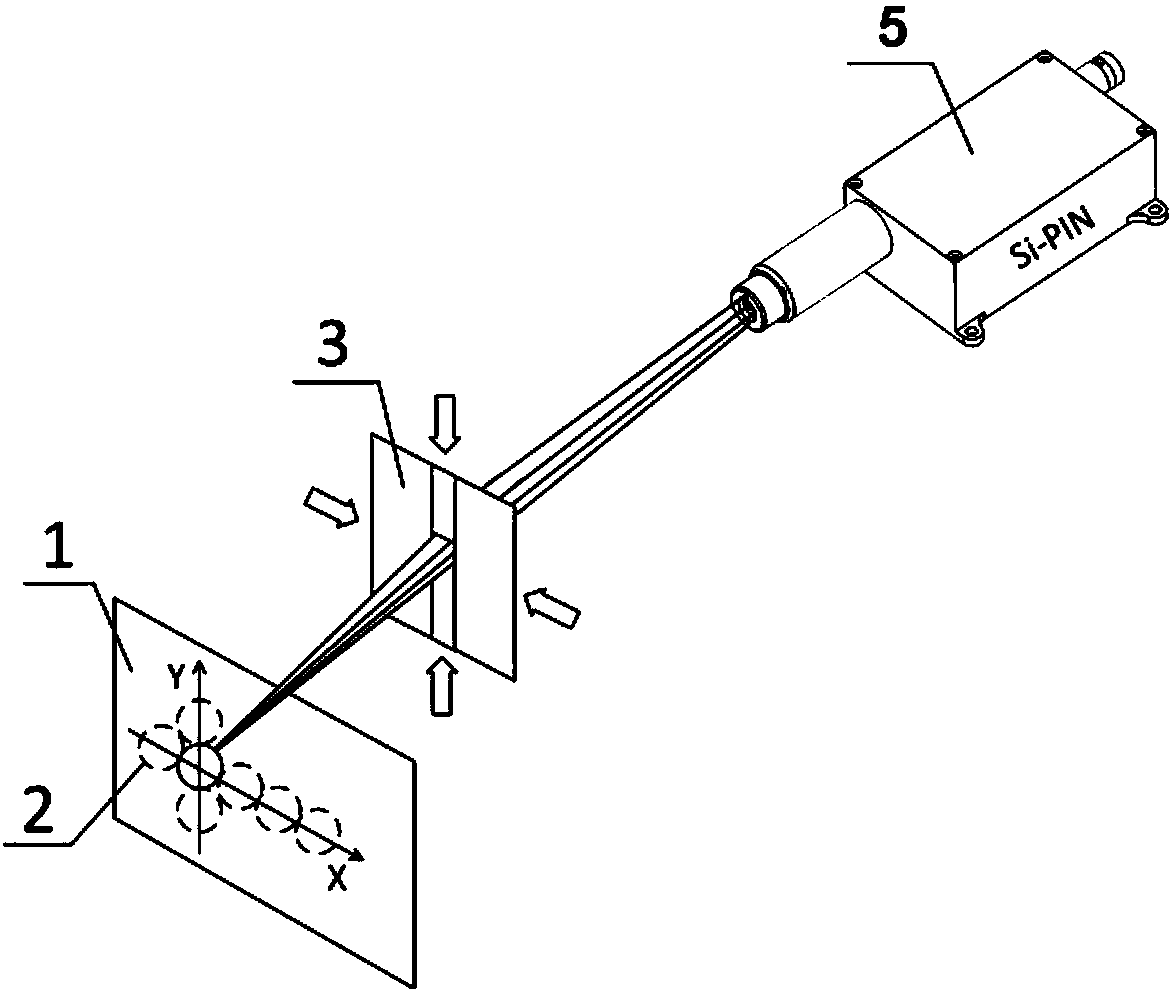
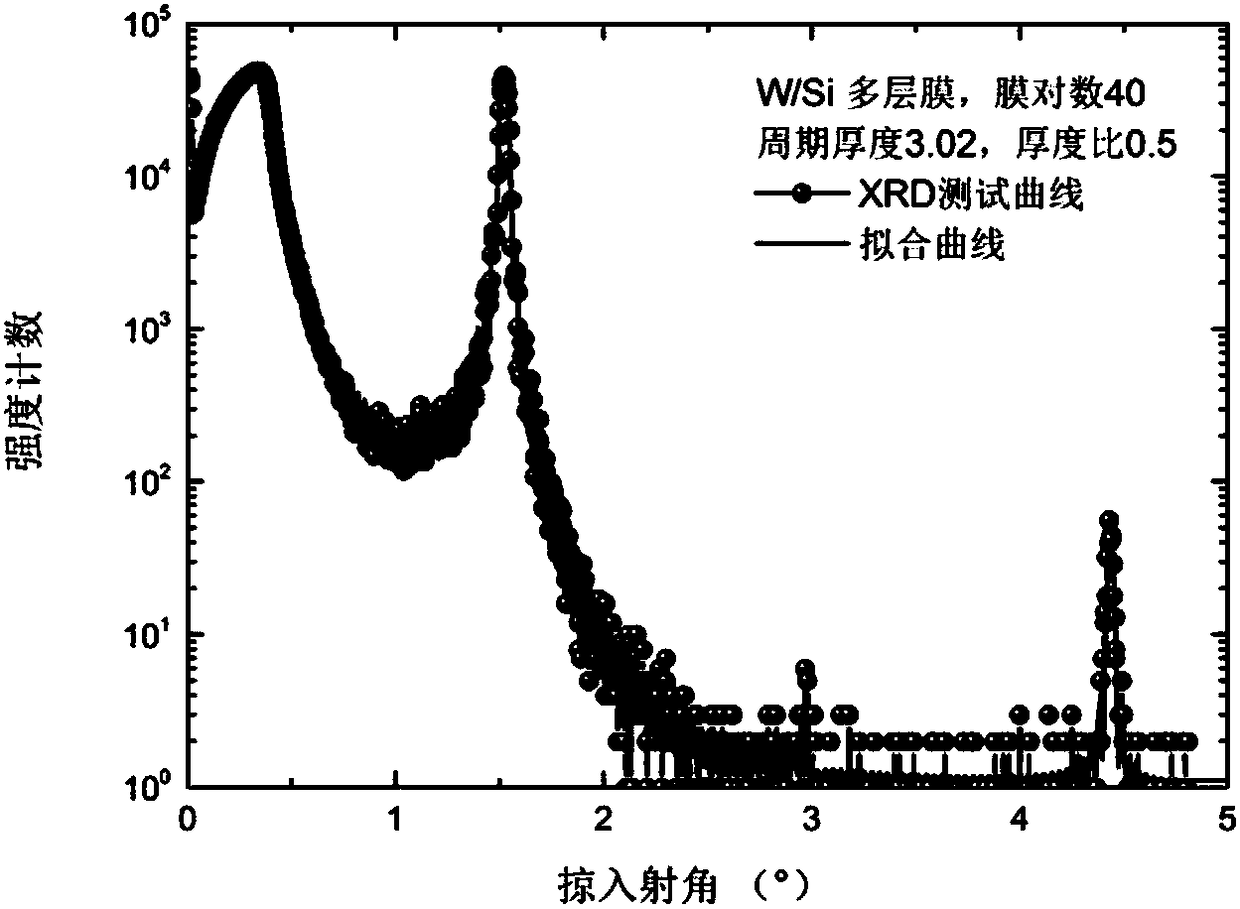
Patents
Literature
69 results about "X-ray microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
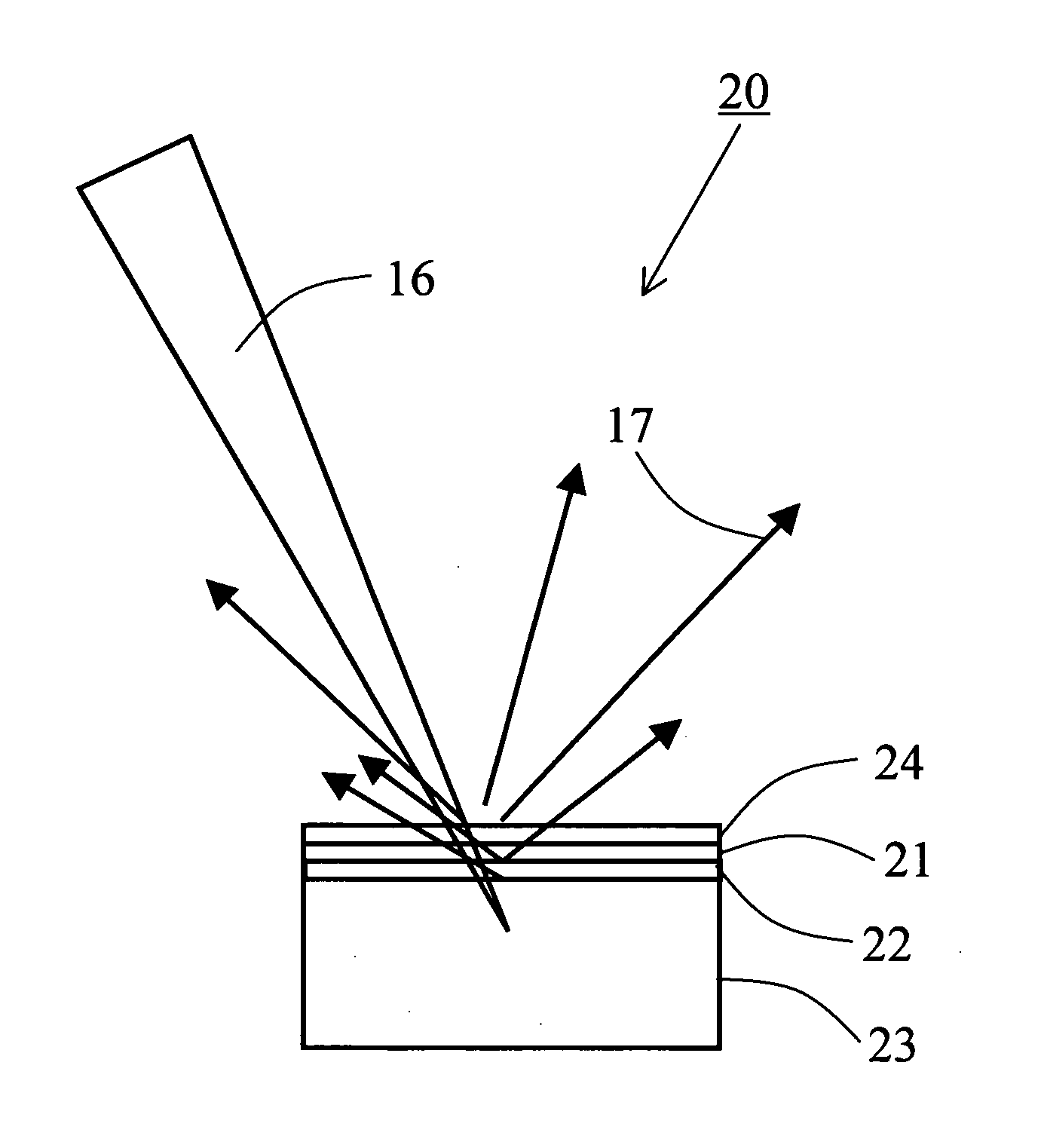
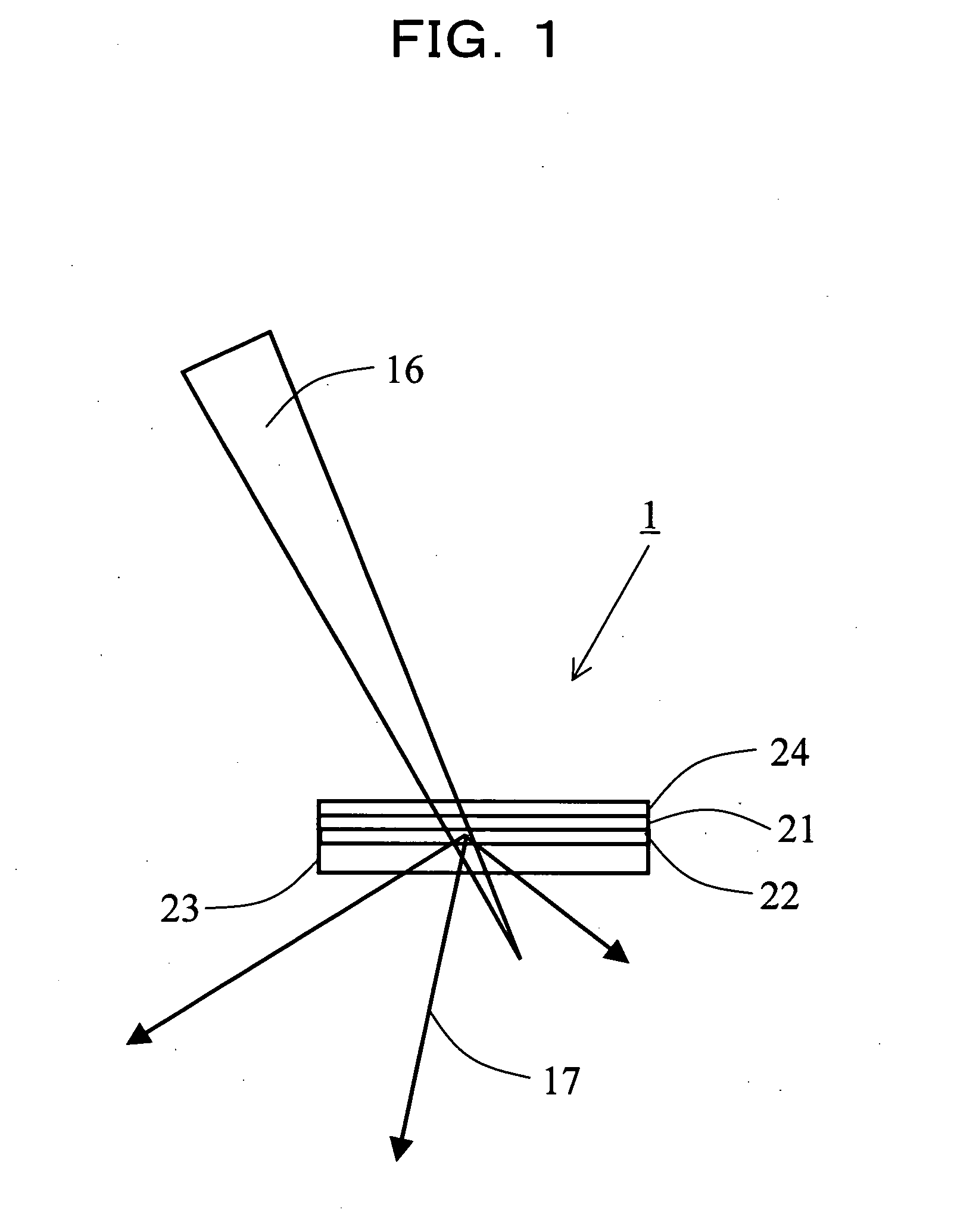
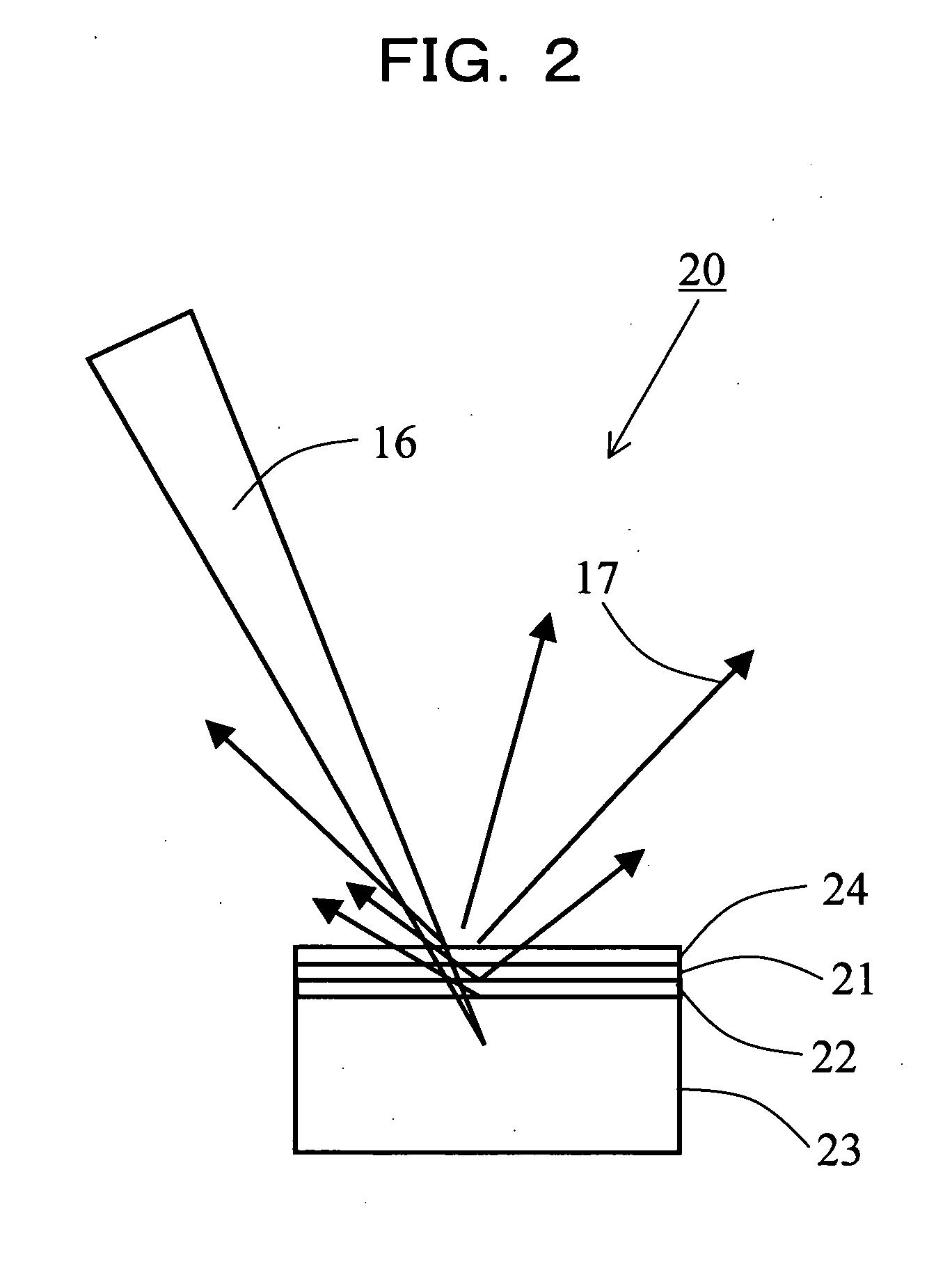
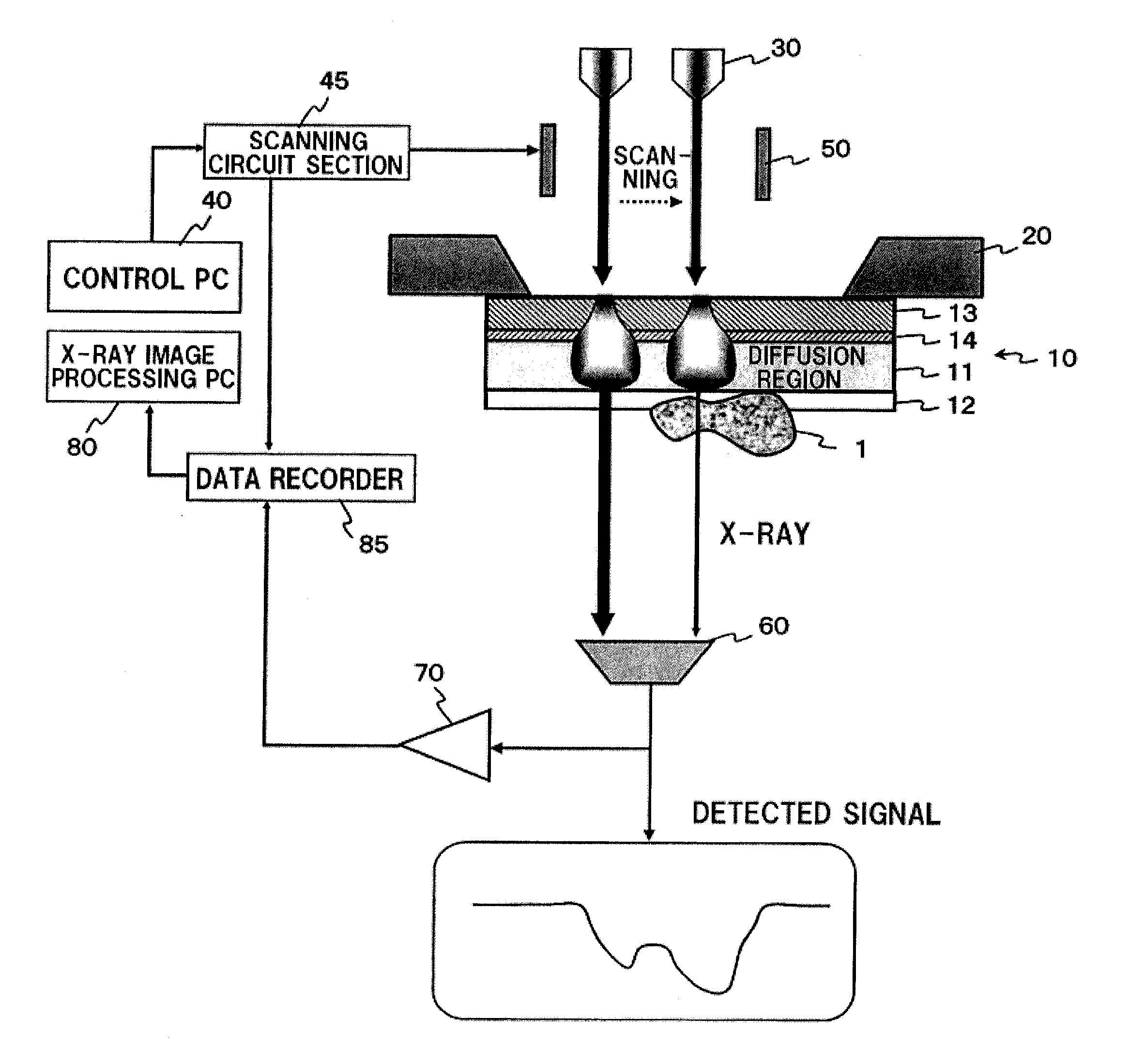
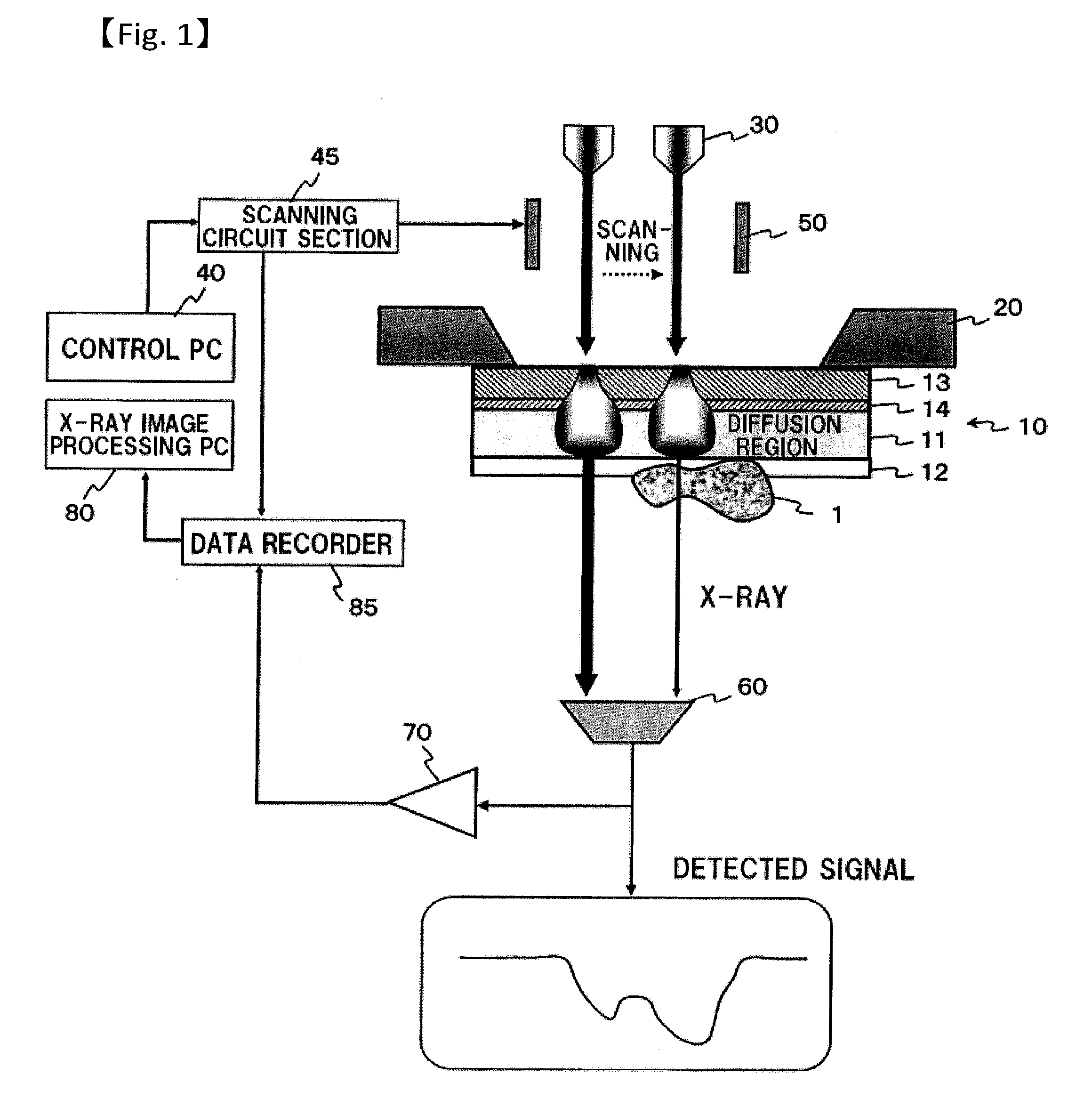
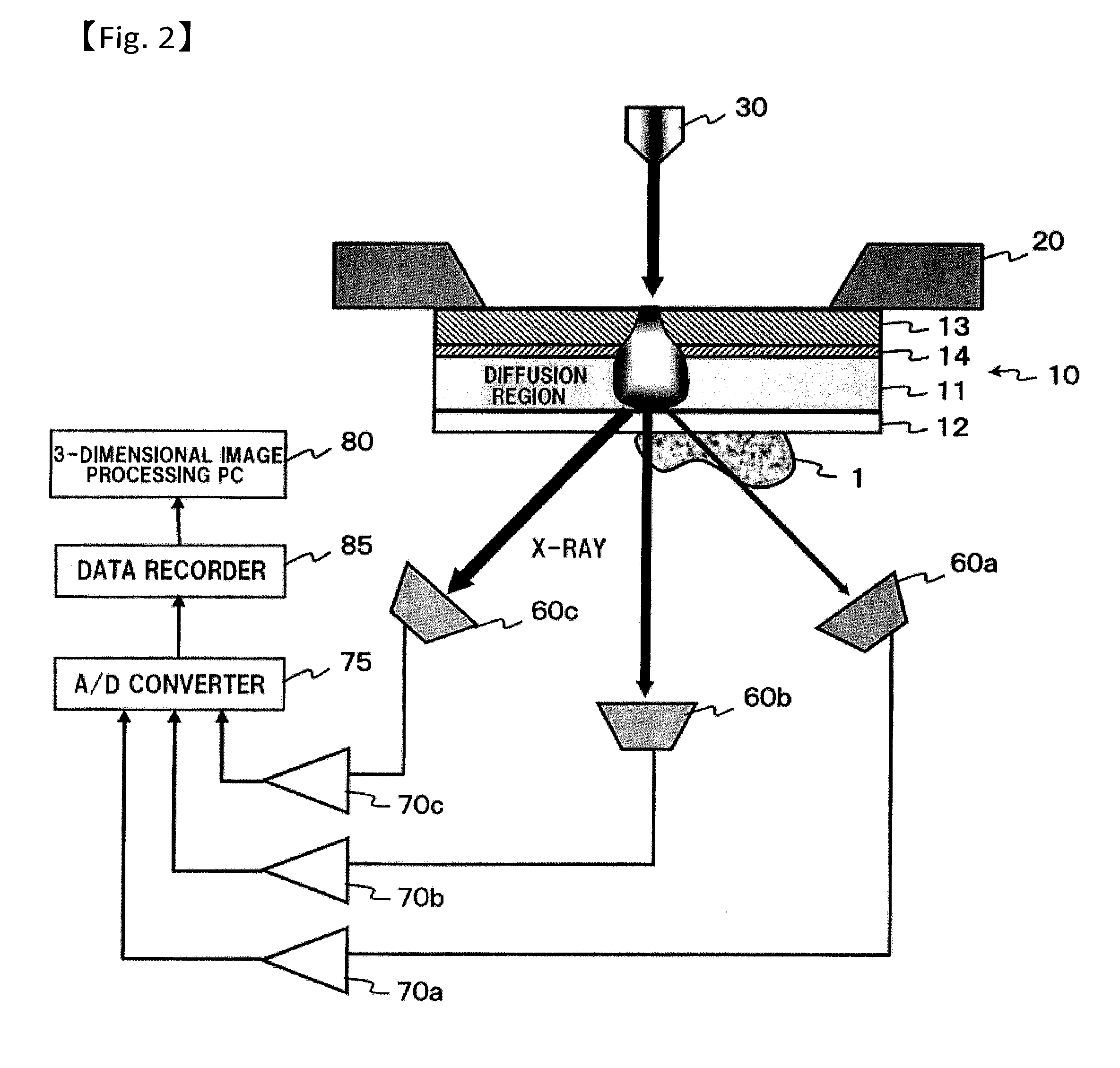
An X-ray microscope uses electromagnetic radiation in the soft X-ray band to produce magnified images of objects. Since X-rays penetrate most objects, there is no need to specially prepare them for X-ray microscopy observations.
