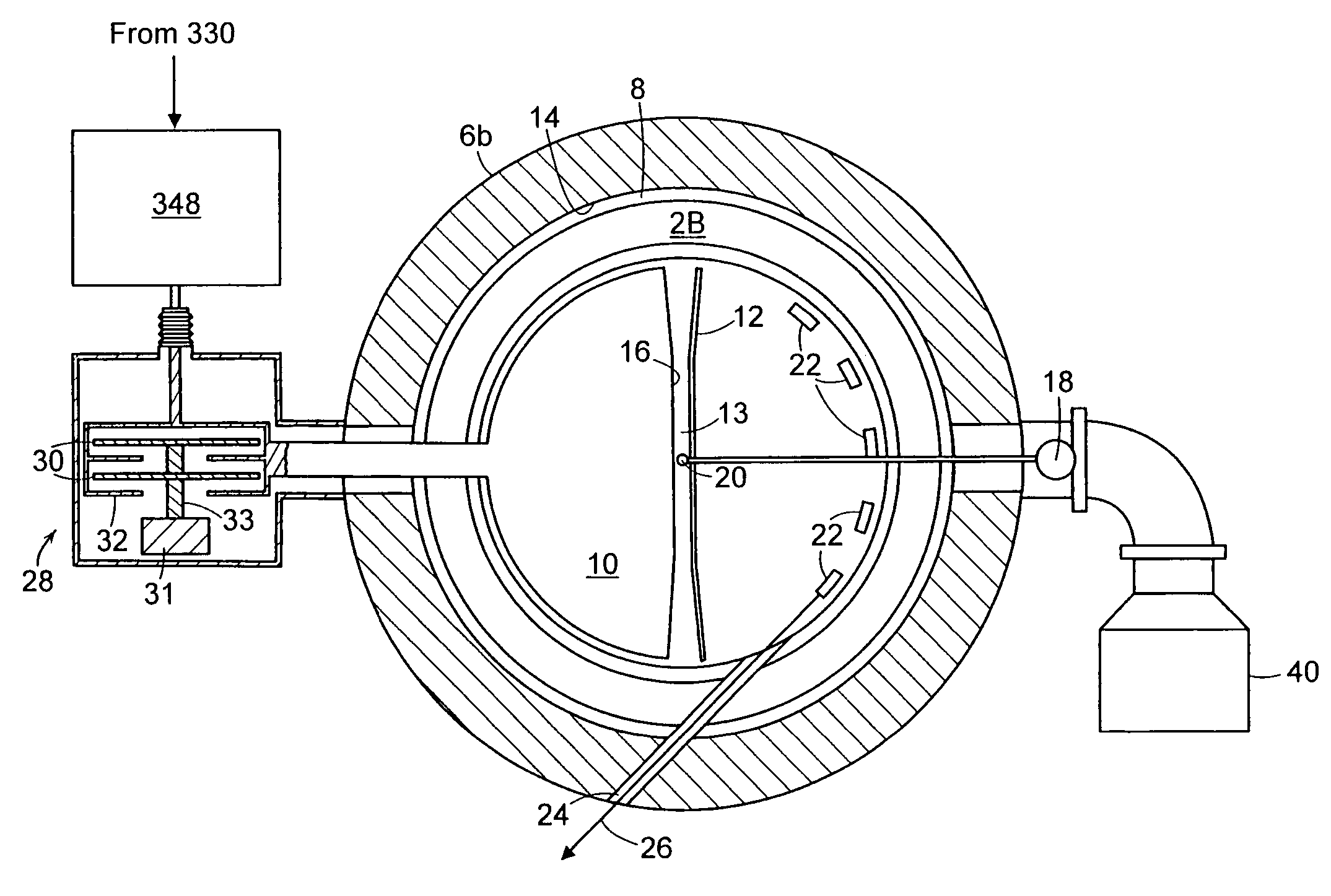
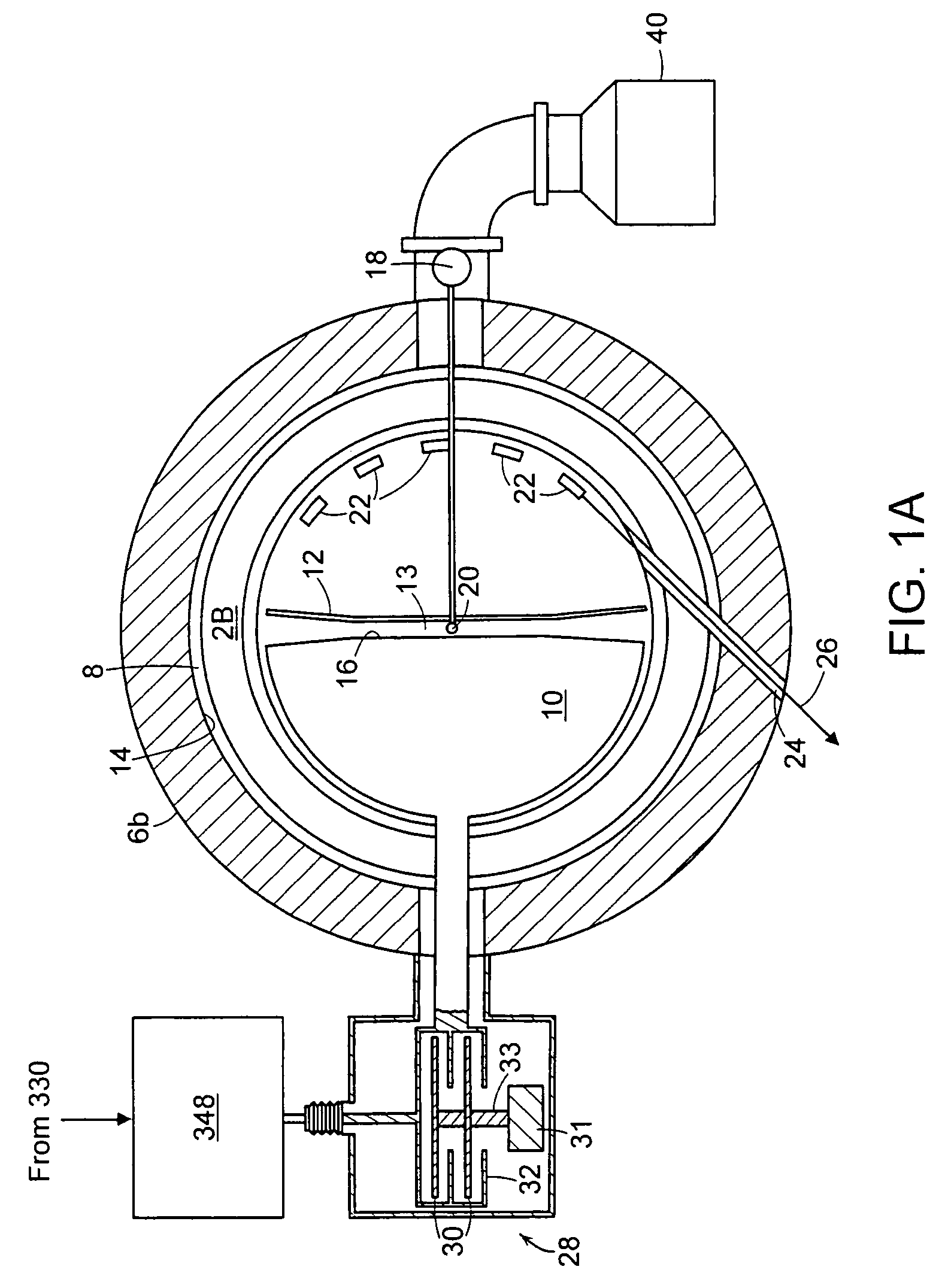
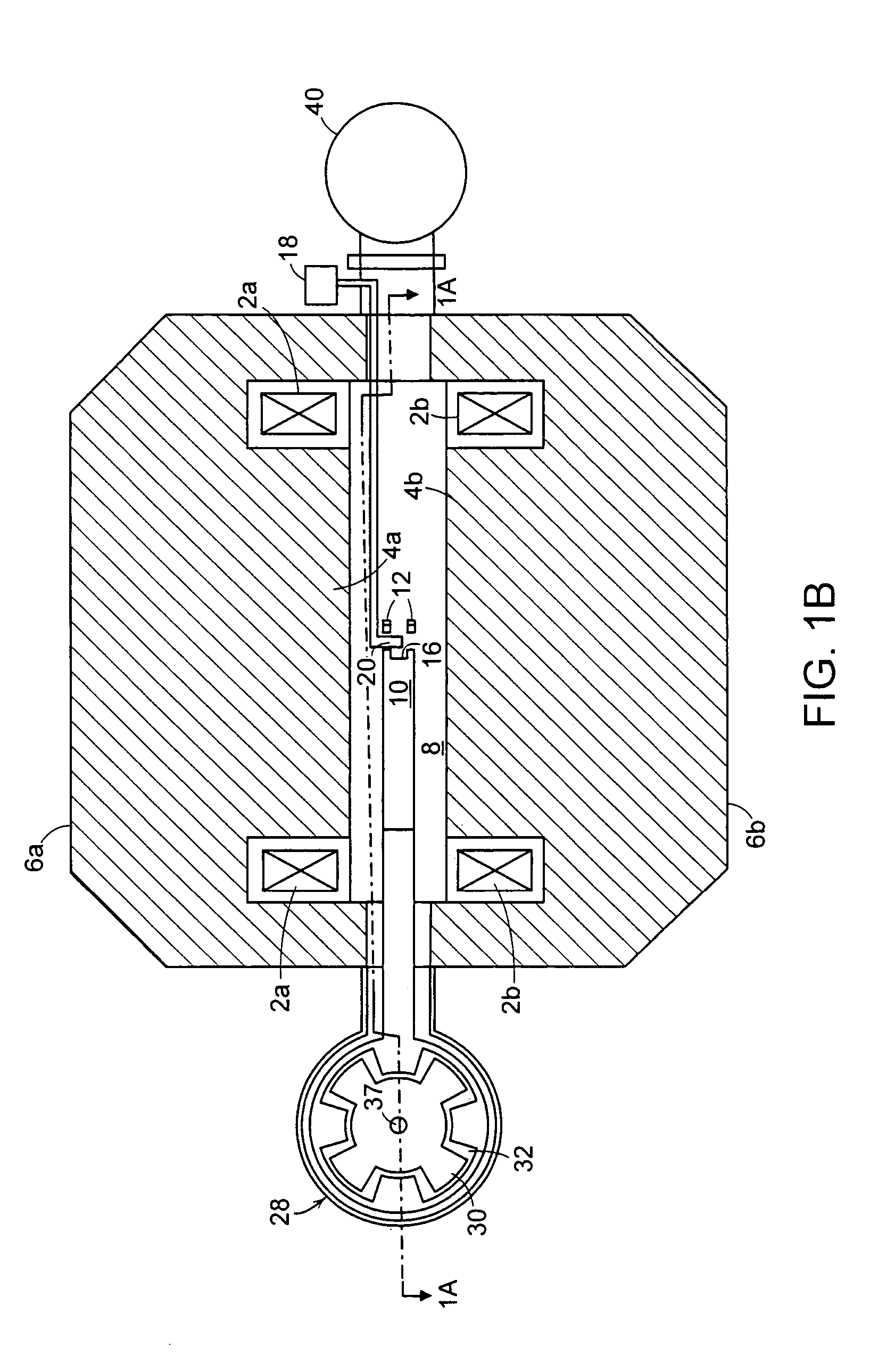
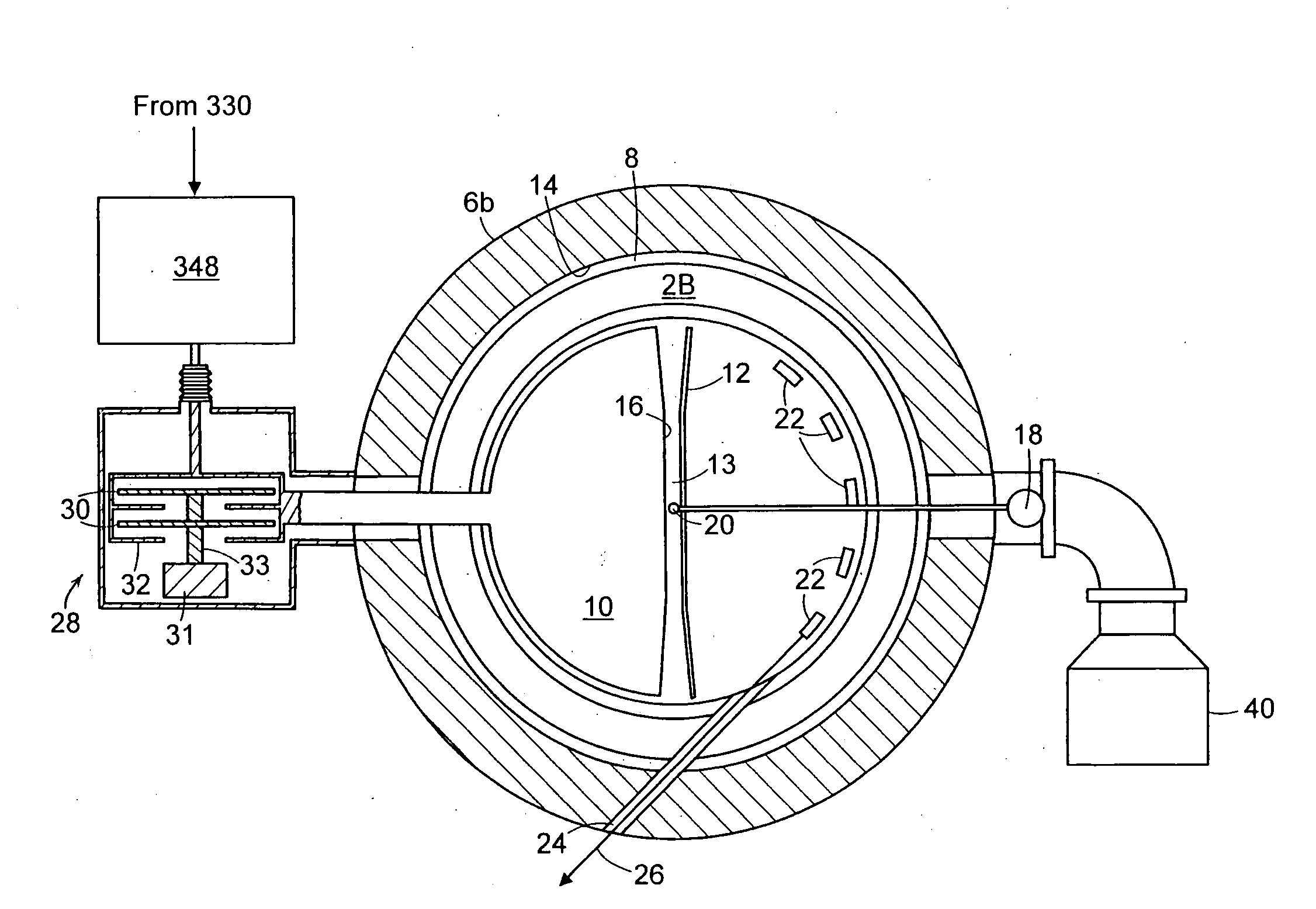
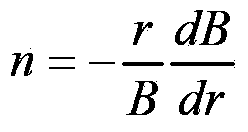Patents
Literature
30 results about "Synchrocyclotron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A synchrocyclotron is a special type of cyclotron, patented by Edwin McMillan, in which the frequency of the driving RF electric field is varied to compensate for relativistic effects as the particles' velocity begins to approach the speed of light. This is in contrast to the classical cyclotron, where this frequency is constant.
Programmable radio frequency waveform generator for a synchrocyclotron
ActiveUS7402963B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsCapacitanceRadio frequency
Owner:MEVION MEDICAL SYST
Programmable radio frequency waveform generator for a synchrocyclotron
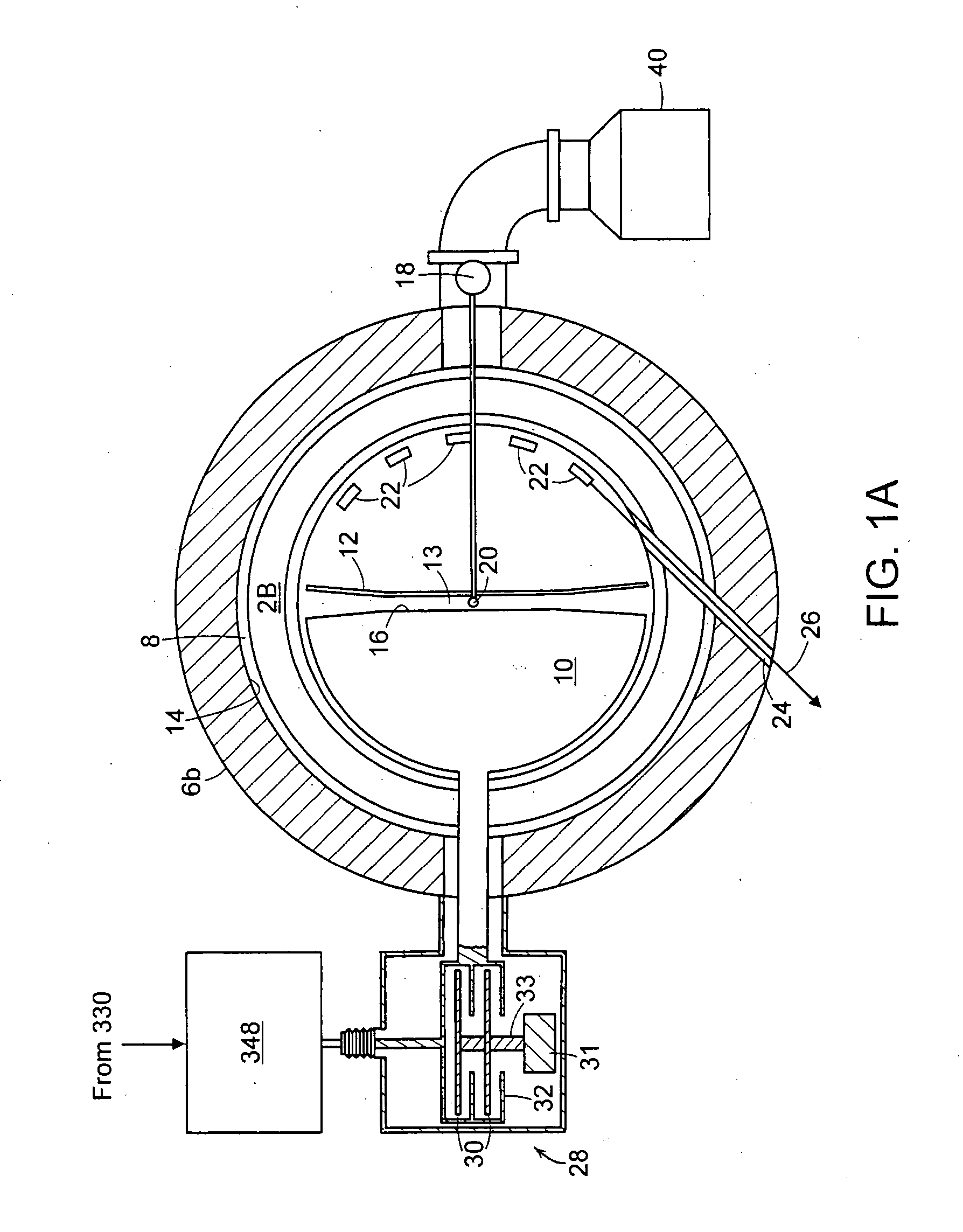
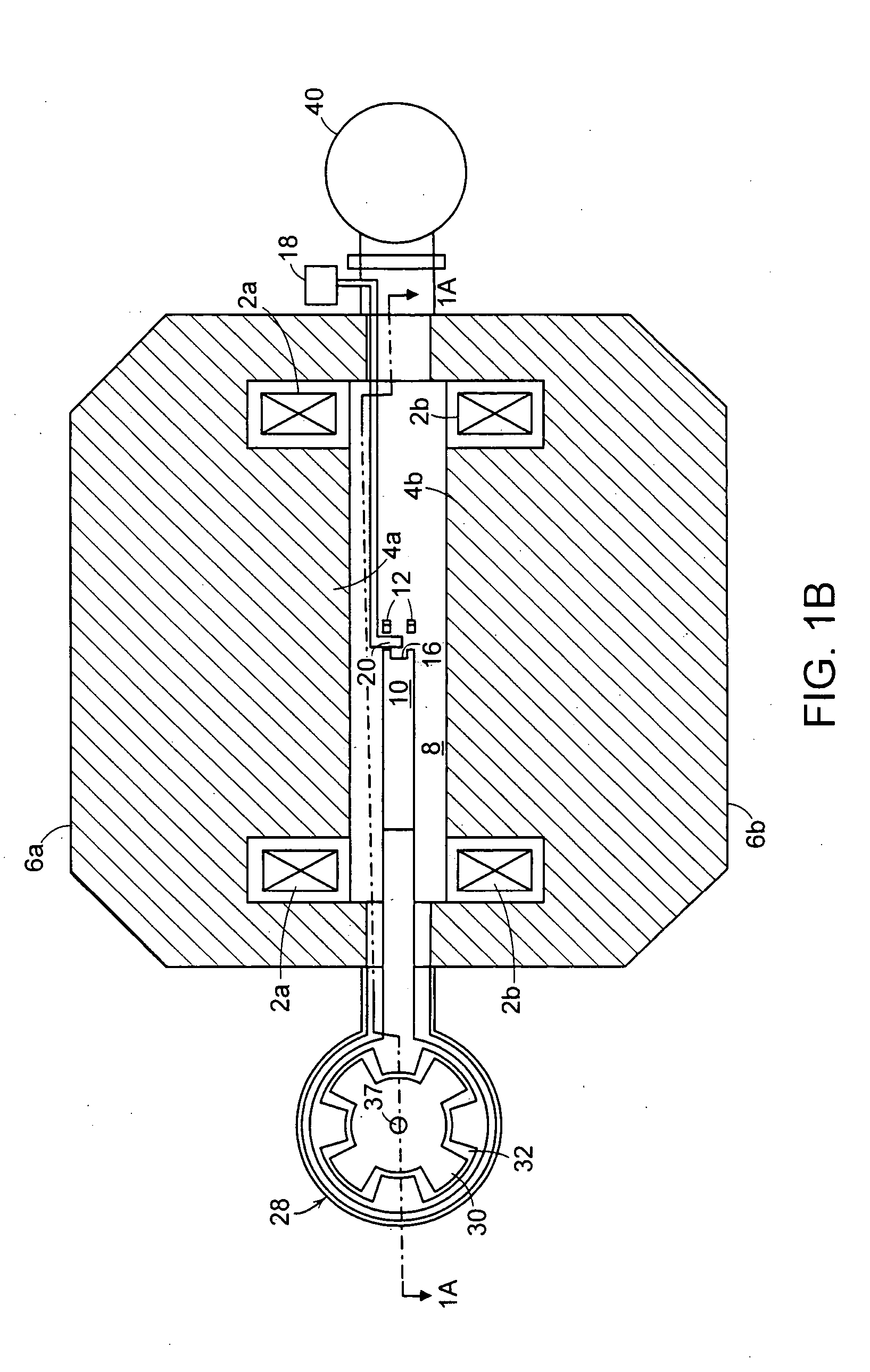
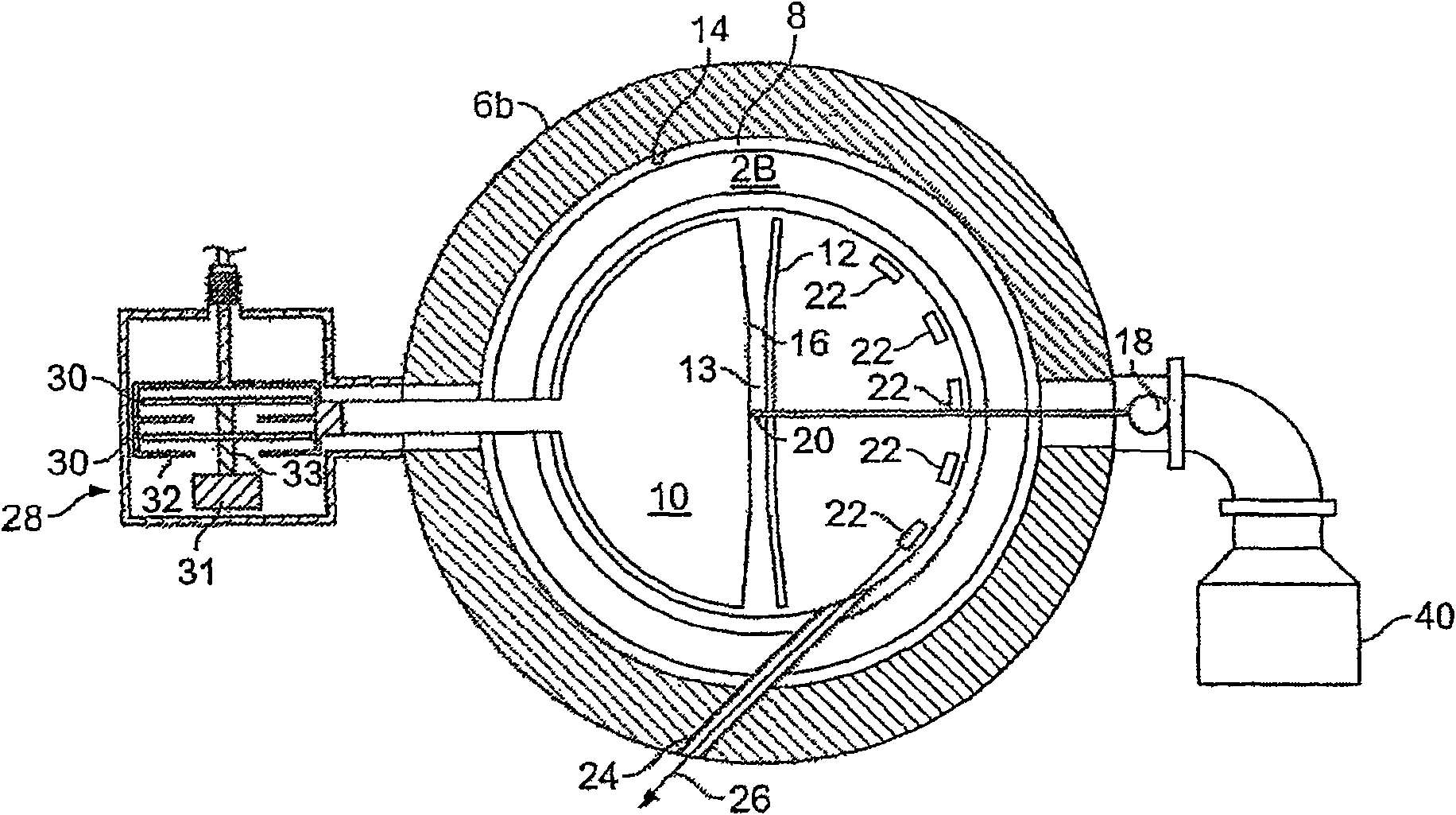
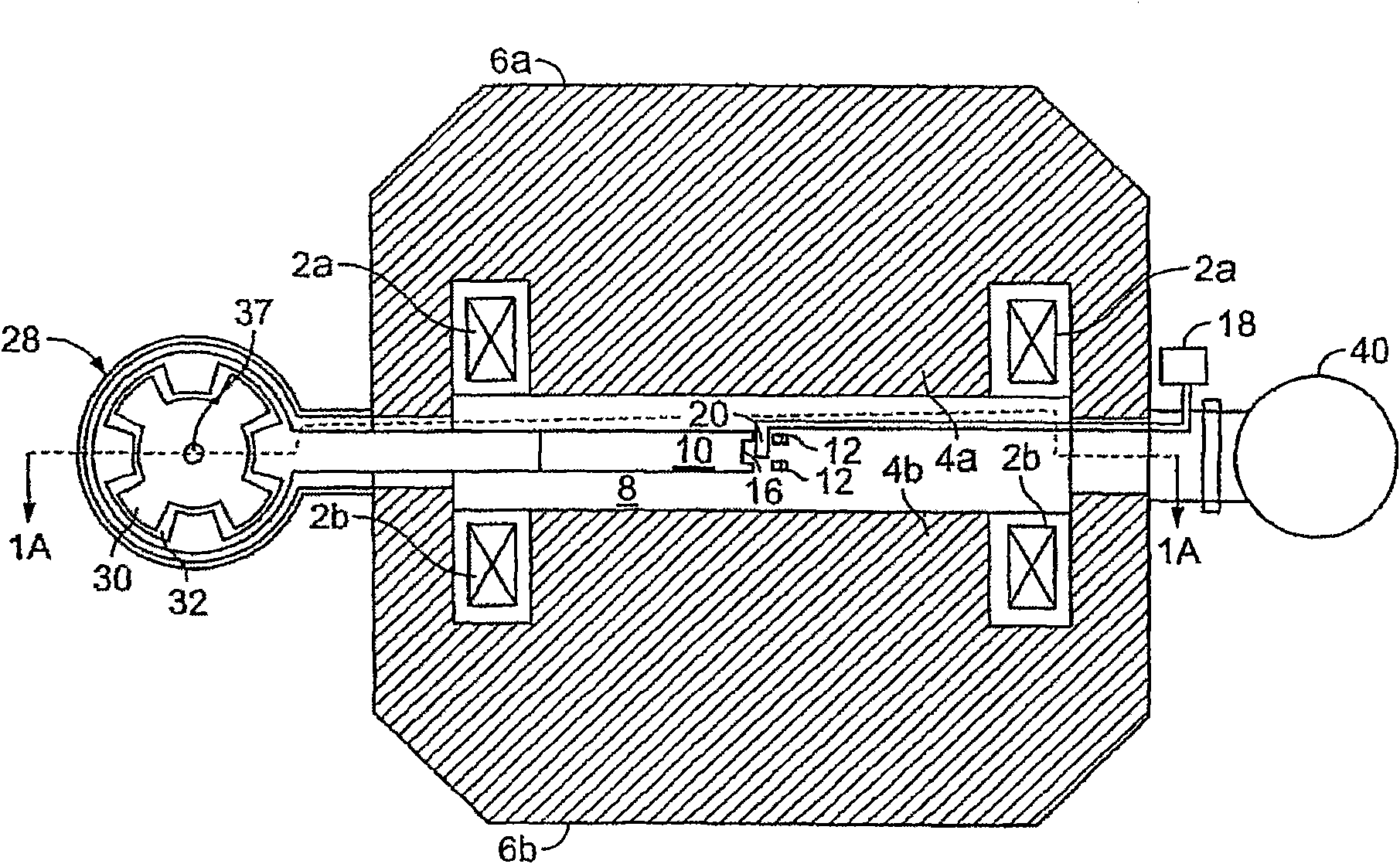
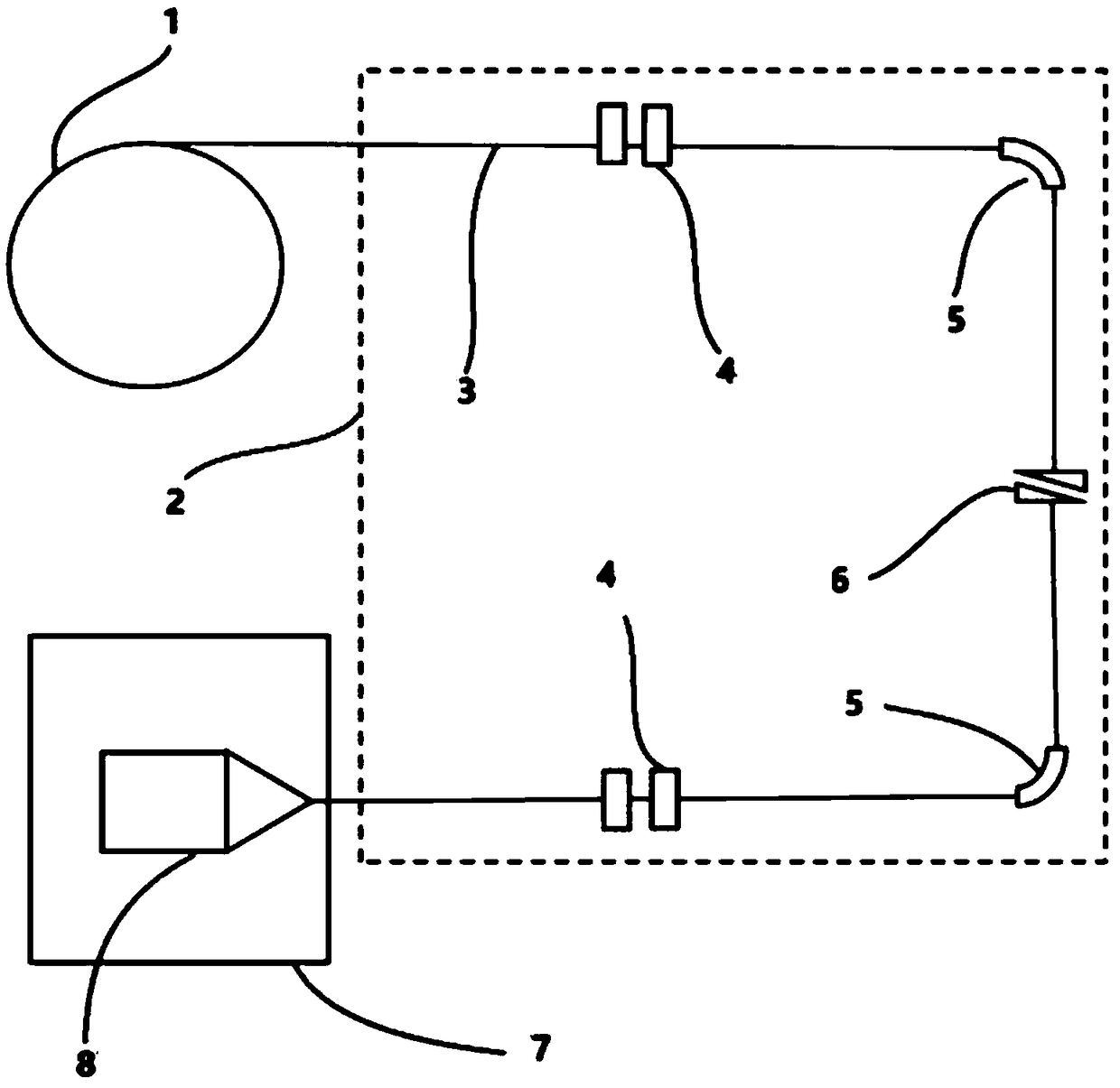
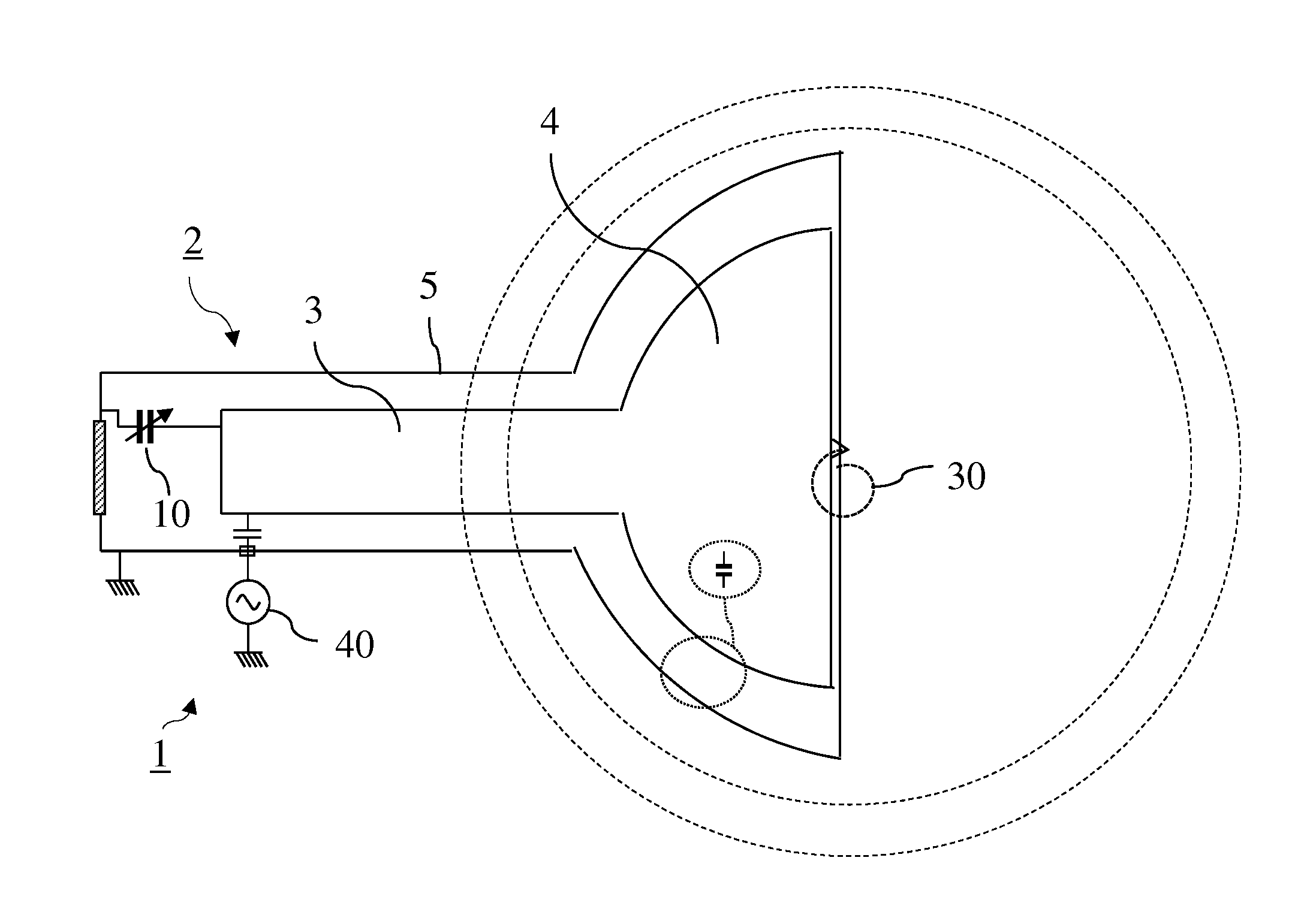
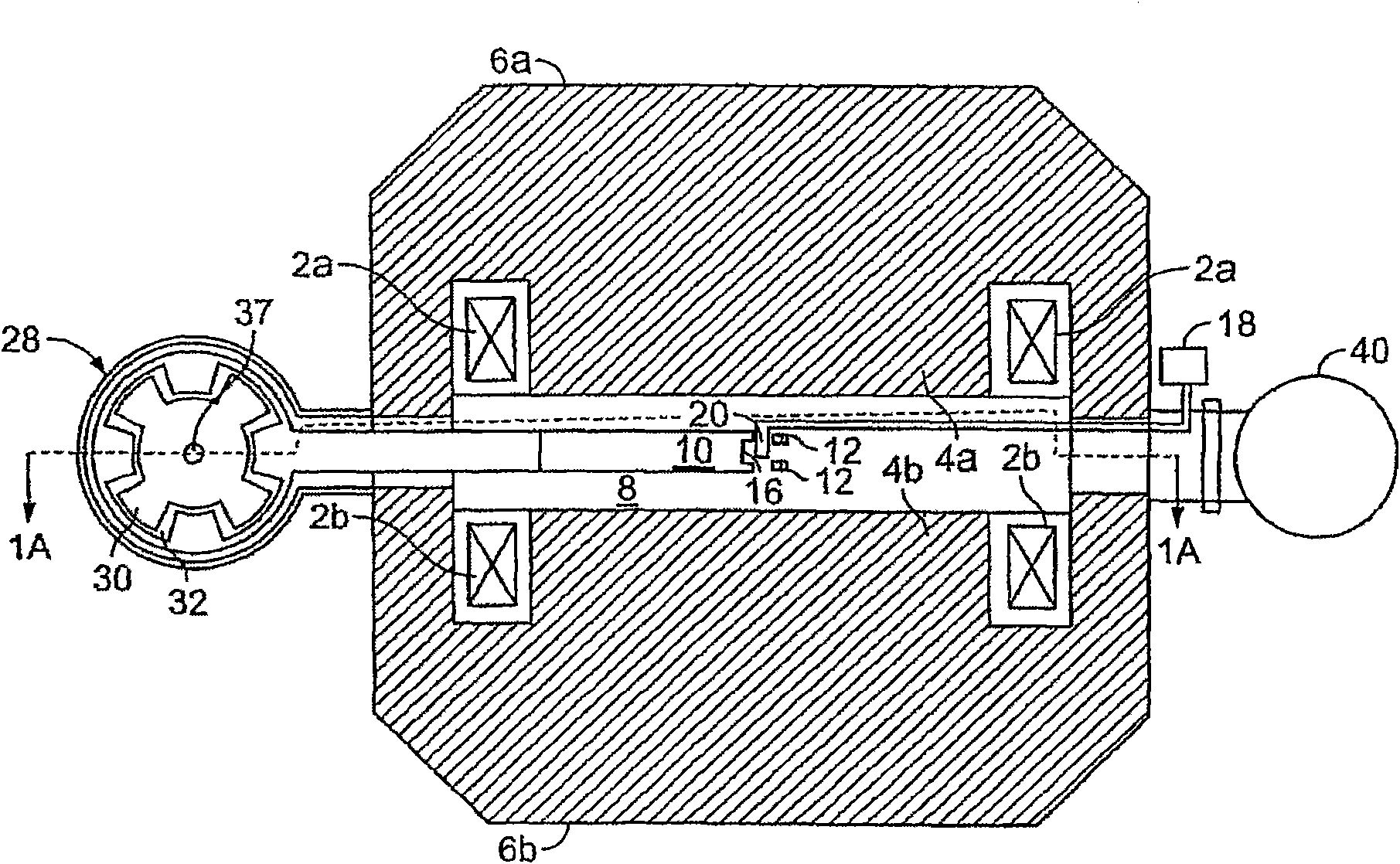
A synchrocyclotron comprises a resonant circuit that includes electrodes having a gap therebetween across the magnetic field. An oscillating voltage input, having a variable amplitude and frequency determined by a programmable digital waveform generator generates an oscillating electric field across the gap. The synchrocyclotron can include a variable capacitor in circuit with the electrodes to vary the resonant frequency. The synchrocyclotron can further include an injection electrode and an extraction electrode having voltages controlled by the programmable digital waveform generator. The synchrocyclotron can further include a beam monitor. The synchrocyclotron can detect resonant conditions in the resonant circuit by measuring the voltage and or current in the resonant circuit, driven by the input voltage, and adjust the capacitance of the variable capacitor or the frequency of the input voltage to maintain the resonant conditions. The programmable waveform generator can adjust at least one of the oscillating voltage input, the voltage on the injection electrode and the voltage on the extraction electrode according to beam intensity and in response to changes in resonant conditions.
