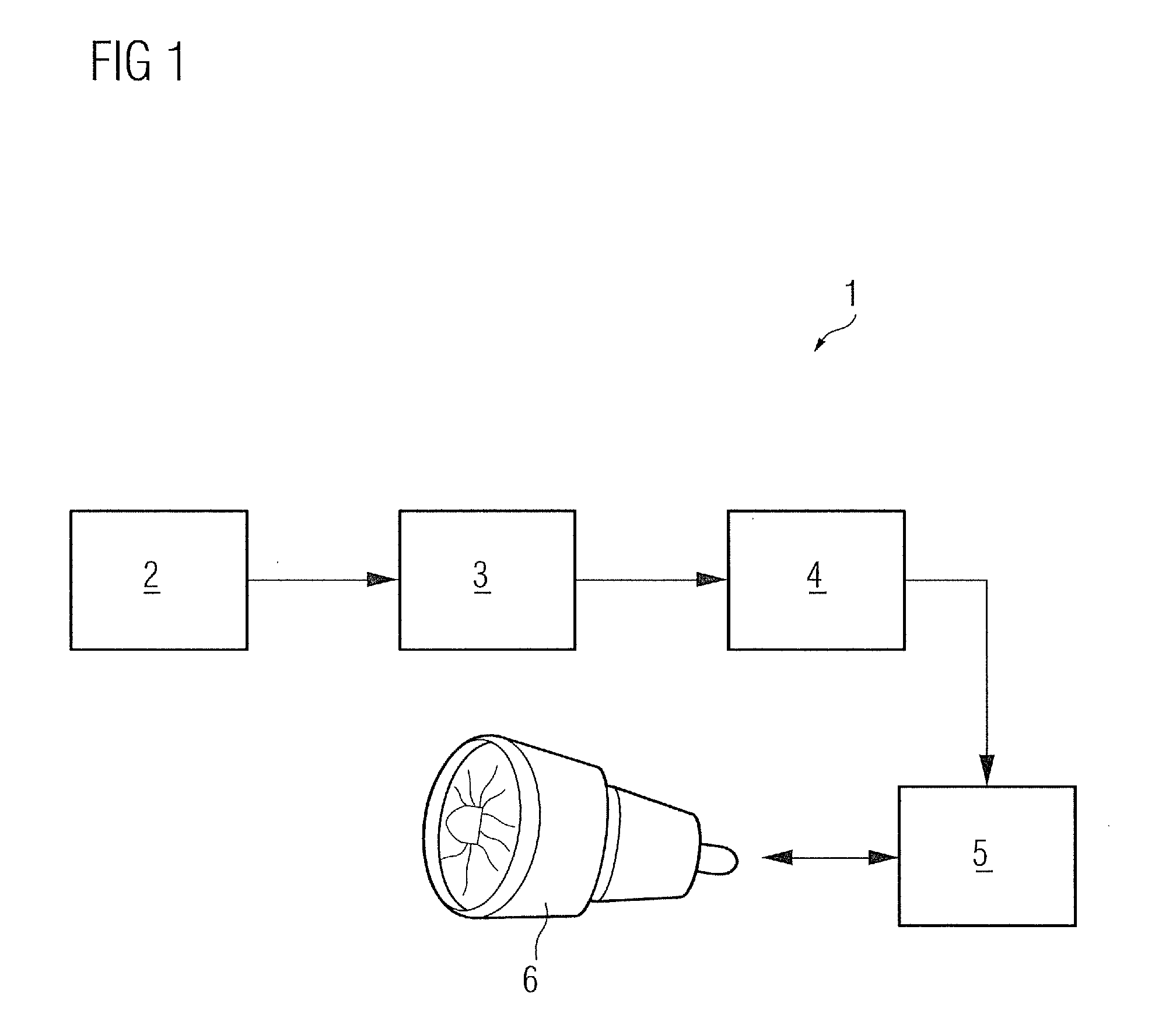
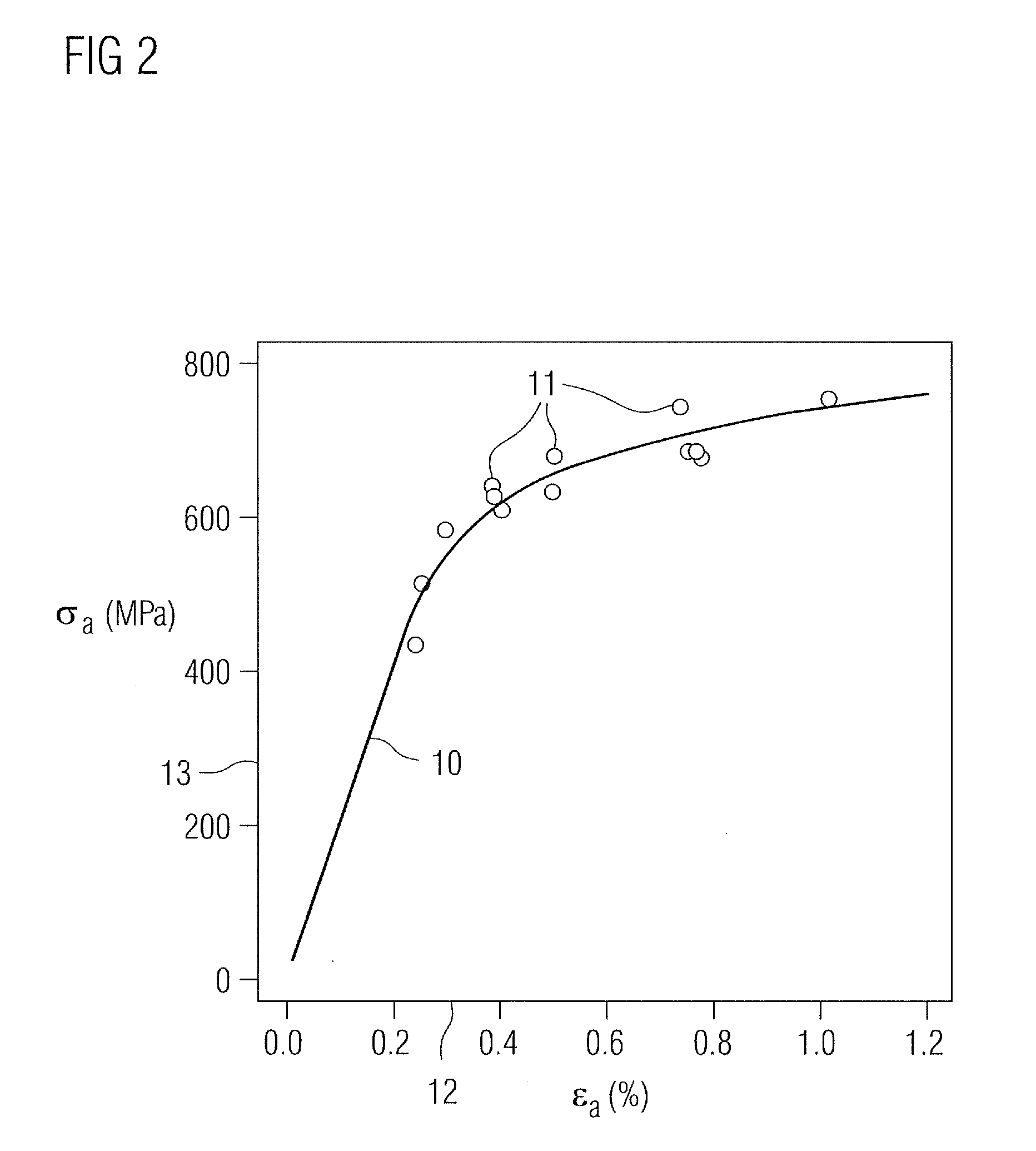
Patents
Literature
350 results about "Low-cycle fatigue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low cycle fatigue has two fundamental characteristics: plastic deformation in each cycle; and low cycle phenomenon, in which the materials have finite endurance for this type of load. The term cycle refers to repeated applications of stress that lead to eventual fatigue and failure; low-cycle pertains to a long period between applications.
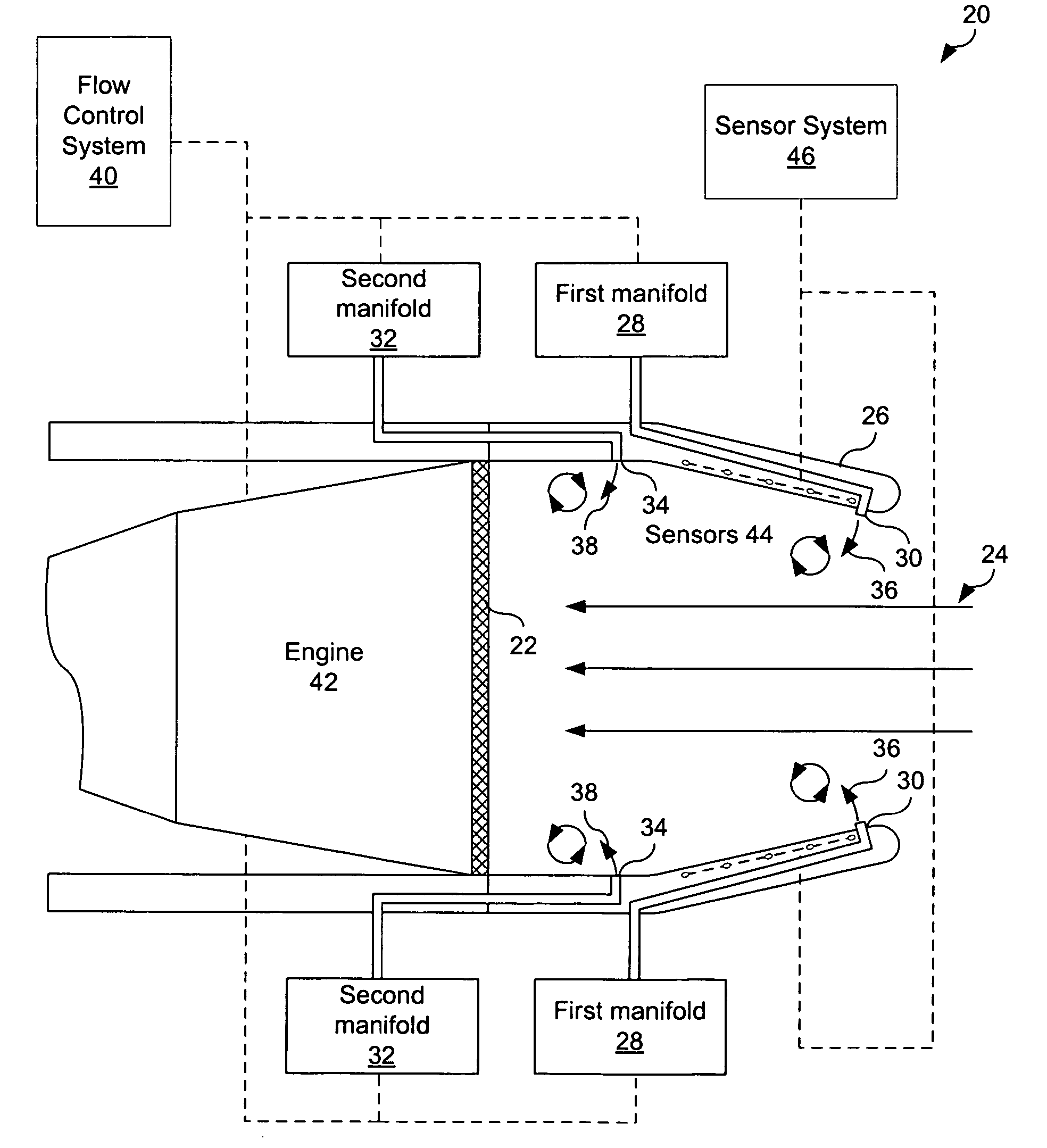
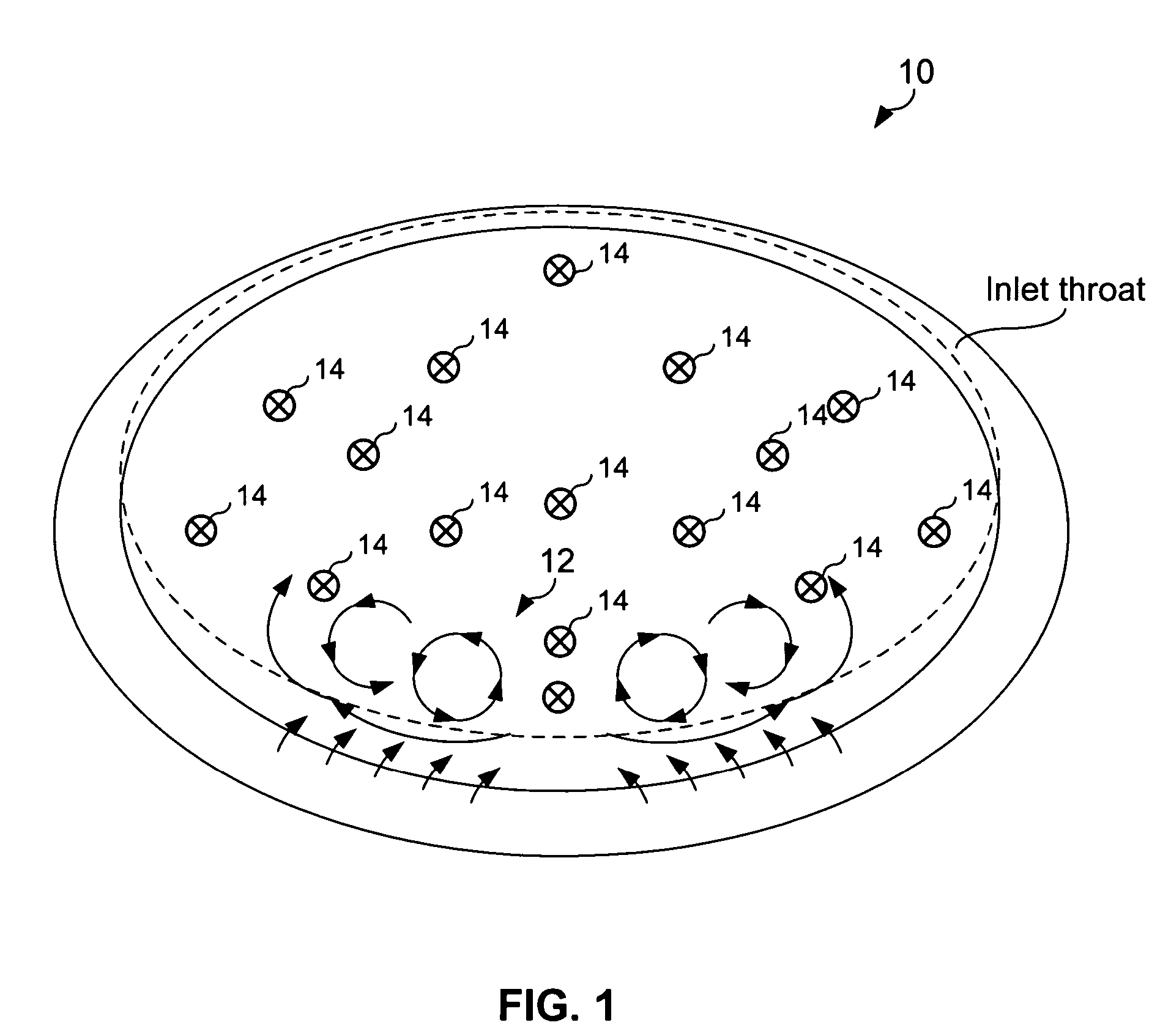
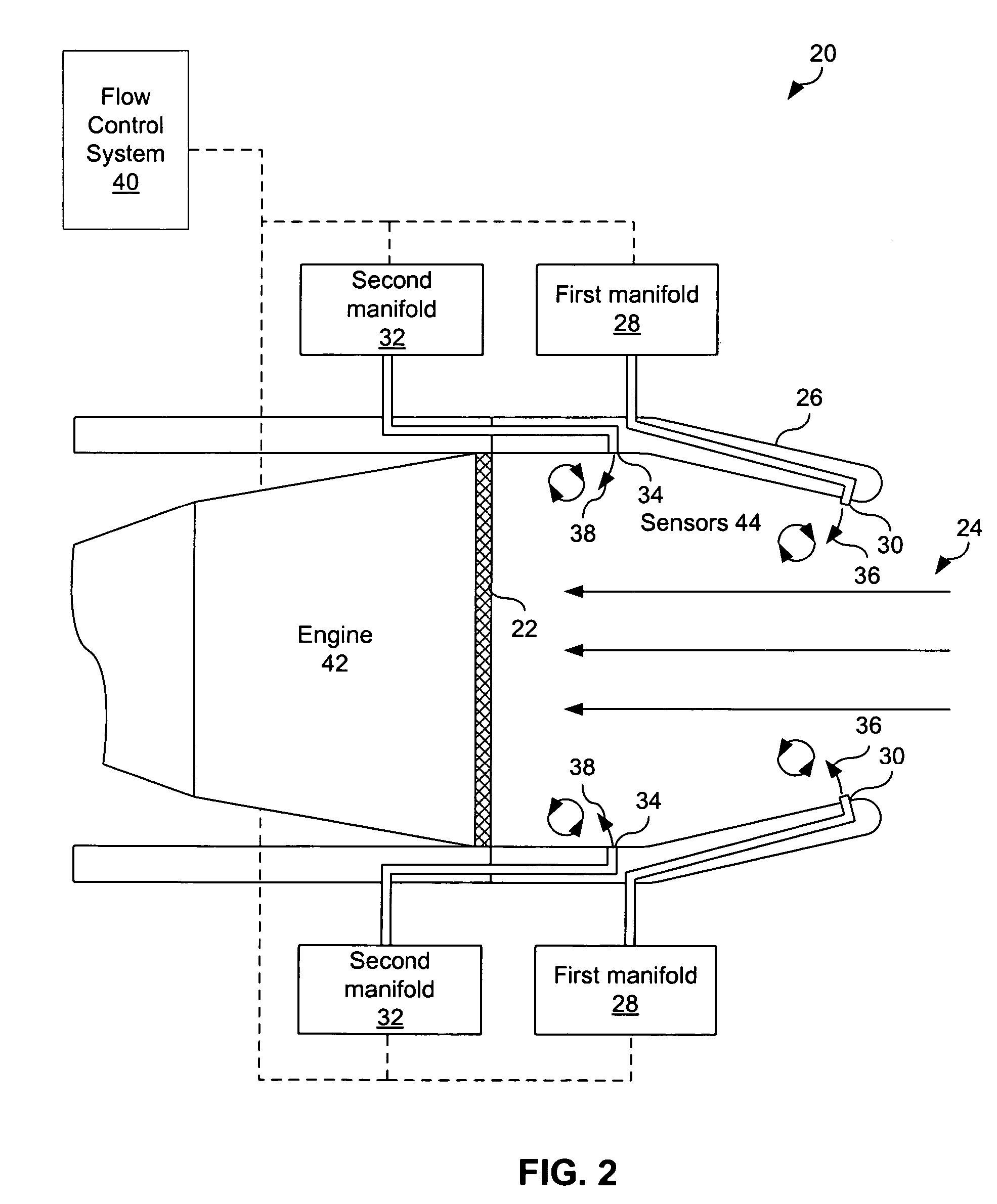
Flow control redistribution to mitigate high cycle fatigue
ActiveUS7617670B2Improve distortionPromote recoveryCombustion enginesGas turbine plantsEngineeringLow-cycle fatigue
A method operable to improve pressure recovery and / or distortion within engine inlet is disclosed. A first fluid flow is provided to primary jet vortex generator(s) operable to inject fluid at a first injection rate into a boundary layer of a primary fluid flow within the inlet. A secondary fluid flow is injected by secondary jet vortex generator(s) at a second injection rate into the boundary layer of the primary fluid flow, The fluid injected at the first injection rate and second injection rate is operable to induce secondary flow structures within the boundary layer. These secondary close structures are then operable to improve or manipulate the pressure recovery of the inlet. At specific engine conditions, this method may redistribute the ratio of the first injection rate and second injection rate in order to improve pressure recovery and / or distortion of the inlet when the particular engine conditions.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
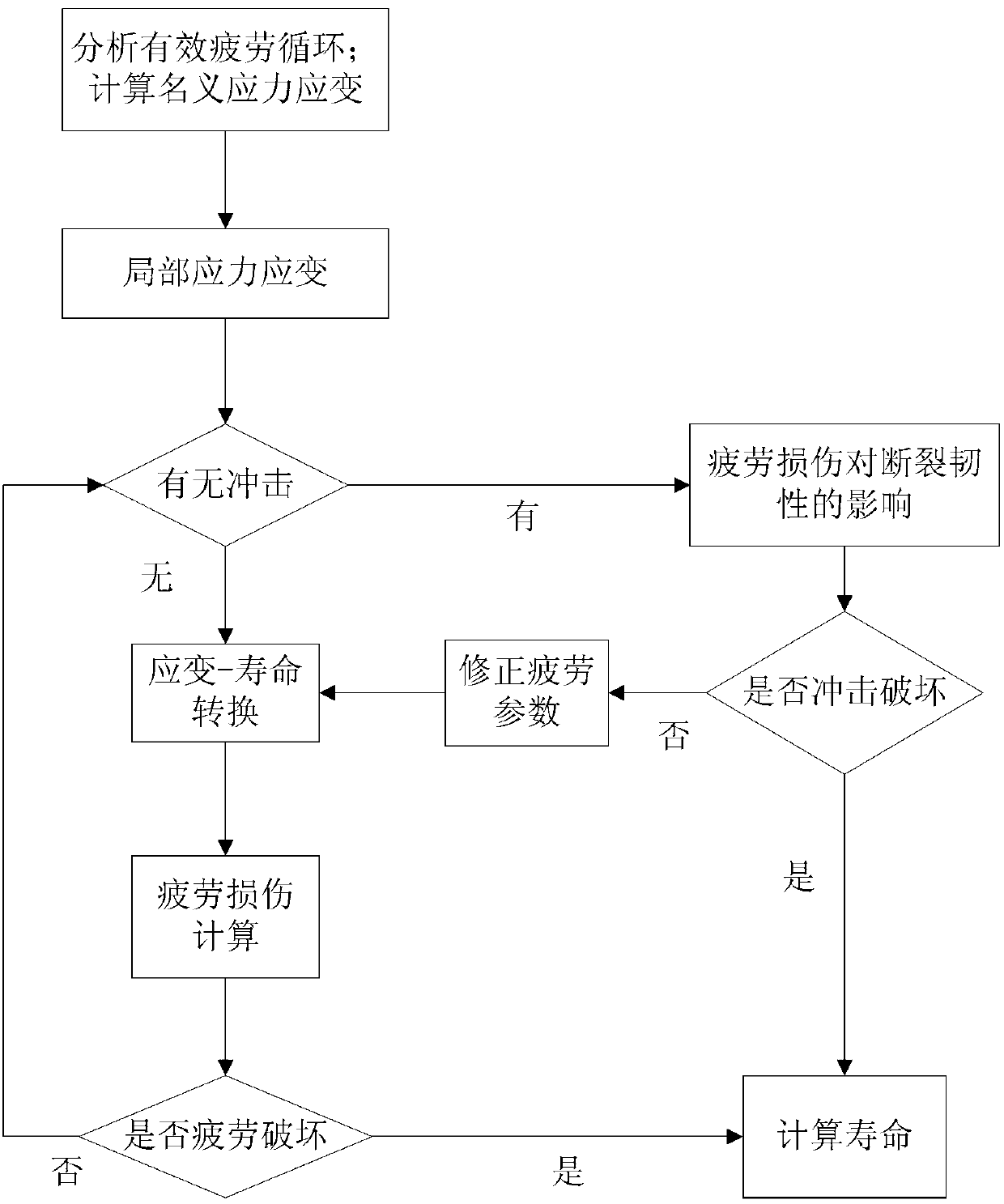
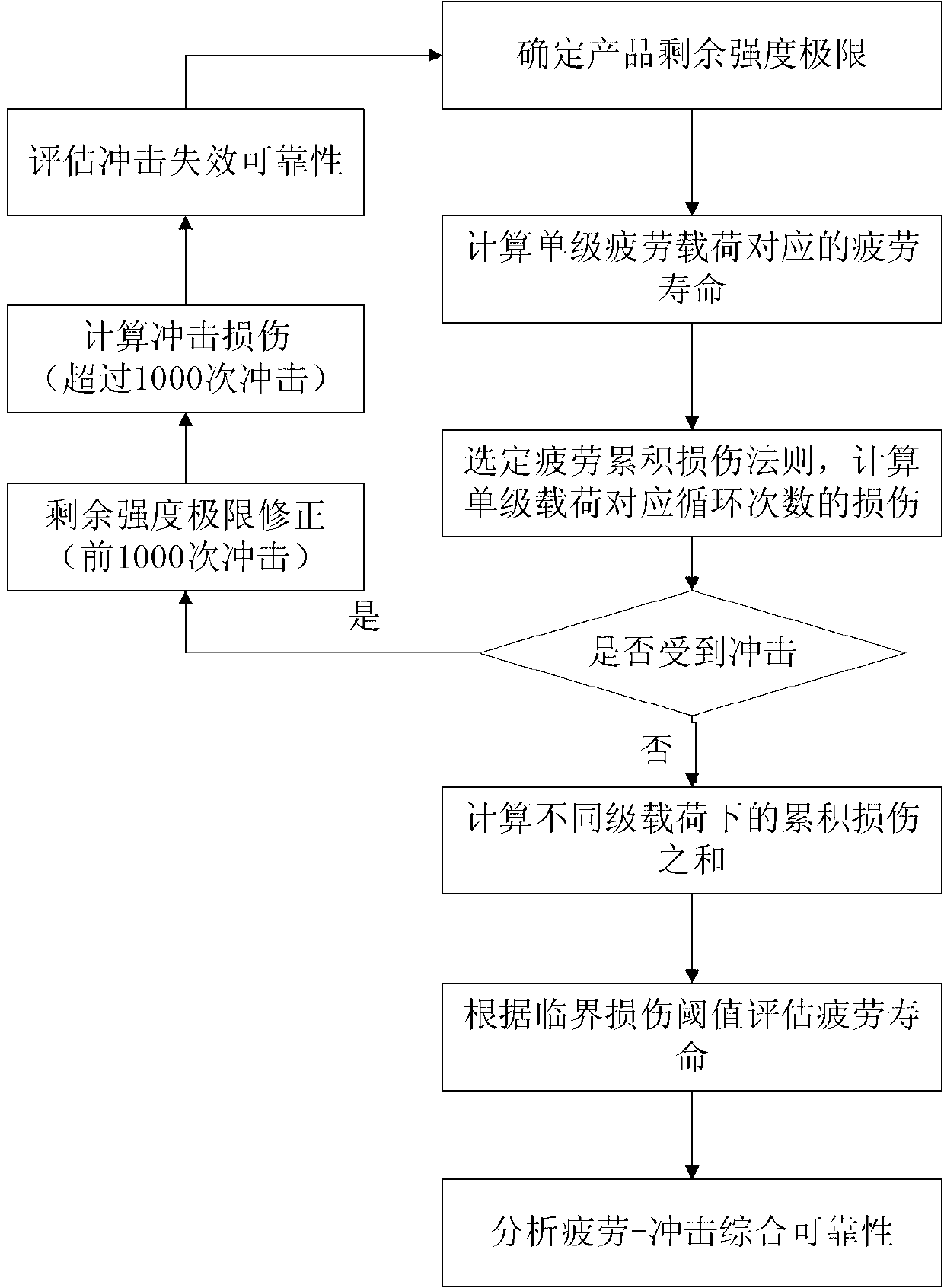
Damage calculation method for low-cycle fatigue and high-strength impact coupling based on local stress strain method
InactiveCN103344515AAccurate fatigue damage analysis resultsMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue damageFatigue loading
The invention relates to a damage calculation method for low-cycle fatigue and high-strength impact coupling based on a local stress strain method. The damage calculation method comprises the following steps of: (1) analyzing a fatigue load spectrum, calculating nominal stress strain of each stage of multiple stages of amplitude-variable fatigue load spectra, and converting the nominal stress strain into local stress strain; (2) calculating fatigue life and damage corresponding to each stage of fatigue load local strain when a product is impacted; (3) calculating the fatigue life and the damage corresponding to each stage of the fatigue load local strain when the product is impacted and the impact is in an influence range, and considering the damage probability in a fatigue circulation unit when the product is impacted; (4) calculating impact performance influenced by fatigue accumulated