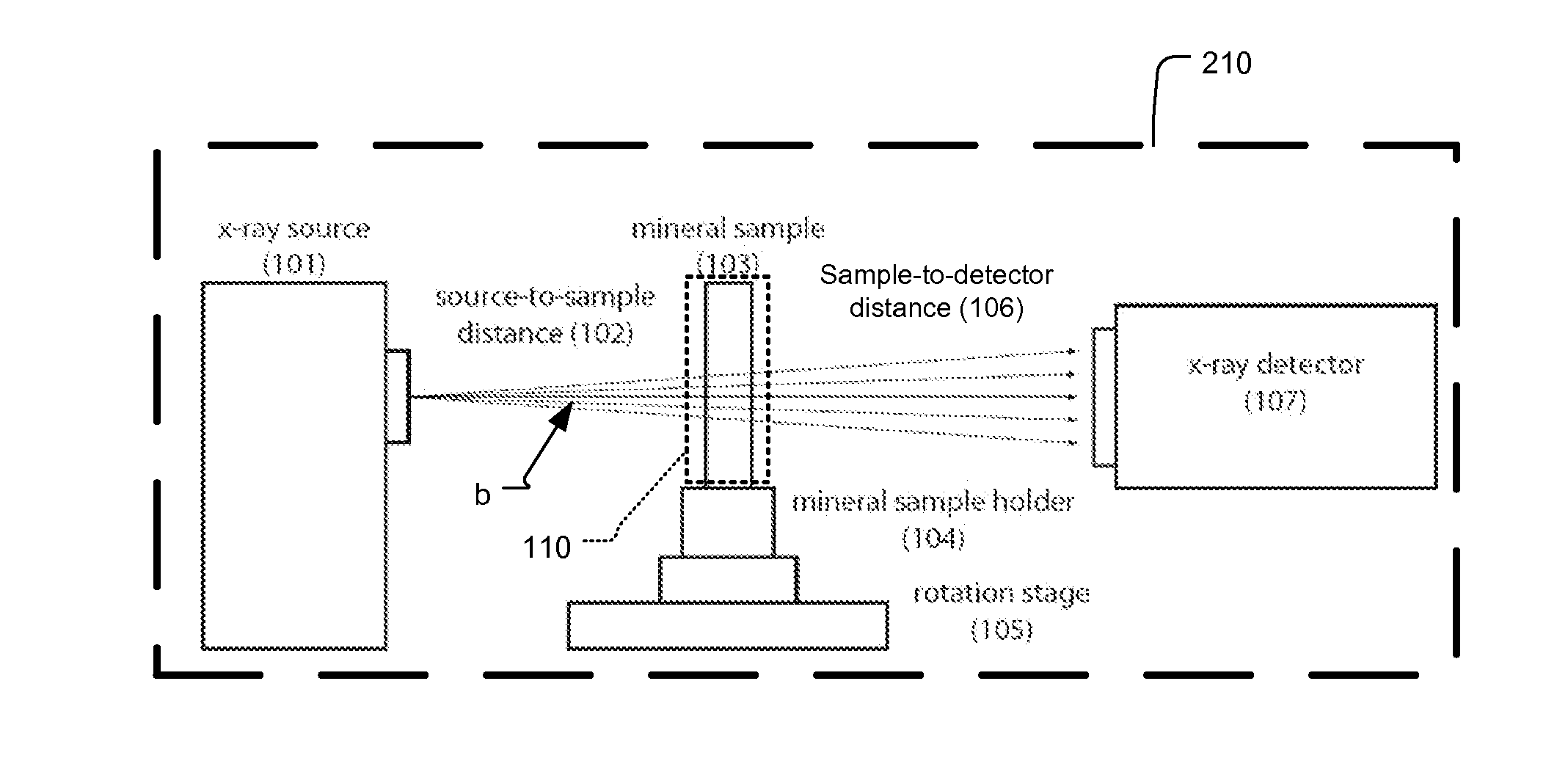
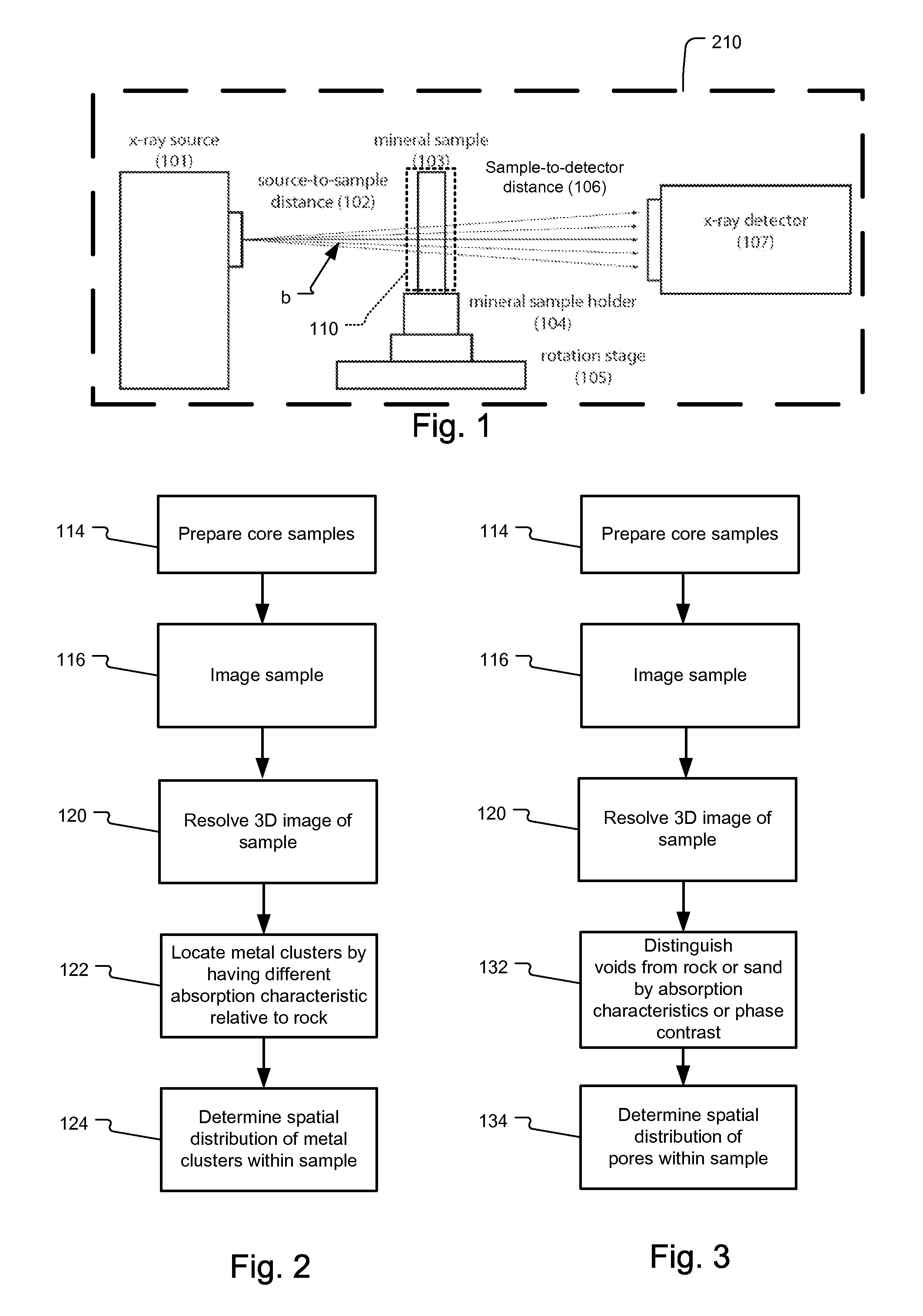
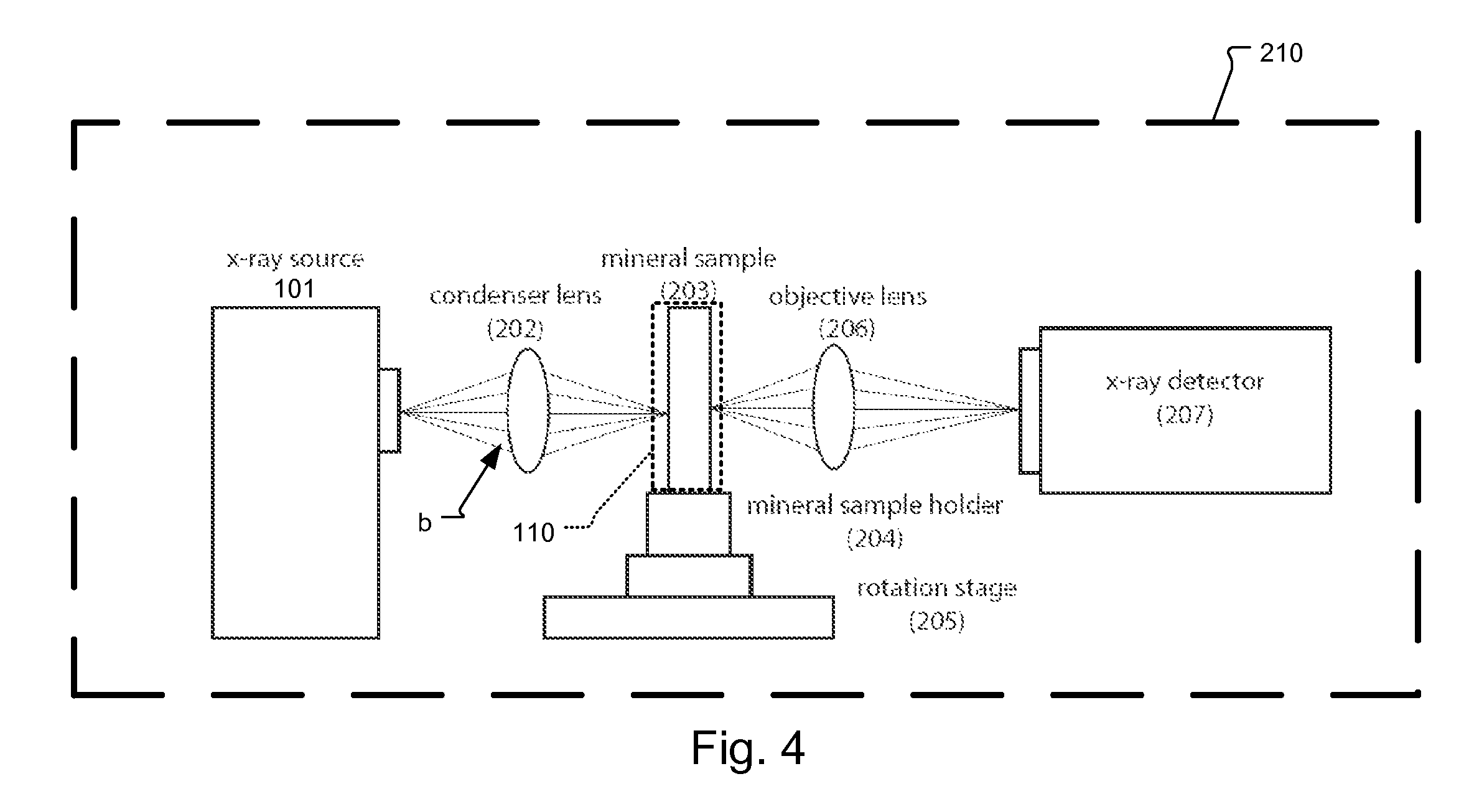
Process for examining mineral samples with X-ray microscope and projection systems
ActiveUS8068579B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPorosityData acquisition
A process to determine the porosity and / or mineral content of mineral samples with an x-ray CT system is described. Based on the direct-projection techniques that use a spatially-resolved x-ray detector to record the x-ray radiation passing through the sample, 1 micrometer or better resolution is achievable. Furthermore, by using an x-ray objective lens to magnify the x-ray image in a microscope configuration, a higher resolution of up to 50 nanometers or more is achieved with state-of-the-art technology. These x-ray CT techniques directly obtain the 3D structure of the sample with no modifications to the sample being necessary. Furthermore, fluid or gas flow experiments can often be conducted during data acquisition so that one may perform live monitoring of the physical process in 3D.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
X-ray anode and process for its manufacture
InactiveUS6850598B1Improve the heating effectReduce absorptionRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayImage resolution
The invention relates to an x-ray anode and a process for its manufacture. The x-ray anode is characterized in that the anode material is embodied as a layer on a diamond window. The x-ray anode is preferably used with x-ray units which require as selective as possible x-radiation production to achieve as high as possible radiation intensity. Use in x-ray microscopes in which a high radiation intensity guarantees the highest resolutions is particularly preferred.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Structured anode X-ray source for X-ray microscopy
ActiveUS7443953B1Improve performanceImprove thermal performanceX-ray tube laminated targetsX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyX-ray
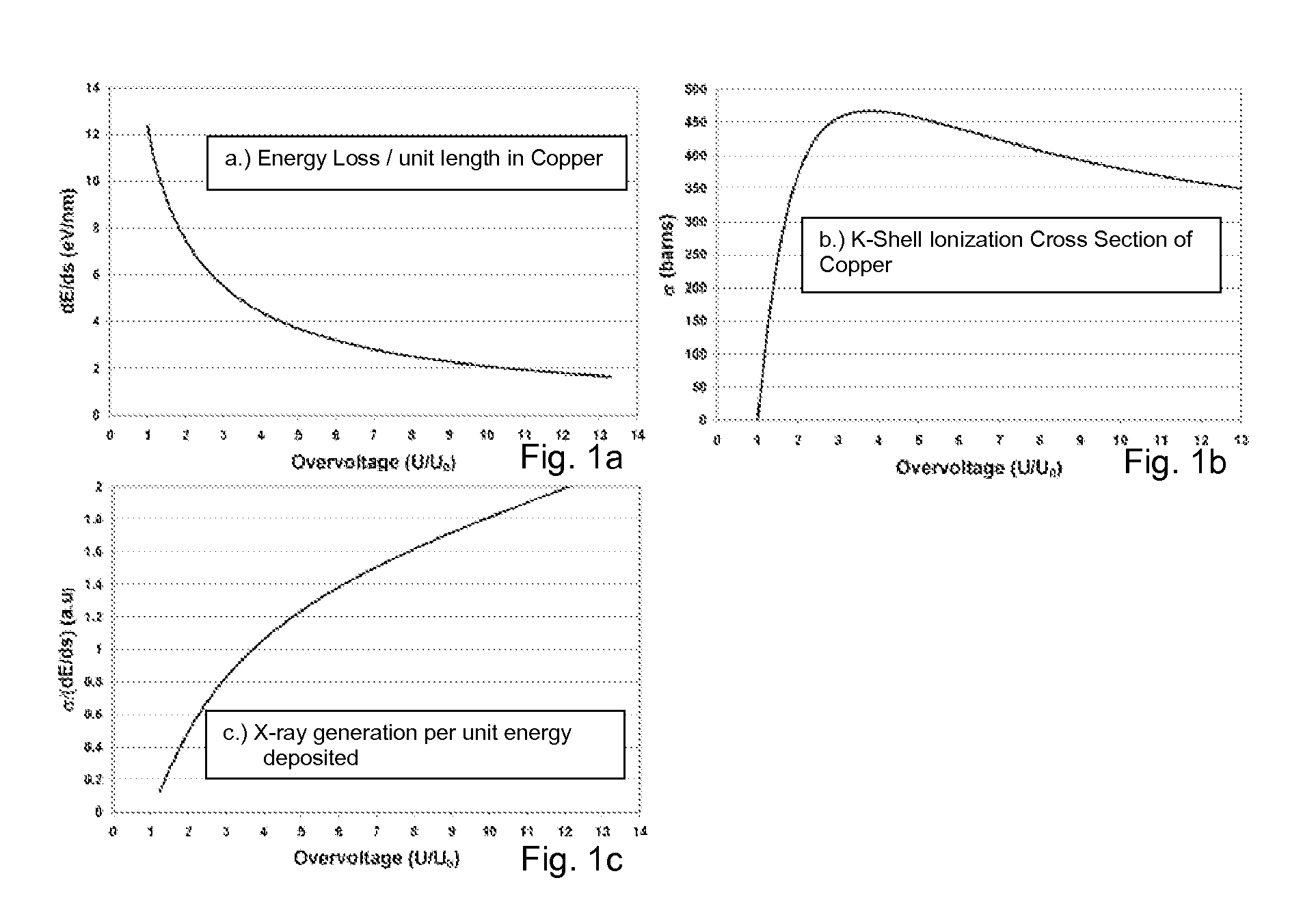
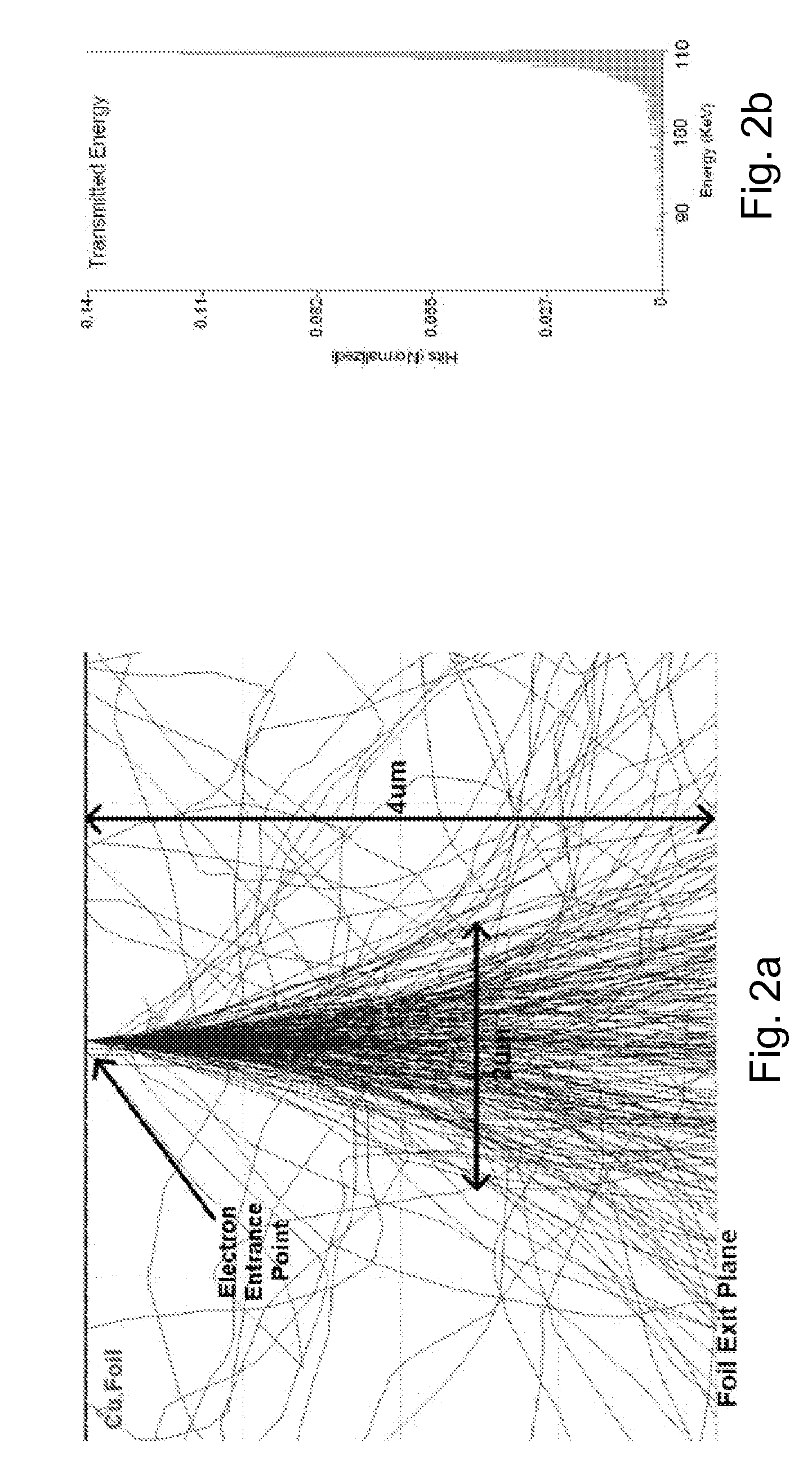
An x-ray source comprises a structured anode that has a thin top layer made of the desired target material and a thick bottom layer made of low atomic number and low density materials with good thermal properties. In one example, the anode comprises a layer of copper with an optimal thickness deposited on a layer of beryllium or diamond substrate. This structured target design allows for the use of efficient high energy electrons for generation of characteristic x-rays per unit energy deposited in the top layer and the use of the bottom layer as a thermal sink. This anode design can be applied to substantially increase the brightness of stationary, rotating anode or other electron bombardment-based sources where brightness is defined as number of x-rays per unit area and unit solid angle emitted by a source and is a key figure of merit parameter for a source.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
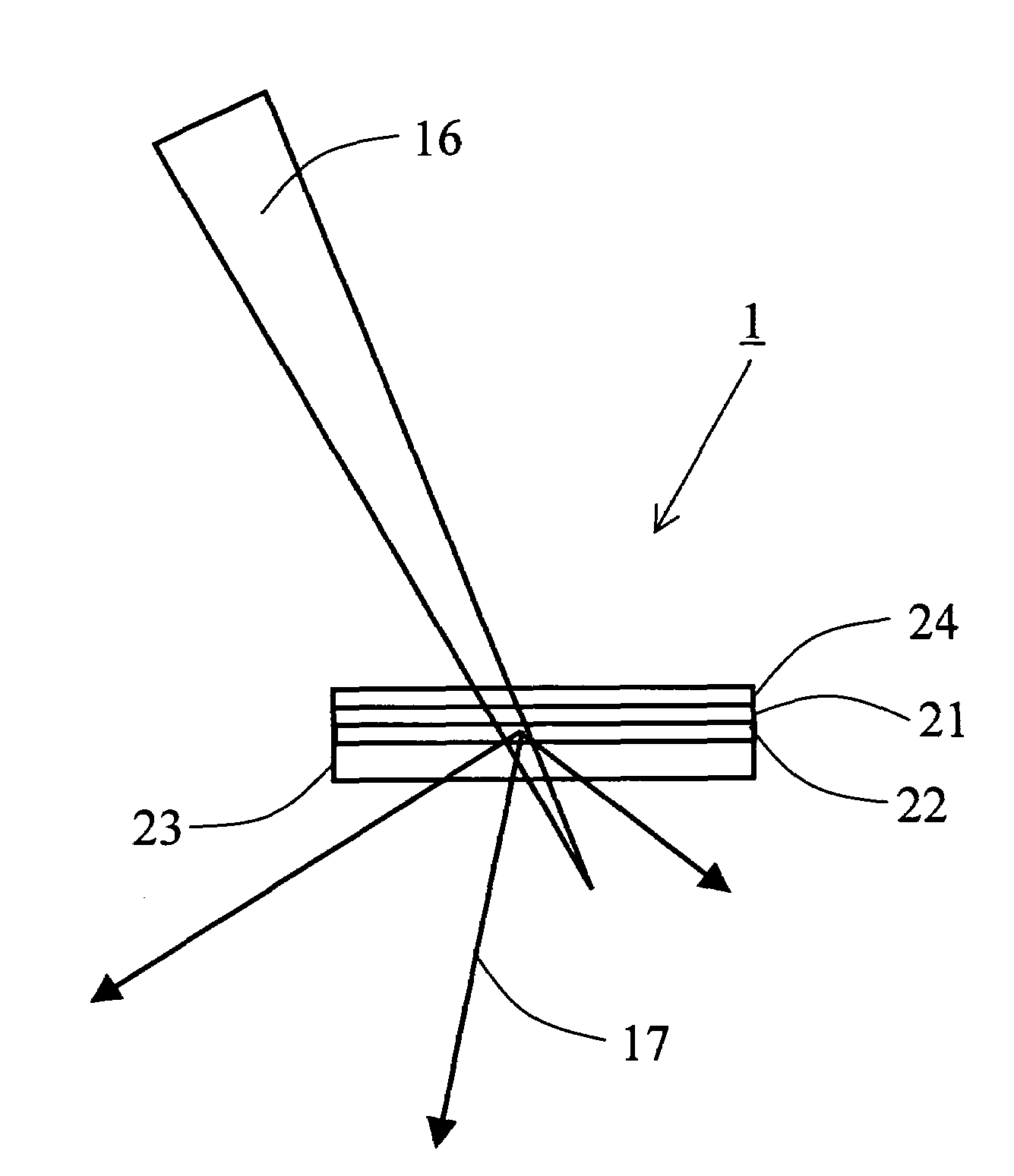
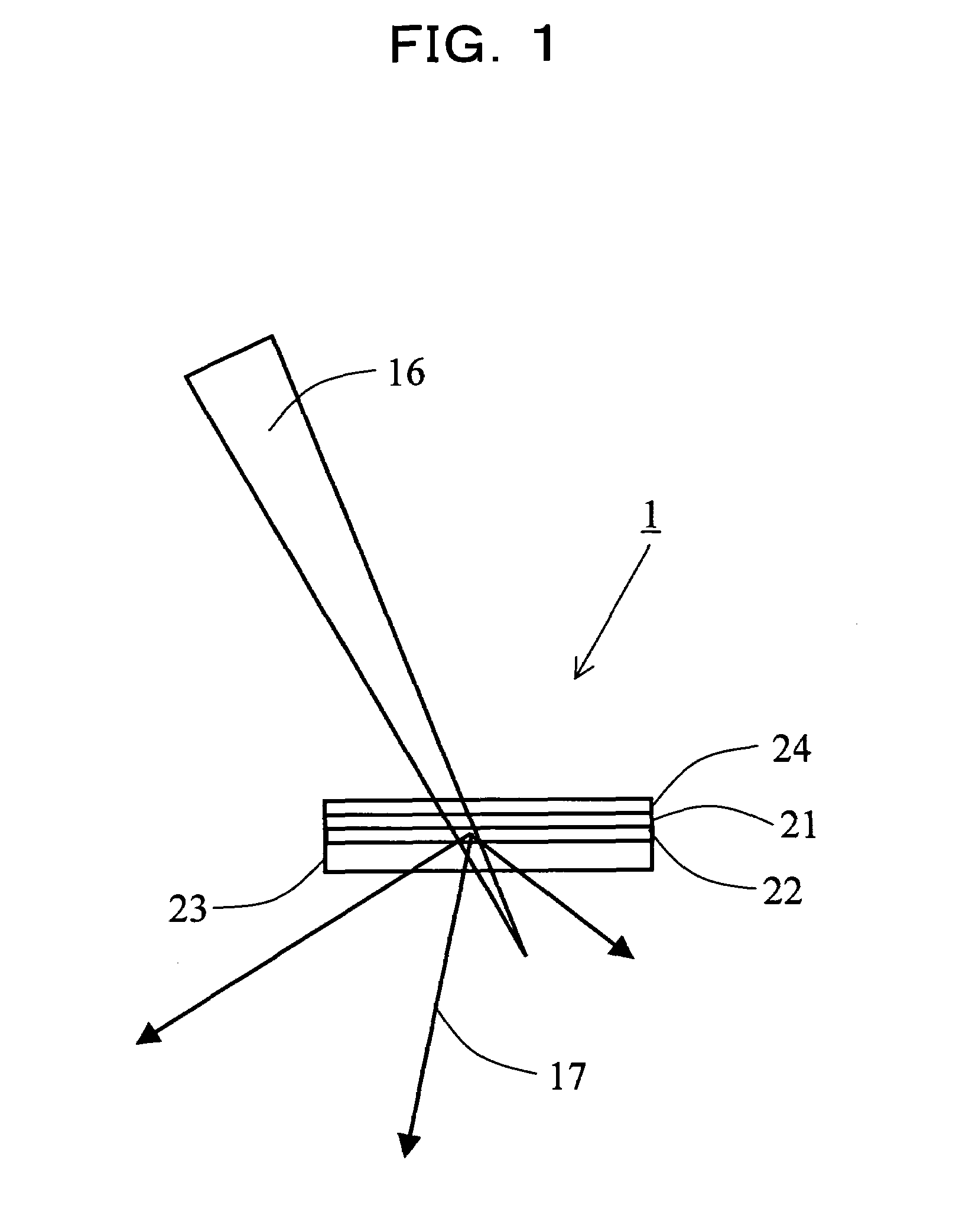
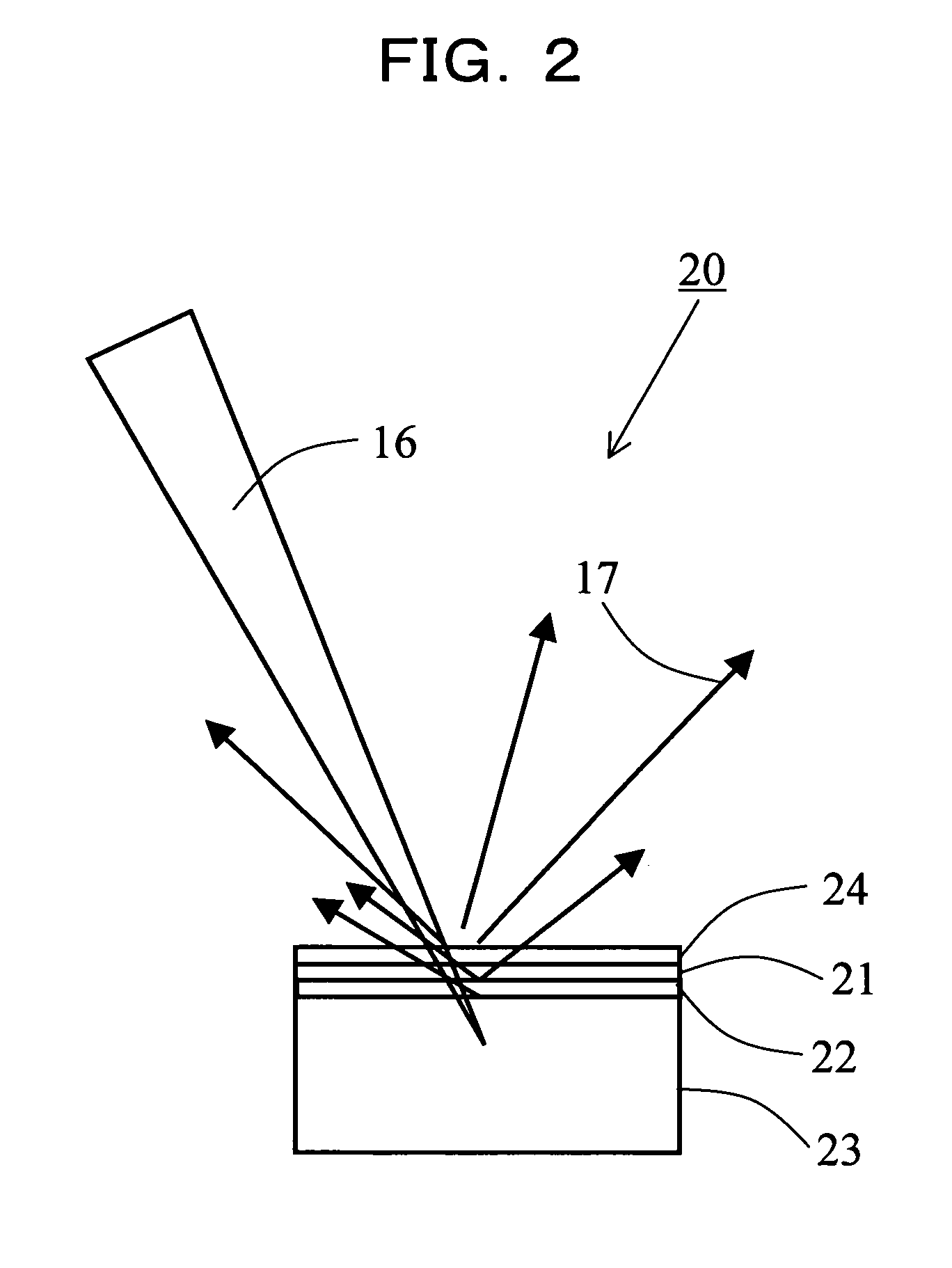
X-Ray Target and Apparatuses Using the Same
InactiveUS20070248215A1Highly convenientElectron beam absorptivityX-ray tube laminated targetsImaging devicesFluorescenceHigh intensity
Disclosed are an X-ray target having a micro focus size and capable of producing X-rays of high intensity, and apparatuses using such an X-ray target. The X-ray target (1) has a structure in which a first cap layer (21), a target layer (22), and a second cap layer (23) are successively laminated, wherein the first and second cap layers (21and 23) are each composed of a material which is lower in electron beam absorptivity than that of which the target layer (22) is composed. An X-ray generator using the X-ray target (1) can generate highly intense and nanofocus (several nm) X-rays (17). Using the X-ray generator, an X-ray microscope allows obtaining a high resolution transmission image, an X-ray diffraction apparatus allows obtaining an X-ray diffraction image of a very small area, and a fluorescent X-ray analysis apparatus allows making the fluorescent X-ray analysis of a minute area.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
