Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Low cycle fatigue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
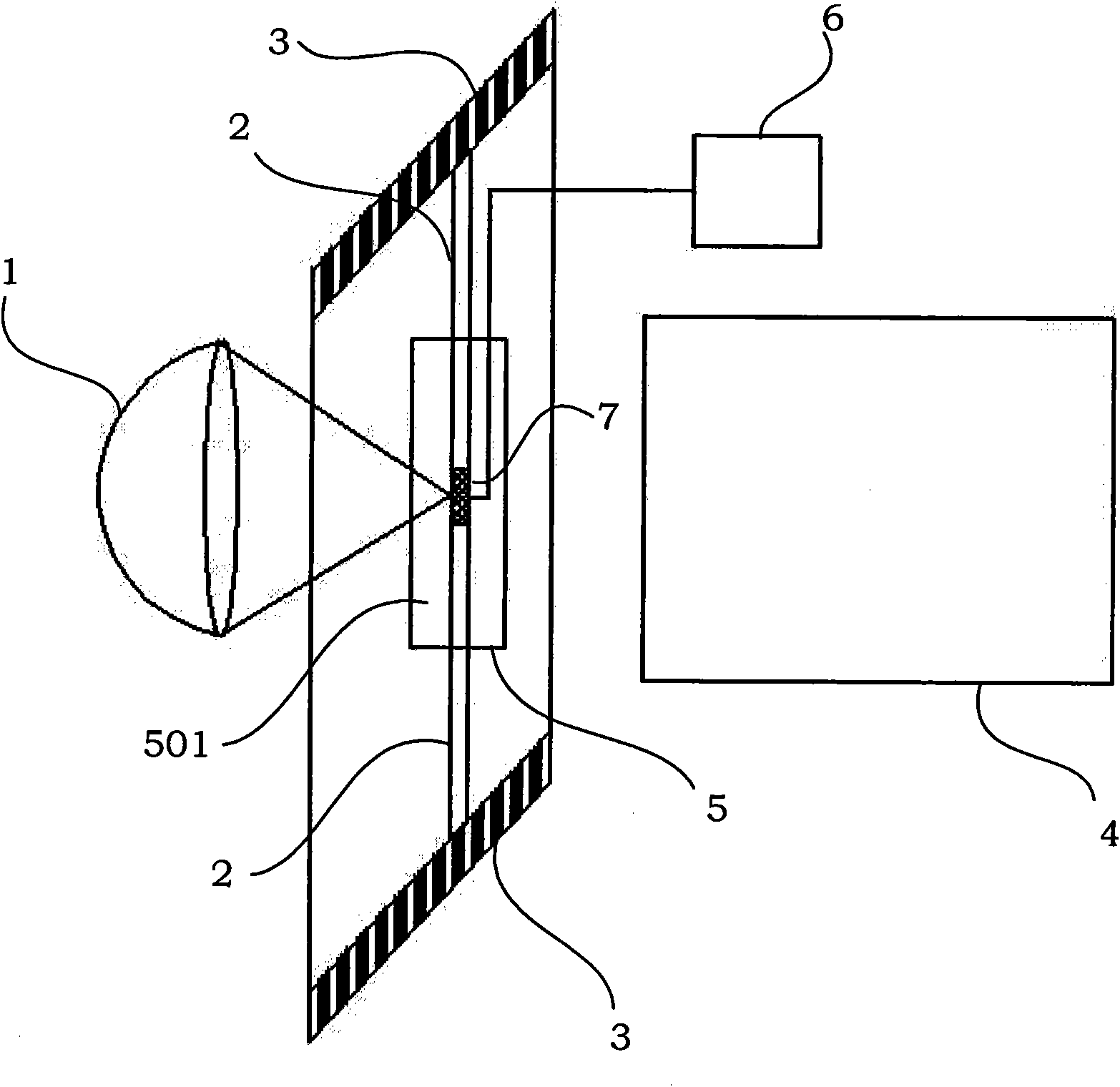
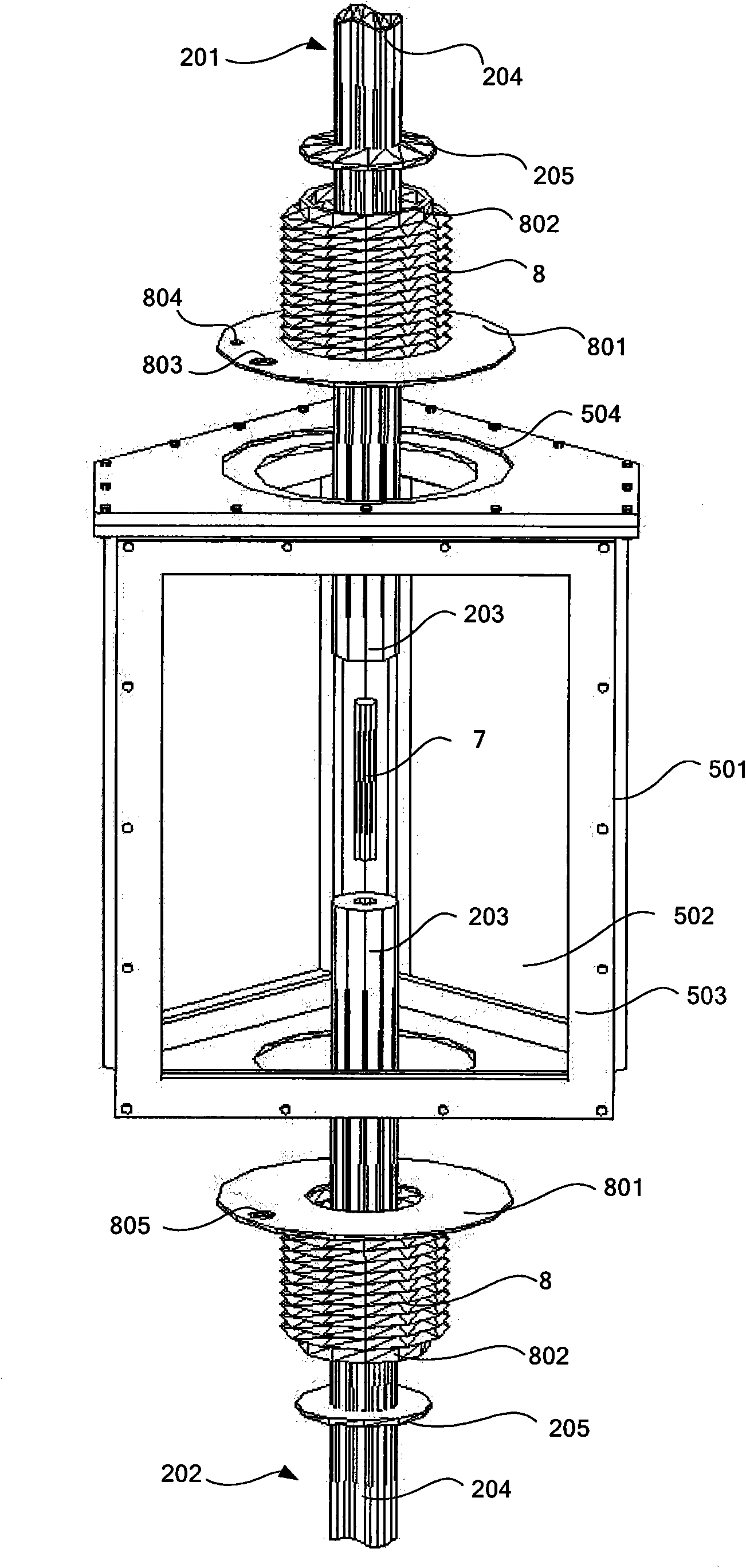
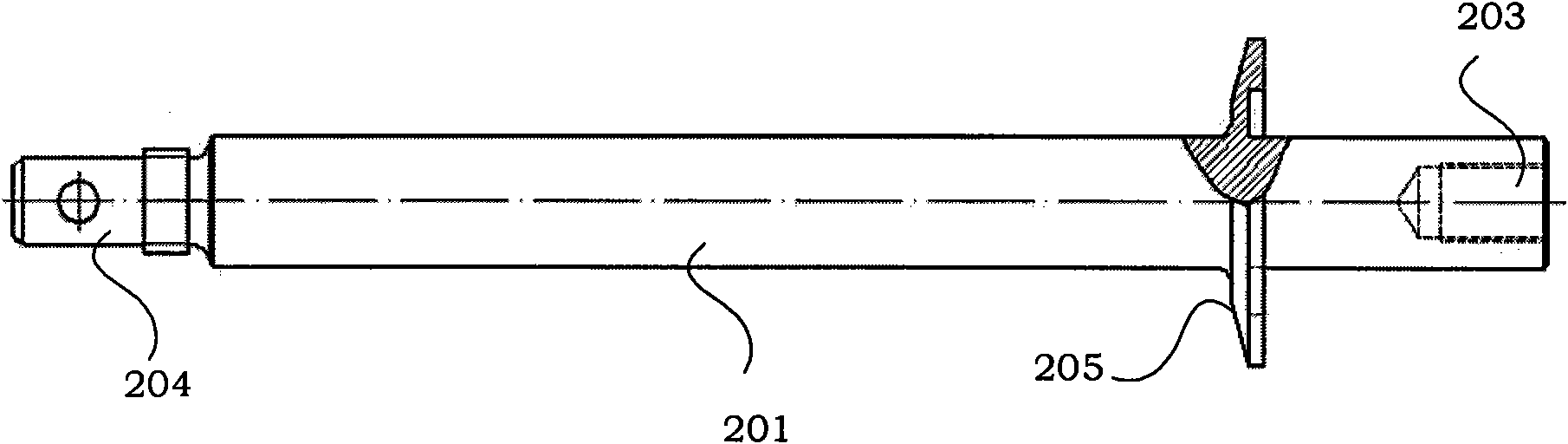
Test device for surface deformation and material and test method thereof
InactiveCN101672749AHeating up fastFast mechanical loadingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansOptical testStrength of materials
The invention discloses a test device for surface deformation of a material and a test method thereof, wherein the device comprises a material mechanical property test machine, an infrared fast heating device, a surface deformation optical test system, a temperature collecting device, a vacuum system and a clamp. The clamp fixes a sample in a vacuum chamber of the vacuum system and is connected with the material mechanical property test machine, the infrared fast heating device supplies thermal load for the sample, and the surface deformation optical test system measures the surface deformation of the sample. The device and the test method can simultaneously heat, apply stress and synchronously test deformation field in the surface. The coupling simulation of an aero-engine under service environment with high temperature and loading level, and the surface deformation condition of the structural material with high temperature under the environment are tested.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
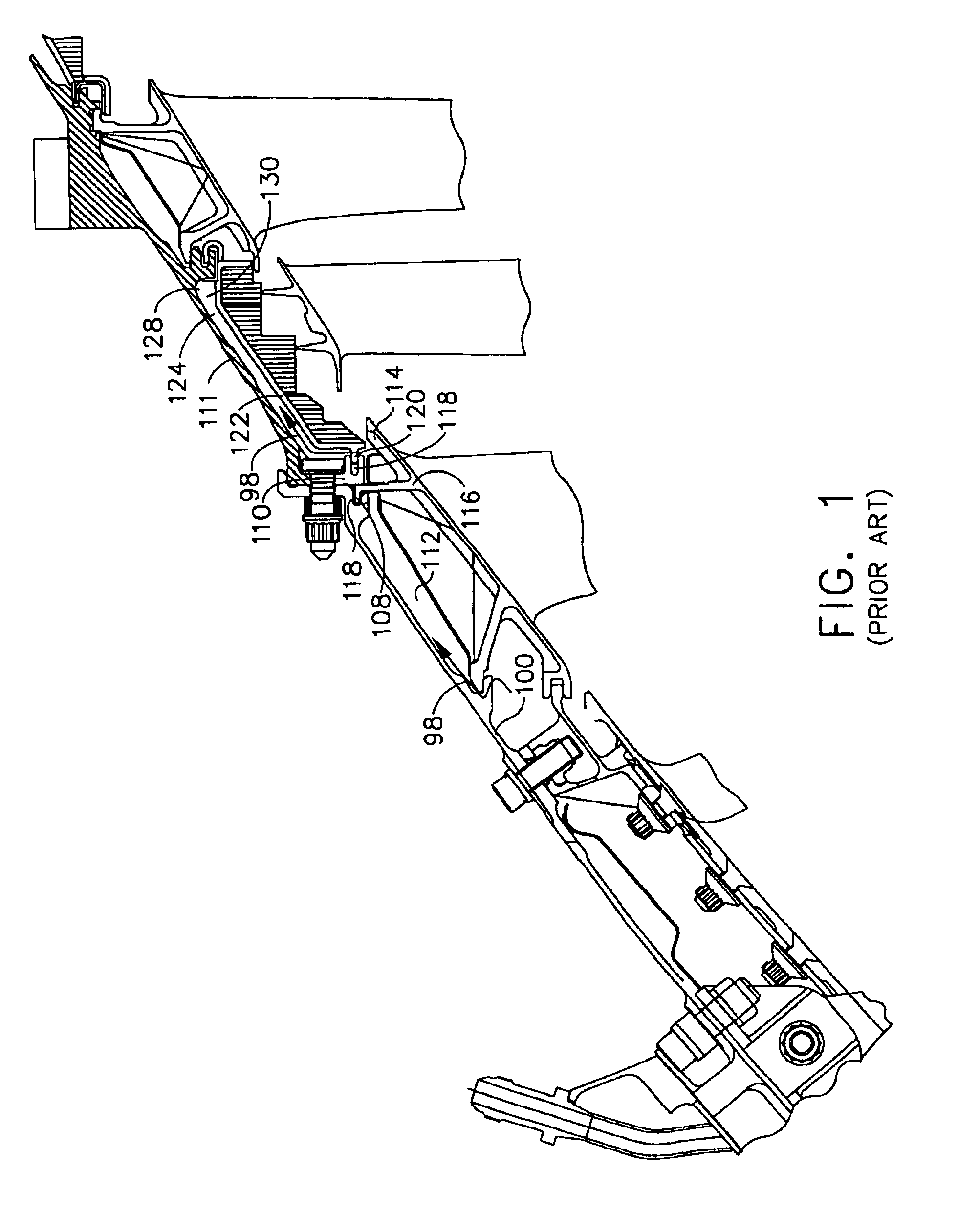
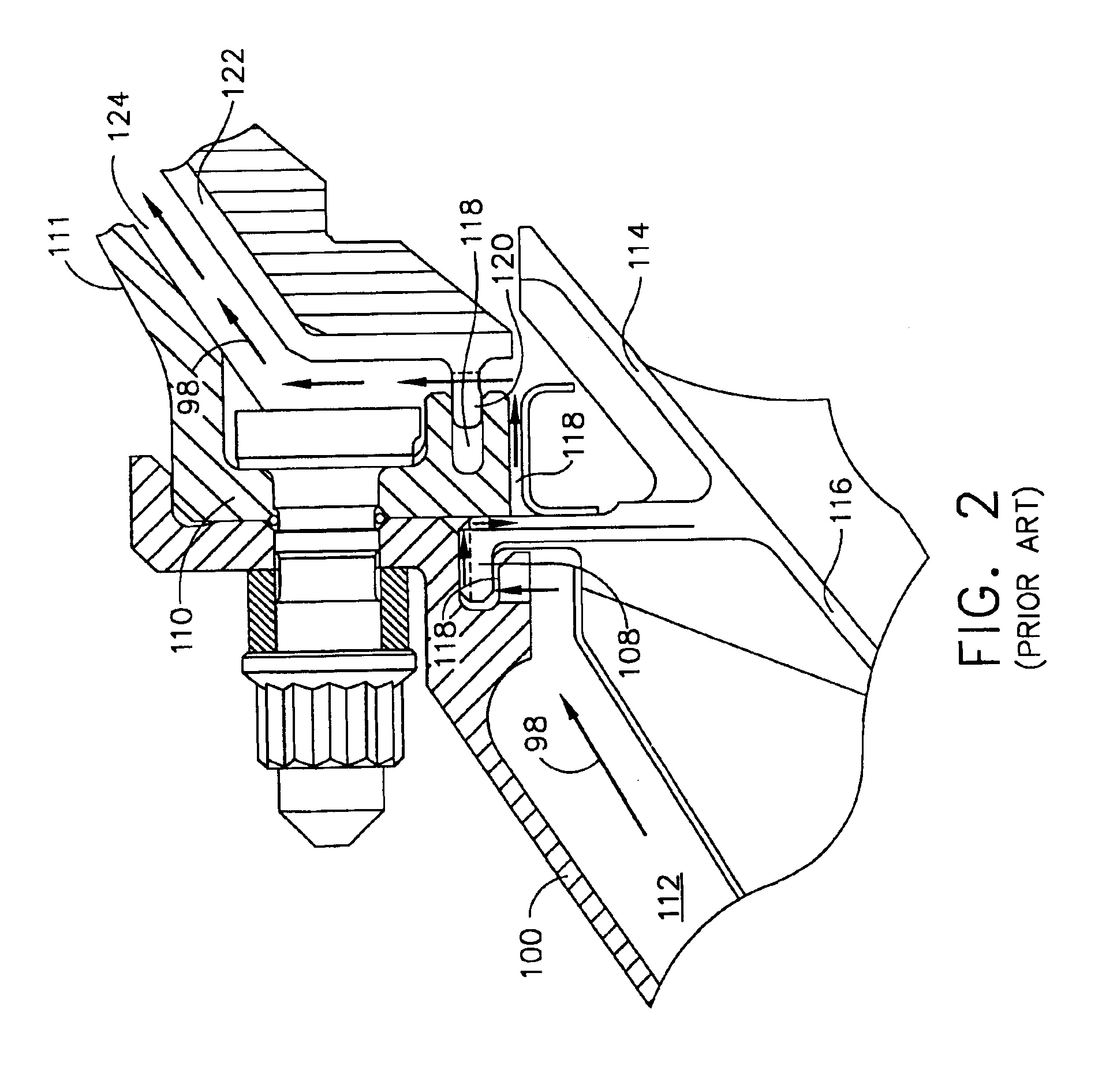
Internal low pressure turbine case cooling
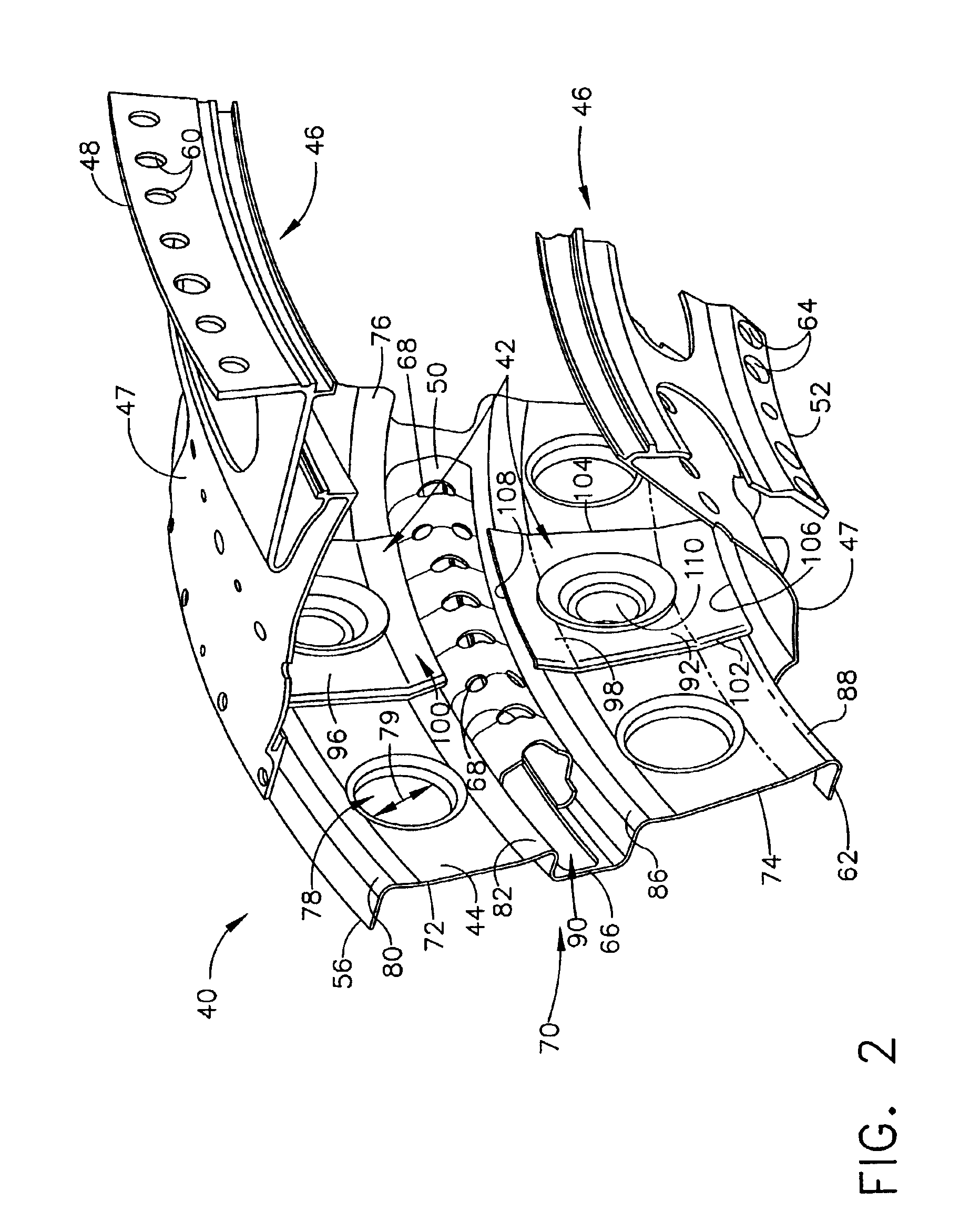
InactiveUS6902371B2Lower operating metal temperatureExtended service lifePump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingOblique angleTurbine
A low pressure turbine casing has a conical annular shell circumscribed about a centerline. A forward flange depends from a forward end of the annular shell and a forward hook extends aftwardly from the forward flange. First and second rails having first and second hooks, respectively, extend aftwardly from the annular shell. First and second cooling holes extend through the first and second rails, respectively. Cooling air feed holes extend through the forward flange. The first and second cooling holes may be radially disposed through the first and second rails, respectively, with respect to the centerline or disposed through the first and second rails at an oblique angle with respect to the centerline. A low pressure turbine casing and shroud assembly further includes a first annular cavity in fluid flow communication with the first cooling holes and the second cooling holes. A second annular cavity is in fluid flow communication with the first and second cooling holes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
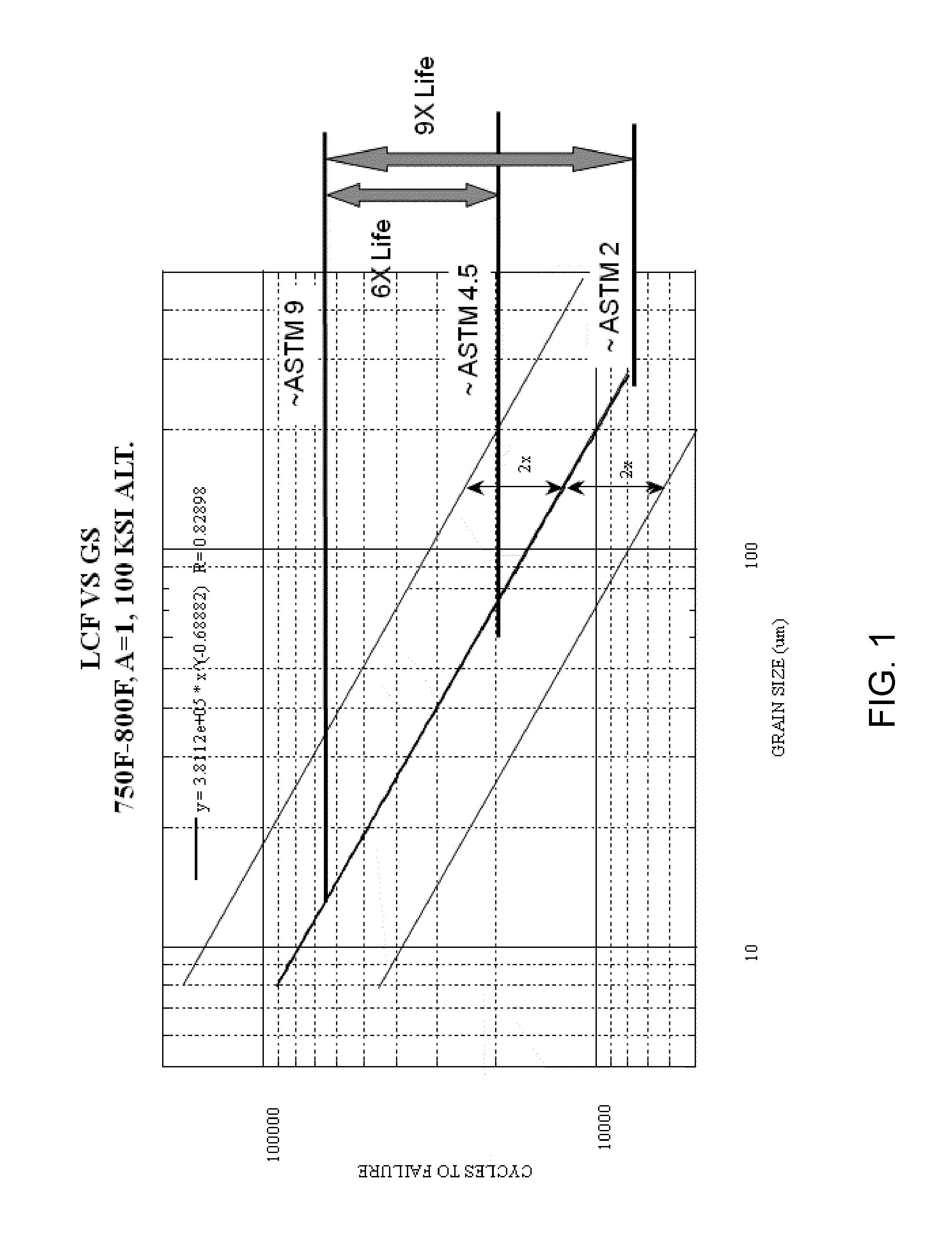
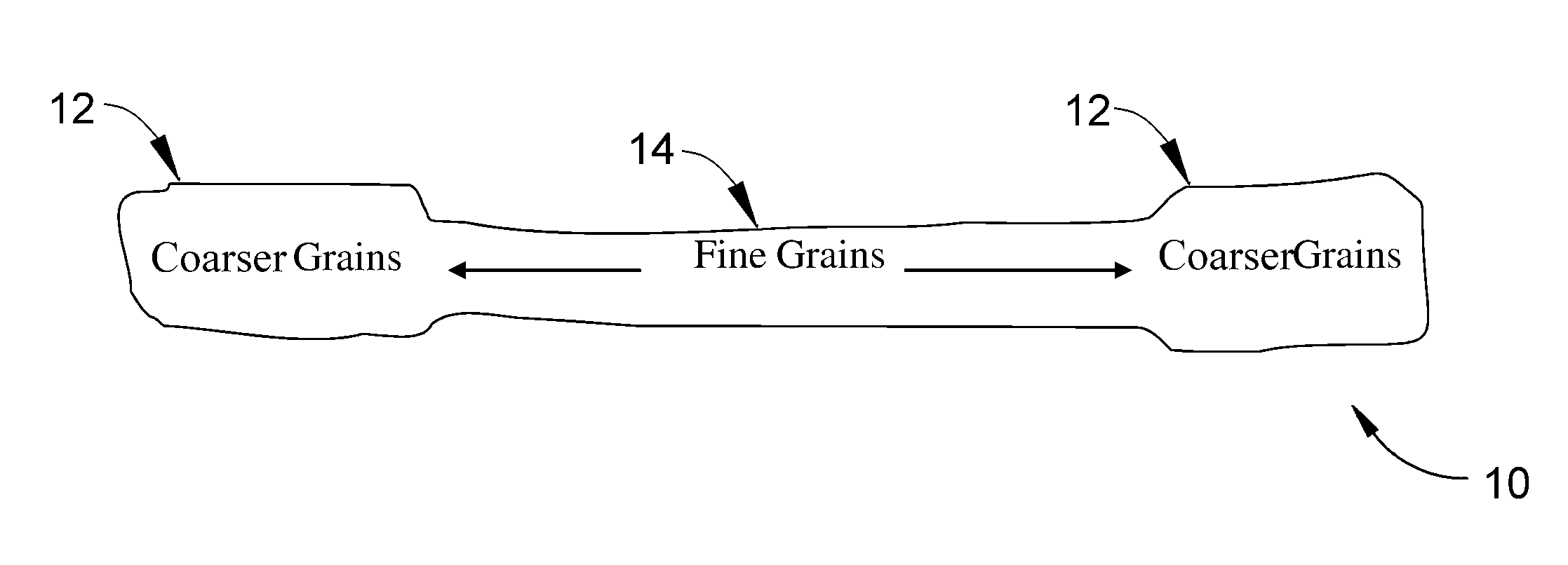
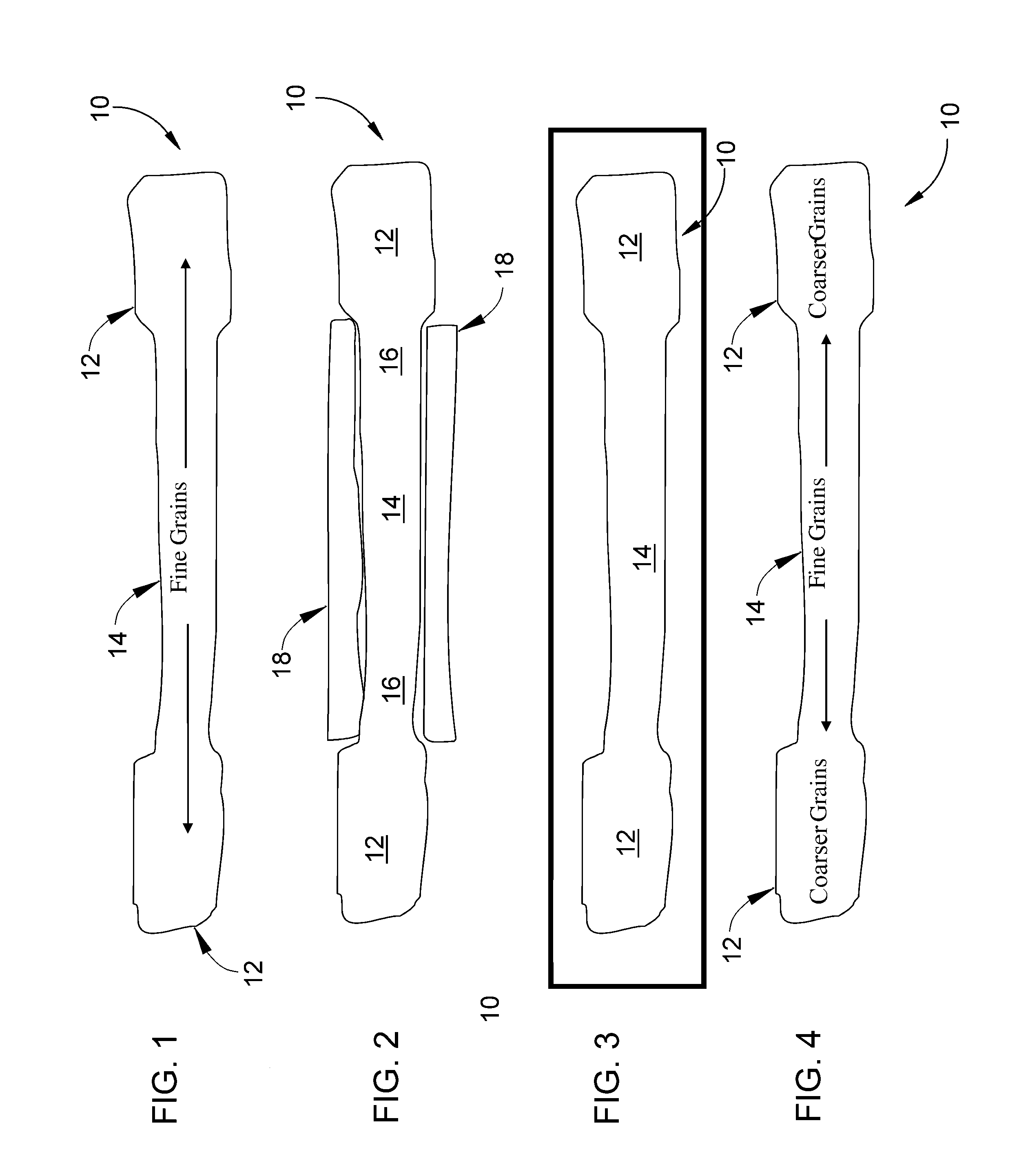
Method of controlling and refining final grain size in supersolvus heat treated nickel-base superalloys
InactiveUS20100329883A1Finer uniform grain sizeImproved low cycle fatigue behaviorPropellersEngine manufactureRheniumNiobium
A gamma prime precipitation-strengthened nickel-base superalloy and method of forging an article from the superalloy to promote a low cycle fatigue resistance and high temperature dwell behavior of the article. The superalloy has a composition of, by weight, 16.0-22.4% cobalt, 6.6-14.3% chromium, 2.6-4.8% aluminum, 2.4-4.6% titanium, 1.4-3.5% tantalum, 0.9-3.0% niobium, 1.9-4.0% tungsten, 1.9-3.9% molybdenum, 0.0-2.5% rhenium, greater than 0.05% carbon, at least 0.1% hafnium, 0.02-0.10% boron, 0.03-0.10% zirconium, the balance nickel and incidental impurities. A billet is formed of the superalloy and worked at a temperature below the gamma prime solvus temperature of the superalloy so as to form a worked article, which is then heat treated above the gamma prime solvus temperature of the superalloy to uniformly coarsen the grains of the article, after which the article is cooled to reprecipitate gamma prime. The article has an average grain size of not coarser than ASTM 7 and is substantially free of critical grain growth.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of controlling grain size in forged precipitation-strengthened alloys and components formed thereby
