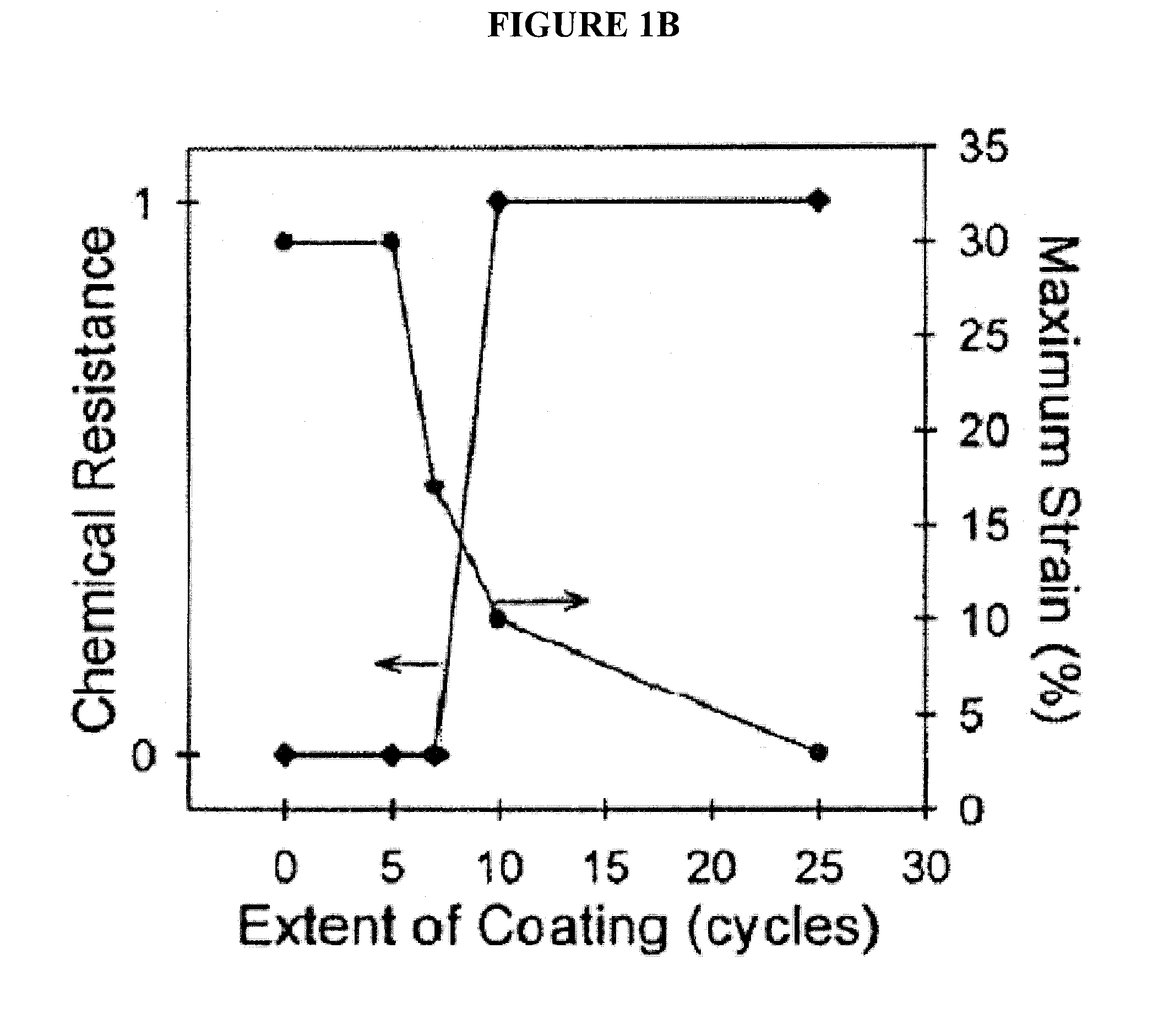
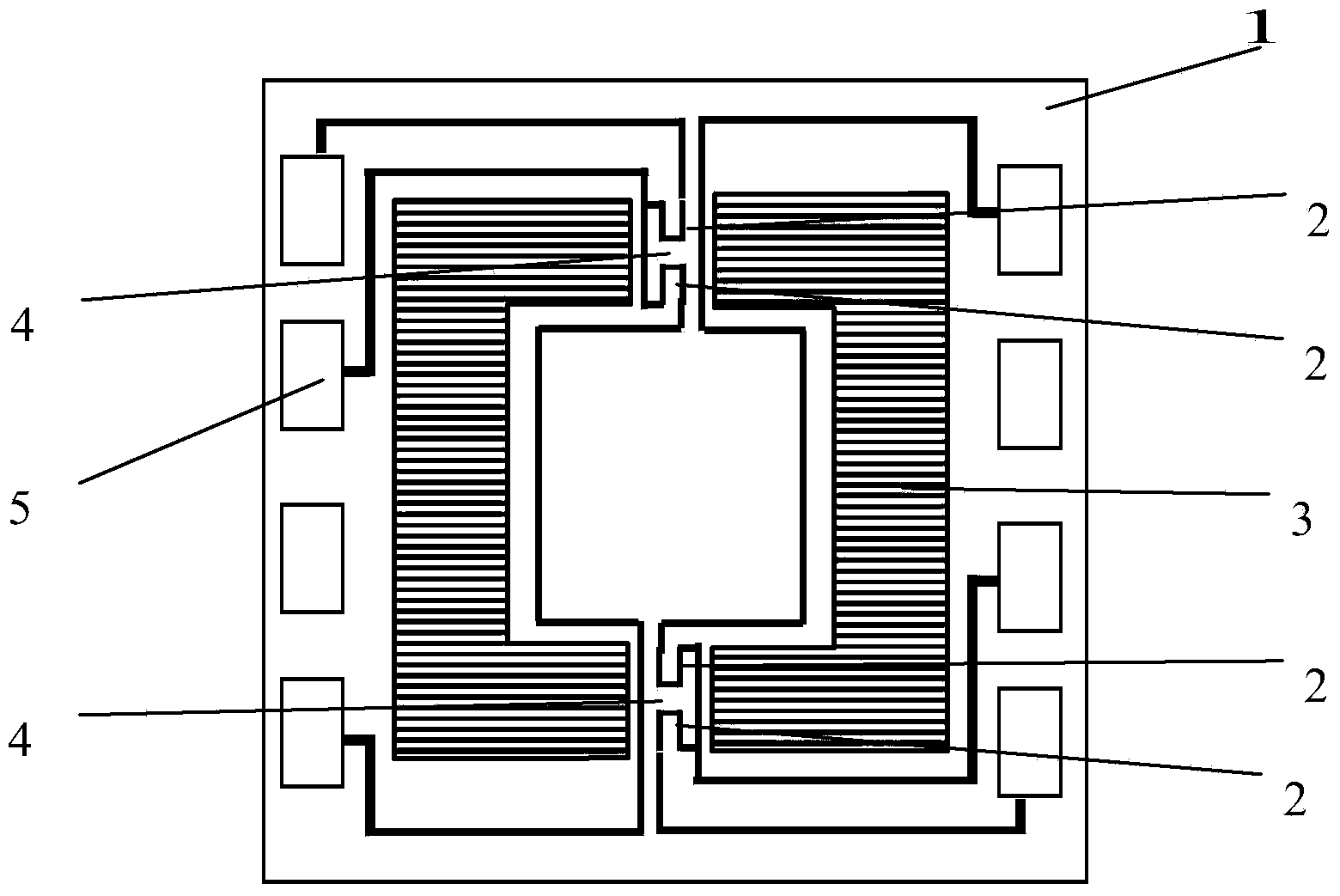
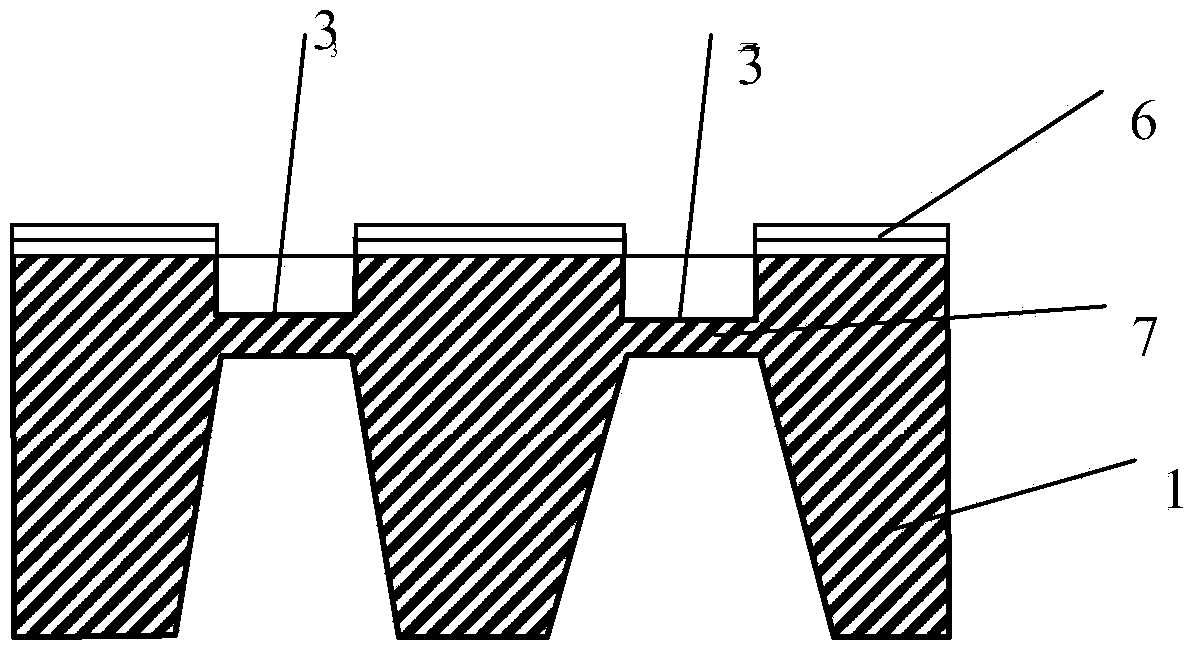
Patents
Literature
238results about How to "Large strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
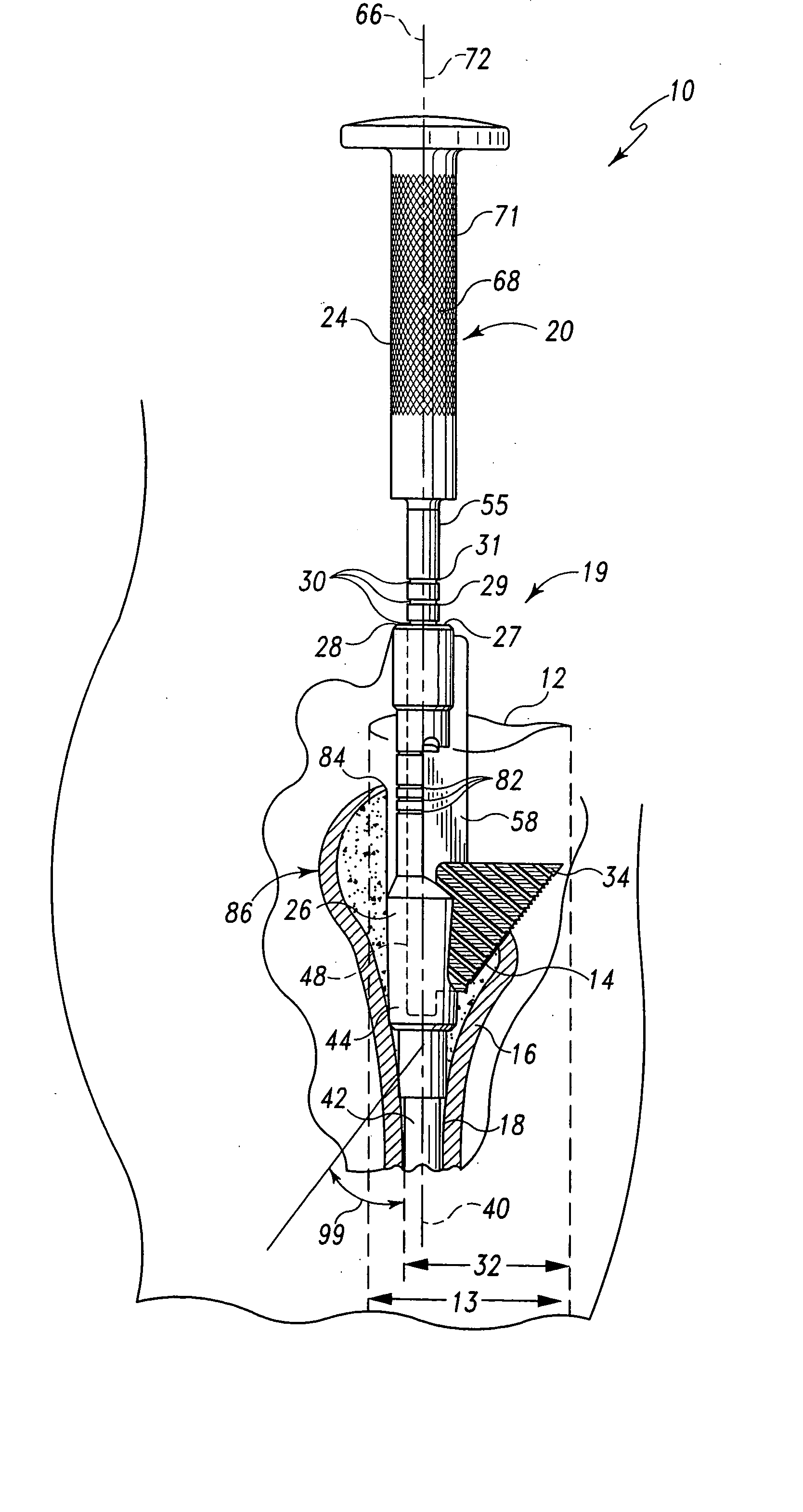
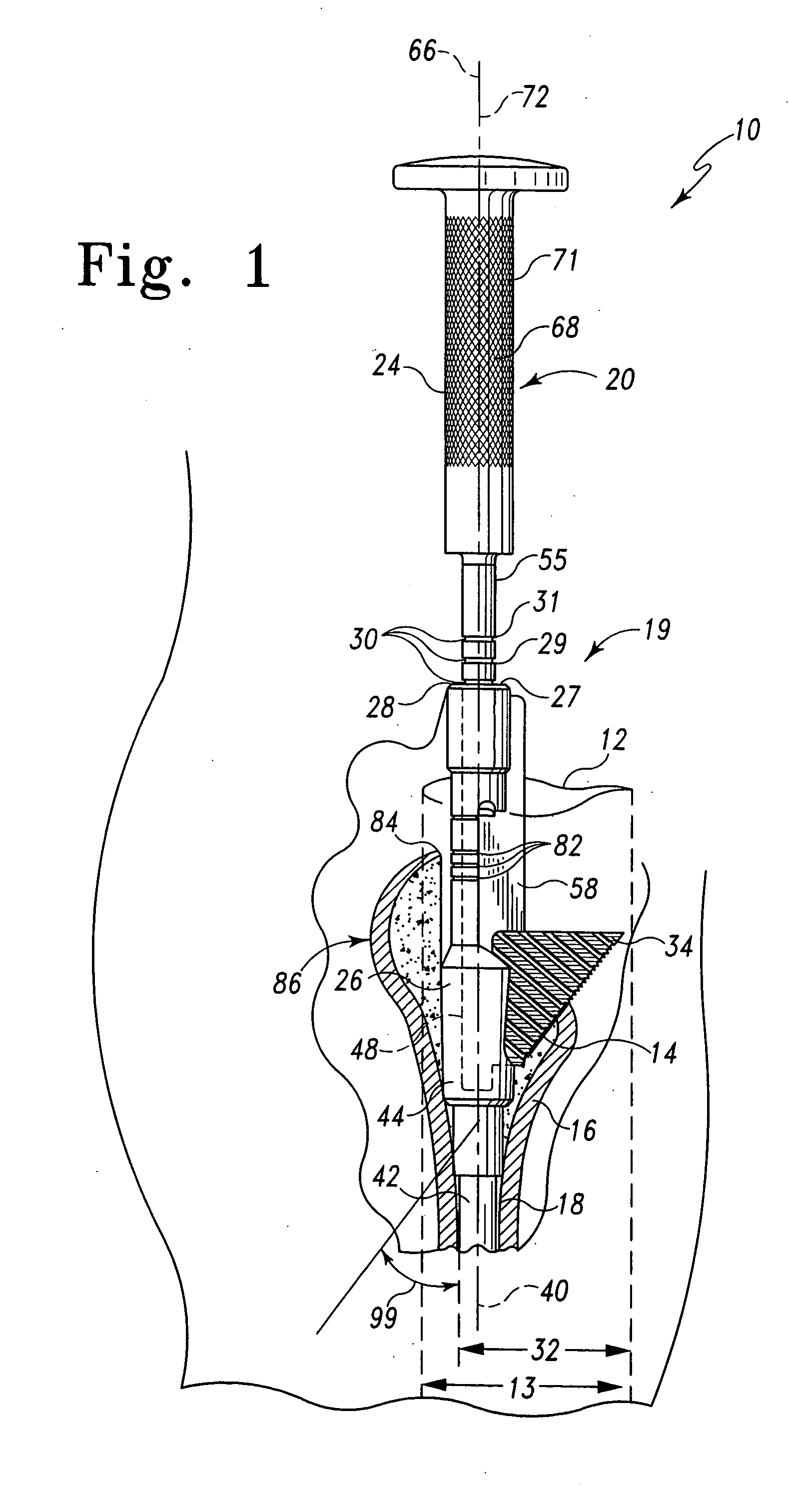
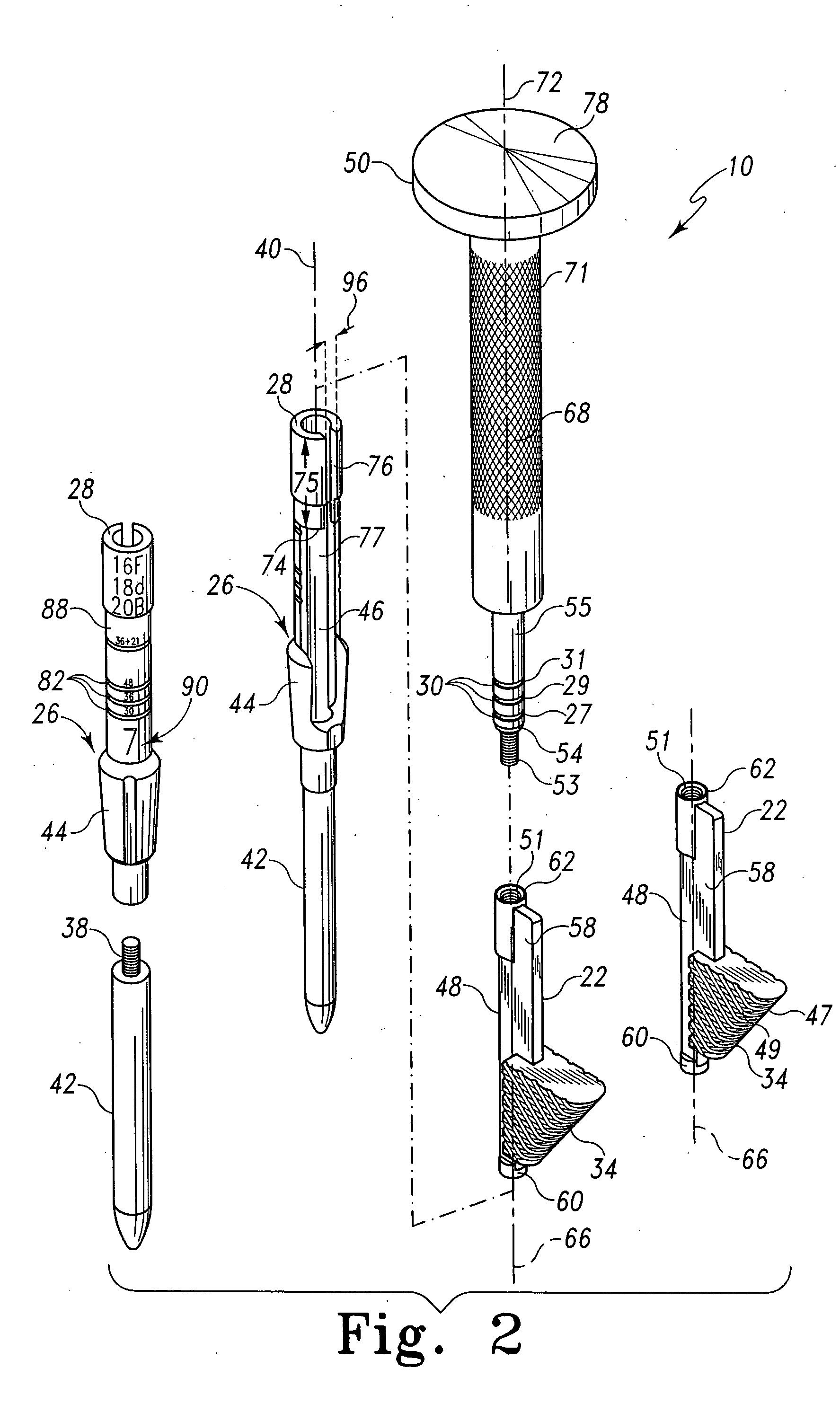
Minimally invasive bone broach
ActiveUS20050288676A1Reduce gapImproving the initial and long-term bone ingrowth/fixationJoint implantsBone drill guidesAcute angleAnatomy
A broaching system is disclosed for creating a cavity in a bone. The cavity has a cross section which has a generally triangular profile having a first side generally parallel with an axis of the bone and a second side forming an acute angle with the first side. The cavity is contiguous with a pre-existing conical cavity in the bone. The apparatus comprises as shaft and a broach. The shaft has a longitudinal axis. The broach is mounted to the shaft and has a first cutting side mounted at the acute angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the shaft. The first cutting side is formed to include teeth. The shaft and broach are configured so that when the longitudinal axis of the shaft is advanced into the bone along the axis of the bone, the teeth of the broach form the triangular cavity. A method for cutting a triangular cavity in bone is also described. The method comprises a providing a shaft step, an incising step and a cutting step. The provided shaft is configured to be movable relative to the bone to be prepared and includes a broach coupled thereto to dispose a cutting surface of the broach at an acute angle relative to the shaft. The shaft and broach have a width defined by the distance between the shaft and the outer most portion of the cutting surface. The incising step includes incising the patient adjacent the bone to be prepared to form an incision having a length approximating the width of shaft and broach. The cutting step includes cutting the cavity by driving the broach by moving the shaft relative to the bone.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
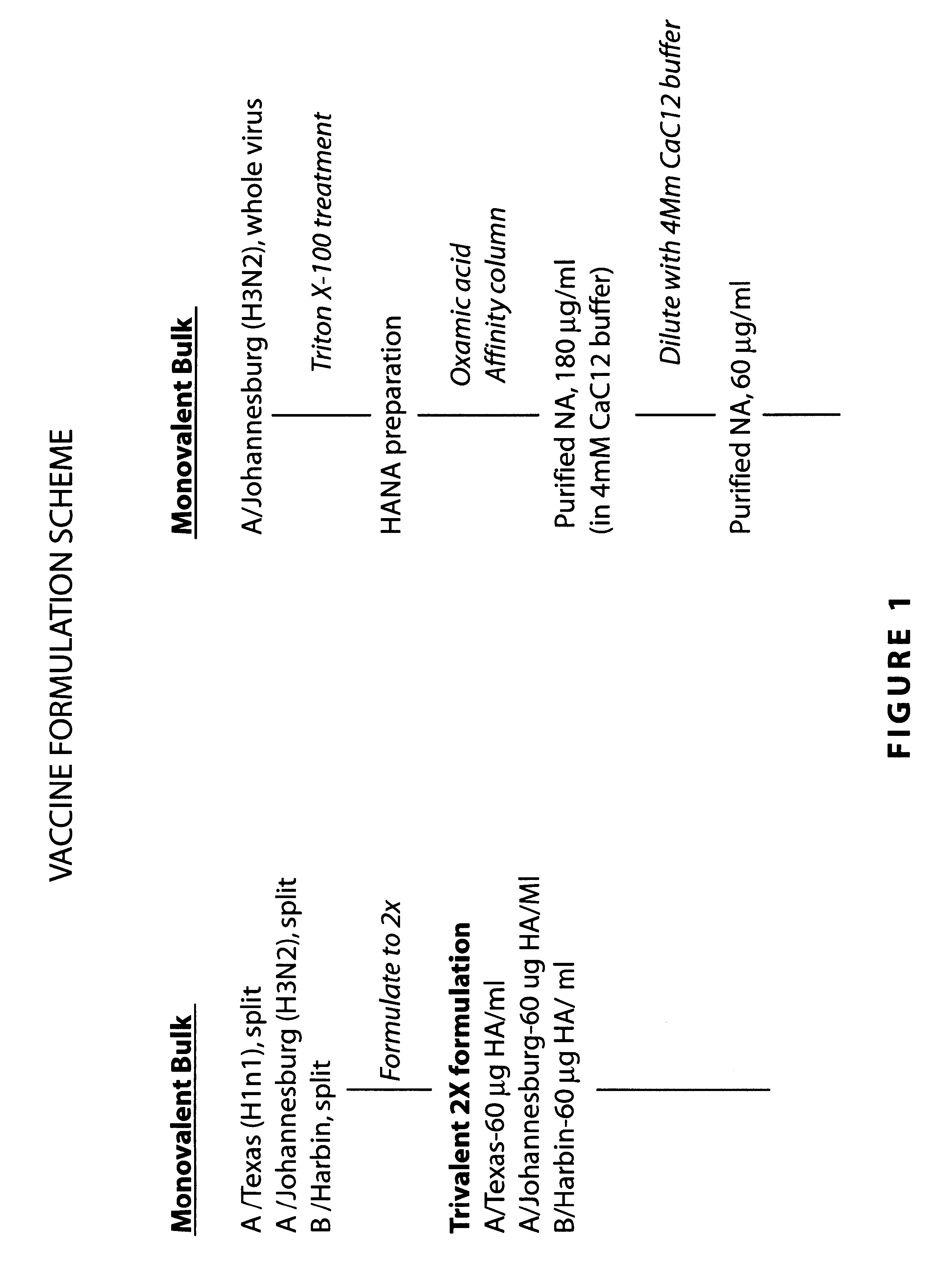
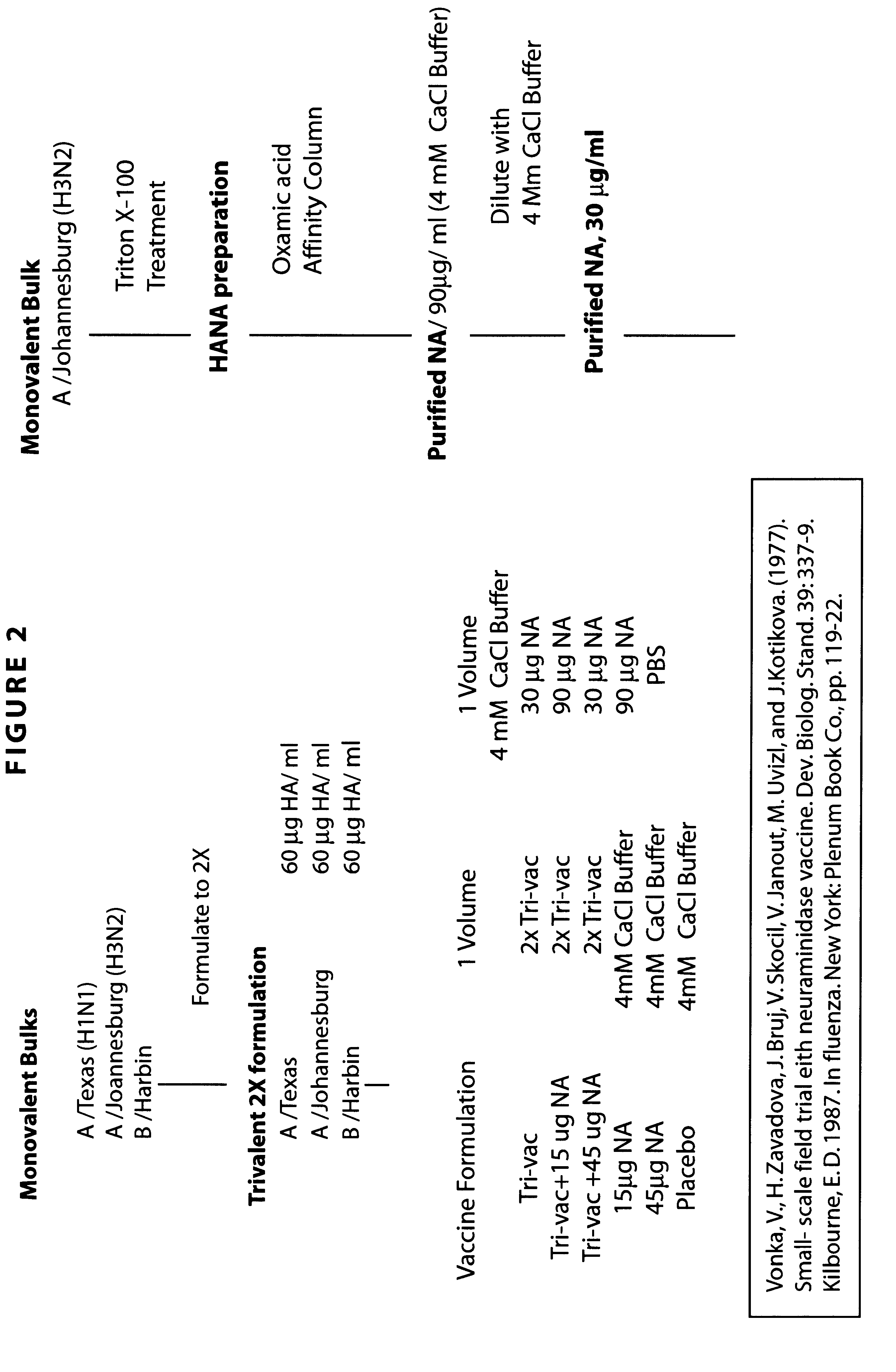
Neuraminidase-supplemented compositions
InactiveUS6485729B1Less importancePrevents and lessens HA immunodominanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNasal cavityAdjuvant
An anti-influenza vaccine composition wherein the improvement is that the vaccine includes, as an additive, neuraminidase (NA). The base anti-influenza vaccine can be any commercially available anti-influenza vaccine. The composition can include and be administered with an adjuvant. The vaccine composition provides protection in a host, animal or human, against influenza infection, including viral replication and systemic infection. Oral, nasal or other mucosal or per needle administration, including intracutaneous, intradermal, intramuscular, intravascular, and intravenous, are included.
