Robot non-redundancy geometric error model analysis modeling method based on spinor theory
A technology of geometric error and modeling method, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems such as the loss of physical meaning of the model, the difficulty of non-redundant geometric error model, and the error deletion of the robot drive joint motion error parameters, so as to achieve easy programming and modeling. The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
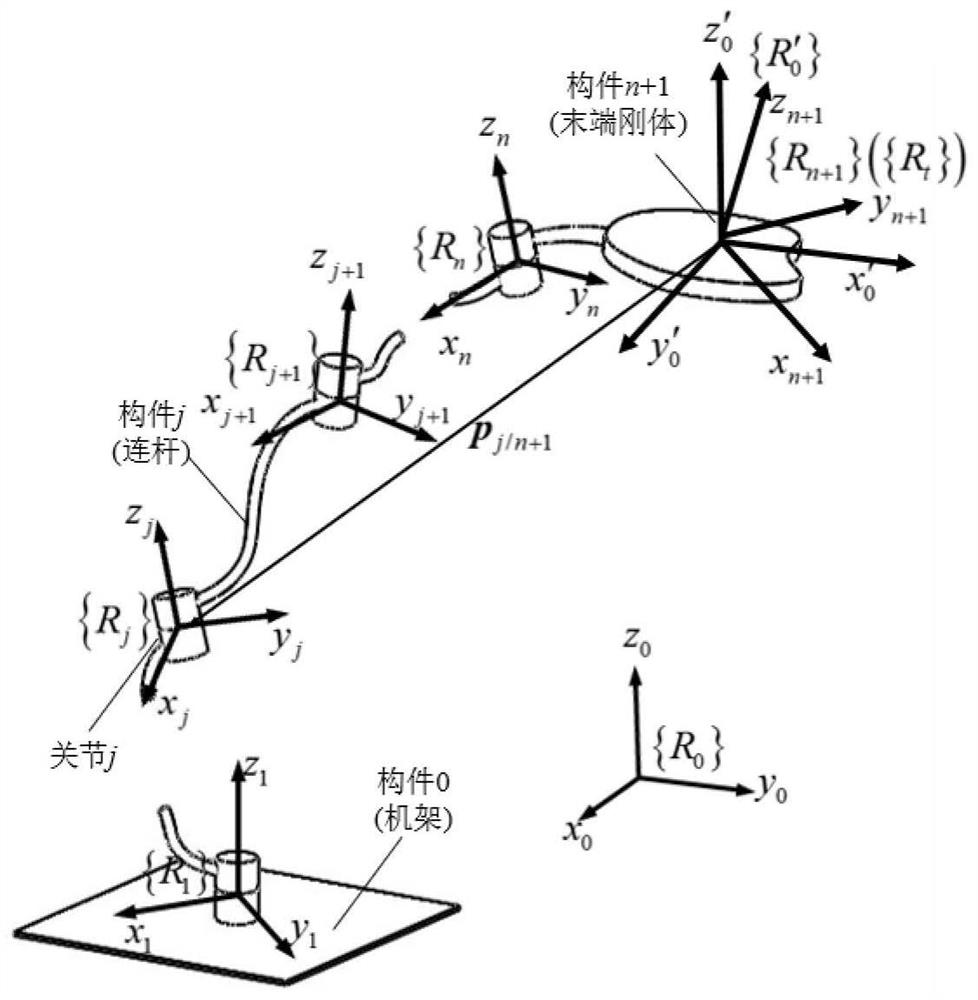
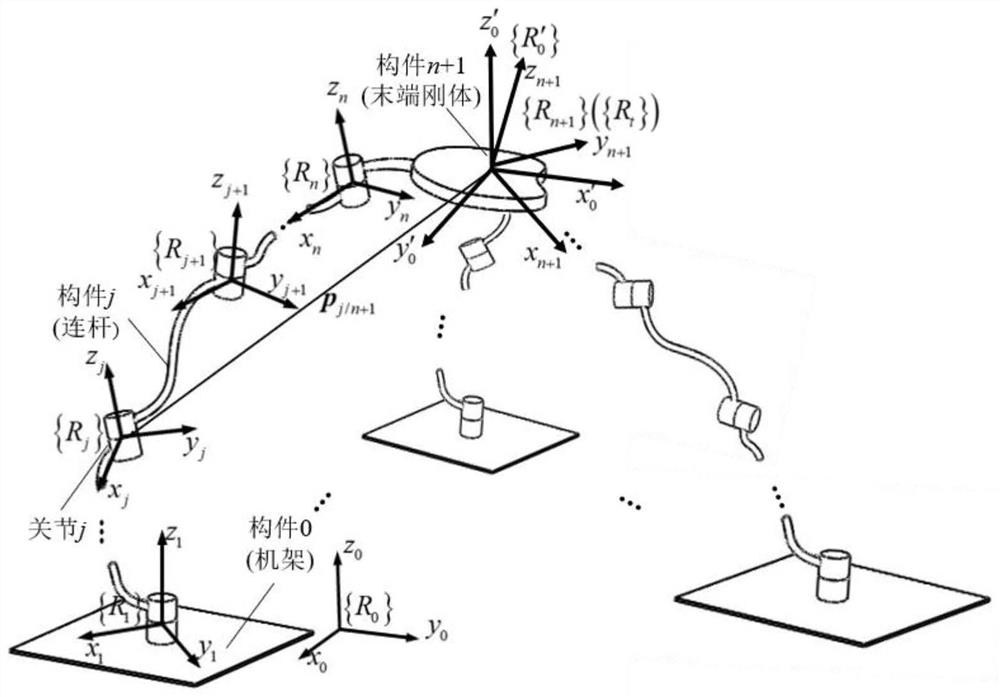
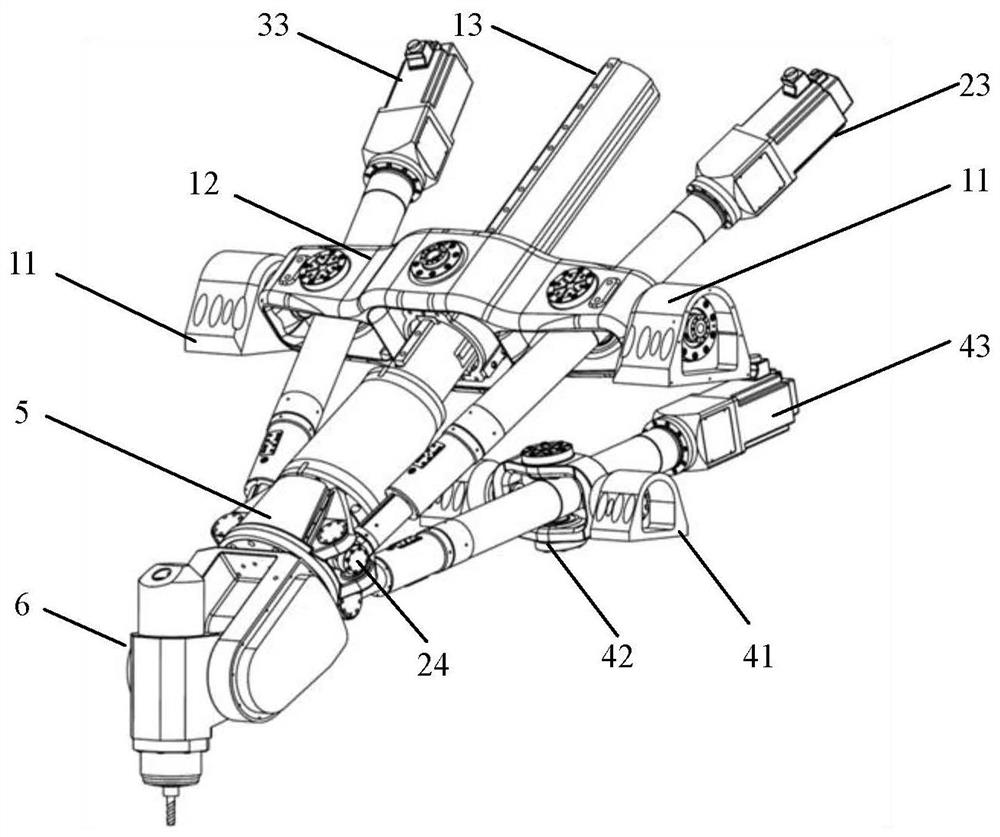
[0118] Embodiment: Utilize the modeling method of the present invention, aiming at the analytical modeling of a non-redundant geometric error model of a five-degree-of-freedom hybrid configuration equipment containing a rotating bracket disclosed in the patent document with the publication number CN104985596A.
[0119] (1) The structure of the five-degree-of-freedom mixed configuration equipment, such as image 3 and Figure 4As shown, the five-degree-of-freedom hybrid configuration equipment is composed of a three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism with one translation and two rotations and a rotor with two rotational degrees of freedom connected in series. The rotor 6 is connected to the dynamic Platform 5 is connected in series. The series-connected rotary head 6 connected in series at the end of the moving platform 5 is a two-degree-of-freedom A / C swing head. The three-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism includes a first length adjustment device 13 , a second length a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com