Owner:MEVION MEDICAL SYST
Matching a resonant frequency of a resonant cavity to a frequency of an input voltage
ActiveCN101933406APulse automatic controlMagnetic resonance acceleratorsResonant cavityPhase detector
A synchrocyclotron includes magnetic structures that define a resonant cavity, a source to provide particles to the resonant cavity, a voltage source to provide radio frequency (RF) voltage to the resonant cavity, a phase detector to detect a difference in phase between the RF voltage and a resonant frequency of the resonant cavity that changes over time, and a control circuit, responsive to the difference in phase, to control the voltage source so that a frequency of the RF voltage substantially matches the resonant frequency of the resonant cavity.
Owner:MEVION MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
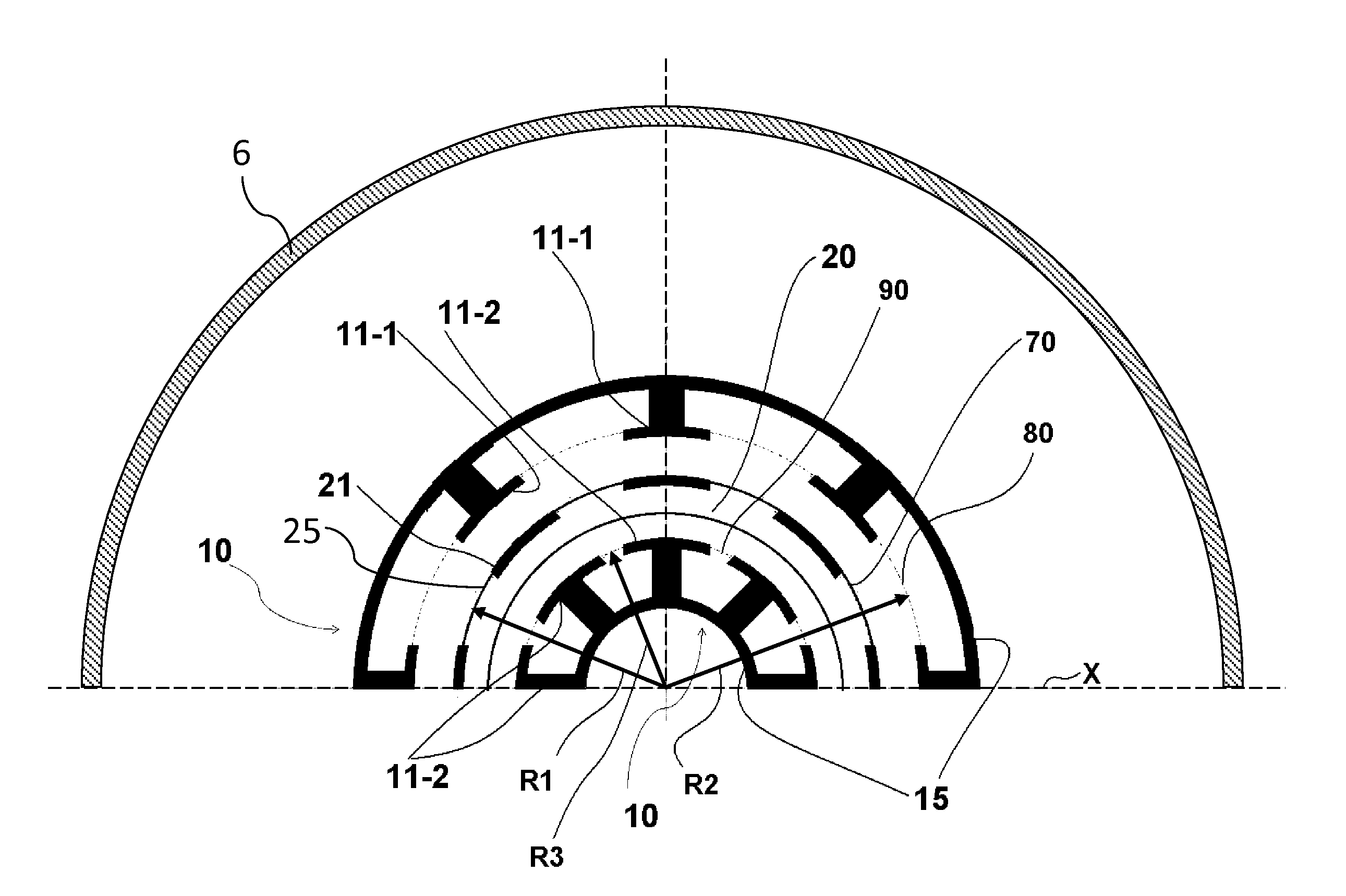
Variable rotating capacitor for synchrocyclotron
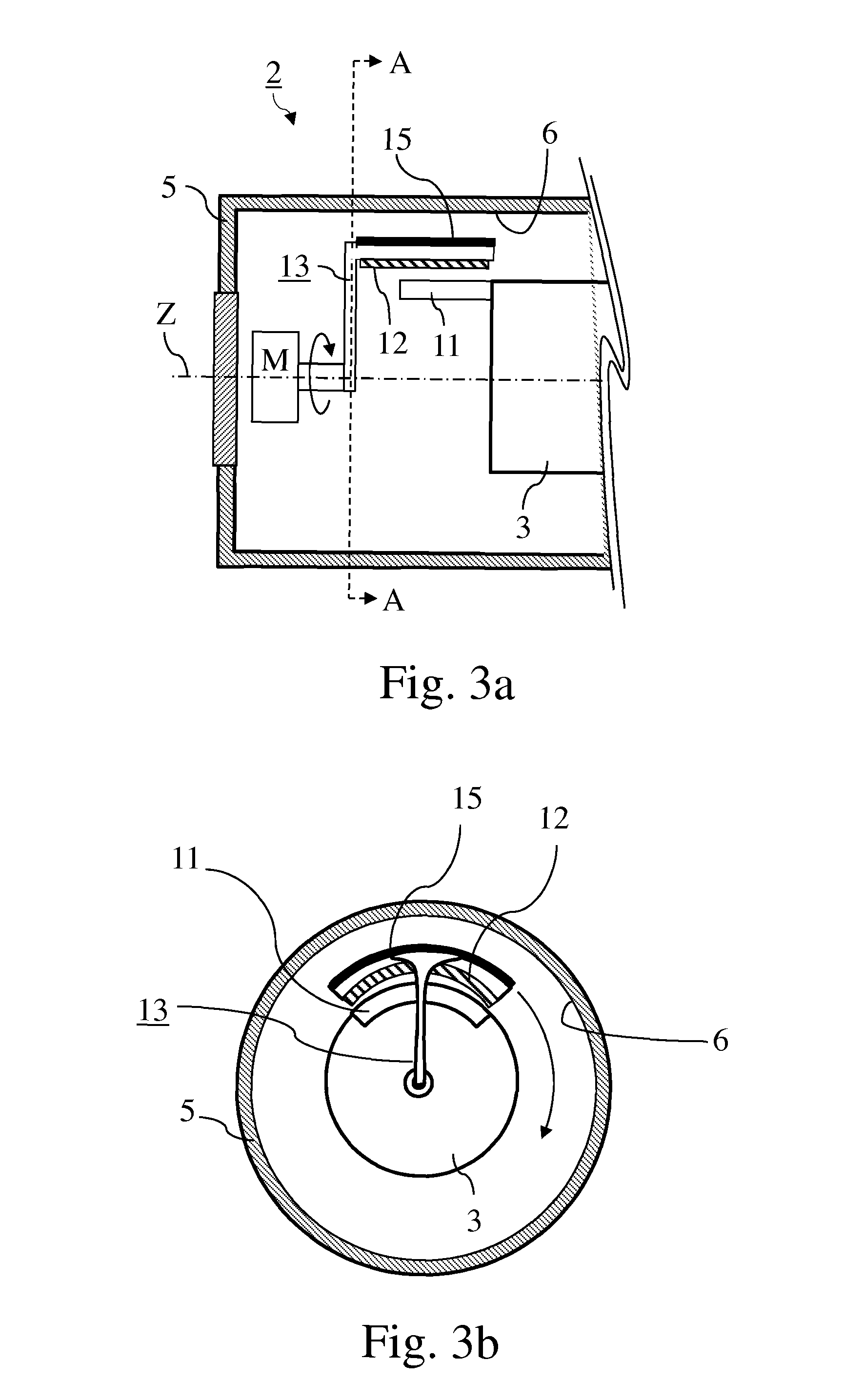
ActiveUS9355784B2Speed up the flowReducing local overheatingCapacitor with electrode area variationMagnetic resonance acceleratorsEngineeringCapacitor
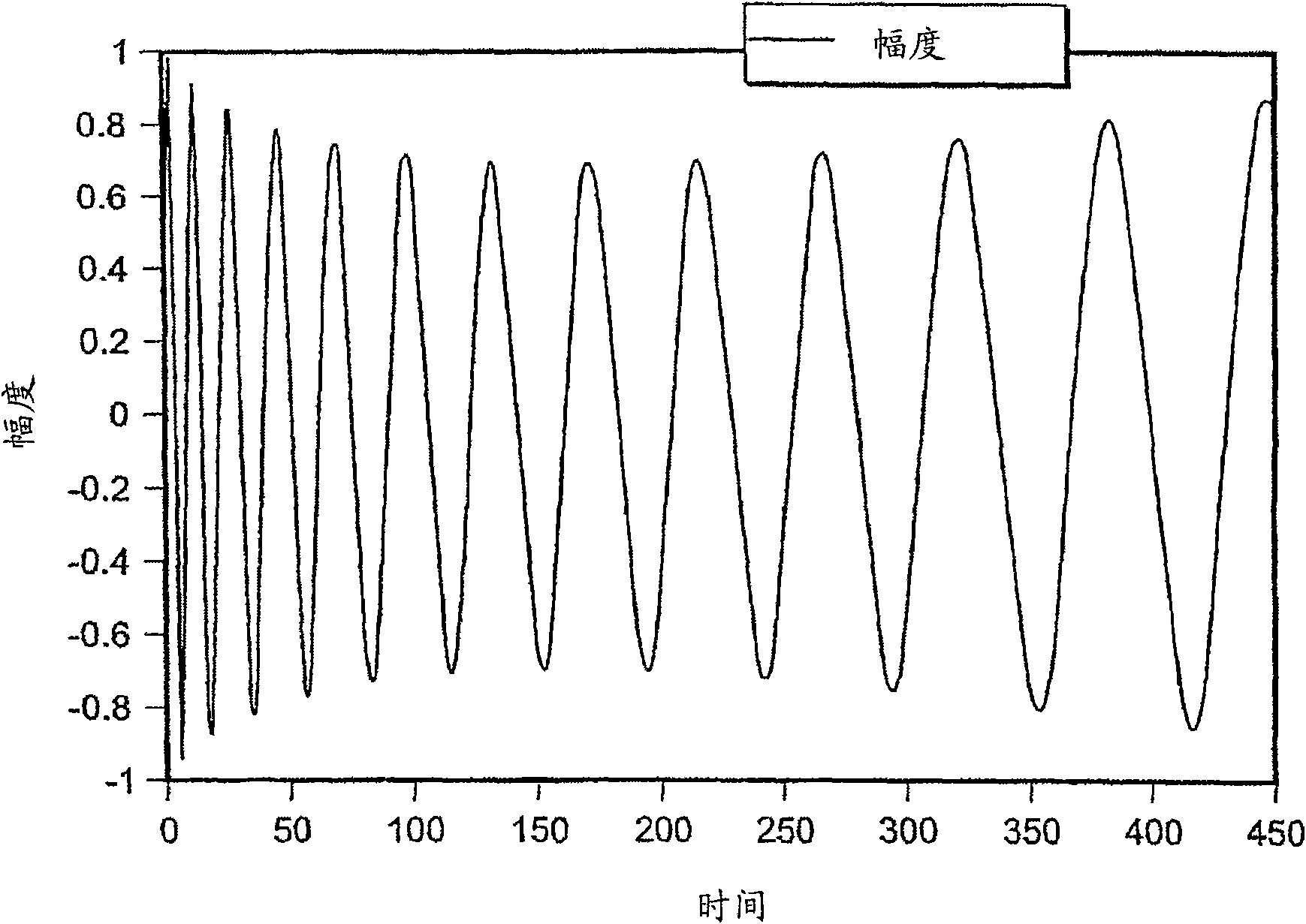
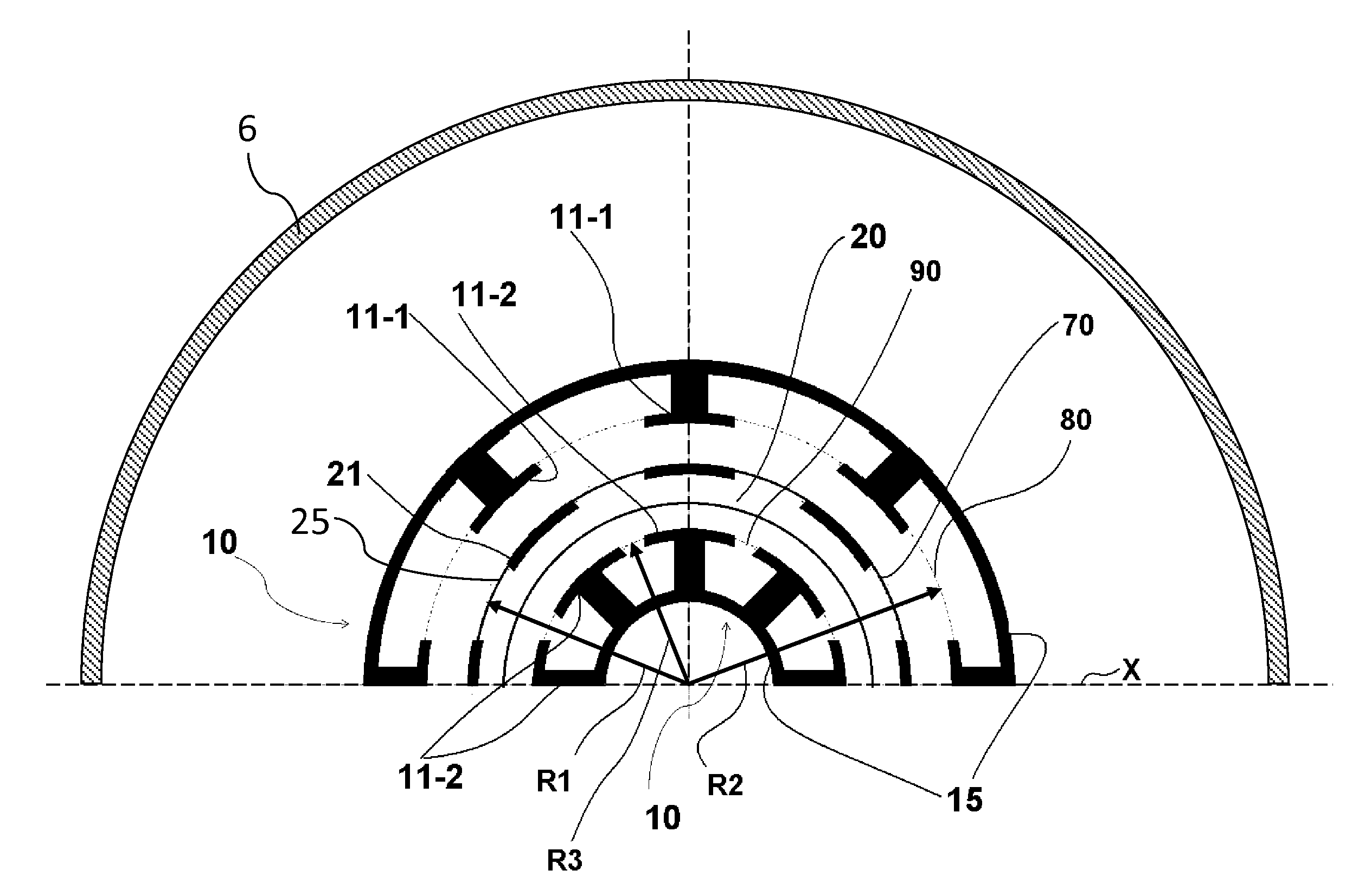
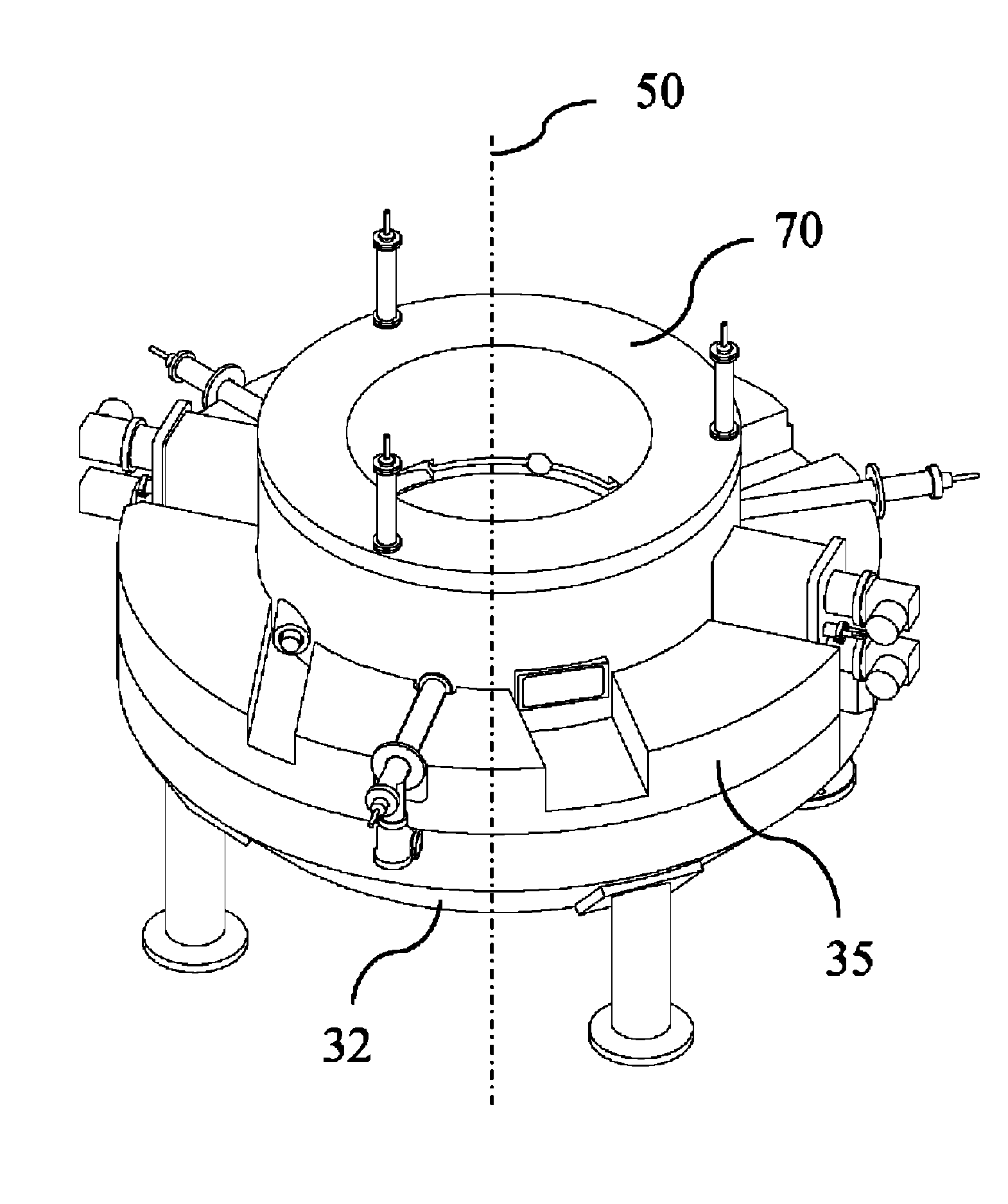
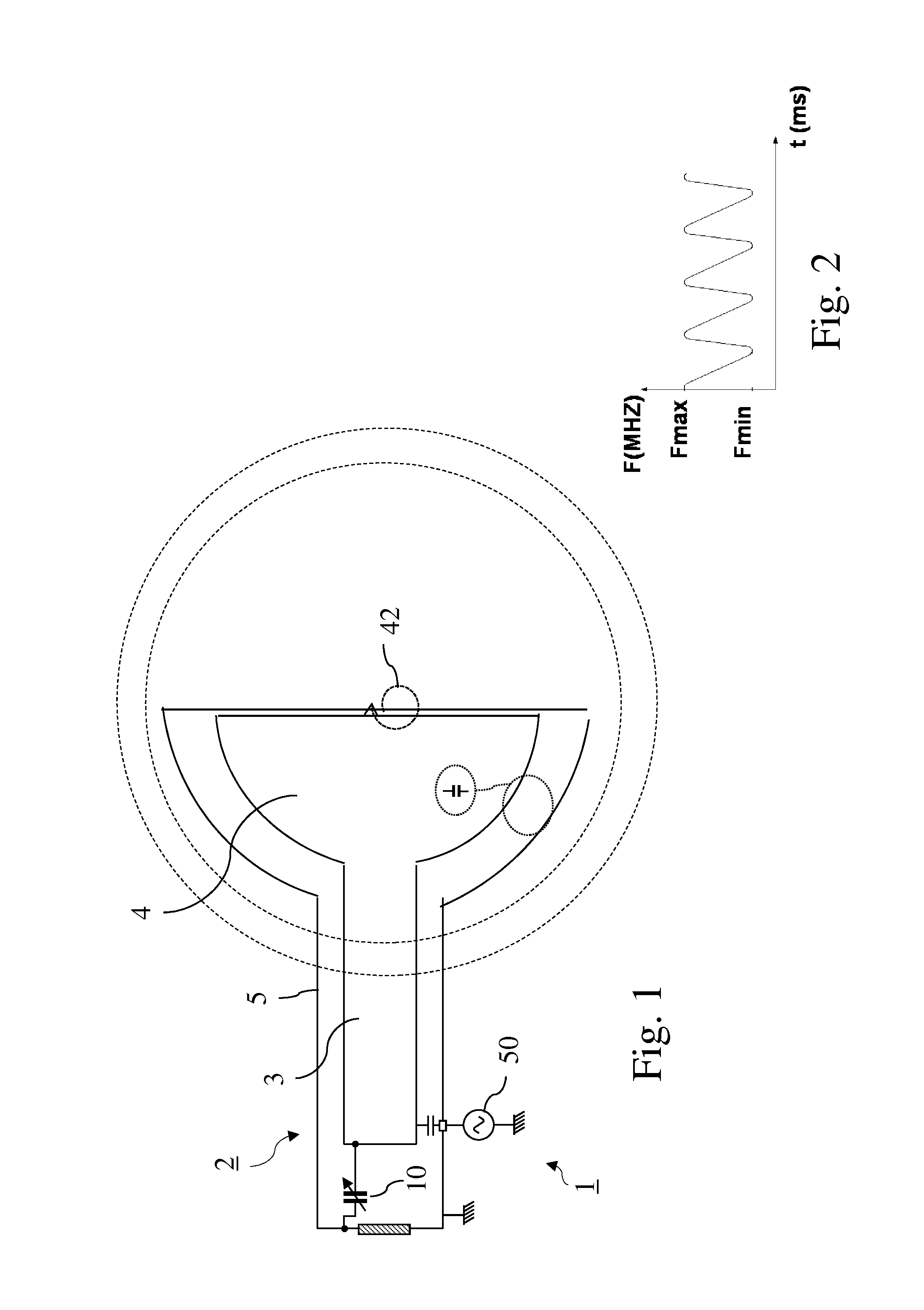
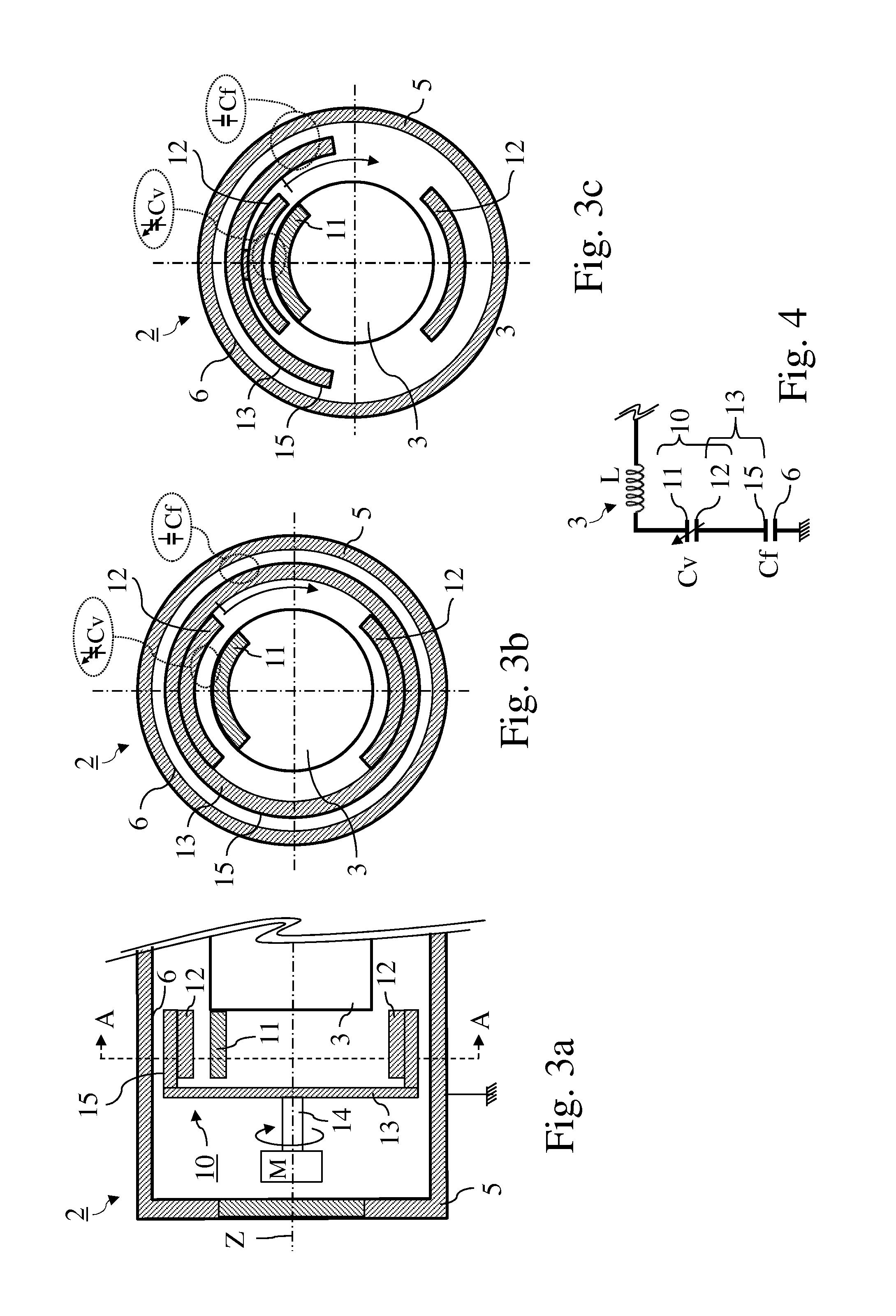
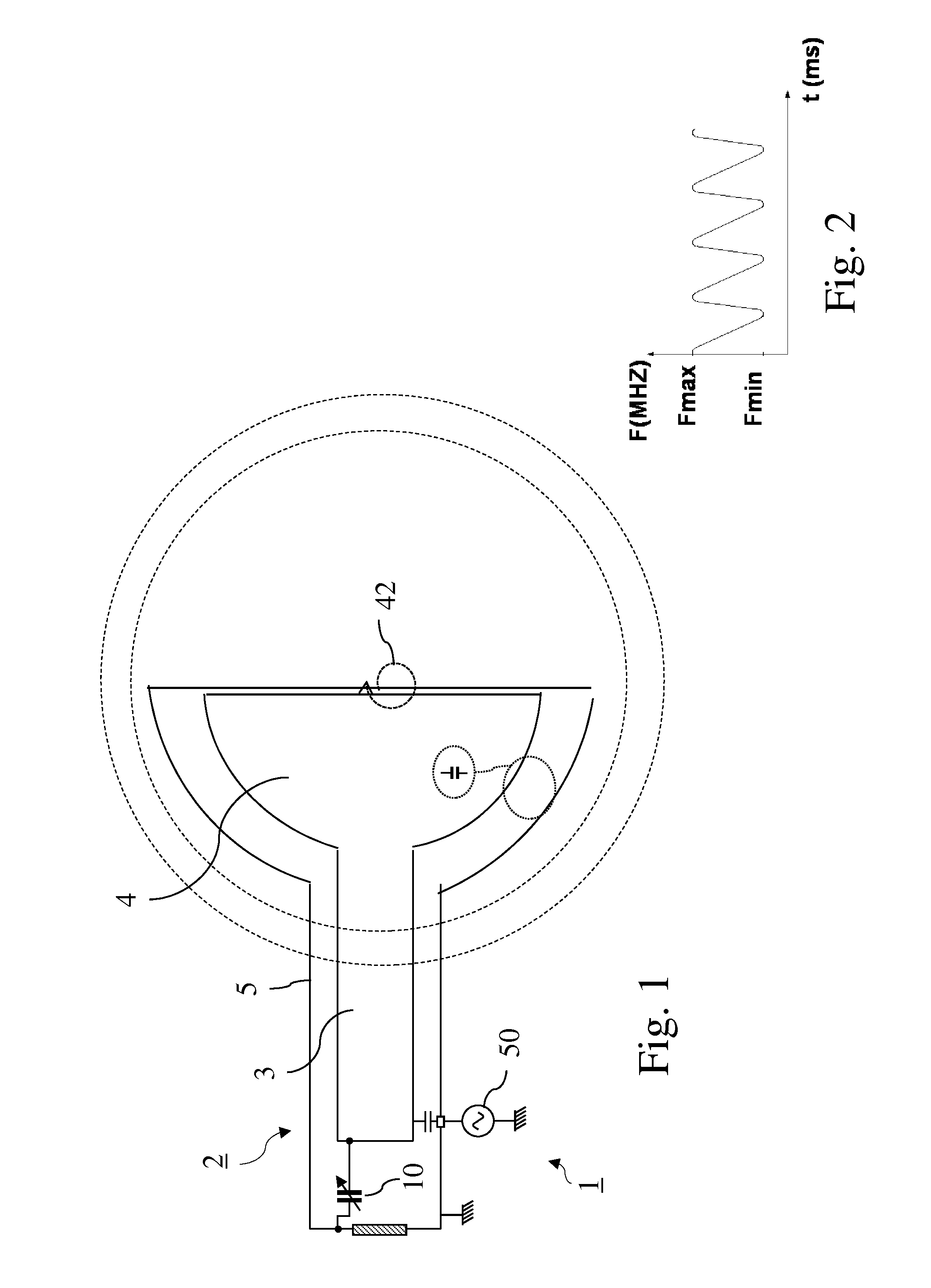
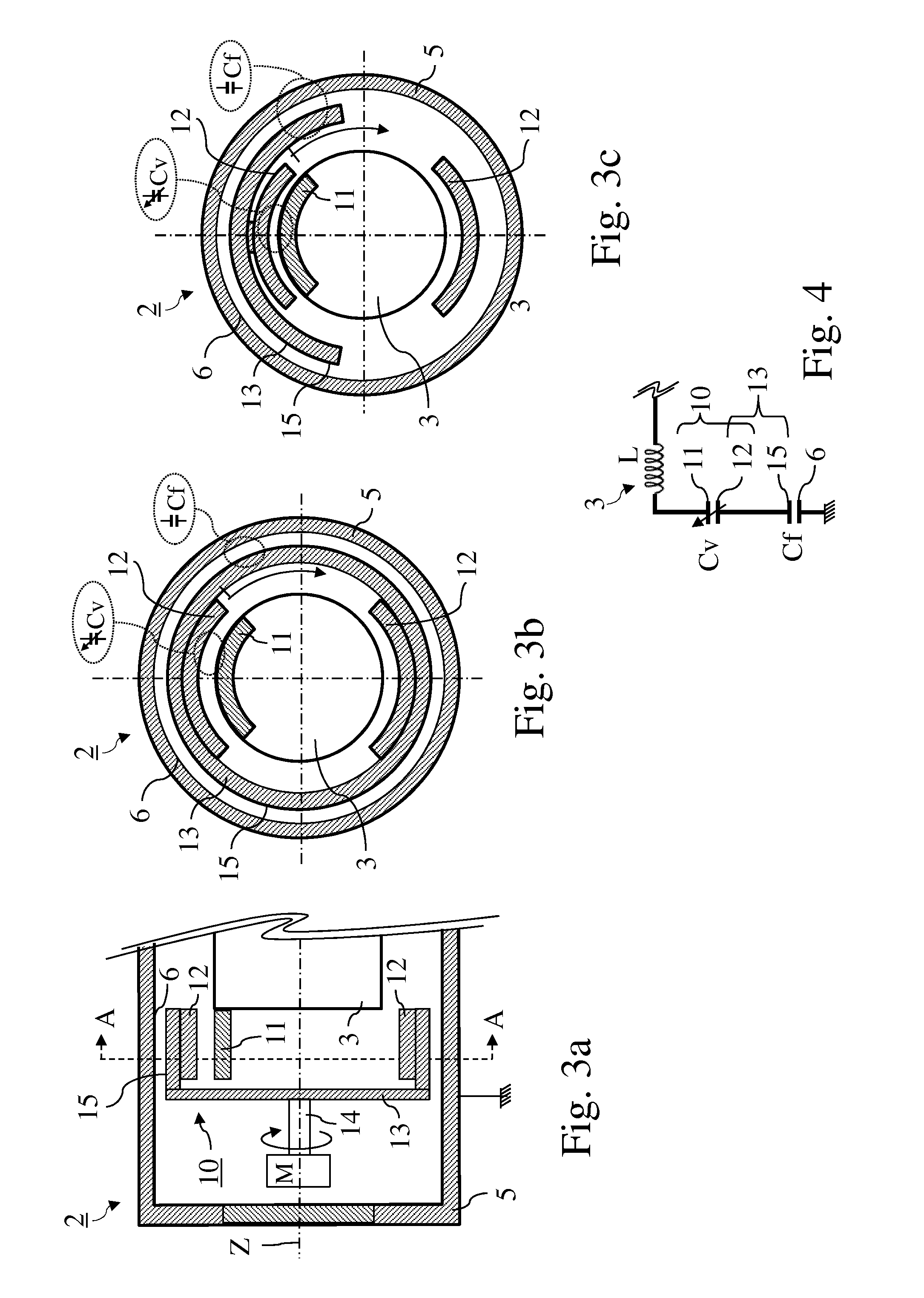
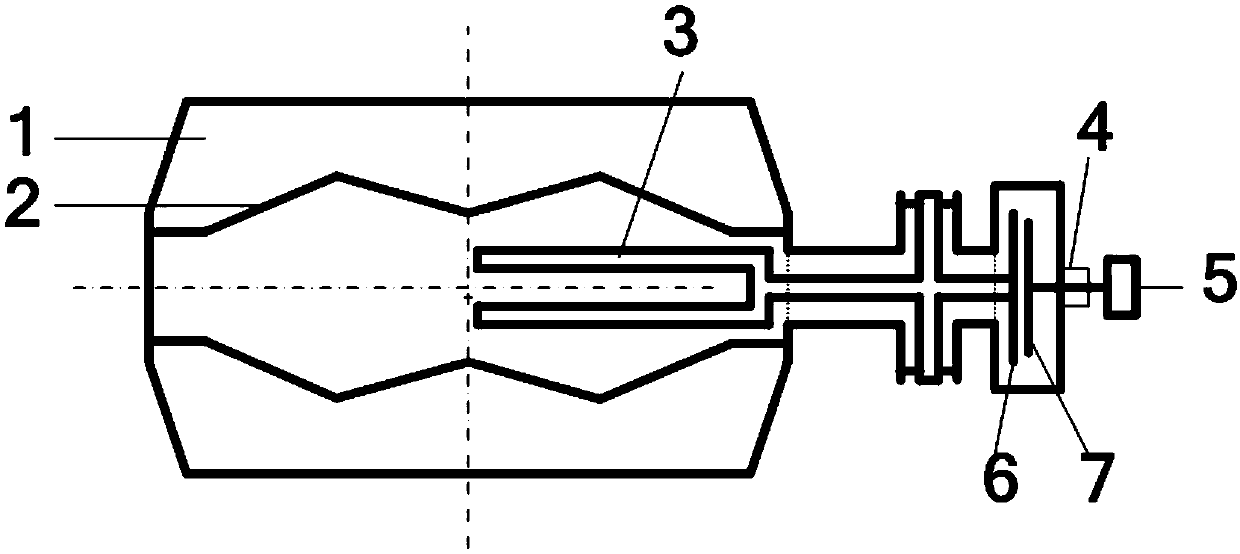
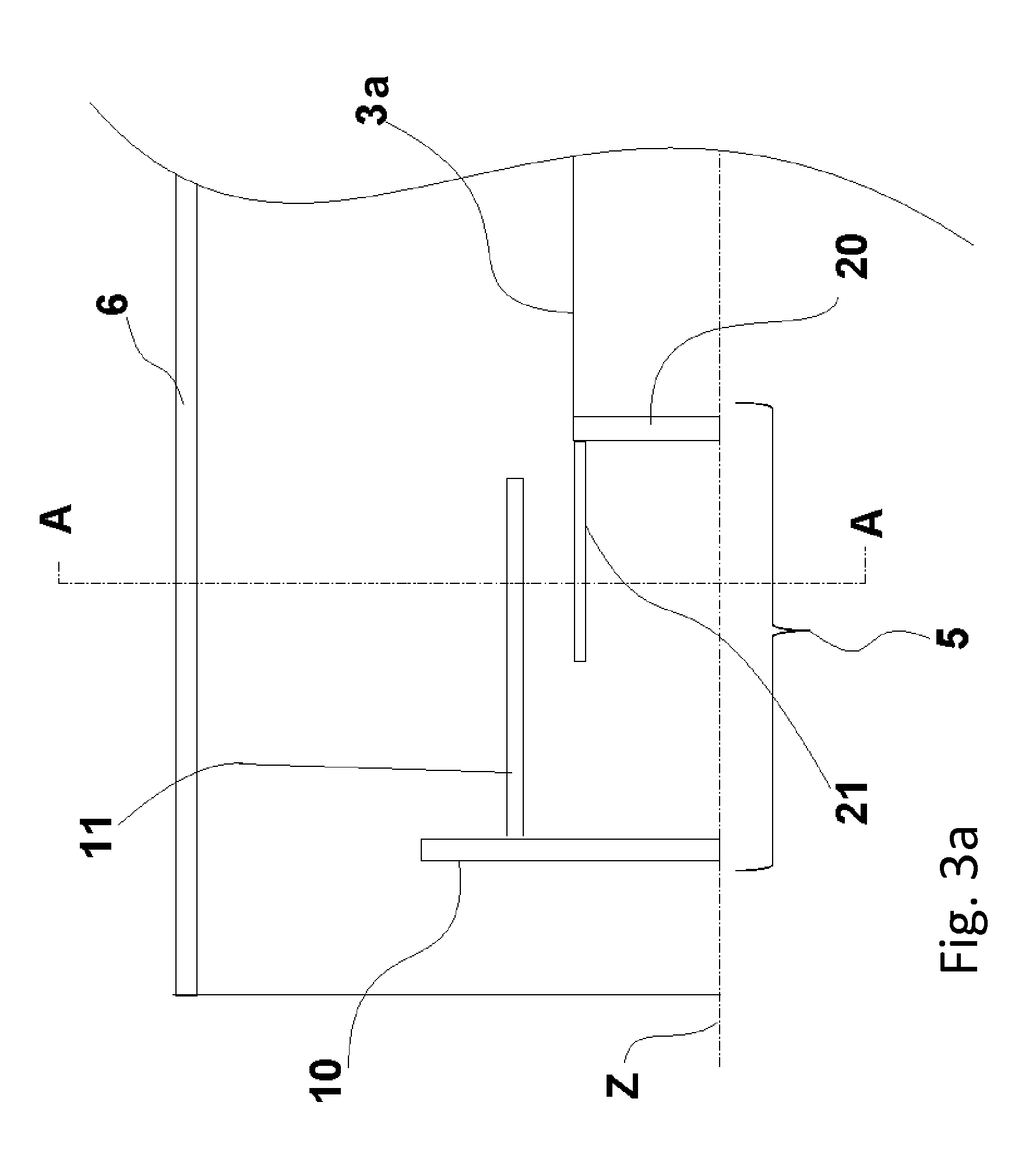
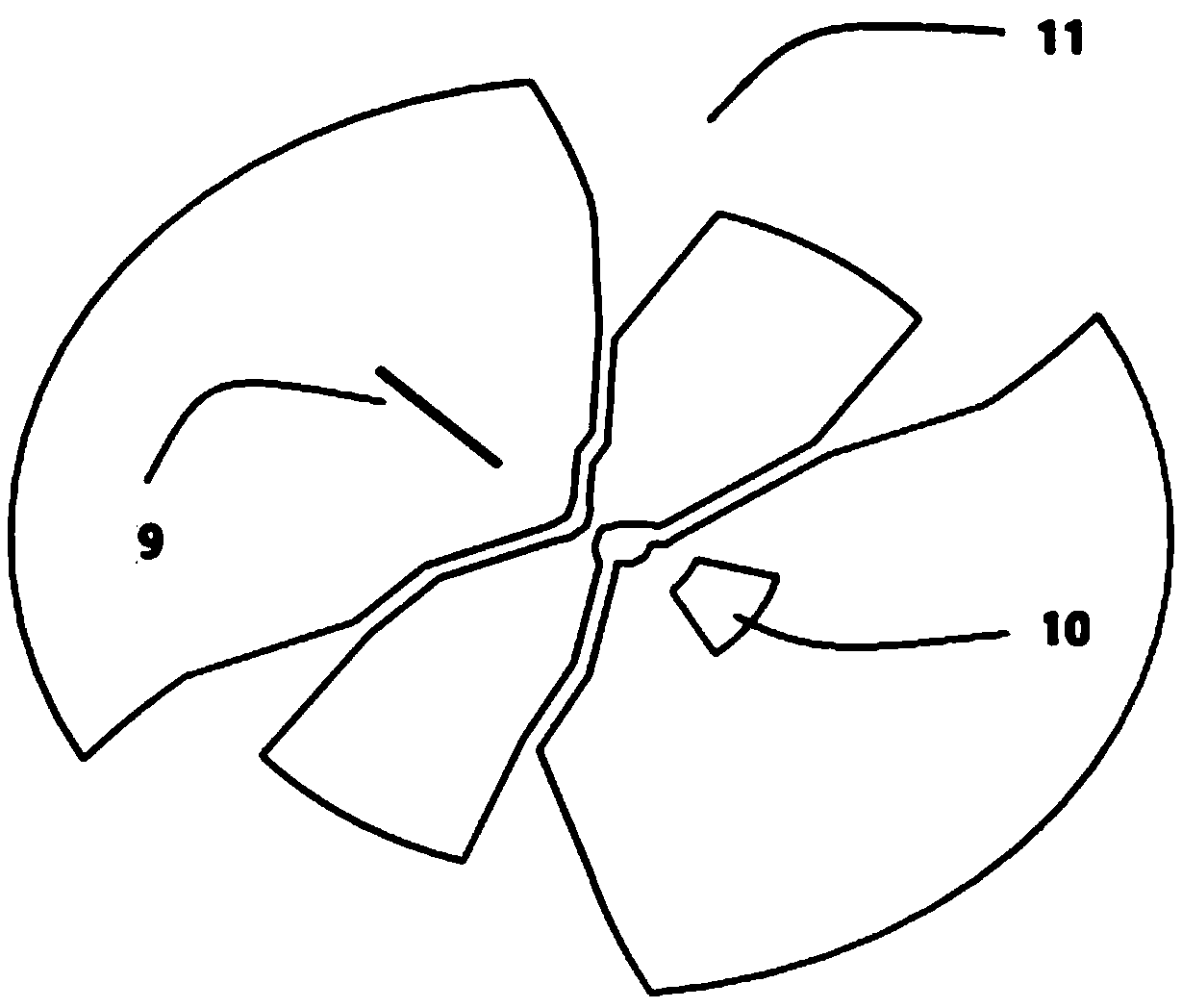
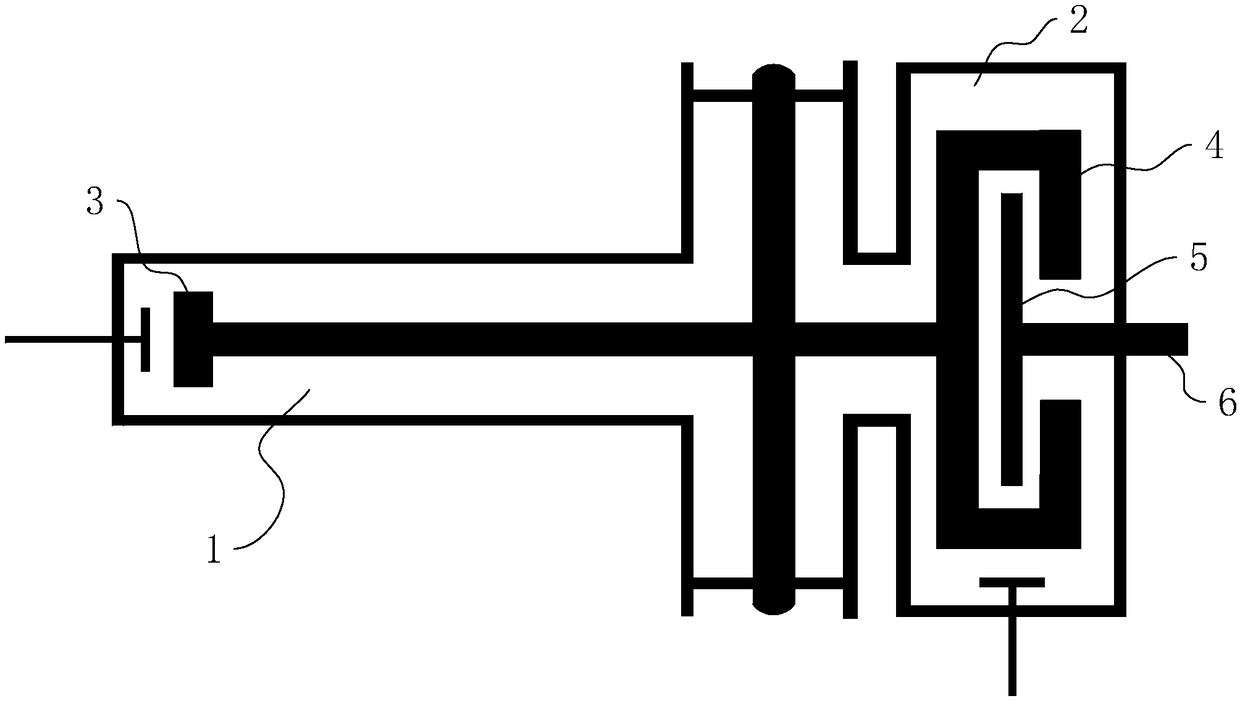
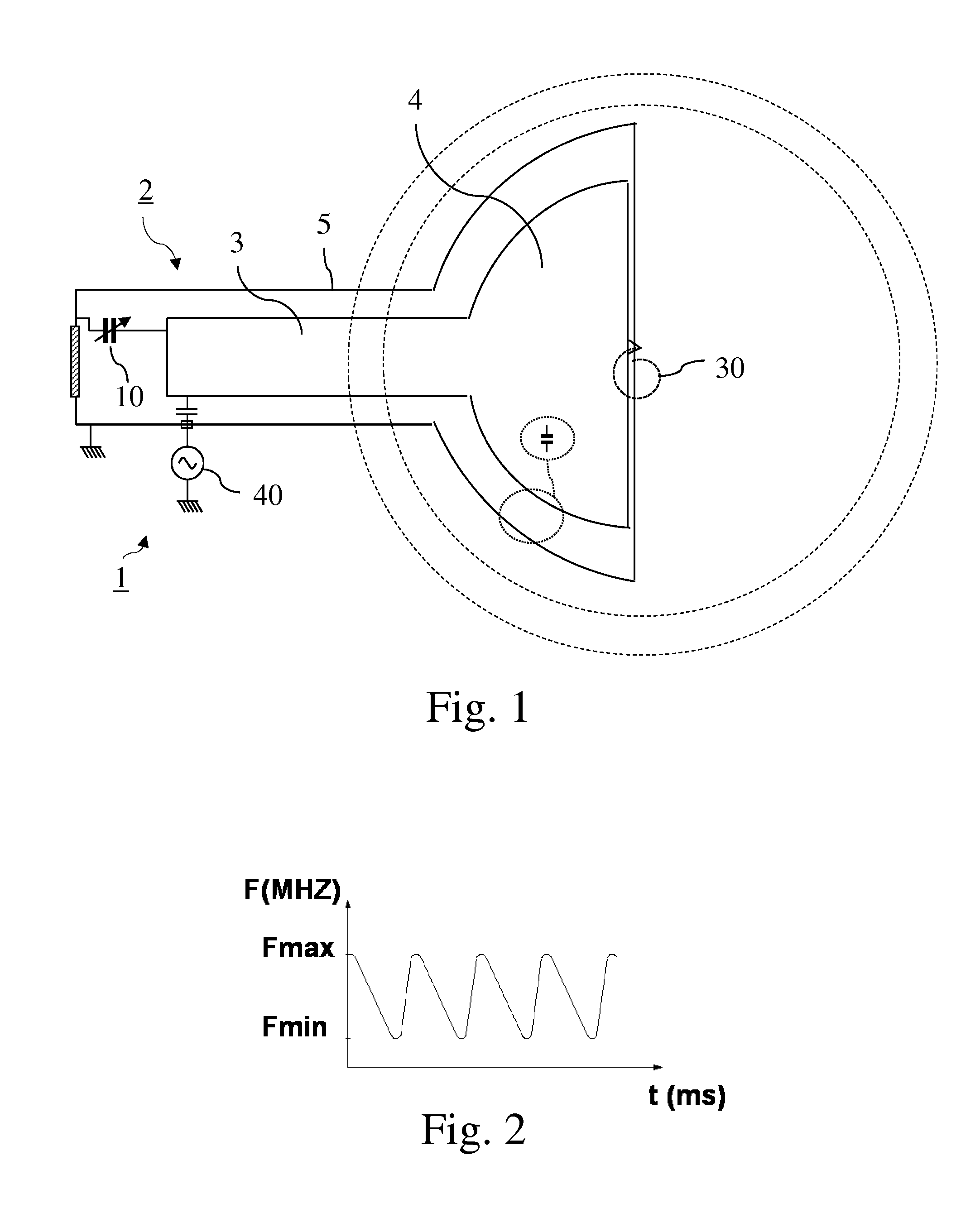
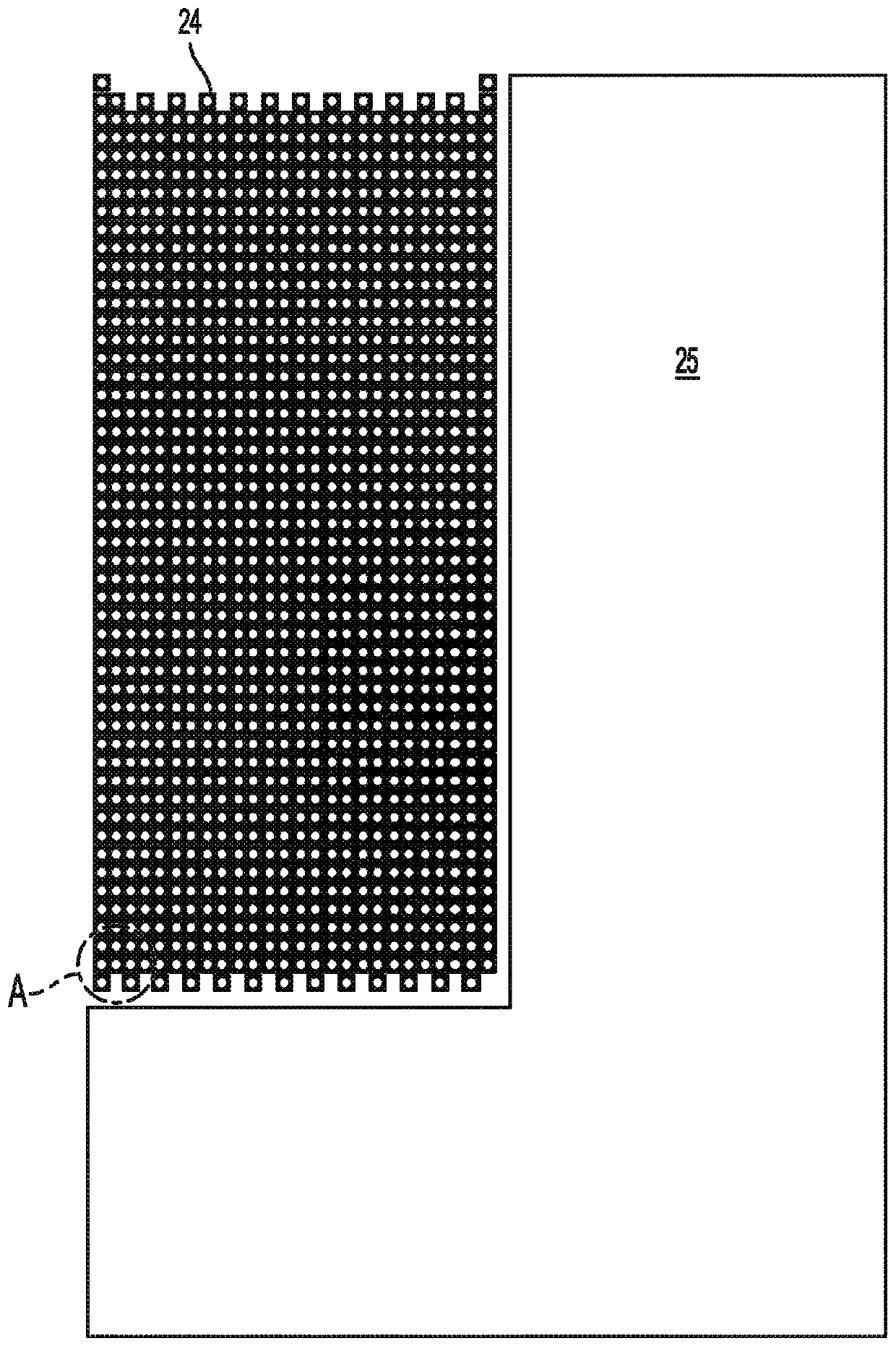
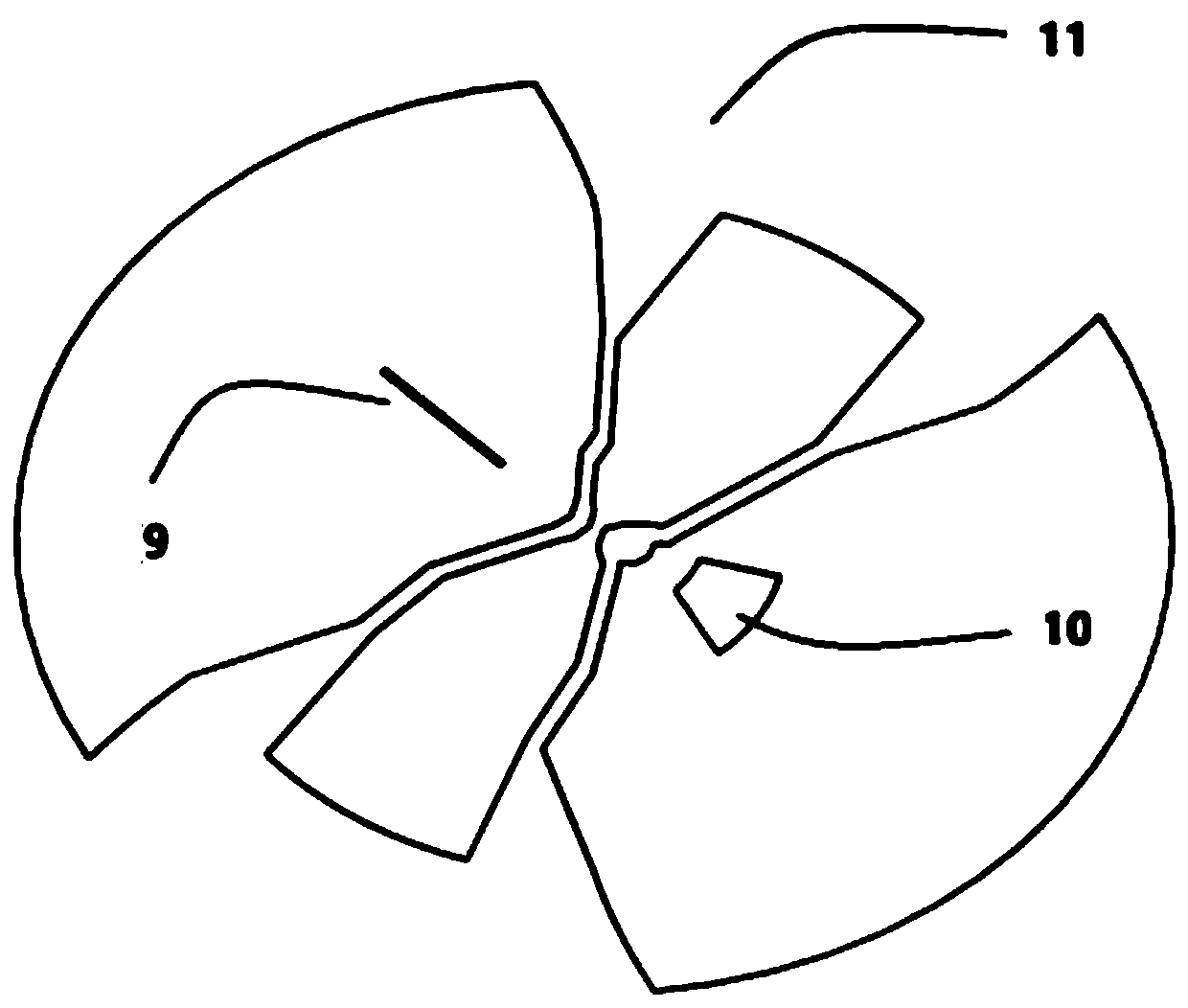
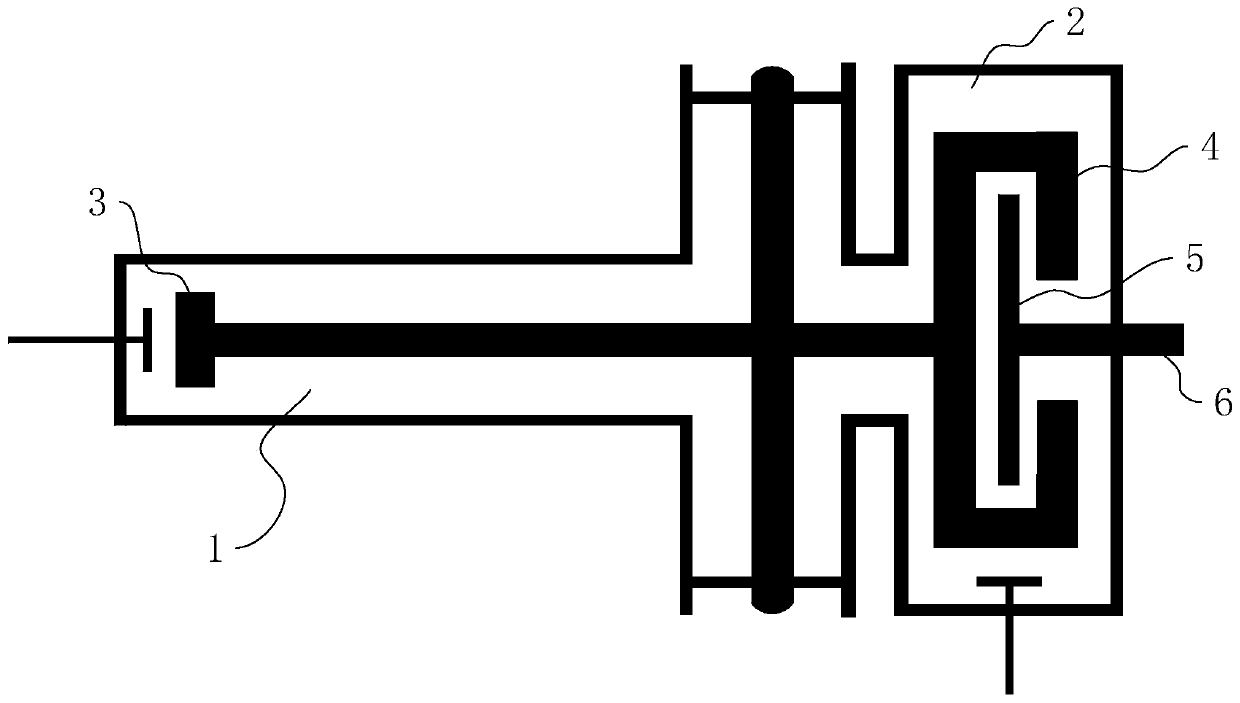
A variable rotating capacitor or RotCo 5 that can be connected via a transmission line 3 to the dee 2 of a synchrocyclotron 1 so as to adjust a resonant frequency of the synchrocyclotron as a function of time and which comprises a cylindrical rotor 10 and a cylindrical stator 20 that are coaxial with the Z axis. The rotor comprises a plurality of circumferentially-distributed rotor electrodes 11 extending parallel to its rotation axis Z. The stator comprises a plurality of circumferentially-distributed stator electrodes 21 extending parallel to the rotation axis Z. Each stator electrode 21 consists of a single metal plate and all said plates are distributed over one and the same stator circumference 25. This makes it possible for the RF currents in the electrodes to be better distributed and thus reduces the local overheating.The present invention also relates to a synchrocyclotron comprising such a RotCo.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Magnetic structure for circular ion accelerator
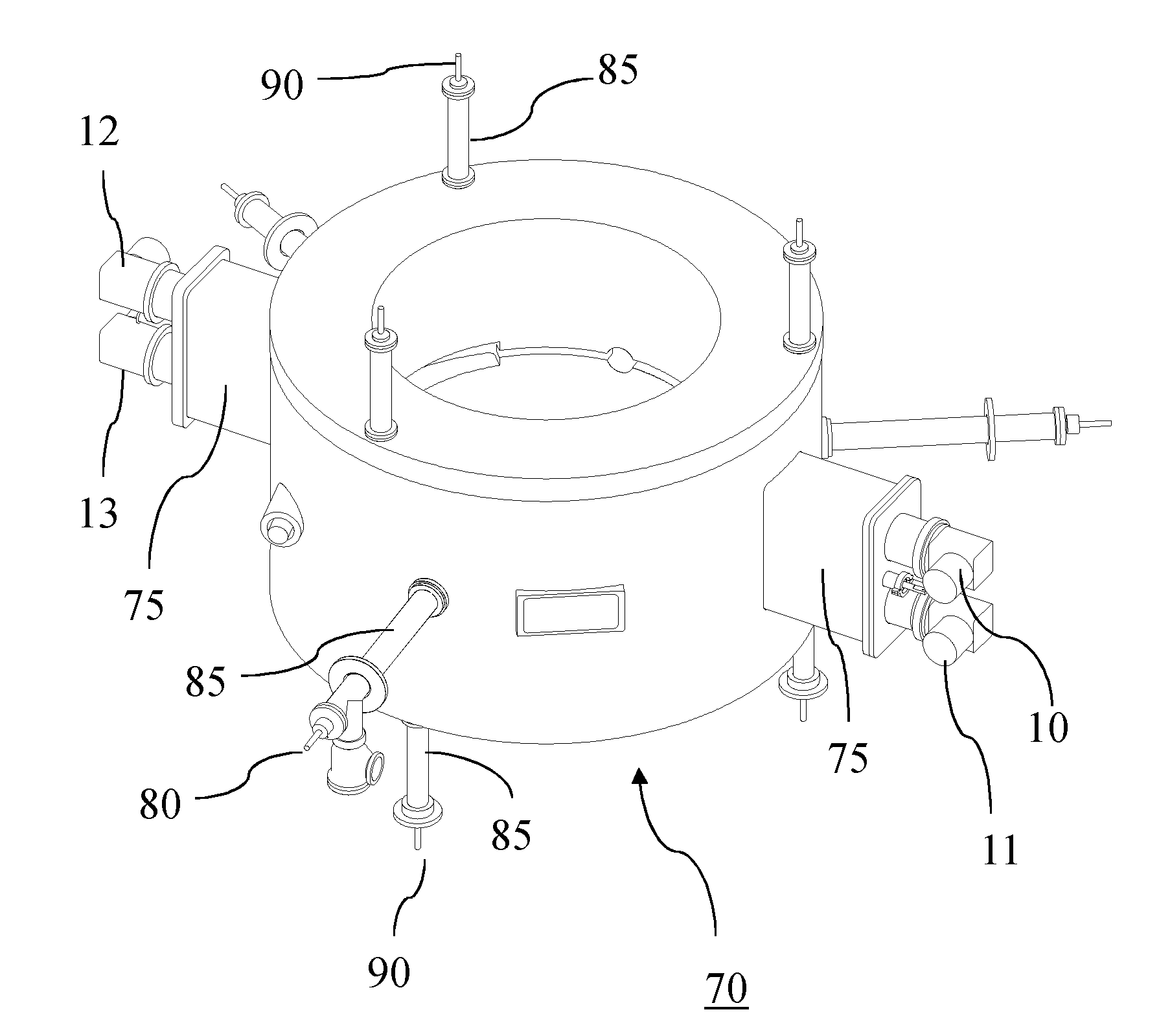
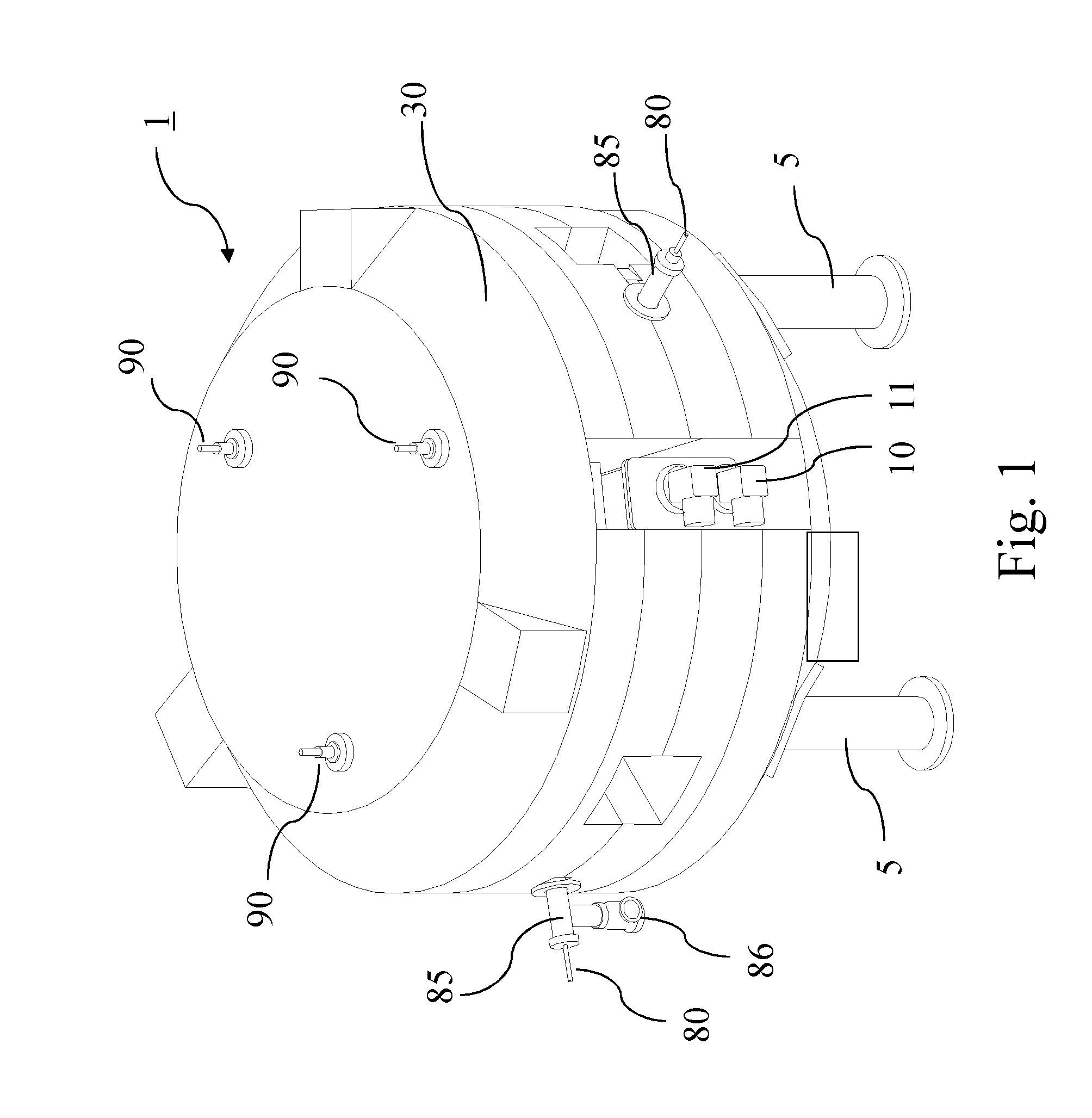
A magnet structure for use in a circular ion accelerator, such as e.g. a synchrocyclotron comprises a cold-mass structure including superconducting magnetic coils (20, 25), at least one dry cryocooler unit (10, 11, 12, 13) coupled with the cold-mass structure for cooling the latter and a magnetic yoke structure (30) with a return yoke (35) configured radially around said coils (20, 25). The return yoke (35) comprises an opening in which said dry cryocooler unit (10, 11, 12, 13) is received so as to be in thermal contact with said cold-mass structure.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