Owner:PROTEIN SCI
Direct assembly process for fabrication of ionomeric polymer devices
InactiveUS20060266642A1Superior transduction performanceLarge strain generationEngine manufactureMachines/enginesPolymer scienceActuator
Ionomeric polymer sensors, actuators, and transducers and methods for fabricating them are disclosed. One embodiment of the sensors, actuators, and transducers possess a high surface area electrode layer that is applied by hot pressing and a highly conductive surface layer. Another embodiment of these sensors, actuators, and transducers possess a high surface area electrode layer that is penetrated by electronically conductive nanowires. Methods for fabricating these sensors, actuators, and transducers are disclosed. These methods involve the formation of the high surface area layer from a liquid mixture that contains ionomeric polymer, electronically conductive particles, and possibly diluent. This mixture is formed into layers either directly on an ionomeric polymer, on a separate transfer decal, or on an electronically conductive layer. This electronically conductive layer may also include an array of nanowires. These electrode layers are then attached to an ionomeric polymer membrane by hot pressing. The ionomeric polymer membrane may be swollen with a diluent either prior to the hot pressing or after the hot pressing step. Also, the ionomeric polymer membrane may be formed by casting from a liquid mixture containing ionomeric polymer and diluent.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Elastomeric dielectric polymer film sonic actuator
InactiveUS7062055B2Optimize power outputLow working voltagePiezoelectric/electrostrictive gramophone pickupsStirling type enginesDielectricConductive polymer
A sonic actuator including a multi-layer membrane having a non-metallic elastomeric dielectric polymer layer with a first surface and a second surface, a first compliant electrode layer contacting the first surface of the polymer layer, and a second compliant electrode layer contacting the second surface of the polymer layer. The actuator further includes a support structure in contact with the sonic actuator film. Preferably, the non-metallic dielectric polymer is selected from the group consisting essentially of silicone, fluorosilicone, fluoroelastomer, natural rubber, polybutadiene, nitrile rubber, isoprene, and ethylene propylene diene. Also preferably, the compliant electrode layer is made from the group consisting essentially of graphite, carbon, and conductive polymers. The support structure can take the form of grid having a number of circular apertures. When a voltage is applied to the electrodes, portions of the film held at the aperture of the support structure can bulge due to the electrostriction phenomenon. The resultant “bubbles” can be modulated to generate sonic vibrations, or can be used to create a variable surface for airflow control.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Low strain optical fiber cable
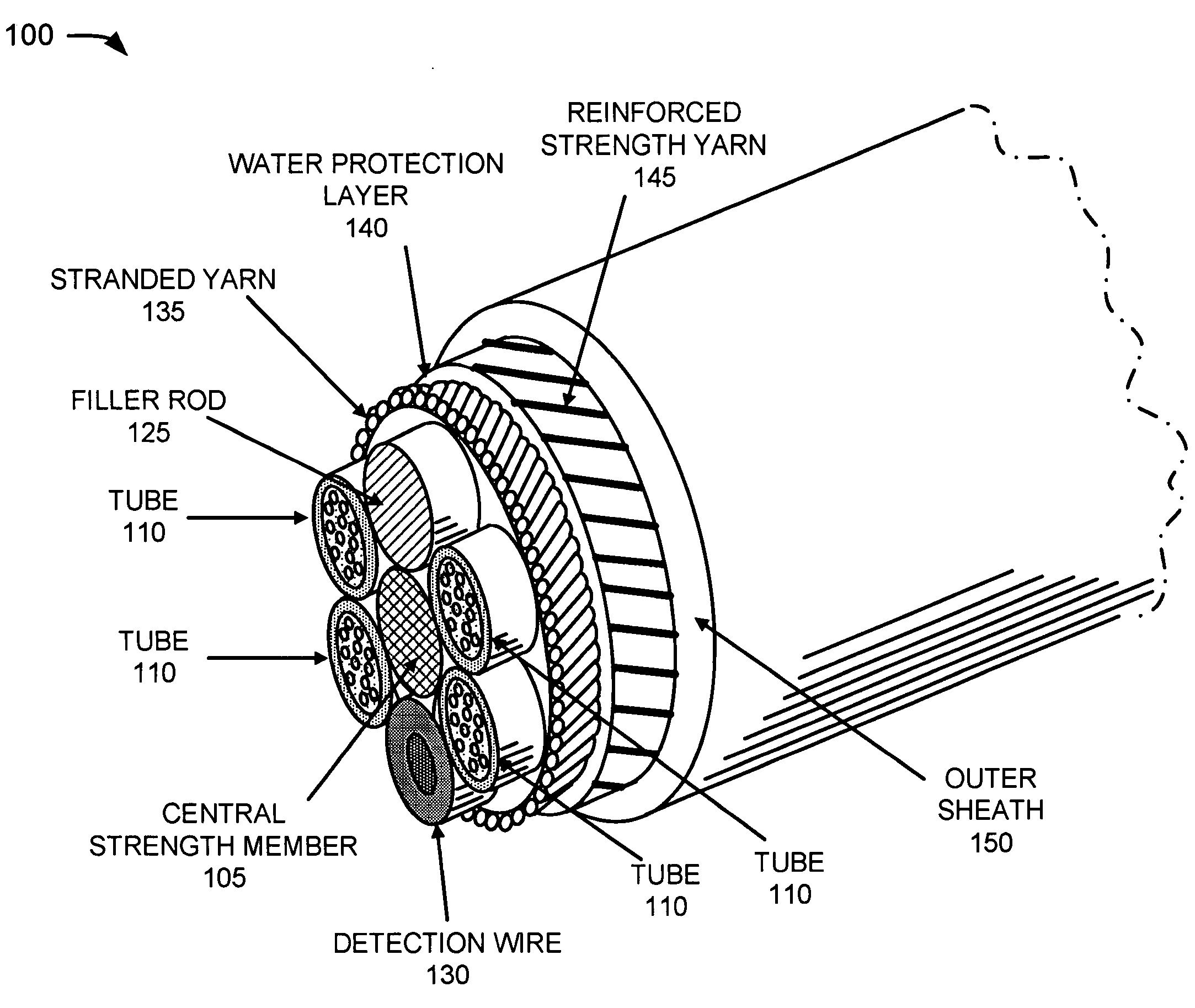
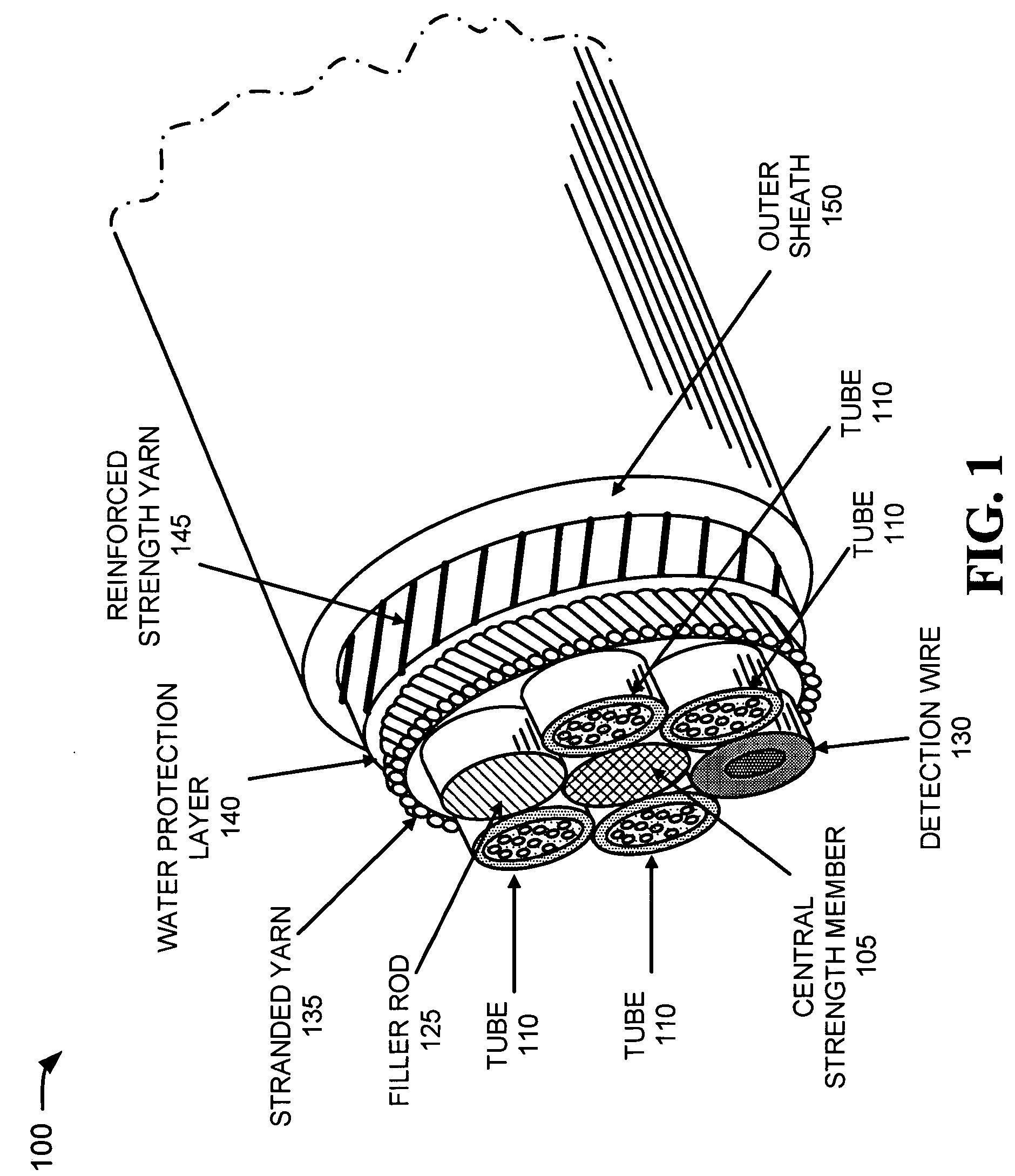
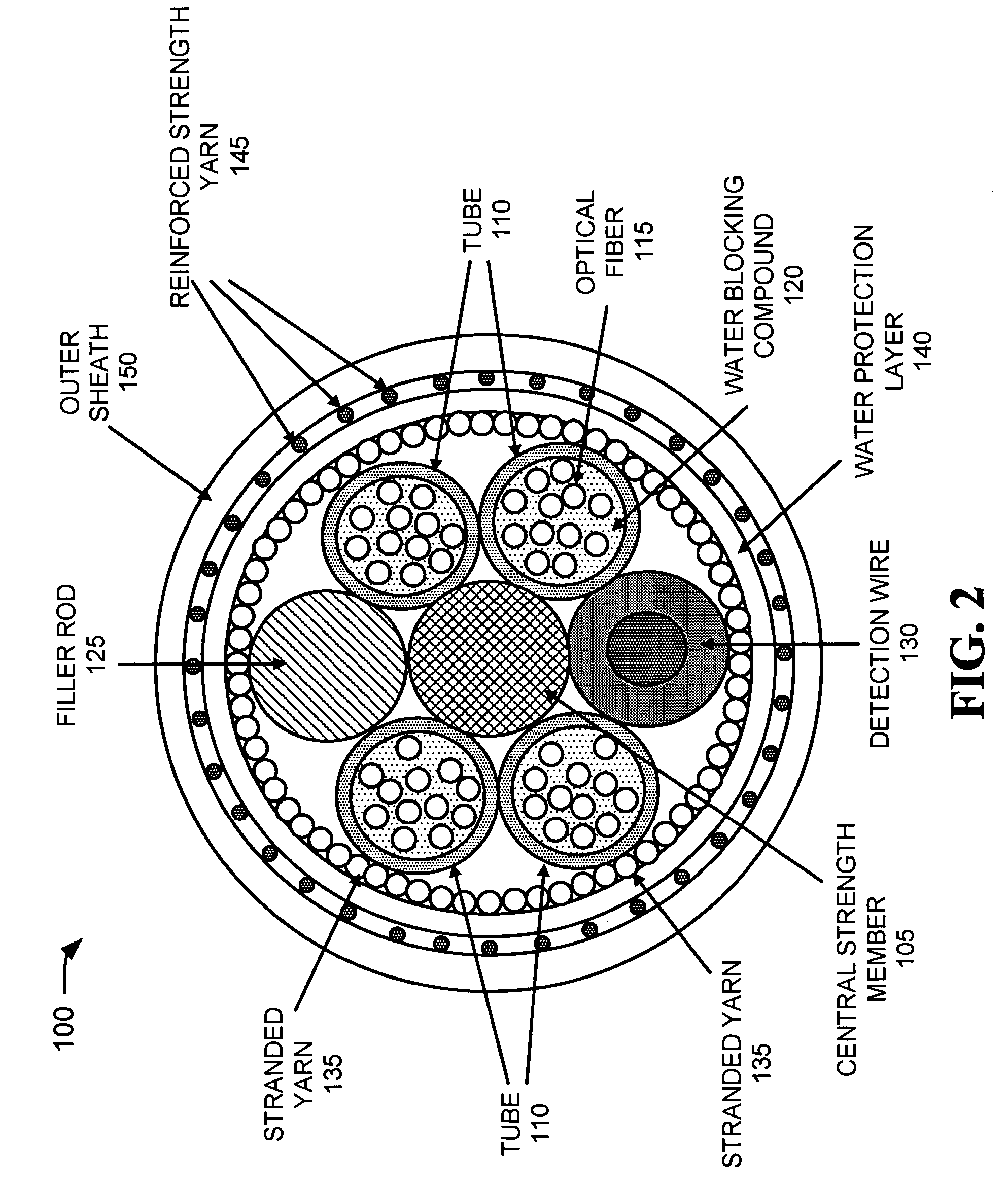
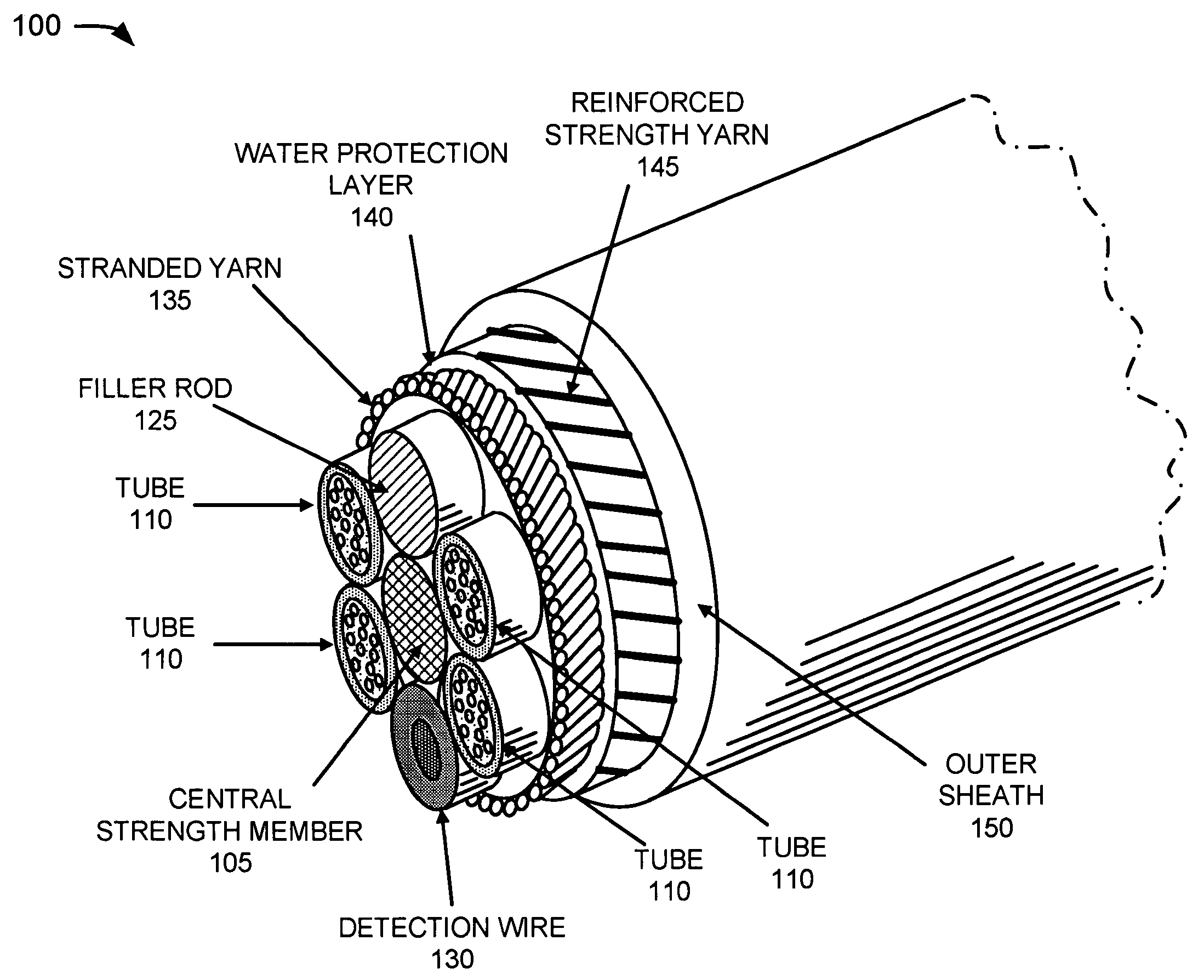
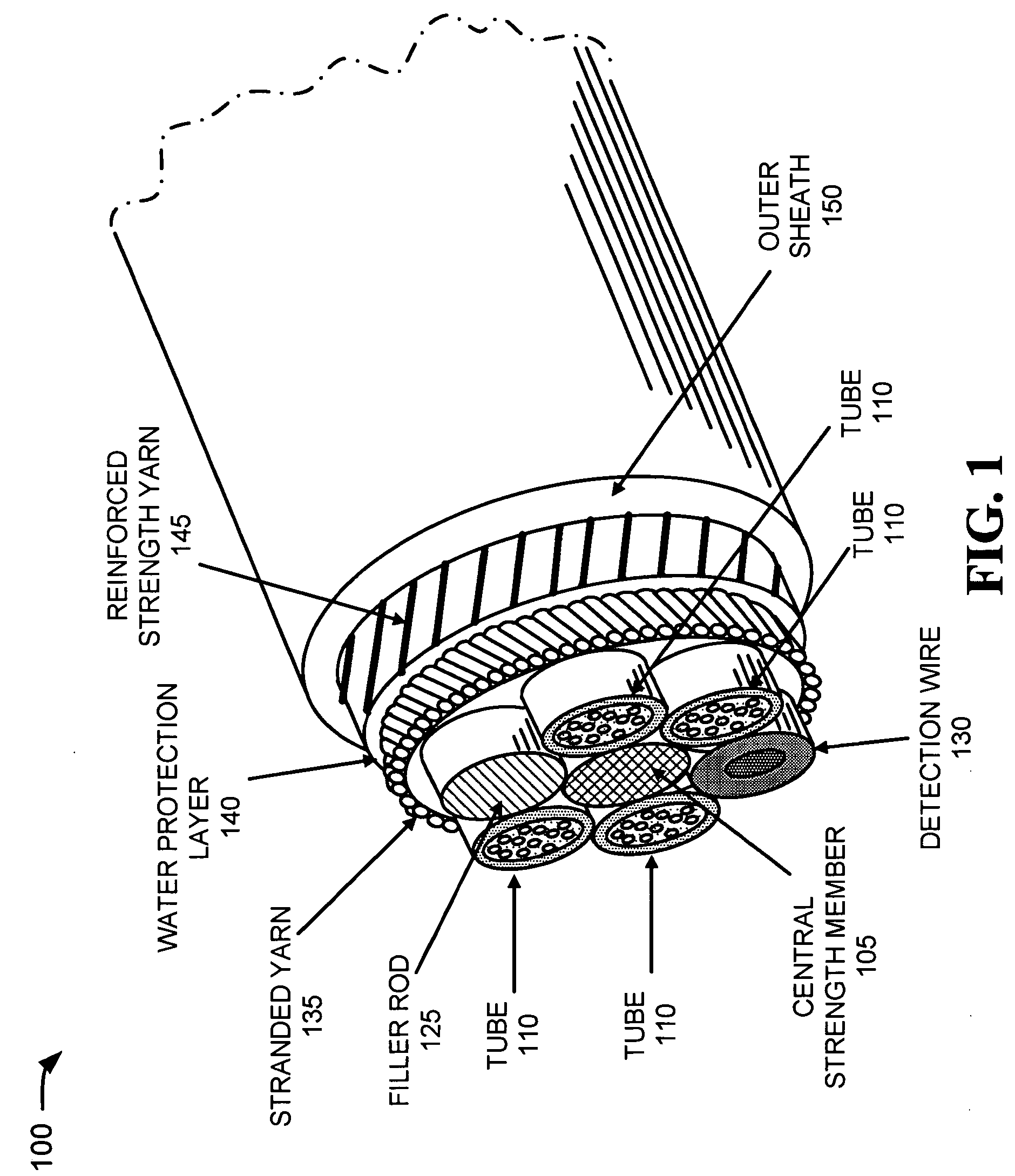
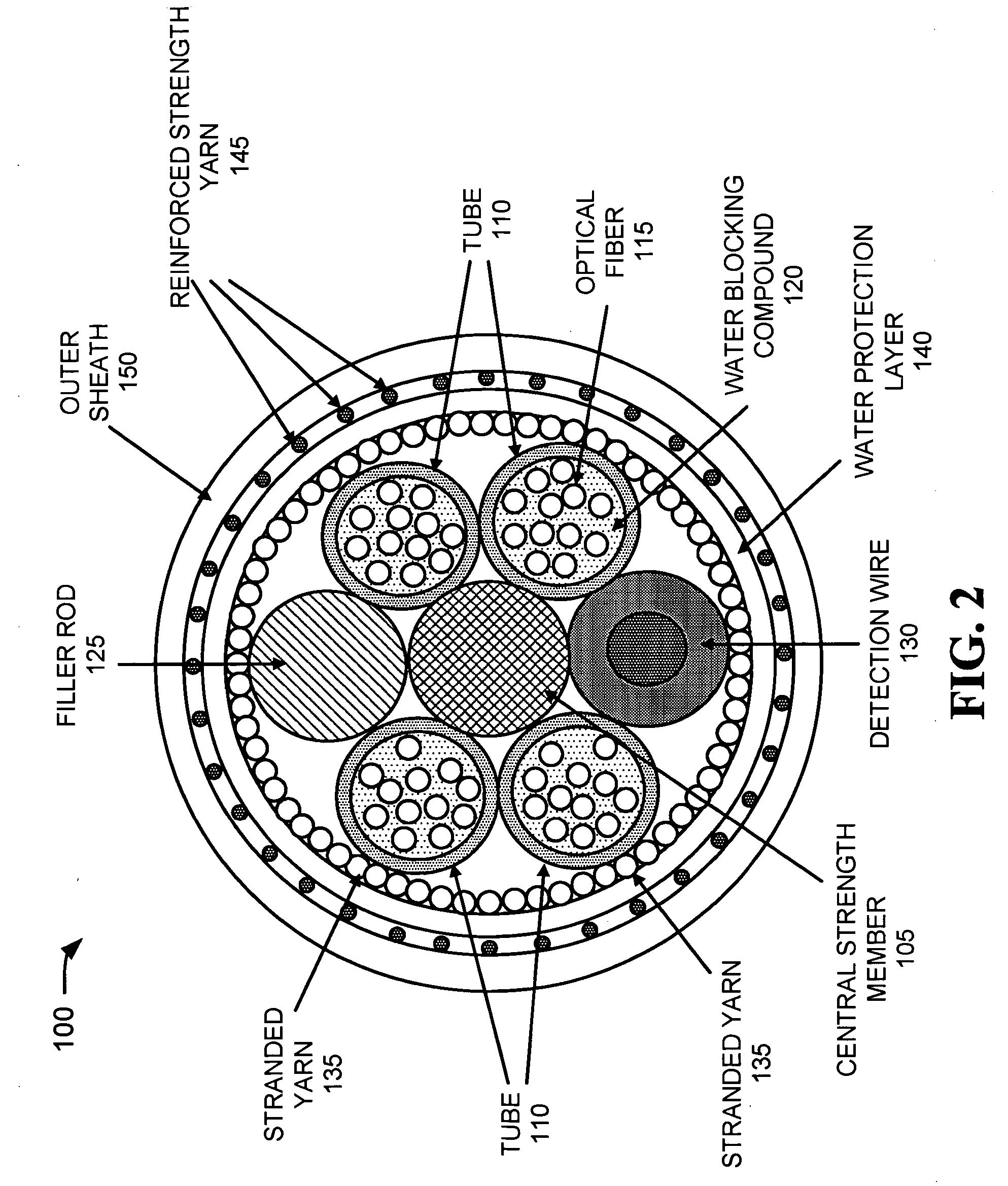
InactiveUS7242831B2Significant degradationLarge strainFibre mechanical structuresYarnProtection layer
An optical fiber assembly includes a central strength member, multiple tubes, stranded yarn, a water protection layer, reinforced strength yarns and an outer sheath. At least one of the multiple tubes has one or more optical fibers disposed within. The stranded yarn is formed around the multiple tubes and the central strength member. The water protection layer is formed around the stranded yarn. The reinforced strength yarns are formed around the water protection layer and the outer sheath is formed around the reinforced strength yarns. The optical fiber assembly has an overall diameter of less than about 11.5 mm and exhibits low strain when subjected to a tension of at least 600 pounds.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Piezoelectric body, piezoelectric device, and liquid discharge apparatus
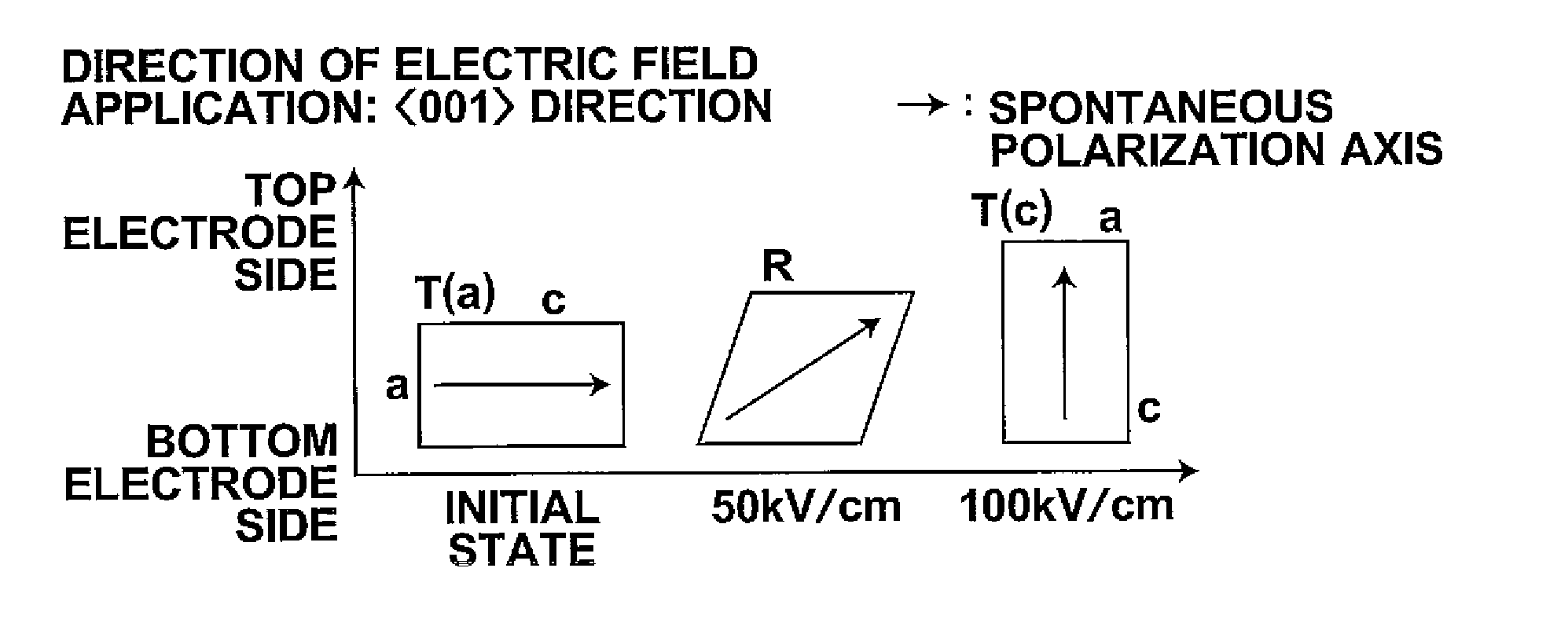
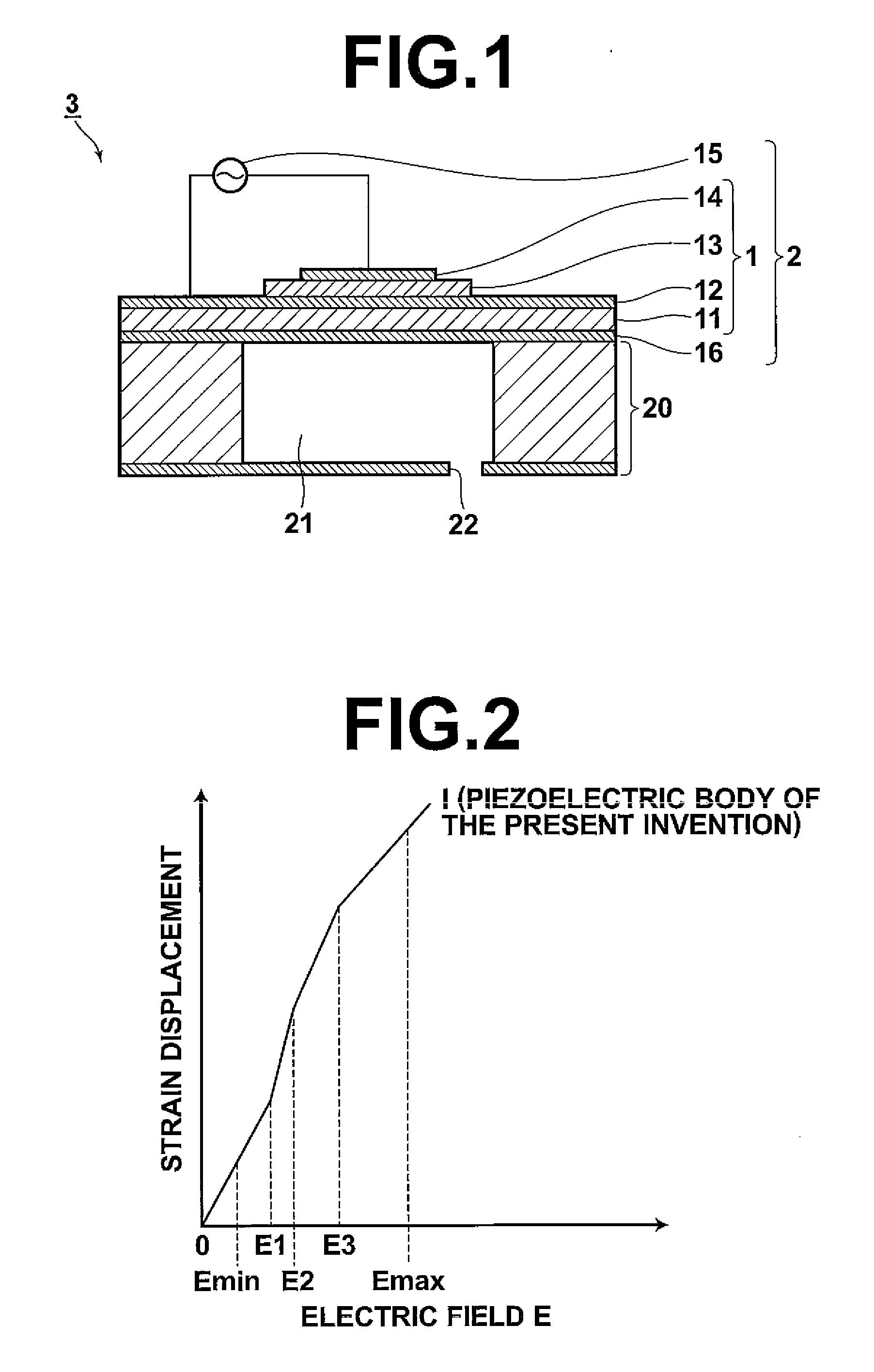
ActiveUS20080265718A1Improve piezoelectric performanceLarge strainPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsCrystal systemElectricity
A piezoelectric body contains a ferroelectric substance phase having characteristics such that, in cases where an applied electric field is increased from the time free from electric field application, phase transition of the ferroelectric substance phase to a ferroelectric substance phase of a different crystal system occurs at least two times. The piezoelectric body should preferably be actuated under conditions such that a minimum applied electric field Emin and a maximum applied electric field Emax satisfy Formula (1):Emin<E1<Emax (1)wherein the electric field E1 represents the electric field at which the first phase transition of the ferroelectric substance phase begins.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
