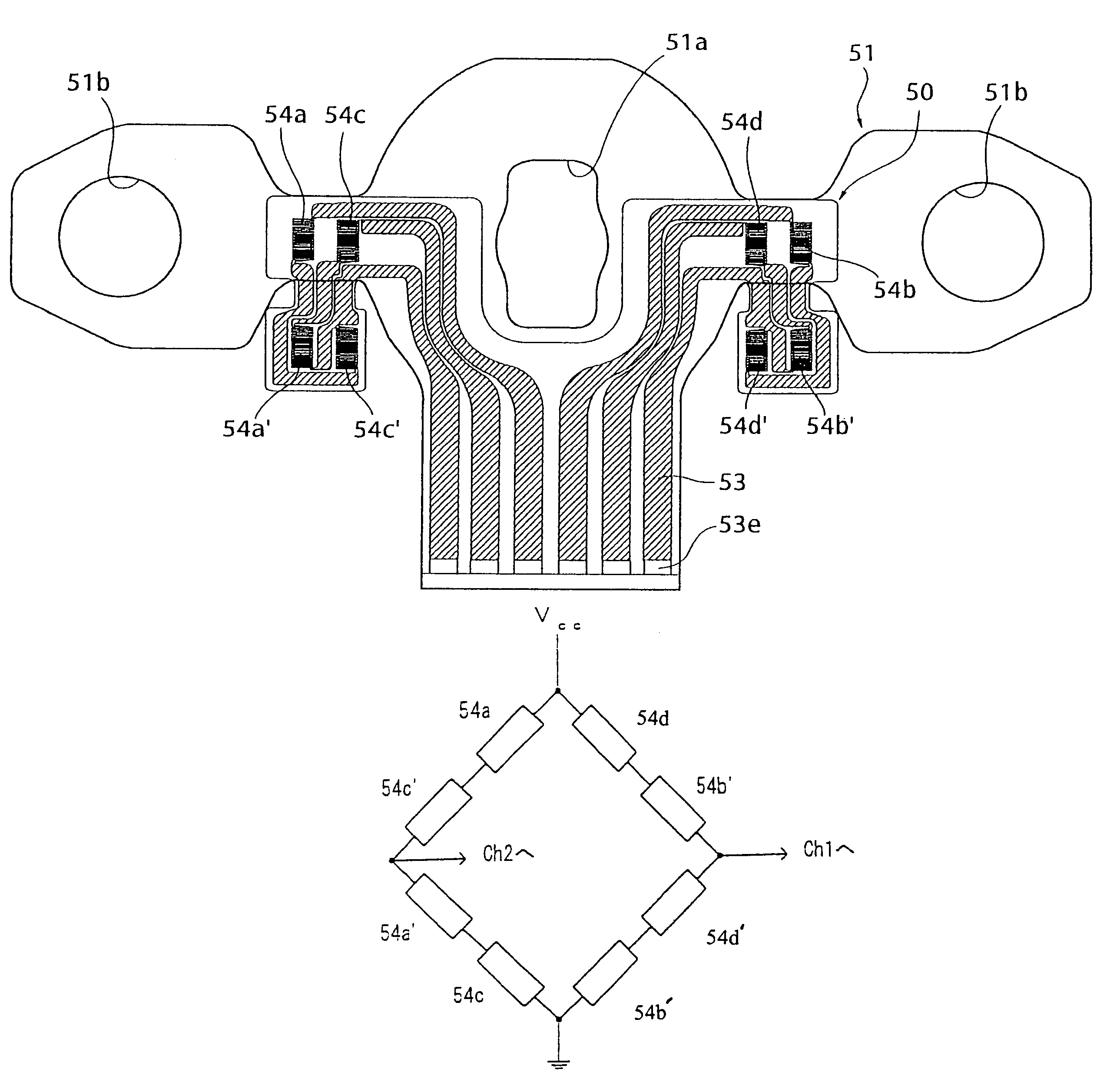
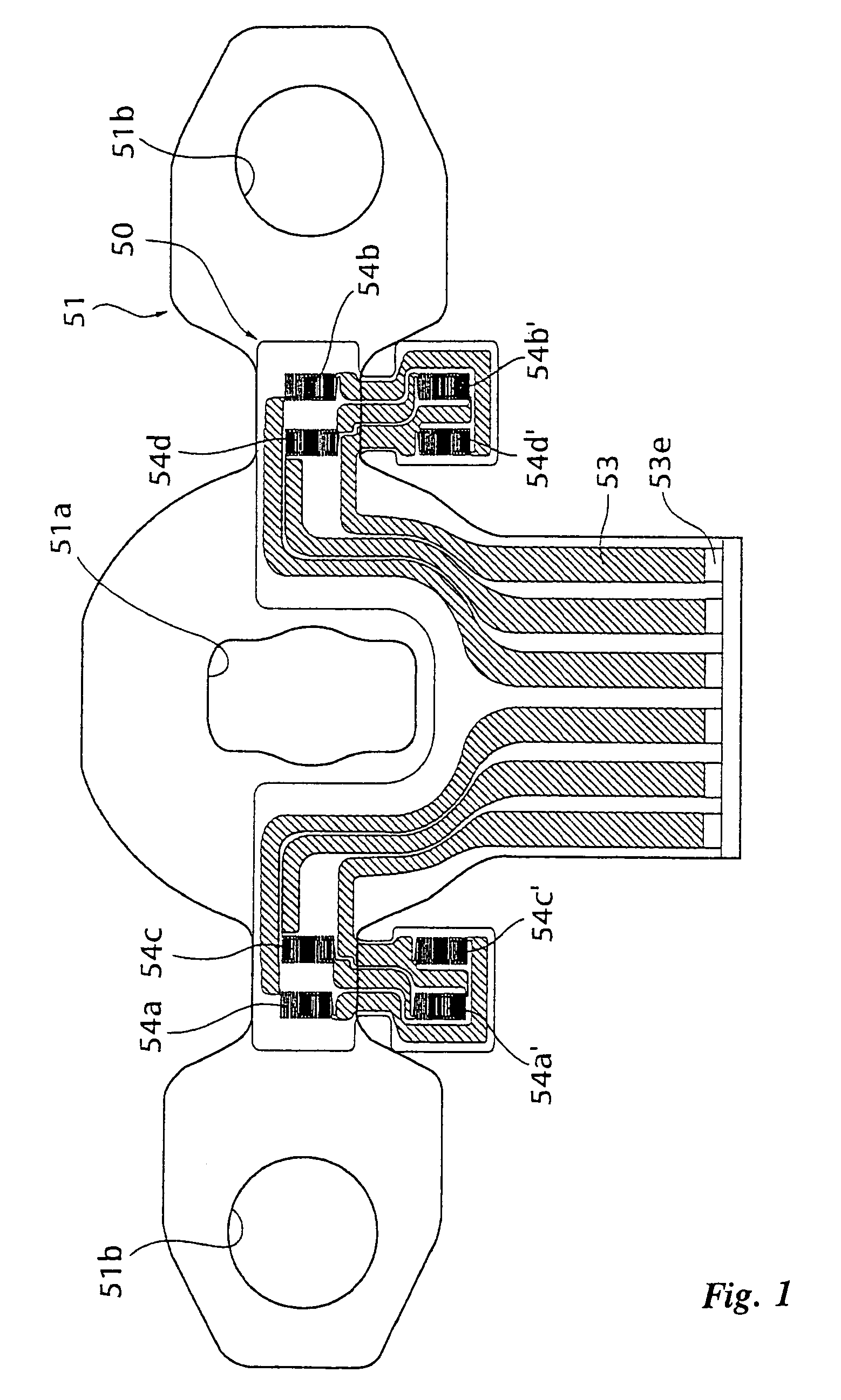
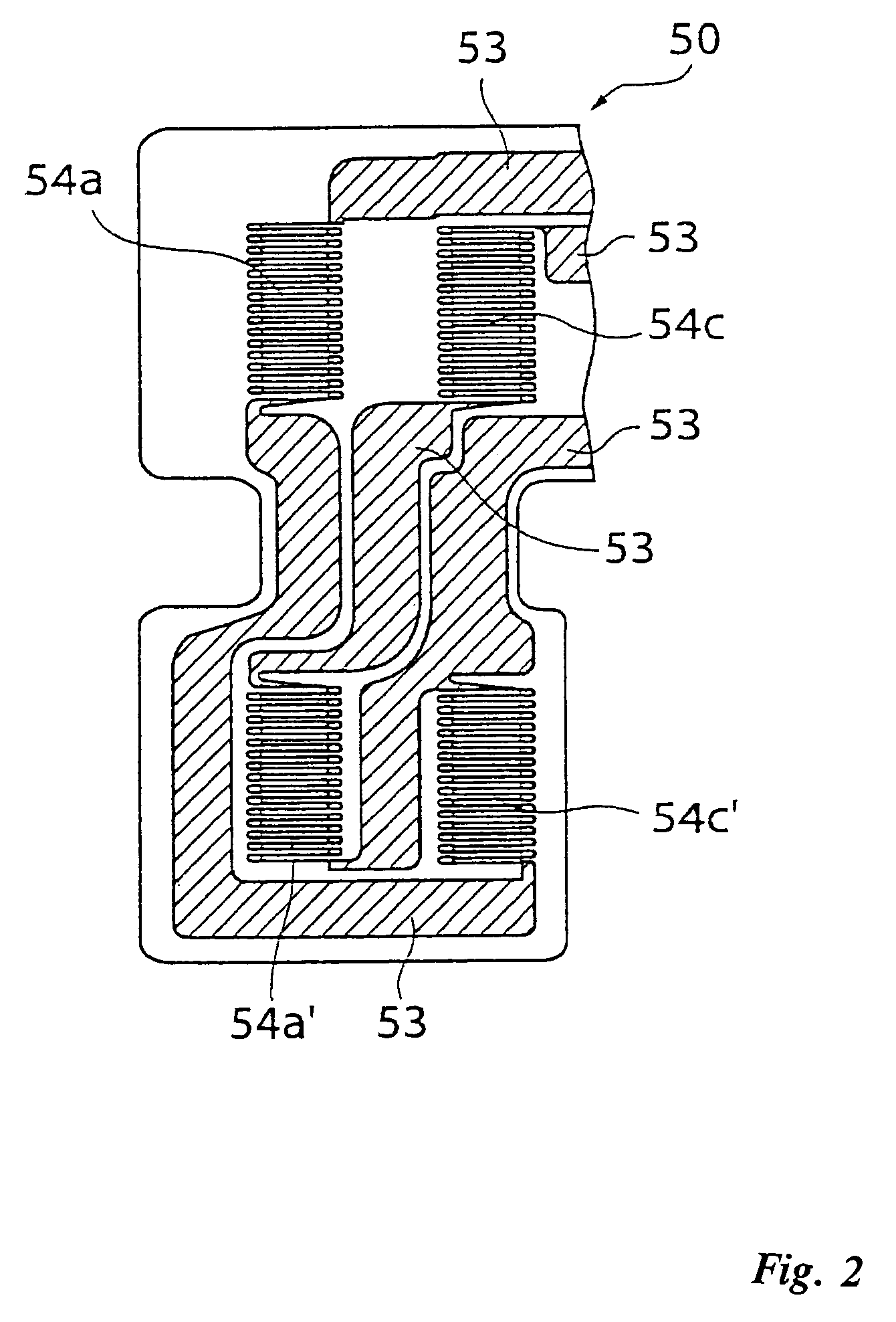
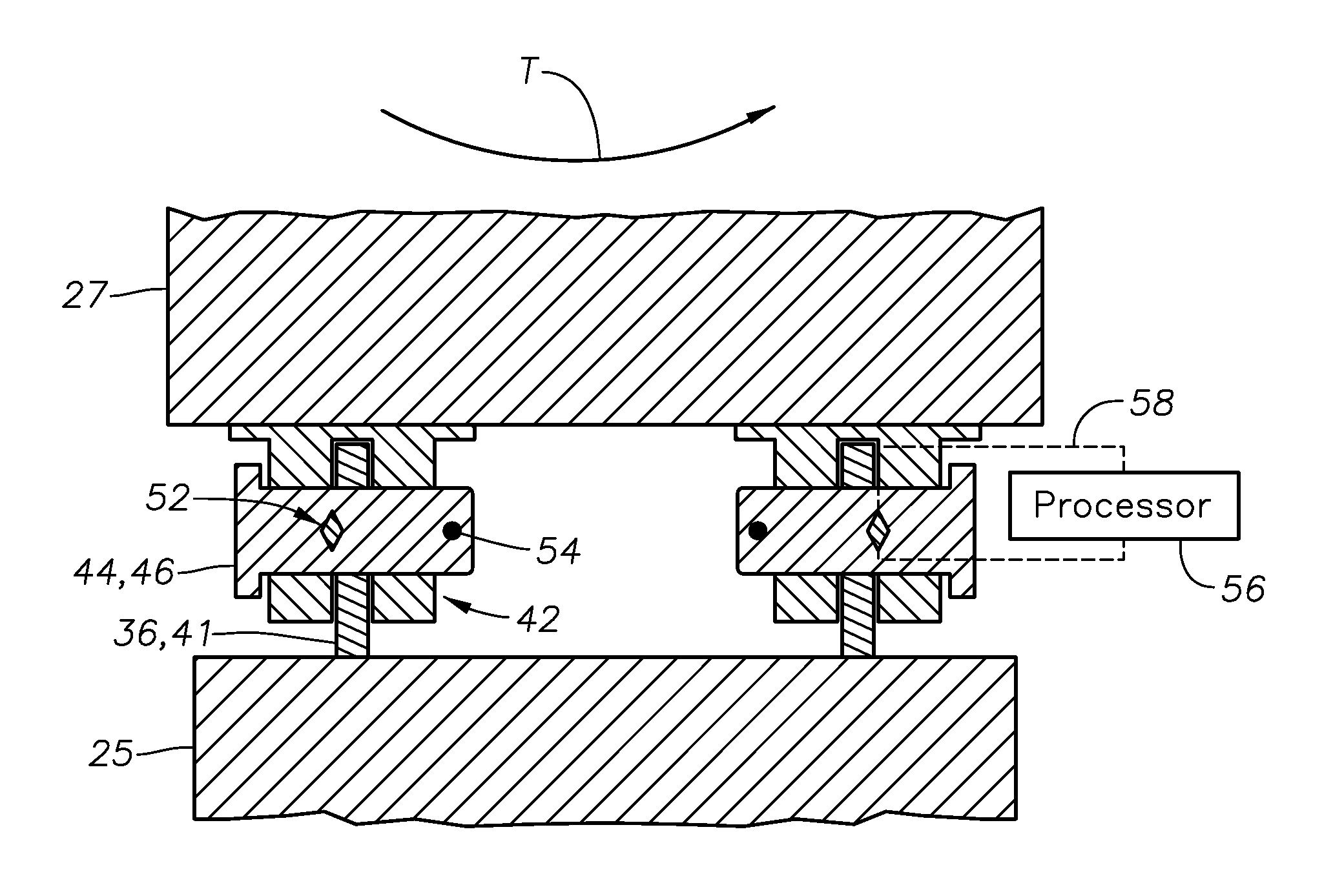
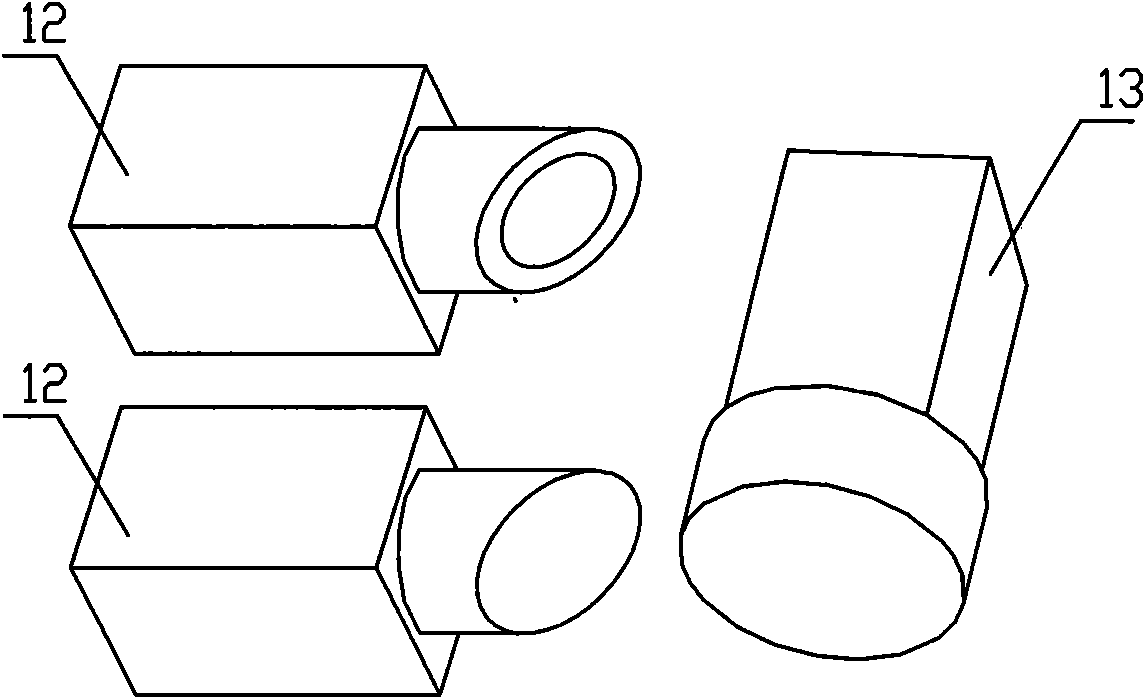Patents
Literature
107 results about "Strainmeter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A strainmeter is an instrument used by geophysicists to measure the deformation of the Earth. Linear strainmeters measure the changes in the distance between two points, using either a solid piece of material (over a short distance) or a laser interferometer (over a long distance, up to several hundred meters). The type using a solid length standard was invented by Benioff in 1932, using an iron pipe; later instruments used rods made of fused quartz. Modern instruments of this type can make measurements of length changes over very small distances, and are commonly placed in boreholes to measure small changes in the diameter of the borehole. Another type of borehole instrument detects changes in a volume filled with fluid (such as silicone oil). The most common type is the dilatometer invented by Sacks and Evertson in the USA (patent 3,635,076); a design that uses specially shaped volumes to measure the strain tensor has been developed by Sakata in Japan.