damage; and (5) calculating comprehensive degree of reliability. Compared with a conventional fatigue damage calculation method, the damage calculation method has the advantages that the influence of high-strength impact on the fatigue damage, the influence of fracture failure caused by direct impact to the life of the product and the influence of the fatigue accumulated damage to the shock resistance of the product are considered, and the fatigue-impact life and the degree of reliability of the product can be well evaluated under a complex environment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method of controlling and refining final grain size in supersolvus heat treated nickel-base superalloys
InactiveUS20100329883A1Finer uniform grain sizeImproved low cycle fatigue behaviorPropellersEngine manufactureRheniumNiobium
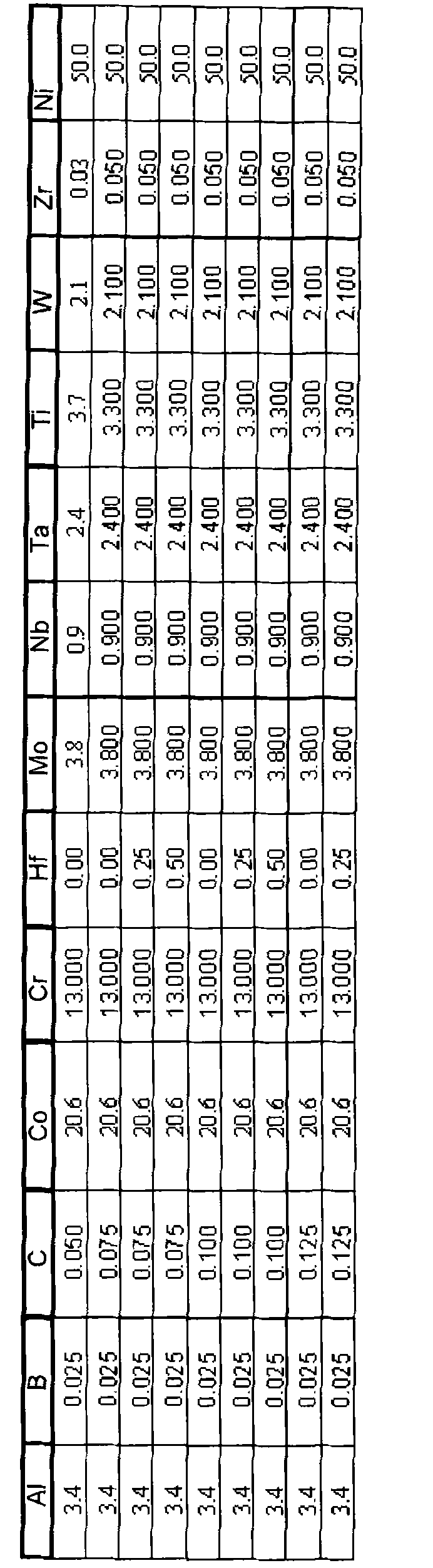
A gamma prime precipitation-strengthened nickel-base superalloy and method of forging an article from the superalloy to promote a low cycle fatigue resistance and high temperature dwell behavior of the article. The superalloy has a composition of, by weight, 16.0-22.4% cobalt, 6.6-14.3% chromium, 2.6-4.8% aluminum, 2.4-4.6% titanium, 1.4-3.5% tantalum, 0.9-3.0% niobium, 1.9-4.0% tungsten, 1.9-3.9% molybdenum, 0.0-2.5% rhenium, greater than 0.05% carbon, at least 0.1% hafnium, 0.02-0.10% boron, 0.03-0.10% zirconium, the balance nickel and incidental impurities. A billet is formed of the superalloy and worked at a temperature below the gamma prime solvus temperature of the superalloy so as to form a worked article, which is then heat treated above the gamma prime solvus temperature of the superalloy to uniformly coarsen the grains of the article, after which the article is cooled to reprecipitate gamma prime. The article has an average grain size of not coarser than ASTM 7 and is substantially free of critical grain growth.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Heat Exchanger Mounting Assembly
InactiveUS20110146944A1Improve gas efficiencyHigh cycle fatigueAir heatersEfficient propulsion technologiesEngineeringThermal expansion
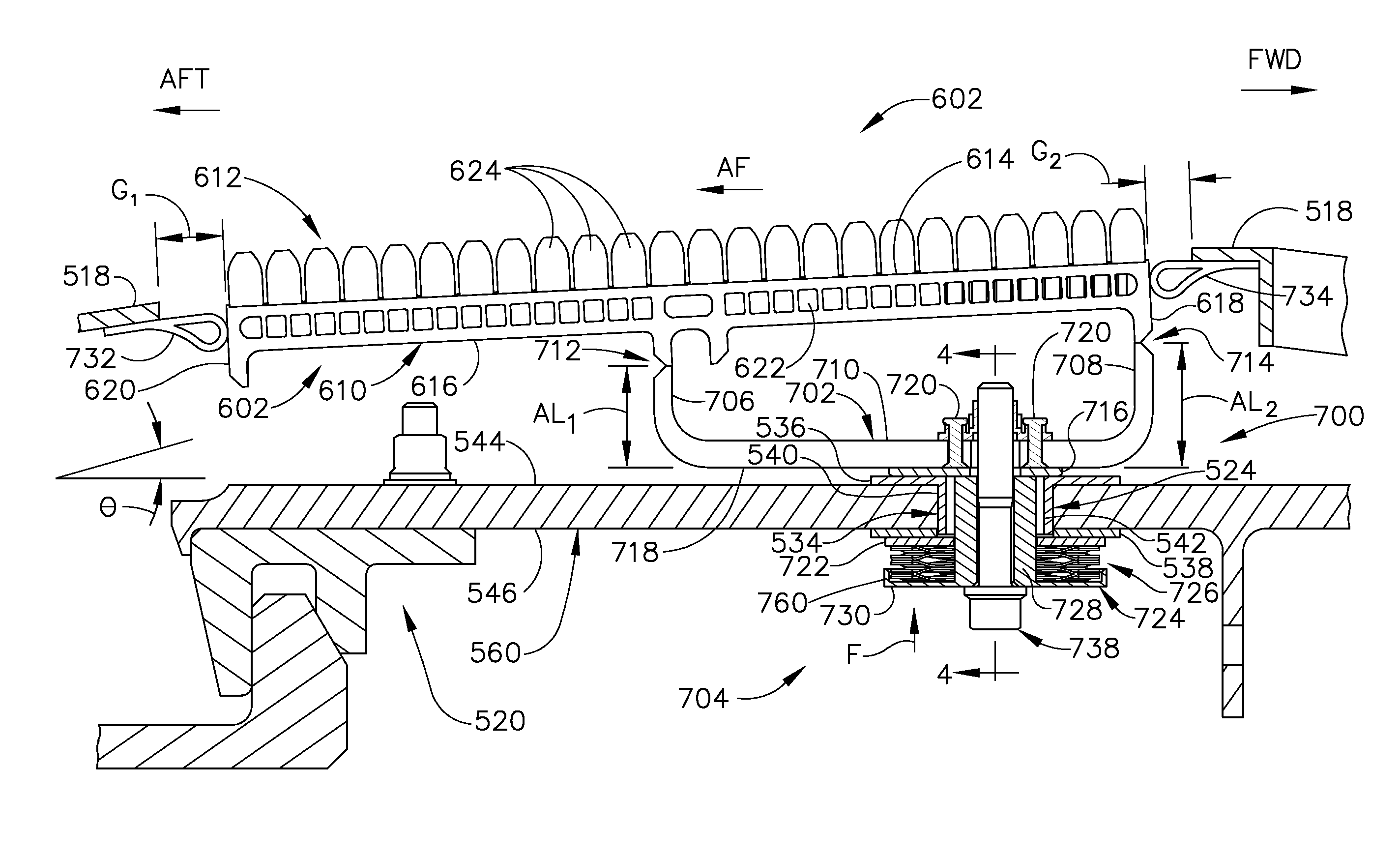
A mounting assembly for a heat exchanger for a gas turbine engine. The heat exchanger assembly includes a plurality of arcuate manifolds each supporting an array of fins extending from a radial inner surface. A plurality of circumferentially extending spaced weld tabs is integrally formed on the radial outer surface. A bracket assembly is utilized to attach the heat exchanger to a structural member of a gas turbine engine assembly, e.g., a fan case, in such a manner as to maximize the surface area available for fin placement, and to not interfere with the cooling circuits within the manifold. The mounting system provides adequate stiffness for high cycle fatigue loads (i.e., vibrations) and allows relative slippage between the heat exchanger and the fan case to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction to address low cycle fatigue loads.