ActiveUS8679269B2Significant control of average grain sizeAvoid grain growthBlade accessoriesReaction enginesAlloyPrecipitation
Components and methods of processing such components from precipitation-strengthened alloys so that the components exhibit desirable grain sizes following a supersolvus heat treatment. The method includes consolidating a powder of the alloy to form a billet having an average grain size. The billet is then forged at a temperature below the solvus temperature to form a forging having an average grain size of not coarser than the grain size of the billet. The billet is then forged at a total strain of at least 5%, after which at least a portion of the forging is heat treated at a temperature below the solvus temperature to pin grains within the portion. The entire forging can then be heat treated at a temperature above the solvus temperature of the alloy without coarsening the grains in the portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
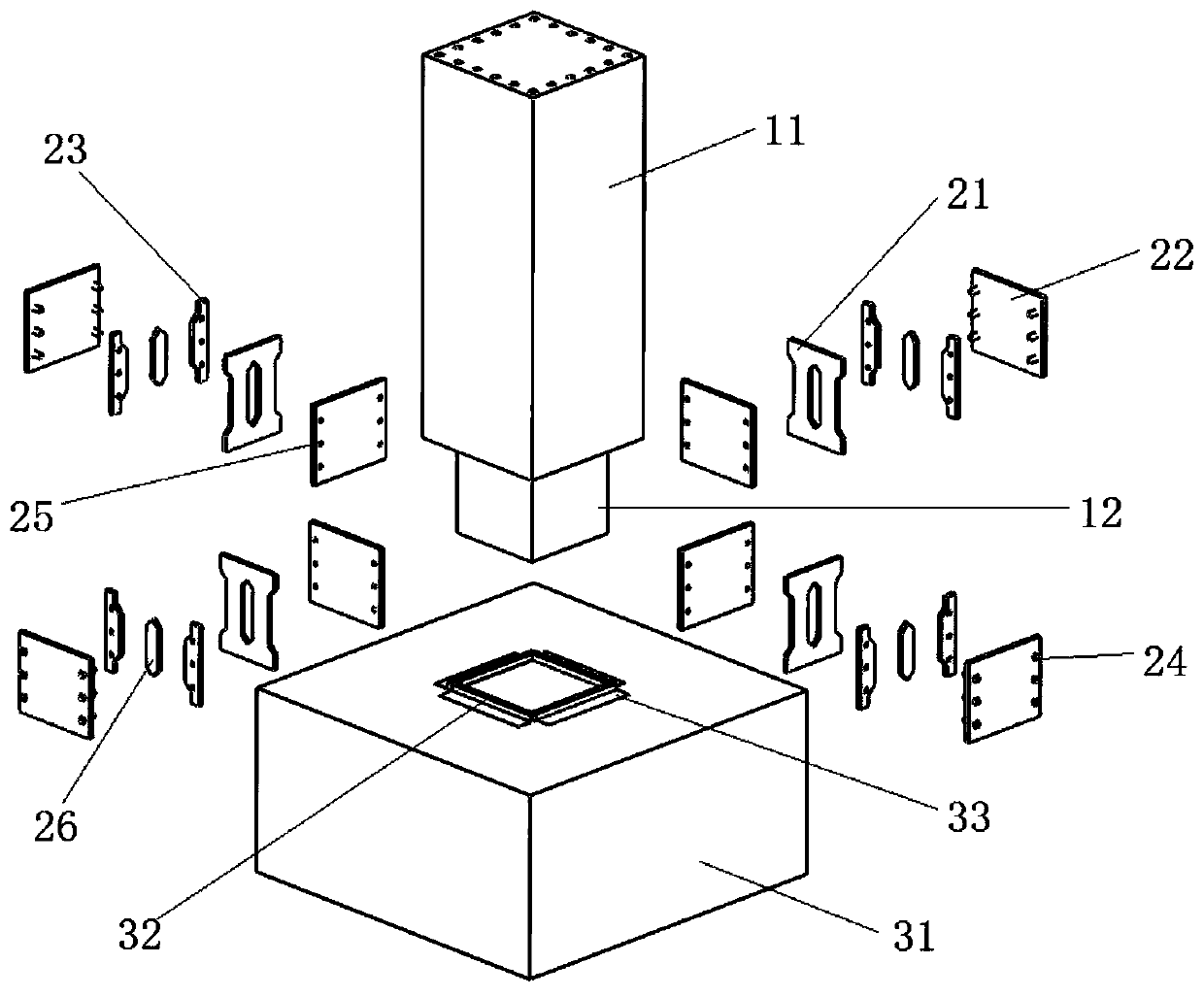
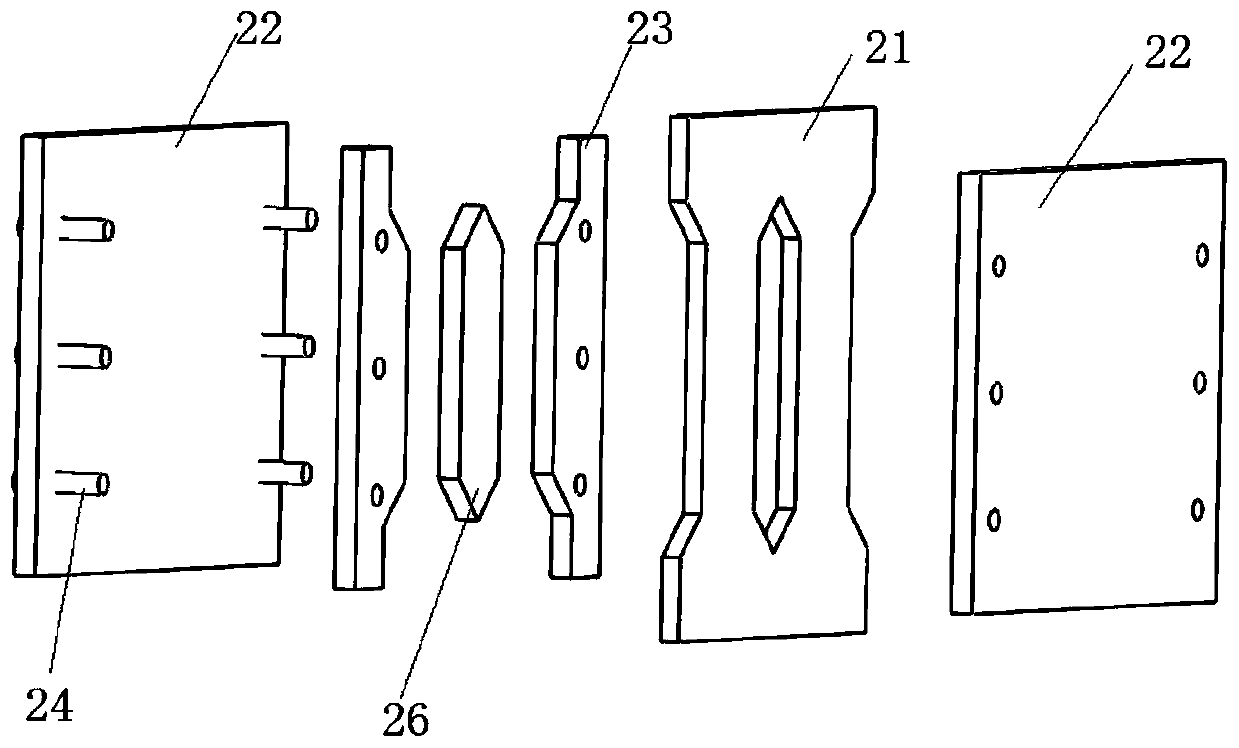
Concrete column base joint containing high-ductility replaceable energy-dissipation connecting assembly
PendingCN110359633AStructural stress division is clearClear division of laborStrutsProtective buildings/sheltersBottom pressurePre embedding
The invention discloses a concrete column base joint containing a high-ductility replaceable energy-dissipation connecting assembly. The concrete column base joint is arranged on the bottom of a rectangular-section column of a concrete structure, and comprises a concrete column, the high-ductility replaceable energy-dissipation connecting assembly and a concrete base, wherein the high-ductility replaceable energy-dissipation connecting assembly is separately welded with the concrete column and a steel connecting block pre-embedded in the concrete base to form a continuous reliable force transmission system. The bottom of the concrete column is equipped with a column bottom reinforcing core column, so that column bottom pressure can be borne under action of an earthquake, and damages are avoided; and the high-ductility replaceable energy-dissipation connecting assembly is mounted on four side surfaces of the column base joint, so that stressed longitudinal bars on the original positionsare replaced, and therefore, hysteretic behavior can be utilized to dissipate earthquake energy during a medium earthquake or a big earthquake, and damages can be controlled inside.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
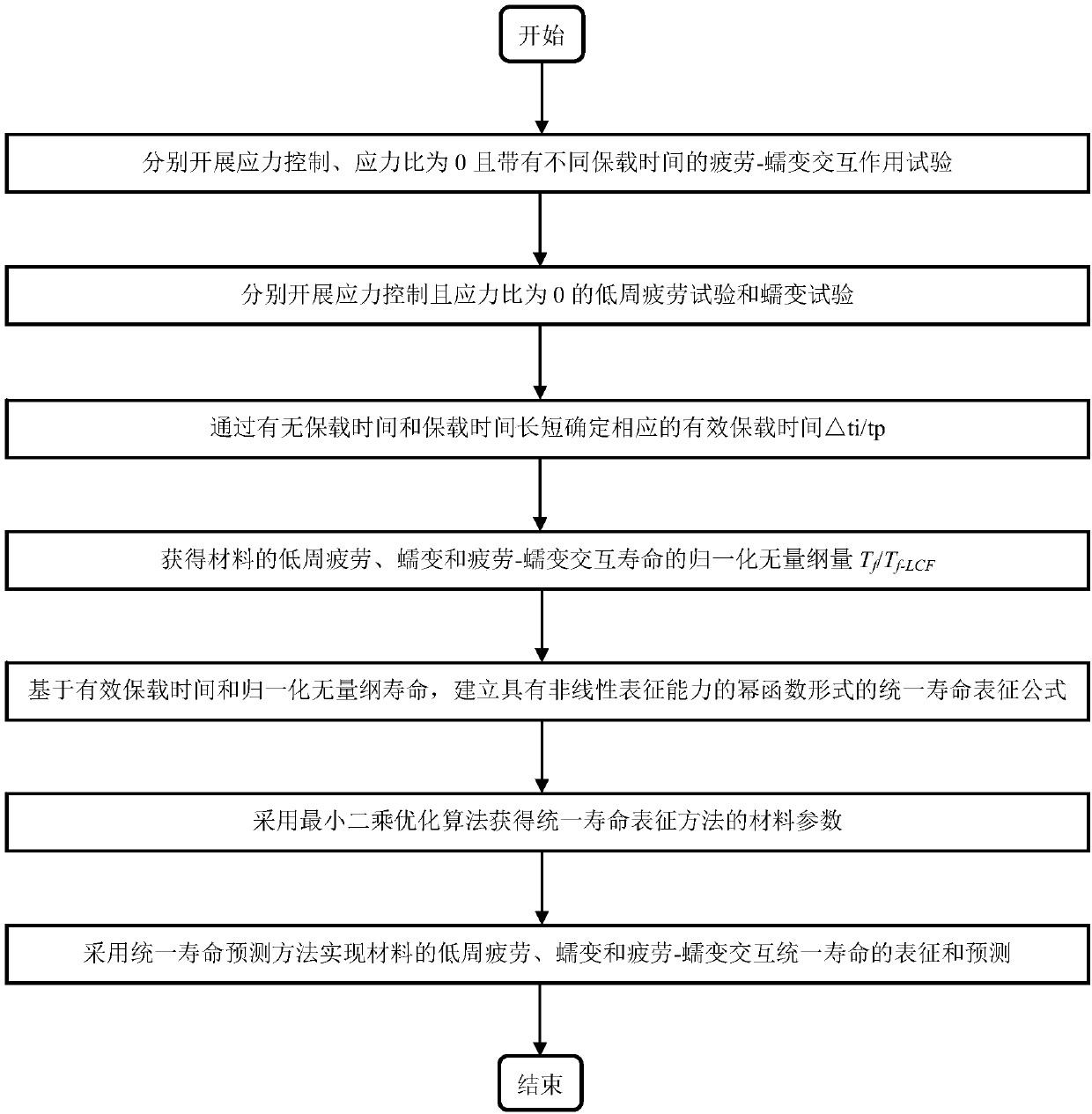
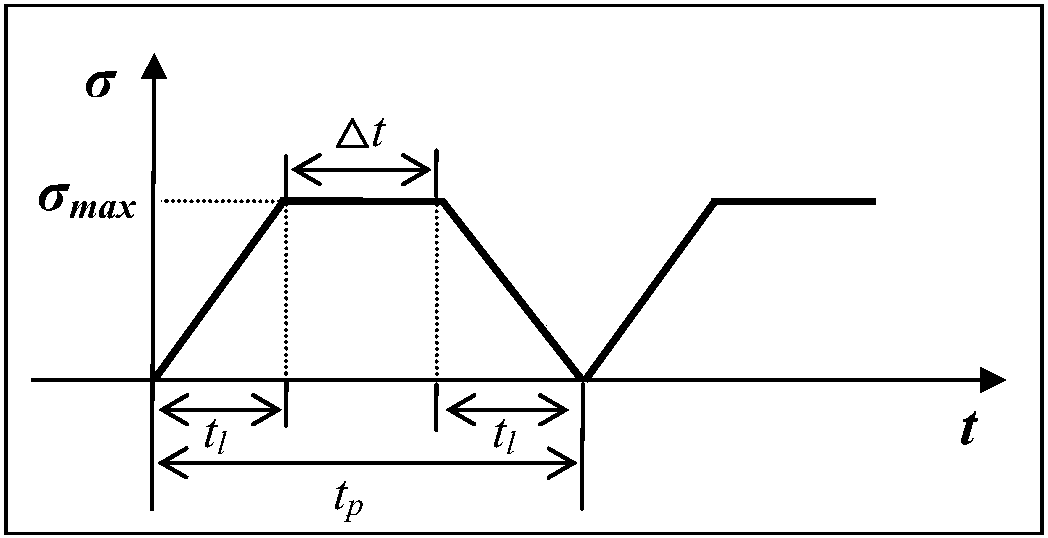
Characterization method of material fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life
ActiveCN107677547ASolid theoretical foundationSimplify the modeling processMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesModel implementationNon linear behavior
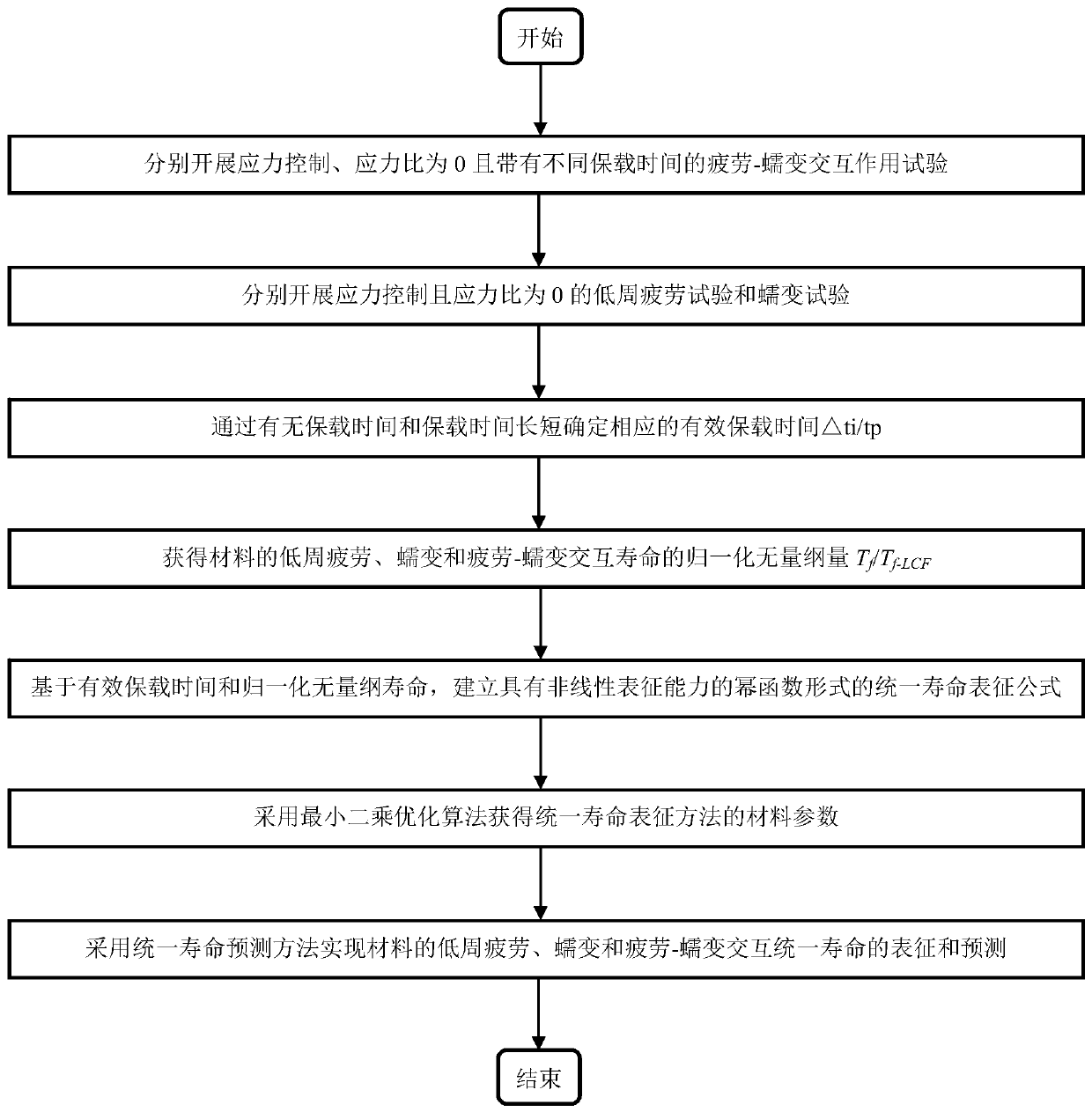
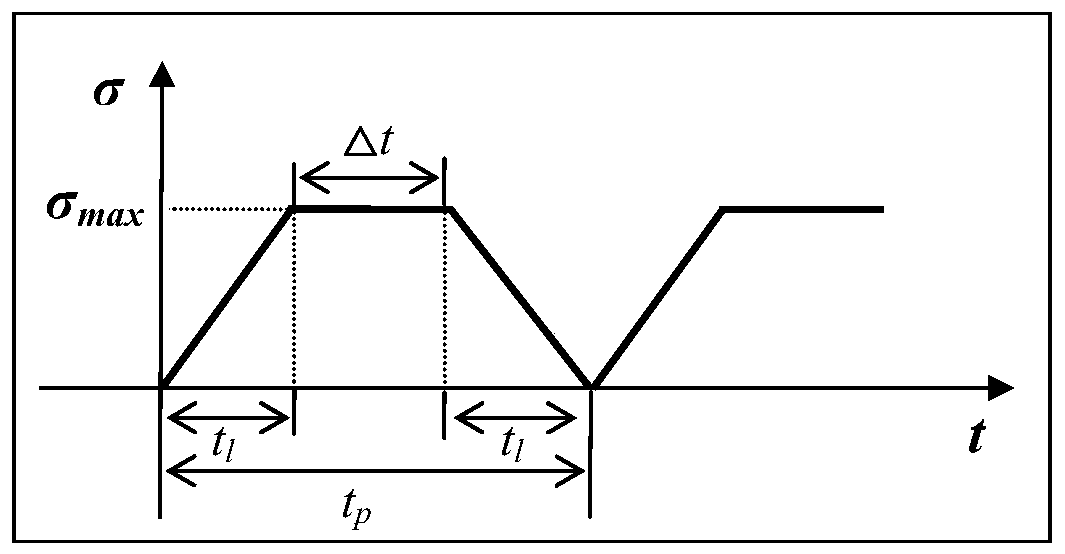
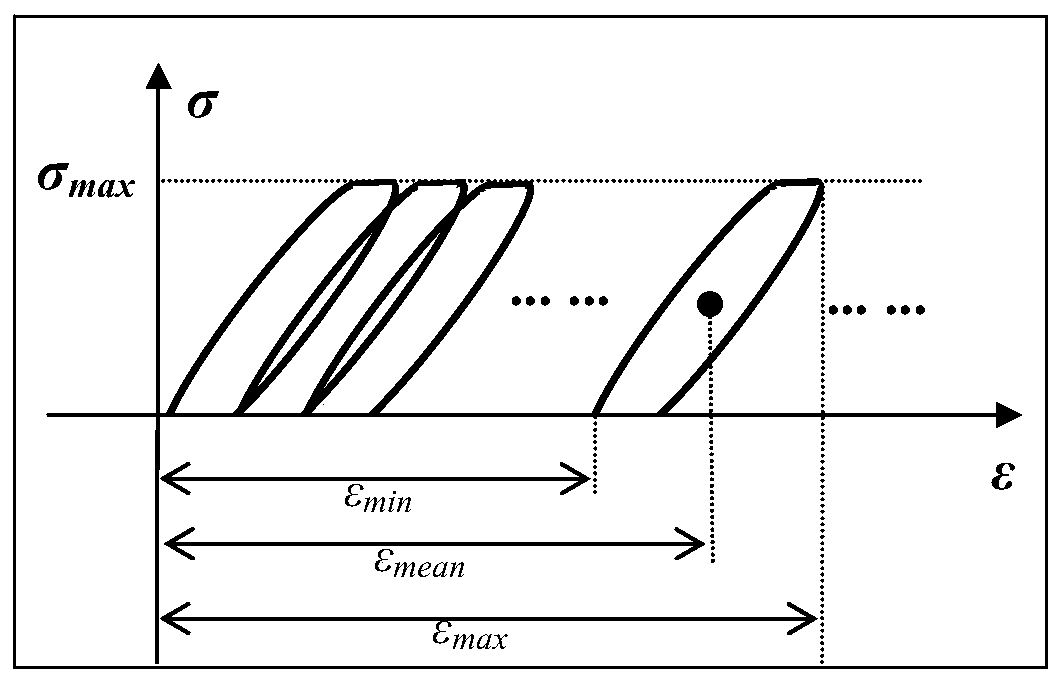
The invention discloses a characterization method of material fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life, and belongs to the field of service life prediction of aero-engine critical materials. The characterization method is used for solving service life characterization and prediction problems of materials under low cycle fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction conditions. According to the principles, a power function form service life prediction method non-linear behavior characterization capacity is established via fatigue-creep interaction, low cycle fatigue, and creeptests of materials at different holding time, and obtaining of effective holding time and normalization dimensionless service life via normalization calculation method. The characterization method iscapable of realizing accurate characterization of service life of materials under low cycle fatigue and fatigue-creep interaction conditions, and especially, consideration and accurate prediction ofcreep service life can be realized. The advantages of the characterization method are that consideration of both physical mechanisms and model implementation convenience is realized, and material lowcycle fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life characterization and prediction problems are solved effectively.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
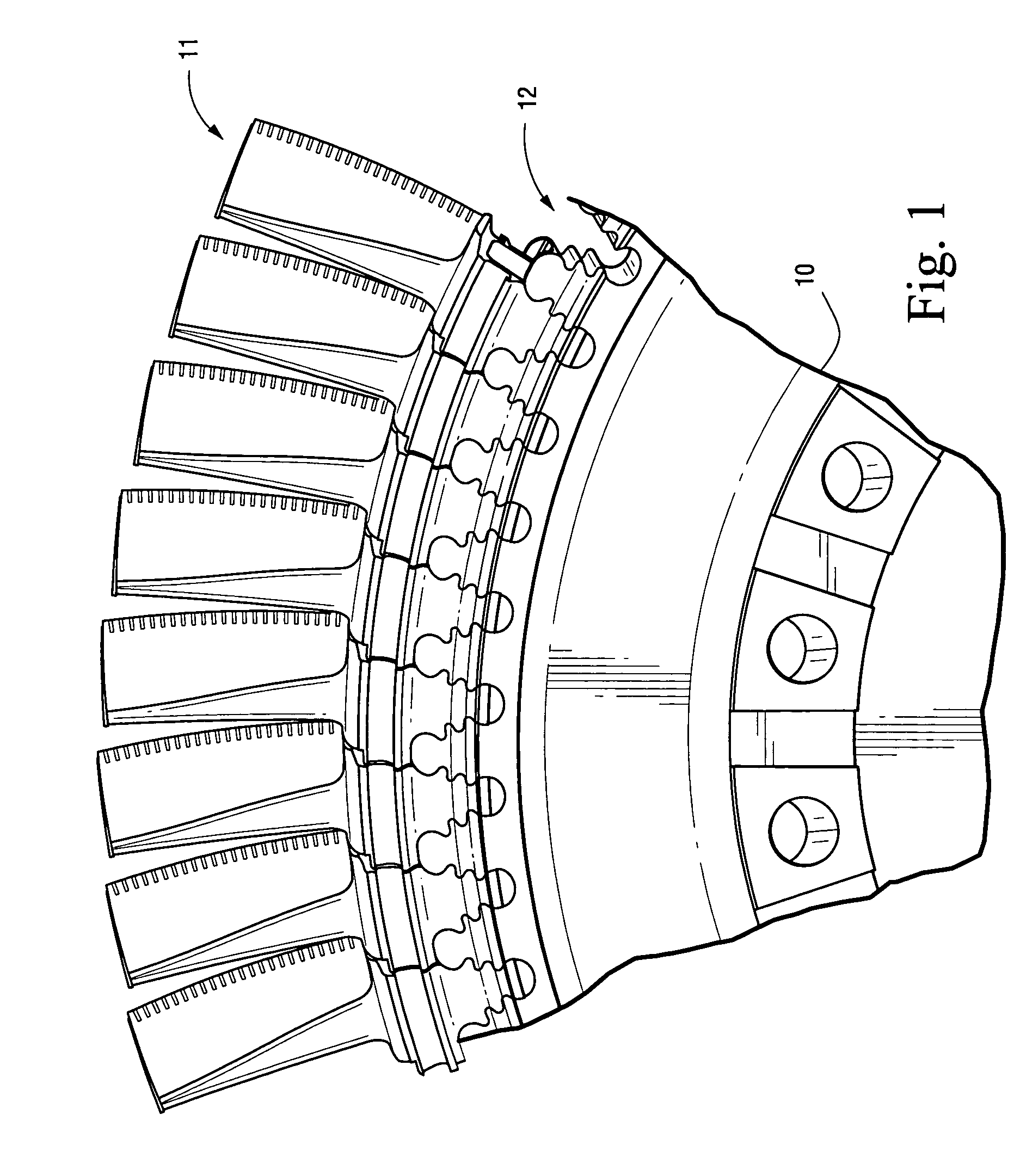
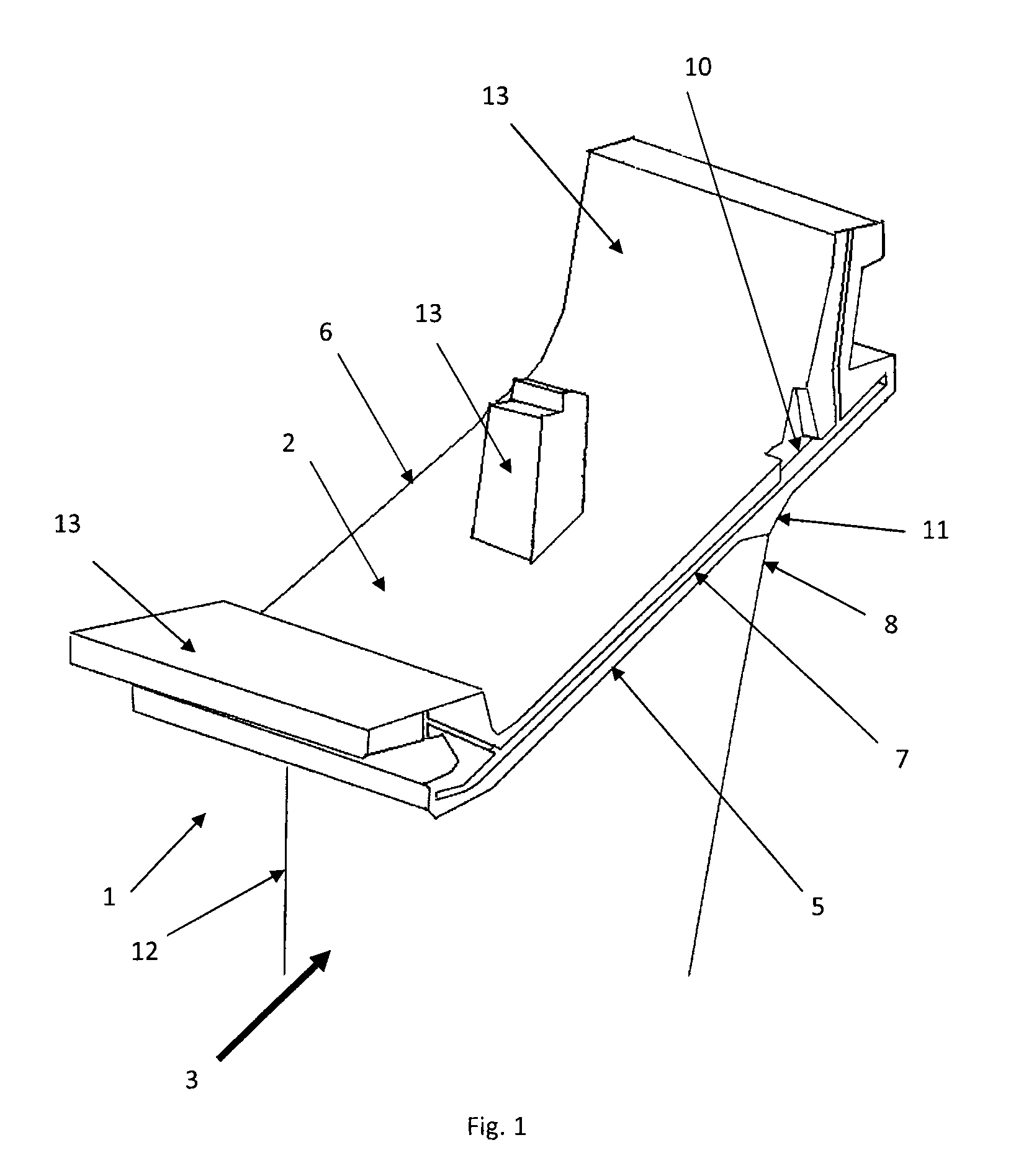