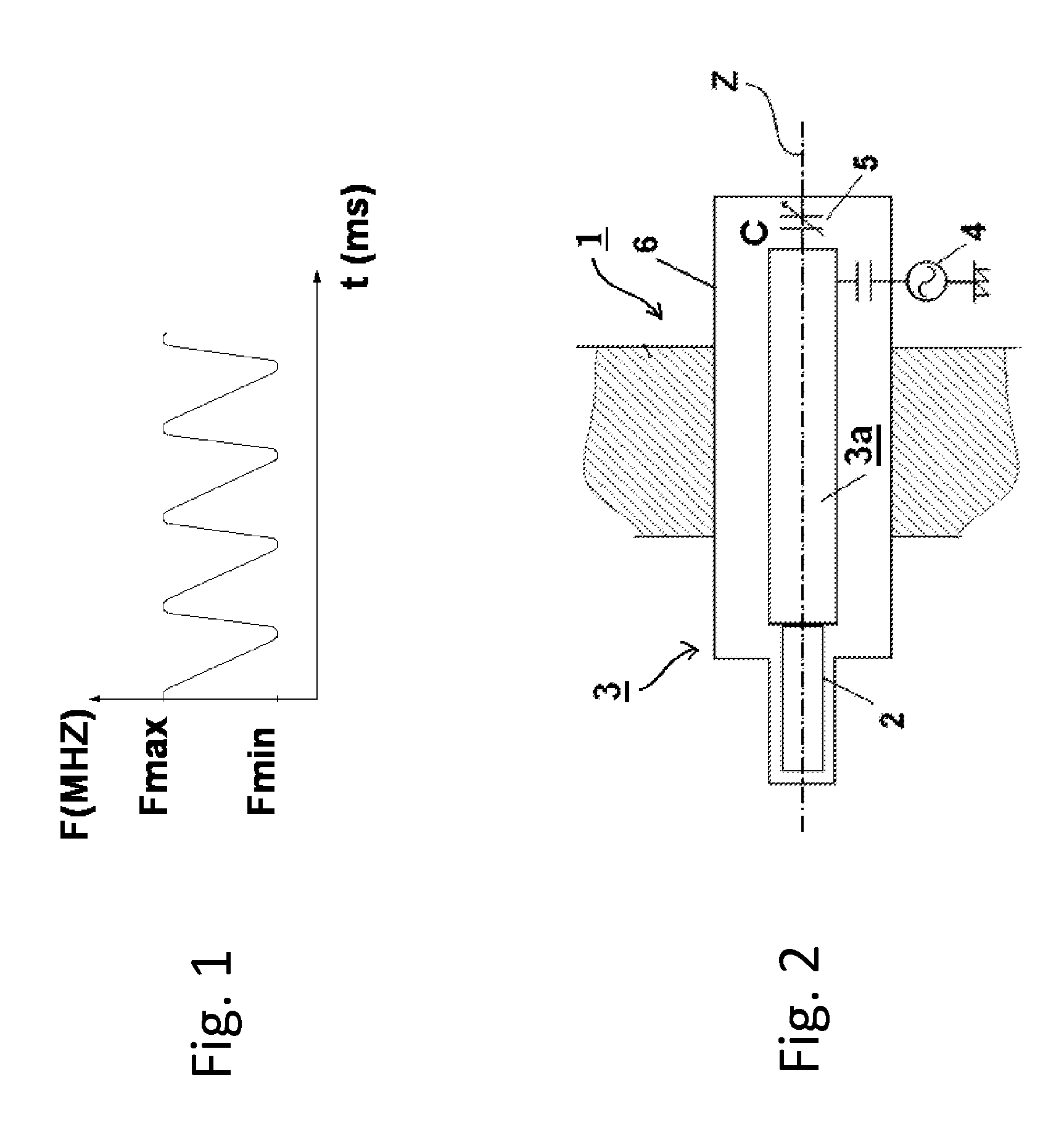
RF device for synchrocyclotron
ActiveUS20140320006A1Low costIncreased durabilityMagnetronsMagnetic resonance acceleratorsCapacitanceResonant cavity
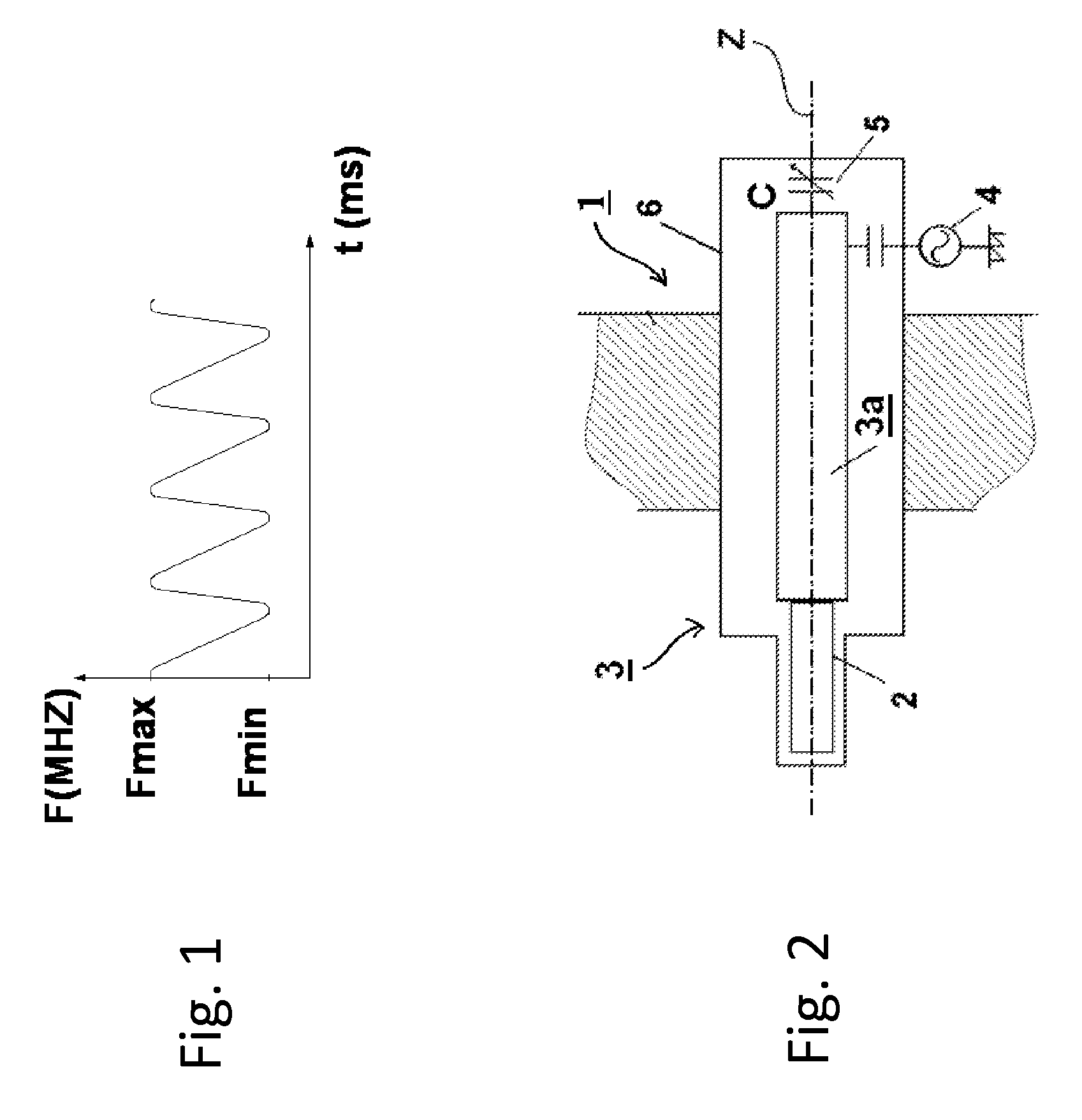
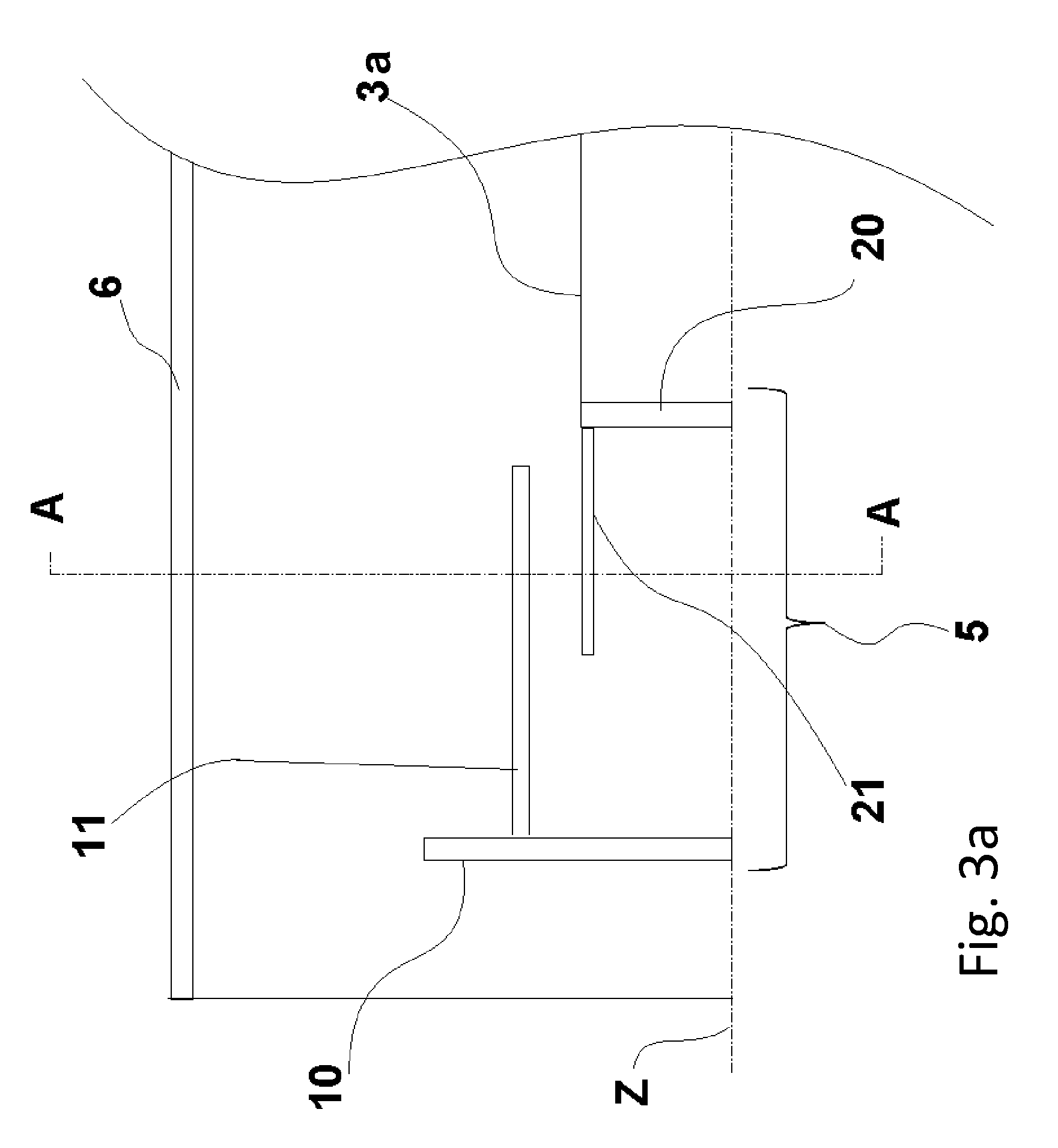
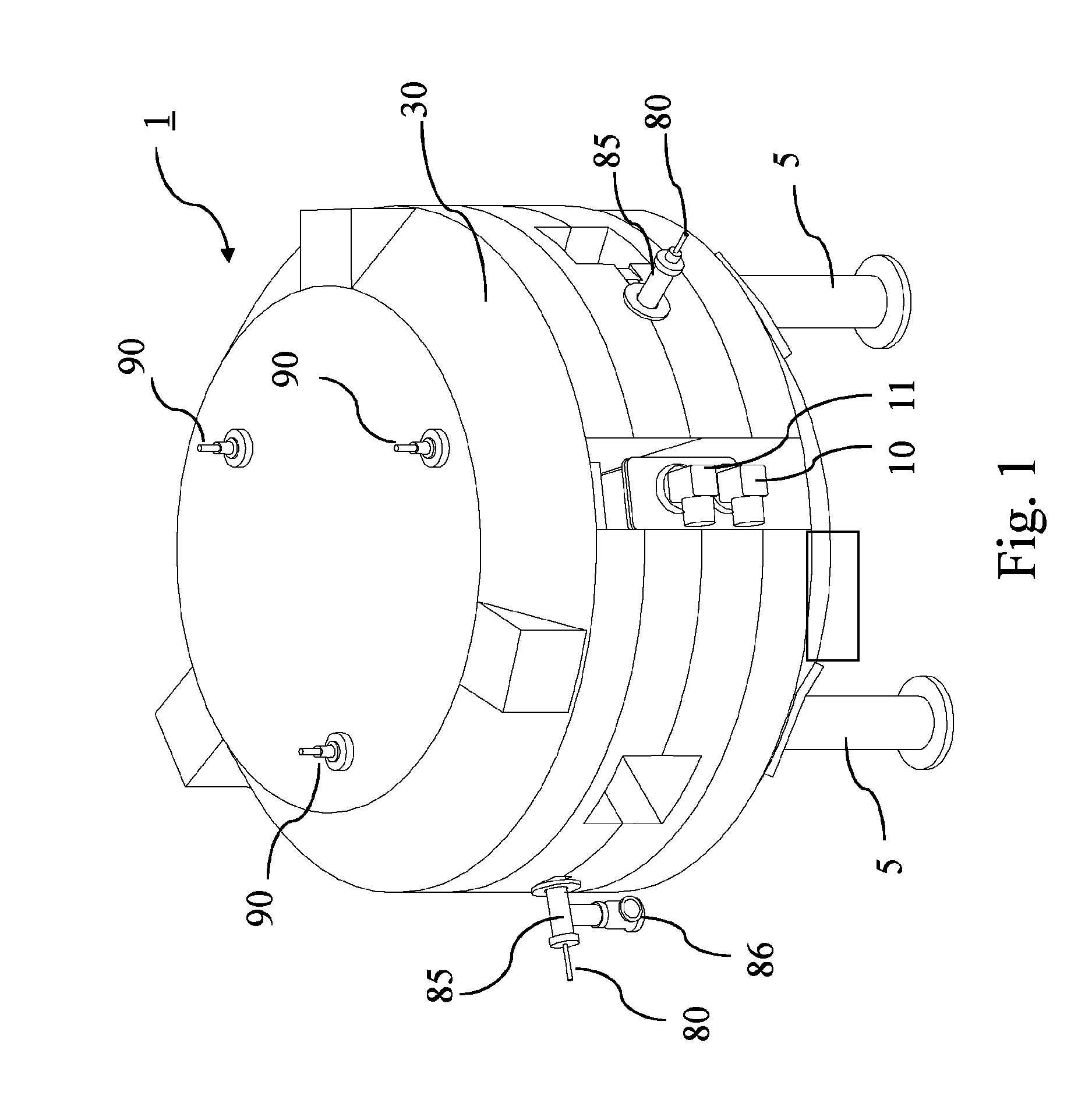
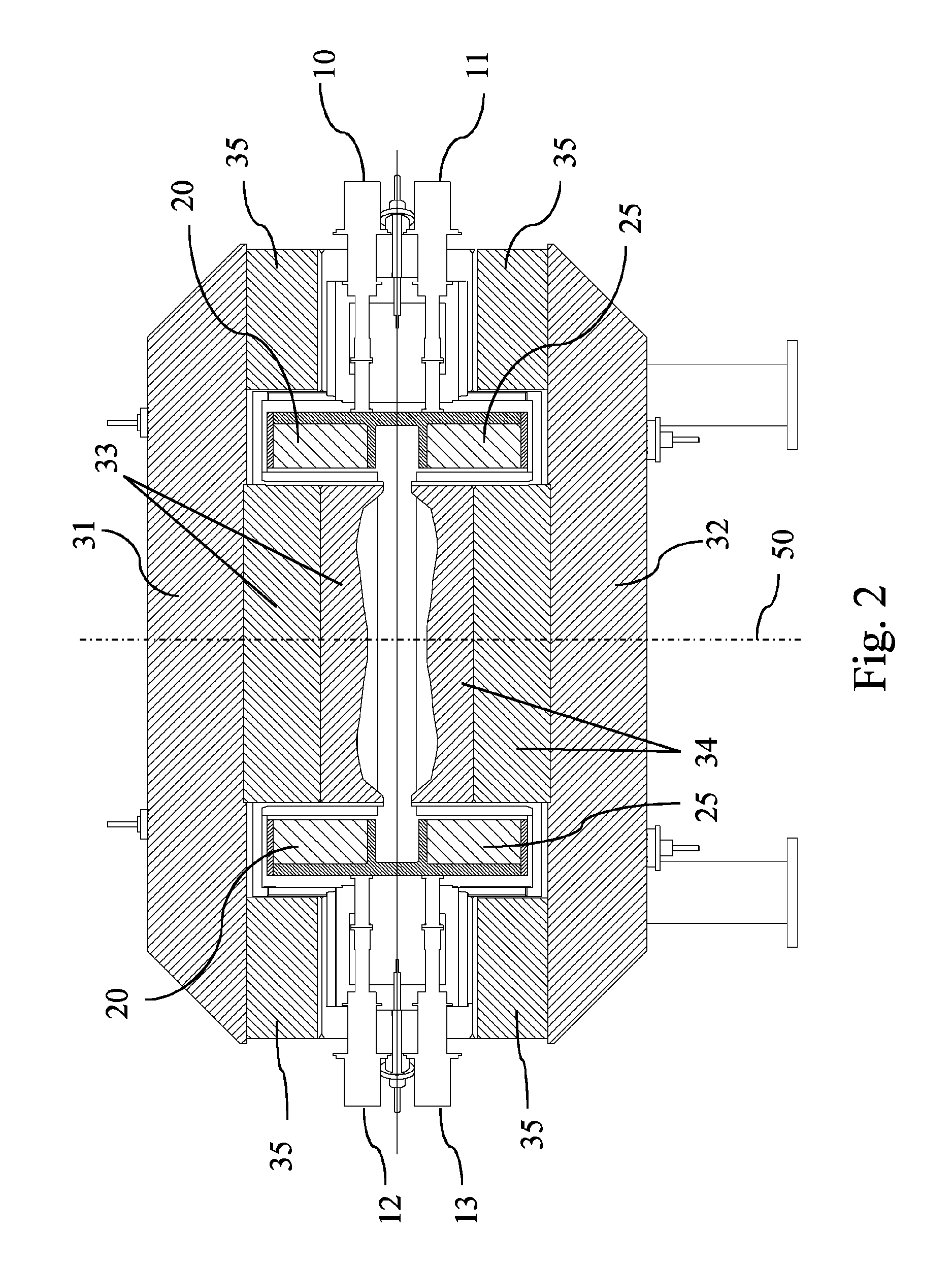
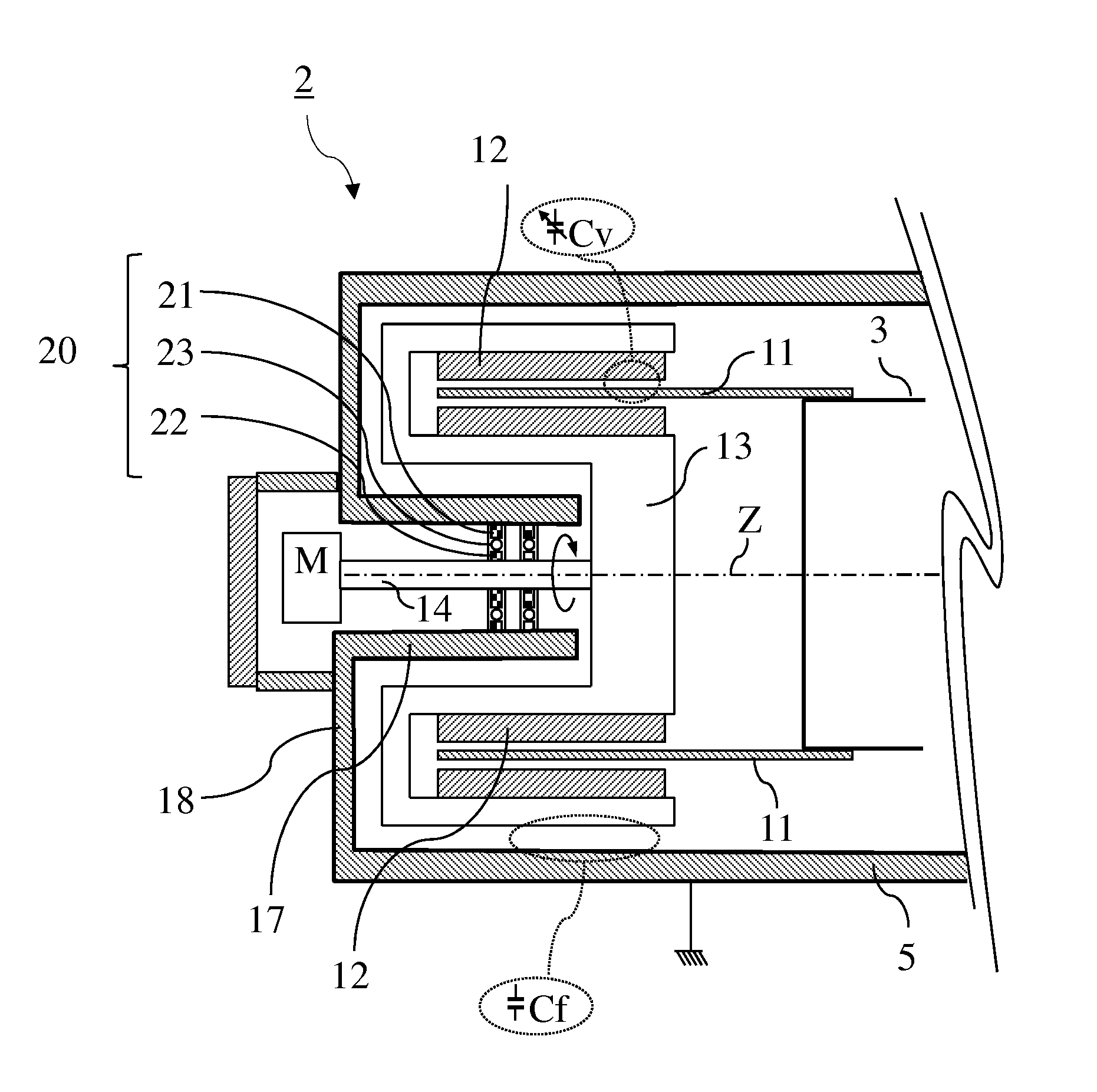
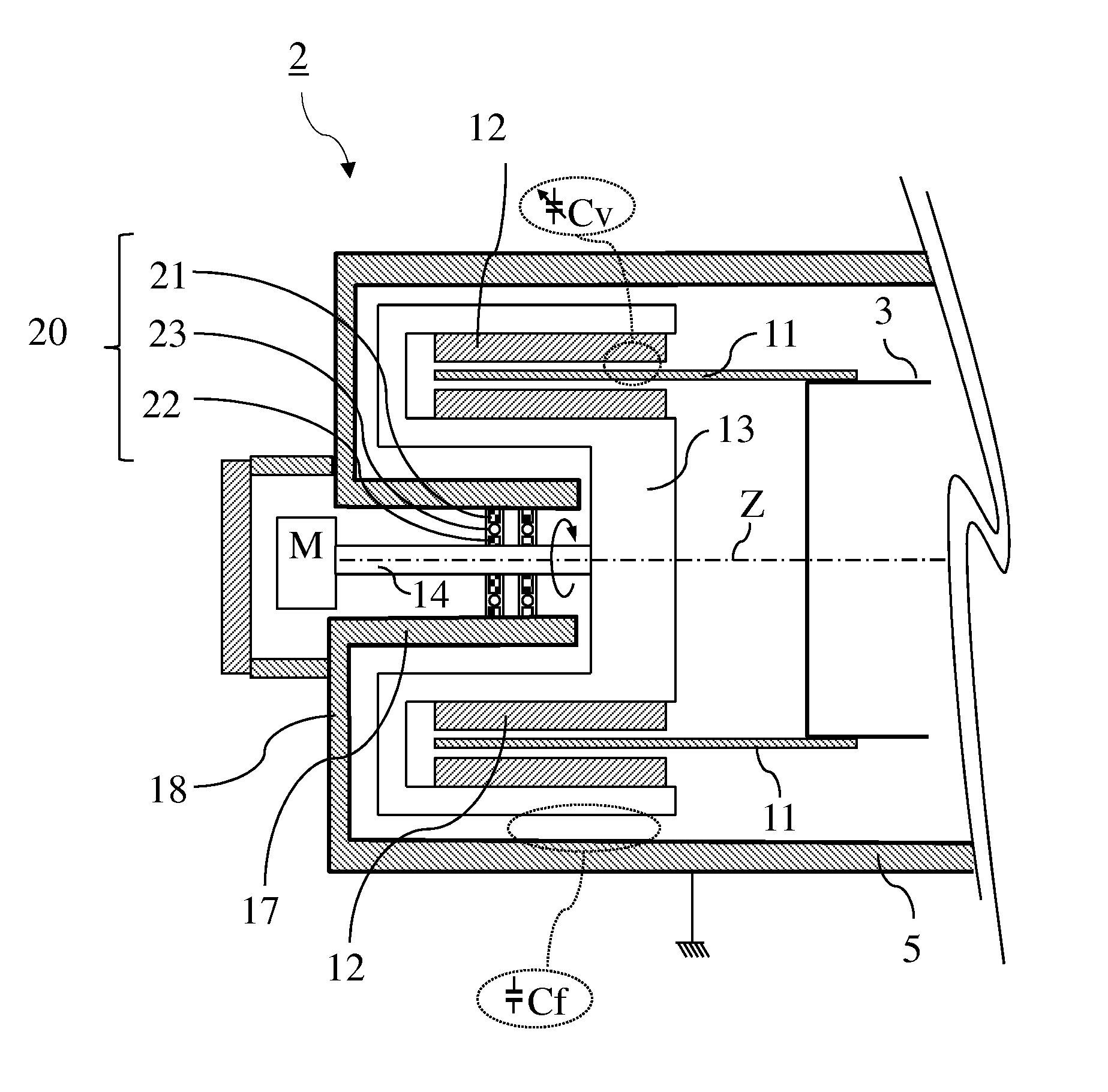
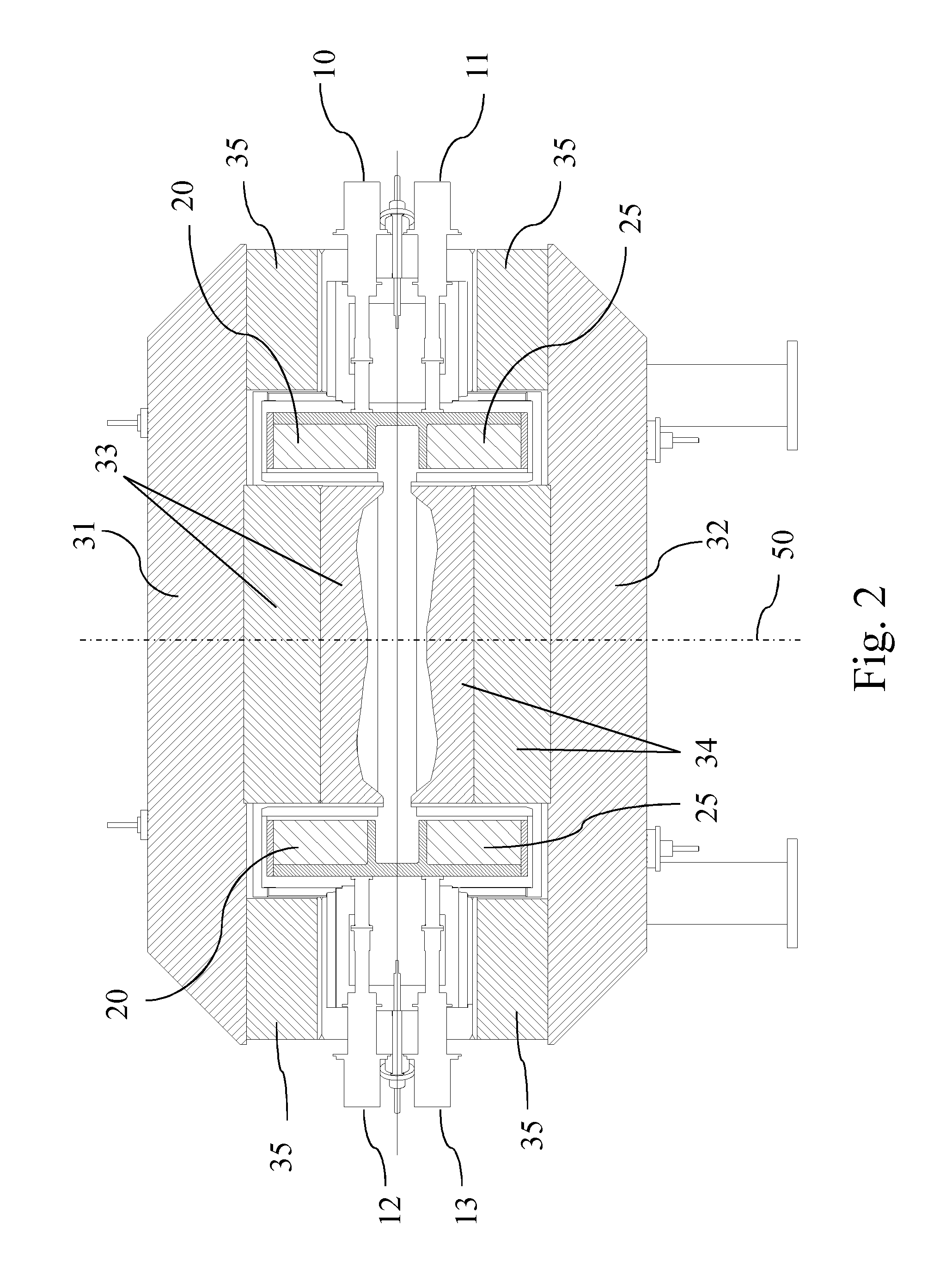
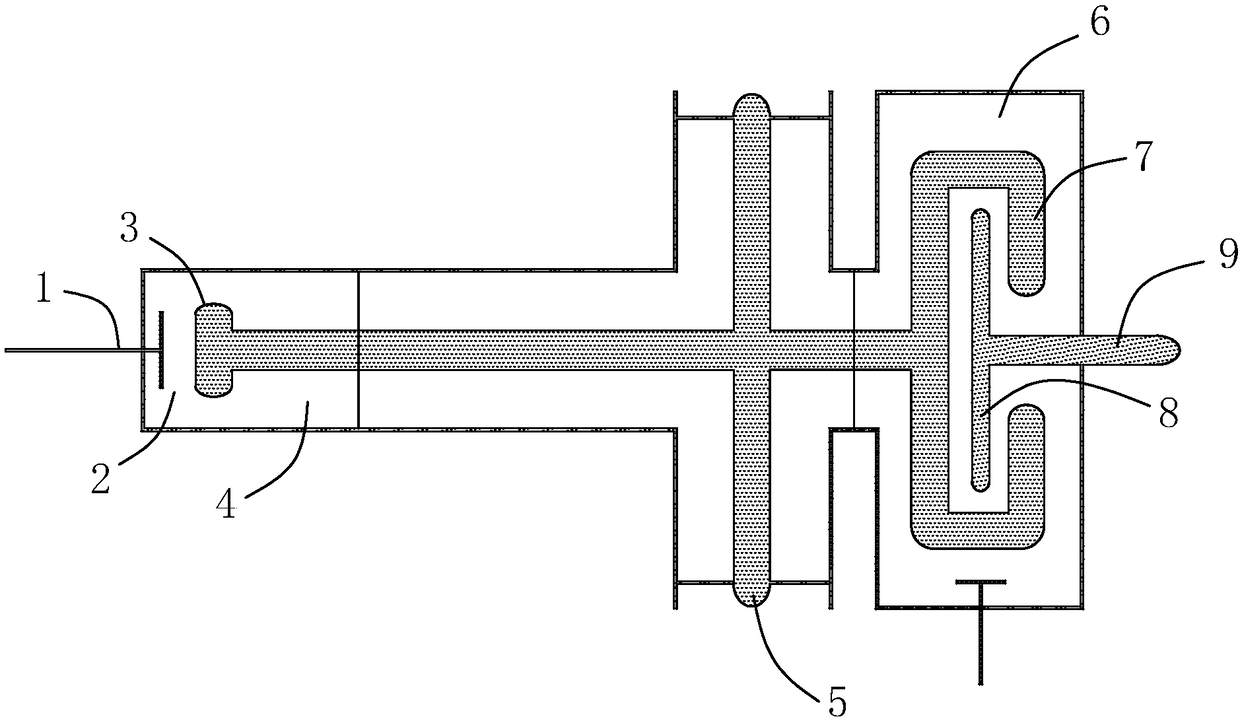
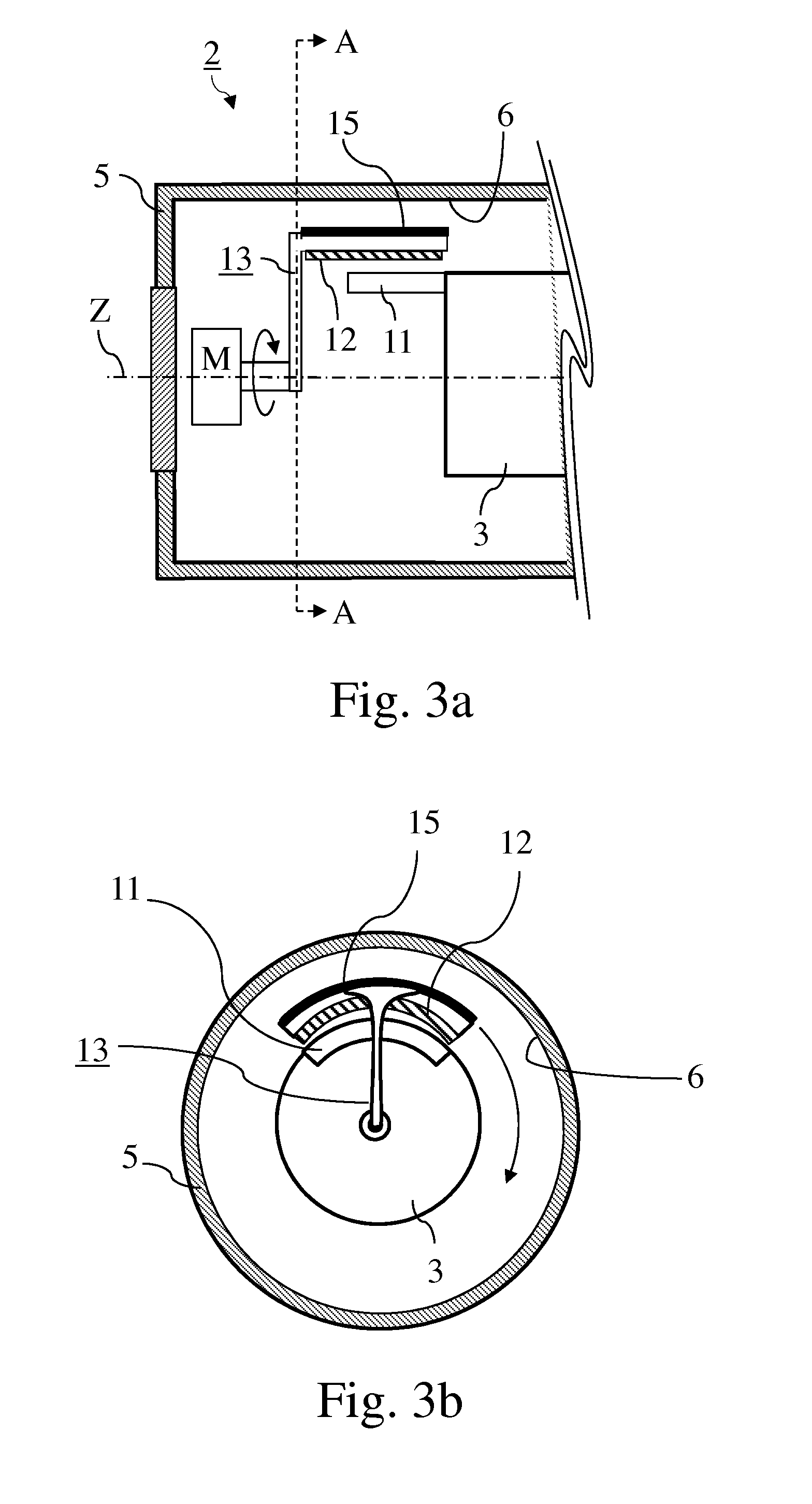
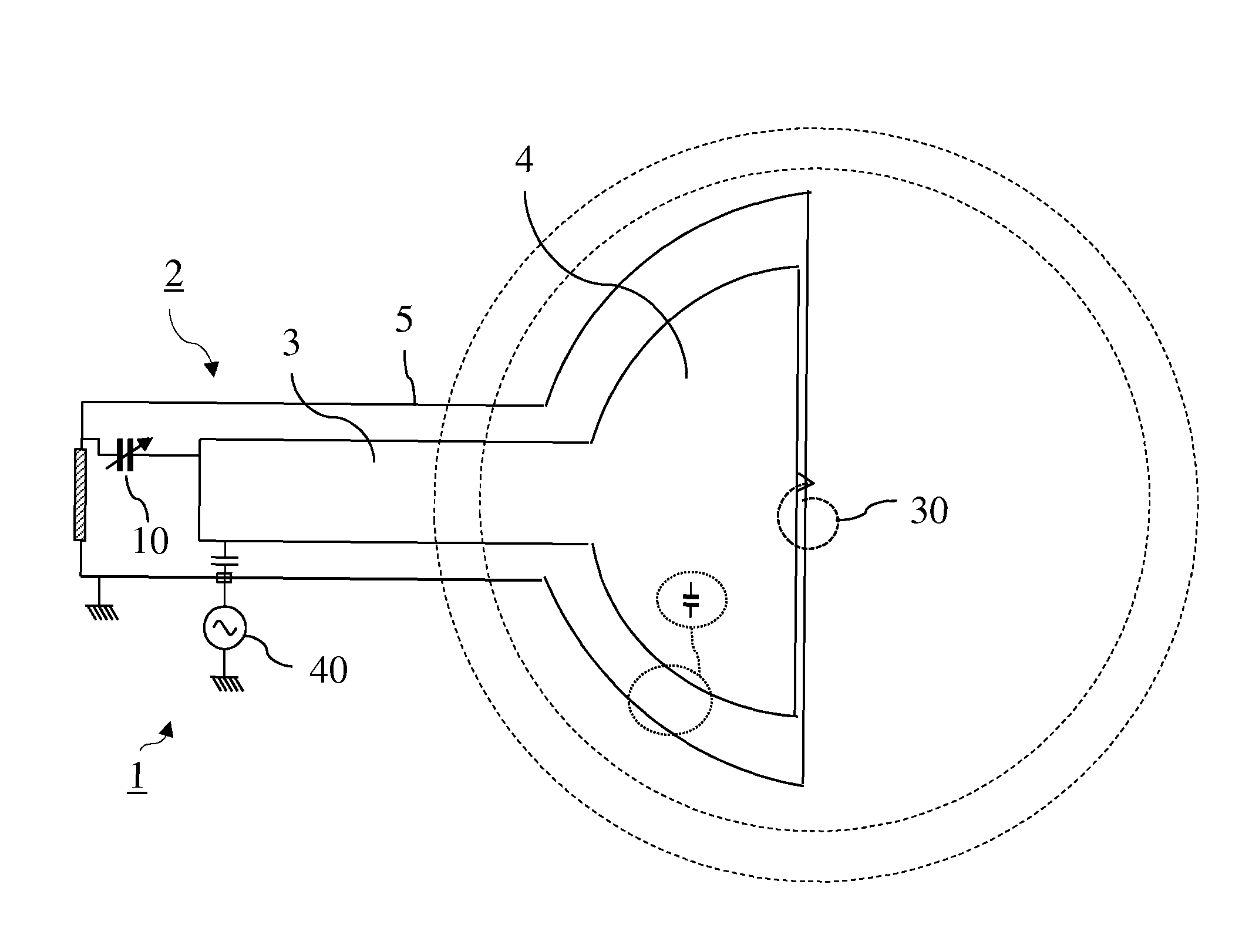
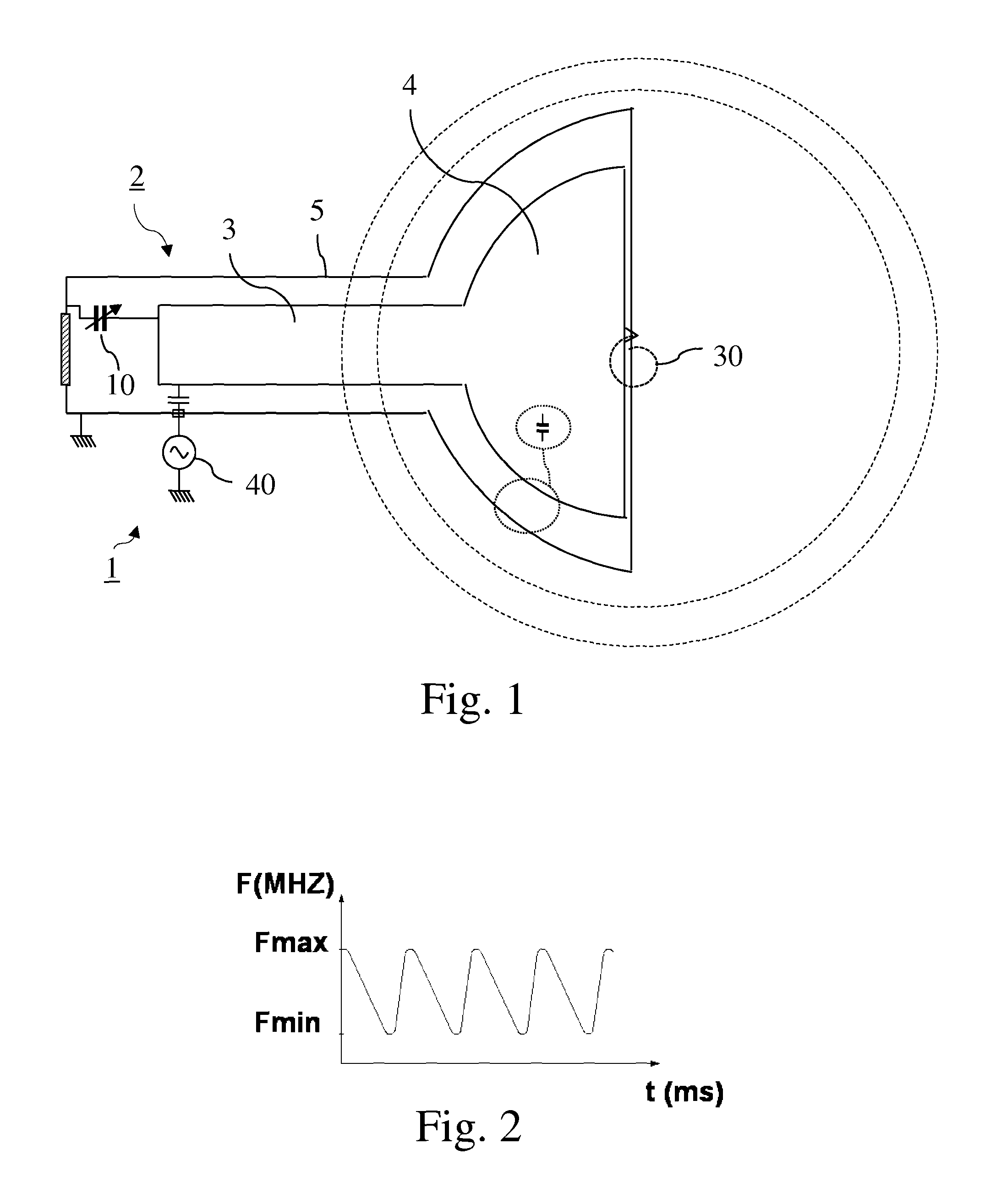
RF device (1) able to generate an RF acceleration voltage in a synchrocyclotron. The device comprises a resonant cavity (2) formed by a grounded conducting enclosure (5) and enveloping a conducting pillar (3) to a first end of which an accelerating electrode (4) is linked. A rotary variable capacitor (10) is mounted in the conducting enclosure at a second end of the pillar, opposite from the first end, comprising at least one fixed electrode (stator) (11) and a rotor (13) exhibiting a rotation shaft (14) supported and guided in rotation by galvanically isolating bearings (20), said rotor (13) comprising one moveable electrode (12) possibly facing the stator (11). When the shaft (14) rotates, the stator and the moveable electrode together form a variable capacitance whose value varies cyclically with time. The rotor (13) is galvanically isolated from the conducting enclosure (5) and from the pillar (3). The stator (11) is connected to the second end of the pillar (3) or to the conducting enclosure (5). The rotor is respectively coupled capacitively to the conducting enclosure or to the pillar. This makes it possible to dispense with sliding electrical contacts between the rotor and respectively the conducting enclosure or the pillar.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
RF device for synchrocyclotron
ActiveUS9237640B2Low costIncreased durabilityMagnetic resonance acceleratorsStrophotronsCapacitanceResonant cavity
RF device (1) able to generate an RF acceleration voltage in a synchrocyclotron. The device comprises a resonant cavity (2) formed by a grounded conducting enclosure (5) and enveloping a conducting pillar (3) to a first end of which an accelerating electrode (4) is linked. A rotary variable capacitor (10) is mounted in the conducting enclosure at a second end of the pillar, opposite from the first end, comprising at least one fixed electrode (stator) (11) and a rotor (13) exhibiting a rotation shaft (14) supported and guided in rotation by galvanically isolating bearings (20), said rotor (13) comprising one moveable electrode (12) possibly facing the stator (11). When the shaft (14) rotates, the stator and the moveable electrode together form a variable capacitance whose value varies cyclically with time. The rotor (13) is galvanically isolated from the conducting enclosure (5) and from the pillar (3). The stator (11) is connected to the second end of the pillar (3) or to the conducting enclosure (5). The rotor is respectively coupled capacitively to the conducting enclosure or to the pillar. This makes it possible to dispense with sliding electrical contacts between the rotor and respectively the conducting enclosure or the pillar.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