Owner:UNISON INDUSTRIES
Turbine disc-based low-cycle fatigue crack propagation life prediction method
InactiveCN106644783AExtended Life SatisfactionMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesElasticity measurementStress intensity factorScanning electron microscope
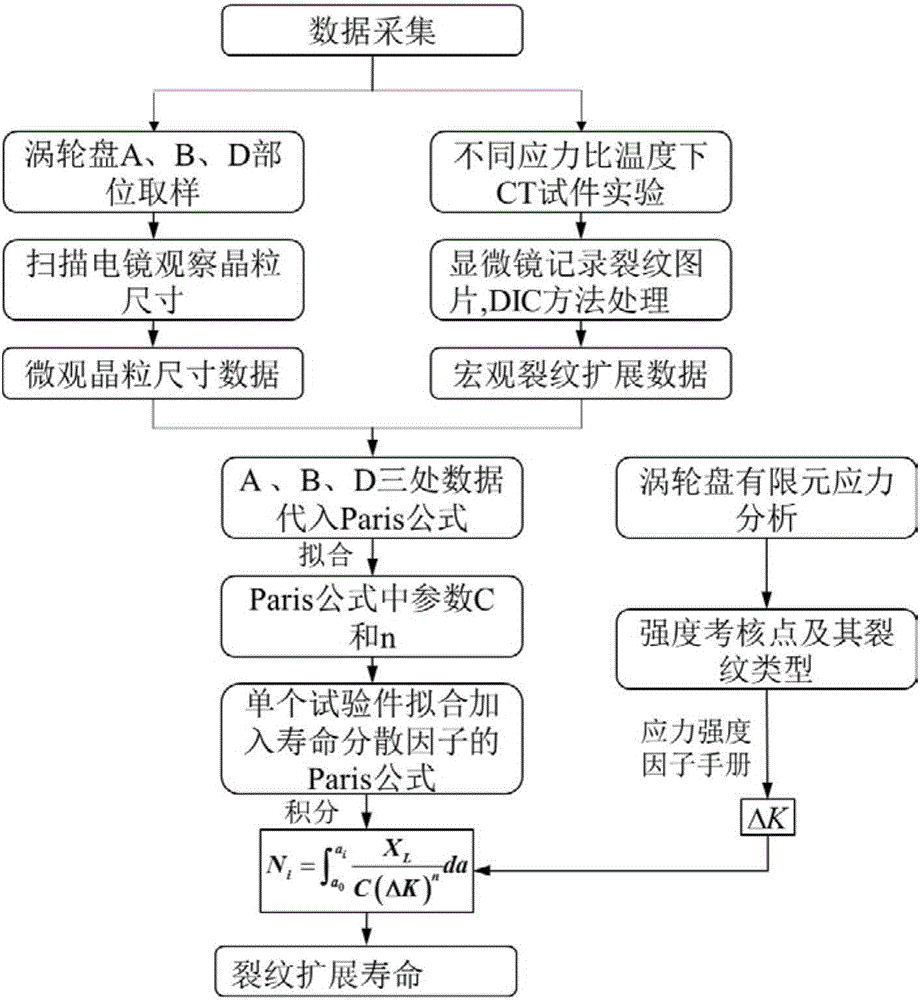
The invention relates to a turbine disc-based low-cycle fatigue crack propagation life prediction method, comprising the following steps: (1) collecting micro-data of different sampling positions of a turbine disc by using a scanning electron microscope, and obtaining a distribution rule; (2) designing a low-cycle fatigue test for the different positions, and collecting macro-data; (3) according to the data collected in steps (1) and (2), obtaining the distribution of a life scattering factor and a Paris formula considering the life dispersibility of the different sampling positions of the turbine disc; (4) performing static strength analysis to obtain a dangerous point position stress intensity factor deltaK, integrating by using the life scattering factor and the Paris formula considering the life dispersibility, which are obtained in step (3), then acquiring the relationship between crack propagation life and crack length, and giving the crack propagation life according to the crack length.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
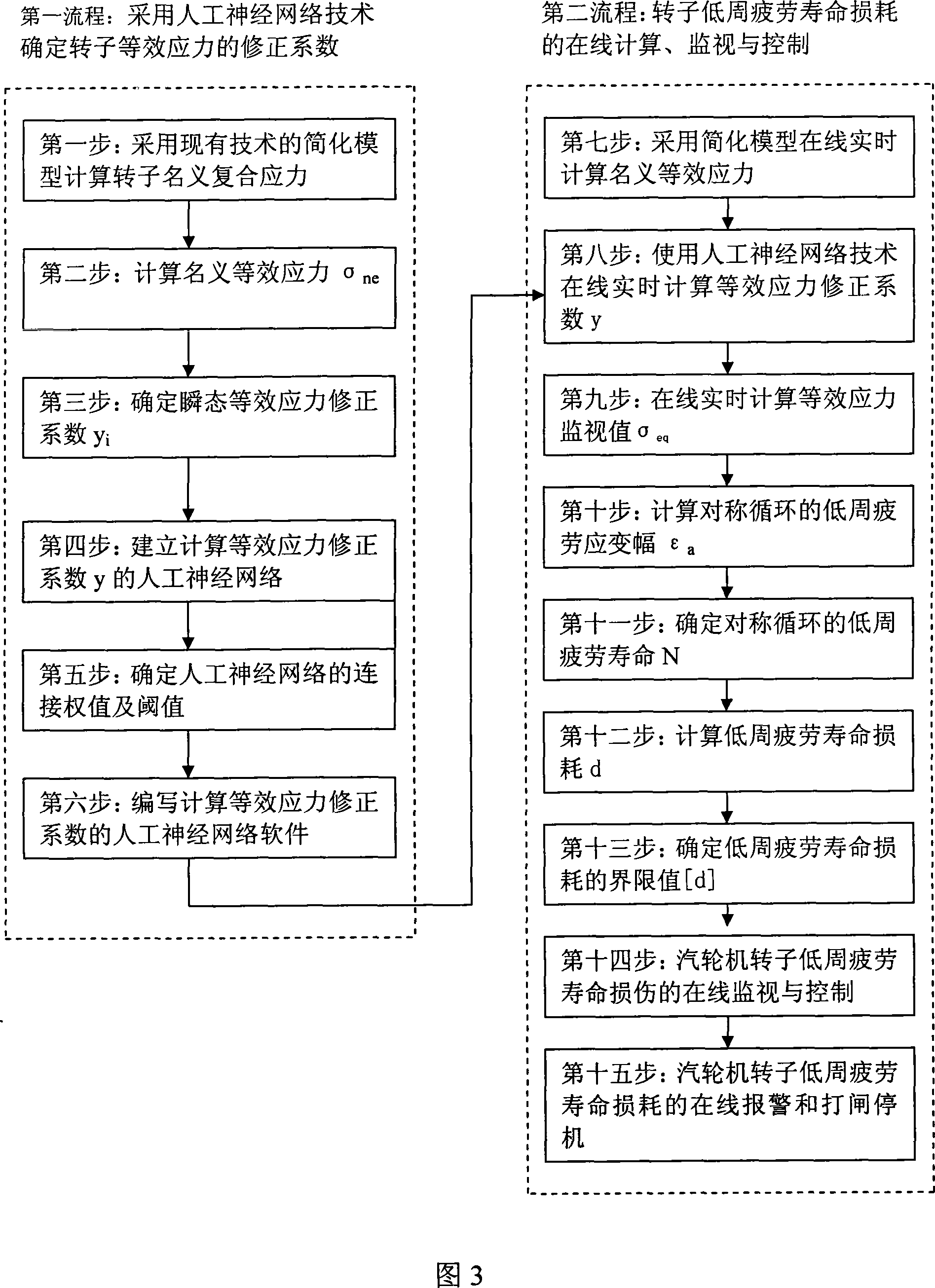
Method and system for on-line monitoring steam turbine roter low-cycle fatigue life consumption
ActiveCN101042059AReduced loss of low cycle fatigue lifeReduced cycle fatigue life lossMachines/enginesSafety/regulatory devicesNerve networkLow-cycle fatigue
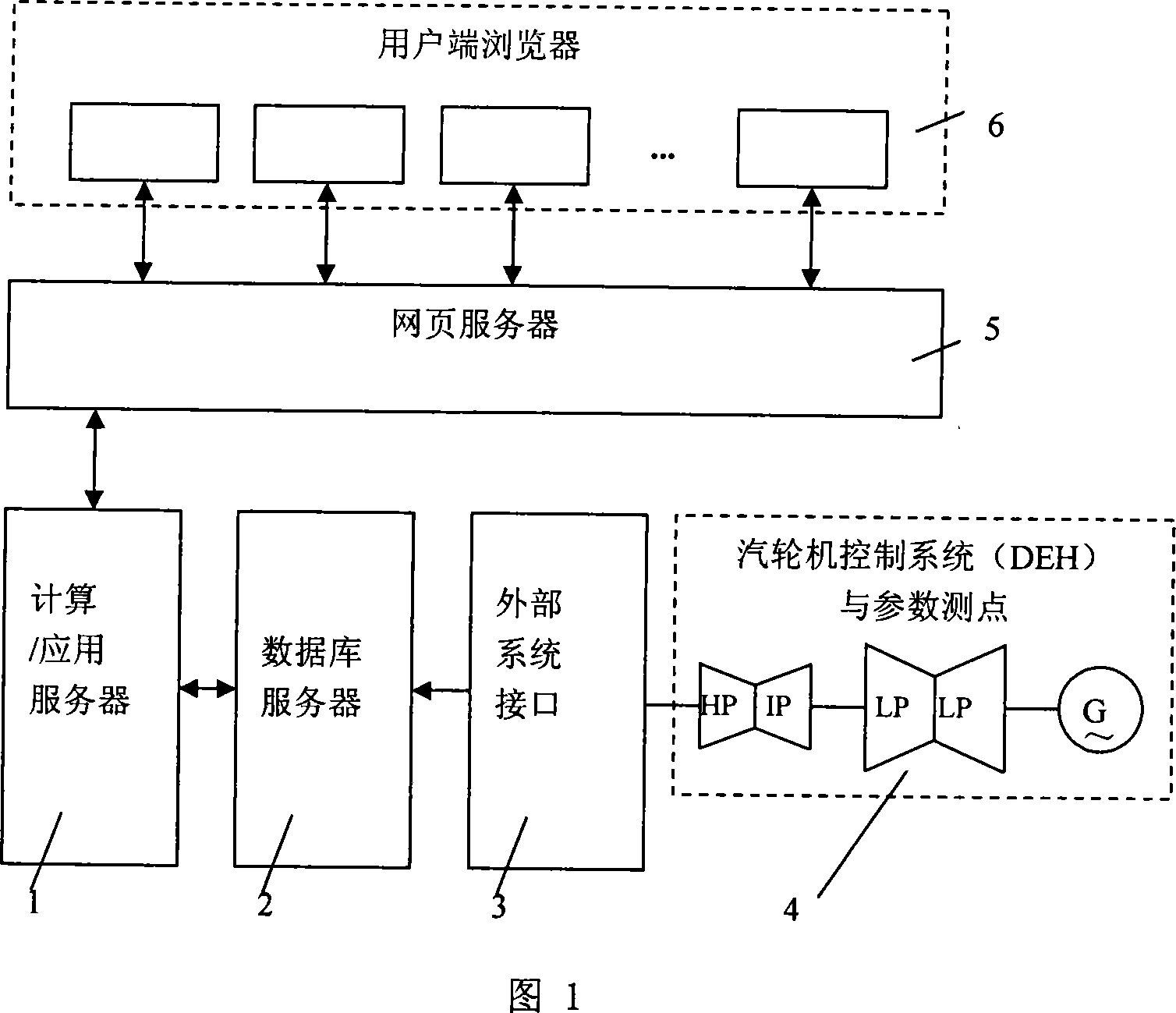
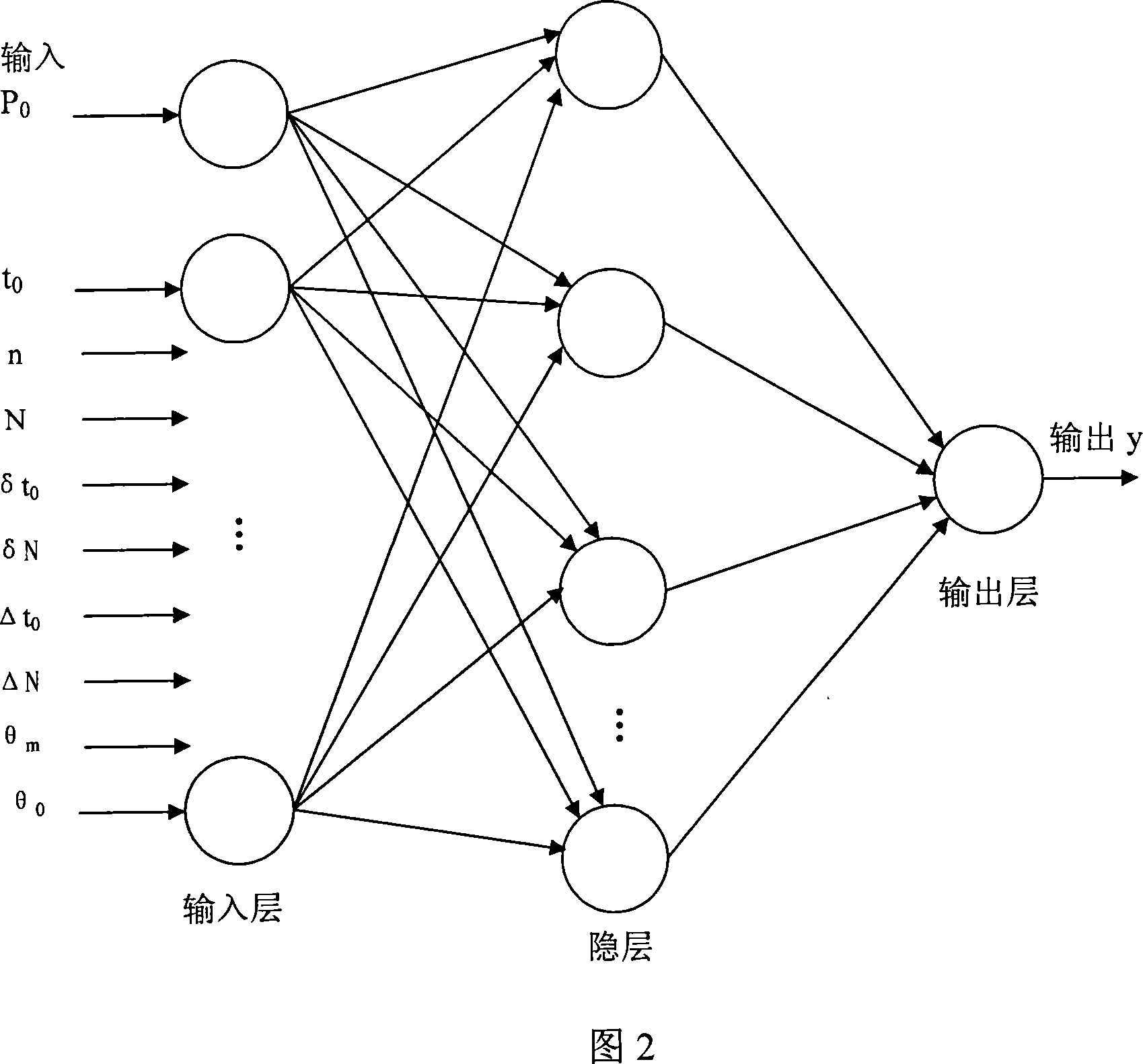
It relates to a turbine rotor low cycle fatigue durability loss on line monitoring system, featuring in its computation, application server and software, database server, outside system interface, turbine control system DEH and parameter testing point, web server and user browser that connects with the computation and application server and each end item user browser respectively, with the computation and application server connecting with the data base server which connects with the turbine control system DEH and parameter testing point through the outside system interface. It is made of two processes, with the no.1 using artificial nerve network to determine turbine rotor equivalent stress coefficient, the no.2 process being on line computation, monitoring and control of the turbine rotor cycle fatigue loss. It realizes the working times of the turbine rotor of 10000 times.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER EQUIP RES INST
Titanium alloy integral bladed disc and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102052342AFlame retardantHigh temperature strengthPump componentsPumpsManufacturing technologyGas compressor
The invention discloses a titanium alloy integral bladed disc and a manufacturing method thereof, which belong to the technical field of titanium alloy material and manufacturing. The integral bladed disc consists of a rotary disc and blades which are integrated, and is characterized in that the rotary disc is made of high-strength titanium alloy and the blades is made of titanium aluminum intermetallic compound. The component transition between the rotary disc and the blades is direct transition. The invention utilizes laser to melt stacked materials layer by layer to directly prepare a near-net-shape titanium alloy integral bladed disc with inflaming retarding and high temperature strength performance without the need of the multi-step hot working process of conventional processing method, remarkably reduces processing amount and improves material utilization rate and structural efficiency; and the rotary disc has high plasticity and strength as well as low-cycle fatigue performance, and the blades have inflaming retarding performance and high temperature strength and rigidity, so as to satisfy the performance requirements of the gas compressor integral bladed disc on the rotarydisc and the blades during the using process.
Owner:有研金属复材技术有限公司
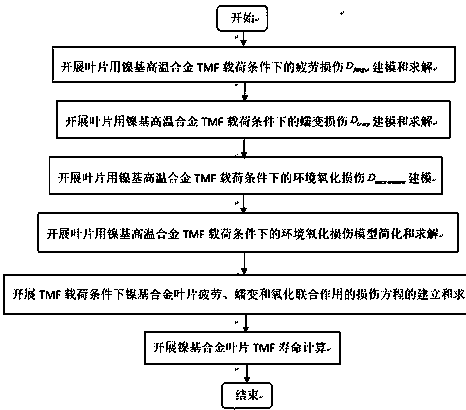
Life prediction method used for nickel-base superalloy blade under thermal mechanical fatigue load
InactiveCN108170905AThe modeling process is clearFully combine structural featuresDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageTime function
The invention discloses a life prediction method used for a nickel-base superalloy blade under a thermal mechanical fatigue load. The problems of life prediction and joint representation of low cyclefatigue damage, creep damage and oxidation environment damage of the nickel-base superalloy blade under the TMF load are effectively solved; according to isothermal low cycle fatigue life data of nickel-base alloy under the condition of not causing high-temperature effects of creep, oxidation and the like, fitting is performed to obtain a strain life equation; in combination with a fatigue damagelinear accumulation theory, a fatigue damage model is obtained; a creep damage model is represented as temperature, stress and time functions; the oxidation environment damage is modeled based on an oxidation-cracking mechanism with a continuous oxidation layer at a crack tip; a continuous damage accumulation mechanism is adopted for the three models; and by virtue of stress, strain and temperature data of dangerous position points of the blade, accurate and reliable unified representation of fatigue, creep and oxidation interactive damage, and life prediction of a combined damage model to a nickel-base superalloy member under the thermal mechanical fatigue load is realized.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Titanium alloy integral blade disc with composite performance and fabricating method thereof
ActiveCN101598139AImprove performanceImprove toughnessPump componentsMetallic material coating processesTitanium matrix compositesCombustion
The invention relates to a titanium alloy integral blade disc with composite performance and a fabricating method thereof. A hub and a spoke of the blade disc are made of titanium alloy, a rim and a blade are made of titanium-base composite materials (or the whole disk is made of titanium alloy, and the blade is made of titanium-base composite materials), and the point of the blade also contains one or more of Cr, V, Mo with higher content so as to have properties of resisting temperature, abrasion and combustion. The hub and the spoke as well as the rim and the blade are sequentially prepared by piling layer by layer through adopting titanium alloy powder, one or more of titanium powder, TiC, B4C, and Cr3C2, and mixture powder of particles of one or more of Cr, V and Mo, which are synchronously conveyed and molten and deposited by adopting laser, so as to obtain the near net-shape titanium alloy integral blade disc with composite performance. The rim and the blade of the blade disc are integer, the hub and the spoke of the disc have high room temperature plasticity and strength as well as low cycle fatigue property, and the rim and the blade have high high-temperature fracture toughness property and high creep resistance.