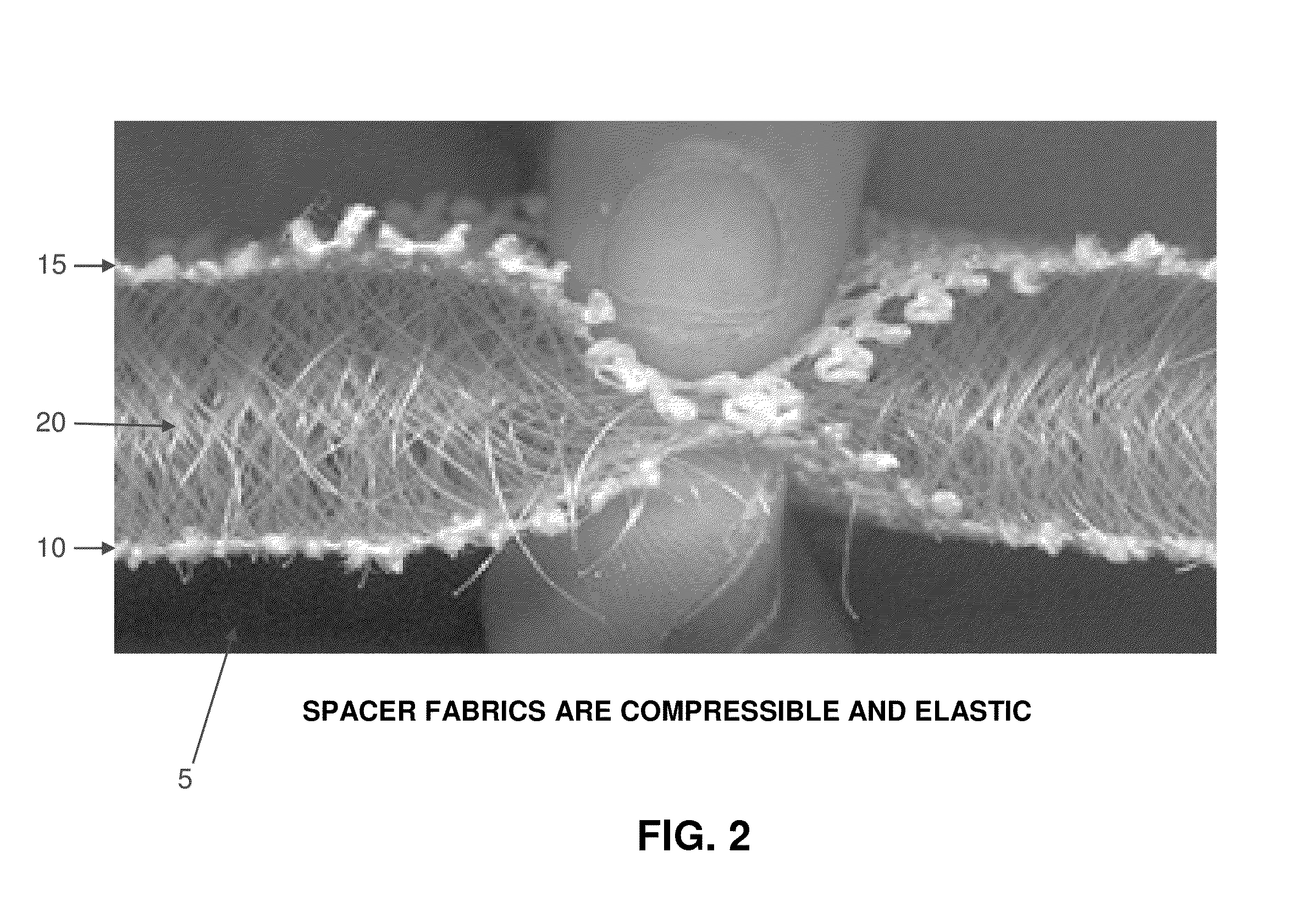
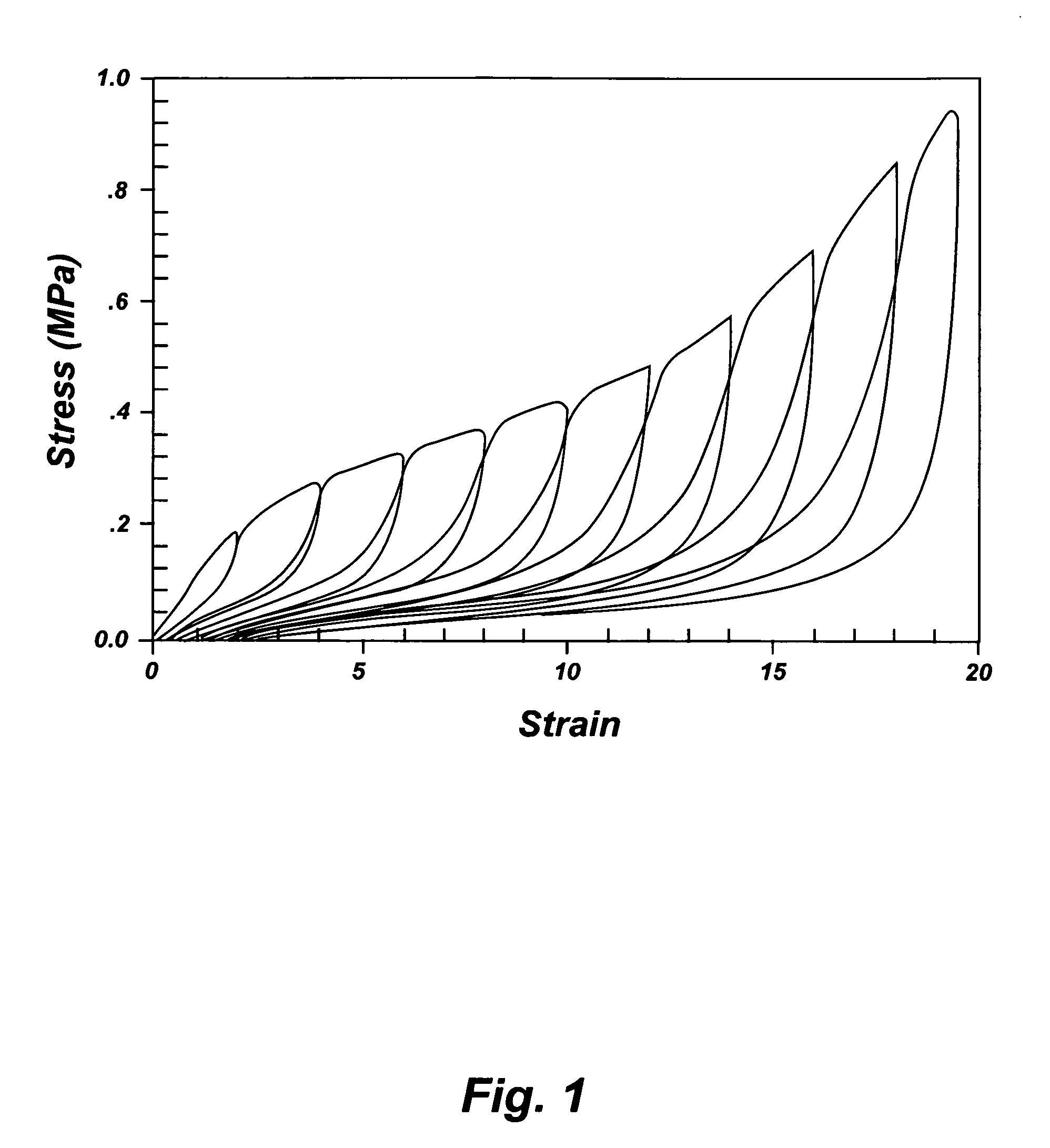
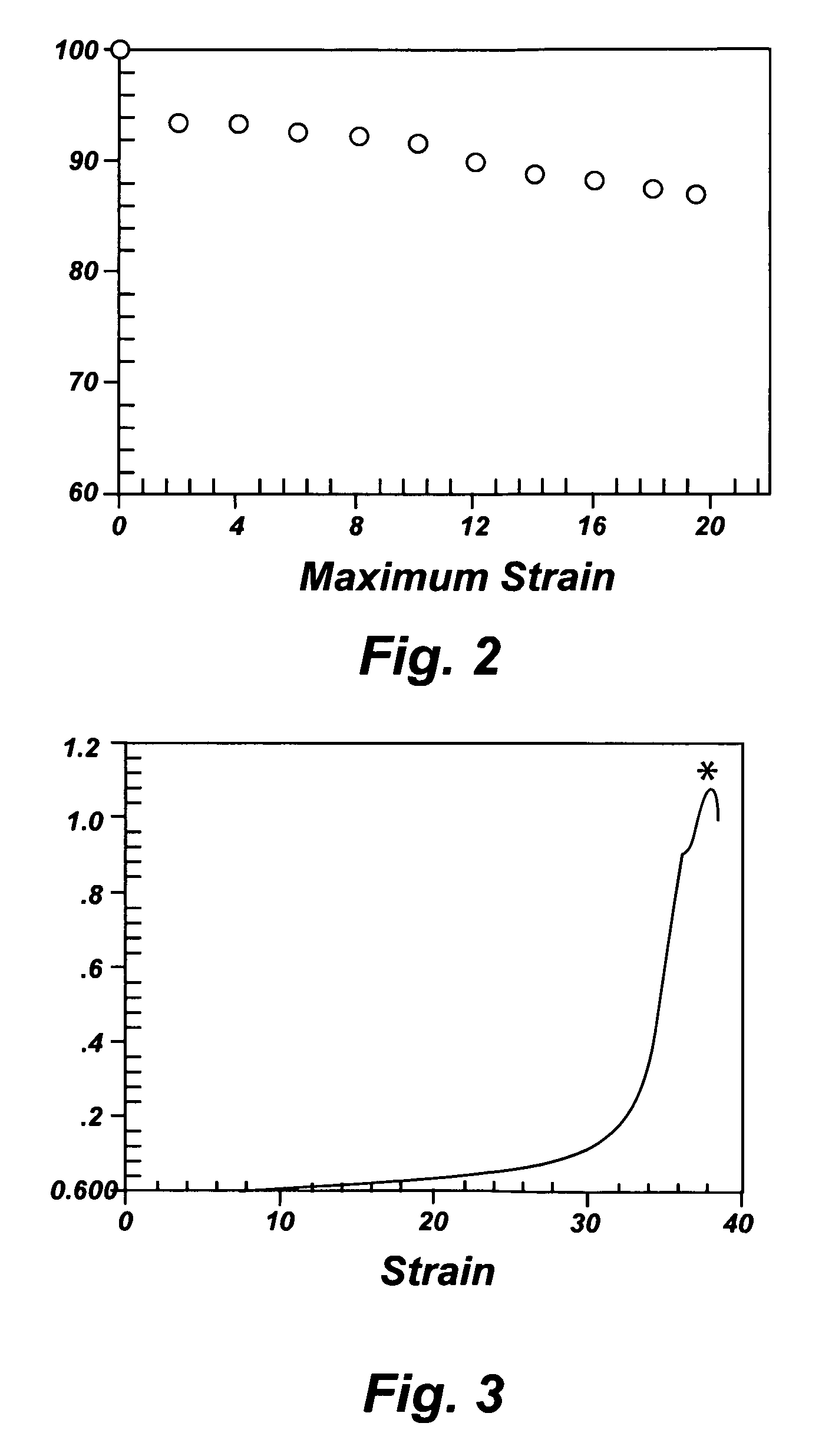
Protective padding utilizing superelastic three-dimensional spacer fabric comprising shape memory materials (SMM)
InactiveUS20130298317A1Highly flexibleShorten lifeChemical protectionHeat protectionBiomedical engineering
Owner:ARTHREX
Soft and strong elastomeric compositions from semicrystalline-amorphous polyolefin block copolymers
ActiveUS20080319116A1Remarkable mechanical propertyExcellent elastic recoveryMixingCeramic shaping apparatusPolyolefinThermomechanical processing
Polyolefin block and graft copolymers comprised of two or more semicrystalline polyolefin blocks or grafts and one or more amorphous polyolefin blocks can be blended with a low molecular weight fluid diluent that preferentially locates within and swells the amorphous domains of the block or graft copolymer, while preserving the crystallinity of the semicrystalline block domains. After mechanical or thermomechanical processing, such compositions combine softness with high strength and high recoverable elasticity. Compositions are also disclosed whereby the diluent species is removed from the composition, either before or after the mechanical or thermomechanical processing, in order to create a strong elastic material with an ultra-low entanglement density within the amorphous domains.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
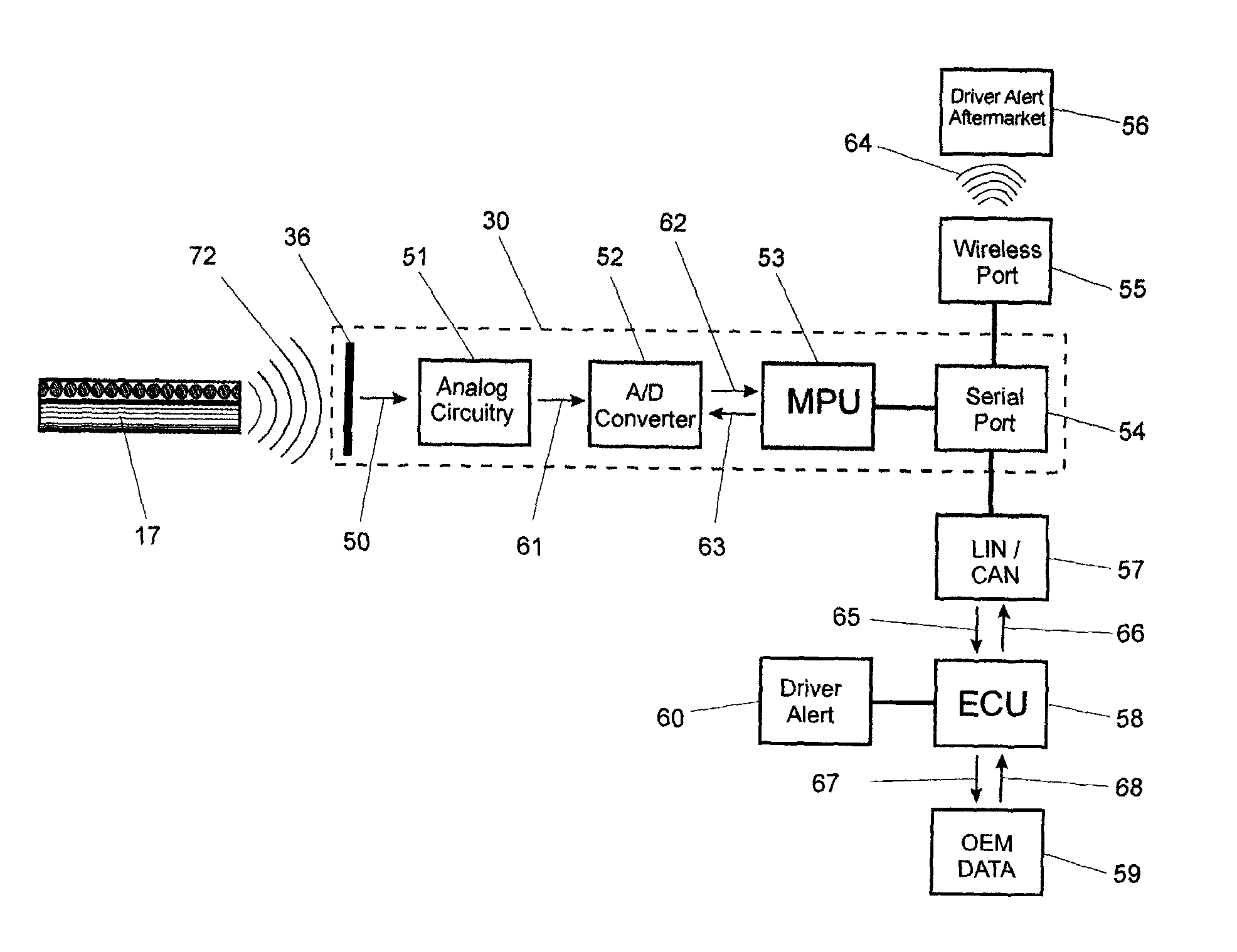
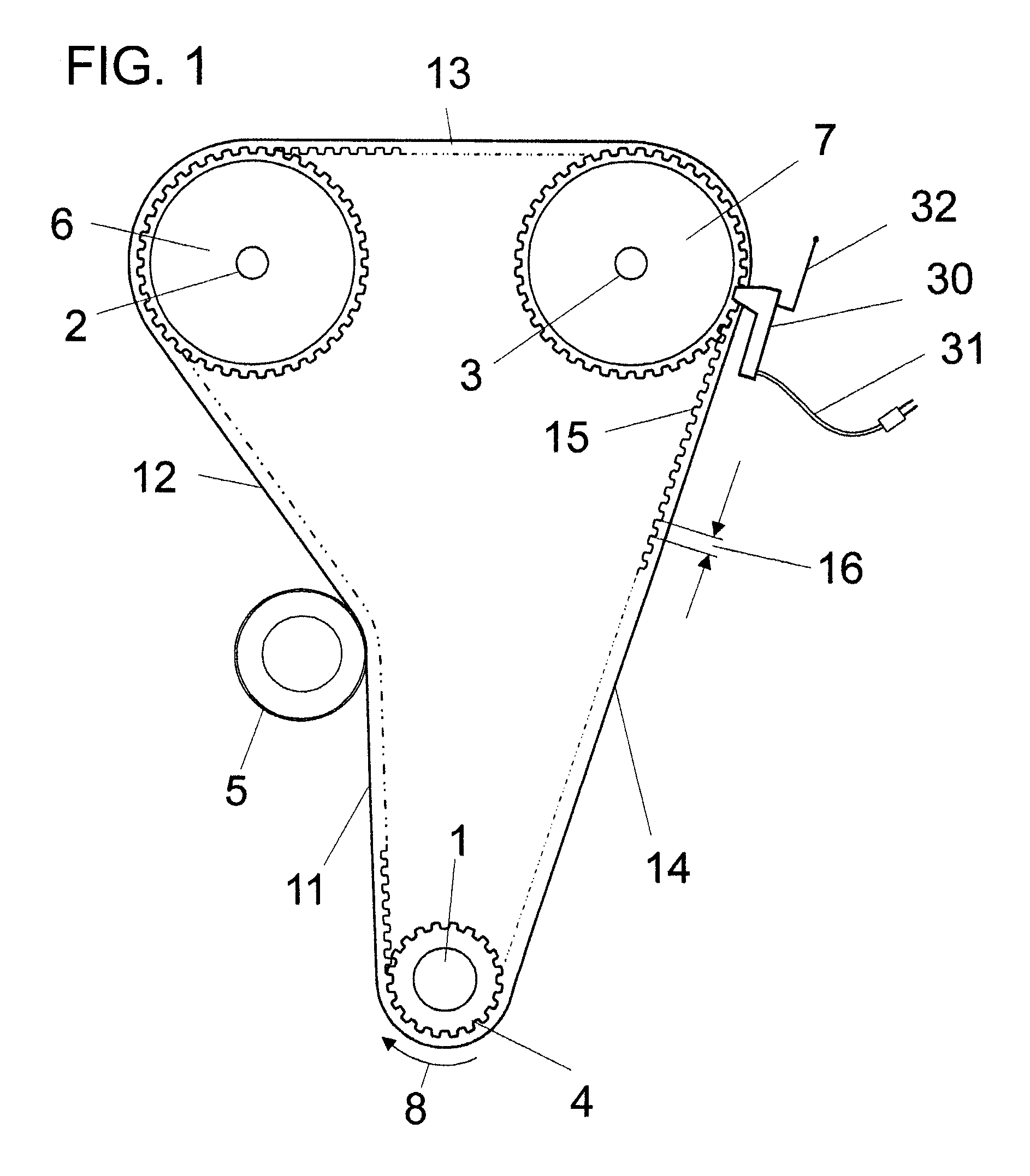
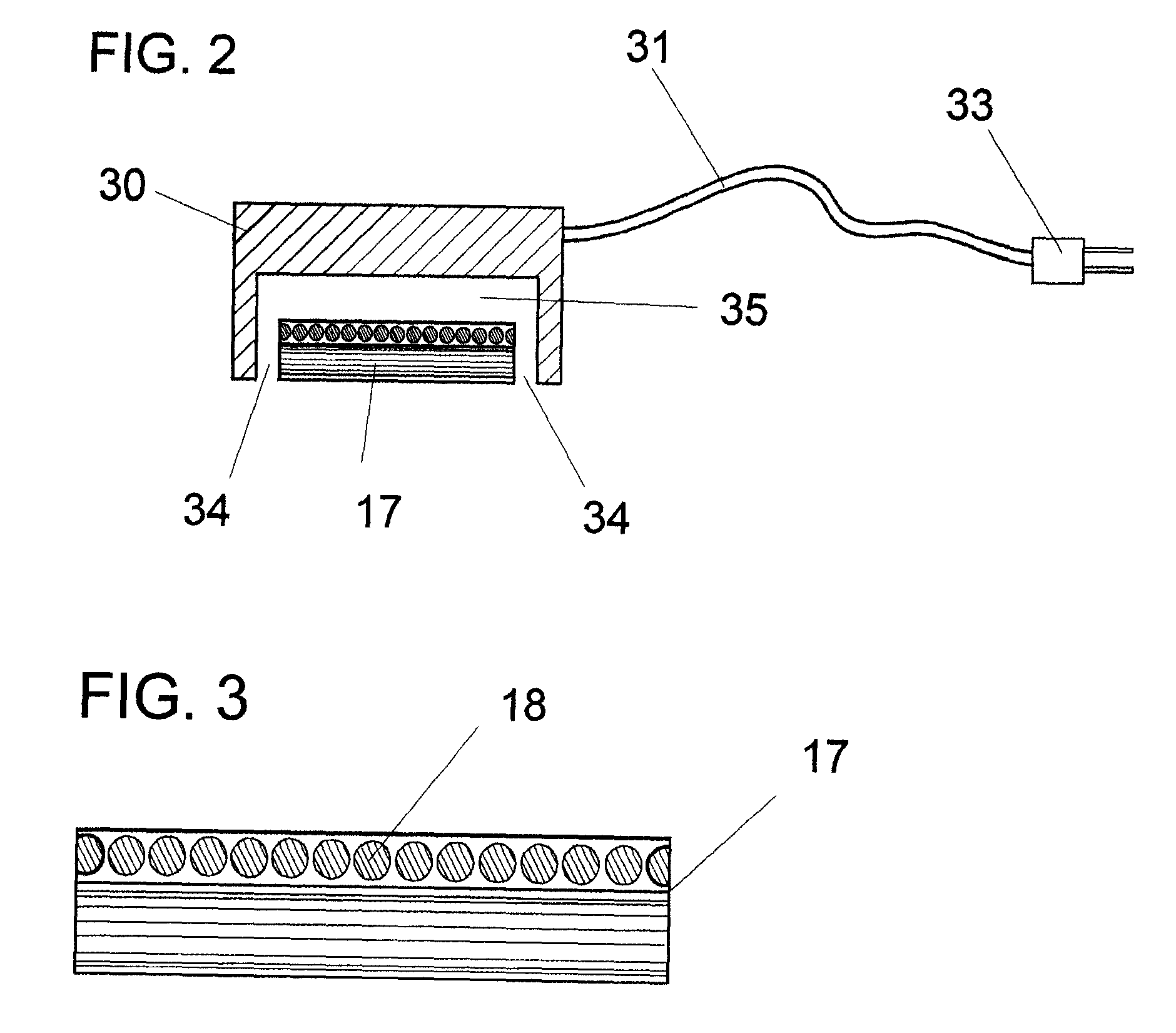
Apparatus And Method For Detecting Transmission Belt Wear And Monitoring Belt Drive System Performance
InactiveUS20090303065A1Improve system qualityPremature failureVehicle testingMachine gearing/transmission testingMicrocontrollerFiber
An apparatus and method to monitor endless belts and related belt drive systems by non-contact sensors for wear or an anomalous function, determining the state of belt drive system and detecting early stages of belt and system failure. A sensing unit featuring one or several independent sensor elements is placed near a belt of a polymer matrix with a fiber cord load bearing core to monitor several simultaneously occurring normal modes of operation. The sensor can determine soundness of the whole timing drive continuously by processing the collected signal and detecting structural damage. The collected data is processed by a microcontroller integrated with the sensor. The apparatus and method uses a non-contacting capacitor array having sensing element(s) connected to electronic circuitry that is adapted to sense the dynamic capacitance change coupled with electrocapacitive and piezoelectric effects exhibited by the belt. The sensor continuously monitors the belt during normal operation.
Owner:LIPOWSKI MATS
Flexible display unit and mobile terminal having the same
ActiveUS20190132947A1Lower yield strengthLarge strainCircuit bendability/stretchabilityDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
A flexible display unit is disclosed including a flexible display, and a flexible frame coupled to the flexible display, the flexible frame including a first rigid portion, a second rigid portion, and a flexible portion located between the first and second rigid portions and configured to permit the frame to be bent, the flexible portion including a first region including a first plurality of holes having a first size, and a second region including a second plurality of holes having a second size, wherein the first size is greater than the second size, the first region is positioned closer to a center axis of the flexible frame than the second region, and an area of the first plurality of holes within a portion of the first region is greater than an area of the second plurality of holes within a portion of the second region having the same area.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Soft support bridge type silicon micro-piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer chip and prepration method thereof
