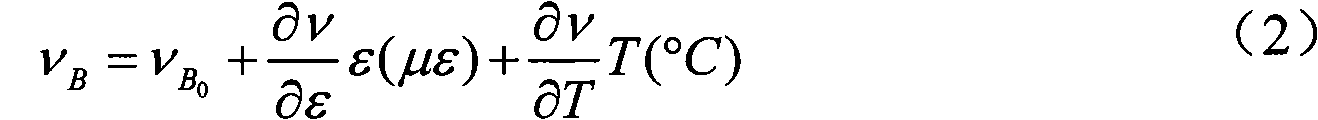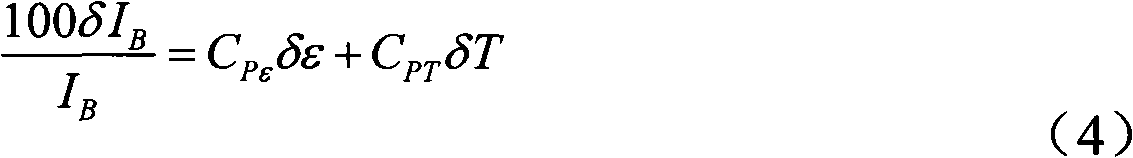Patents
Literature
400 results about "Fiber optic splitter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
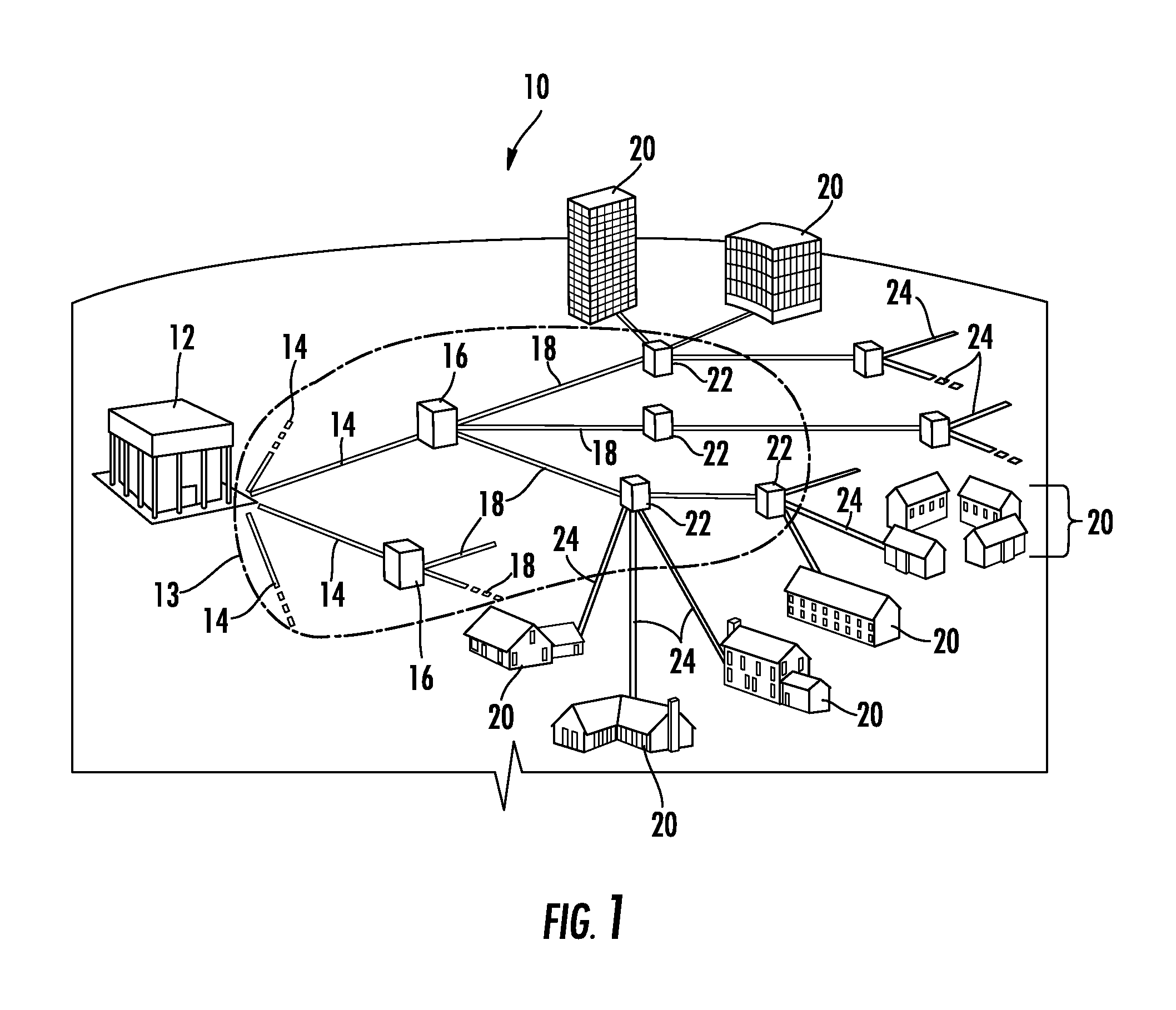
A fiber-optic splitter, also known as a beam splitter, is based on a quartz substrate of an integrated waveguide optical power distribution device, similar to a coaxial cable transmission system. The optical network system uses an optical signal coupled to the branch distribution. The fiber optic splitter is one of the most important passive devices in the optical fiber link. It is an optical fiber tandem device with many input and output terminals, especially applicable to a passive optical network (EPON, GPON, BPON, FTTX, FTTH etc.) to connect the MDF and the terminal equipment and to branch the optical signal.
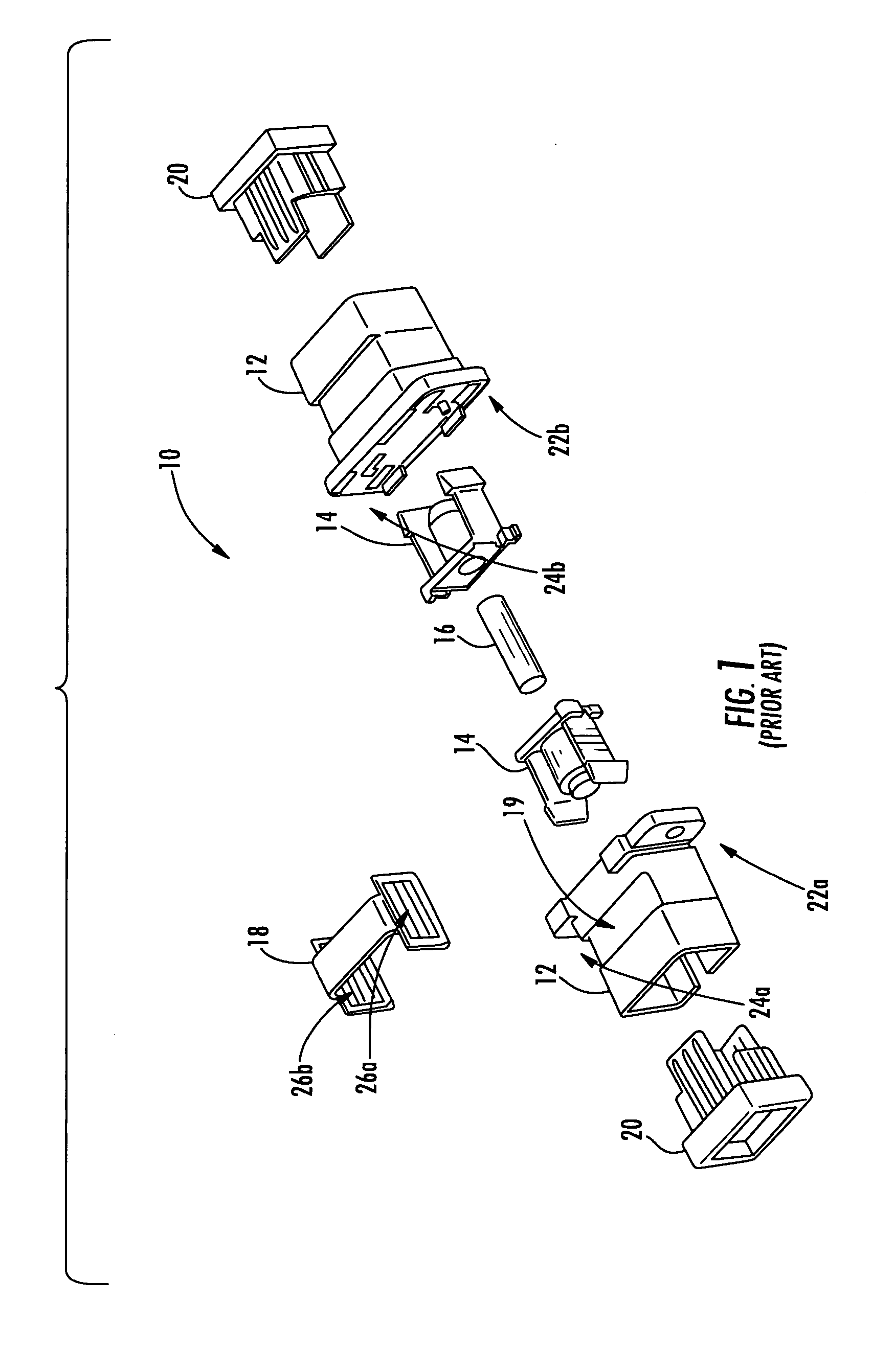
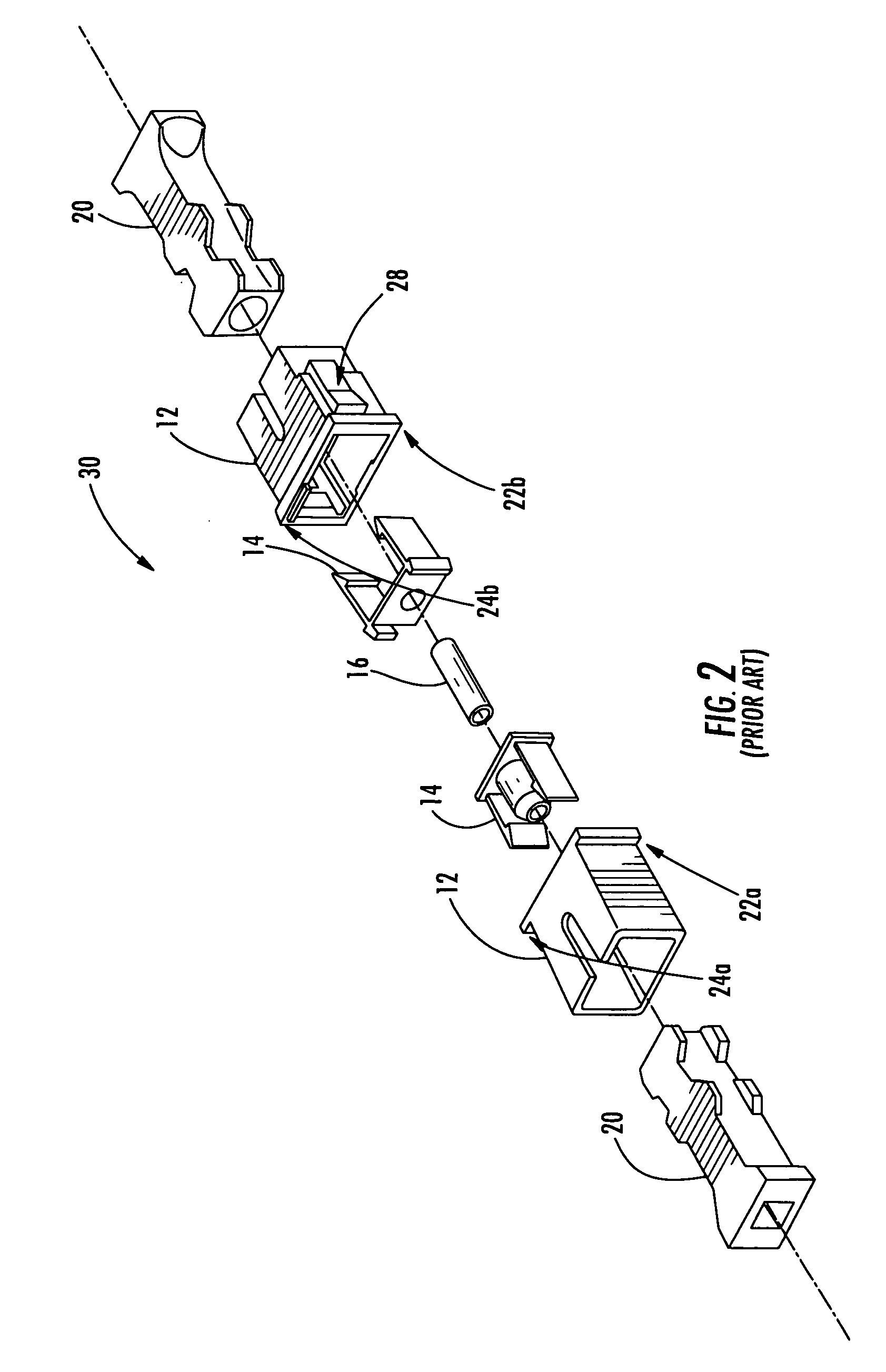
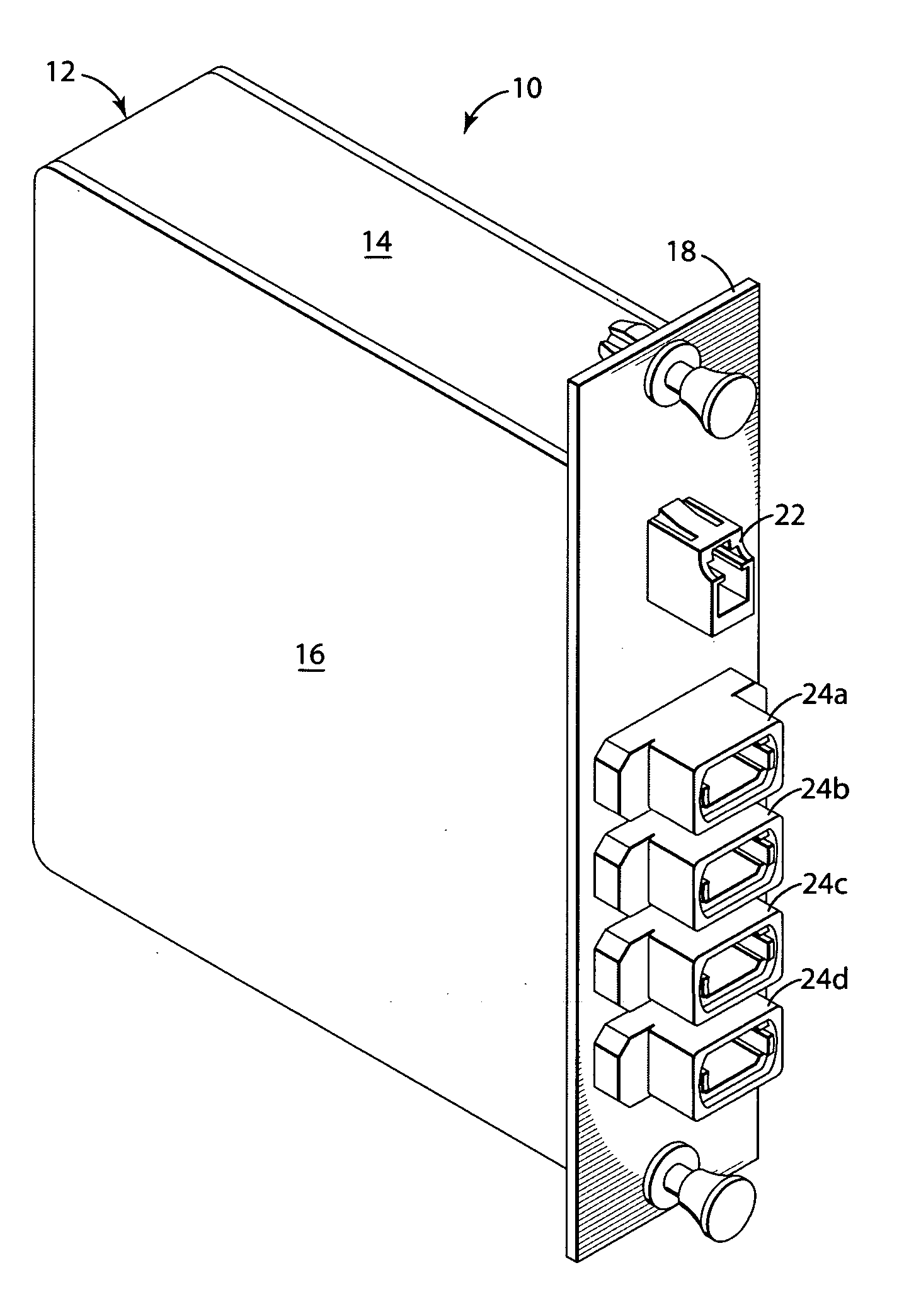
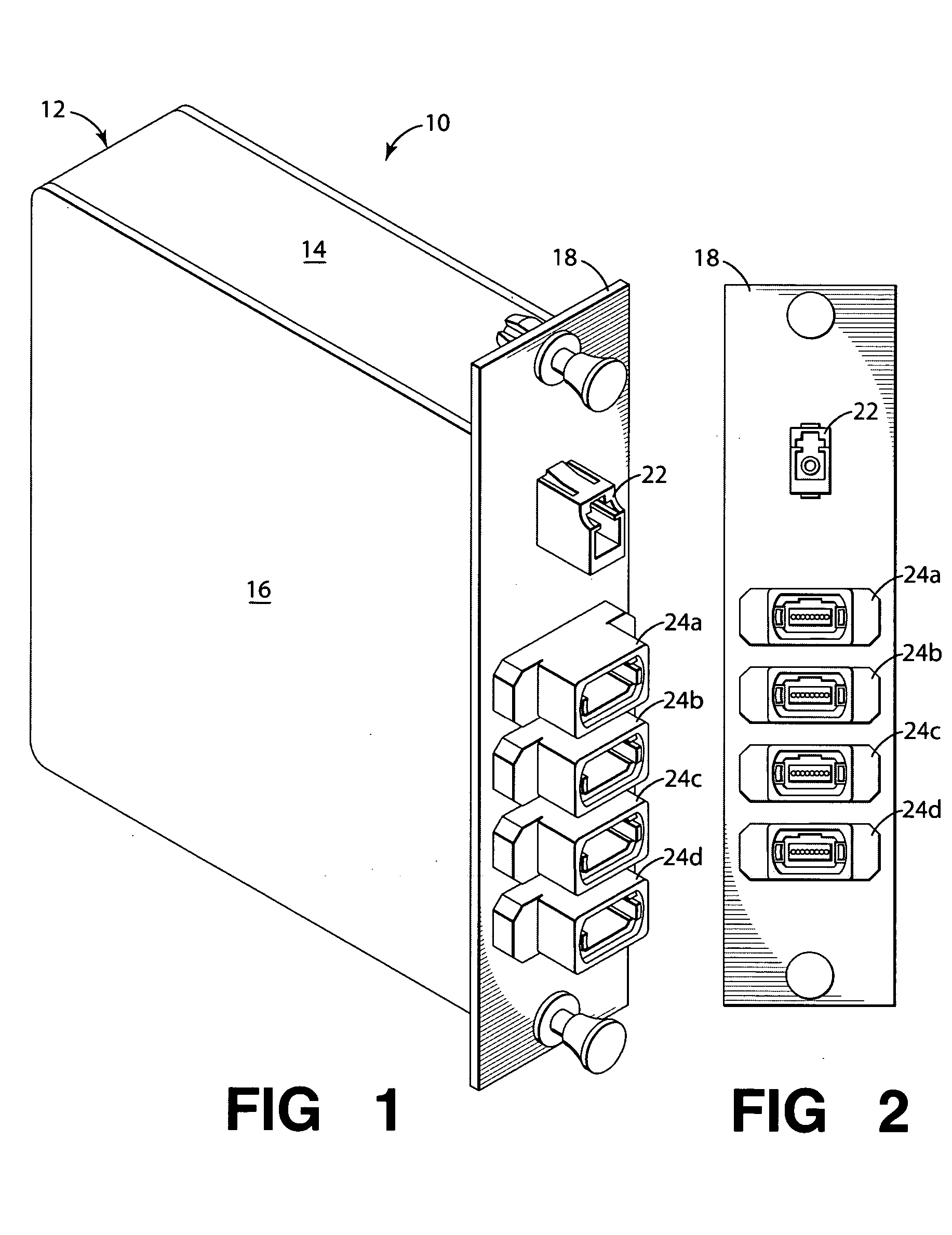
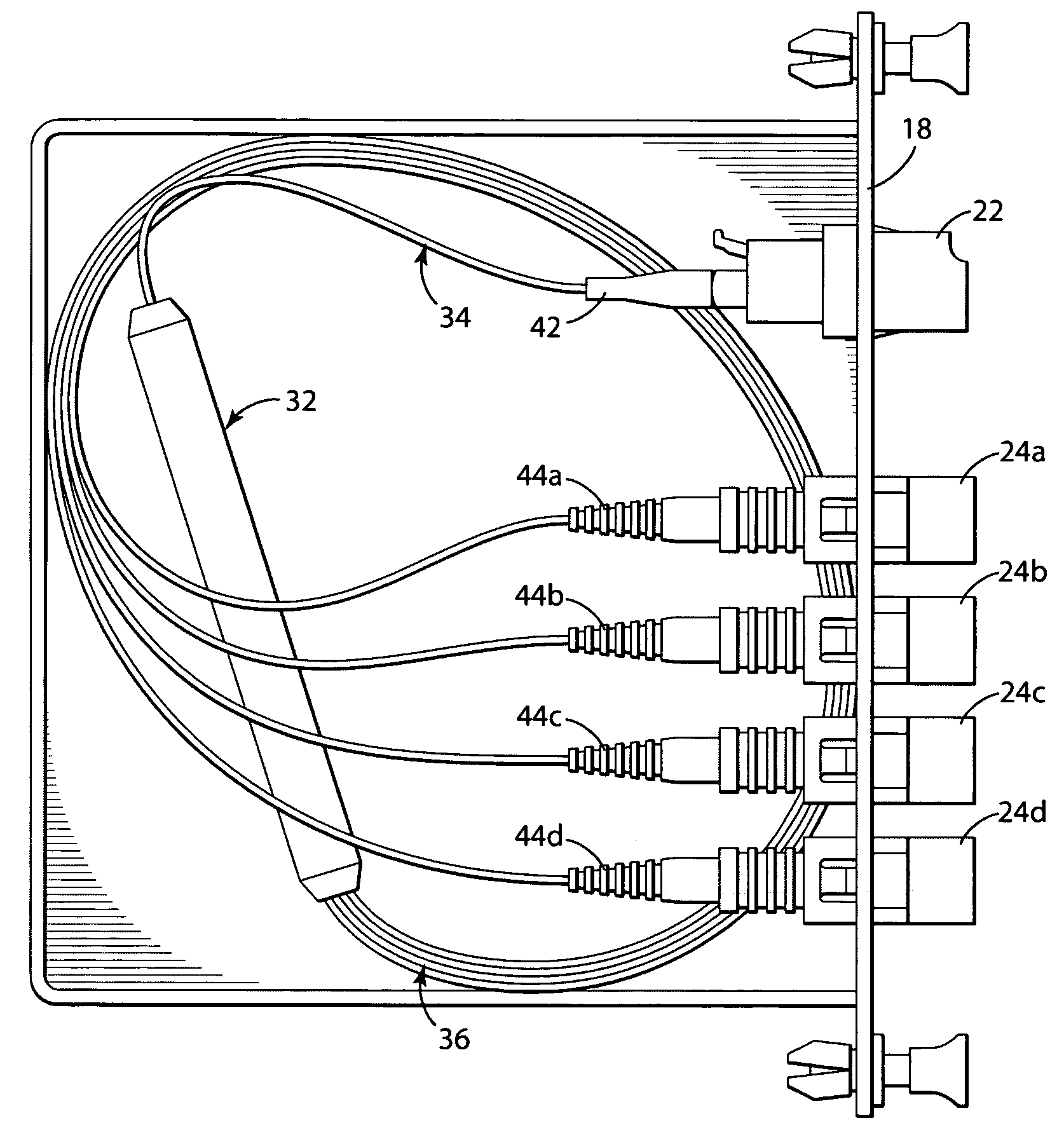
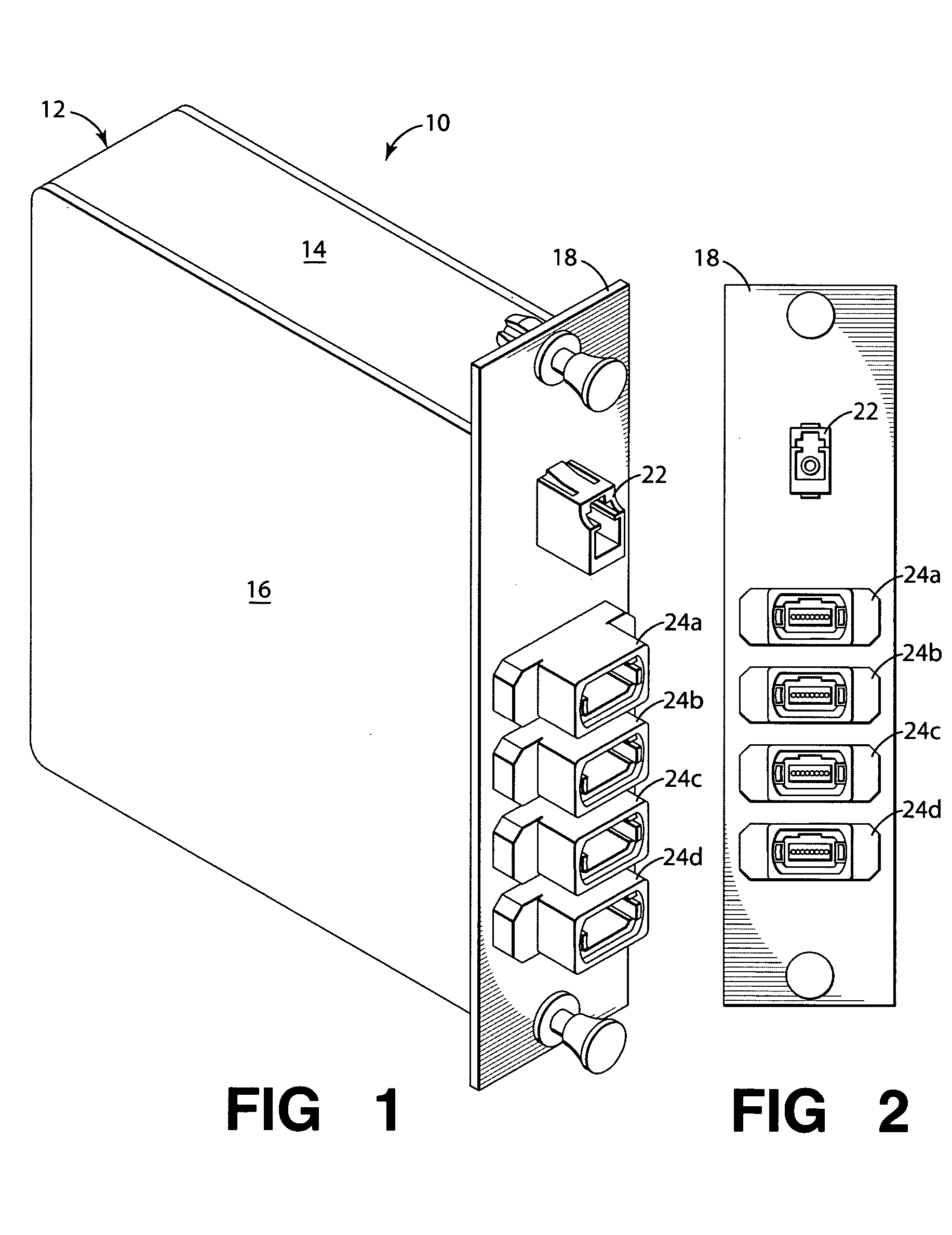
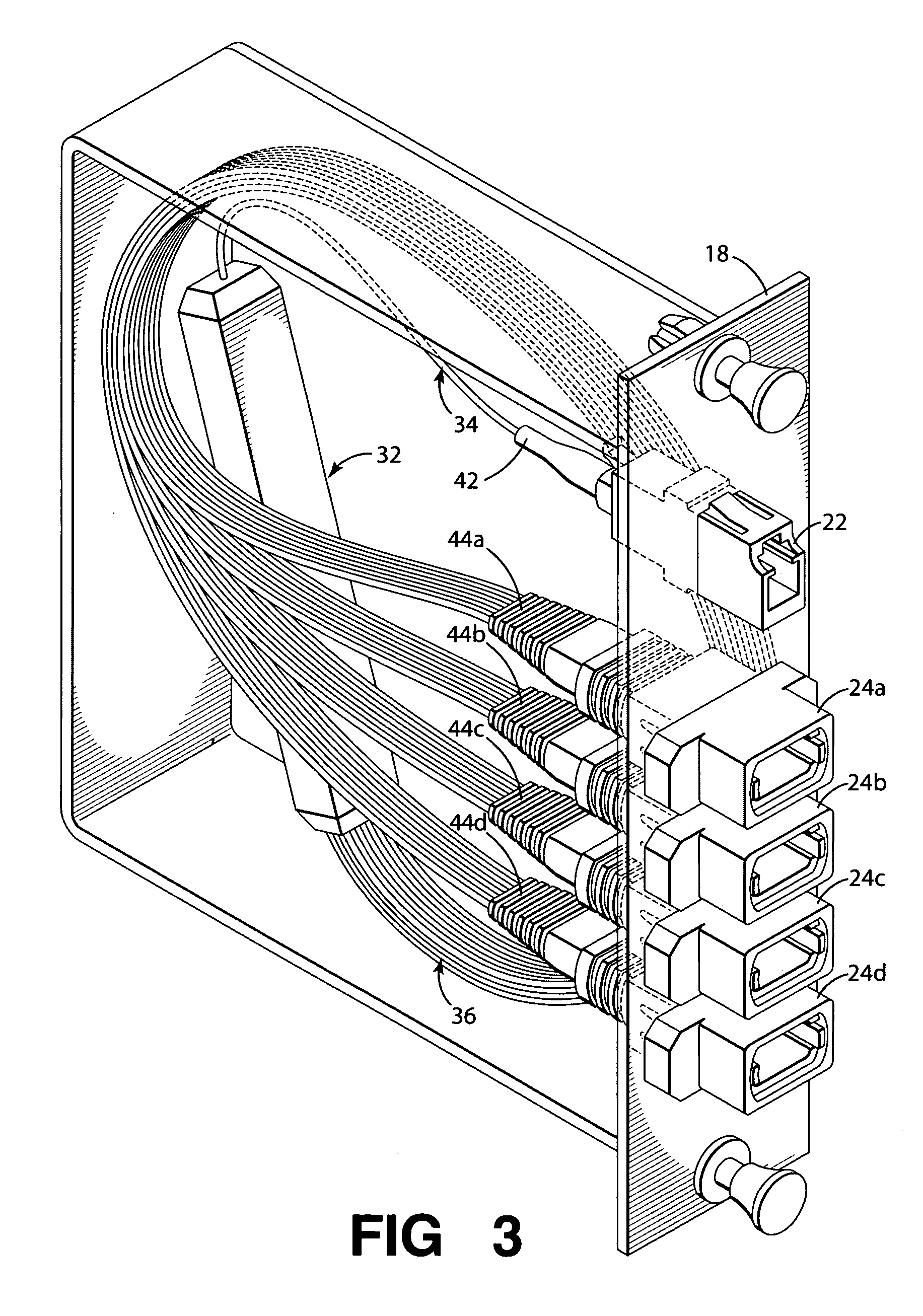
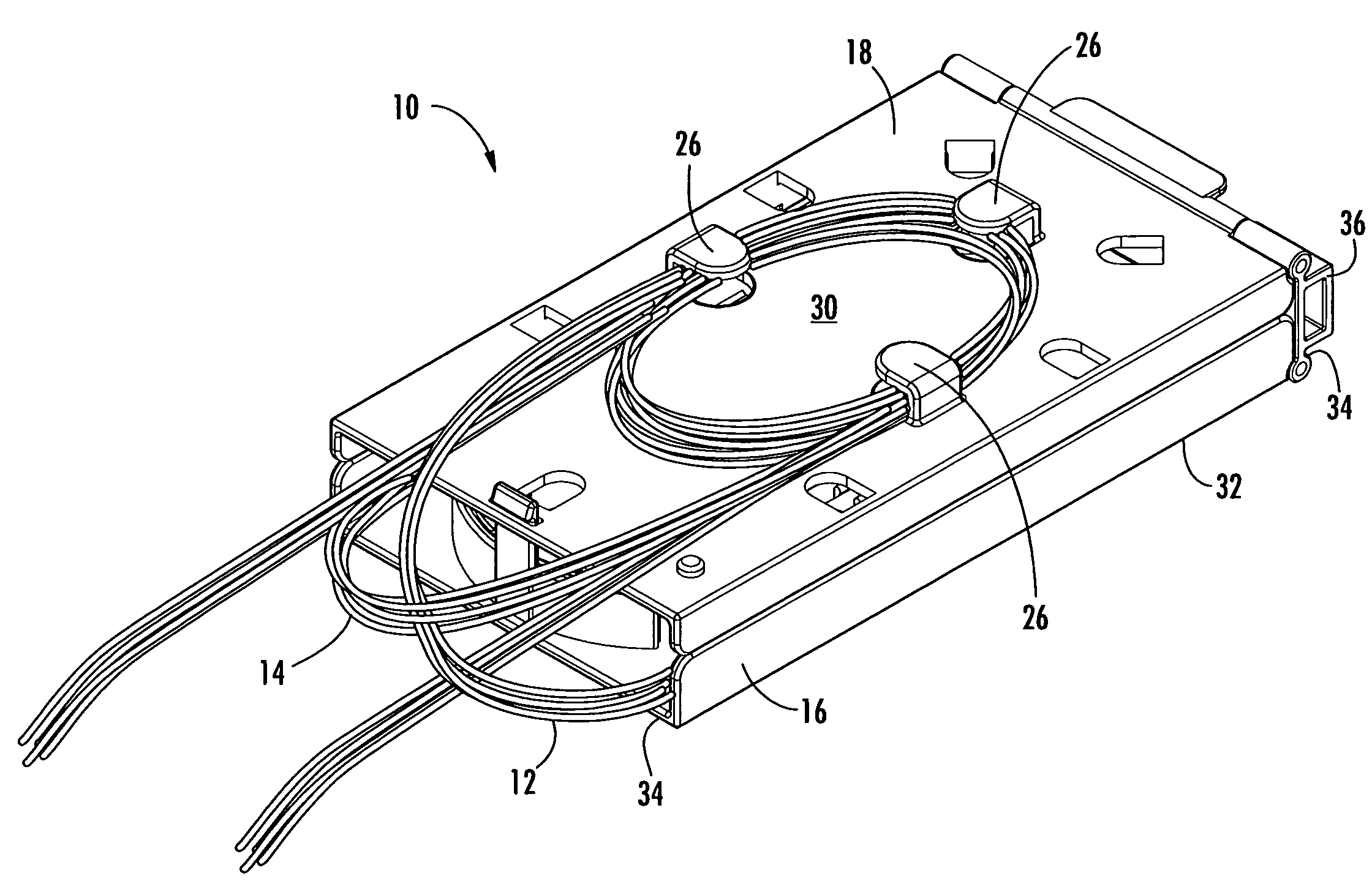
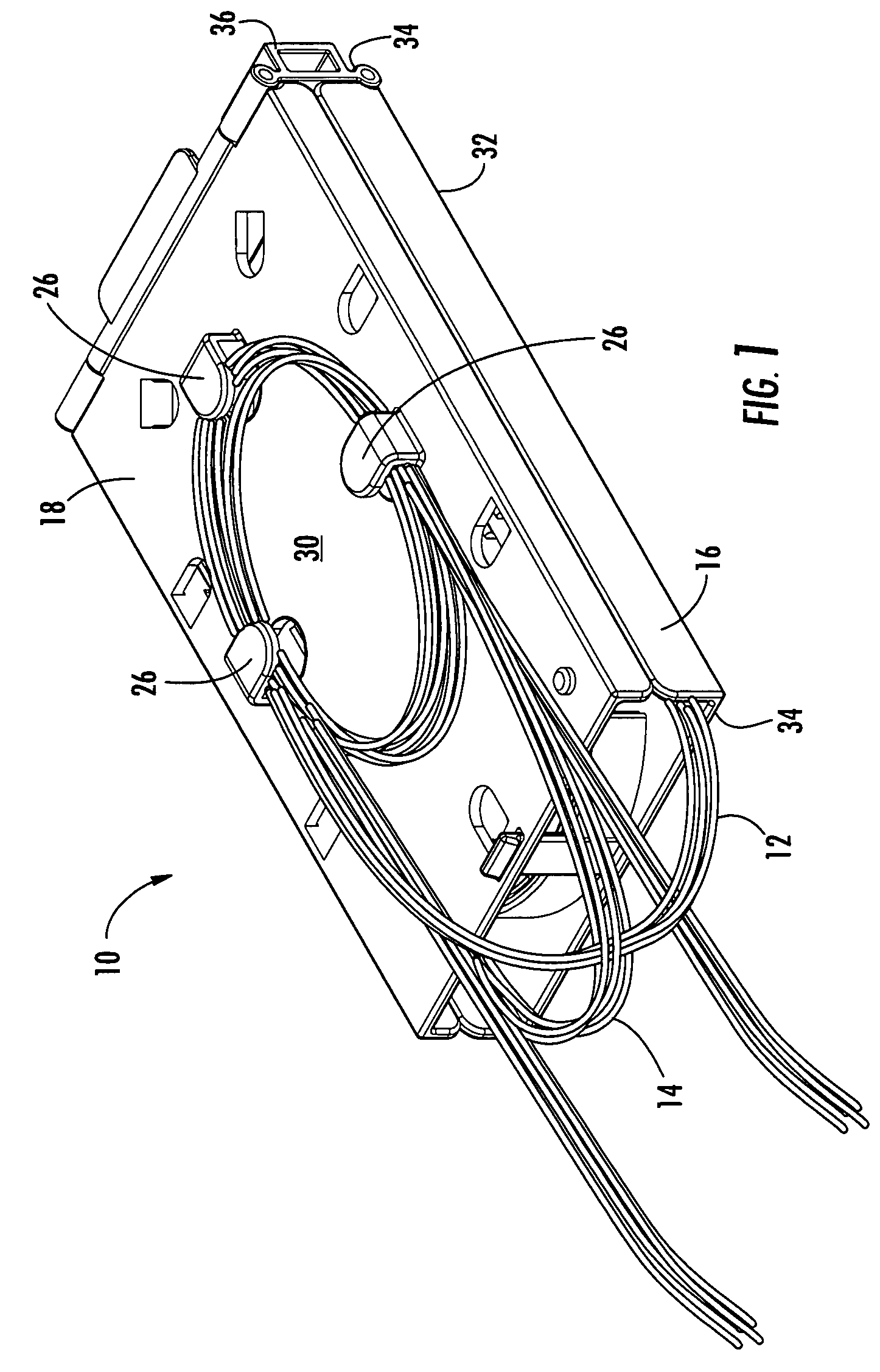
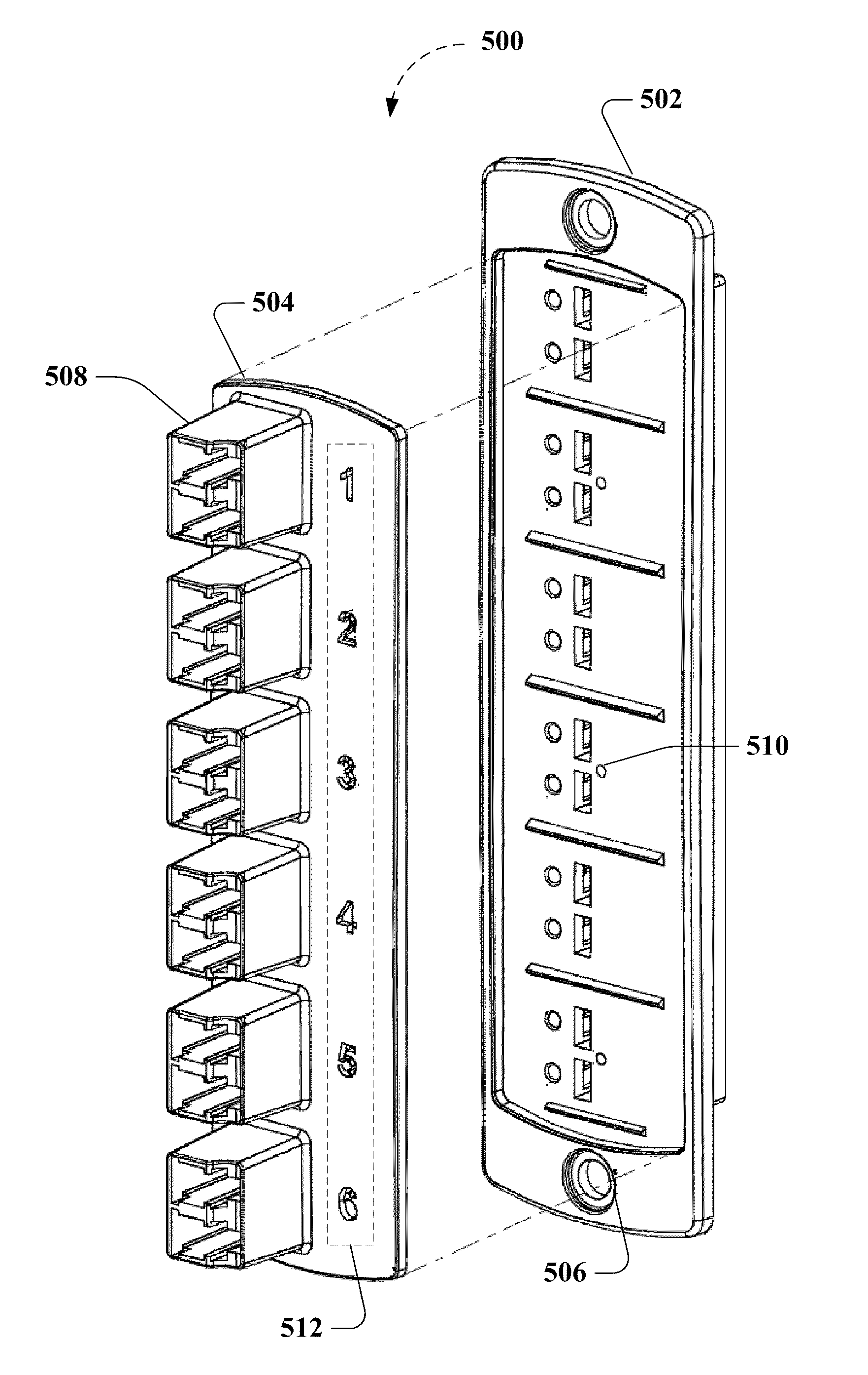
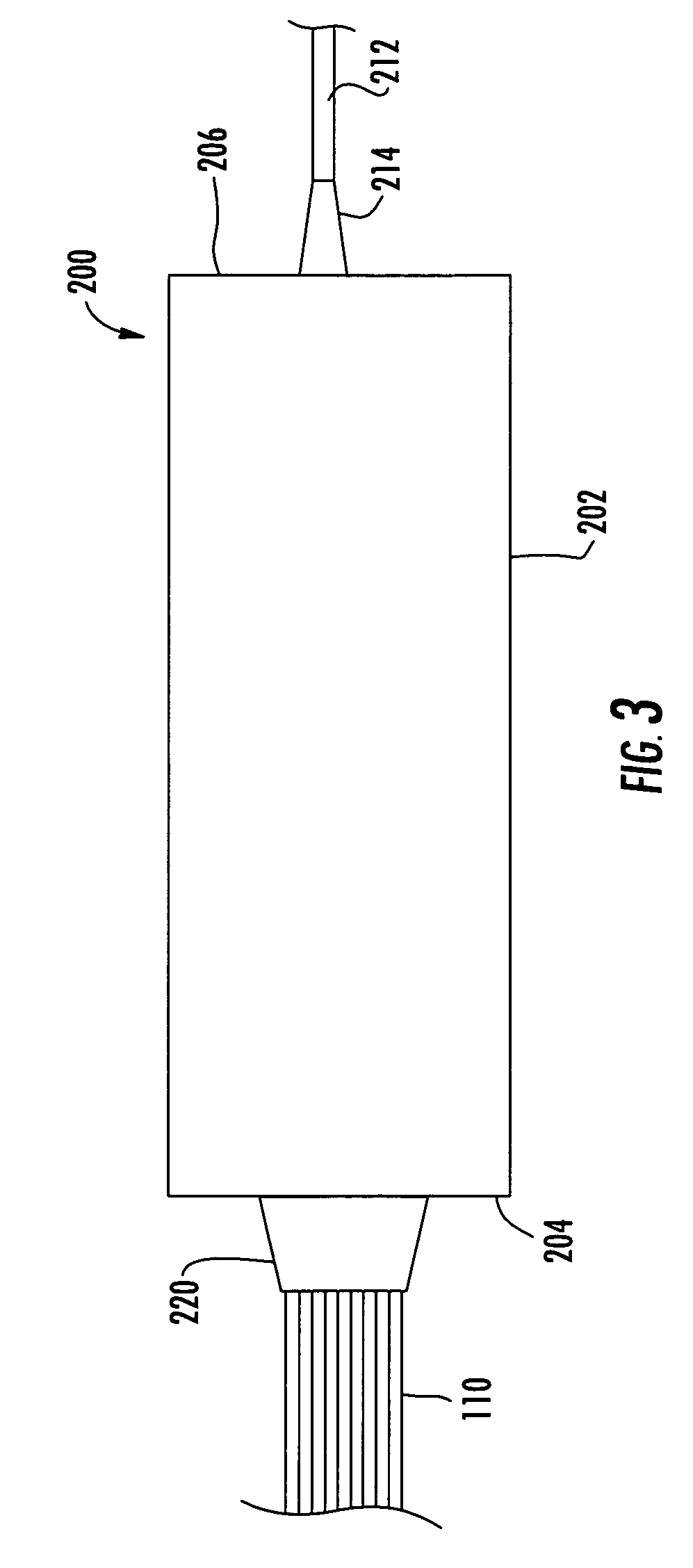
Fiber optic adapter module and tray
ActiveUS20090067800A1Enhanced convenient accessNeat routingFurniture partsCabinetsFiberInterior space
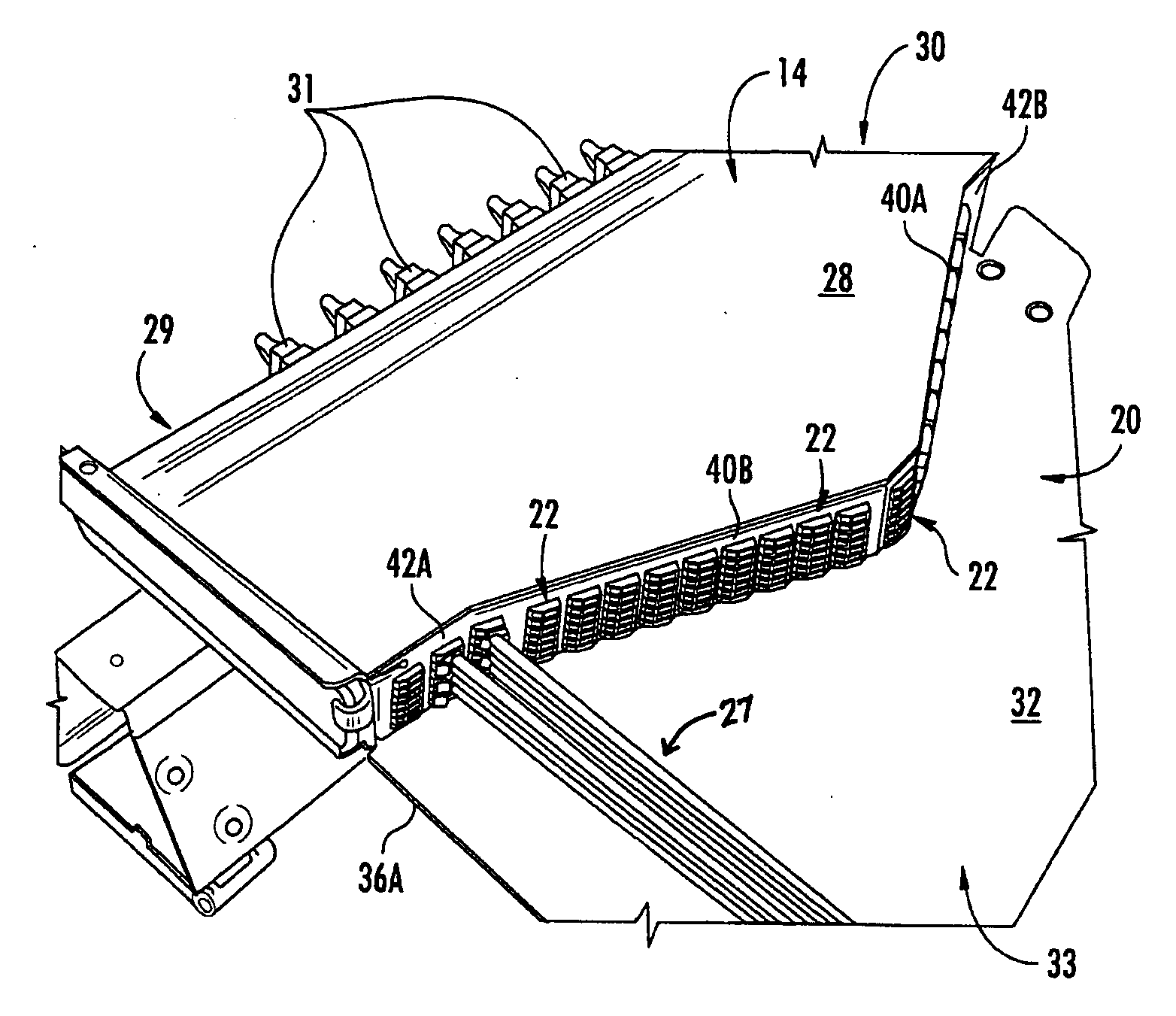
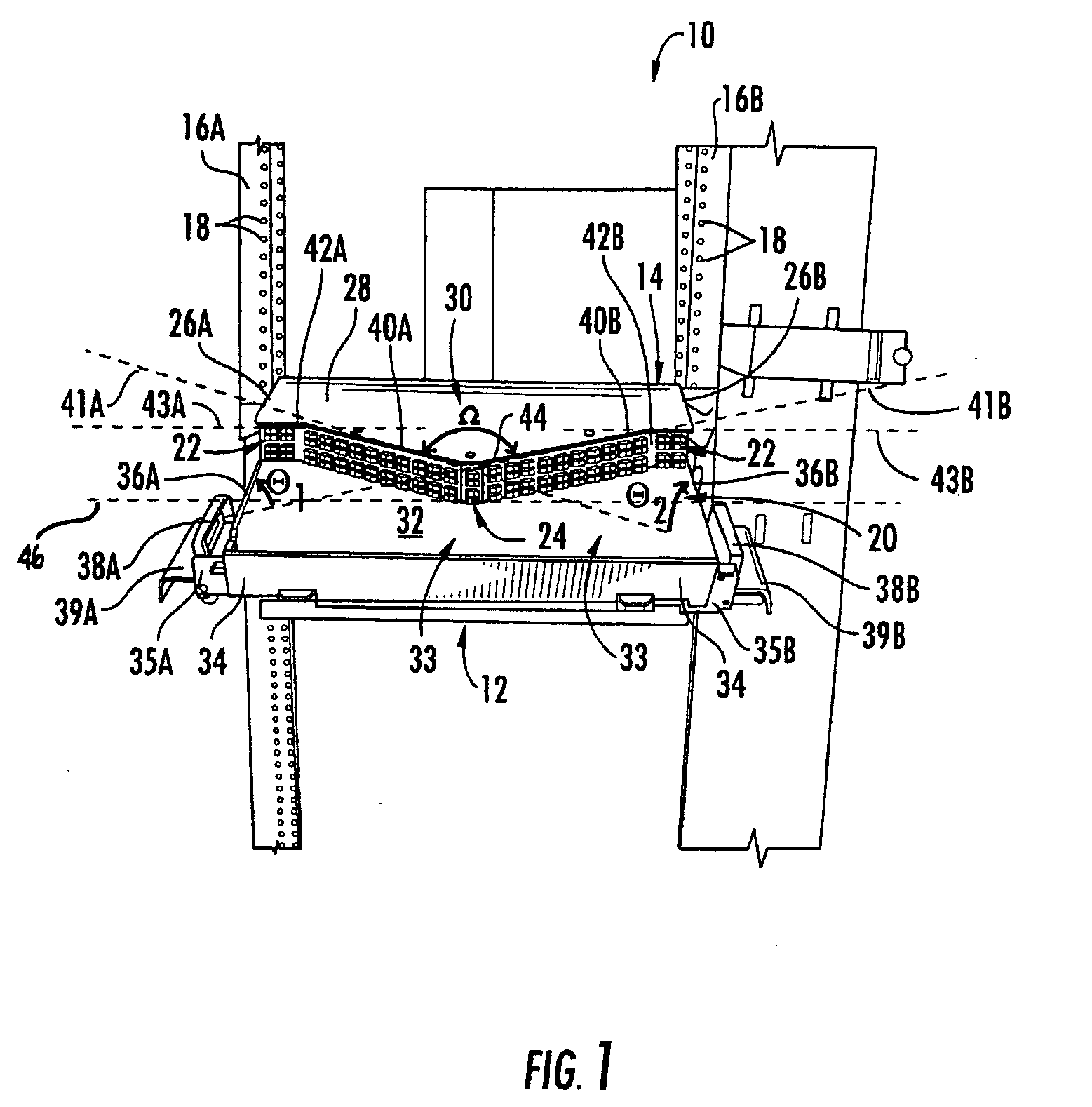
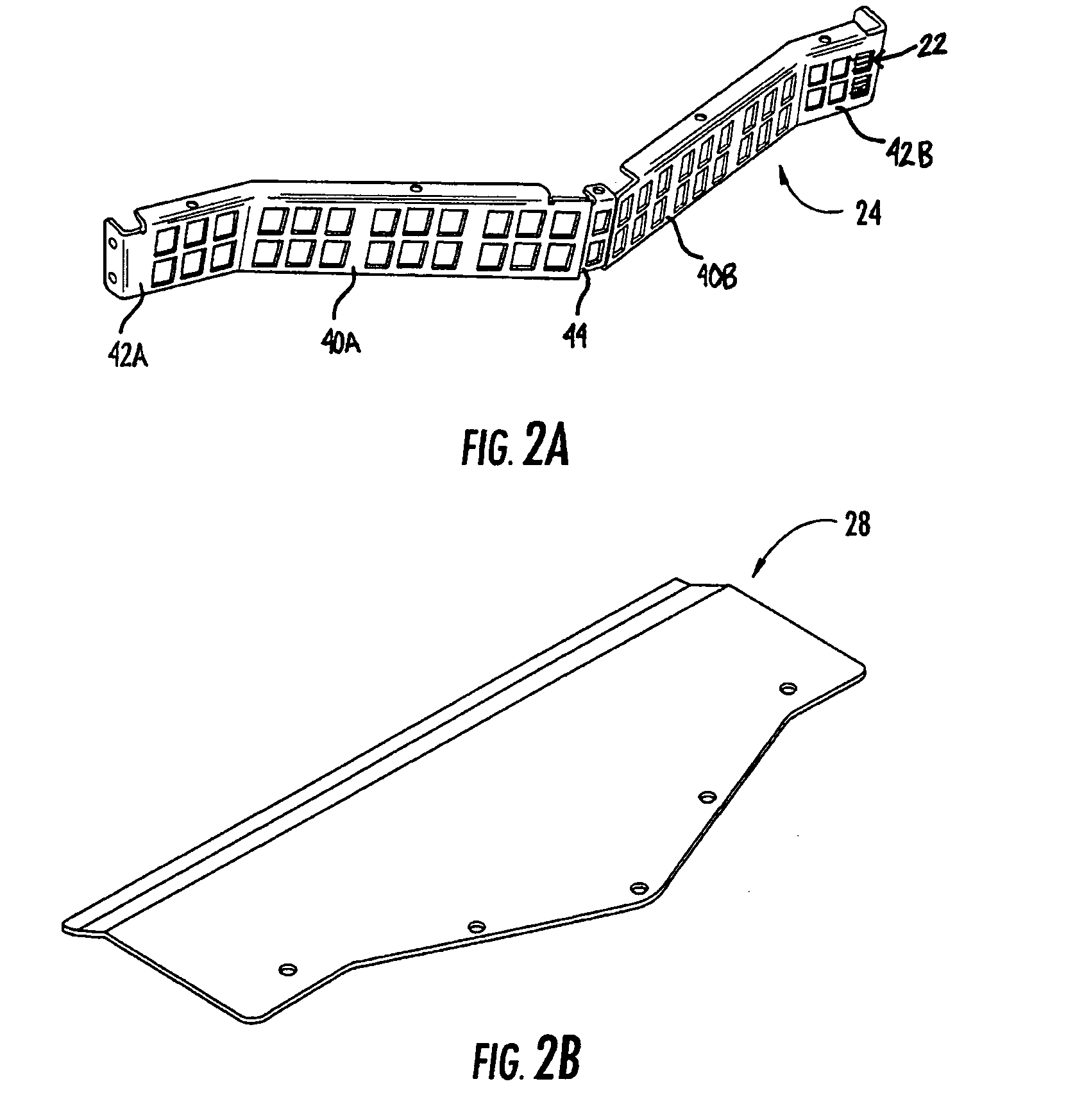
A fiber optic adapter module and tray. The fiber optic adapter module supports fiber optic adapters for fiber optic connections. The fiber optic adapter module may be included on an extendible tray portion of a fiber optic equipment tray and selectively configured to be tilted when extended for providing enhanced access to the fiber optic adapter module. In one embodiment, an adapter module panel of the fiber optic adapter module that supports fiber optic adapters contains at least two forward facing panel surfaces angled to one another to provide more surface area for supporting a higher density of fiber optic adapters and / or for neat routing and organizing of fiber optic connections. One or more fourth flared panel surfaces may also be included on an end(s) of the adapter module panel to provide sufficient interior space for fiber optic connections adjacent or proximate to sides of the fiber optic equipment tray.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Radio frequency identification of component connections
ActiveUS20080100467A1Subscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesFiberEmbedded system