Owner:有研金属复材技术有限公司
High-cycle fatigue and low-intensity impact coupled damage calculation method based on nominal stress method
ActiveCN103344514AWide selectionWide applicabilityMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue damageFatigue loading
The invention relates to a high-cycle fatigue and low-intensity impact coupled damage calculation method based on a nominal stress method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, determining the initial fatigue limit of a product, and calculating the fatigue life corresponding to single step of load under the action of fatigue load by utilizing the Baskin formula; 2, determining whether random impact or fixed impact exists according the frequency of impact; 3, calculating the accumulated fatigue damage after first 1000 times of impact according to the damage calculation method of the accumulated fatigue damage rule selected in the step 1; 4, calculating the accumulated fatigue damage after more than 1000 times of impact and the total accumulated damage value of the product at the t moment; 5, calculating the probability of no fatigue failure and the probability of random impact failure respectively, thereby finally obtaining the reliability of the product. The method provided by the invention can be used for evaluating the fatigue life and reliability of the product under the complex environment, and then discussing the impact and accumulated fatigue damage models in different cases, and is wide in selection area and application space, simple and convenient in analysis and calculation process and strong in engineering practicability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method of controlling and refining final grain size in supersolvus heat treated nickel-base superalloys
A gamma' prime precipitation-strengthened nickel-base superalloy and method of forging an article from the superalloy to promote a low cycle fatigue resistance and high temperature dwell behavior of the article. The superalloy has a composition of, by weight, 16.0-22.4% cobalt, 6.6-14.3% chromium, 2.6-4.8% aluminum, 2.4-4.6% titanium, 1.4-3.5% tantalum, 0.9-3.0% niobium, 1.9-4.0% tungsten, 1.9-3.9% molybdenum, 0.0-2.5% rhenium, greater than 0.05% carbon, at least 0.1% hafnium, 0.02-0.10% boron, 0.03-0.10% zirconium, the balance nickel and incidental impurities. A billet is formed of the superalloy and worked at a temperature below the gamma' prime solvus temperature of the superalloy so as to form a worked article, which is then heat treated above the gamma' prime solvus temperature of the superalloy to uniformly coarsen the grains of the article, after which the article is cooled to reprecipitate gamma' prime. The article has an average grain size of not coarser than ASTM 7 and is substantially free of critical grain growth.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Low cycle fatigue life (LCF) impeller design concept
InactiveUS6935840B2Improving low cycle fatigue (LCF) lifeImprove LCFPropellersRotary propellersImpellerEngineering
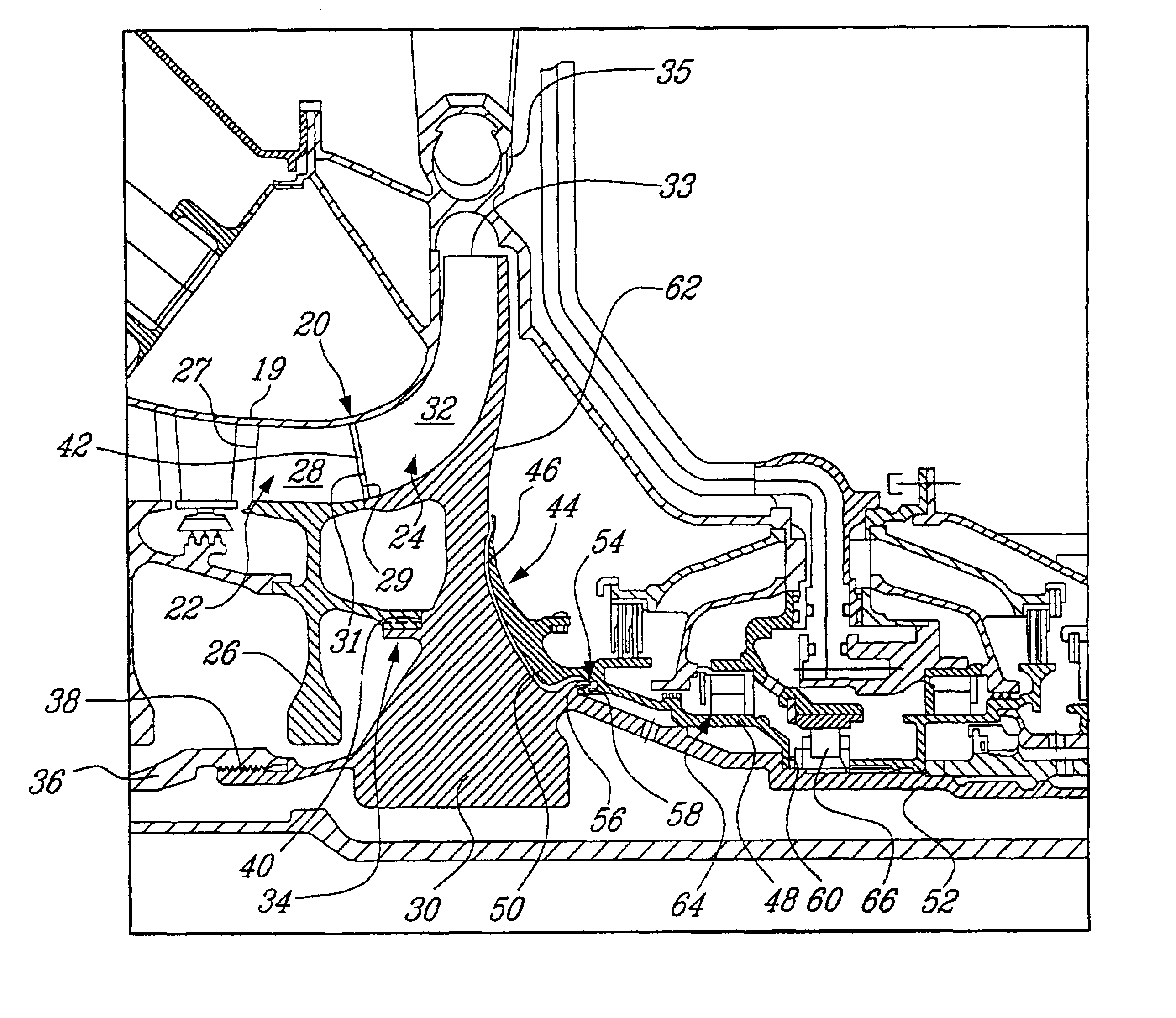
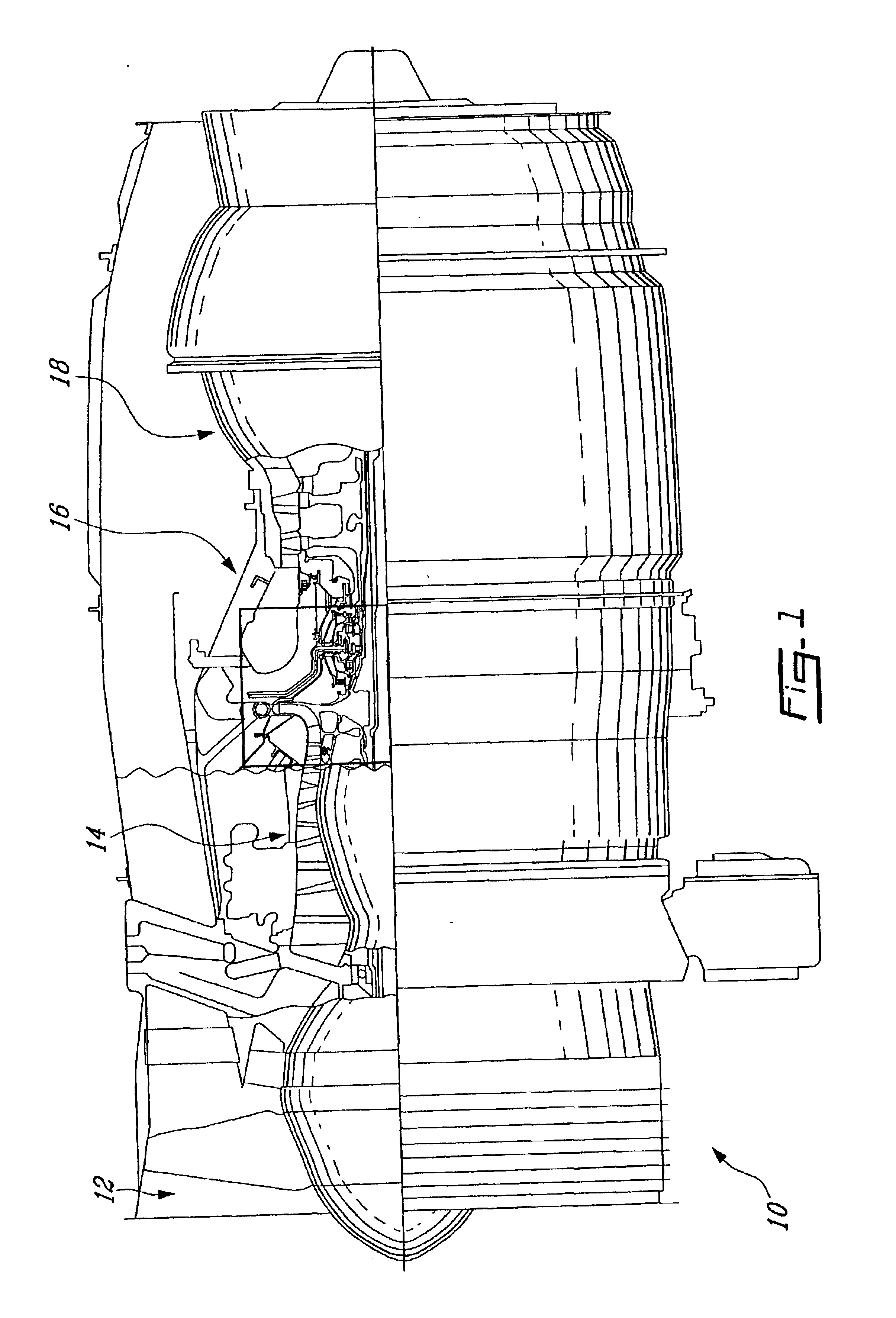
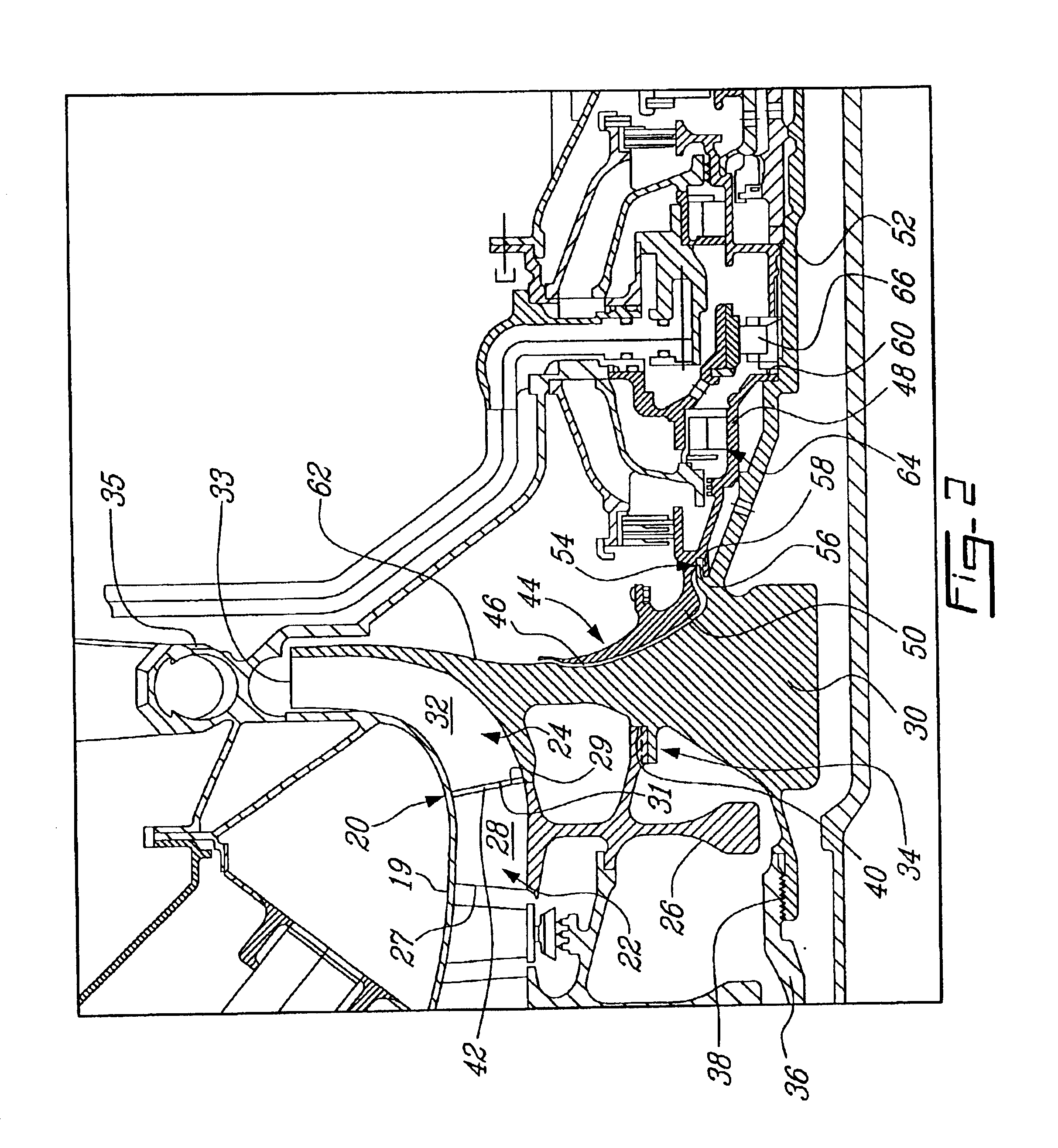
A rotor assembly for a gas turbine engine, having a rotor member with axially spaced-apart front and rear end portions. A thermal shield is located axially downstream of the rear end portion of the rotor for thermally shielding the same from the hot surrounding environment. The thermal shield includes a rear coverplate and an axial gap between the rear coverplate and the rear end portion of the rotor member.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Once variable cross-section cross buckling-restrained bracing member
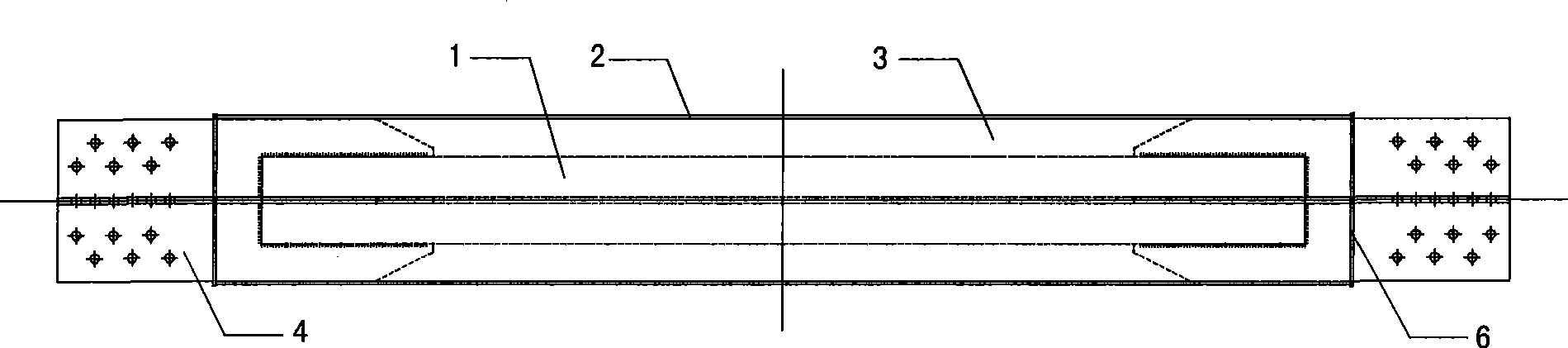
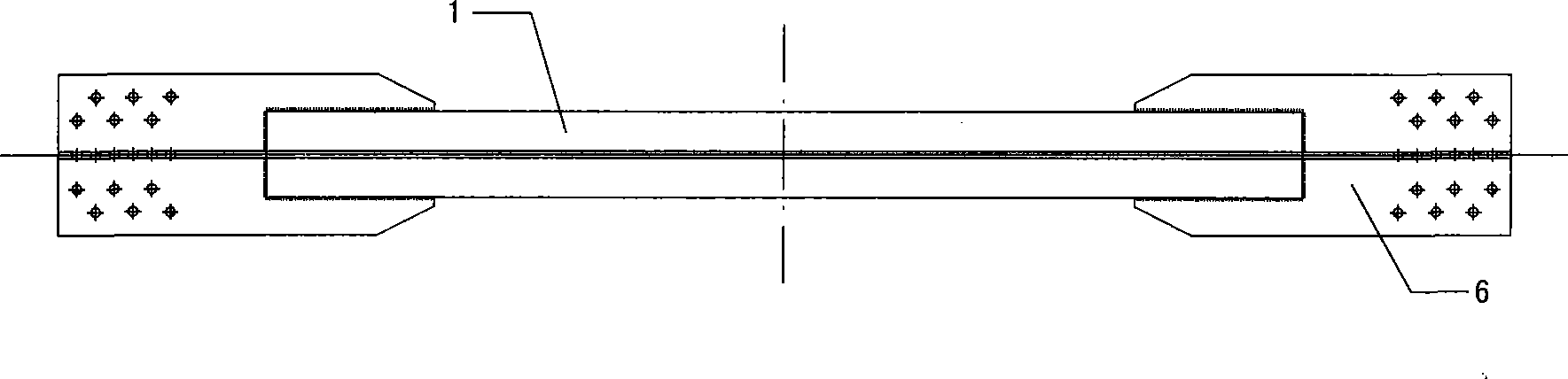
The invention discloses a cross-shaped buckling constraint support component with a primary variable cross-section. The support component comprises a core material part, a support end node and a sleeve part, wherein, the core material part is formed by welded core plates, the support end node part consists of gusset plates which are directly welded with the core plates, and the sleeve part consists of a square or quadrate steel sleeve and an internal filling material; a delaminating material is arranged between the internal filling material of the steel sleeve and the core plates. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the improved buckling constraint support component. The buckling constraint support has very good hysteresis characteristic and energy dissipation performance, is a very effective energy dissipation component, can achieve 1 / 80 deformation to satisfy 1 / 50 floor displacement deformation requirement of an architecture under an infrequent earthquake action and accumulates plastic deformation greater than 200 times of yielding displacement; the buckling constraint support has stable hysteresis characteristic and good low-cycle fatigue characteristic, can greatly improve seismic capability of the architecture, greatly reduce cost of the support and lay a foundation for popularization and application.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