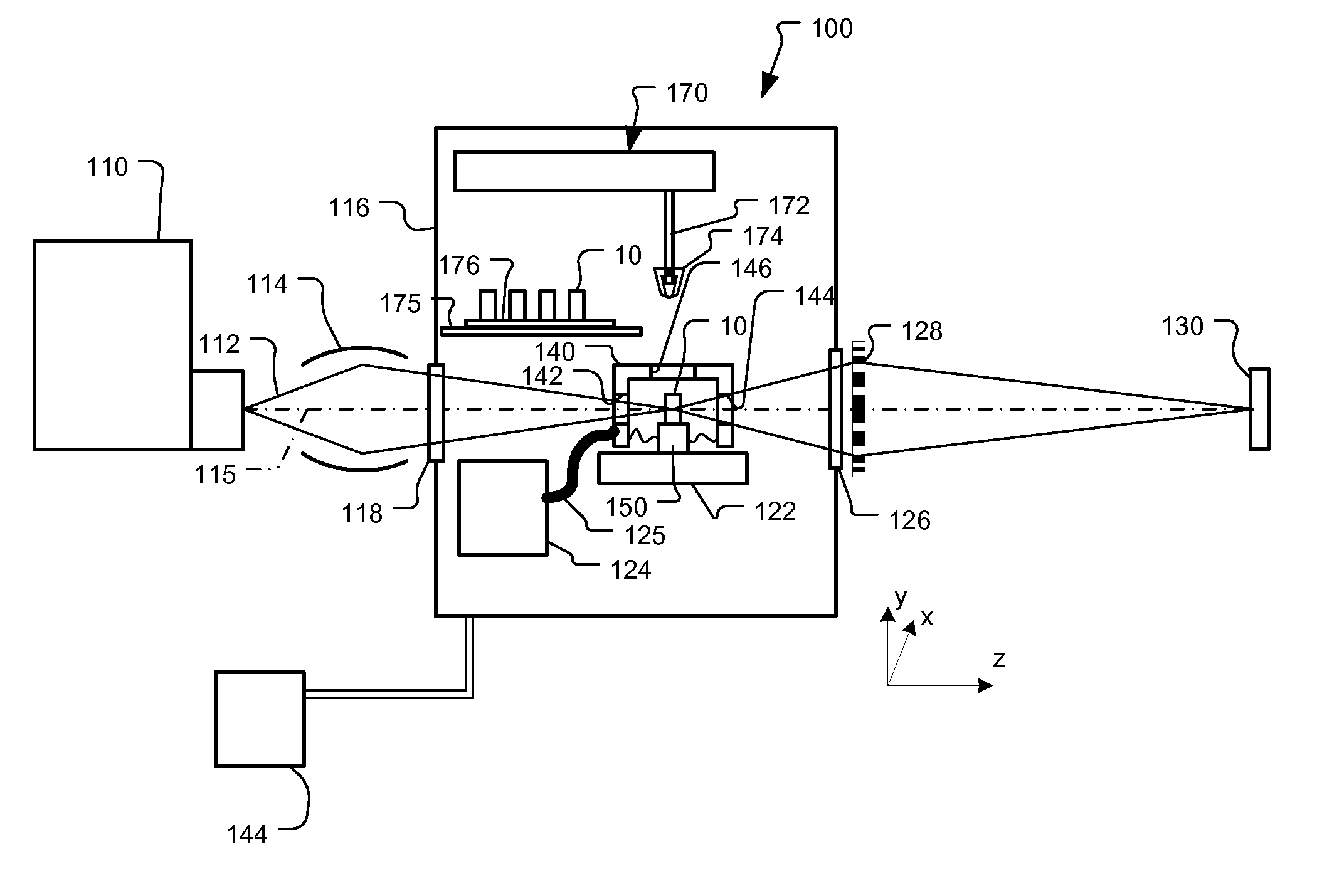
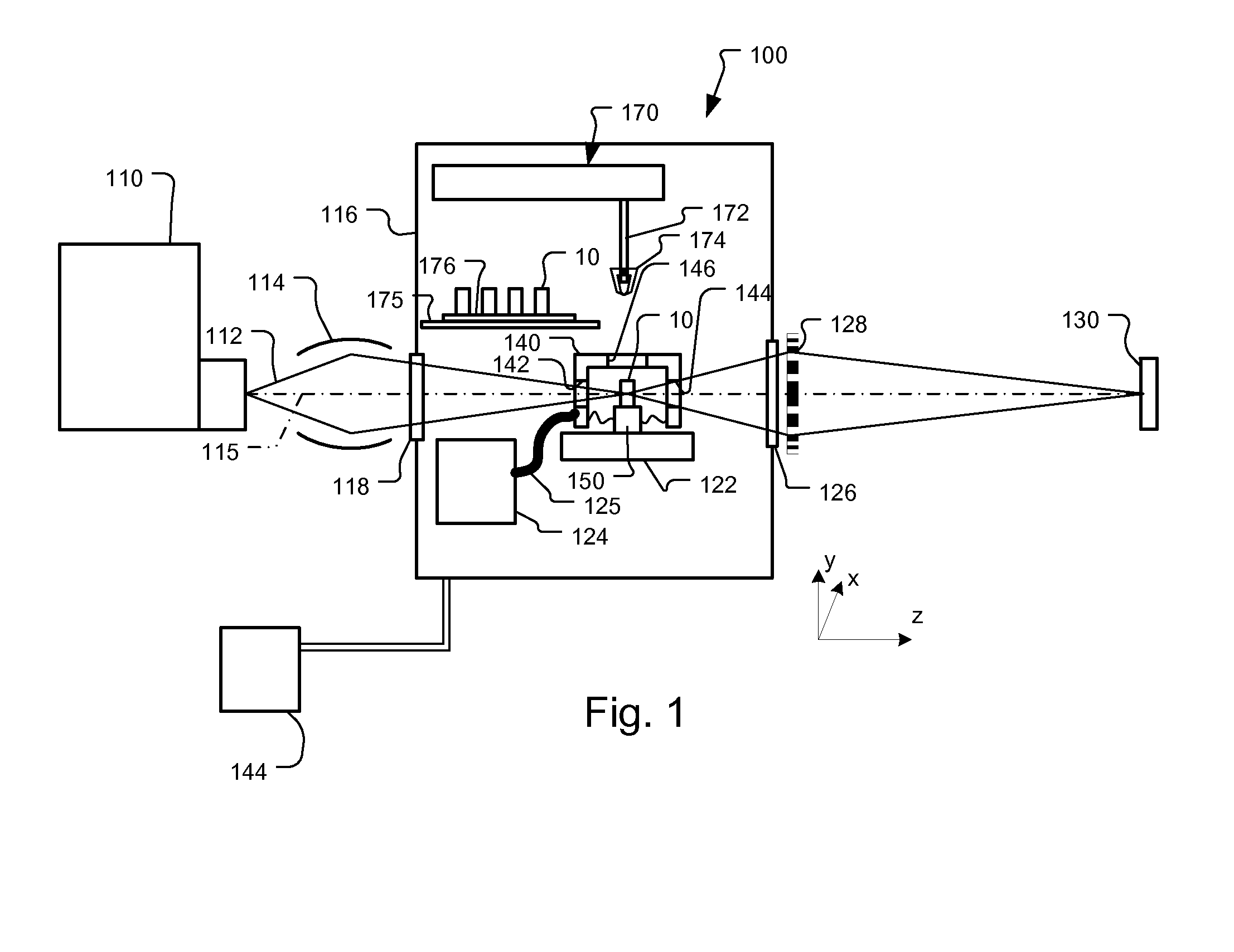
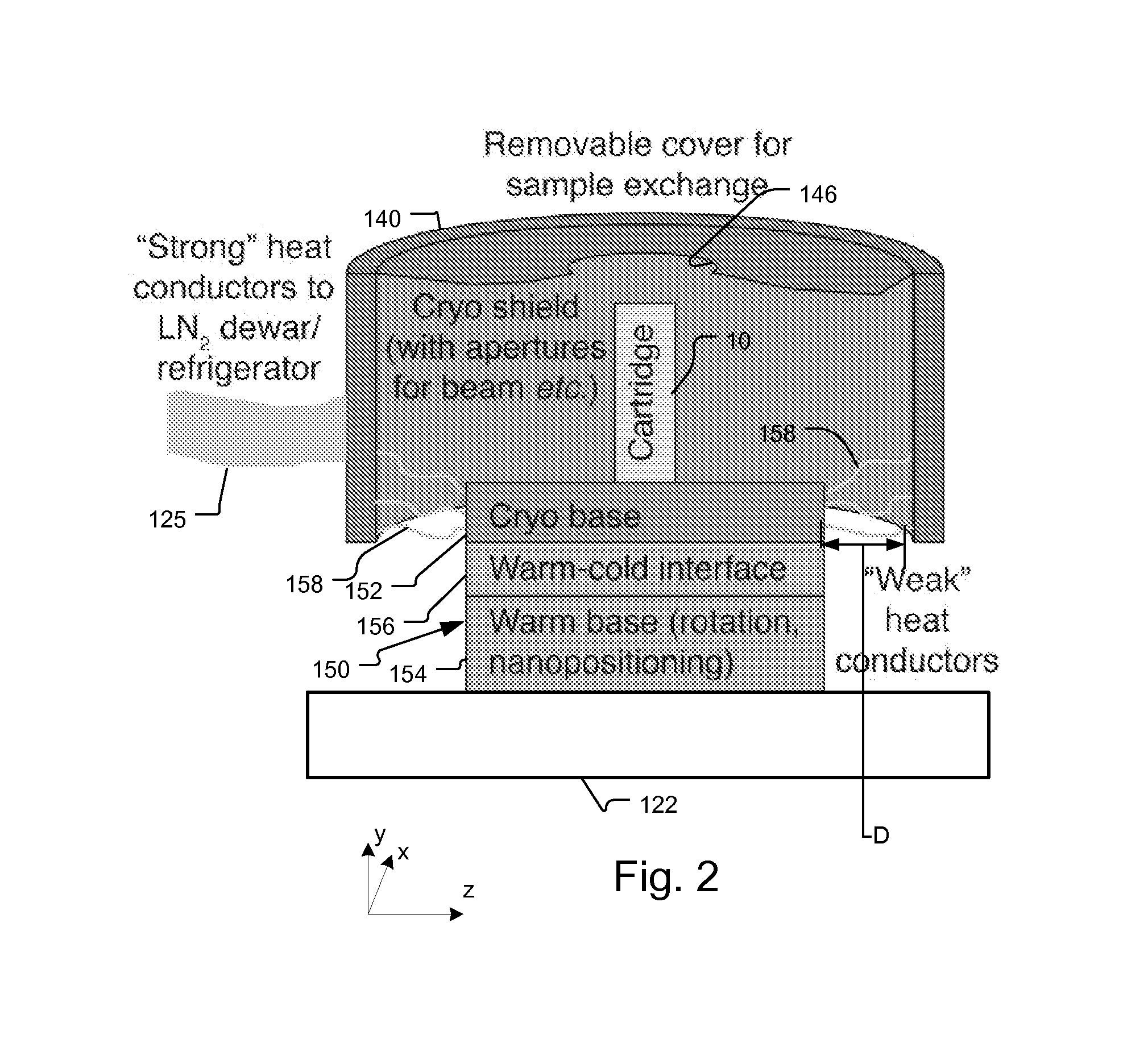
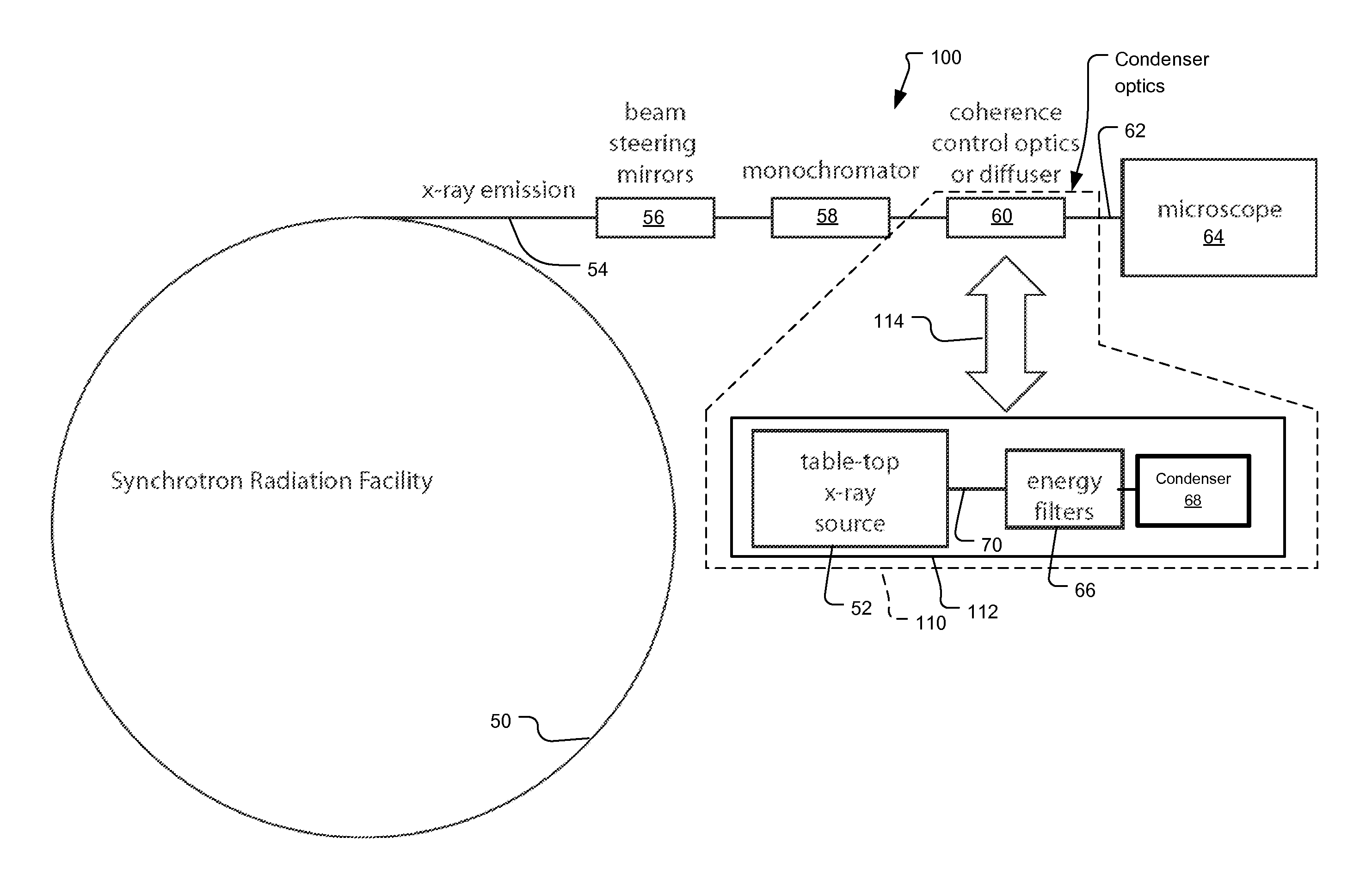
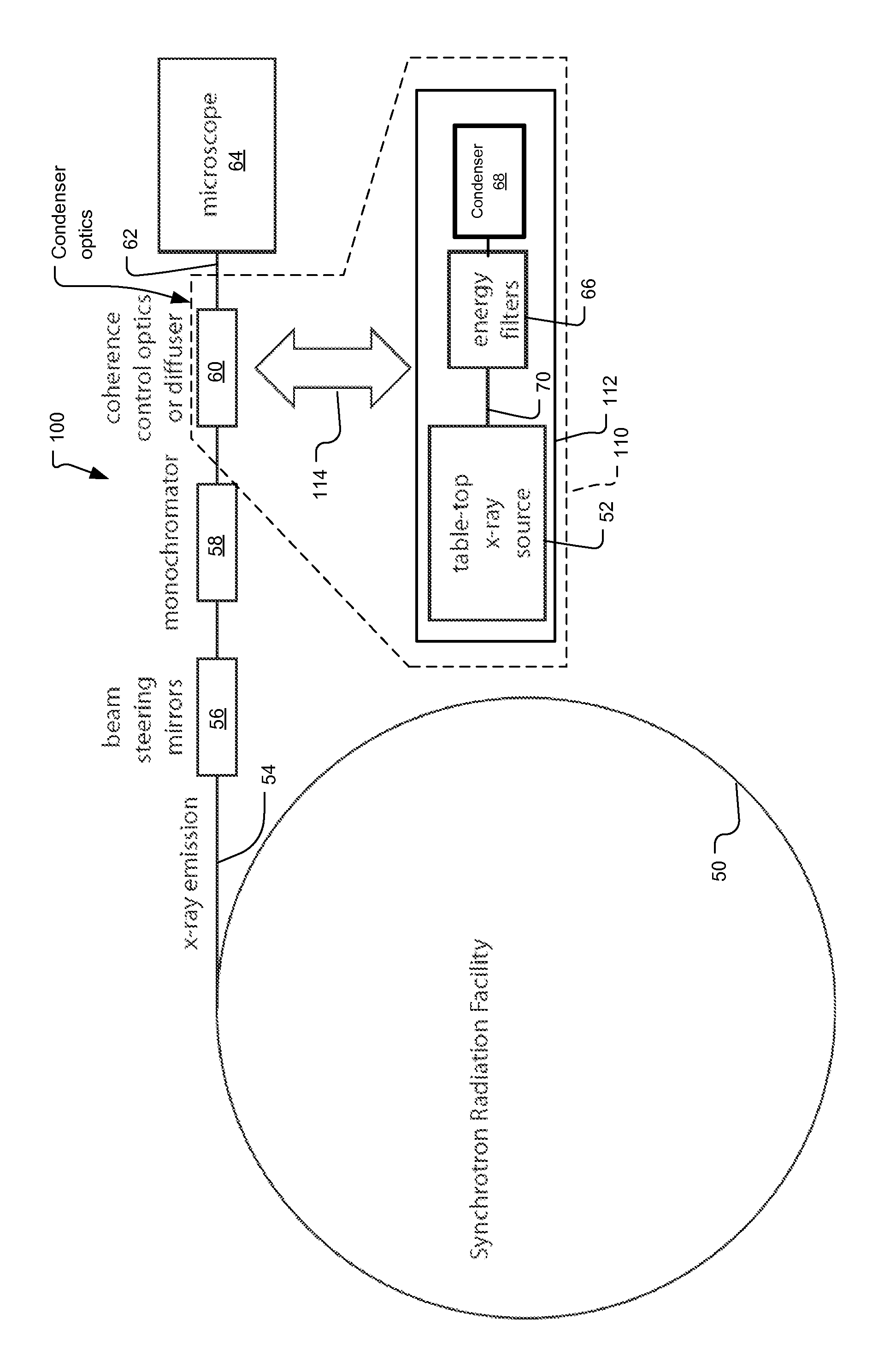
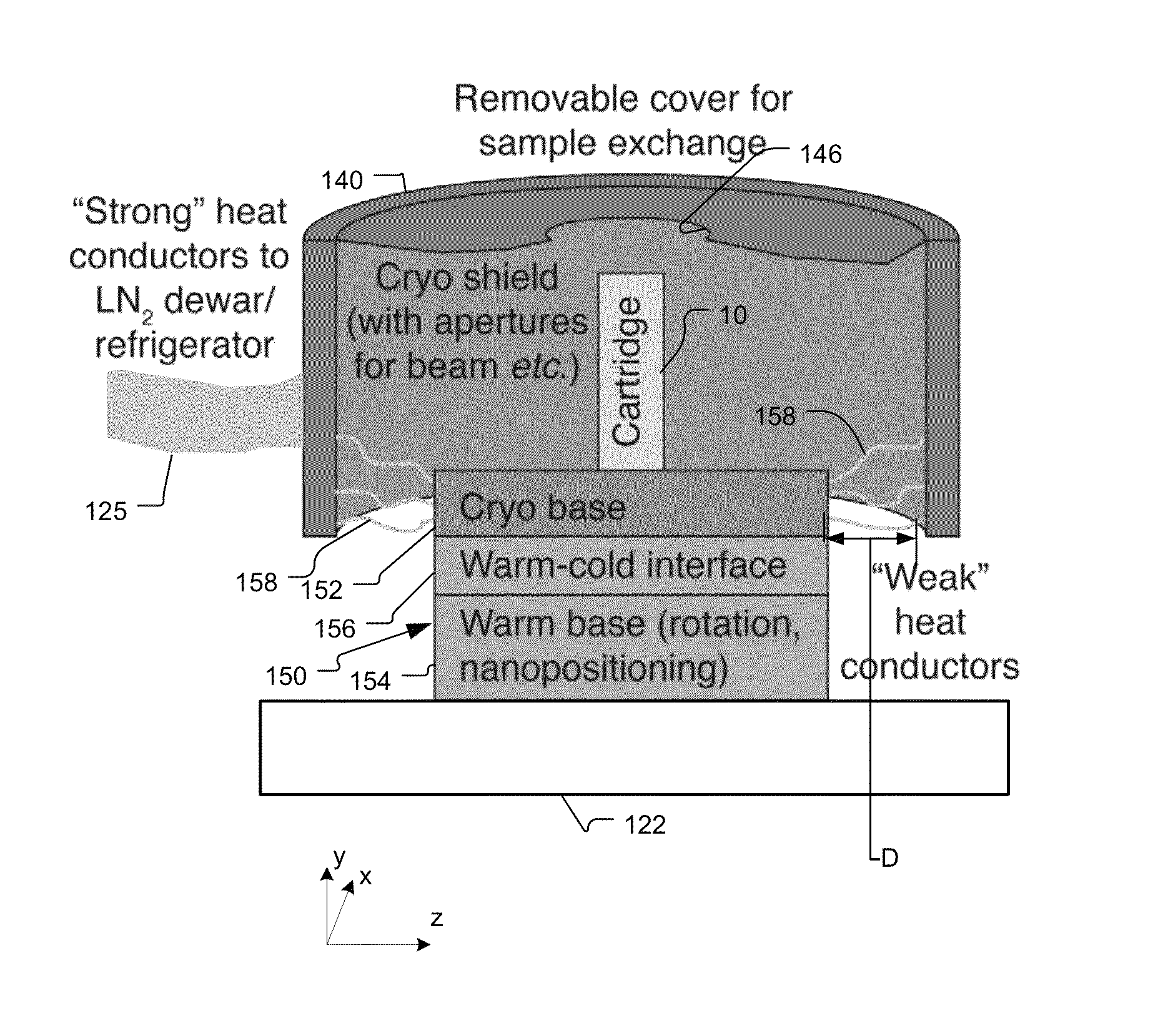
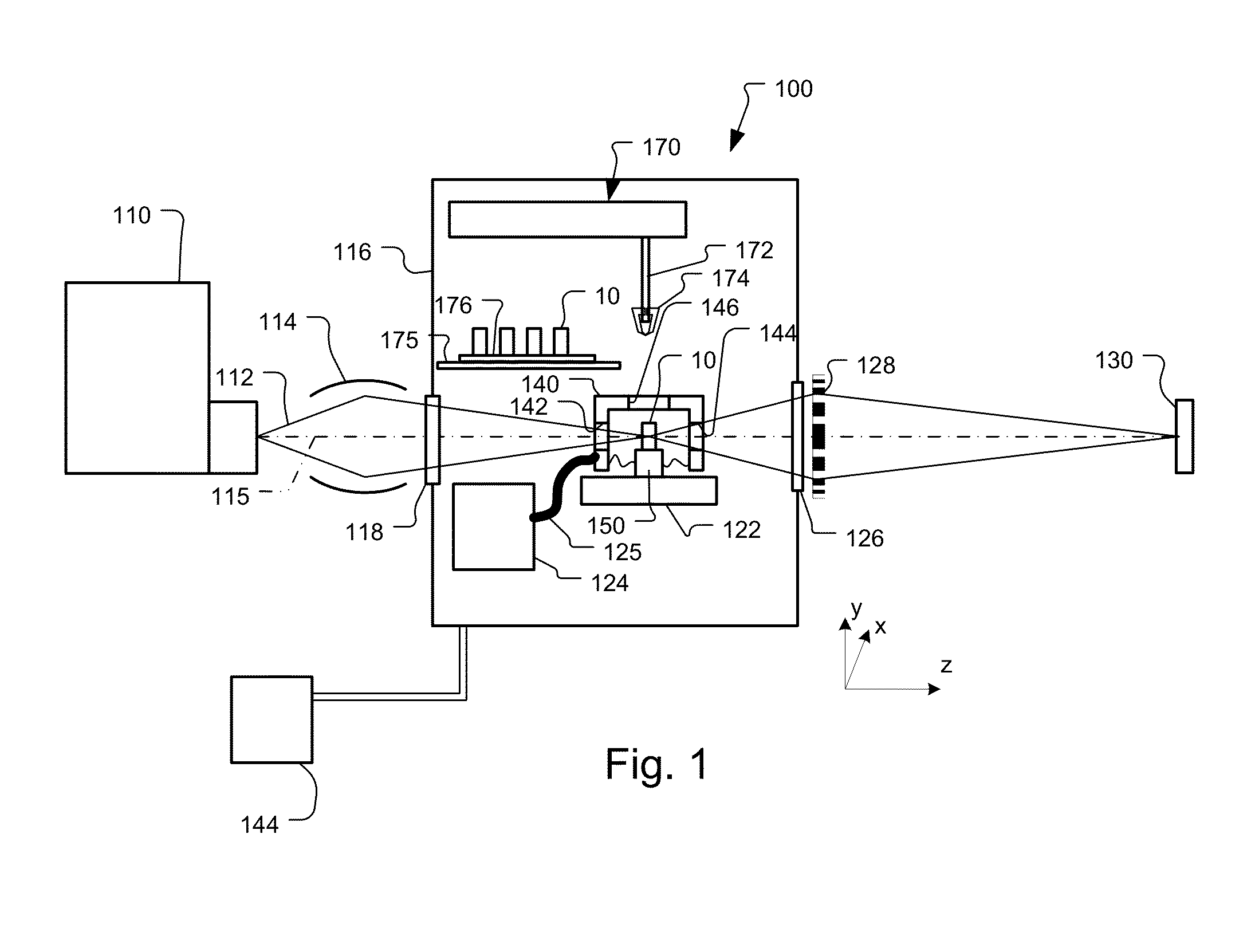
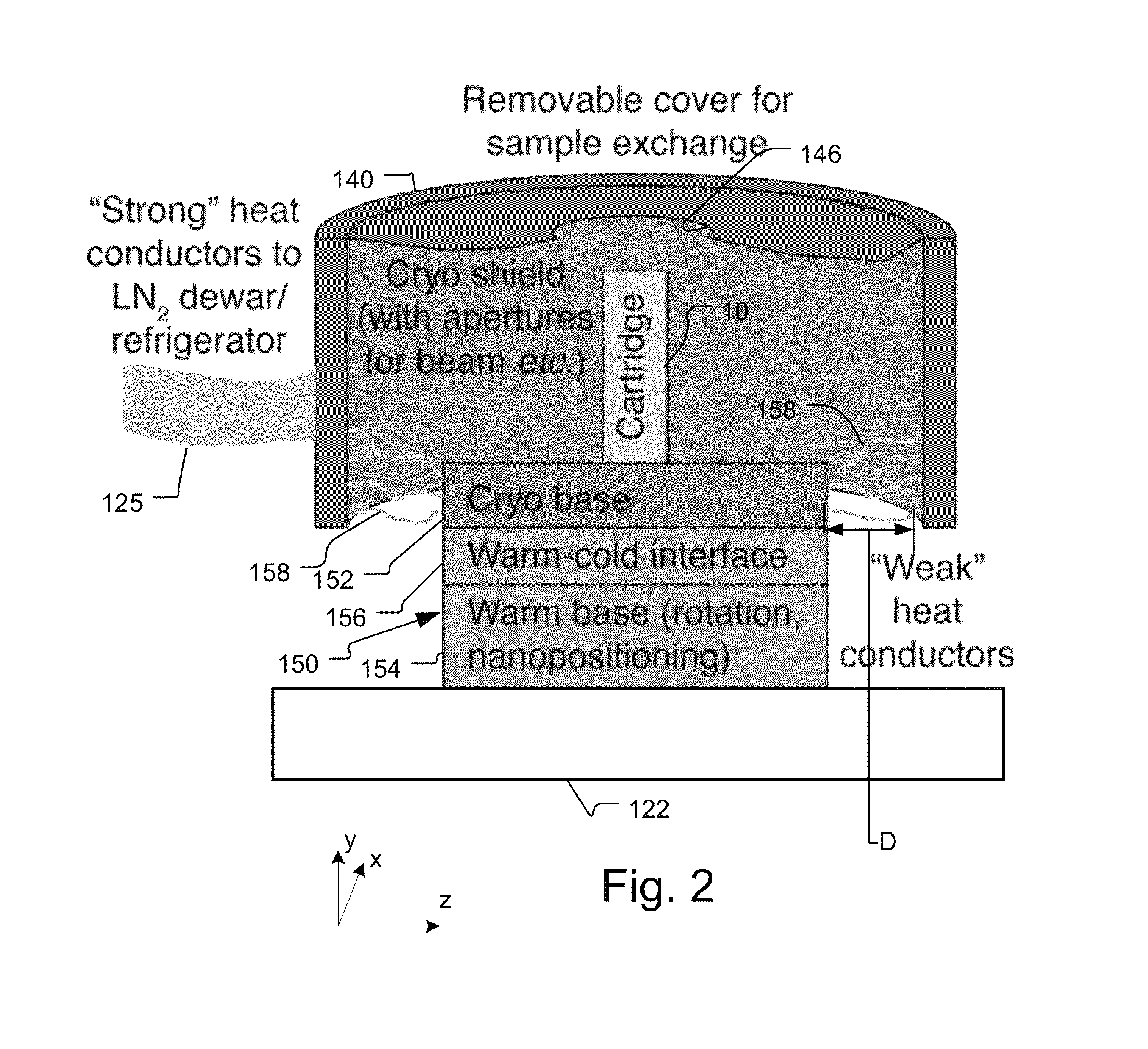
X-Ray Microscope System with Cryogenic Handling System and Method
ActiveUS20140072104A1High-resolution imageLarge rotation rangeMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGamma-ray/x-ray microscopesX-rayEngineering
A cartridge-based cryogenic imaging system includes a sample handling system. This system uses a kinematic base and cold interface system that provides vertical loading to horizontally mounted high-precision rotation stages that are able to facilitate automated high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) imaging with computed tomography (CT). Flexible metal braids are used to provide cooling and also allow a large range of rotation. A robotic sample transfer and loading system provides further automation by allowing a number of samples to be loaded and automatically sequentially placed on the sample stage and imaged, These characteristics provide the capability of high-throughput and highly automated cryogenic x-ray microscopy and computed tomography.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
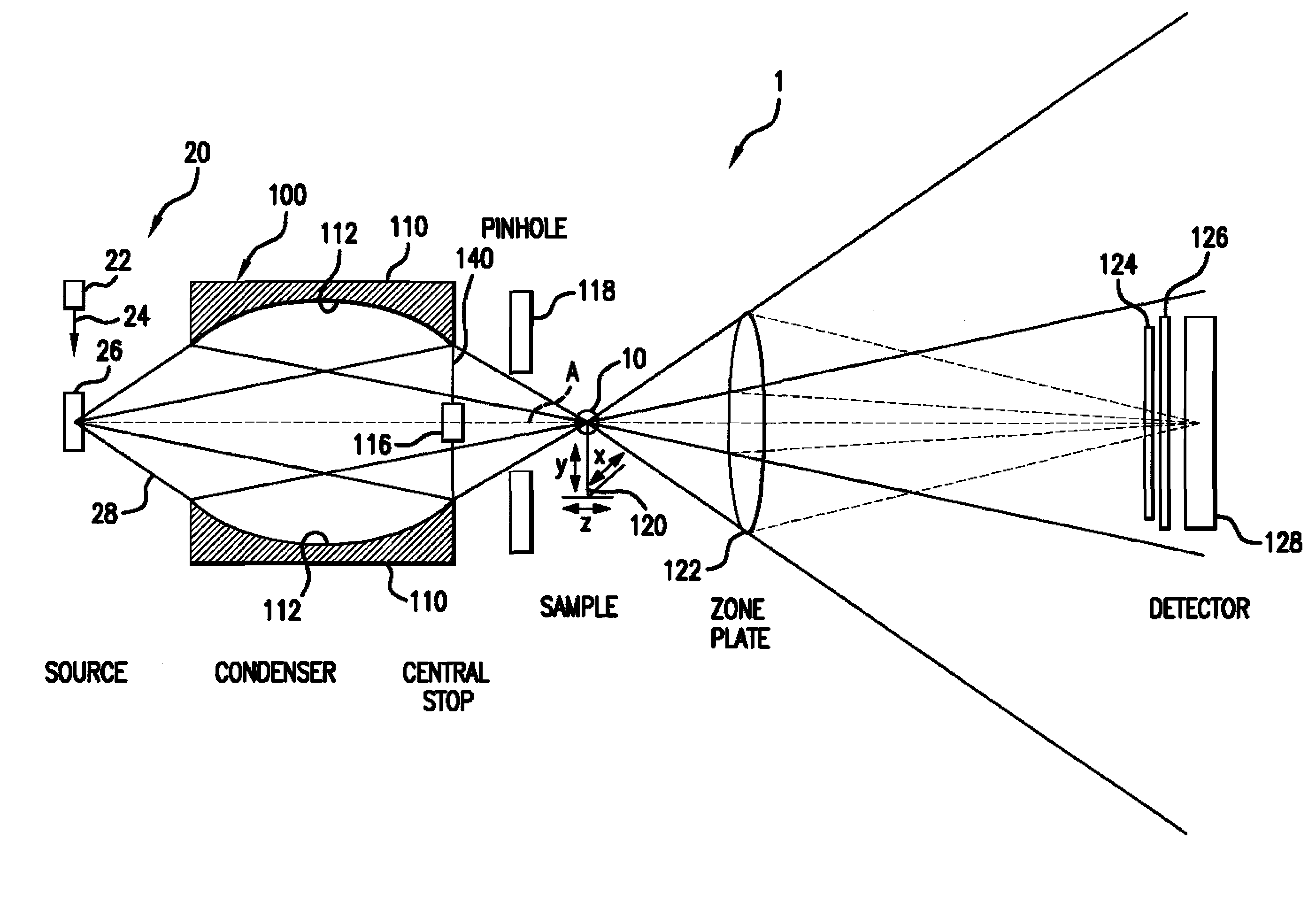
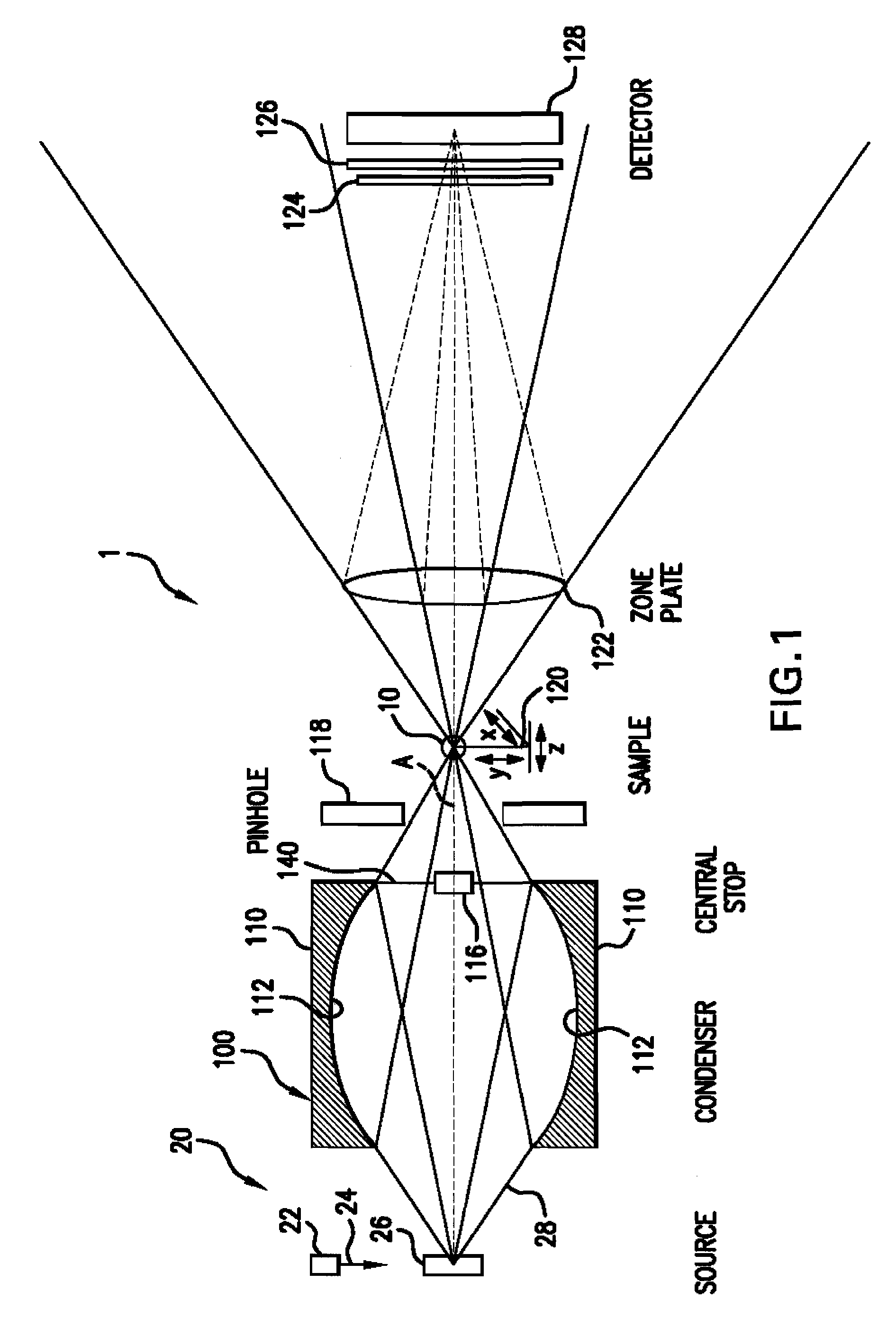
X-ray microscope capillary condenser system
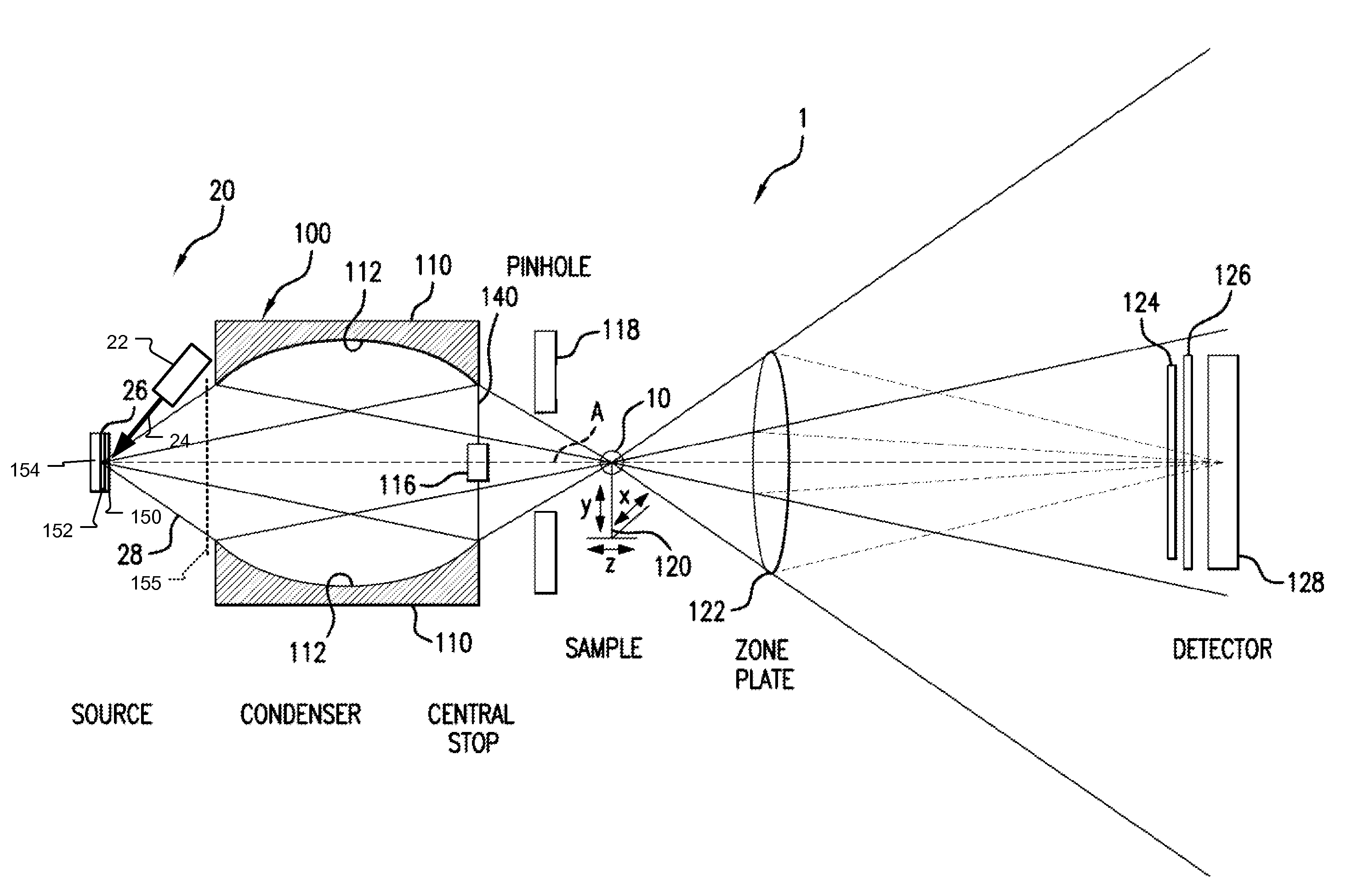
ActiveUS7170969B1Efficient collectionEfficient relayHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionGamma-ray/x-ray microscopesZone platePhysics
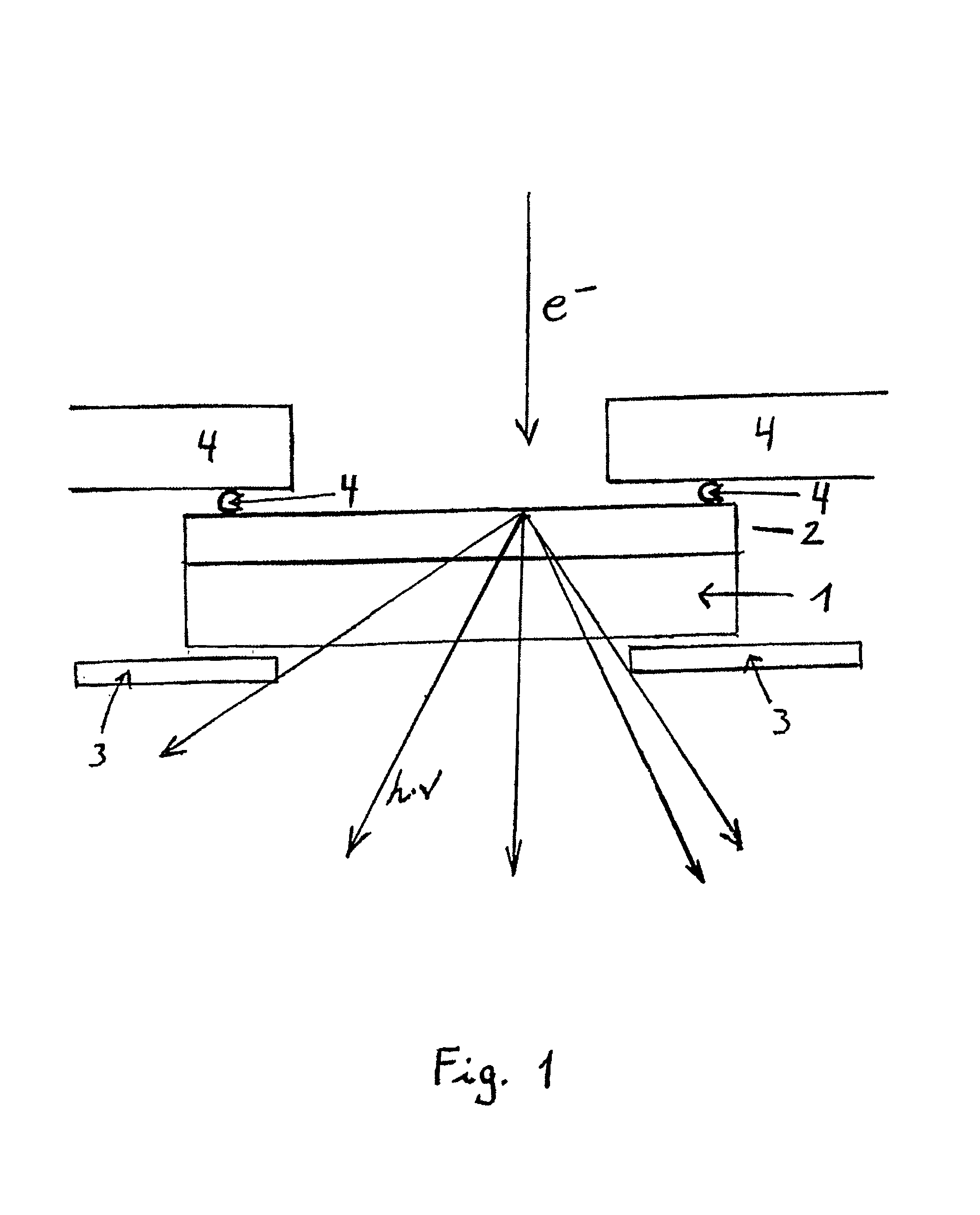
A radiation condenser system for an X-ray microscope allows for the efficient collection and relay of radiation from a source to the sample. It generates a converging hollow cone of radiation that can be used in the imaging of a sample or target using a zone plate lens. This system comprises a capillary tube for receiving and focusing radiation onto a sample. A center stop is provided for blocking radiation being transmitted along an axis of the capillary tube.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
X-ray microscope with switchable x-ray source
An x-ray imaging system uses a synchrotron radiation beam to acquire x-ray images and at least one integrated x-ray source. The system has an imaging system including sample stage controlled by linear translation stages, objective x-ray lens, and x-ray sensitive detector system, placed on a fixed optical table and a mechanical translation stage system to switch x-ray sources when synchrotron radiation beam is not available.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
X-ray microscope system with cryogenic handling system and method
ActiveUS8602648B1Facilitate automated high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) imagingLarge rotation rangeX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayEngineering
A cartridge-based cryogenic imaging system includes a sample handling system. This system uses a kinematic base and cold interface system that provides vertical loading to horizontally mounted high-precision rotation stages that are able to facilitate automated high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) imaging with computed tomography (CT). Flexible metal braids are used to provide cooling and also allow a large range of rotation. A robotic sample transfer and loading system provides further automation by allowing a number of samples to be loaded and automatically sequentially placed on the sample stage and imaged. These characteristics provide the capability of high-throughput and highly automated cryogenic x-ray microscopy and computed tomography.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
