Patents
Literature
392 results about "Synchrotron radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when charged particles are accelerated radially, e.g., when they are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (a ⊥ v). It is produced, for example, in synchrotrons using bending magnets, undulators and/or wigglers. If the particle is non-relativistic, then the emission is called cyclotron emission. If, on the other hand, the particles are relativistic, sometimes referred to as ultrarelativistic, the emission is called synchrotron emission. Synchrotron radiation may be achieved artificially in synchrotrons or storage rings, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over the entire electromagnetic spectrum which is also called continuum radiation.
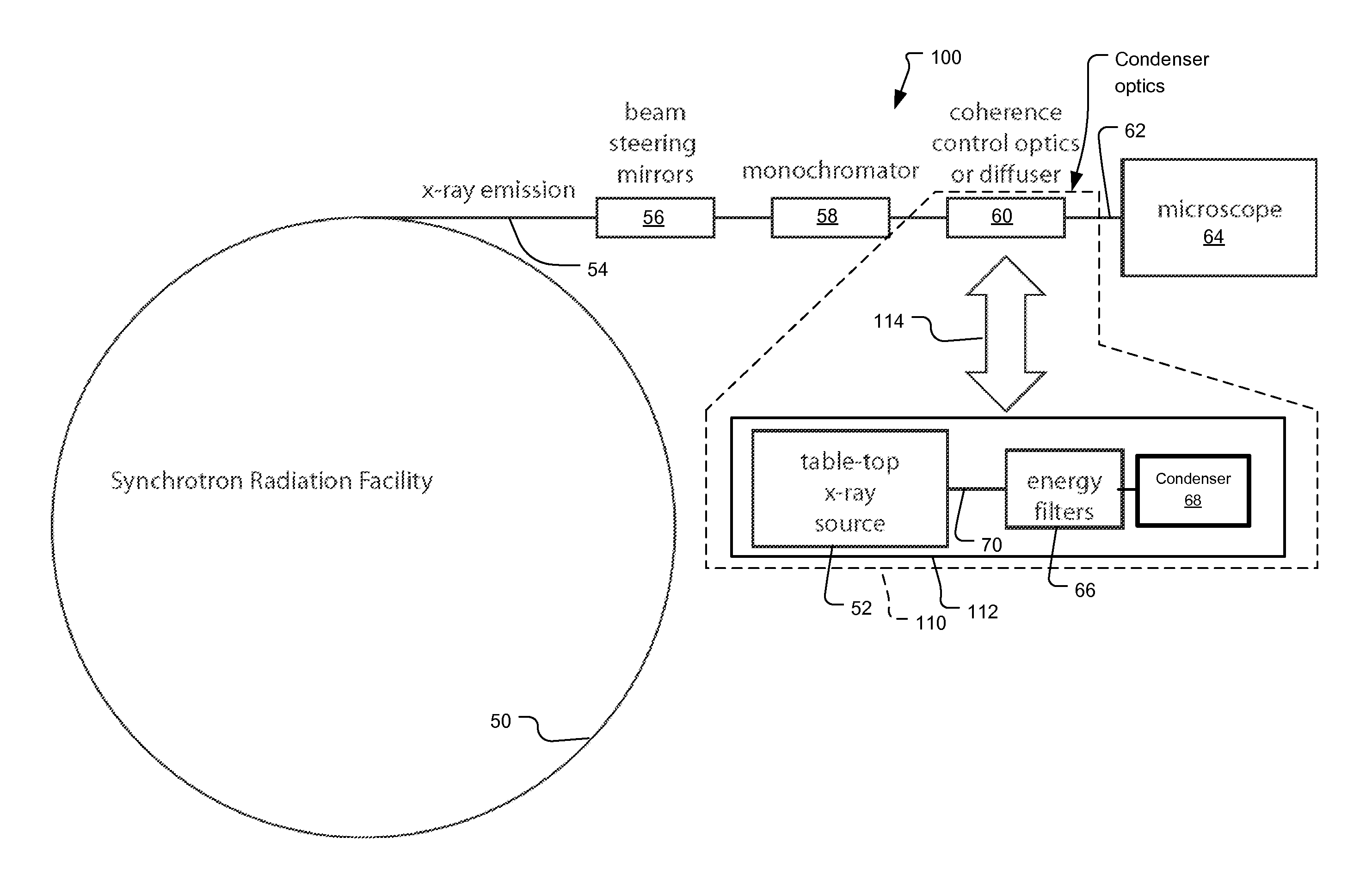
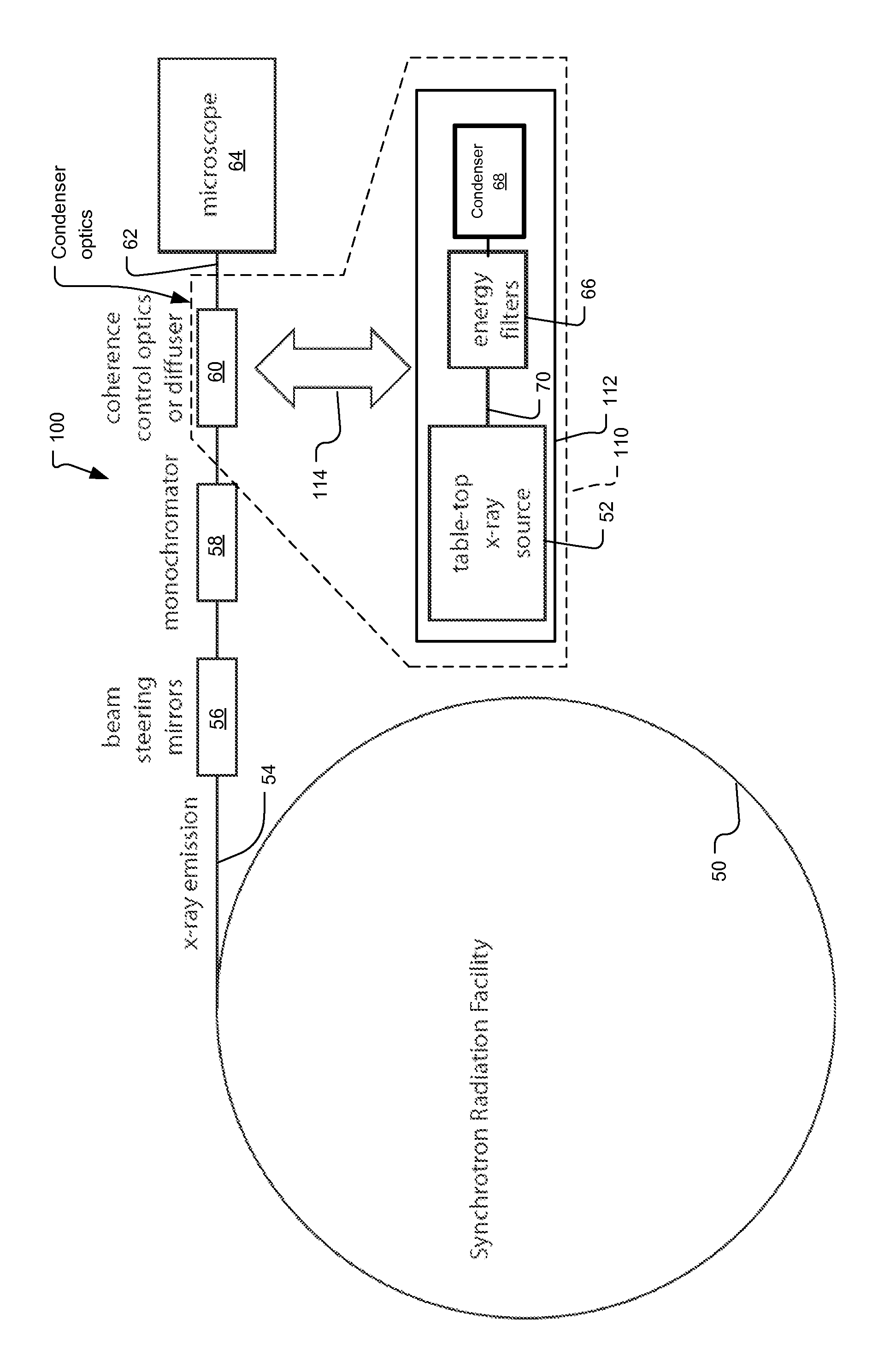
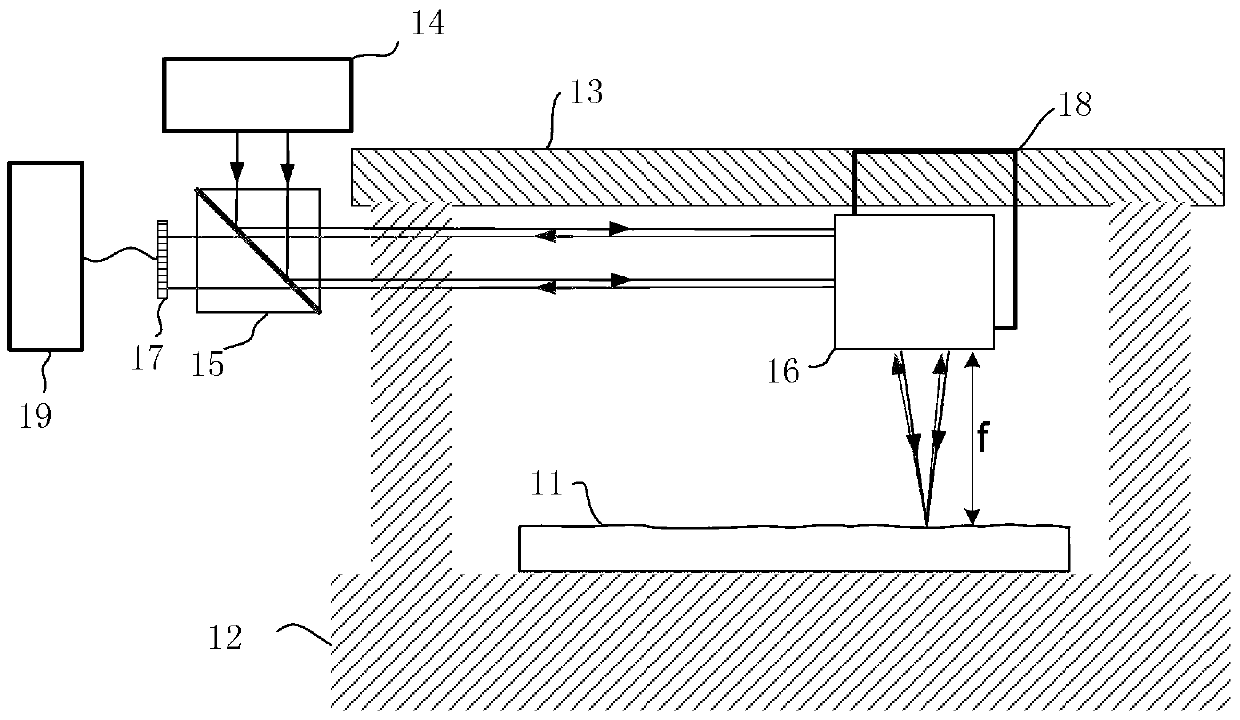
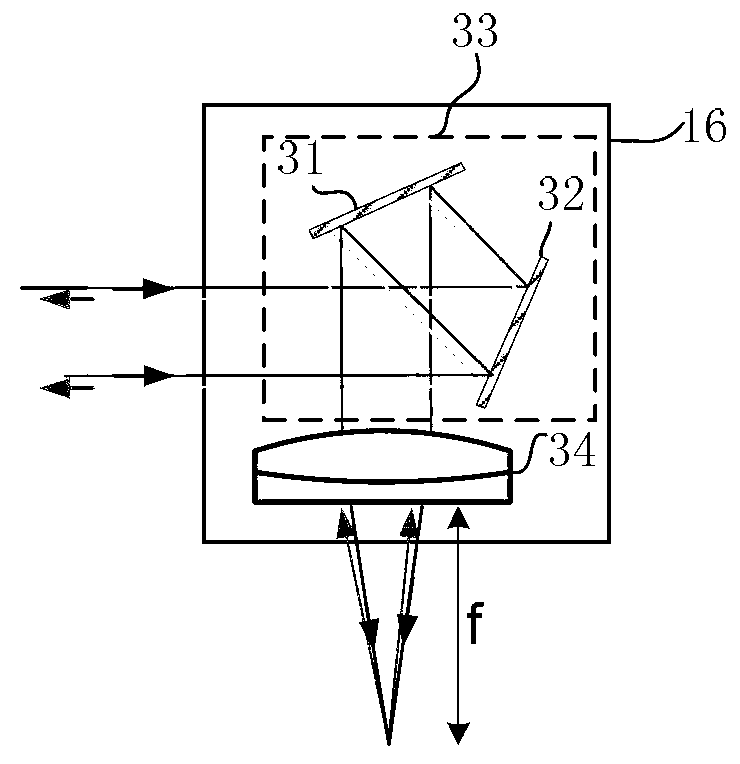
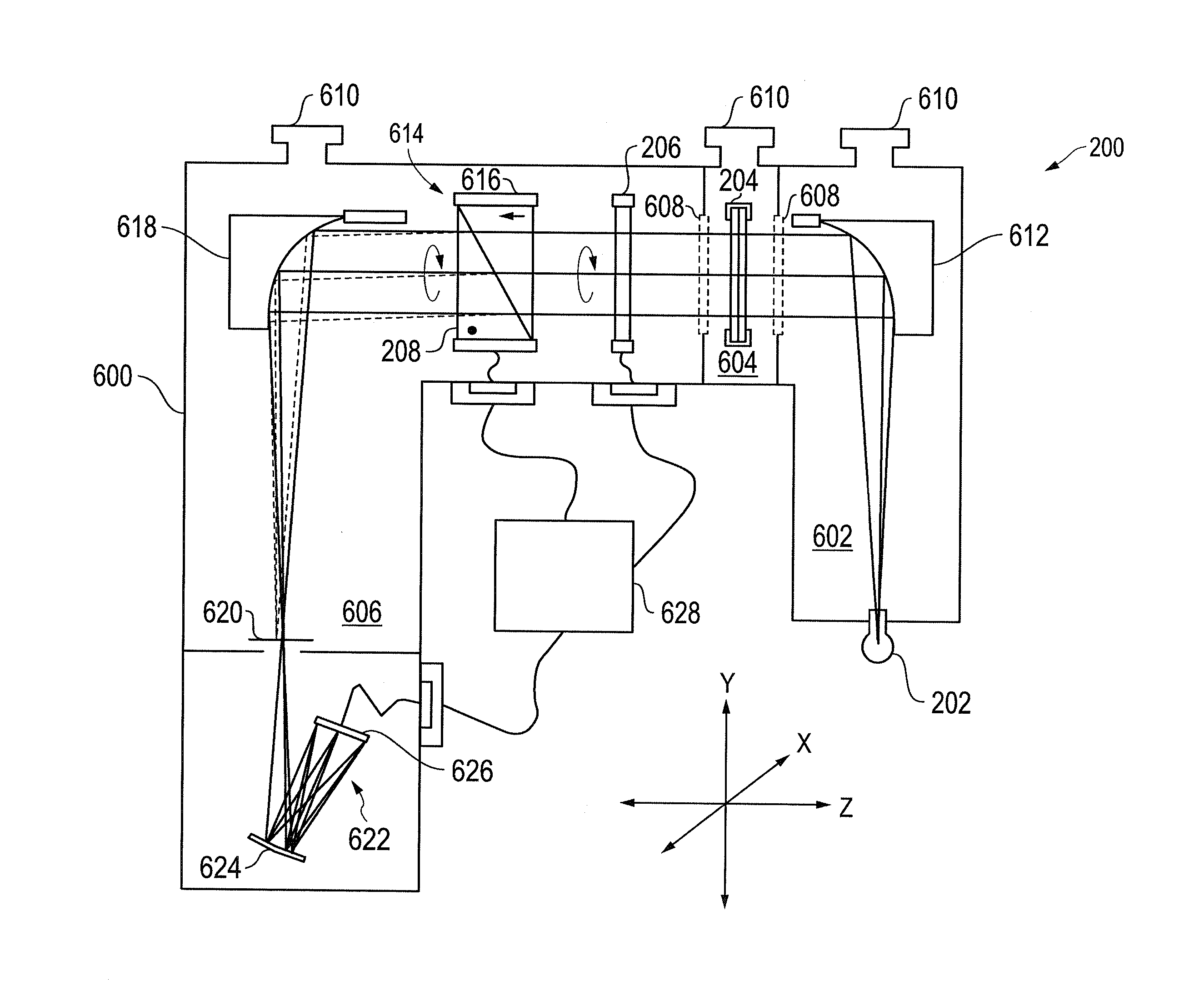
X-ray microscope with switchable x-ray source
An x-ray imaging system uses a synchrotron radiation beam to acquire x-ray images and at least one integrated x-ray source. The system has an imaging system including sample stage controlled by linear translation stages, objective x-ray lens, and x-ray sensitive detector system, placed on a fixed optical table and a mechanical translation stage system to switch x-ray sources when synchrotron radiation beam is not available.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
High-temperature fused salt synchrotron radiation in-situ research device
InactiveCN102590253AEliminate phenomena that introduce artifactsExpand the detection angleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescenceIonization chamber
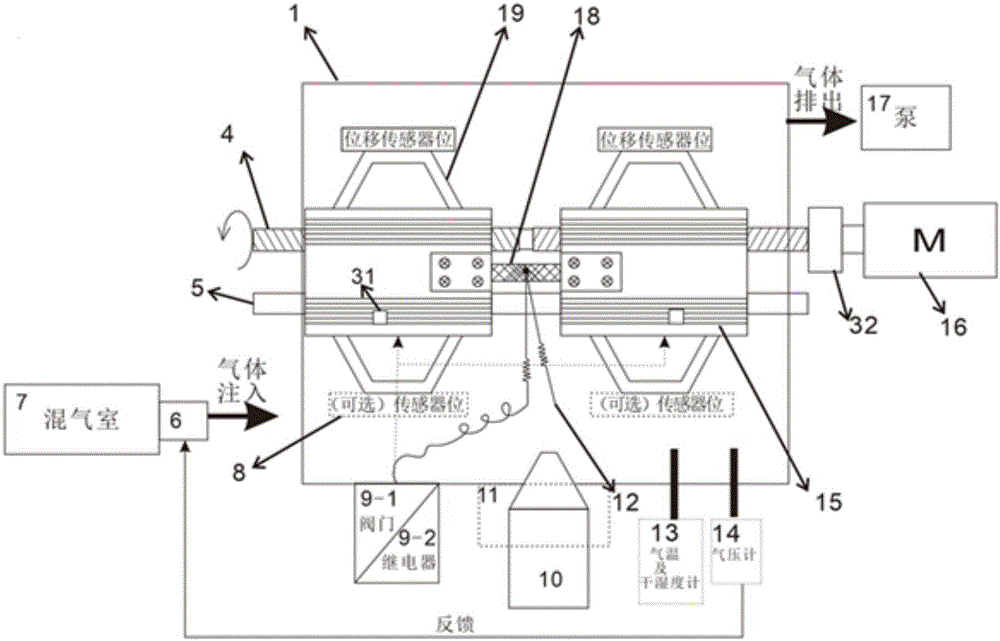
The invention discloses a high-temperature synchrotron radiation in-situ research device. The high-temperature fused salt synchrotron radiation in-situ research device comprises a fused salt test tube, a vacuum furnace, a heating device, a first ionization chamber, a second ionization chamber or a charge coupled device (CCD) detector and an external fluorescence detector, wherein a cavity is formed in the vacuum furnace; an incident window, a transmission window and a fluorescence window are arranged on the furnace wall of the vacuum furnace; the incident window and the transmission window are arranged coaxially and collinearly; the axial line of the fluorescence window is vertical to that of the incident window and / or the transmission window; the heating device is arranged in the cavity of the vacuum furnace and is used for heating the fused salt test tube arranged in the heating device; an incident hole, a transmission hole and a fluorescence hole corresponding to the incident window, the transmission window and the fluorescence window respectively are formed on the heating device; the first ionization chamber corresponding to the incident window is arranged outside the vacuum furnace; the second ionization chamber or the CCD detector corresponding to the transmission window is arranged outside the vacuum furnace; and the external fluorescence detector corresponding to the fluorescence window is arranged outside the vacuum furnace.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Support structures for planar insertion devices
InactiveUS7956557B1Prevents detrimental deformation reactionMagnetic induction acceleratorsMagnetsSynchrotronInsertion device
A planar insertion device and supporting structure for a planar insertion device for treating a synchrotron radiation beam includes a primary frame on which at least two secondary C-frames are mounted. An upper and a lower girders are mounted on the secondary C-frames forming a gap between girders and arranged substantially horizontally and parallel to each other and to the synchrotron radiation beam. Magnetic arrays rigidly mounted on the girders are facing each other and facing the gap between girders, with the synchrotron radiation beam passing between the magnetic arrays through the gap. The planar insertion device supporting structure prevents detrimental deformation reactions to variations of magnetic loadings with changes in the gap and subsequent geometrical misalignments.