InactiveCN101645484AHigh sensitivityGood process compatibilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionVertical projectionUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a soft support bridge type silicon micro-piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer chip which comprises a silicon substrate with a square conical hole which is small at the top andbig at the bottom in the center; a silicon layer and a first oxidation layer are sequentially covered on the front surface of the silicon substrate, and a second oxidation layer is covered on the backsurface; the corresponding silicon layer and the first oxidation layer above the square hole of the front surface of the silicon substrate constitute a square vibration membrane, one pair of oppositesides of the square vibration membrane respectively etch a vertical narrow slot, and the vertical projection of each narrow slot is positioned on the inner side of the hole edge above the front surface of the silicon substrate; a lower electrode, a piezoelectric membrane and an upper electrode are sequentially deposited on the square vibration membrane; a polyimide membrane is deposited on various parts on the front surface of the silicon substrate; and the square vibration membrane which is etched with the vertical narrow slots and the polyimide membrane commonly constitute a soft support anti-sound leakage bridge type vibration membrane. The anti-sound leakage bridge type structure is used on the vibration membrane of the transducer; in order to avoid sound leakage through the narrow slots, the soft polyimide membrane is deposited on the narrow slots, which has little effect on vibration of the vibration membrane and can still keep high sensitivity.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite substrate, elastic wave device using the same, and method for manufacturing composite substrate
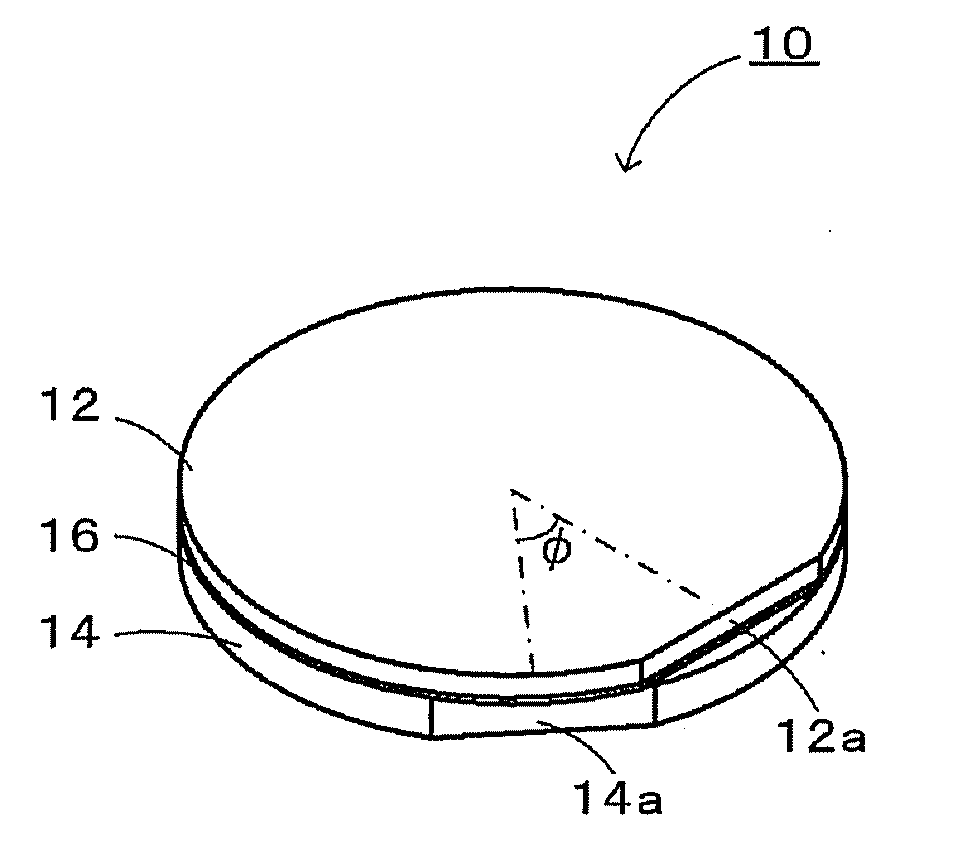
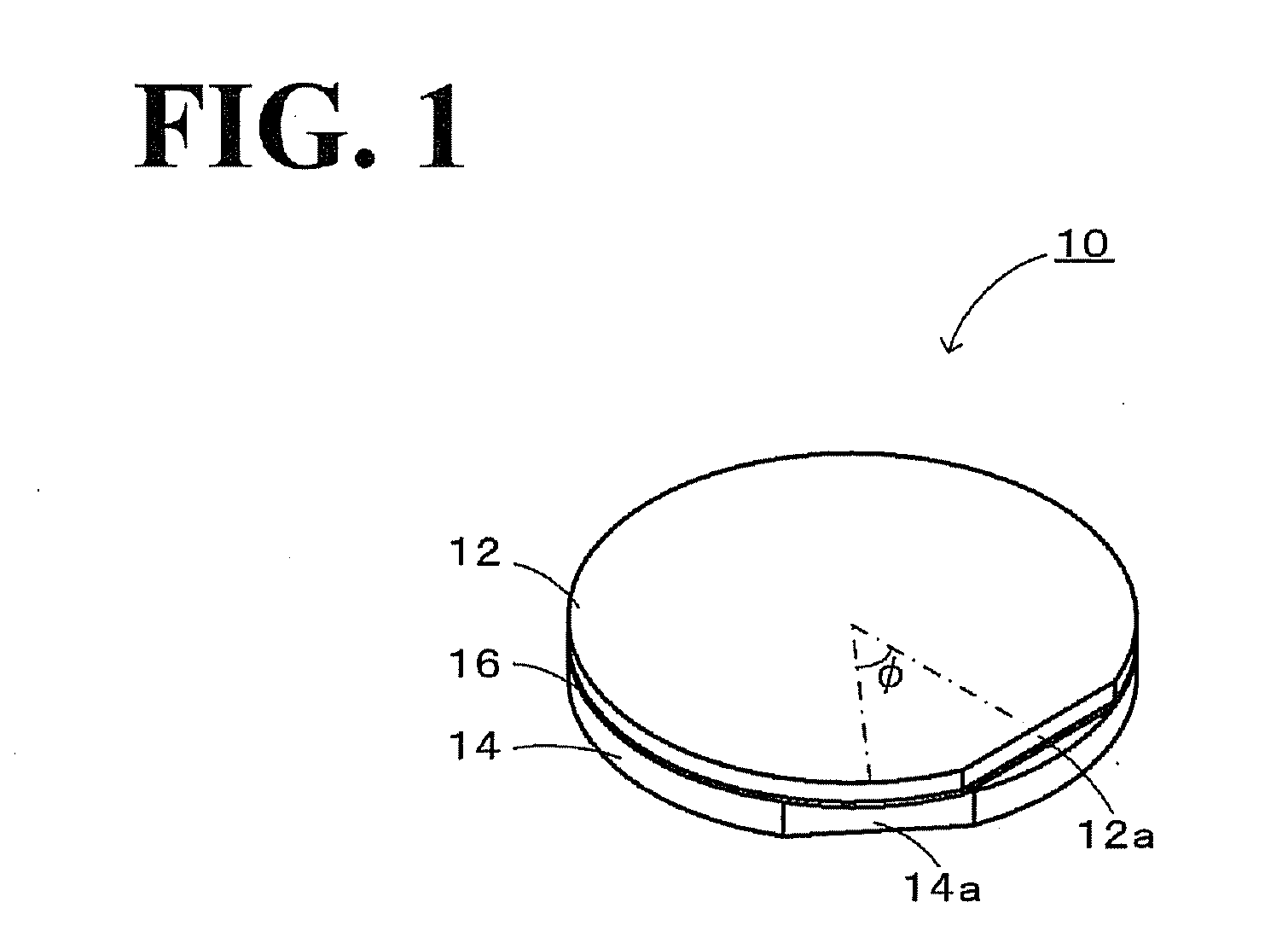
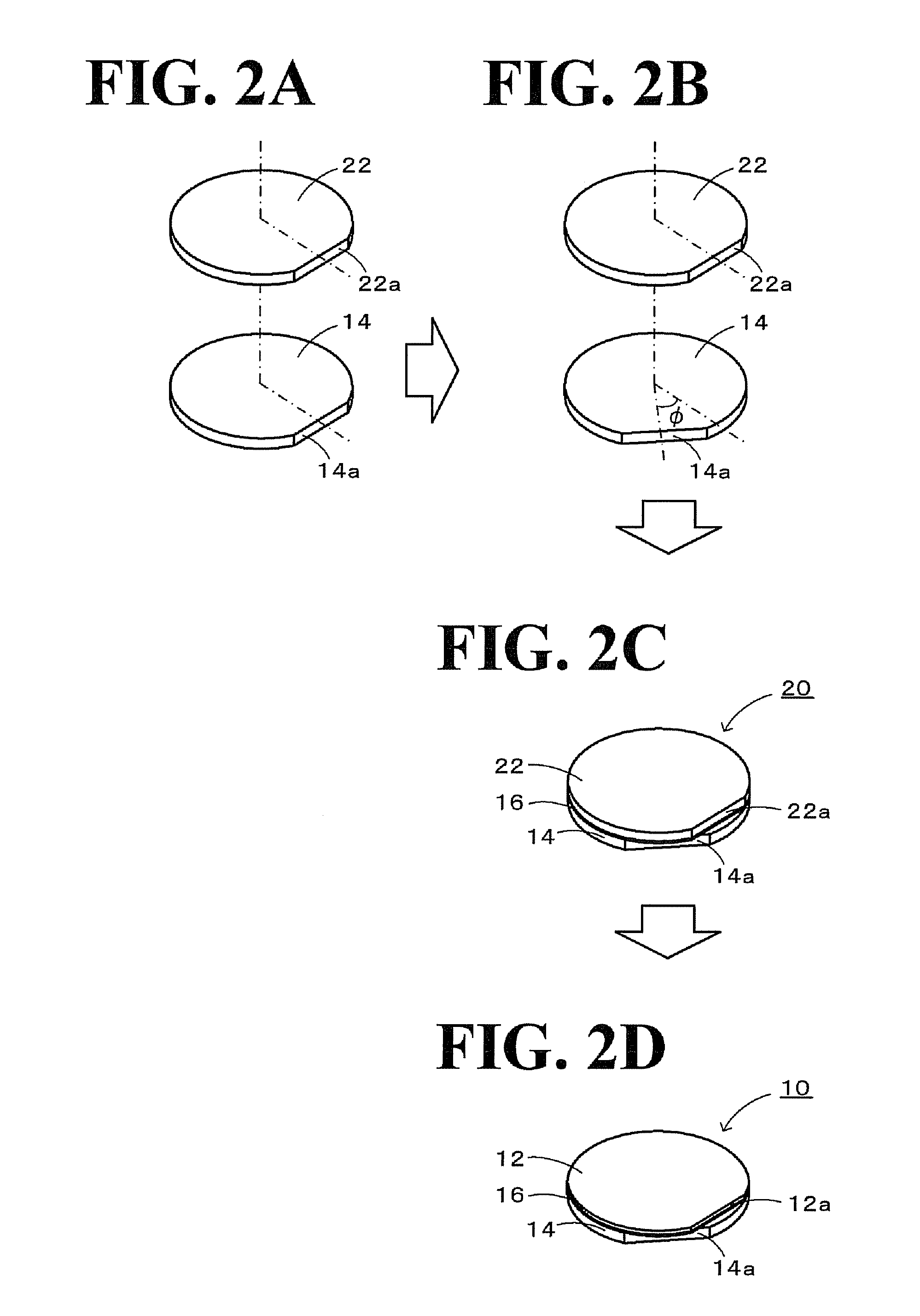
ActiveUS20100244631A1Easy to manufactureInhibit the generation of cracksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeComposite substrate
In a composite substrate 10, the piezoelectric substrate 12 which is capable of transmitting an elastic wave and a support substrate 14 which a smaller thermal expansion coefficient than the piezoelectric substrate 12 are bonded to each other. The in-plane maximum thermal strain amount which is the largest thermal strain amount in the plane of the composite substrate 10 has a minimum value and a maximum value when the piezoelectric substrate 12 and the support substrate 14 are relatively rotated 0° to 360°, and the piezoelectric substrate 12 and the support substrate 14 are bonded to each other so that the in-plane maximum thermal strain amount has the minimum value or a value in the vicinity thereof.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Low strain optical fiber cable
InactiveUS20050201696A1Significant degradationLarge strainFibre mechanical structuresYarnProtection layer
An optical fiber assembly includes a central strength member, multiple tubes, stranded yarn, a water protection layer, reinforced strength yarns and an outer sheath. At least one of the multiple tubes has one or more optical fibers disposed within. The stranded yarn is formed around the multiple tubes and the central strength member. The water protection layer is formed around the stranded yarn. The reinforced strength yarns are formed around the water protection layer and the outer sheath is formed around the reinforced strength yarns. The optical fiber assembly has an overall diameter of less than about 11.5 mm and exhibits low strain when subjected to a tension of at least 600 pounds.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Systems and methods for mounting landing gear strain sensors
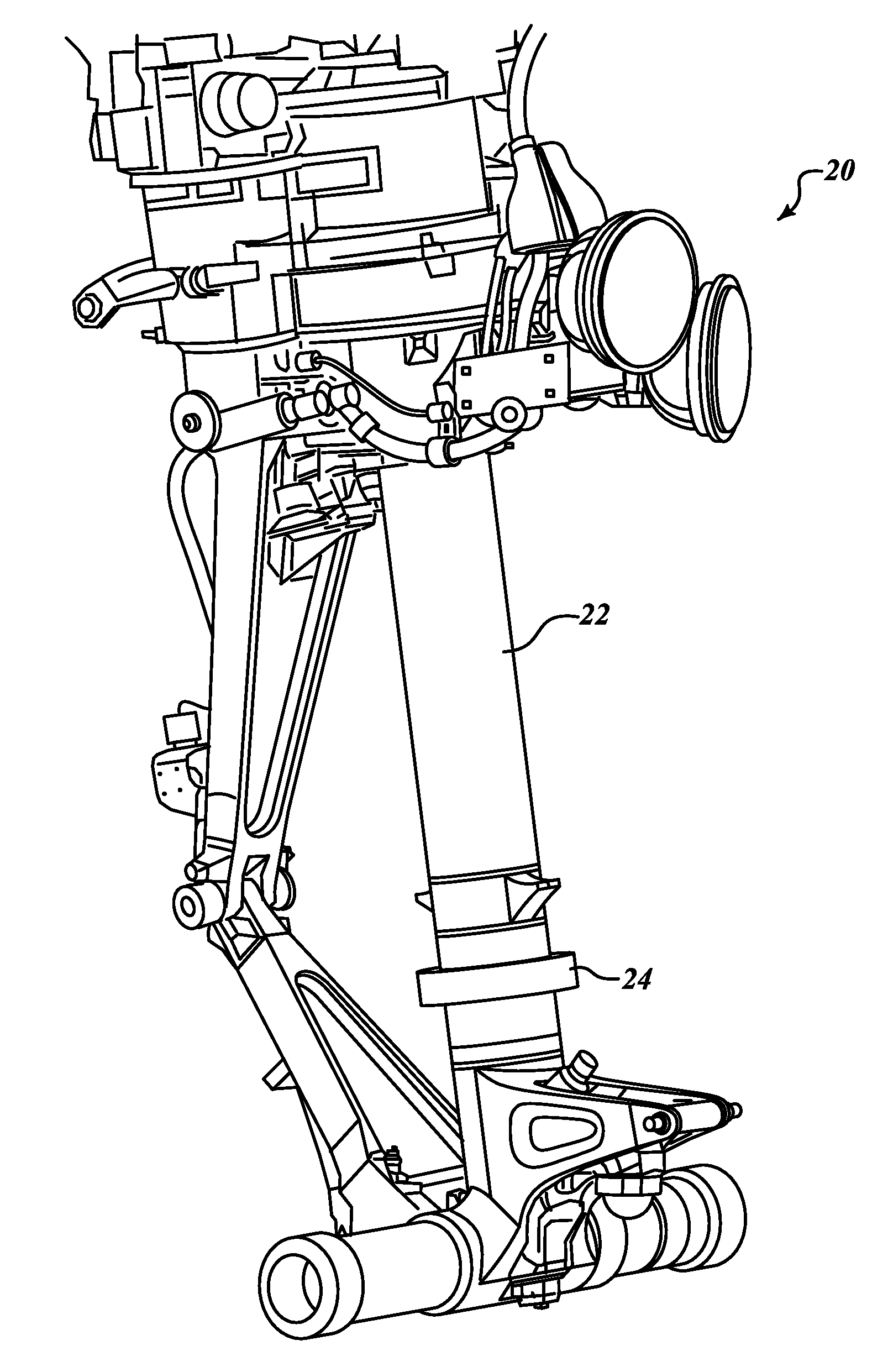
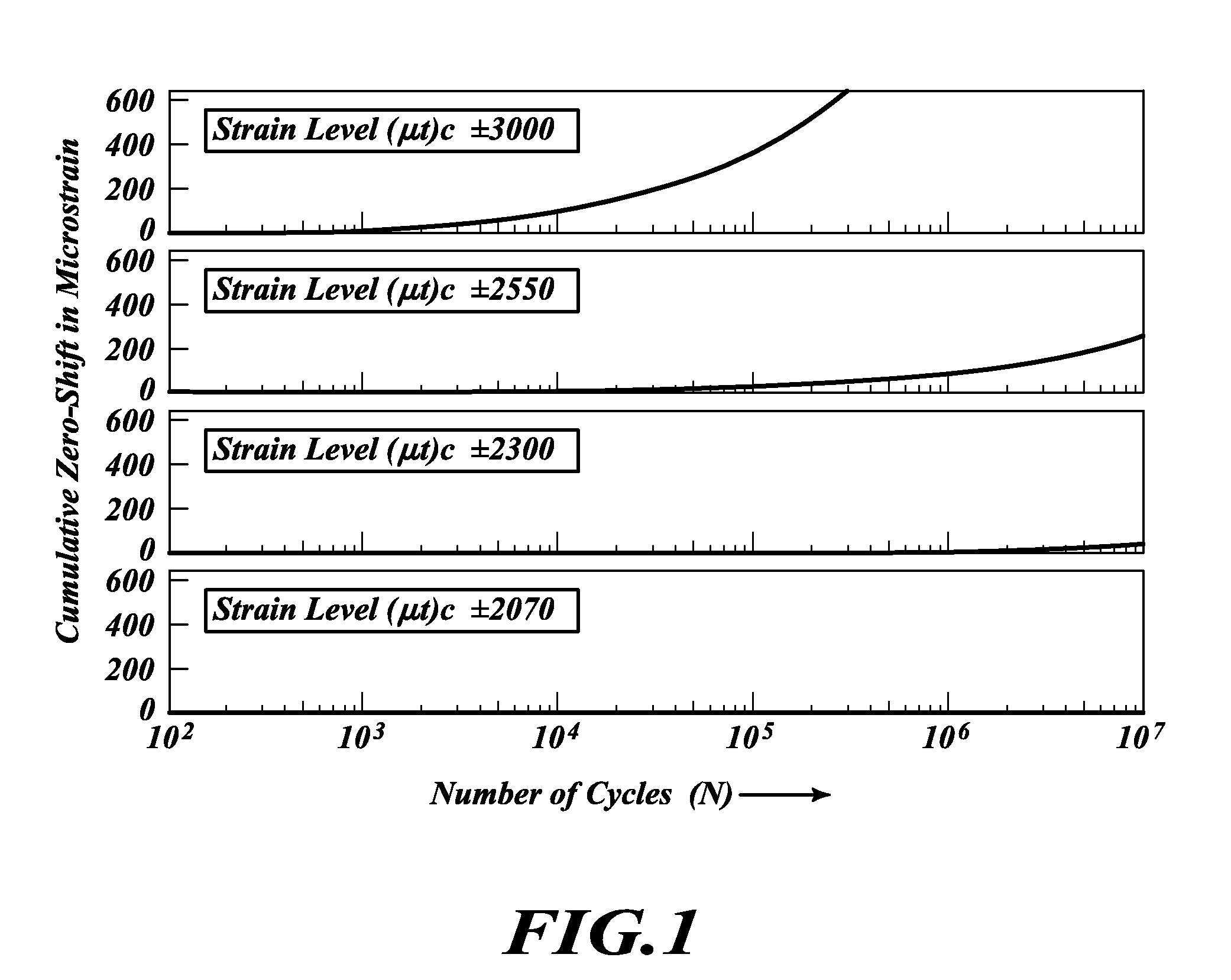
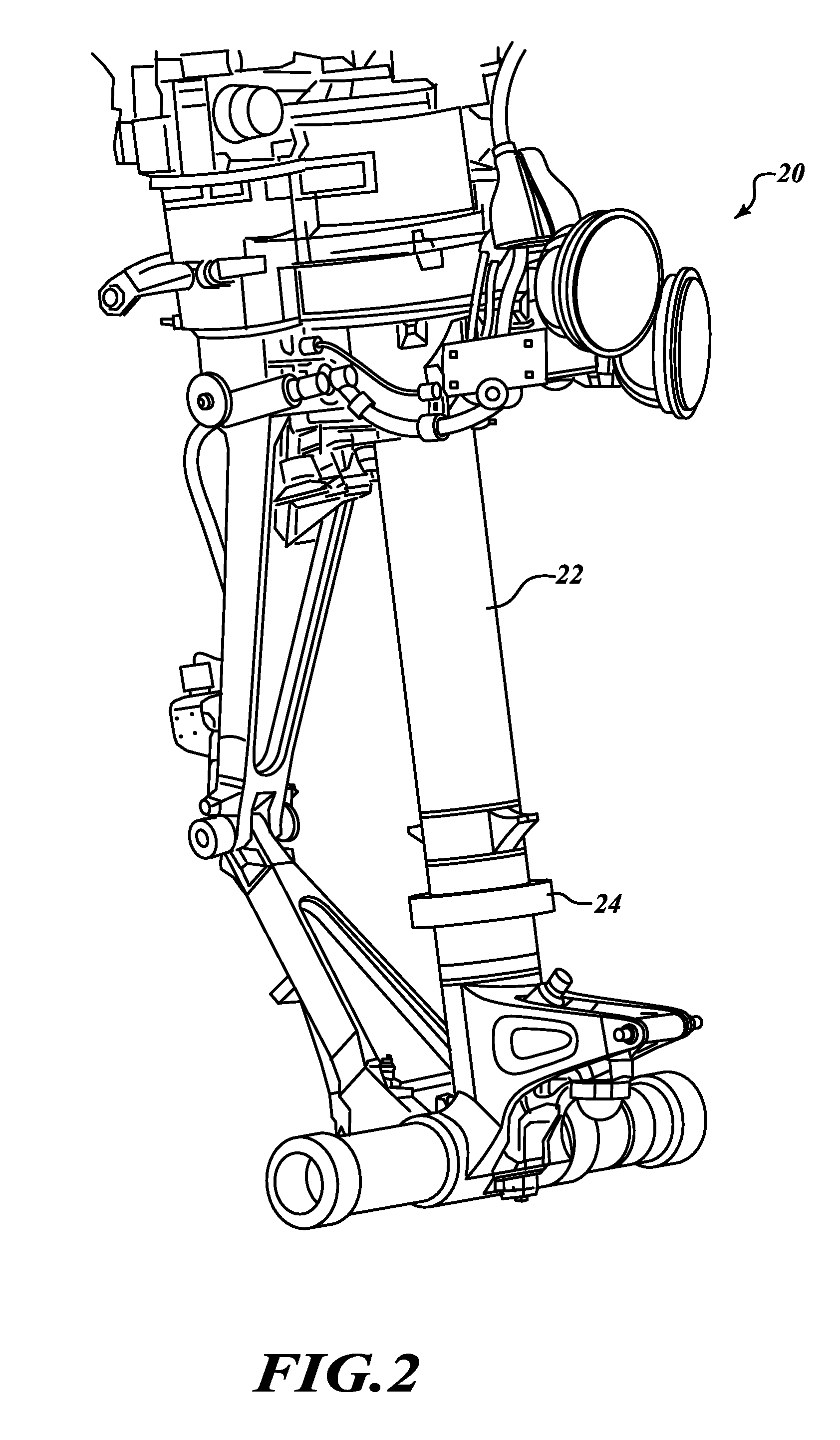
ActiveUS20120011946A1Large strainImprove accuracyForce measurementUsing electrical meansImage resolutionAircraft landing
A strain sensor device for measuring loads on aircraft landing gear. This is done by measuring strains in the lower end of the strut, by which we infer the loading in the entire landing gear structure. These strains can be very large (as high as 10,000 microstrain) and can be imposed in numerous random directions and levels. The present invention includes a removable sensor assembly. An electromechanical means is presented that can accommodate large strains, be firmly attached to the strut, and provide good accuracy and resolution.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Optical fibre grating accelerometer based on cantilever beam deflection
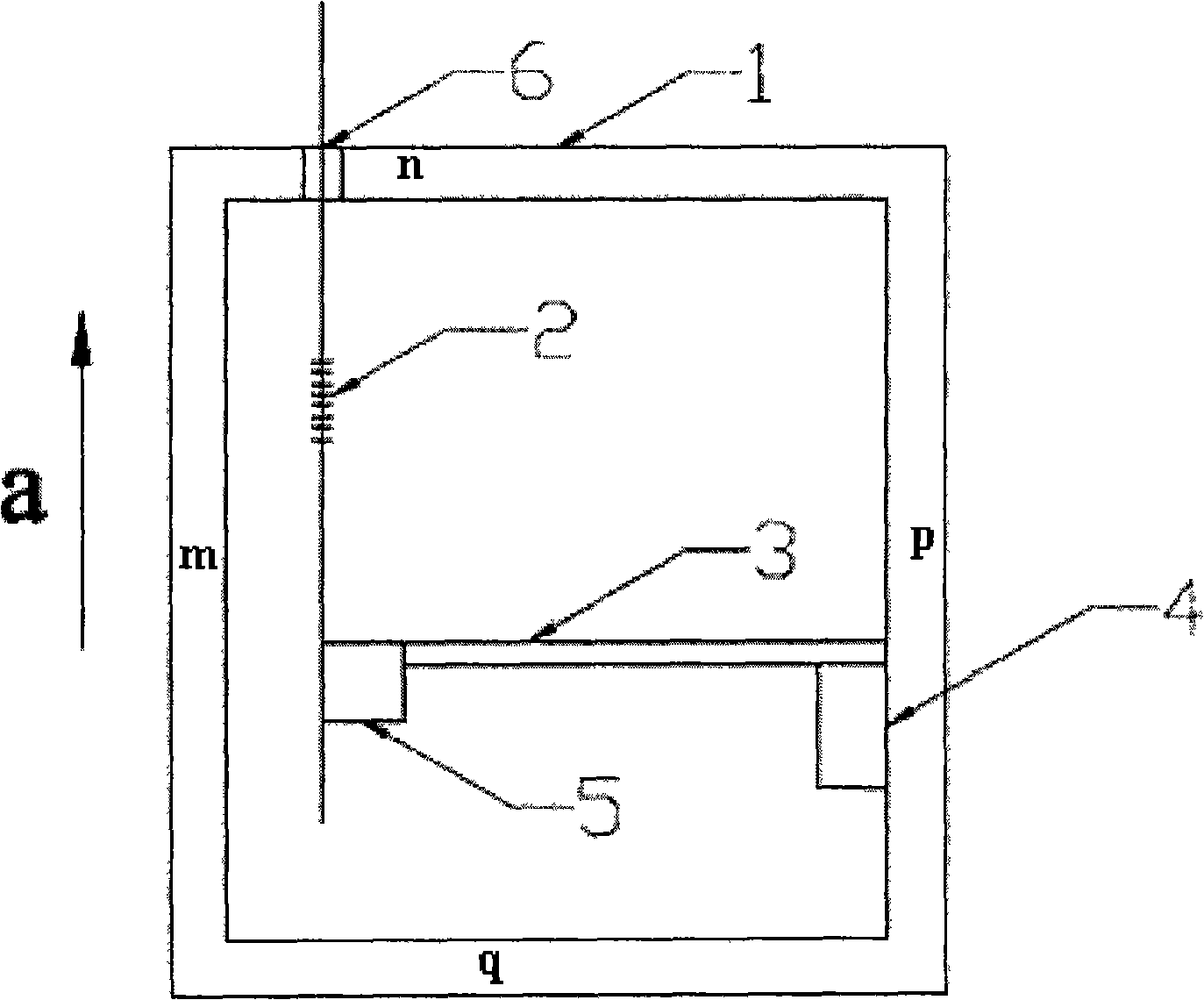
InactiveCN101285846AHigh sensitivityLarge strainTelevision system detailsImpedence networksCantilevered beamAccelerometer