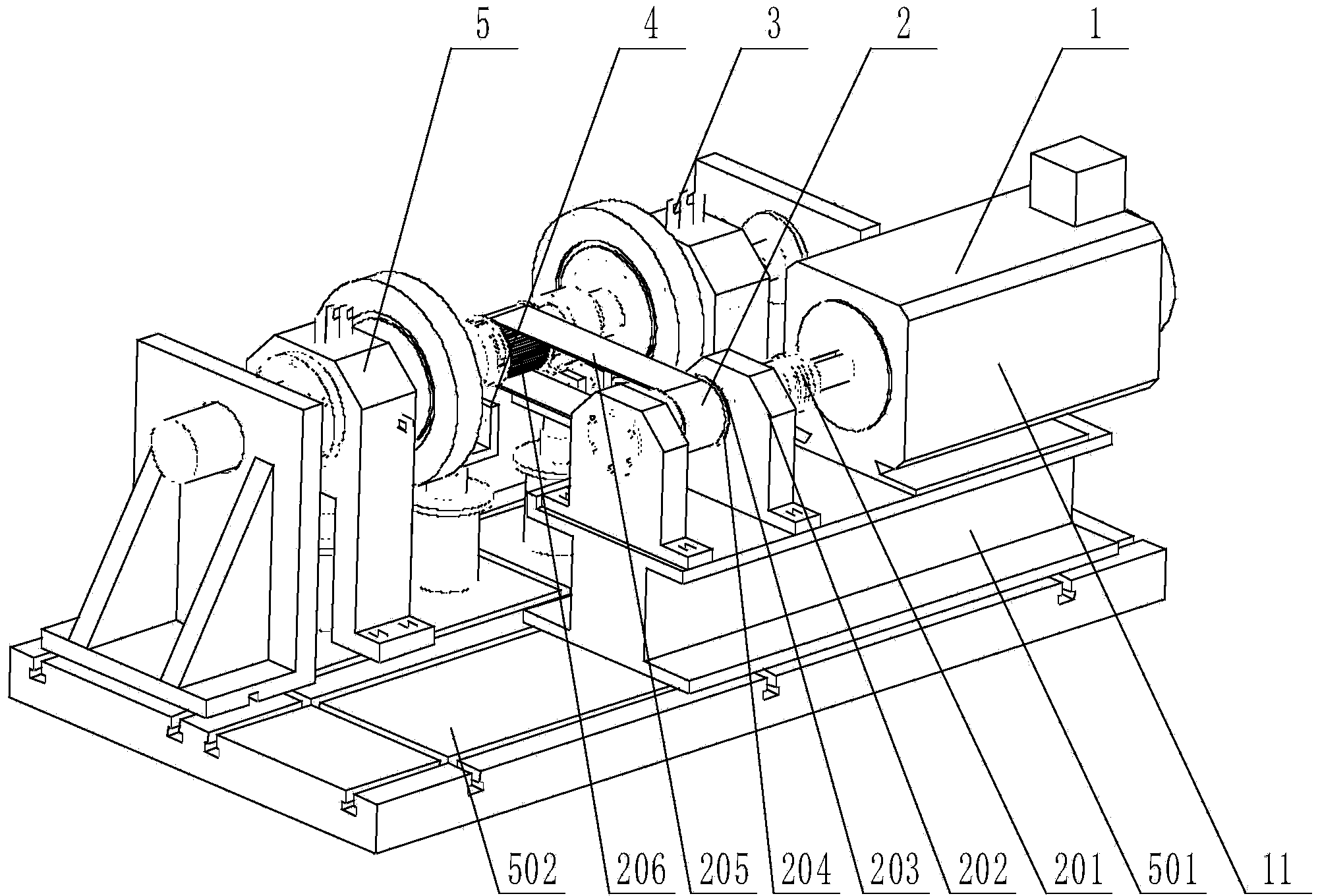
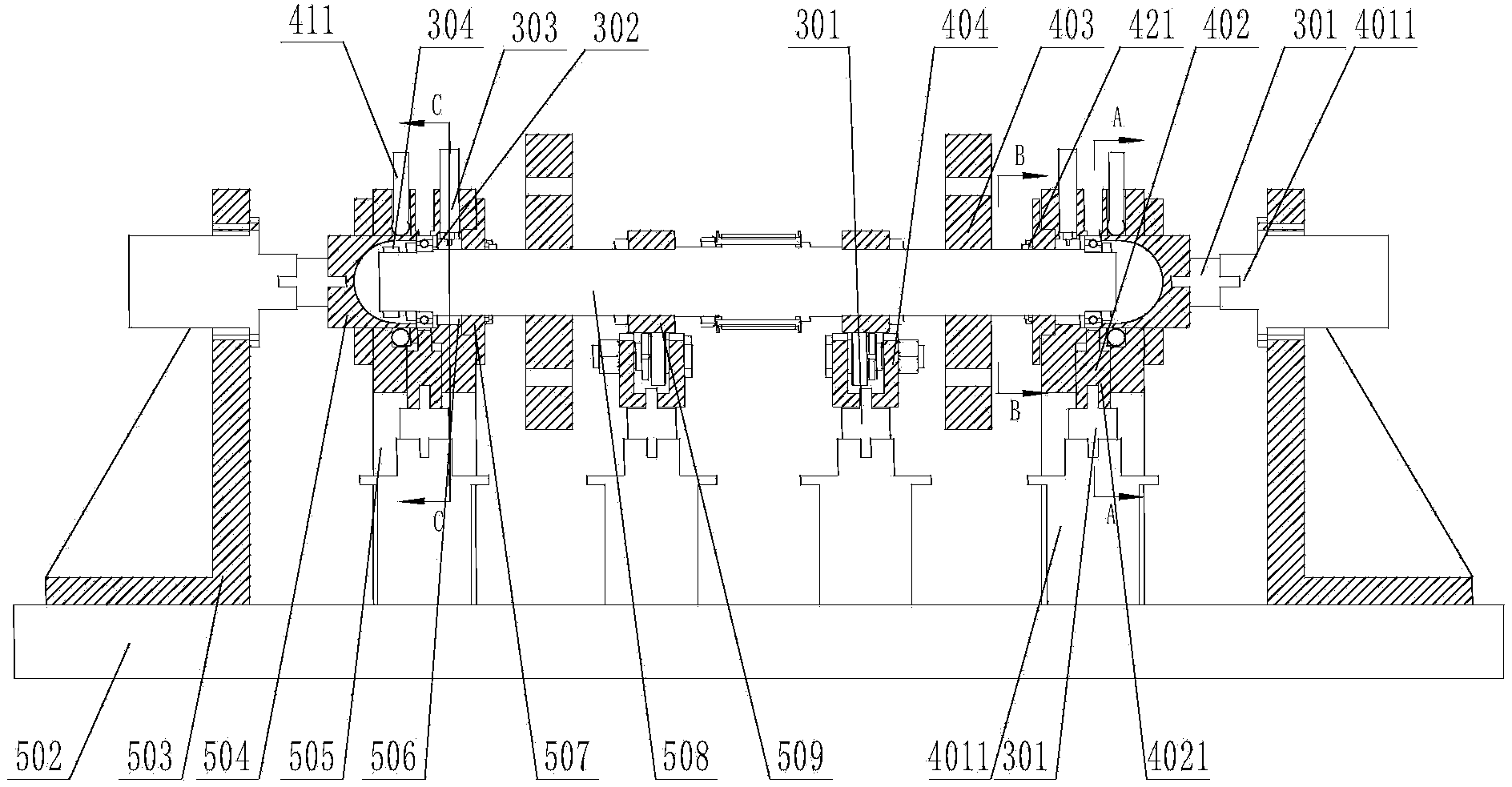
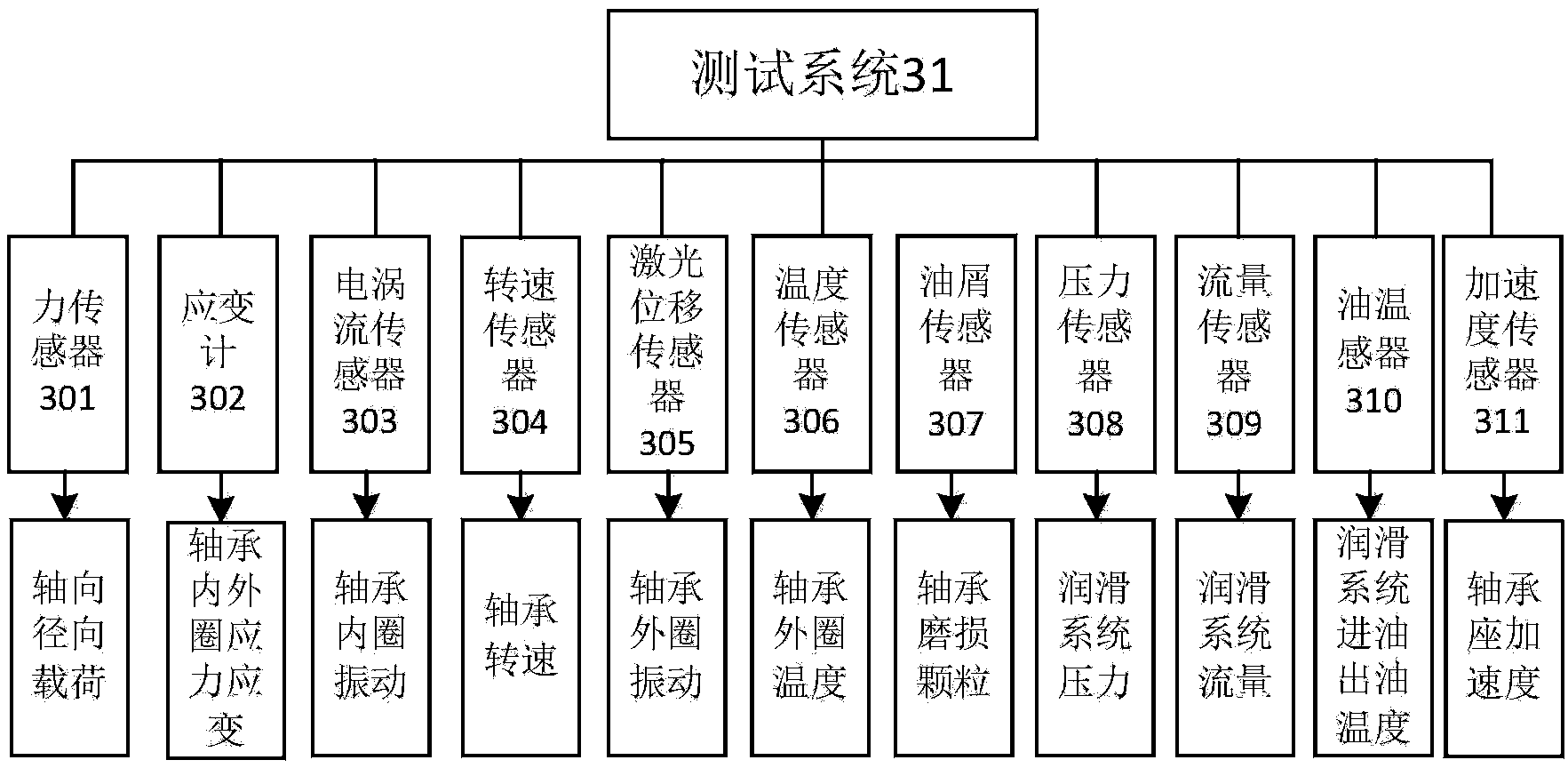
Bearing integrated dynamic performance test device and method
The invention relates to the technical field of bearing testing, in particular to a bearing integrated dynamic performance test device and method. The bearing integrated dynamic performance test device comprises a drive system, a transmission system, a measurement and control system, an environmental simulation system and a mechanical body structure. A motor is adopted by the drive system for driving. The measurement and control system controls the rotation speed of the motor. The transmission system is in a belt transmission mode or a coupler transmission mode. The measurement and control system is provided with a force sensor, a strainmeter, an eddy current transducer, a rotation speed sensor, a laser displacement sensor, a temperature sensor, a magnetic oil residue sensor, a pressure sensor, a flow sensor, an oil temperature sensor, an acceleration sensor and other related sensors used for bearing testing. The control system is driven in a servo mode, and is composed of a frequency converter, a hydraulic solenoid valve, a heating controller, a flow control device and a pressure control device. The environmental simulation system is adopted for simulating a real bearing testing working condition, and the performance and service life testing of the real bearing testing working condition is achieved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
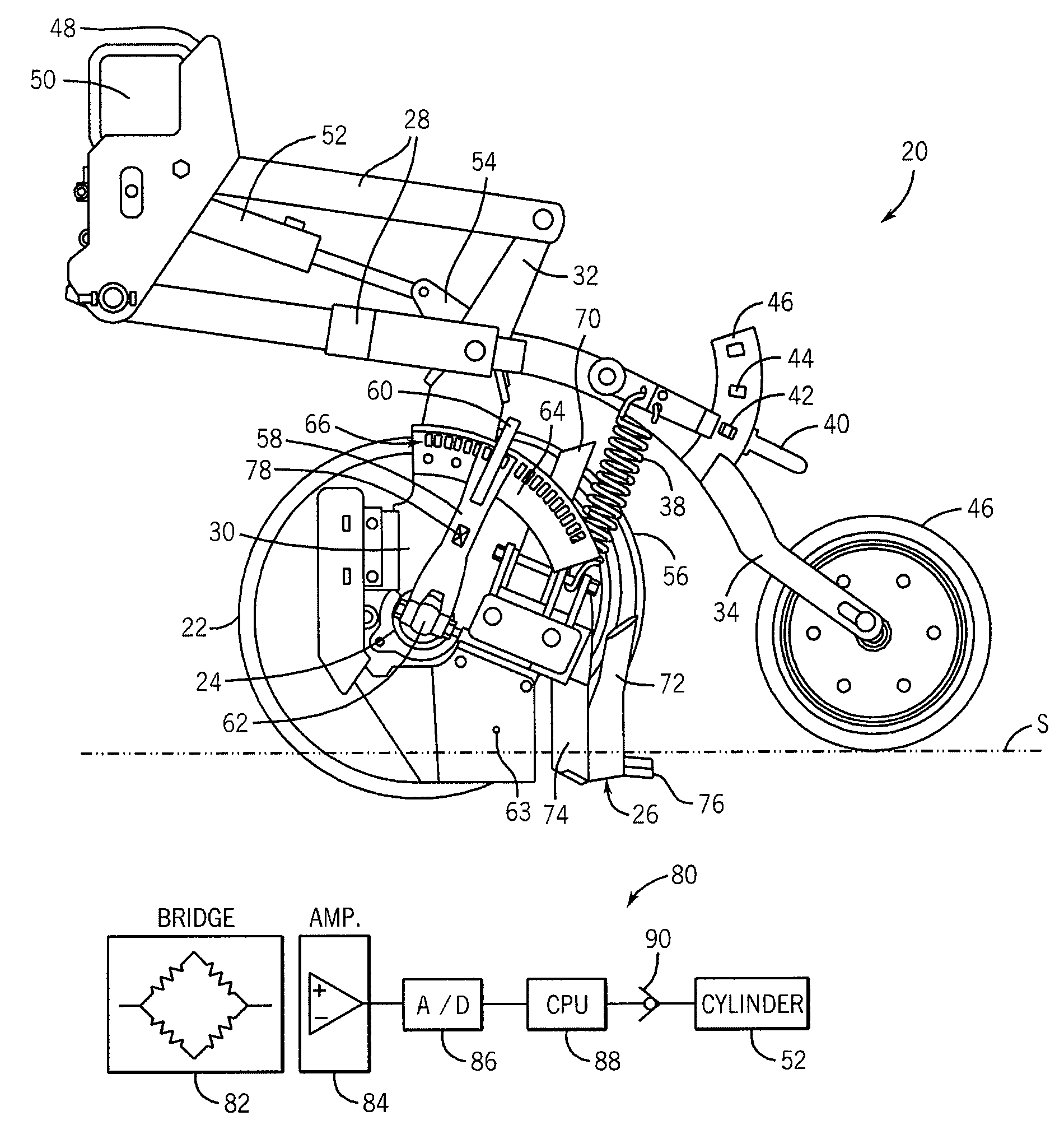
Automatic down pressure adjustment system for set of ganged disc openers
A disc opener unit for an agricultural implement has a down pressure adjustment device that automatically adjusts the amount of down pressure applied on a furrowing disc based on strain measurements taken by a strain gauge or load cell. The strain gauge, which may be mounted to an arm that is used to set the position of a depth setting gauge wheel, provides feedback to a processor that in turn controls the amount of hydraulic fluid in a hydraulic cylinder to adjust the down force applied on the disc. The amount of down pressure is therefore adjusted in substantially real-time in response to changes in field conditions, which improves furrow depth consistency and reduces wear on the gauge wheel and its components.
Owner:CNH IND CANADA
Set of multiaxial force and torque sensor and assembling method
A multiaxial force / torque sensor assembly and method for assembling such a sensor assembly are disclosed. The sensor assembly includes a set of at least two sensors each being made of strain gauges, which are each arranged at a definite angle and distance relative to each other and which are each fixed to a transducer body, which is mechanical contact with a printed circuit board. The printed circuit board includes clearances for each strain gauge as well as associated electronic components and wiring located on the remaining area of the printed circuit board which will monitor compressive and tensile stresses in the measurement directions of the sensors. The method includes positioning the strain gauges on the plane measurement surface of a transducer body in a definite arrangement; fixing the strain gauges to the transducer body by means of adhesives, and connecting the strain gauges to respective conductors by means of electrically bonding.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Catheter with strain gauge sensor
A medical probe, including a flexible insertion tube, having a distal end for insertion into a body cavity of a patient and which is configured to be brought into contact with tissue in the body cavity. The probe further includes a sensor tube of an elastic material, contained inside the distal end of the insertion tube and configured to deform in response to forces exerted by the tissue on the distal end. The probe also includes a plurality of strain gauges fixedly attached to a surface of the sensor tube at different, respective locations and configured to generate respective signals in response to deformations of the sensor tube.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Load sensor and seat weight measuring apparatus with a plurality of strain gauges
InactiveUS7055365B2Vehicle seatsBelt control systemsElectrical resistance and conductanceMeasurement device
Owner:TAKATA CORPORATION
Top drive output torque measurement method
A top drive assembly that includes a gauge for measuring strain in a linkage coupling the top drive to a drilling rig frame. The strain measuring gauge, which can be a strain gauge, is disposed on a pin that pivotingly links members of the linkage coupling. When a motor in the top drive assembly operates to rotate an associated pipe string, the torque generated by the motor can be estimated by monitoring strain measured in the pin.
Owner:NABORS DRILLING TECH USA INC
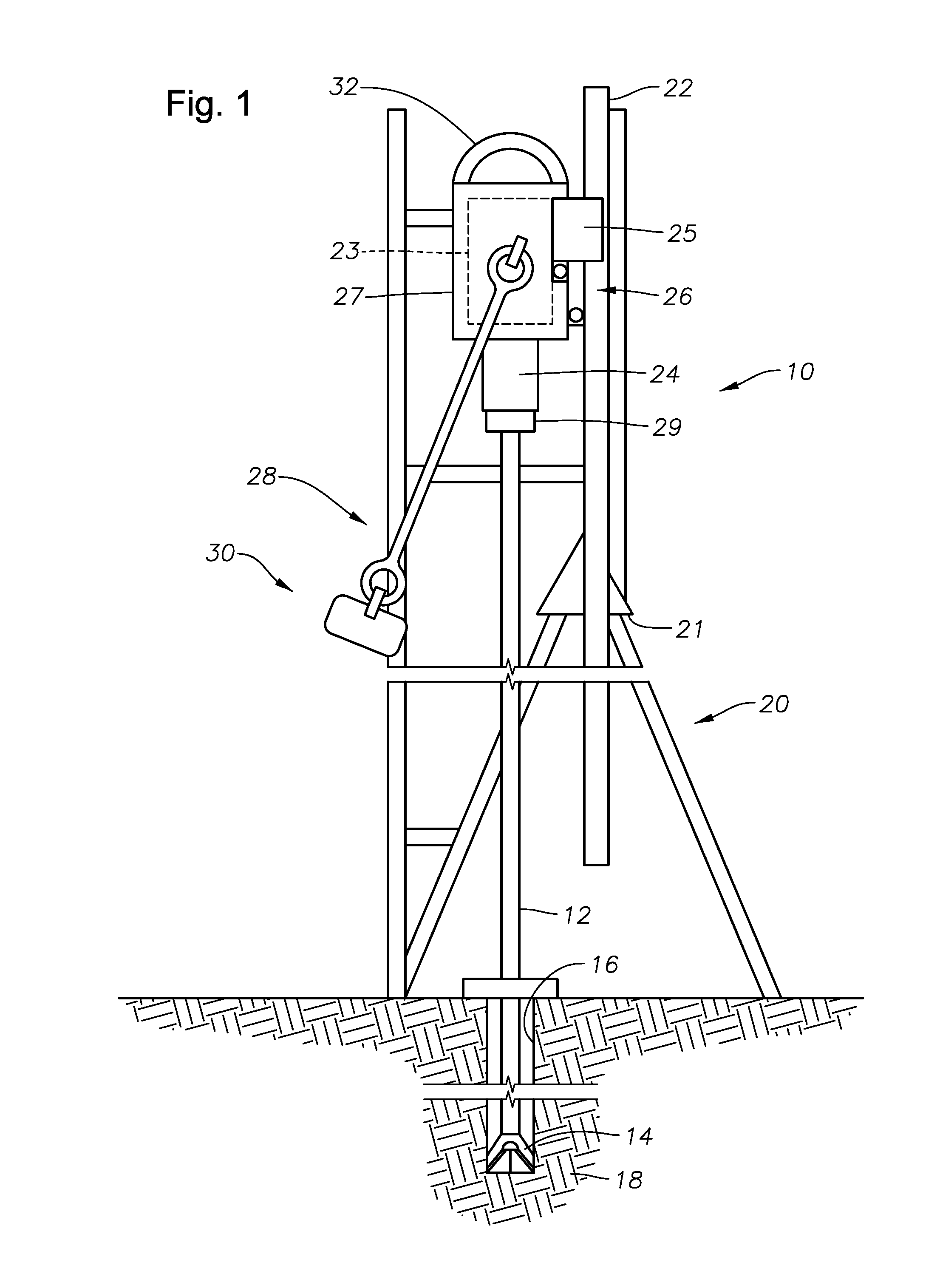
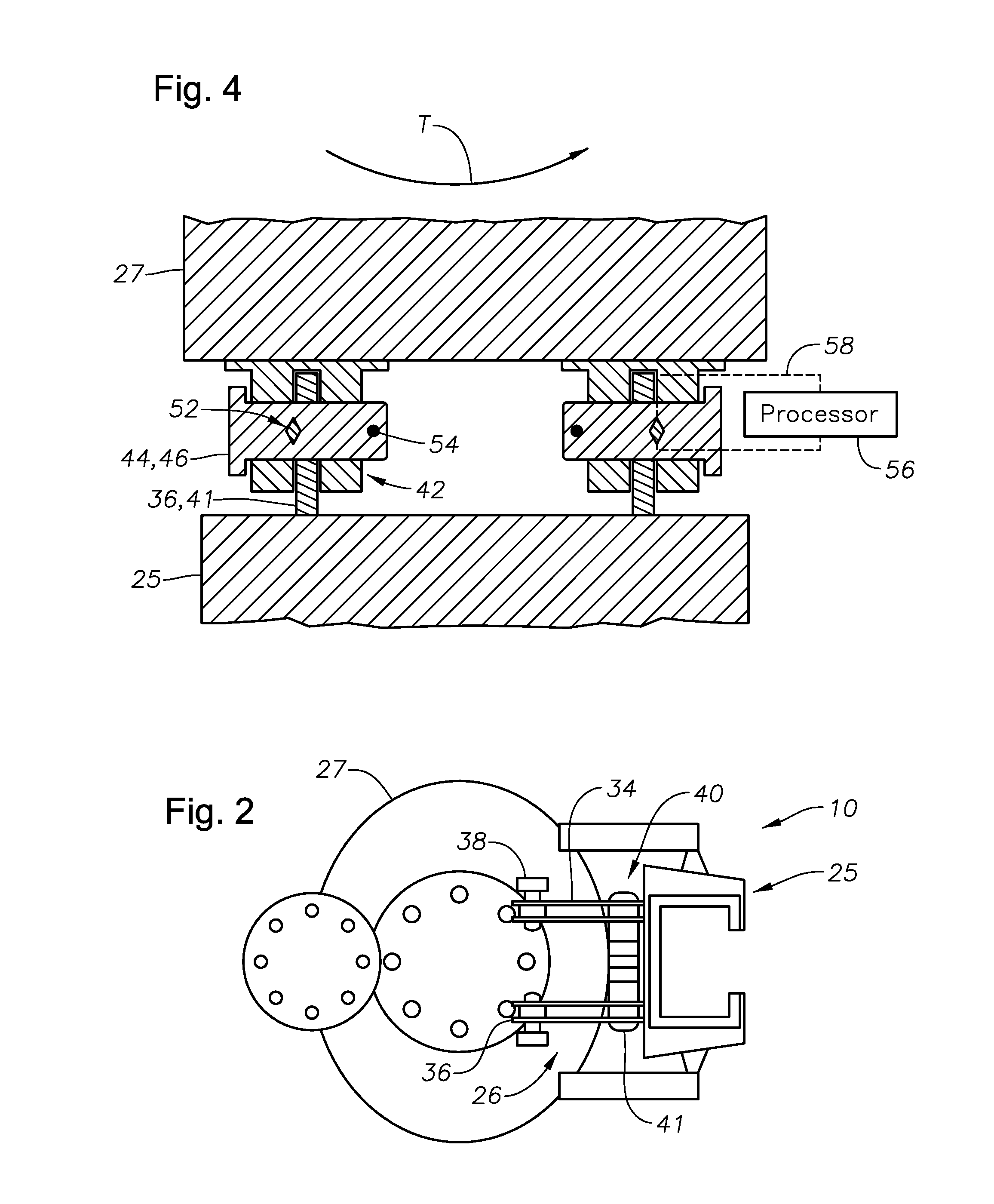
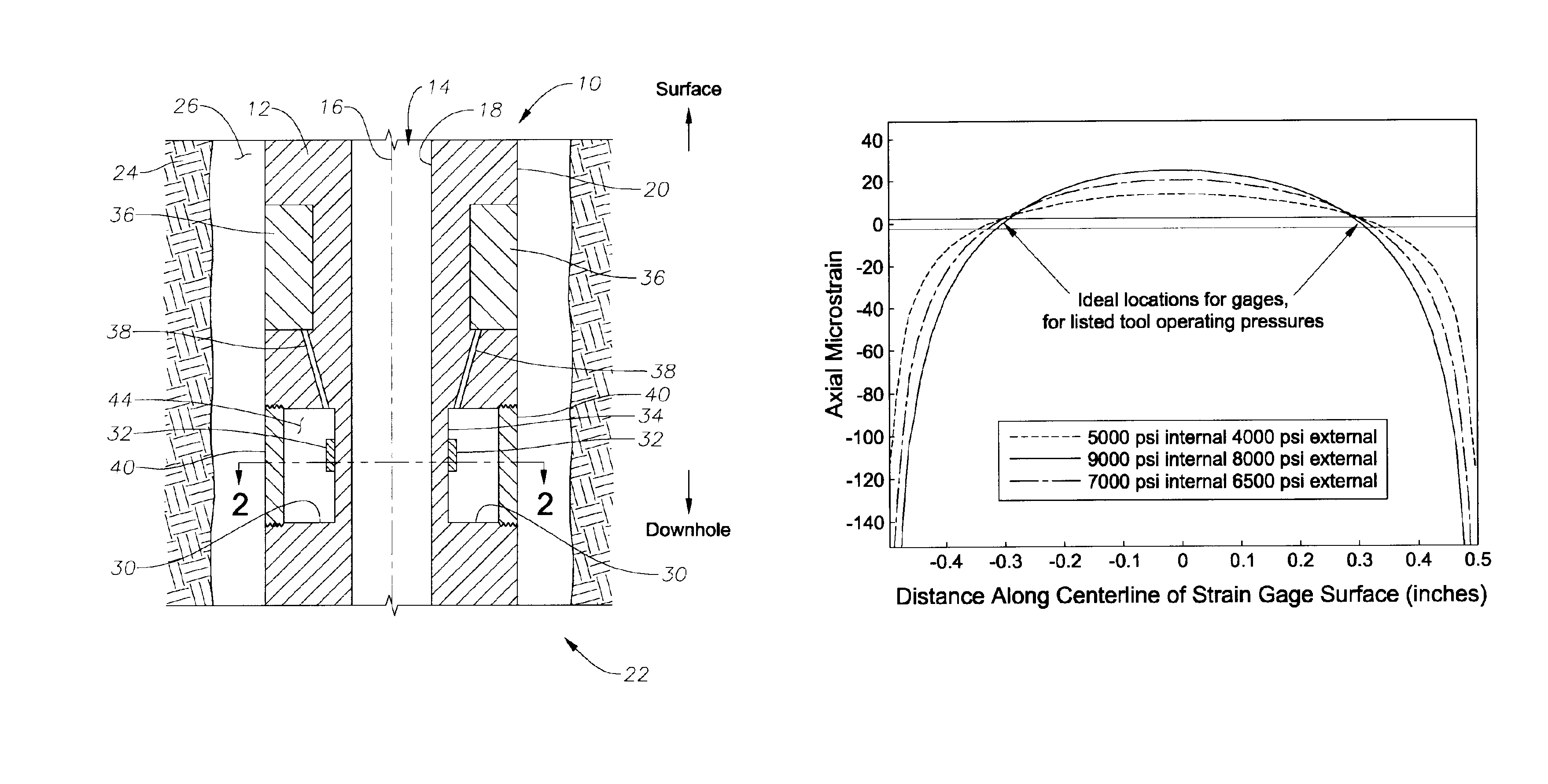
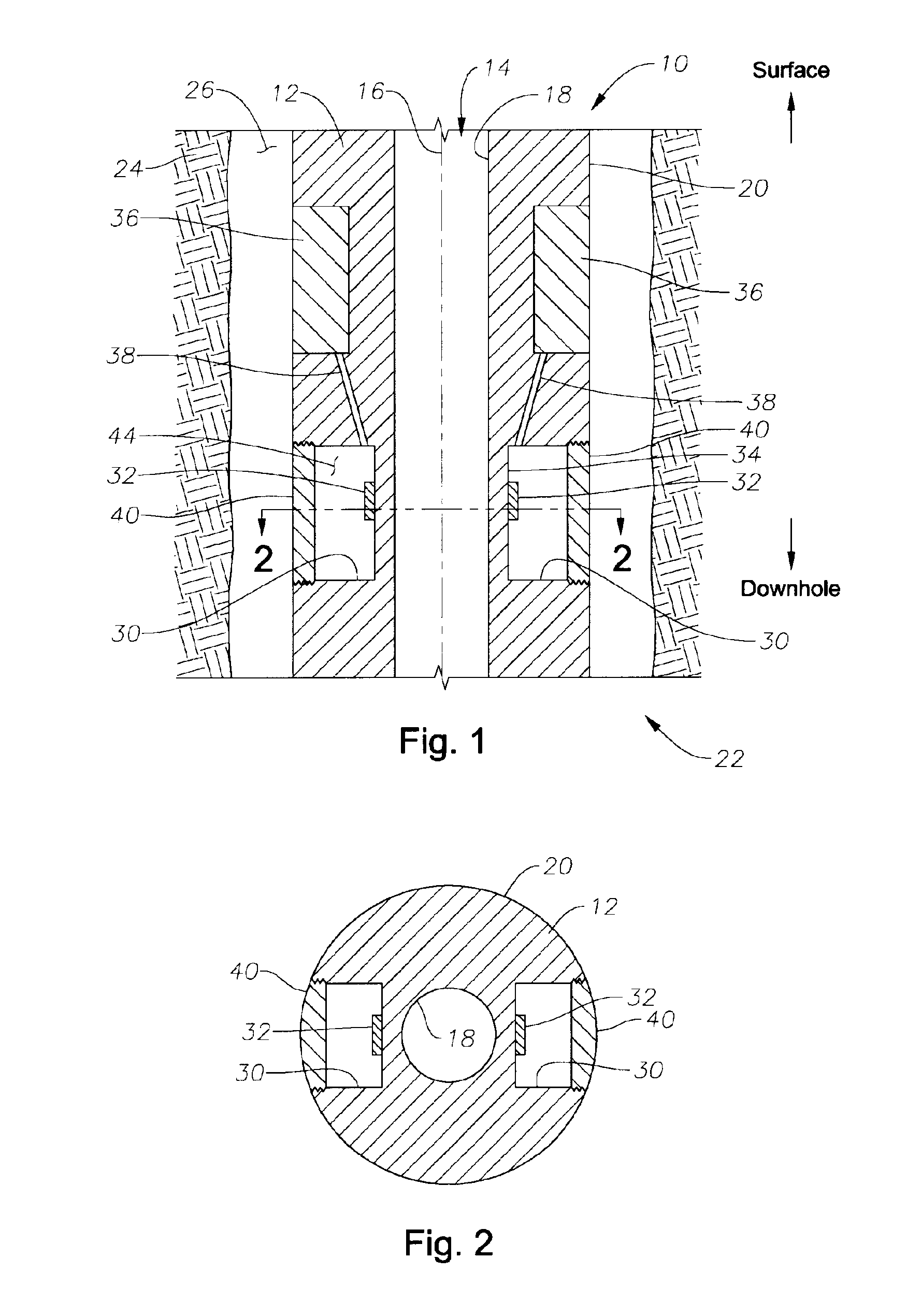
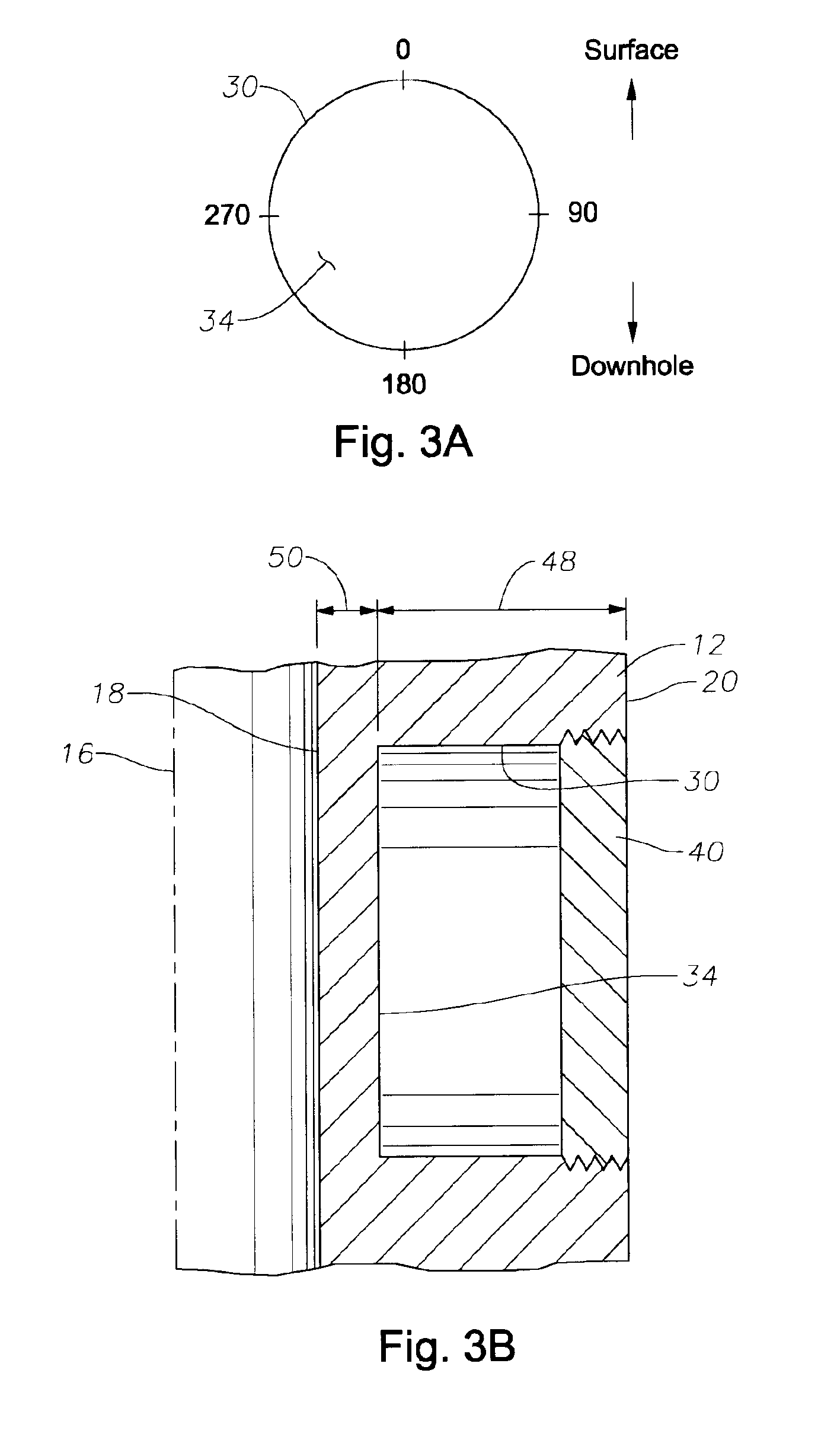
Apparatus for weight on bit measurements, and methods of using same
The present invention is generally directed to a tool for obtaining downhole measurements and methods of using such a tool. In one illustrative embodiment the tool comprises a body, at least one strain gauge cavity in the body, the strain gauge cavity having a strain gauge mounting surface that is located at a position such that a region of approximately zero strain due to at least one downhole operating condition exists on the mounting surface when the tool is subjected to downhole operating conditions, and a strain gauge operatively coupled to the mounting face above the region of approximately zero strain. In another illustrative embodiment, the method comprises providing a measurement tool comprised of a body, at least one strain gauge cavity in the body, the strain gauge cavity having a strain gauge mounting surface that is located at a position such that a region of approximately zero strain due to at least one downhole operating condition exists on the mounting surface when the tool is subjected to downhole operating conditions, and a strain gauge coupled to the mounting face above the region of approximately zero strain. The method further comprises positioning the tool in a subterranean well bore and obtaining measurement data using the strain gauge in the tool.
Owner:GP USA HLDG LLC
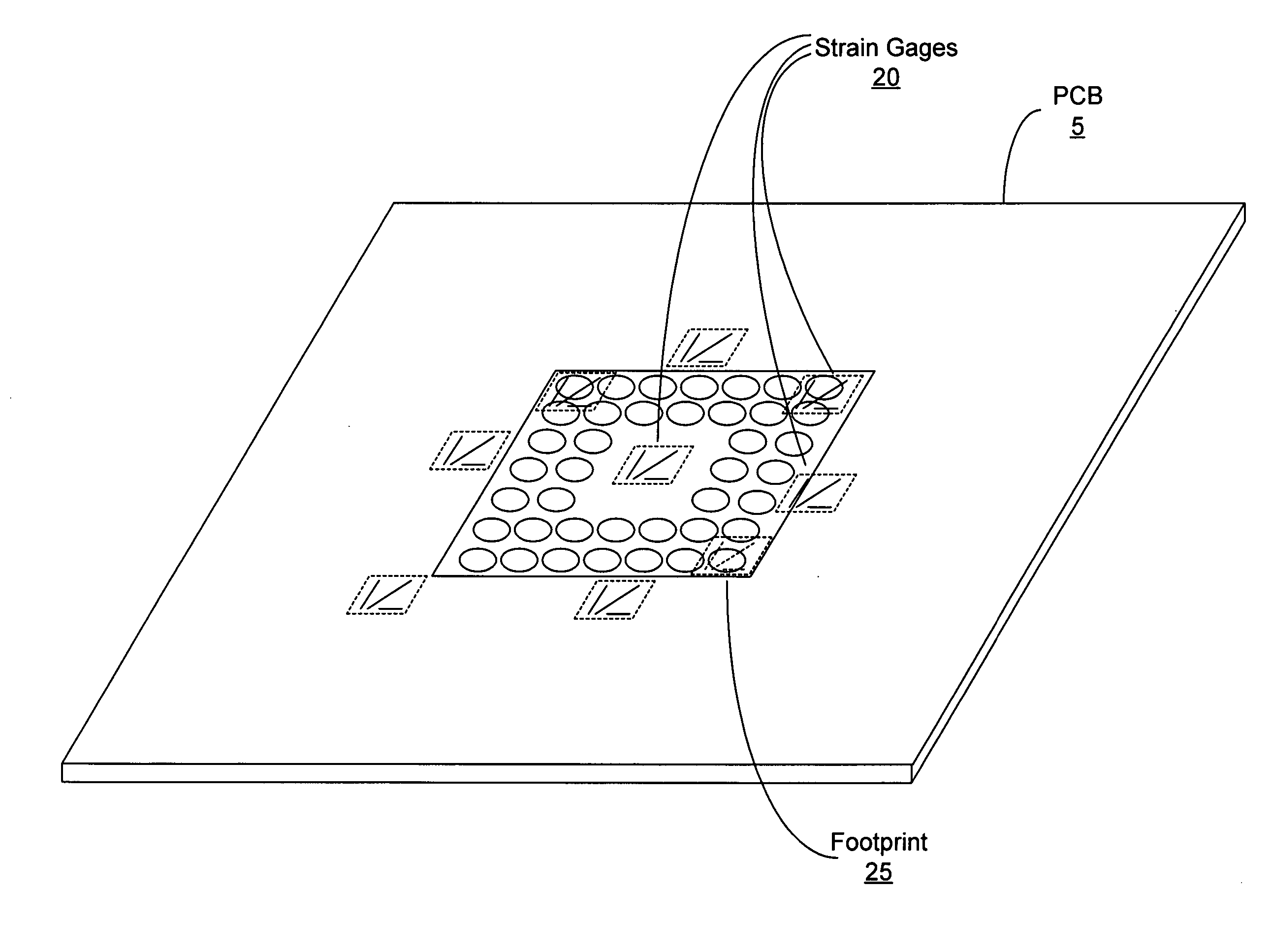
Integrated strain gages for board strain characterization
ActiveUS20050252311A1Testing/calibration apparatusBy pulling from meltElectrical conductorElectronic component