Owner:ADVANCED DESIGN CONSULTING USA
Neutron diffraction residual stress determination device and method
ActiveCN102435623AReduce absorptionNo need to overcome Coulomb barrierMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayNeutron diffraction
The invention discloses a neutron diffraction residual stress determination device and a method. The device is characterized by using the reactor neutron source, carrying out monochromatization by a monochromator to obtain a required monochromatic neutron beam at a certain wavelength, and using the neutron beam to detect the residual stress. According to the invention, because the neutrons are uncharged, and when the neutrons interact with substance, the neutrons have no effect with extranuclear electons, charge Coulombian force obstacle has no need to overcome, thus low energy neutrons can enter in atoms; the neutron absorption of great majority of materials is low, thus the penetration depth of incoming neutron beam is deep. Simultaneously by collimator and slit collimation, the limitedneutron beam has high space resolution ratio, a three-dimensional lossless and deep stress test of a test piece is realized by translation of three directions which are vertical to each other and rotation around testing central point, and the defect that an X-ray and a synchrotron radiation residual stress determination device can only losslessly determine the residual stress of the crystal material surface and subsurface is overcome.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
A method for pattern recognition of cancer cells using soft x-ray microscopic imaging
InactiveCN102297873APreparing sample for investigationBiological neural network modelsMicroscopic imageSoft x ray
This invention discloses a method for utilizing soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition. The method comprises the steps of 1) sample preparation; 2) pathological examination; 3) soft X-ray imaging; and 4) analysis and recognition. This invention applies soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition, successfully obtains the soft X-ray microscopic image of a cancer cell by scanning the cancer cell with synchrotron radiation soft X-ray microimaging, provides recognition steps and experimental data, and establishes a method for utilizing soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition. This invention creates a method for analyzing soft X-ray microscopic images, provides a novel synchrotron radiation soft X-ray pathological diagnosis method for cancer diagnosis, and provides an extremely valuable basis for the creation and clinical application of soft X-ray pathology in the 21st century.
Owner:NO 128 HOSPITAL OF HANGZHOU
Crystal geometrically necessary dislocation automatic analysis method based on synchrotron radiation
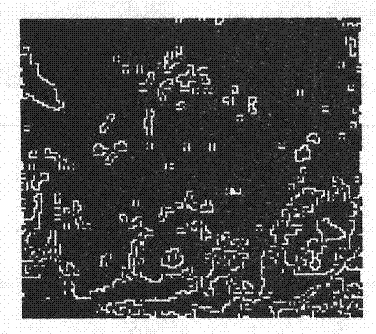
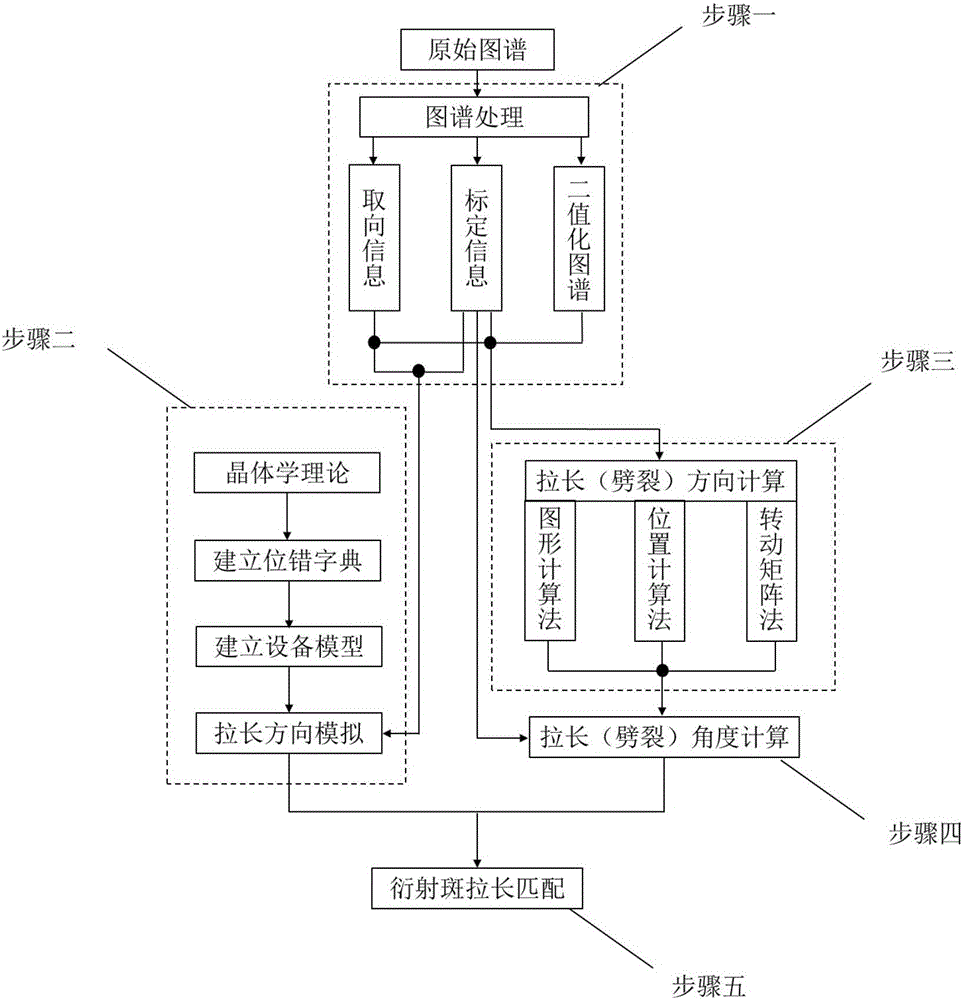
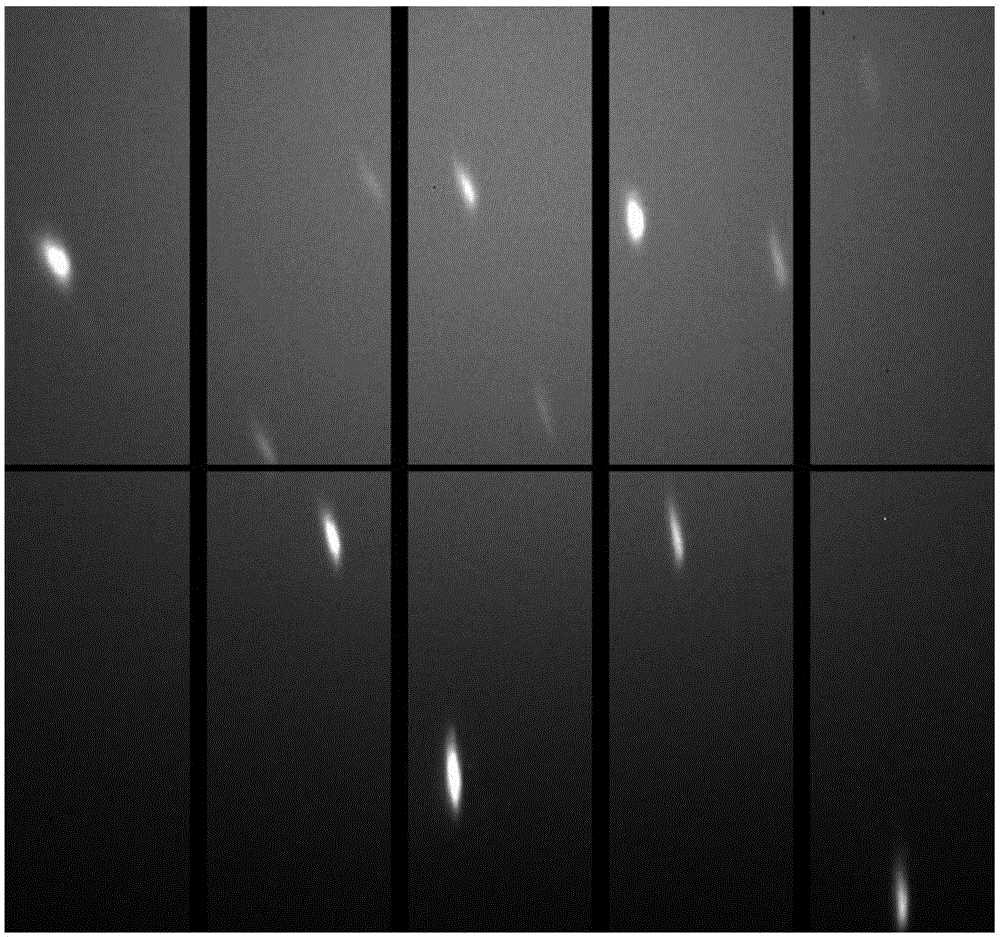
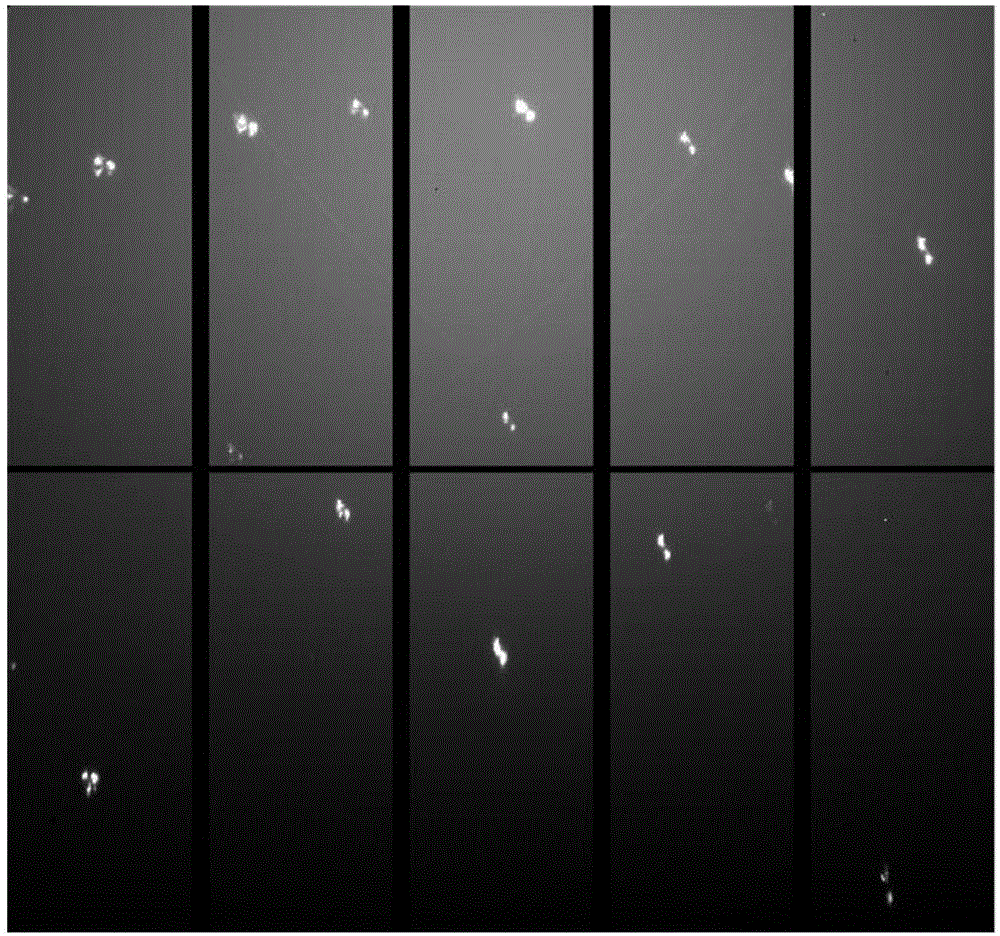
ActiveCN106055899AProcessing speedRealize analysisMolecular entity identificationSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsCrystal orientation
The invention relates to a crystal geometrically necessary dislocation automatic analysis method based on synchrotron radiation. The method comprises the following steps: step one, acquiring a binary map, diffraction spot calibration information and crystal orientation information from an original map through the map processing; step two, establishing a dislocation dictionary through the crystallographic theory, establishing equipment model and simulating an elongation direction in combination with the diffraction spot calibration information and the crystal orientation information so as to obtain a candidate elongation direction; step three, using the binary map, the diffraction spot calibration information and the crystal orientation information to compute a diffraction spot elongation or splitting direction and elongation diffraction spot vertex through the graphic computation method of a diffraction map, the position computation method of the diffraction spot position and a rotation matrix method of the crystal orientation; step four, computing the diffraction spot elongation or splitting angle through the elongation diffraction spot vertex and the splitting diffraction spot calibration information; step five, identifying and matching the diffraction spot elongation or splitting according to the candidate elongation direction produced through simulation, computed elongation or splitting direction and elongation or splitting angle.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device and application