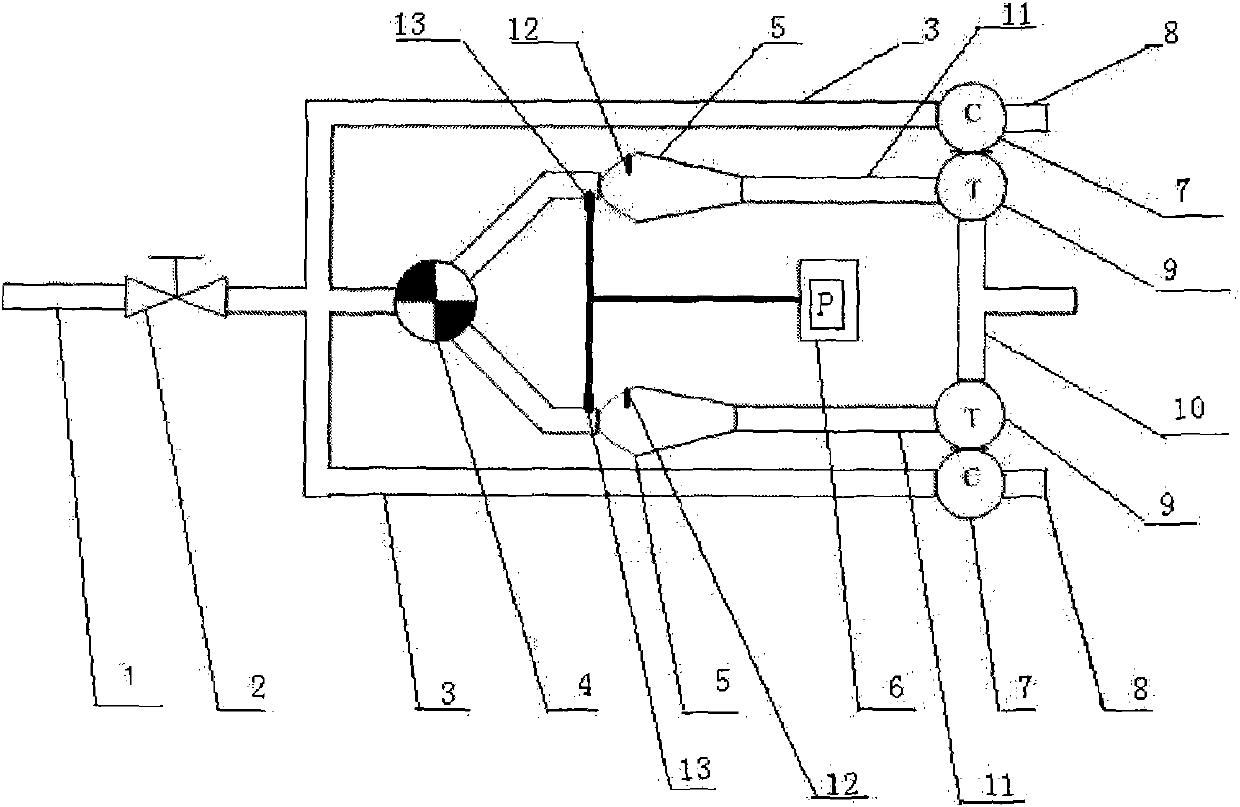
Test bench with double combustion chambers, double superchargers and low cycle fatigue based on self-circulation mode
InactiveCN101793619AReduce dependenceReduce consumptionInternal-combustion engine testingCombustion chamberPrice ratio
The invention relates to a test bench with double combustion chambers, double superchargers and low cycle fatigue based on a self-circulation mode, belonging to the technical field of power machinery. When the test bench with superchargers and low cycle fatigue which adopts a self-circulation principle is started and works, an external gas source firstly supplies gas to the combustion chambers and is closed after the superchargers stably runs, and a turbine and a compressor form self circulation, thereby reducing the dependency to power and the consumption of power, only needing fuel oil with a certain quantity and lowering the requirement of a low cycle fatigue test to compressed air and further reducing the requirement to an air compressor. In the test bench, air flows are respectively supplied to turbines of the two superchargers by adopting the two combustion chambers, and a measure that a flow distribution valve is installed before each combustion chamber enables the test bench with the double combustion chambers, the double superchargers and the low cycle fatigue to realize different gas inlet temperatures of each supercharger, thereby the mechanical load and the heat load needed by the low cycle fatigue test is changed, and the high temperature resistance requirements of materials of the flow distribution valve is reduced with high performance price ratio.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
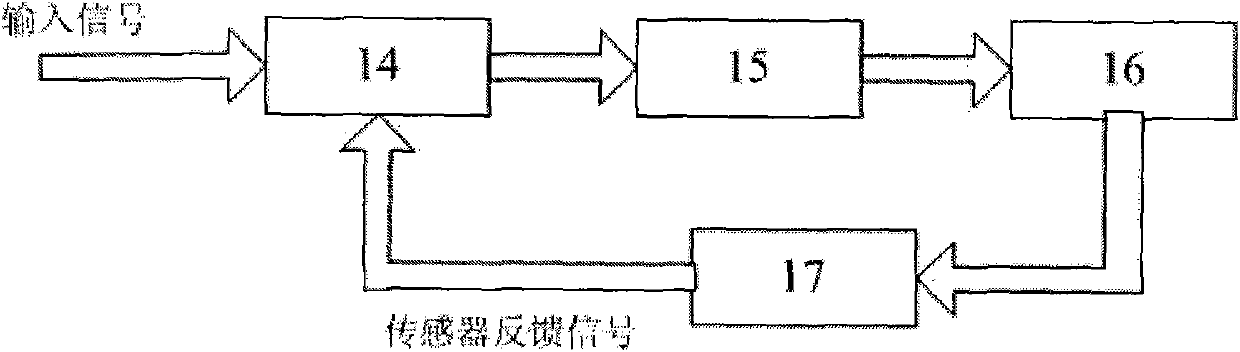
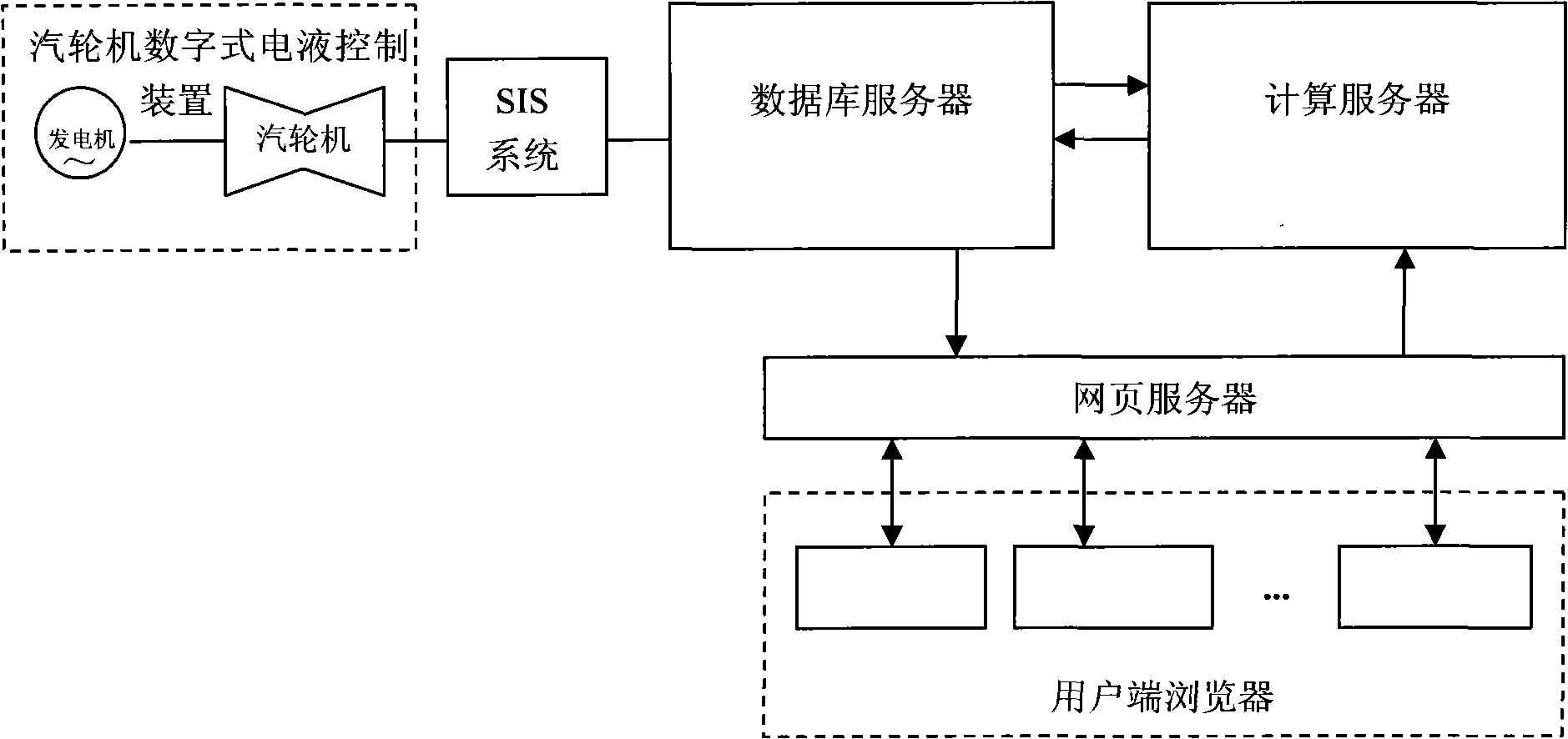
Device for online monitoring and controlling low cycle fatigue life consumption of components of steam turbine and method
ActiveCN101561669ALow cycle fatigue life lossReduced cycle fatigue life lossProgramme controlComputer controlDatabase serverMonitoring and control
The invention relates to a device for online monitoring and controlling low cycle fatigue life consumption of components of a steam turbine and a method, belonging to the technical field of the steam turbine. The invention is characterized in that the device consists of a compute server, a database server, a web server, a user browser and a plant supervisory information device; the web server is connected with the user browser, the database server and the compute server respectively; the compute server is connected with the database server which is connected with a digital electric-hydraulic control device of the steam turbine by the plant supervisory information device. The invention has the advantages of being capable of realizing online computing and controlling of transient low cycle fatigue life consumption of a plurality of components of the steam turbine.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER EQUIP RES INST +2
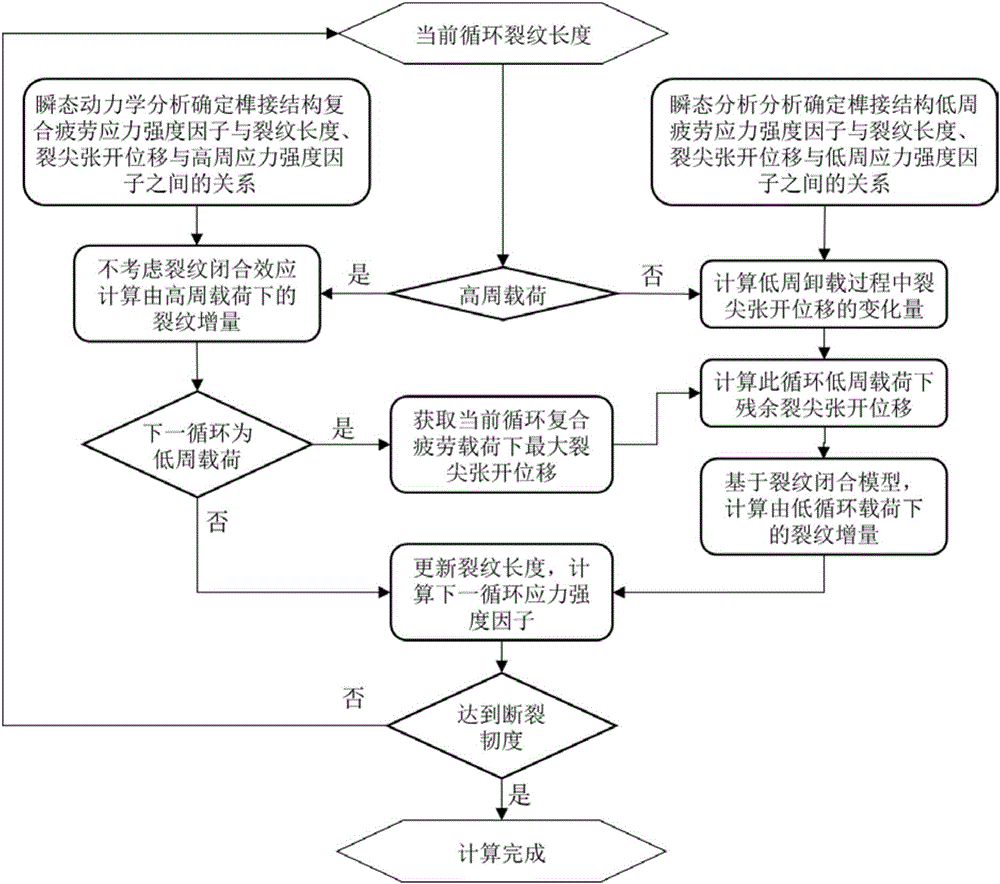
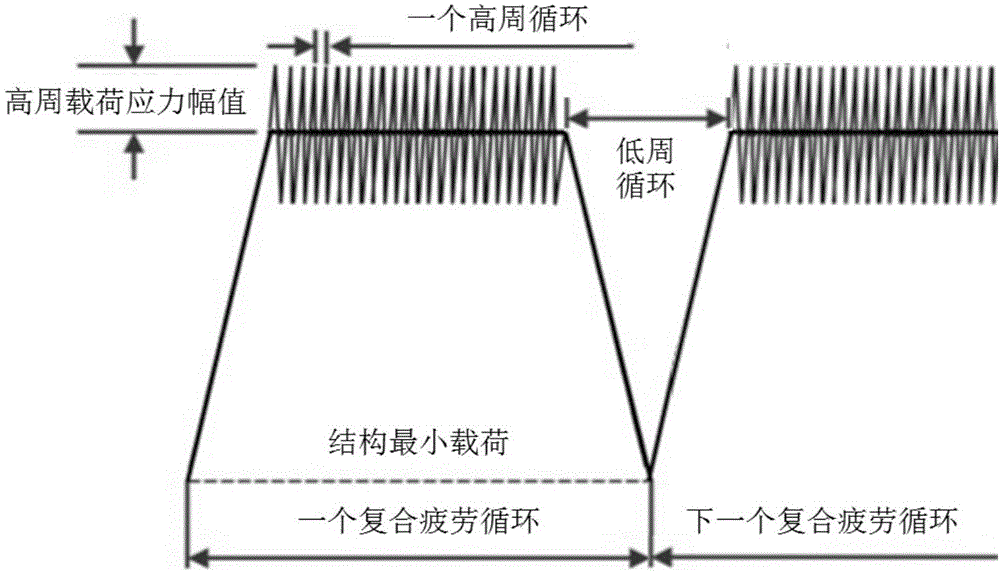
Method for predicting high-low-cycle composite fatigue crack growth life of turbine joggle structure
ActiveCN106644490AImprove scalabilityInhibit expansionEngine testingCrack tip opening displacementEngineering
The invention relates to a method for predicting the high-low-cycle composite fatigue crack growth life of a turbine joggle structure, and the method comprises the steps: (1), building a crack growth model giving consideration to a crack closure effect; (2), determining a high-cycle load stress intensity factor model; (3), determining a low-cycle load stress intensity factor model; (4), judging whether a current cycle is a high-cycle load or not: executing step (5) if the current cycle is the high-cycle load, or else executing step (6); (5), calculating a composite fatigue lower crack increment, judging whether a next cycle is a low-cycle fatigue load or not: obtaining the maximum crack tip opening displacement of the current cycle if the next cycle is the low-cycle fatigue load, and executing step (7), or else executing step (8); (6), calculating the variance of the low-cycle load lower crack tip opening displacement; (7), calculating the residual crack tip opening displacement and crack increment according to the results inputted at steps (5) and (6); (8), updating the crack length, repeatedly carrying out the steps (4)-(7) if the maximum stress intensity factor is less than the fracture toughness, or else completing the calculation, and obtaining the crack growth life.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Preparation method of functional gradient performance coil