A printed circuit board (PCB) having an integrated strain gage. In one embodiment, a PCB includes a component footprint suitable for mounting an electronic component. A strain gage is integrated into the PCB in a location under the component footprint. The strain gage includes at least one electrical conductor that is accessible for resistance measurements.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Water and soil pressure monitoring rod for shield tunnel
ActiveCN105258824AOvercome the difficulty of measuring the pore water pressure on the surface of the segmentOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to achieve the same positionForce measurementFluid pressure measurementPore water pressureEngineering
The invention relates to a water and soil pressure monitoring rod for a shield tunnel, and the rod comprises a pressure monitoring rod body. The pressure monitoring rod body comprises a cylindrical rod body, an end compartment connected to one end part of the cylindrical rod body, and a sealing box which is disposed at the other end of the cylindrical rod body in a sleeving manner. The interior of the end compartment is provided with a soil pressure sensor and a pore water pressure sensor, wherein leading-out wires disposed on the soil pressure sensor and the gap water pressure sensor pass through the cylindrical rod body to be connected with a strain gauge. During soil pressure monitoring, the pressure monitoring rod body sequentially passes through a pipe piece and a grouting layer to reach soil. A joint of the pipe piece with the pressure monitoring rod body is sealed by the sealing box. The soil pressure sensor and the pore water pressure sensor are used for measuring soil pressure and pore water pressure at the same time, and the measurement results are transmitted to the strain gauge through the leading-out wires. Compared with the prior art, the rod is convenient to install and use, is high in reliability, and can measure the soil pressure and the pore water pressure at the same time.
Owner:上海瓴云土木工程咨询有限公司
Catheter with strain gauge sensor
A medical probe, including a flexible insertion tube, having a distal end for insertion into a body cavity of a patient and which is configured to be brought into contact with tissue in the body cavity. The probe further includes a sensor tube of an elastic material, contained inside the distal end of the insertion tube and configured to deform in response to forces exerted by the tissue on the distal end. The probe also includes a plurality of strain gauges fixedly attached to a surface of the sensor tube at different, respective locations and configured to generate respective signals in response to deformations of the sensor tube.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Strain gauge apparatus having a point-distributed sensor
InactiveUS20050279177A1Improve accuracyForce measurementUsing electrical meansClassical mechanicsStrain gauge
A strain gauge apparatus having a point-distributed sensor for measuring the strain of a mechanical structure. The strain gauge comprises a thin elongated piezoresistive lamina with a shape contour that is symmetric with respect to the longitudinal axis thereof, and the width of the lamina at the center along the longitudinal axis is minimum for the entire lamina length. The point-distributed strain gauge apparatus measures both static and dynamic deformation in the measured structure at a precise location aligned to the targeted center of the sensor lamina.
Owner:LEE CHIH KUNG
Force-sensing catheter with bonded center strut
ActiveUS9101734B2Maximize cross-sectional areaDiameter minimizationElectrocardiographyStrain gaugeMetallic foilCatheter
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter and method
InactiveCN103162889AQuick installationReduce measurement linksTransmission systemsApparatus for force/torque/work measurementMicrocontrollerAudio power amplifier
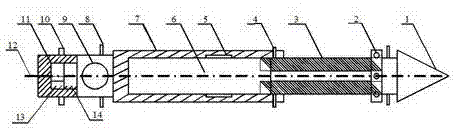
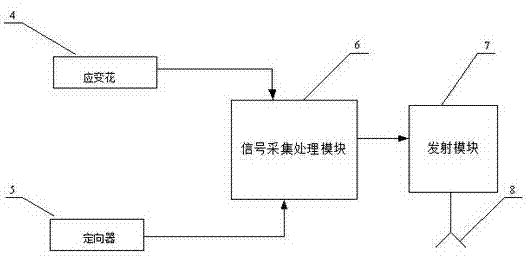
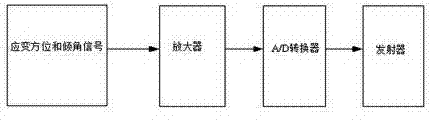
The invention discloses a wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter and a method for measuring ground stress. The wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter for measuring the ground stress is characterized in that a shell body of the wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter is sealed by epoxy resin, a base material of the shell body is composite ceramic, the wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter for measuring the ground stress comprises a strain measurement portion, an emitting portion and a guiding portion, wherein the strain measurement portion, the emitting portion and the guiding portion are all detachable and recyclable, a directional sensor, a power source and an emitting module are sequentially sealed on the rear portion of the wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter, resistance strain rosettes are inlaid in the middle along the same circumference of the wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter at intervals, and the strain measurement portion, the emitting portion and the directional portion of the wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter can be detached and separated. Three groups of strain rosettes and three groups of direction finders are arranged on the wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter. The strain rosettes and the direction finders are used for respectively transmitting collected signals to an amplifier, and then the signals enter an analog to digital (A / D) converter, analog signals are converted into digital signals, a singlechip is used for sampling, and data are sent out through a wireless module. The wireless hollow inclusion strainmeter for measuring the ground stress has integration and telemetering, and can be recovered and repeatedly used.
Owner:付志亮
Pressure sensor containing mechanically deforming elements
The invention has the objective of offering a sensor the allows for measuring the pressure force of the springs on the carbon brushes as well as the actual brush pressure on its contact surface. This is obtained by measuring between the carbon brush, and there is limited space through its holder, and the contact surface and is therefore characterized by the fact that the sensor is thinner than 4 mm, and that it is provided with a target (4) which is suspended in the sensor (1) by means of a mechanically deformable section (3), and where the sensor is fitted with one or more strain gauges (2) that is / are set up as such that it can detect the shearing of the mechanical deformable measuring section under pressure. In contrast to the existing measuring sensors, the measuring strips also connect the suspension points of the mechanically deformable elements with the sensor and / or the suspended target or measuring point through which sensitivity increases and makes the sensor useful for such applications.