There is provided a system for identifying a connection of two or more components in which one or more RFID transponders are associated with the two or more components. A plug is associated with the first component, such as a fiber optic connector, and a socket is associated with the second component, such as a fiber optic adapter. An RFID transponder is associated with each component and at least one of the RFID transponders is activatable when the plug is received by the socket to enable the activated RFID transponder to communicate with the RFID reader. The antennas and integrated circuit chips that define the RFID transponders are positioned relative to the plug and socket to enable the one or more RFID transponders to activate when the plug is received by the socket. In addition, the RFID transponders may communicate with one another to identify other RFID transponders in order to communicate identities of two or more RFID transponders.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
Fiber optic adapter with integrated shutter
InactiveUS20090028507A1Reduce in quantityLower component costsCoupling light guidesFiberUltrasonic welding
The present invention relates generally to fiber optic connectors and adapters, and more specifically to a simplified fiber optic adapter assembly and integrated shutter mechanism. In various embodiments, the simplified fiber optic adapter assembly includes a one-piece outer housing, a one or two-piece inner housing, and several different clip arrangements, reducing the number of parts associated with conventional fiber optic adapter assemblies and eliminating the need for ultrasonic welding or the like. In various embodiments, the integrated shutter mechanism includes one or more shutter doors that are opened internally via the motion required for connector installation.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC
Optical fiber power splitter module apparatus
Embodiments of the invention include an optical power splitting module apparatus. The module apparatus includes at least one input port, one or more multi-fiber output ports, and an optical fiber-splitter device coupled therebetween. The optical splitter device has a first end configured as at least one single optical fiber, and a second end configured as one or more multi-fiber groups. The first end of the splitter device is coupled to the input port and the second end of the splitter device is coupled to the output ports. The first end of the splitter device is, e.g., an LC connector. The second end of the splitter device is, e.g., one or more Multi-fiber Push On (MPO) connectors. The optical splitter device is, e.g., a 1×N planar lightwave circuit (PLC) splitter, such as a 1×32 PLC splitter with an LC input connector and four 8-fiber MPO output connectors.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Optical fiber power splitter module apparatus