The invention provides a preparation method of a functional gradient performance coil and belongs to the technical field of rapidly freezing powder metallurgy superalloys. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, powders with different particle sizes are adopted at different parts of a turbine disk to carry out direct hot isostatic pressing formation, and a coil after heat treatment acquires gradient grain structures with different grain sizes along the radial direction and has different gradient performances along the radial direction. With the adoption of the preparation method, a hub is strong in the tensile strength and excellent in the low-cycle fatigue performance, the mechanical property between the hub and a rim is good in transition, the rim has strong durability and strong creep resistance, and the requirements of the functional gradient performance coil are satisfied.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
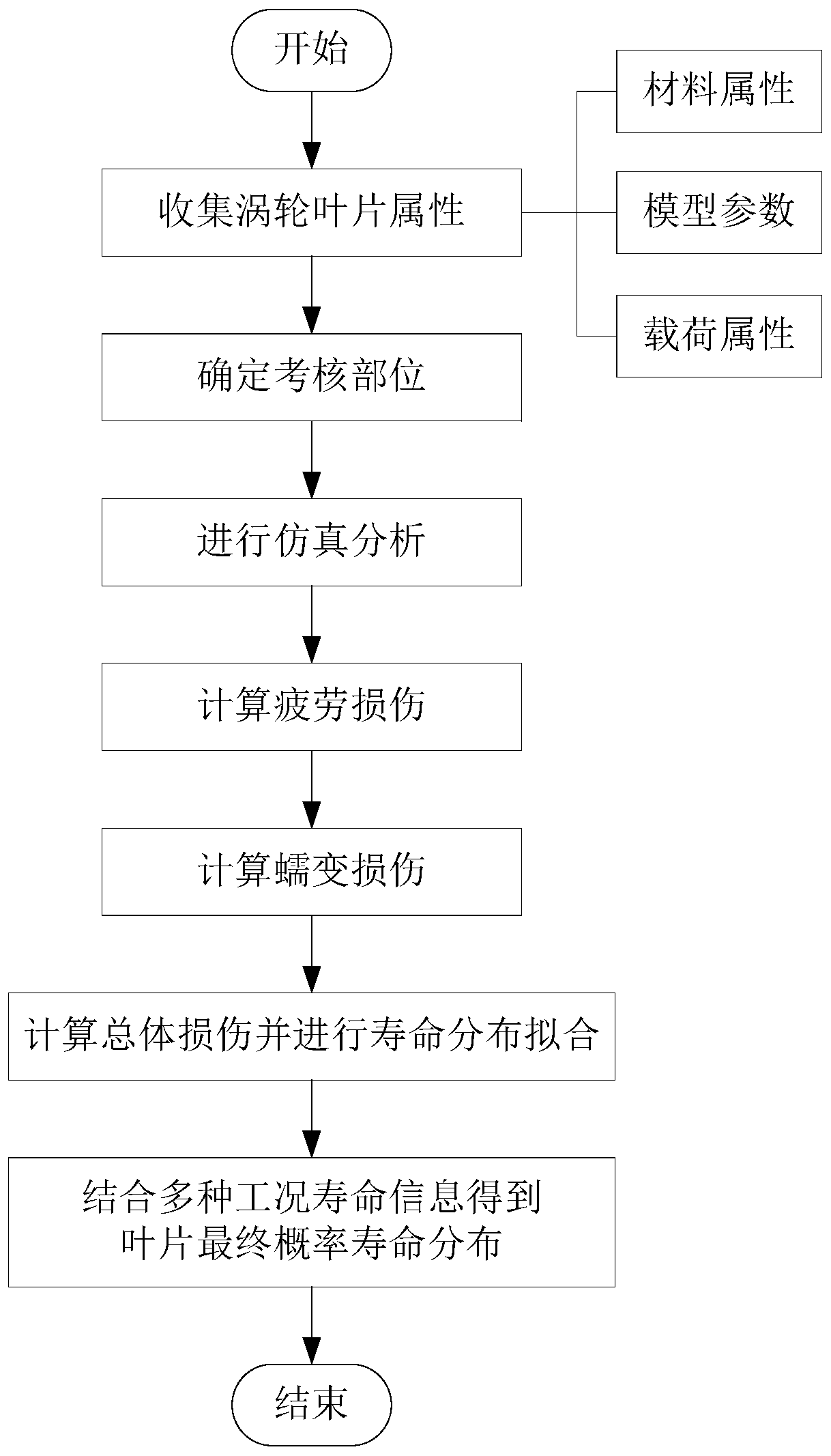
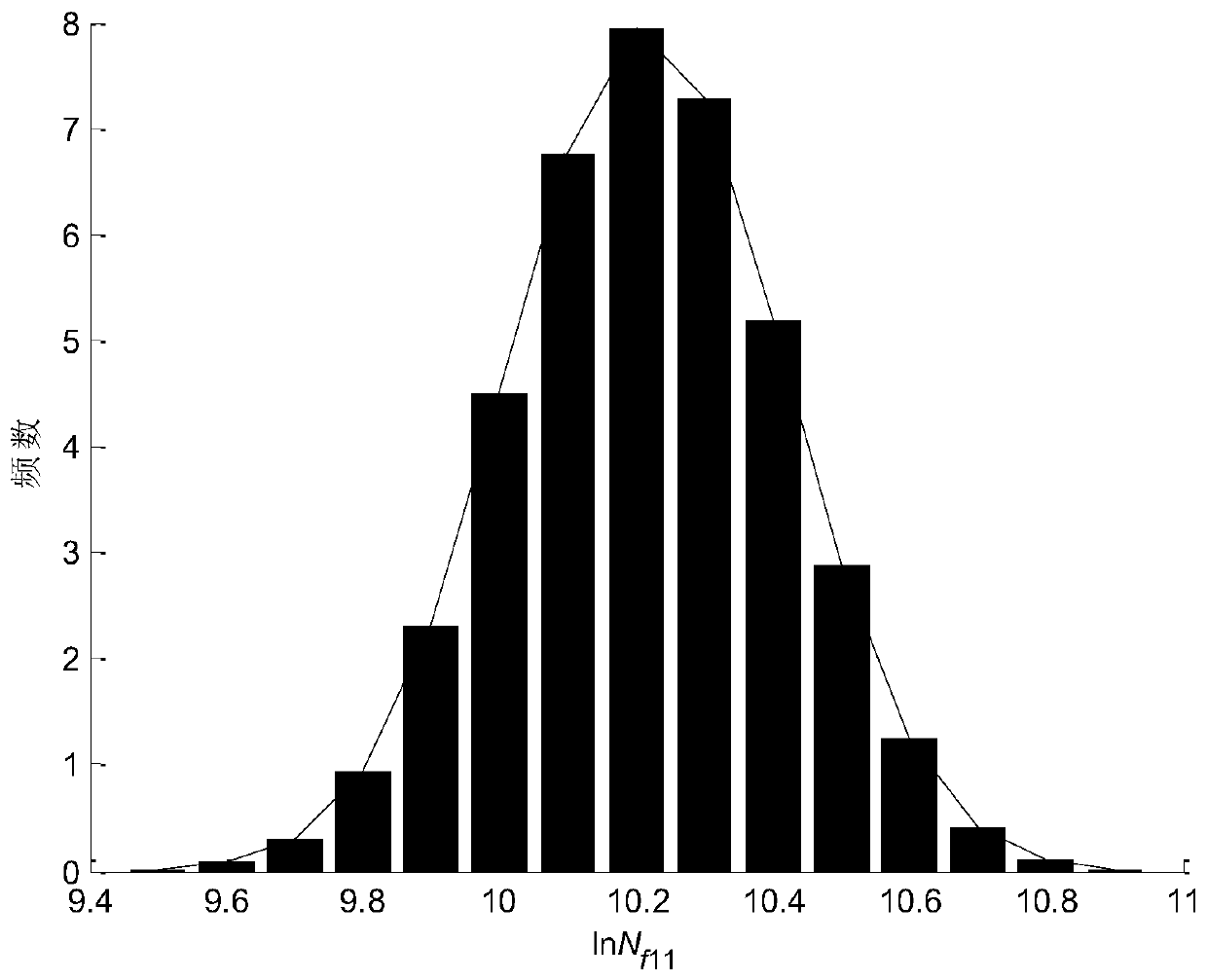
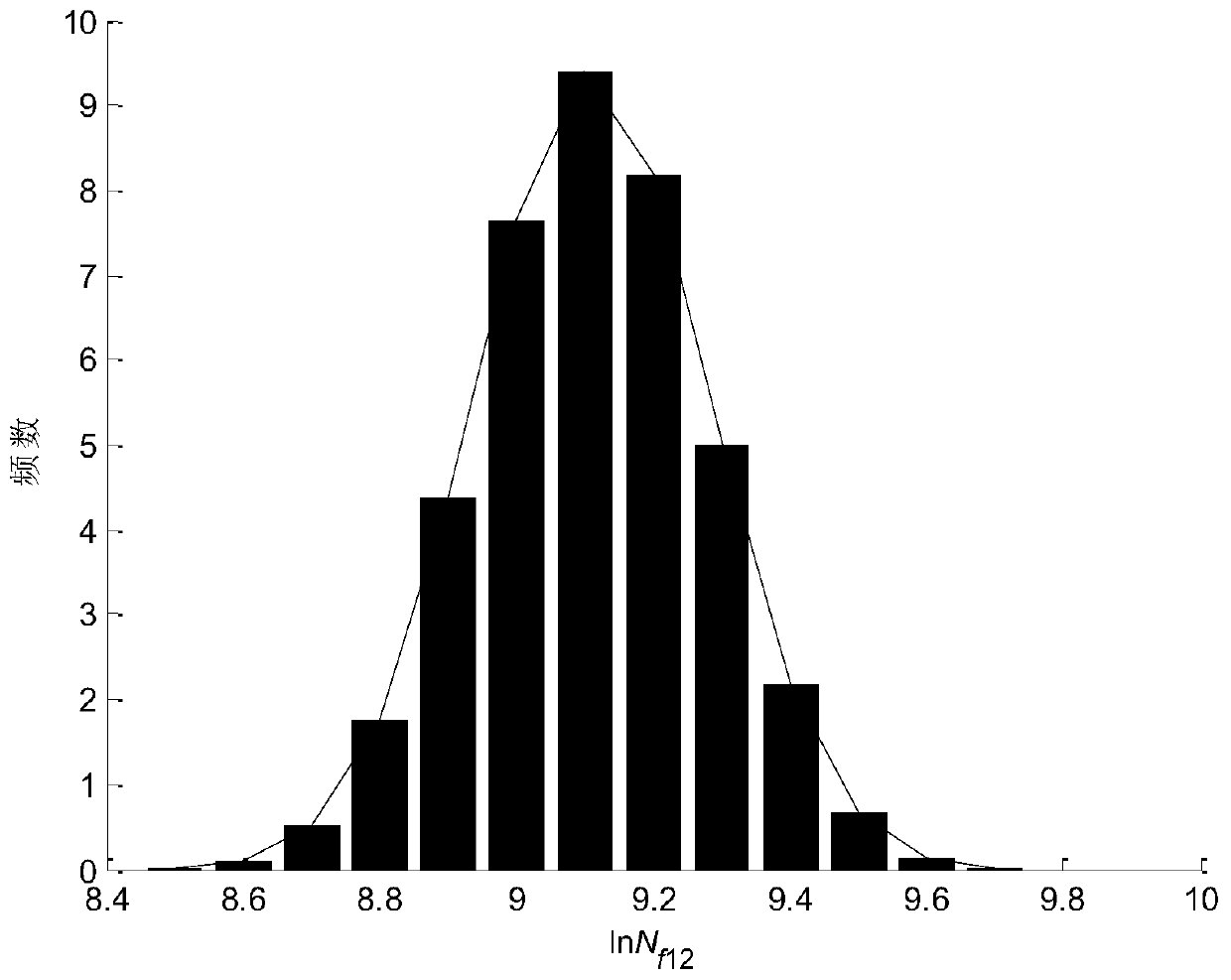
Turbine blade fatigue-creep damage coupling probability life prediction calculation method
InactiveCN110175394AHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageTurbine blade
The invention discloses a turbine blade fatigue-creep damage coupling probability life prediction calculation method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, collecting the turbine blade attributes; S2, determining an examination part; S3, performing finite element simulation on the turbine blade to obtain the turbine blade examination point stress strain information; S4, calculating fatigue damage, calculating the fatigue life and the fatigue damage information through a low-cycle fatigue life model; S5, calculating the creep damage, calculating the creep life and the creep damage information through a creep life model; S6, calculating the total damage and carrying out life distribution fitting; and S7, on the basis of the cumulative damage theory, obtaining the final probabilitylife distribution of the blade in combination with various working condition life information. According to the method, the uncertainty factors caused by the material performance, the load history, the geometric dimension, the prediction model error and the like of the turbine blade are represented by the probability, the service life of the turbine blade is predicted by using the probability service life prediction model, and the precision of the turbine blade service life prediction can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fatigue Life Estimation Method and System
ActiveUS20120053858A1Low cycle fatigueRobust and reliable determinationVehicle testingPlug gaugesEstimation methodsEngineering
A method to estimate the fatigue life of a component operable under cyclic stress is provided. A system including testing means for performing a strain controlled test of a component or a representative specimen of the component, to obtain therefrom a first set of data samples including measured stress amplitude values for varying applied strain levels, and a second set of data samples including measured number of cycles to crack initiation for varying applied strain levels is also provided. The system further includes a modeling means for fitting a first low cycle fatigue material curve on the first set of data samples and a second low cycle fatigue material curve on the second set of data samples.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Turbocharger including cast titanium compressor wheel
InactiveUS20080289332A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyComplex designPropellersReaction enginesImpellerWax
An air boost device such as a turbocharger, wherein the compressor wheel thereof is re-designed to permit die inserts (20), which occupy the air passage and define the blades (4, 5) during a process of forming a wax pattern (21) of a compressor wheel, to be pulled without being impeded by the blades. This modified blade design enables the automated production of wax patterns (21) using simplified tooling. The compressor wheel improves low cycle fatigue, withstands high temperatures and temperature changes, and permits operation at high boost pressure ratio while, on the other hand, having low weight, low inertial drag, and high responsiveness.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