Owner:MERSEN BENELUX BV
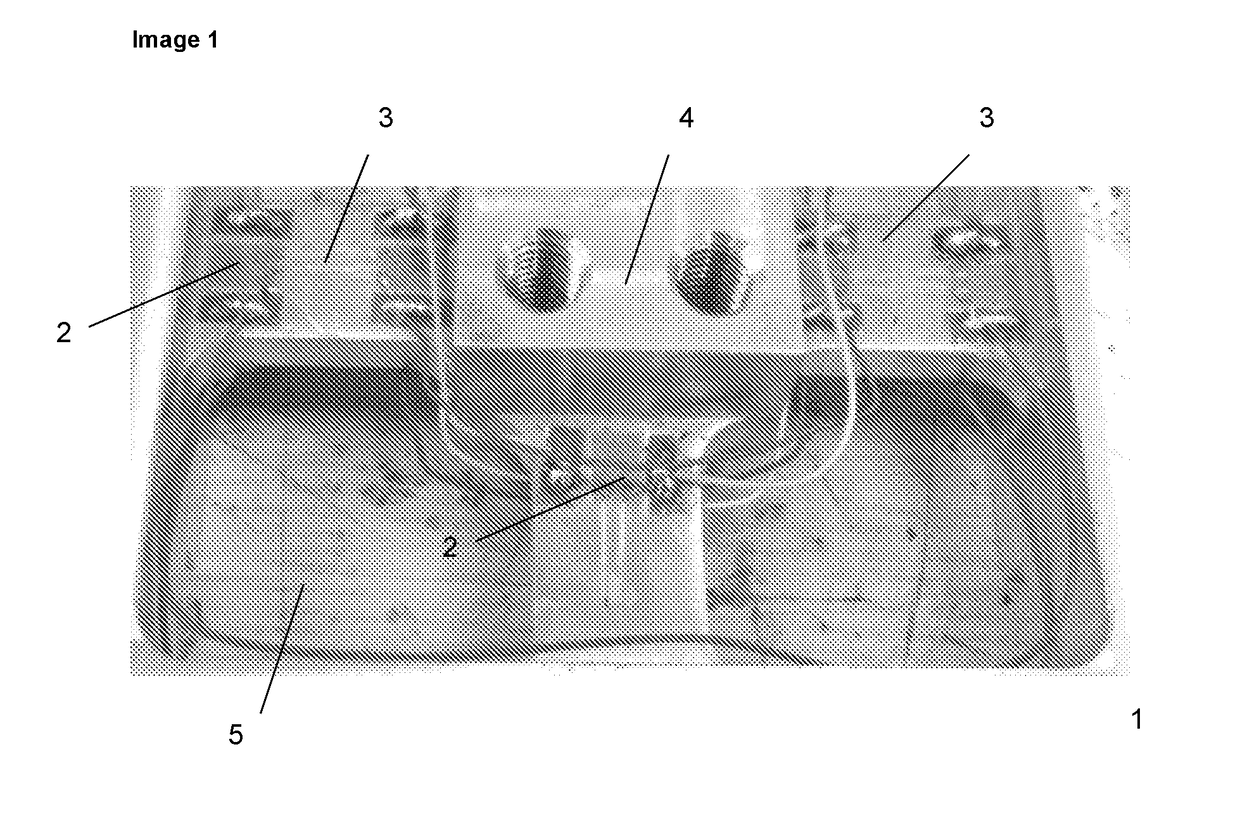
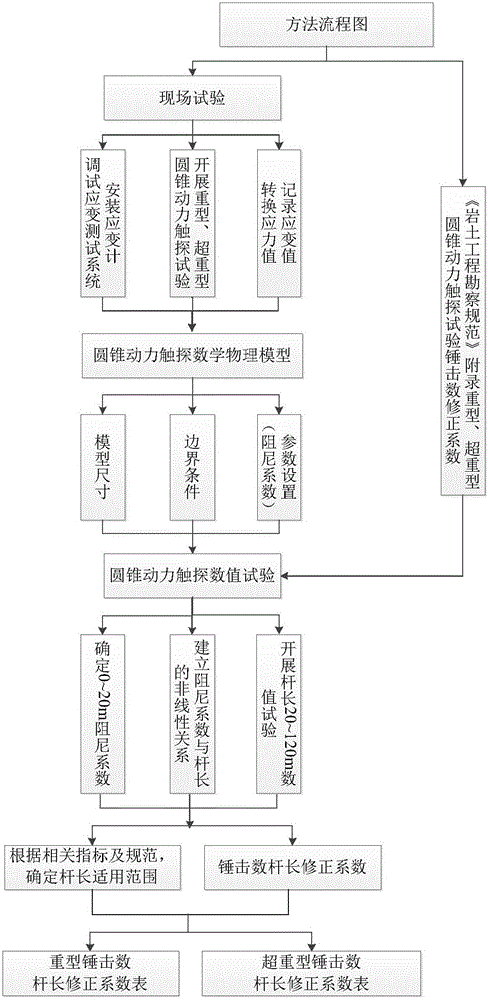
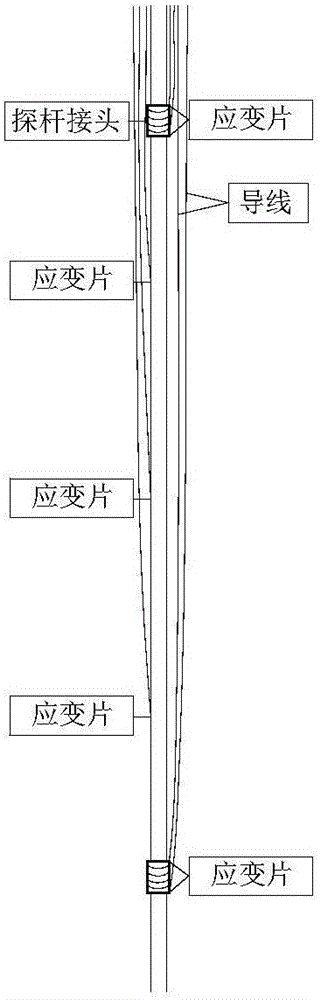
Super long rod heavy-type/super heavy-type cone dynamic penetration blow counts correction method
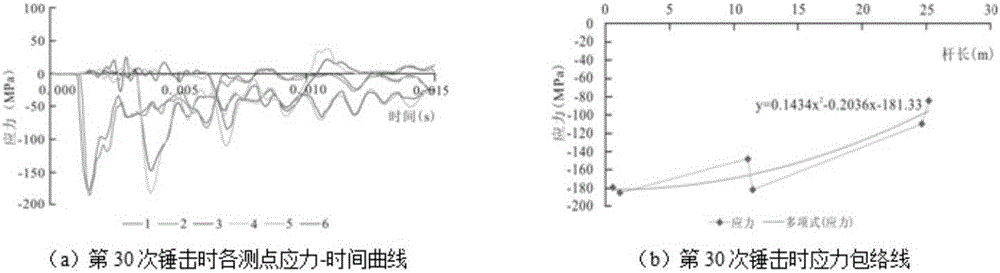
The invention discloses a super long rod heavy-type / super heavy-type cone dynamic penetration blow counts correction method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) arranging strainmeters on a detecting rod, the strainmeters are arranged on the detecting rod at intervals; 2)according to requirement of a cone dynamic penetration test technology prescribed in Geotechnical Engineering Test Monitoring Manual, performing on-site tests, recording the blow counts when penetration depth is 10 cm for each time, storing the strain value at a measuring point of the strainmeter when each time of hammering is carried out; 3) establishing a cone dynamic penetration value calculating model; 4) determining a damping coefficient; and 5) using the obtained damping coefficient and performing the value test with the rod having length of 20-120 m, calculating impact force and effective energy at the bottom of the rod, and obtaining the blow counts correction coefficient. The invention provides the calculating method of heavy-type / super heavy-type cone dynamic penetration blow counts correction coefficient of the rod having length of 20 m, which fills the epitaxial blank of the dynamic penetration blow counts correction coefficient in domestic geotechnical engineering investigation.
Owner:长江三峡勘测研究院有限公司(武汉)
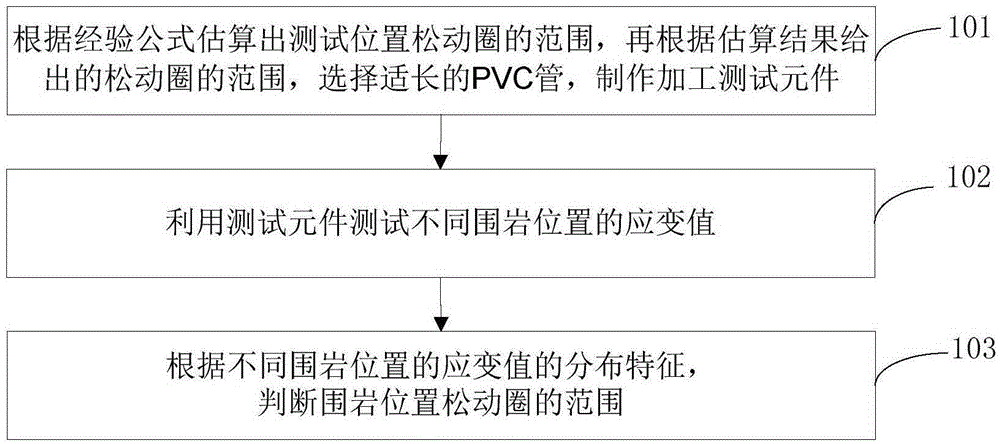
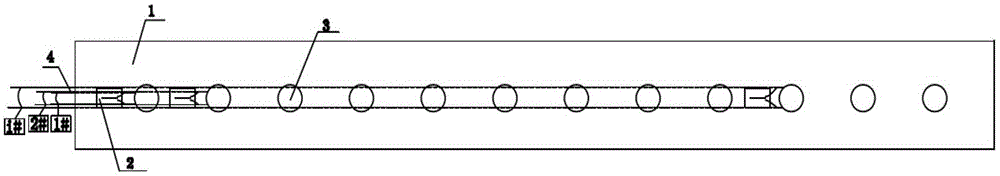
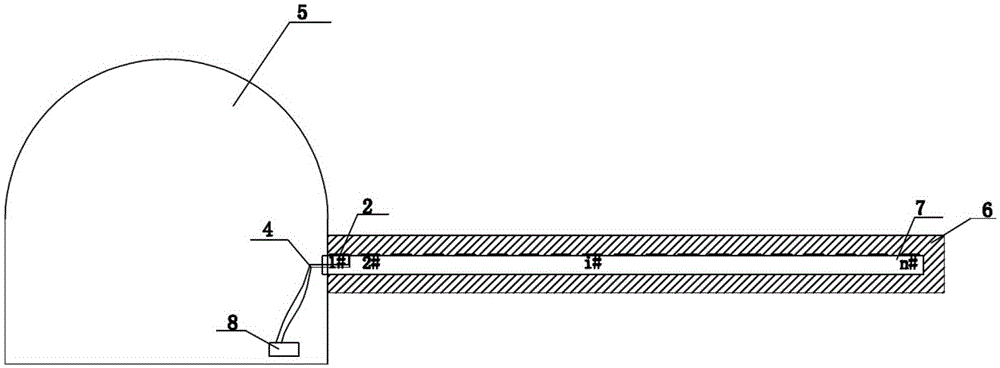
A method for measuring loose circles of surrounding rocks based on distributed resistance strain gauges
ActiveCN105318824AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementBorehole/well accessoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceStrain gauge
The invention provides a method for measuring loose circles of surrounding rocks based on distributed resistance strain gauges. The method comprises the steps of: making and processing a test element and numbering resistance strain gauges on the surface of a PVC pipe body; performing construction drilling, placing the test element in the drilled hole and performing grouting and hole sealing to make the test element and surrounding rocks effectively coupled; measuring the surrounding rock strain value reflected by each resistance strain gauge successively by using a strain meter, drawing a relation curve of different surrounding rock positions and the strain values and obtaining the result that the surrounding rocks between the strain peak position to the drilling position are in the loose circle range through analysis. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the distribution range of loose circles is analyzed by using the resistance strain gauges to measuring the strain of coal-rock bodies at different positions. The operation is convenient, rapid and economical, the sensitivity is high, the data processing for the measuring results is easy, and the method facilitates field implementation.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Load cell and large load measuring method capable of carrying out calibration in multiple angles for air craft
InactiveCN103454025AImprove structural strengthImprove carrying capacityApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectricityLoad cell
The invention provides a load cell which is suitable for being mounted on a connector of an air craft structure. The load cell comprises a cylindrical pin body, a pin seat, a first strainmeter, a second strainmeter, a first strainmeter connecting line and a second strainmeter connecting line, wherein an axial straight groove (a first groove) and an annular groove (a second groove) perpendicular to the straight groove are formed in the body wall of the cylindrical pin body, a line leading hole communicated with the straight groove is formed in the pin seat, the first strainmeter is located at the intersection position of the first groove and the second groove, the second strainmeter is located in the second groove and forms a 90 degree central angle with the first strainmeter, the first strainmeter line and the second strainmeter line are electrically connected with an external sensing signal collecting instrument, and the length direction of the first strainmeter and the length direction of the second strainmeter are identical with the axial direction of the pin body. The invention further provides a large load measuring method capable of carrying out calibration in multiple angles for an air craft. Through the data sensed by the load cell, the size and the direction of the load borne by the air craft structure can be determined, and the load cell can be used for sensing large loads.
Owner:COMAC +1
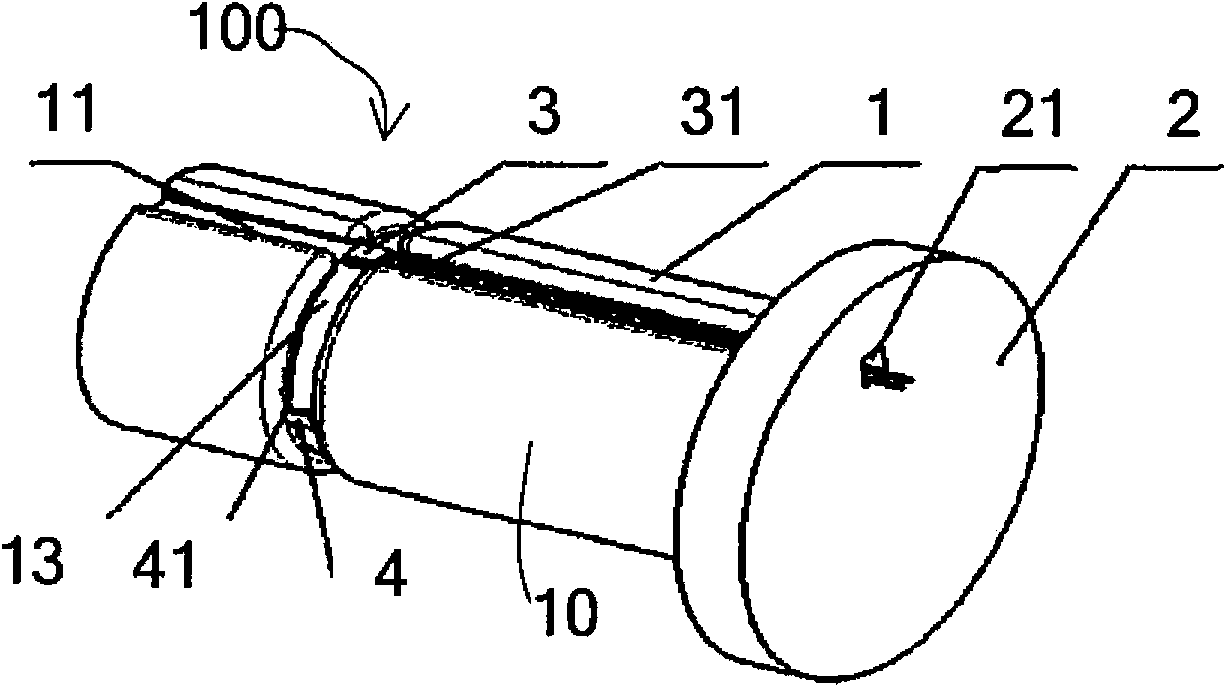
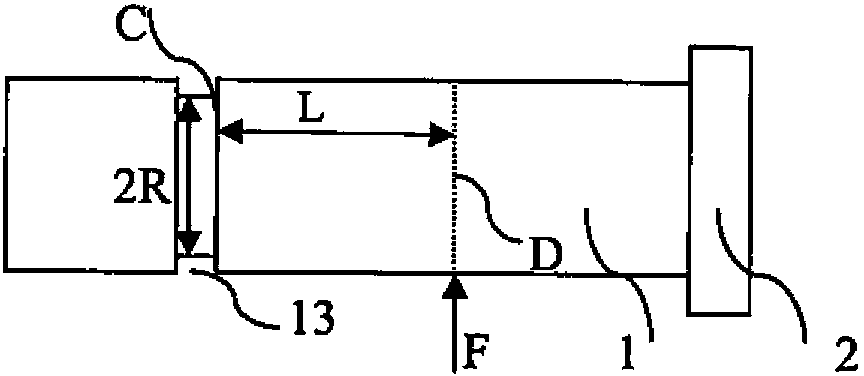
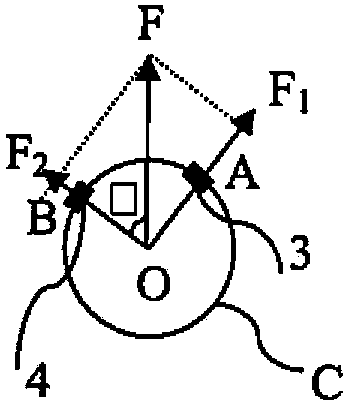
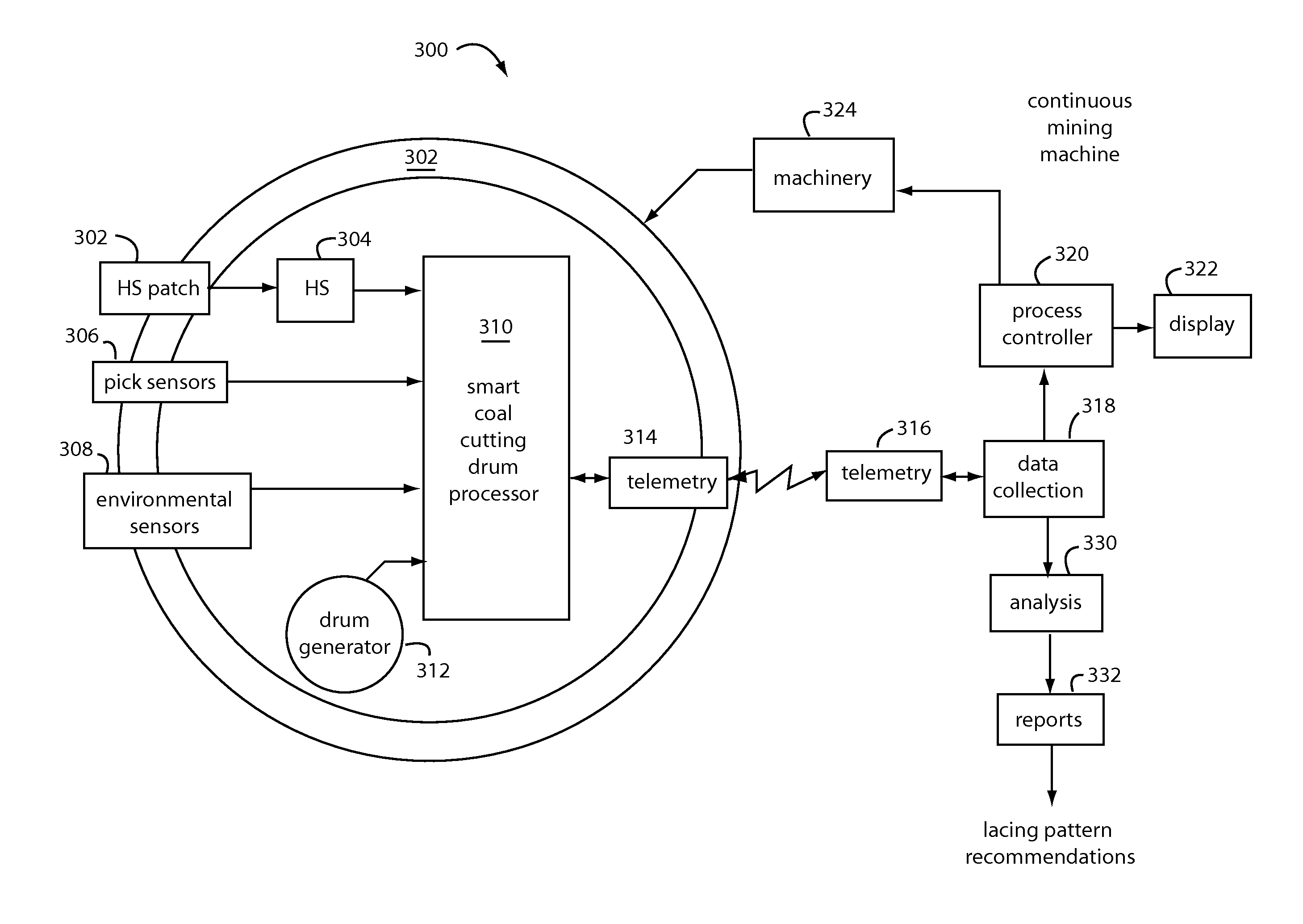
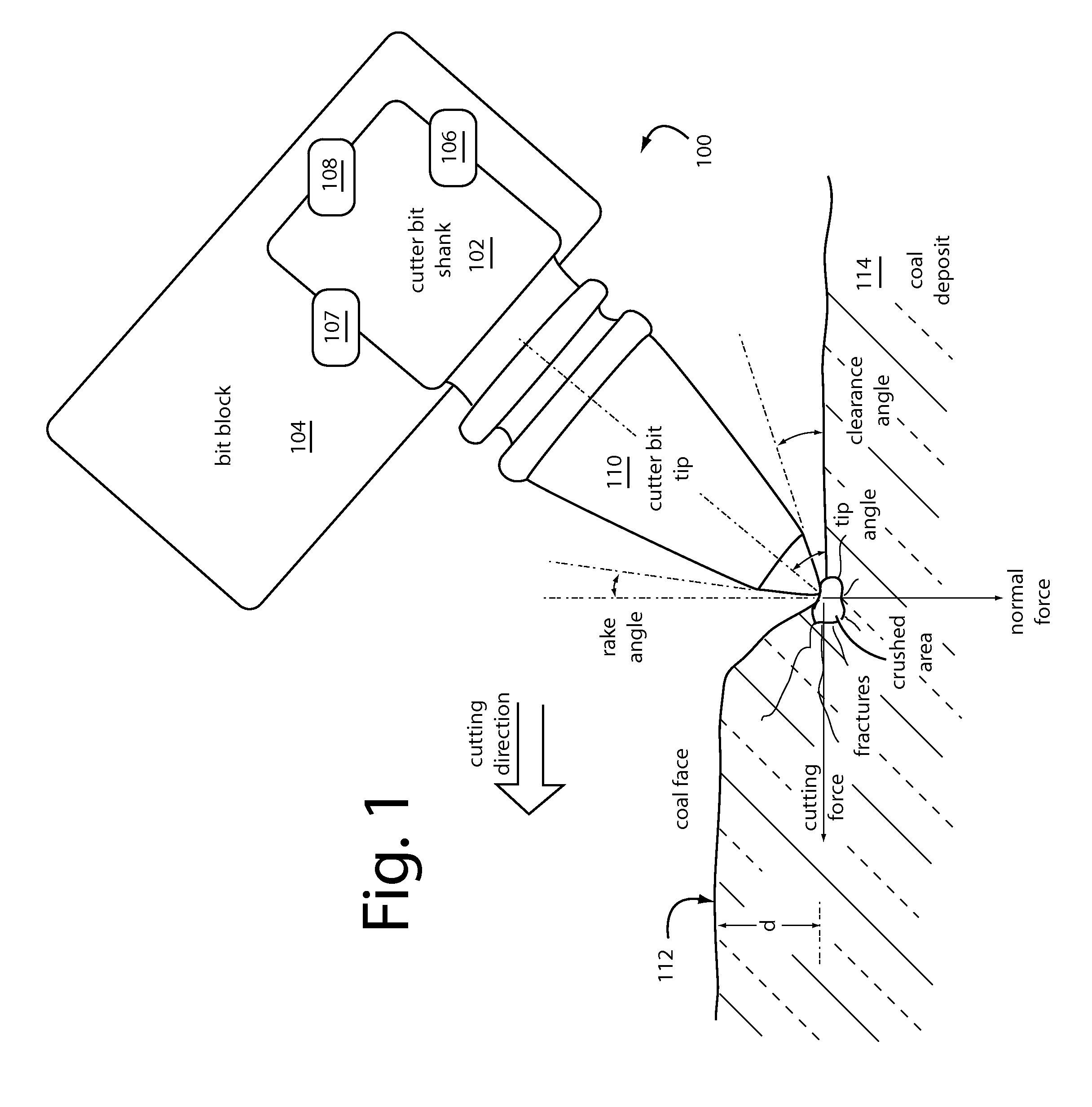
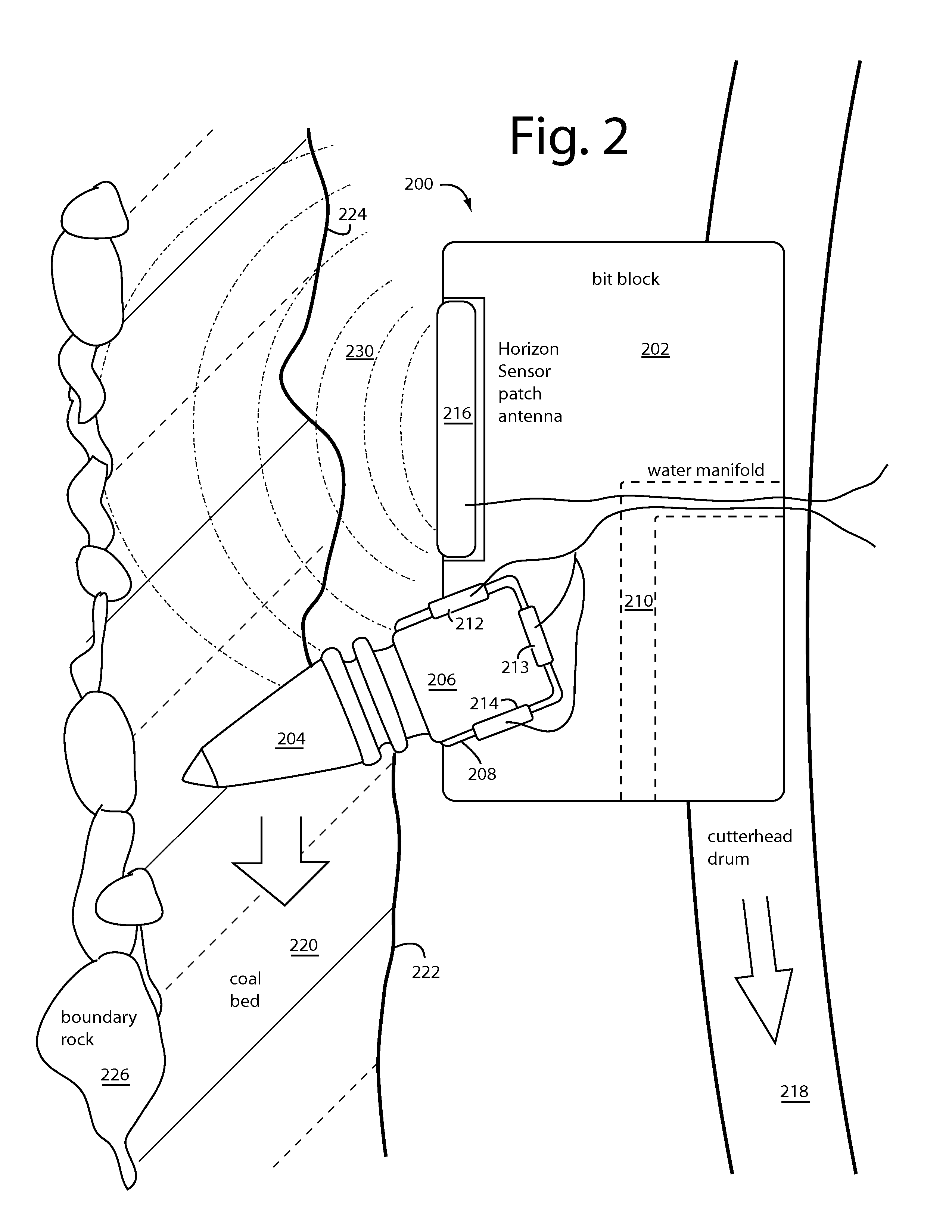
Mining machine automation
An automated coal mining system outfits rotating cutterhead drums with bit blocks and replaceable bit picks according to a lacing pattern. A set of strain gauges are configured to measure the mechanical forces experienced by the bit picks during coal cutting. Measurements are taken that can be processed for indications that the replaceable bit picks have encountered a boundary layer of rock during coal cutting operations, or they are working harder than necessary to cleave coal, or that a better lacing pattern is possible. A resonant microwave patch antenna is mounted on a top surface shoulder of the bit blocks to take impedance measurements of the coal face. The impedance measurements are calibrated according to indications that the replaceable bit picks have encountered a boundary layer of rock. The rotating drum sensor data is wirelessly transmitted back to the machine for analysis and control purposes.
