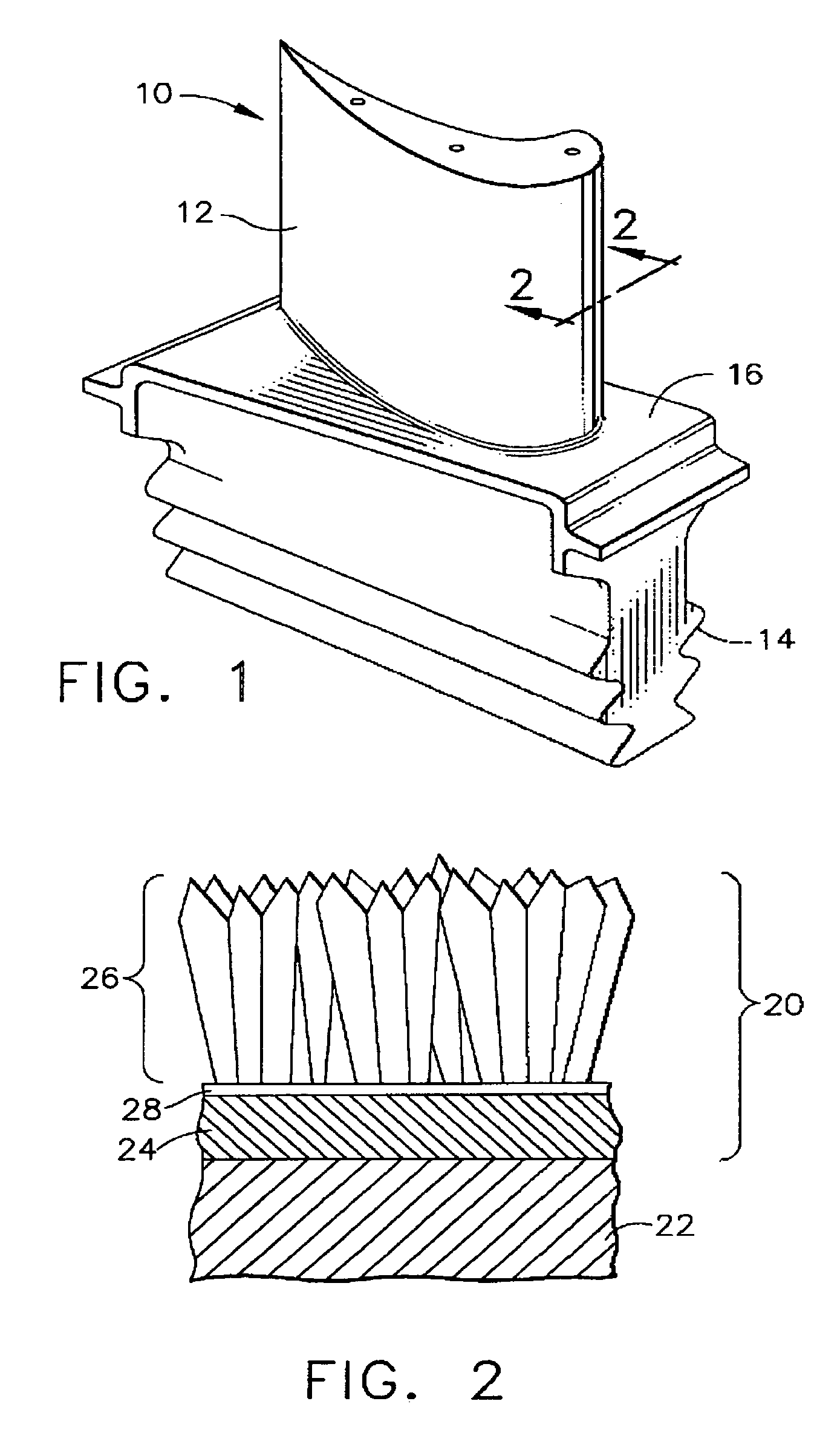