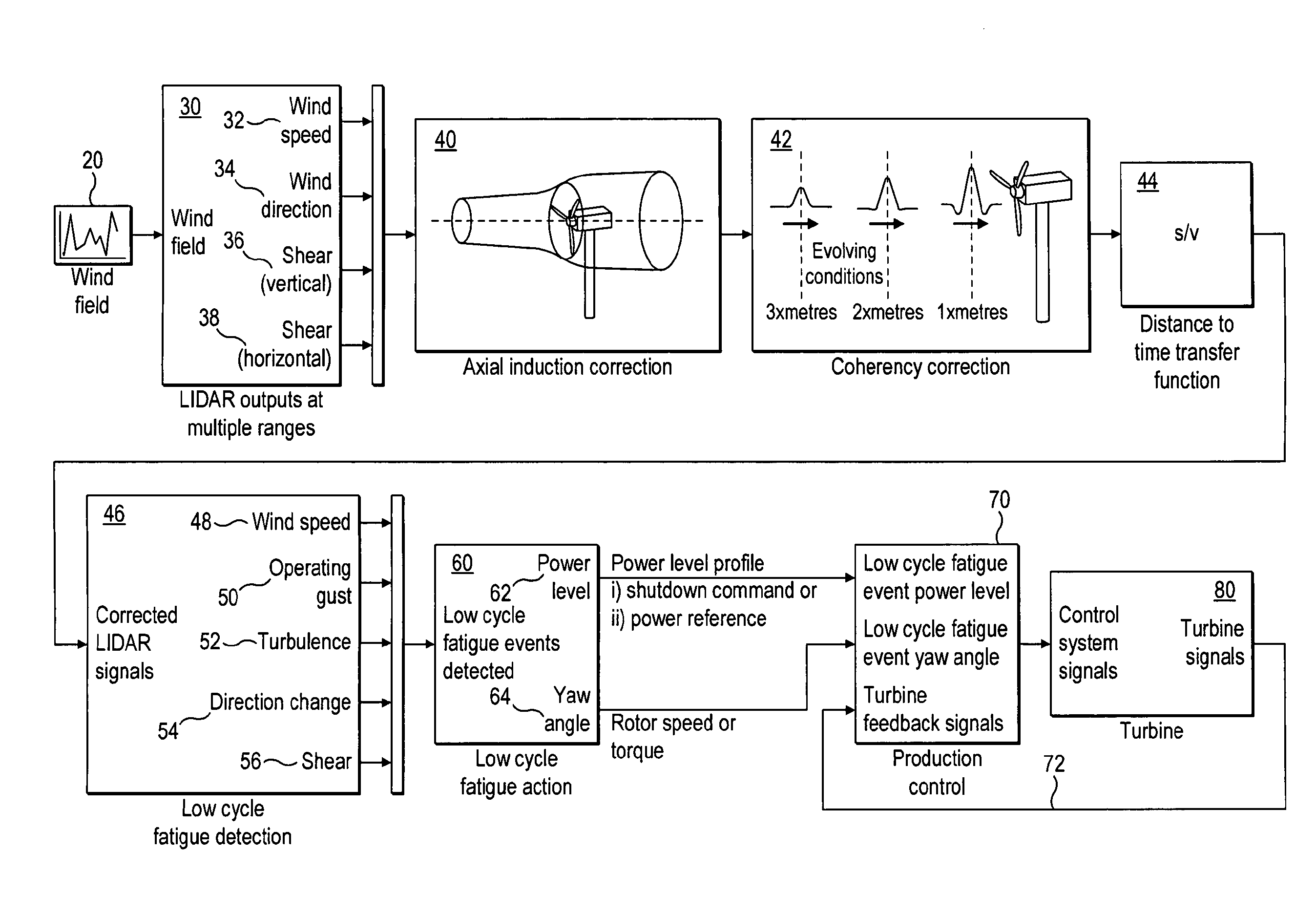
Method and apparatus for protecting wind turbines from fatigue damage
ActiveUS8928164B2Enough can be detectedCatastrophic effectWind motor controlEngine fuctionsFatigue damageNacelle
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method of manufacture of a dual alloy impeller
InactiveUS20100215978A1Promote oxidationHigh strengthTurbinesPump componentsLow-cycle fatigueMaterials science
There is provided a method for fabricating a dual alloy structure that may in turn be machined to fabricate a rotary component for use in a gas turbine engine. The method provides a powder metal (PM) nickel based superalloy and a nickel aluminide intermetallic based alloy. The powder metal (PM) nickel based superalloy displays characteristics, such as improved strength, low cycle fatigue resistance, fracture toughness, and crack growth resistance. The nickel aluminide intermetallic based alloy displays characteristics, such as high temperature creep and oxidation resistance, suitable for use in the outer radial area of an impeller. A bore sub-element is fabricated from the powder metal (PM) nickel based superalloy. A body sub-element is fabricated from the nickel aluminide intermetallic based alloy. The bore sub-element and body sub-element are joined by inertia welding or diffusion bonding at a common mating surface.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Nickel alloy and method of direct aging heat treatment
Embodiments of the present disclosure relate to nickel-base alloys and methods of direct aging nickel-base alloys. More specifically, certain embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods of direct aging 718Plus< TM > nickel-base alloy to impart improved mechanical properties, such as, but not limited to, tensile strength, yield strength, low cycle fatigue, fatigue crack growth, and creep and rupture life to the alloys. Other embodiments of the present disclosure relate to direct aged 718Plus< TM >nickel-base alloy, and articles of manufacture made therefrom, having improved mechanical properties, such as, but not limited to, tensile strength, yield strength, low cycle fatigue, fatigue crack growth, and creep and rupture life.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES
Compressor rotor and method for making
ActiveUS7370787B2Improved property and performanceIncrease pressurePump componentsBlade accessoriesTitaniumProcess engineering
A method an apparatus for a gas turbine compressor rotor is provided which offers improved characteristics to the rotor when used with at least titanium IMI 834. Mechanical work is optimized through forging to provide at least improved low cycle fatigue life to the part.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
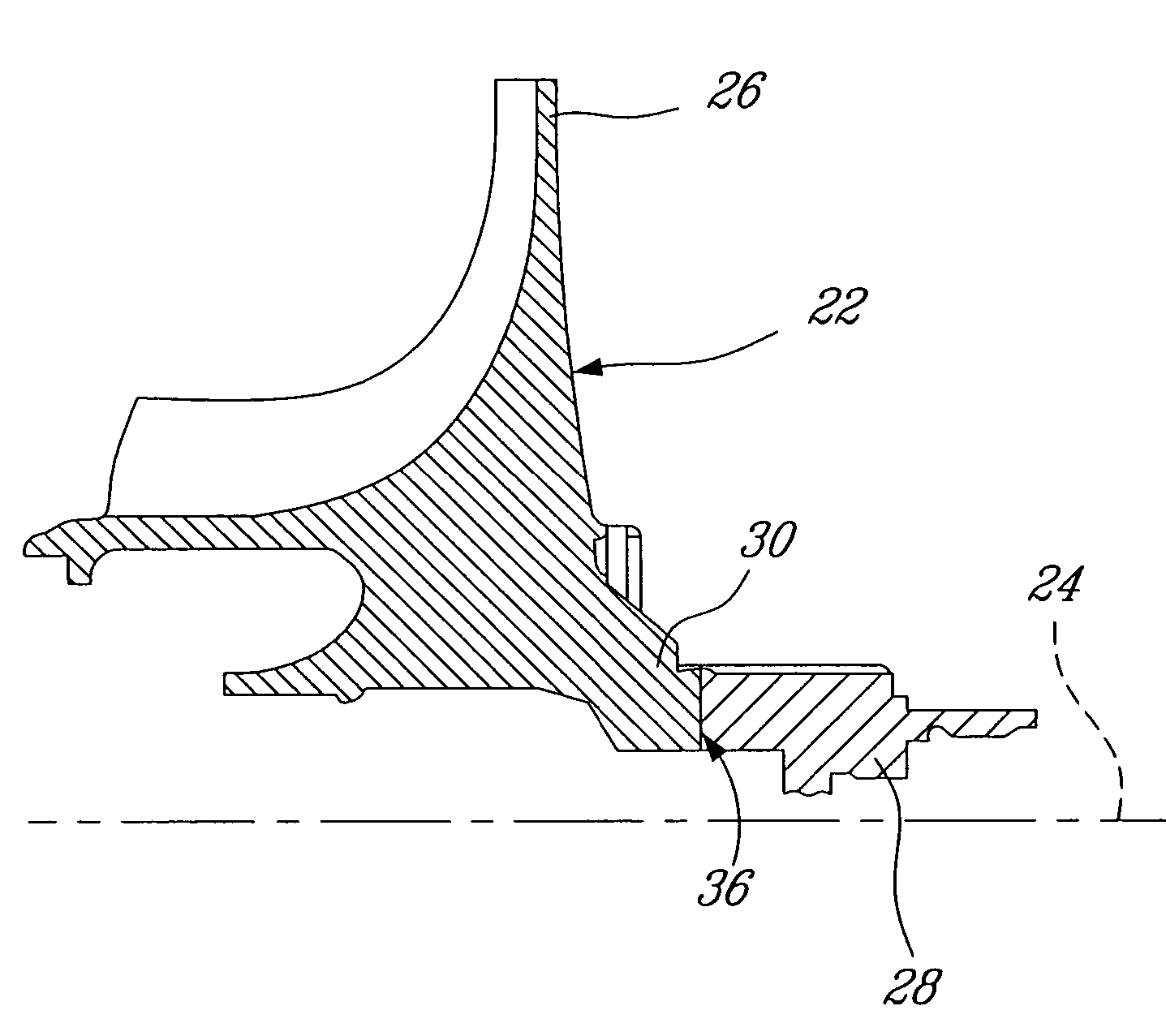
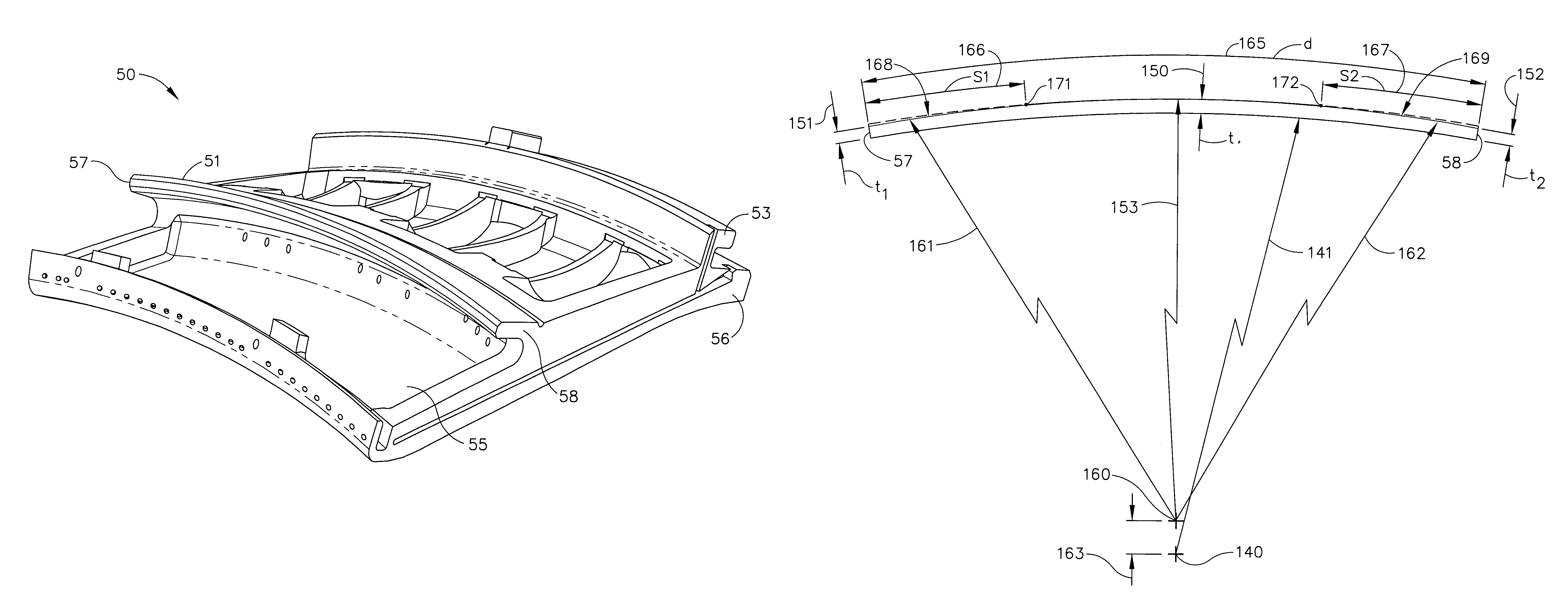
Cantilevered nozzle with crowned flange to improve outer band low cycle fatigue
A flange for supporting arcuate components comprising at least one arcuate rail, each arcuate rail having an inner radius, a first taper location, a first taper region, a second taper location, a second taper region, wherein the thickness of at least a portion of the first taper region is tapered and wherein the thickness of at least a portion of the second taper region is tapered.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rhenium-free low-density high-performance nickel-based monocrystalline high-temperature alloy and heat treatment technology thereof
ActiveCN105200521ADurable cycle fatigue performanceDurable high temperature oxidation resistancePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsRheniumChemical composition
The invention discloses a rhenium-free low-density high-performance nickel-based monocrystalline high-temperature alloy and a heat treatment technology thereof, and belongs to the field of nickel-based monocrystalline high-temperature alloys. The alloy comprises 6.0-8.0wt% of Cr, 8.0-10.0wt% of Co, 6.0-9.0wt% of W, 1.0-3.0wt% of Mo, 0-2wt% of Nb, 3.0-6.0wt% of Al, 1.0-3.0wt% of Ti, 1.0-5.0wt% of Ta, 0.02-0.06wt% of C, 0.001-0.003wt% of B, 0-0.02wt% of Ce, 0-0.01wt% of Y and the balance Ni. The alloy has excellent low-temperature, middle-temperature and high-temperature strength and antioxidation performances, has lasting and low-cycle fatigue behavior the same to that of a second monocrystalline high temperature alloy CMSX-4 with Re content of 3wt%, does not contain a noble element Re, reduces an alloy cost by 70% or more and reduces alloy density by about 3%.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Characterization method of material fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life