ActiveUS7218828B2Optical fibre/cable installationCoupling light guidesOptical powerElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
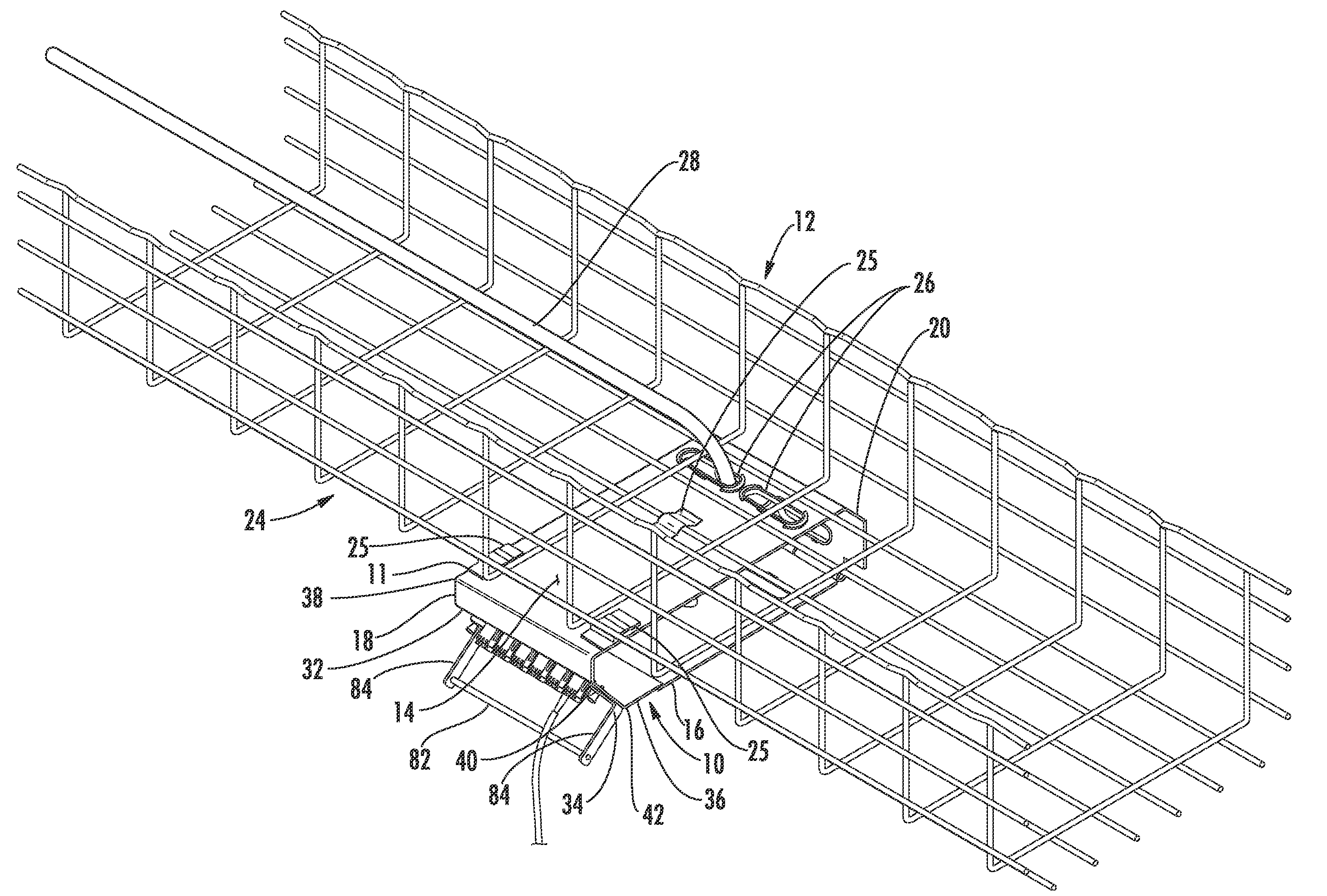
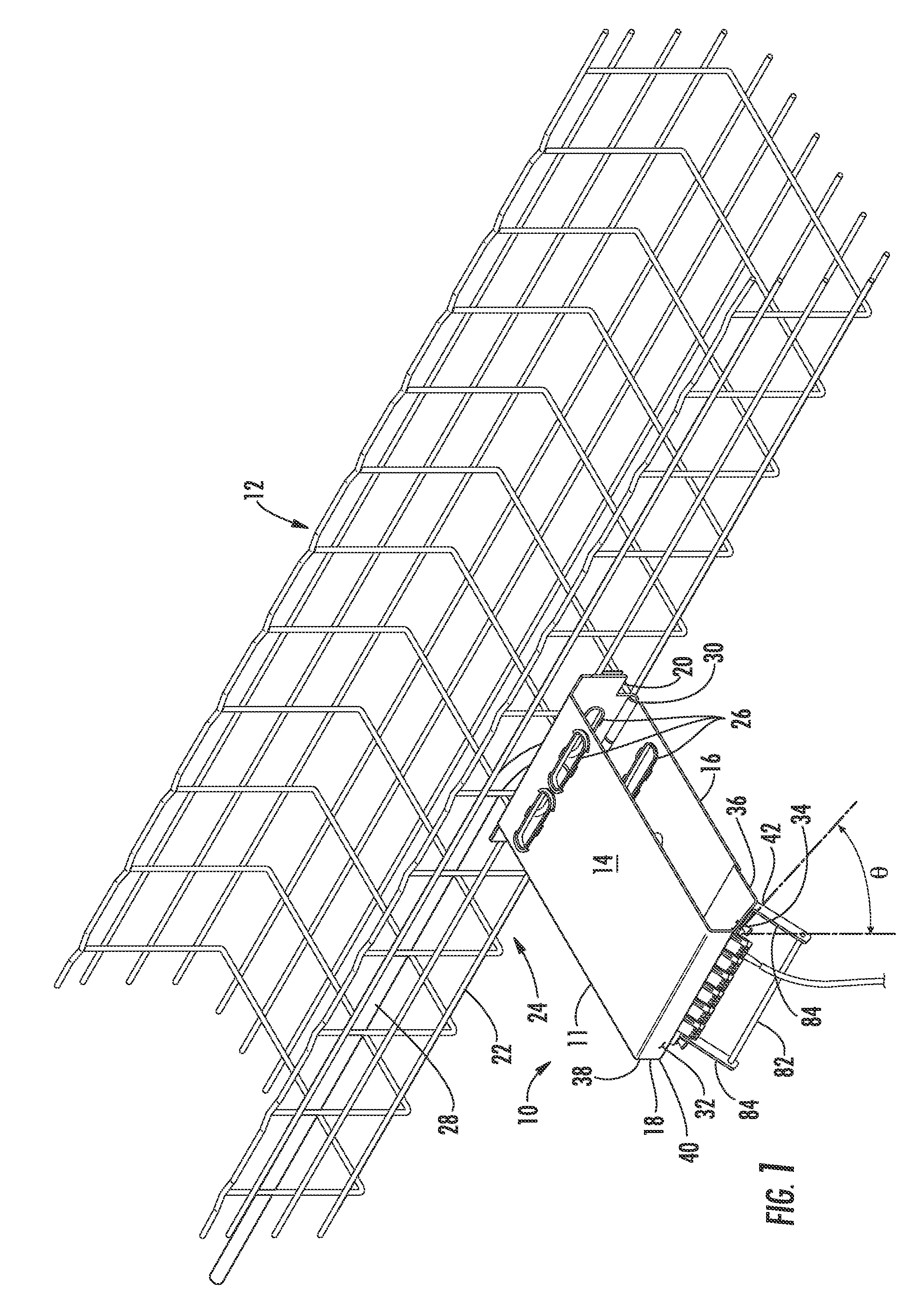
Fiber optic splice trays
InactiveUS7822310B2Reduce areaFunction increaseElectrically conductive connectionsCable junctionsFiberOptical fiber connector
There is provided splice trays and splice assemblies that provide convenient access to optical fiber slack within a relatively small area or volume. Some splice trays are adapted for use with microstructured optical fibers to further reduce the size of the splice tray or splice assembly. Some splice trays provide fiber routing devices on the cover of the splice tray. The fiber routing device may be positioned on an inside surface of the cover and / or on an outside surface of the cover. The splice trays and / or splice assemblies may be used with or as fiber drop terminals used within multiple dwelling units.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
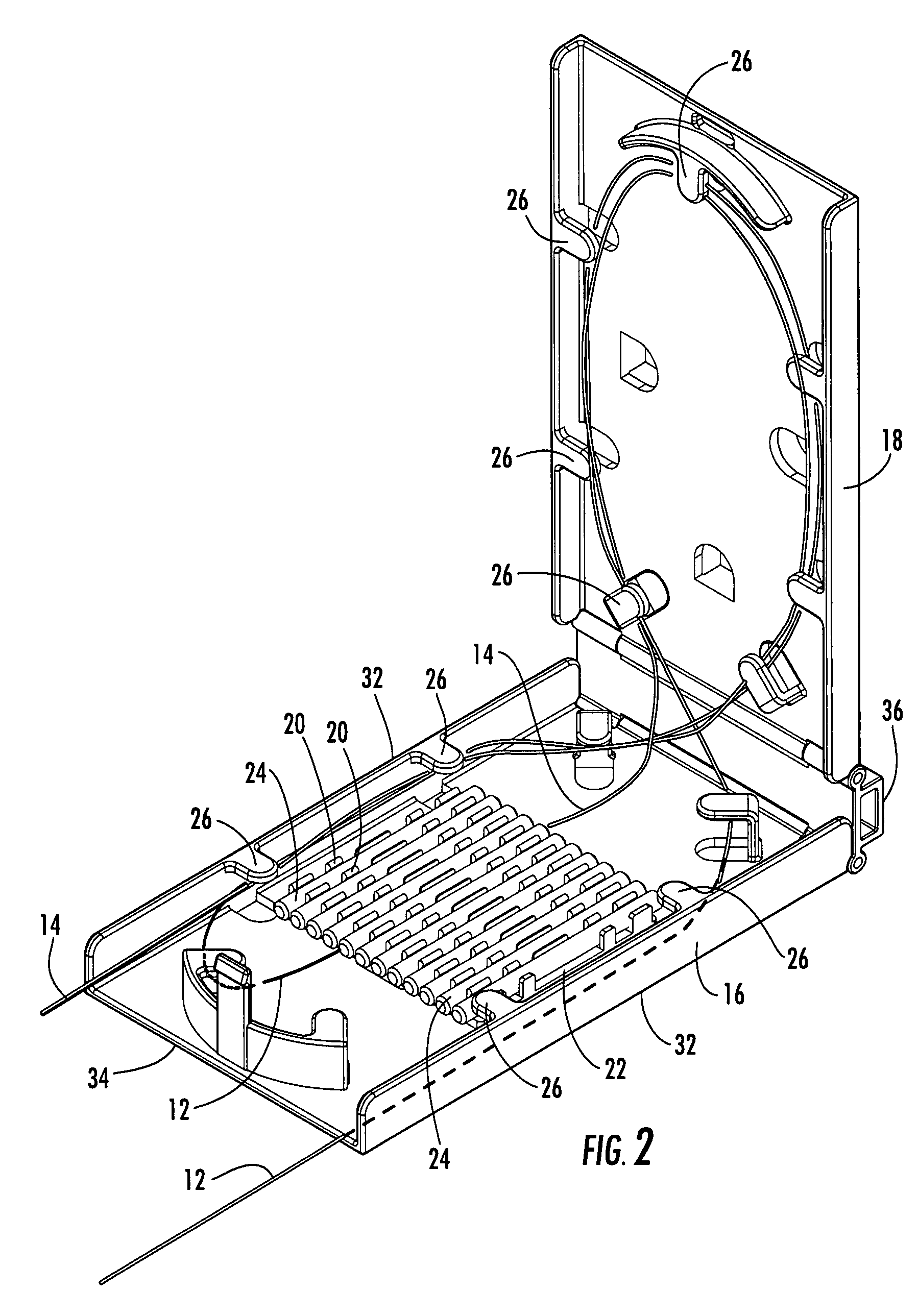
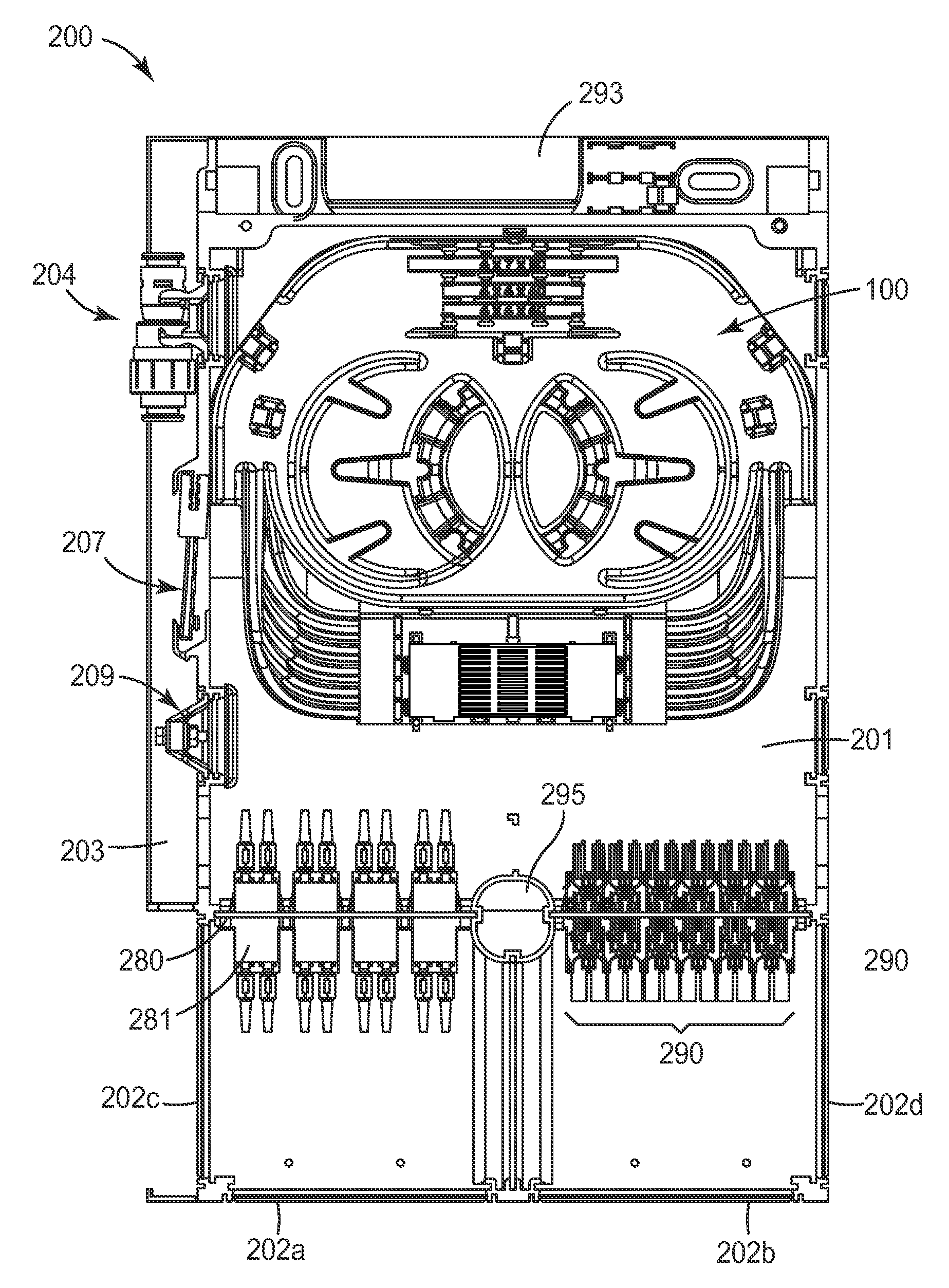
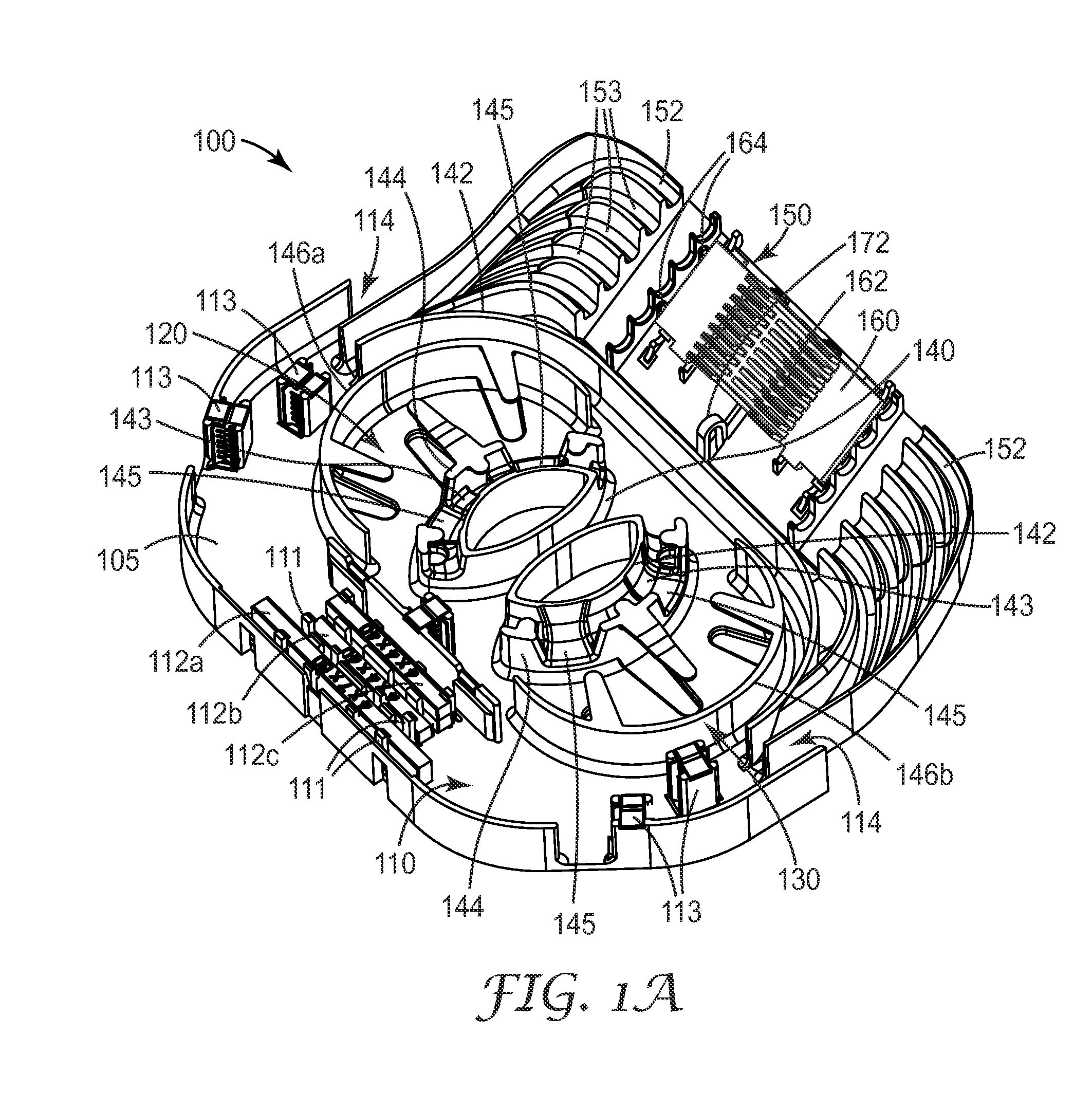
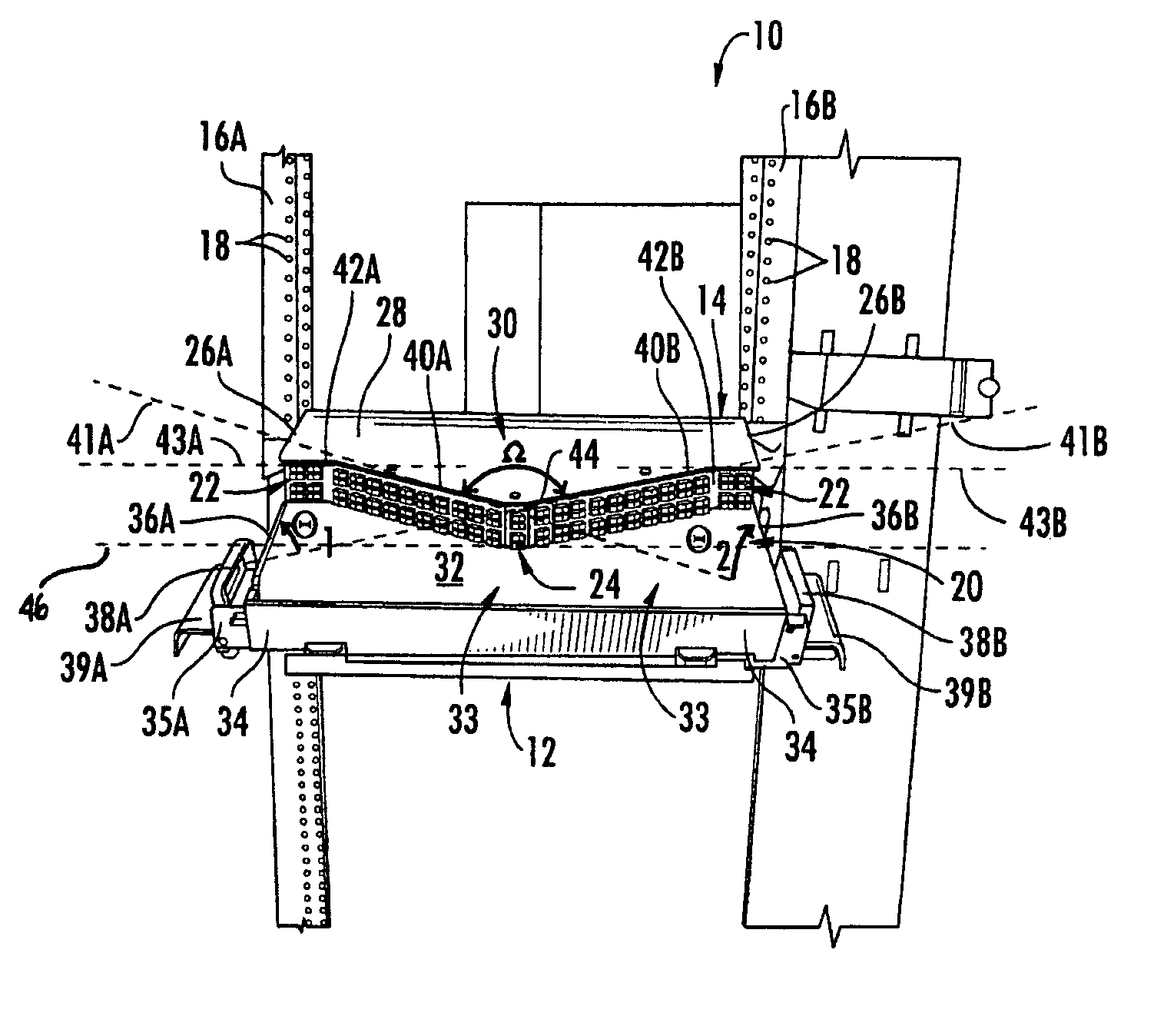
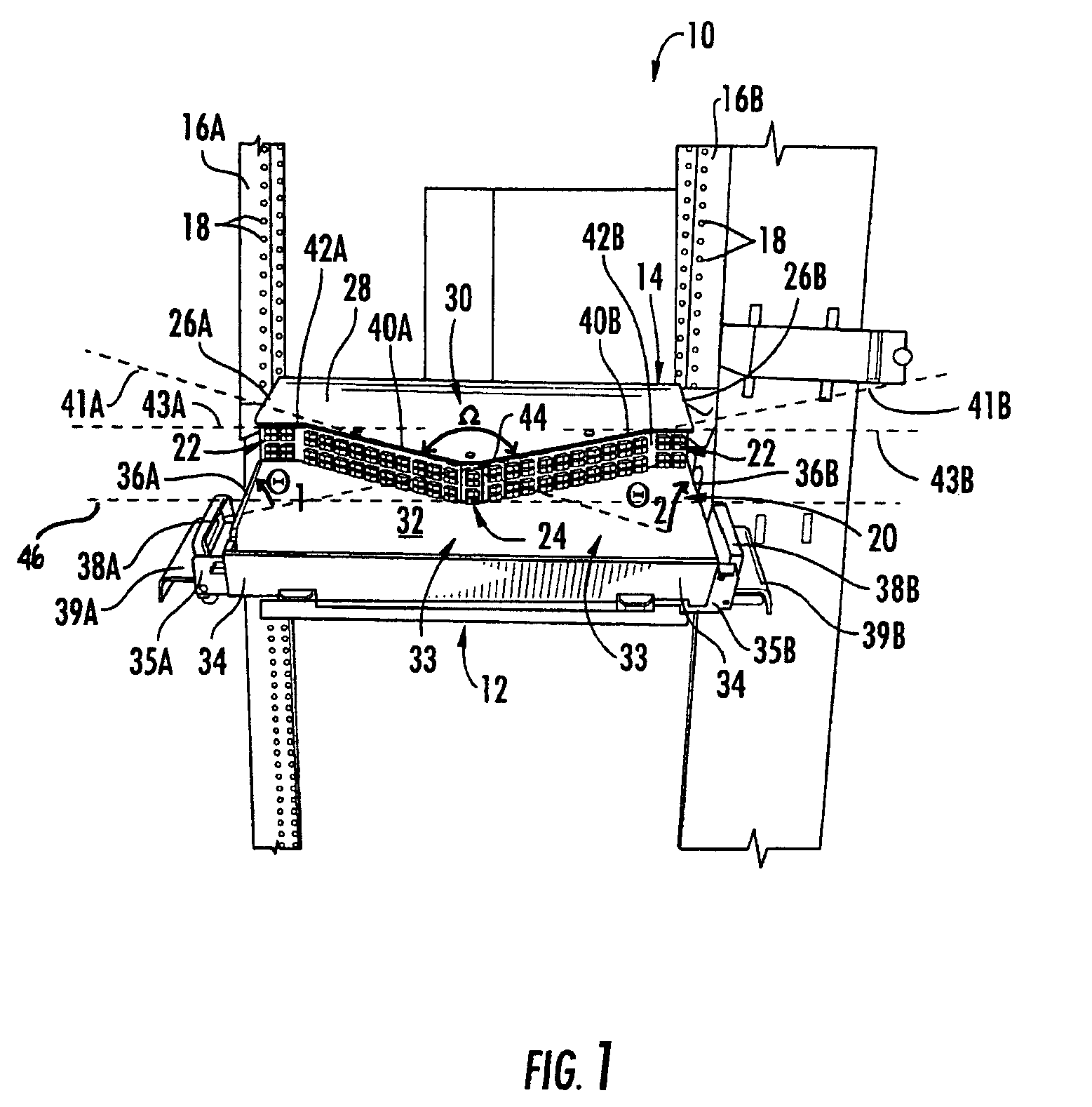
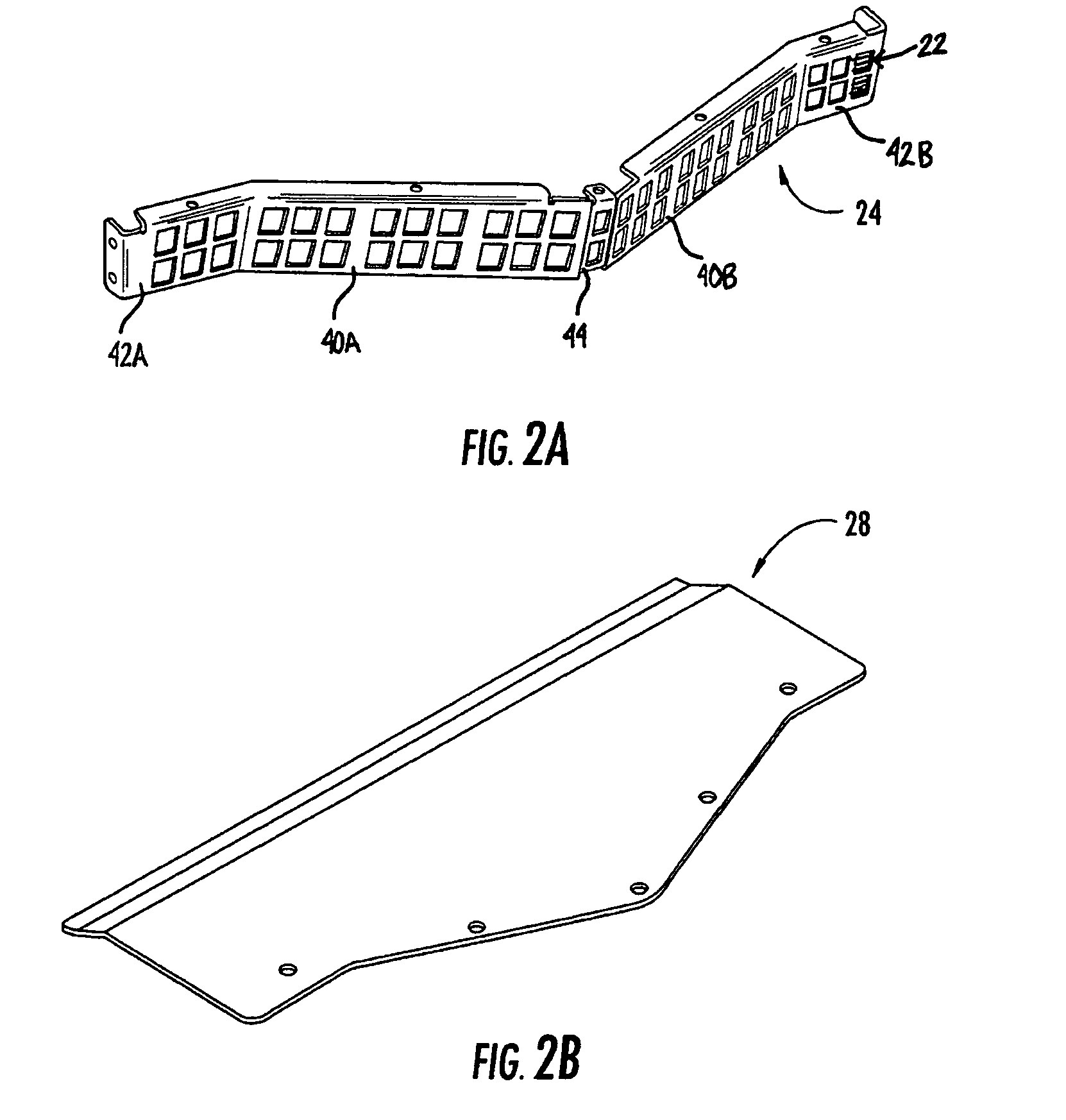
Fiber organizer and distribution box
ActiveUS20130243386A1Reduce axial strainAvoid displacementFibre mechanical structuresFiberEngineering
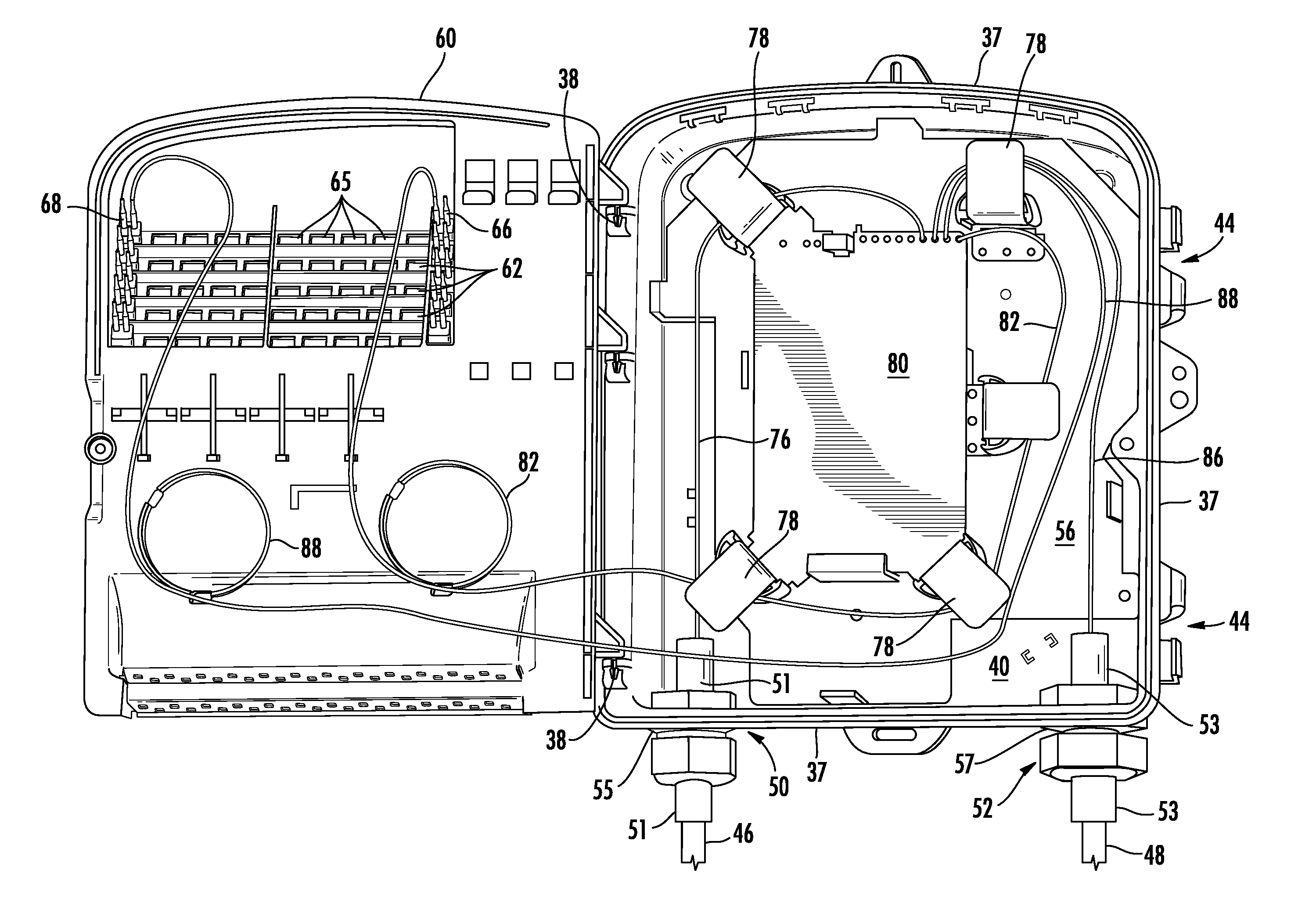
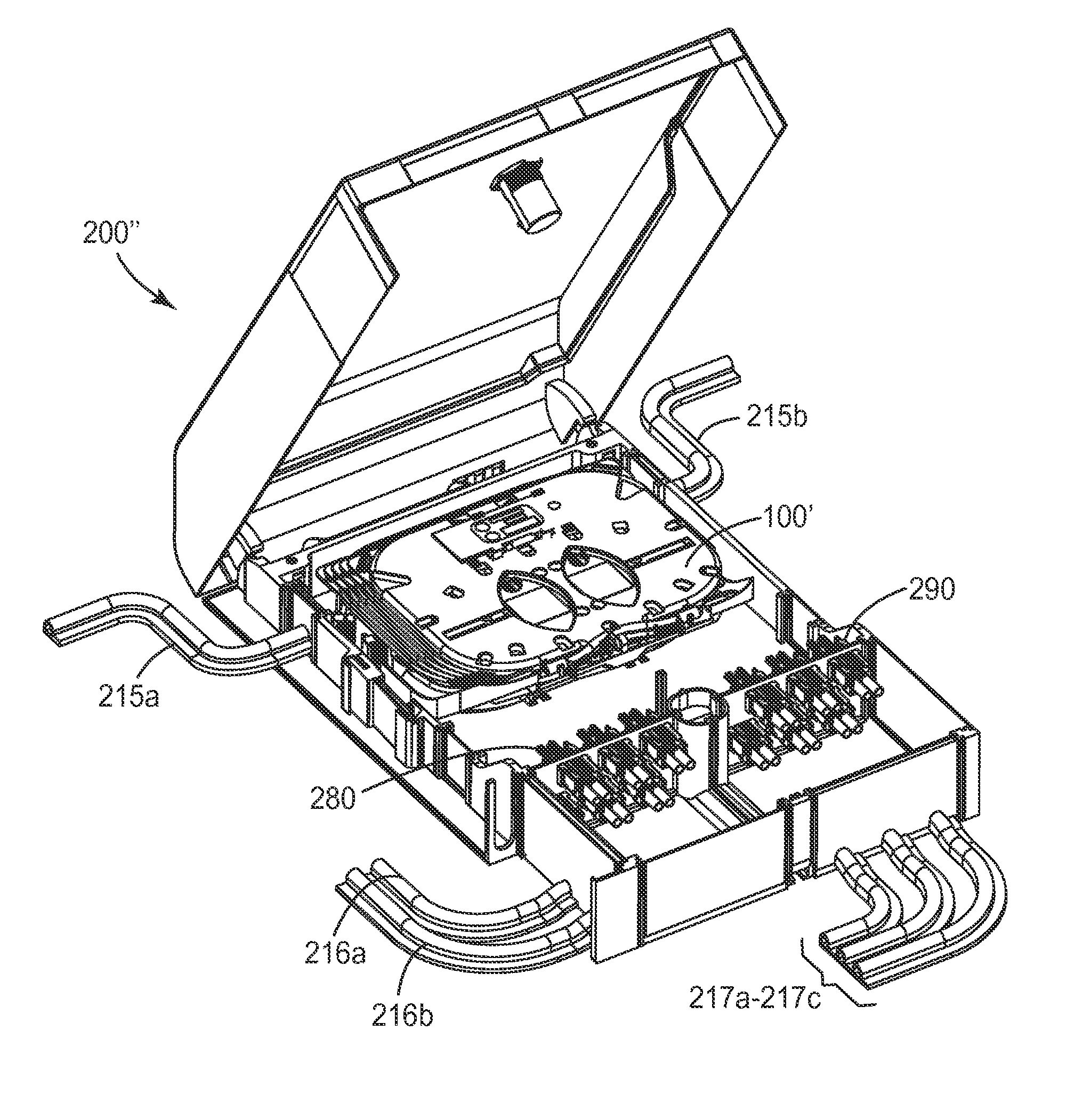
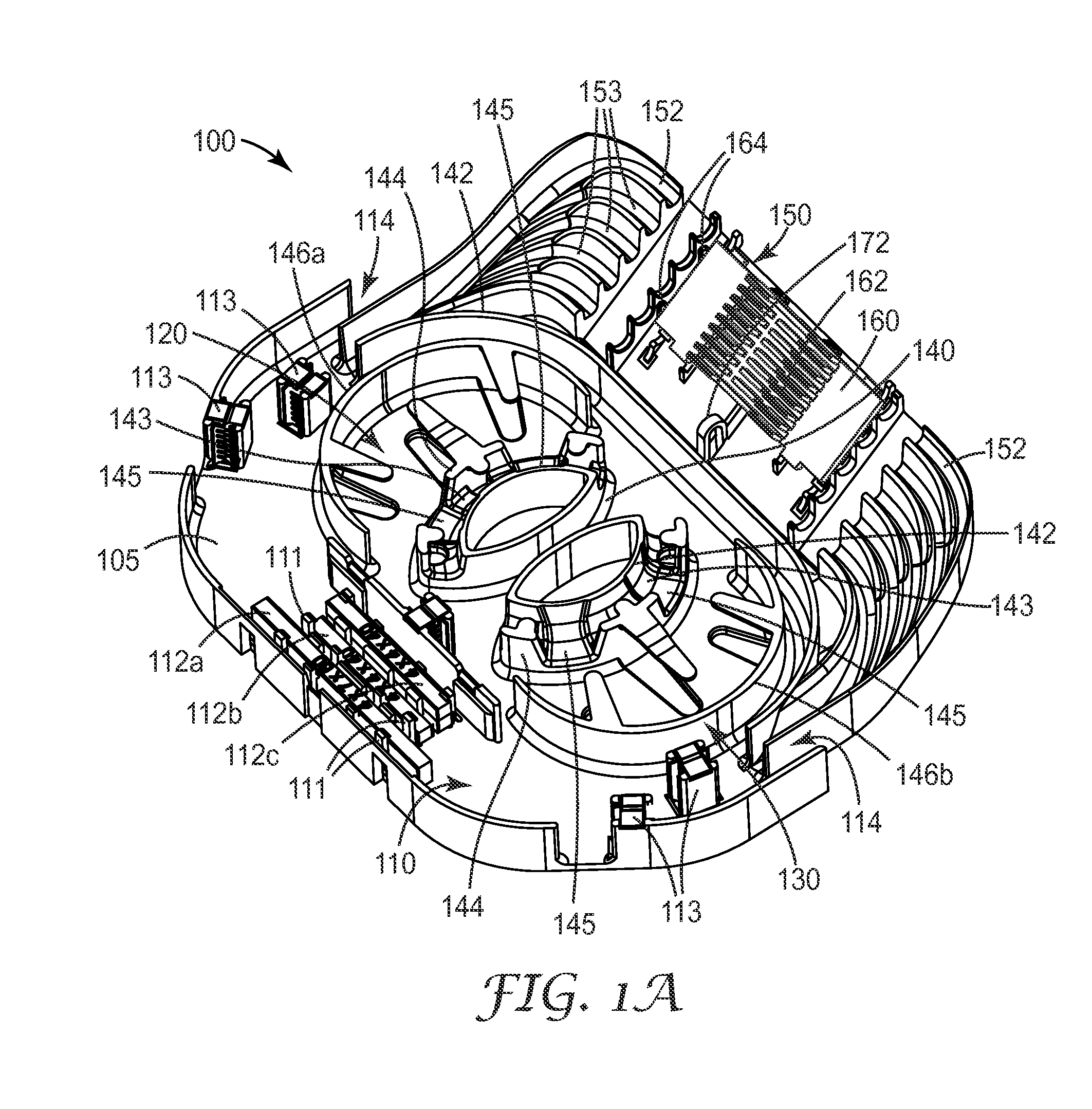
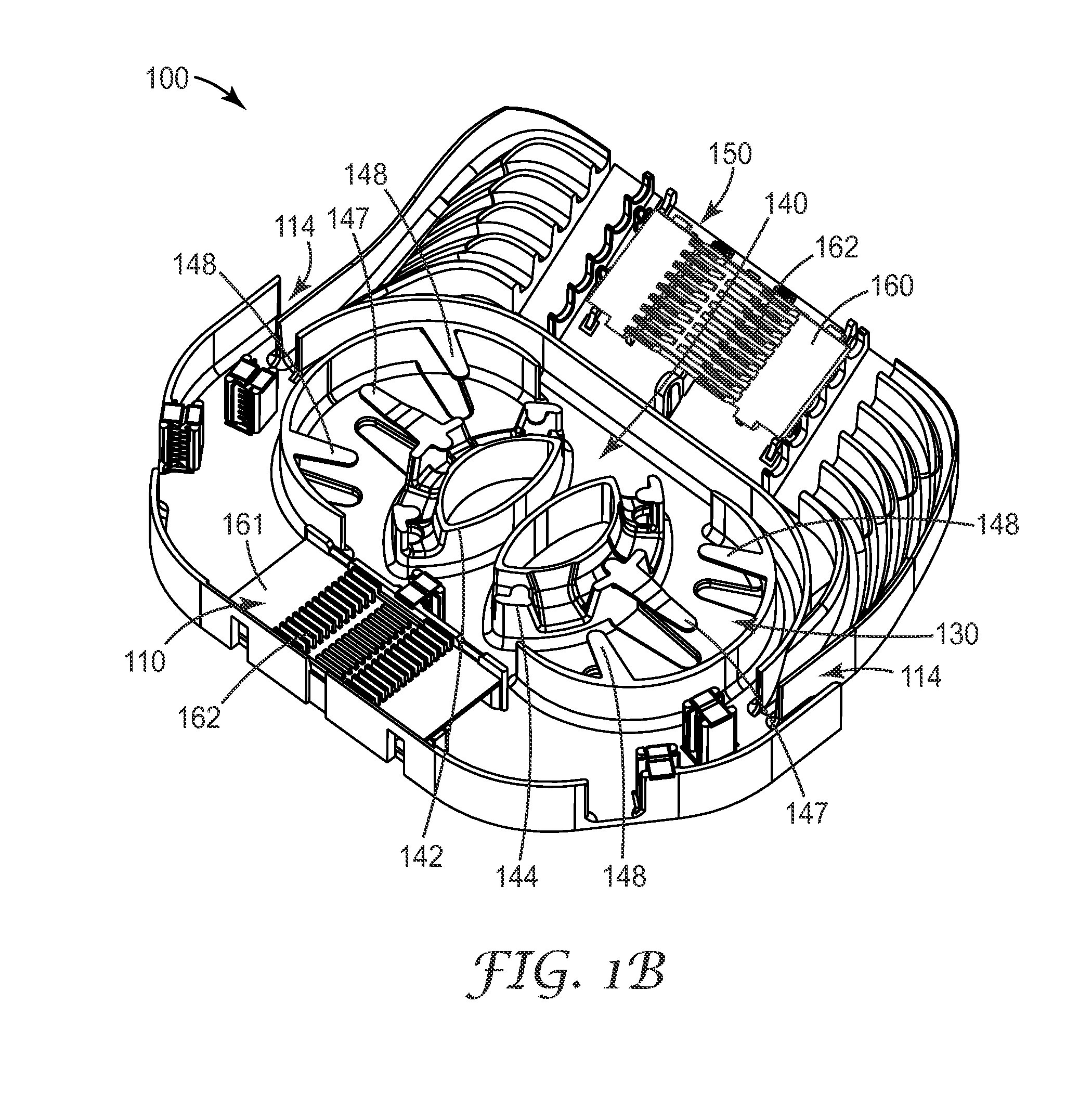
An organizer (100) for fiber cable management comprises a generally planar base (105) having a splitter holding section (110), a slack and unterminated fiber storage section (120), and a splice and splice tray holding section (150). The splitter holding section (110) is configured to optionally hold one or more fiber splitters. The slack and unterminated fiber storage section includes a slack storage region (130) having a plurality of fiber routing structures (146a, 146b) to support and retain slack fiber and an unterminated fiber storage region having one or more spool type structures (142) to support and retain unterminated fiber separate from the slack fiber. The splice and splice tray holding section is configured to optionally hold one of a first fiber splice insert (160) and a splice tray holder (170) configured to engage one or more splice trays. A distribution box (200) for distributing optical fibers for communications includes a base, a cover, and the organizer described above.