Owner:STOLAR
Contact stress sensor
InactiveCN103411712AApplicable measurementHigh sensitivity factorForce measurementLead bondingEngineering
The invention discloses a contact stress sensor. The contact stress sensor comprises a flexible supporting base, a strainmeter, a flexible transmission line and a flexible medium, wherein the flexible supporting base is provided with a plurality of through holes and located at the bottommost position, the strainmeter and the flexible transmission line adhere to the upper surface of the flexible supporting base after being connected into a whole in a lead bonding mode, and the flexible medium covers and adheres to the upper surface of a combination of the strainmeter and the flexible transmission line. Due to the adoption of the flexible supporting base, the flexible transmission line and the flexible medium, the contact stress sensor is capable of bending and deforming along with changes of installation environments, and particularly applicable to measuring contact stress of an upper contact surface and a lower contact surface of an article located in a curved surface structure; due to the fact that the through holes are formed in the supporting base, the contact stress sensor can be used for measuring not only pulling stress but also compressive stress, and measuring accuracy is enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Seismic test device and test method for ultrahigh-voltage direct current single-pole composite post insulator
ActiveCN106124151ASimple structureDoes not affect mechanical propertiesVibration testingAccelerometerMarine engineering
The invention discloses a seismic test device and test method for an ultrahigh-voltage direct current single-pole composite post insulator. The seismic test device for the ultrahigh-voltage direct current single-pole composite post insulator comprises a vibrating table, a support installed on an installation platform of the vibrating table and a single-pole post insulator with the lower end installed on the installation platform of the support, wherein a counterweight is arranged at the upper end of the single-pole post insulator, a hardware fitting is arranged at the upper end of the counterweight, and at least one accelerometer and at least one strainmeter are arranged on the installation platform of the support; at least one accelerometer, at least one strainmeter and at least one displacement meter are arranged on the single-pole post insulator; at least one accelerometer is arranged on the hardware fitting; and at least one displacement meter is arranged on the installation platform of the vibrating table. The seismic test device and test method for the ultrahigh-voltage direct current single-pole composite post insulator are low in test cost, and can be used for effectively assessing the seismic performance of the single-pole post insulator.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Optic fiber connection for a force sensing instrument
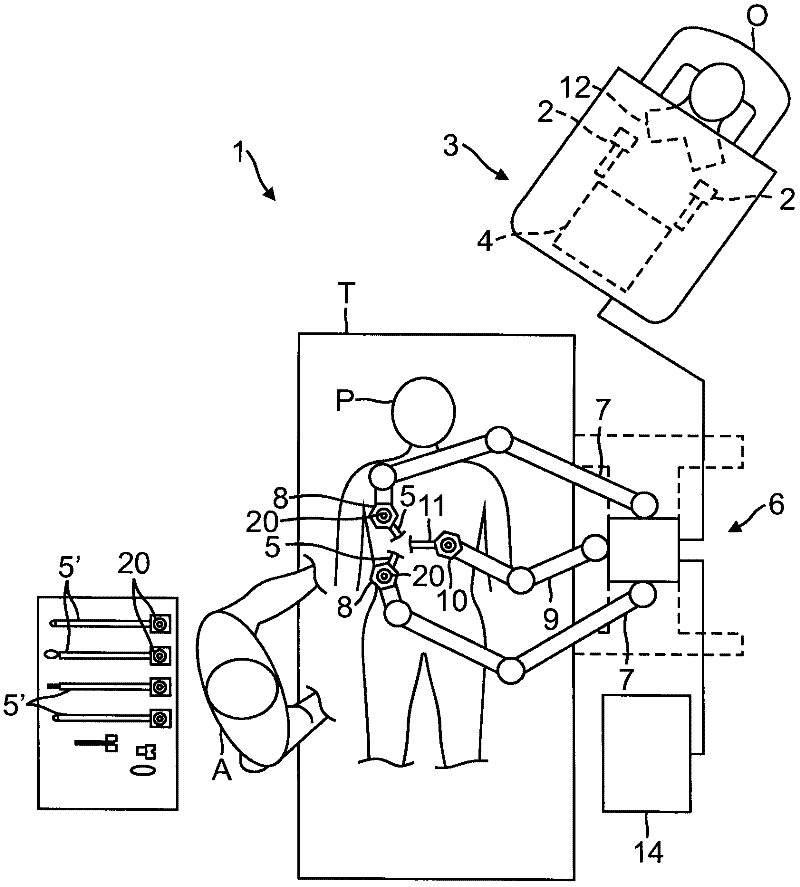
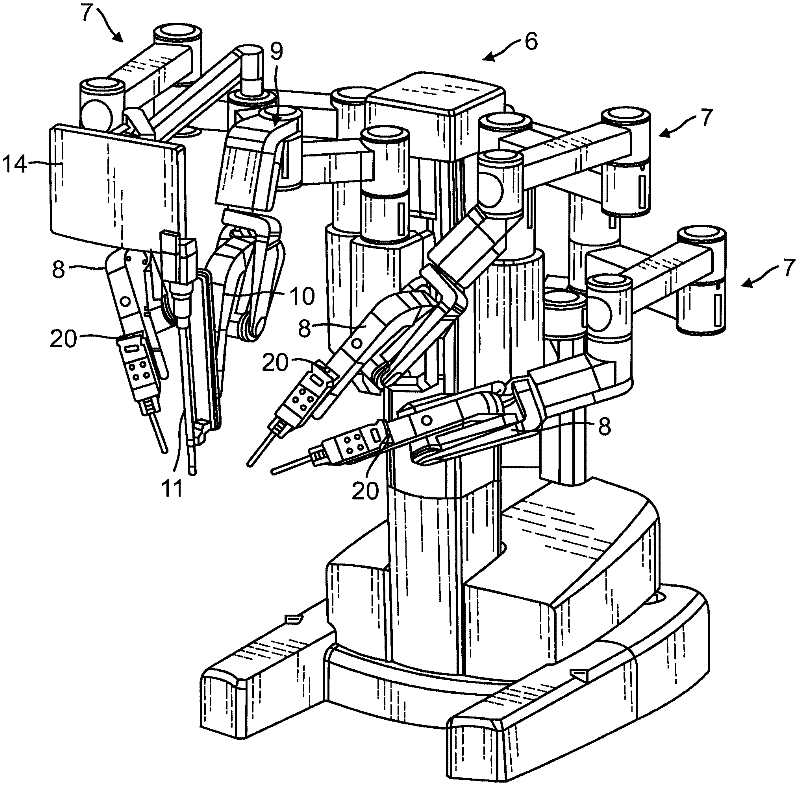
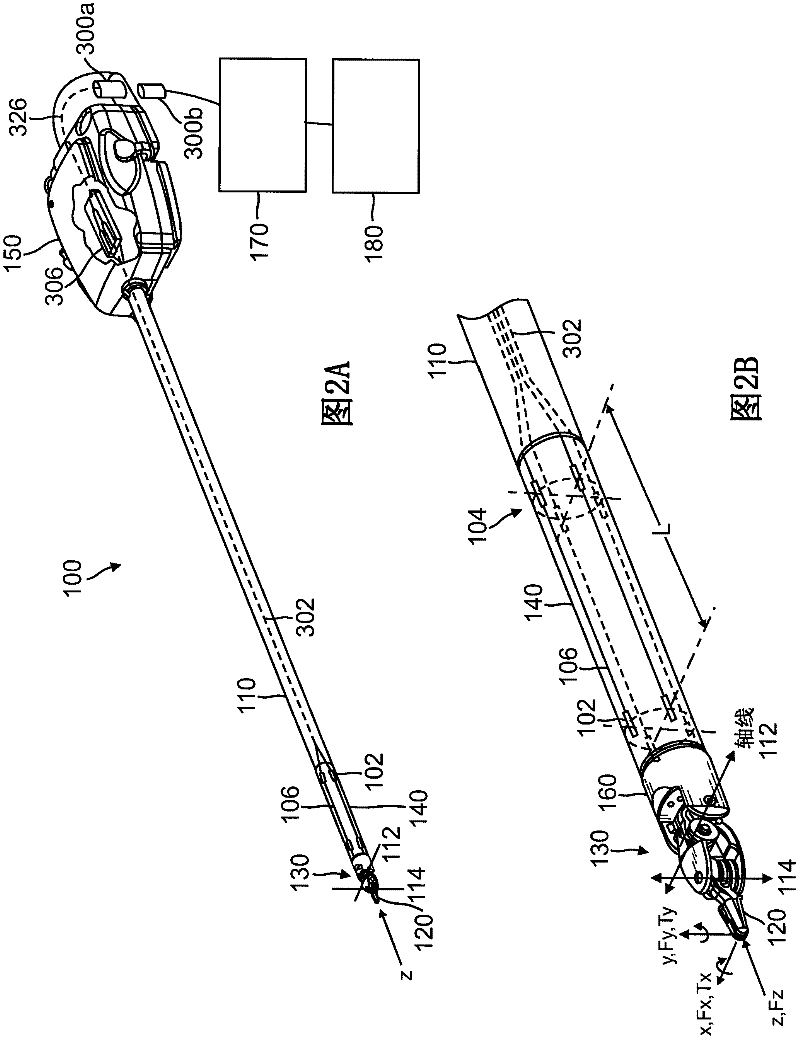
In one embodiment, a surgical instrument includes a housing linkable with a manipulator arm of a robotic surgical system, a shaft operably coupled to the housing, a force transducer on a distal end of the shaft, and a plurality of fiber optic strain gauges on the force transducer. In one example, the plurality of strain gauges are operably coupled to a fiber optic splitter or an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) multiplexer. A fiber optic connector is operably coupled to the fiber optic splitter or the AWG multiplexer. A wrist joint is operably coupled to a distal end of the force transducer, and an end effector is operably coupled to the wrist joint.; In another embodiment, a robotic surgical manipulator includes a base link operably coupled to a distal end of a manipulator positioning system, and a distal link movably coupled to the base link, wherein the distal link includes an instrument interface and a fiber optic connector optically linkable to a surgical instrument. A method of passing data between an instrument and a manipulator via optical connectors is also provided.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
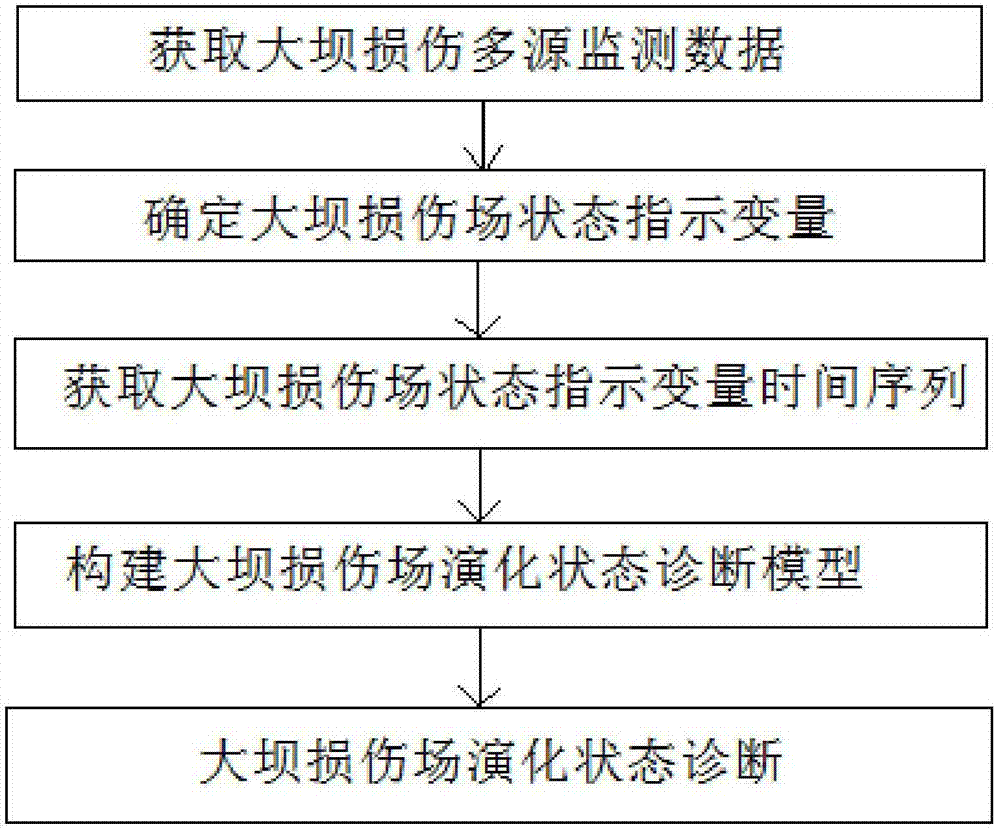
Diagnostic method of evolution state of damage field of concrete dam
ActiveCN103162982AFully reflect the state of healthStructural/machines measurementStrain energyEngineering
The invention discloses a diagnostic method of an evolution state of a damage field of a concrete dam. The method includes the steps of (1) building a damage field indication variable based on entropy, and defining the entropy of a system as H=F(Q,qi,L,T); (2) calculating the damage field indication variable, and extracting sizes influenced by stress, strain and strainmeter of the damage field from a dam safety monitoring system, wherein the number of strainmeter groups is n, strain energy of a unit of a portion where an ith strainmeter group is located is qi (i=1,2,......,n), total strain energy Q of the area is obtained, and therefore an information entropy function H of a local area is shown in the description, (qi=0, lambada i ln lambada i= 0); and (3) expressing the entropy of the damage field of the concrete dam at a certain moment as F(H)=F(Hh)+F(HT)+F(Htheta) according to a time sequence of the damage field indication variable, and obtaining influence degrees of water pressure, temperature and aging for the damage field and changing trends of the damage field according to an entropy formula to achieve diagnosis and prediction for the damage field. The diagnostic method solves the problems that a traditional method can only diagnose a single measurement point and is lack of relevant diagnosis for changes of measured values of multiple measure points, and comprehensively reflects health states of the dam.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Device and method for testing lateral impact friction