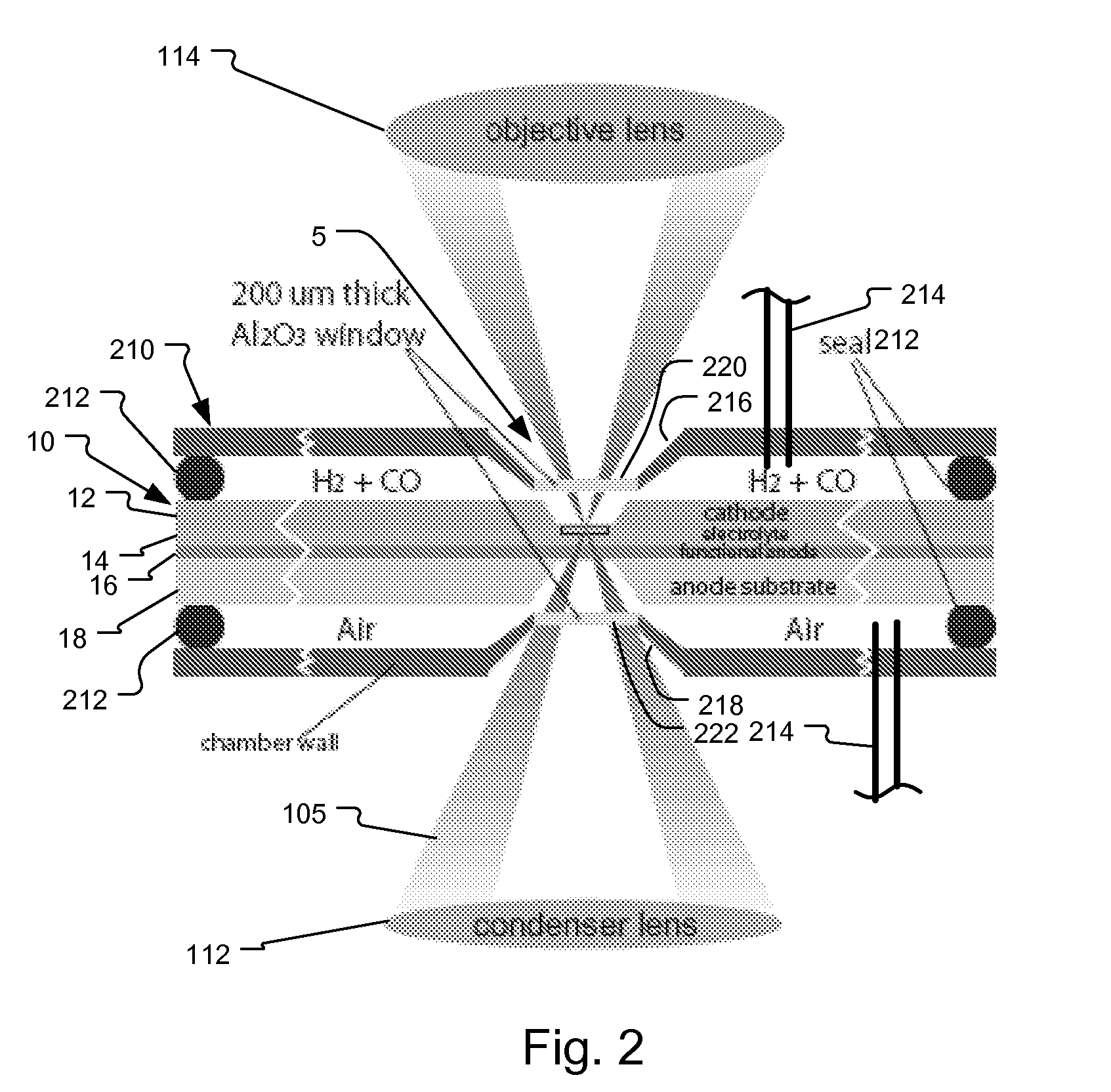
System and method for fuel cell material x-ray analysis
ActiveUS7499521B2Shorten development timeImprove reliabilityRadiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansHard X-raysMetrology
An imaging technology for fuel cells is based on x-ray microscopy. A metrology system images the electro-chemical interaction areas of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFC) in-situ. This system takes advantage of both the penetrating power and elemental absorption contrast of hard x-ray radiation to image the internal interaction areas in a SOFC. The technology can further take advantage of the strong dependence of the x-ray absorption on material type and energy to distinguish the four major material types: cathode, electrolyte, air, and low-Z contaminants such as sulfur.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
X-ray target and apparatuses using the same
InactiveUS7551722B2Electron beam absorptivitySmall in focus sizeX-ray tube laminated targetsImaging devicesHigh intensityX ray analysis
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for x-ray microscopy
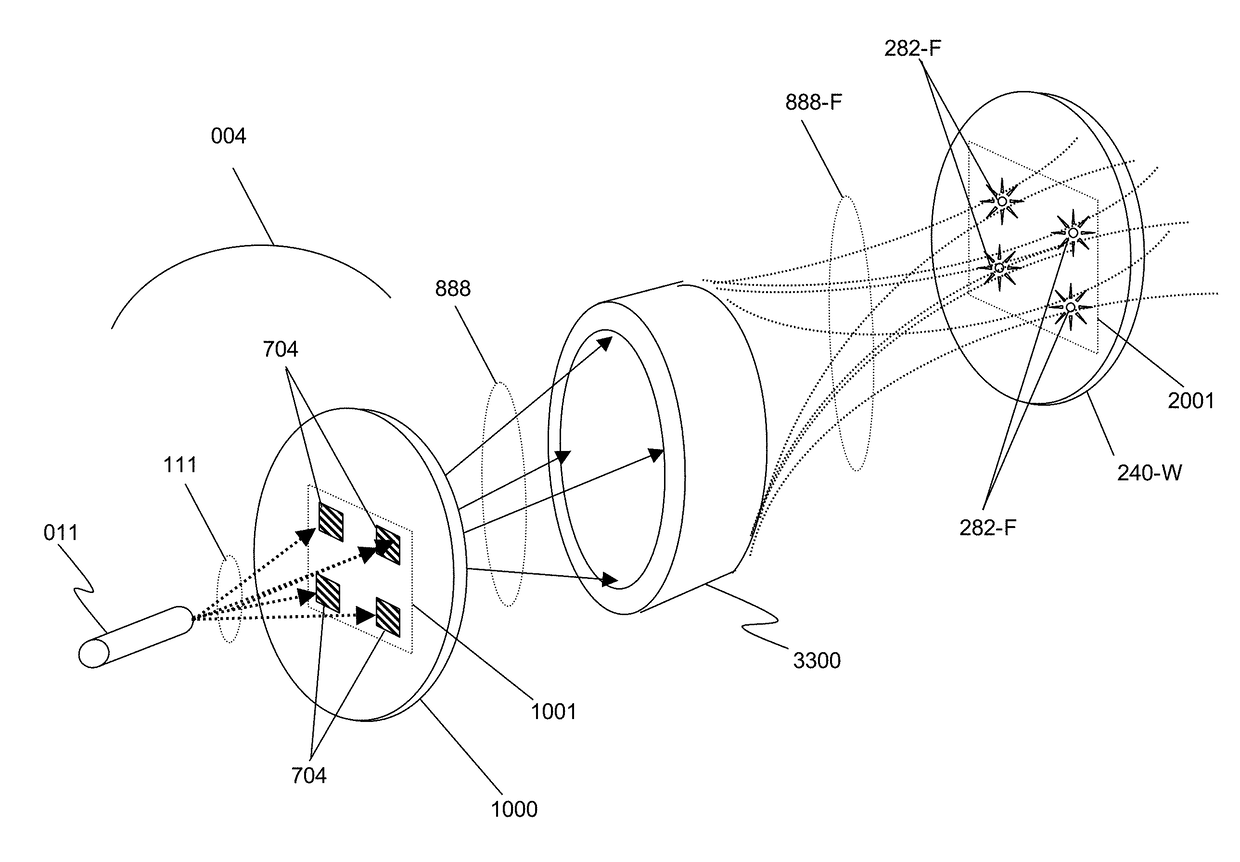
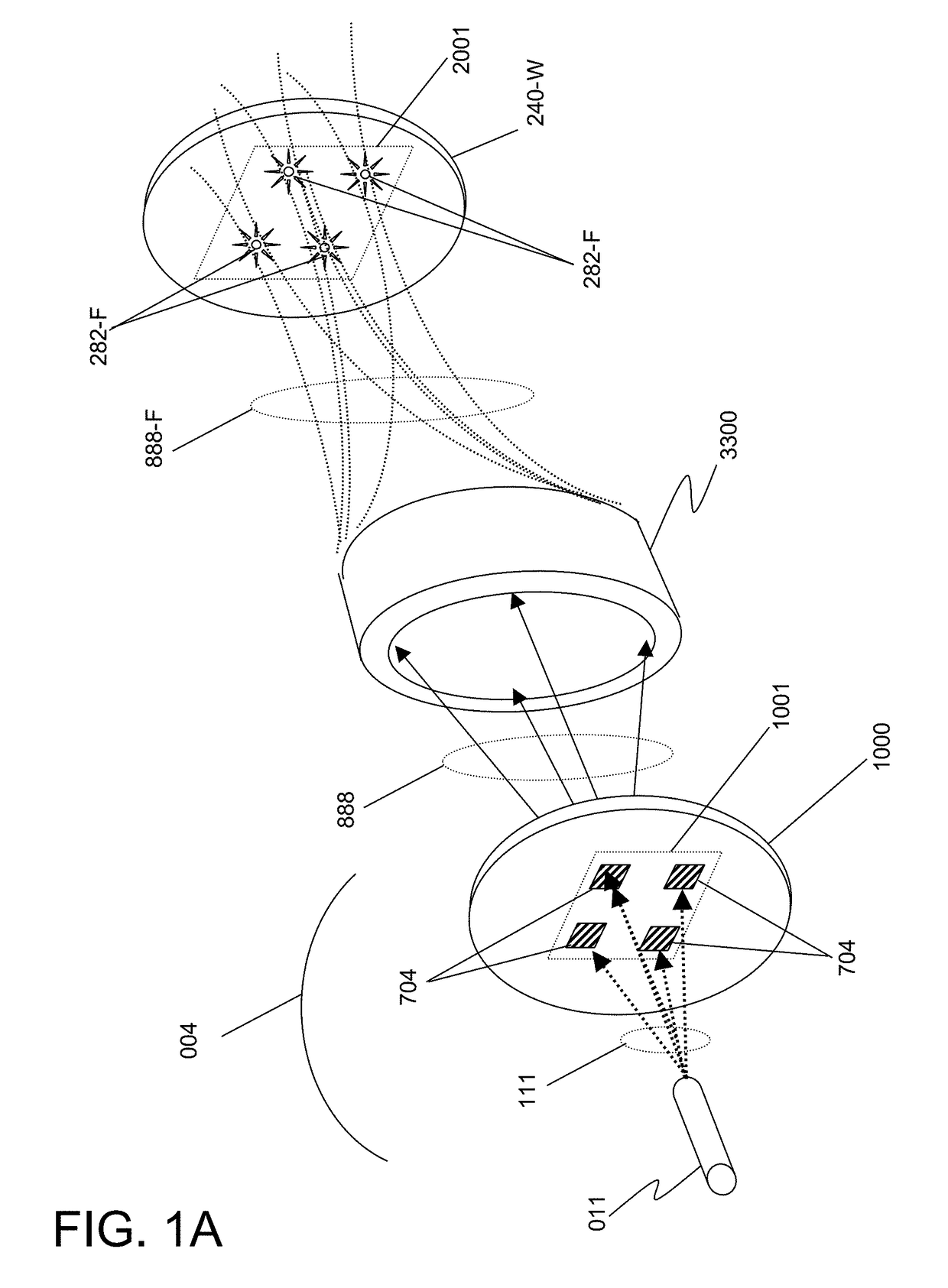
ActiveUS20170261442A1Large pixel sizeImprove detection efficiencyImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-rayNanoscopic scale
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray microscopy using an array of micro-beams having a micro- or nano-scale beam intensity profile to provide selective illumination of micro- or nano-scale regions of an object. An array detector is positioned such that each pixel of the detector only detects x-rays corresponding to a single micro- or nano-beam. This allows the signal arising from each x-ray detector pixel to be identified with the specific, limited micro- or nano-scale region illuminated, allowing sampled transmission image of the object at a micro- or nano-scale to be generated while using a detector with pixels having a larger size and scale. Detectors with higher quantum efficiency may therefore be used, since the lateral resolution is provided solely by the dimensions of the micro- or nano-beams. The micro- or nano-scale beams may be generated using an arrayed x-ray source or a set of Talbot interference fringes.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
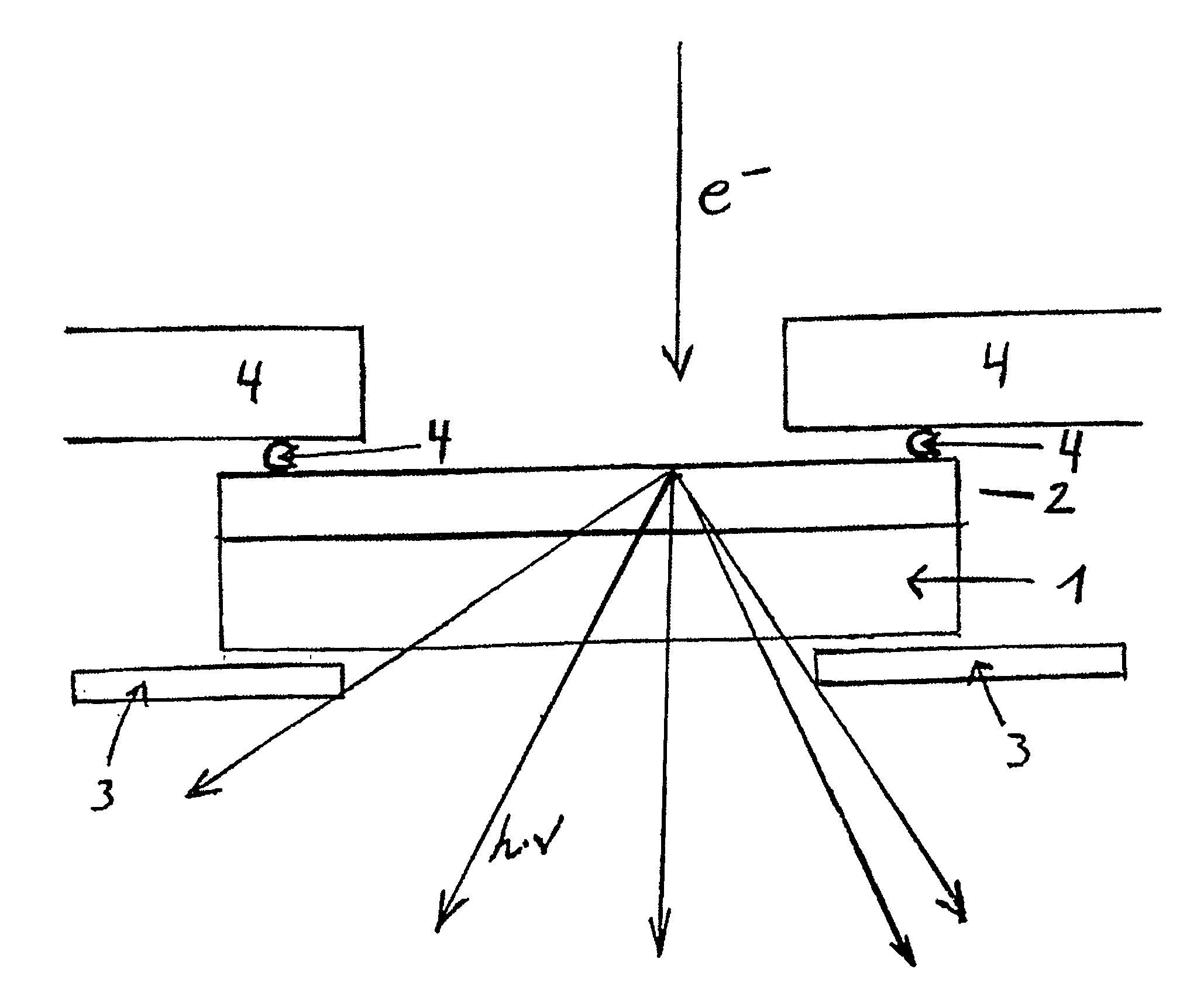
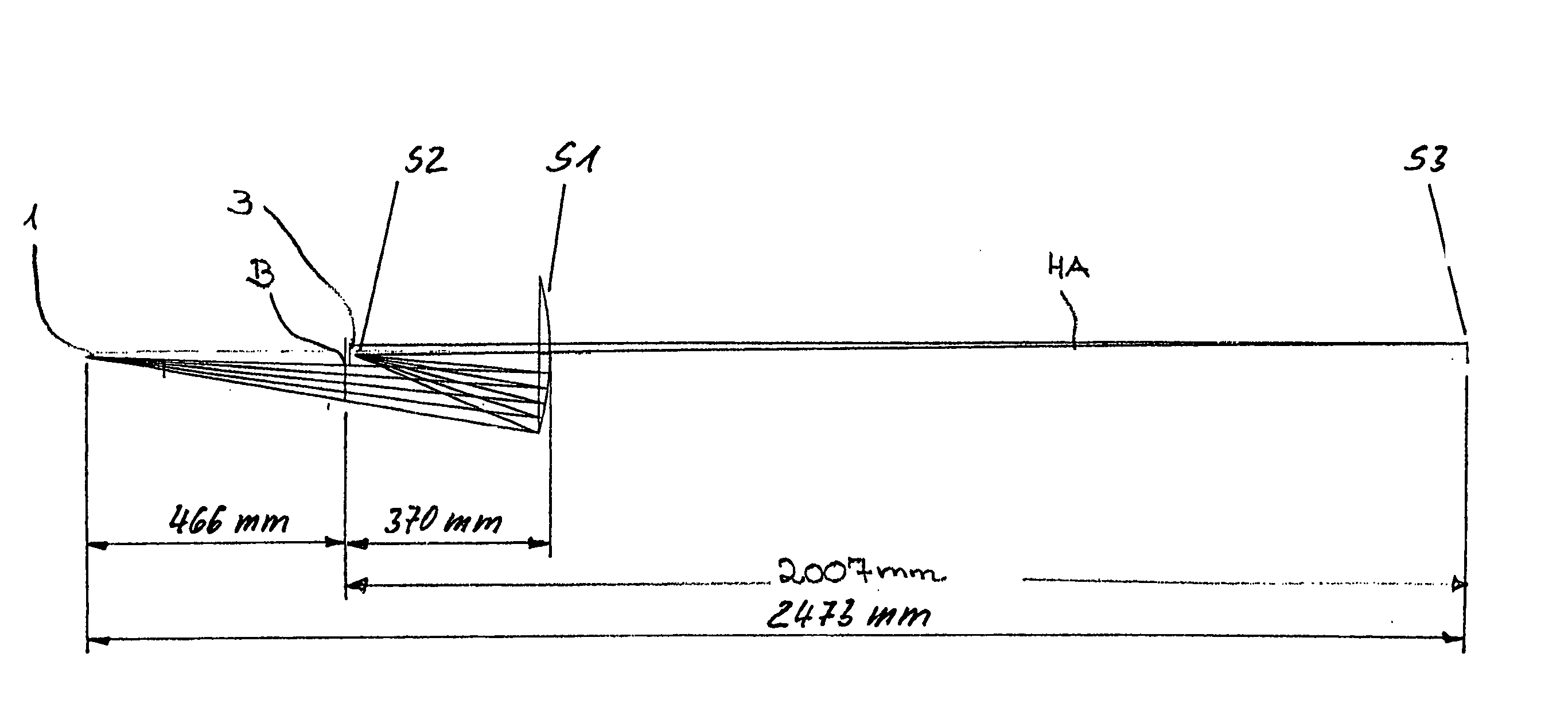
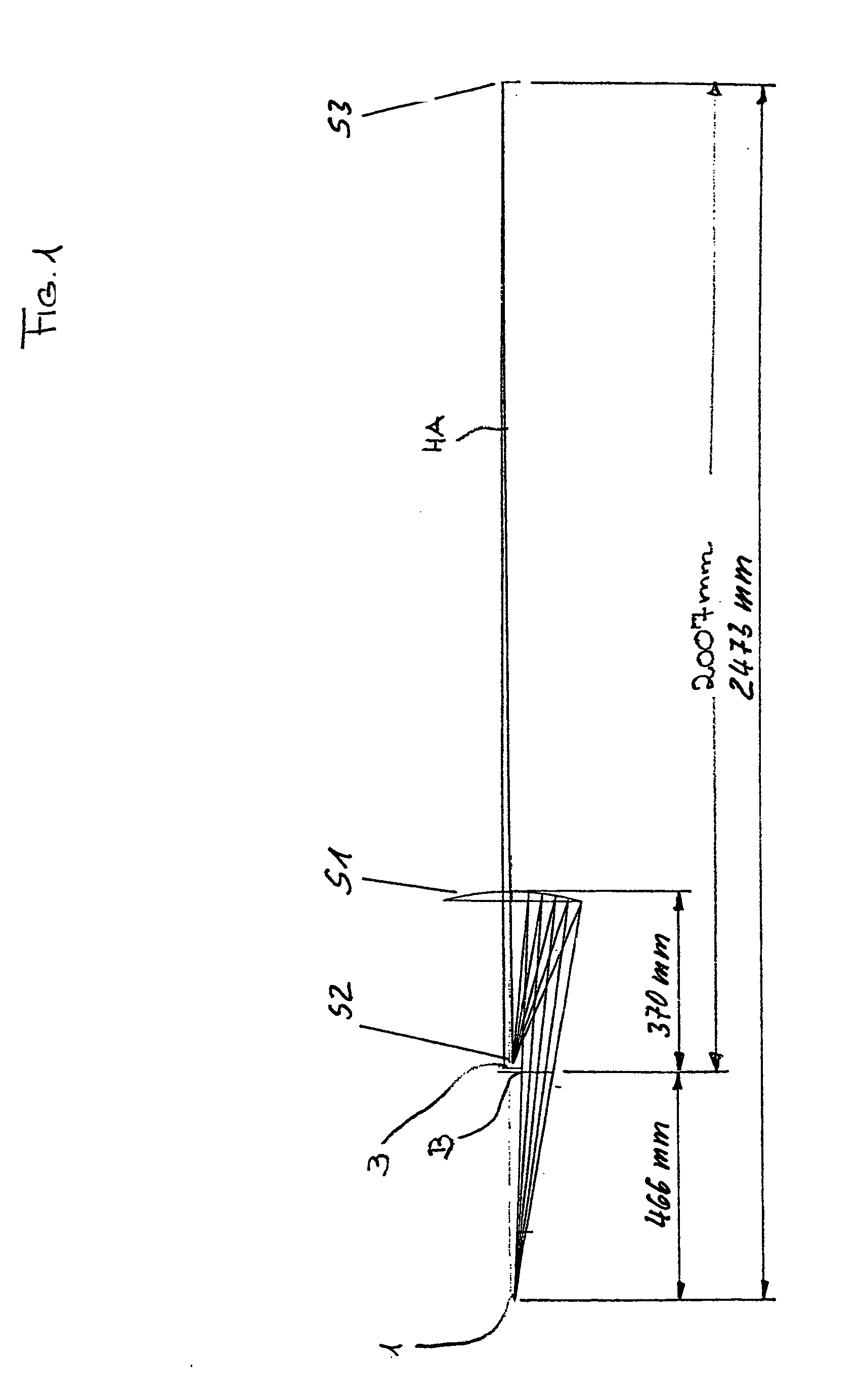
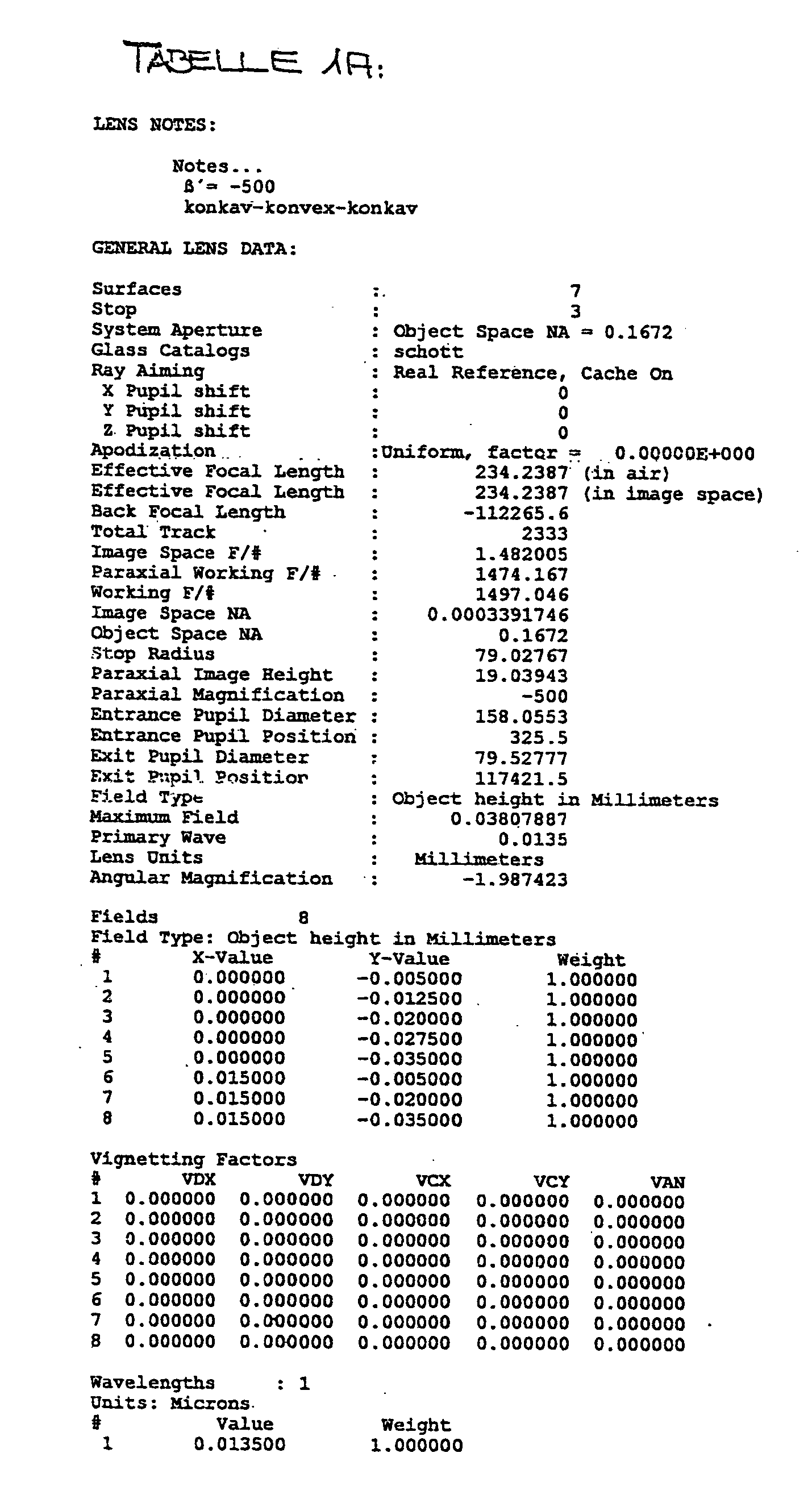
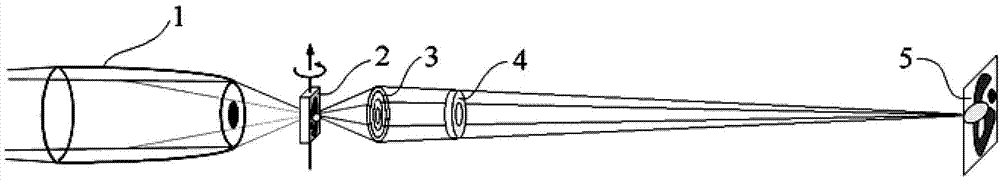
X-ray microscope
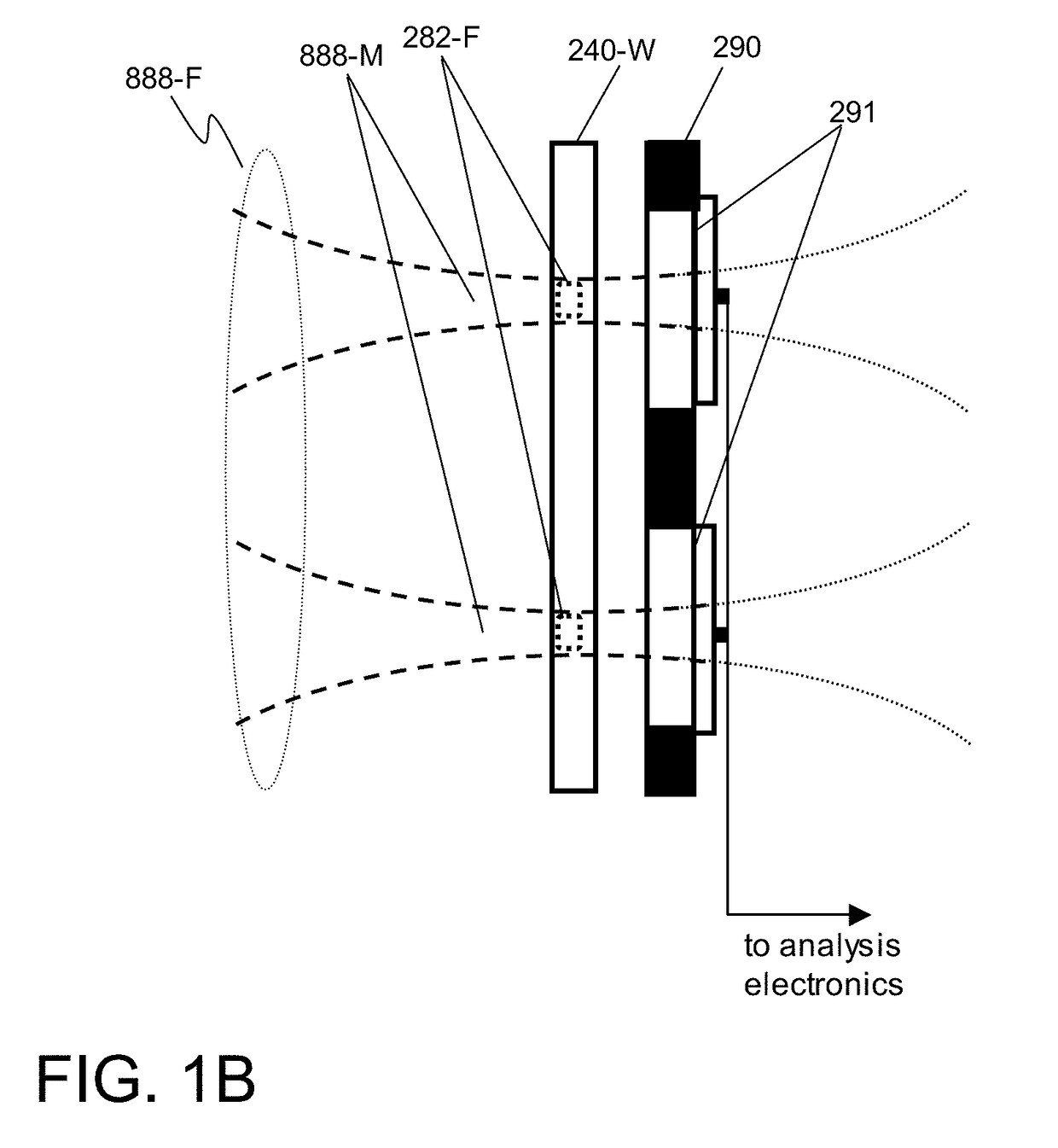
ActiveUS20180261352A1Reducing optical distanceHigh industrial applicabilityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPath lengthOptical axis
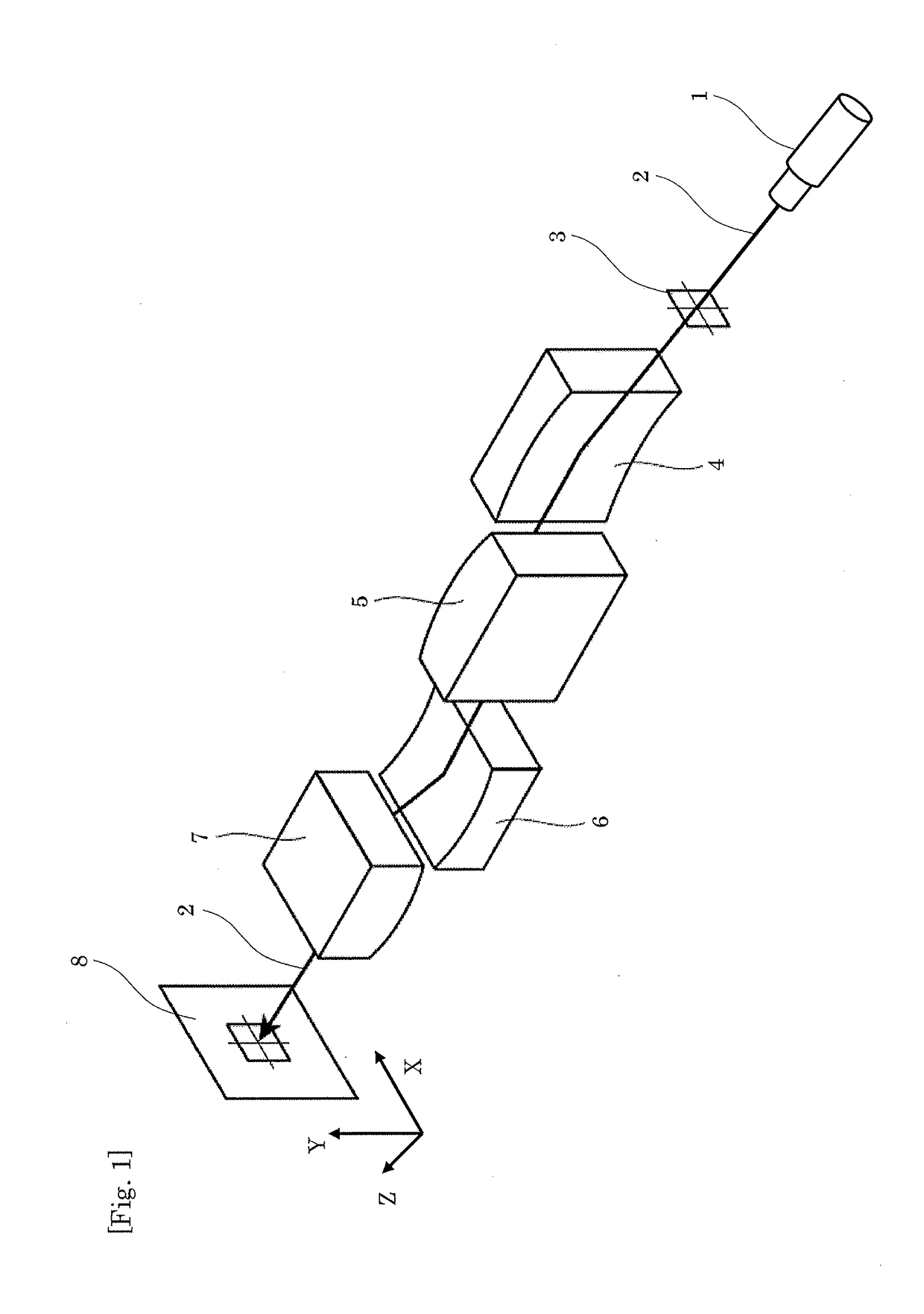
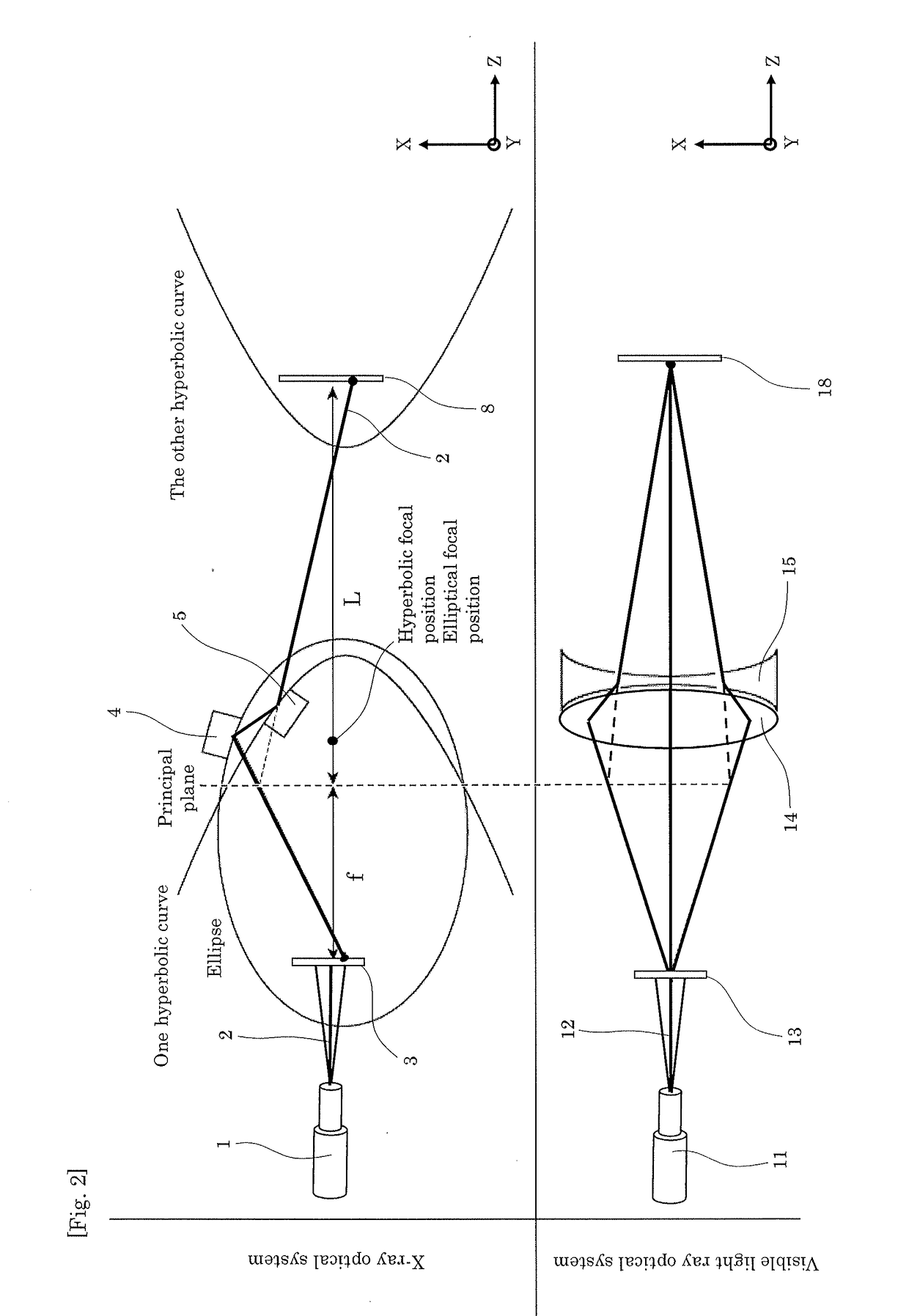
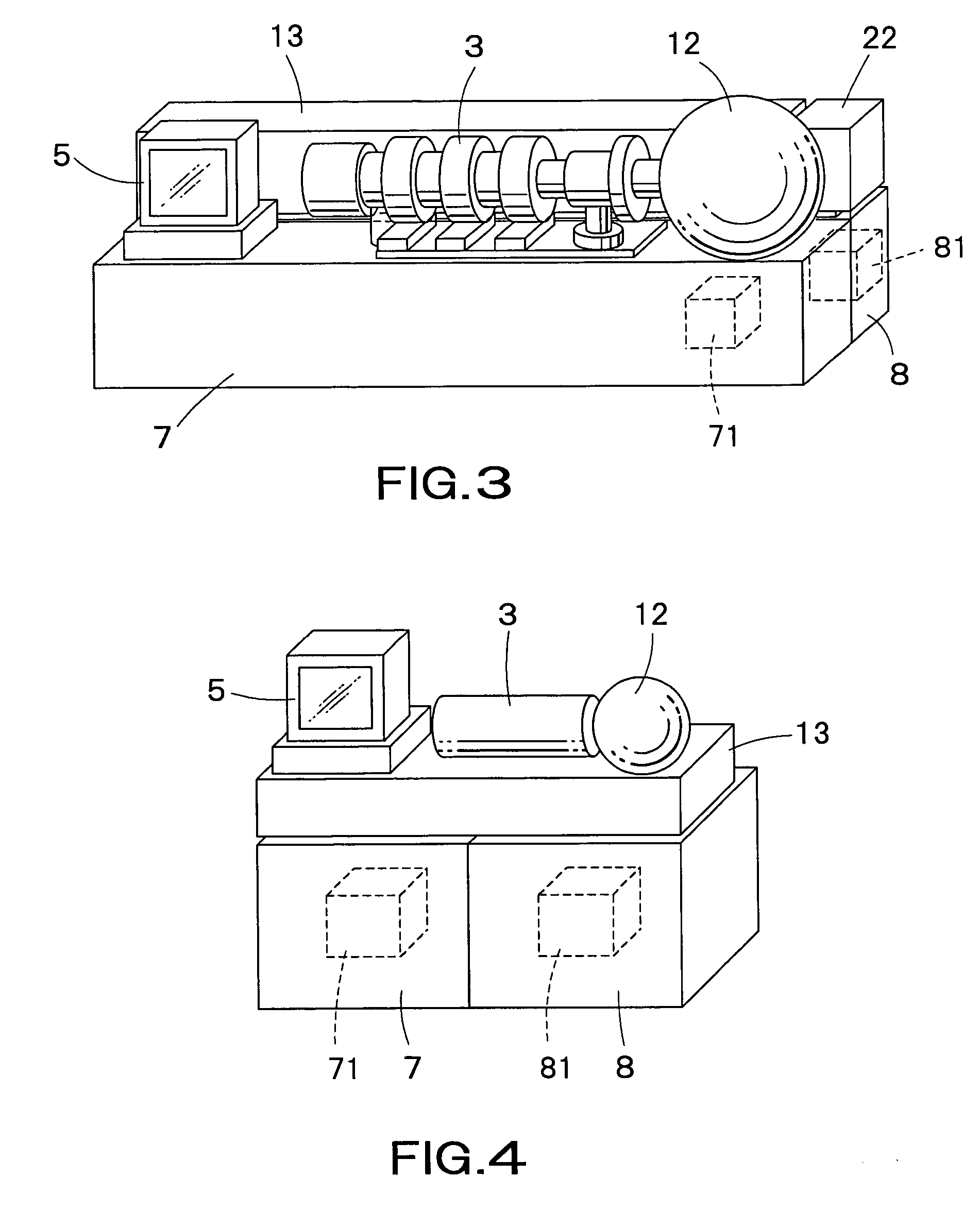
To provide an X-ray microscope that has a size small enough to be brought into a room by shortening the path length, an X-ray microscope including at least one of each of an X-ray source 1, a sample holding part 3, a concave KB mirror 4, a convex KB mirror 5, and a light receiving part 8 located at a position in an imaging relation to a position of the sample holding part 3 in this order along an optical axis is fabricated.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
X-ray microscope apparatus
InactiveUS7039157B2Small sizeEasy to useImage-conversion/image-amplification tubesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging processingPhotocathode
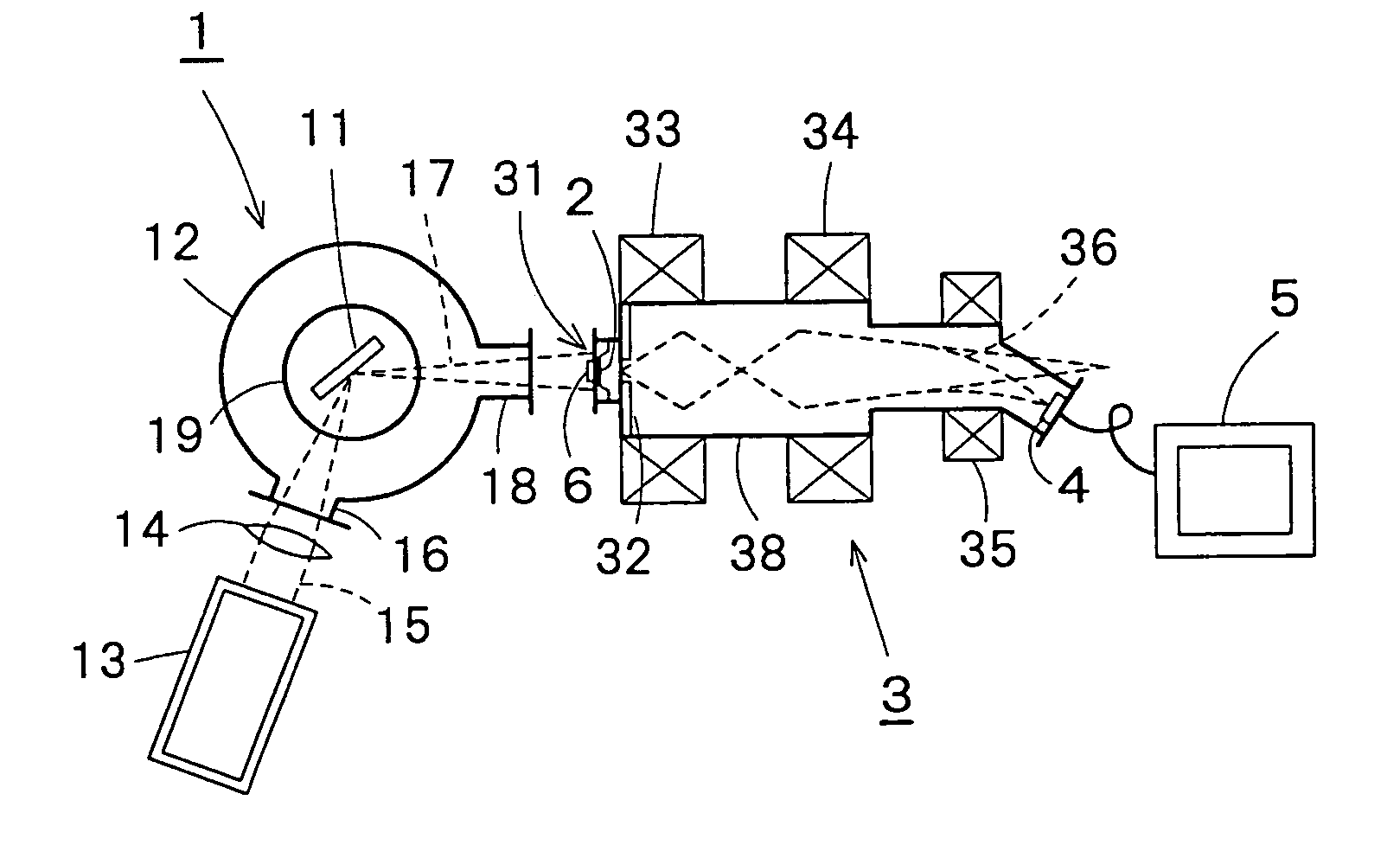
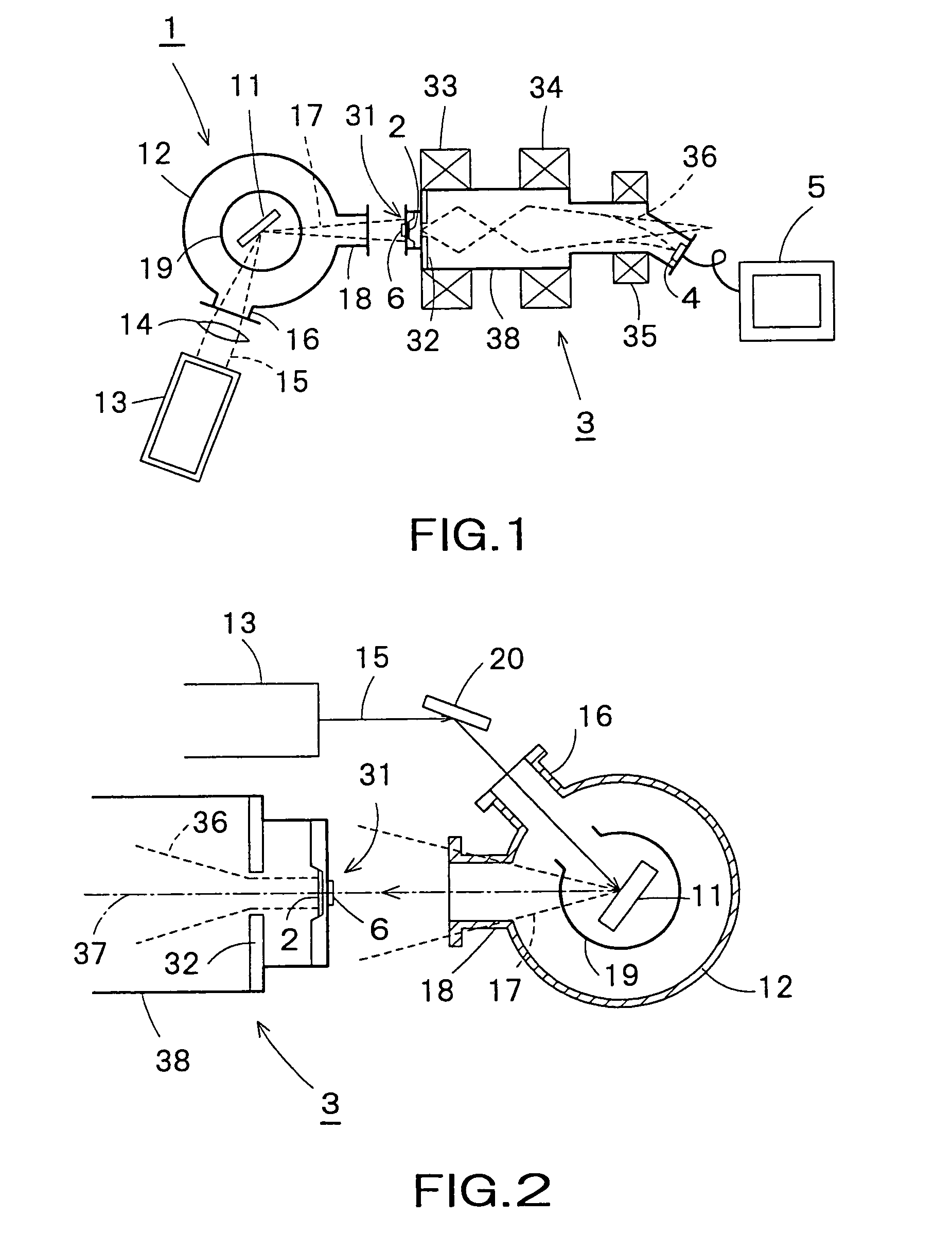