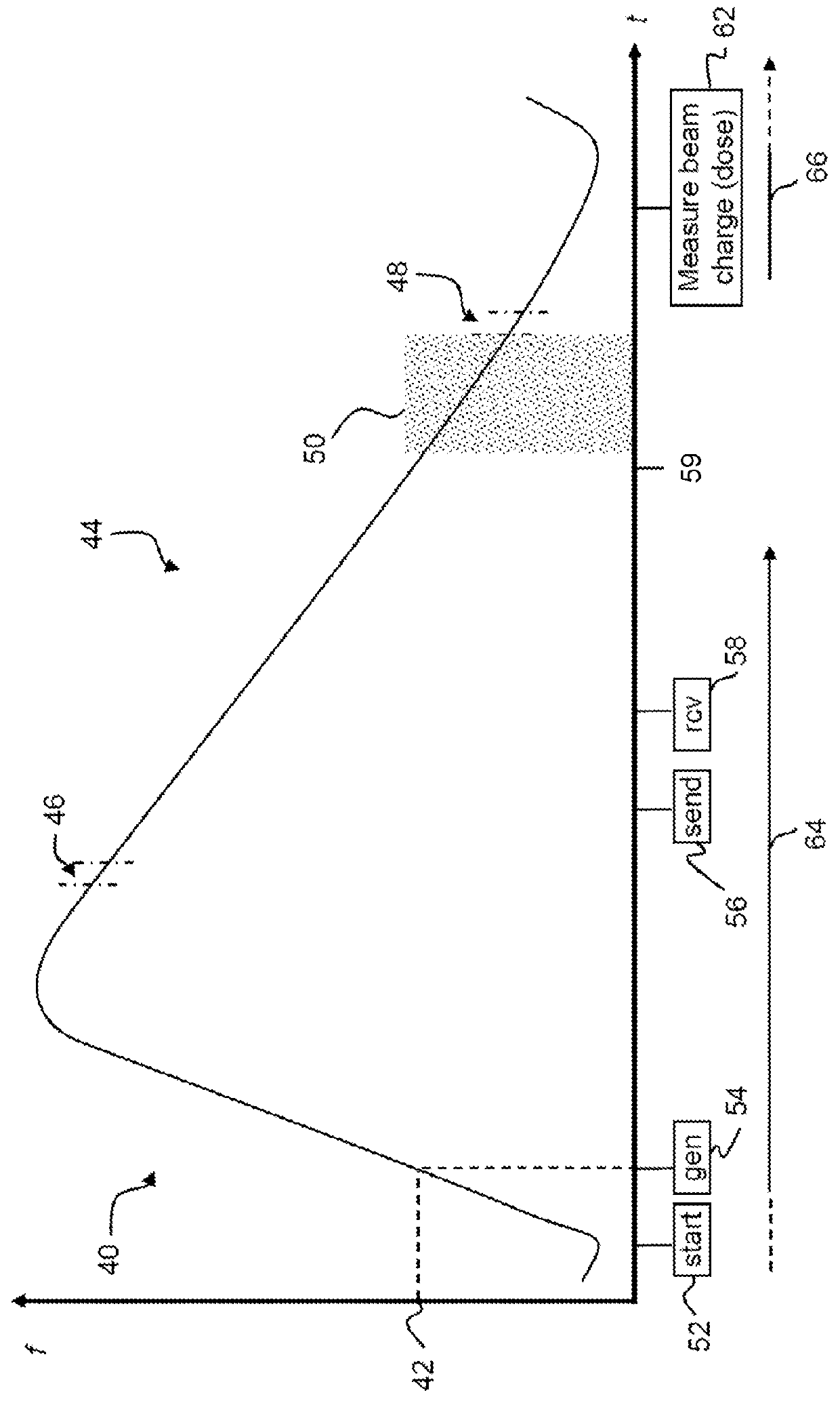
Synchrocyclotron beam orbit and RF drive synchrocyclotron
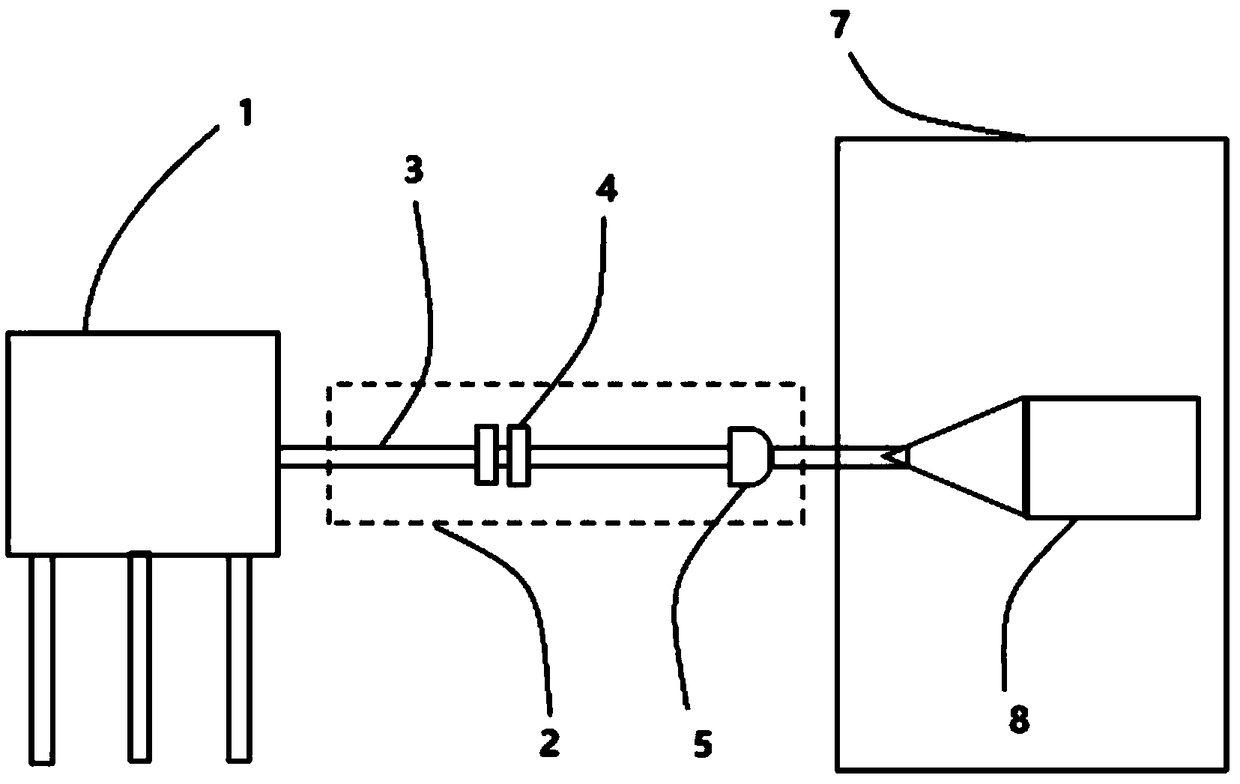
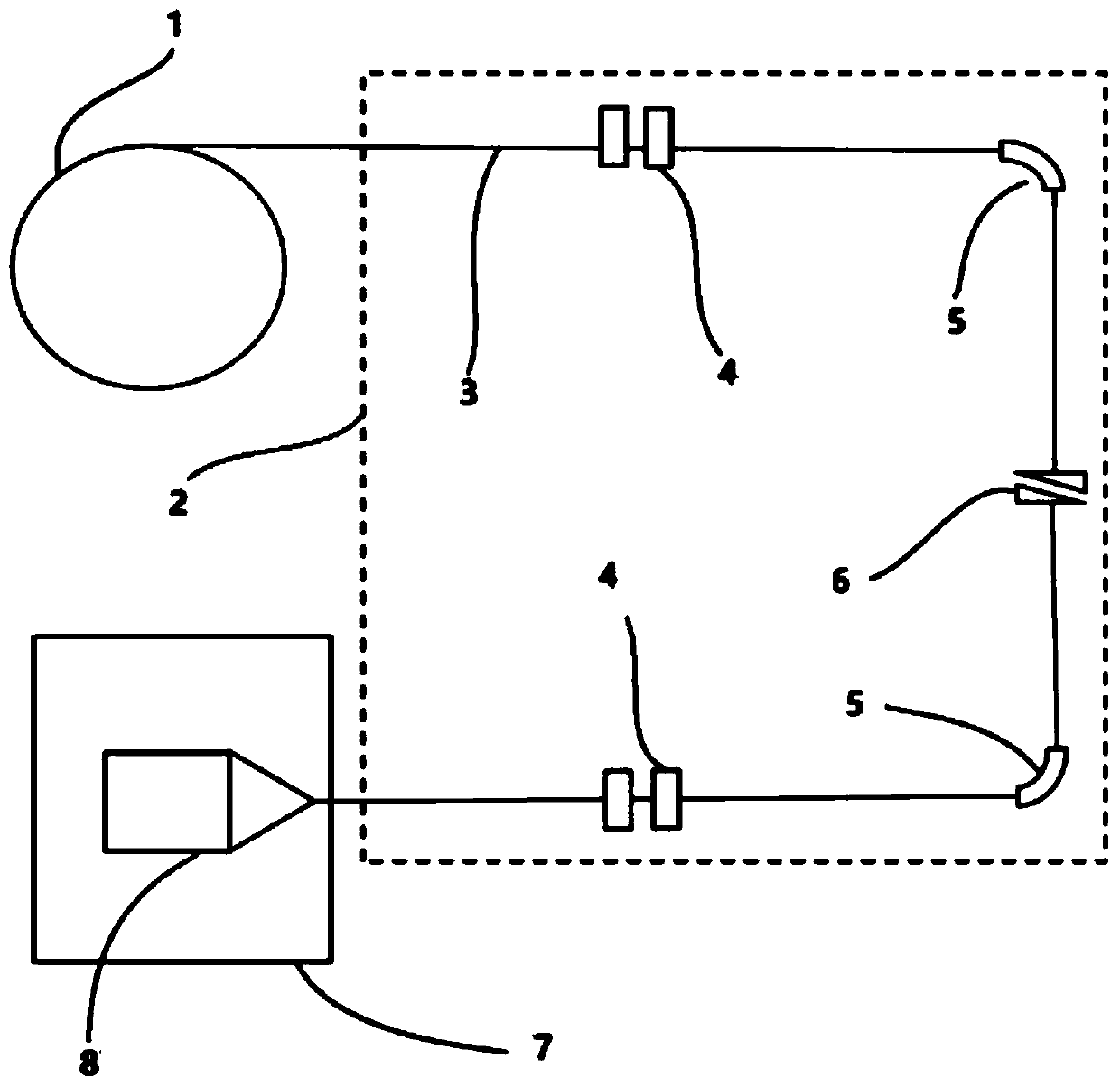
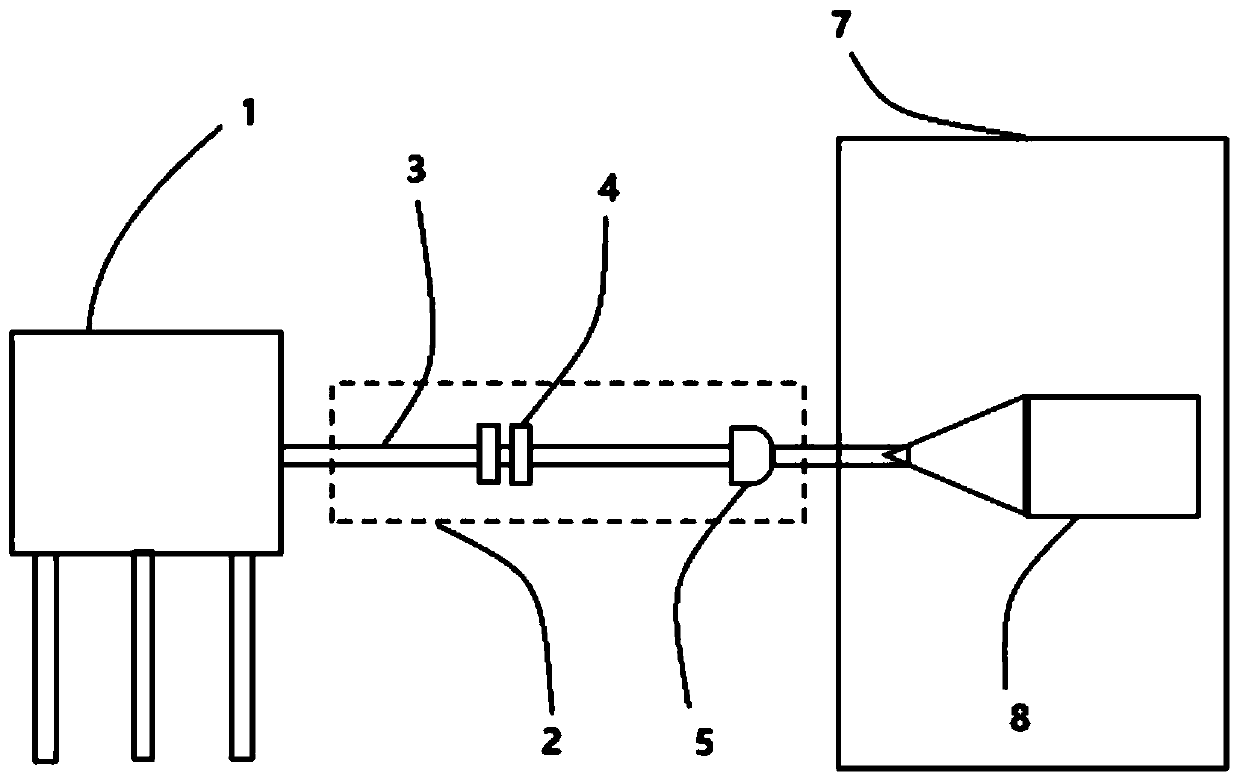
The invention specifies the use of feedback in the radio frequency (RF) drive for a synchrocyclotron, controlling the phase and / or amplitude of the accelerating field as a means to assure optimal acceleration of the beam, to increase the average beam current and to alter the beam orbit in order to allow appropriate extraction as the beam energy is varied. The effect of space charge is reduced by rapid acceleration and extraction of the beam, and the repetition rate of the pulses can be increased. Several means are presented to monitor the phase of the beam in synchrocyclotrons and to adjust the phase and amplitude of the RF to optimize the acceleration of the beam and to adjust the extraction and injection of the beam. Also, the use of a pulsed ion source that matches the acceptance window of the synchrocyclotron is described.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Magnetic Structure For Circular Ion Accelerator
ActiveUS20130270451A1Improve cooling effectStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsThermal contactIon acceleration
A magnet structure for use in a circular ion accelerator, such as e.g. a synchrocyclotron comprises a cold-mass structure including superconducting magnetic coils (20, 25), at least one dry cryocooler unit (10, 11, 12, 13) coupled with the cold-mass structure for cooling the latter and a magnetic yoke structure (30) with a return yoke (35) configured radially around said coils (20, 25). The return yoke (35) comprises an opening in which said dry cryocooler unit (10, 11, 12, 13) is received so as to be in thermal contact with said cold-mass structure.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
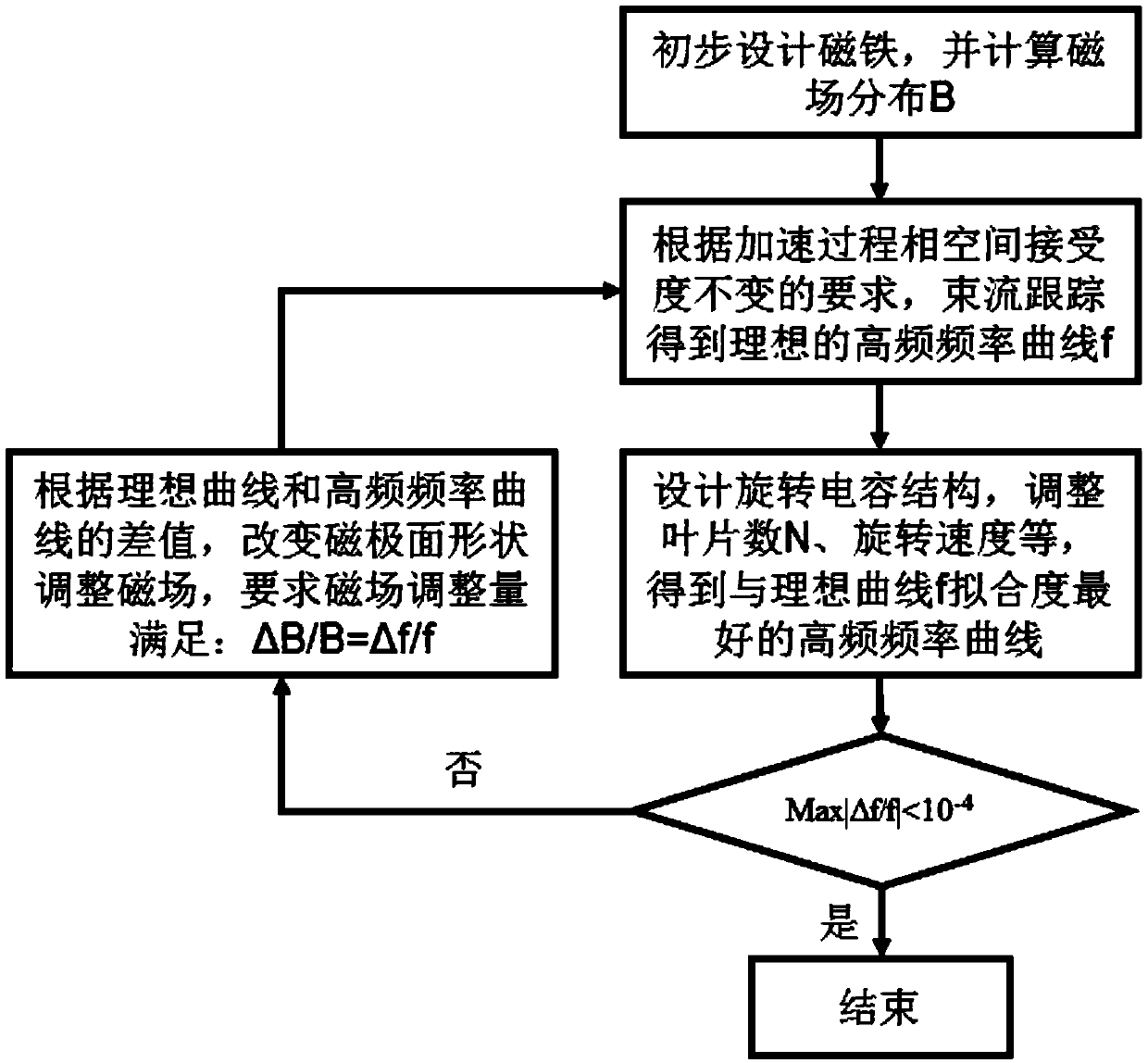
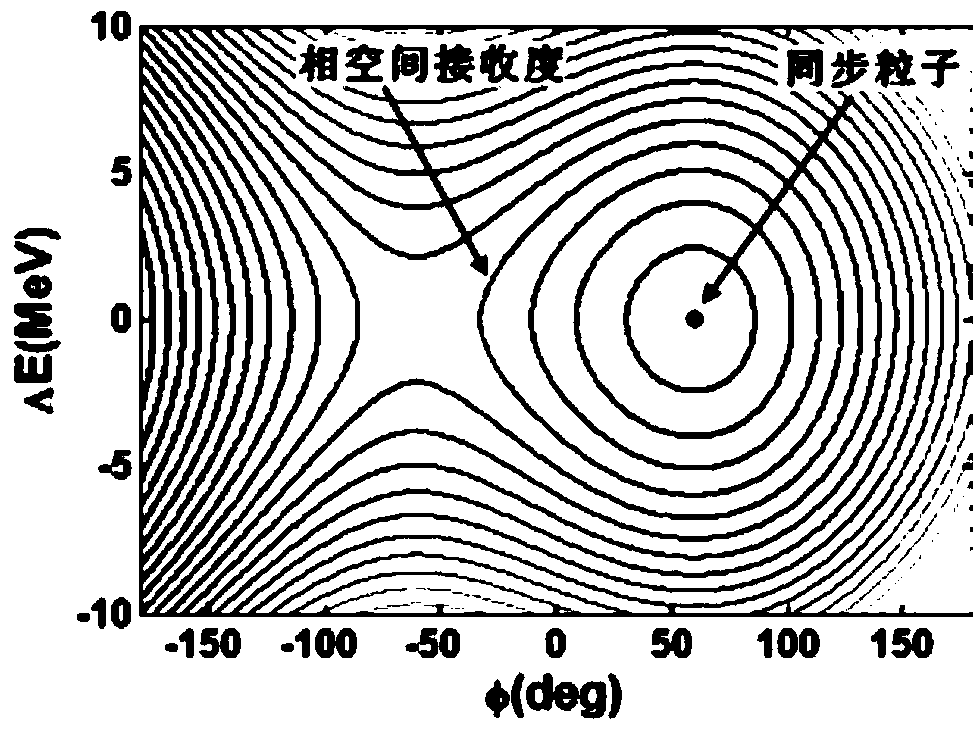
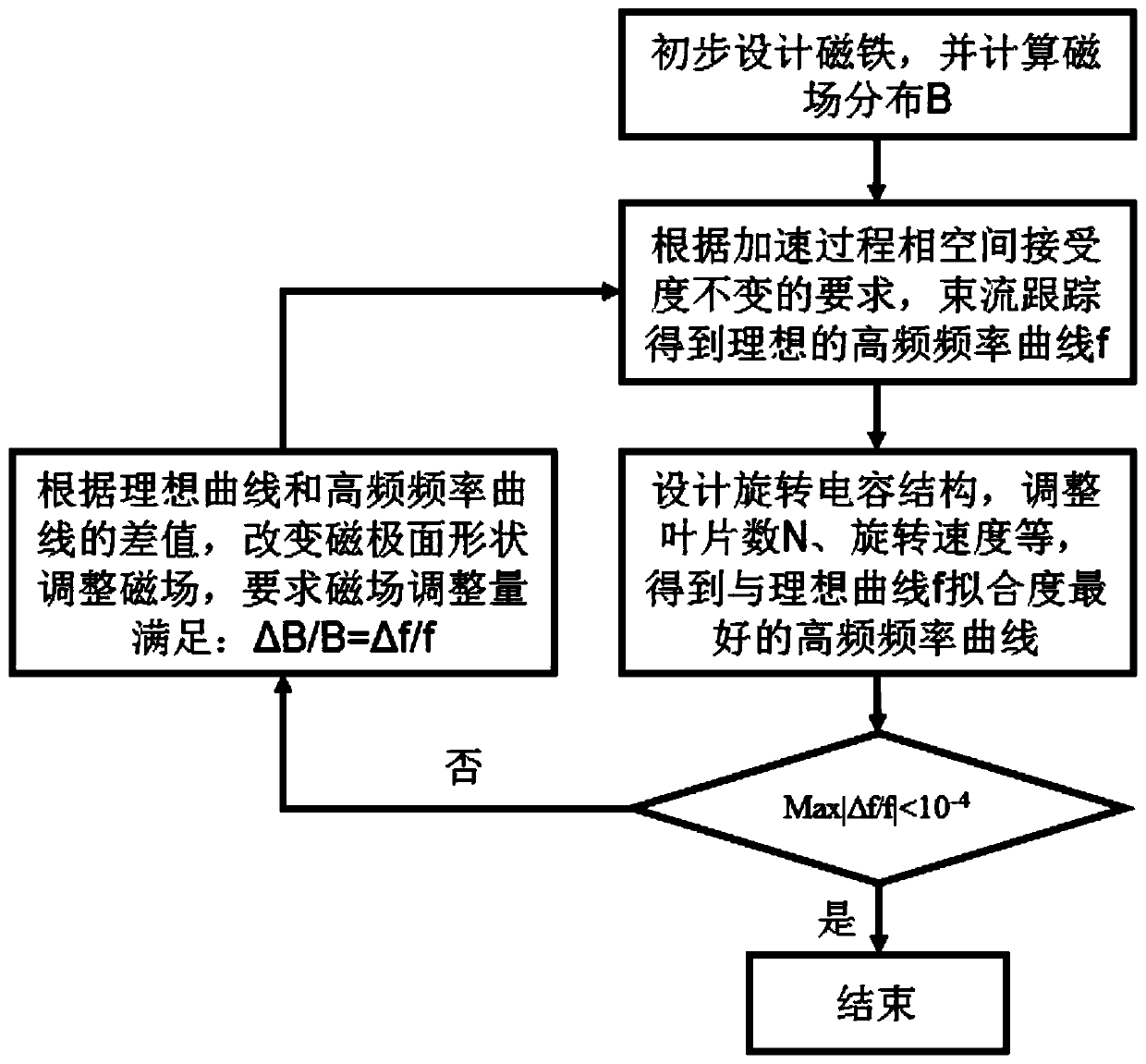
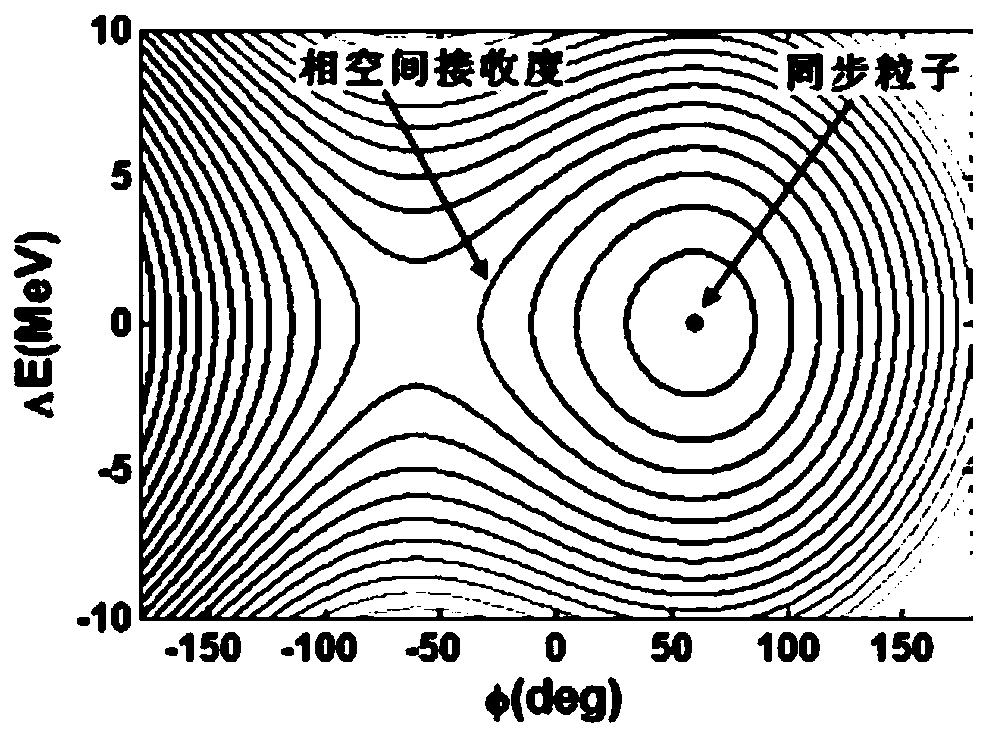
Synchrocyclotron and method for matching high-intensity magnetic field thereof with high-frequency frequency modulation curve
ActiveCN108684132AMinimized beam lossReduce activation levelMagnetic resonance acceleratorsCapacitanceMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a synchrocyclotron and a method for matching a high-intensity magnetic field thereof with a high-frequency frequency modulation curve, belongs to the field of particle cyclotron acceleration, and solves the problem that the magnetic field distribution of a flat magnetic pole does not match the high-frequency frequency modulation curve. The synchrocyclotron mainly includes amain magnet. The two