InactiveCN103134825ARealize free switchingRealize acquisitionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicroscopic imageX-ray
The invention discloses a multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device. A synchrotron radiation X-ray light source, an undulator, a monochromator crystal, an X-ray shutter, a first lifting platform, a focusing device cavity, a vacuum piping, a second lifting platform, a multi-purpose sample room, a vacuum piping, a third lifting platform, a detector, and a computer which is used for collecting data and controlling an electric controlled translation platform are sequentially and coaxially arranged along the forward motion direction of light beam, wherein the monochromator crystal, the X-ray shutter and the first lifting platform are arranged on an electrical rotary platform, the focusing device cavity, the vacuum piping and the second lifting platform are arranged on the first lifting platform, the multi-purpose sample room, the vacuum piping and the third lifting platform are arranged on the second lifting platform, and the detector and the computer are arranged on the third lifting platform. According to the multi-purpose synchrotron radiation coherent X-ray diffraction microscopic imaging device, a low vacuum operating mode, a ventilation working mode, a freezing operating mode, X-ray focusing mode imaging or X-ray non-focusing mode imaging are achieved, the collection of three-dimension diffraction signals of samples are achieved by using a three-dimension rotating platform, a high quality three-dimension rebuilding result is obtained by using computer software, dying treatment and slicing treatment to the samples are needless, and train of thought is supplied to enrich a synchrotron radiation beam line imaging method.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
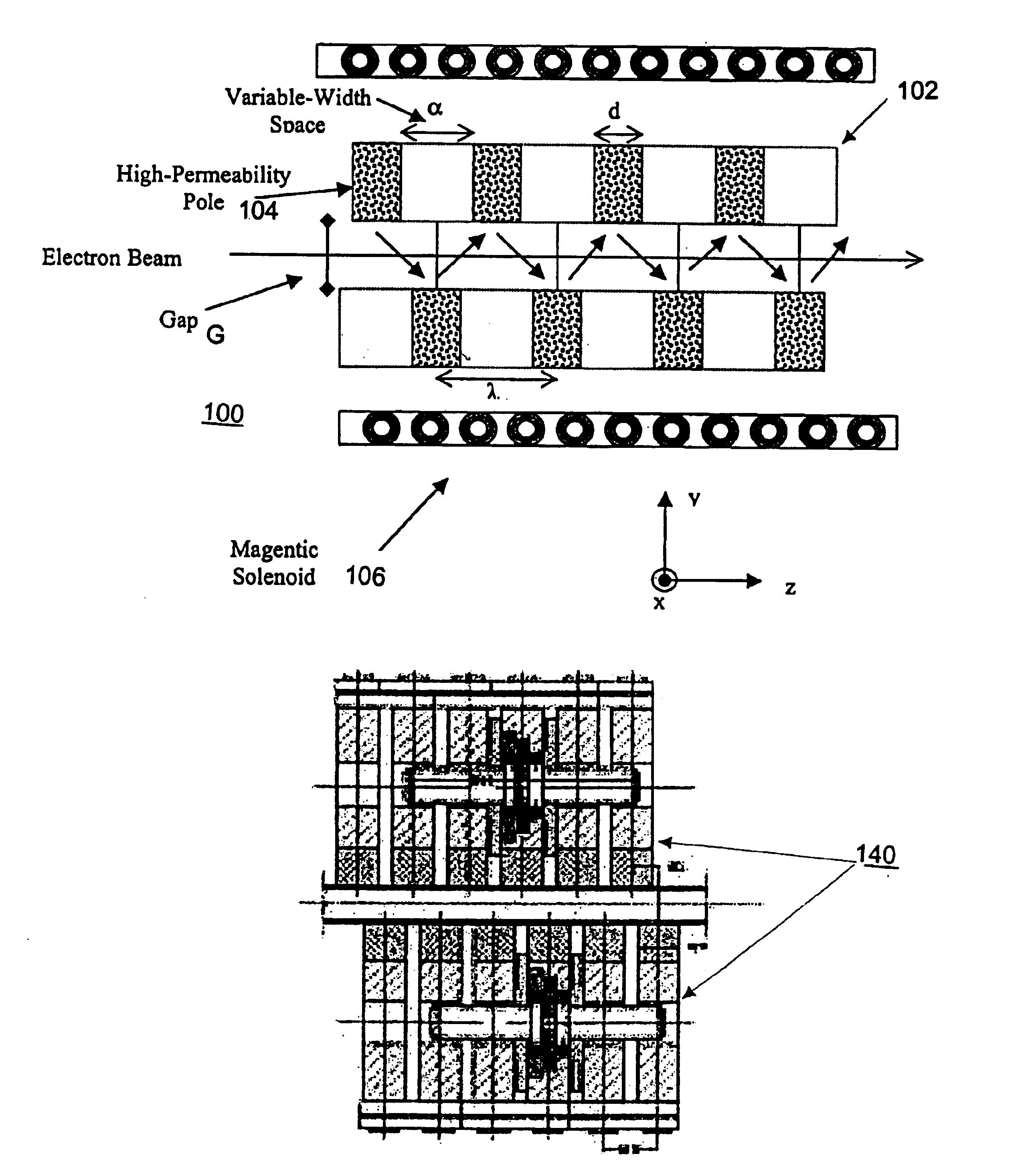
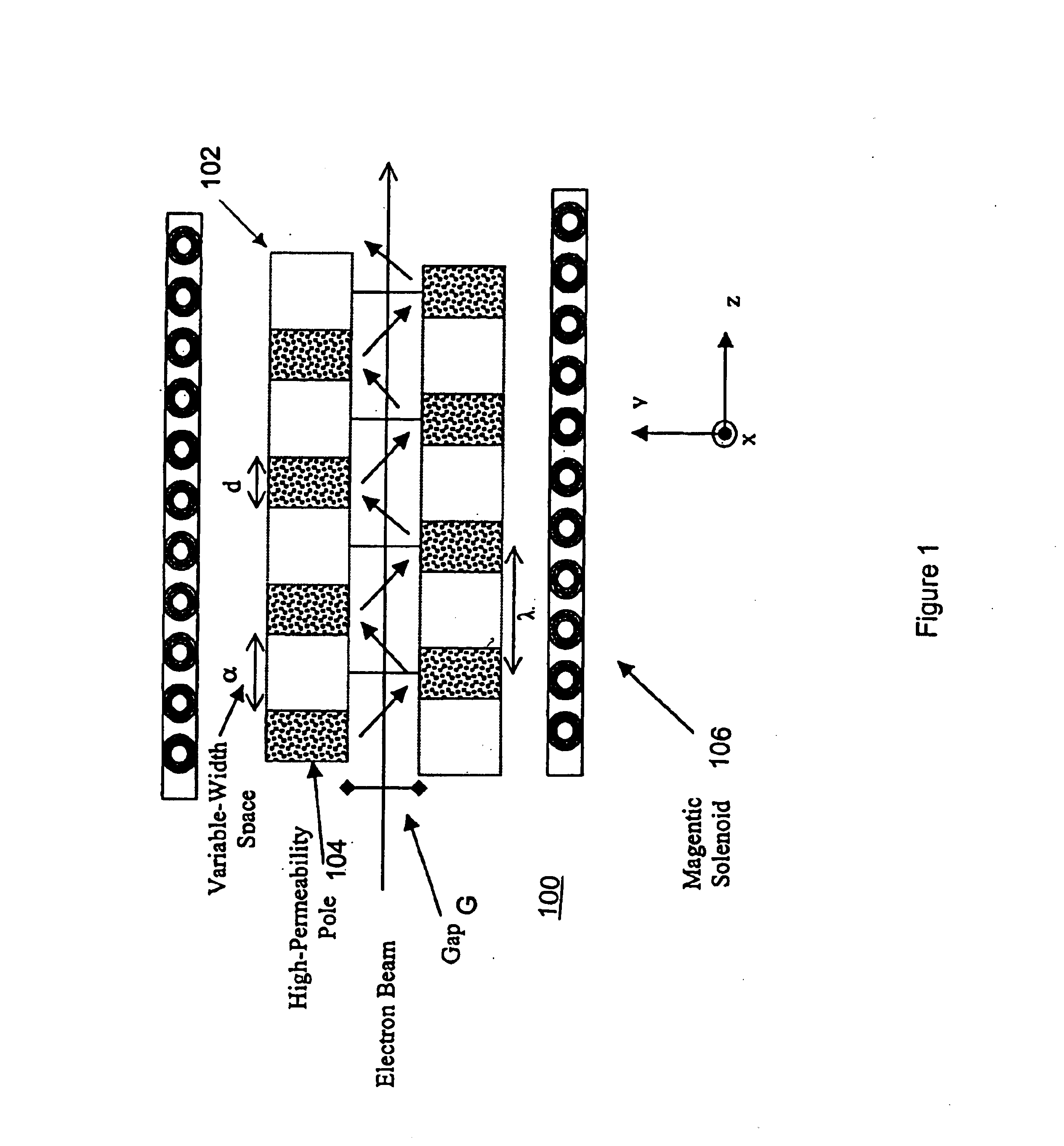
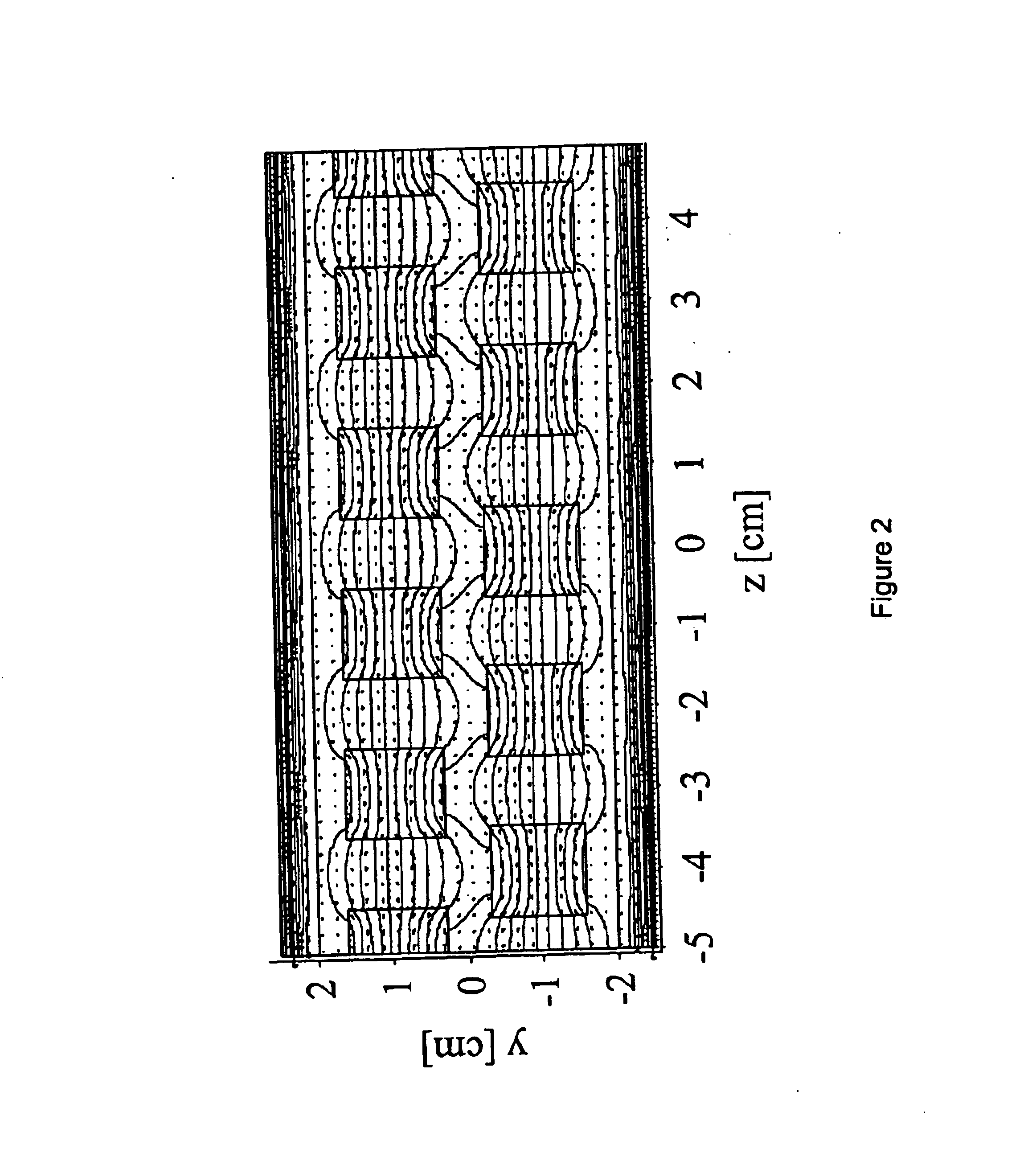
Variable-period undulators for synchrotron radiation
A new and improved undulator design is provided that enables a variable period length for the production of synchrotron radiation from both medium-energy and high-energy storage rings. The variable period length is achieved using a staggered array of pole pieces made up of high permeability material, permanent magnet material, or an electromagnetic structure. The pole pieces are separated by a variable width space. The sum of the variable width space and the pole width would therefore define the period of the undulator. Features and advantages of the invention include broad photon energy tunability, constant power operation and constant brilliance operation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Shale gas reservoir character prediction method
The invention relates to a shale gas reservoir character prediction method. In the method, scanning lines in the horizontal direction are formed through focusing by a reflective mirror in a mirror box with a synchrotron radiation light source. Vertical scanning is achieved through rotating vibration of the reflective mirror for obtaining micro-structure three-dimensional data of a shale gas occurrence porous sample. Three-dimension reconstruction is carried out to the obtained micro-structure three-dimensional data and porosity and an inherent permeability of a shale three-dimensional digital rock core are obtained through calculation in a manner of coupling between molecular dynamics and crystal lattice Boltzmann method and are expressed by mathematic expressions. In the invention a synchrotron radiation light and a computer technology are employed for researching the porosity and the inherent permeability of the shale three-dimensional digital rock core. The method is economic and environmental-protective, is easy to operate, can provide required important evaluation parameters for exploration and development of shale gas, can predict an adsorption / desorption principle of free gas and adsorbed gas in the shale gas, can be used for researching the porosity and the inherent permeability of the shale three-dimensional digital rock core, and provides technical support for development of the shale gas.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
High-accuracy high-spatial resolution long range profile detection system
ActiveCN103278106AEasy to measureHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansBeam splittingHigh spatial resolution