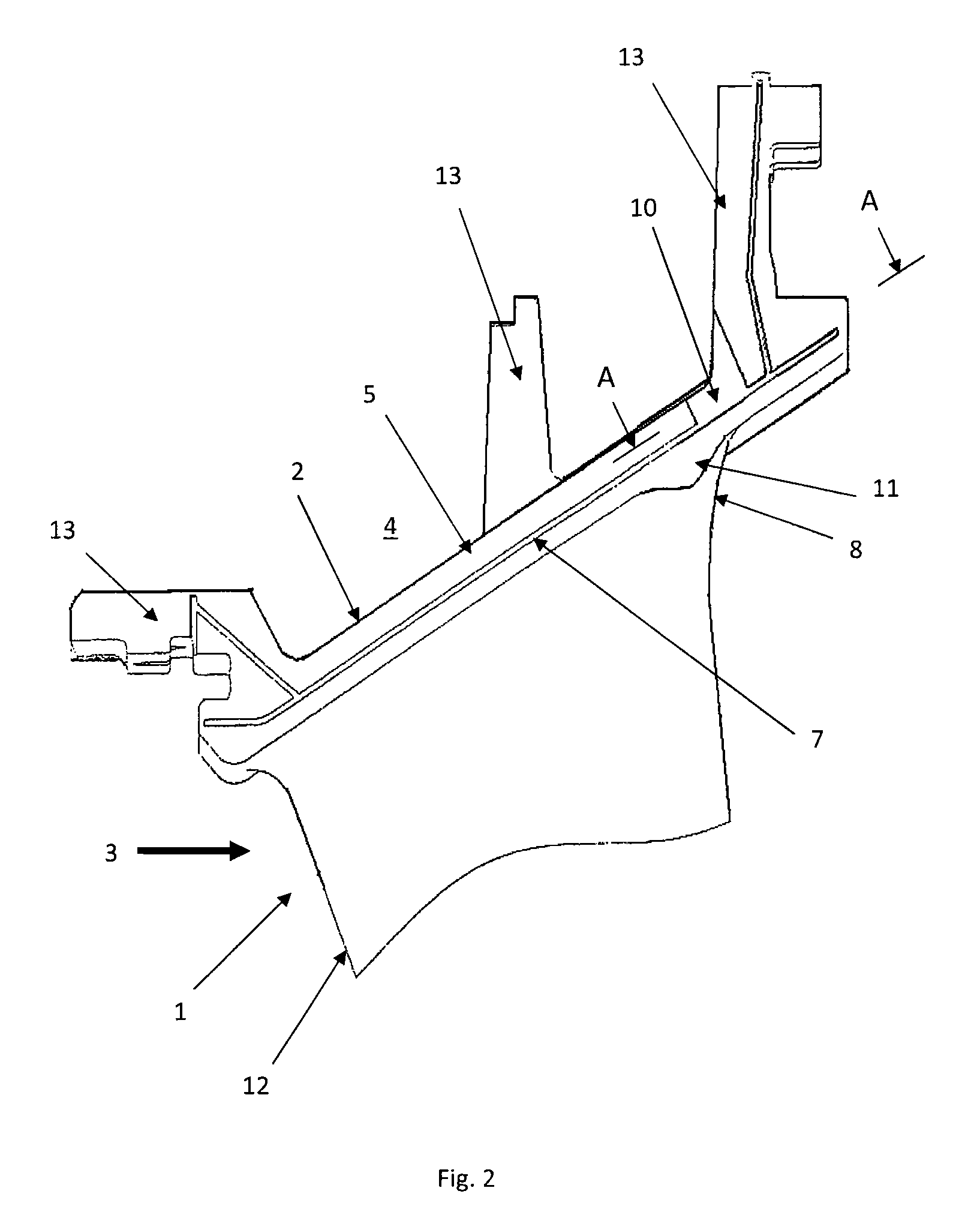
Stator vane for a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20100150710A1Reduce stress concentrationLow cycle fatigueEngine manufacturePump componentsLeading edgeEngineering
A guide vane for a gas turbine includes a vane body having a leading edge and a trailing edge and a shroud extending at least between the leading edge and the trailing edge. The shroud has a first side wall and a second side wall extending essentially radially and in a longitudinal direction of the gas turbine. The first side wall has a groove disposed in a region of the trailing edge extending in a longitudinal direction of the shroud and is configured to receive a sealing plate. The first side wall also has a clearance extending from the groove in a region of the trailing edge, wherein a depth of the clearance in a circumferential direction of the gas turbine is equal to a depth of the groove, and wherein a width of the clearance in the longitudinal direction of the shroud is between one to three times the depth of the clearance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Efficient automatic polishing processing method for molding surface of closed inner chamber, and dedicated equipment adopting method
InactiveCN102873629AImproves machined surface integrityEnsure consistencyEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesPolishingEngineering
The invention aims to provide an efficient automatic polishing processing method for a molding surface of a closed inner chamber, and dedicated equipment adopting the method. According to the method, a part is processed by adopting a vibrating polishing machine; and the method adopts the technological processes of clamping the part, adding grinding material into a work bin, and carrying out vibrating and polishing. The method is characterized in that the molding surface of the closed inner chamber is polished and processed automatically by adopting the dedicated vibrating polishing machine; the processing process comprises a roughing step and a finishing step; rough grinding material used in the roughing step is required to have sharp edges; fine grinding material used in the finishing step is required to have round corners; during clamping, the effective vertical lifting height of the part is guaranteed to be larger than twice the thickness of the part, and the vertical deflection of the part is not smaller than 30 degrees; and the vibration frequency of the work bin is 1,000 to 1,450 per minute, the vibration and swing frequency of a machine head is 15 to 30 per minute, and the lifting speed of the part is 1.5 to 2 m per minute.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Replaceable energy consumption connecting assembly for connecting fabricated frame beam column
ActiveCN106499247AEase of implementation of design principlesSmall plastic strainProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingHysteresisSteel bar
The invention provides a replaceable energy consumption connecting assembly for connecting a fabricated frame beam column. According to the technical scheme, a replaceable energy consumption assembly is arranged at the connecting position of the fabricated frame beam column and consists of an energy consumption steel rod, a constraint part and a connecting part, one end of the replaceable energy consumption assembly is connected with a node anchor steel bar embedded into the column, and the other end of the replaceable energy consumption assembly is connected with a beam-end longitudinal steel bar embedded into a beam. Under an earthquake effect, the energy consumption steel rod yields prior to other members and parts and utilizes plastic hysteresis to consume earthquake energy. The replaceable energy consumption connecting assembly is used for connecting the fabricated frame beam column, can induce the plastic damage of the structure in a middle earthquake and a large earthquake to be concentrated on the energy consumption steel rod, the damage of abeam column member can be avoided while the seismic ductility of the structure is improved, and the structure can be rapidly repaired after the earthquake in a simple energy consumption part changing mode, so that the structure repair efficiency after the earthquake is remarkably improved. The application of the replaceable energy consumption connecting assembly meets the industrialization development requirements of buildings.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for increasing heat transfer from combustors