magnetic pole faces with opposite magnetic poles of the main magnet are curved surfaces. The two magnetic poles are disposed centrally symmetrically. The method, based on the fine adjustment of an ideal frequency curve by the compensation of a high-intensity magnetic field and the large-range modulation of the high-frequency frequency curve by a rotary capacitor, repeatedly performs iteration to realize the optimum matching of the high-intensity magnetic field and the high-frequency frequency modulation curve, thereby ensuring the stability of the longitudinal phase spaceacceptance during an acceleration process, minimizing the beam loss in the synchrocyclotron and achieving a low level of excitation.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Variable Rotating Capacitor for Synchrocyclotron
ActiveUS20140103839A1Reduce mechanical deformationLess sensitiveCapacitor with electrode area variationMagnetic resonance acceleratorsPower flowCapacitor
A variable rotating capacitor or RotCo 5 that can be connected via a transmission line 3 to the dee 2 of a synchrocyclotron 1 so as to adjust a resonant frequency of the synchrocyclotron as a function of time and which comprises a cylindrical rotor 10 and a cylindrical stator 20 that are coaxial with the Z axis. The rotor comprises a plurality of circumferentially-distributed rotor electrodes 11 extending parallel to its rotation axis Z. The stator comprises a plurality of circumferentially-distributed stator electrodes 21 extending parallel to the rotation axis Z. Each stator electrode 21 consists of a single metal plate and all said plates are distributed over one and the same stator circumference 25. This makes it possible for the RF currents in the electrodes to be better distributed and thus reduces the local overheating.The present invention also relates to a synchrocyclotron comprising such a RotCo.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Fluid dynamic machine with rotating wheel and rotary vane synchrocyclotron mechanism
PendingCN104912598AImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesRotary piston pumpsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a fluid dynamic machine with a rotating wheel and rotary vane synchrocyclotron mechanism. The fluid dynamic machine comprises a machine body (2), a cylinder cover (6), a cylinder sleeve (3), a rotating wheel (4), a transmission shaft (7), a rotary vane wheel (5) and a rotating wheel cycloid mechanism (11). A left cylinder chamber (15) and a right cylinder chamber (16) are symmetrically distributed in the rotating wheel (4), the left cylinder chamber (15) is divided into a first volume chamber (20) and a second volume chamber (21) by a left rotary vane (19) on the rotary vane wheel (5), the right cylinder chamber (16) is divided into a third volume chamber (23) and a fourth volume chamber (24) by a right rotary vane (22) on the rotary vane wheel (5), the rotary vane wheel (5) and the rotating wheel (4) are synchronously rotated under the effect of the rotating wheel cycloid mechanism (11), the rotating wheel (4) are rotated for one circle, and suction and discharge work by eight times of a fluid (32) are carried out.