Owner:CORNING RES & DEV CORP
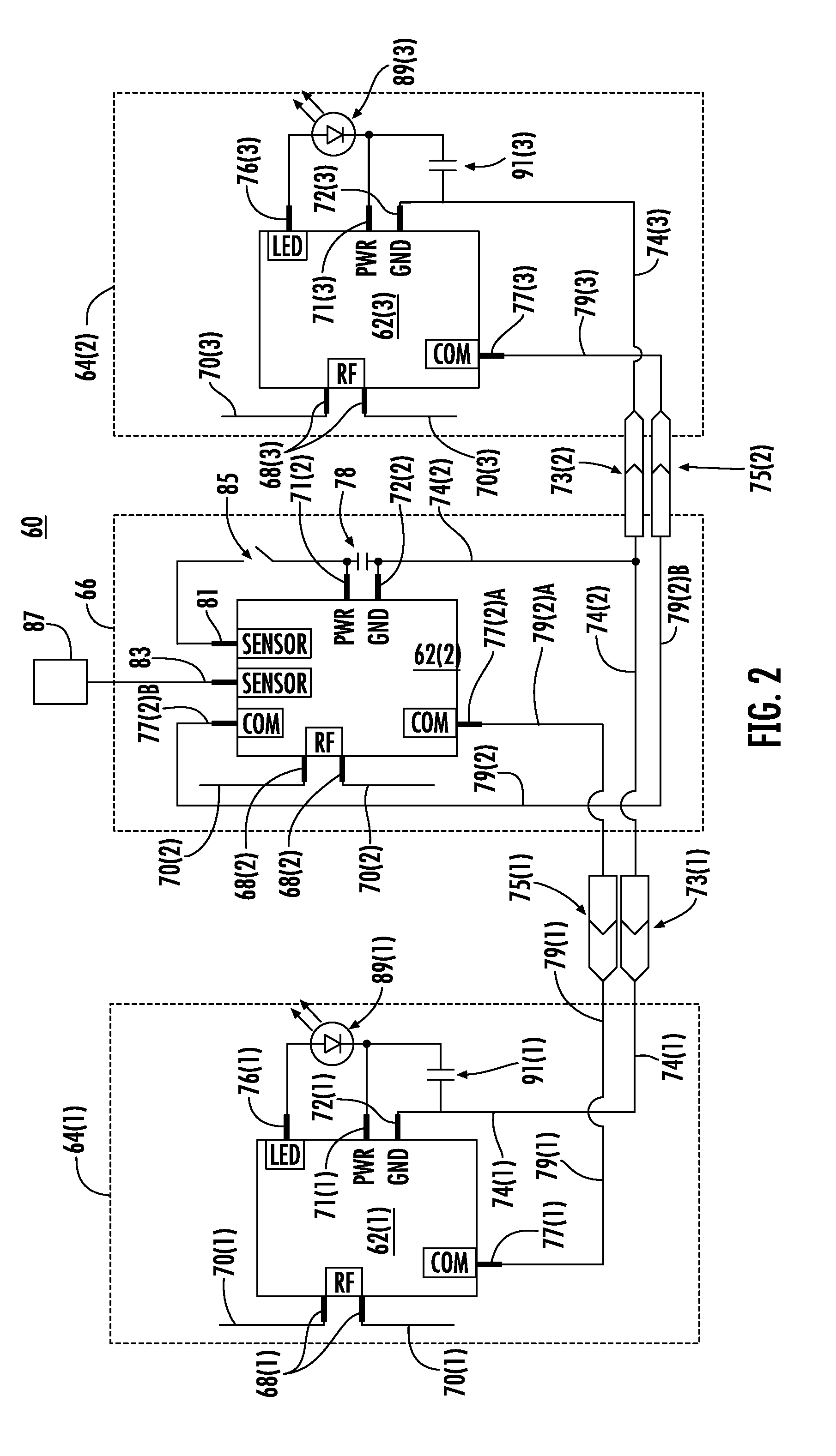
Radio frequency identification (RFID) in communication connections, including fiber optic components
ActiveUS20110274437A1Reduce and eliminate overlapEasy to receiveCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionElectricityFiber
Radio frequency identification (RFID)-equipped communication components are disclosed. The communication components can include fiber optic components, such as fiber optic connectors and fiber optic adapters as examples. An RFID-equipped circuit is provided in the communication components to communicate information. In order that the electrical circuit be provided in the communication component without altering the communication component connection type, the circuit may be disposed in at least one recessed area of the communication component housing. In this manner, the communication component maintains its connection type such that it is compatible with a complementary communication component connection type for backwards compatibility while also being RFID-equipped. The circuit may also be provided in a substrate containing one or more electrical contacts coupled to the circuit such that a wired coupling is established with one or more electrical contacts provided in another communication component when connected.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
Fiber optic adapter plates with integrated fiber optic adapters
Structures, devices and methods are provided for creating fiber optic adapter plates with integrated fiber optic adapters. In one aspect, fiber optic adapter plates having integrated fiber optic adapter subassemblies are formed from a moldable plastic. For example, a molded plastic fiber optic adapter plate can include a molded plastic adapter back plate having a plurality of integrated fiber optic adapter subassemblies and one or more attachment mechanisms that facilitate locating and attaching an adapter front plate having a corresponding plurality of integrated fiber optic adapter subassemblies on the adapter front plate. Advantages provided by integrating fiber optic adapters into the molded plastic assemblies include superior mechanical strength, manufacturing cost reductions and adapter placement flexibility among other advantages.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
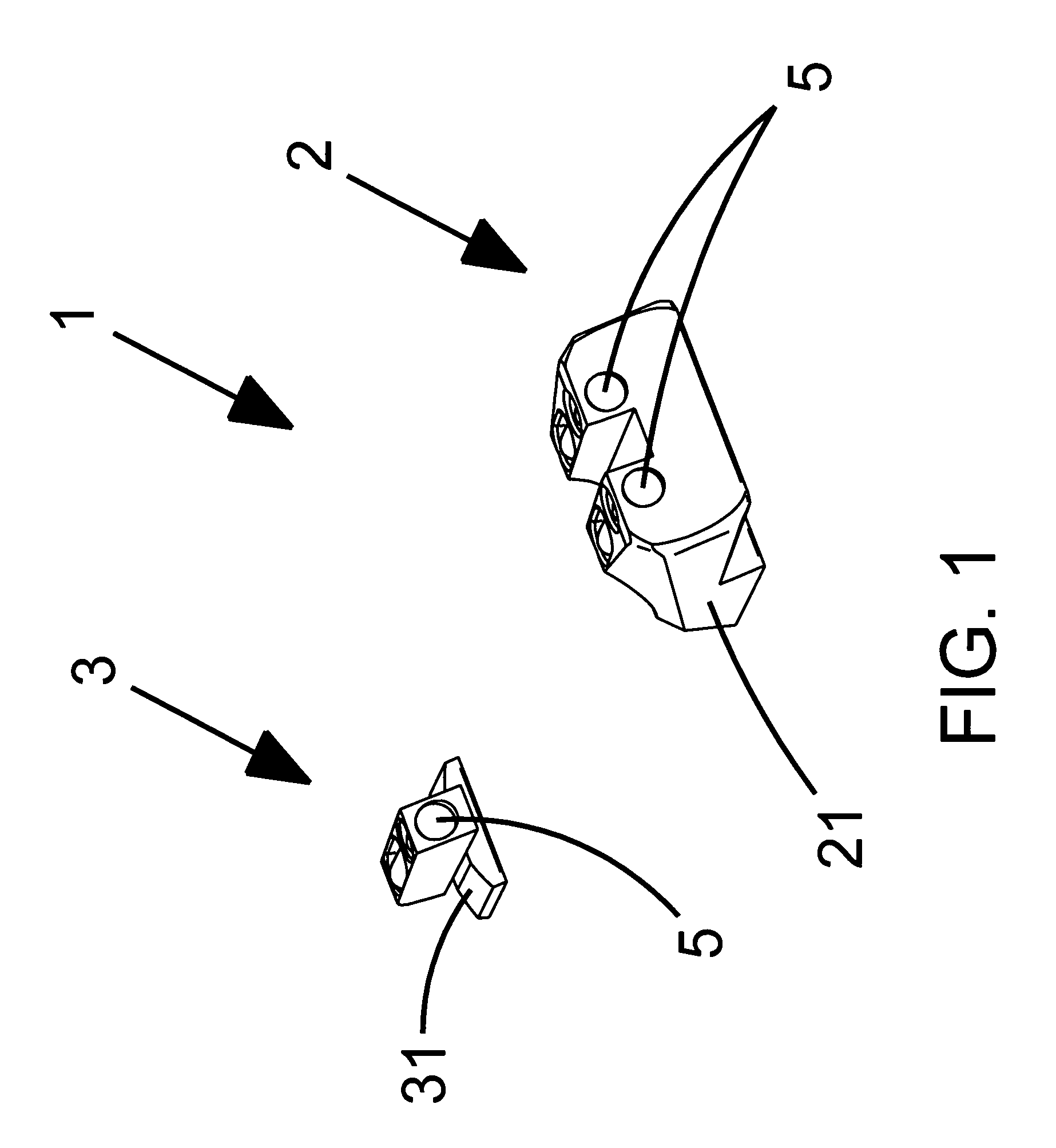
Fiber optic sight for firearms with nighttime capabilities
InactiveUS7627976B1Increase the amount of lightSufficient protectionSighting devicesEpoxyNight vision
New and unique improvements of prior known fiber optic sights for firearms with day and night time capabilities are disclosed that comprise (A) a sight base, (B) a fiber optic rod mounted in said base having an angle cut at the distal end which is positioned on the underside of the rod, and (C) an artificial light insert that is positioned in a cavity in the fiber optic rod. The cavity is sealed with a fiber optic rod plug and epoxied using an optically clear epoxy. The sight provides increased light output, co-located day and night sight views with increased illumination during the day, and uses a low power tritium insert for night time use. At night the sight achieves a transition from a bright ring during the day to a small central dot at night while maintaining the same color light for both.
Owner:WILSONS GUN SHOP
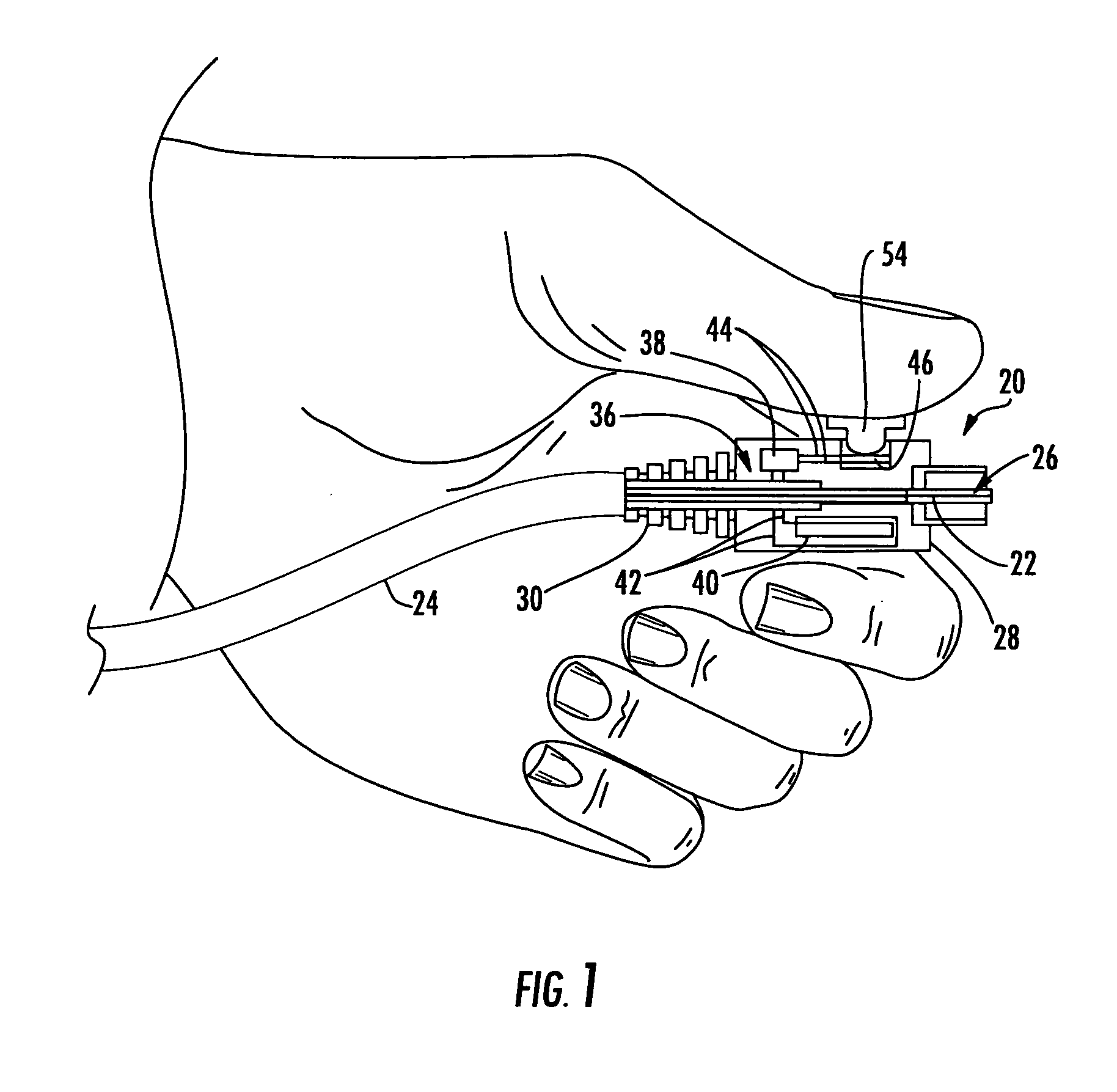
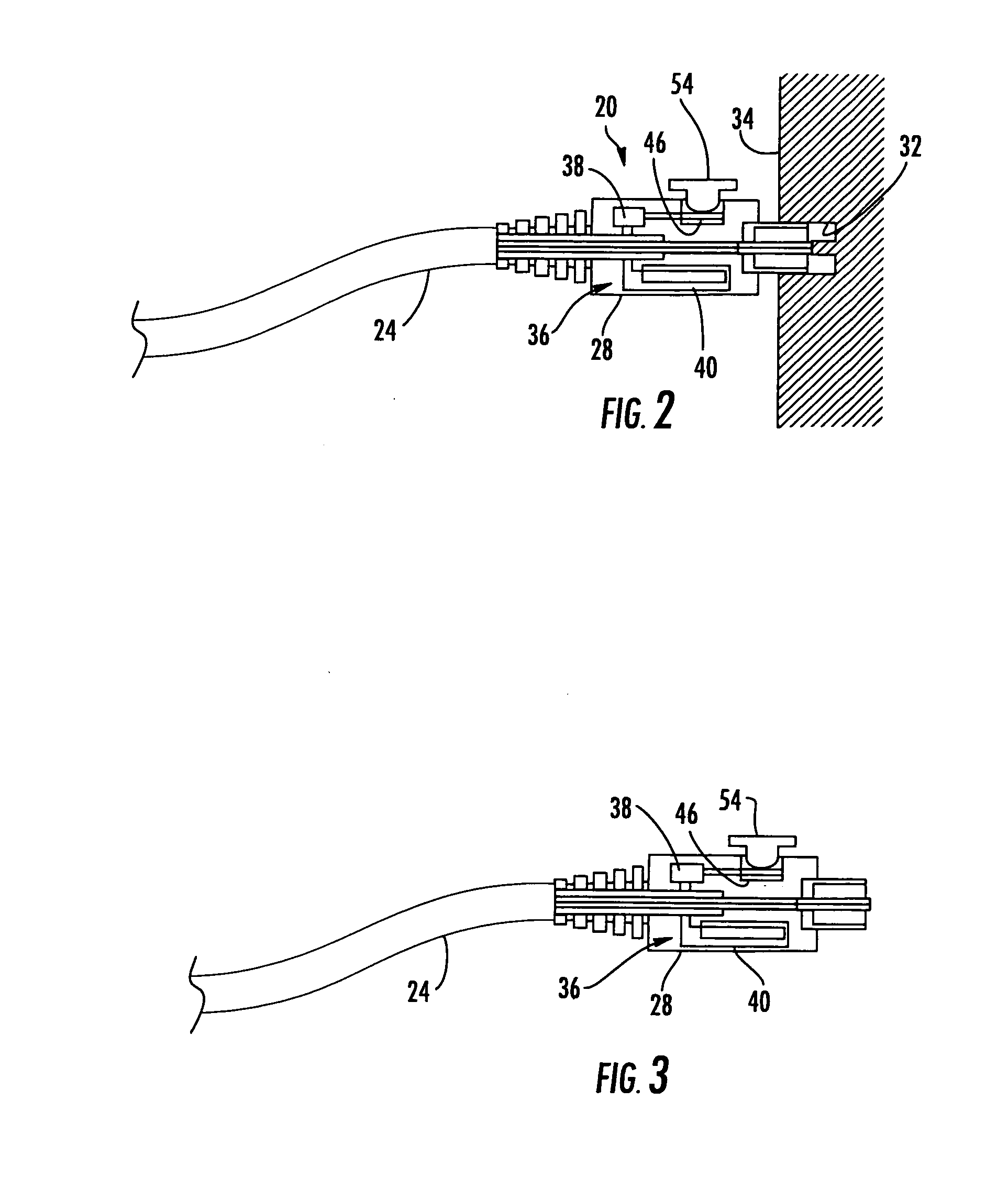
Methods, Apparatuses for Providing Secure Fiber Optic Connections
Methods and apparatuses for providing secure fiber optic connections are disclosed. In one embodiment, a locking apparatus comprising a locking plate to secure fiber optic connections is disclosed. The locking plate is configured to be attached to a fiber optic adapter panel and adjustably positioned to a selected position such that when a fiber optic connector on the end of a fiber optic cable is connected to a fiber optic adapter on the fiber optic adapter panel, the fiber optic cable is allowed to pass through a cut-out area of the locking plate but a finger portion of the locking plate does not allow the fiber optic connector to pass through the cut-out area. A lock disposed on the locking plate is configured to keep the locking plate in the selected position. The locking apparatus may also be used to securely store unused or unconnected ports of an optical splitter in a separate enclosure, such as a parking lot compartment.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
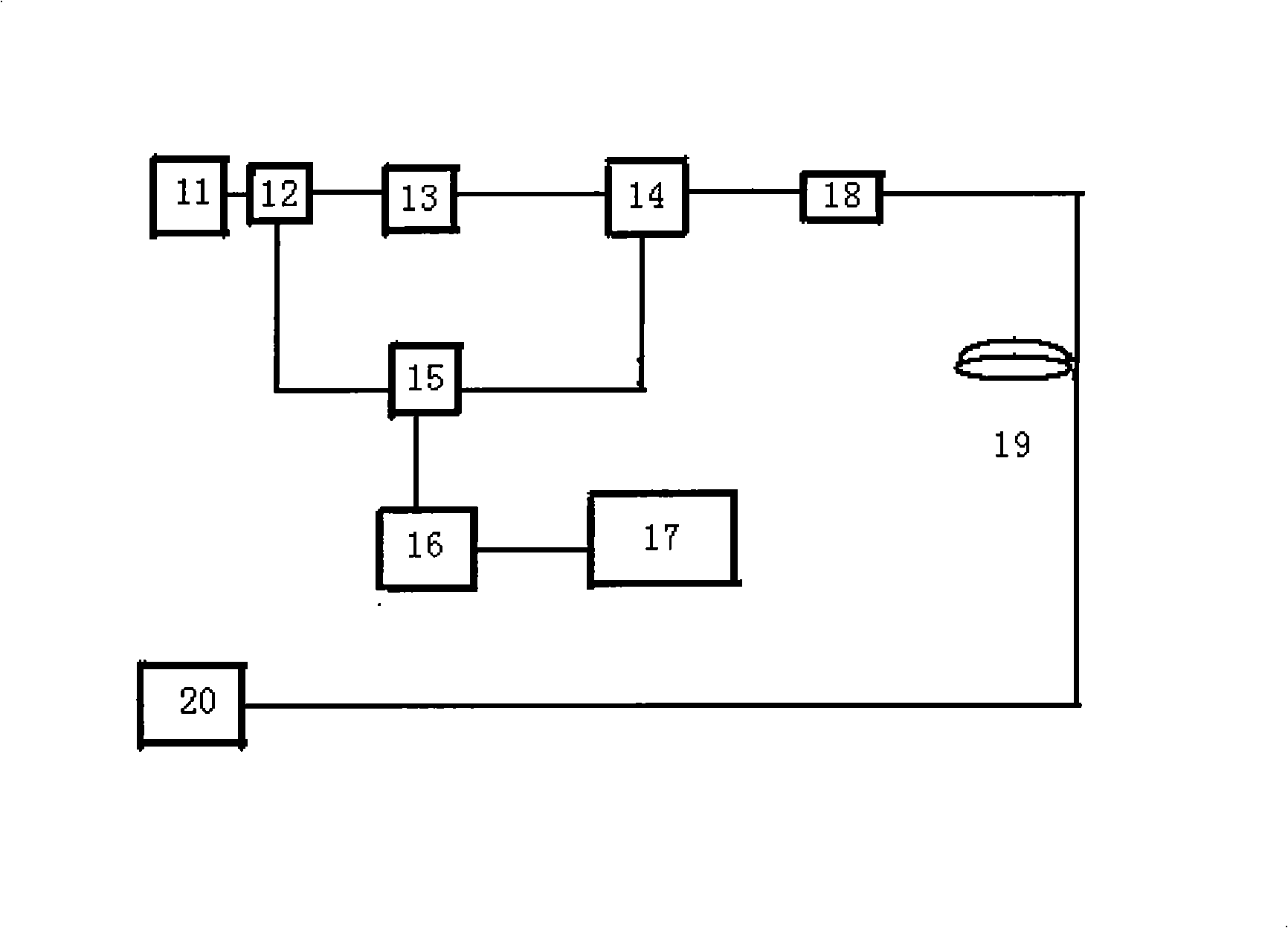
Instrument and method for real time monitoring optical fibre distributed multi-point mash gas
InactiveCN101281127AEliminate distractionsConcentration sensitiveColor/spectral properties measurementsData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses an optical fiber distributed multi-point methane real-time monitor based on the light wave modulation spectrometry and the monitoring method, a semiconductor DFB laser, an optical fiber splitter, a gas calibration pond, a laser control circuit board, a signal generative circuit board, a lock-in amplified board, a data acquisition card, a control module, a multi-channel analog signal selection switch and a driving circuit are arranged in the main case of the monitor, the main case is connected with miniature optical sensors in various underground detection optical path through dingle mode fibers. The wavelength modulation of a gas laser absorption spectrum is realized by a low frequency scanning signal and a high frequency modulation signal generated by a signal generative circuit. The laser wavelength shift is carried out adaptive adjustment by the built-in gas calibration pond so as to realize the locking of a methane absorption line. The distributed multi-point methane concentration monitoring in the underground coal mine is realized by the switching of the multi-channel analog signal selection switch.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