The invention relates to the optical fiber sensor technical field, disclosing an optical fiber grating accelerometer based on cantilever beam deflection. The accelerometer comprises an outer casing 1 used as a support structure of the accelerometer, an optical fiber grating 2 used to measure acceleration, a cantilever beam 3 with one end horizontally fixed on the third sidewall p of the accelerometer and a mass block 5 fixed at the other end of the cantilever beam 3, wherein the outer casing 1 has a first sidewall m, a second sidewall n, a third sidewall p and a fourth sidewall q; one end of the optical fiber grating 2 is fixed with the mass block 5, while the other end is parallel to the first sidewall m and passes through the hole 6 on the second sidewall n of the accelerometer to extend outside the accelerometer; the cantilever beam 3 is used to send vibration signal to the optical fiber grating 2; and the mass block 5 is used to adjust the sensitivity and the natural vibration frequency of the accelerometer. The optical fiber grating accelerometer increases sensitivity and improves packaging technology.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for measuring temperature and strain of isotactic ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber gratings simultaneously based on Brillouin scattering
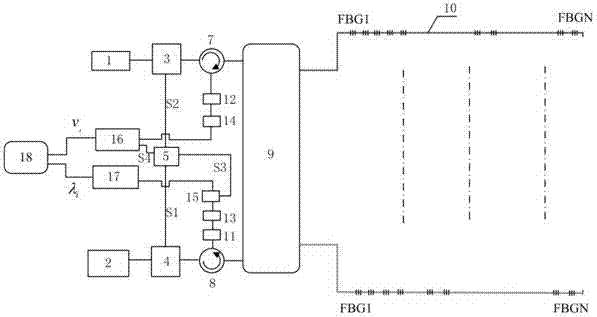
InactiveCN103674086AOptimize layoutLower deployment costsThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiberCross sensitivity
The invention discloses a method and device for measuring the temperature and strain of isotactic ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber gratings simultaneously based on Brillouin scattering. The method includes the steps that the ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber gratings are continuously and dynamically etched through monopulse laser energy based on the drawing tower technology to obtain high-capacity optical fiber grating array sensing fibers, wherein m optical fibers and 2*m optical switches are connected to serve as a sensing probe; the reflection center wavelength lambda[i] and Brillouin frequency shift v[i] of each optical fiber grating are obtained through a high-speed CCD wavelength demodulation module and a Brillouin frequency shift heterodyne demodulation module; solving is carried out according to the Brillouin frequency shift and temperature and strain parameters of the optical fiber gratings to obtain the temperature and strain of the optical fiber gratings at each position. The method and device overcome the defects that the Brillouin sensing technology is low in precision and low in speed, simplify high-capacity ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber grating array optical fiber cabling complexity, improve high-capacity ultralow-reflectivity optical fiber grating array optical fiber cabling operability, overcome the cross sensitivity of the temperature and strain of the optical fiber gratings and improve distributed sensing detection precision.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Polycrystalline foams exhibiting giant magnetic-field-induced deformation and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS20110064965A1Reduce constraintsLarge poresInorganic material magnetismThin material handlingAlloySingle crystal
Magnetic materials and methods exhibit large magnetic-field-induced deformation / strain (MFIS) through the magnetic-field-induced motion of crystallographic interfaces. The preferred materials are porous, polycrystalline composite structures of nodes connected by struts wherein the struts may be monocrystalline or polycrystalline. The materials are preferably made from magnetic shape memory alloy, including polycrystalline Ni—Mn—Ga, formed into an open-pore foam, for example, by space-holder technique. Removal of constraints that interfere with MFIS has been accomplished by introducing pores with sizes similar to grains, resulting in MFIS values of 0.12% in polycrystalline Ni—Mn—Ga foams, close to the best commercial magnetostrictive materials. Further removal of constraints has been accomplished by introducing pores smaller than the grain size, dramatically increasing MFIS to 2.0-8.7%. These strains, which remain stable over >200,000 cycles, are much larger than those of any polycrystalline, active material.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
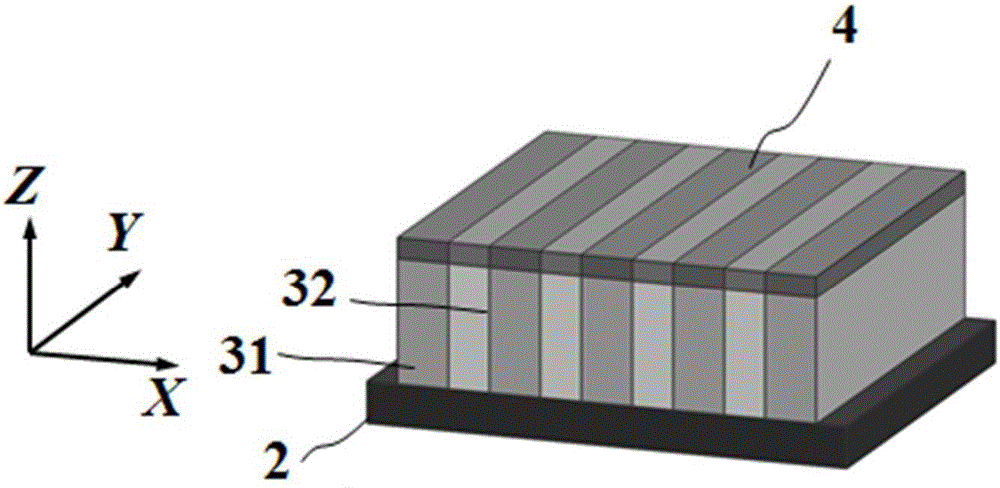
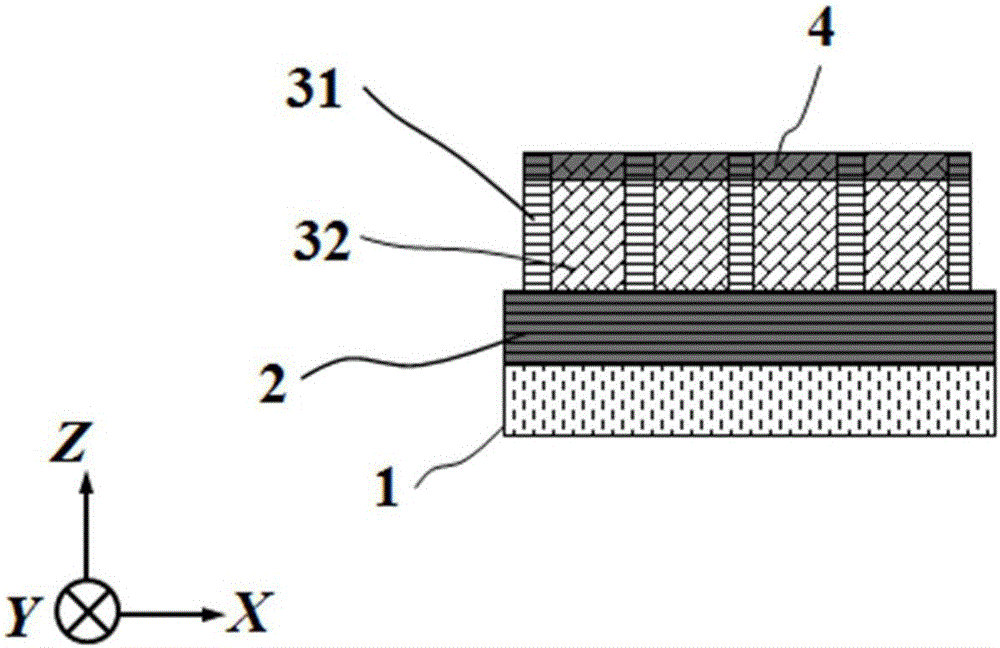
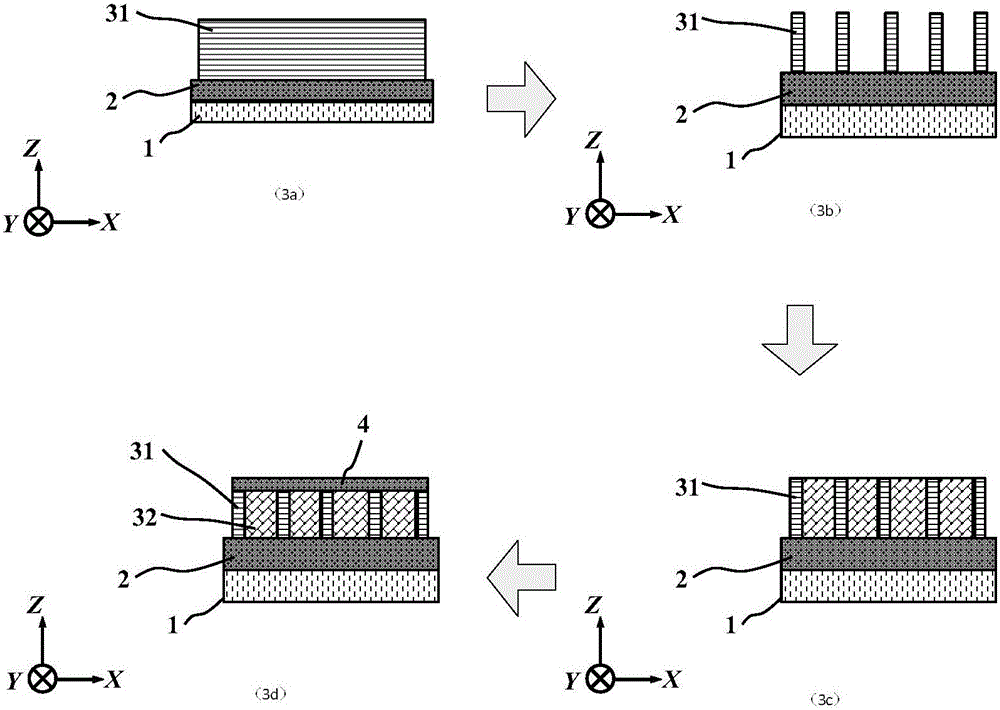
Transverse IV-clan element quantum well photoelectric detector and preparation method
ActiveCN105006500AImprove the effect of bandgap adjustmentEffective adjustment of absorption wavelength rangeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSpectral responseSingle crystal