InactiveCN103743668AEnables side impact friction measurementsUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisTest sampleEngineering
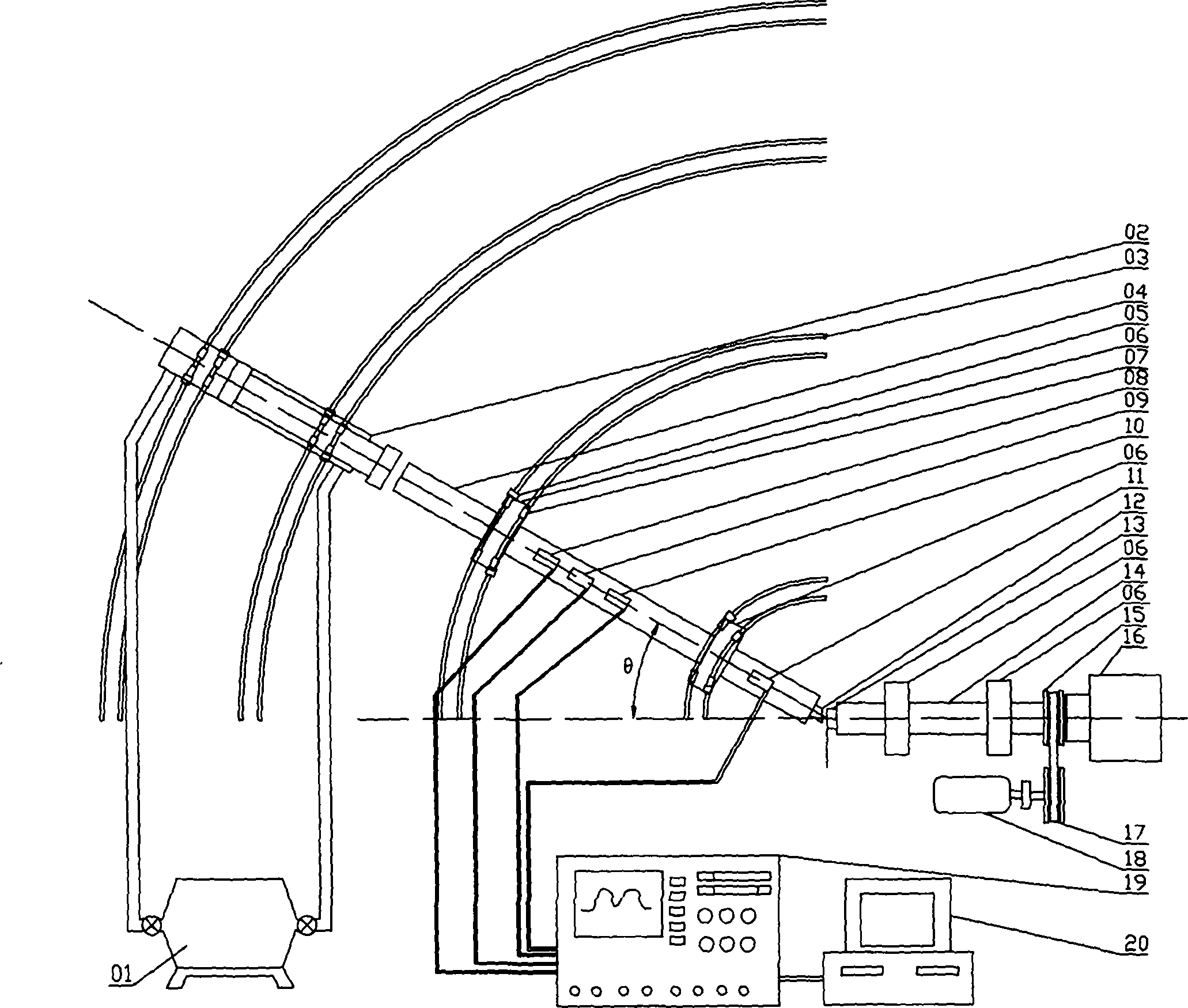
The invention discloses a device and a method for testing lateral impact friction. The device for testing lateral impact friction factors comprises a pneumatic pump, a pneumatic impact device, an arc-shaped rail, an incidence column, a clamp, a support, truckles, an acceleration sensor, a speed sensor, a first strainmeter, a second strainmeter, a first test sample, a second test sample, a transmission column, a belt pulley, a shock absorber, a belt, a variable-frequency motor, a signal acquisition device and a computer. Due to the arrangement of the truckles at the bottoms of the pneumatic impact device and the support, the pneumatic impact device and the support can move on the arc-shaped rail so as to regulate the impact incidence angles of the test samples. Lateral impact friction of materials can be tested by the device. The shapes of the test samples which are used in the invention can be changed, so that the lateral impact friction properties of different types of materials can be tested.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +2
Isolating type triaxial test device
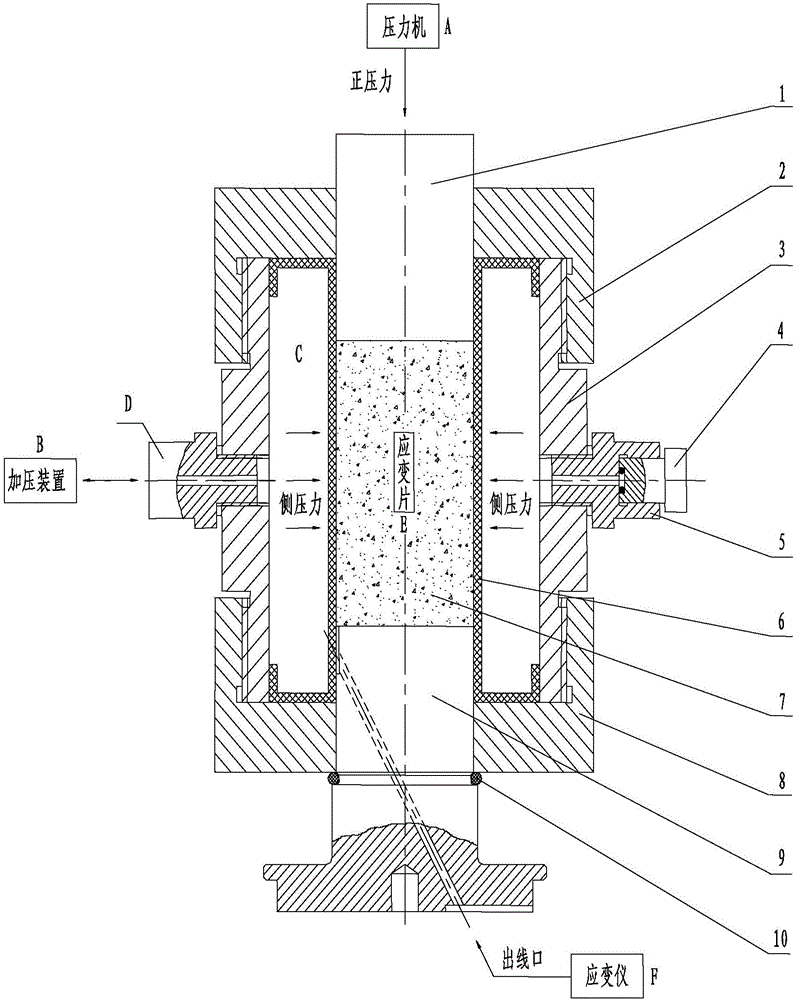
InactiveCN106153469ASimple structureReduce volumeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTriaxial shear testAxial pressure
The invention disclose an isolating type triaxial test device, and relates to a device for carrying out mechanical property tests on rock and concrete materials in a pressure state. According to the main structure of the device, the upper portion and the lower portion of a pressure chamber are connected with an upper penetrating cover and a lower penetrating cover respectively to form an overall space, a lower pressing head, a sample and an upper pressing head are sequentially arranged along the center line of the overall space from bottom to top, and the lower pressing head is sleeved with an elastic cushion and isolated from the inner wall of the pressure chamber through an isolating sleeve; hydraulic oil is injected into the space formed by the pressure chamber and the isolating sleeve through the pressurizing device; a strain gage attached to the side face of the sample is connected with a strain gauge to test strain; a press applies test axial pressure to the sample through the upper pressing head. According to the device, pressure oil is located in an airtight space, repeated oil charge or drainage is not needed, and the sample does not need to be wrapped. Due to the fact that the device is simple in structure, small in size and light, operation is easy and convenient, and working efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
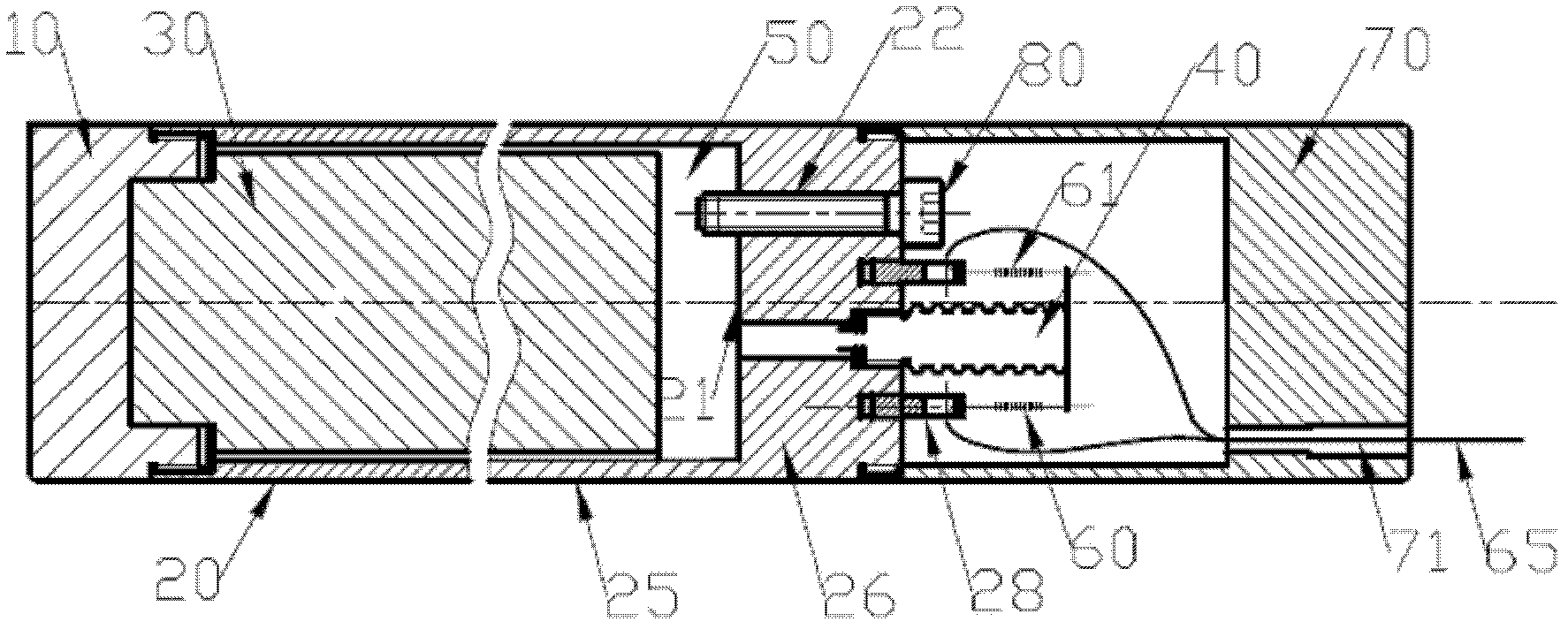
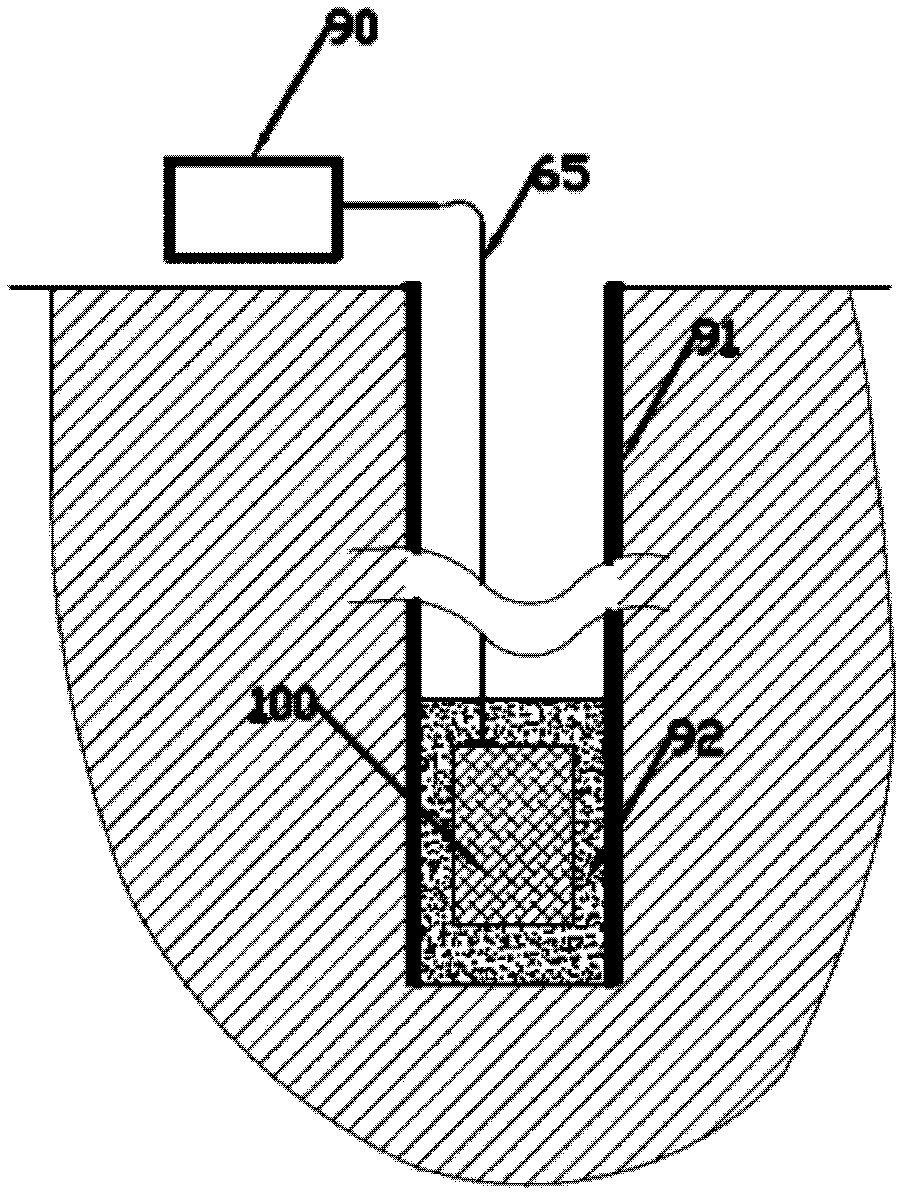
Optical fiber drilling strain gauge
The invention discloses an optical fiber drilling strain gauge, which comprises a strain cylinder, liquid, an end cover, a corrugated pipe, a bolt, measurement gratings, a protective cover, an optical cable and ground demodulation equipment, wherein the strain cylinder is used for sensing strain; the liquid is filled in the strain cylinder and used for transferring the strain sensed by the strain cylinder; the end cover is used for sealing; the corrugated pipe is arranged at the bottom of the strain cylinder and used for sensing the change of pressure in the strain cylinder; the bolt is arranged at the bottom of the strain cylinder and used for filling liquid and sealing; the measurement gratings are fixed at the end of the corrugated pipe and the bottom of the strain cylinder and used for measuring the end displacement of the corrugated pipe; the protective cover is arranged at the bottom of the strain cylinder and used for protecting the internal structure of the optical fiber drilling strain gauge; the optical cable is connected with the optical fiber drilling strain gauge arranged at the bottom of a well and the ground demodulation equipment; and the ground demodulation equipment is used for demodulating the wavelength change of the measurement gratings so as to obtain a ground strain value. By using the optical fiber drilling strain gauge, the problems of electromagnetic interference, lightning stroke resistance and null shift of the conventional drilling strain gauge are solved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
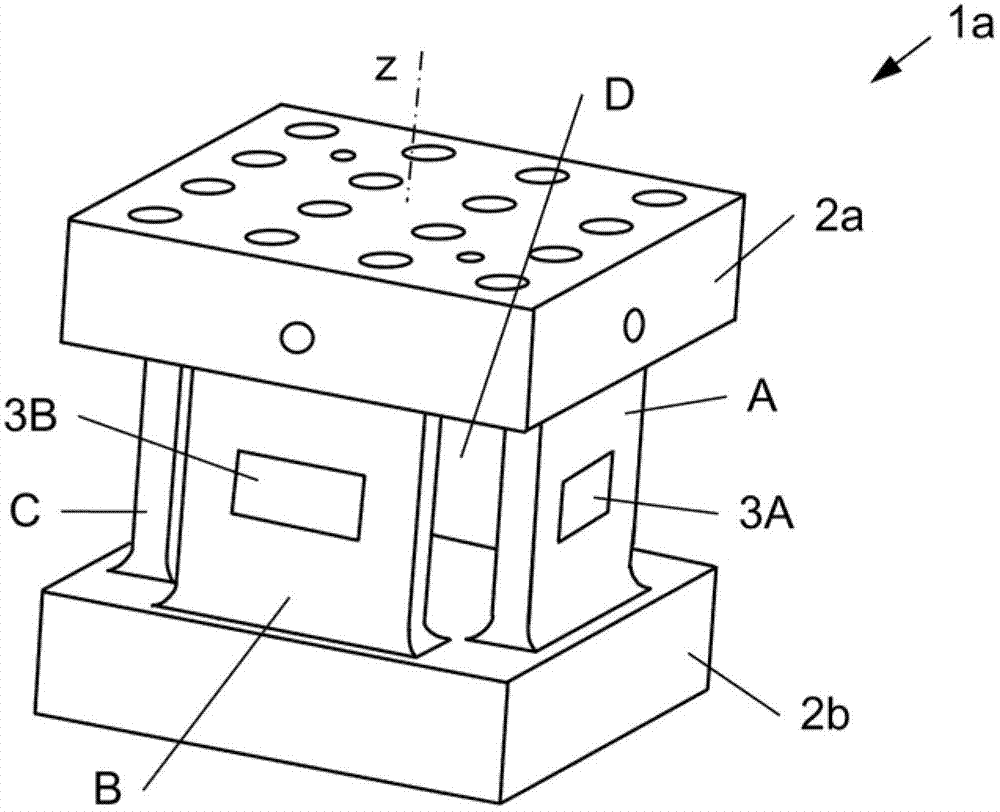
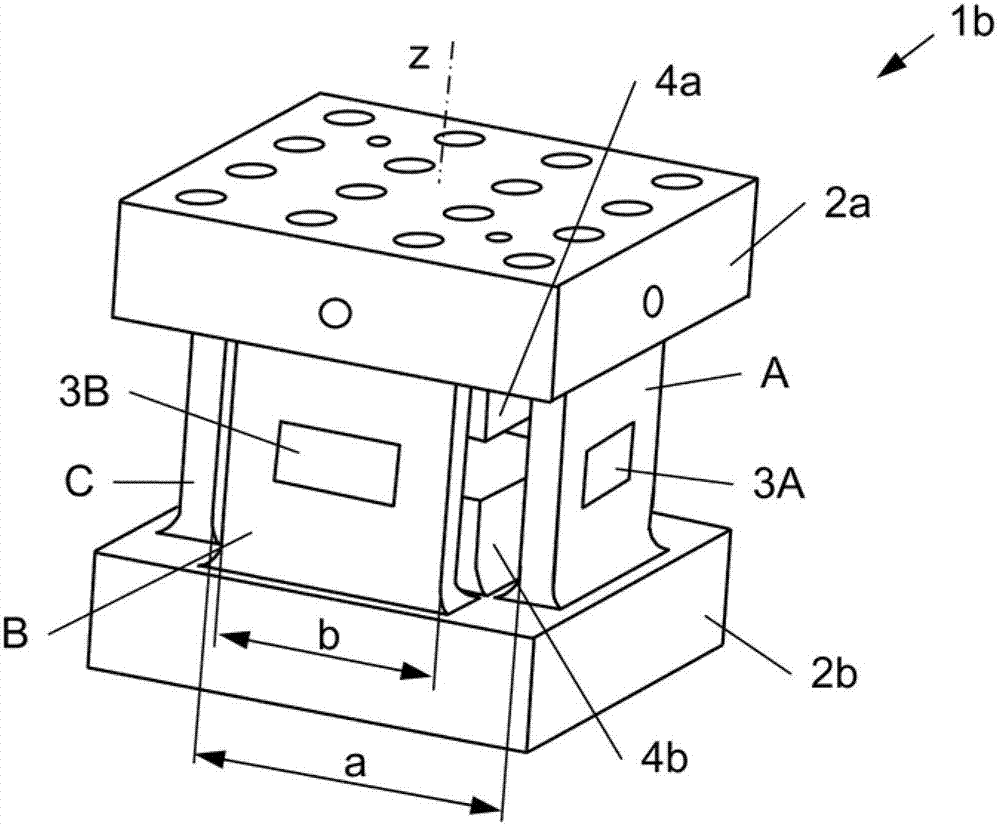
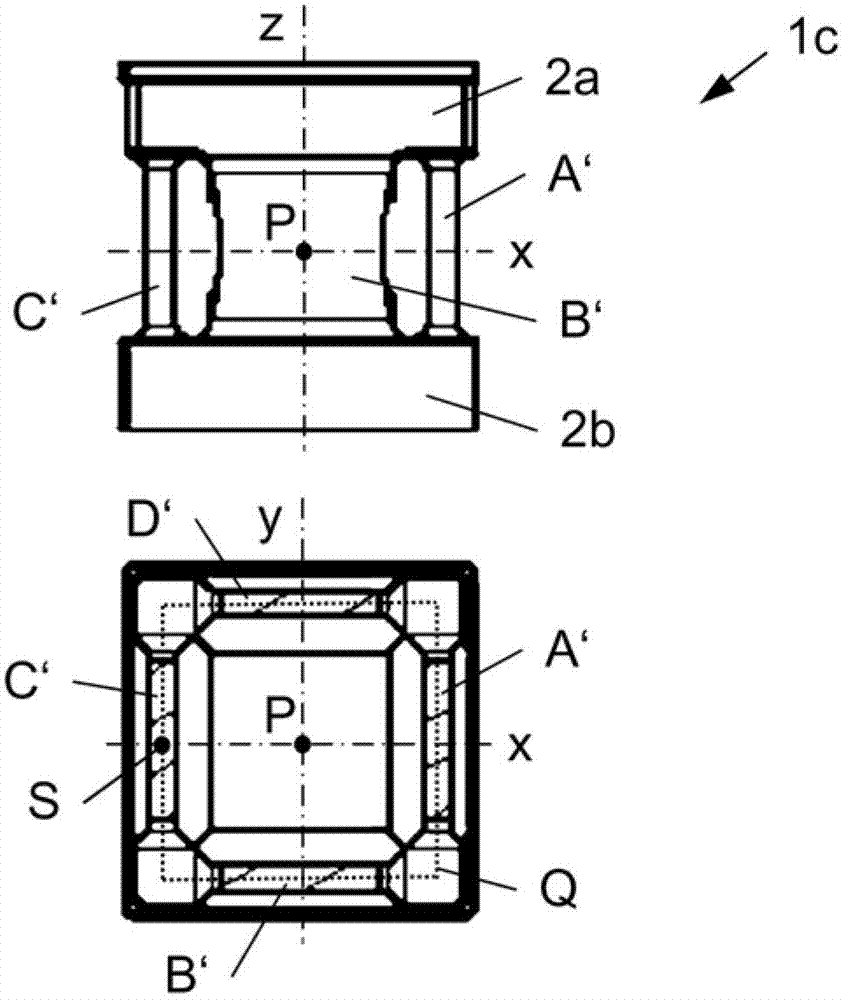
Measuring element, force sensor and measuring assembly for measuring forces
ActiveCN102889953AForce measurementApparatus for force/torque/work measurementEngineeringStrain gauge
The invention relates to a measuring element, a force sensor and a measuring assembly for measuring forces. The measuring element (1a..1c) for measuring forces comprises two spaced-apart core portions (2a, 2b) and four identical spaced-apart webs (A..D, A'..D') which are aligned along a longitudinal axis (z) and are arranged in a square (Q), connecting the two core portions (2a, 2b). Force sensors (3a, 3b, 3A..3D, 11, 12, 21, 22, 31..34) are only provided to the webs (A..D, A6..D6). Further, the force sensors (3a, 3b, 3A..3D) include two first strain gauges (11, 12) for measuring a force in a first direction (z), two second strain gauges (21, 22) for measuring a force perpendicular to the first direction (z), at least one third strain gauge (31, 33) for measuring a force at an angle of +45 degrees to the first direction (z) and at least one fourth strain gage (32, 34) for measuring a force at an angle of -45 degrees to the first direction (z). The strain gages (11, 12, 21, 22, 31..34) are arranged on a common substrate. Finally, a measuring assembly to be used with the measuring element (1a..1c) is provided.
