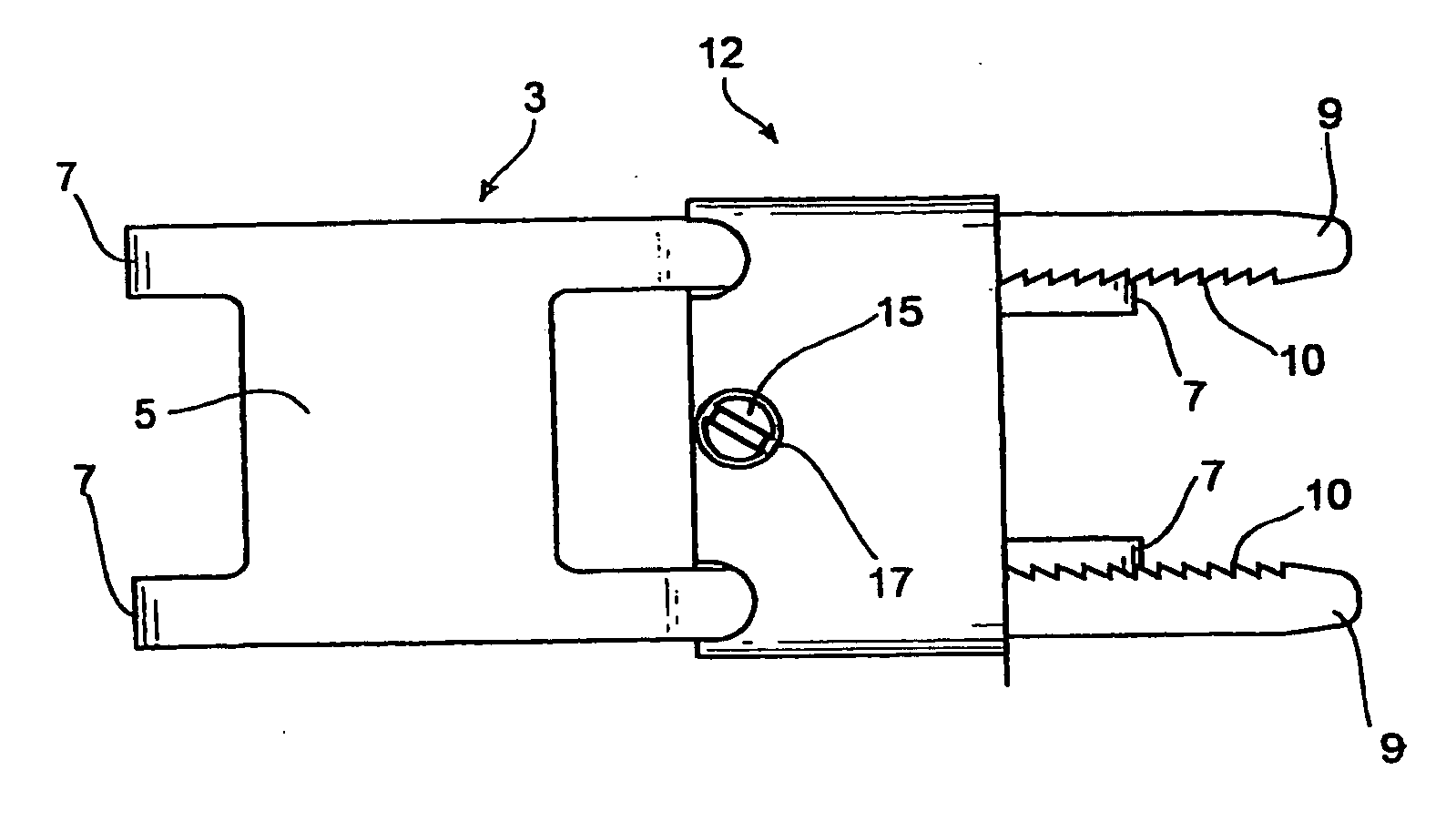
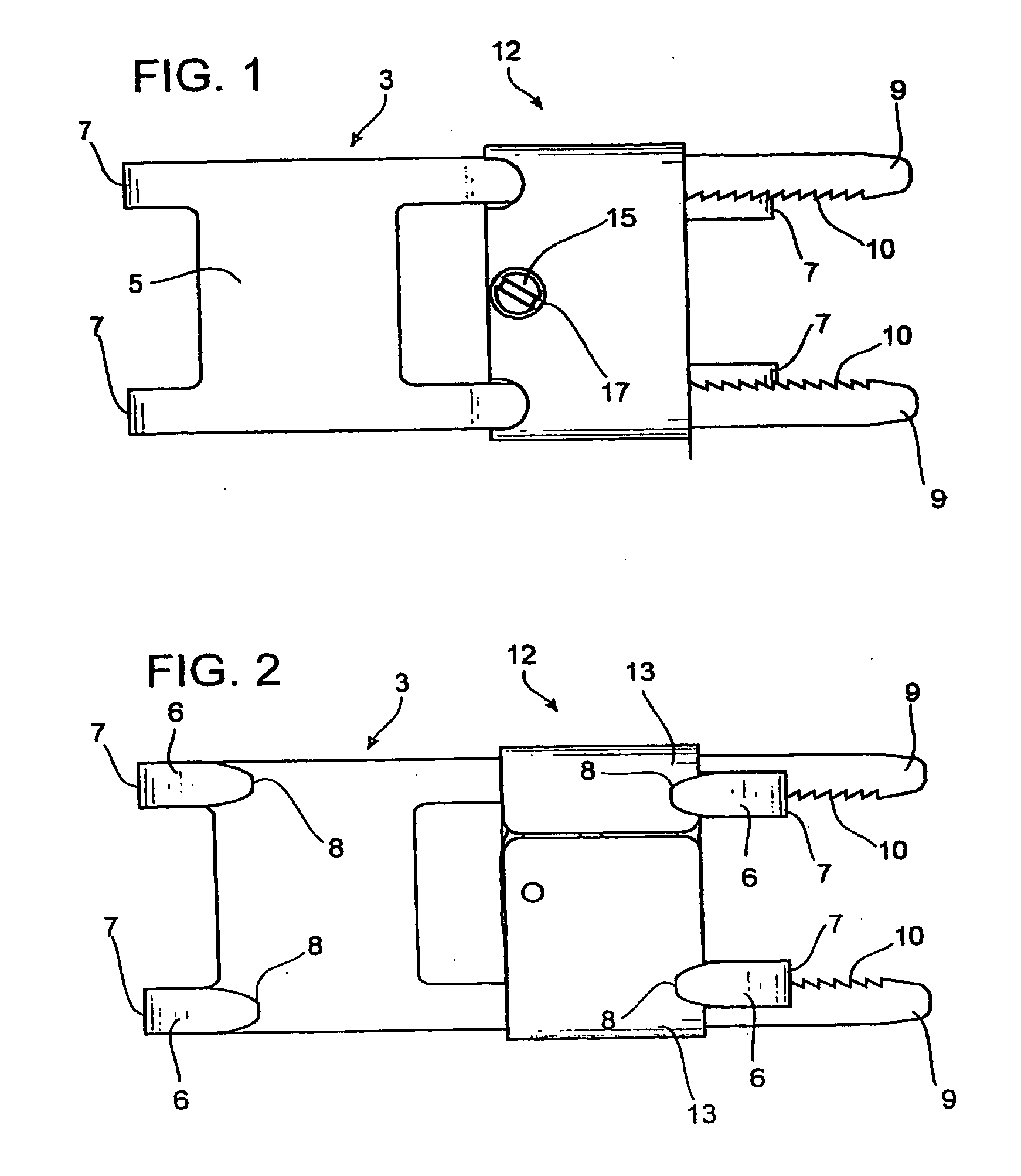
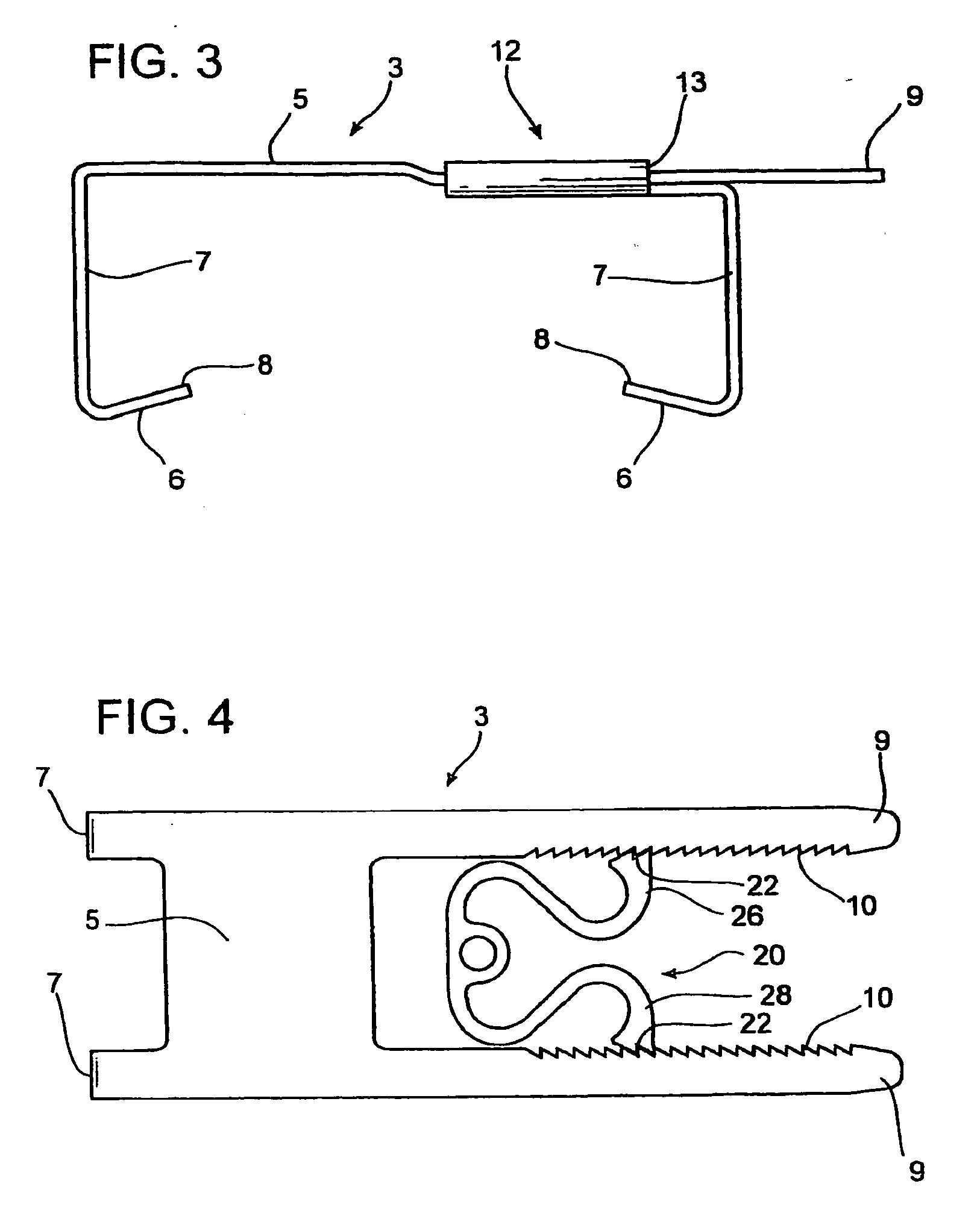
Sternum closure device having locking member
a technology of sternum and locking member, which is applied in the field of surgical devices, can solve the problems of sternal non-union, steel wires can and do break, and steel wires are difficult to maneuver and place around the sternum, and achieve the effect of convenient access
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] While the making and using of various embodiments of the present invention are discussed in detail below, it should be appreciated that the present invention provides for inventive concepts capable of being embodied in a variety of specific contexts. The specific embodiments discussed herein are merely illustrative of specific manners in which to make and use the invention and are not to be interpreted as limiting the scope of the present invention.
[0022] While the invention has been described with a certain degree of particularity, it is clear that many changes may be made in the details of construction and the arrangement of components without departing from the spirit and scope of this disclosure. It is understood that the invention is not limited to the embodiments set forth herein for purposes of exemplification, but is to be limited only by the scope of the attached claim or claims, including the full range of equivalency to which each element thereof is entitled.
[002...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com