The invention discloses a high-accuracy high-spatial resolution long range profile detection system, which comprises a workbench, a transmission platform, a laser light source, a scanning optical head, a beam splitting prism and a signal acquisition processing unit, wherein the scanning optical head is arranged on the transmission platform; the beam splitting prism is used for deflecting light output from the laser light source for incidence into the scanning optical head, and an incident direction is consistent with the scanning direction of the transmission platform; the scanning optical head is used for deflecting and focusing incident light beams to the surface of an object to be detected in a detection area, for the object to be detected, of the workbench; and light reflected by the surface of the object to be detected in the detection area for the object to be detected sequentially passes through the scanning optical head and the beam splitting prism, and enters the signal acquisition processing unit. The system can be used for the high-spatial frequency sampling measurement of the surface to be detected, and the measurement accuracy is high; and the system can be used for measuring a large-sized object, and is particularly suitable for the detection of an optical element on a synchrotron radiation beam.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Construction and analysis of high-resolution digital cores for organic shales
PendingCN109285222AAccurate realization of resolutionDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementKerogenHigh resolution imaging
A construction and analysis of high-resolution digital cores for organic shales is disclosed. The method is characterized by comprising such steps as A, performing synchrotron radiation scanning on said synchrotron radiation scanning data; B. carrying out threshold filtering processing on that gray-scale image of the shale core, so that the boundary between the rock pores and the skeleton becomesmore obvious and smoother, and noise point generated in the process of CT scanning and reconstruction are eliminated; C. performing threshold segmentation of CT images to divide the rock framework andporosity. The invention has the beneficial effects that the method and the process of organic shale high-resolution imaging and digital core construction are completely introduced. In the calculationof the threshold value of skeleton and pore, the ratio of the property difference between the two groups to the difference within the group reaches the maximum to determine the threshold value, and the pore composition, mineral, kerogen and other components can be accurately distinguished.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
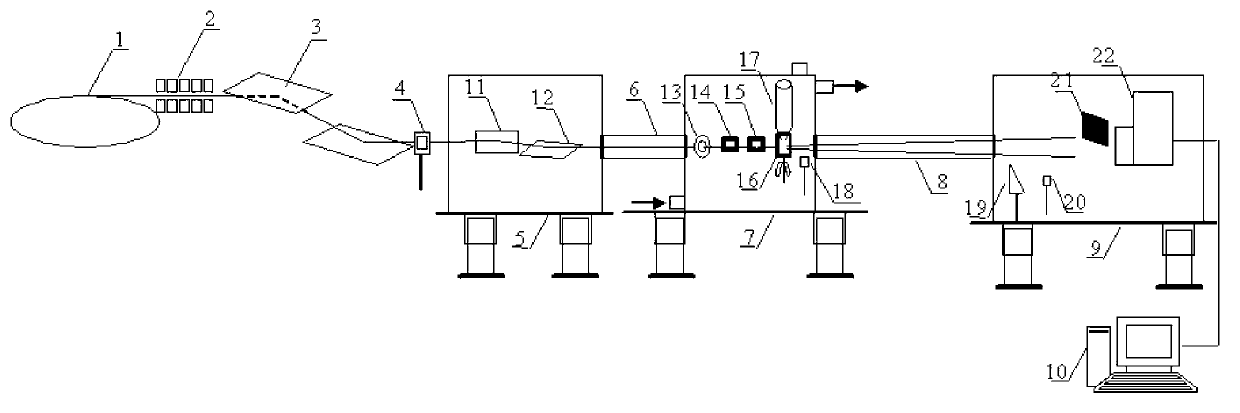
synchrotron radiation x-ray phase contrasting computed tomography and experimental method thereof
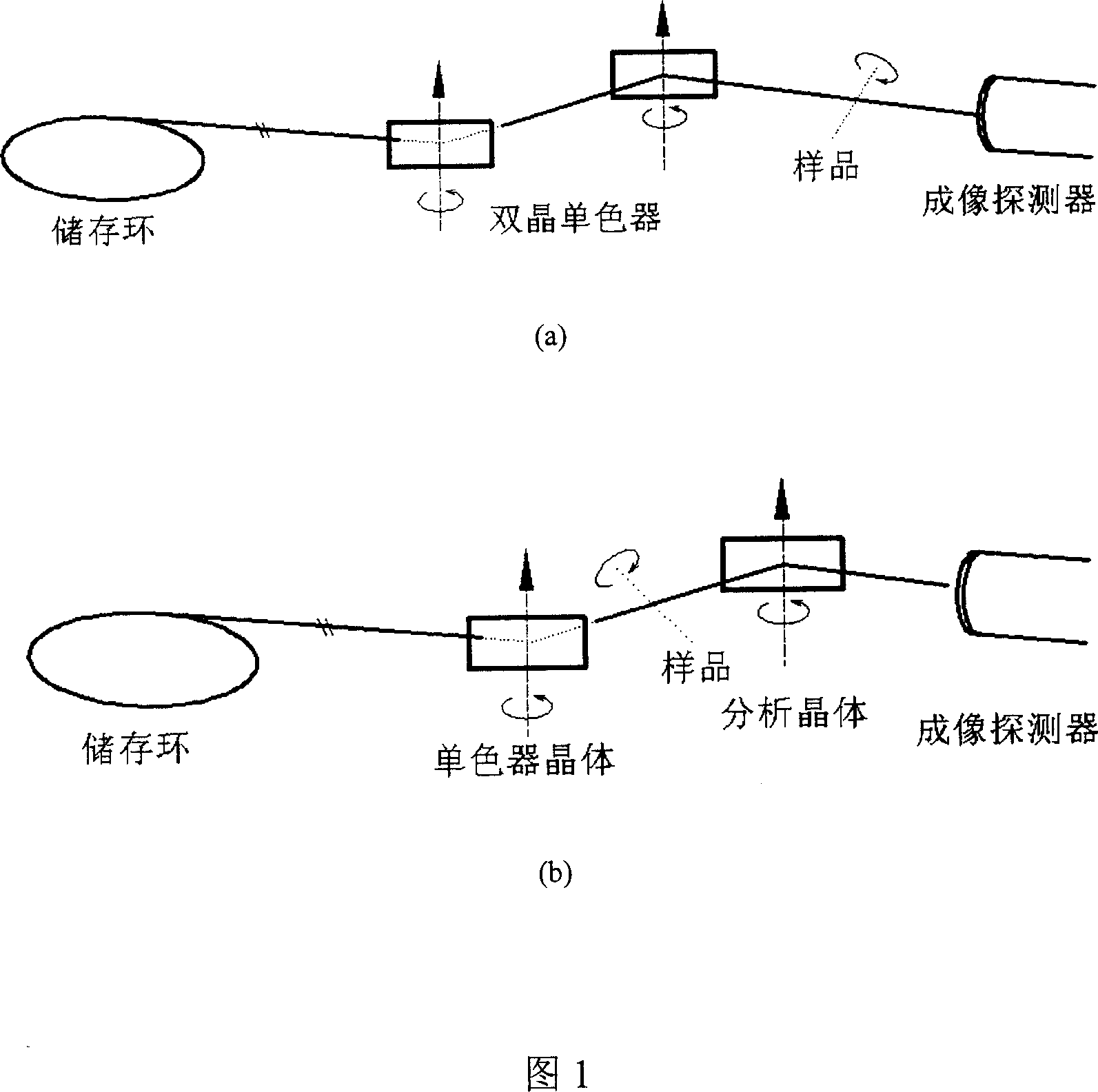
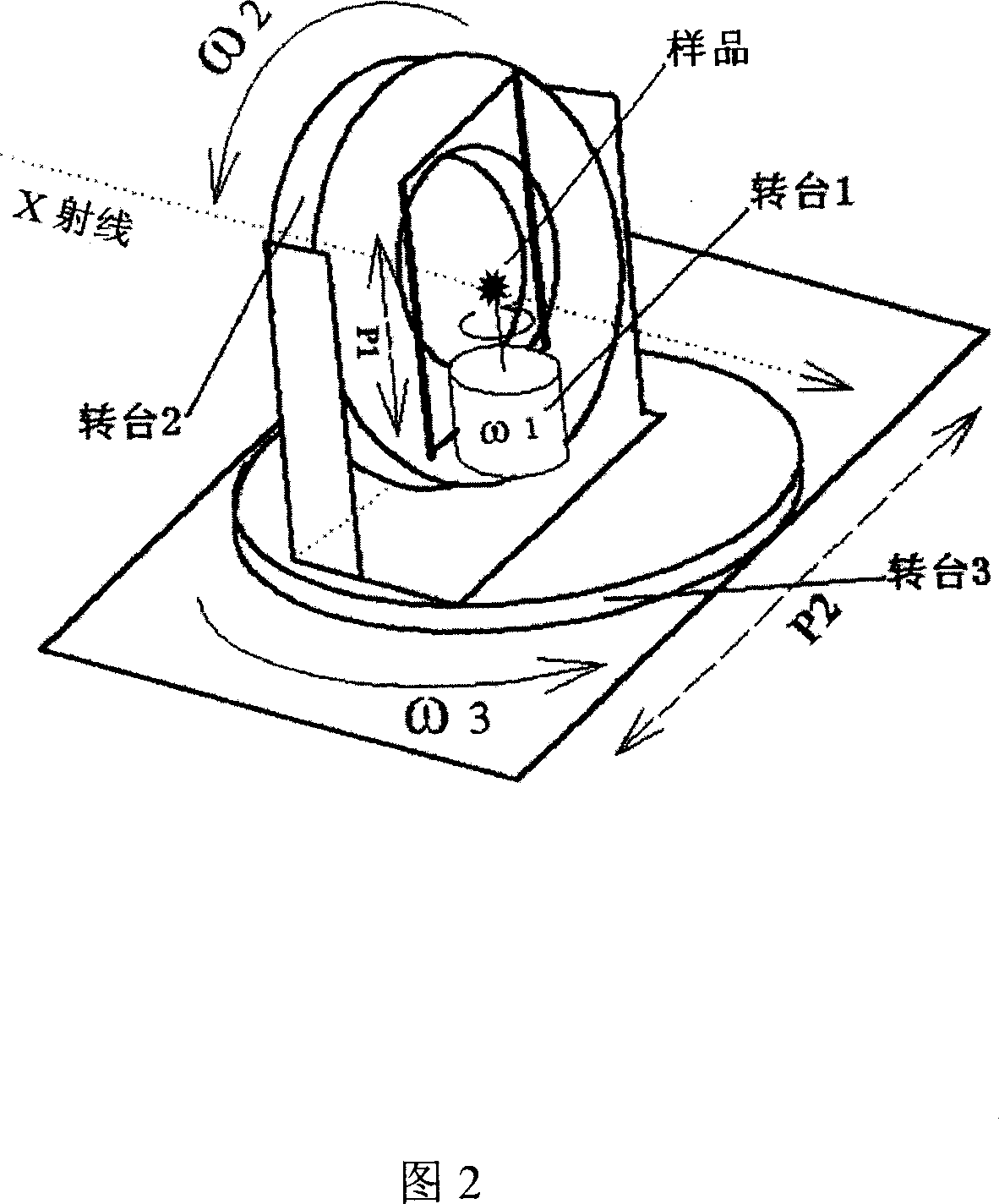
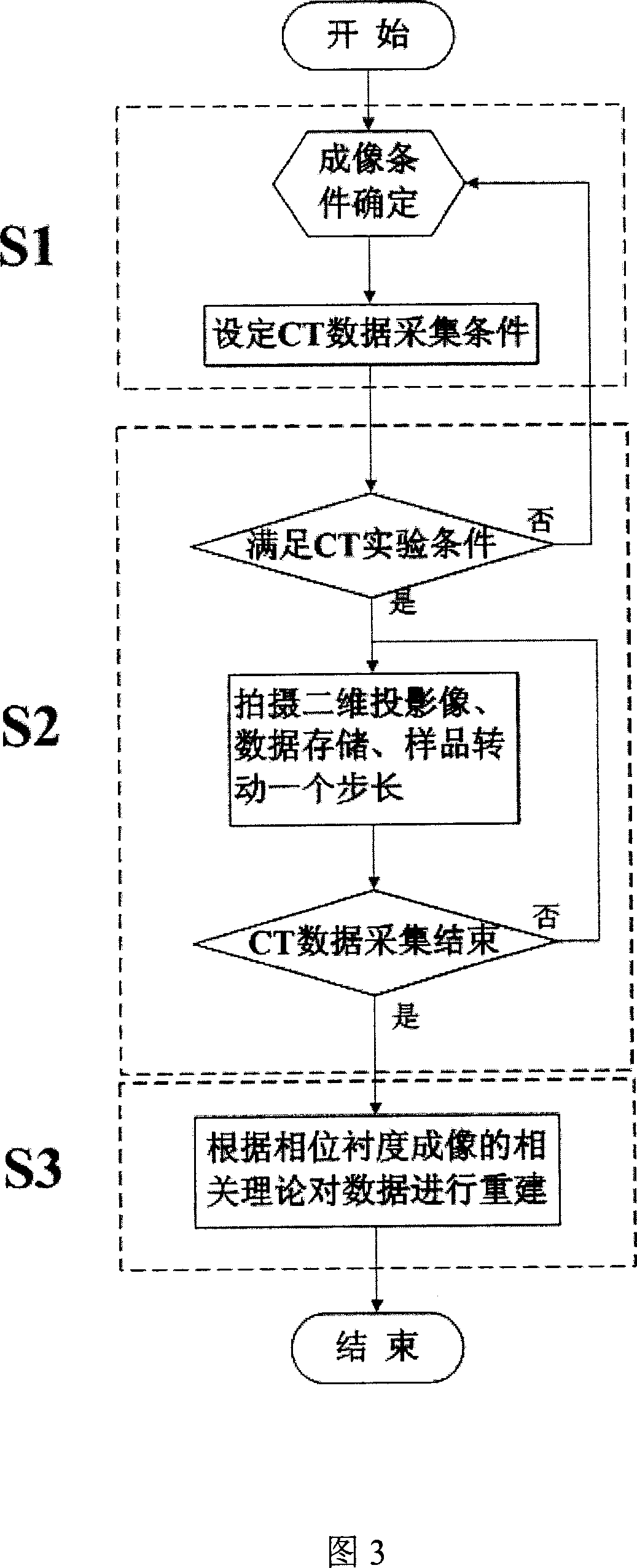
The invention relates to a computer tomography imaging technique, especially a synchronous radiation X-ray phase contrast CT imager and test method, wherein it is formed by monochromator crystal, sample table, analysis crystal, ionize room, and image detector; the sample table is formed by three rotations and two translations; the method comprises that S1 , finding the image conditions of phase contrasts in different image modes; S2, obtaining phase contrast CT test data; S3, rebuilding the test data.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods and apparatus for vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) or shorter wavelength circular dichroism spectroscopy
A highly efficient vacuum ultraviolet circular dichroism spectrometer is provided; the spectrometer suitable for laboratory use or for integration into a beam line at a synchrotron radiation facility. In one embodiment, a spectroscopic circular dichroism instrument is provided; the instrument configured so as to enable circular dichroism data to be simultaneously obtained for multiple wavelengths of light. The instrument may be further configured to operate in at least a portion of the vacuum ultraviolet wavelength region.
Owner:VUV ANALYTICS
Constant width film stretching device combined with X-ray scattering, and experimental method thereof
ActiveCN103063689AAchieve stretchAccurate temperatureMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionLabview softwareTwo temperature
