Life prediction method used for nickel-base superalloy blade under thermal mechanical fatigue load
A nickel-based superalloy, thermomechanical fatigue technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
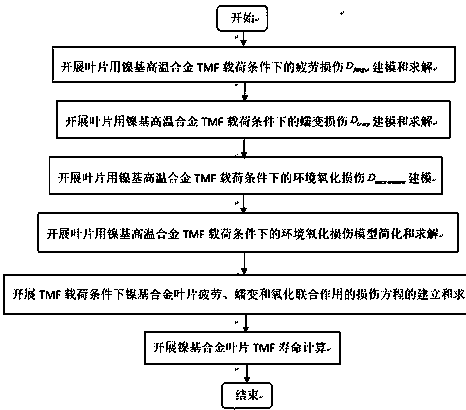
[0047] Example: Damage Characterization and Life Prediction Method of DZ125 Alloy Under TMF Condition of Blade
[0048] In step S1, the fatigue damage modeling and solution of the nickel-based alloy blade under the TMF load condition are carried out.
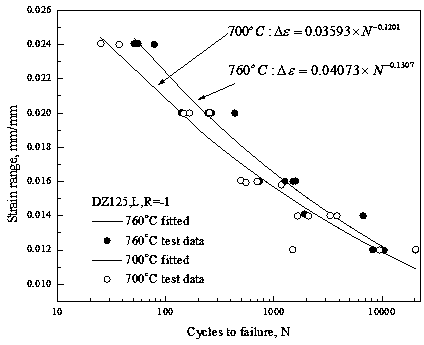
[0049] Δε mech =c(N fatigue ) d (1)
[0050] D. fatigue =1 / N fatigue (2)
[0051] In formulas (1) and (2), D fatigue Indicates the low-cycle fatigue damage under thermal-mechanical fatigue conditions; N fatigue Indicates the number of fatigue cycles, the unit is week N; Δε mech Indicates the plastic strain amplitude in mm / mm.
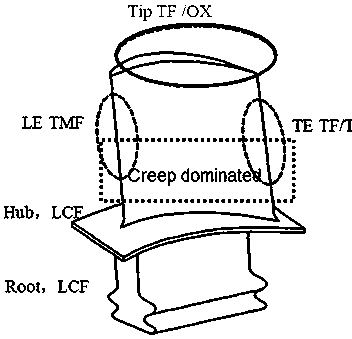
[0052] For an aero-engine DZ125 directionally solidified nickel-based superalloy blade, TMF fatigue damage modeling based on low-cycle fatigue experimental data was carried out. Depend on figure 2It can be seen intuitively that the dominant damage distribution in each area of the blade, where LE represents the leading edge of the blade, TE represents the trailing edge of the blade, Hub rep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com