InactiveUS6842980B2Improve heat transfer performanceMinimizes low cycle fatigue stressContinuous combustion chamberMolten spray coatingHigh densityCombustor
A combustor for a gas turbine engine includes a deflector assembly that enhances heat transfer from the combustor and minimizes low cycle fatigue stresses induced within the combustor. The deflector assembly includes a plurality of deflectors secured to a spectacle plate. Each deflector has tapered edges and includes a plurality of cylindrical projections extending outward from the deflector to facilitate heat transfer. The projections include rounded edges and are arranged in a high density pattern. The deflector is coated with a thermal barrier coating and a bondcoat to minimize exposure to hot combustion gases or flame radiation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
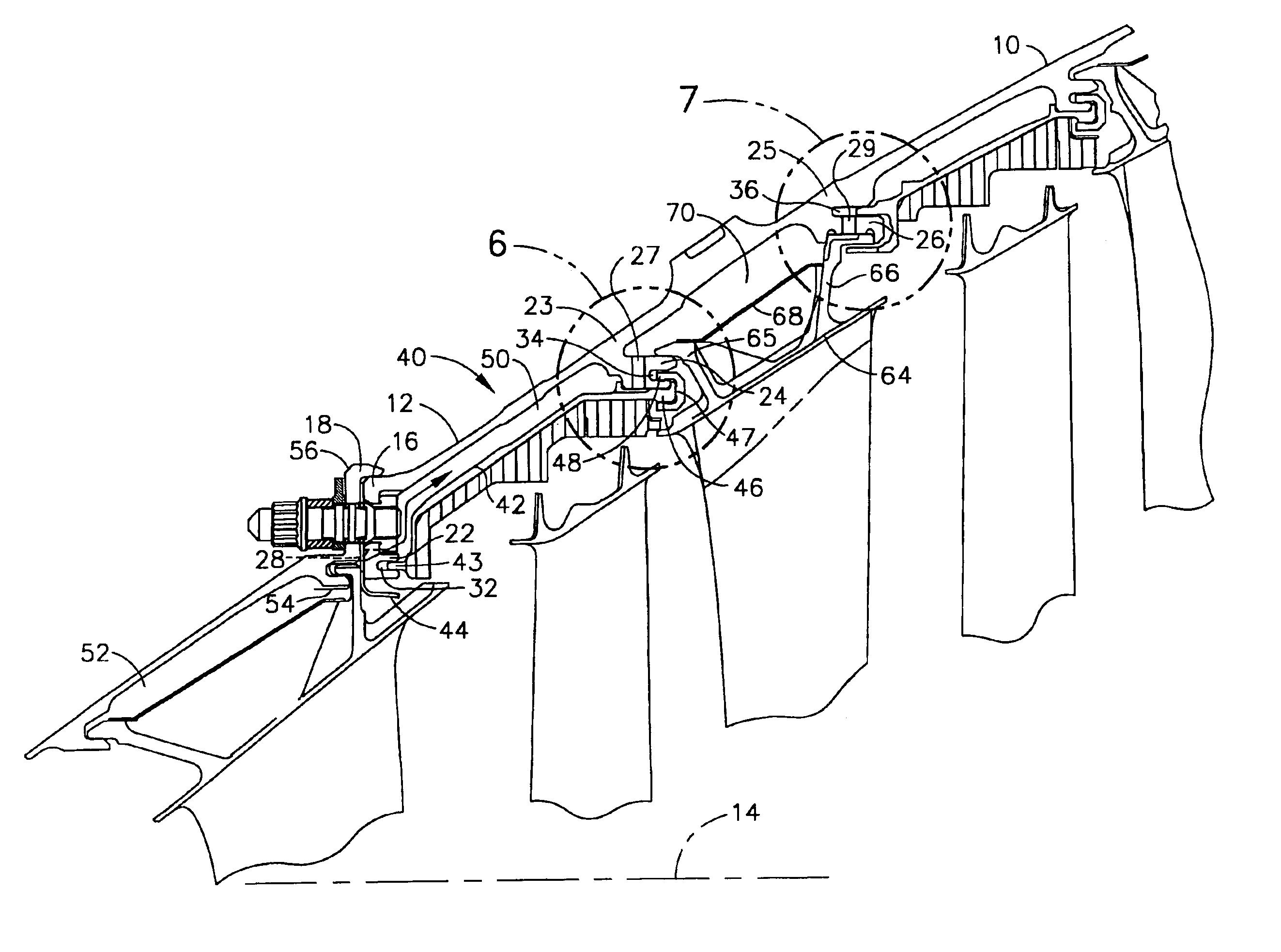
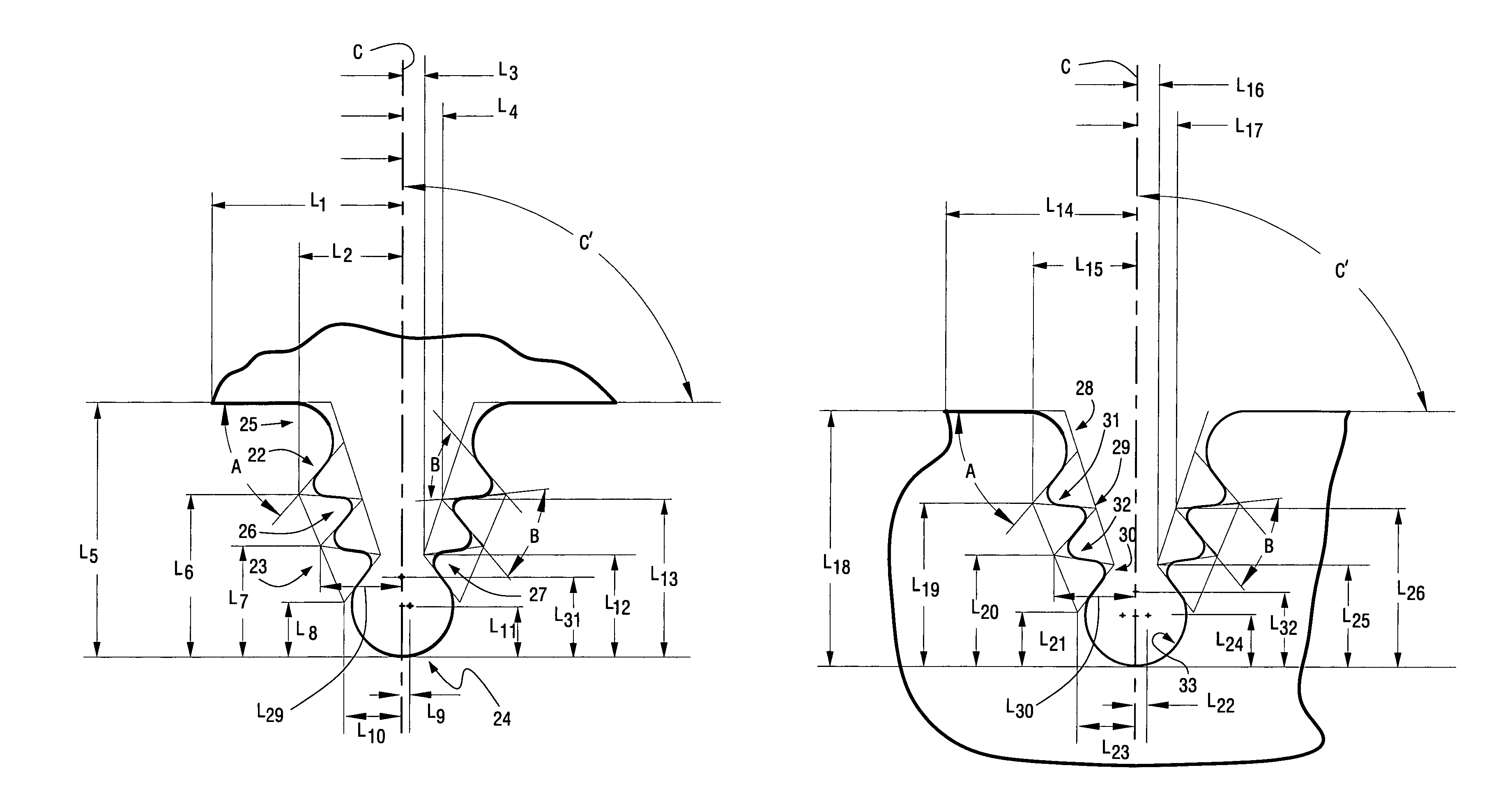
Advanced firtree and broach slot forms for turbine stage 3 buckets and rotor wheels
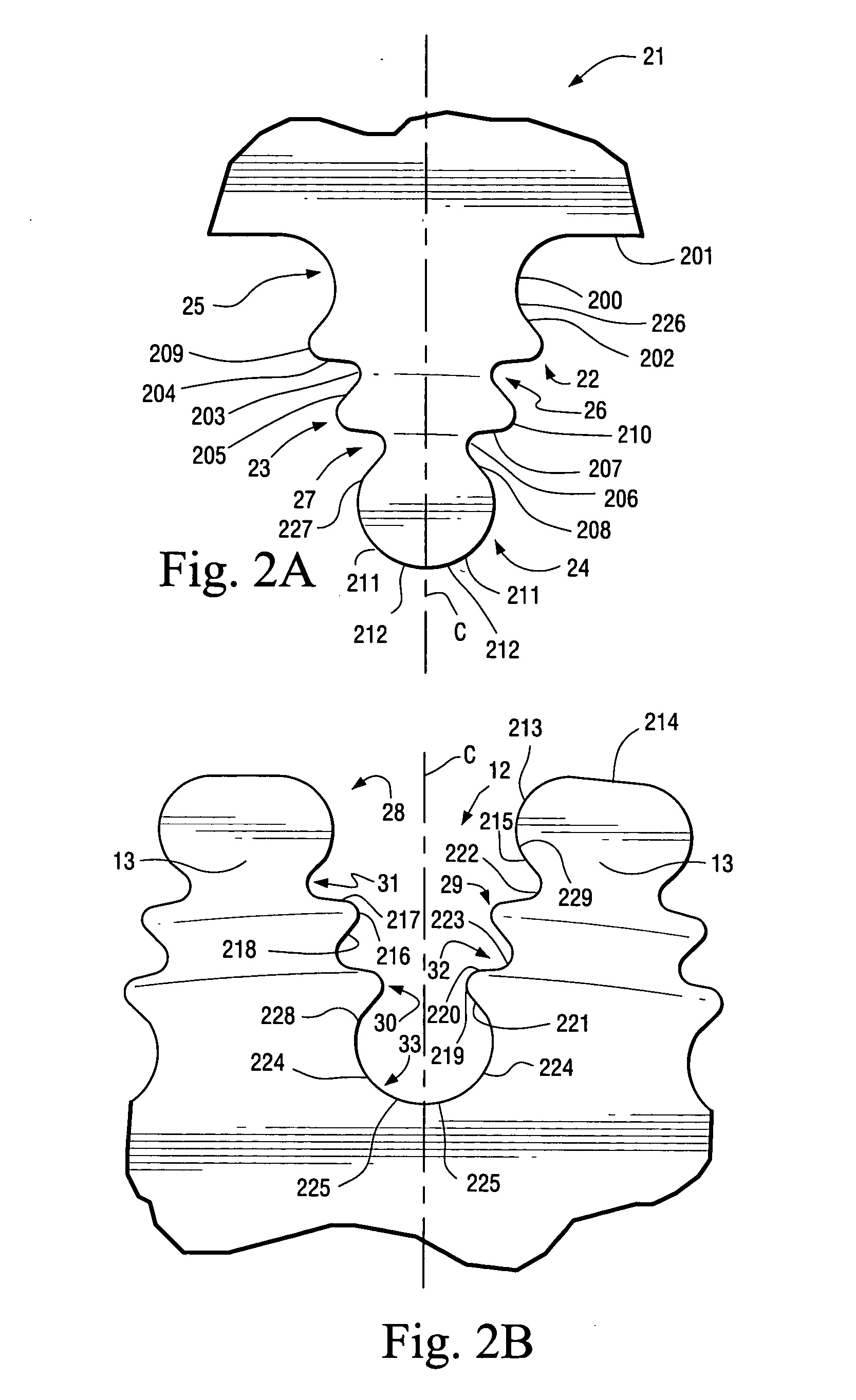
ActiveUS20050175461A1Enhance transfer of loadRaise transfer toPropellersRotary propellersImpellerTurbine blade
A turbine bucket and wheelpost assembly reduces the number of buckets in the third stage of the turbine from ninety-two to ninety while reducing stresses at the assembly points of the buckets and wheelposts. The buckets and wheelposts are formed with complementary fillets and tangs that provide for the insertion of the bucket into the broach slot between two wheelposts. The angles of the fillets on both the bucket and wheelpost range from 50° to 59°. The upper surface of the wheelpost is scalloped to reduce weight and the tangs and fillets of both the bucket and wheelpost are formed from curved and straight surfaces to reduce stresses on the assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of controlling grain size in forged precipitation-strengthened alloys and components formed thereby
ActiveUS20120282106A1Significant control of average grain sizeAvoid grain growthBlade accessoriesReaction enginesAlloyHeat treated
Components and methods of processing such components from precipitation-strengthened alloys so that the components exhibit desirable grain sizes following a supersolvus heat treatment. The method includes consolidating a powder of the alloy to form a billet having an average grain size. The billet is then forged at a temperature below the solvus temperature to form a forging having an average grain size of not coarser than the grain size of the billet. The billet is then forged at a total strain of at least 5%, after which at least a portion of the forging is heat treated at a temperature below the solvus temperature to pin grains within the portion. The entire forging can then be heat treated at a temperature above the solvus temperature of the alloy without coarsening the grains in the portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Advanced firtree and broach slot forms for turbine stage 3 buckets and rotor wheels
A turbine bucket and wheelpost assembly reduces the number of buckets in the third stage of the turbine from ninety-two to ninety while reducing stresses at the assembly points of the buckets and wheelposts. The buckets and wheelposts are formed with complementary fillets and tangs that provide for the insertion of the bucket into the broach slot between two wheelposts. The angles of the fillets on both the bucket and wheelpost range from 50° to 59°. The upper surface of the wheelpost is scalloped to reduce weight and the tangs and fillets of both the bucket and wheelpost are formed from curved and straight surfaces to reduce stresses on the assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
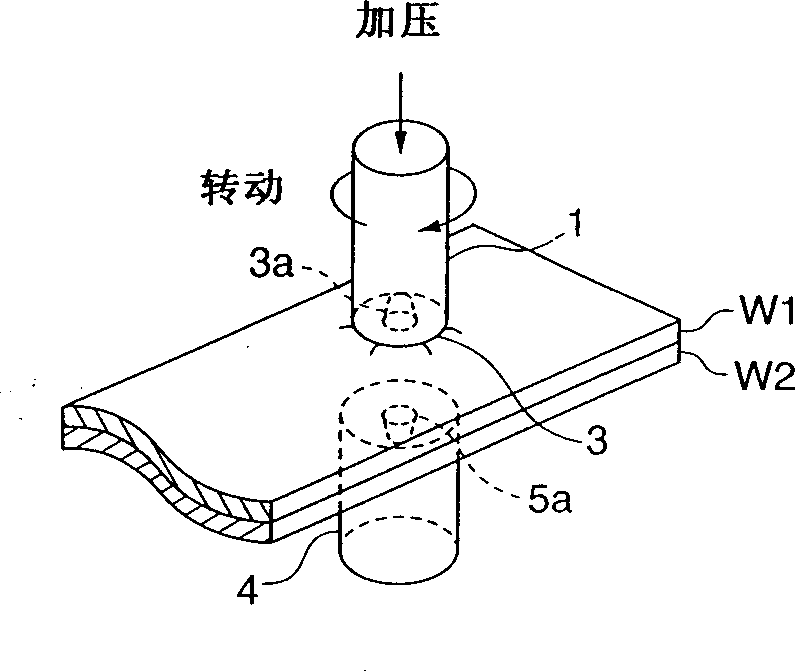
Method of processing metal members
The first and second metal members (W1, W2) are connected by the following steps: overlapping at least two metal members with each other; pressing a rotary tool (1) on the outermost surface of the overlapping metal members, i.e., Pressed on the first metal member (W1); the frictional heat generated by the rotation of the rotating tool (1) stirs the metal structure between the first and second metal members (W1, W2), while maintaining the metal member in a non-melted state .