The invention provides a constant width film stretching device combined with X-ray scattering, and an experimental method thereof. The device employs two Yaskawa servo motors to drive a ball screw to stretch a sample. The rotation of the motors is controlled by a Labview software. One end of the device is configured to a tension sensor for tracking tension change during a stretching process. During the stretching process, scissor mechanism fixtures are employed perpendicular to the stretching direction, so as to guarantee that the width of the sample can be kept constant during the stretching process and chuck points move uniformly along with the sample. The device employs a forced nitrogen stream to equalize temperature distribution in a sample cabin and reduce thermal degradation of the sample at a high temperature. Two temperature monitoring points are pre-set in the sample cabin. The temperature is precisely controlled by the temperature controller. The device has the advantages of easy disassembly and assembly and the like, is very suitable for combination with synchrotron radiation line stations, and is a very good device for studying the relationship between a structural evolution behavior and the film properties in film stretching and processing.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA +4
In-situ device for small-angle X-ray scattering experiment
ActiveCN106290426ASimple structureImprove performanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSmall-angle X-ray scatteringSpecial design
The invention discloses an in-situ device for small-angle X-ray scattering experiment. The in-situ device comprises a vacuum and atmosphere protection system, a stress load and measurement system and a temperature load and measurement system. Self-alignment of samples during stress load is realized in the stress load system by adopting design of pull-press stress transformation. Special design is adopted in the temperature load and measurement system, wide X-ray channels are realized while uniform of temperature field is guaranteed, and meanwhile, heating temperature of the samples can reach 1100 DEG C. By the arrangement, the in-situ device is simple in structure, reliable in performance, high in measurement accuracy and capable of loading in temperature and stress simultaneously on the samples under the vacuum or atmosphere protection environment. The in-situ device is used in cooperation with a synchrotron-radiation small-angle X-ray scattering line station, in-situ measurement of to-be-measured samples on microscopic deformation, damage and fracture process under the mechanics use environment can be performed, and an effective and reliable measurement method for discovering changes of deformation and microstructure of brittle material samples under the stress is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-watt THz generator
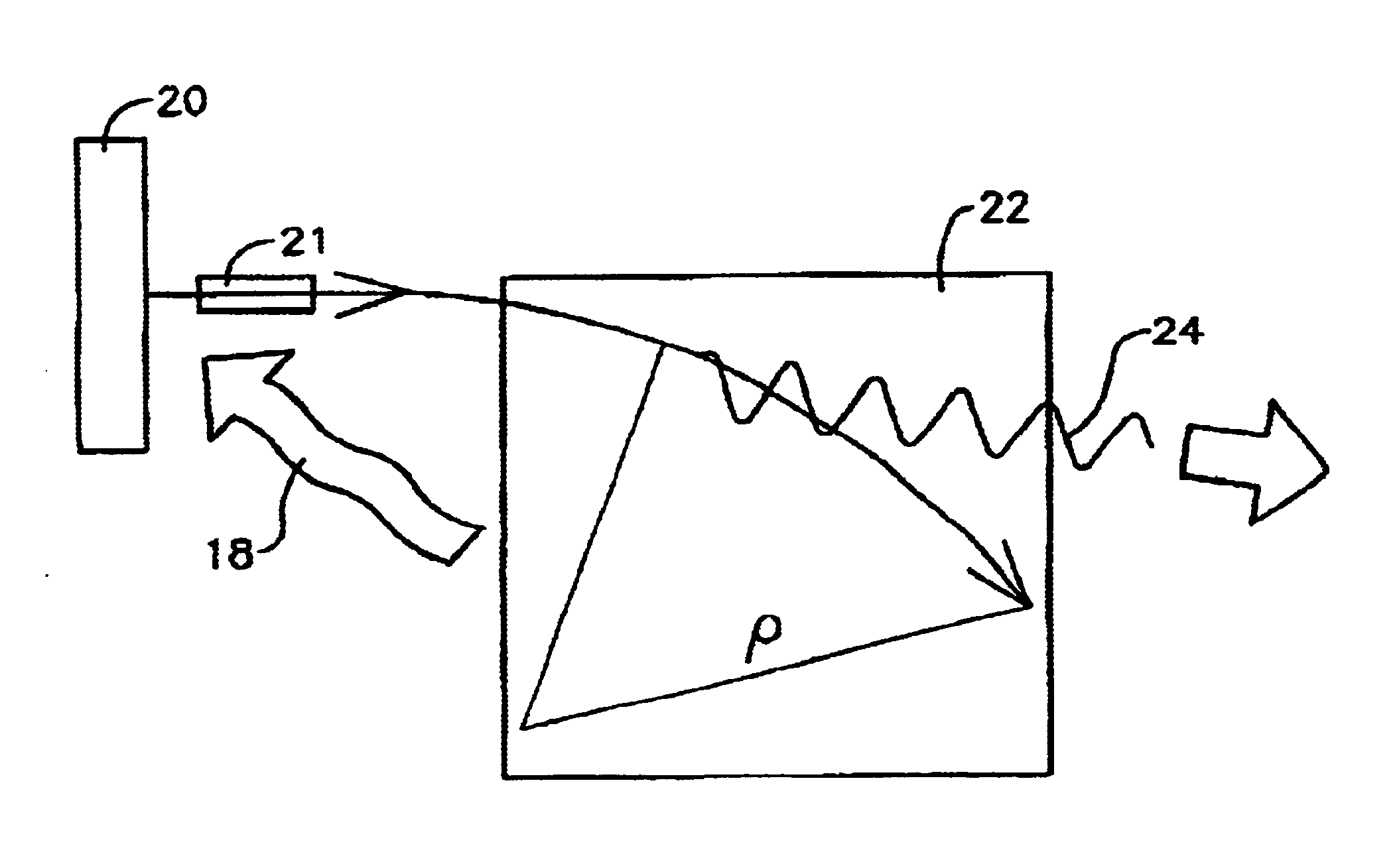
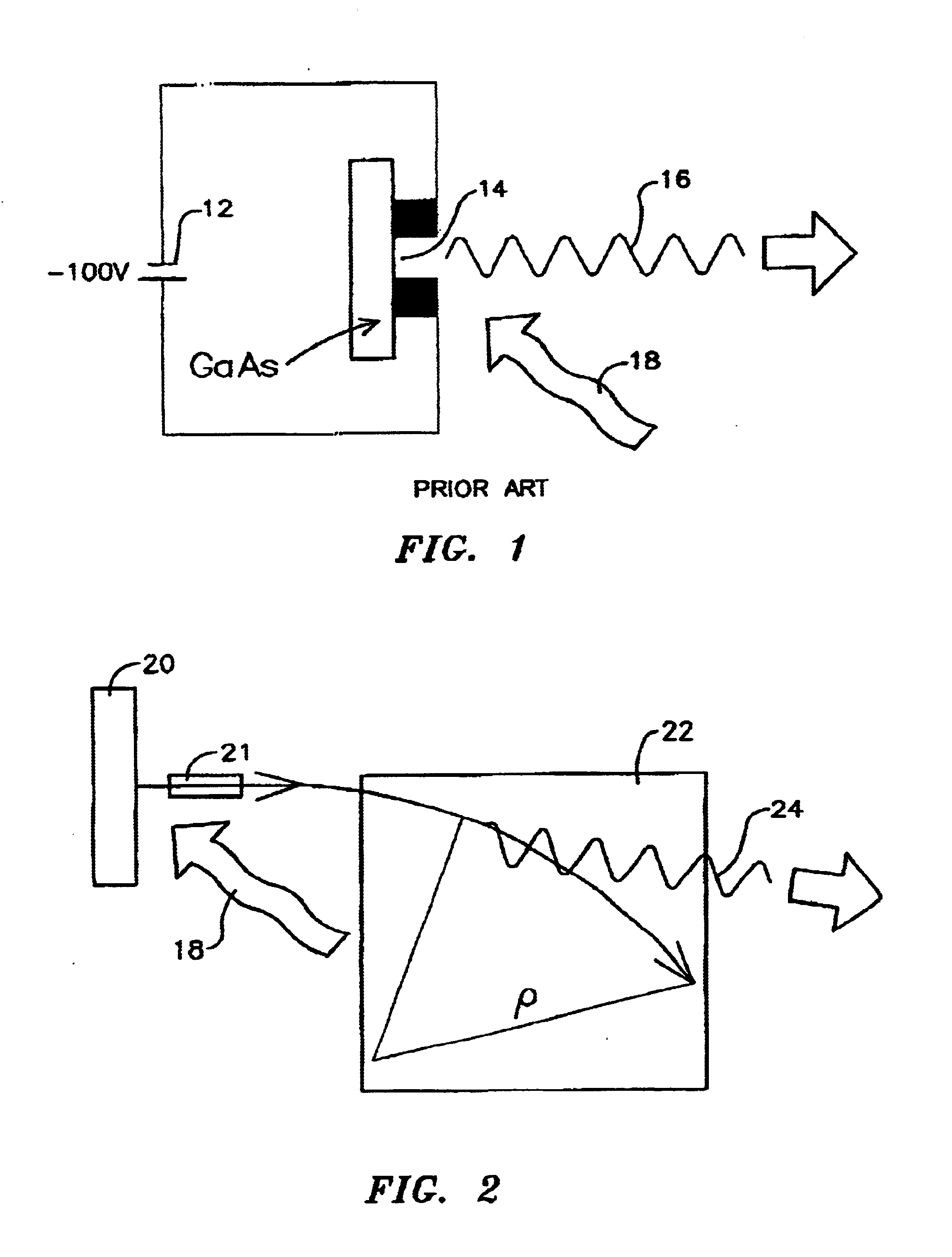
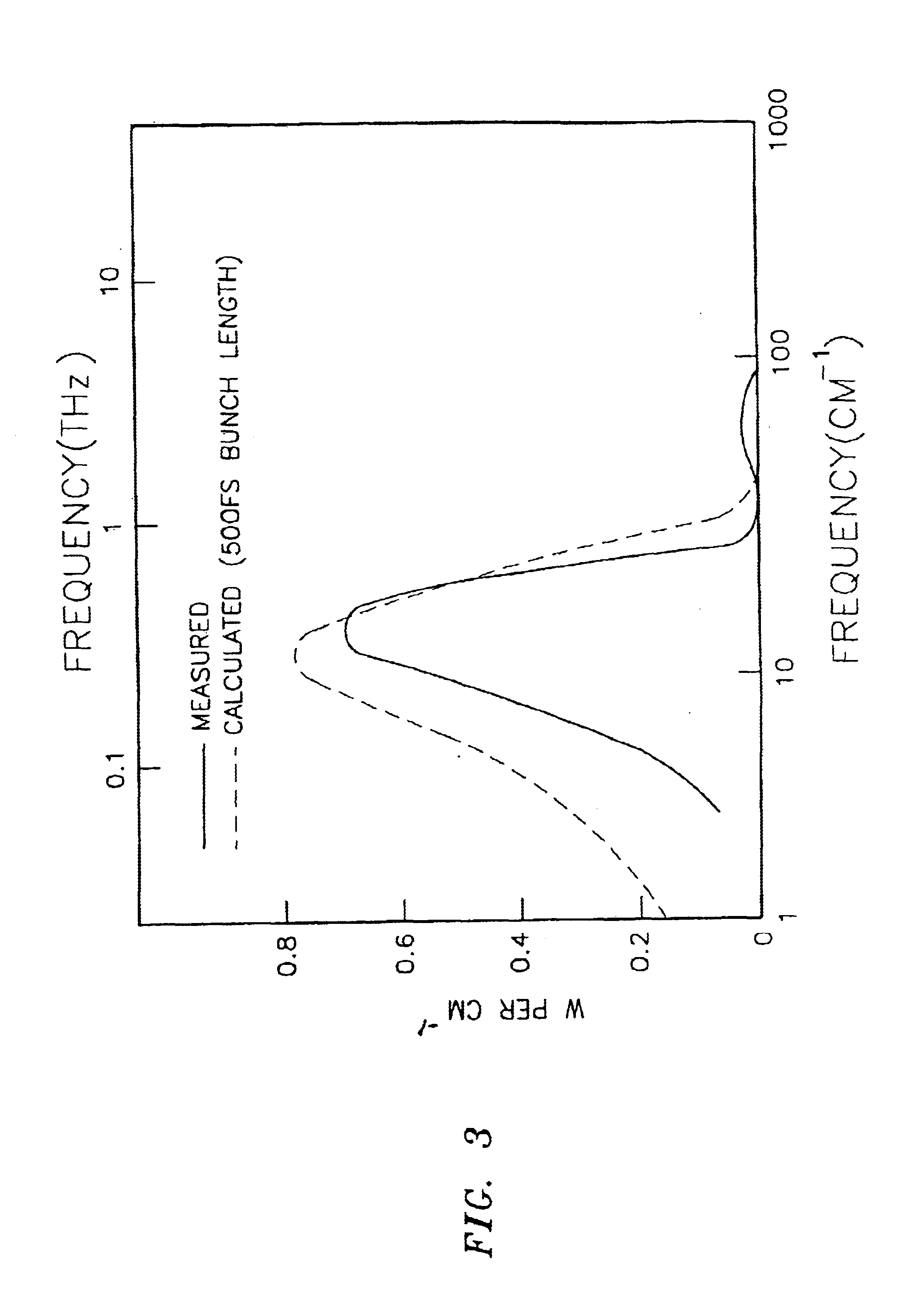
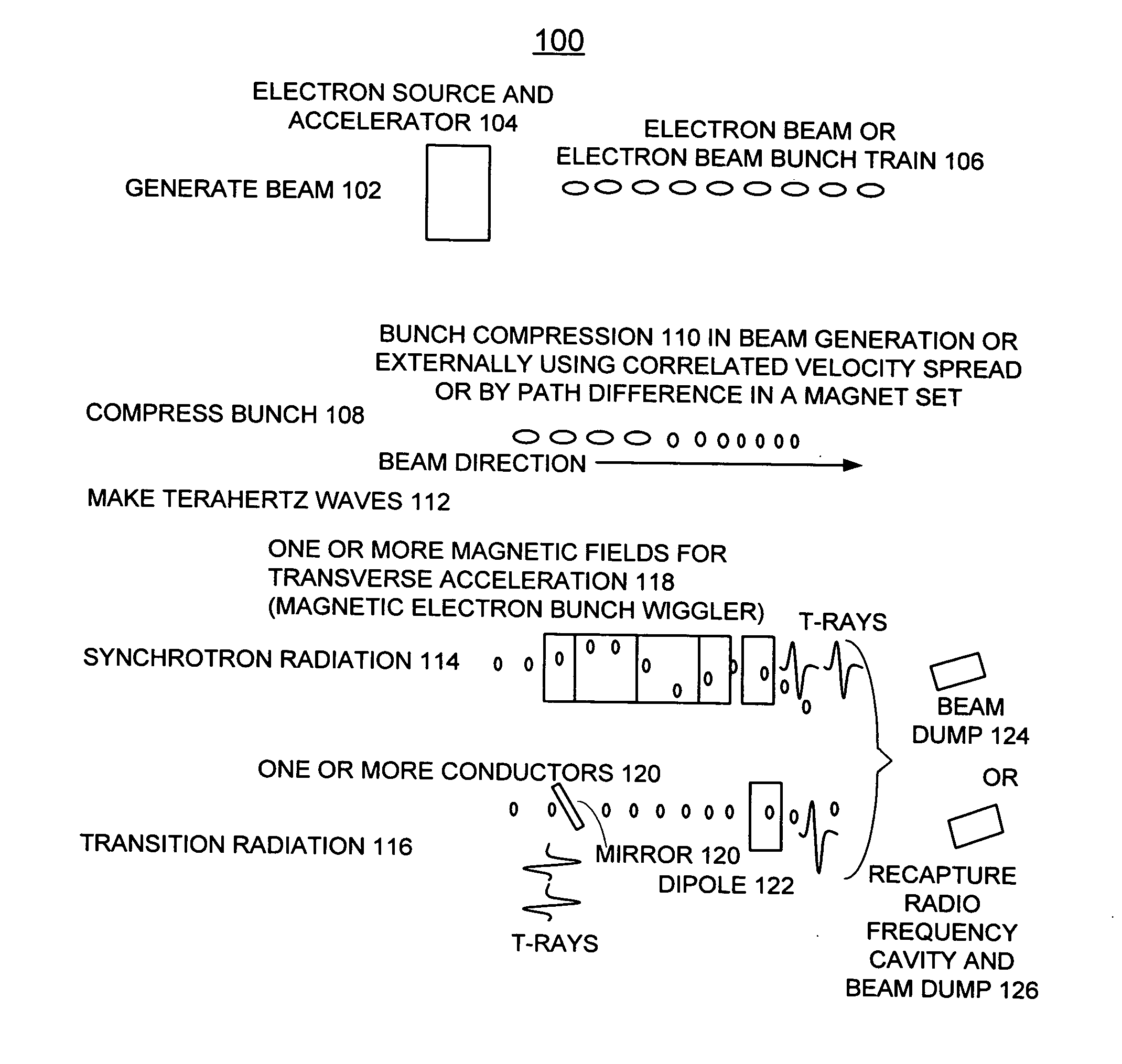
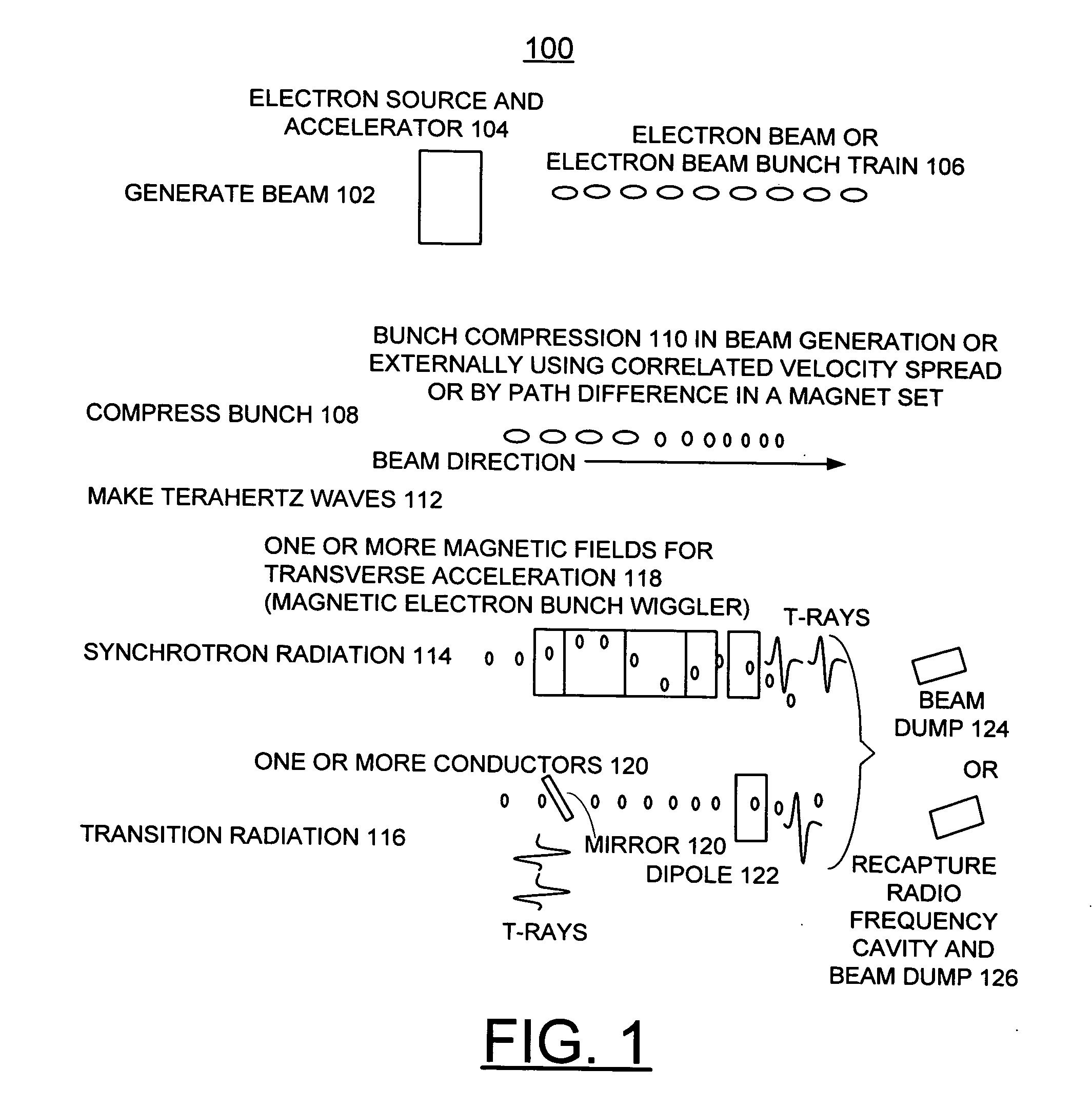
Stable THz radiation in the multi-watt range, upwards of 2 watts and even up to 100 watts, is produced through the acceleration of electrons in bunches less than about 500 femtoseconds in length as measured at full width and half maximum, at relativistic speeds (>˜40 MeV) and at a high repetition rate (>˜5 MHz) followed by transverse acceleration thereof by a magnetic field to produce the desired THz emission as synchrotron radiation.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
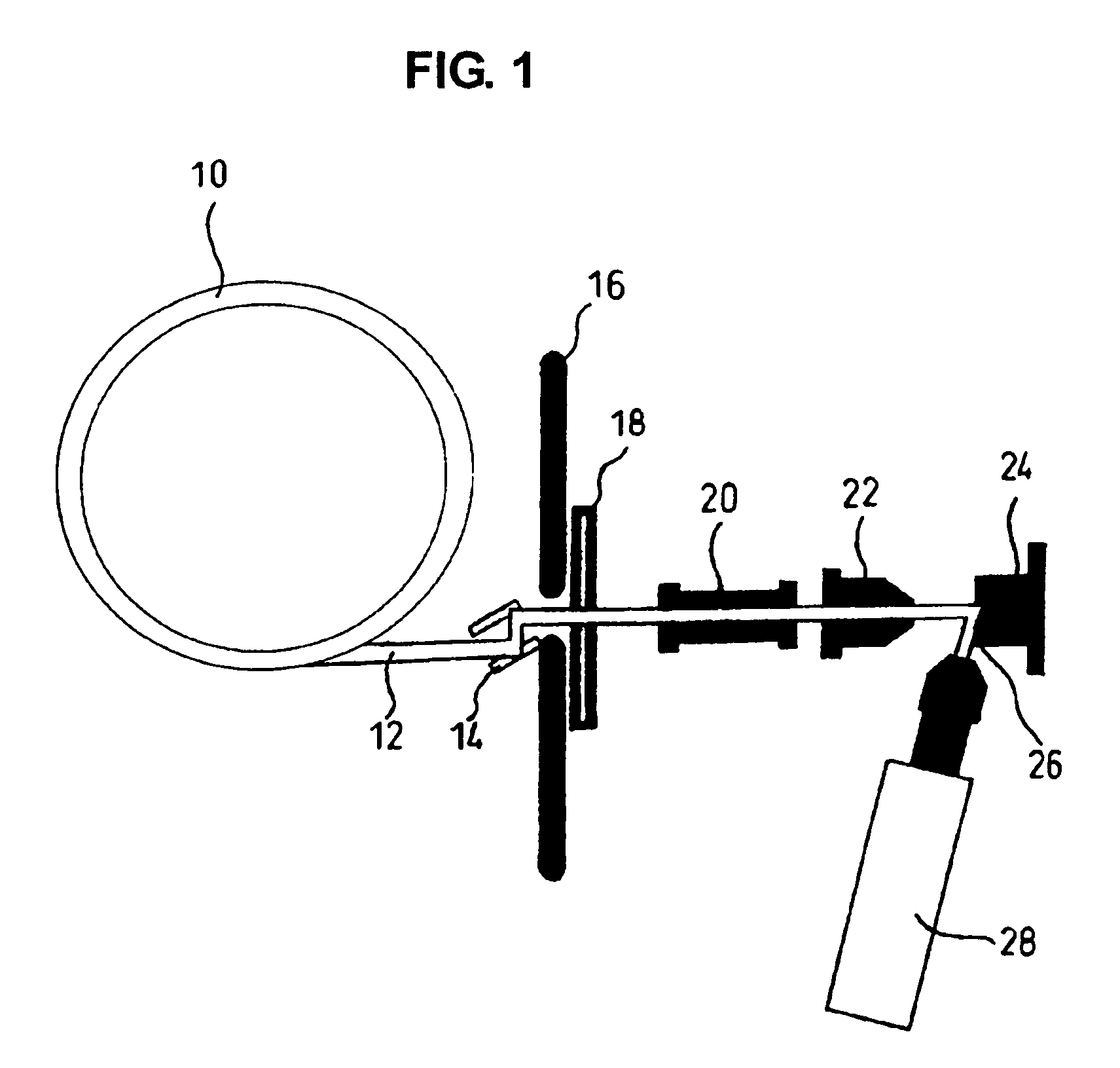
Method for evaluating physical conditions using head hair or body hair
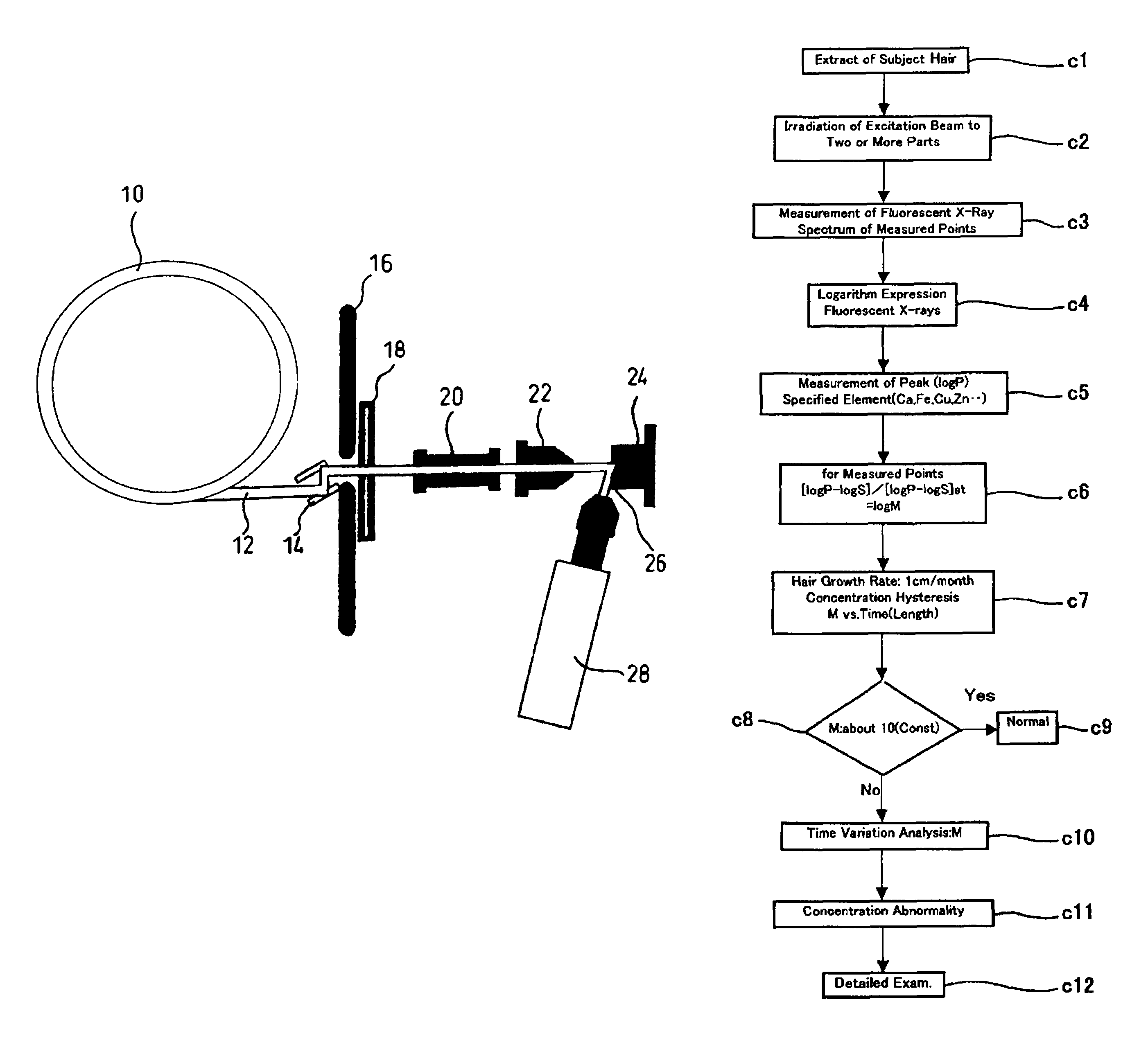
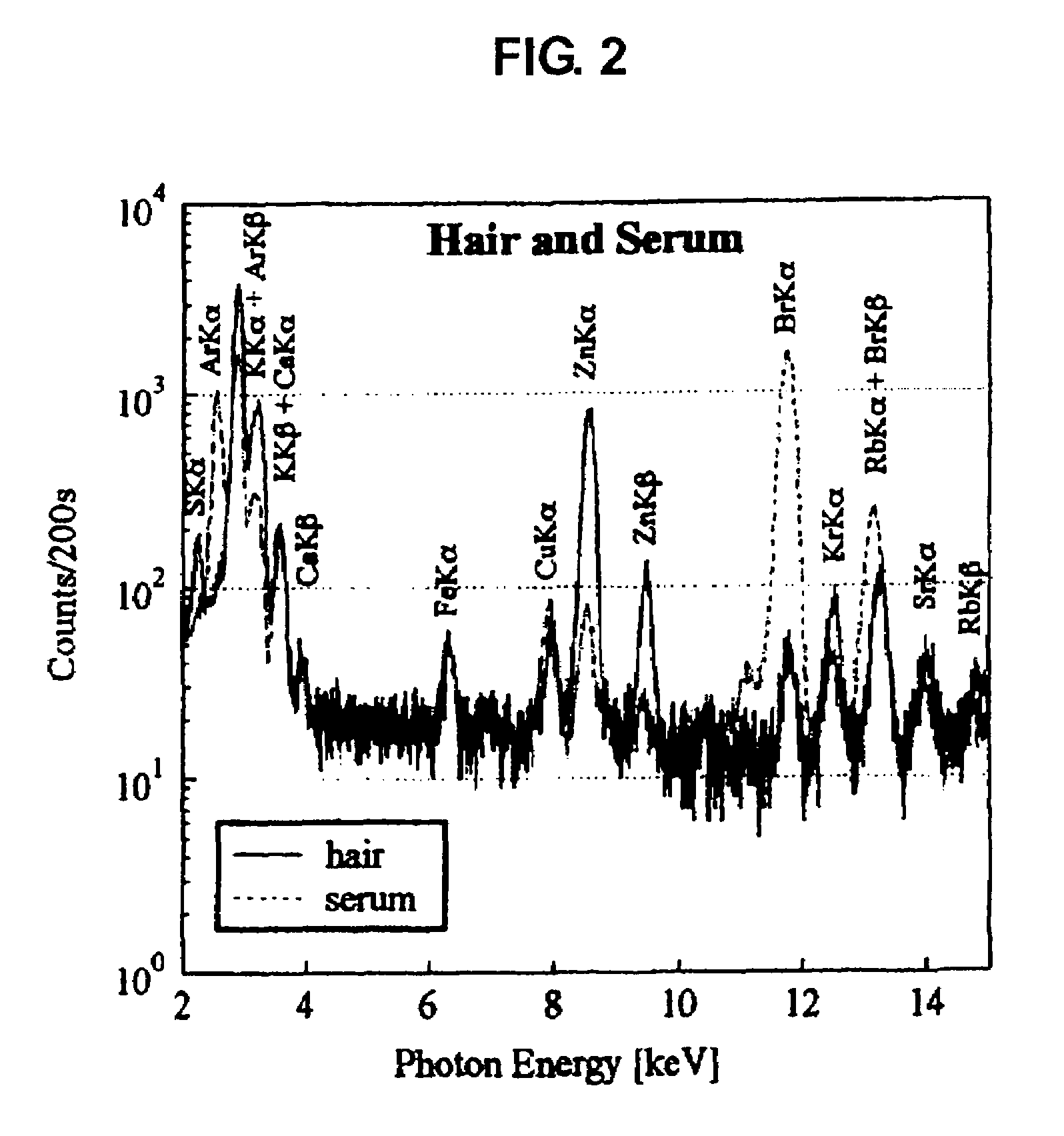
InactiveUS7688943B2Easy to handleEasy to implementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementFluorescent spectraSerum protein
Elemental concentrations in hair (head and body hair) and dried serum have been measured by x-ray fluorescence analysis using synchrotron radiation. The relative concentration defined by log P−log S are obtained from the fluorescent spectra, where P is the peak height for the element and S is the background height. The observation shows that hair has two separate [Ca] concentration levels, the upper level and lower level. Since the content in hair growing at a steady state must be equal to the supply from serum, the upper and the lower level of hair [Ca] are attributed to open and close Ca ion channels of the hair matrix cells and can be derived from the serum concentrations of Ca ion and Ca atoms included in serum protein, respectively. The hair analysis is useful for cancer detection and protection as well as for diagnosing the Ca metabolism.