The invention discloses a transverse IV-clan element quantum well photoelectric detector and mainly solves problems of high material toxicity and high cost of a conventional infrared photoelectric detector. The transverse IV-clan element quantum well photoelectric detector comprises a substrate (1), a bottom electrode (2), an absorption region (3), and a top electrode (4). A quantum well (31) uses a GeSn strain monocrystalline material with a Sn component more than or equal to 0 but less than 0.3. A barrier layer (32) uses a monocrystalline material with a Sn component more than or equal to 0 but less than 0.3 and a Ge component more than or equal to 0 but less than 1. The quantum well (31) and the barrier layer (32) are stacked transversely to form the absorption region arranged between the bottom electrode and the top electrode. According to the invention, SiGeSn monocrystalline material changes in size in an epitaxial process so as to generate transverse tensile strain in the GeSn quantum well material, thereby changing a GeSn material band gap and enlarging the spectral response range of the detector. The SiGeSn monocrystalline material can be used for producing large-scale integrated circuit.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Hub unit with sensor
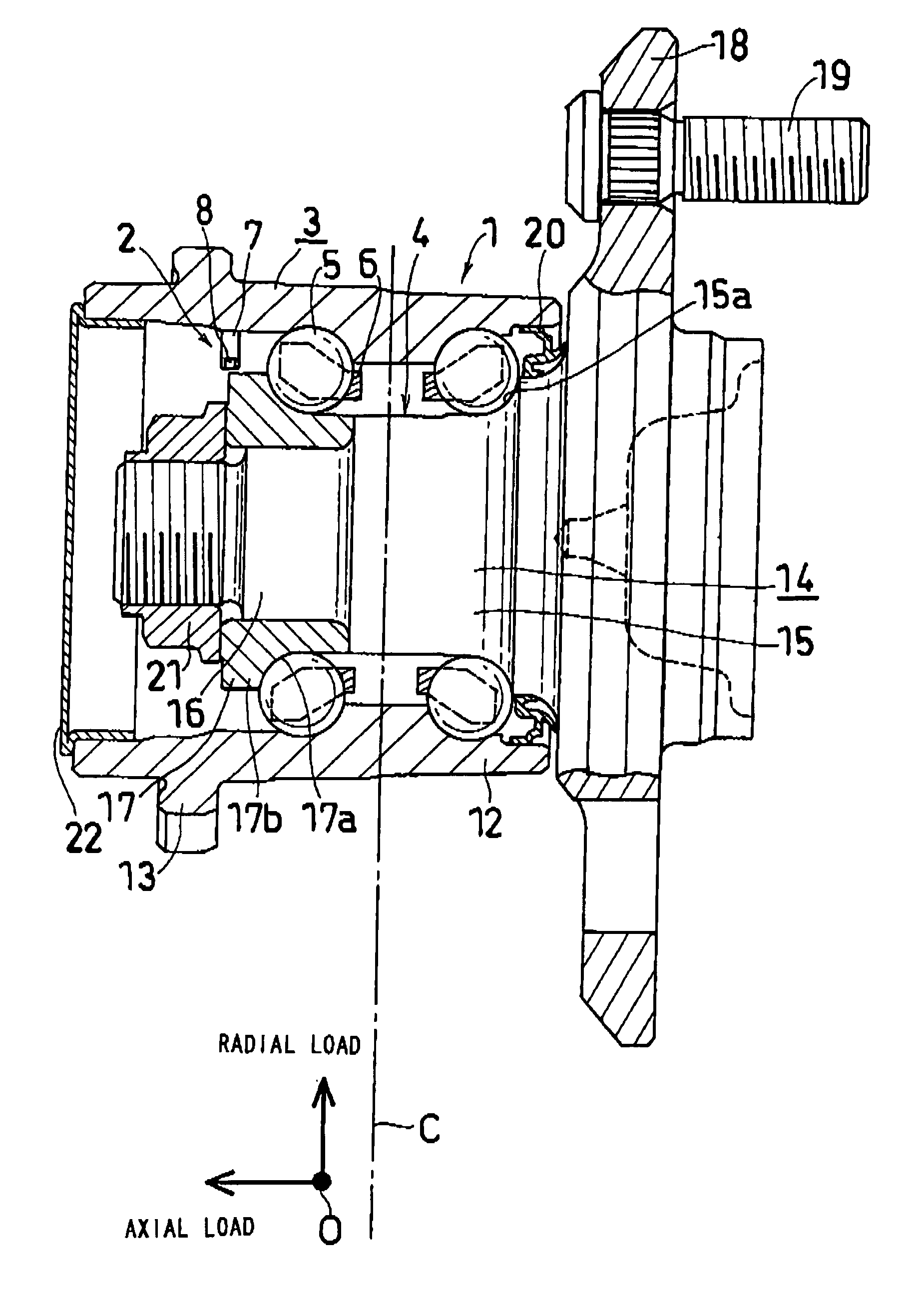
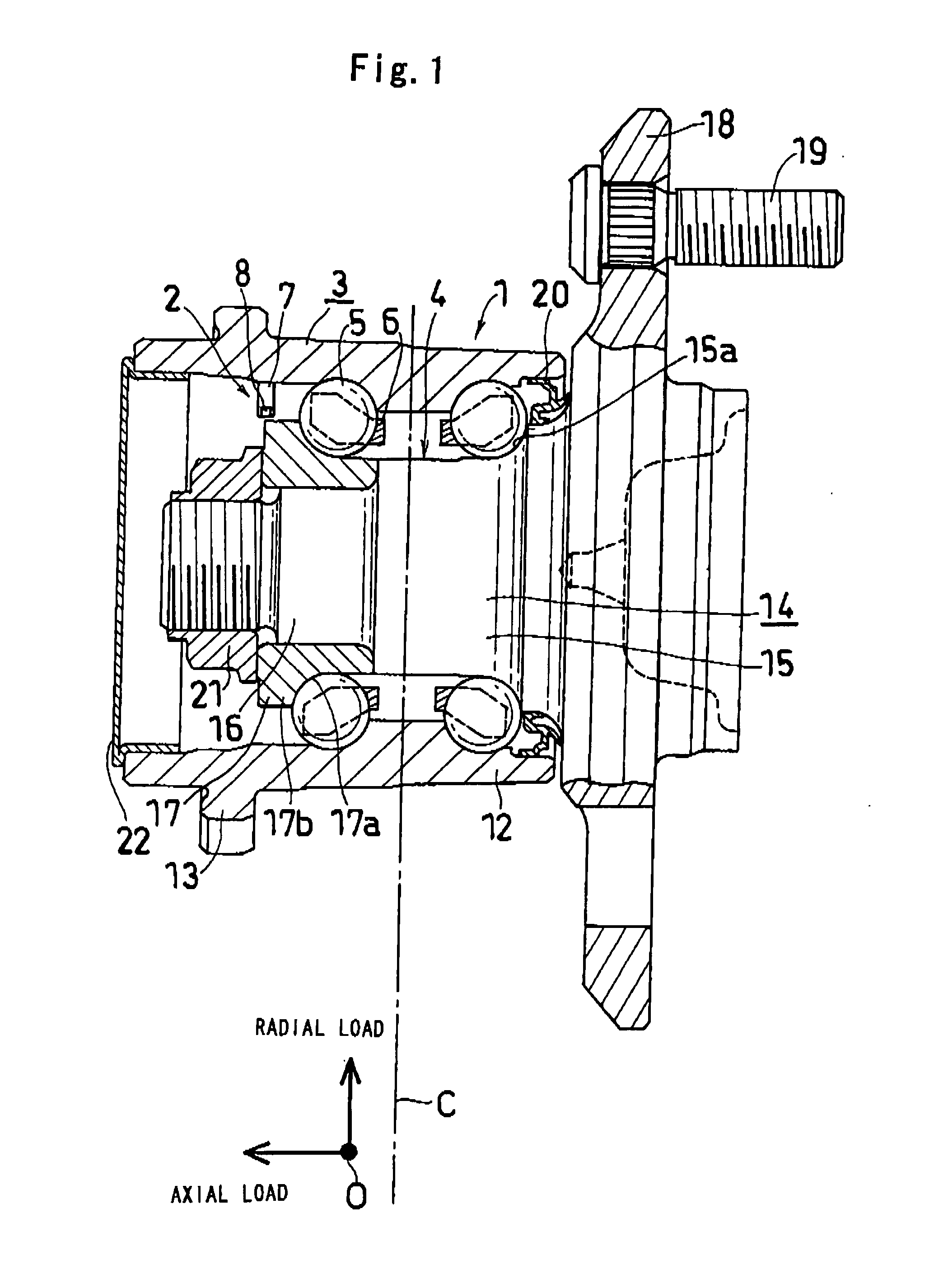
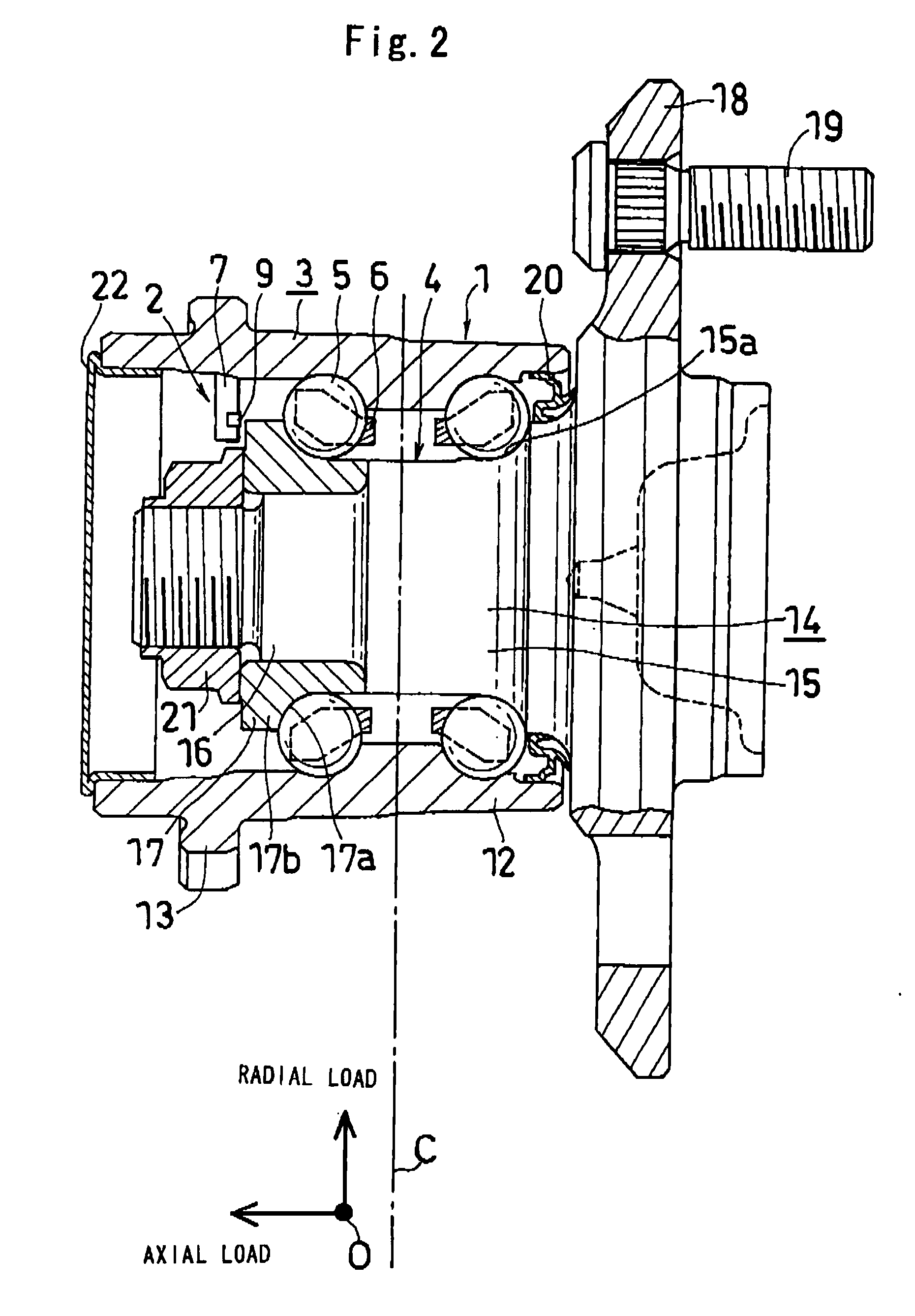
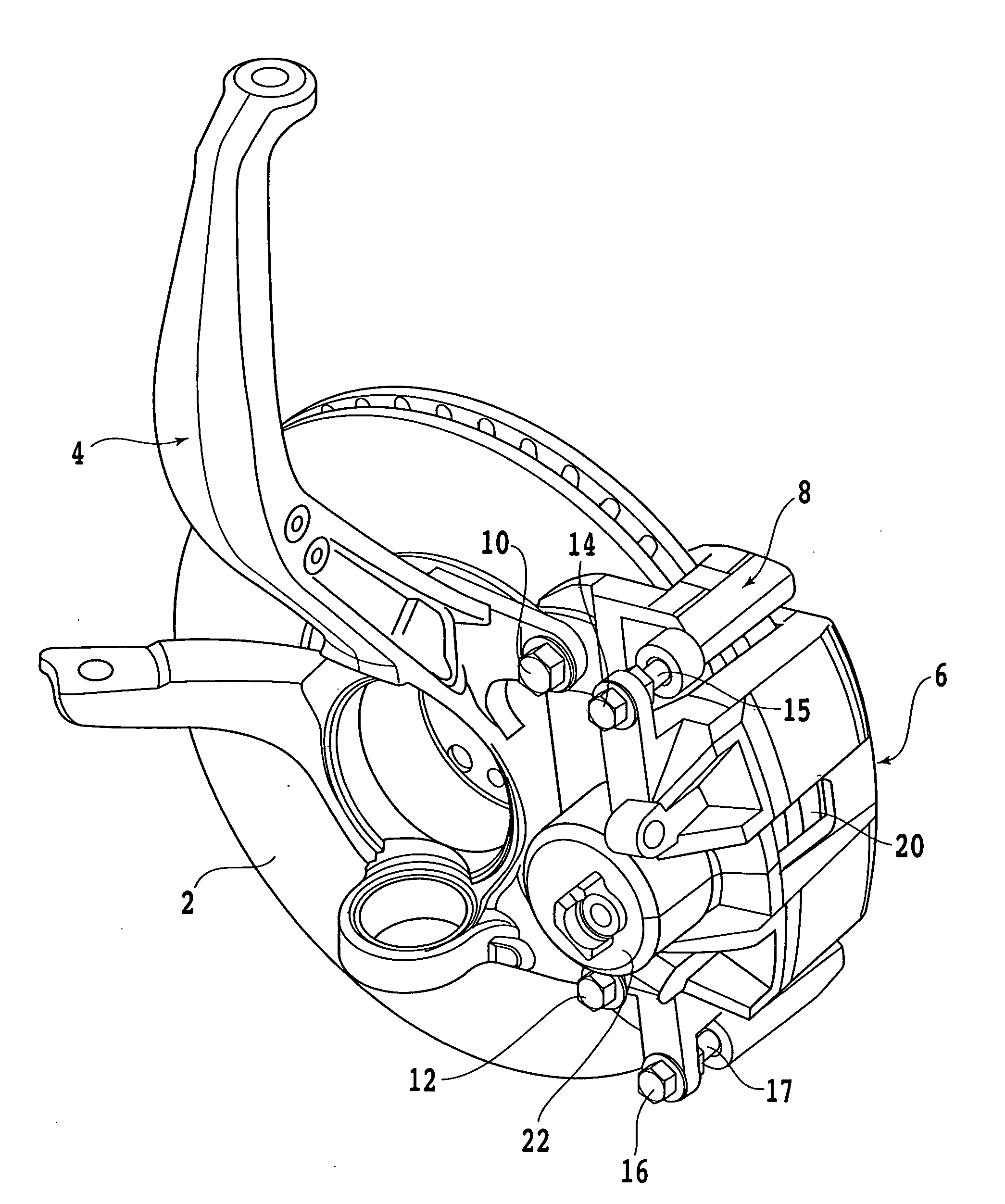
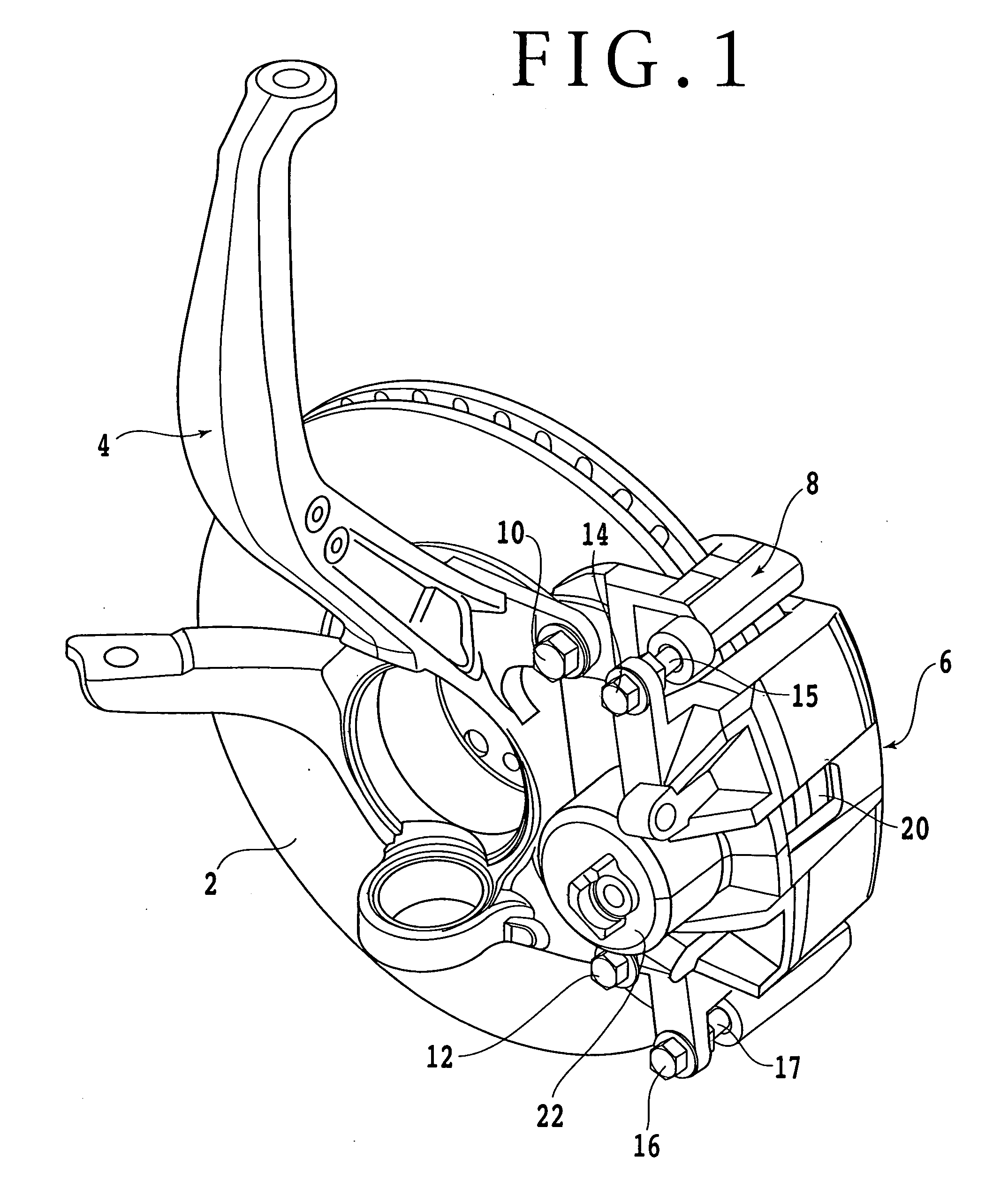
InactiveUS20070157742A1High accuracyImprove accuracyRolling contact bearingsBearing assemblyInverse magnetostrictive effectTensile strain
A hub unit with a sensor comprises a hub unit 1 including a body-side raceway member 3, a wheel-side raceway member 4 and two rows of rolling elements 5, and a sensor device 2. The sensor device 2 includes a magnetostrictive sensor 8 for detecting the inverse magnetostrictive effect, and the magnetostrictive sensor 8 is mounted to the body-side raceway member 3 so as to be capable of measuring the tensile strain in the uppermost part of an inner wheel 17 of the wheel-side raceway member 4. From the output of the magnetostrictive sensor 8, the tire grounding load and the rotational velocity are detected.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
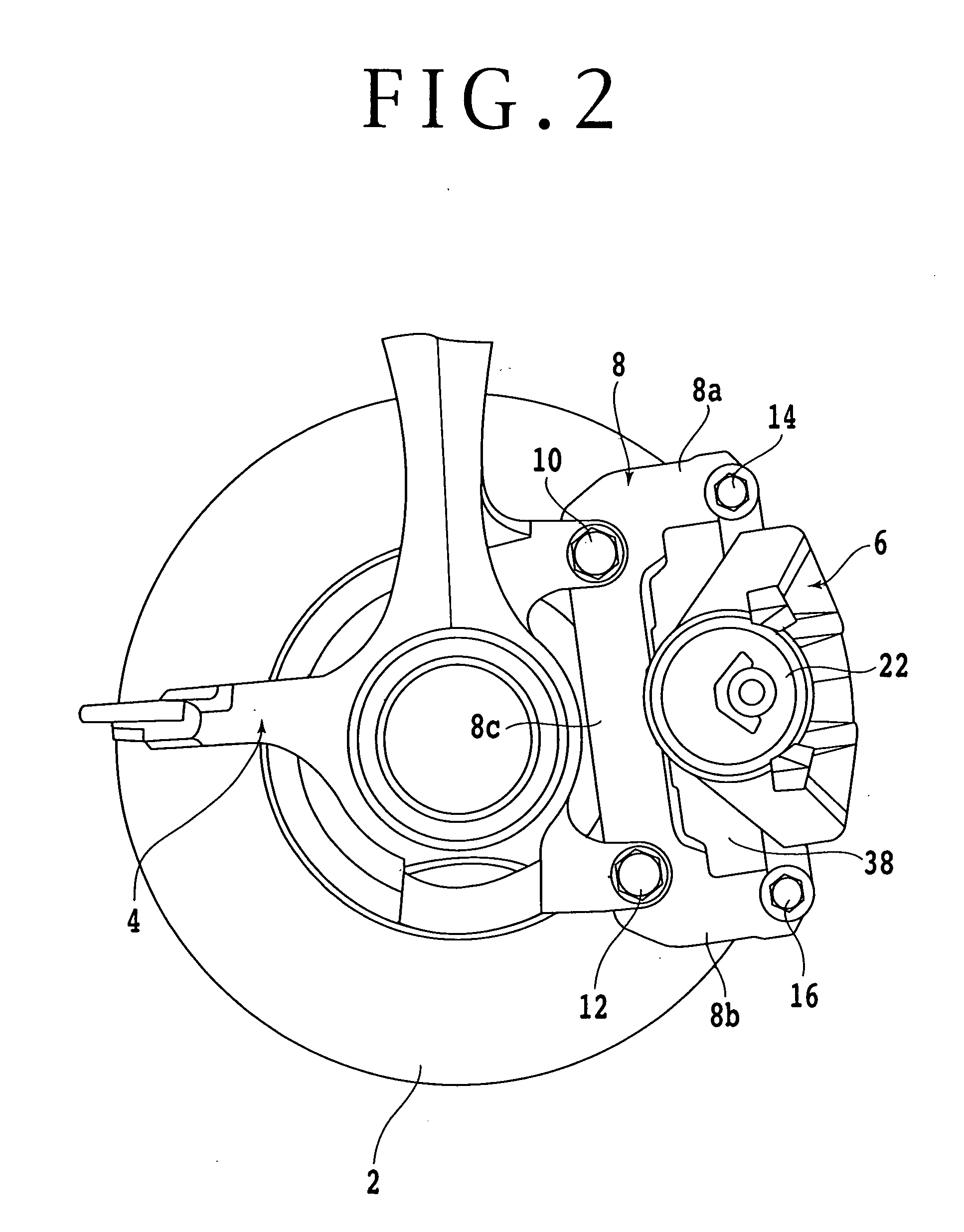
Brake force detecting device
InactiveUS20080077302A1Stable outputStable detectionAxially engaging brakesDigital data processing detailsStrain gaugeEngineering
A brake force detecting device for detecting strain in a caliper bracket. The brake force detecting device includes a sensor plate fixed to the outside surface of a brake load receiving portion of the caliper bracket in the circumferential direction of a brake disc and a strain gauge attached to the sensor plate for detecting strain generated in the sensor plate. The strain gauge is connected to an amplifier.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
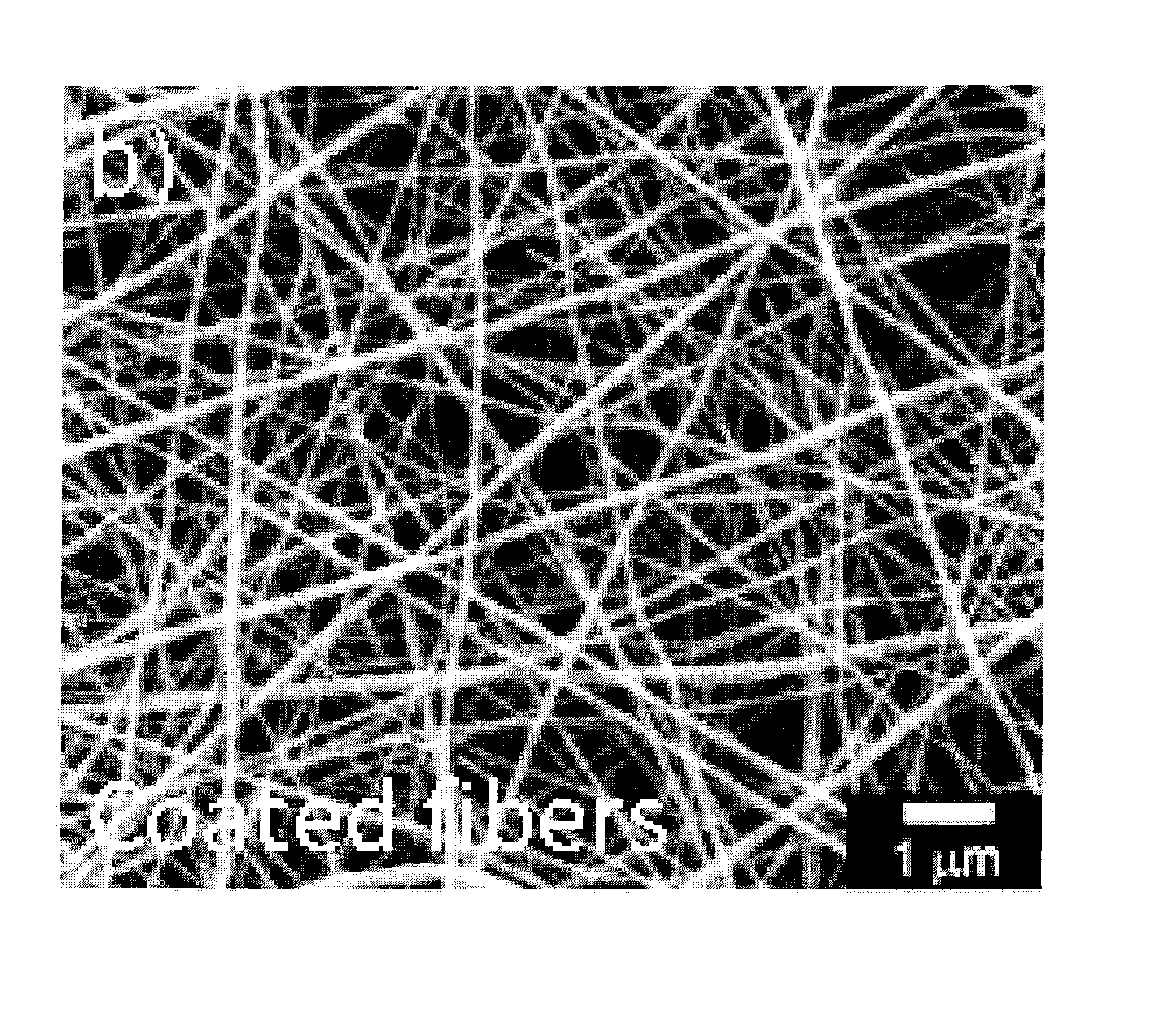
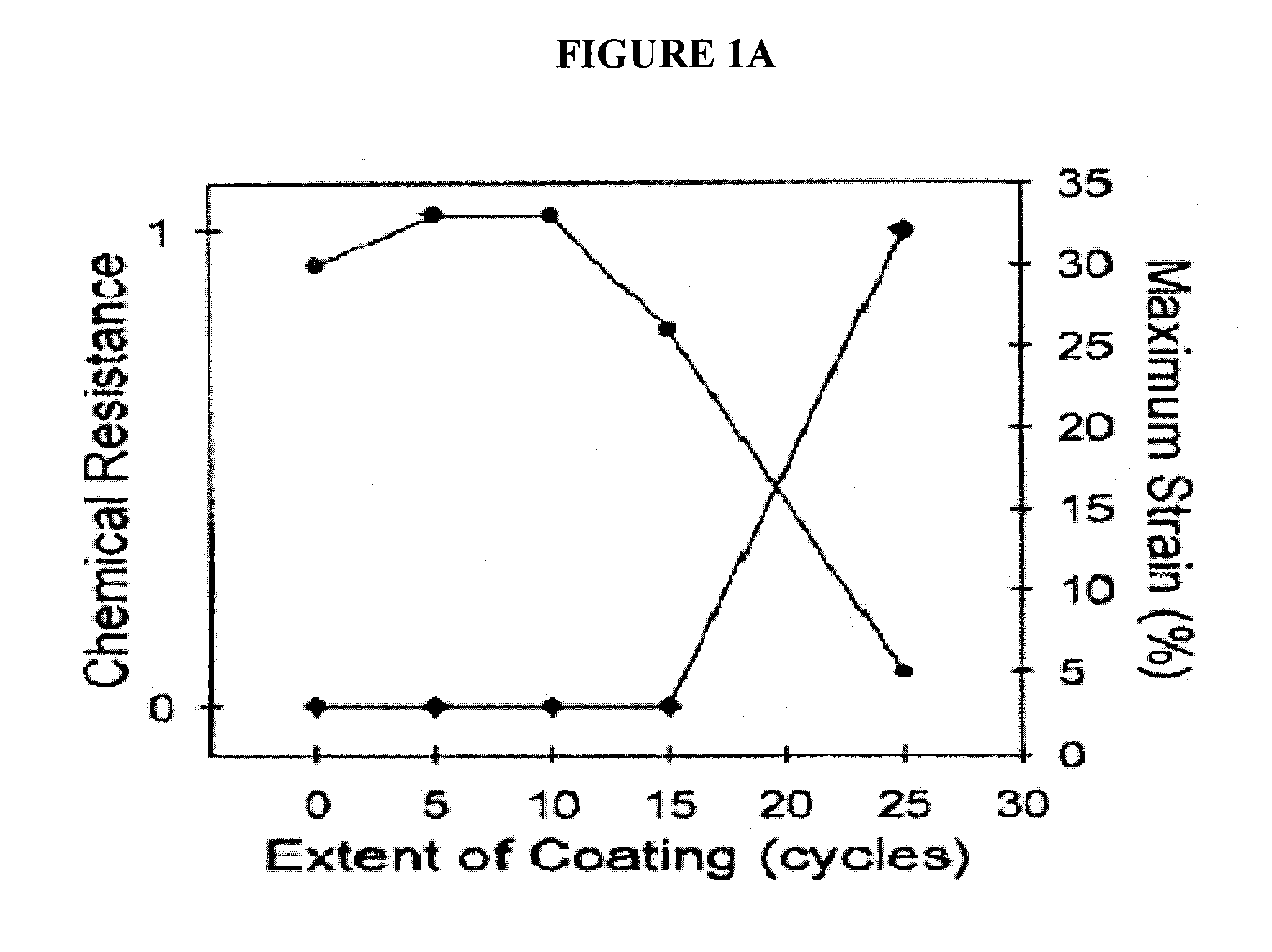
Nanostructured polymer-inorganic fiber media
A fiber media and a filter device. The fiber media has a plurality of nanofibers formed of a polymer material, having diameters less than 1 micron, and formed into a fiber mat. A barrier layer is disposed on the nanofibers to prevent dissolution of the nanofibers in the fiber mat upon exposure of the fiber mat to a solvent of the polymer material. The barrier layer coated nanofibers have a maximum strain before breakage of at least 2%. The filter device includes the fiber media and a support attached to the fiber mat.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST +1
High-power overload 1KPa silicon micropressure sensor chip and manufacturing method
InactiveCN103487178ALow costProcess is easy to implementFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationForce measurementBatch productionMicro structure
Provided are a high-power overload 1KPa silicon micropressure sensor chip and a manufacturing method. The high-power overload 1KPa silicon micropressure sensor chip is characterized by being of a beam-single-island double-sided double-piece micro structure. A U-shaped pressure sensitive resistor is arranged on an I beam in the front side of an upper chip body, an aluminum electrode lead and a lead welding pad are arranged at the periphery of a shallow groove, a residue membrane is connected with a central square support on the back side of the upper chip body at the portion opposite to the shallow groove to form a single hard core-shaped sensitive membrane, a peripheral sealing face and an overpressure stopping groove are arranged on the front side of a lower chip body, a pressure tap through hole is formed in the center of the front side of the lower chip body, the upper chip body and the lower chip body are sealed by rubber and are divided in a scribing mode to form the single micropressure sensor chip. An MEMS technique is utilized to manufacture the pressure sensitive resistor and the I beam structure, a KOH wet method is used for etching and manufacturing the single hard core-shaped sensitive membrane, and the KOH wet method is further used for etching the structure of the lower chip body. The high-power overload 1KPa silicon micropressure sensor chip has the advantages that due to the stress concentration effect of a beam structure, the pressure sensitive resistor can obtain the largest strain; the flexibility for acquiring a micropressure range can reach to 20mV / 1KPa (1mA excitation); the linearity reaches to 0.05%FS; the overpressure stopping groove achieves 50-time overpressure resistance protection in 1KPa pressure measurement; batch production of wafers is achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG ACAD OF INSTR SCI