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Automobile chassis part excellent in low cycle fatigue characteristics and method of production of same
ActiveUS20130056115A1Excellent in low cycle fatigue characteristicConvenient amountFurnace typesVehicle componentsX-rayMethods of production
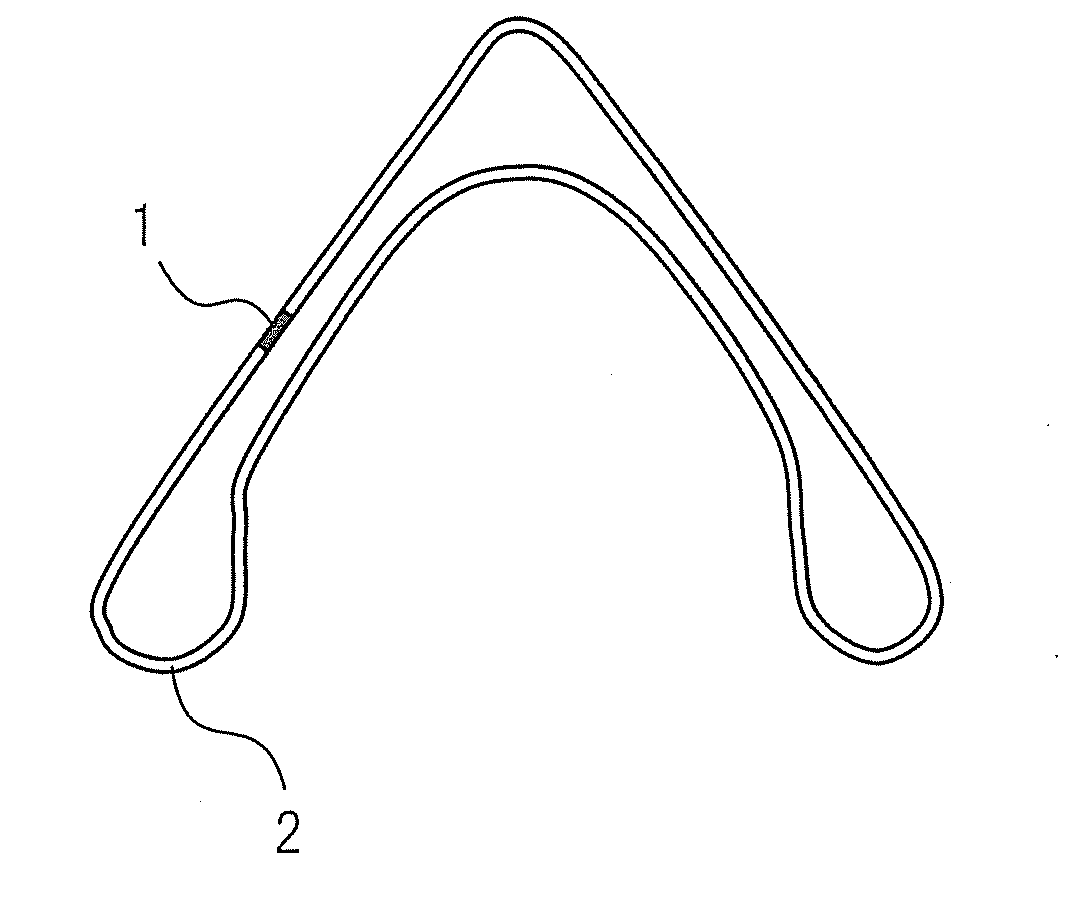
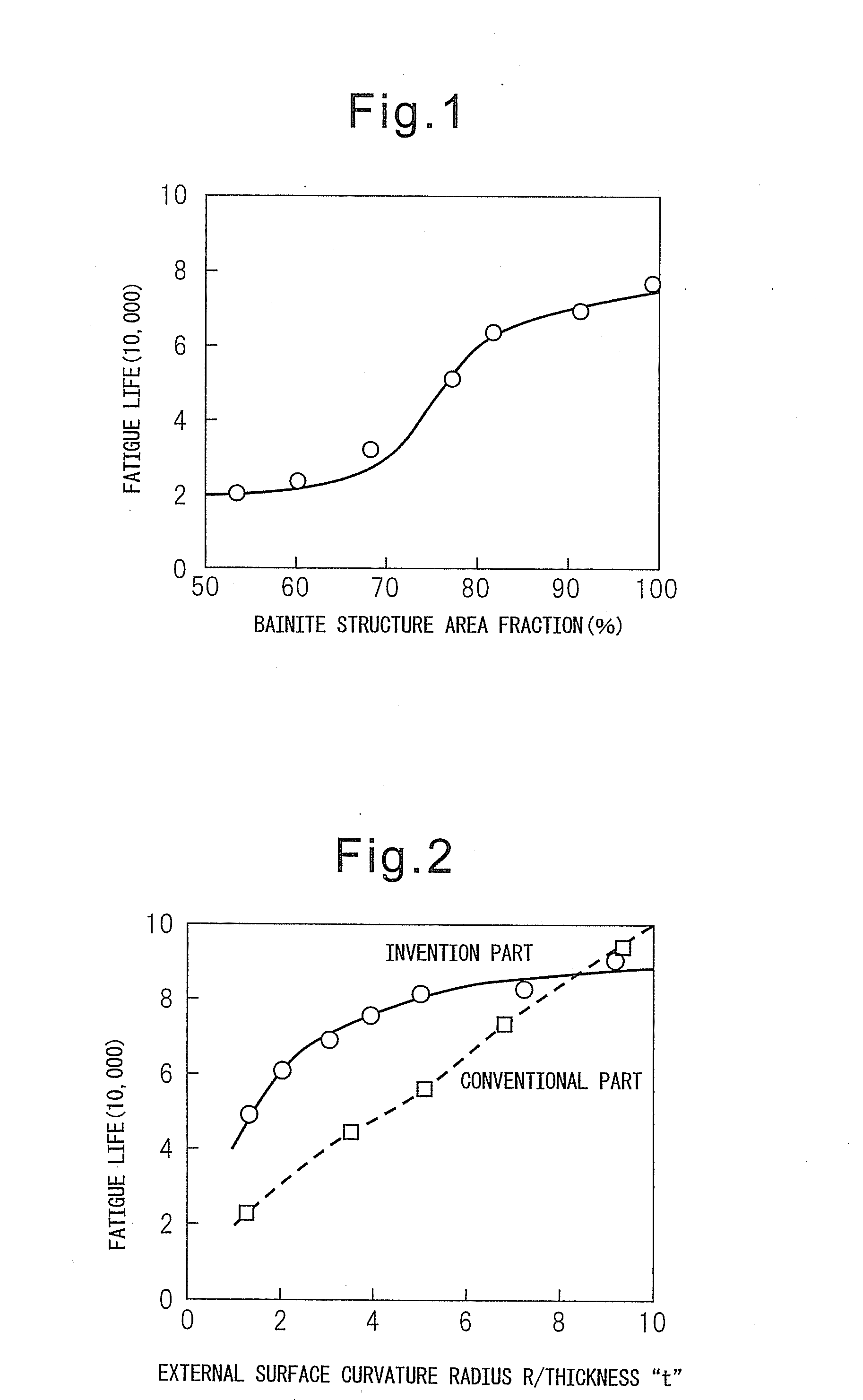
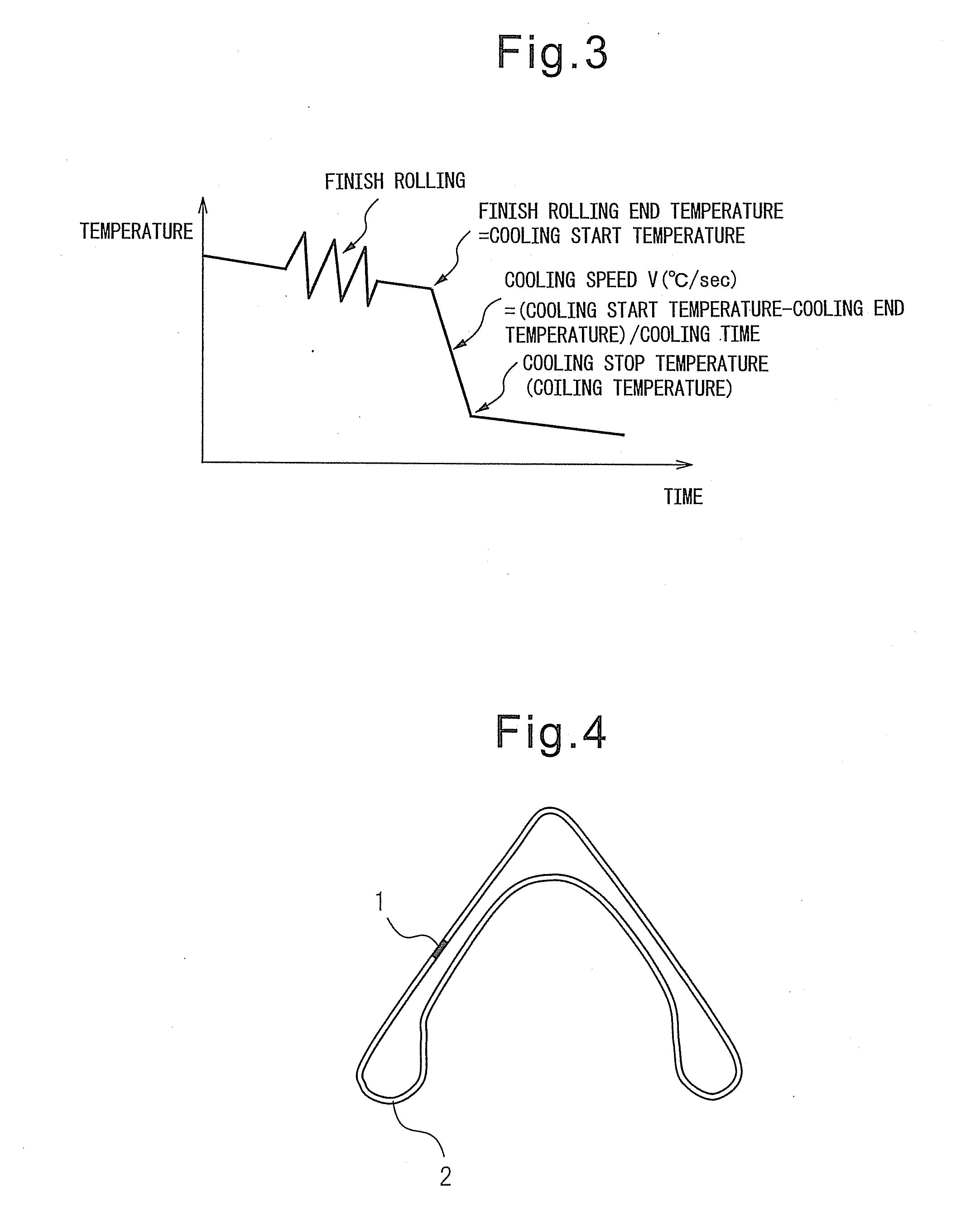
An automobile chassis part which is excellent in low cycle fatigue characteristics, characterized by being formed by steel which contains, by mass %, C: 0.02 to 0.10%, Si: 0.05 to 1.0%, Mn: 0.3 to 2.5%, P: 0.03% or less, S: 0.01% or less, Ti: 0.005 to 0.1%, Al: 0.005 to 0.1%, N: 0.0005 to 0.006%, and B: 0.0001 to 0.01 and has a balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities, in which 80% or more of the part structure comprises a bainite structure and in which a portion where a ratio R / t of the thickness “t” and external surface curvature radius R is 5 or less has an X-ray half width of an (211) plane of 5 (deg) or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Stator vane for a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS8152454B2Reduce stress concentrationLow cycle fatigueEngine manufacturePump componentsLeading edgeEngineering
A guide vane for a gas turbine includes a vane body having a leading edge and a trailing edge and a shroud extending at least between the leading edge and the trailing edge. The shroud has a first side wall and a second side wall extending essentially radially and in a longitudinal direction of the gas turbine. The first side wall has a groove disposed in a region of the trailing edge extending in a longitudinal direction of the shroud and is configured to receive a sealing plate. The first side wall also has a clearance extending from the groove in a region of the trailing edge, wherein a depth of the clearance in a circumferential direction of the gas turbine is equal to a depth of the groove, and wherein a width of the clearance in the longitudinal direction of the shroud is between one to three times the depth of the clearance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
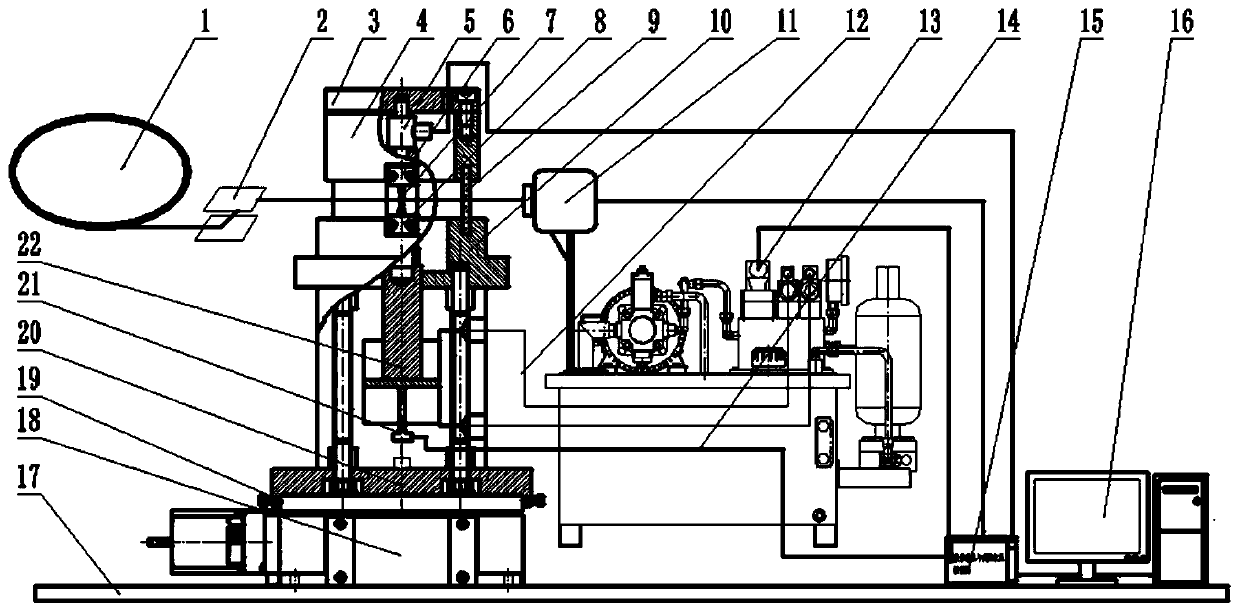
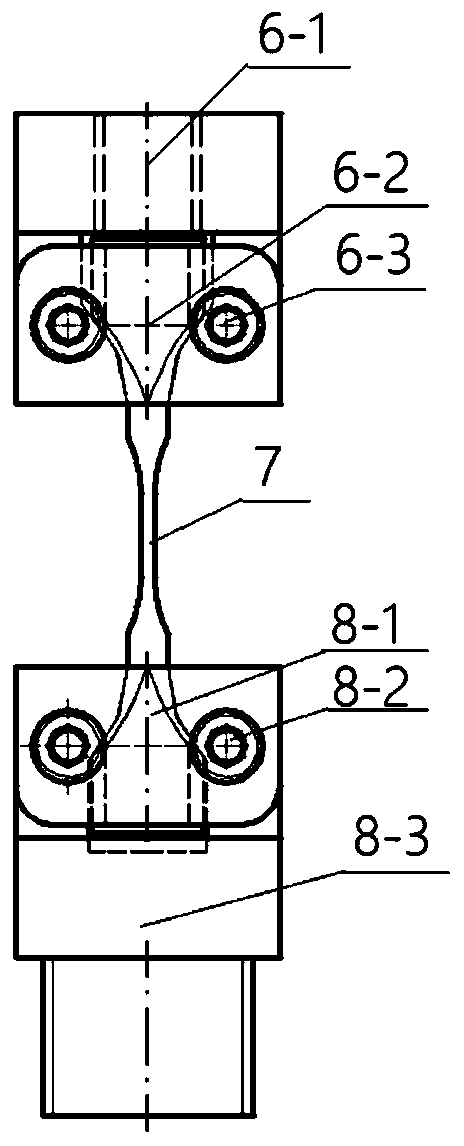
Large-load and high-frequency in-situ tension and fatigue tester based on X-ray imaging
PendingCN109883847AIncrease loadFast frequency responseMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue testingHigh frequency
The invention discloses a large-load and high-frequency in-situ tension and fatigue tester based on X-ray imaging. An imaging displacement stage can be rotatably mounted on a test platform; a base isfixed on the imaging displacement stage, a rack is arranged on the base, a servo hydraulic cylinder is arranged on the rack, a lower clamp is rotatably connected to an upper end of a piston rod of thehydraulic cylinder, a support seat platform is fixed on four uprights of the rack; a support tube is located at an upper side of the support seat platform, a transparent cover is embedded between thesupport seat platform and the support tube; an upper clamp is fixed on the support tube; an electrolyte servo valve is connected with an upper oil chamber and a lower oil chamber of the hydraulic cylinder; a load sensor, the electrolyte servo valve and a X-ray detector are orderly connected with a data collection and control unit and a data processing unit. The tester disclosed by the invention has the features of being large in load, high in frequency, small in volume, and high in precision.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
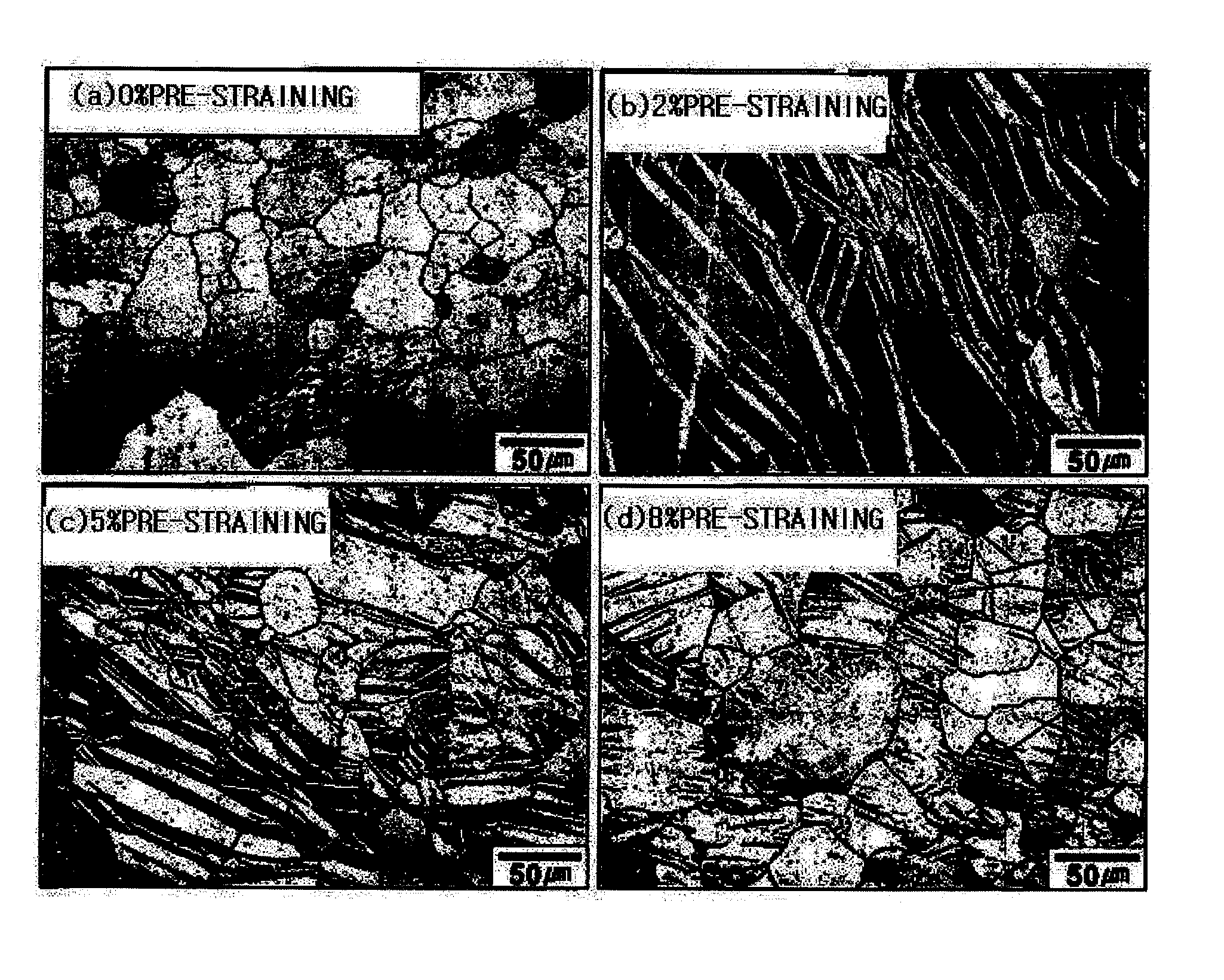
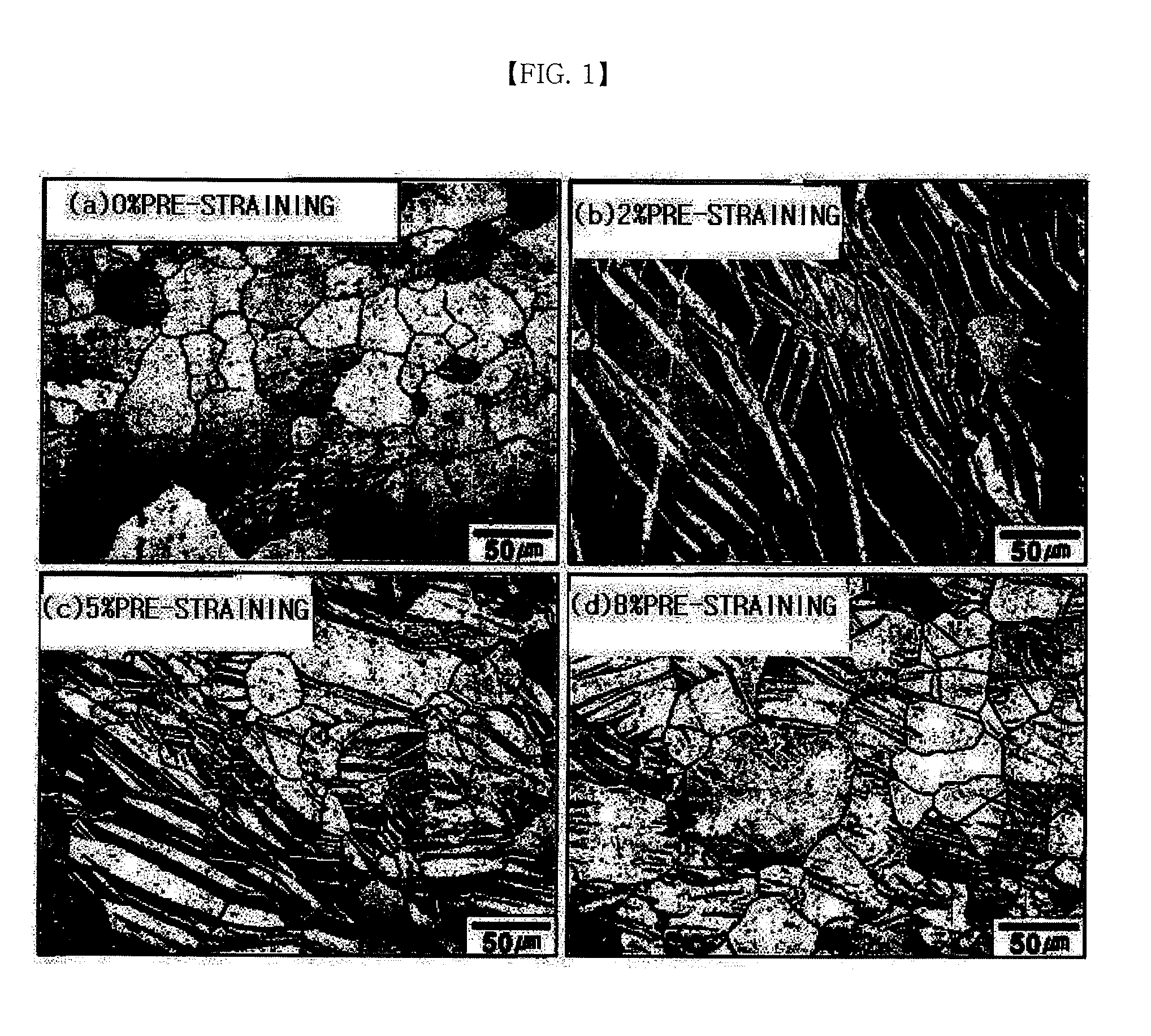
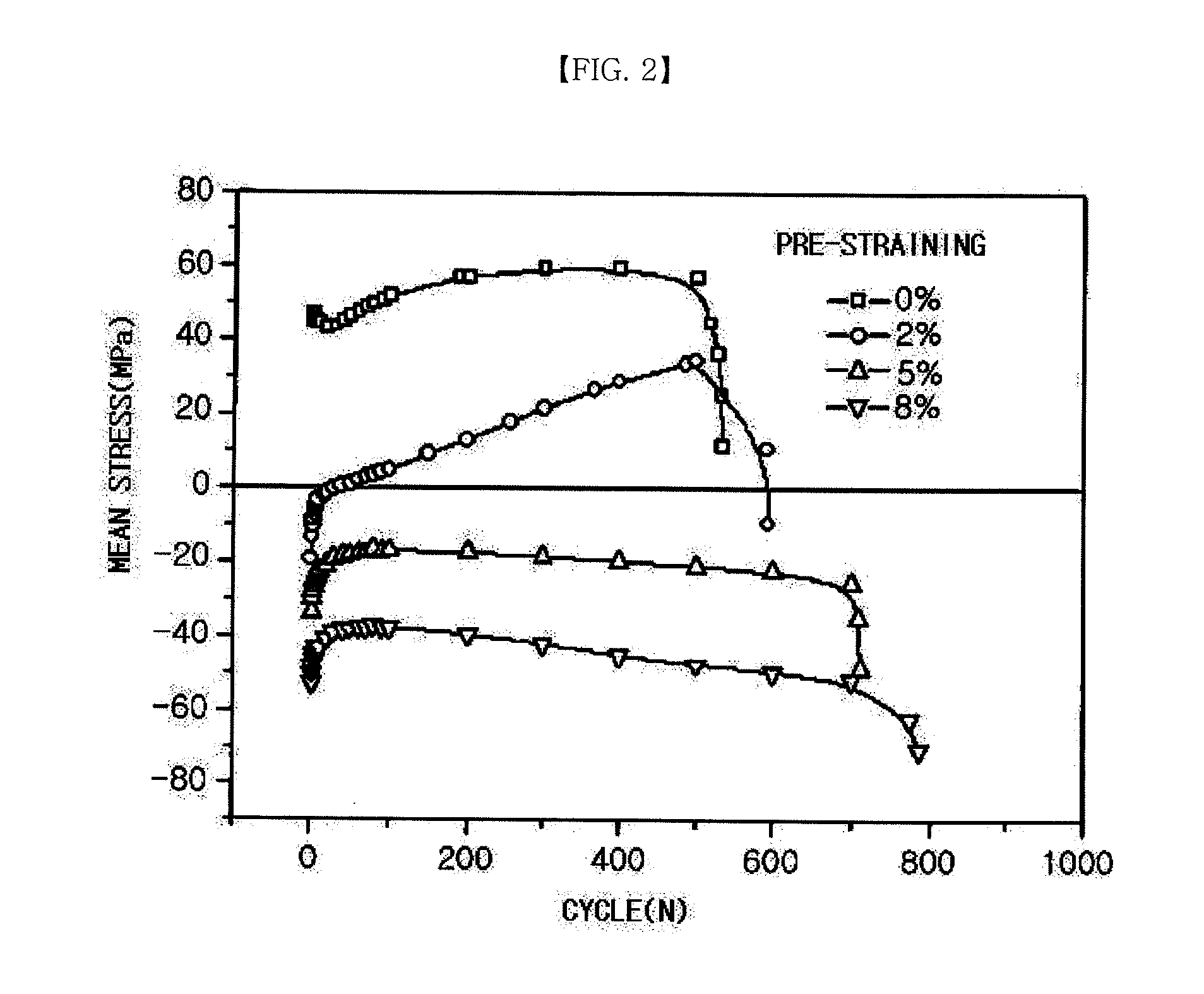
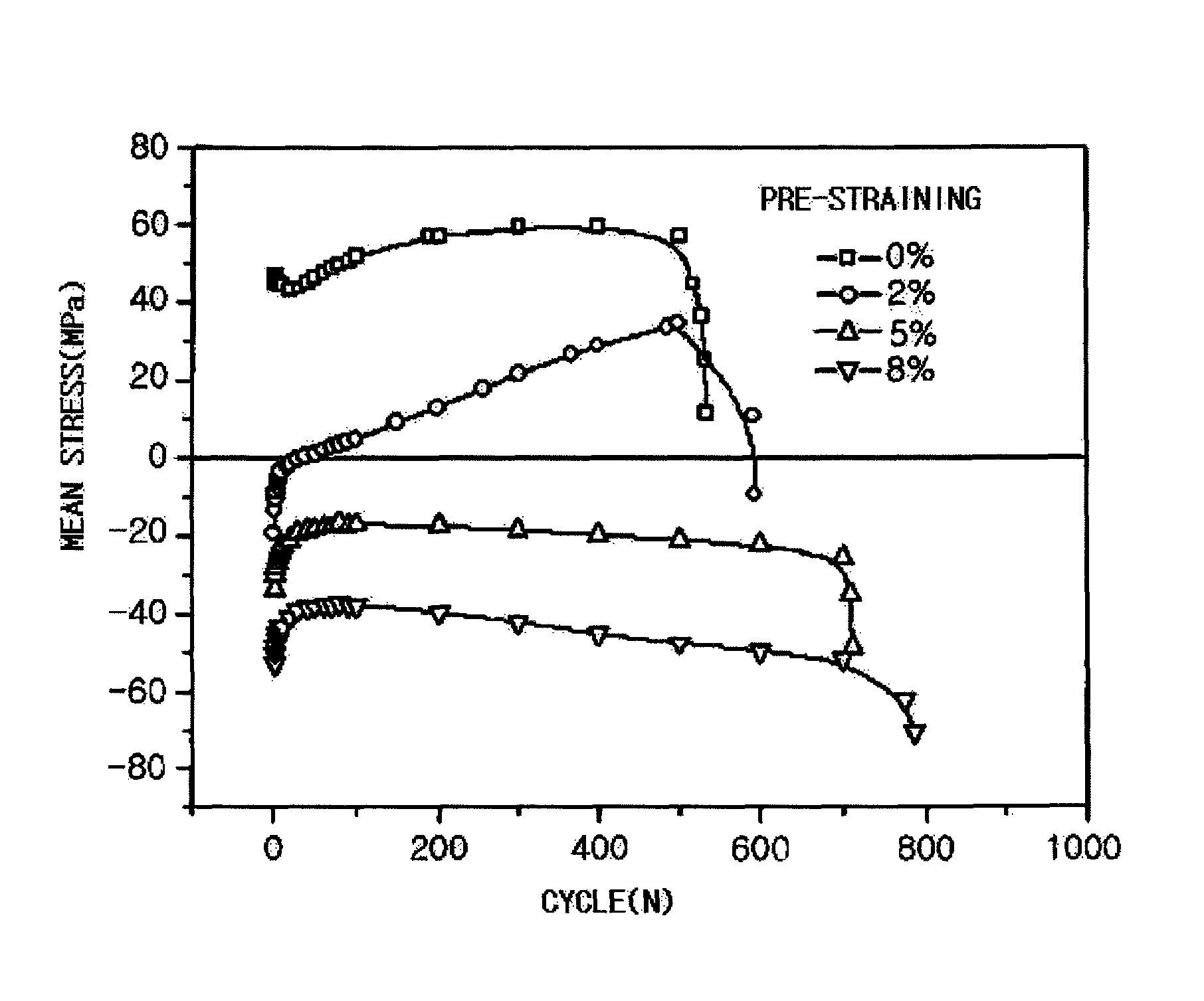