An X-ray microscope apparatus includes an X-ray generator, a photocathode disposed on a path of X-rays for producing electrons when irradiated with X-rays generated by the X-ray generator, an electron image enlarging device having an acceleration anode for accelerating electrons produced by the photocathode and a magnetic lens for enlarging and focusing an electron beam of electrons emitted by the photocathode, an electron beam detecting device for detecting the electron beam focused thereon by the electron image enlarging device; and an image processing device for processing an electron image formed by the electron beam detecting device. The X-ray microscope apparatus can be formed in compact construction.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
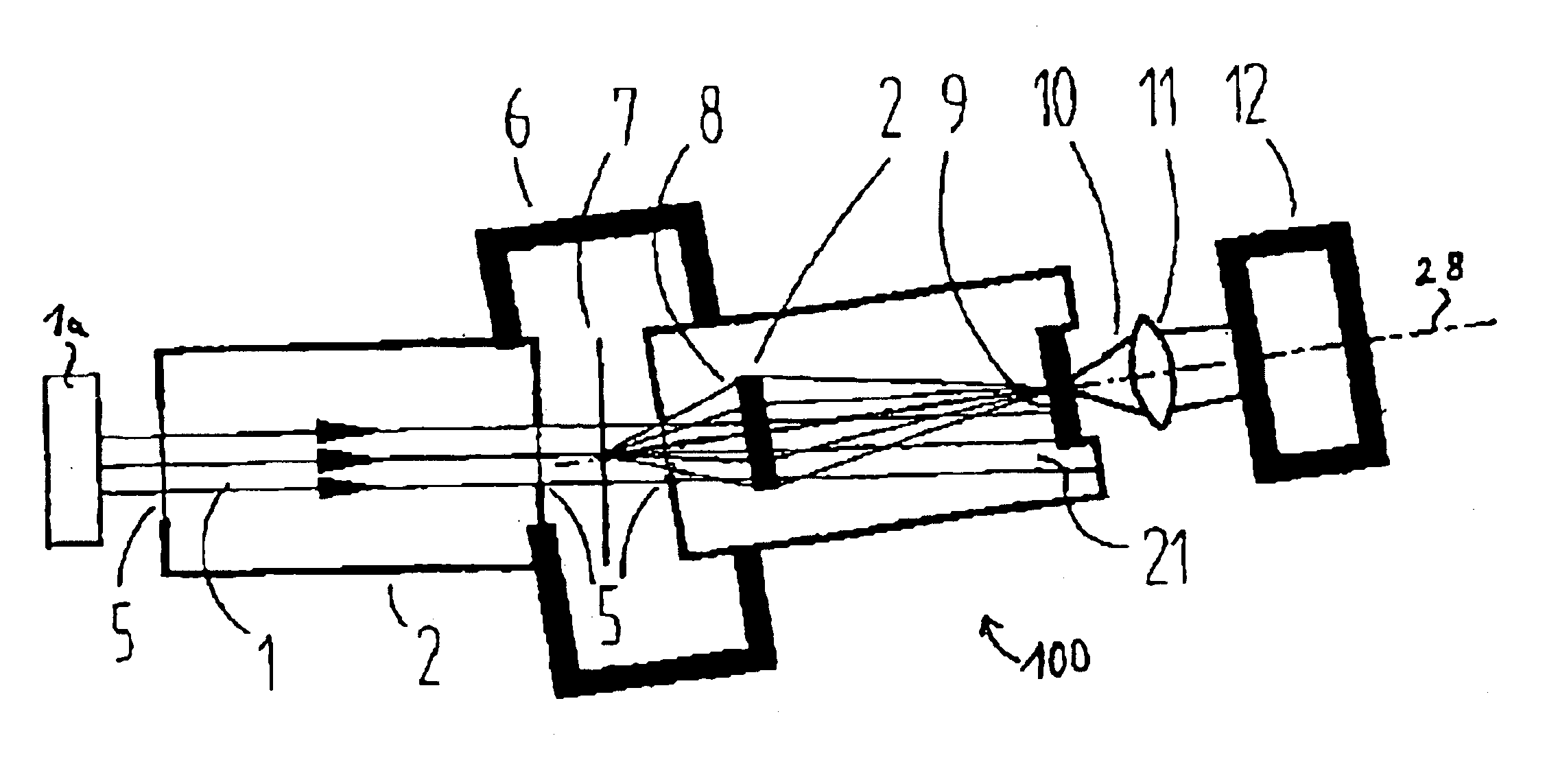
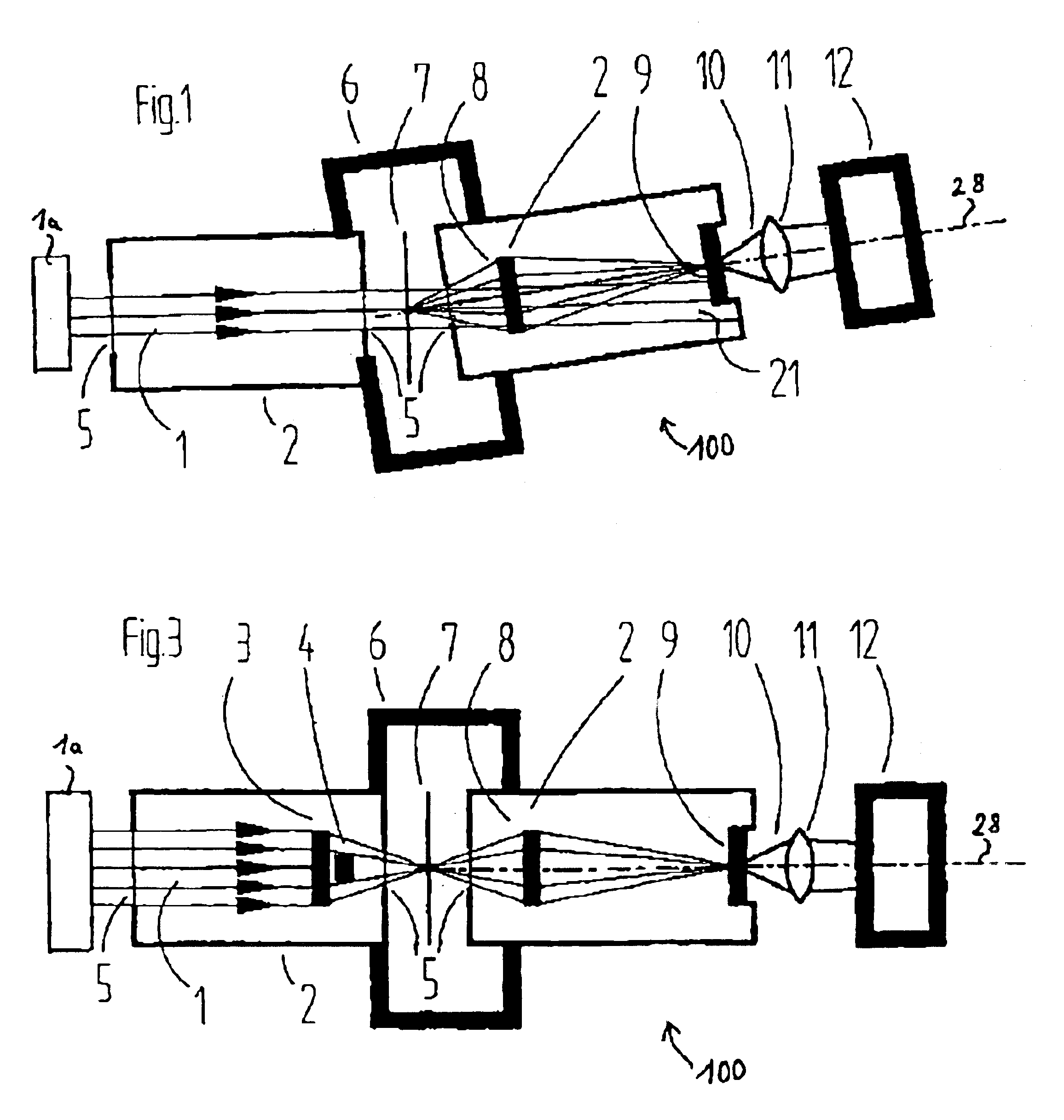
Reflective X-ray microscope and inspection system for examining objects with wavelengths <100 nm
ActiveUS7623620B2Small sizeNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionFluenceLight beam
There is provided a reflective X-ray microscope for examining an object in an object plane. The reflective X-ray microscope includes (a) a first subsystem, having a first mirror and a second mirror, disposed in a beam path from the object plane to the image plane, and (b) a second subsystem, having a third mirror, situated downstream of the first subsystem in the beam path. The object is illuminated with radiation having a wavelength <100 nm, and the reflective X-ray microscope projects the object with magnification into an image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
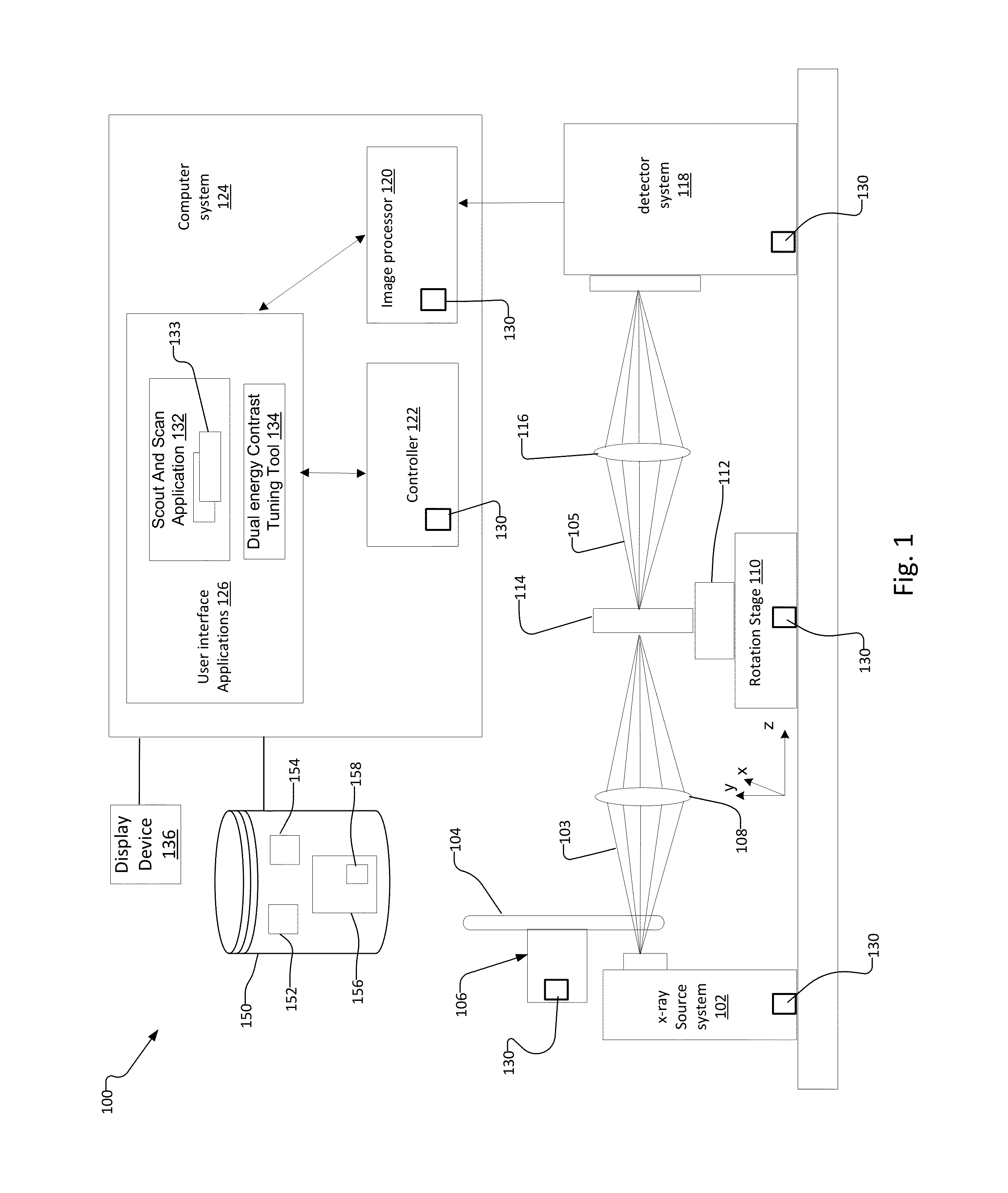
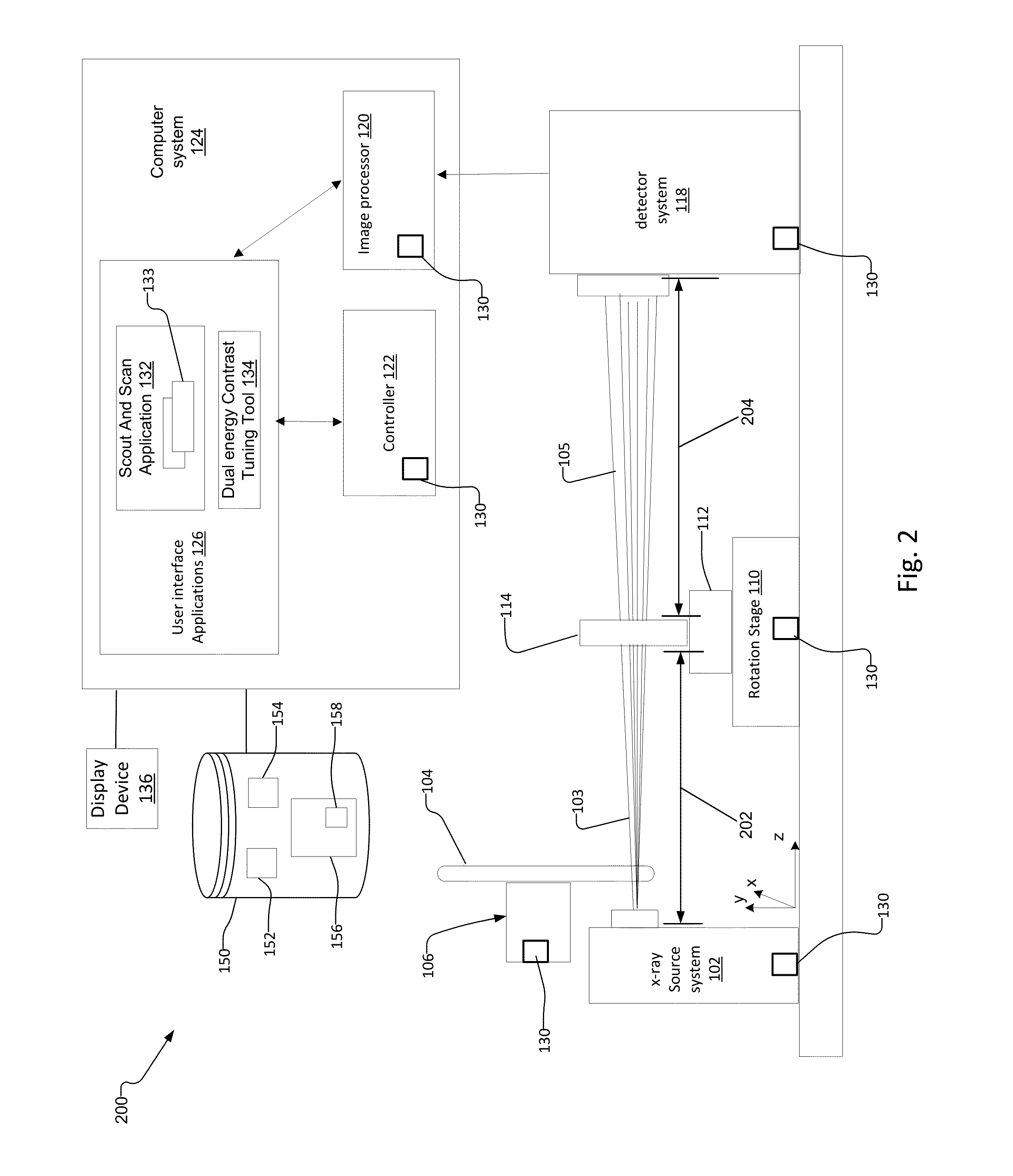
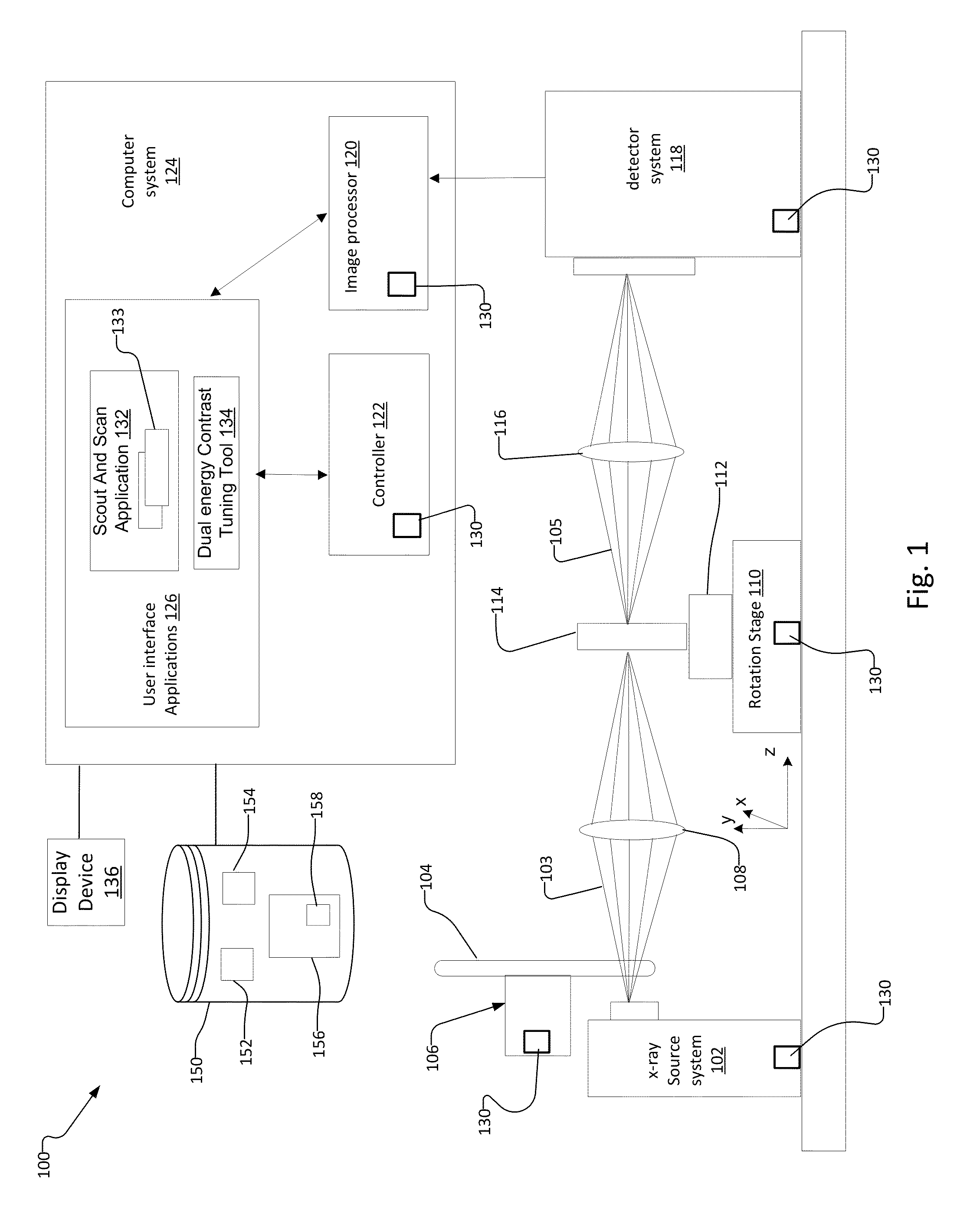
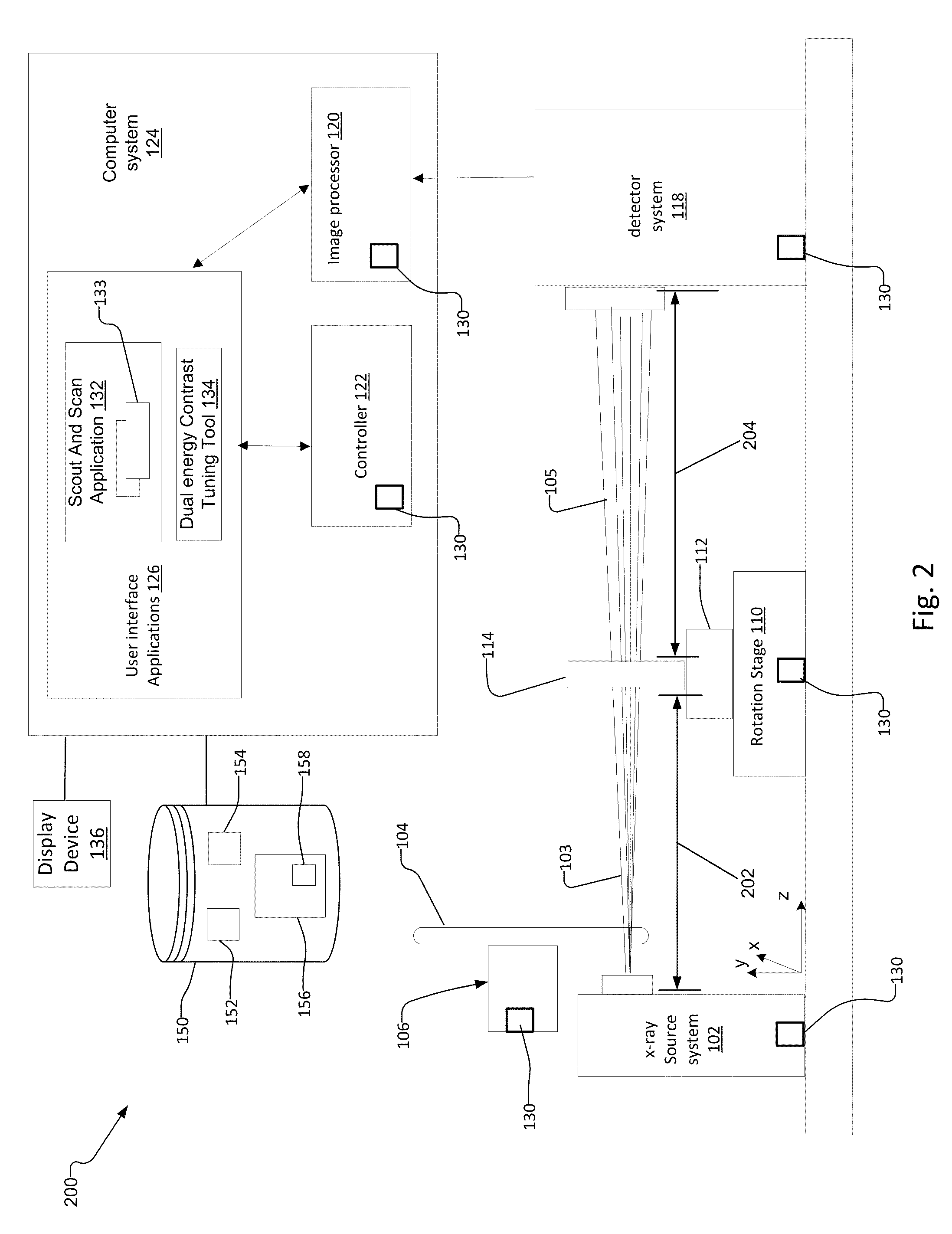
Multi Energy X-Ray Microscope Data Acquisition and Image Reconstruction System and Method
ActiveUS20140233692A1Increase contrastImprove image qualityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setHigh energy
A multi energy, such as dual-energy (“DE”), x-ray imaging system data acquisition and image reconstruction system and method enables optimizing the image contrast of a sample. Using the DE x-ray imaging system and its associated user interface applications, an operator performs a low energy (“LE”) and high energy (“HE”) x-ray scan of the same volume of interest of the sample. The system creates a low-energy reconstructed tomographic volume data set from the set of low-energy projections and a high-energy tomographic volume data set from the set of high-energy projections. This enables the operator to control the image contrast of selected slices, and apply the information associated with optimizing the contrast of the selected slice to all slices in the low-energy and high-energy tomographic data sets. This creates a combined volume data set from the LE and HE volume data sets with optimized image contrast throughout.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Method for examining structures on a semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS6859516B2Avoid damageShort exposure timeImaging devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSoft x rayImage resolution
Owner:SCHNEIDER GERD DR +1
Method and apparatus for x-ray microscopy
ActiveUS10352880B2Increase in sizeImprove detection efficiencyImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesQuantum efficiencyImage resolution
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray microscopy using an array of micro-beams having a micro- or nano-scale beam intensity profile to provide selective illumination of micro- or nano-scale regions of an object. An array detector is positioned such that each pixel of the detector only detects x-rays corresponding to a single micro- or nano-beam. This allows the signal arising from each x-ray detector pixel to be identified with the specific, limited micro- or nano-scale region illuminated, allowing sampled transmission image of the object at a micro- or nano-scale to be generated while using a detector with pixels having a larger size and scale. Detectors with higher quantum efficiency may therefore be used, since the lateral resolution is provided solely by the dimensions of the micro- or nano-beams. The micro- or nano-scale beams may be generated using an arrayed x-ray source or a set of Talbot interference fringes.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Reflective X-ray microscope and inspection system for examining objects with wavelengths < 100 nm