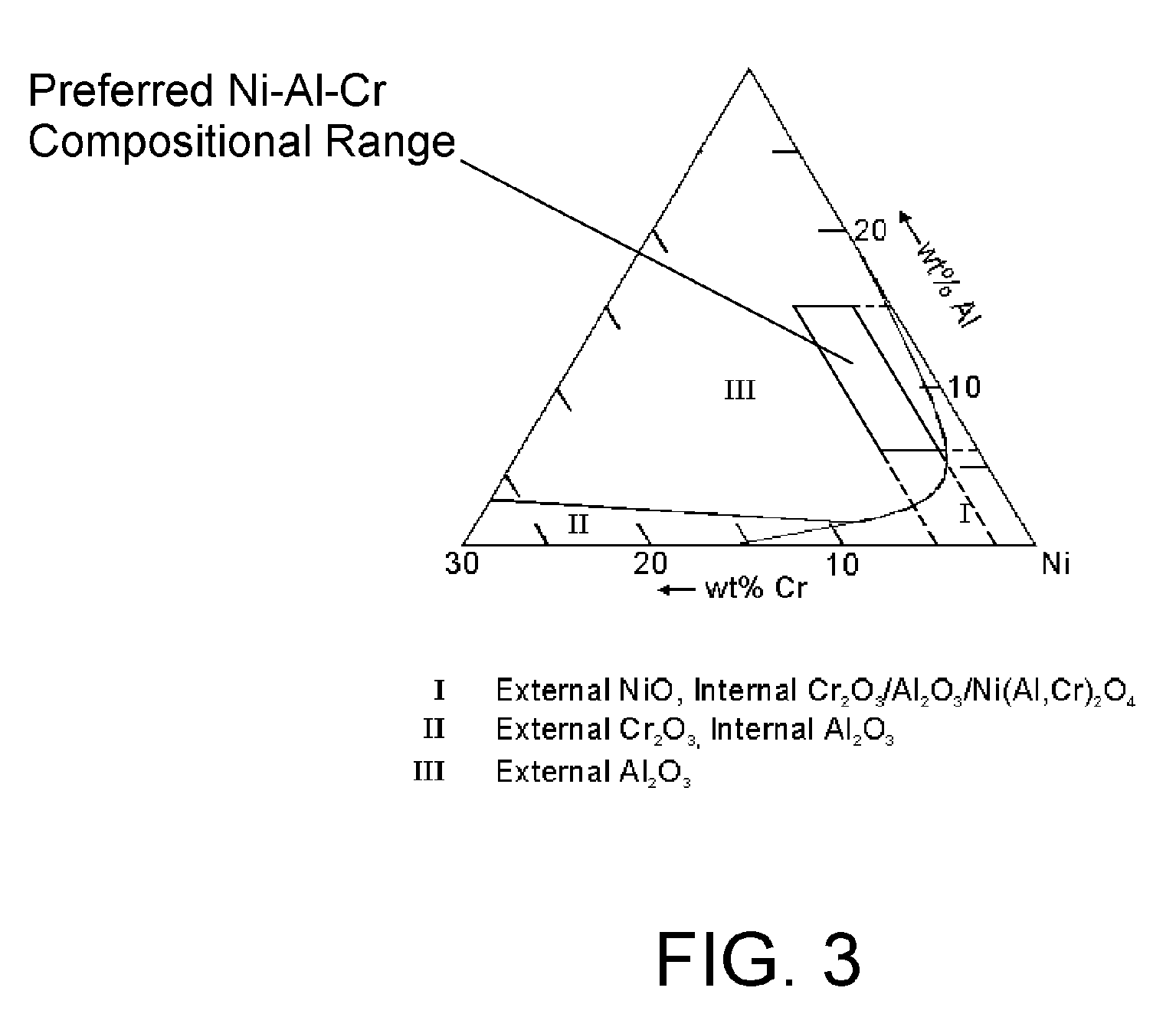