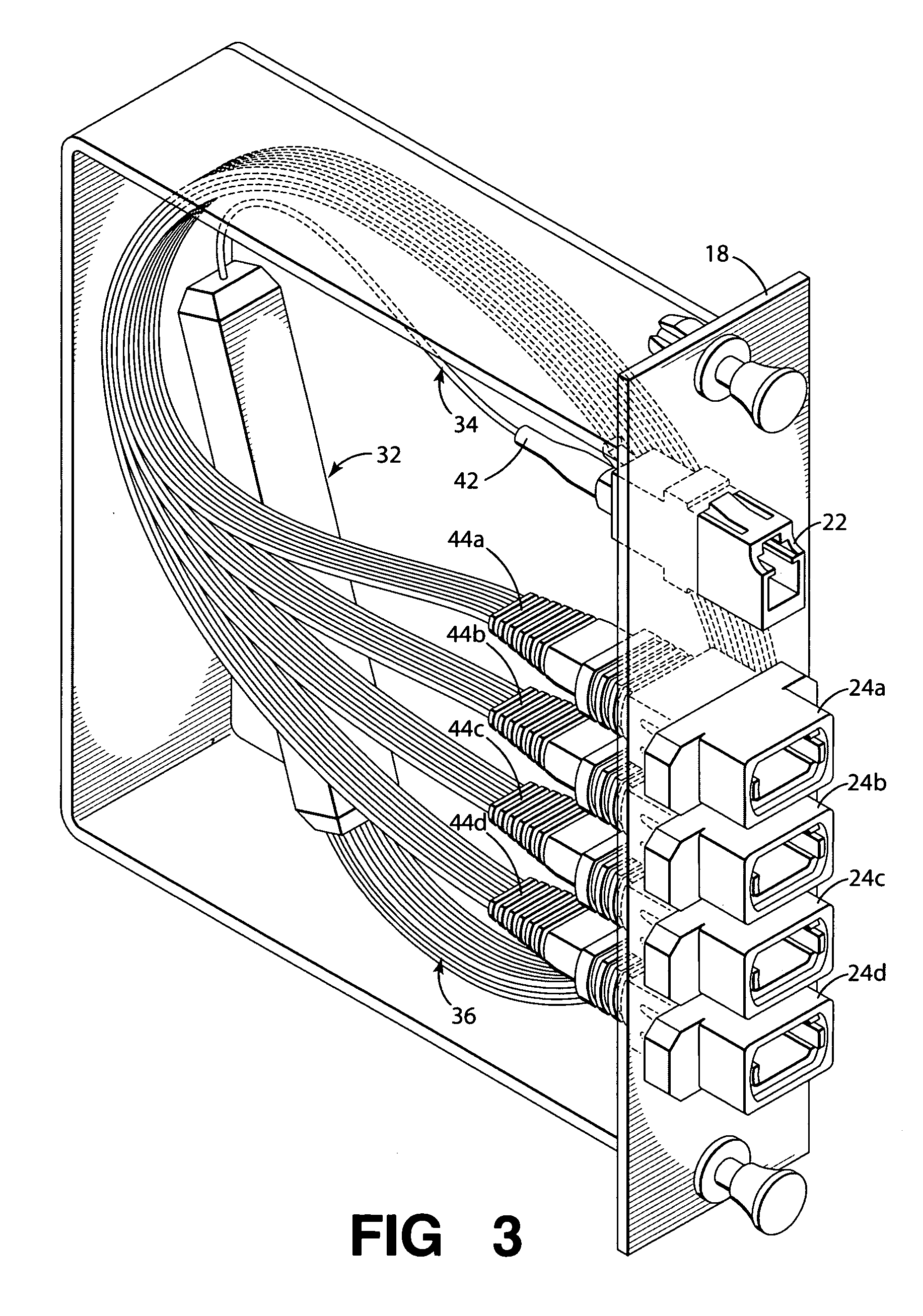
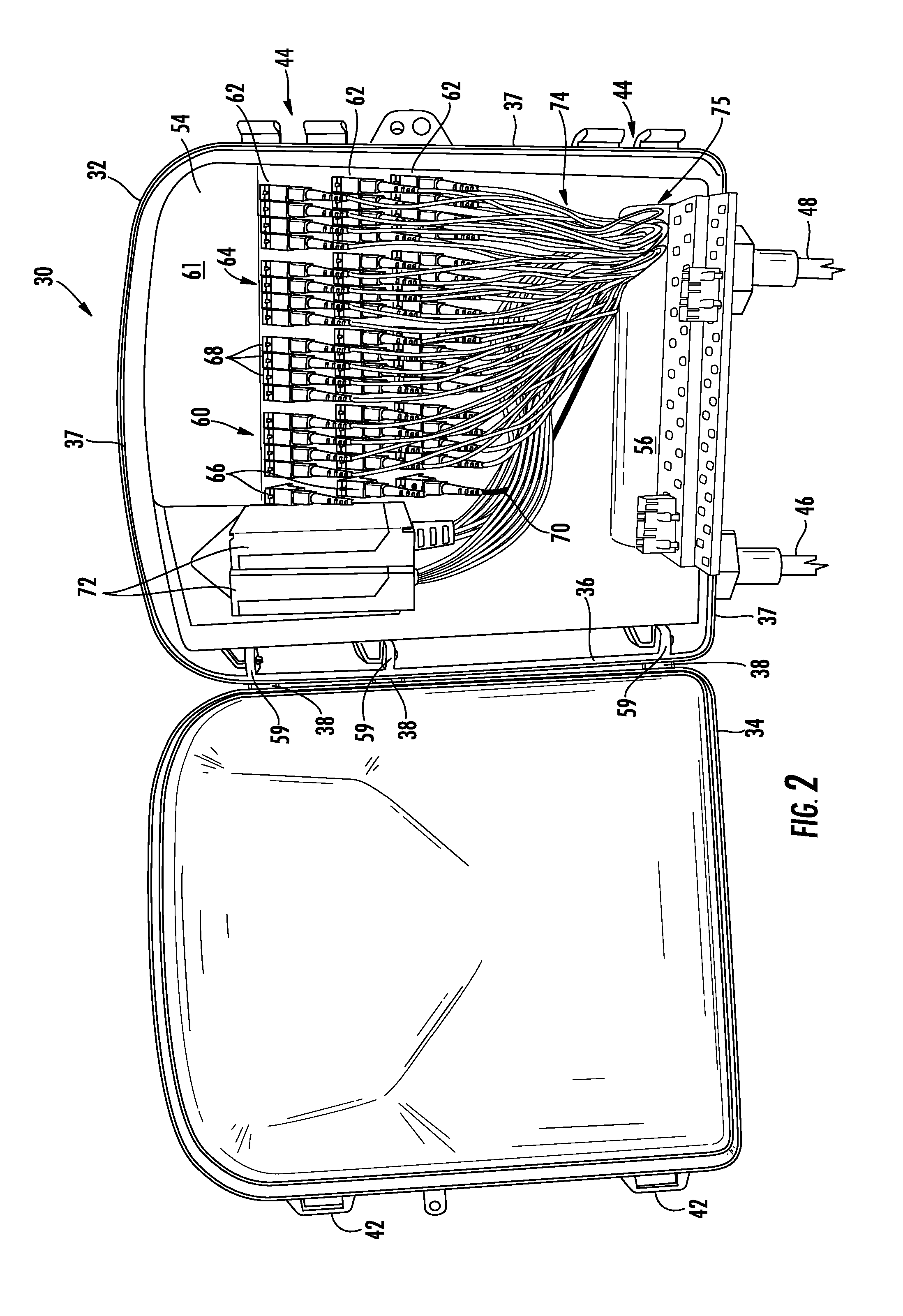
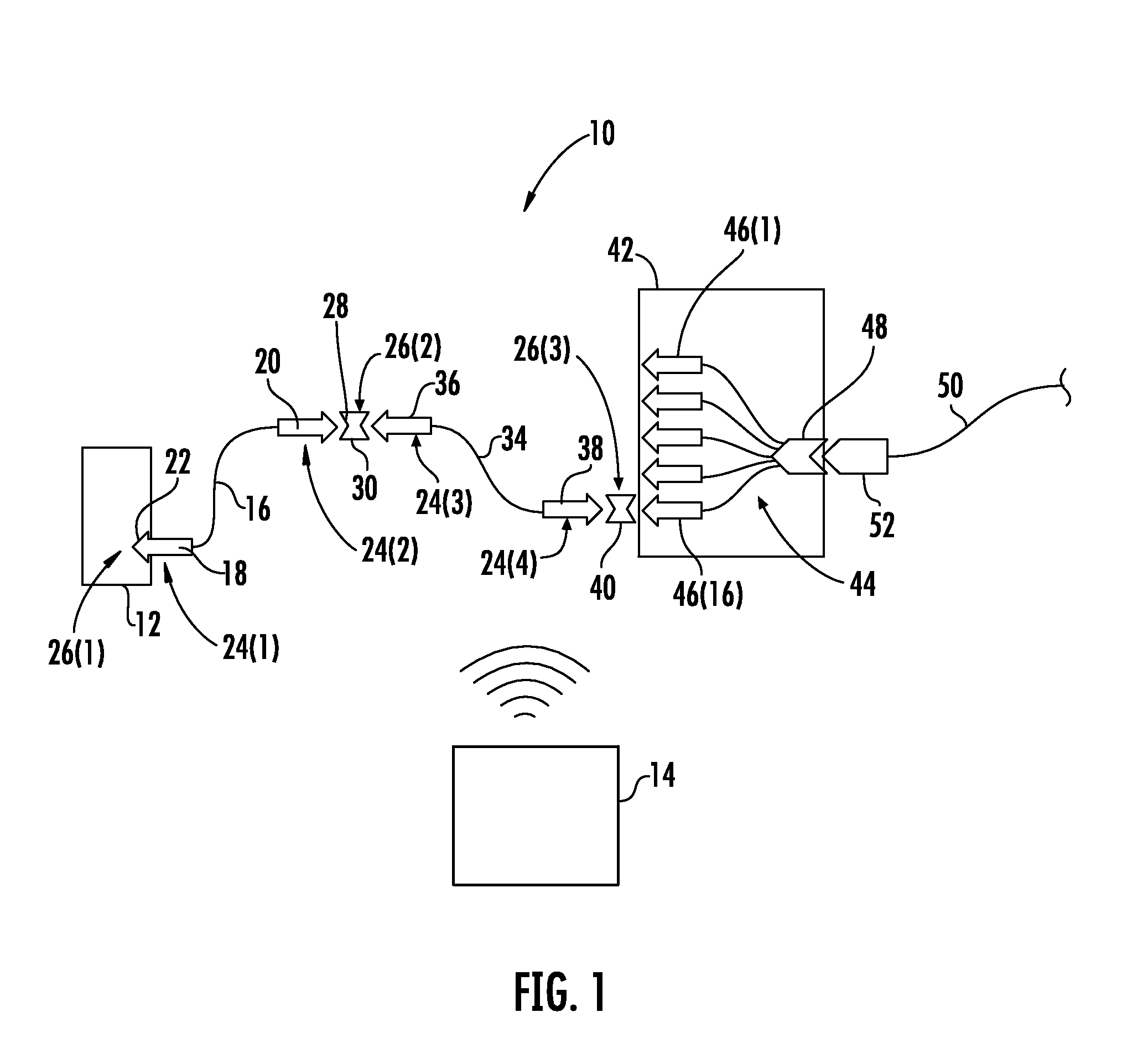
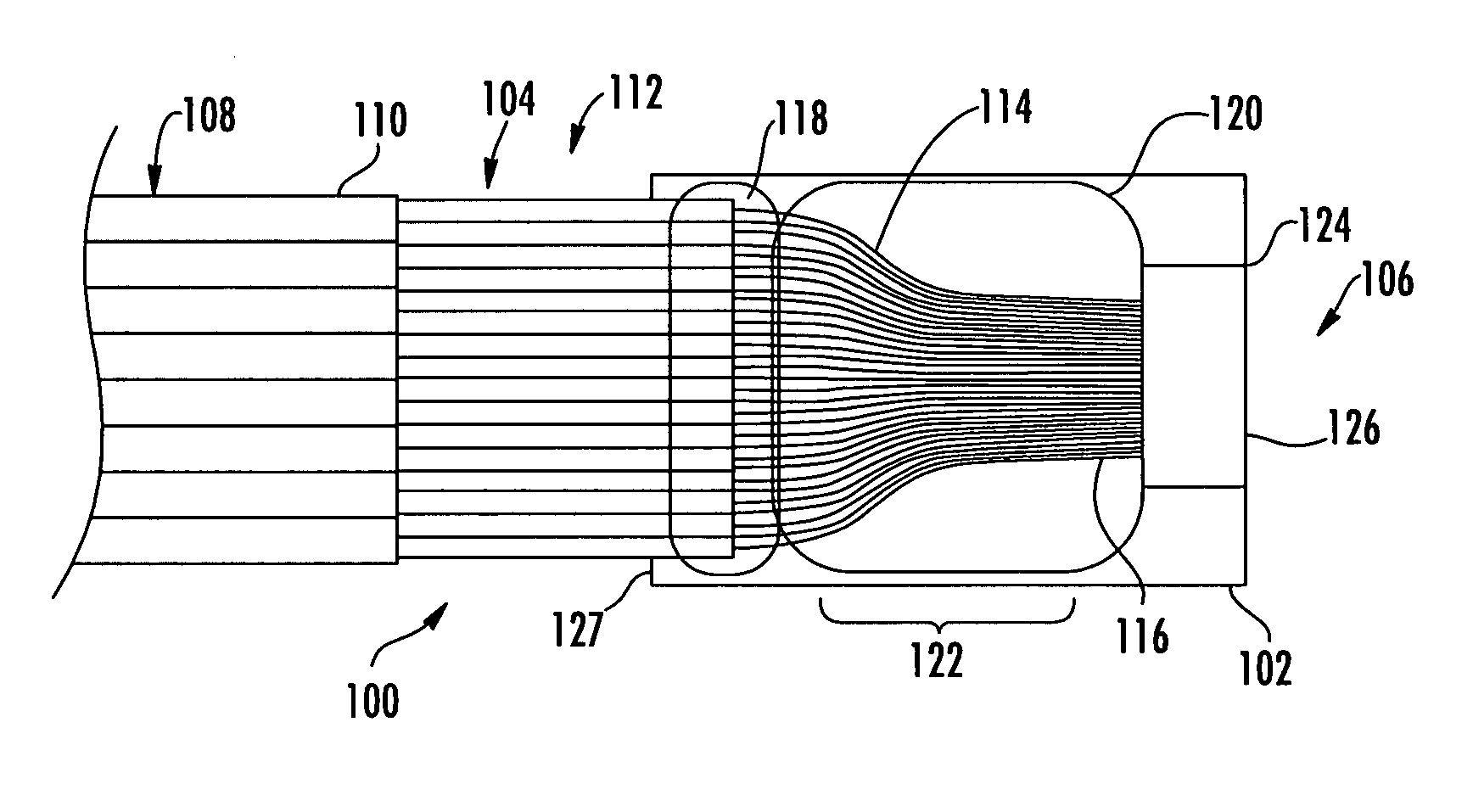
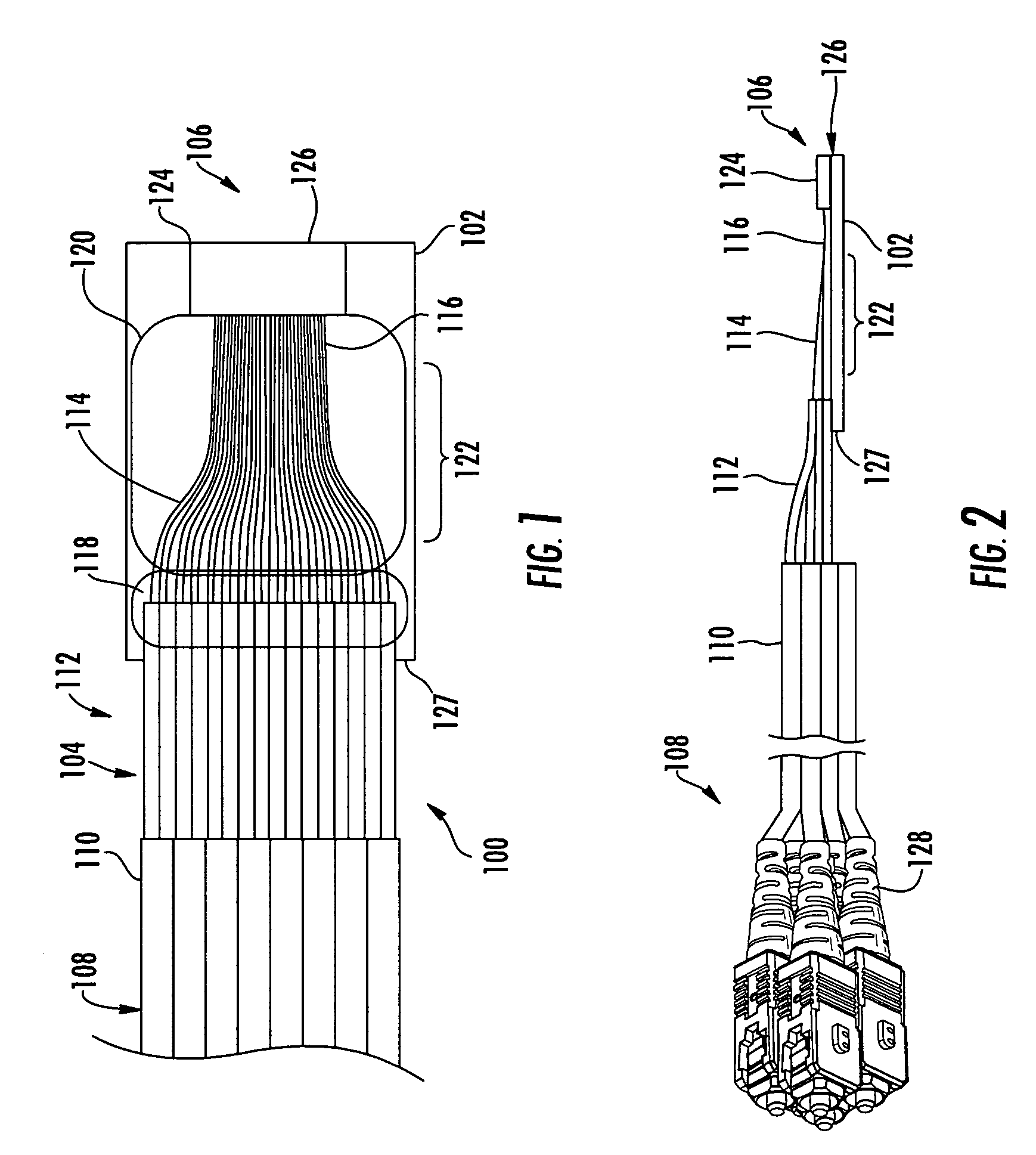
Optical fiber splitter module and fiber optic array therefor
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Radio frequency identification (RFID) in communication connections, including fiber optic components
ActiveUS8172468B2Reduce and eliminate overlapEasy insertion and removalCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionElectricityFiber
Radio frequency identification (RFID)-equipped communication components are disclosed. The communication components can include fiber optic components, such as fiber optic connectors and fiber optic adapters as examples. An RFID-equipped circuit is provided in the communication components to communicate information. In order that the electrical circuit be provided in the communication component without altering the communication component connection type, the circuit may be disposed in at least one recessed area of the communication component housing. In this manner, the communication component maintains its connection type such that it is compatible with a complementary communication component connection type for backwards compatibility while also being RFID-equipped. The circuit may also be provided in a substrate containing one or more electrical contacts coupled to the circuit such that a wired coupling is established with one or more electrical contacts provided in another communication component when connected.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
Removably mountable fiber optic terminal
A zero-U, high-density fiber optic terminal for data centers and central offices is disclosed. The terminal may be used for optical fiber interconnection and / or optical fiber and fiber optic cable storage. The terminal is removably mountable to a cable tray above fiber optic equipment, in a subfloor below fiber optic equipment or on a wall in proximity of fiber optic equipment. Additionally, the terminal may have an adapter panel with fiber optic adapters for optically connecting the optical fiber of a first fiber optic cable received from the cable tray and the optical fiber of a second fiber optic cable. The second fiber optic cable is intended to extend to the fiber optic equipment. The adapter panel and the fiber optic adapters are angled generally in the direction in which the second fiber optic cable is intended to extend. Angling the fiber optic adapters in this manner accommodates routing of second fiber optic cable, and provides ease of access to the fiber optic adapters for connecting and disconnecting fiber optic connectors and to slack storage components for cable management mounted in the terminal.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
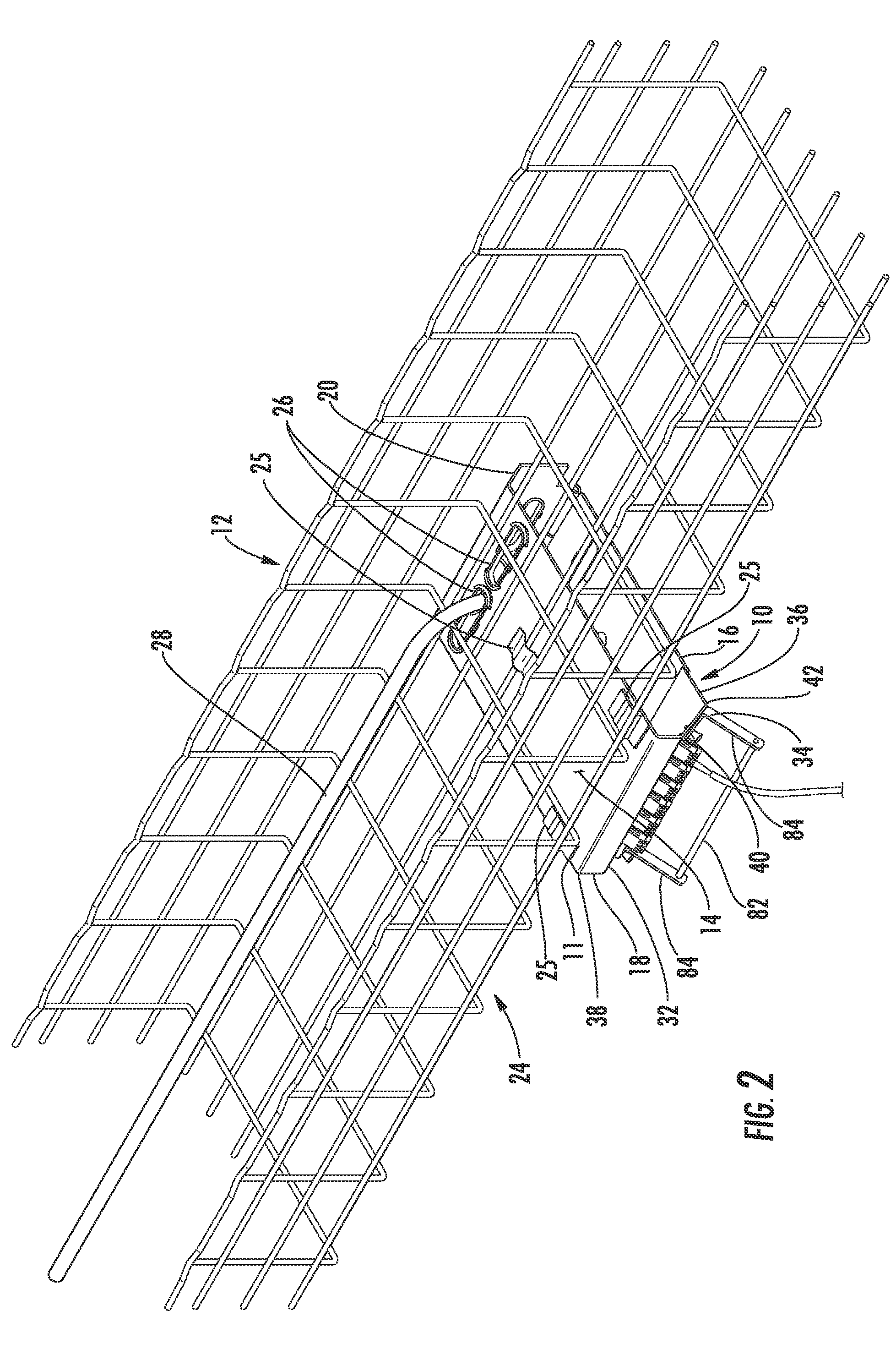
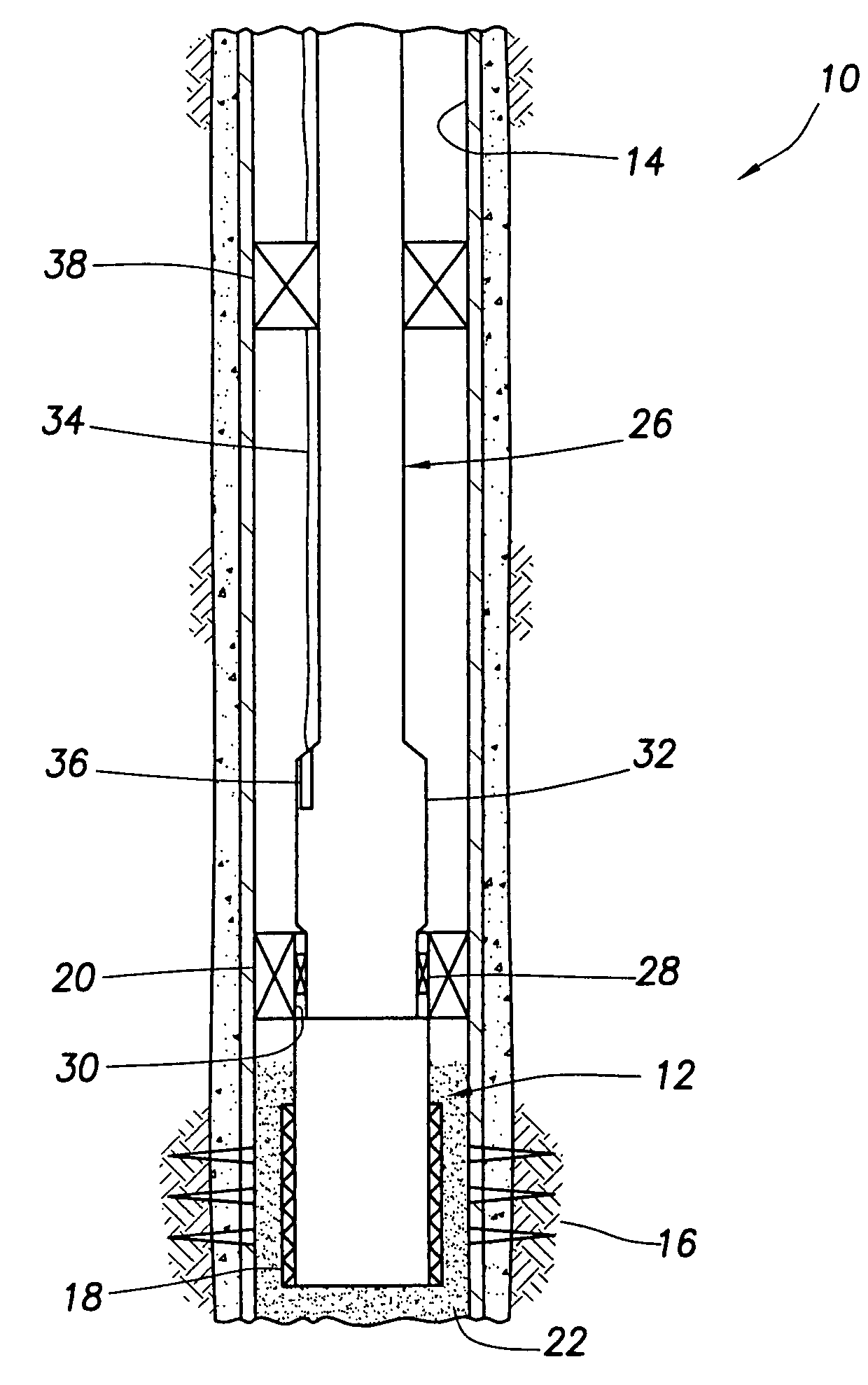
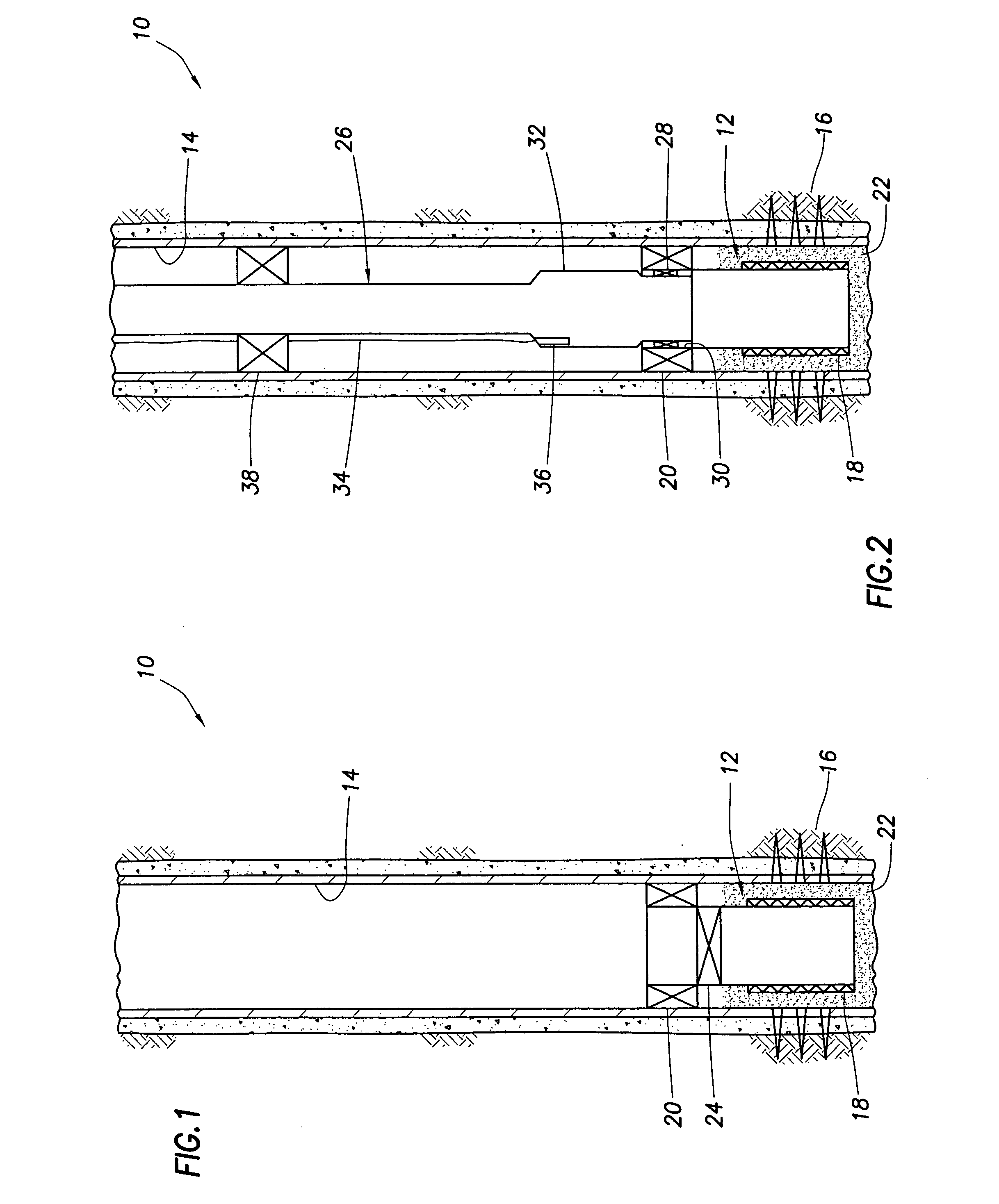
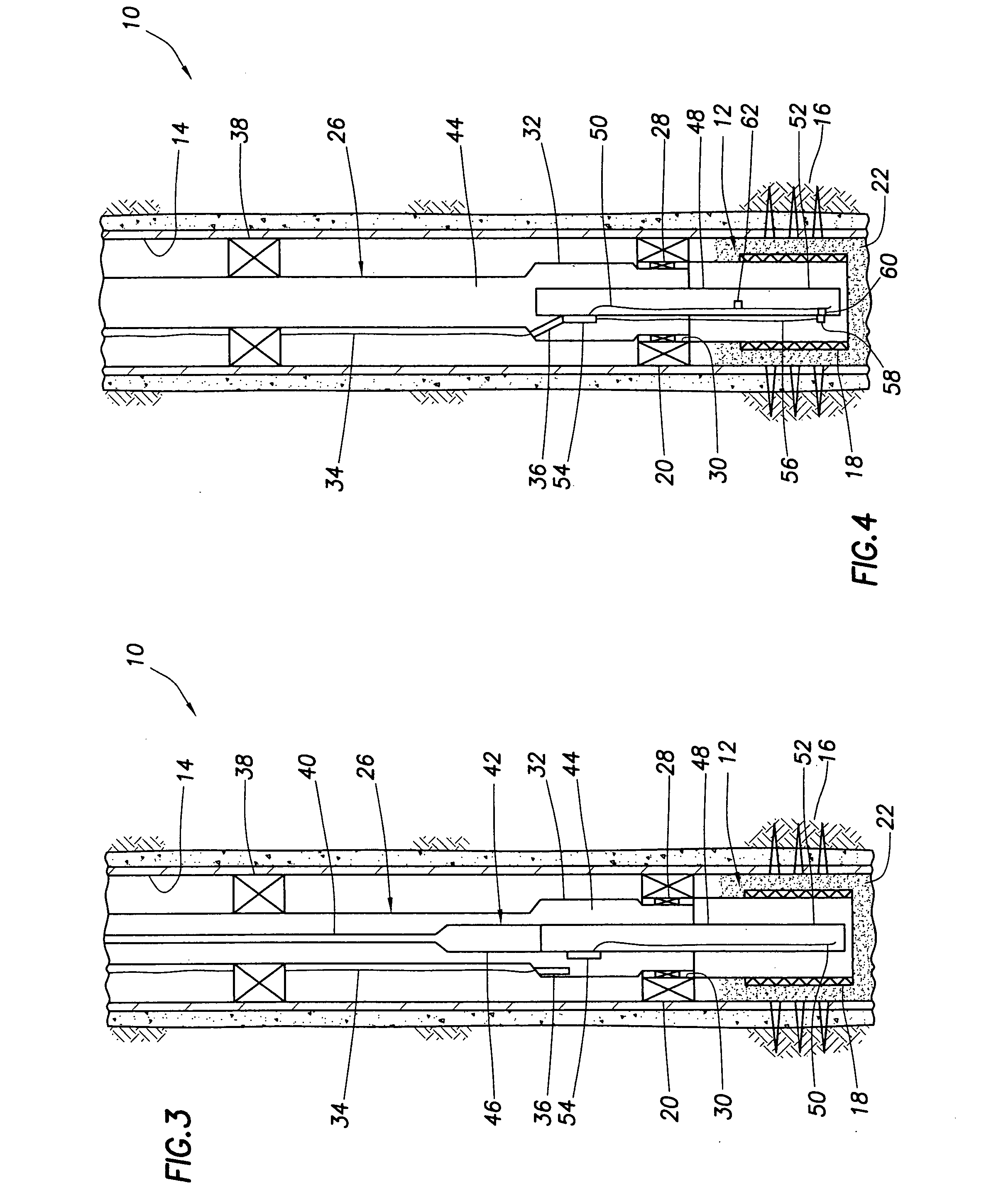
Downhole fiber optic wet connect and gravel pack completion
A downhole fiber optic wet connect and gravel pack completion. In a described embodiment, a system for making fiber optic connections in a subterranean well includes a first fiber optic connector positioned in the well and a second fiber optic connector operatively connected to the first fiber optic connector after the first fiber optic connector is positioned in the well. A method of monitoring a subterranean well includes the steps of: positioning a fiber optic line in the well, the fiber optic line extending in a formation intersected by the well; positioning another fiber optic line in the well, the fiber optic line extending to a remote location; operatively connecting the fiber optic lines while the fiber optic lines are in the well; and monitoring a well parameter using a sensor operatively coupled to the fiber optic line extending in the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
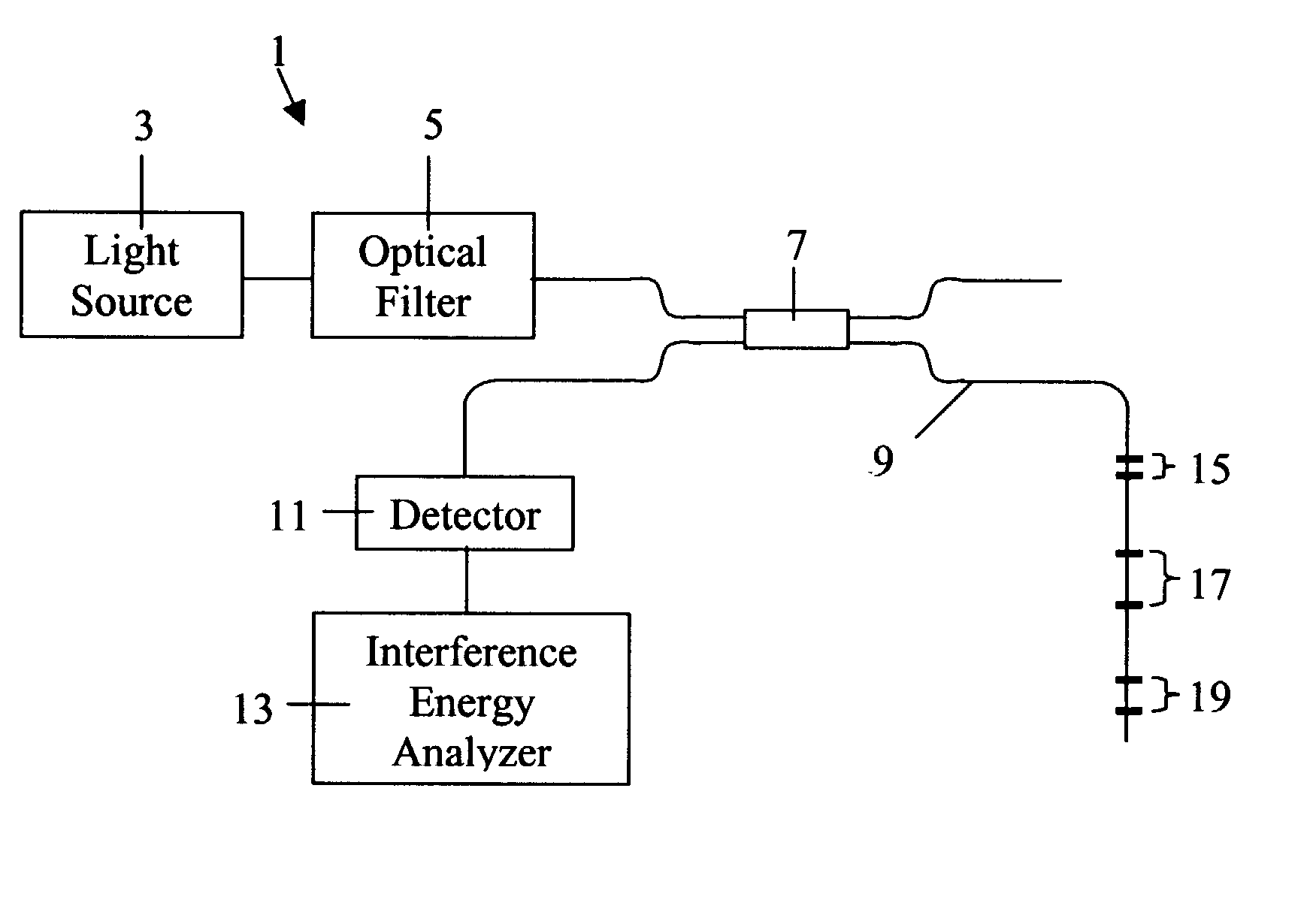
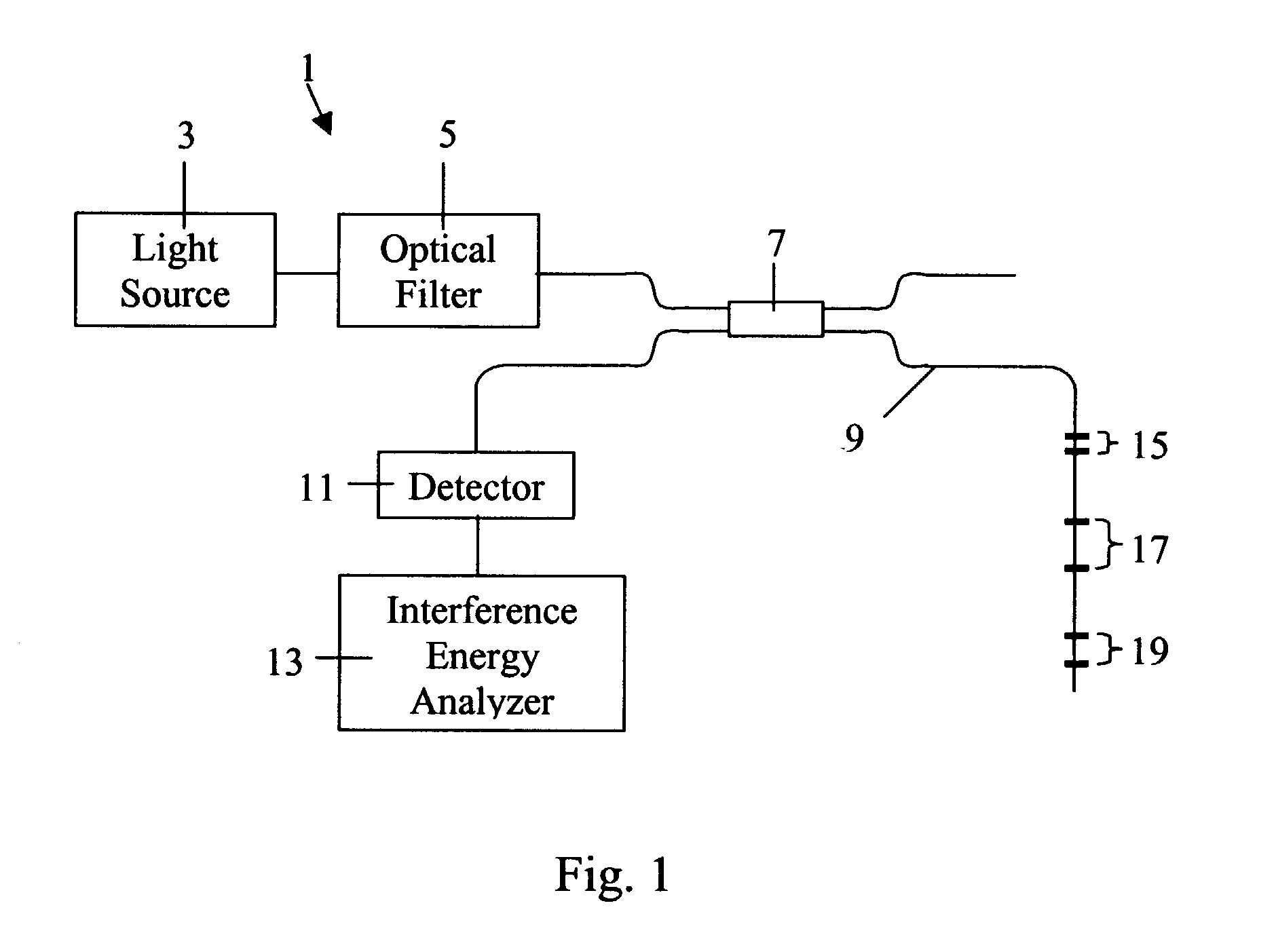
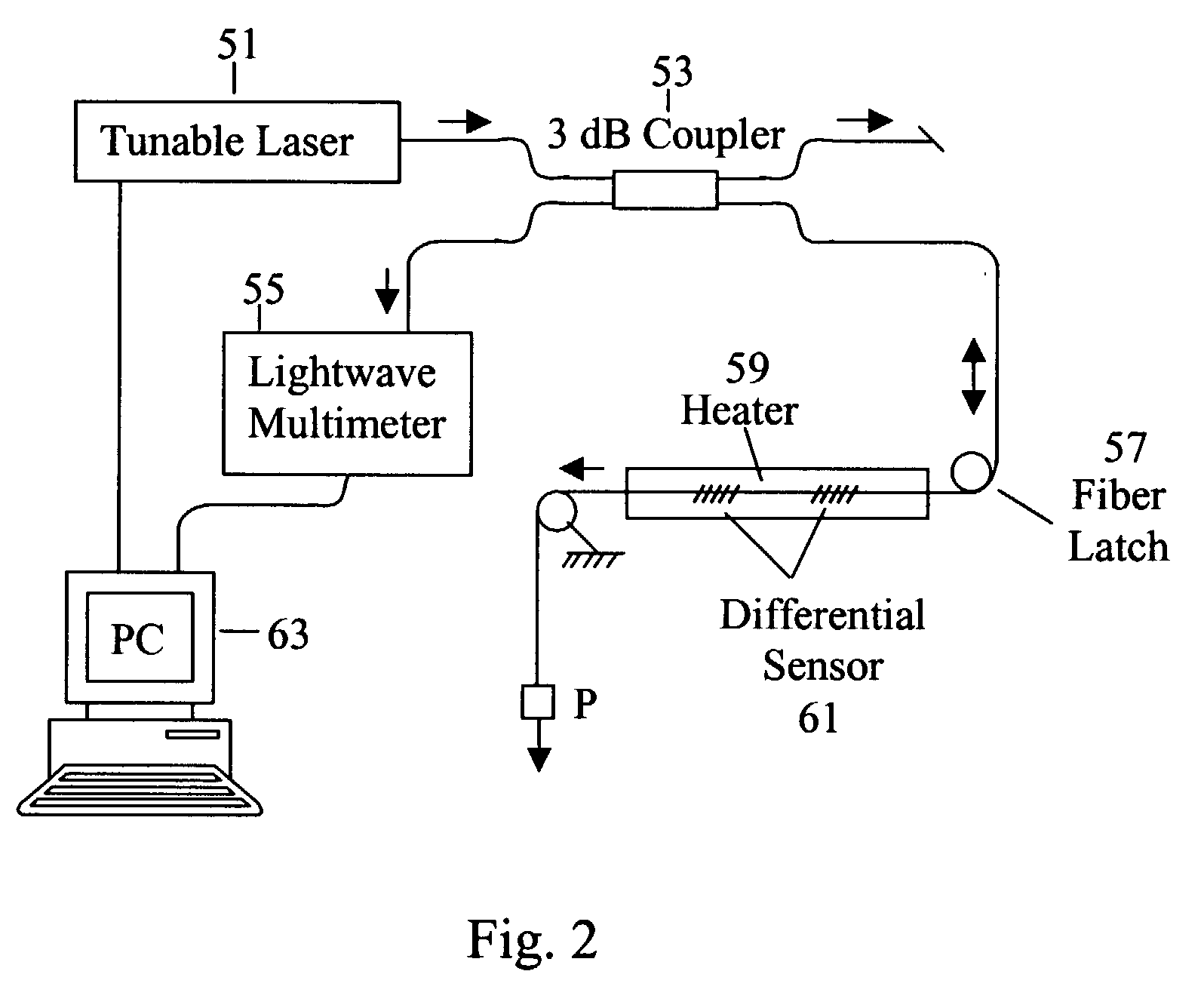
Differential fiber optical sensor with interference energy analyzer
InactiveUS20020176647A1Reduce temperature sensitivityForce measurement by measuring optical property variationCoupling light guidesOptical reflectionGrating
A fiber optic sensor, which includes an interference energy analyzer, is used to measure strain and temperature distribution along a test fiber. The sensor includes the following: a plurality of double-Bragg grating elements positioned along a test fiber, a broadband light source which produces a broadband spectral profile that propagates along the test fiber, an optical filter that is able to change the parameters of the broadband spectral profile, an optical reflection detector, a fiber optic beamsplitter, and an interference energy analyzer. Each double-Bragg grating element consists of two weak Bragg gratings, separated by a distance unique to each element. The interference energy analyzer calculates the energies of the interference patterns, which are created by beams reflected from double-Bragg grating elements. The energy of the interference signal changes when the gratings in one element non-uniformly change its parameters due to non-equal temperature or strain influence on two gratings.