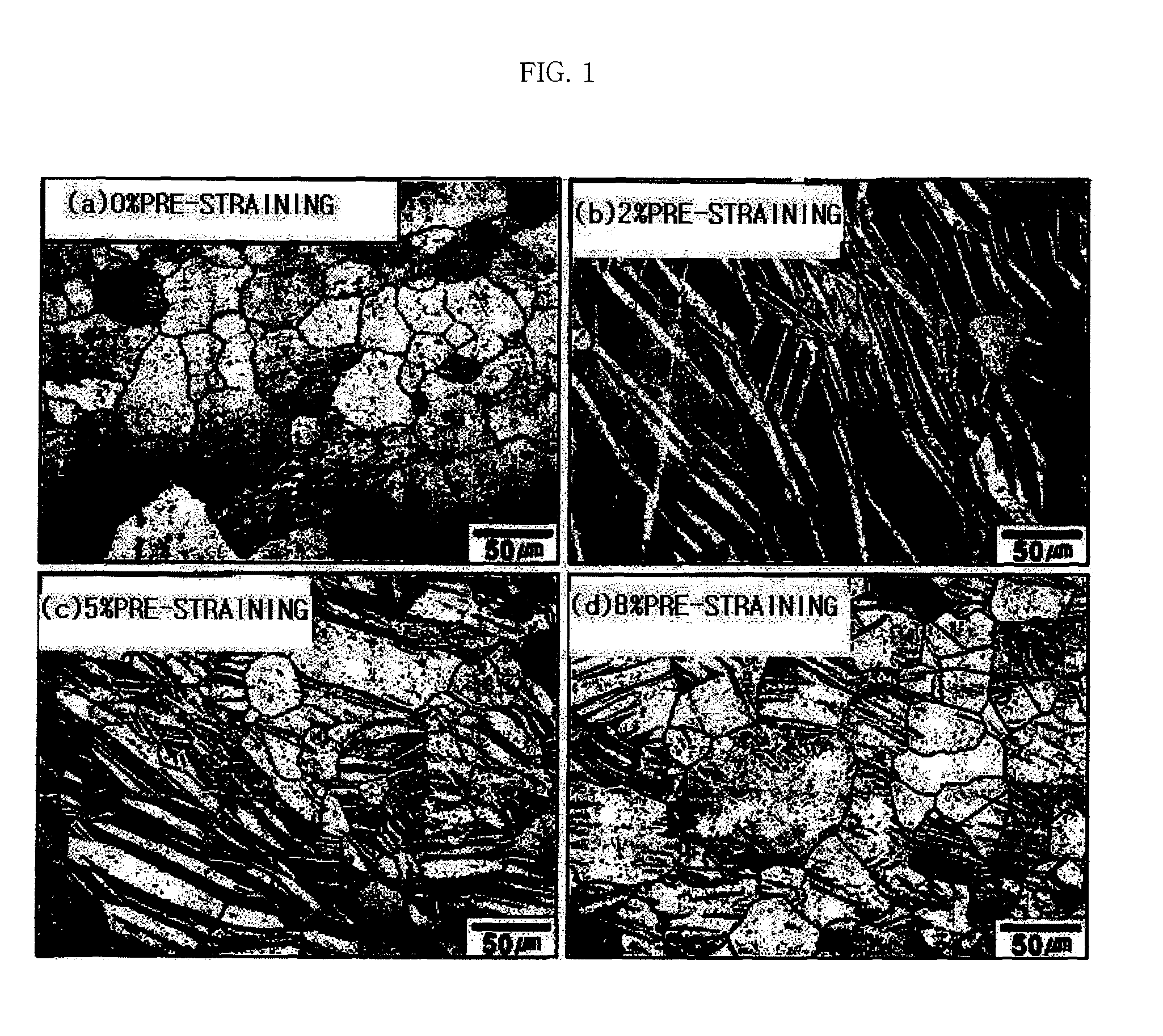
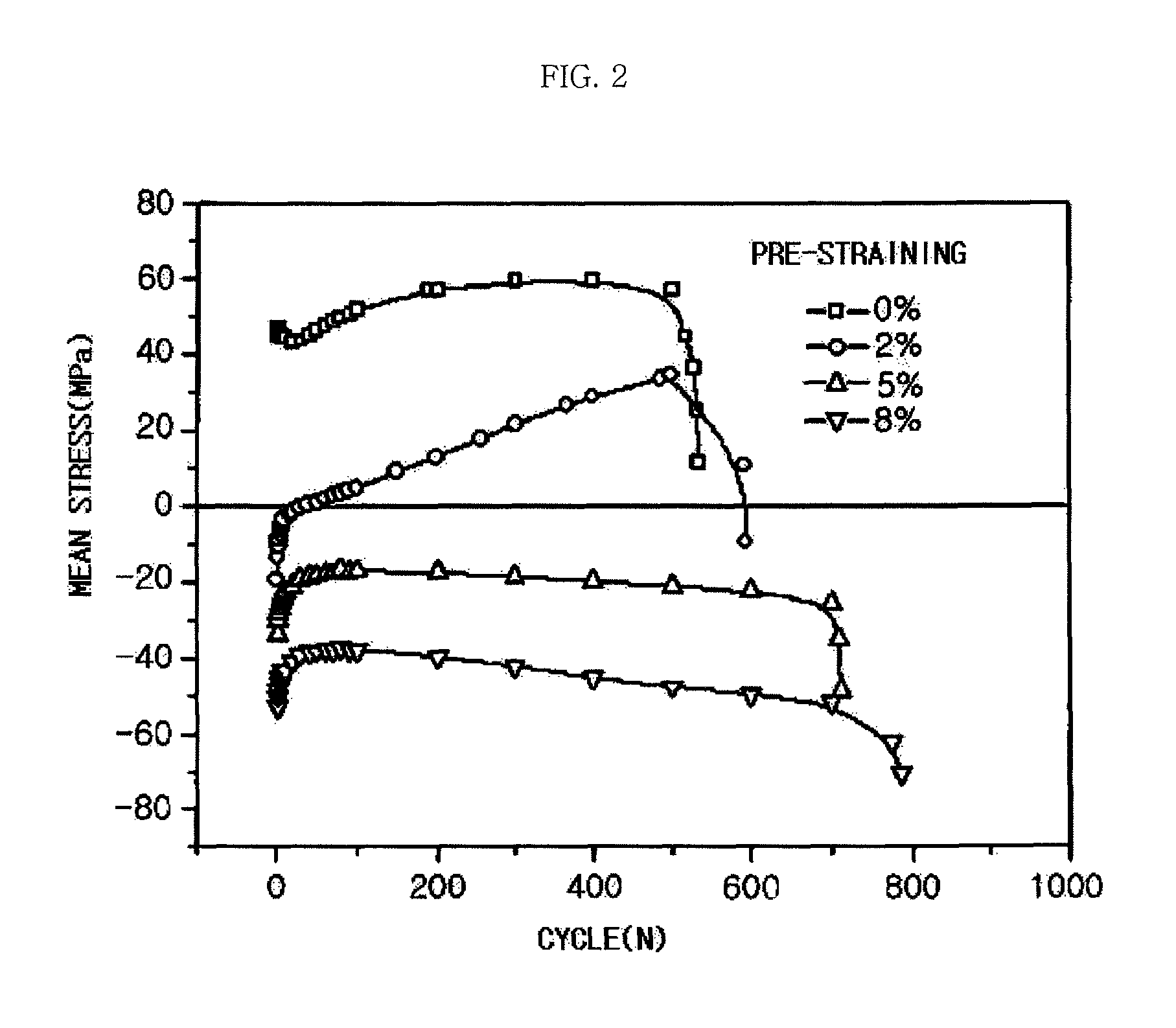
Method of manufacturing magnesium alloy processing materials with low cycle fatigue life improved by pre-straining
ActiveUS20120111081A1Process safety and stabilityLow cycle fatigueMetal rolling arrangementsPre strainingLow-cycle fatigue
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing magnesium alloy processing materials capable of improving low cycle fatigue life. The manufacturing method for magnesium alloy processing materials with improved low cycle fatigue life comprises pre-straining a magnesium alloy processing material which is processed.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
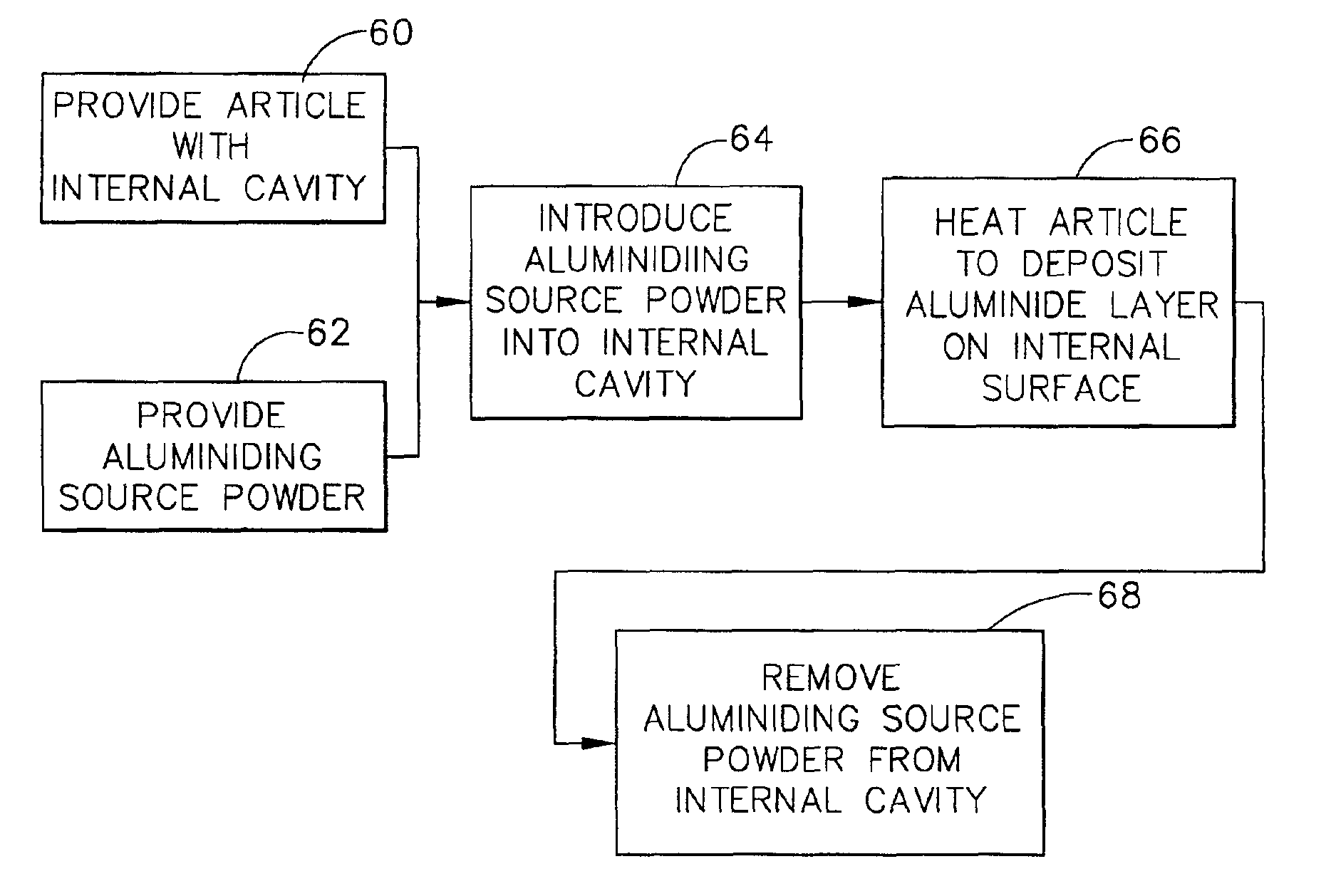
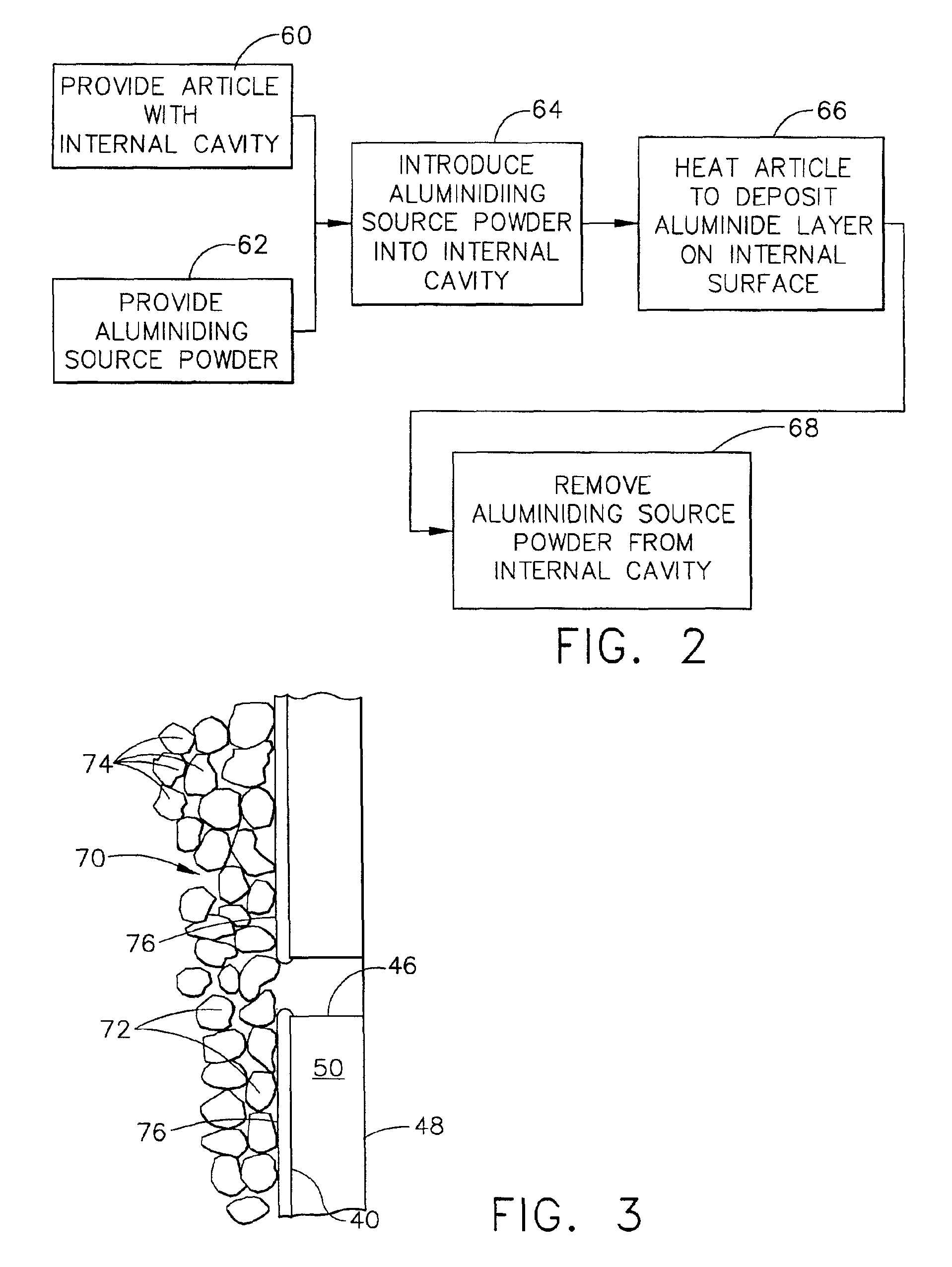
Dimensionally controlled pack aluminiding of internal surfaces of a hollow article
InactiveUS7094445B2Readily introduced into the internal cavityLow cycle fatigueLiquid surface applicatorsPropellersInternal cavityGas turbines
An article such as a hollow gas turbine blade has an internal cavity therein with an inlet and outlet. The outlet has an outlet minimum transverse dimension of from about 0.009 inch to about 0.012 inch. An aluminiding source powder has a minimum particle size of greater than about 0.0015 inch and not greater than about 0.005 inch. The aluminiding source powder is a mixture of from about 5 to about 15 percent by weight of a metallic aluminum-containing powder and from about 85 to about 95 percent by weight of a ceramic powder. The aluminiding source powder is flowed into the internal cavity through the inlet, and the article is heated with the aluminiding source powder in the internal cavity to a temperature of from about 1750° F. to about 2000° F., and for a time of from about 2 hours to about 12 hours, to deposit an aluminum-containing coating on the internal surface of the internal cavity. The aluminiding source powder is thereafter removed from the internal cavity through the inlet.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cobalt-chromium ceramic-metal alloy disc for engraving fixed dentures and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110819851AHigh strengthImprove creep resistanceImpression capsDentistry preparationsCeriumWire cutting
The invention relates to oral medical materials, in particular to a cobalt-chromium ceramic-metal alloy disc for engraving fixed dentures. The cobalt-chromium ceramic-metal alloy disc is prepared fromthe following raw materials in percentage by weight: 50%-65% of cobalt, 20%-35% of chromium, 3%-6% of molybdenum, 1%-3% of titanium, 5%-7% of tungsten, 0.08%-0.3% of lanthanum, 0.1%-0.5% of cerium, 0.09%-0.3% of yttrium and 0.06%-0.2% of strontium. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 1, after the tungsten is firstly melt in a high-frequency high-temperature furnace, the cobalt, the chromium and the molybdenum are added in sequence; 2, the metals are introduced into a vacuum smelting furnace after melting, and then the cerium, the lanthanum, the titanium, the yttrium andthe strontium are added for vacuum melting; 3, a smelted and molten metal solution is introduced into a rectangular parallelepiped mold, and is cooled after being formed in a vacuum; and 4, for a cooled alloy metal ingot, residues in an alloy are cut off and separated from the alloy by a material reducing method, the remaining materials are machined by wire cutting and lathe turning, and the cobalt-chromium ceramic-metal alloy disc with the diameter being 98mm and the thickness being 10mm-25mm is machined. Compared with existing products, the cobalt-chromium ceramic-metal alloy disc is high inengraving machining yield and stable in quality, and is suitable for promotion and use.