Owner:MAGNA STEYR FAHRZEUGTECHN
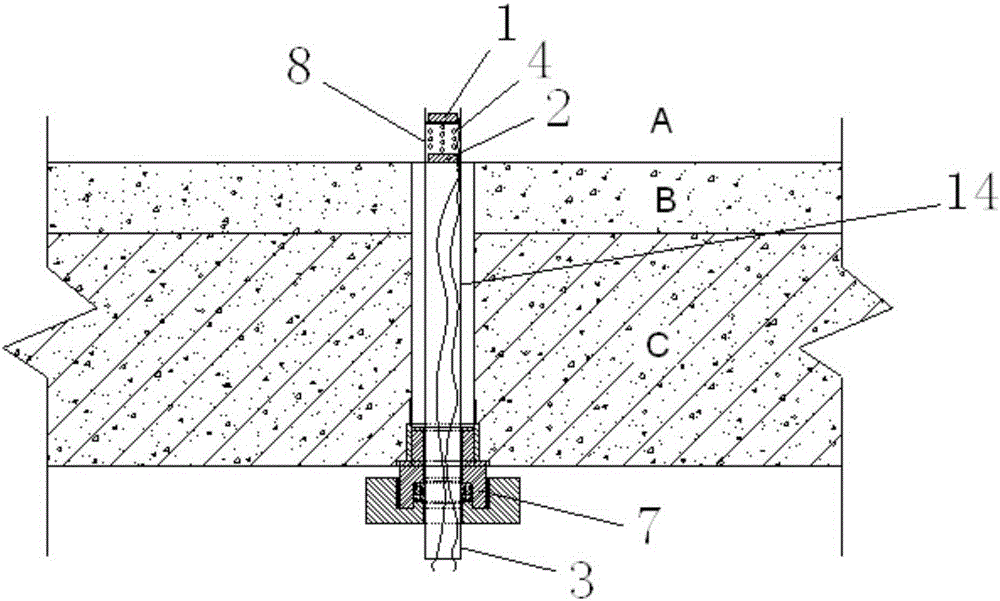
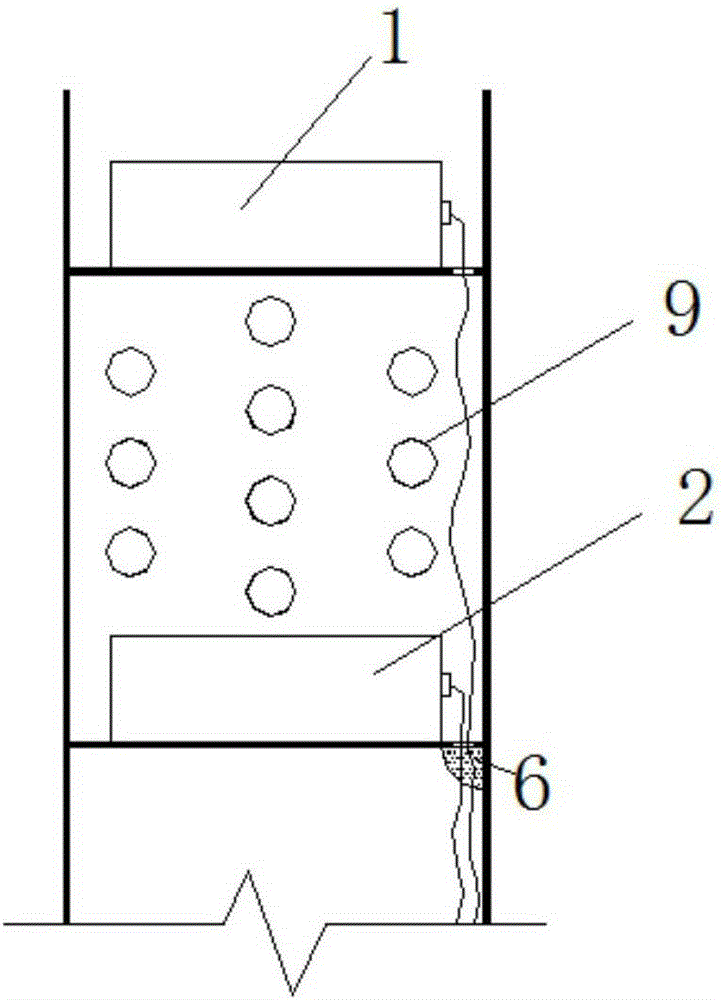
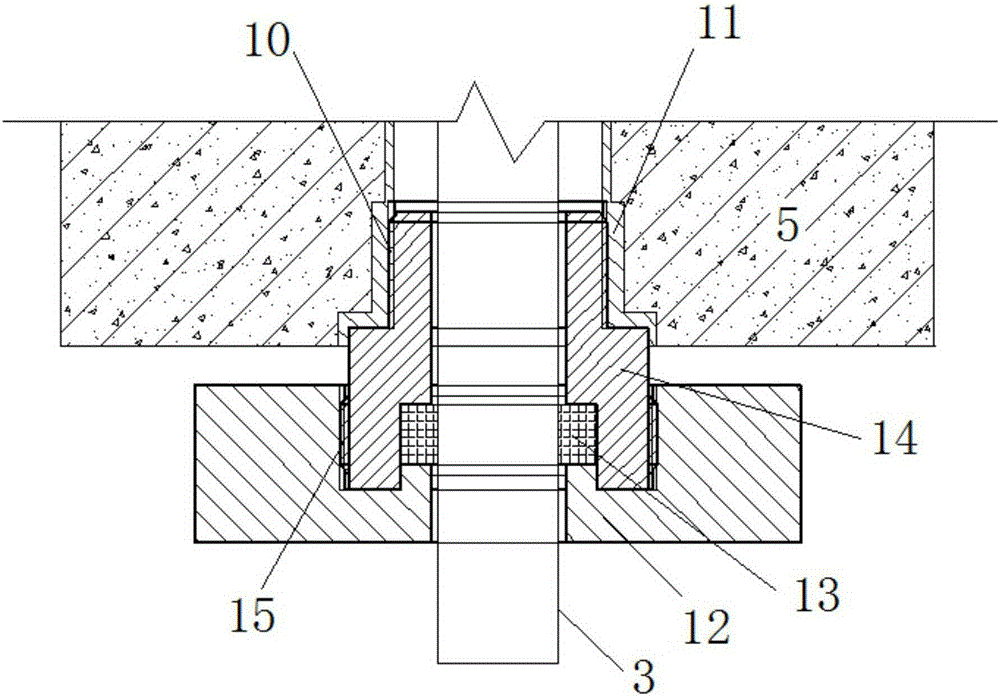
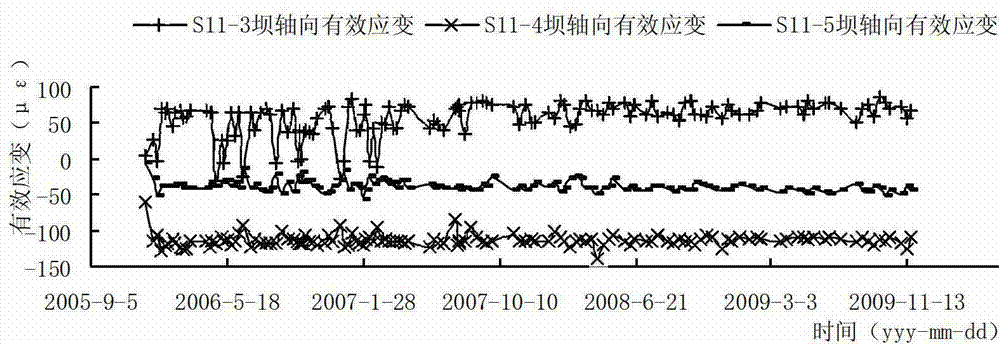
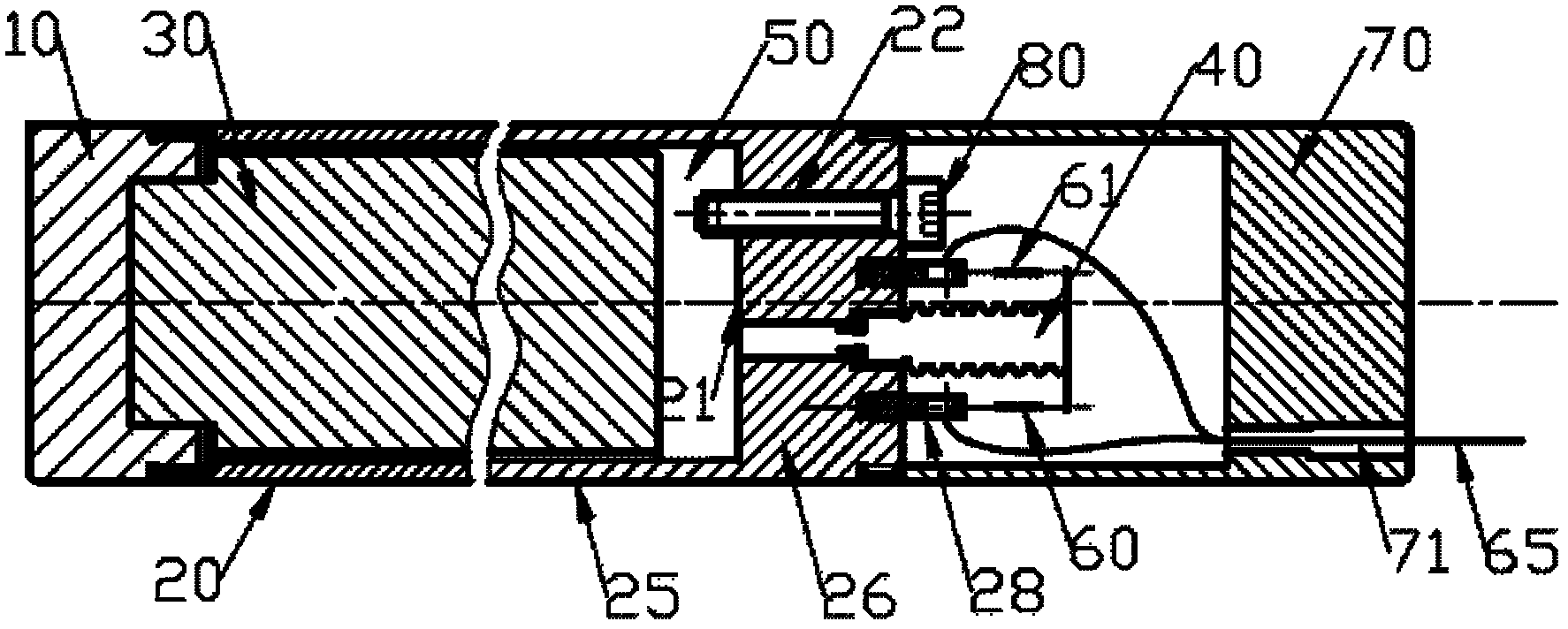
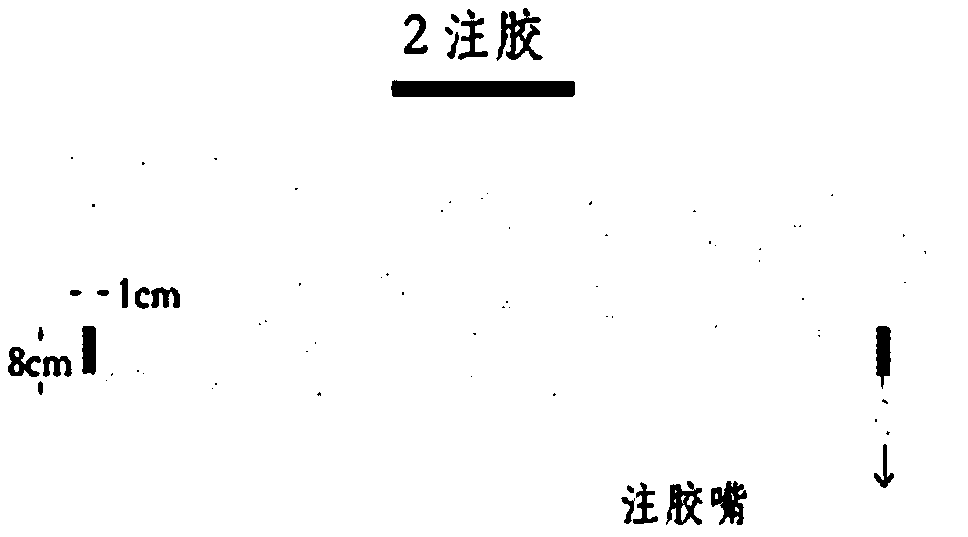
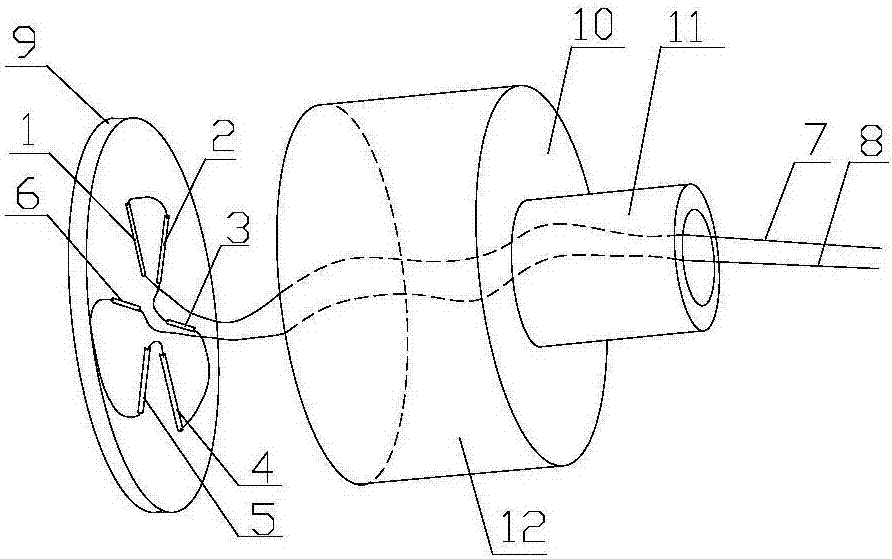
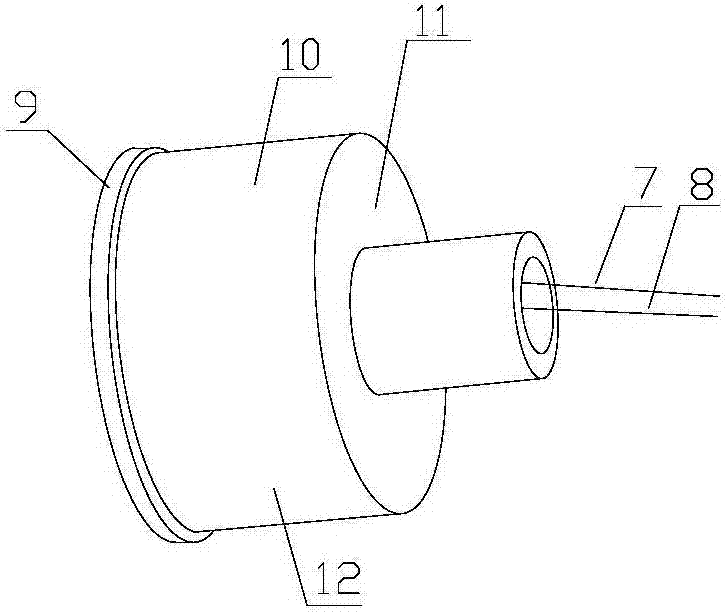
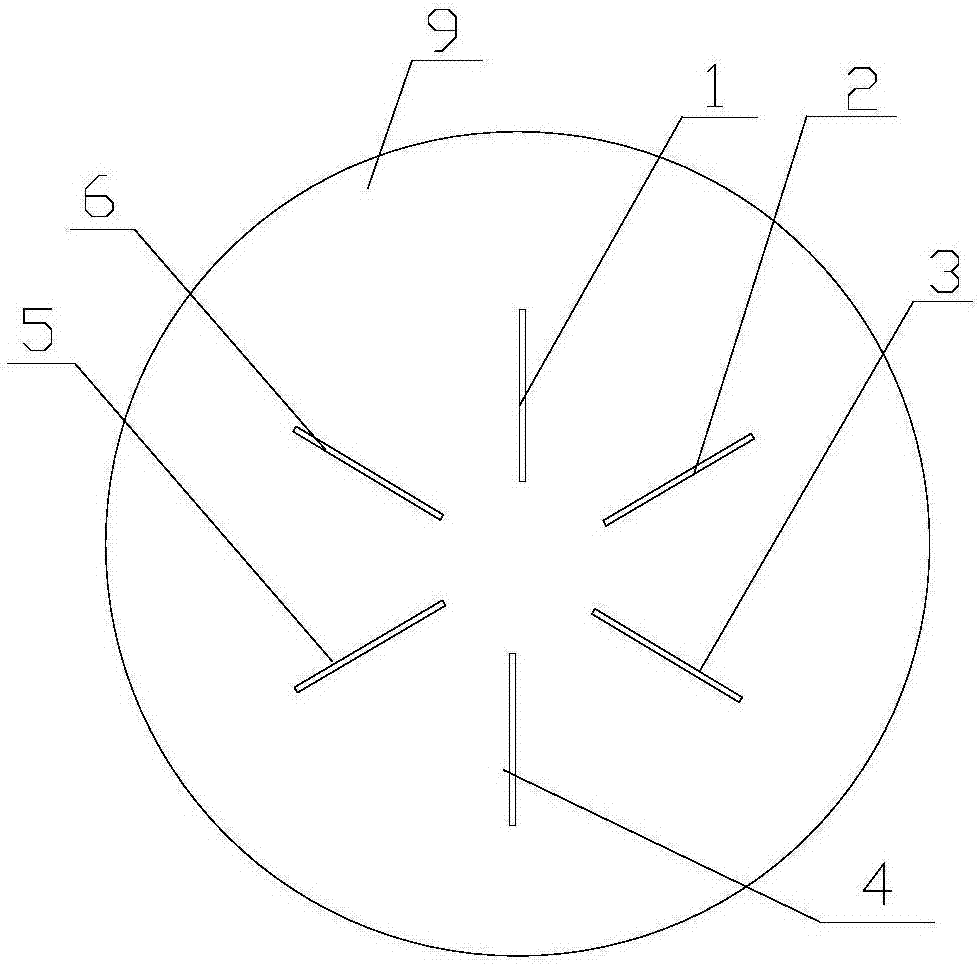
Concrete strainmeter subassembly and installation method
The invention relates to construction and especially relates to a subassembly for fixing a strainmeter in concrete, and an installation method. The invention discloses a subassembly for fixing a strainmeter in concrete and an installation method aiming at solving the problem of inaccurate measurement data of strainmeters in the prior art. The concrete strainmeter subassembly comprises a strainmeter and fixing rebars. The strainmeter comprises wafers, a force transferring rod, and a strain sensor. A fixing device is arranged between the strainmeter and the fixing rebars and is used for fixing the strainmeter on the fixing rebars. The fixing device is arranged on the strainmeter and makes the wafers of the strainmeter and the force transferring rod keep in an indirect contact status; the fixing device comprises a fixing tube, one end of the fixing tube is connected with the strainmeter. A guide line, connecting to the strain sensor, of the strainmeter extends outward through the pipeline of the fixing tube. By installing the fixing device between the fixing rebars and the strainmeter and adjusting the outlet mode of the guide line, the influence of external factors is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
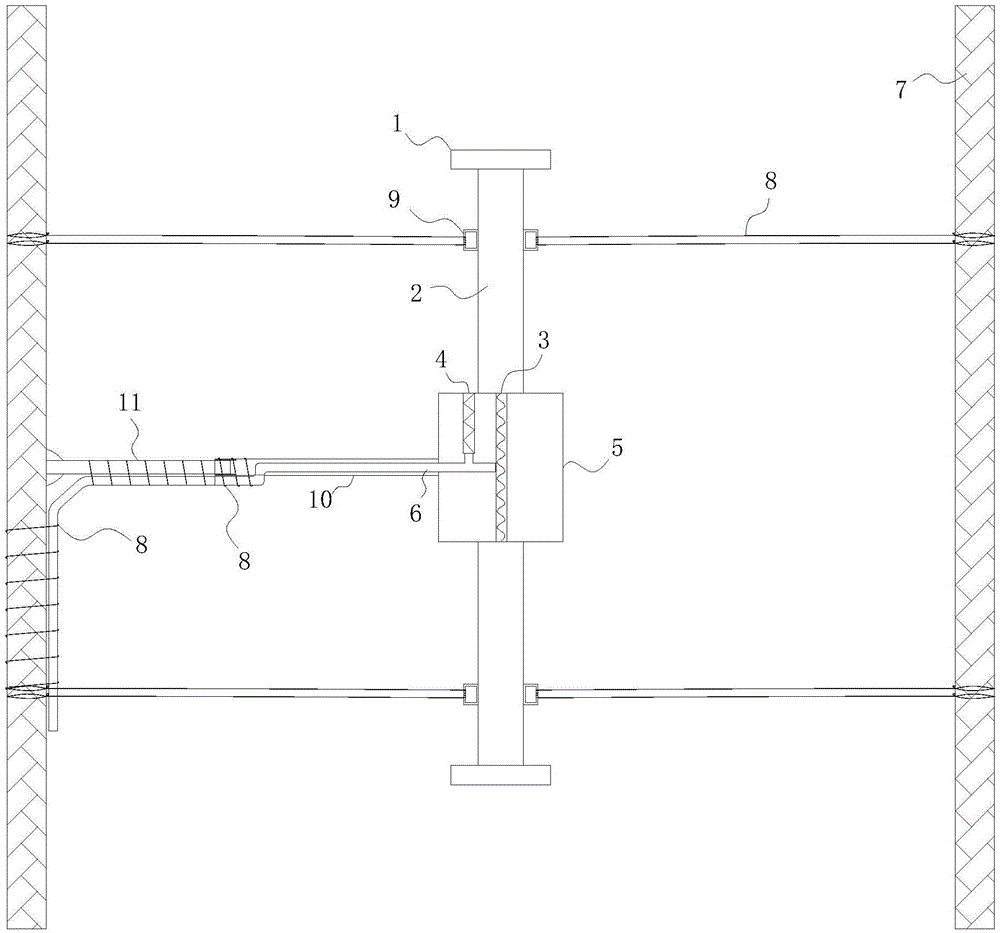
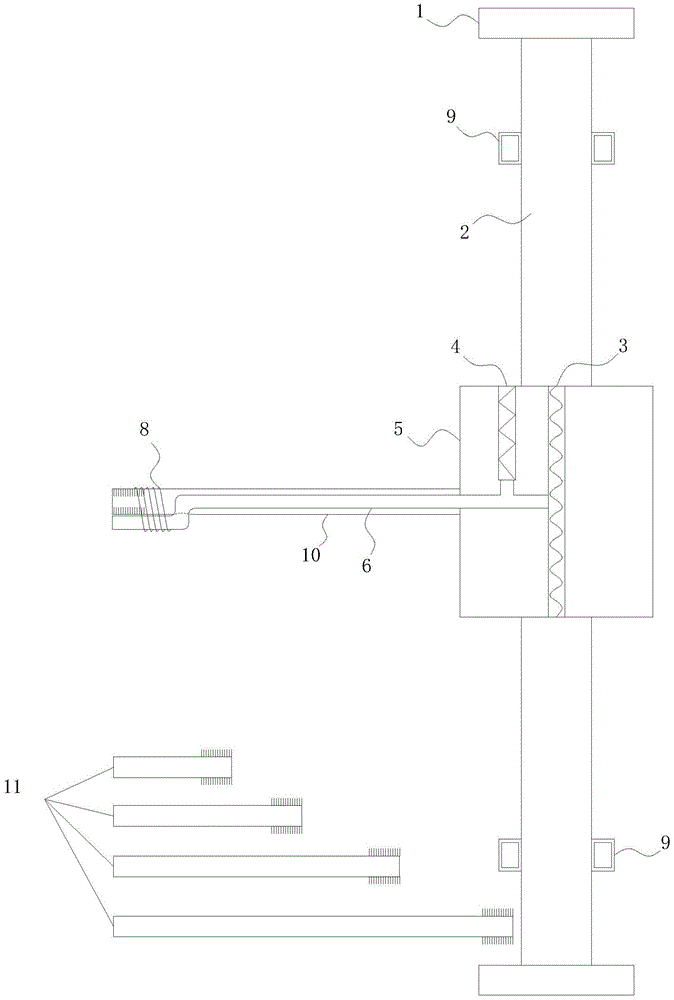
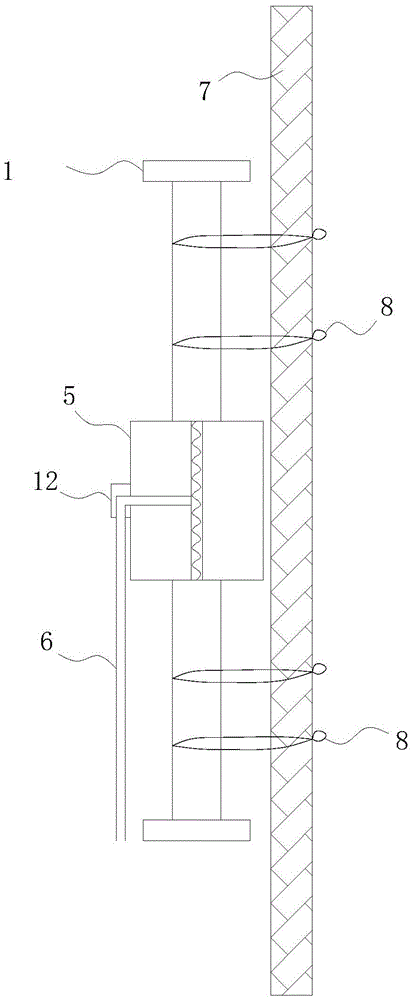
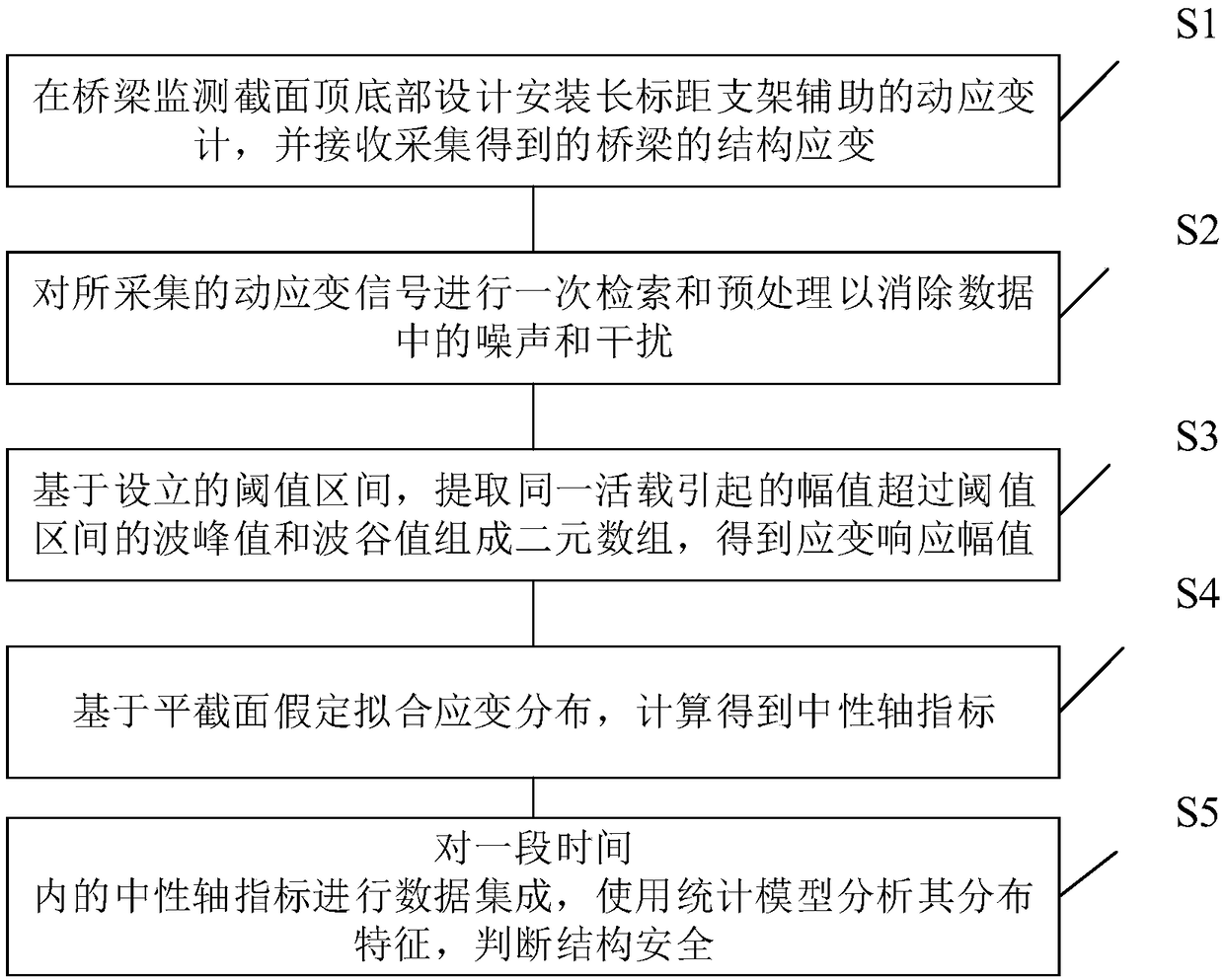
Long-term monitoring method based on beam-type bridge cross section neutral axis safety index
ActiveCN109506615AReduce distractionsImprove accuracyMeasurement devicesSafety indexSafety indicators
The invention relates to a long-term monitoring method based on a beam-type bridge cross section neutral axis safety index. The method comprises the following steps: step S1: designing and installinga dynamic strainmeter assisted by a long scale distance bracket at the top and bottom of a bridge monitoring cross section, receiving and collecting obtained structure strain of the bridge; step S2: searching and preprocessing collected dynamic strain signals once so as to eliminate noise and interference in data; step S3: based on a setting threshold section, extracting an amplitude value causedby same living load and forming a binary array by wave crest values and wave trough values exceeding the threshold section, to obtain a strain response amplitude value; step S4: fitting strain distribution based on plane cross section assumption, and calculating to obtain a neutral axis index; and step S5: performing data integration on the neutral axis indexes within a period of time, analyzing distribution characteristics thereof by using a statistic model, and judging structure safety. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of strong pertinence, stable long-term performance, easy popularization and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
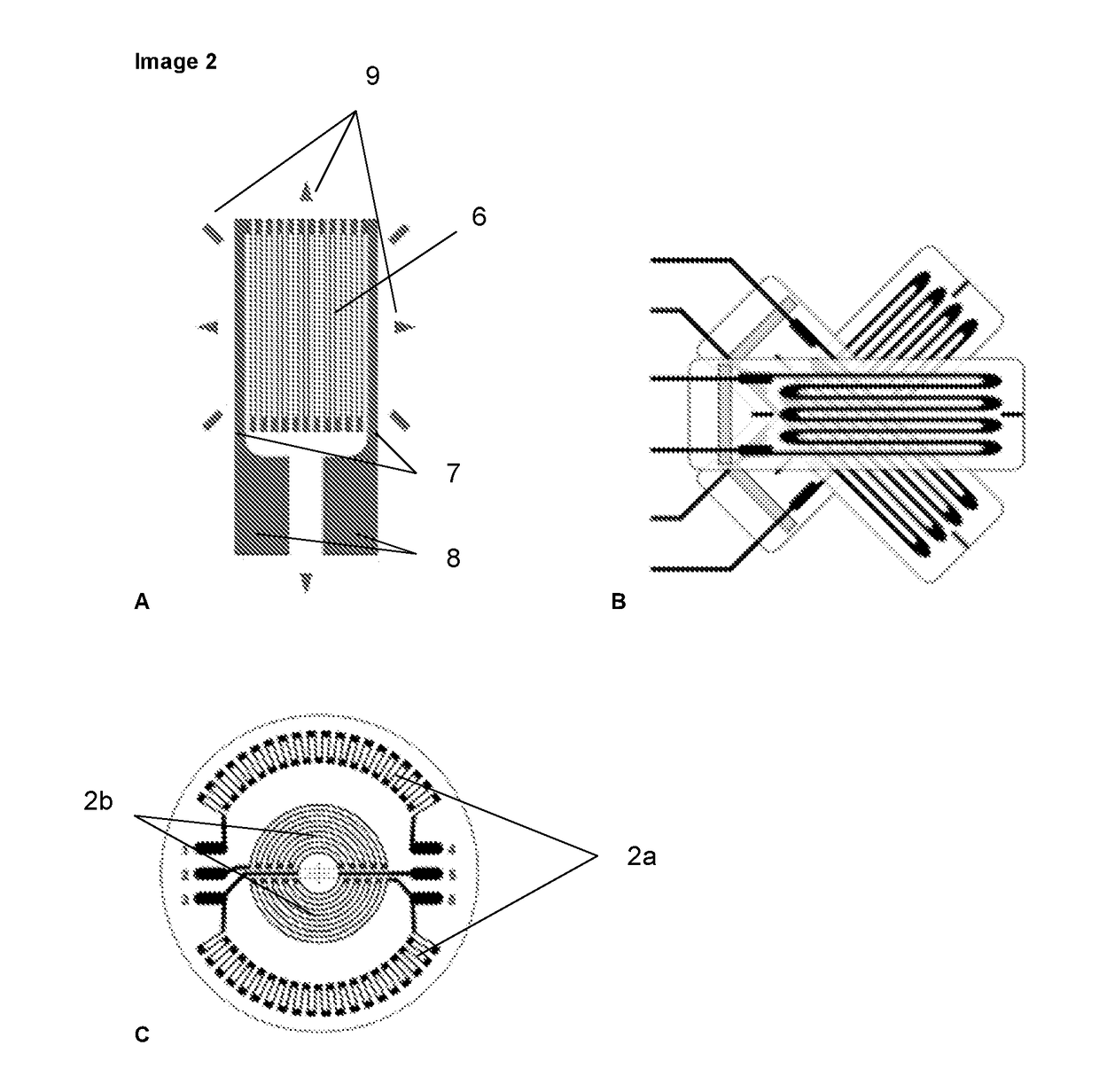
Semi-implanted hole bottom fiber bragg grating strainmeter geostress measuring device and method
ActiveCN106918415AWide measurement rangeHigh measurement accuracyForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFiberGrating
The invention provides a semi-implanted hole bottom fiber bragg grating strainmeter geostress measuring device and method. The device includes a fiber bragg grating strainmeter probe, an injection end optical cable, a transmission end optical cable, a fiber bragg grating adjustment analyzer, a signal line, a data acquisition host and an installing rod with an installer. The fiber bragg grating strainmeter probe includes a pedestal and a semi-implantable epoxy resin substrate installed in the pedestal, six fiber bragg grating strainmeters are fixed on the epoxy resin substrate around the circumference at an interval of 60 degrees, after the six fiber bragg grating strainmeters are connected in series, two ends are connected with the injection end optical cable and the transmission end optical cable, the injection end optical cable and the transmission end optical cable are connected with the fiber bragg grating adjustment analyzer, and the fiber bragg grating adjustment analyzer is connected with the data acquisition host through the signal line. The semi-implanted hole bottom fiber bragg grating strainmeter geostress measuring device couples a fiber bragg grating sensor and a hole bottom strain technology, has the advantages of small size, wide measuring range, easy installation, high measuring accuracy, long serving time and the like, and provides a new approach with relatively high precision to complicated rock mass geostress measurement.
Owner:CHANGJIANG RIVER SCI RES INST CHANGJIANG WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
Remote calibration device of borehole deformation instrument for borehole ground deformation measurement
ActiveCN104089571AEasy to controlHigh precisionElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementDisplacement controlData treatment
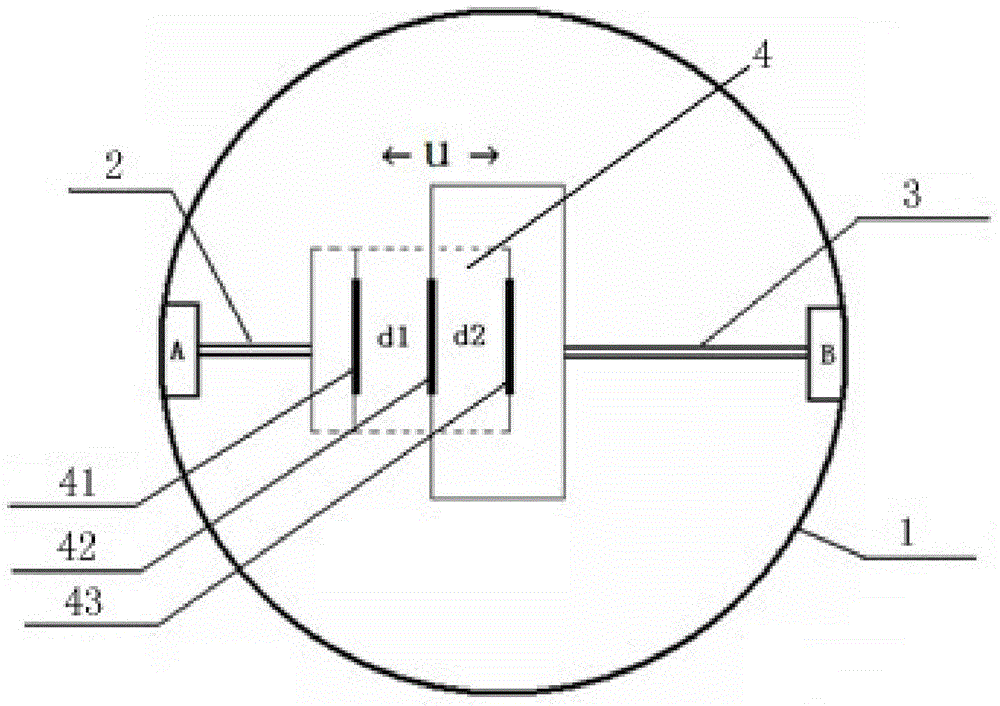
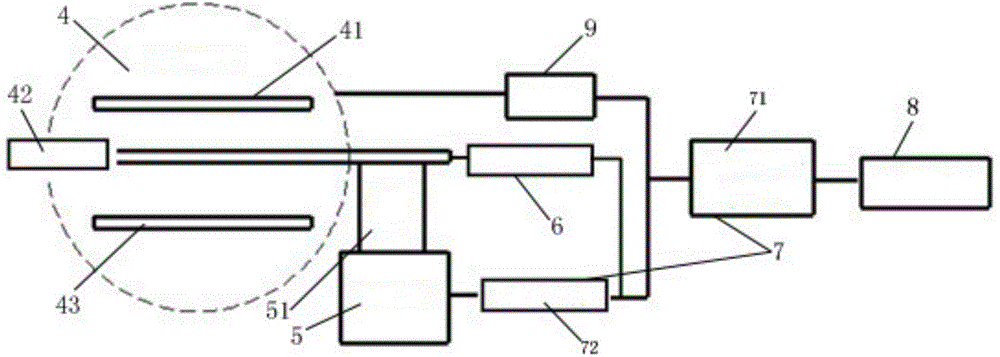
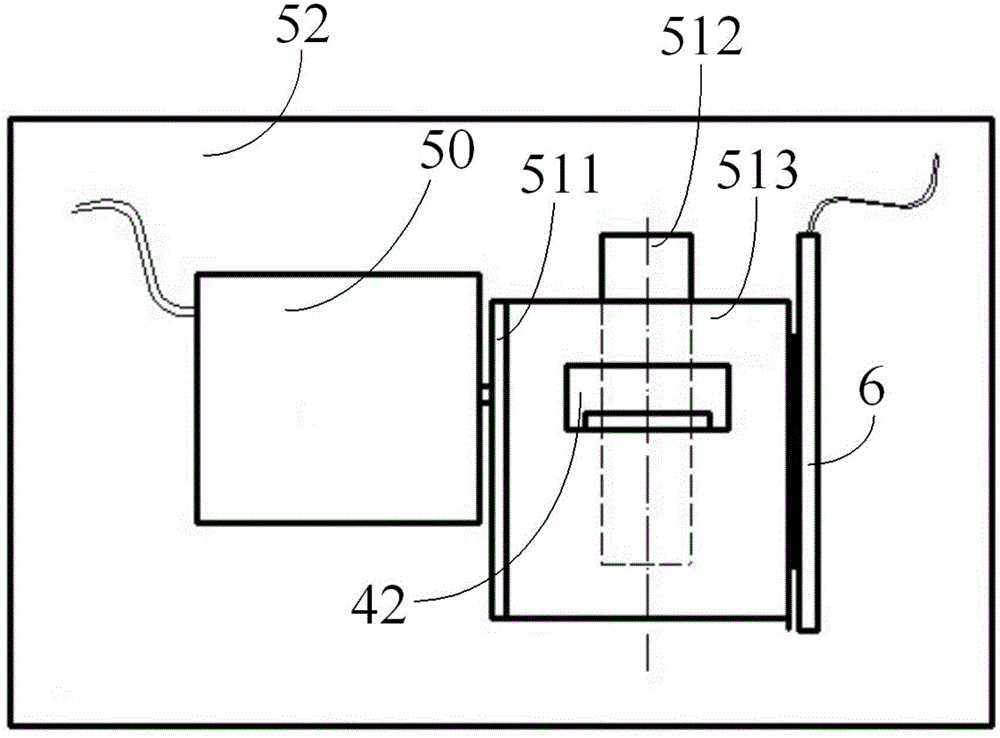
The invention discloses a remote calibration device of a borehole deformation instrument for borehole ground deformation measurement. The device comprises a micro-displacement device, a calibration device body and a calibration and control device, wherein the micro-displacement device is provided with a movable displacement driving portion which is connected with the measuring polar plate in the middle of a tripolar differential capacitor type micro-displacement sensor of a borehole strainmeter and can measure the measuring polar plate; the calibration device body is arranged on one side of the measuring polar plate of the tripolar differential capacitor type micro-displacement sensor and can detect the displacement variation of the measuring polar plate; the calibration and control device is respectively in communication with the micro-displacement device and the calibration device body and can send the received displacement variation of the measuring polar plate to a remote data processing terminal, wherein the displacement variation is detected by the calibration device body; a displacement control signal sent by the data processing terminal is transmitted to the micro-displacement device, so that the displacement driving portion of the micro-displacement device is controlled to move the measuring polar plate of the tripolar differential capacitor type micro-displacement sensor according to the displacement control signal. The remote calibration device is simple in structure and facilitates remote calibration of the borehole deformation instrument.
Owner:NAT INST OF NATURAL HAZARDS MINISTRY OF EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com