ActiveUS20050201514A1Small sizeAvoid disadvantagesNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionLight beamMagnification
There is provided a reflective X-ray microscope for examining an object in an object plane. The reflective X-ray microscope includes (a) a first subsystem, having a first mirror and a second mirror, disposed in a beam path from the object plane to the image plane, and (b) a second subsystem, having a third mirror, situated downstream of the first subsystem in the beam path. The object is illuminated with radiation having a wavelength <100 nm, and the reflective X-ray microscope projects the object with magnification into an image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
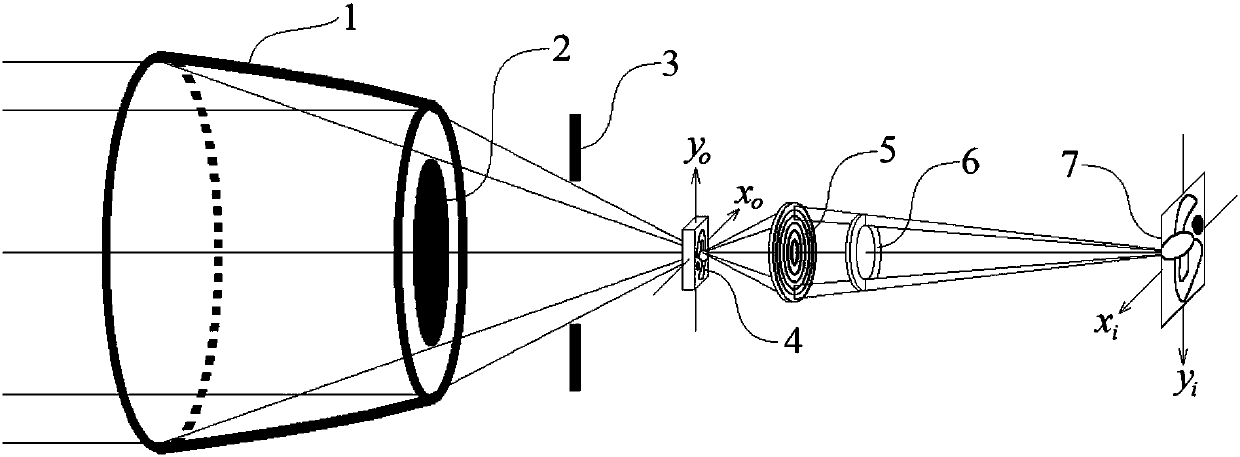
X ray differential phase contrast microscopic imaging system and imaging method
ActiveCN103364416AFast imagingSimple structureMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionRapid imagingSoft x ray
The invention relates to the technical field of nanometer resolution X ray wave zone plate microscopic imaging and specifically discloses an X ray differential phase contrast microscopic imaging system and an imaging method. The system sequentially comprises an X ray light source, a collecting lens, a sample stage, an X ray wave zone plate, an absorbing ring and an imaging detector along the X ray propagation direction. The X ray differential phase contrast microscopic imaging system is provided to overcome the defects of an X ray microscope taking a wave zone plate as an objective lens, and the X ray differential phase contrast microscopic imaging system and the two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional imaging method provided by the invention can be used for quickly imaging objects.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Talbot X-ray microscope
ActiveUS10304580B2Improve detection efficiencyIncrease in sizeImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationQuantum efficiencyImage resolution
Owner:SIGRAY INC
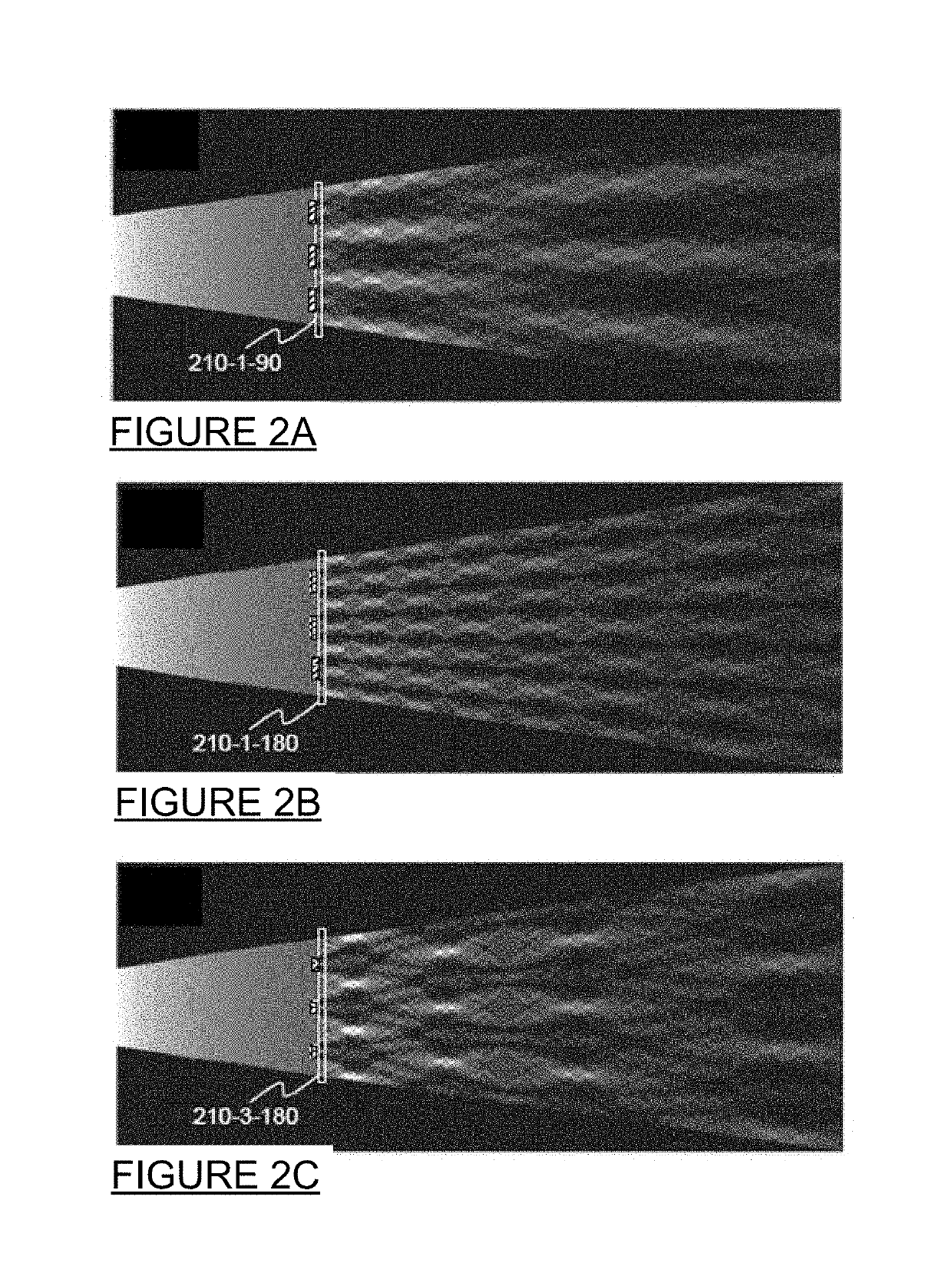
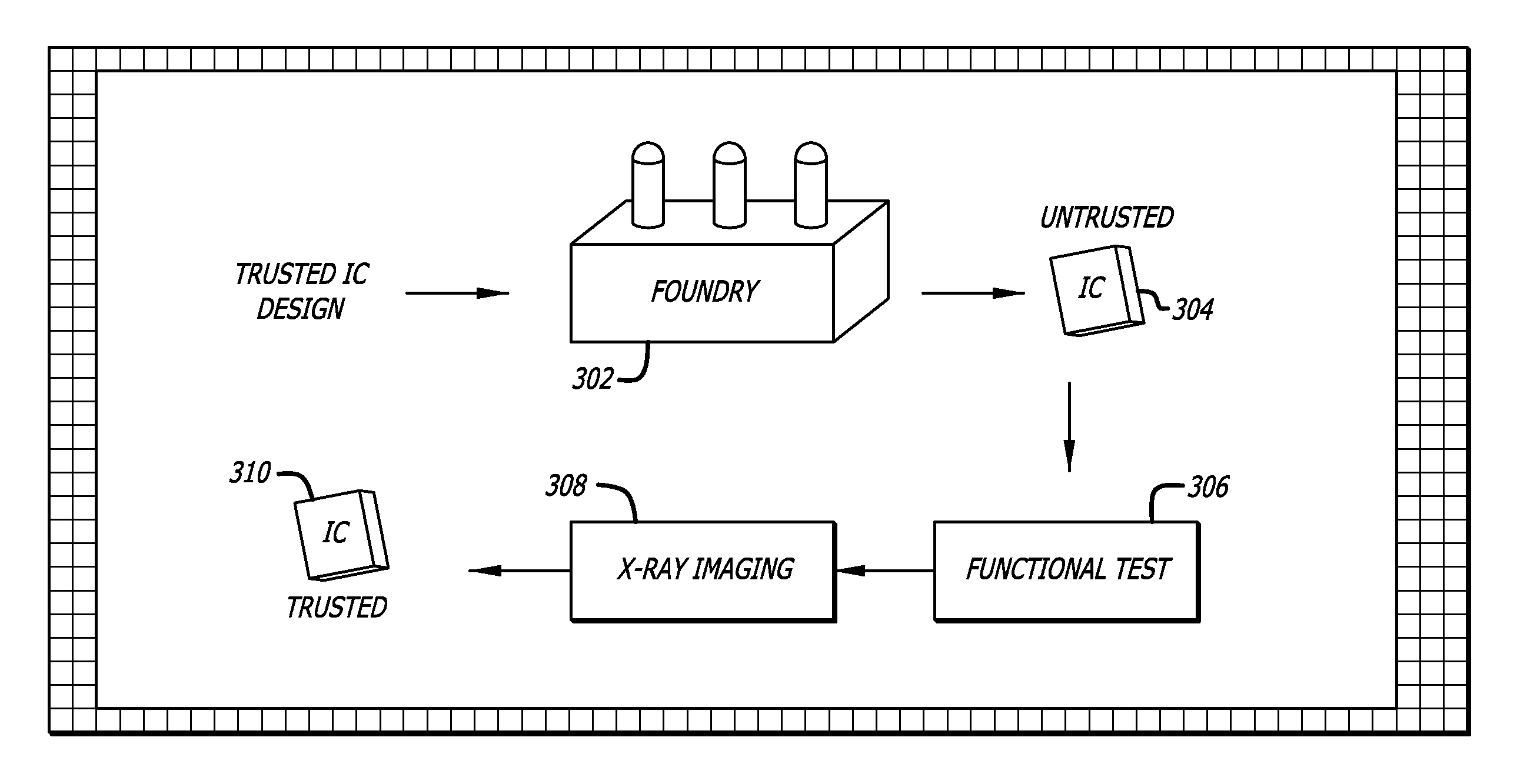
Verification of integrated circuits against malicious circuit insertions and modifications using non-destructive X-ray microscopy
ActiveUS8139846B2Low costBetter-facilitate x-ray inspectionImage enhancementImage analysisNon destructiveFoundry
A method and system for verifying the integrity of integrated circuits (ICs) by detecting the presence of unauthorized circuit insertions or modifications using non-destructive x-ray microscopy is disclosed. A reference image based on a trusted IC or a trusted design file may be generated. An un-trusted IC may be received from an un-trusted foundry, which IC is manufactured in response to the trusted design file provided to the foundry. An x-ray microscope may record a plurality of sets of base images of the un-trusted IC, each set corresponding to a different viewing angle. One or more un-trusted images may be produced from the base images. The reference images may be compared with the un-trusted images to illuminate any additions or modifications in circuit elements or other parameters.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY +1
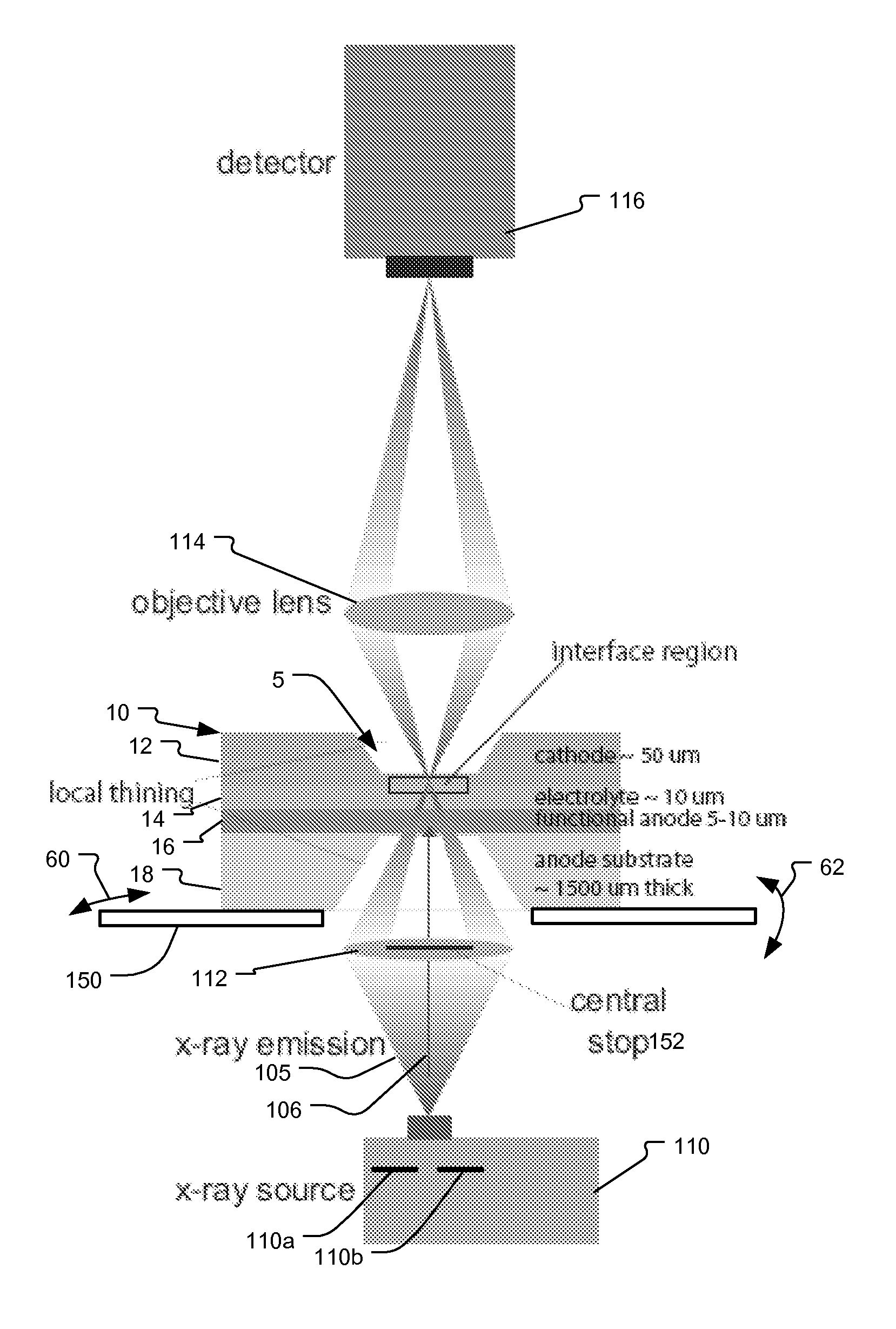
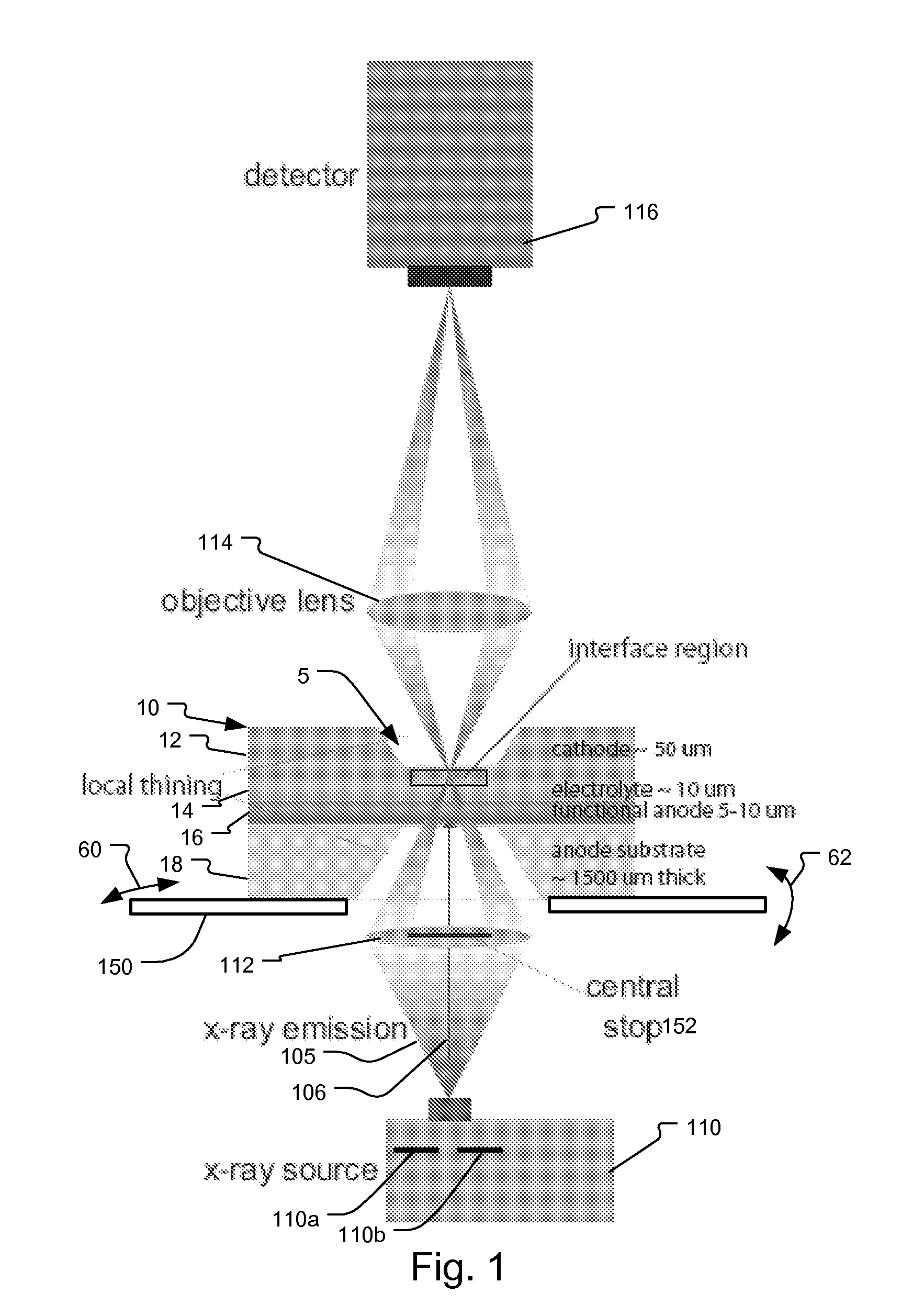
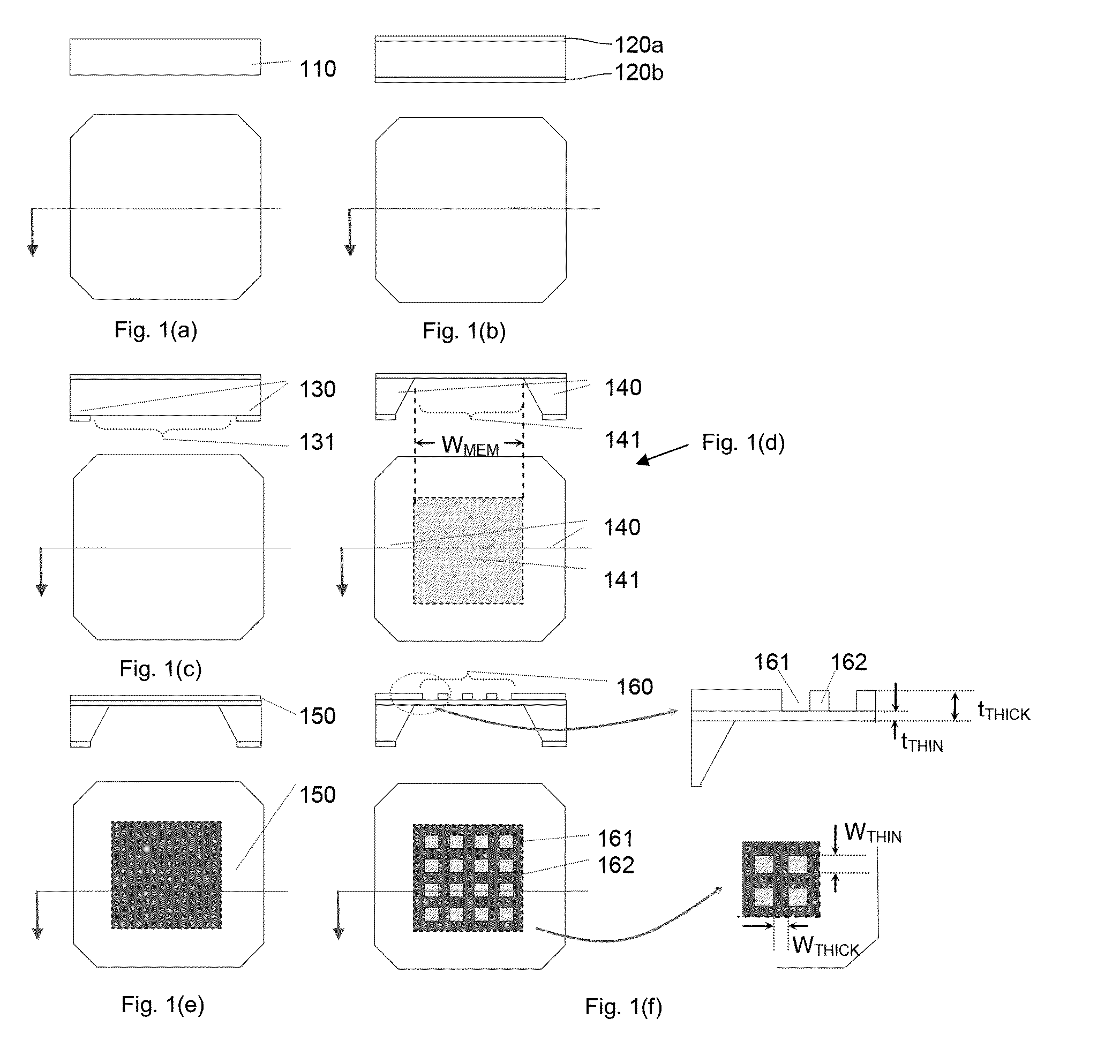
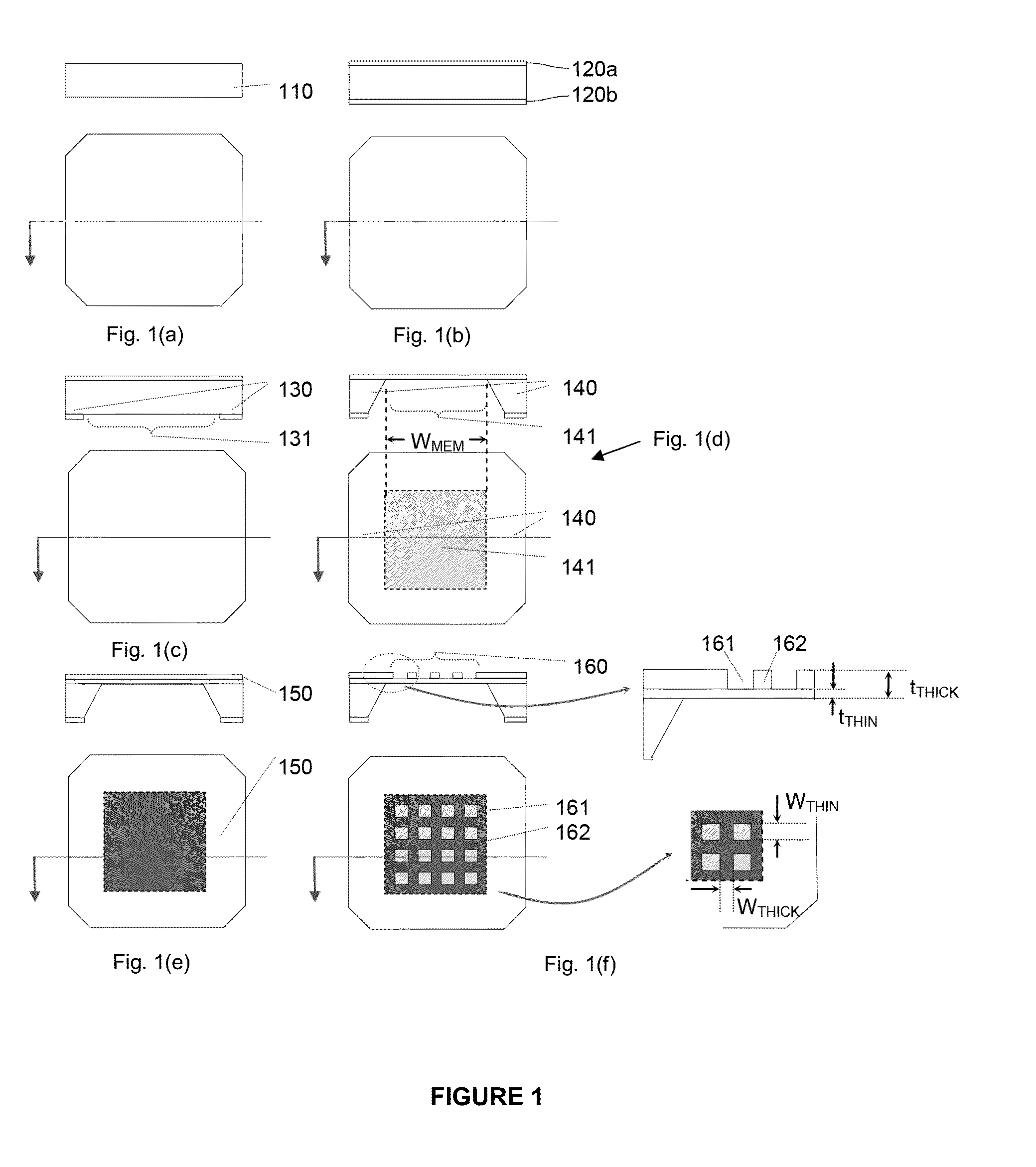
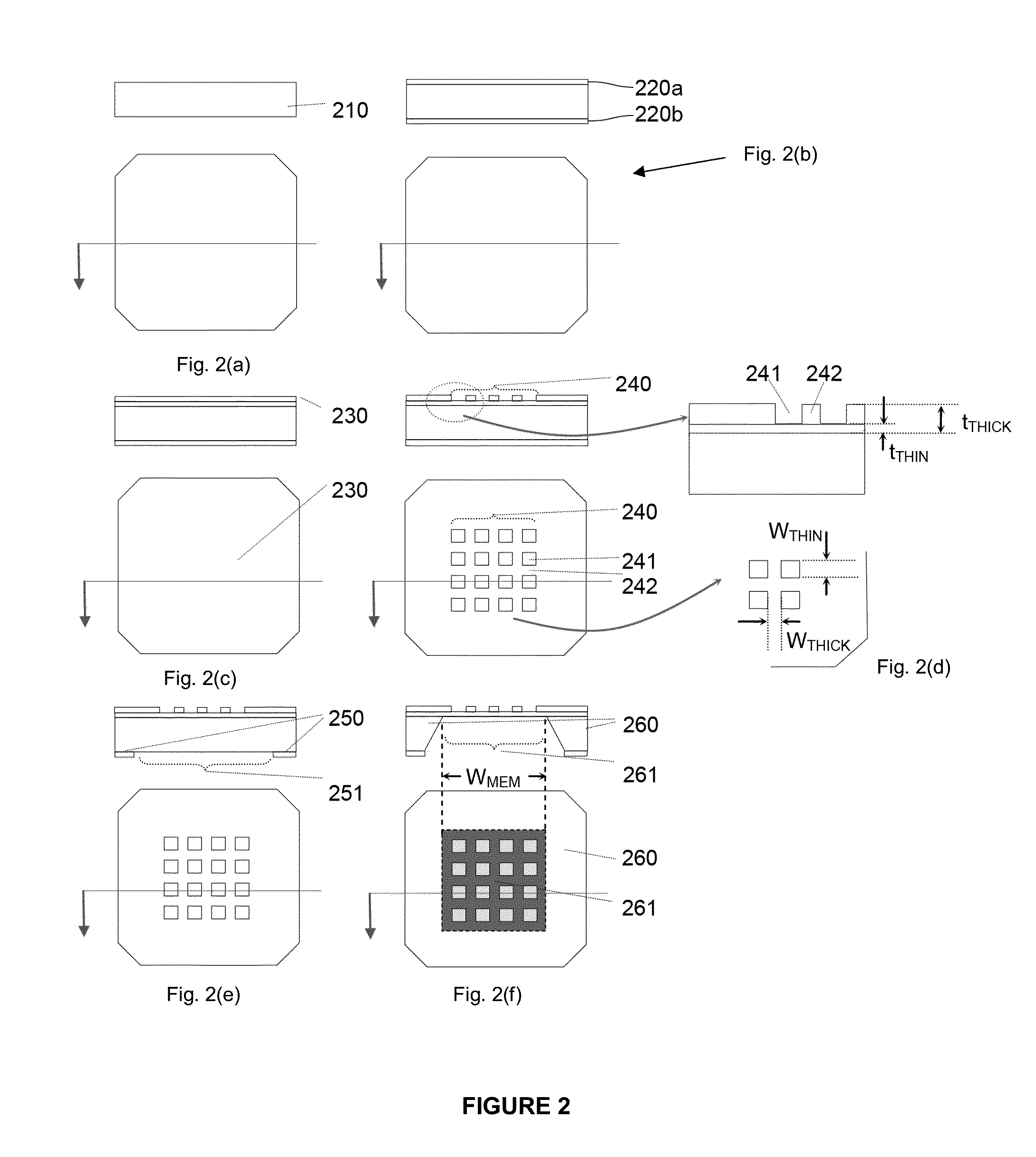
Specimen supporting member for x-ray microscope image observation, specimen containing cell for x-ray microscope image observation, and x-ray microscope
InactiveUS20120321037A1Reduce harmConveniently performedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesCarbon filmX-ray