Owner:南通今日高科技新材料股份有限公司
Replaceable energy-dissipating connection components for beam-to-column connections of fabricated frames
ActiveCN106499247BEase of implementation of design principlesSmall plastic strainProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingArchitectural engineeringRebar
The present invention proposes and invents a replaceable energy-dissipating connection assembly applied to the beam-column connection of the assembled frame. It is composed of rods, restraining parts and connecting parts. One end is connected to the node anchor reinforcement embedded in the column, and the other end is connected to the beam end longitudinal reinforcement embedded in the beam. Under the action of earthquake, the energy-dissipating steel bar yields before other components and components and uses plastic hysteresis to dissipate the seismic energy. This kind of replaceable energy-dissipating connection component is used for the connection of prefabricated beams and columns in prefabricated frame structures. It can induce the plastic damage of the structure to concentrate on the energy-dissipating steel rods under moderate and large earthquakes, and can improve the seismic ductility of the structure while avoiding the damage of beams and columns. For component damage, the structure can be quickly repaired by simply replacing energy-consuming components after an earthquake, so that the post-earthquake repair efficiency of the structure is significantly improved. The application of replaceable energy-consuming connection components meets the requirements of building industrialization development.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of manufacturing magnesium alloy processing materials with low cycle fatigue life improved by pre-straining
ActiveUS8505353B2Process safety and stabilityLow cycle fatigueMetal rolling arrangementsPre strainPre straining
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
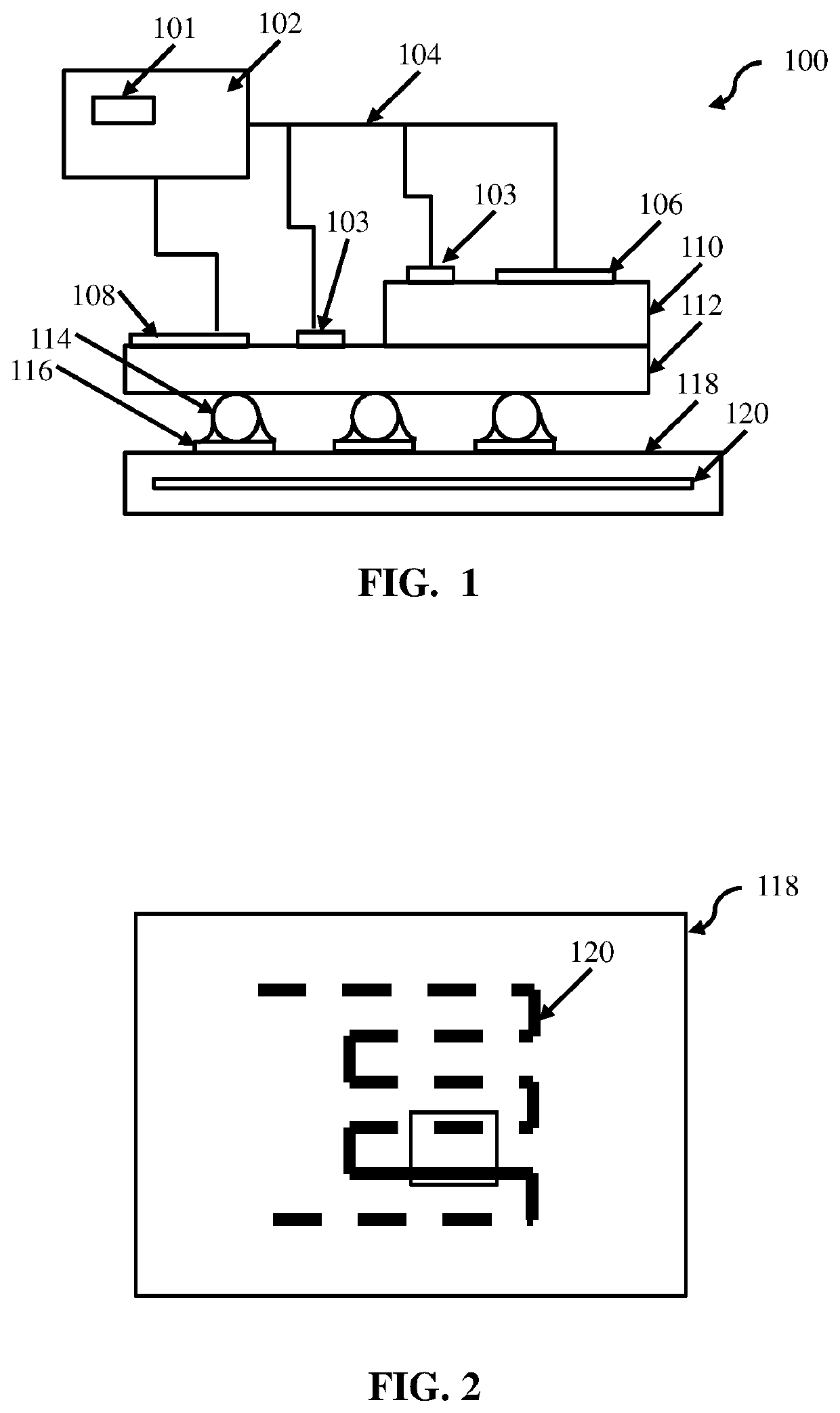
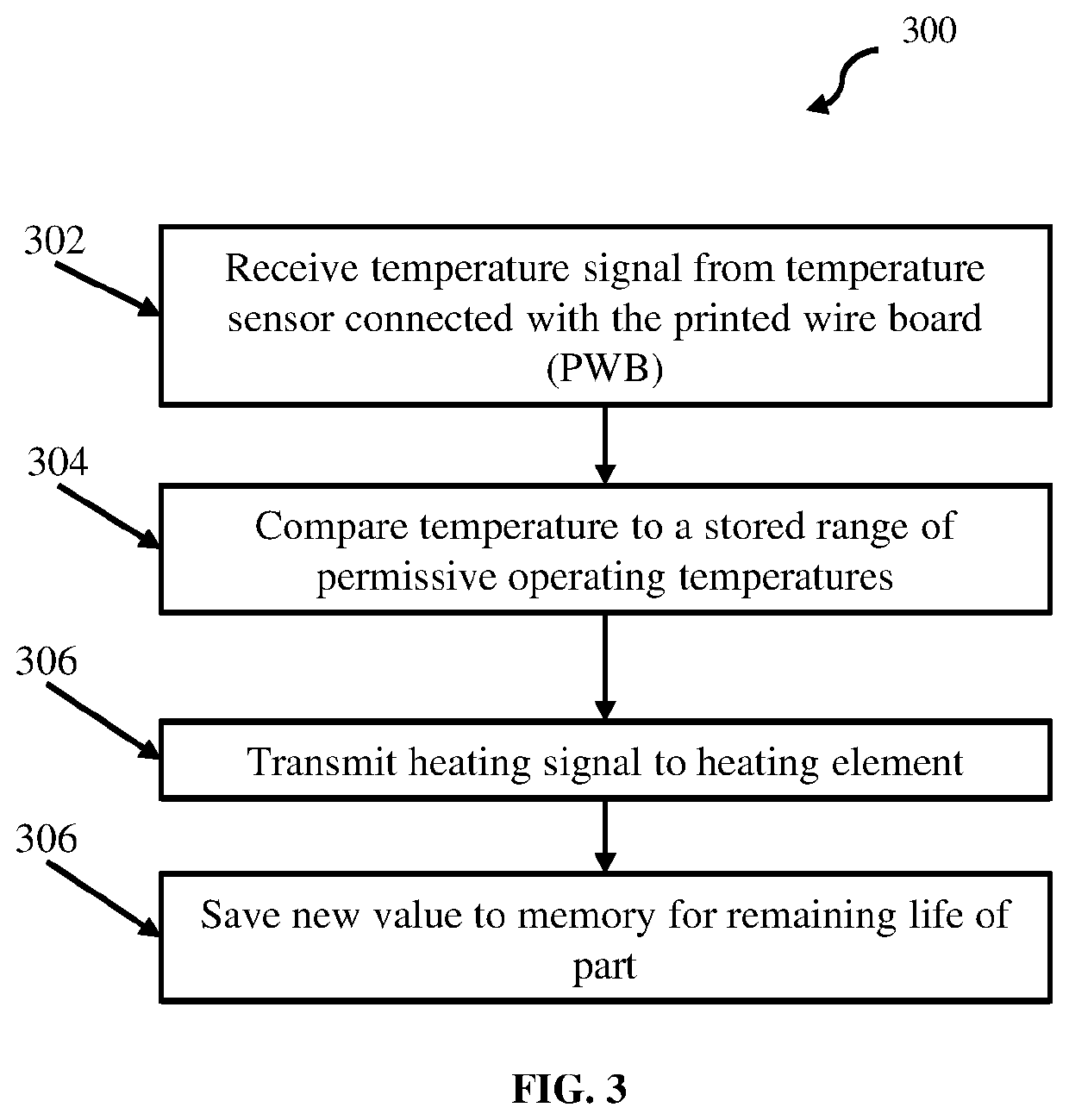
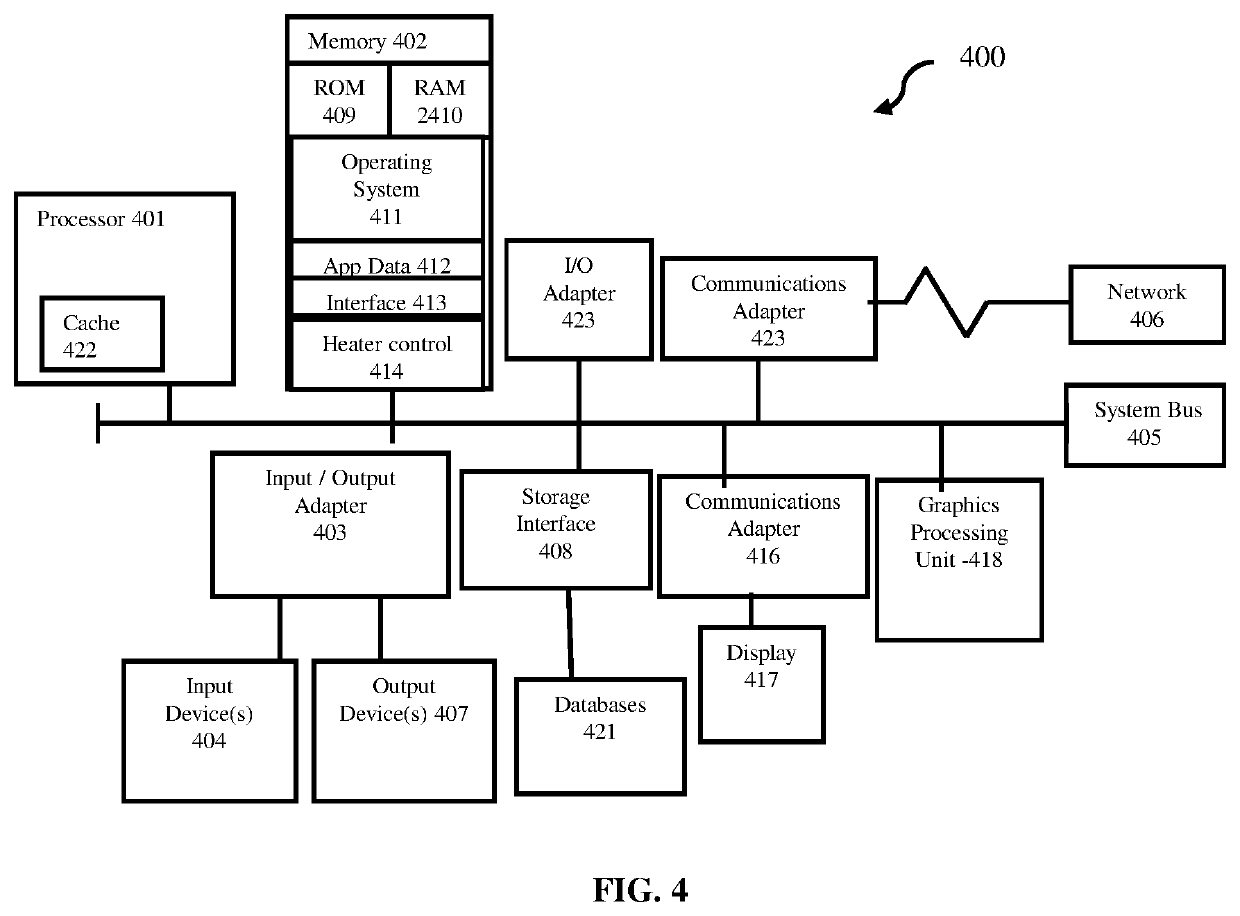
Low cycle fatigue prevention
ActiveUS10887979B2Low cycle fatiguePrinted circuit assemblingElectronic circuit testingOperating temperature rangeElectronic component
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Characterization method of fatigue, creep and fatigue-creep interaction unified life of materials
ActiveCN107677547BSolid theoretical foundationSimplify the modeling processMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesModel implementationNon linear behavior
The invention discloses a characterization method of material fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life, and belongs to the field of service life prediction of aero-engine critical materials. The characterization method is used for solving service life characterization and prediction problems of materials under low cycle fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction conditions. According to the principles, a power function form service life prediction method non-linear behavior characterization capacity is established via fatigue-creep interaction, low cycle fatigue, and creeptests of materials at different holding time, and obtaining of effective holding time and normalization dimensionless service life via normalization calculation method. The characterization method iscapable of realizing accurate characterization of service life of materials under low cycle fatigue and fatigue-creep interaction conditions, and especially, consideration and accurate prediction ofcreep service life can be realized. The advantages of the characterization method are that consideration of both physical mechanisms and model implementation convenience is realized, and material lowcycle fatigue, creep, and fatigue-creep interaction service life characterization and prediction problems are solved effectively.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for simulating fatigue test of inter-pole connection wire
InactiveCN109342224ALow cycle fatigue injuryLow cycle fatigueMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesRelative displacementUnit operation
The invention discloses a method for simulating a fatigue test of an inter-pole connection wire, wherein a periodic load can be applied to an actual assembly of the inter-pole connection wire by usinga low cycle fatigue tester, and an alternating load generated by the circumferential relative displacement between the two magnetic poles can be simulated when a hydraulic generator is operated in arated running state and a runaway state; meanwhile, the inter-pole connection wire can be heated to simulate the actual temperature rise in the unit operation, so that the startup and shutdown times prediction of the inter-pole connection wire of the hydraulic generator in the rated running or the runaway state are obtained through the number of fatigue cycles of the corresponding inter-pole connection wire under different loads; and the structural optimization of the inter-pole connection wire is guided, so that the data support is provided for the service life prediction of reliable startupand shutdown times of the large hydraulic generator including the pumped-storage unit.