Owner:CHIKAWA JUN ICHI
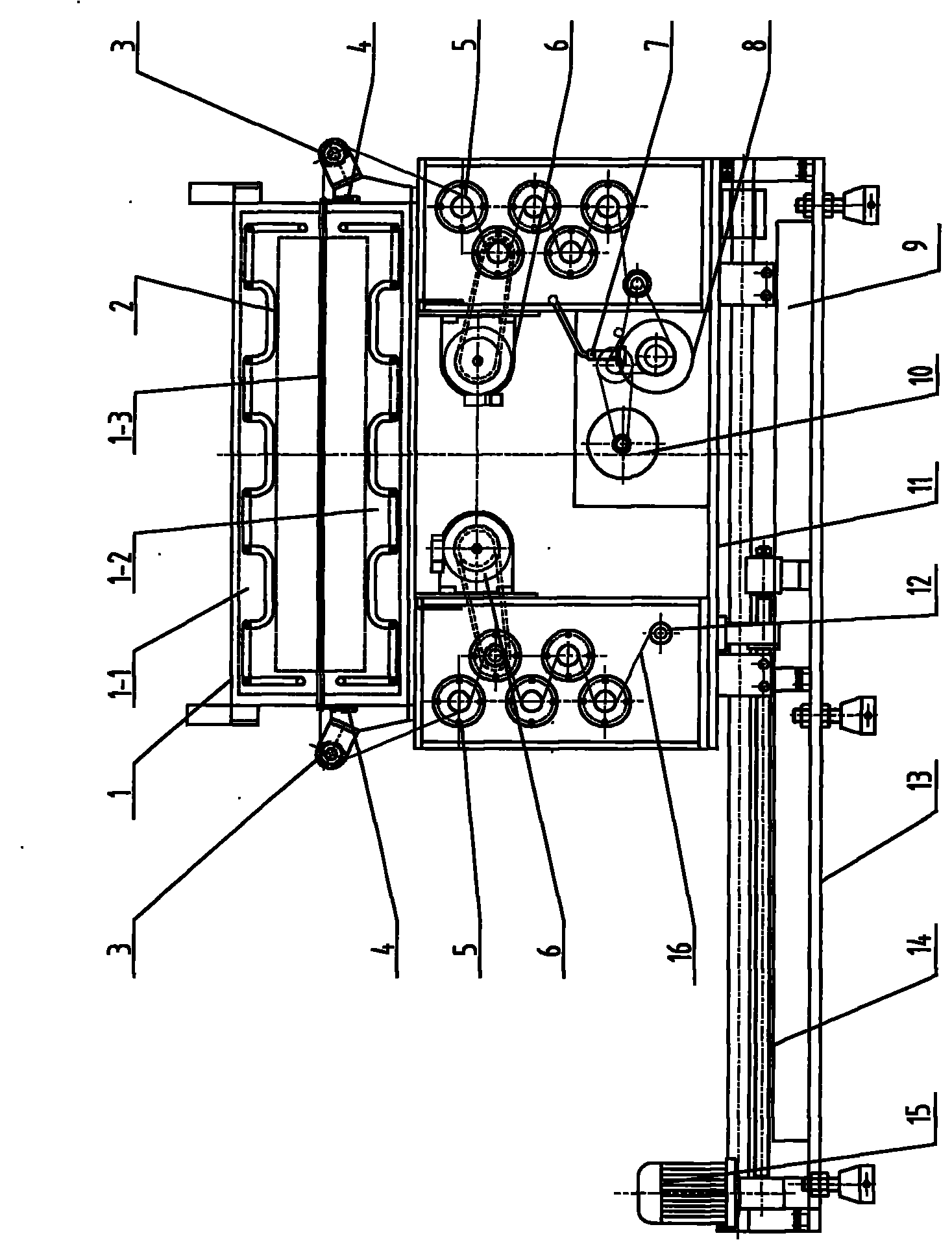
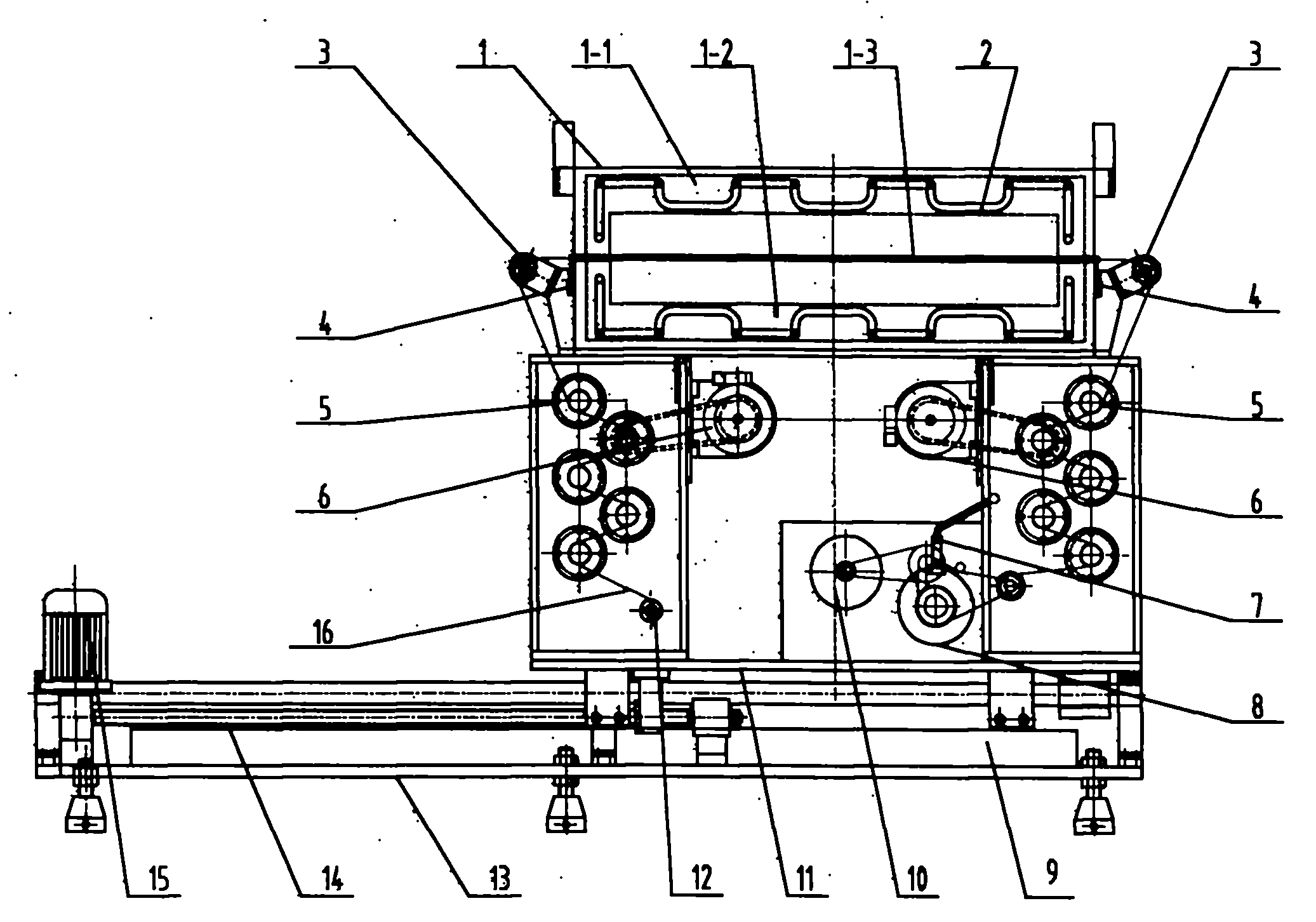
High-performance fiber synchrotron radiation in-situ testing machine
ActiveCN101831719AGuarantee product qualityReasonable structureInspecting textilesArtificial filament heat treatmentHot boxFiber
The invention provides a high-performance fiber synchrotron radiation in-situ testing machine. The testing machine comprises a base, a chassis, a drafting hot box, a front drafting mechanism, a back drafting mechanism, a winding mechanism and a translating mechanism, wherein the drafting hot box is used to heat fibre tows, one side of the box body opposite to the heat fibre tows is provided with a working gap; the front and back drafting mechanisms are used to provide drafting force for drafting the heated heat fibre tows; the winding mechanism is used to wind the heat fibre tows after hot stretching; and the translating mechanism is used to move the chassis horizontally and contains a translation motor, a turn-screw and a slideway. The testing machine has reasonable structure and convenient operation and is used commonly with the synchrotron radiation device so as to timely and accurately test the molecular changes of the high-strength and high-modulus polyethylene fibre tows under hot stretching, provide powerful technical support for the hyperploid hot stretching technology of the production of high-performance fiber, shorten debugging period and ensure the quality of fiber products.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENTAI SCI & TECH DEV
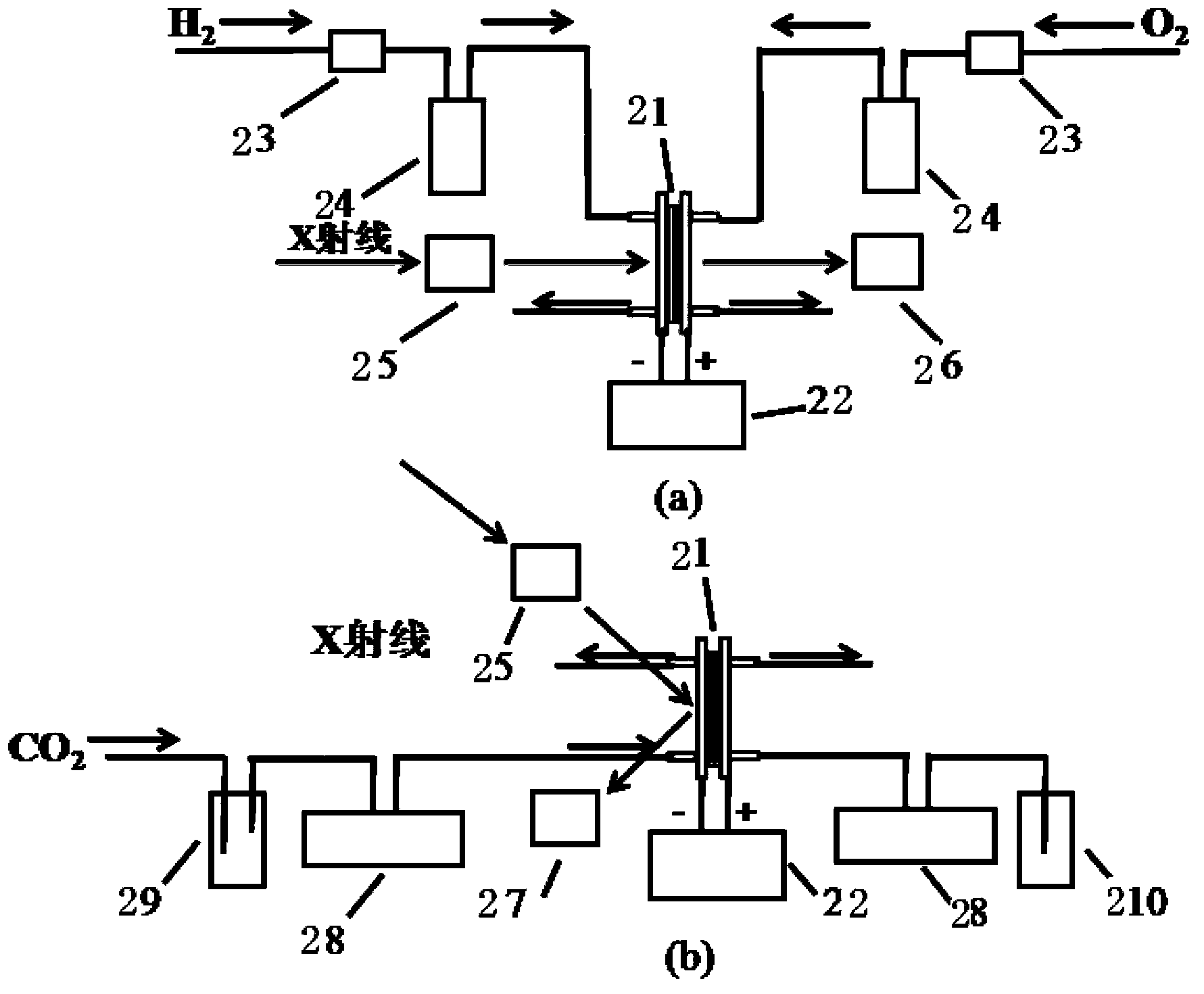
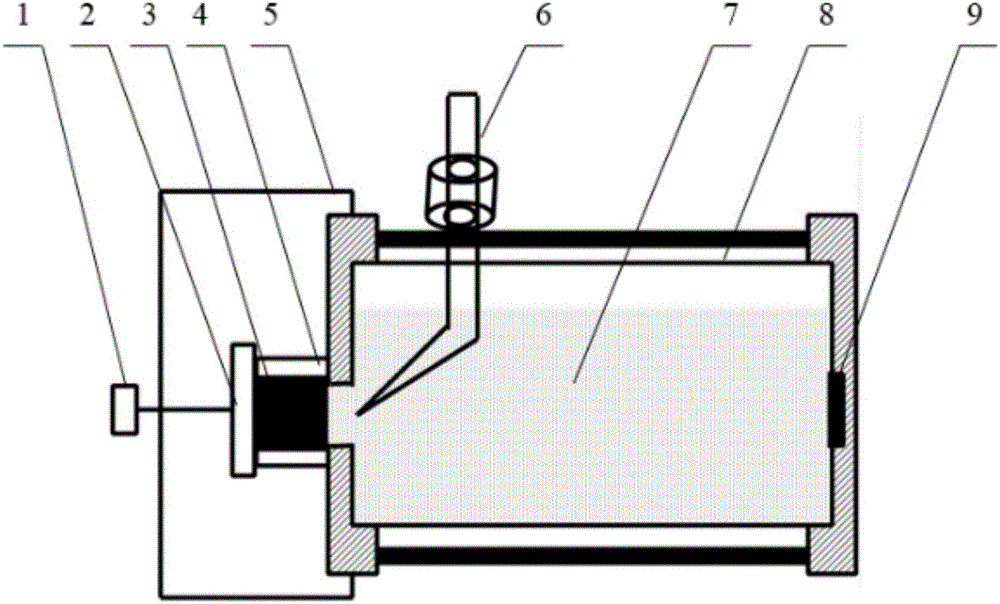
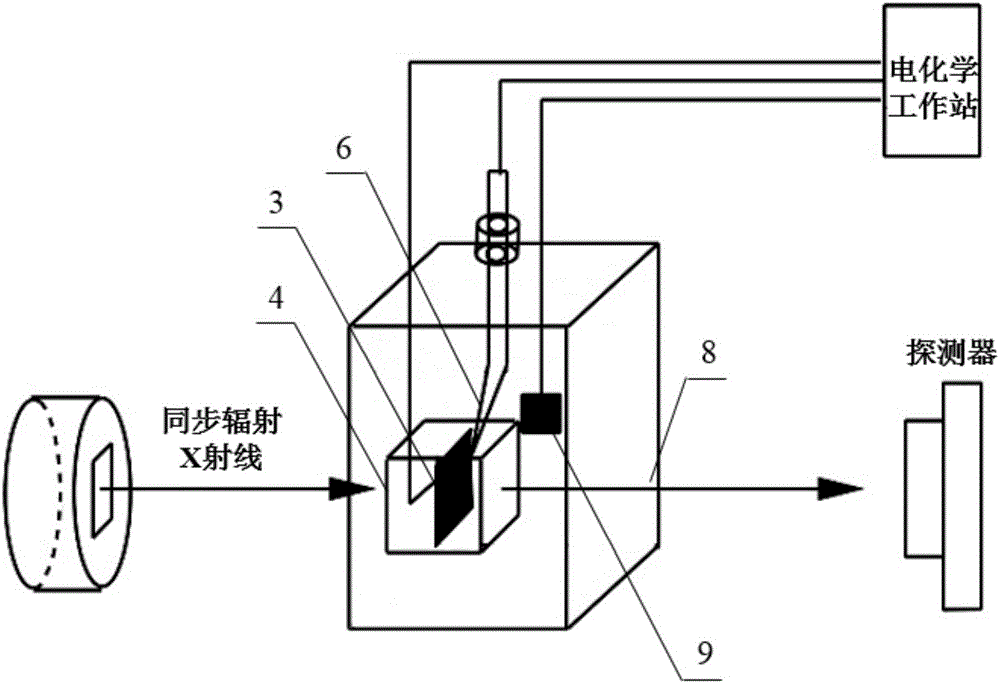
Synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device used for electrocatalysis reaction
ActiveCN103884728AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSoft x rayElectricity
The invention discloses a synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device used for electrocatalysis reaction. The synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device comprises a synchrotron radiation X ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) line station front ionization chamber, a synchrotron radiation XAFS line station back ionization chamber (or a fluorescence detector) and an in-situ pool. A membrane electrode for electrocatalysis reaction is arranged in the in-situ pool, and in the condition that detection windows of components of the in-situ pool are in the same center line, X-ray irradiates onto the membrane electrode, and then reaches, in a transmission or reflection way, to the synchrotron radiation XAFS line station back ionization chamber or the fluorescence detector so as to achieve in-situ detection of the catalyst structure in the electrocatalysis reaction process; the detection windows of the in-situ pool are in the center of a flow field plate, the dead volume is less, the accuracy and reliability of experimental data can be improved, a heating plate and the flow field plate in the in-situ pool are fixed together by bolts, the detection windows on the flow field plate are sealed, and the assembly and replacement of the membrane electrode are facilitated. The synchrotron radiation in-situ detection device is a set of detection device suitable for the study of the electrocatalytic reaction process and mechanism.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modular multi-atmosphere in-situ environmental stress instrument with wide temperature ranges
ActiveCN106840852AUniversalReal-time and high-precision mechanicsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringExtreme temperature
The invention discloses a modular multi-atmosphere in-situ environmental stress instrument with wide temperature ranges. The modular multi-atmosphere in-situ environmental stress instrument comprises a mechanical loading module, a temperature varying module, an optical imaging and positioning module, an atmosphere module and a sensor system. The modular multi-atmosphere in-situ environmental stress instrument has the advantages that high-temperature and low-temperature modules can be switched over, so that mechanical tests can be carried out at extreme temperatures in the wide temperature ranges; a closed shell can be filled with different types of atmospheres, accordingly, single-axis in-situ mechanical tests can be carried out in multi-atmosphere environments, and displacement measurement, temperature measurement and mechanical measurement can be immediately carried out; the modular multi-atmosphere in-situ environmental stress instrument is mainly designed for synchronous radiation in-situ mechanical experiments and is modular, the wide temperature ranges, the multiple environments and multiple fields are coupled with one another, and mechanical, displacement and temperature measurement and feedback can be immediately carried out.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Device and test method of alloy solidification synchronous radiation imaging static magnetic field composite direct current effect
ActiveCN105136824ASimple structureReasonable structureMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation imagingX-ray
The invention provides a device and a test method of alloy solidification synchronous radiation imaging static magnetic field composite direct current effect. The device includes a power supply circuit and a micro heating furnace. A heating unit is arranged in a cavity of the micro heating furnace. Two opposite side walls of the micro heating furnace are respectively provided with light passing holes, wherein the axial lines of the light passing holes are coincided. Permanent magnets are arranged on outer sides of the two side walls having the light passing holes on the micro heating furnace. A sample bracket for fixing a sample is arranged in the micro heating furnace at the position that an X-ray passing through the light passing holes can be irradiated vertically on the plane the sample arranged. The power supply circuit includes a direct current generation device and electrodes, wherein the two electrodes are detachably fixed on two ends of the sample respectively and are connected to the direct current generation device through wires. The device is simple in structure and can achieve synchronous radiation imaging of alloy solidification under a static magnetic field composite direct current field effect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