A specimen supporting member (10) includes: a specimen supporting film (11) such as a silicon nitride film, a carbon film, and a polyimide film; an X-ray radiation film (13) provided on one principal surface of the specimen supporting film, and for radiating a characteristic X-ray in a soft X-ray region upon irradiation with charged particles; and a specimen adsorption film (12) which is a metal film provided on another principal surface of the specimen supporting film (11), and which fixes by adsorption a specimen (1) to be observed. Since a protein which is a constitutive substance of a biological specimen has a characteristic to easily adsorb to a metallic ion, a specimen adsorption film (12) is formed on one principal surface of the specimen supporting film (11) so that an observation specimen adsorbs thereto.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
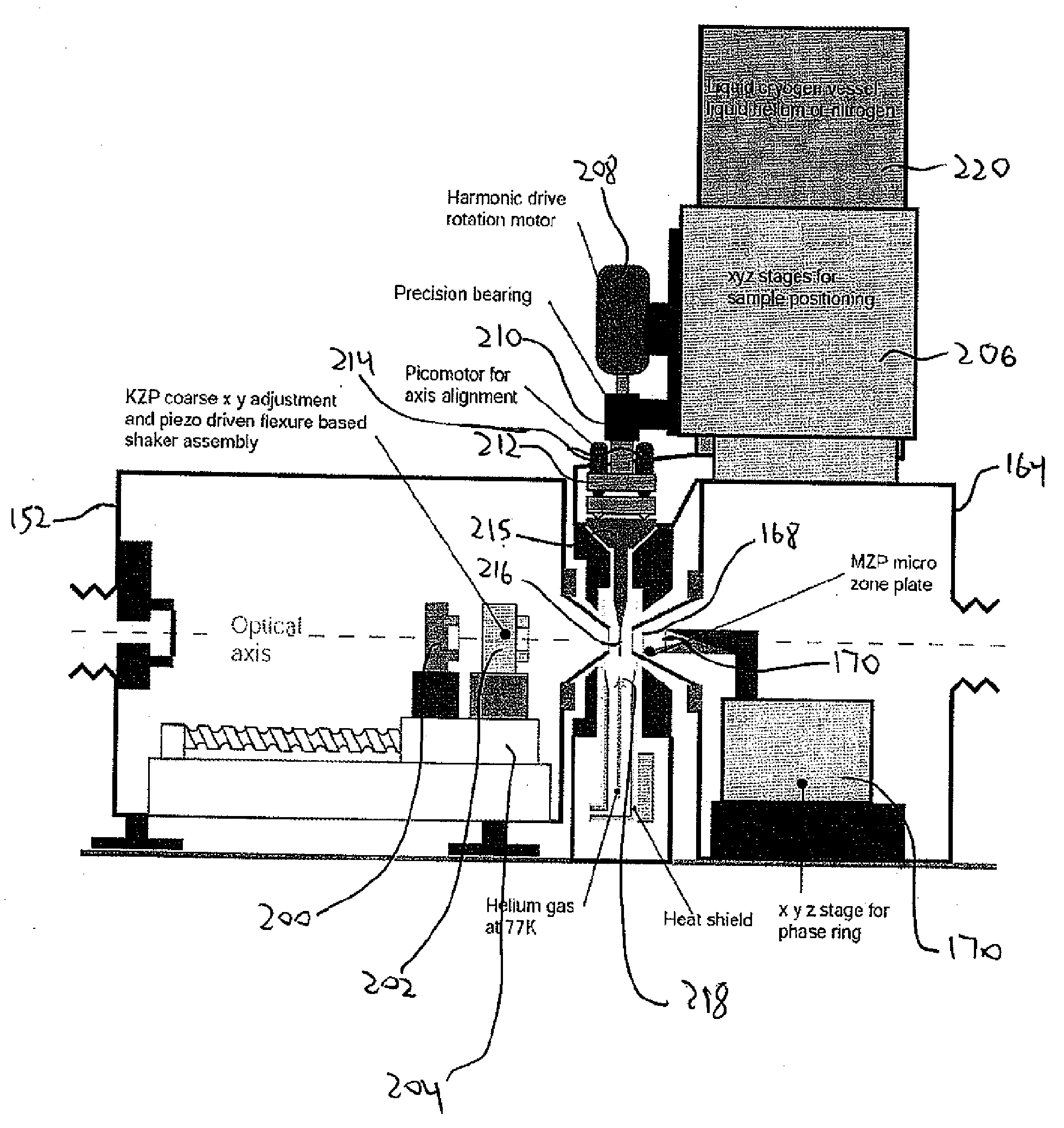
Cryotomography X-Ray Microscopy State
An x-ray microscope stage enables alignment of a sample about a rotation axis to enable three dimensional tomographic imaging of the sample using an x-ray microscope. A heat exchanger assembly provides cooled gas to a sample during x-ray microscopic imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi energy X-ray microscope data acquisition and image reconstruction system and method
ActiveUS9128584B2Improve image contrastIncrease contrastImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setHigh energy
A multi energy, such as dual-energy (“DE”), x-ray imaging system data acquisition and image reconstruction system and method enables optimizing the image contrast of a sample. Using the DE x-ray imaging system and its associated user interface applications, an operator performs a low energy (“LE”) and high energy (“HE”) x-ray scan of the same volume of interest of the sample. The system creates a low-energy reconstructed tomographic volume data set from the set of low-energy projections and a high-energy tomographic volume data set from the set of high-energy projections. This enables the operator to control the image contrast of selected slices, and apply the information associated with optimizing the contrast of the selected slice to all slices in the low-energy and high-energy tomographic data sets. This creates a combined volume data set from the LE and HE volume data sets with optimized image contrast throughout.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Membrane supports with reinforcement features
ActiveUS9040939B2Electric discharge tubesPreparing sample for investigationNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceX-ray
Owner:PROTOCHIPS
High-precision x-ray microscope sample scanning table with metering rotary shaft
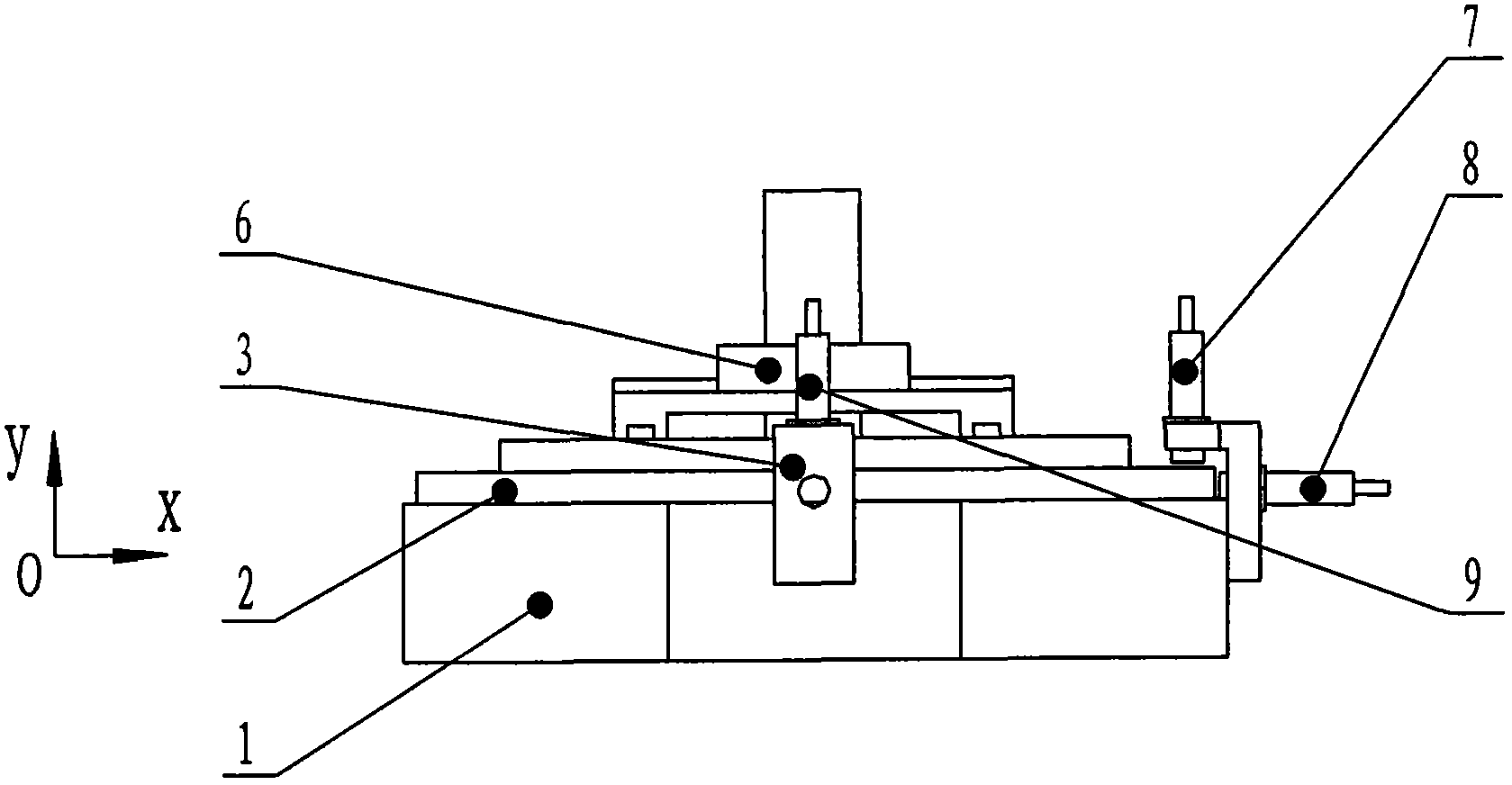
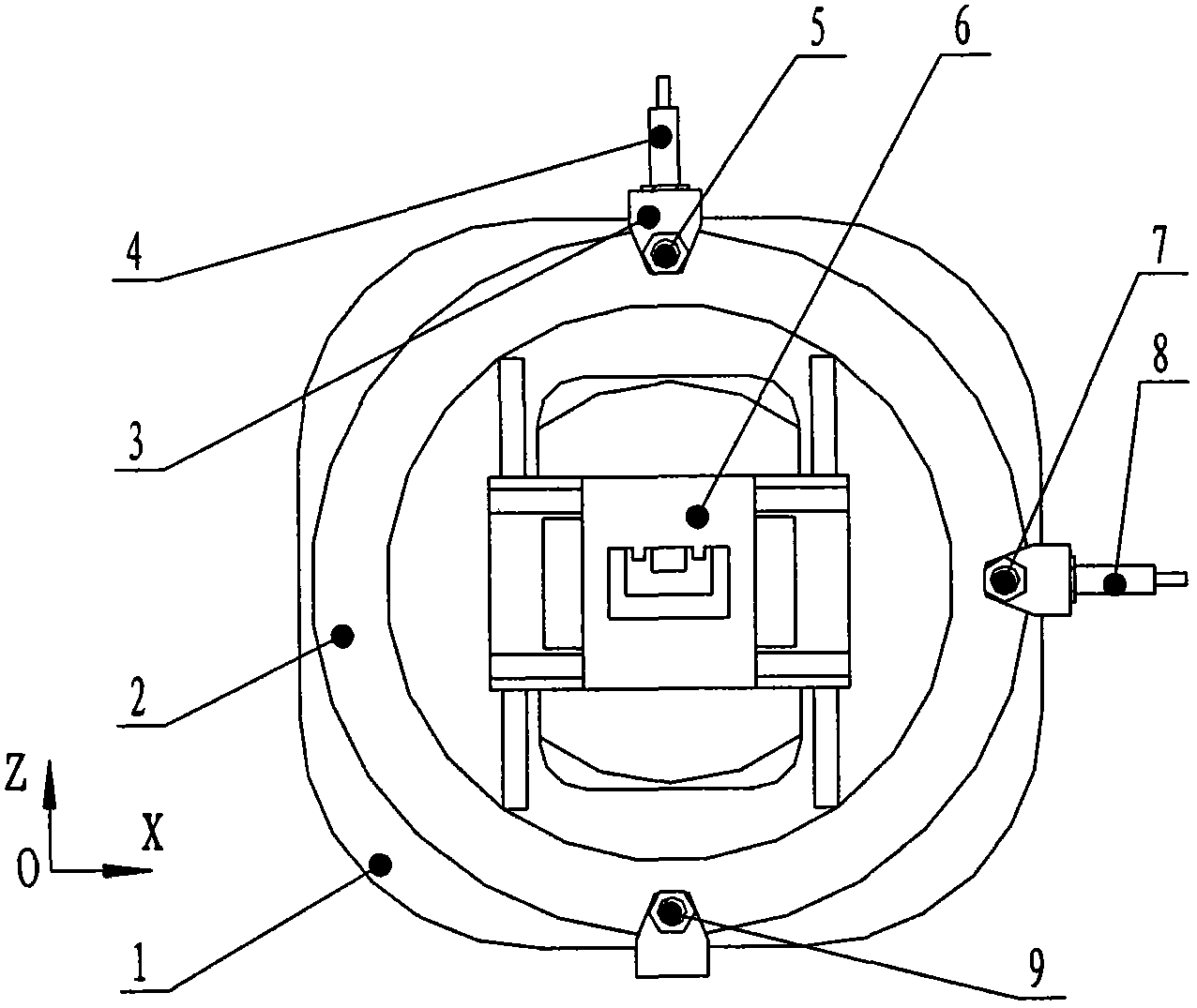
ActiveCN102692421AReduce or eliminate distortionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPosition errorDistortion problem
The invention discloses a high-precision x-ray microscope sample scanning table with a metering rotary shaft. A scanning rotary table (2) is arranged on a fixed base (1); a drive device of the scanning rotary table (2) is arranged outside the fixed base (1) and is used for driving the scanning rotary table (2) to rotate; a three-dimensional positioning platform (6) is fixedly arranged on the upper part of the scanning rotary table (2); a sensor installation seat (3) is arranged outside the fixed base (1); a Z-direction run-out error measuring sensor (4), an X-direction run-out error measuring sensor (8), a first swing error measuring sensor (5), a second swing error measuring sensor (7) and a third swing error measuring sensor (9) are respectively arranged on the sensor installation seat (3); the error correction is carried out on the scanning rotary table (2) by using an active correction control method according to the size of the errors measured by each sensor, and the run-out error correction is also can be carried out in a three-dimensional image reconstructing process by using a mathematical algorithm, so that a scanned image distortion problem caused by position error precision of the rotary table rotary shaft can be reduced or eliminated.