Owner:南通金鼎天轮动力科技有限公司
Synchrocyclotron-based proton heavy ion therapy system
ActiveCN109224321AReduce size and weightLow costX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBeam energyHigh energy
The invention discloses a synchrocyclotron-based proton heavy ion therapy system. The system is characterized in that the treatment system adopts a synchrocyclotron to accelerate protons or heavy ionsto the highest energy required for treatment; For protons, the maximum energy is 235 MeV. The beam output from the synchrocyclotron enters the high energy transport line for focusing and deflection and is fed to the energy selector. The energy selector makes the beam energy continuously adjustable through the graphite energy reducer. The beam enters a single room and is sent to a rotating gantrysystem, which rotates by +- 185 DEG, allowing the beam to exit in all directions of 360 DEG. Compared with the cyclotron and the synchrotron, the invention can use a magnetic field of up to more than5T to reduce the volume weight of the accelerator, so as to be more compact; And the acceleration voltage requirements are small, reducing the cost of RF system and design difficulties.
Owner:HEFEI CAS ION MEDICAL & TECHNICAL DEVICES CO LTD +1
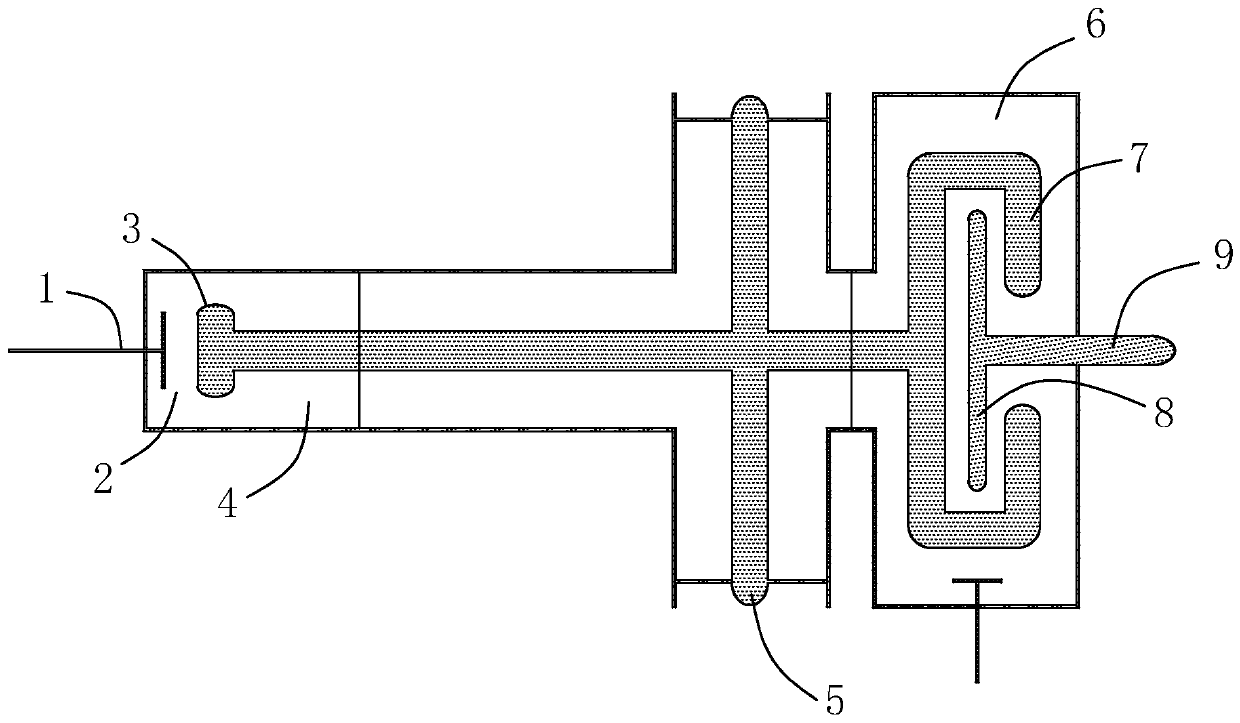
Synchrocyclotron
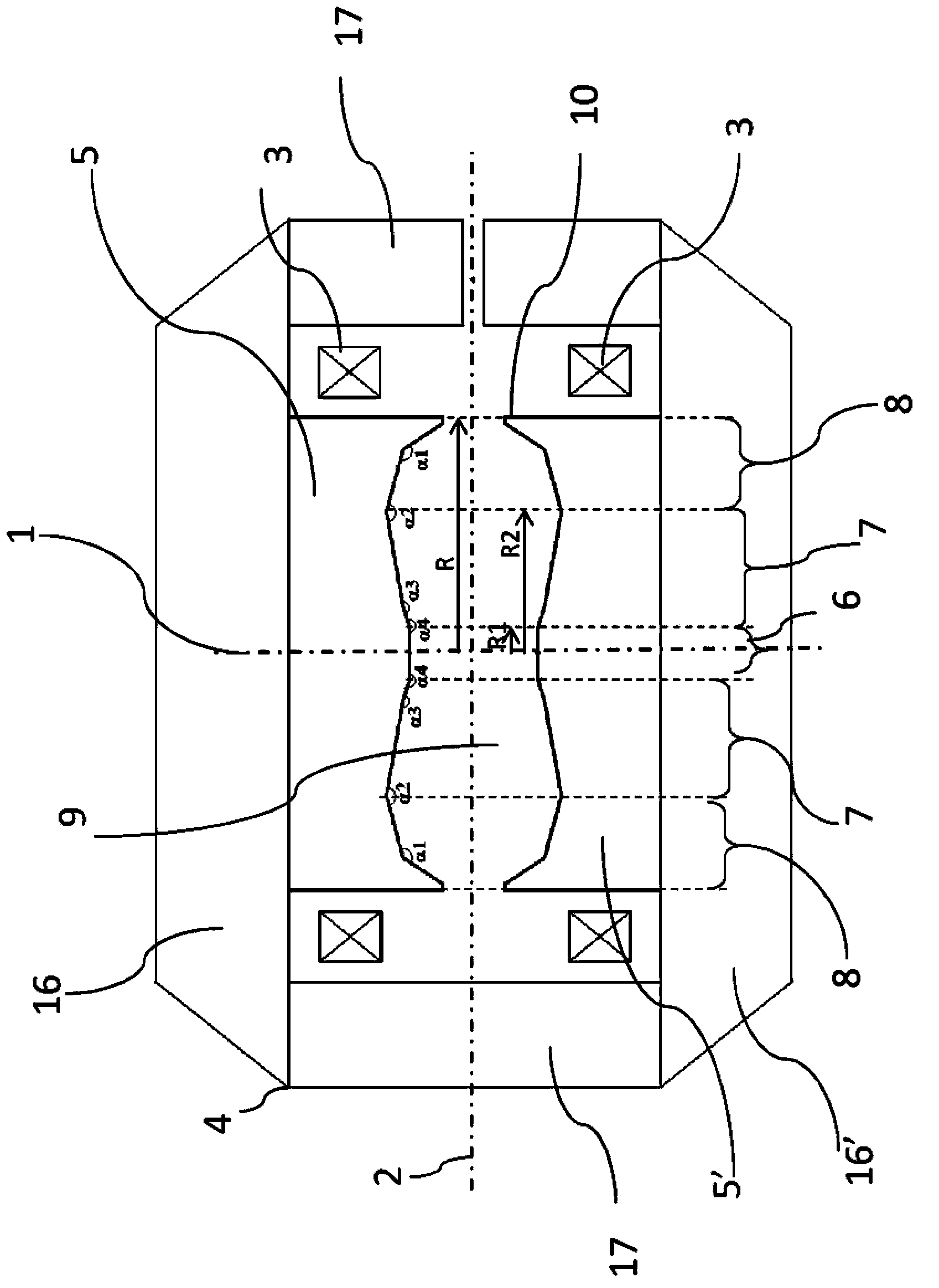
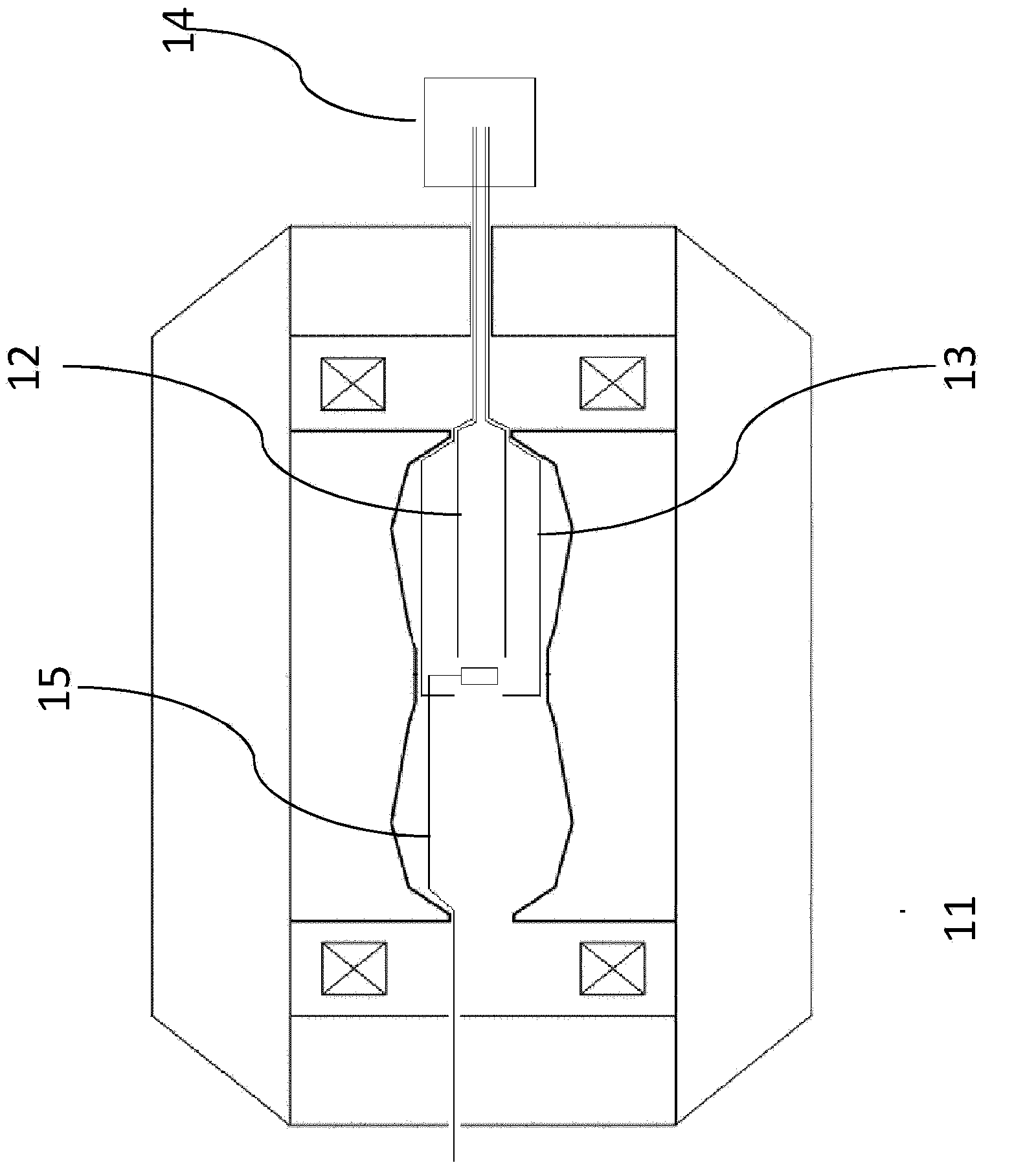
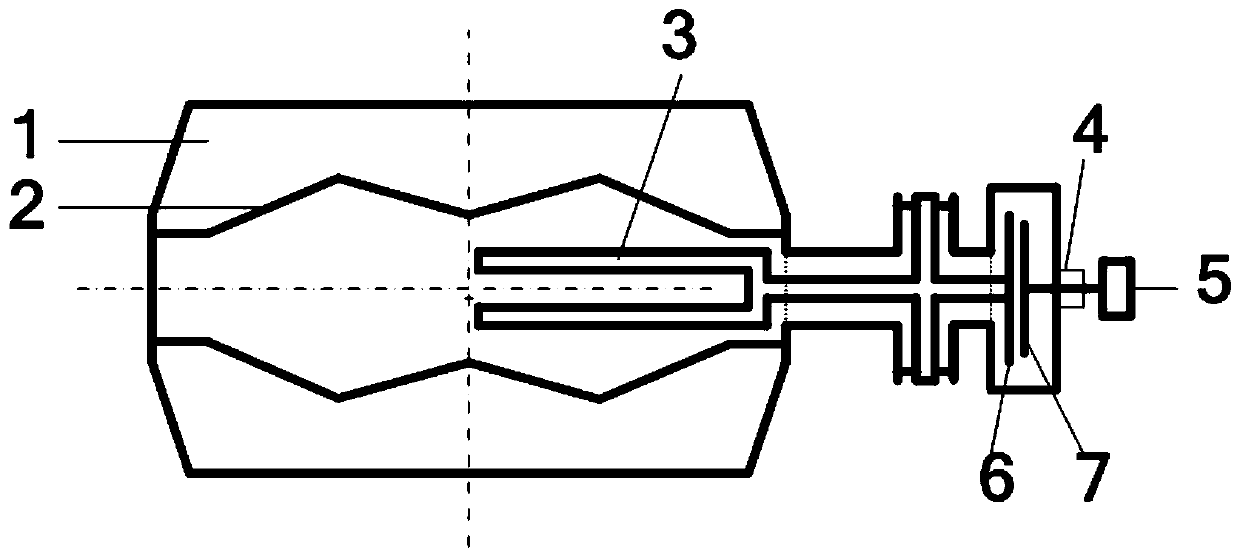
A synchrocyclotron comprises a ferromagnetic structure (4) with a pair of poles (5, 5'), which have a generally circular cross section of radius R which are placed on either side of a mid-plane (2) and centred on a central axis (1). These poles (5, 5') are separated by a gap forming a cavity (9) having a profile substantially symmetrical with respect to the mid-plane (2). The height of this gap varies radially and the profile of the gap comprises, in succession, starting from the central axis (1): a first portion (6, 7) of circular section with a radius R2, which is centred on the central axis (1), the height of the gap at the centre thereof being equal to Hcentre, and which includes an annular subportion (7) in which the height of the gap progressively increases up to a maximum height Hmax at the radius R2, and a second portion, of annular section (8), which surrounds the first portion (6, 7) and in which the height of the gap progressively decreases down to a height Hedge at the edges of the poles (5, 5'). The height Hcentre is greater than 10 cm and the ratio of the maximum height Hmax to the height Hcentre is between 1.1 and 1.5.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
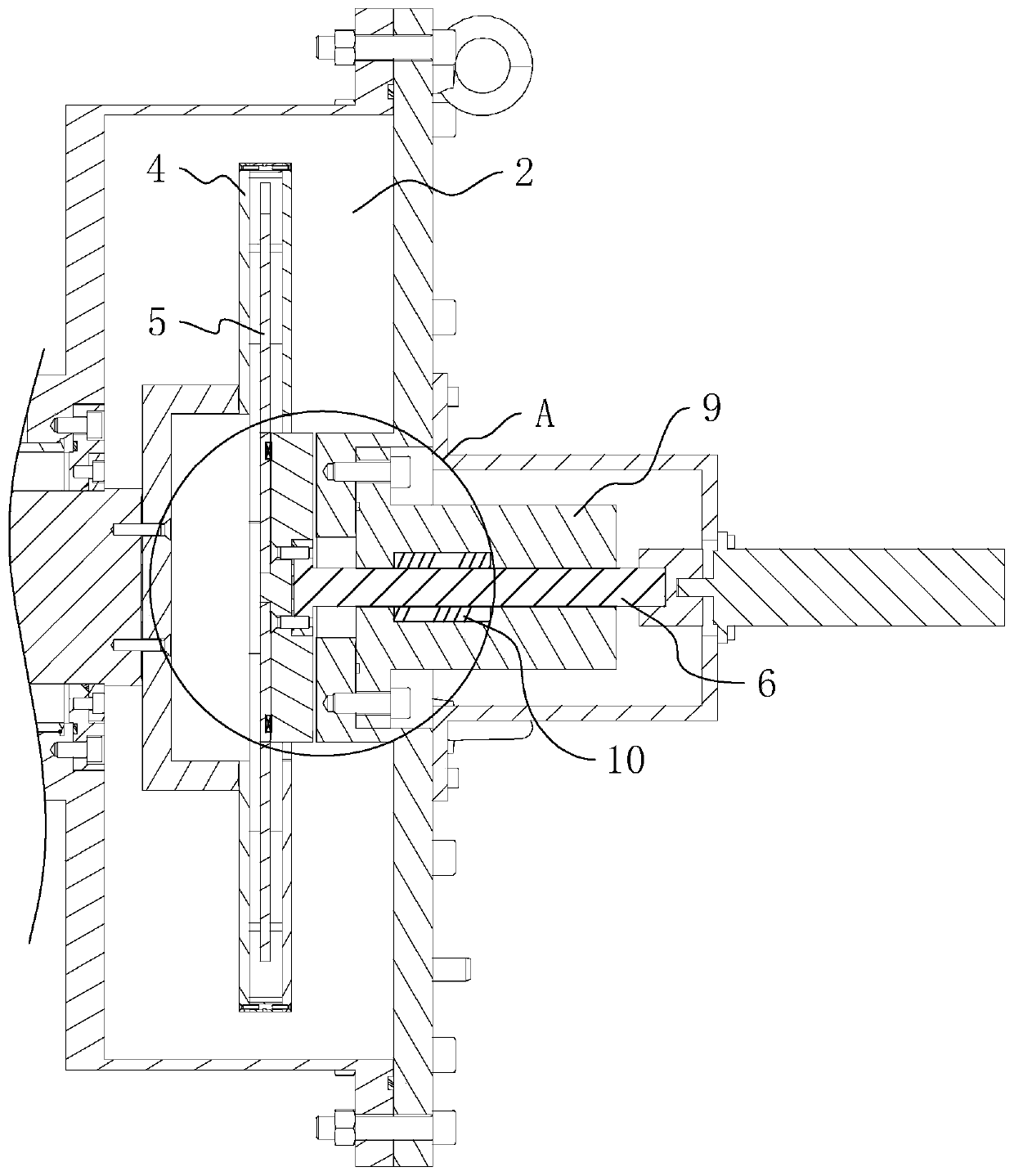
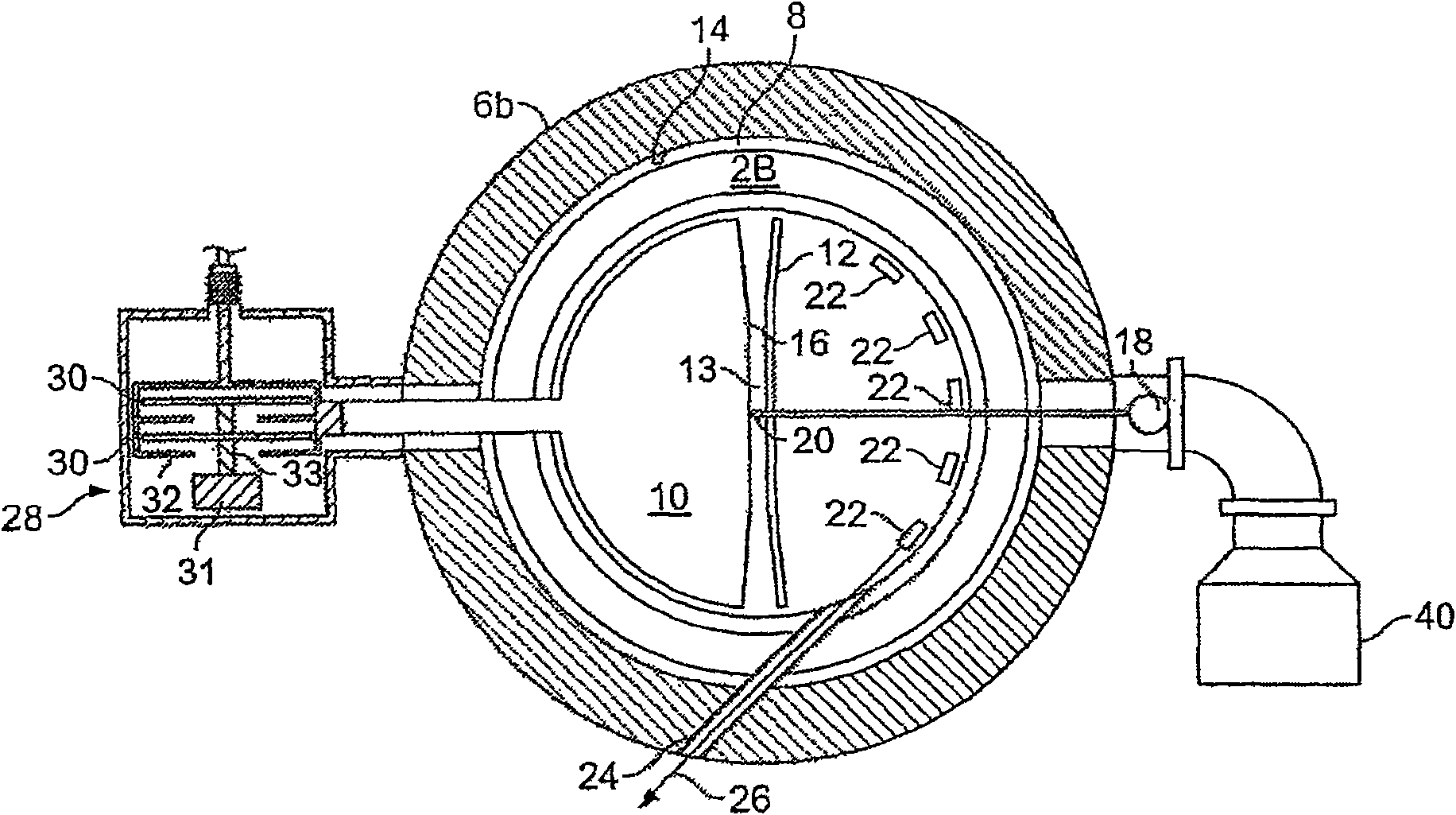
Electric contact method and structure of rotation of capacitance rotor in synchrophasotron
ActiveCN108834301AExtended service lifeIncrease speedMagnetic resonance acceleratorsElectricityCapacitance
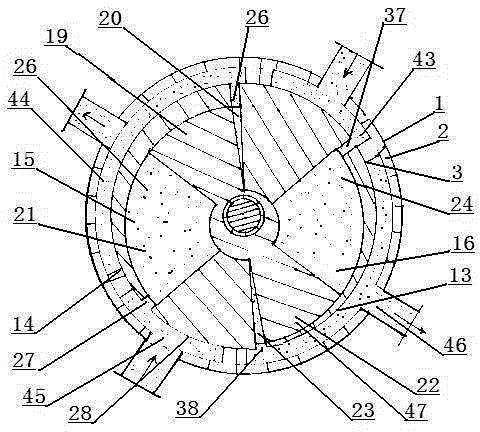
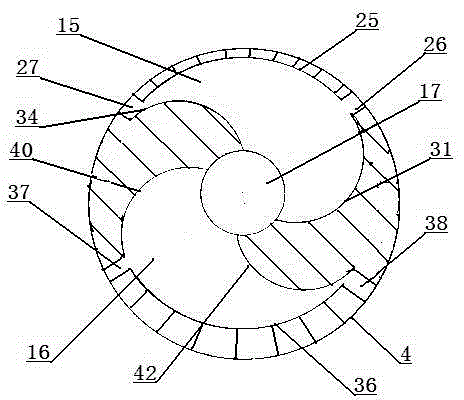
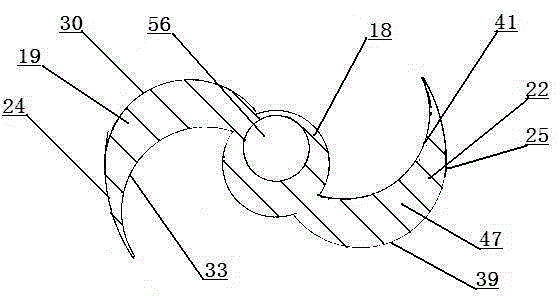
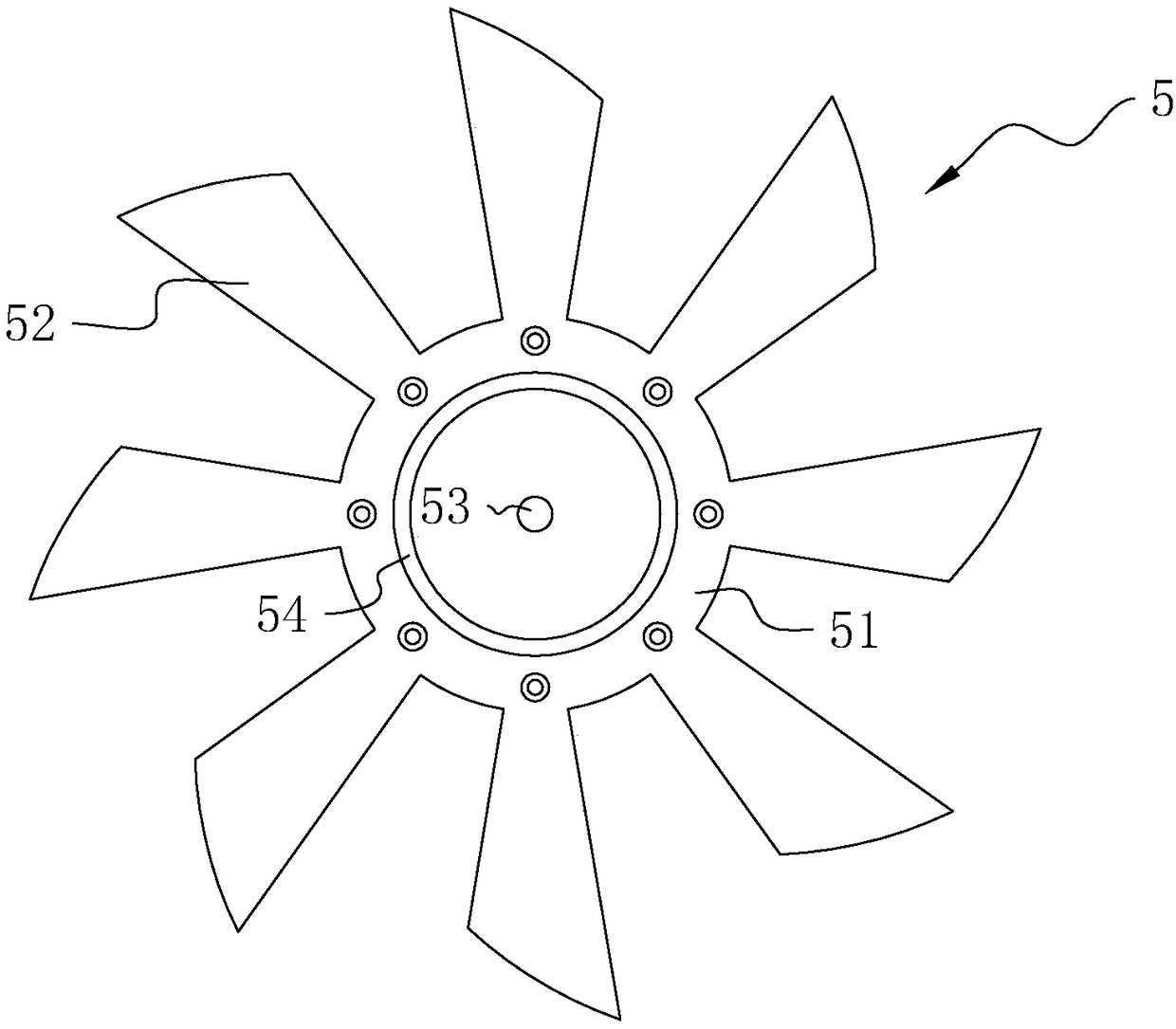
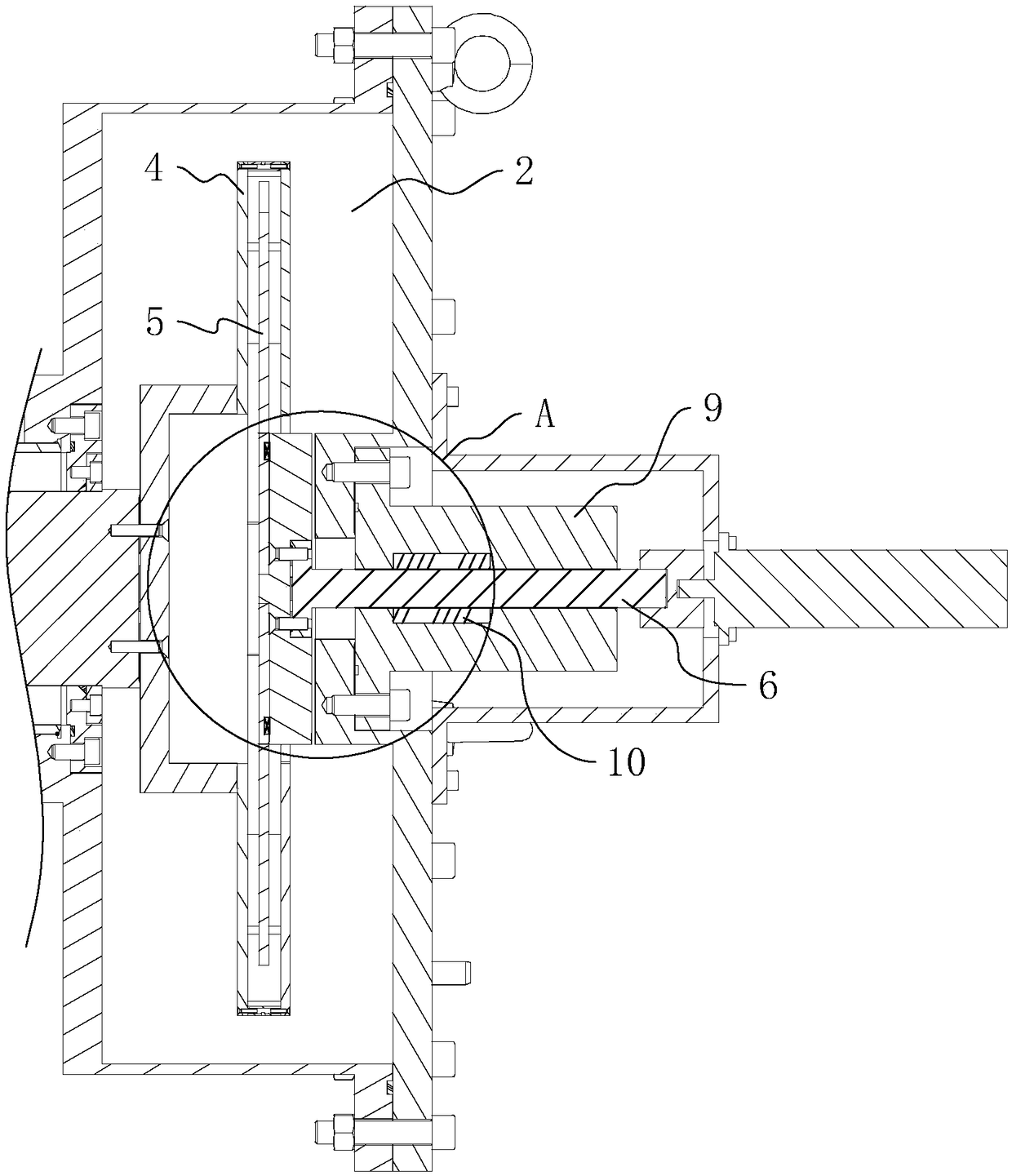
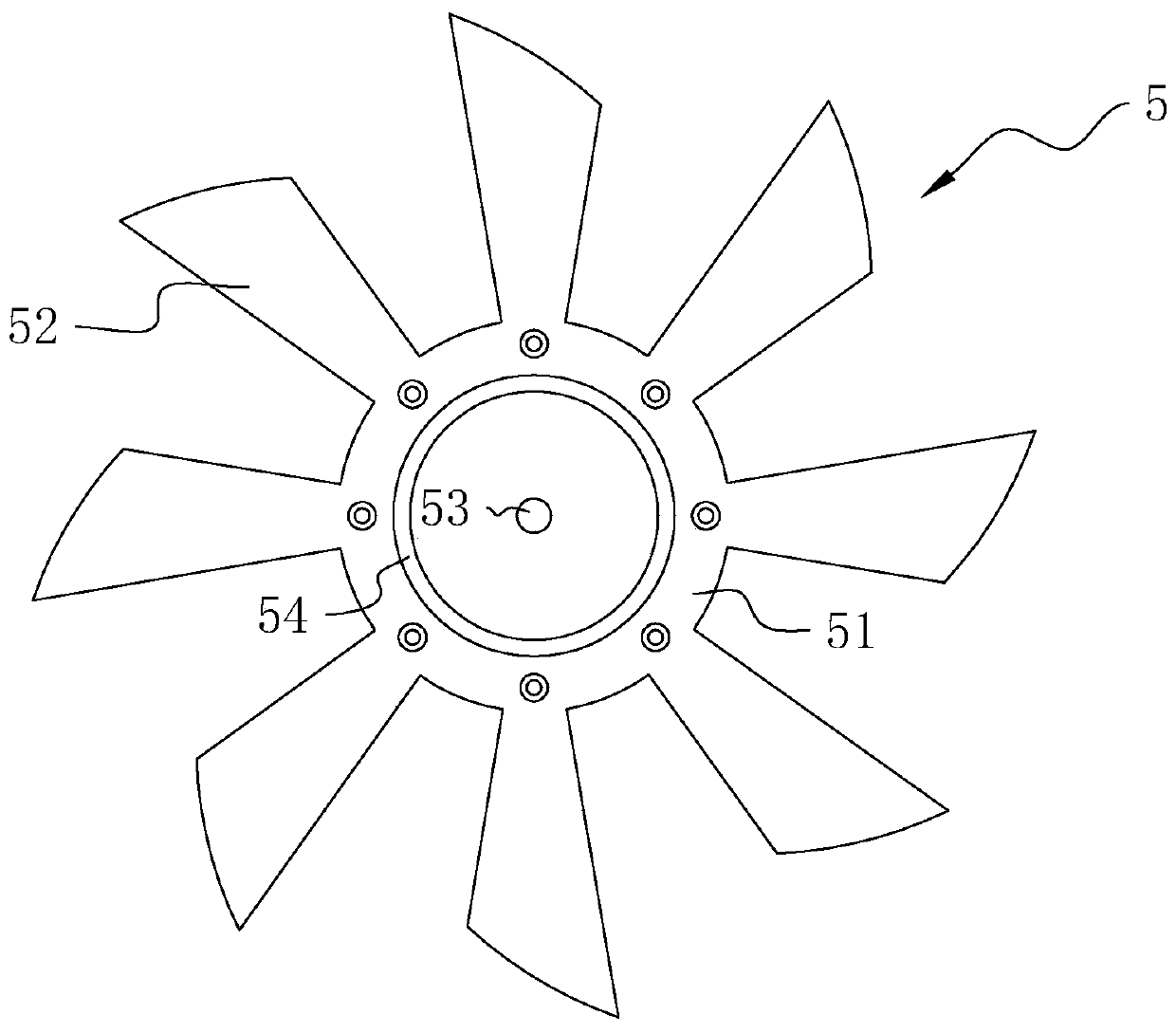
The present invention discloses an electric contact structure of rotation of a capacitance rotor in synchrophasotron and a structure thereof. The structure comprises a capacitance vacuum chamber, a capacitance rotor rotationally arranged in the capacitance vacuum chamber and a rotation shaft fixedly connected with one end of the capacitance rotor and configured to drive the rotation of the capacitance rotor. The capacitance rotor comprises a disc portion arranged at the middle portion and a blade portion distributed towards the outer side along the disc portion, the rotation shaft is providedwith an electric connection rotary table having an interval with the disc portion, and an electric connection copper mesh is crimped between the disc portion and the electric connection rotary table;and a planar narrow gap configured to perform high-frequency earthing is arranged between one side, far away from the disc portion, of the electric connection rotary table and the side wall of the capacitance vacuum chamber. The effect of electric contact can be stably achieved in a high-speed rotation condition.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
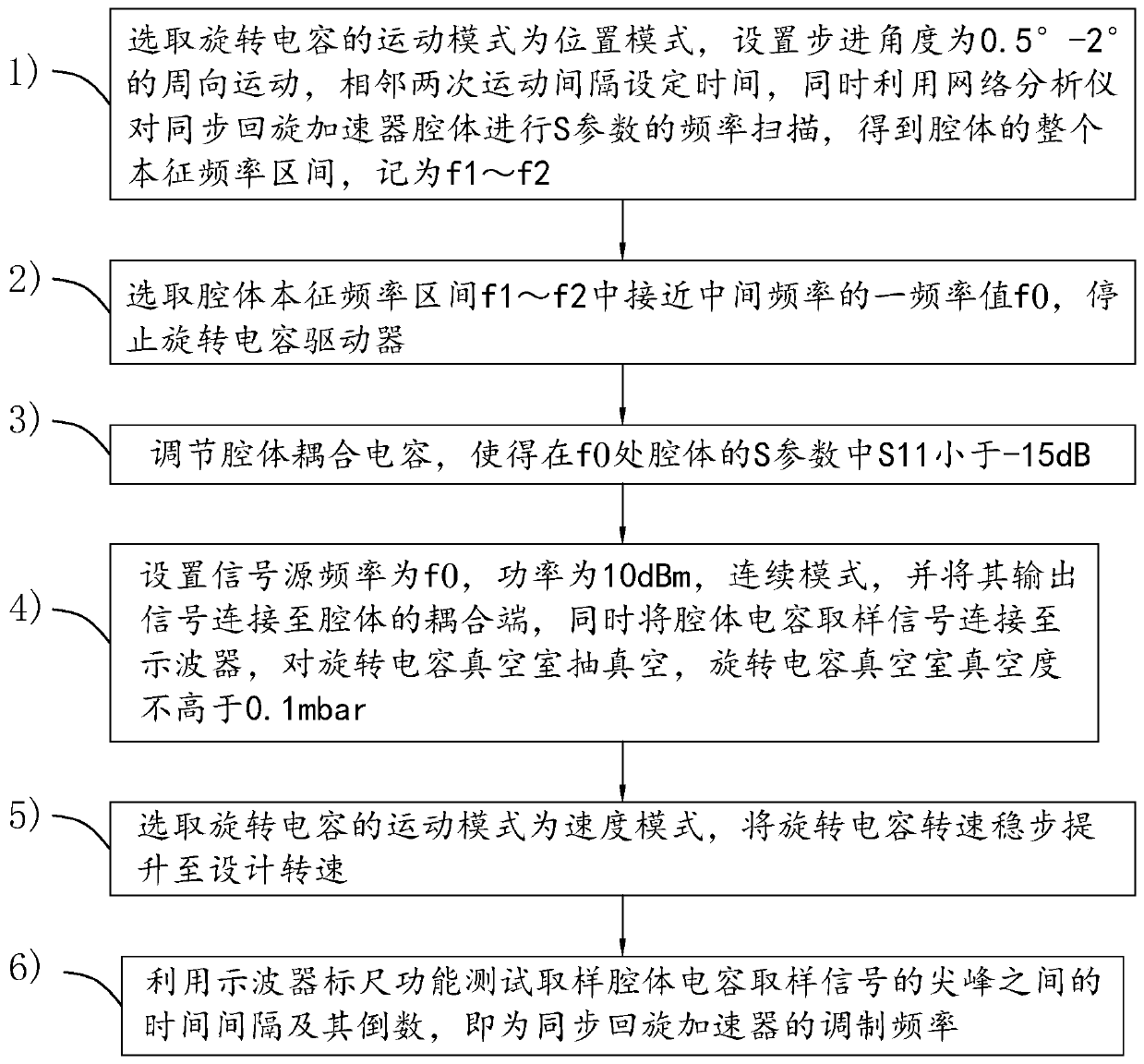
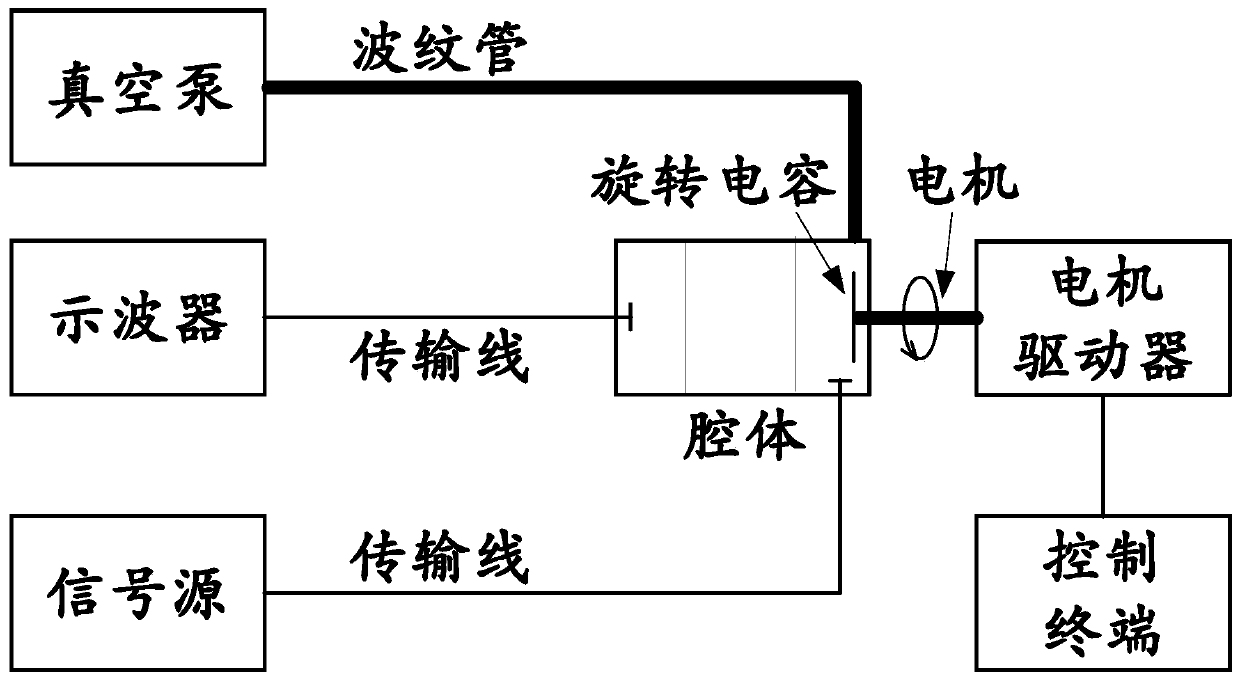
Synchrocyclotron modulation frequency test method
ActiveCN109100567AModulation frequency results are accurateFrequency measurement arrangementCapacitanceEigen frequency
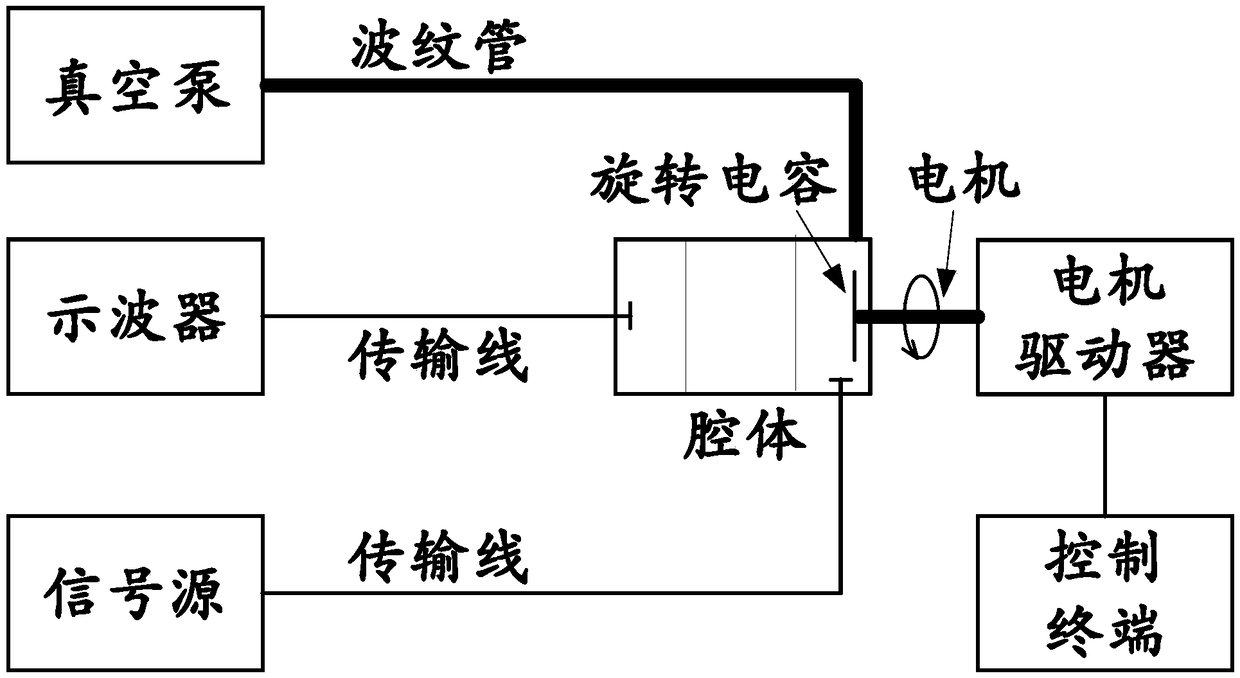
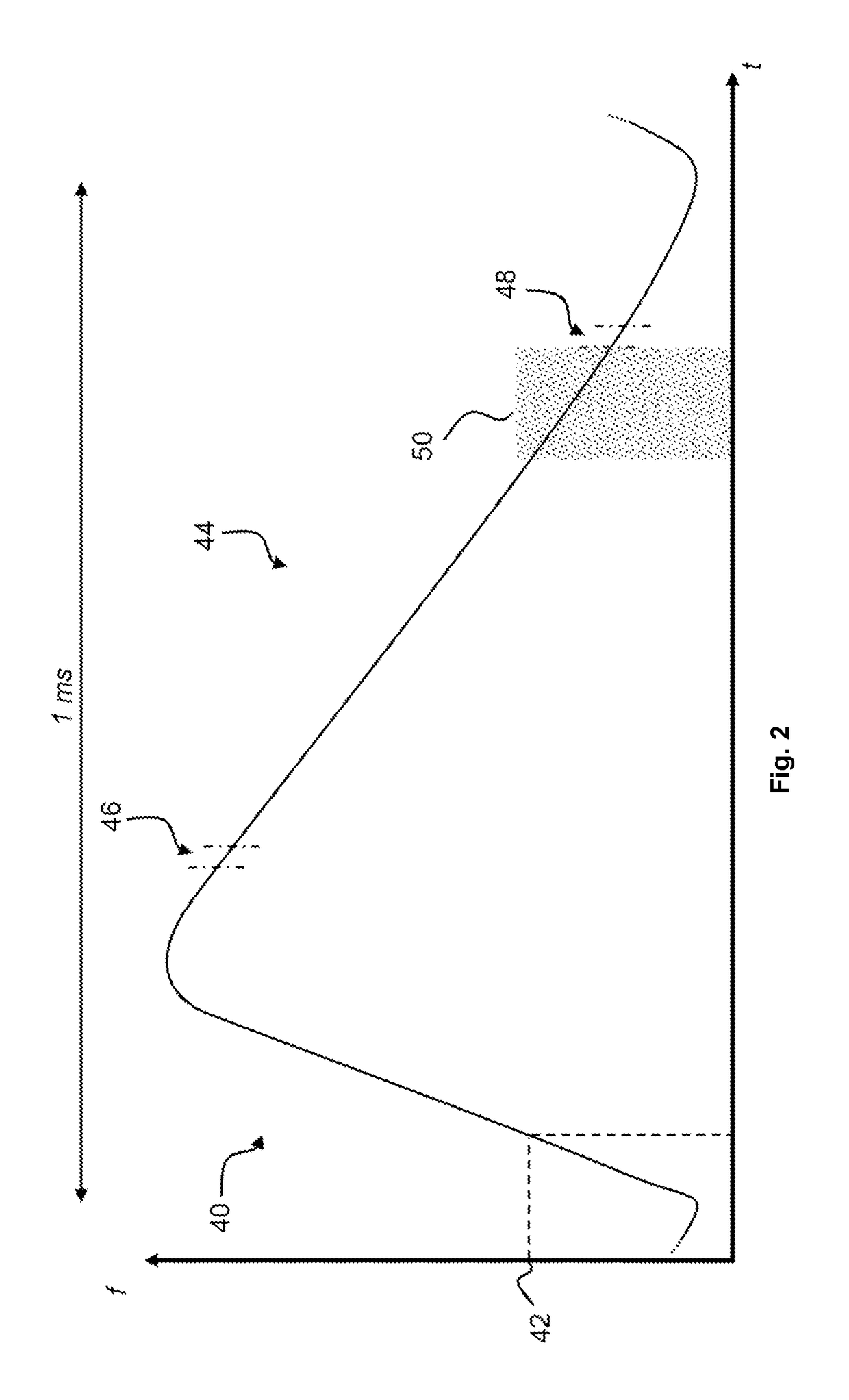
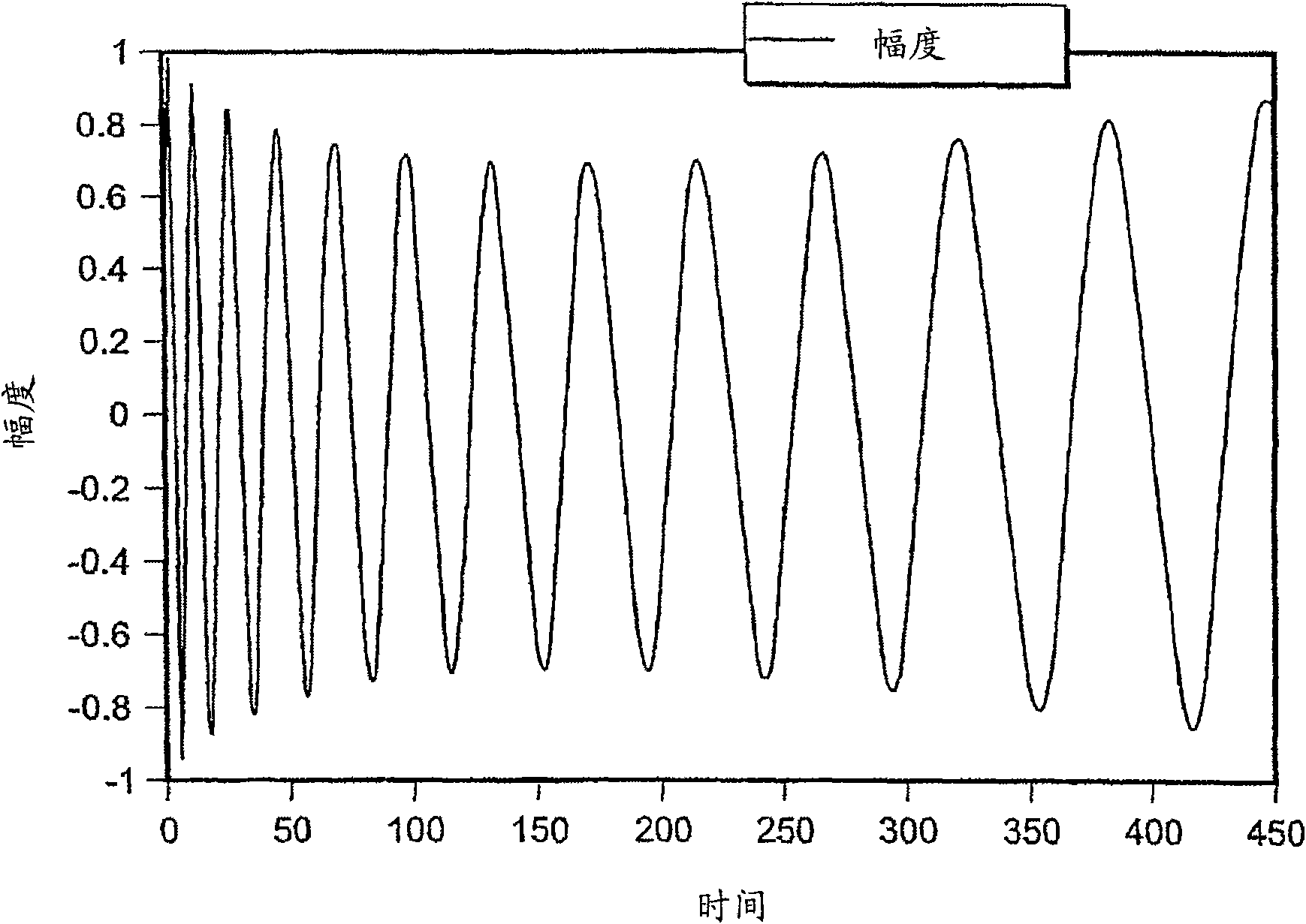
The invention discloses a synchrocyclotron modulation frequency test method and relates to the technical field of synchrocyclotrons. The test method comprises the following steps: selecting a motion mode of a rotary capacitor as a position mode, setting a circumferential motion with a fixed step angle, and carrying out frequency scanning on the cavity of the synchrocyclotron to obtain a cavity eigenfrequency range f1~f2; selecting a frequency value f0 in the cavity eigenfrequency range and stopping a rotary capacitor driver; adjusting cavity coupling capacitance so that S11 in an S parameter of the cavity at f0 is less than -15dB; setting the signal source frequency to be f0 and the power to be 10dBm in a continuous mode, connecting an output signal to a coupling end of the cavity and connecting a cavity capacitance sampling signal to an oscilloscope; selecting the motion mode of the rotary capacitor as a speed mode, and lifting the rotational speed of the rotary capacitor to a designed rotational speed; using the oscilloscope to test and sample the time interval delta X between peaks of the cavity capacitance sampling signal, wherein 1 / delta X is the modulation frequency of the synchrocyclotron.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