Owner:NAGANO KEIKI
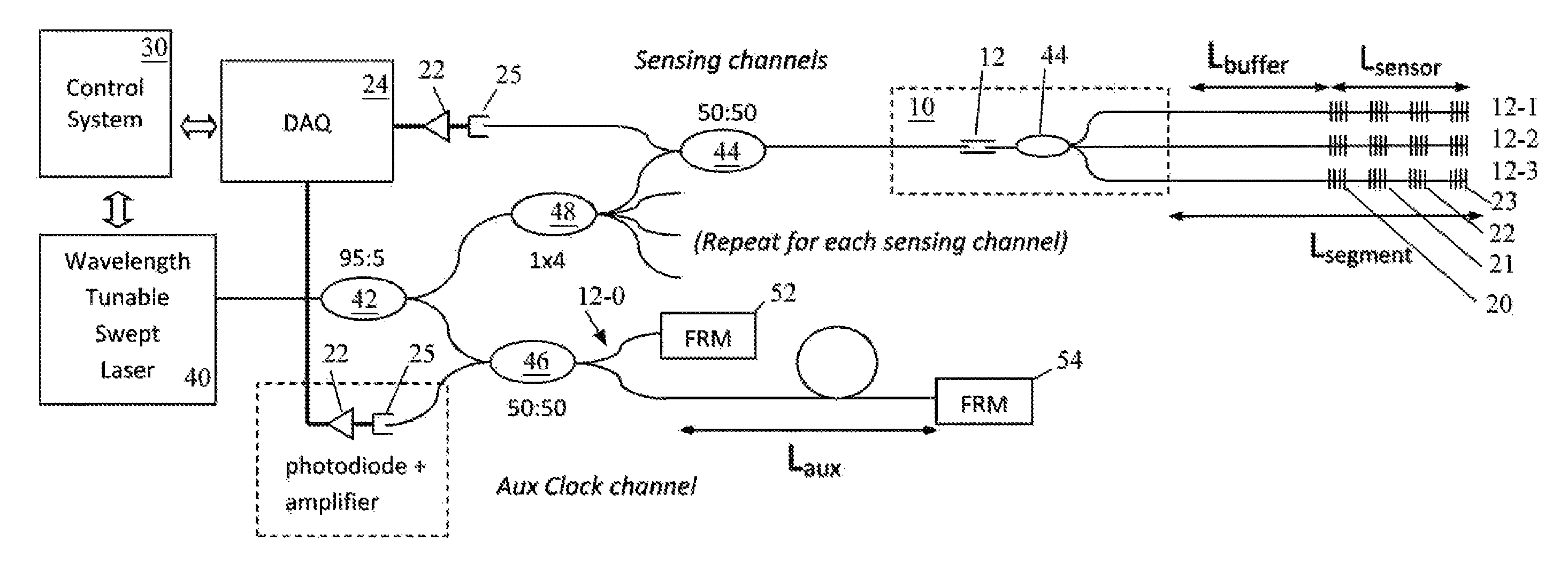
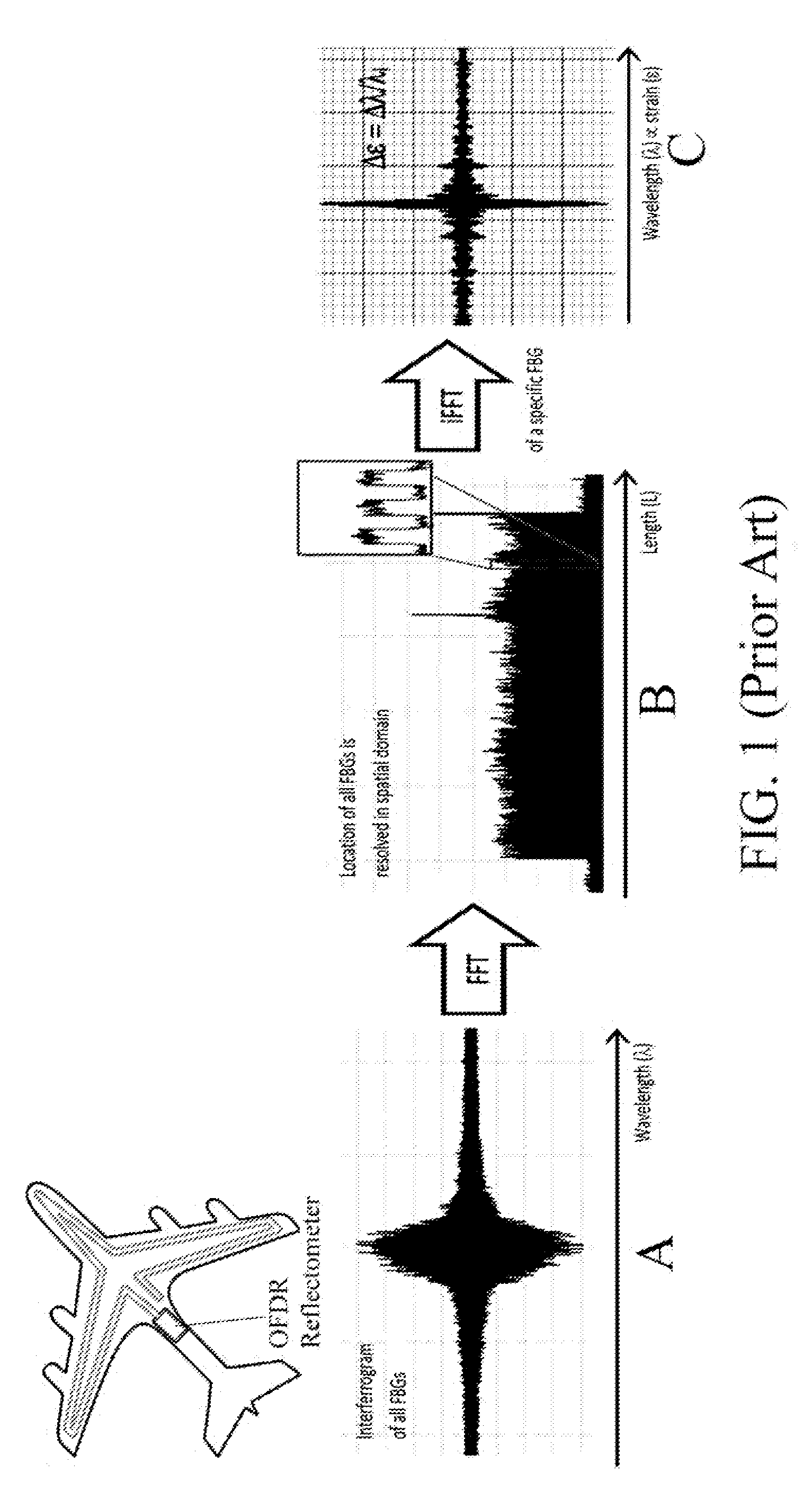
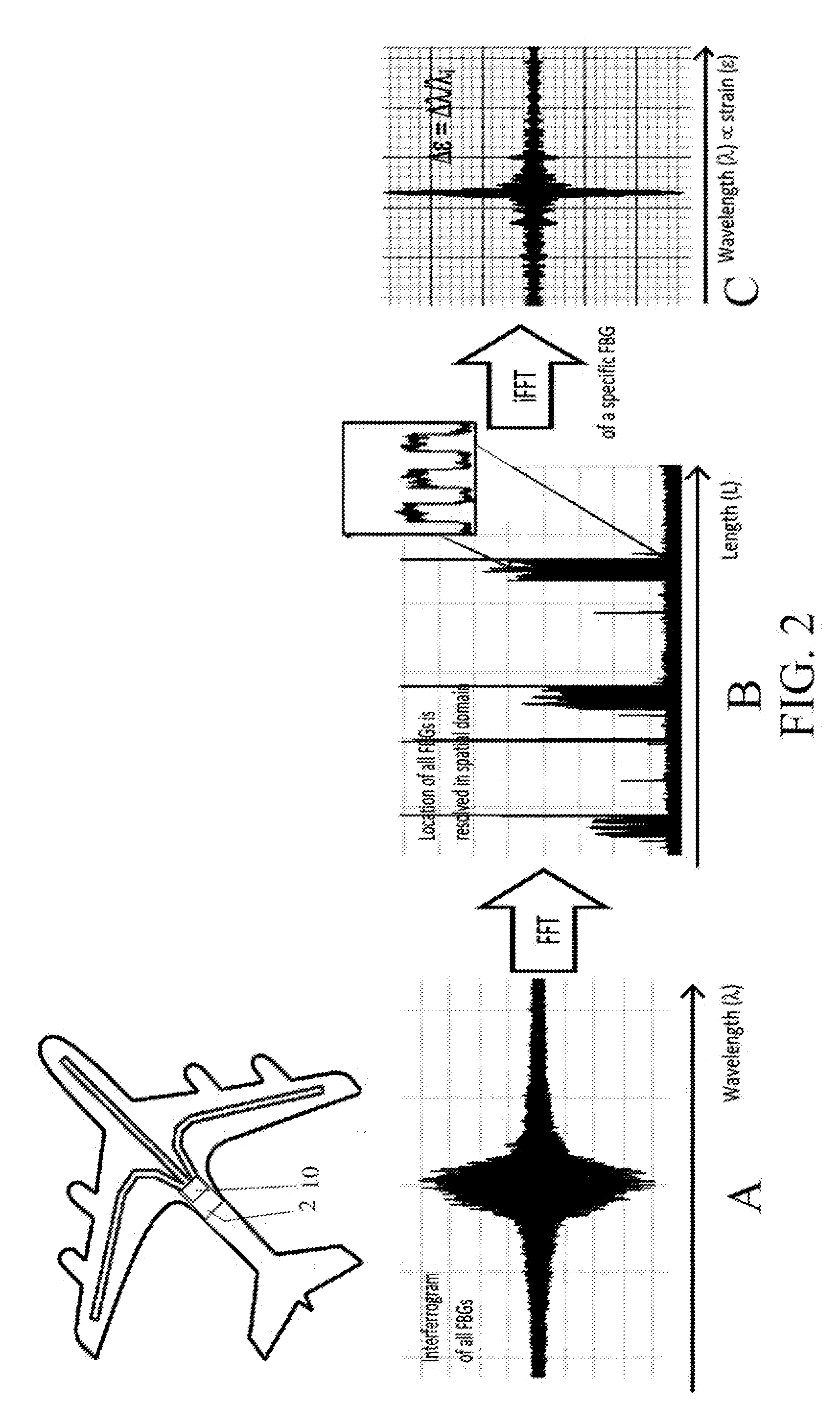
Method and apparatus of multiplexing and acquiring data from multiple optical fibers using a single data channel of an optical frequency-domain reflectometry (OFDR) system
ActiveUS8909040B1Simplifies opticalSimplifies electronicWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingMeasurement point
A method and system for multiplexing a network of parallel fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor-fibers to a single acquisition channel of a closed Michelson interferometer system via a fiber splitter by distinguishing each branch of fiber sensors in the spatial domain. On each branch of the splitter, the fibers have a specific pre-determined length, effectively separating each branch of fiber sensors spatially. In the spatial domain the fiber branches are seen as part of one acquisition channel on the interrogation system. However, the FBG-reference arm beat frequency information for each fiber is retained. Since the beat frequency is generated between the reference arm, the effective fiber length of each successive branch includes the entire length of the preceding branch. The multiple branches are seen as one fiber having three segments where the segments can be resolved. This greatly simplifies optical, electronic and computational complexity, and is especially suited for use in multiplexed or branched OFS networks for SHM of large and / or distributed structures which need a lot of measurement points.
Owner:NASA
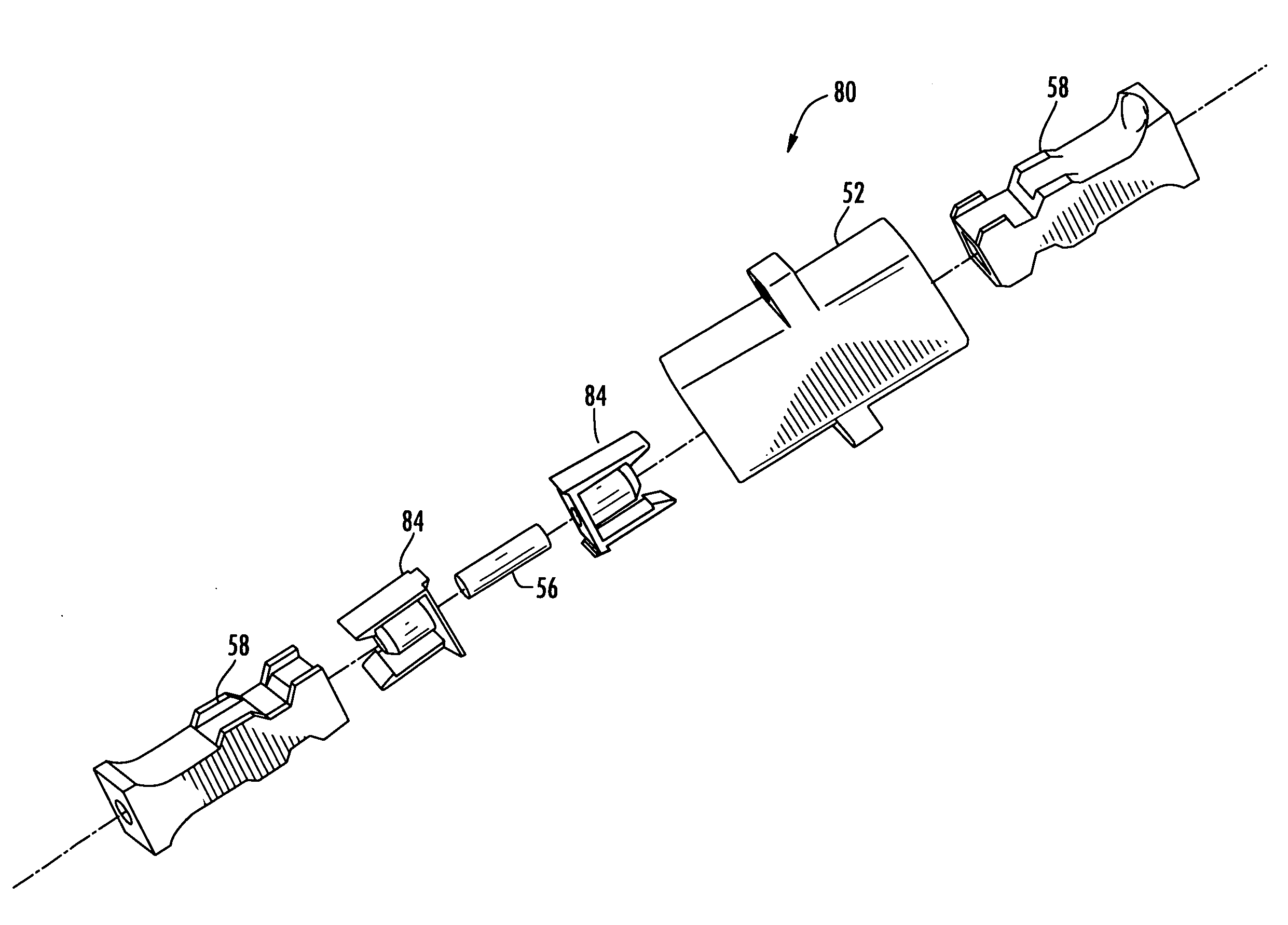
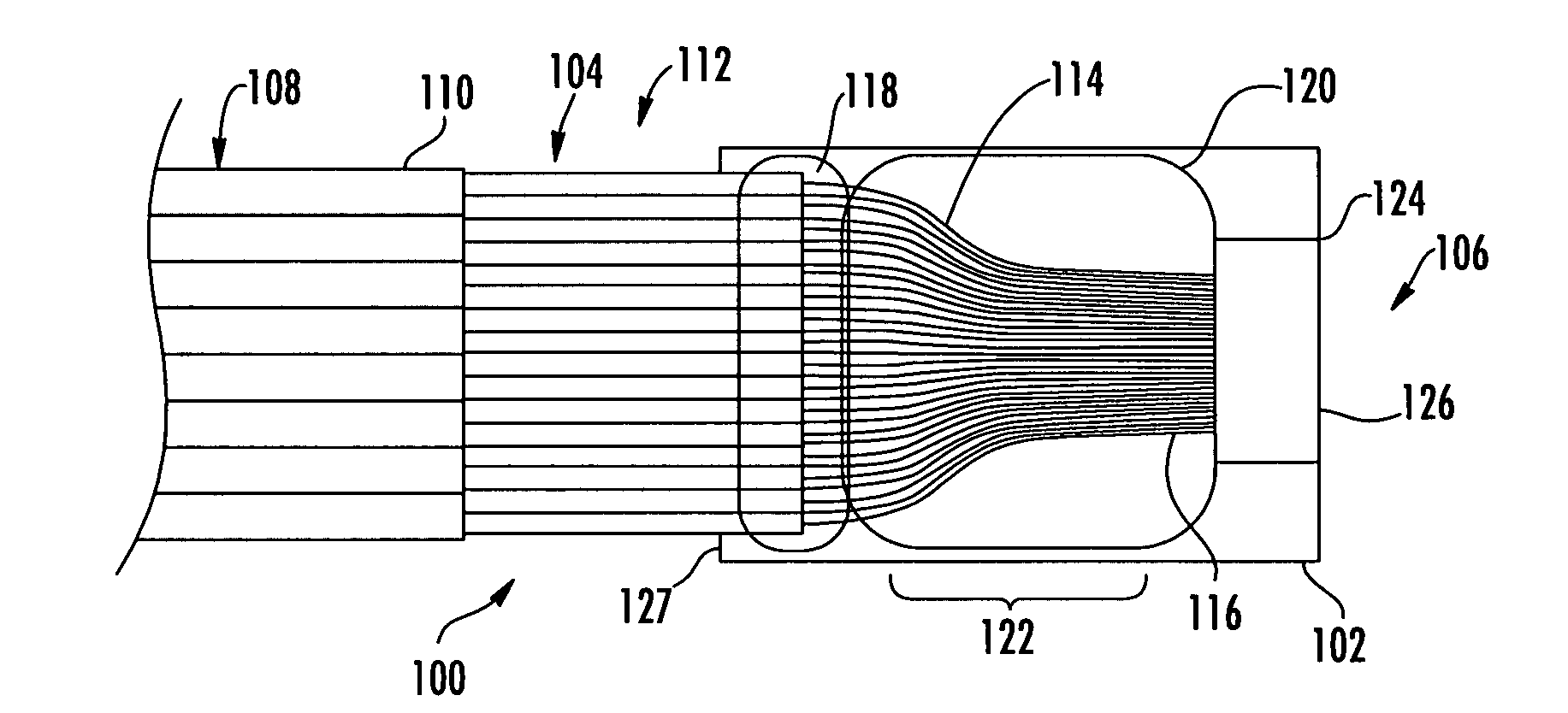
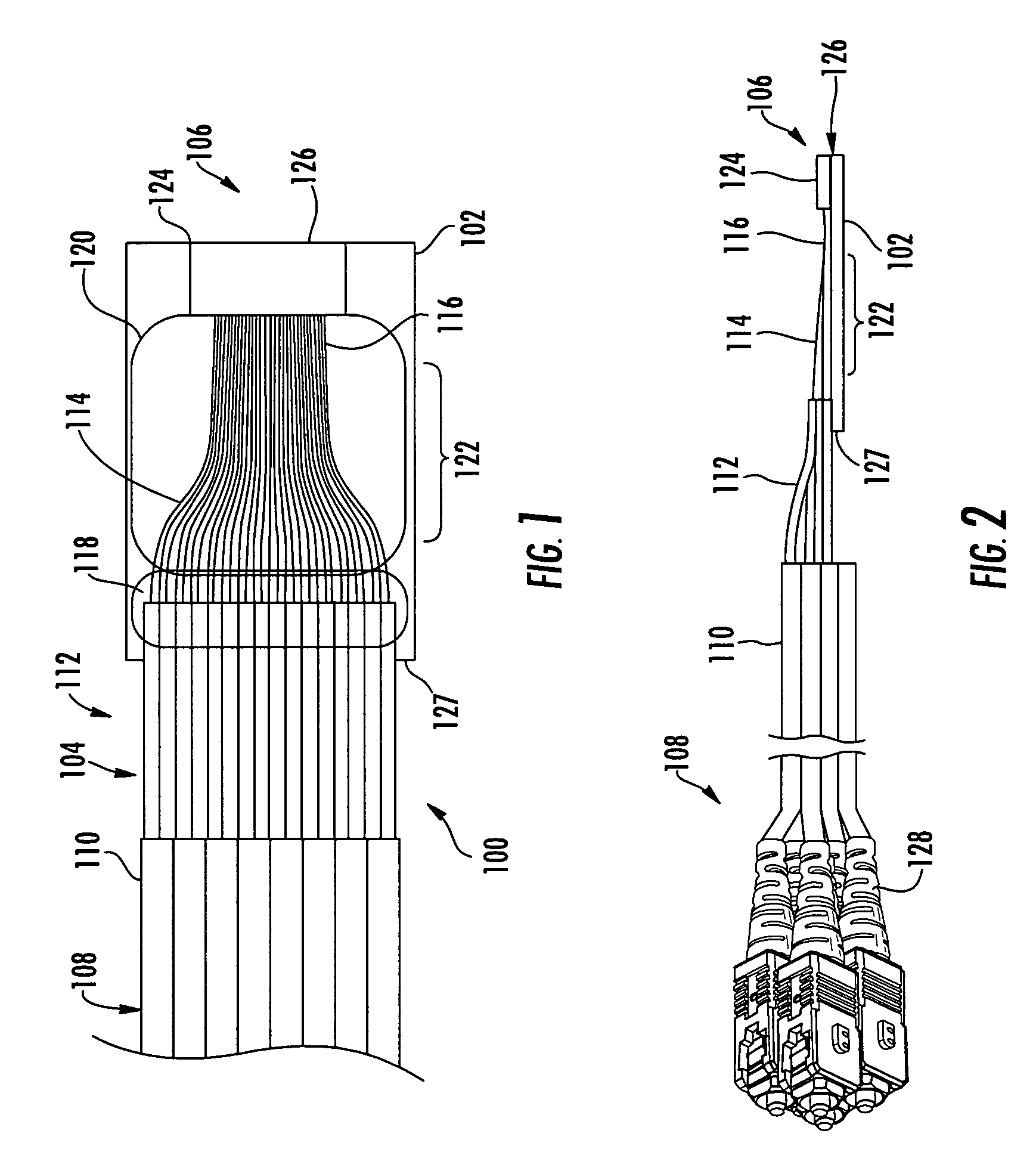
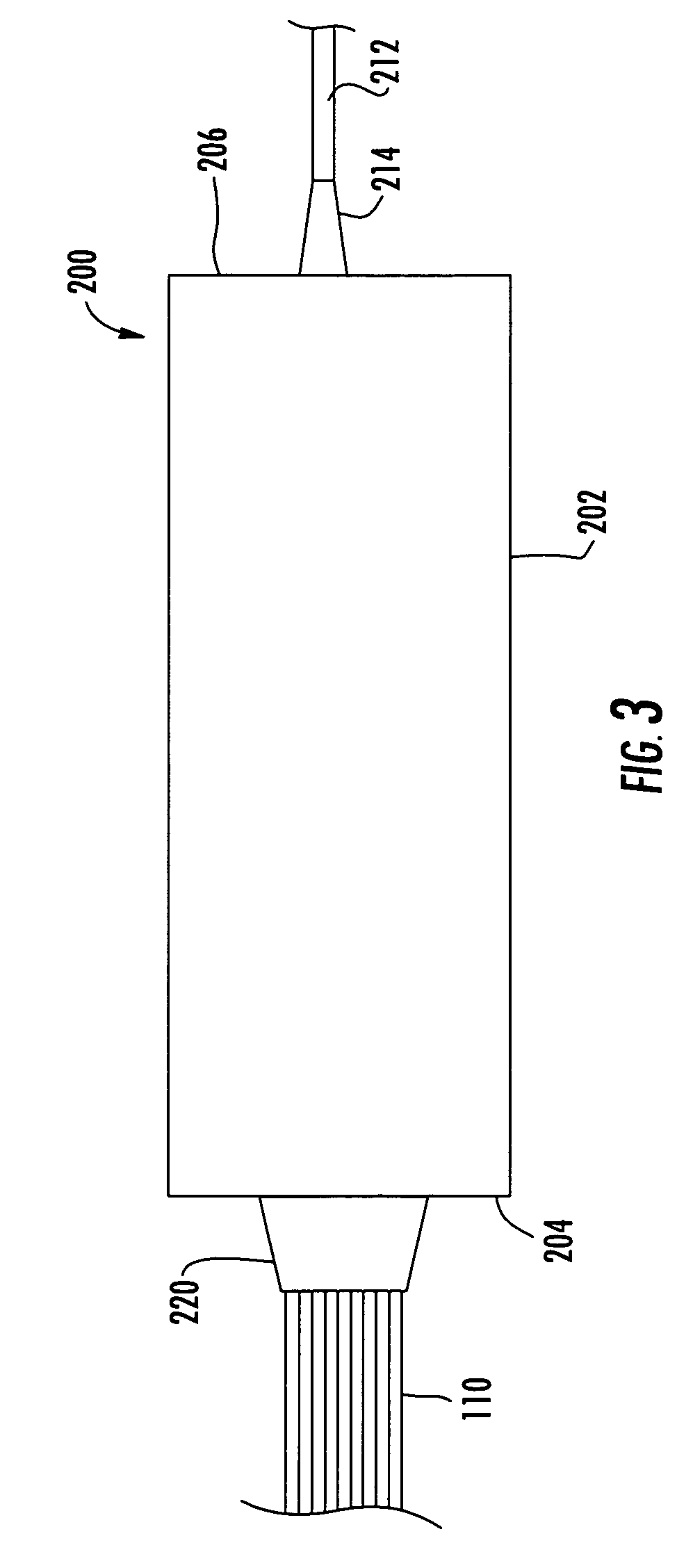
Optical fiber splitter module and fiber optic array therefor
An optical fiber splitter has a higher density fiber optic array that allows for smaller packaging. The optical fibers that extend from the optical fiber splitter have one end connectorized and their spacin at the other end reduced, thereby eliminating components that were heretofore required. A method of making the fiber optic array includes interleaving the optical fibers to reduce the overall dimensions of the fiber optic array and the fiber optic splitter. A tool is used to reduce the spacing of the optical fibers in the fiber optic array.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
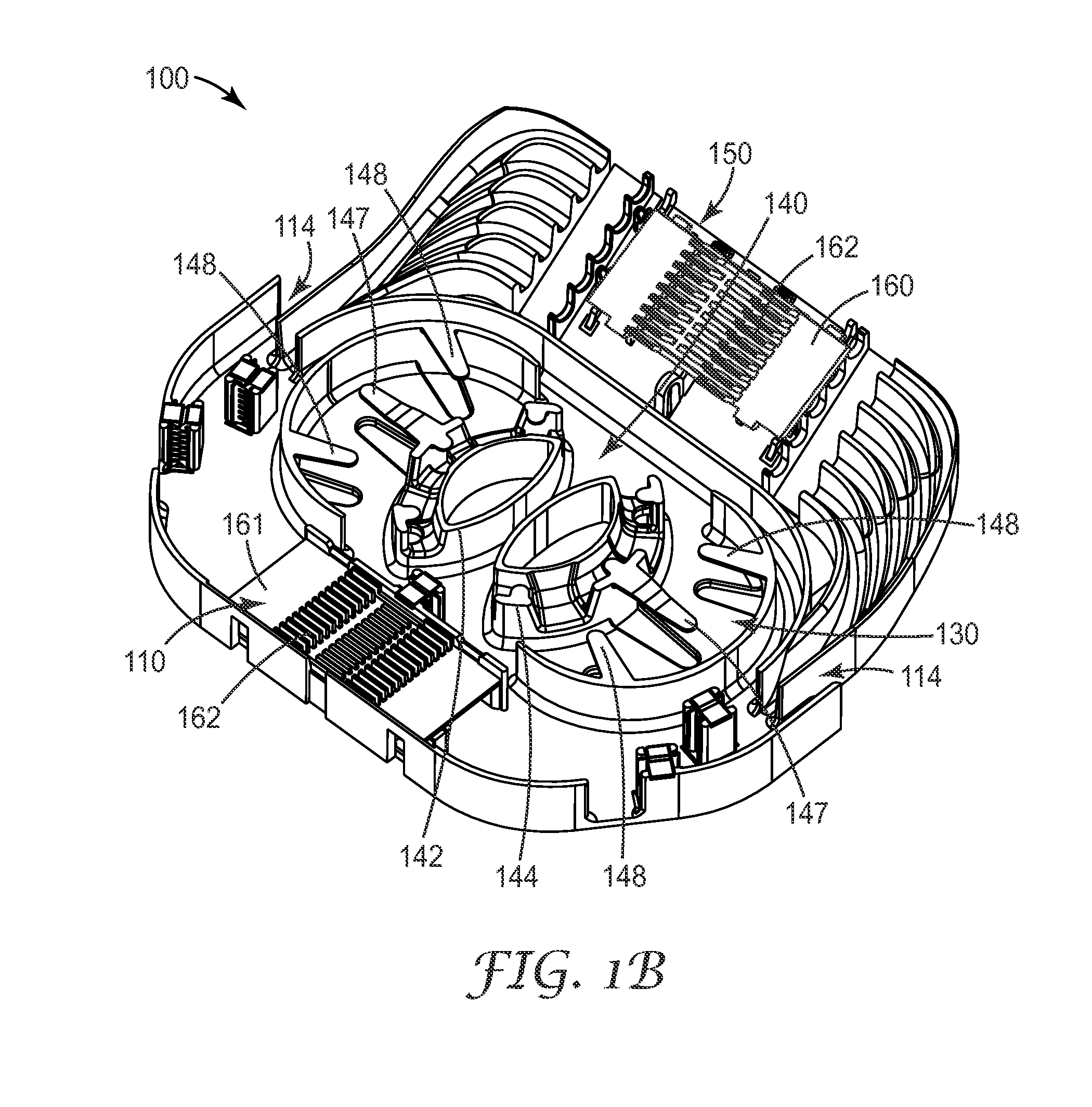
Fiber optic adapter module and tray
A fiber optic adapter module and tray. The fiber optic adapter module supports fiber optic adapters for fiber optic connections. The fiber optic adapter module may be included on an extendible tray portion of a fiber optic equipment tray and selectively configured to be tilted when extended for providing enhanced access to the fiber optic adapter module. In one embodiment, an adapter module panel of the fiber optic adapter module that supports fiber optic adapters contains at least two forward facing panel surfaces angled to one another to provide more surface area for supporting a higher density of fiber optic adapters and / or for neat routing and organizing of fiber optic connections. One or more fourth flared panel surfaces may also be included on an end(s) of the adapter module panel to provide sufficient interior space for fiber optic connections adjacent or proximate to sides of the fiber optic equipment tray.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Novel optical fiber Brillouin light time domain analyzer
InactiveCN101324424AHigh gainAvoid difficultiesThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansBeam splitterFiber gratings
The invention discloses an optical fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer, which is made based on optical fiber broadband nonlinear light amplification effect and strain, temperature effect and optical light domain analysis principle of coherent amplified Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer comprises a narrowband single-frequency fiber laser, a fiber beam splitter, a pulse modulator, two optical fiber circulators, a heterodyne receiver, a digital signal processor, a fiber-grating filter, a monomode fiber and a continuous-operating fiber Raman pump laser. The continuous-operating high-power fiber Raman pump laser is used as the pump light source of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer, which can overcome the difficulty in strictly locking the frequency of a detection laser and the pump laser of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer; and boardband fiber nonlinear scattering amplification is used for substituting for narrowband Brillouin amplification to increase the gain of stimulated Brillouin scattering with back amplification, thus improving the S / N ratio of the system, increasing the measurement length, and improving the accuracy for simultaneous measurement of stain and temperature.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
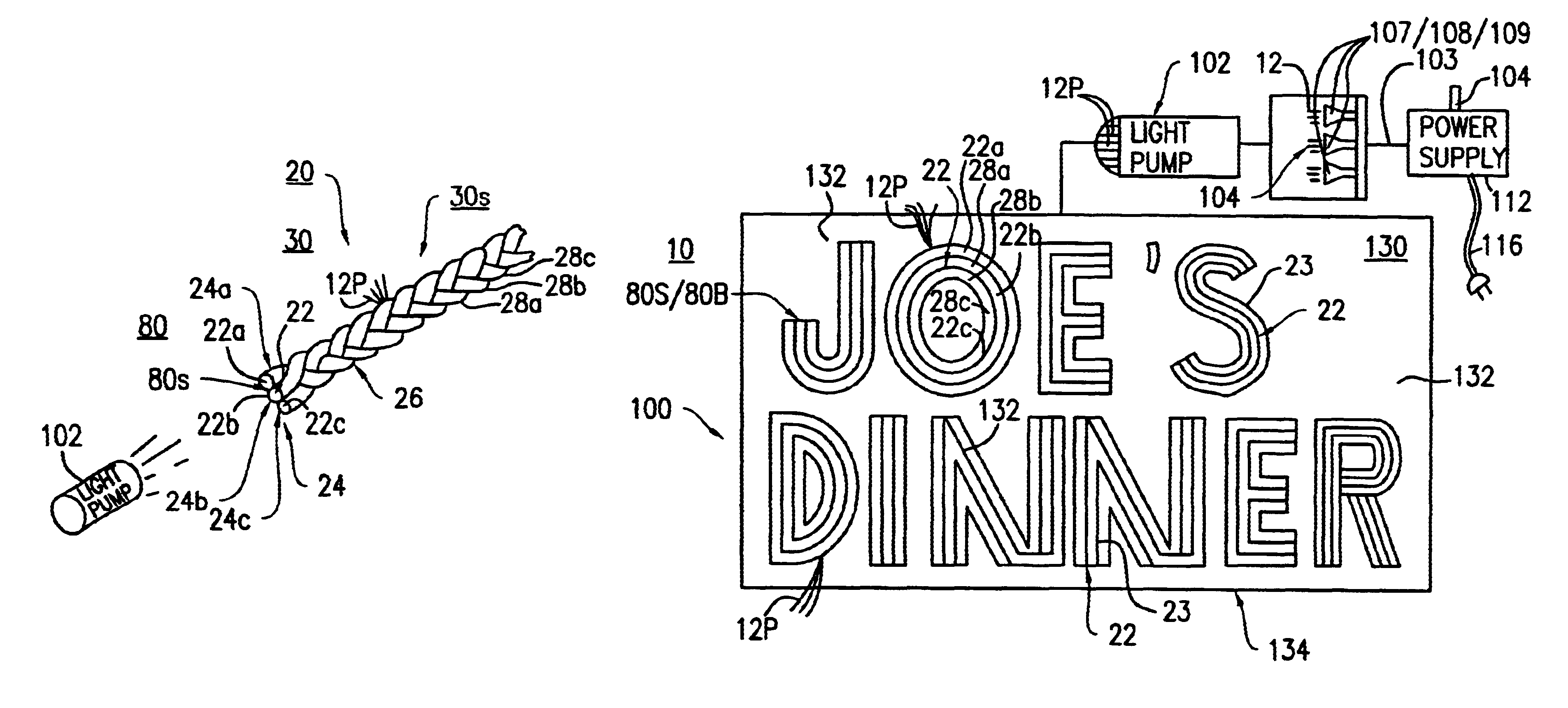
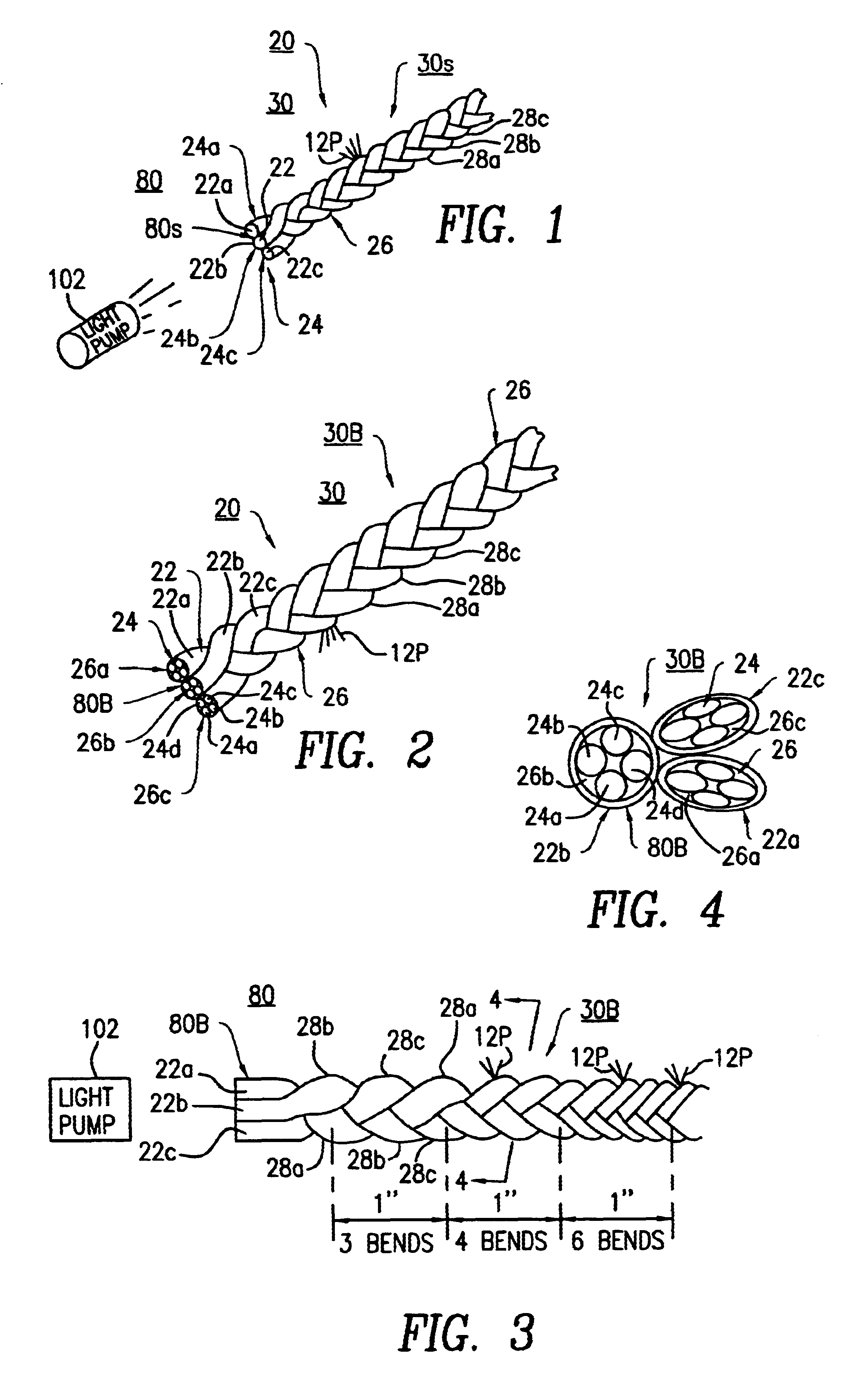
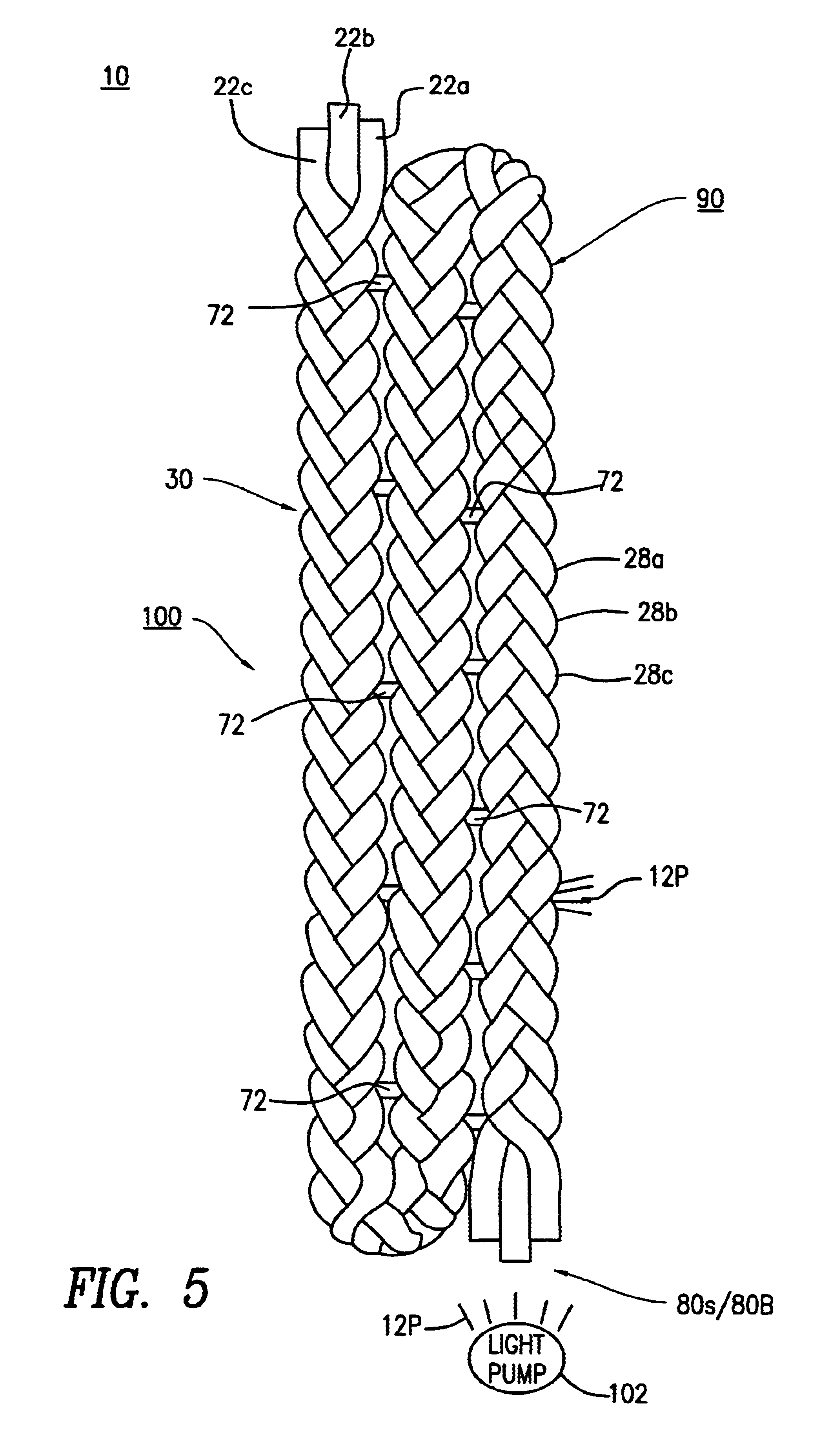
Braided optical fiber bundles
A fiber optic light-emitting panel having one or more braided fiber optic strand assemblies formed into a light-transmitting device. The fiber optic light-emitting panel includes a plurality of three or more fiber optic strands braided together to form a braided fiber optic strand assembly. Each of the fiber optic strands includes a single optical fiber or a plurality of optical fibers to form a bundle. Each of the fiber optic strands within the braided fiber optic strand assembly has at least three (3) bends per inch along the length thereof for transmitting light laterally at the bends to form the light-transmitting device. The fiber optic light-emitting panel includes plastic ties for connecting at least two (2) of the braided fiber optic strand assemblies to form the fiber optic light-emitting panel. The fiber optic light-emitting panel further includes a light pump having a light source for applying an optical light signal to the braided strand assemblies for transmitting light from the bends of the fiber optic light-emitting panel.