Owner:HARBIN ELECTRIC MASCH CO LTD
Replaceable energy-dissipating connection components for beam-to-column connections in fabricated concrete frames
ActiveCN106592807BEase of implementation of design principlesSmall plastic strainProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingClassical mechanicsAssembly (construction)
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of manufacturing metal member
InactiveUS20210040594A1Sufficient creep characteristicLow cycle fatigue characteristicAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySolution treatmentLow-cycle fatigue
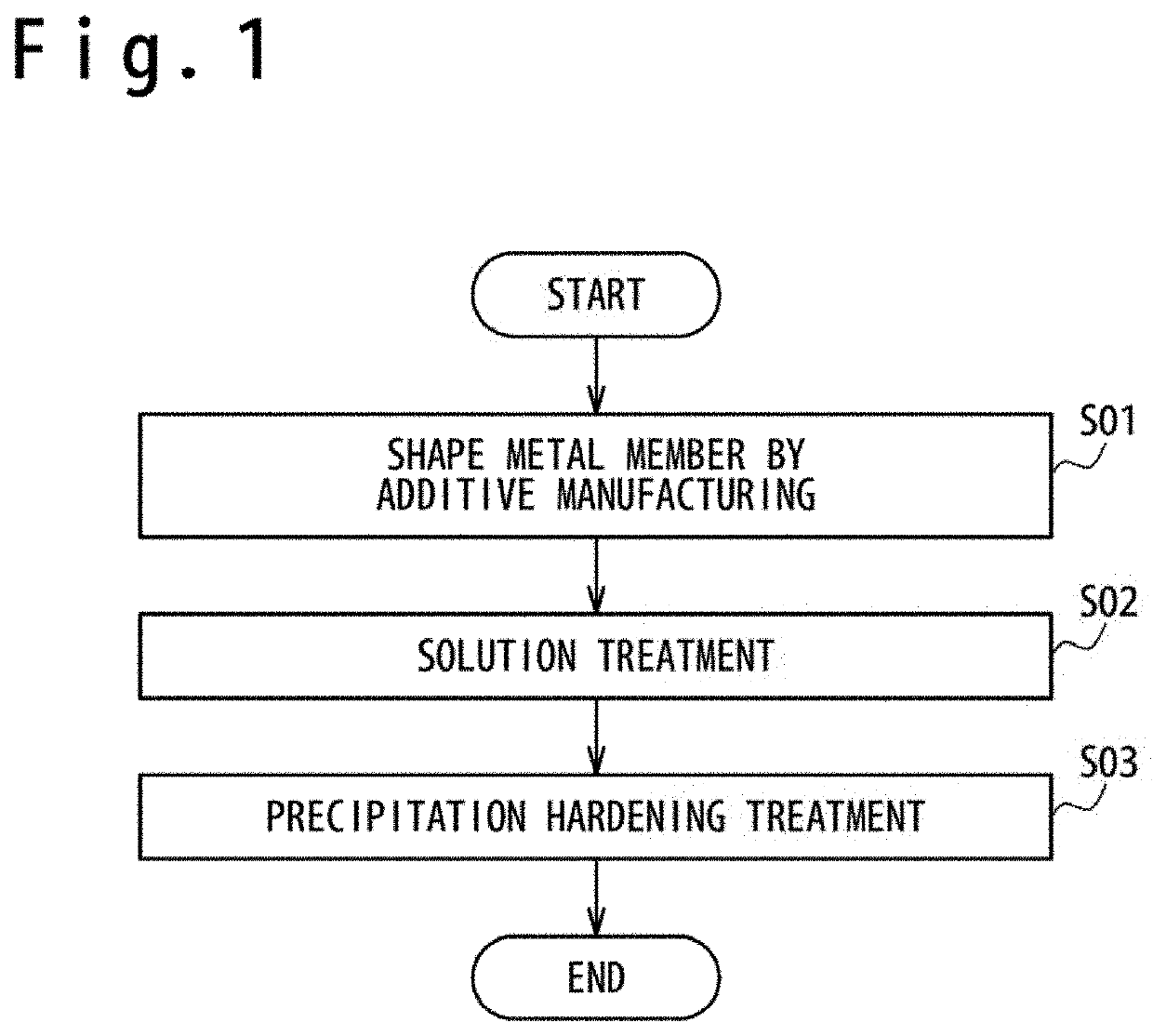
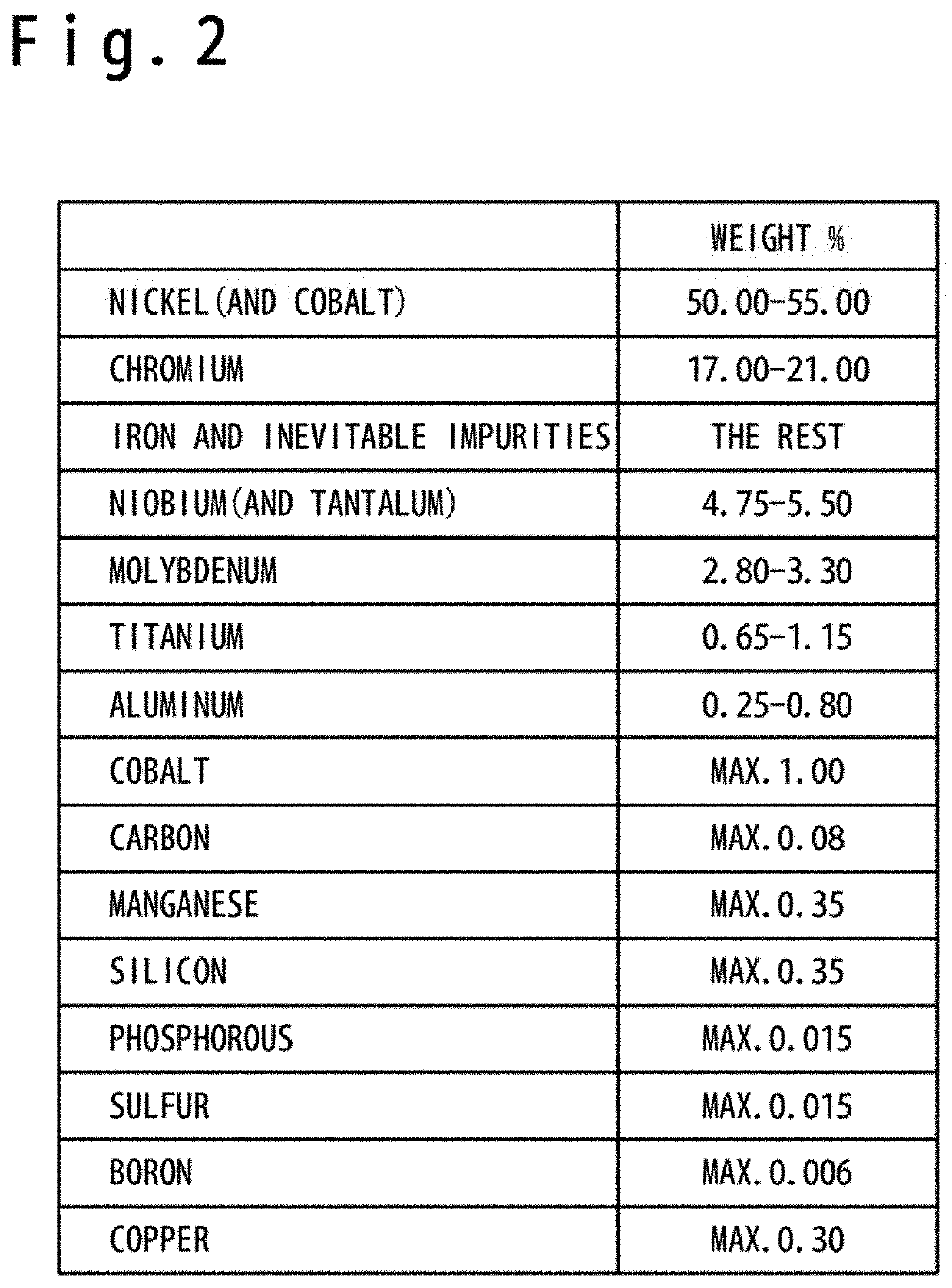
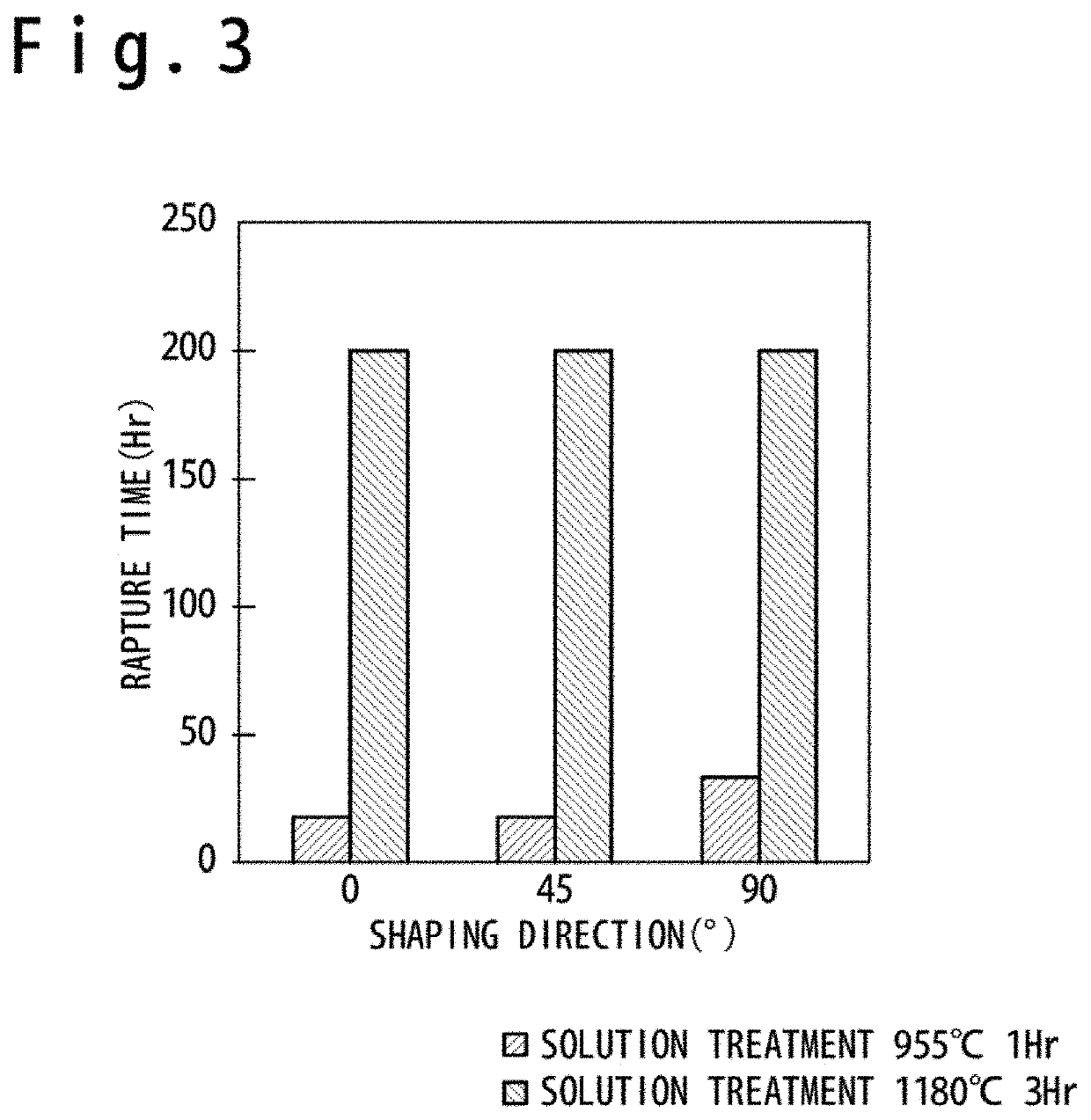
A method of manufacturing a metal member, includes shaping a metal member configured of Ni-based alloy by an additive manufacturing; and carrying a solution treatment to the metal member. In the solution treatment, a heat treatment is carried out at a temperature in a temperature range of (TC−100)° C. to (TC−50)° C. (TC is a solid solution temperature of Ni-based alloy). In this way, a creep characteristic and a low cycle fatigue characteristic have been secured sufficient in the metal member shaped by the additive manufacturing.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
A kind of high temperature resistant tungsten-molybdenum alloy and its preparation method
The invention provides a high-temperature resistant tungsten-molybdenum alloy and a preparation method thereof. The weight percentages of each group are as follows: tungsten: 50-80%, molybdenum: 35-50%, rhenium: 10-30%, zirconium: 2-5%, Impurities: 0.1-1%. The preparation method is to mix various metal powders evenly, dehydrate in a vacuum, sieve, and mix. After pressing, they are placed in a smelting furnace for sintering. After sintering, they are cooled and made into filaments or ribbons. The preparation method of the invention has a simple process, good material properties, and good high temperature resistance, and is particularly suitable for making high temperature resistant accessories such as filaments for LED car lights.
Owner:天津市程田新能源股份有限公司
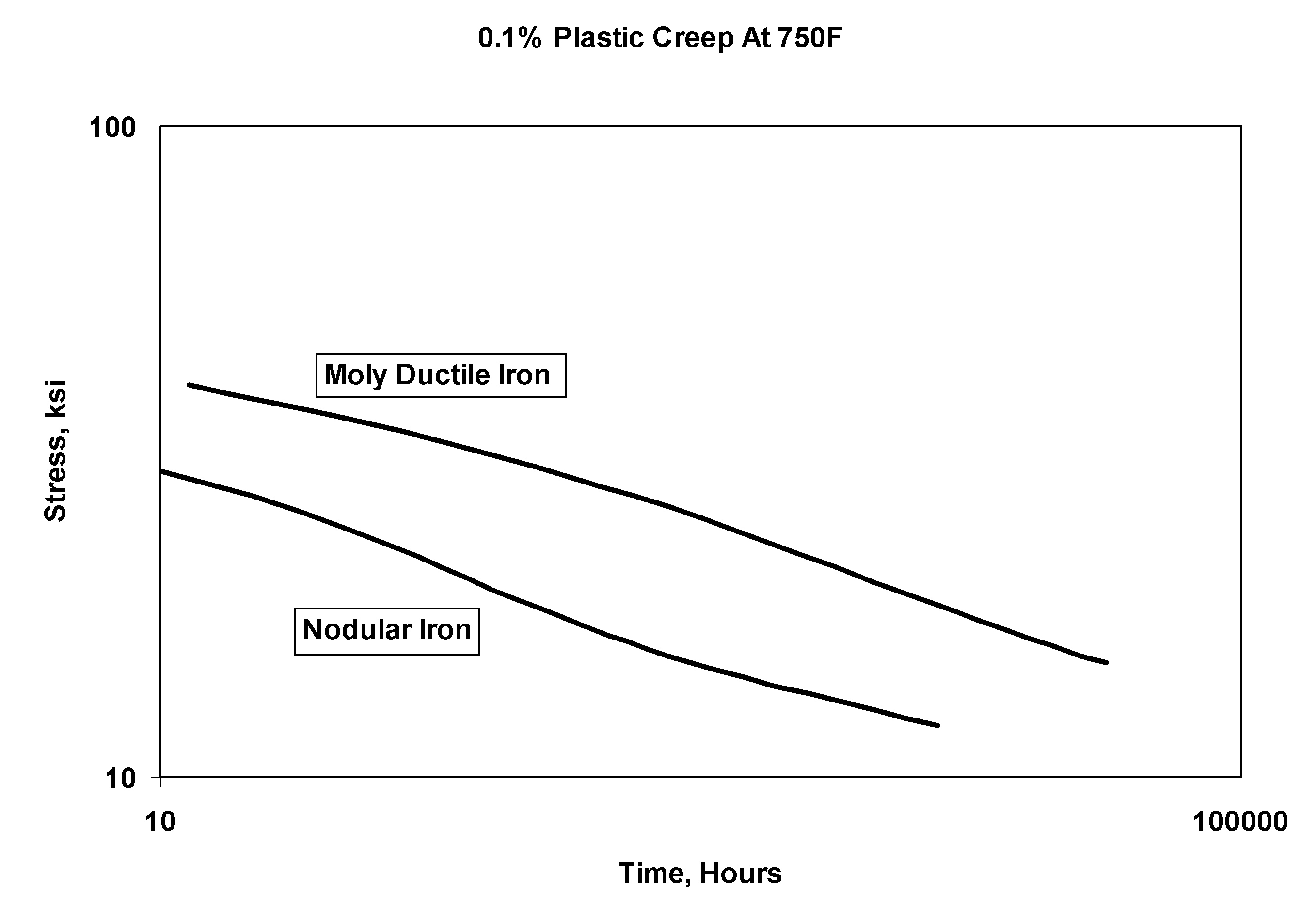
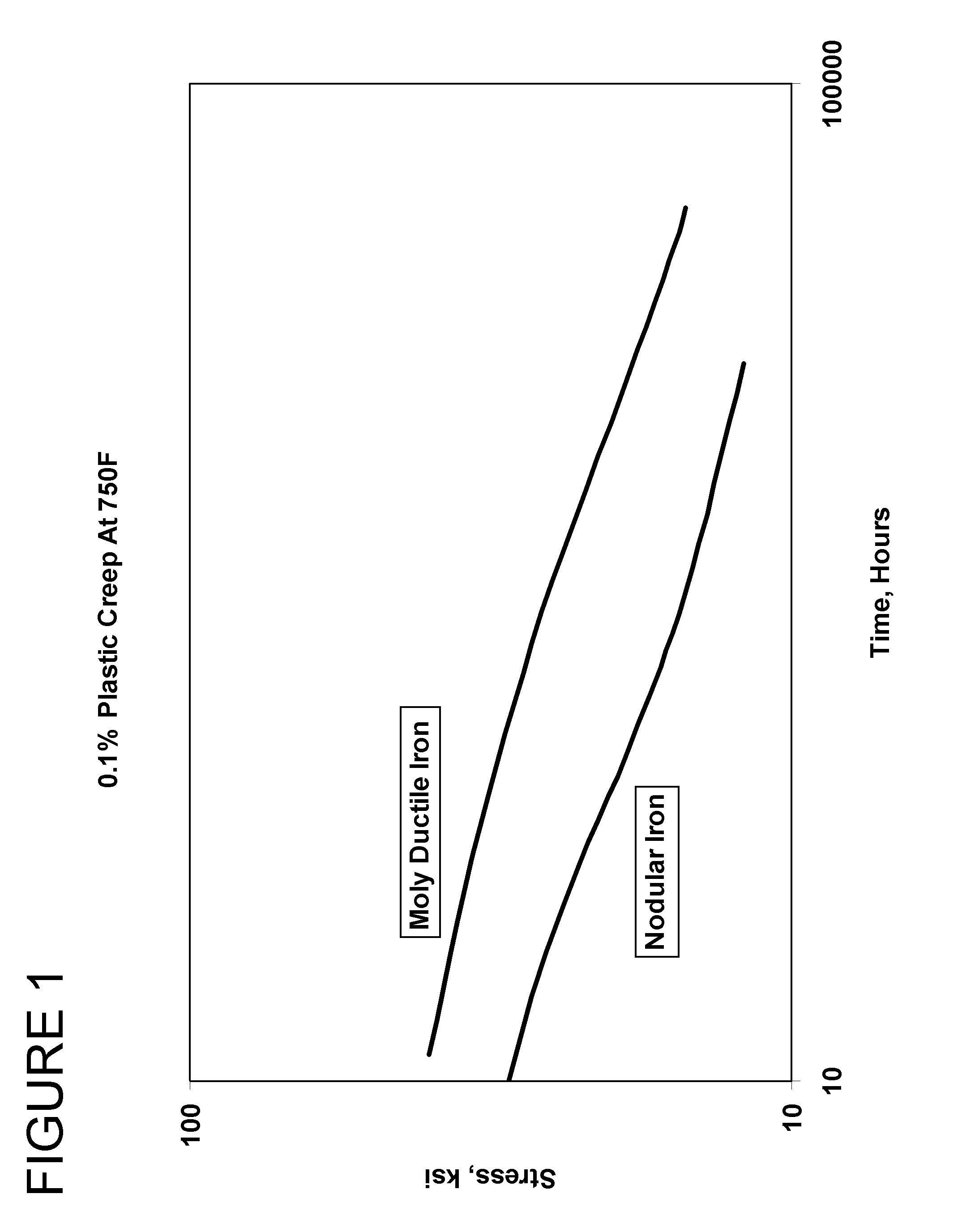
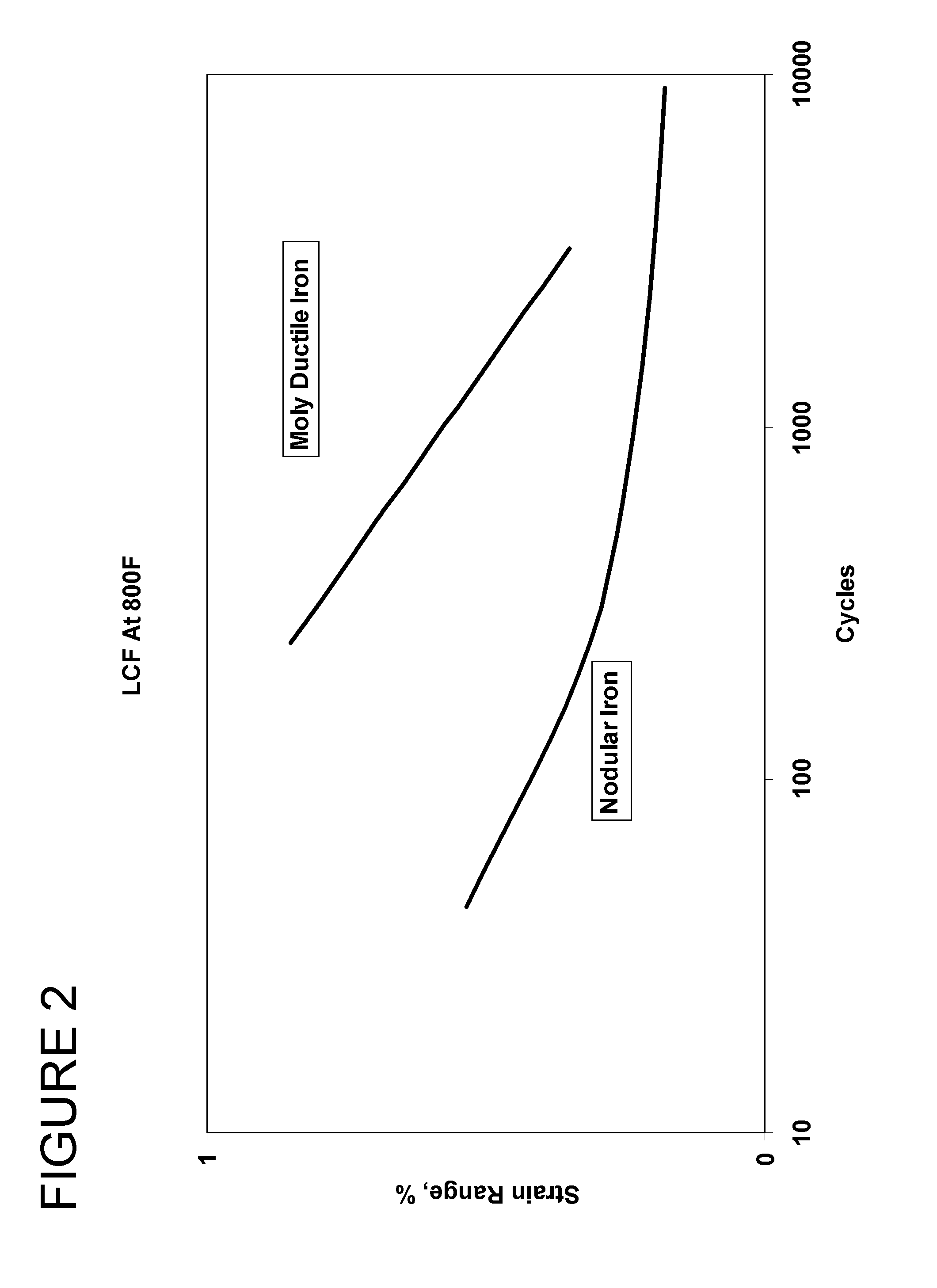
Method for improving creep resistance and low cycle fatigue properties of pressure-containing components
A method by which high temperature properties of a ductile iron alloy, including creep and LCF properties, can be increased for pressure-containing components that are subject to creep and low cycle fatigue. The method comprises modifying the ductile iron alloy to contain 0.4 to 0.8 weight percent molybdenum. A casting of the modified ductile iron alloy is produced and then annealed at a temperature of at least 725° C. for not less than five hours to eliminate carbides and / or stabilize pearlite in the casting. The annealed casting of the modified ductile iron alloy exhibits improved creep resistance and low cycle fatigue properties in comparison to an identical casting of a ductile iron alloy that does not contain molybdenum.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
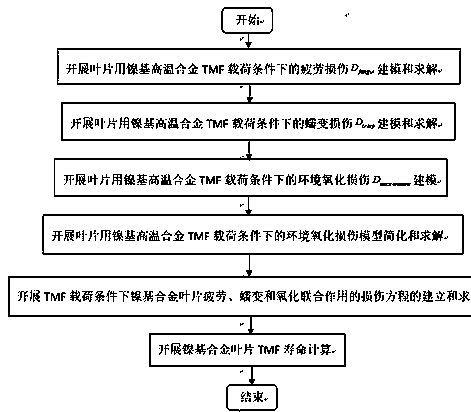
A LIFE PREDICTION METHOD FOR NICKEL-BASED SUPERALLOY BLADE UNDER THERMOMECHANICAL FATIGUE LOAD
InactiveCN108170905BThe modeling process is clearFully combine structural featuresDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageSuperalloy
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com