RF system for synchrocyclotron
ActiveUS20140320044A1Increase absorbanceImprove cooling effectLine/current collector detailsMagnetic resonance acceleratorsCapacitanceResonant cavity
The present invention relates to an RF system (1) able to generate a voltage for accelerating charged particles in a synchrocyclotron, the RF system (1) including a resonant cavity (2) comprising a conducting enclosure (5) within which are placed a conducting pillar (3) of which a first end is linked to an accelerating electrode (4) able to accelerate the charged particles, a rotary variable capacitor (10) coupled between a second end opposite from the first end of the pillar (3) and the conducting enclosure (5), the said capacitor (10) comprising fixed electrodes (11) and a rotor (13) comprising mobile electrodes (12), the fixed electrodes (11) and the mobile electrodes (12) forming a variable capacitance able to vary a resonant frequency of the resonant cavity (2) in a cyclic manner over time, an exterior layer of the rotor (13) having a conductivity of greater than 20,000,000 S / m at 300 K. At least one part of the exterior surface (15) of the rotor (13) is a surface possessing a normal total emissivity of greater than 0.5 and less than 1, thereby allowing better cooling of the rotor and / or making it possible to dispense with a system for cooling the rotor by conduction and / or by convection.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Design method of superconductor focusing synchrocyclotron
InactiveCN103228093ASmall radiusEnhanced magnetic fieldMagnetic resonance acceleratorsSuperconductor classificationMaterials science
The invention discloses a superconductor focusing synchrocyclotron, and belongs to the field of physics. The available magnetic field intensity is insufficient, so that sizes of accelerators are very large; the superconductor focusing synchrocyclotron solves the problem; the sizes of the accelerators are reduced greatly; and a main technology is that magnetic force lines are focused by a superconductor to greatly improve the magnetic field intensity, so that charged particles can be accelerated to very high speeds with very small sizes.
Owner:胡明建 +1
Superconducting coil configuration
PendingUS20180122544A1Improve current carrying capacityLarge sectionSuperconducting magnets/coilsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyElectrical conductorPower flow
An example particle therapy system includes: a synchrocyclotron, and a gantry on which the synchrocyclotron is mounted to rotate around a patient position to position the synchrocyclotron relative to a treatment area of the patient. The synchrocyclotron includes a magnet having a coil to receive electrical current and to generate a magnetic field in response to the electrical current. The magnetic field causes the particles to move orbitally within a cavity at an energy that corresponds to the electrical current, and the coil includes multiple integrated conductors that are wound together. An integrated conductor includes: a core including conductive or superconducting material; and at least six strands wound around the core, with each of the at least six strands including a superconducting material. The synchrocyclotron includes an extraction channel to receive the particles from the cavity and to output the particles received from the cavity.
Owner:MEVION MEDICAL SYST
Superconducting coil configuration
ActiveCN110121791APermanent superconductor devicesSuperconducting magnets/coilsElectrical conductorSuperconducting Coils
An example particle therapy system includes: a synchrocyclotron, and a gantry on which the synchrocyclotron is mounted to rotate around a patient position to position the synchrocyclotron relative toa treatment area of the patient. The synchrocyclotron includes a magnet having a coil to receive electrical current and to generate a magnetic field in response to the electrical current. The magneticfield causes the particles to move orbitally within a cavity at an energy that corresponds to the electrical current, and the coil includes multiple integrated conductors that are wound together. Anintegrated conductor includes: a core including conductive or superconducting material; and at least six strands wound around the core, with each of the at least six strands including a superconducting material. The synchrocyclotron includes an extraction channel to receive the particles from the cavity and to output the particles received from the cavity.
Owner:MEVION MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
A Proton Heavy Ion Therapy System Based on Synchrocyclotron
ActiveCN109224321BReduce weight and sizeLow costMagnetic resonance acceleratorsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBeam energyHigh energy
The invention discloses a synchrocyclotron-based proton heavy ion therapy system. The system is characterized in that the treatment system adopts a synchrocyclotron to accelerate protons or heavy ionsto the highest energy required for treatment; For protons, the maximum energy is 235 MeV. The beam output from the synchrocyclotron enters the high energy transport line for focusing and deflection and is fed to the energy selector. The energy selector makes the beam energy continuously adjustable through the graphite energy reducer. The beam enters a single room and is sent to a rotating gantrysystem, which rotates by +- 185 DEG, allowing the beam to exit in all directions of 360 DEG. Compared with the cyclotron and the synchrotron, the invention can use a magnetic field of up to more than5T to reduce the volume weight of the accelerator, so as to be more compact; And the acceleration voltage requirements are small, reducing the cost of RF system and design difficulties.