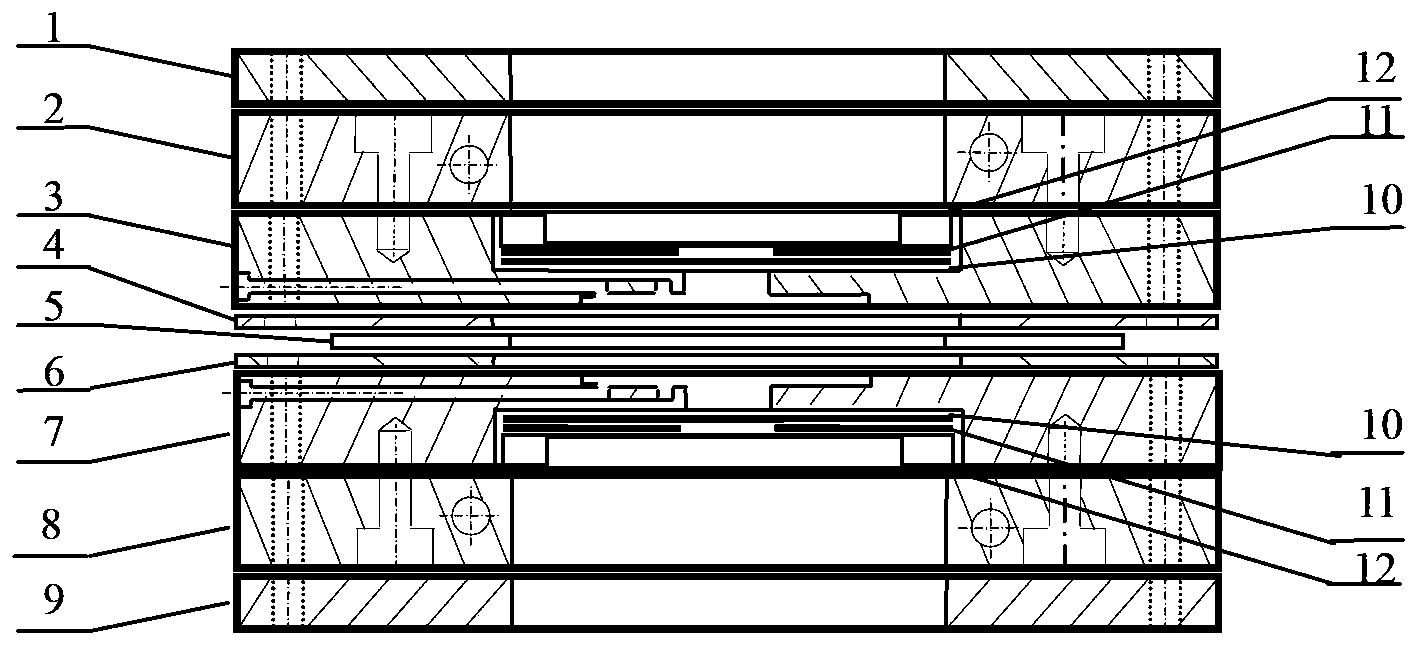
Synchrotron-radiation X-ray diffraction apparatus for analyzing electrochemical property of electrode material and application thereof
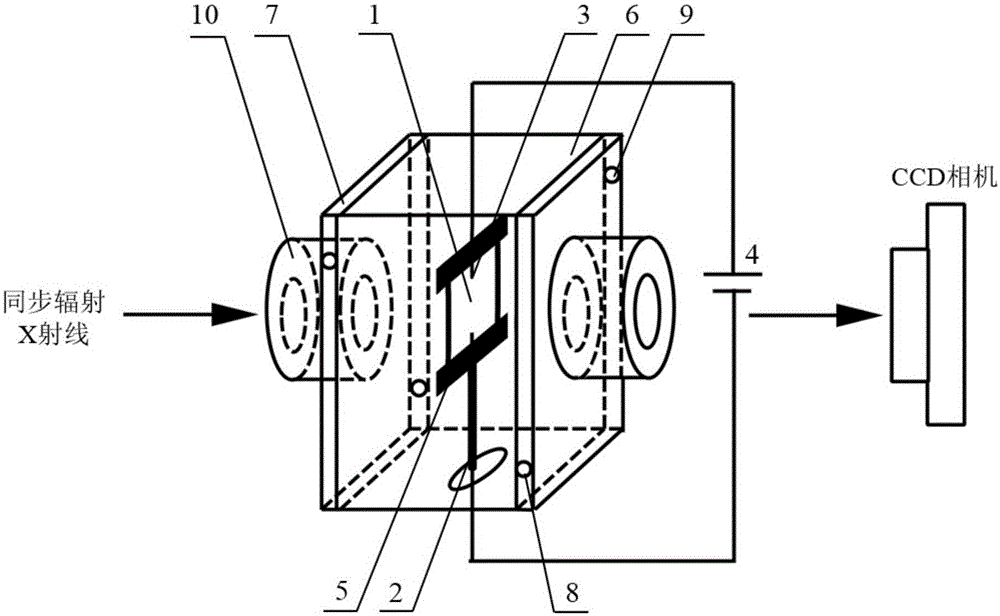
ActiveCN102980903AAchieve reuseMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSoft x rayX-ray
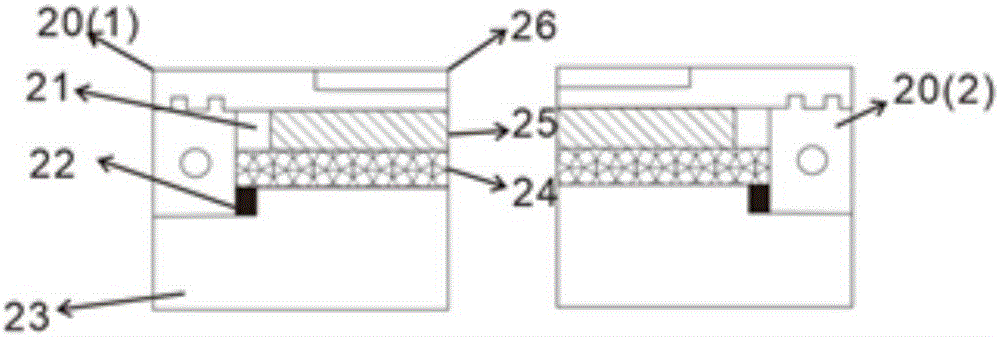
The invention discloses a synchrotron-radiation X-ray diffraction apparatus for analyzing electrochemical properties of an electrode material and an application thereof. The apparatus comprises a component A and a component B, wherein the component A comprises a stainless steel plate a, a Be glass window a and an insulating board; through holes are respectively formed in the stainless steel plate a and the insulating board; the Be glass window a is positioned at the through hole between the stainless steel plate a and the insulating board; the Be glass window a is fixed between the stainless steel plate a and the insulating board by fixing the stainless steel plate a and the insulating board; the component B comprises a stainless steel plate b and a Be glass window b; a through hole is formed in the stainless steel plate b; and the Be glass window b is fixed in the through hole of the stainless steel plate b in an insulating manner through a fixing element, and the component A and the component B are fixedly connected. The device disclosed by the invention can realize in-situ or non-in-situ measurement on synchrotron-radiation X-ray diffraction data of an electrode material in an X-ray transmission or reflection manner, can be recycled, and has a great application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
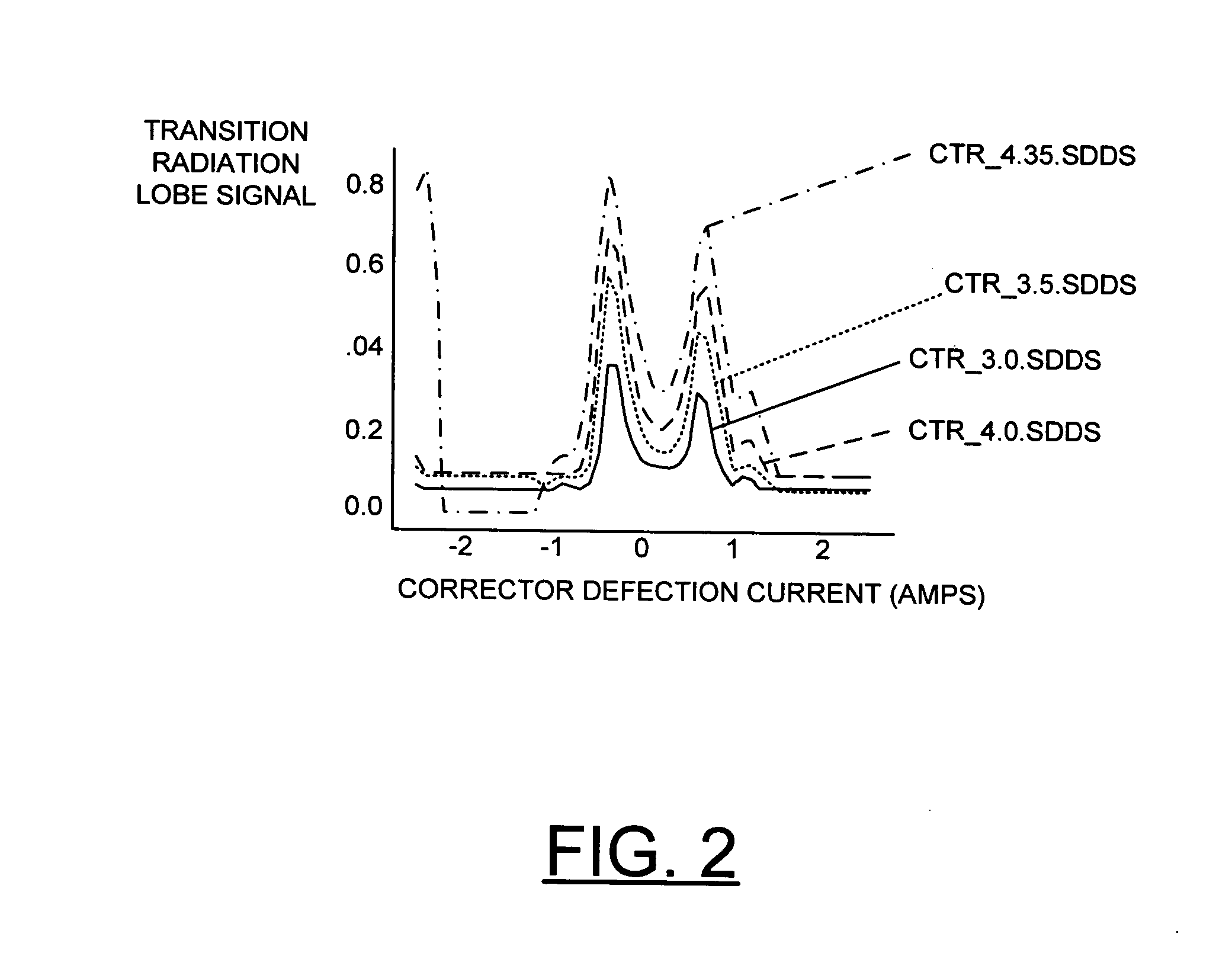
Compact system and method for the production of long-wavelength, electromagnetic radiation extending over the terahertz regime
InactiveUS20060039417A1Improve efficiencyEfficiently electromagnetic radiationLaser detailsCharged particle masersTransition radiationBroadband
A compact system and method are provided for implementing the generation of electromagnetic radiation extending over mm-wavelength to sub-mm-wavelength or terahertz range. The generated electromagnetic radiation can be broadband or have a variable bandwidth. Electrons are accelerated to a chosen energy and undergo subsequent or simultaneous temporal or spatial compression. The degree of compression is chosen such that the electron beam pulse length is near to or less than that of the terahertz wavelength desired to be generated. The radiation is produced by one or combination of methods of synchrotron radiation or transition radiation.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
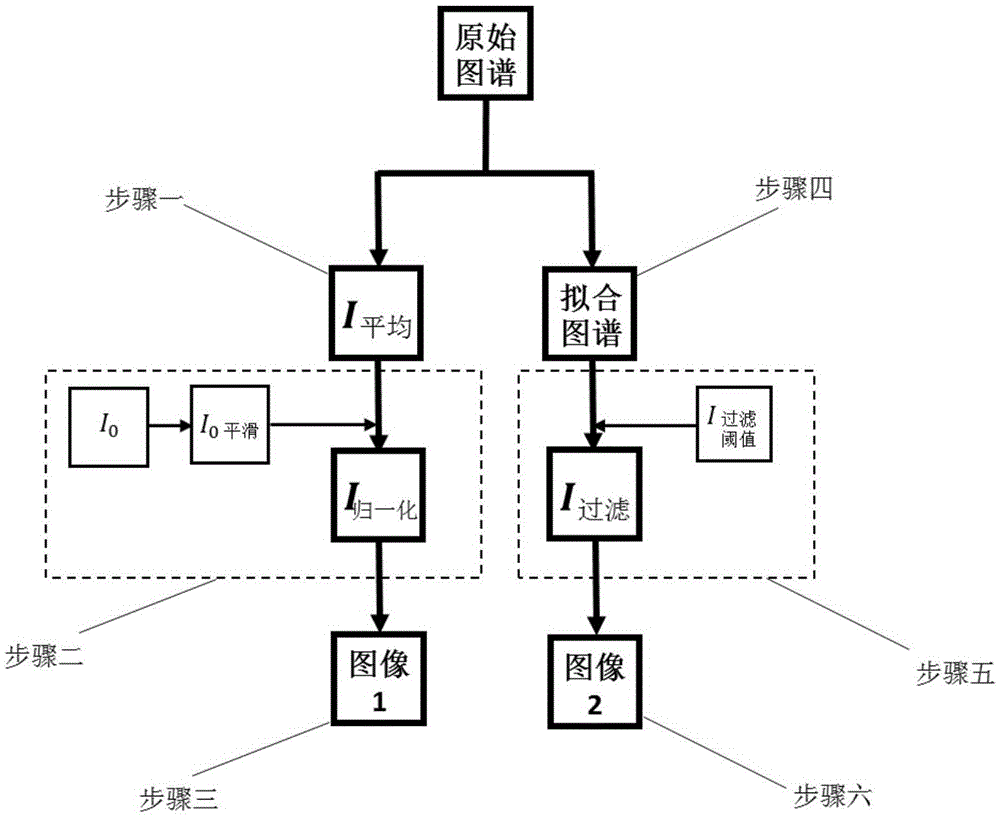
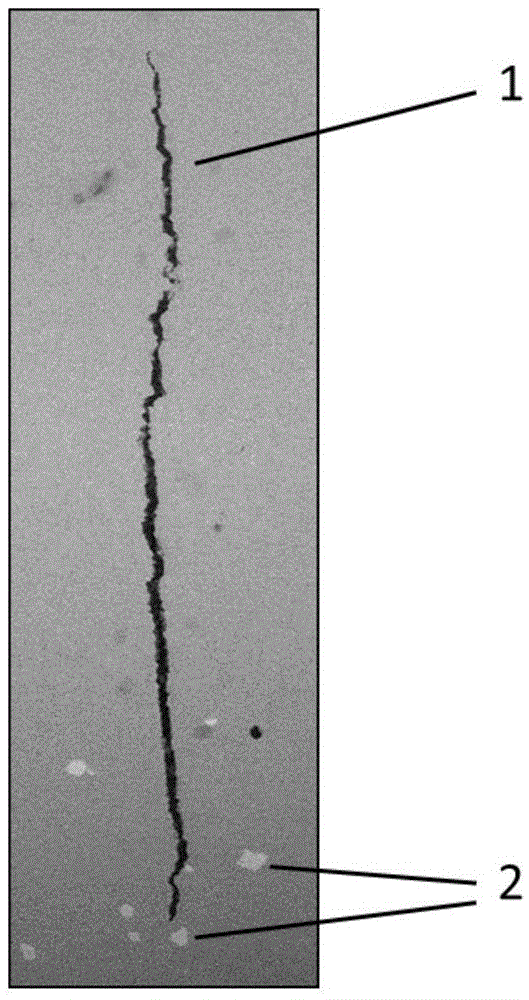
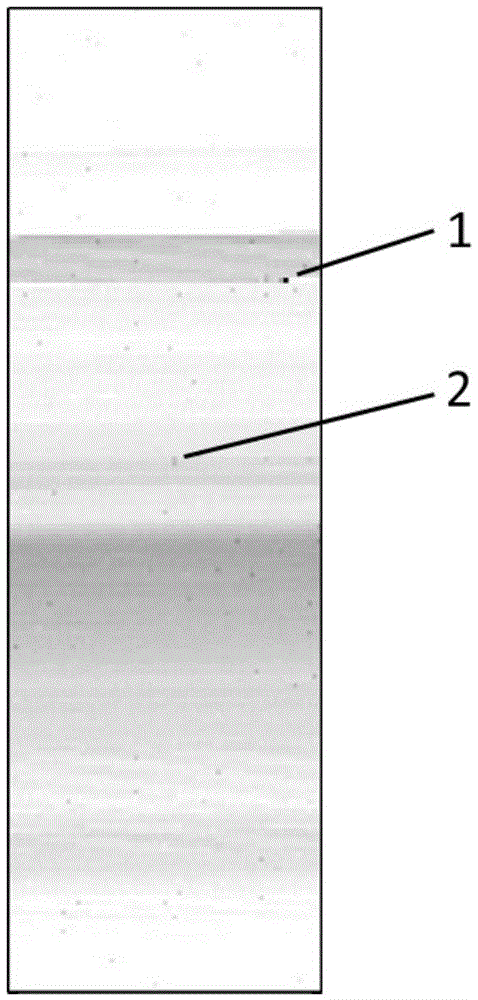
Universality efficient synchrotron radiation visual representation method of crystal microstructure
ActiveCN105675638AData processing is simpleProcessing speedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiation2D-image generationX-rayMicroscopic scale
The invention relates to a universality efficient synchrotron radiation visual representation method of crystal microstructure. The method includes following steps: step 1, acquiring average intensity in an original spectrum obtained at each point on a synchrotron radiation micro-area Laue diffraction experiment scanning sample; step 2, using a normalization means to eliminate influence of incident X-ray intensity in the average intensity acquired in the step 1 to acquire diffraction spectrum average intensity after normalization; step 3, drawing an image 1 related to contrast in a whole scanning area and microstructure according to the normalized diffraction spectrum average intensity acquired in step 2; step 4, fitting abnormal numeric values in the original spectrum; step 5, performing threshold filtering on the spectrum after being fitted in the step 4, and calculating average intensity of a diffraction spectrum; step 6, drawing an image 2 related to the contrast in the whole scanning area and the microstructure according to the diffraction spectrum average intensity acquired after threshold filtering so as to realize high-universality efficient synchrotron radiation visual representation of the crystal microstructure.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Improved actuation mechanism for fatigue testing machine achieving in-situ imaging of synchrotron radiation light source
ActiveCN106018140AIncrease brightnessImprove image signal-to-noise ratioMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesTest sampleCam
The invention discloses an improved actuation mechanism for a fatigue testing machine achieving in-situ imaging of a synchrotron radiation light source. The actuation mechanism is arranged on a cylinder-shaped base plate on a platform of the synchrotron radiation light source and used for applying a vertical reciprocating displacement load to a test sample on the fatigue testing machine achieving in-situ imaging of the synchrotron radiation light source. Compared with the last generation of fatigue testing machines, further improvement is conducted, friction generated by a cam actuation mode is reduced, therefore, energy consumption of the fatigue testing machine is reduced, and the noise reduction performance of the fatigue testing machine is further improved; the load applied to the test sample is further guaranteed, and compared with the last generation of the fatigue testing machines, the details in the test implementation process are considered more detailedly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Shale gas reservoir characteristic simulation method
InactiveCN104239602AEasy to operateSpecial data processing applications3D modellingMicro structurePorous medium