Owner:天津三英精密仪器股份有限公司
Membrane supports with reinforcement features
InactiveUS20150338322A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceX-ray
A sample support structure with integrated support features and methods of making and using the reinforced membrane. The sample support structures are useful for supporting samples for analysis using microscopic techniques, such as electron microscopy, optical microscopy, x-ray microscopy, UV-VIS spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques.
Owner:PROTOCHIPS
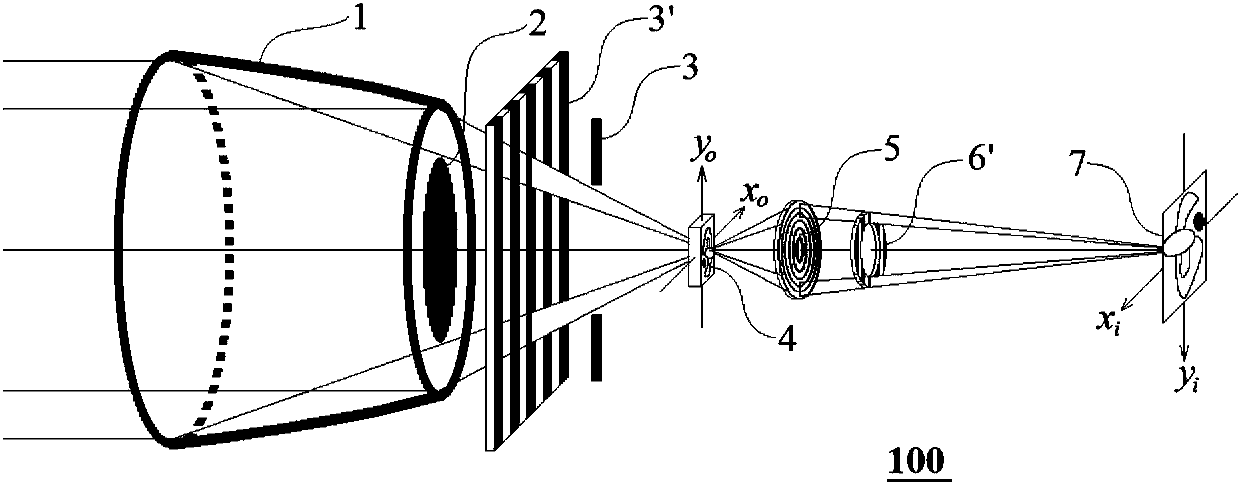
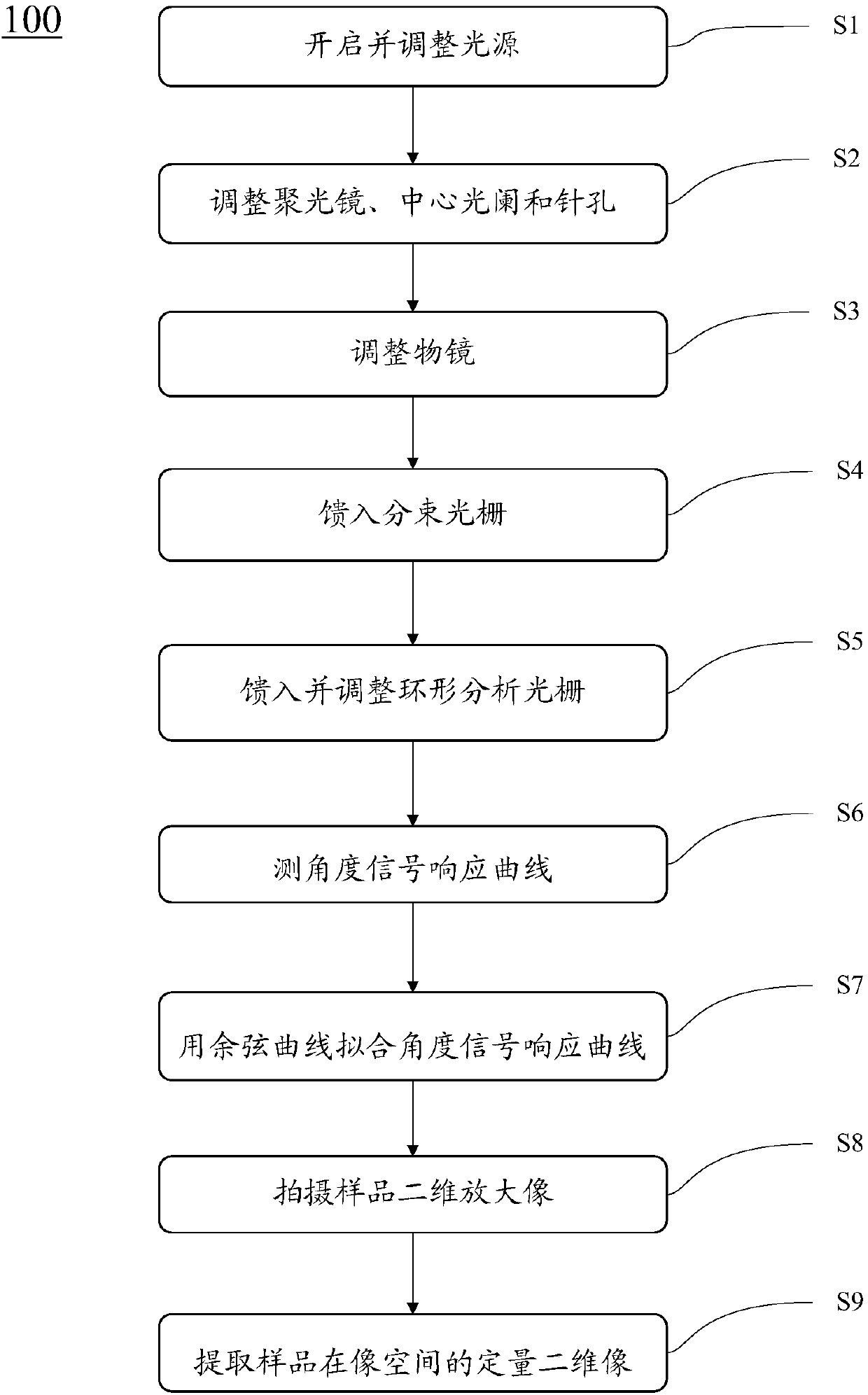
X-ray differential phase contrast microscope system and two-dimensional imaging method thereof
ActiveCN107664648AShorten the lengthReduce manufacturing costMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayConventional X-Ray
The invention discloses an X-ray differential phase contrast microscope system and a two-dimensional imaging method thereof. The X-ray differential phase contrast microscope system comprises a light source, a convergent lens, a center diaphragm, a beam splitting grating, a pin hole, a sample table, an object lens, an annular analysis grating and an imaging detector, wherein the light source is used for generating X rays; the convergent lens, the center diaphragm, the beam splitting grating, the pin hole, the sample table, the object lens, the annular analysis grating and the imaging detector are sequentially arranged in the X-ray spreading direction. The X-ray differential phase contrast microscope system has the beneficial effects that the X-ray differential phase contrast microscope system can realize the phase contrast quantitative imaging only through adding the beam splitting grating and the annular analysis grating in the conventional X-ray microscope; the advantages of simple structure and easy popularization are realized. In addition, the X-ray light source, the convergent lens and the beam splitting grating can be integrated into an X-ray annular grating source element; the length of the whole X-ray phase contrast microscope system can be further reduced; the manufacturing cost of the X-ray microscope system can be reduced; in addition, the light utilization efficiencyis further improved.
Owner:济南汉江光电科技有限公司
Intensity calibration method of grazing incidence X-ray microscope
ActiveCN108169790ARealize full spectrum measurementIncrease brightnessRadiation measurementRaman microscopeEnergy spectrum
The present invention relates to an intensity calibration method of a grazing incidence X-ray microscope. The method comprises the following steps of: installing each experiment part in a system and performing regulation of the experiment parts to allow the system to achieve an optimal resolution; moving a pin hole diaphragm to measure the emitting spectrum of each field-of-view position; moving out an X-ray microscope from an optical path, and measuring the incident spectrum of the system in each field of view at the rear portion of the aperture diaphragm; employing the measured emitting spectrums and the incident spectrums to perform counting of photons in an energy resolution range, and calculating the object lens reflectivity of each field of view; and employing the object lens reflectivity to calculate the system response efficiency; and according to the system response efficiency of the microscope, the filter disc transmittance and the camera quantum efficiency, calculating and obtaining the source intensity of an implosion pellet. Compared to the prior art, the intensity calibration method of the grazing incidence X-ray microscope considers the consistency of the fields of view, completes the calibration of the optical system energy spectrum response efficiency, and is more suitable for laboratories.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com