High-strength cold-rolled steel sheet and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20140377582A1Improve bending performanceHigh tensile strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingManganeseHardness
A high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet includes, as a component composition, by mass %: C: 0.075% to 0.300%; Si: 0.30% to 2.50%; Mn: 1.30% to 3.50%; P: 0.001% to 0.050%; S: 0.0001% to 0.0100%; Al: 0.001% to 1.500%; and N: 0.0001% to 0.0100%, in which a surface microstructure contains residual austenite of 3% to 10% and ferrite of 90% or less by volume fraction, an inner microstructure at a depth of t / 4 from the surface assuming that a sheet thickness is t contains residual austenite of 3% to 20% by volume fraction, a ratio Hvs / Hvb between a surface hardness Hvs of the steel sheet surface and a hardness Hvb at a depth of ¼ of the thickness is more than 0.75 to 0.90, and a maximum tensile strength is 700 MPa or more.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Semiconductor device which employs an interlayer insulating film of a low mechanical strength and a highly reliable metal pad, and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7202565B2Avoid crackingPrevent peelingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectEngineering
A semiconductor device includes: multiple kinds of interlayer insulating films formed on a semiconductor substrate and having different elastic moduli, respectively; a metal pad arranged on said multiple kinds of interlayer insulating films; the interlayer insulating film of a low elastic modulus having the lowest elastic modulus and having an opening located under the metal pad, the interlayer insulating film of a not-low elastic modulus having the elastic modulus larger than the elastic modulus of the interlayer insulating film of the low elastic modulus, being layered in contact with the interlayer insulating film of the low elastic modulus, and continuously extending over the opening and a region surrounding the opening and a metal interconnection layer arranged under the metal pad, filling the opening in the interlayer insulating film of the low elastic modulus, and being in contact with the interlayer insulating film of the not-low elastic modulus.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
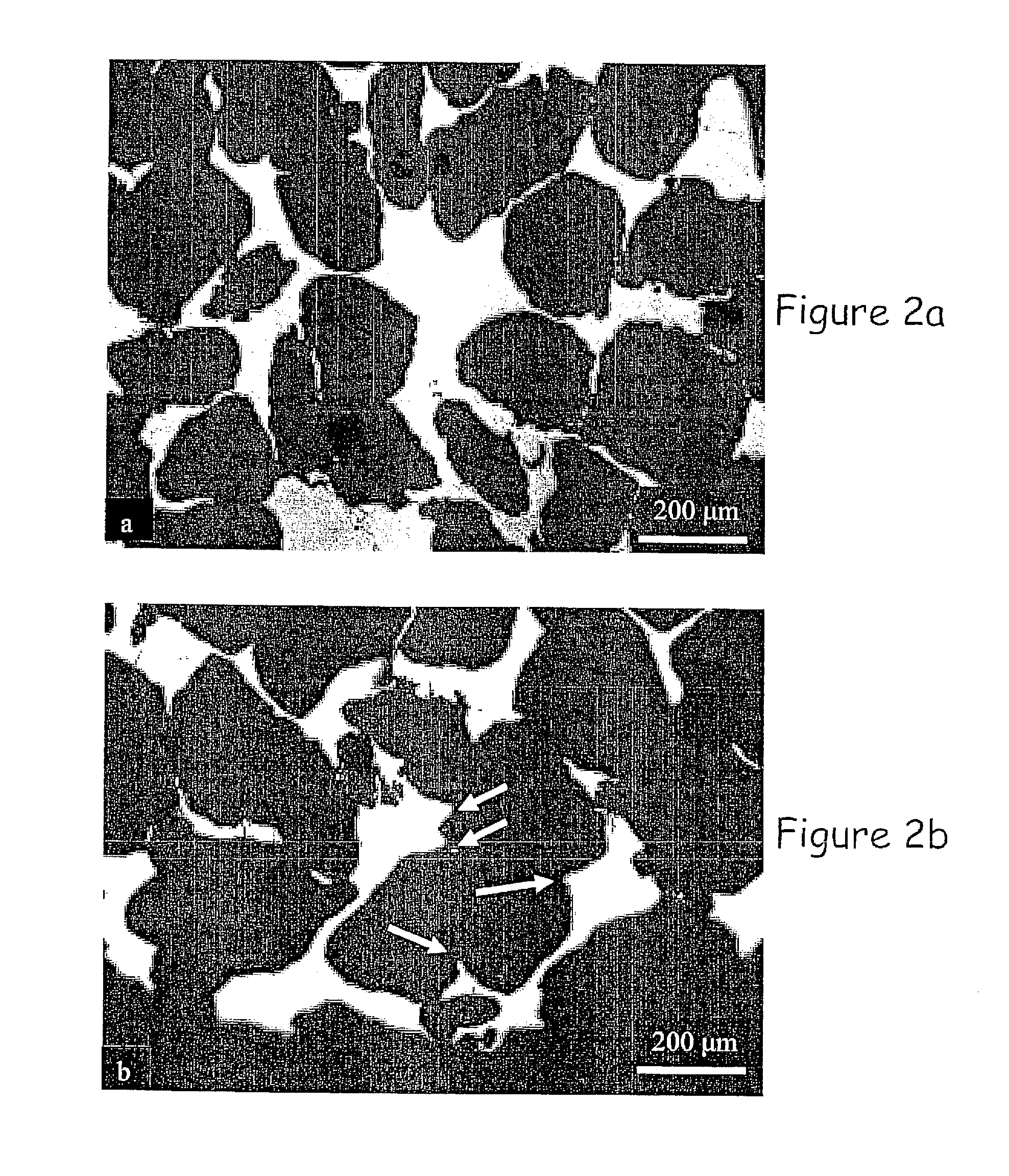
Forging method for efficiently healing hole flaws inside blank with large height-diameter ratio
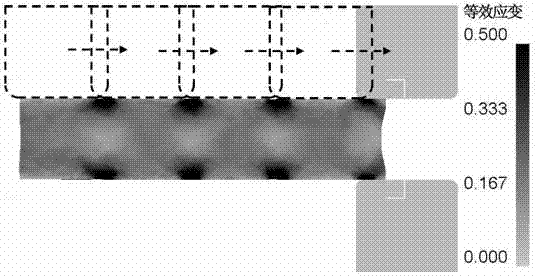
ActiveCN102756062APromote healingLarge strainMetal-working apparatusThermal insulationDiameter ratio
The invention belongs to the field of forging, and specifically relates to a forging method with a small screw-down rate, which is capable of efficiently healing hole flaws inside a blank with a height-diameter ratio. The forging method adopts a numerical simulation technique to research the distribution status of strain inside the blank in the conventional forging process, thus providing a radial wide anvil compaction process which comprises the following steps of: pressing down the blank by virtue of the radial wide anvil compaction process, wherein flat plates serve as upper and lower anvil; after radial the wide anvil compaction process, returning the blank to a furnace to be re-heated and be subjected to thermal insulation; and turning over the blank by 90 degrees and drawing out the blank by the upper and lower anvil. The forging method is suitable for a free forging process for various blanks (for example continuous-casting blanks) or steel ingots with a large height-diameter ratio and the like, and particularly has good effects on the blank with the large height-diameter ratio and serious centre looseness. Forged pieces produced by the forging method can ensure the healing of the hole flaws inside the blank with the large height-diameter ratio, so that the possibility of forged piece scrapping caused by the loosened and non-forged center of the forged piece is greatly reduced; and moreover, a forged piece with a larger size can be manufactured by virtue of a small screw-down rate.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Liquid-ejecting head, liquid-ejecting apparatus, piezoelectric element, and piezoelectric material