Owner:HEFEI CAS ION MEDICAL & TECHNICAL DEVICES CO LTD +1
synchrocyclotron beam orbit and rf driven synchrocyclotron
The present invention provides for the use of feedback in the radio frequency (RF) drive of a synchrocyclotron to control the phase and / or amplitude of the accelerating field as a means of ensuring optimal acceleration of the beam, increasing the average beam current, and modifying the beam trajectory to follow Variations in beam energy allow proper extraction. Space charge effects are reduced by rapid acceleration and extraction of the beam, and the pulse repetition rate can be increased. Several measures have been proposed for monitoring the phase of the beam in a synchrocyclotron and adjusting the phase and amplitude of the RF in order to optimize the acceleration of the beam and adjust the extraction and injection of the beam. Also described is the use of a pulsed ion source matched to the acceptance window of the synchrocyclotron.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and system for controlling ion beam pulses extraction
ActiveUS10070510B2Weakening rangeMedical devicesMagnetic resonance acceleratorsState parameterIon beam
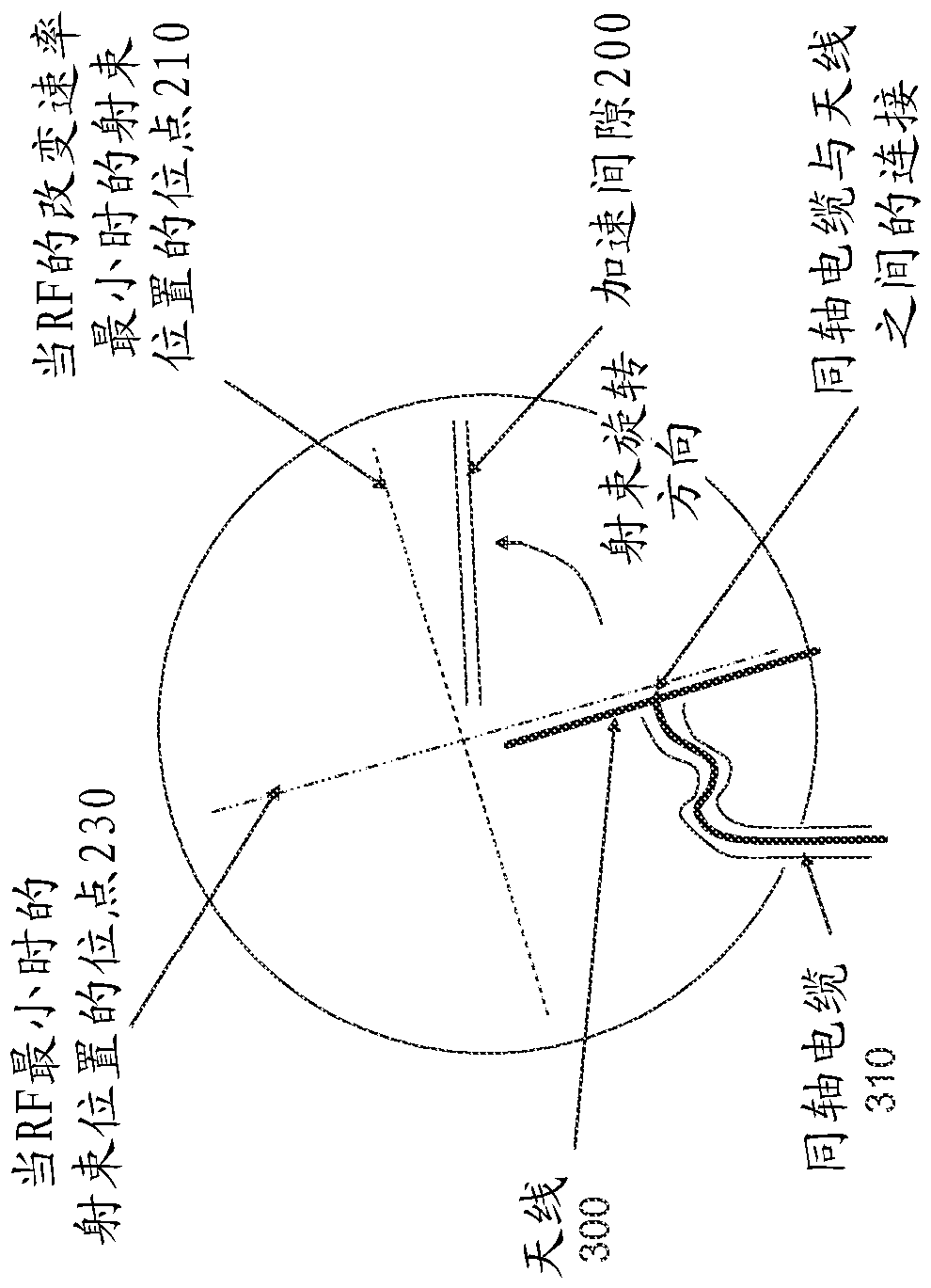
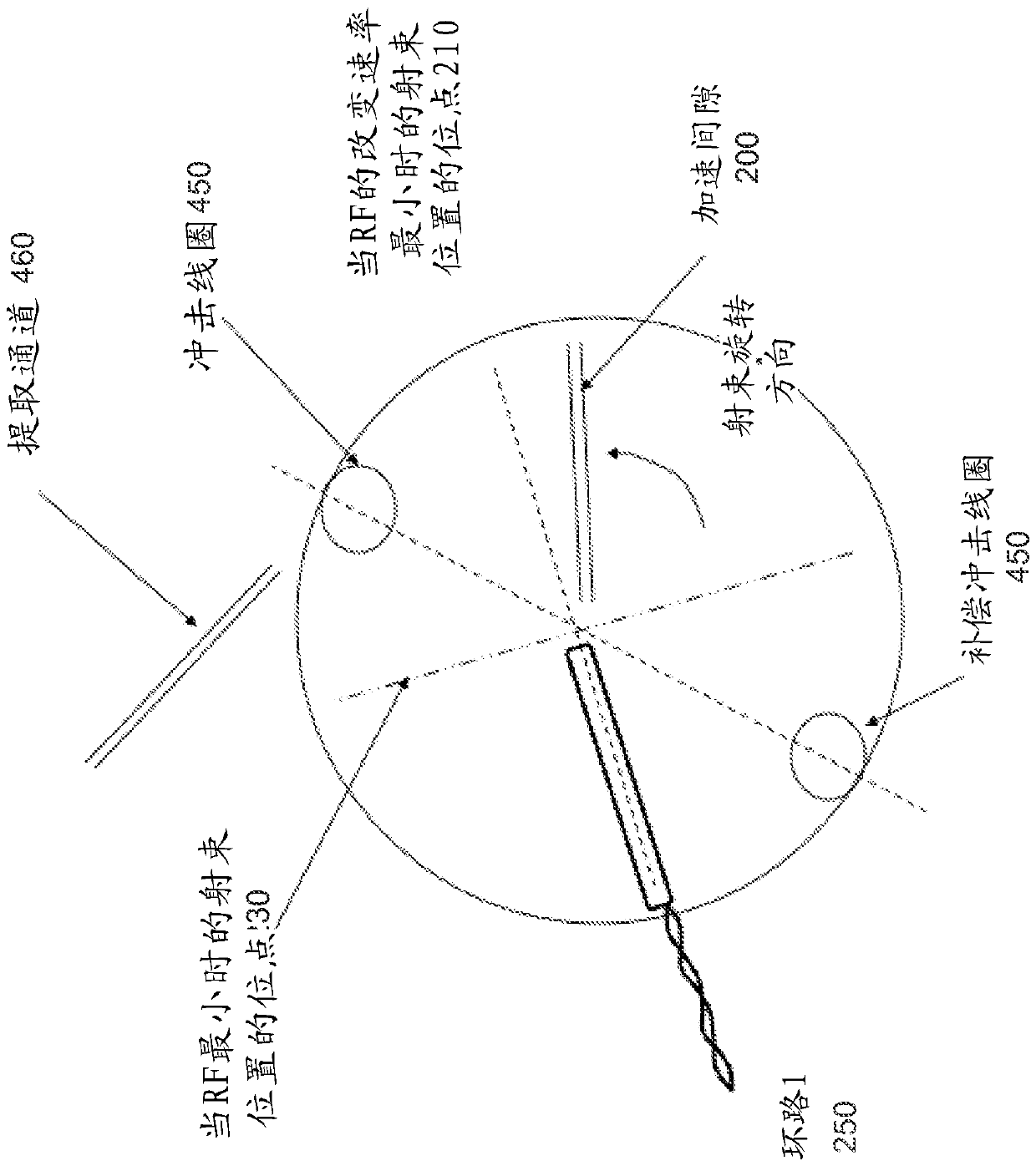
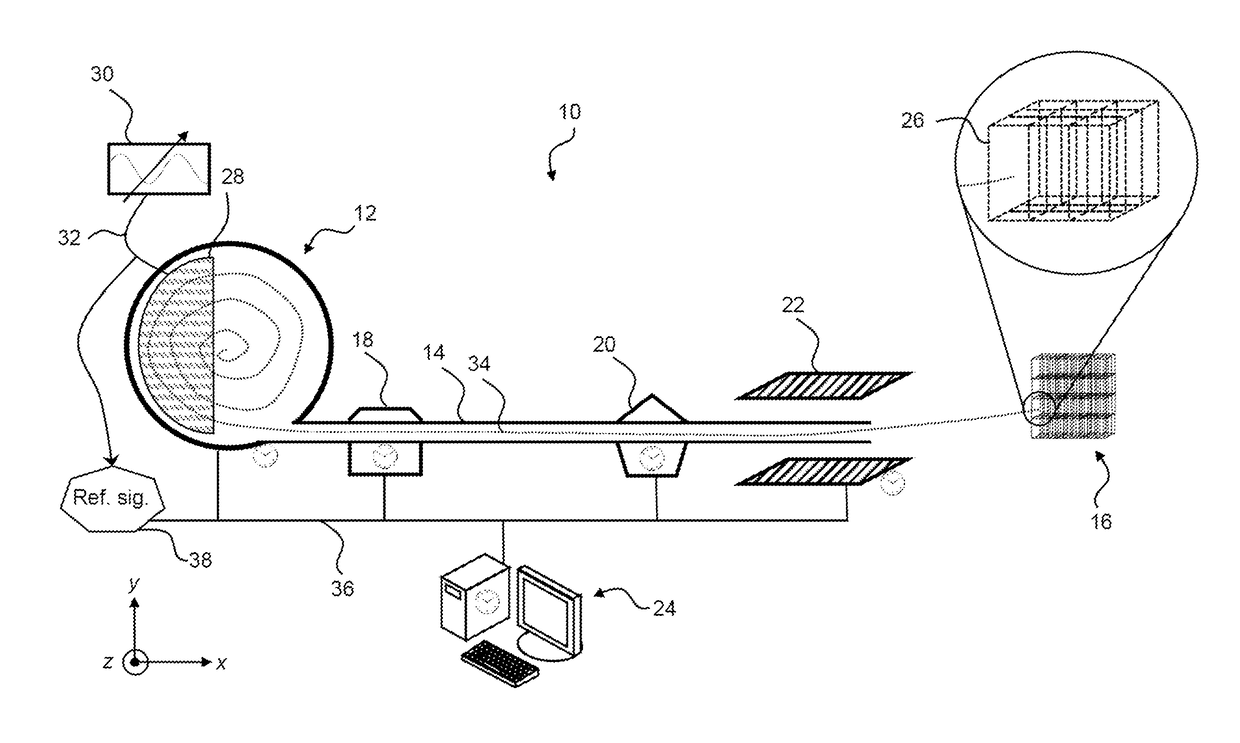
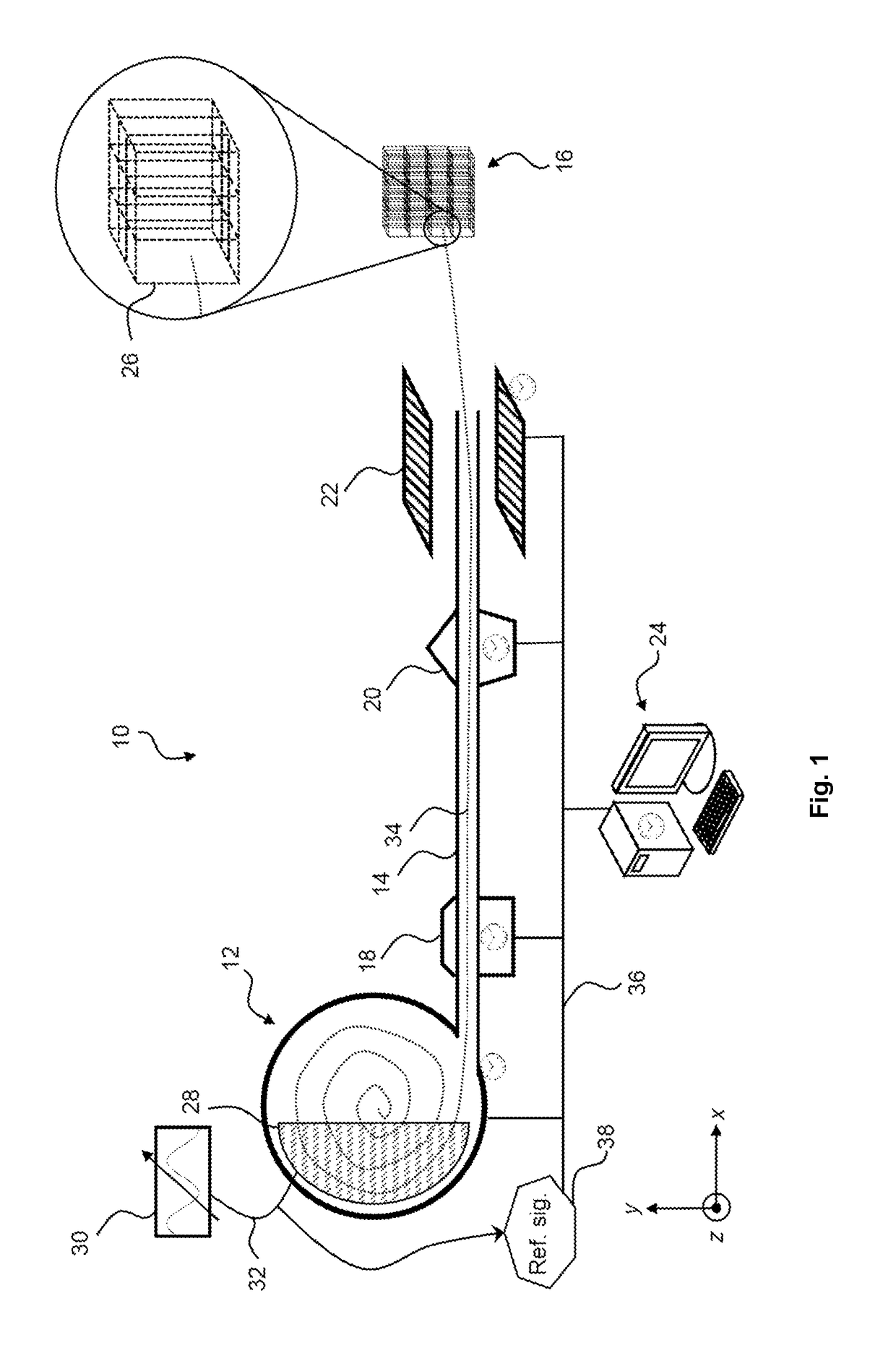
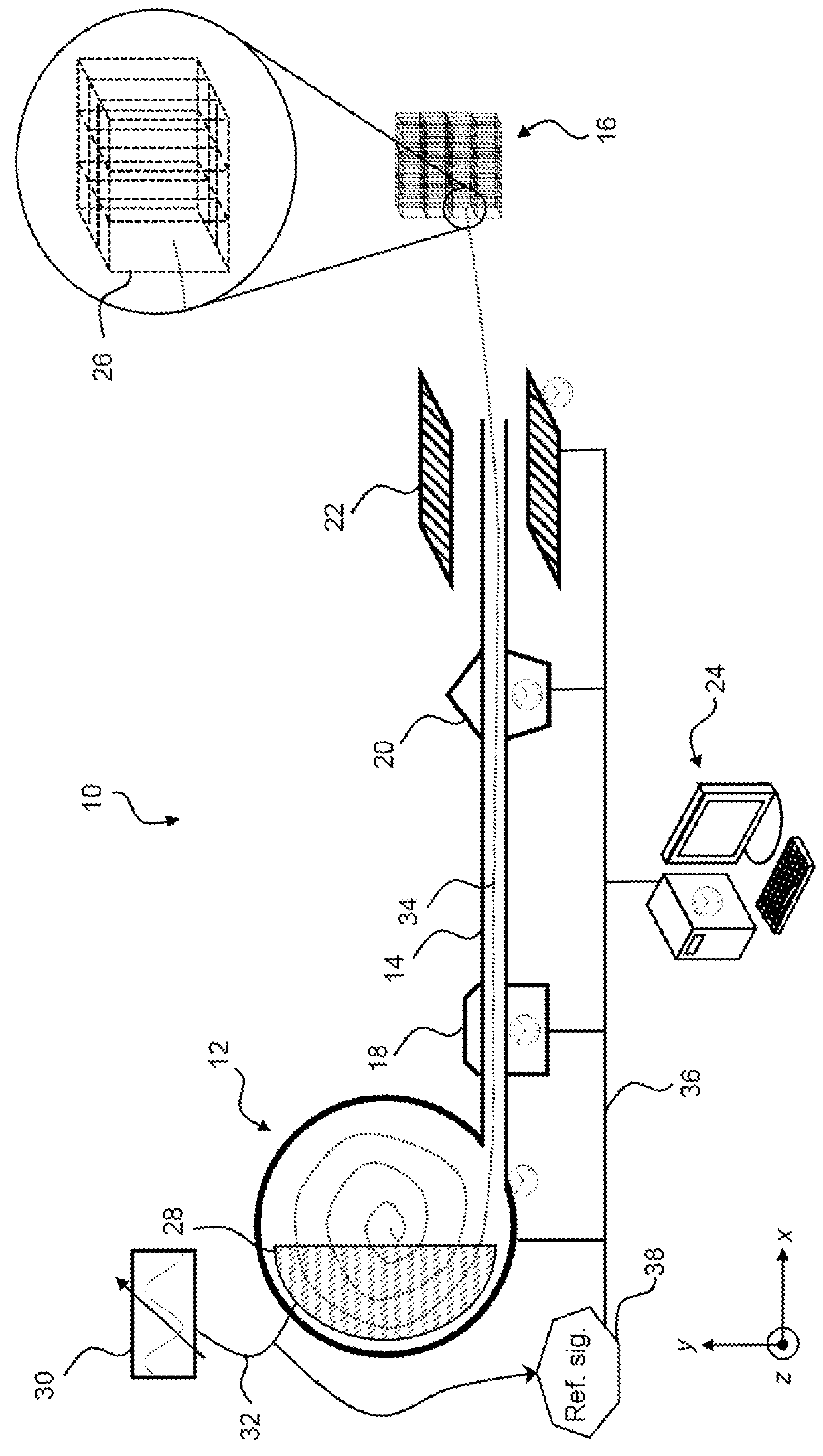
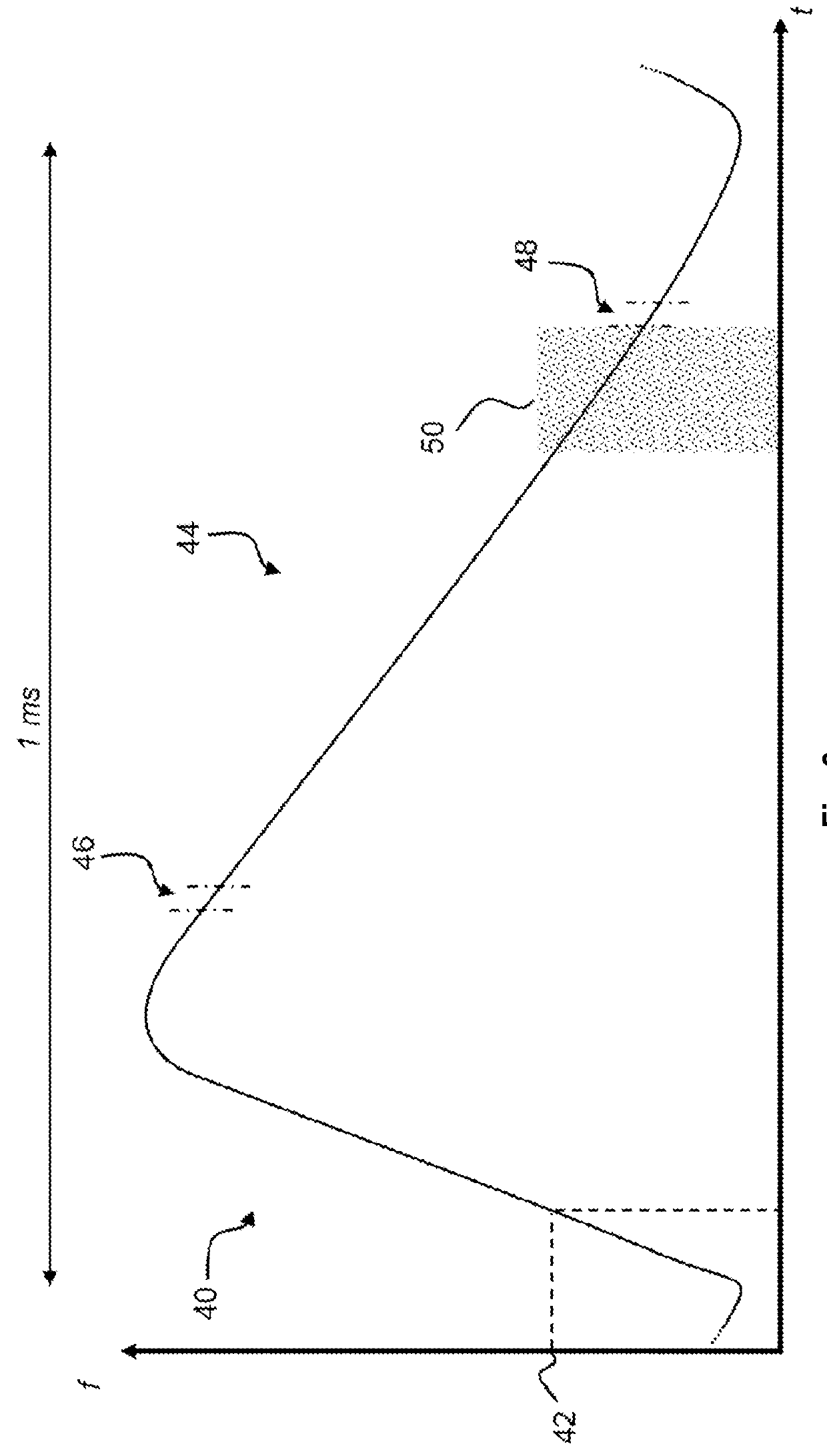
The embodiments of the present disclosure relate to a method and system for controlling the extraction of ion beam pulses produced by a synchrocyclotron. The synchrocyclotron comprises electrodes configured to be placed in a magnetic field. An alternating voltage is applied between the electrodes, and the frequency of the alternating voltage is modulated in a cyclic manner. In other embodiments, the method further comprises the steps of starting an acceleration cycle of the synchrocyclotron, generating a reference signal when the modulated frequency reaches a predefined value, communicating the time, at which the reference signal is generated, to the beam control elements, assessing one or more status parameters of the one or more beam control elements, and cancelling or proceeding with the extraction of the beam pulse depending on the results of the assessment.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Electrical Contact Method and Structure of Rotating Capacitor Rotor in Synchrocyclotron
ActiveCN108834301BExtended service lifeIncrease speedMagnetic resonance acceleratorsCapacitanceCircular disc
The present invention discloses an electric contact structure of rotation of a capacitance rotor in synchrophasotron and a structure thereof. The structure comprises a capacitance vacuum chamber, a capacitance rotor rotationally arranged in the capacitance vacuum chamber and a rotation shaft fixedly connected with one end of the capacitance rotor and configured to drive the rotation of the capacitance rotor. The capacitance rotor comprises a disc portion arranged at the middle portion and a blade portion distributed towards the outer side along the disc portion, the rotation shaft is providedwith an electric connection rotary table having an interval with the disc portion, and an electric connection copper mesh is crimped between the disc portion and the electric connection rotary table;and a planar narrow gap configured to perform high-frequency earthing is arranged between one side, far away from the disc portion, of the electric connection rotary table and the side wall of the capacitance vacuum chamber. The effect of electric contact can be stably achieved in a high-speed rotation condition.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Matching method of strong magnetic field and high frequency frequency conversion in synchrocyclotron
ActiveCN108684132BMinimized beam lossReduce activation levelMagnetic resonance acceleratorsCapacitanceMagnetic poles
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Synchrotron Modulation Frequency Test Method
ActiveCN109100567BModulation frequency results are accurateMagnetic resonance acceleratorsFrequency measurement arrangementCapacitanceEigen frequency
The invention discloses a synchrocyclotron modulation frequency test method and relates to the technical field of synchrocyclotrons. The test method comprises the following steps: selecting a motion mode of a rotary capacitor as a position mode, setting a circumferential motion with a fixed step angle, and carrying out frequency scanning on the cavity of the synchrocyclotron to obtain a cavity eigenfrequency range f1~f2; selecting a frequency value f0 in the cavity eigenfrequency range and stopping a rotary capacitor driver; adjusting cavity coupling capacitance so that S11 in an S parameter of the cavity at f0 is less than -15dB; setting the signal source frequency to be f0 and the power to be 10dBm in a continuous mode, connecting an output signal to a coupling end of the cavity and connecting a cavity capacitance sampling signal to an oscilloscope; selecting the motion mode of the rotary capacitor as a speed mode, and lifting the rotational speed of the rotary capacitor to a designed rotational speed; using the oscilloscope to test and sample the time interval delta X between peaks of the cavity capacitance sampling signal, wherein 1 / delta X is the modulation frequency of the synchrocyclotron.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Matching a resonant frequency of a resonant cavity to a frequency of an input voltage
ActiveCN101933406BPulse automatic controlMagnetic resonance acceleratorsPhase detectorResonant cavity
A synchrocyclotron includes magnetic structures that define a resonant cavity, a source to provide particles to the resonant cavity, a voltage source to provide radio frequency (RF) voltage to the resonant cavity, a phase detector to detect a difference in phase between the RF voltage and a resonant frequency of the resonant cavity that changes over time, and a control circuit, responsive to the difference in phase, to control the voltage source so that a frequency of the RF voltage substantially matches the resonant frequency of the resonant cavity.
Owner:MEVION MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Method and system for controlling ion beam pulses extraction
ActiveUS20180098413A1Weakening rangeMagnetic resonance acceleratorsMedical devicesState parameterIon beam
The embodiments of the present disclosure relate to a method and system for controlling the extraction of ion beam pulses produced by a synchrocyclotron. The synchrocyclotron comprises electrodes configured to be placed in a magnetic field. An alternating voltage is applied between the electrodes, and the frequency of the alternating voltage is modulated in a cyclic manner. In other embodiments, the method further comprises the steps of starting an acceleration cycle of the synchrocyclotron, generating a reference signal when the modulated frequency reaches a predefined value, communicating the time, at which the reference signal is generated, to the beam control elements, assessing one or more status parameters of the one or more beam control elements, and cancelling or proceeding with the extraction of the beam pulse depending on the results of the assessment.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
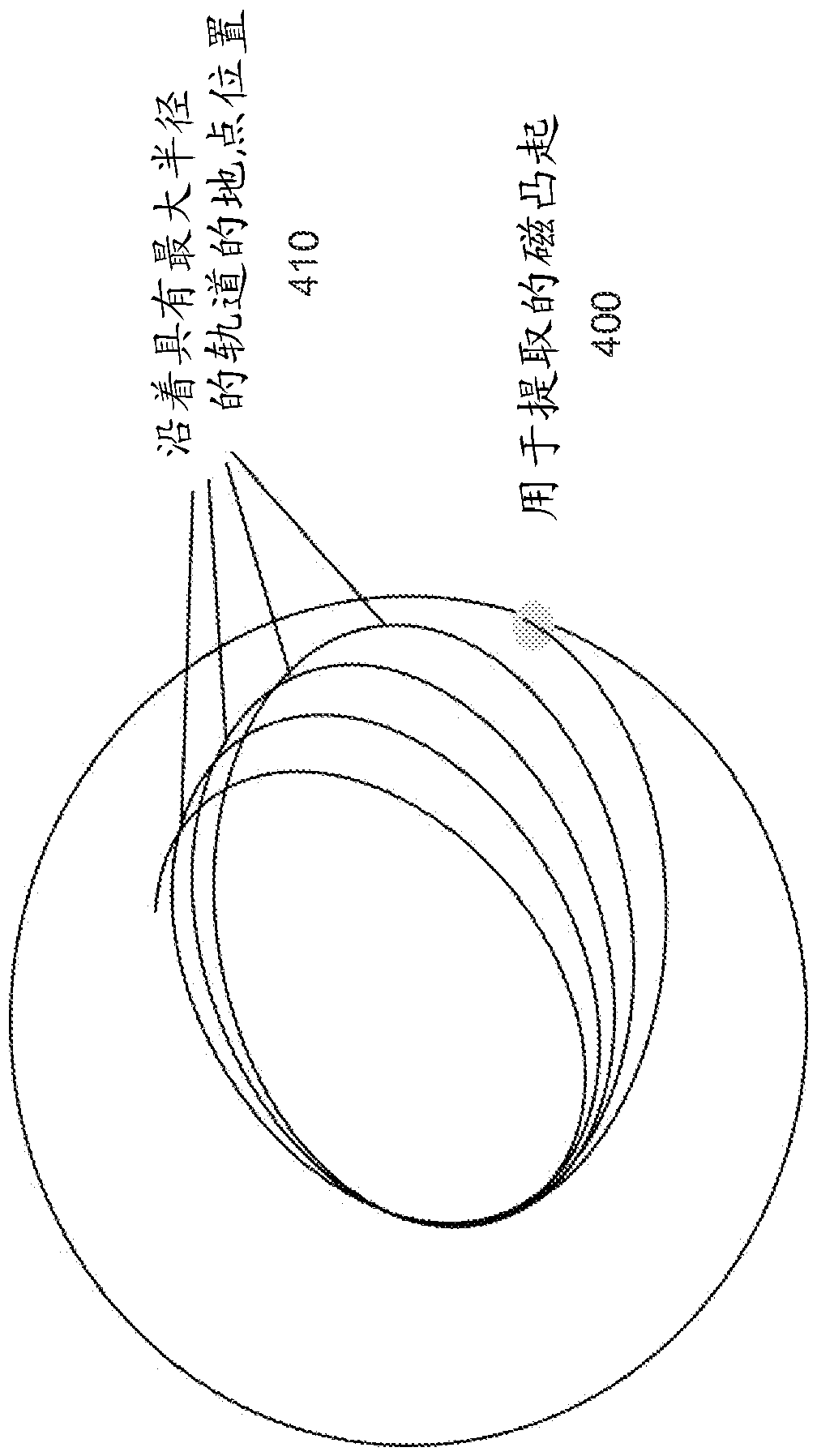
Synchrocyclotron for extracting beams of various energies
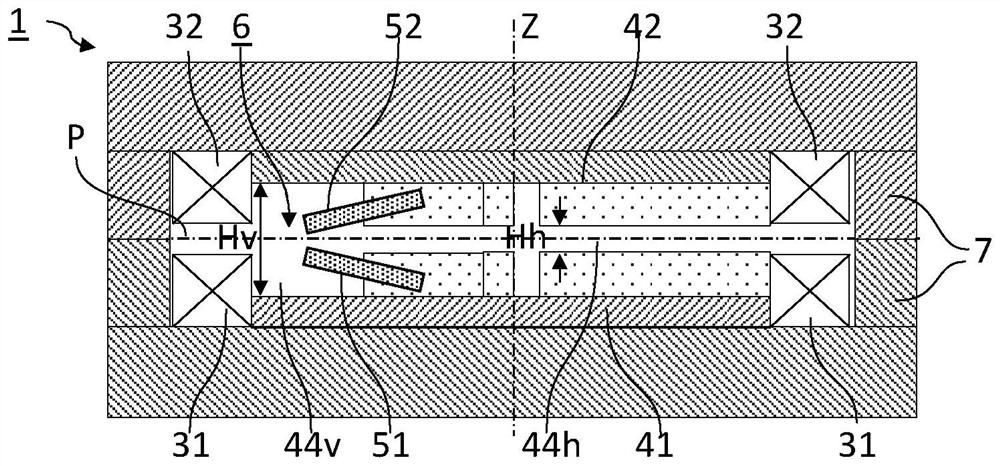
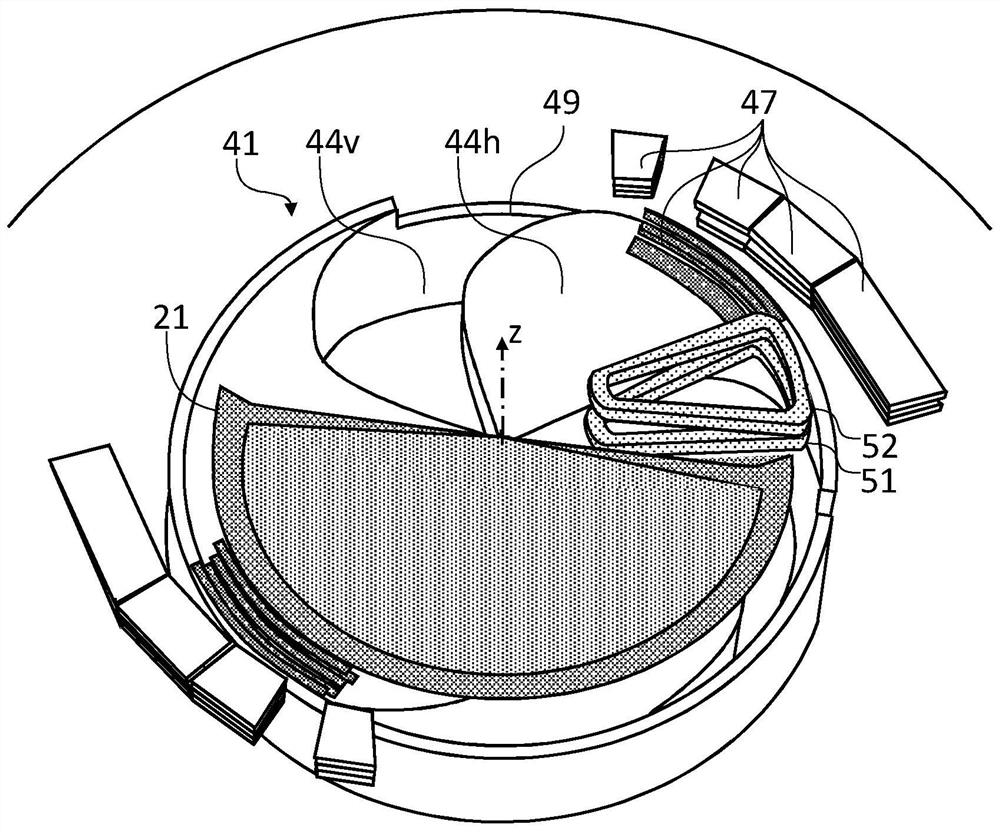
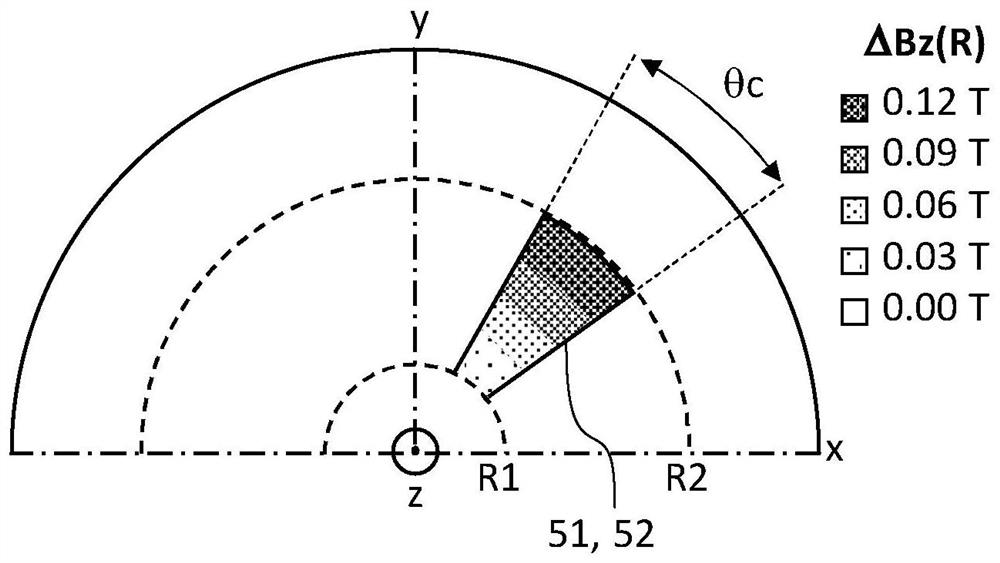
A synchrocyclotron for extracting charged particles accelerated to any extraction energy (Ei) between a low energy (E1) and a high energy (E2) is provided. The synchrocyclotron comprises a magnetic unit comprising N valley sectors and N hill sectors and configured for generating a z-component (Bz) of a main magnetic field. The synchrocyclotron is characterized in that the radial tuning ([nu]r) of successive orbits is not 1 and is in the range of 1 + / - 0.1 for all values of an average radius (R) between a low radius (R1) and a high radius (R2) corresponding to respective average radius positions of charged particles at low and high energies (E1, E2). The synchrocyclotron comprises a first labile coil unit (51) and a second labile coil unit (52) configured for generating a field bump of a radially increasing amplitude ([Delta]Bz(R)) when activated by a power source.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
RF system for synchrocyclotron
ActiveUS9351391B2Raise transfer toImprove cooling effectMagnetic resonance acceleratorsCapacitanceResonant cavity
The present invention relates to an RF system (1) able to generate a voltage for accelerating charged particles in a synchrocyclotron, the RF system (1) including a resonant cavity (2) comprising a conducting enclosure (5) within which are placed a conducting pillar (3) of which a first end is linked to an accelerating electrode (4) able to accelerate the charged particles, a rotary variable capacitor (10) coupled between a second end opposite from the first end of the pillar (3) and the conducting enclosure (5), the said capacitor (10) comprising fixed electrodes (11) and a rotor (13) comprising mobile electrodes (12), the fixed electrodes (11) and the mobile electrodes (12) forming a variable capacitance able to vary a resonant frequency of the resonant cavity (2) in a cyclic manner over time, an exterior layer of the rotor (13) having a conductivity of greater than 20,000,000 S / m at 300 K. At least one part of the exterior surface (15) of the rotor (13) is a surface possessing a normal total emissivity of greater than 0.5 and less than 1, thereby allowing better cooling of the rotor and / or making it possible to dispense with a system for cooling the rotor by conduction and / or by convection.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com