Owner:BELFER BRUCE D
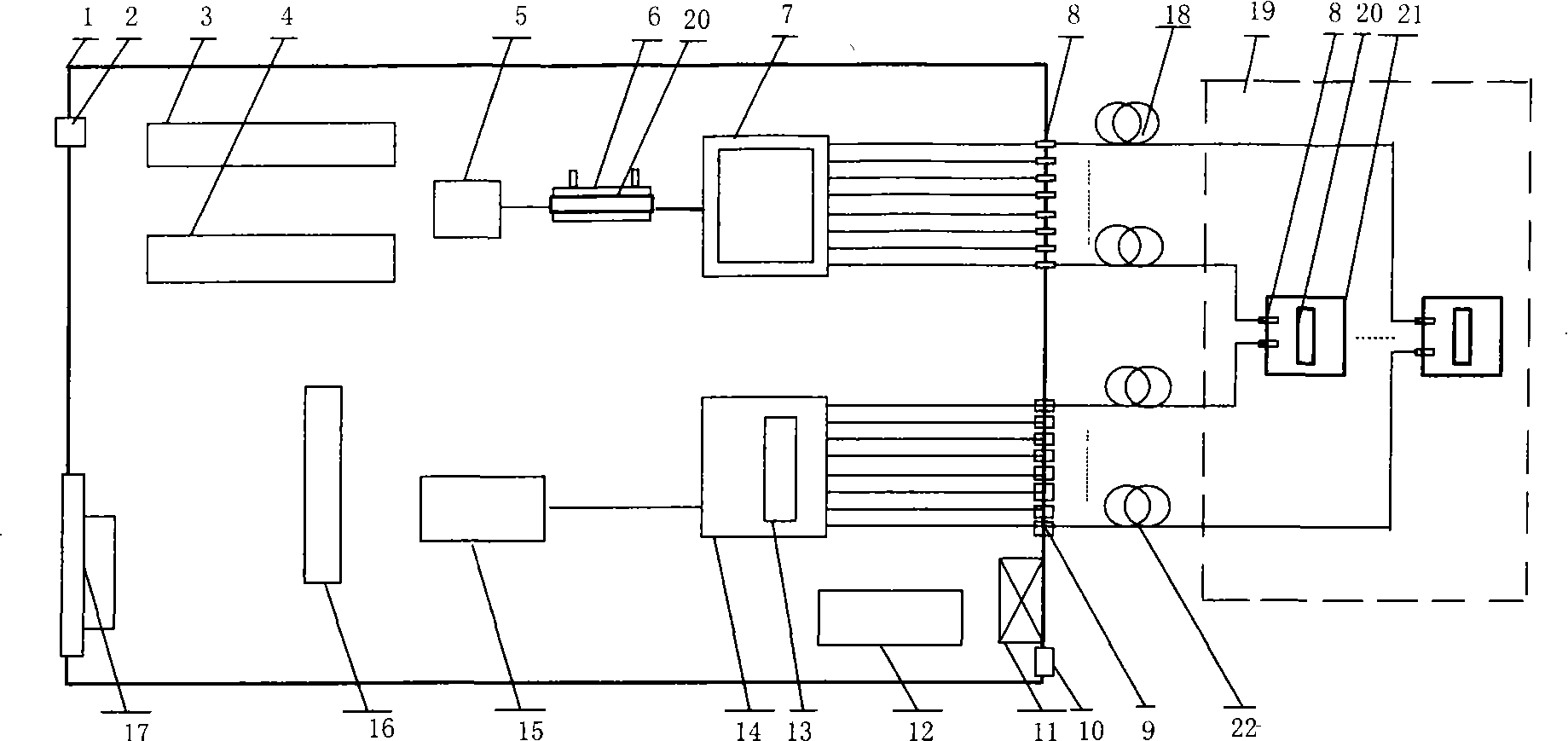
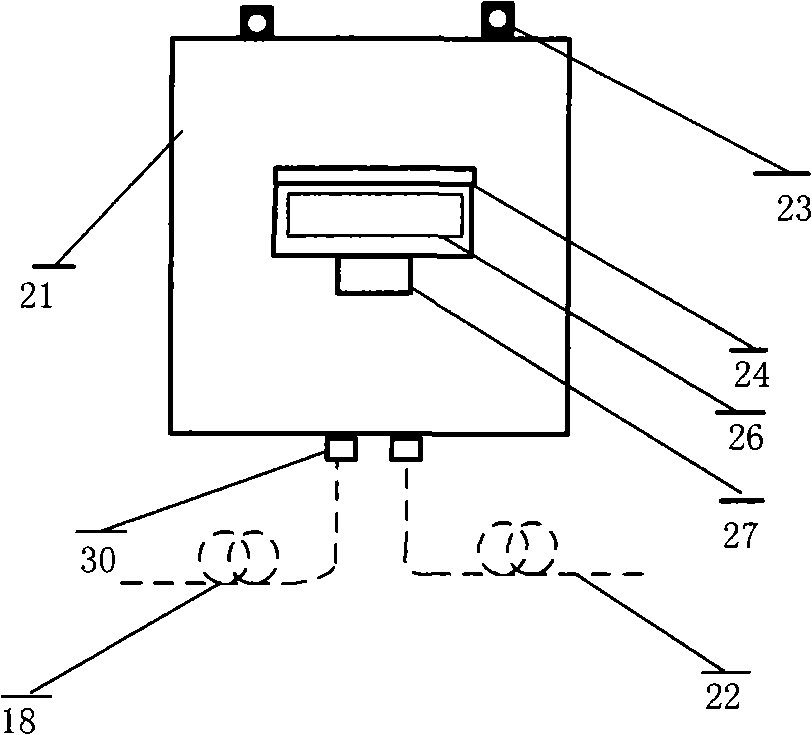
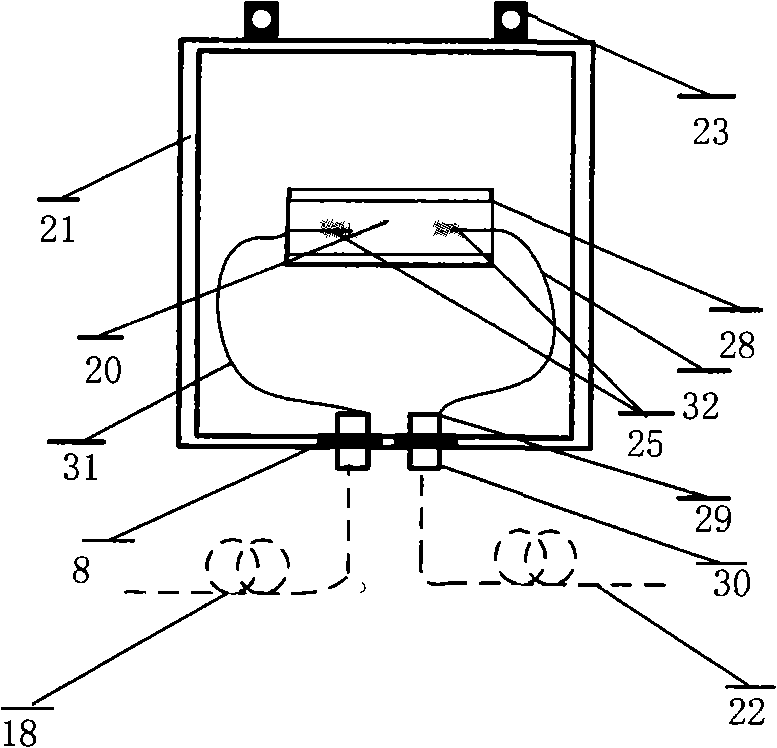
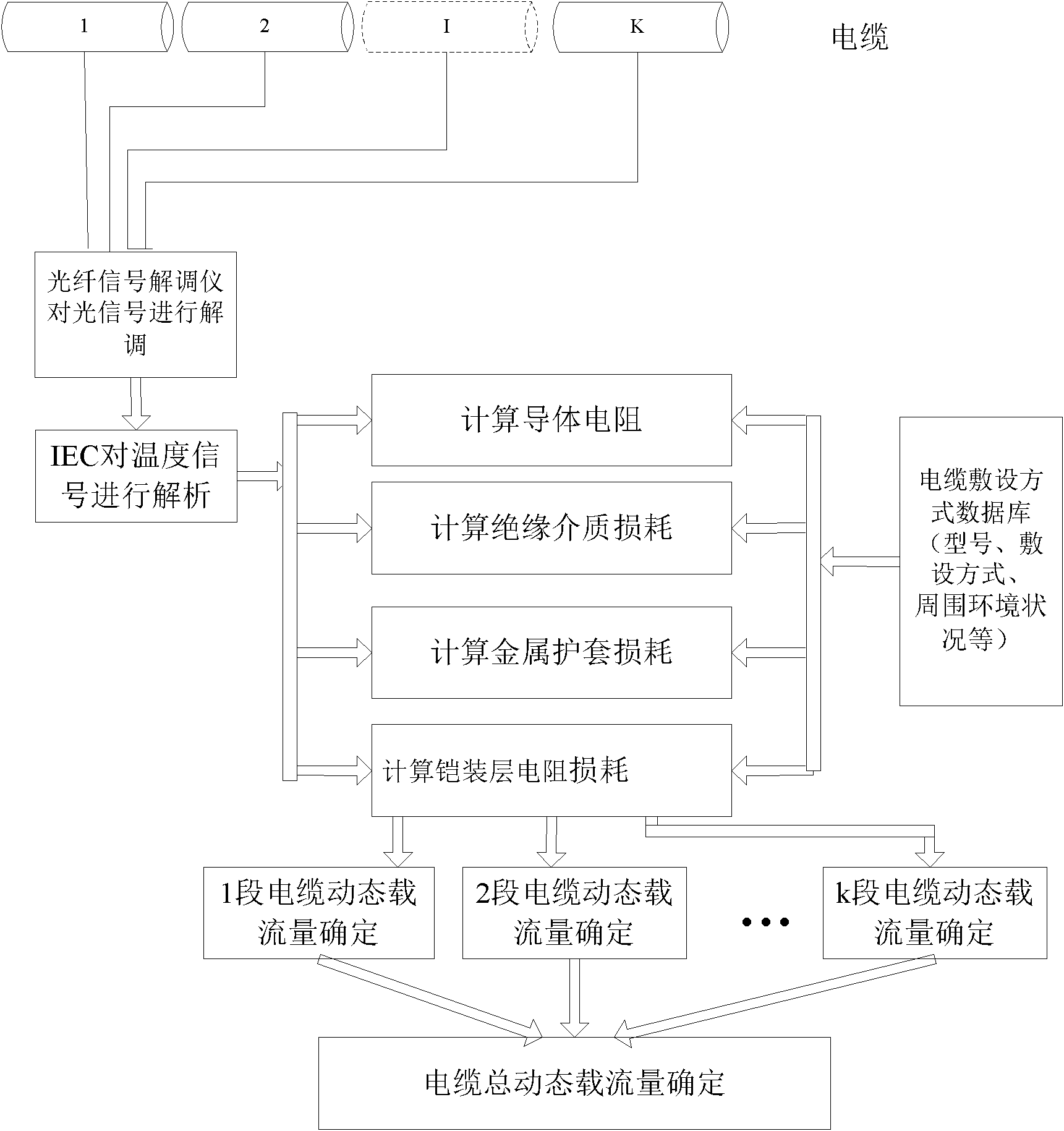
Method and system for monitoring current-carrying capacity of cable based on distributed optical fiber temperature measuring method
InactiveCN102103173AMonitor operating temperatureReduce mistakesThermometers using physical/chemical changesFault locationCarrying capacityEthernet
The invention relates to a method and a system for monitoring current-carrying capacity of a cable based on a distributed optical fiber temperature measuring method. The system comprises a laser drive device which is matched with a temperature sensing device in a cable; the temperature sensing device is matched with the corresponding optical fiber splitter; the output end of each optical fiber splitter is connected with one end of the cable; the other end of the cable is connected with a wire distribution cabinet which is matched with demodulating equipment; and the output end of the demodulating equipment is connected with a cable integrated Ethernet chip (IEC) compute server which is output to a client terminal. Combining the distributed optical fiber temperature measuring method, by the method and system provided by the invention, the important parameters of the cable operation can be acquired; the stimulated accuracy is greatly improved through the comprehensive analysis of the current-carrying capacity, thus providing the decision standard for ensuring the safe operation of the city cables and the reasonable configuration of the transmission capacity.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER
Fiber optic coupler with in-line optical component
InactiveUS20030007739A1Easy to disconnectPromote exchangeCoupling light guidesFiberOptical fiber cable
A coupler for coupling first and second fiber optic cables terminating in first and second connectors having first and second ferrules, respectively. The coupler includes a holder element and a mating element. The holder element defines a channel for receiving the first ferrule and a socket aligned with the channel for receiving an optical component The holder element further defines a first cable connector adapted for connection to the first connector and a first element connector opposite said first cable connector. The mating element defines a channel for receiving the second ferrule, a second cable connector adapted for connection to the second connector and a second element connector opposite the second cable connector. Accordingly, the holder element and mating element are connectable to house an optical component aligned with the channels and positionable substantially contiguous with the first and second ferrules when attached thereto.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Fiber organizer and distribution box
An organizer (100) for fiber cable management comprises a generally planar base (105) having a splitter holding section (110), a slack and unterminated fiber storage section (120), and a splice and splice tray holding section (150). The splitter holding section (110) is configured to optionally hold one or more fiber splitters. The slack and unterminated fiber storage section includes a slack storage region (130) having a plurality of fiber routing structures (146a, 146b) to support and retain slack fiber and an unterminated fiber storage region having one or more spool type structures (142) to support and retain unterminated fiber separate from the slack fiber. The splice and splice tray holding section is configured to optionally hold one of a first fiber splice insert (160) and a splice tray holder (170) configured to engage one or more splice trays. A distribution box (200) for distributing optical fibers for communications includes a base, a cover, and the organizer described above.
Owner:CORNING RES & DEV CORP
Fiber mine water inrush precursor information monitor
InactiveCN101696639AAchieve separationRealize quasi-distributed real-time monitoringMining devicesThermometers using physical/chemical changesSensor arrayReal time analysis
The invention provides a fiber mine water inrush precursor information monitor comprising a sensor array, a fiber splitter, a fiber grating demodulation device and a computer. The sensor array comprises a fiber temperature sensor, a fiber strain sensor, a fiber displacement sensor and a fiber osmotic pressure sensor which are all fiber grating sensors, and temperature, strain, displacement, osmotic pressure, and other physical quantities collected by the fiber grating sensors are sent to the fiber grating demodulation device by the fiber splitter through optical fibers; and the fiber grating demodulation device converts collected light wavelength signals into electric signals and finally sends the electric signals to the computer, and the computer analyzes and monitors on-site information by a software system in real time.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
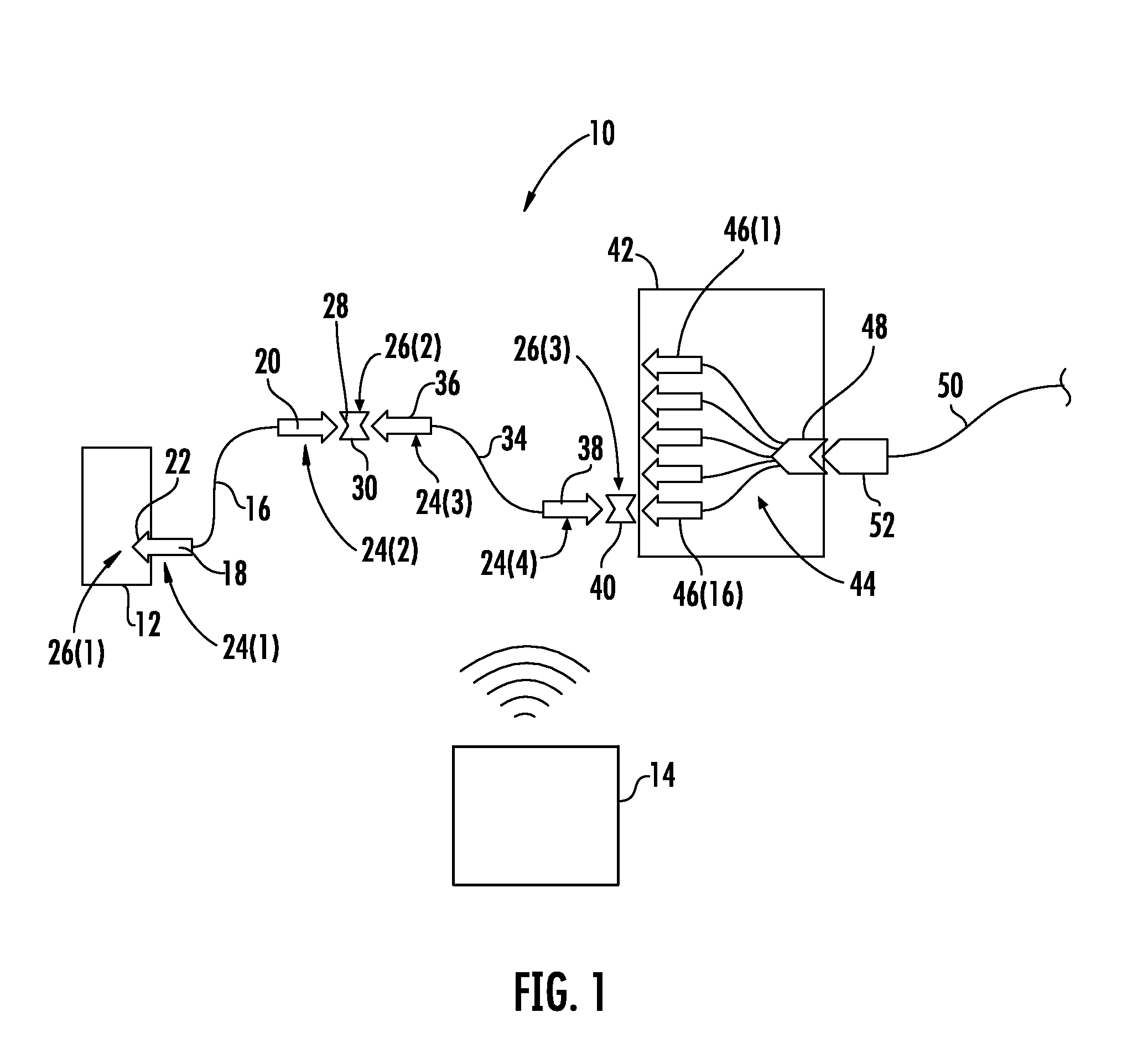
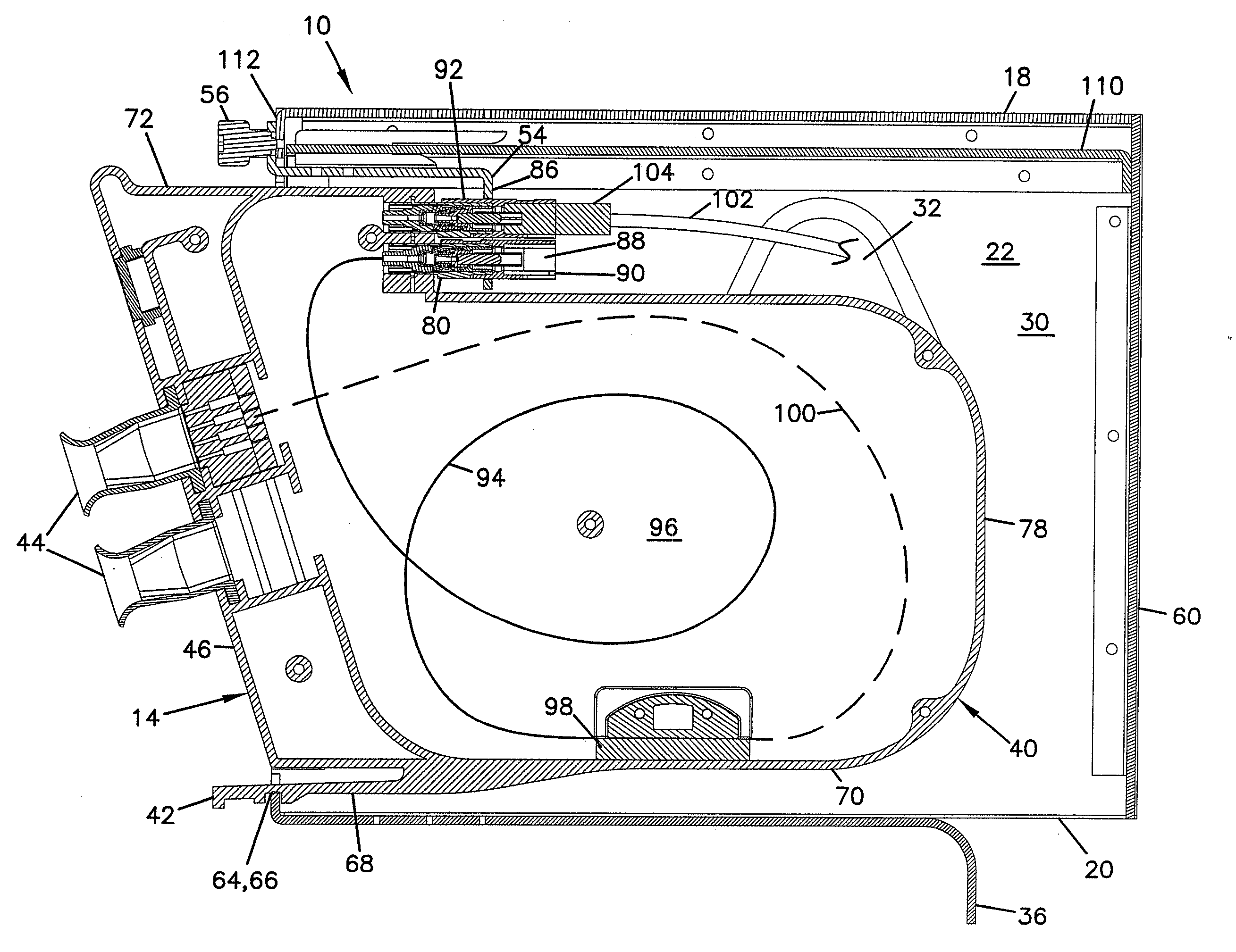
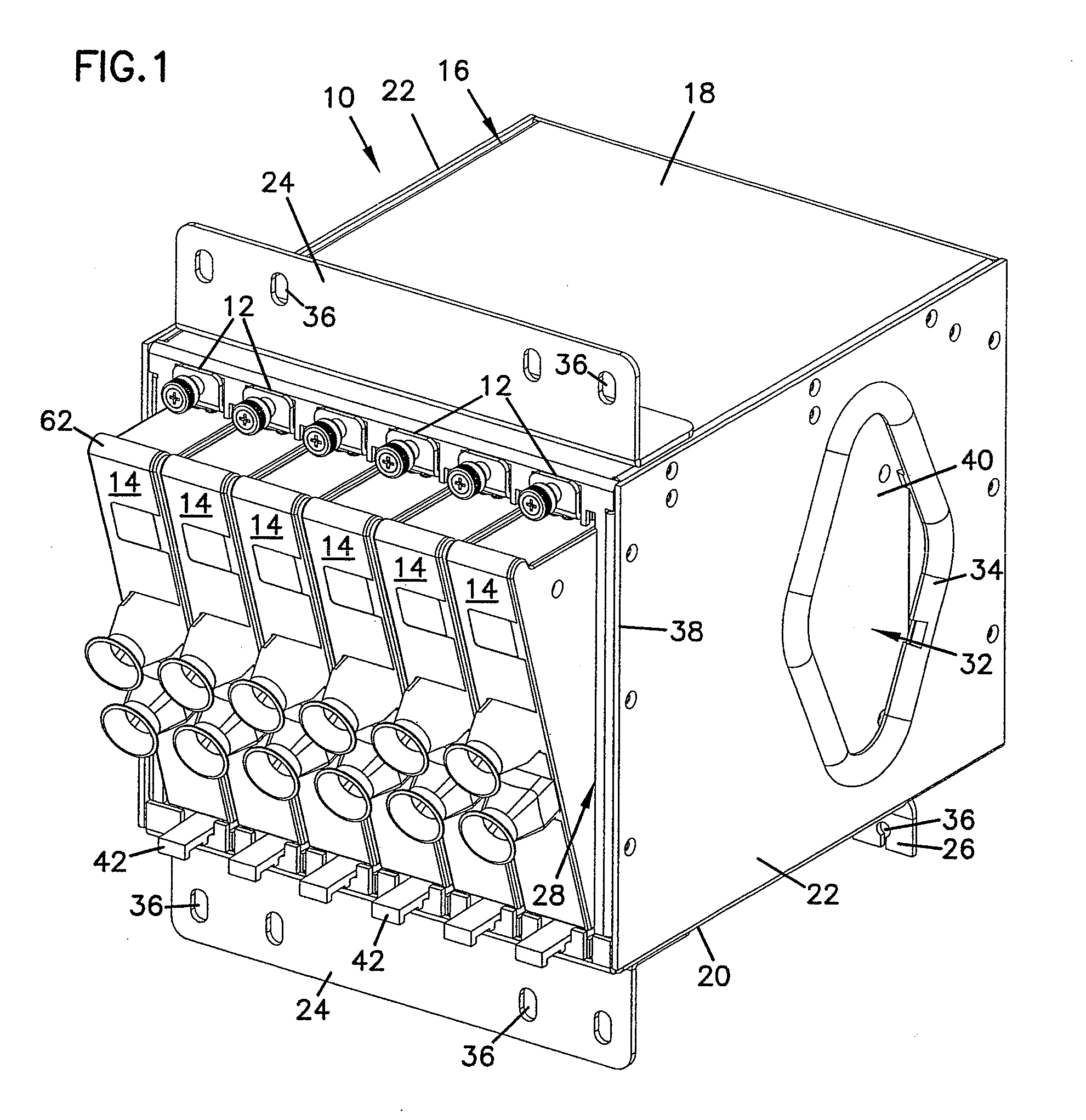
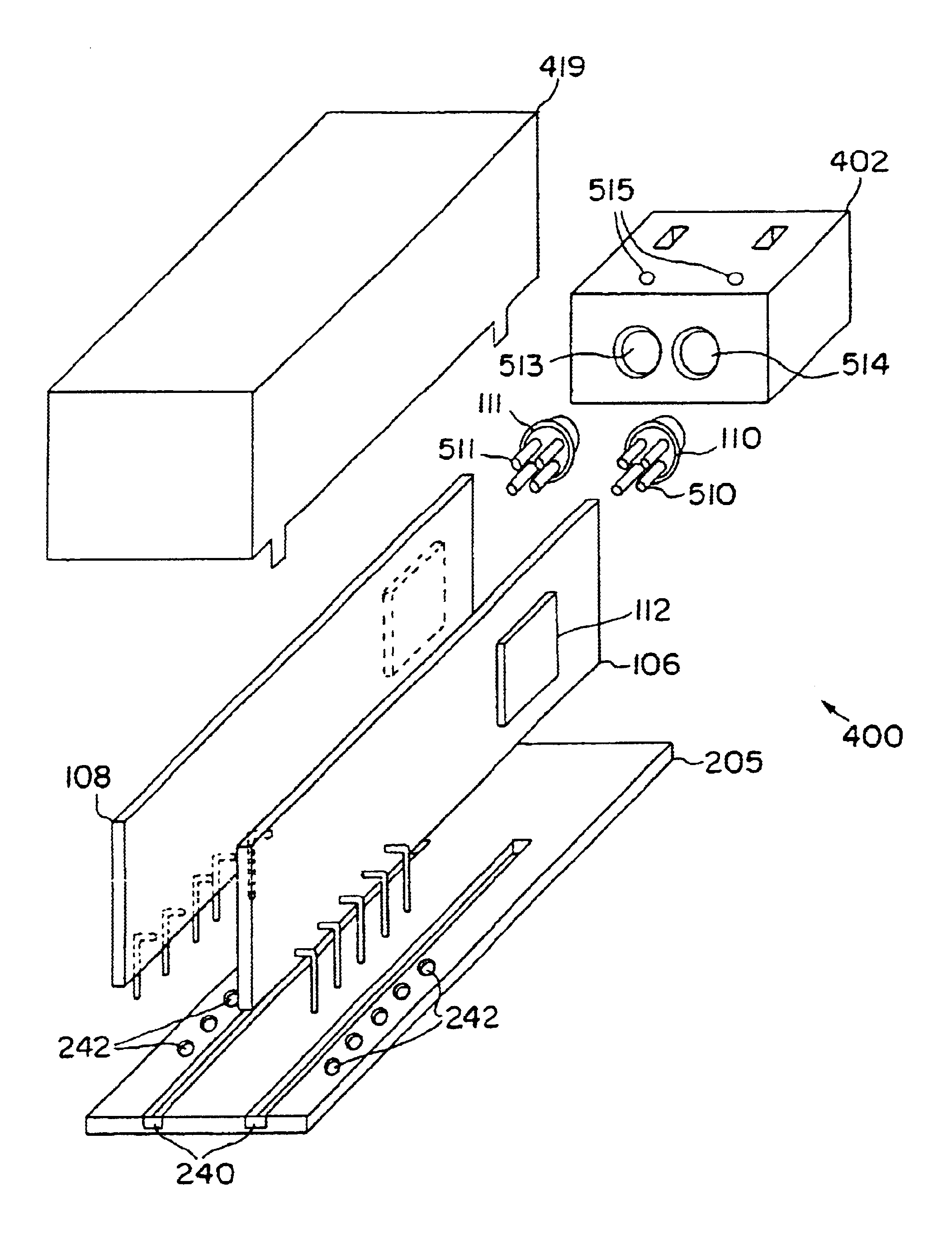
Fiber optic splitter module
A telecommunications assembly including a housing and a plurality of modules mounted within the housing. The modules includes a rear face in which is mounted at least one fiber optic connector. Within an interior of the housing are positioned at least one fiber optic adapters. Inserting the module through a front opening of the housing at a mounting location positions the connector of the module for insertion into and mating with the adapter of the housing. The adapters within the interior of the housing are integrally formed as part of a removable adapter assembly. A method of mounting a telecommunications module within a chassis.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
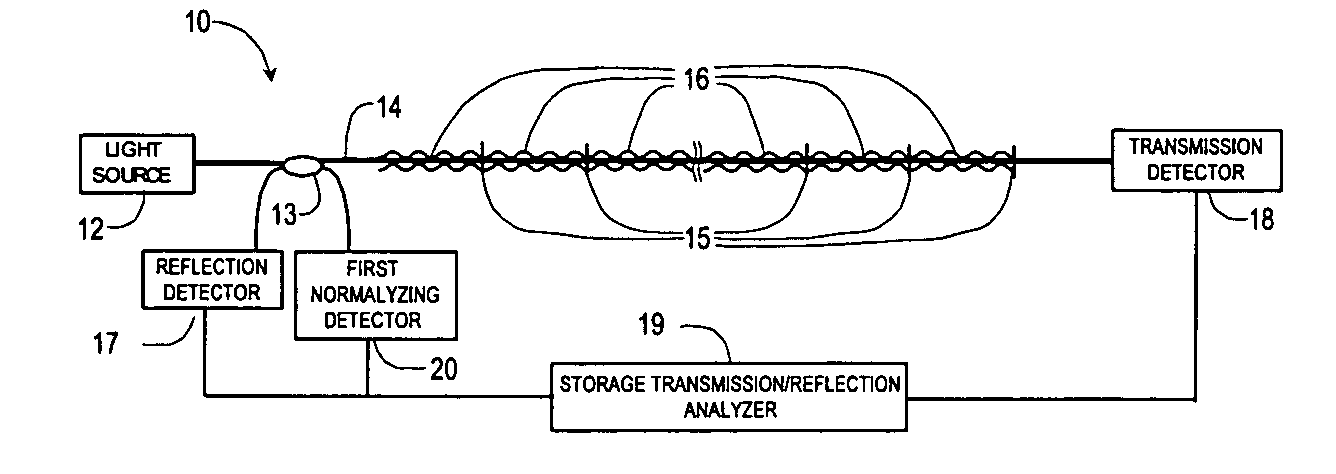
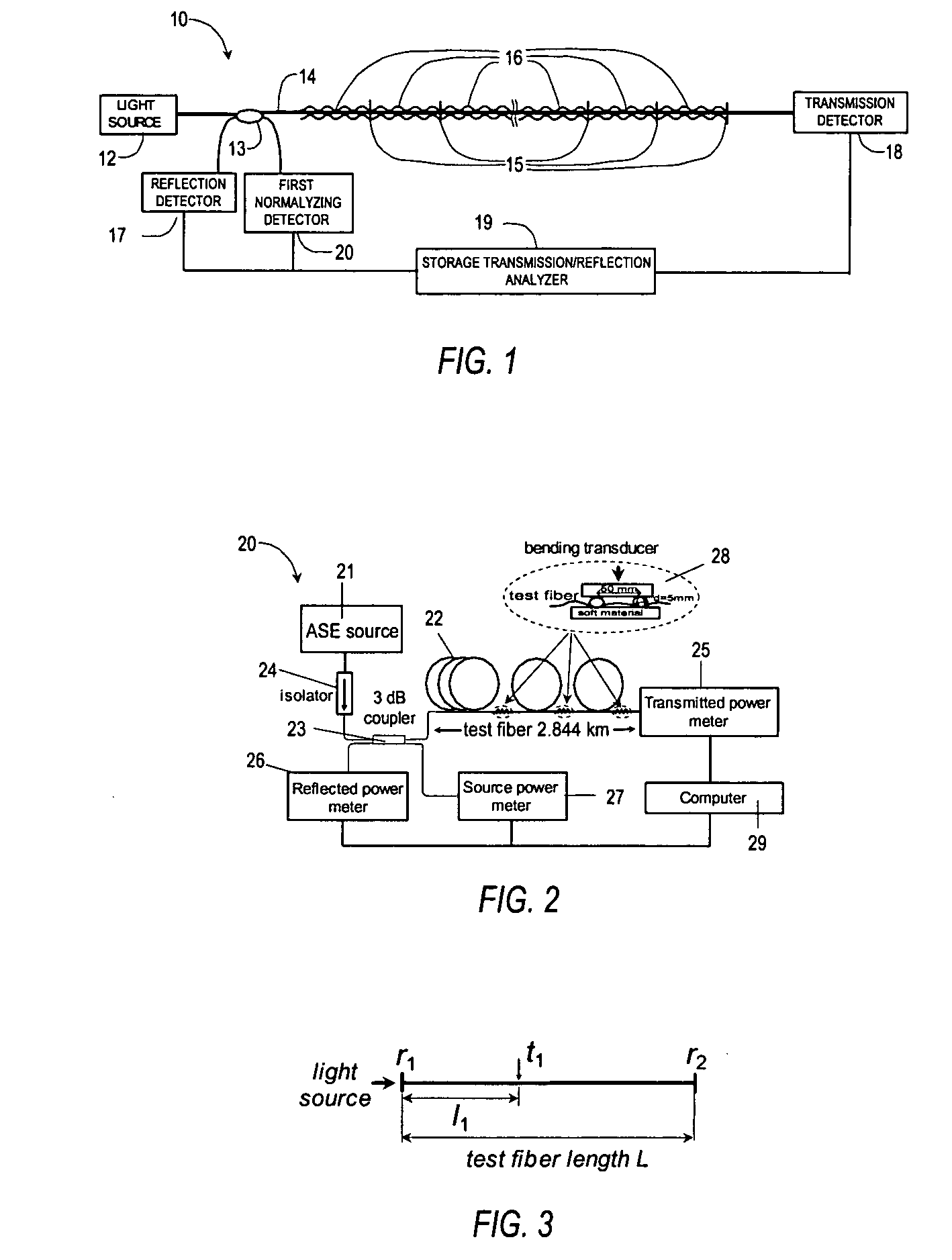
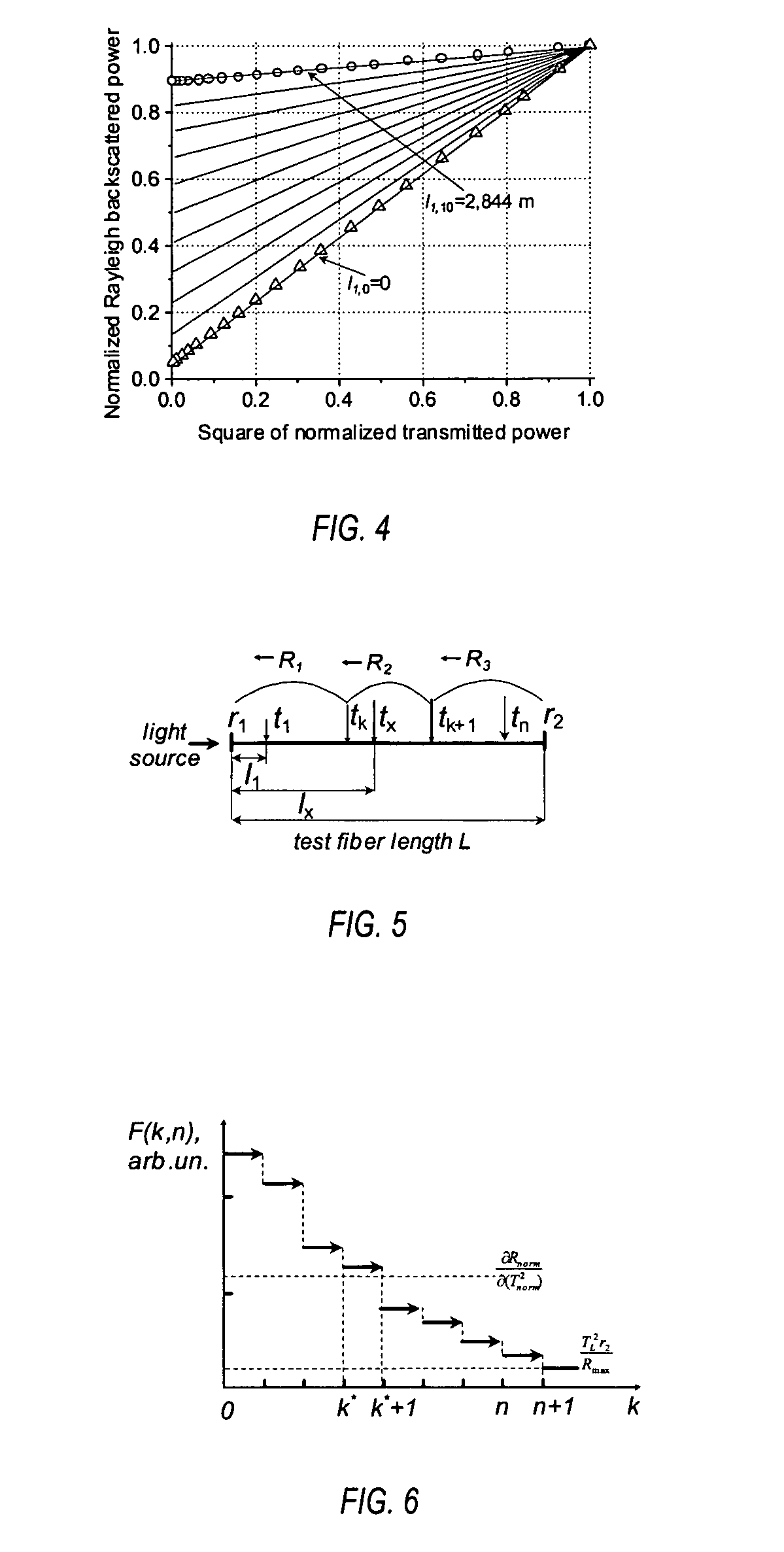
Alarm condition distributed fiber optic sensor with storage transmission-reflection analyzer
InactiveUS20040240769A1Detection of fluid at leakage pointForce measurement by measuring optical property variationOptical reflectionMeasurement test
This invention pertains to alarm condition fiber optic sensor with storage transmission-reflection analyzer for detection and localization of any number of consecutive loss-inducing disturbances along the test fiber. The sensor includes a test fiber having a first port and a second port; a light source for producing a beam of light propagating along the test fiber; a fiber optic beamsplitter having a first port connected to the light source, a second port connected to the first port of the test fiber, and a third and a fourth port; a plurality of reflectors positioned along the test fiber and a plurality of loss-inducing members positioned along the test fiber, wherein said each of the reflectors is matched to each loss-inducing members, wherein at least one reflector is placed between each consecutive loss-inducing members; an optical reflection detector to receive a light flux, the optical reflection detector connected to the third port of optic beamsplitter, wherein the reflection detector is adapted to sense changes in the average power of the light reflected from the reflectors; an optical transmission detector adapted to receive the light flux, connected to the second port of test fiber, said transmission detector being operable to sense changes in the average power of the light transmitted through the test fiber; and a storage transmission-reflection analyzer connected to reflection and transmission detectors, and adapted to measure time-behavior of the transmission-reflection dependencies of test fiber, said analyzer being operable to identify the locations and values of any number of consecutive loss-inducing disturbances along the test fiber by using stored locations and values of previous perturbations and the slope of dependence of normalized reflected average power versus the square of normalized transmitted average power for current loss-inducing perturbation.