ActiveUS20110102518A1Low environmental loadLarge strainInking apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesElectric fieldPhase transition
A liquid-ejecting head includes a pressure-generating chamber communicating with a nozzle opening, and a piezoelectric element. The piezoelectric element has piezoelectric layer contains a perovskite complex oxide containing Bi, La, Fe, and Mn and can undergo electric-field-induced phase transition.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Hyper-redundant continuum robot driven by shape memory alloy
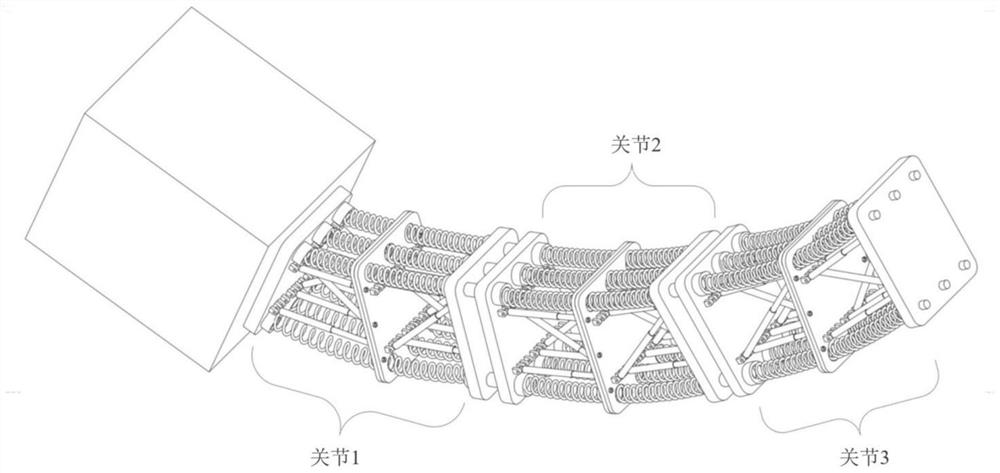
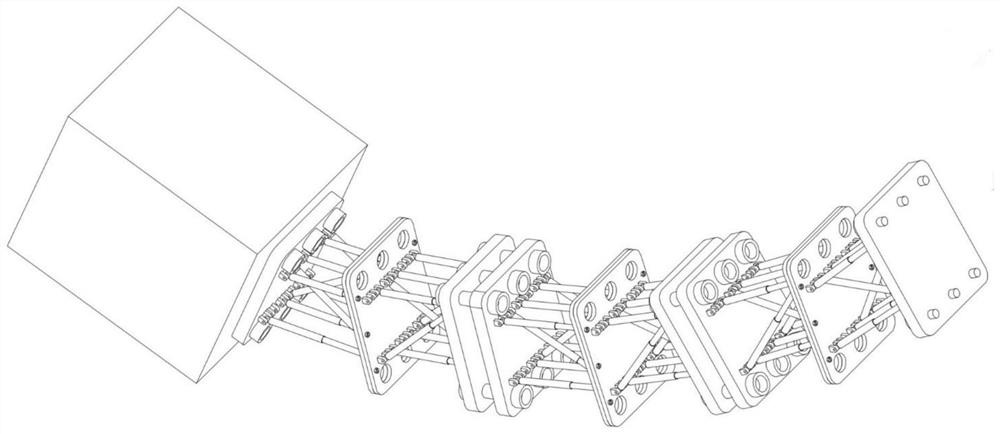
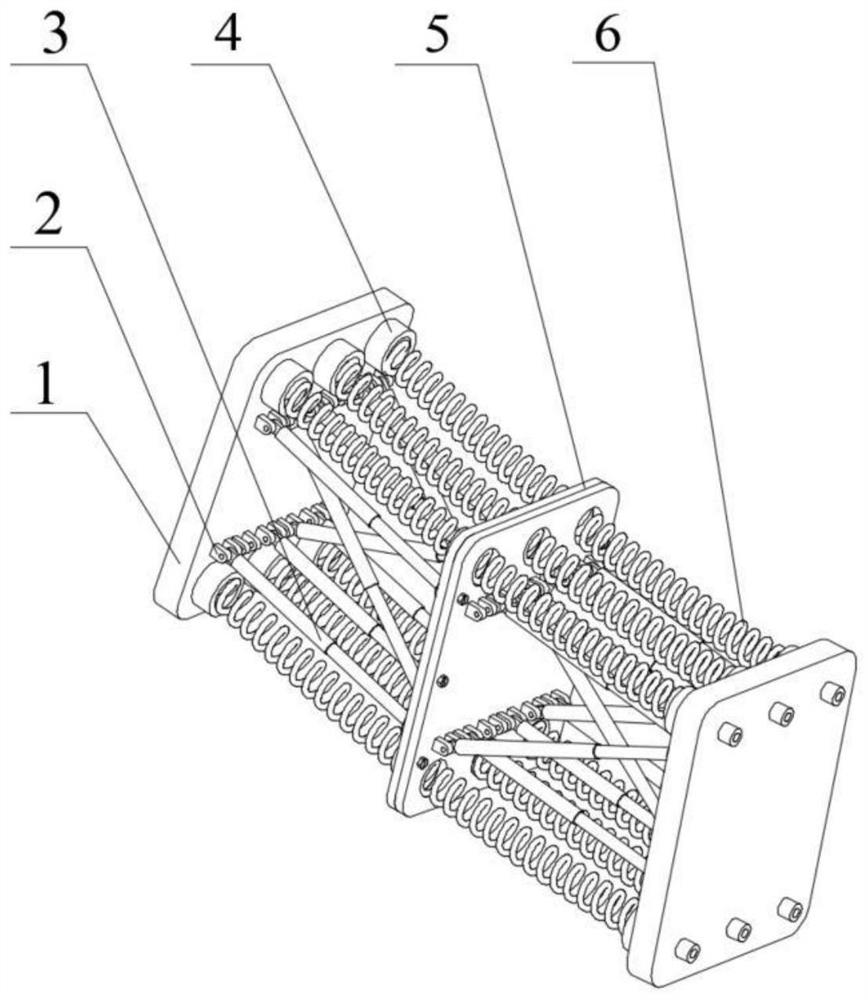
ActiveCN112091957AProminent substantive naturePrecise Feedback ControlProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl engineeringShape-memory alloy
The invention relates to a hyper-redundant continuum robot driven by a shape memory alloy. The hyper-redundant continuum robot is formed by connecting a control box and three joints which are arrangedon one side of the control box and are of the same structure through connecting pieces end to end in series, and each joint consists of two groups of deformable truss units with three degrees of freedom of a plane. Each joint is provided with a shape memory alloy spring as a driver; through arrangement of a circuit board in a proper size between every two joints, and by utilizing the characteristic that the shape memory alloy spring is powered on and heated to generate phase change shrinkage, the bending deformation of three different joints can be controlled separately; and the movement of the continuum robot is achieved through coupled motion between different joints. According to the hyper-redundant continuum robot, the shape memory alloy spring can be directly driven through current heating, the robot has the advantages of simple structure, light weight and easy control, and the degree of freedom of each joint can be independently controlled through the shape memory alloy spring.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
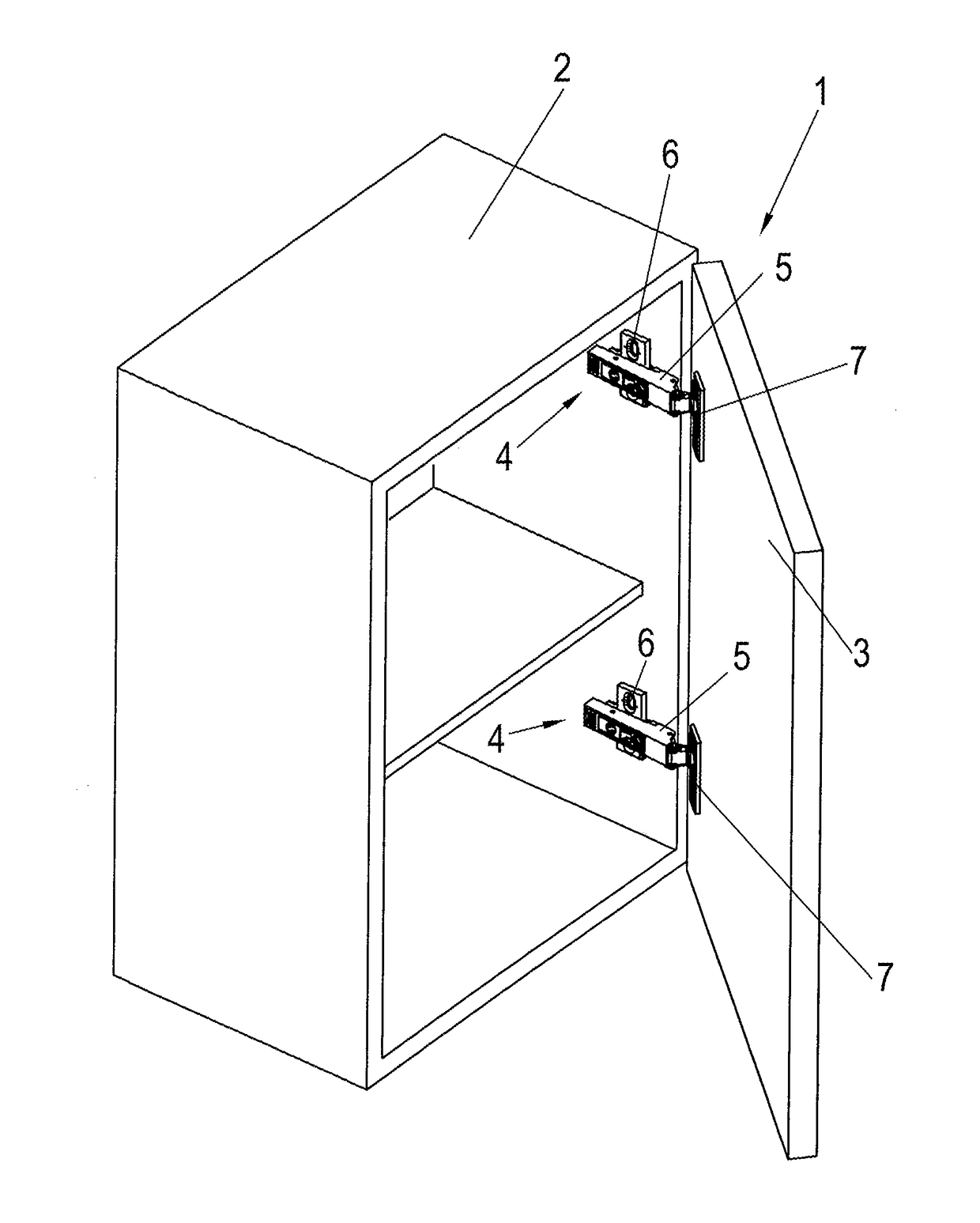
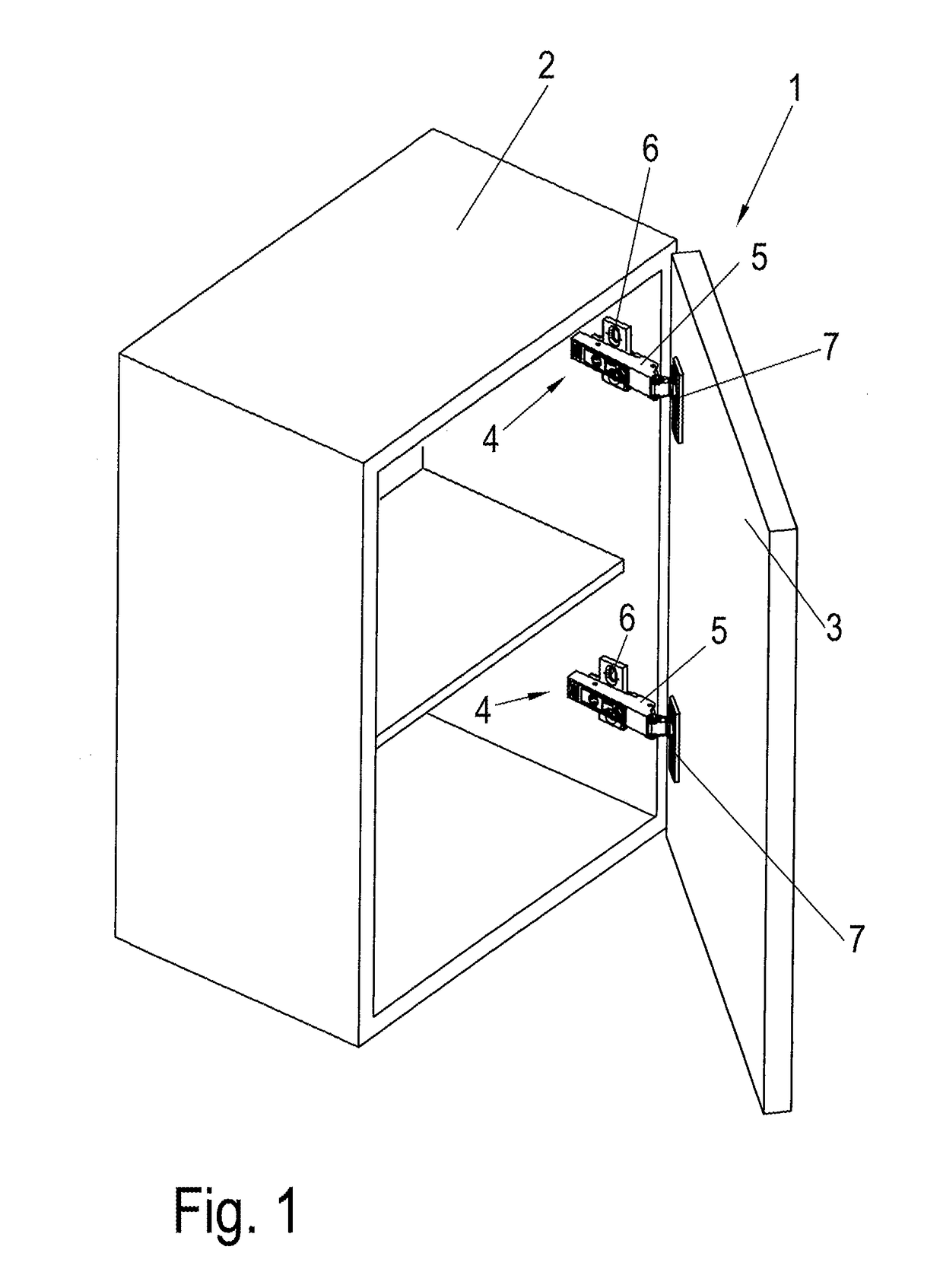
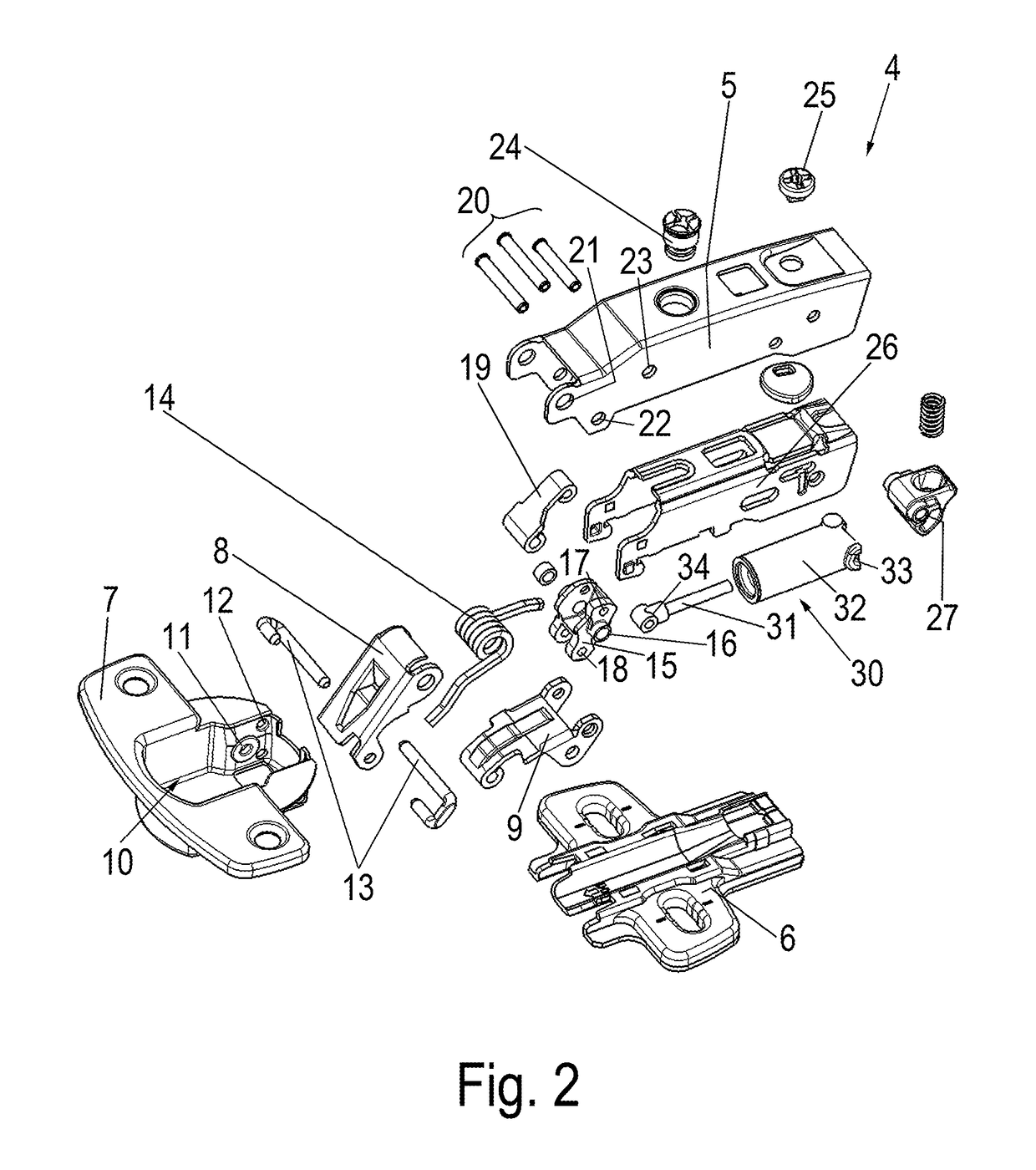
Hinge
ActiveUS20170138106A1Great damp forceLow damping forceBuilding braking devicesHingesHinge angleEngineering
Owner:HETTICH ONI
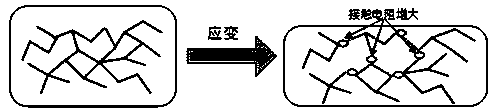
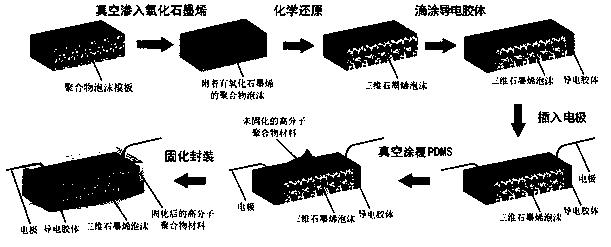
Three-dimensional graphene foam flexible strain sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109520410ANo breakage issuesReduce duplicationElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementColloidGraphene
The invention discloses a three-dimensional graphene foam flexible strain sensor and a preparation method thereof. The three-dimensional graphene foam flexible strain sensor comprises three-dimensional graphene foam; the two ends of the three-dimensional graphene foam are coated with conductive colloid; electrodes are arranged in the center of the upper surfaces of the conductive colloid, and cured high-molecular polymers are arranged on the peripheries of the three-dimensional graphene foam and the conductive colloid. According to the preparation method of the three-dimensional graphene foamflexible strain sensor, graphene is attached to a polymer template, and the three-dimensional graphene foam flexible strain sensor based on the polymer template is prepared after permeation of a high-molecular polymer material. The sensor disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high strain capacity, high sensitivity, flexibility, low cost, simple preparation method and good repeatabilityand consistency.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
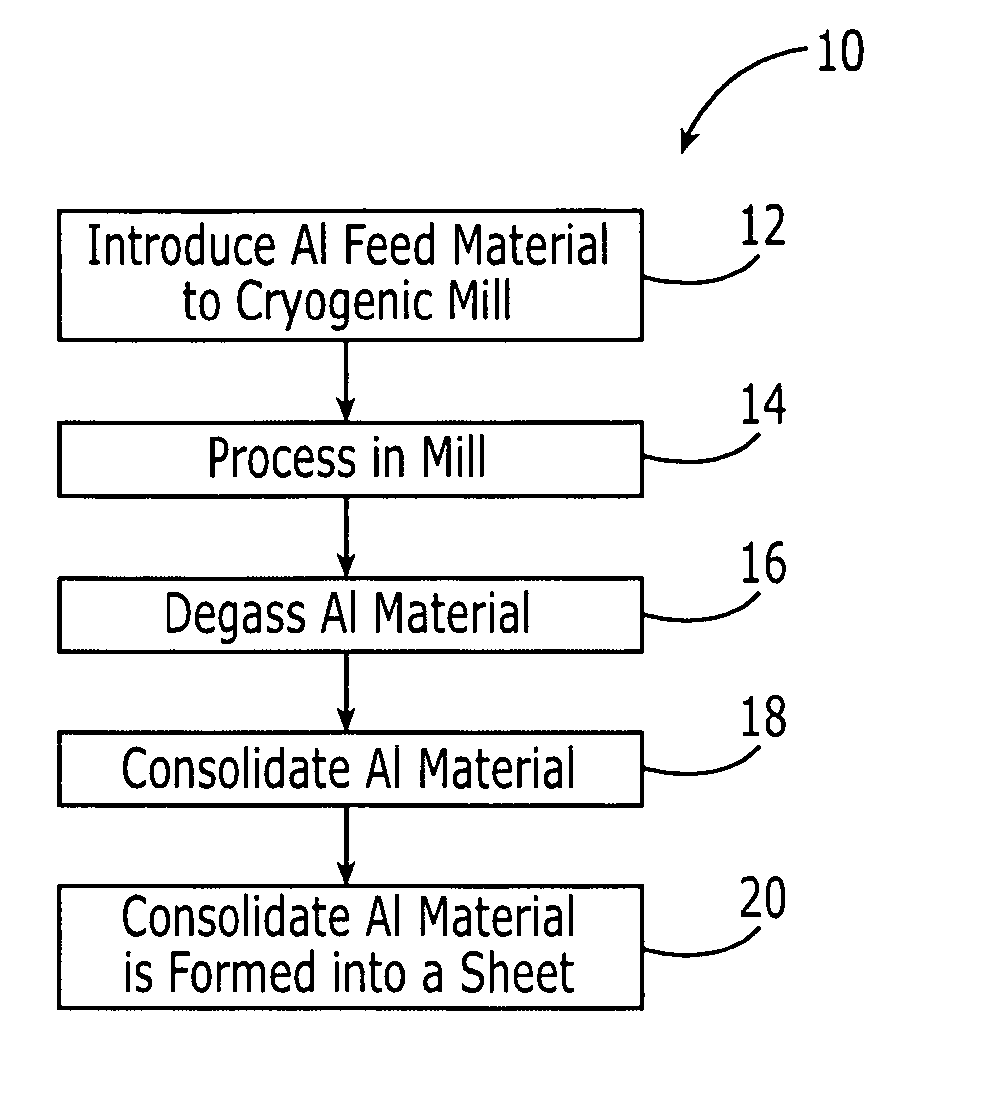
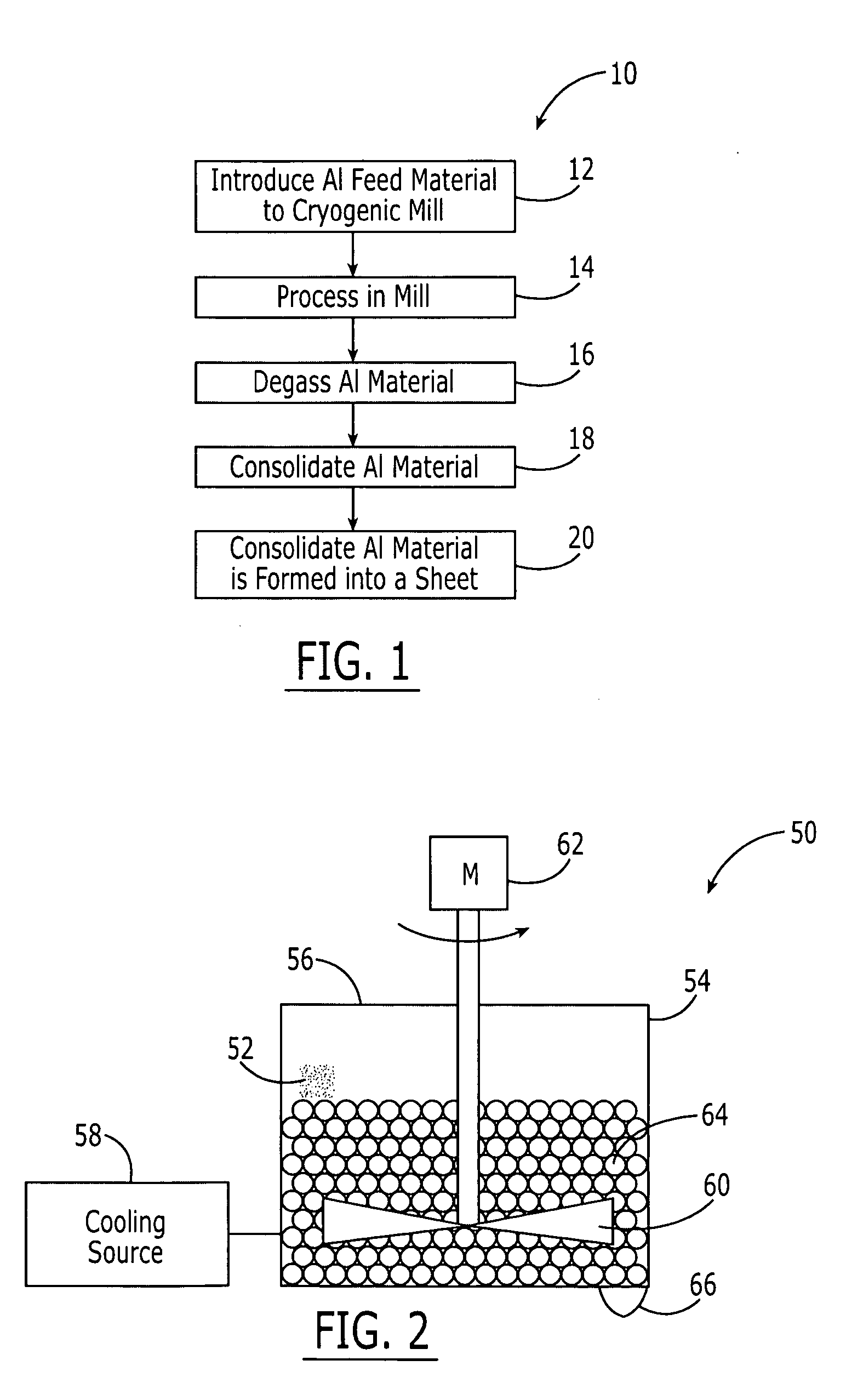
Method for preparing high-temperature nanophase aluminum-alloy sheets and aluminum-alloy sheets prepared thereby
ActiveUS20060198754A1Improve material performanceLow work hardening rateMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingUltra fineGrain structure
An aluminum or aluminum-alloy material sheet comprised of an aluminum material having an ultra-fine, submicron grain structure. The strength and physical properties of the aluminum or aluminum-alloy material sheet are improved over previous aluminum and aluminum-alloy material sheets because the aluminum is produced by cryomilling the aluminum or aluminum-alloy materials into a metal powder with ultra-fine, submicron grain structure. The powder is consolidated and rolled into the form of a sheet.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com