ActiveCN107677547ASolid theoretical foundationSimplify the modeling processMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesModel implementationNon linear behavior
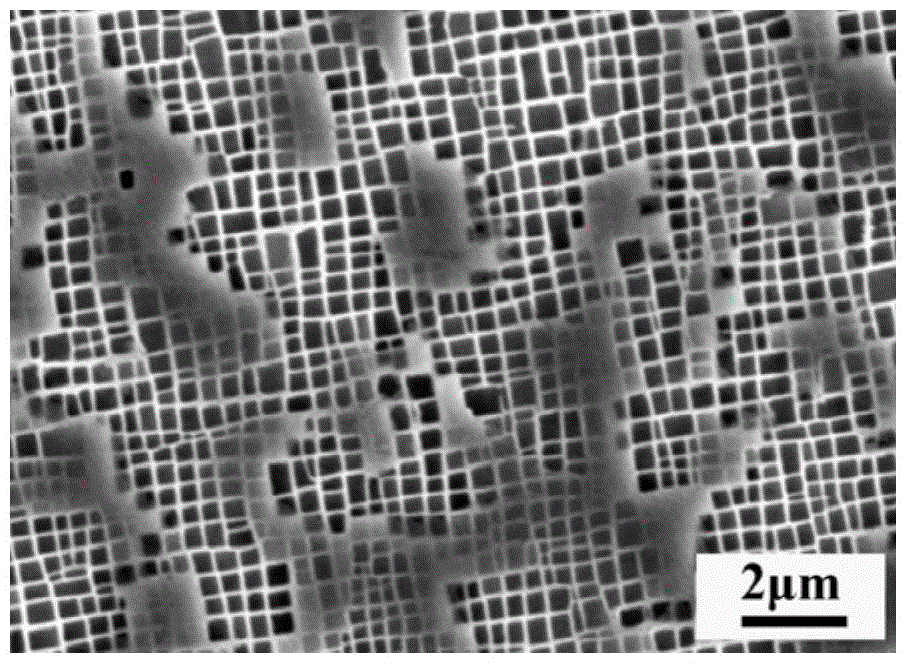
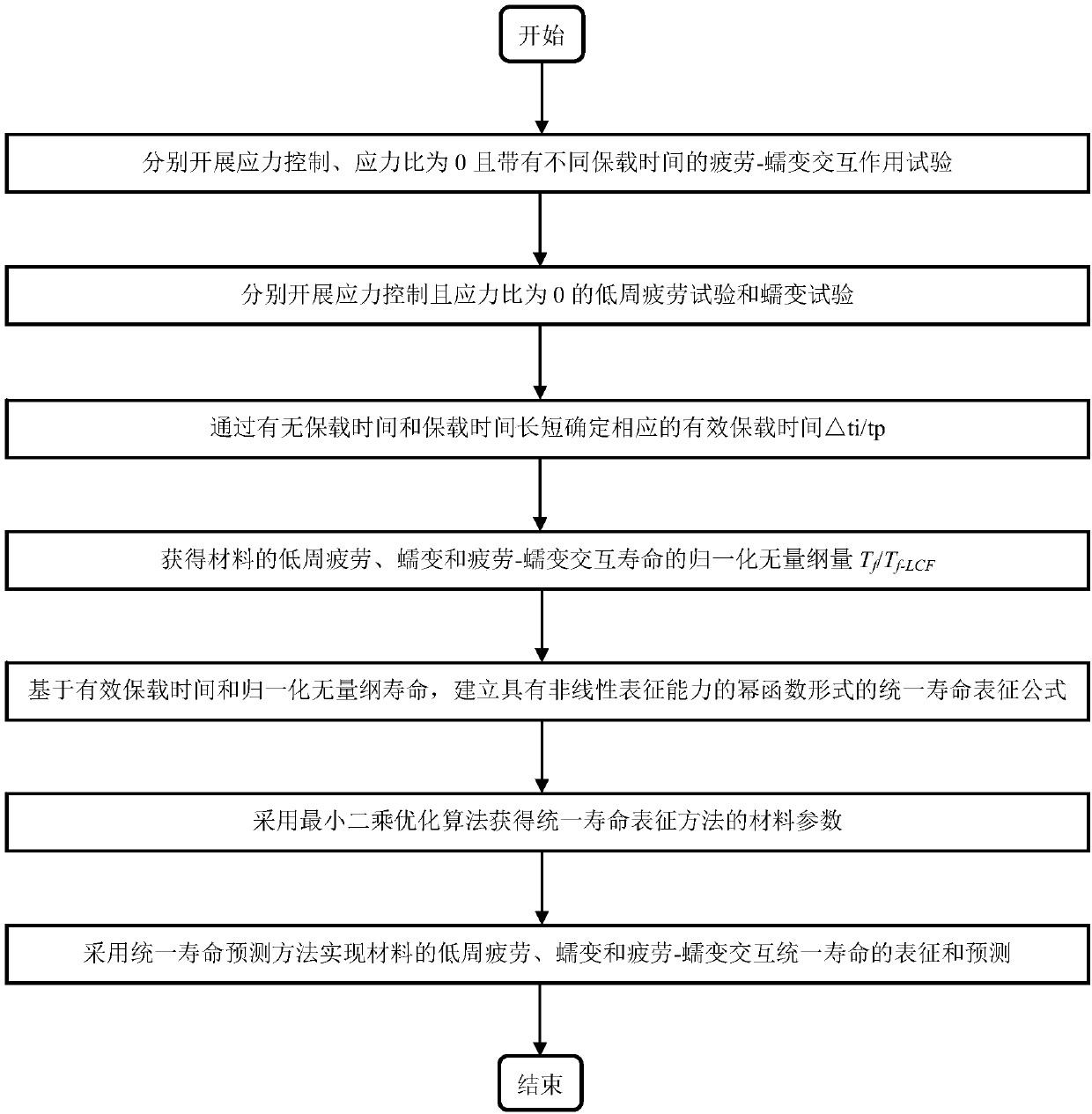
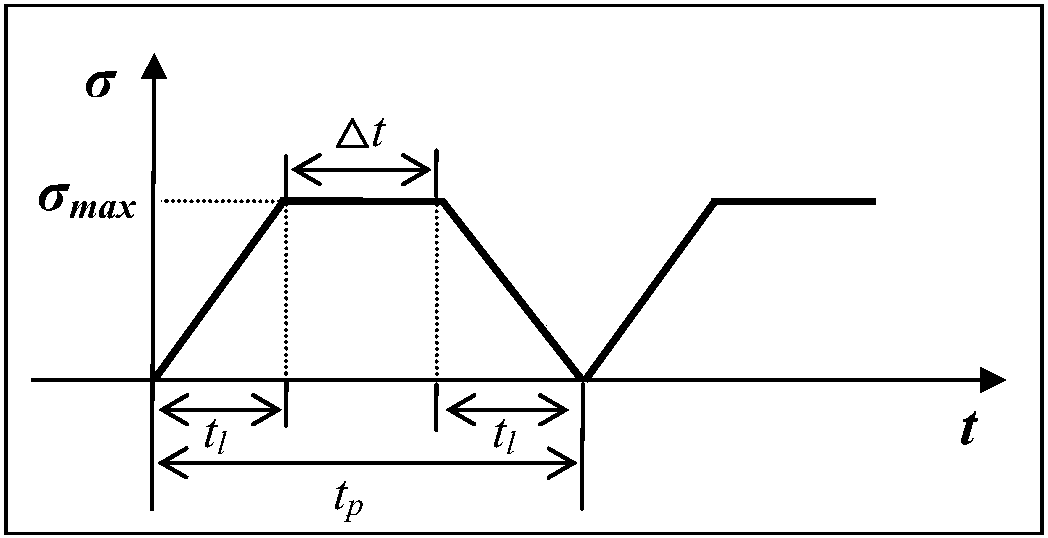
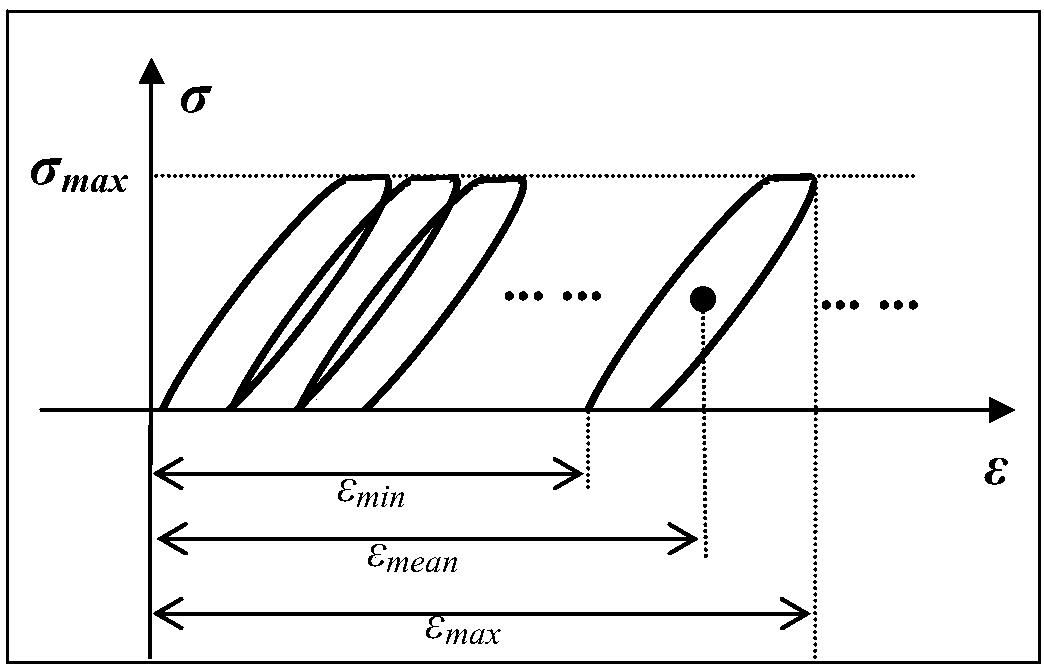
The invention discloses a characterization method of material fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life, and belongs to the field of service life prediction of aero-engine critical materials. The characterization method is used for solving service life characterization and prediction problems of materials under low cycle fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction conditions. According to the principles, a power function form service life prediction method non-linear behavior characterization capacity is established via fatigue-creep interaction, low cycle fatigue, and creeptests of materials at different holding time, and obtaining of effective holding time and normalization dimensionless service life via normalization calculation method. The characterization method iscapable of realizing accurate characterization of service life of materials under low cycle fatigue and fatigue-creep interaction conditions, and especially, consideration and accurate prediction ofcreep service life can be realized. The advantages of the characterization method are that consideration of both physical mechanisms and model implementation convenience is realized, and material lowcycle fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life characterization and prediction problems are solved effectively.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
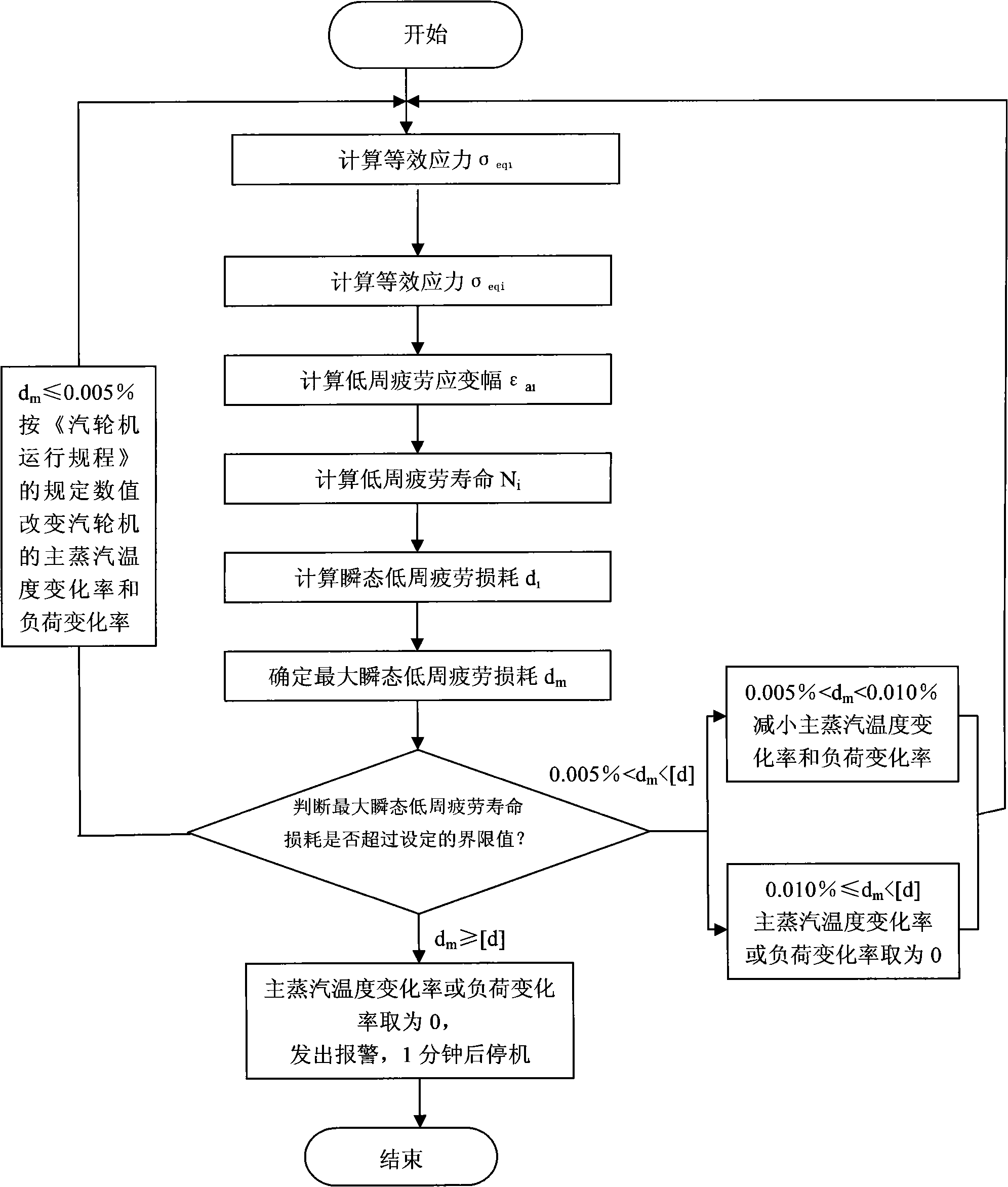
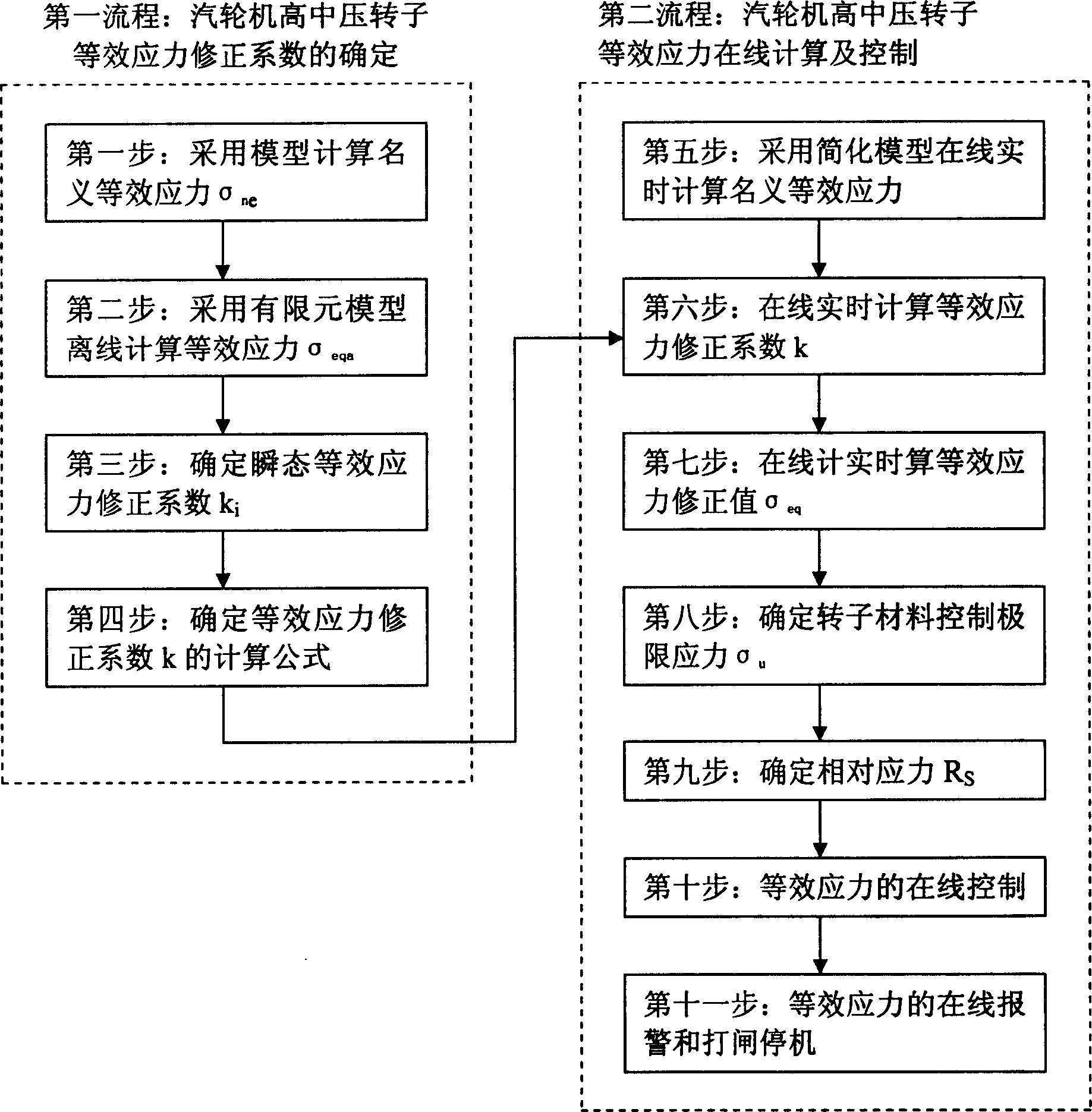
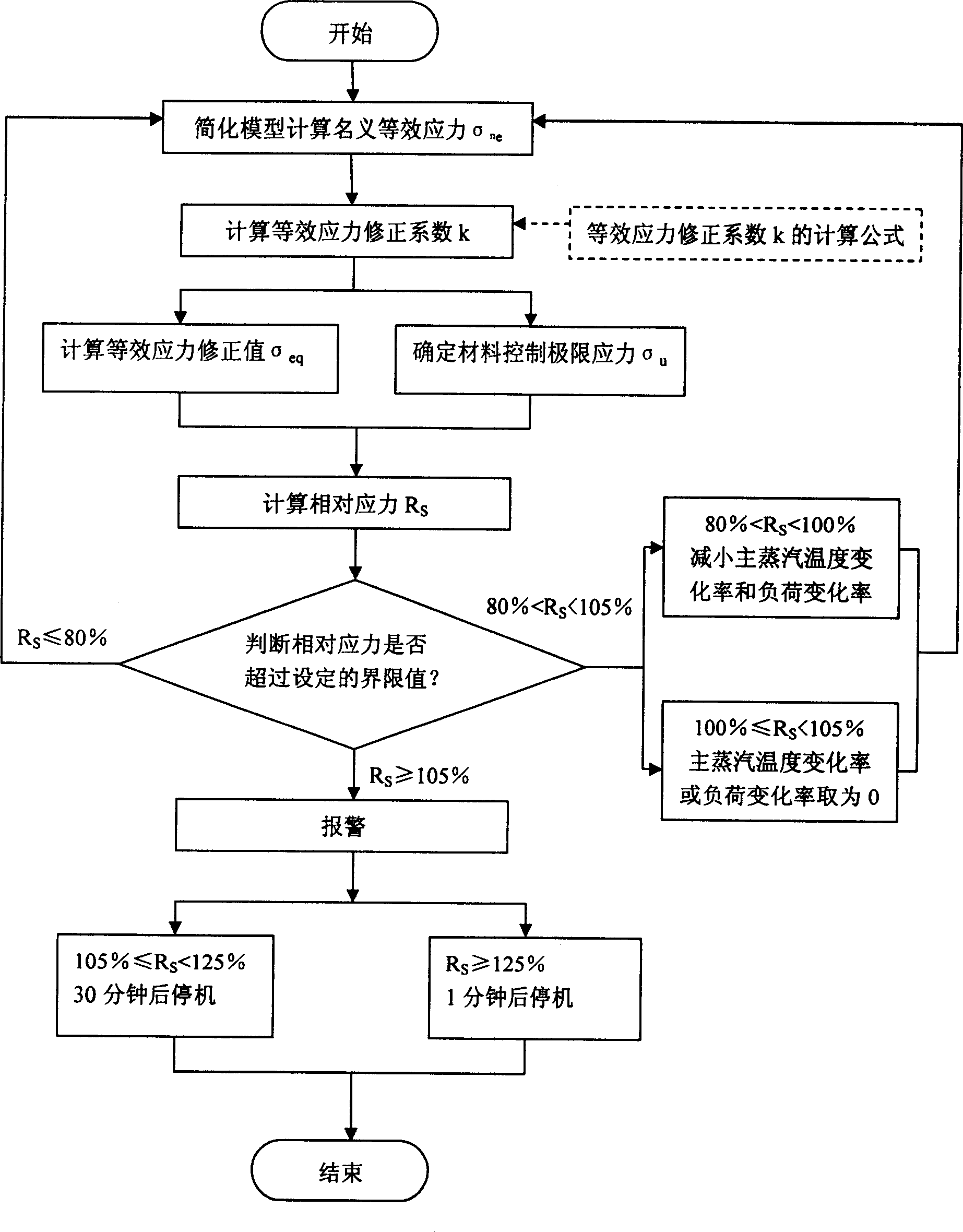
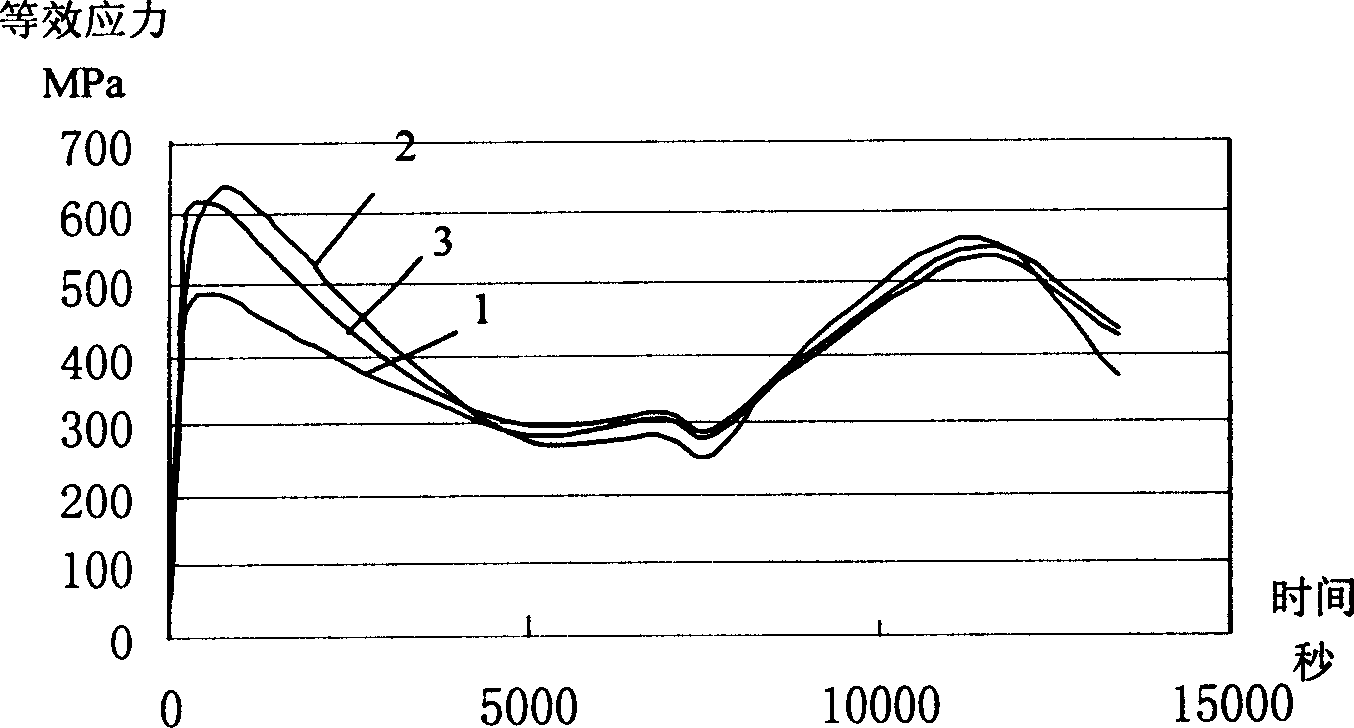
Online computing and controlling method for steam turbine high and medium pressure rotator equivalent stress
ActiveCN1908381AEasy to controlReduces low cycle fatigue life damageMachines/enginesSafety/regulatory devicesEngineeringTurbine
The invention relates to an online calculation-control method on the equivalent stress of the high-middle-pressure rotor of turbine, wherein if said factor is over preset value, it can online control the temperature change rate of main steam, and the load change rate to improve equivalent stress and prolong the service life. If the factor reaches the alarm value, it will alarm, and stop in preset time to control the equivalent stress and prolong the service life.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER EQUIP RES INST +1
In on or Relating to Rotating Machines
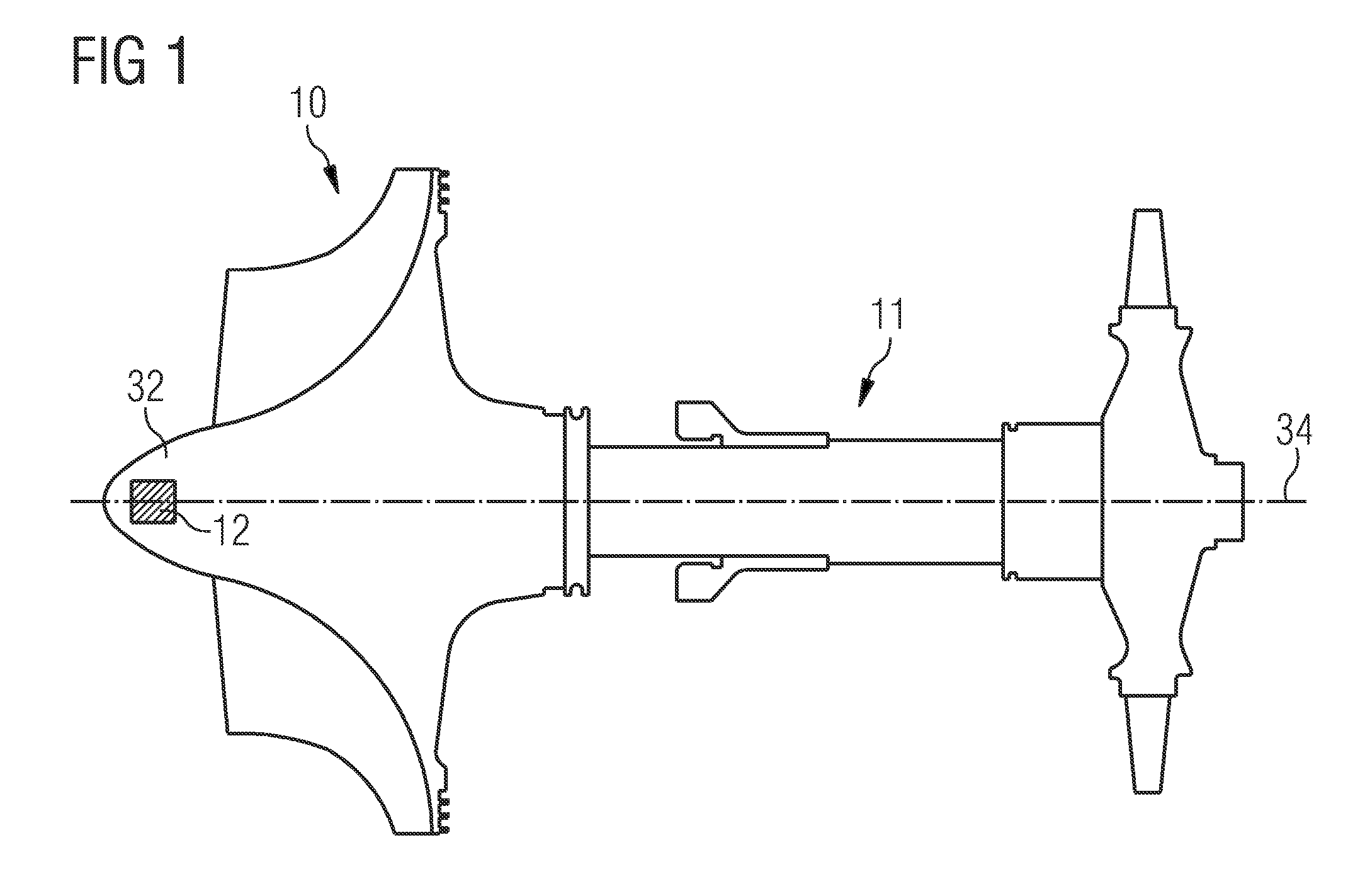
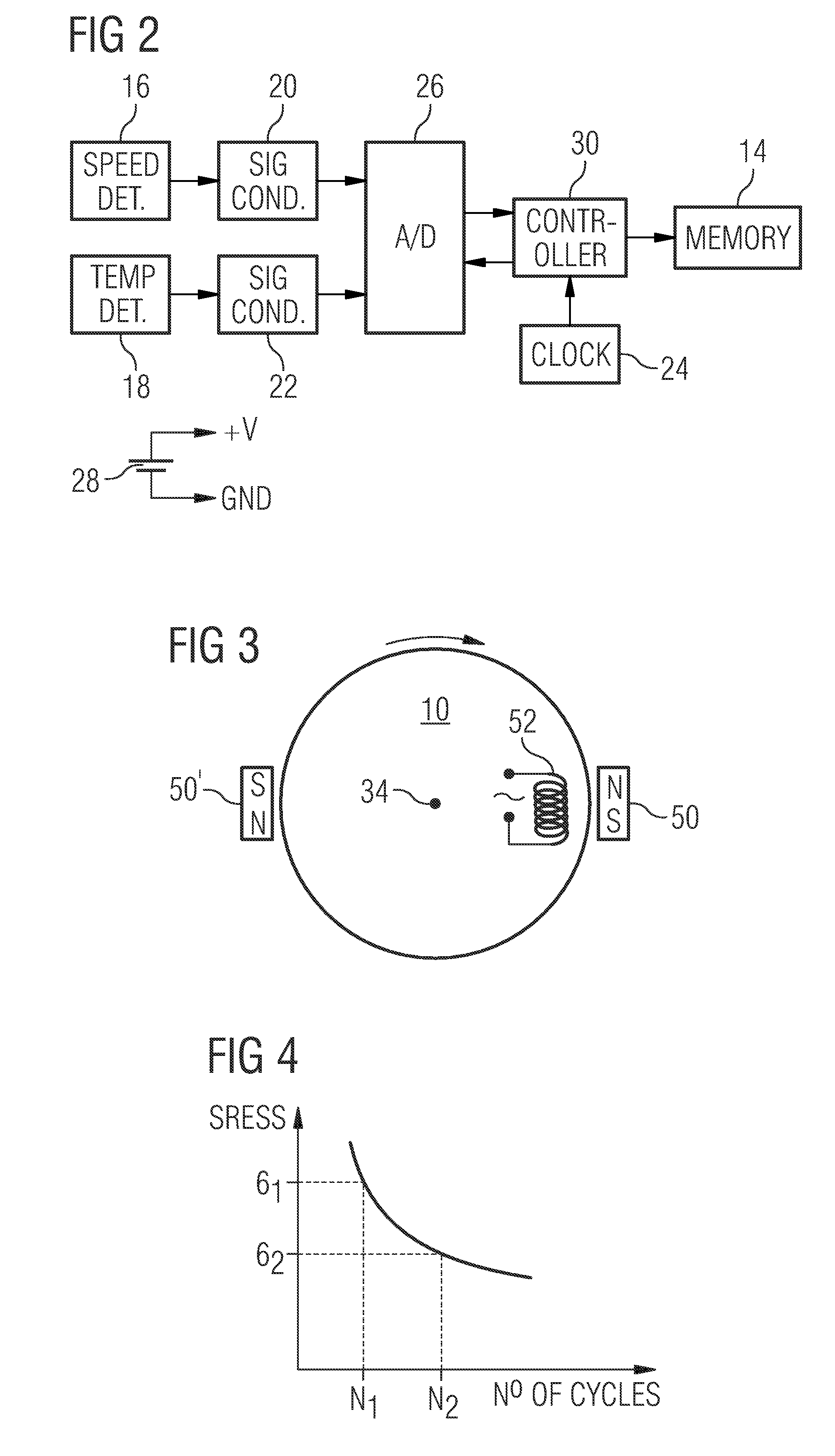
A rotating machine, has a rotary component, which includes a memory device for storing data relating to the past use of the component. The data are associated with rotational speed and ambient temperature, which are detected by detectors either on or off the rotary component. The stored data may be the raw temperature and speed data as sampled over time, which are then used to derive values of low-cycle fatigue and creep damage. These fatigue and creep values are, in turn, correlated with the load profiles of the component to arrive at a value of elapsed lifespan for the component. Alternatively, the stored data may be the fatigue and creep values and / or, preferably, values of elapsed and remaining lifespan of the component. In a second embodiment the detectors are located on the machine casing along with an evaluation unit.
Owner:WABTEC UK LTD
Usage Based Lifing
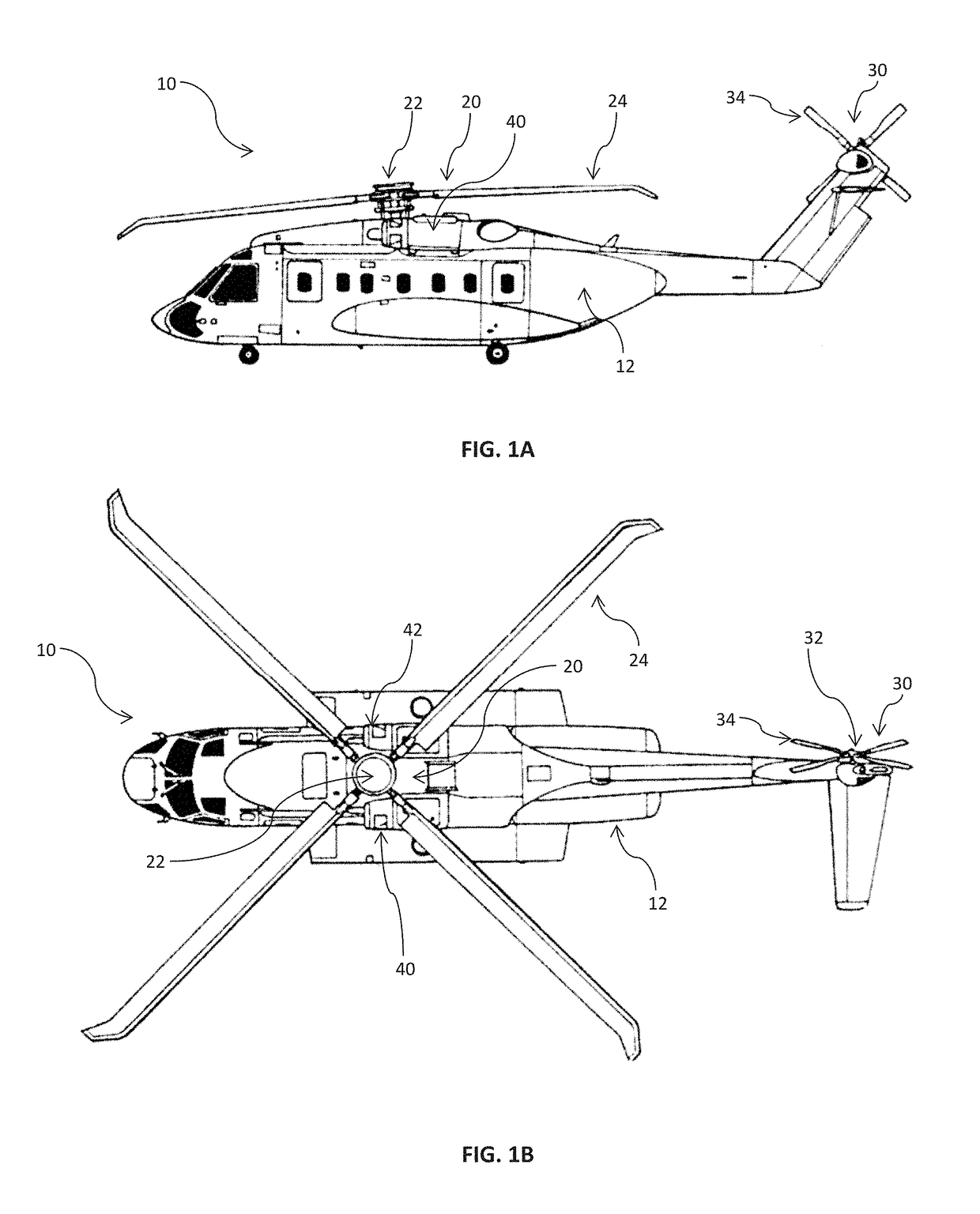
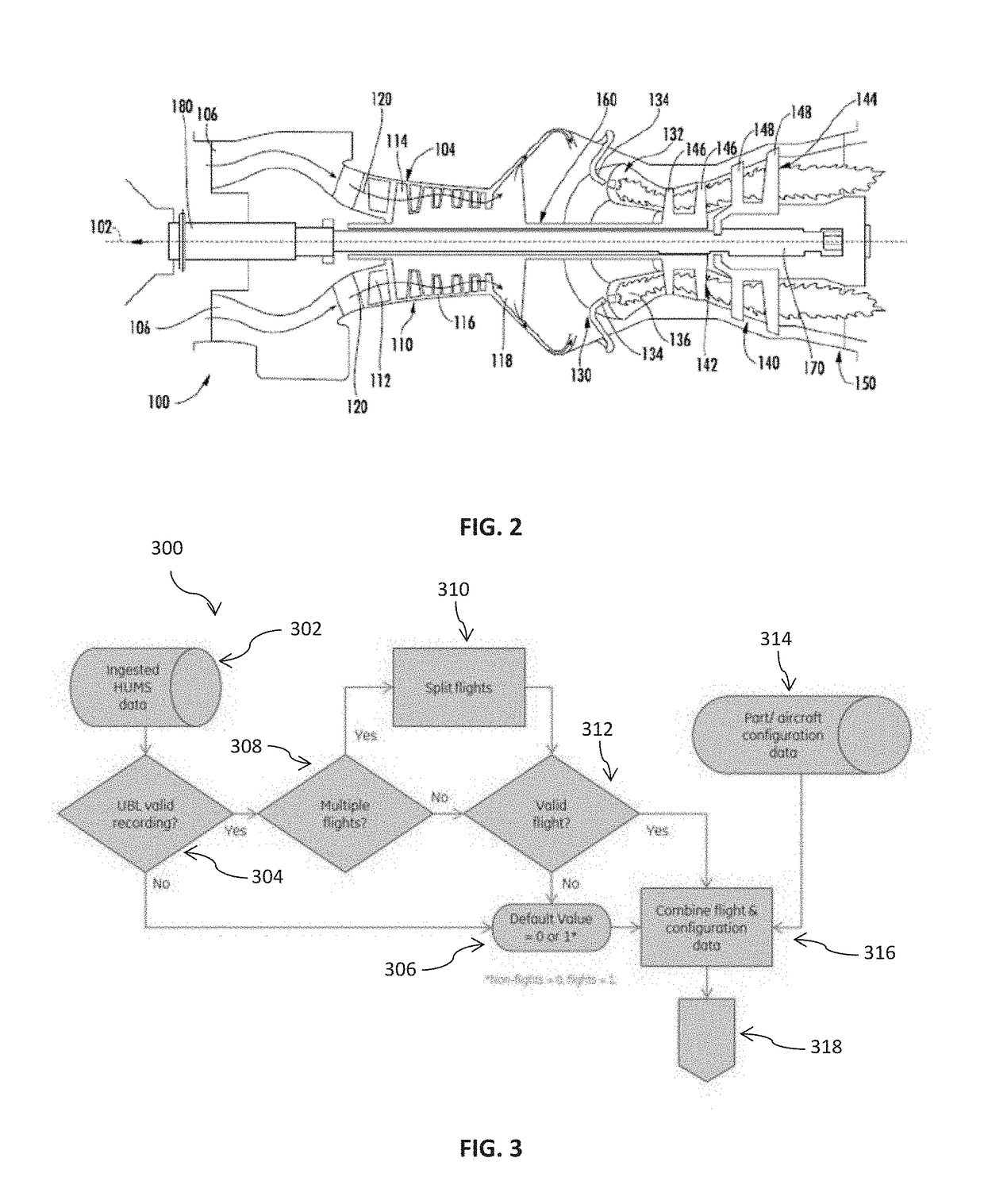
ActiveUS20180307784A1Geometric CADAircraft health monitoring devicesLow-cycle fatigueOperant conditioning
Systems and methods for predicting usage based lifing and low cycle fatigue consumption are provided. In one example embodiment, a method can include obtaining historical flight data associated with one or more gas turbine engines of an aerial vehicle; obtaining data indicative of one or more operational conditions of the aerial vehicle during an operating period; determining whether the flight data is indicative of a usable flight; and constructing a model correlating low cycle fatigue consumption with flight data using a machine learning technique.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com