Owner:CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION CIENTIFICA Y DE EDUCACION SUPERIOR DE ENSENADA +1
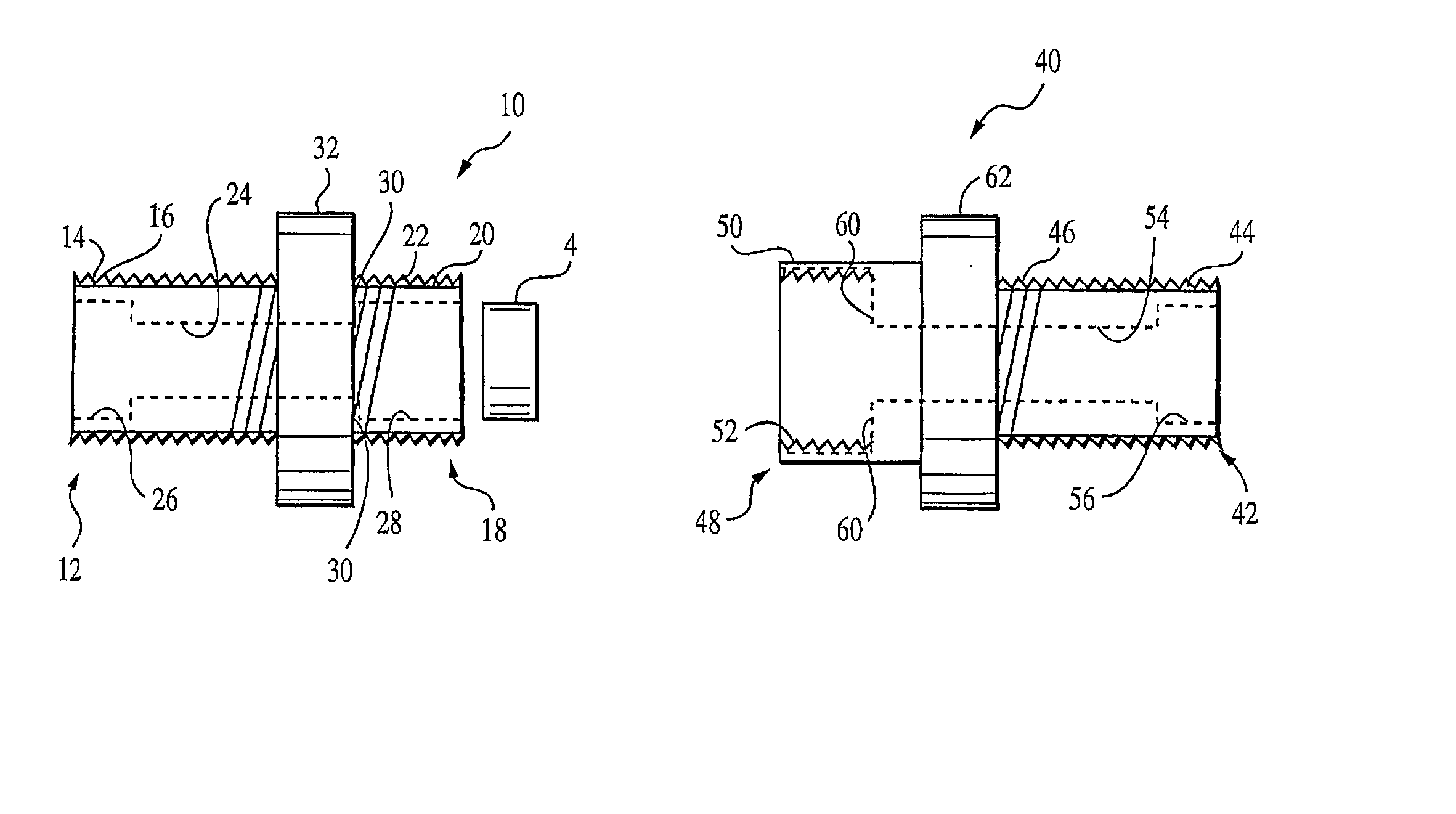
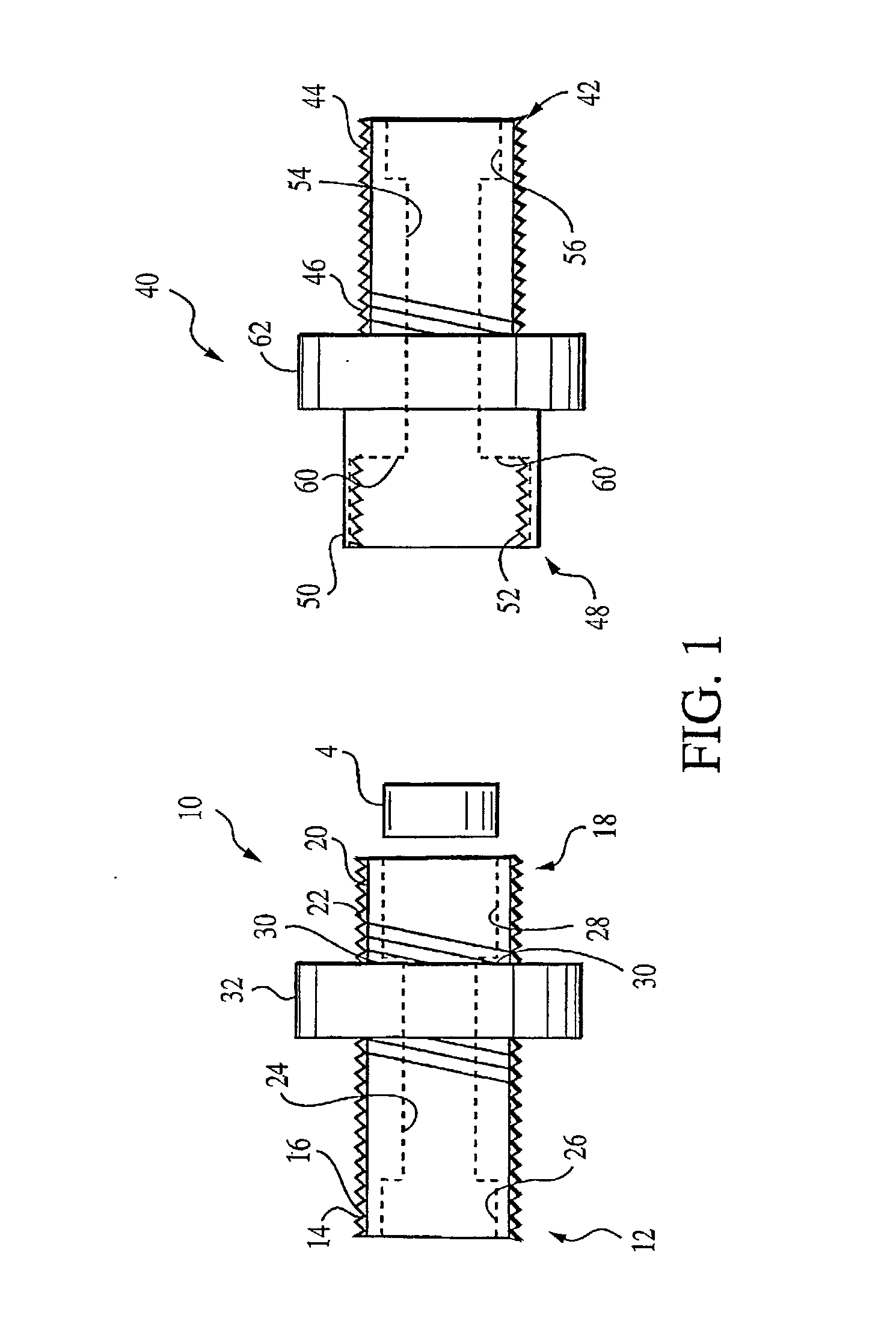
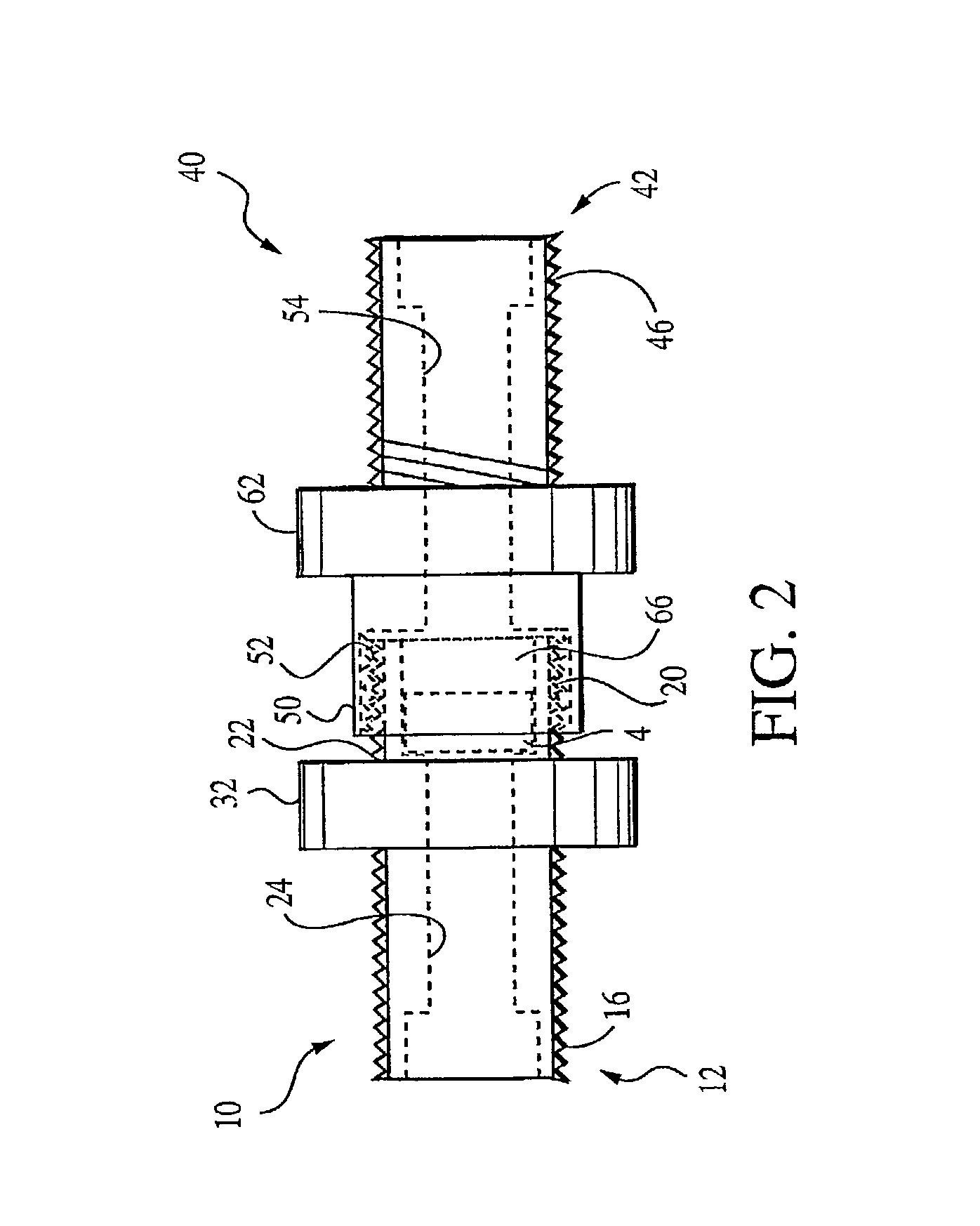
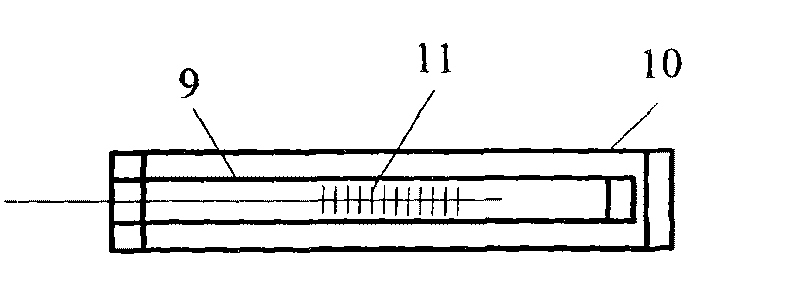
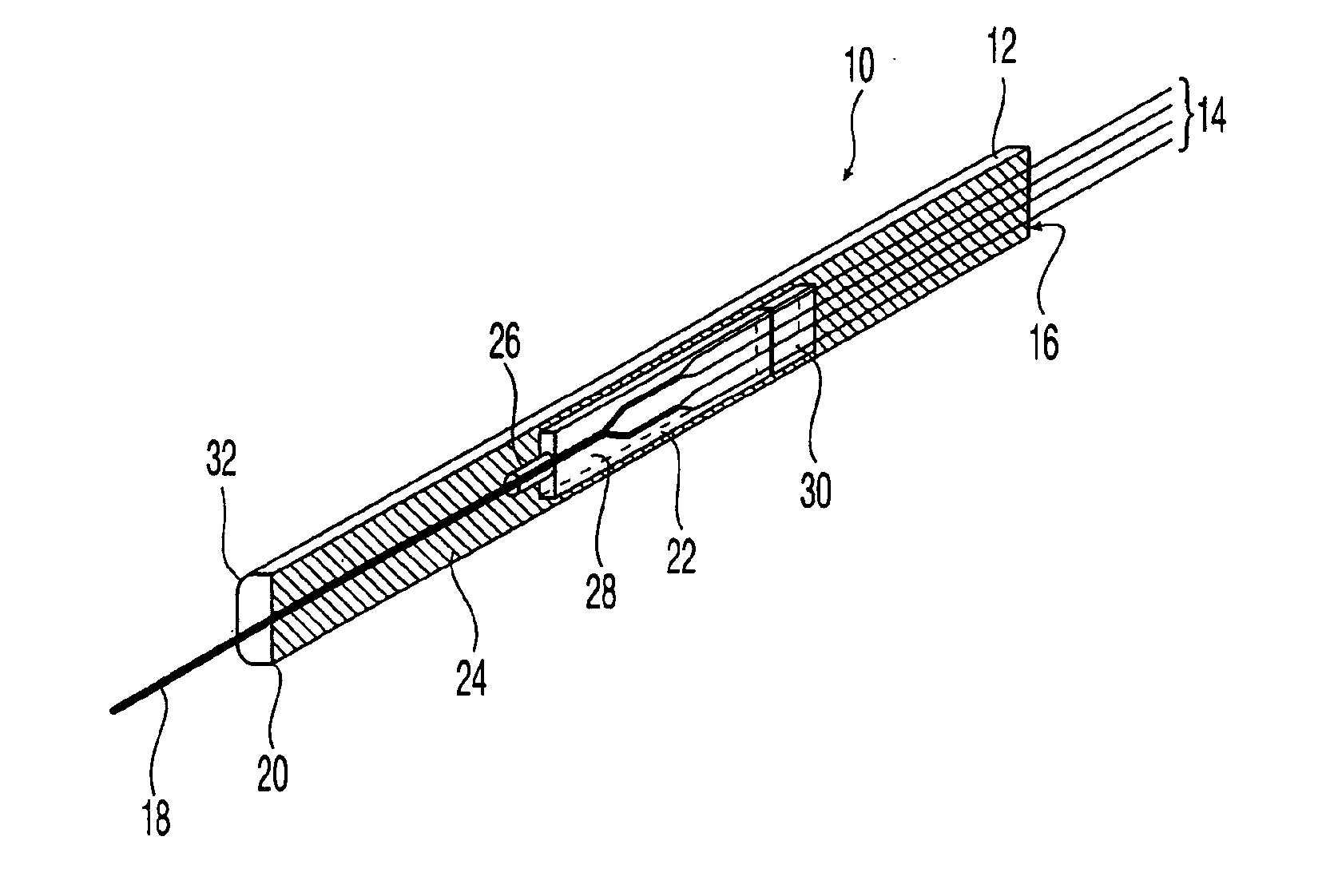
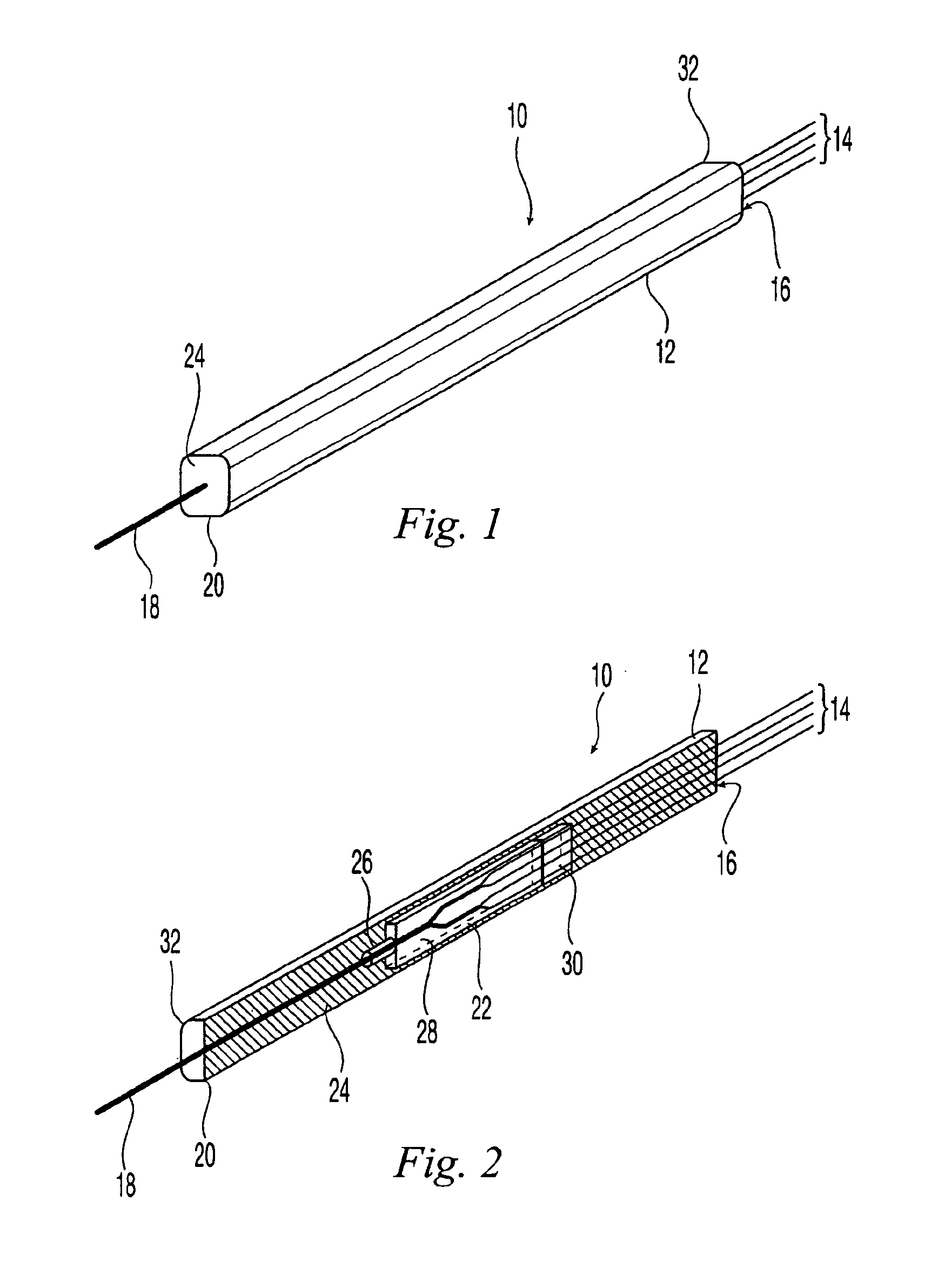
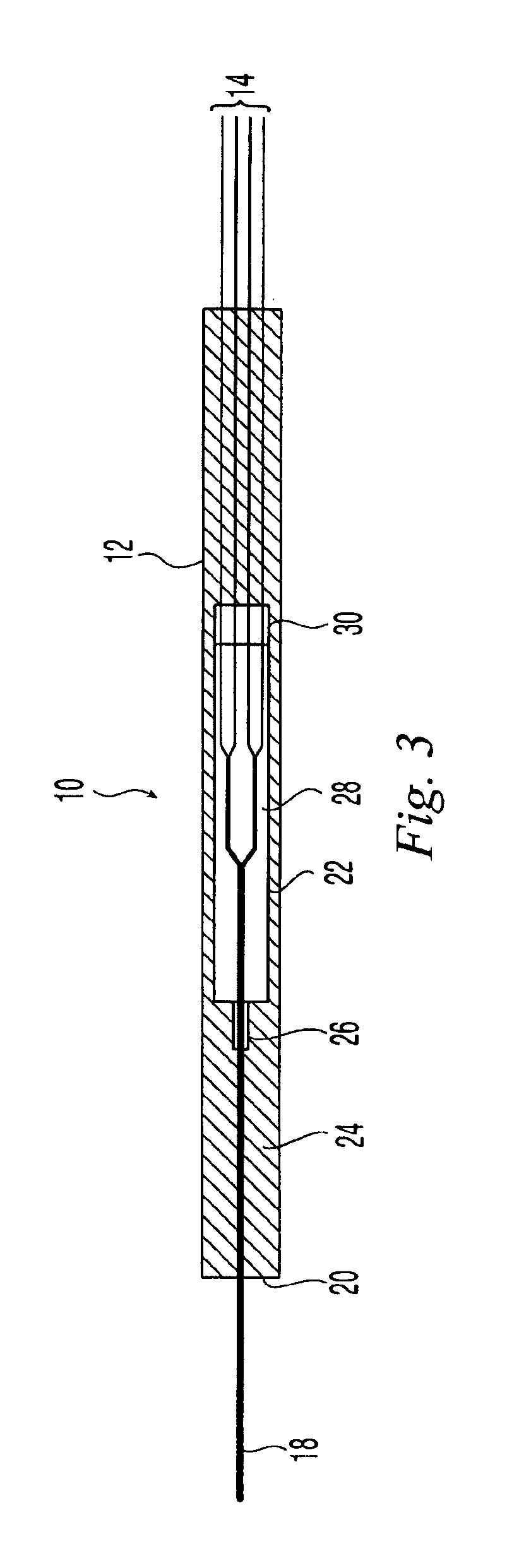
Fiber optic splitter package and method of manufacture
A fiber optic splitter package and method are provided for protecting a fiber optic splitter assembly while preventing adverse affects from temperature cycling. The fiber optic splitter package includes a housing, a fiber optic splitter assembly, and a flexible retainer member that holds the fiber optic splitter assembly in the housing. The flexible retainer member has a modulus of about 30 to about 80 on a Shore A hardness scale, thereby insulating the fiber optic splitter assembly from stress due to differences in the coefficients of thermal expansion of the housing and the fiber optic splitter assembly.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Method and apparatus for vertical board construction of fiber optic transmitters, receivers and transceivers
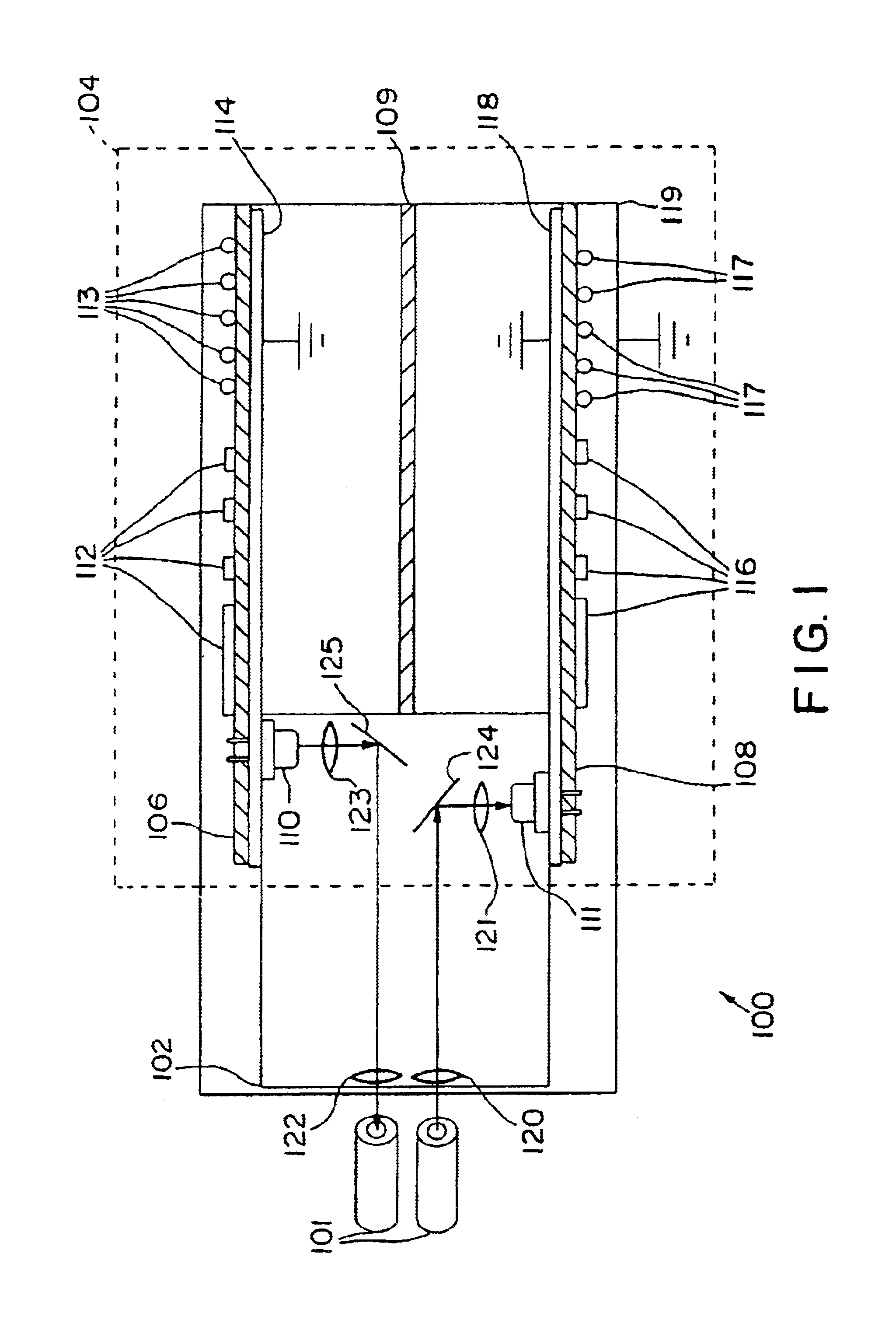
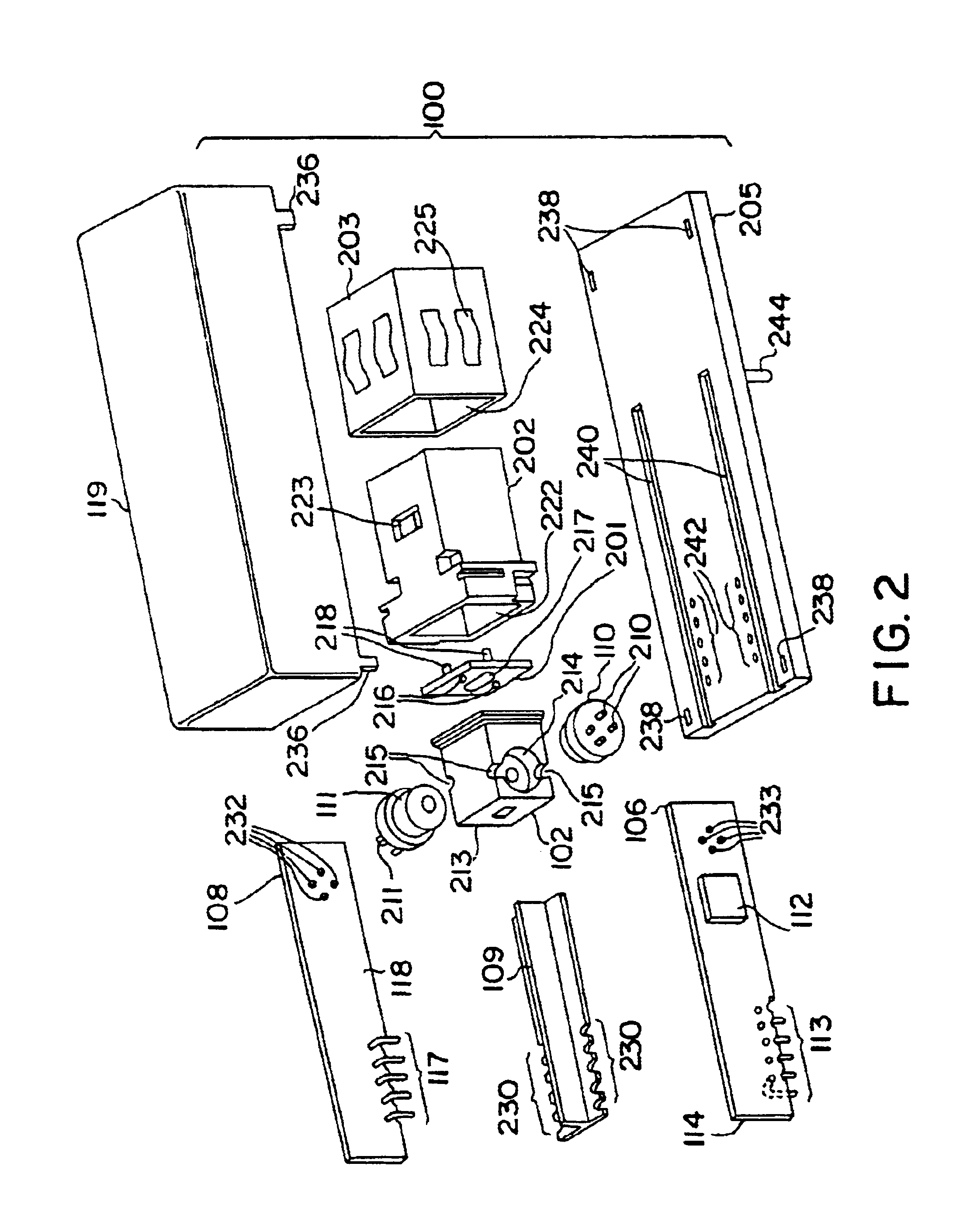
InactiveUS6840686B2Reduced footprintReduce manufacturing costLaser detailsCoupling light guidesFiberTransceiver
Fiber optic transmitter and receiver electrical elements are implemented on separate vertical boards in fiber optic modules. A single optical block implements lenses and reflecting surfaces to minimize manufacturing costs. In one embodiment the receiver and transmitter are mounted to receive and transmit vertical boards respectively to nearly face each other but being offset to avoid optical cross talk. In a second embodiment, receiver and transmitter are mounted parallel with the printed circuit boards to save additional space. The vertical boards have ground planes to minimize electrical cross talk. A shielded housing provides further shielding for EMI. Manufacturing steps of the fiber optic transceiver are disclosed which provide reduced manufacturing costs.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com