The invention relates to a shale gas reservoir characteristic simulation method. The shale gas reservoir characteristic simulation method comprises the steps of focusing light into scanning lines in the horizontal direction through a reflection mirror of a mirror box by utilizing synchrotron radiation light sources, realizing vertical scanning through rotational vibration of the reflection mirror, and obtaining three-dimensional micro-structure data of a shale gas occurrence porous medium sample; then, carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction on the obtained three-dimensional micro-structure data, obtaining a percolation mechanism in unconventional shale gas occurrence medium through coupling computation by utilizing molecular dynamics and a lattice boltzmann method, and using a mathematical expression to express the percolation mechanism. According to the shale gas reservoir characteristic simulation method disclosed by the invention, a microcosmic percolation mechanism in the unconventional shale gas occurrence medium is researched by utilizing synchrotron radiation light and a computer technology, economy and environmental protection are realized, and the operation is simple; necessary and important evaluation parameters are provided for exploring and developing shale gas; an adsorption / analysis law of free gas and adsorbed gas in the shale gas can be simulated, and technical support is provided for mining the shale gas.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Radiation detector, as well as a method for synchronized radiation detection
InactiveCN1673772AFulfil requirementsReduced precision requirementsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesTime segmentModularity
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Synchrotron radiation in-situ imaging tensile testing machine simulating multiple environments and testing method thereof
ActiveCN107036888AImprove accuracyObserving the Microstructure MorphologyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationTemperature controlHigh humidity
The invention discloses a synchrotron radiation in-situ imaging tensile testing machine simulating multiple environments and a testing method thereof and belongs to the field of material tensile testing machine. The material tensile testing machine comprises a rotatable single-pull base, wherein a digital display pull and push dynamometer is arranged above the single-pull base and is fixedly connected with the lower portion of a lower clamp, the upper portion of an upper clamp is fixedly connected to a sleeve, a spring and a sleeve shaft are arranged in the sleeve, the top of the sleeve shaft is connected to the loading connection position of a loading mechanism, and the loading mechanism is provided with a ratchet wheel and a pawl for achieving a self-locking function. The testing machine is further provided with an in-situ imaging system, a humidification device and a temperature control device. The testing machine reasonably applies a dynamical tensile test and a synchrotron radiation imaging technique and conveniently obtains a three-dimensional image of the inside of a material, microstructure change and microcosmic deformation damage of material organization under complicated environments such as high temperature, low temperature, high humidity and rich oxygen can be obtained, and the microstructure morphology and defects of the material can be better observed.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Metal material electrochemical test in situ diffraction and imaging experiment method
ActiveCN106124396AObserve changeObservation generationWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionEpoxyX-ray
The invention provides a metal material electrochemical test in situ diffraction and imaging experiment method. The method comprises the following steps: cutting the metal material to be detected into a rectangular sheet sample with thickness of 50-500 mum; coating a corrosion resistant paint on both sides of the rectangular sheet sample; embedding the rectangular sheet sample in epoxy resin; fixing embedded resin sample on a detection slit of a side wall of an electrochemical cell; placing the electrochemical cell fixed with embedded resin sample in a synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction / imaging working platform, so as to put the X-ray spot on a contact interface of a working electrode surface and an electrolyte; opening a synchrotron radiation X-ray optical shutter, adjusting the X-ray energy and exposure time, opening an electrochemical workstation, stabilizing the potential, and collecting data by the detector. The metal material electrochemical test in situ diffraction and imaging experiment method can realize in situ diffraction and visualization of metal material in the electrochemical testing process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
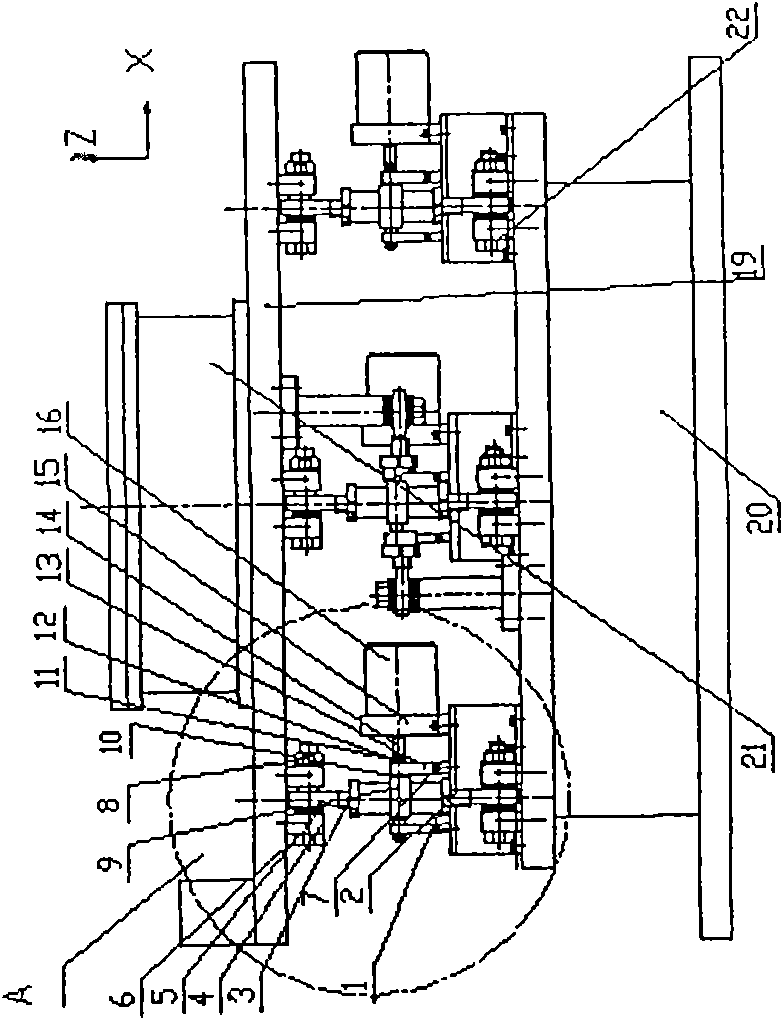
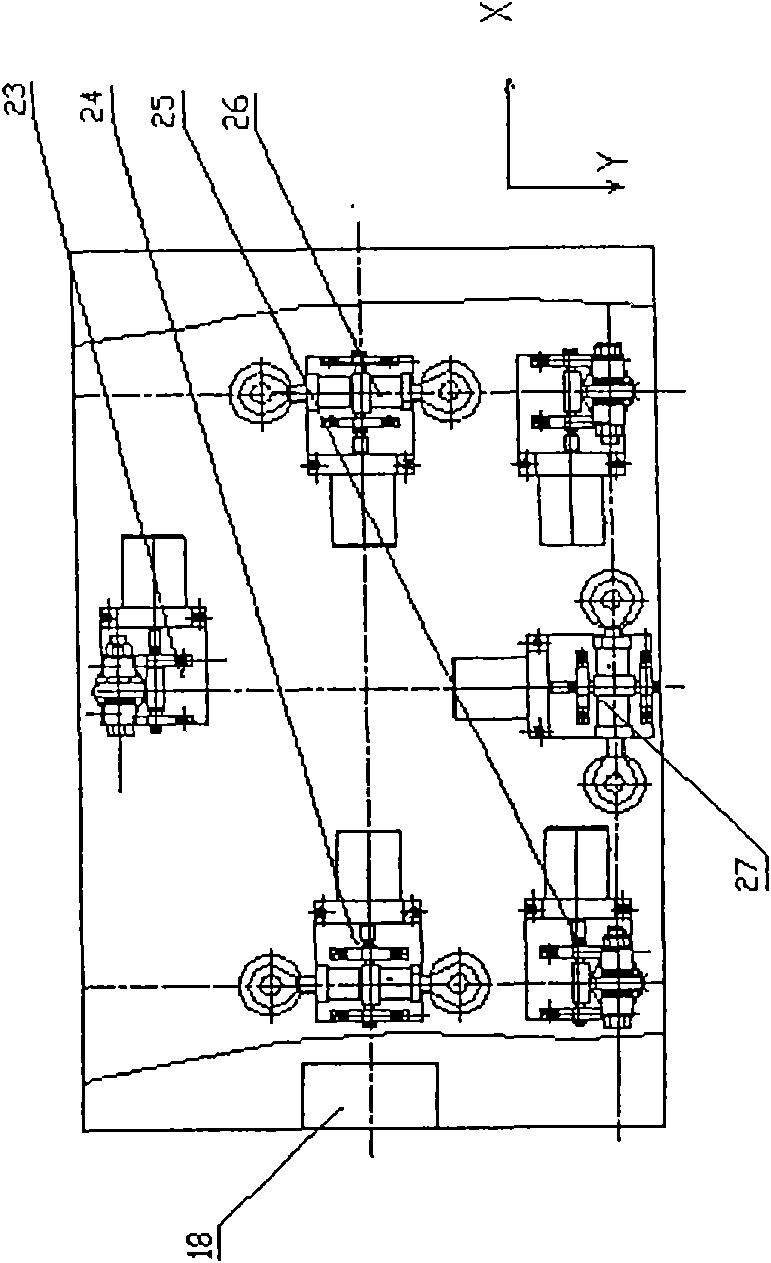
Automatic adjustment positioning device in a six-dimensional space
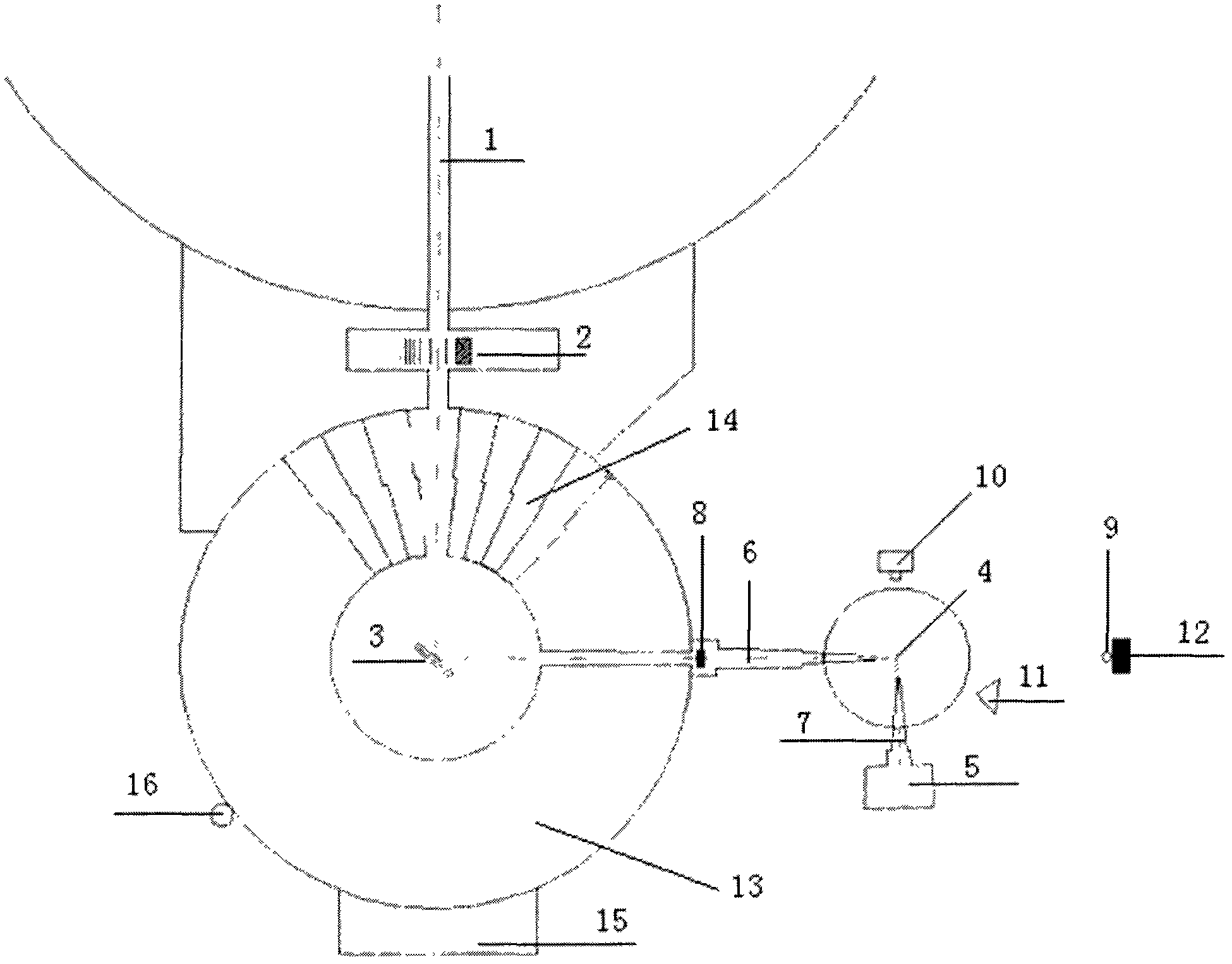
InactiveCN101567222AReduce loadSimple and reliable adjustmentInstrumental componentsPosition/direction controlAuto regulationClosed loop
The invention discloses an automatic adjustment positioning device in a six-dimensional space, which can be used for automatically adjusting and positioning an optical element supporting case; the device comprises a threaded sleeve, an A screw rod, a B screw rod, supports, a joint bearing, bolts, screws, a washer, worm wheels, worm screws, a bearing, a locking nut, a bearing support, a shaft coupler, a motor frame, a servo motor, a power source, a computer, a movable plate, a fixed bracket, a vacuum mirror cabinet and six sets of driving components which consist of spiral struts, the worm wheels and the worm screws; the supports at one side of each set of the driving components are arranged on the movable plate, while the supports at the other side thereof are arranged, positioned and fastened on the fixed bracket; the servo motor is matched and the computer adopts closed-loop parallel control to finish adjustment and positioning of the vacuum mirror cabinet in beam lines of synchrotron radiation in the space six-dimension, i.e., moving along X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis and rotating around the X axis, the Y axis and the Z axis. The invention realizes the adjustment of the six-dimensional space, simplifies structure, reduces the load of instruments, is simple and reliable in adjustment, and lowers processing cost.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com