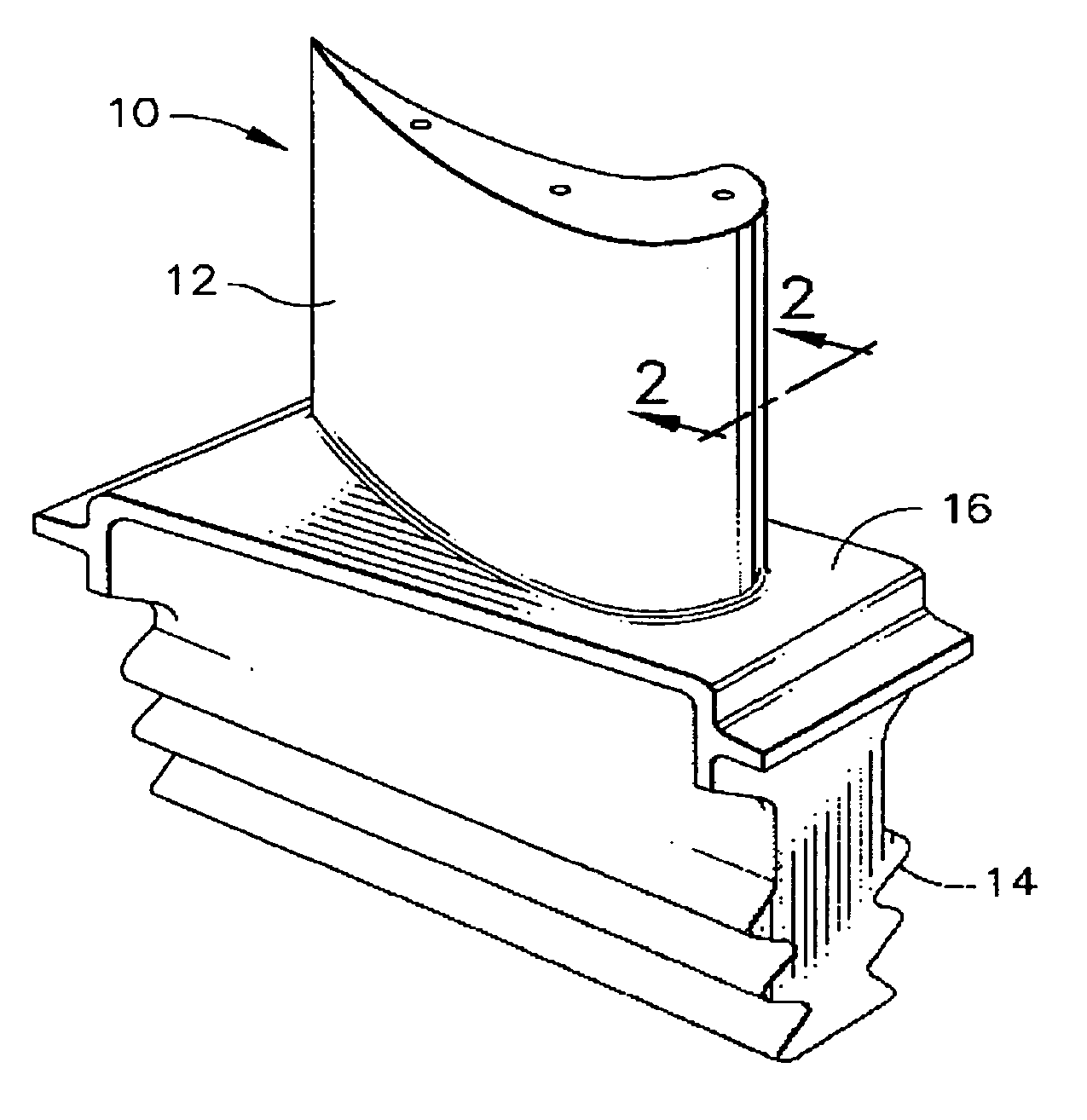
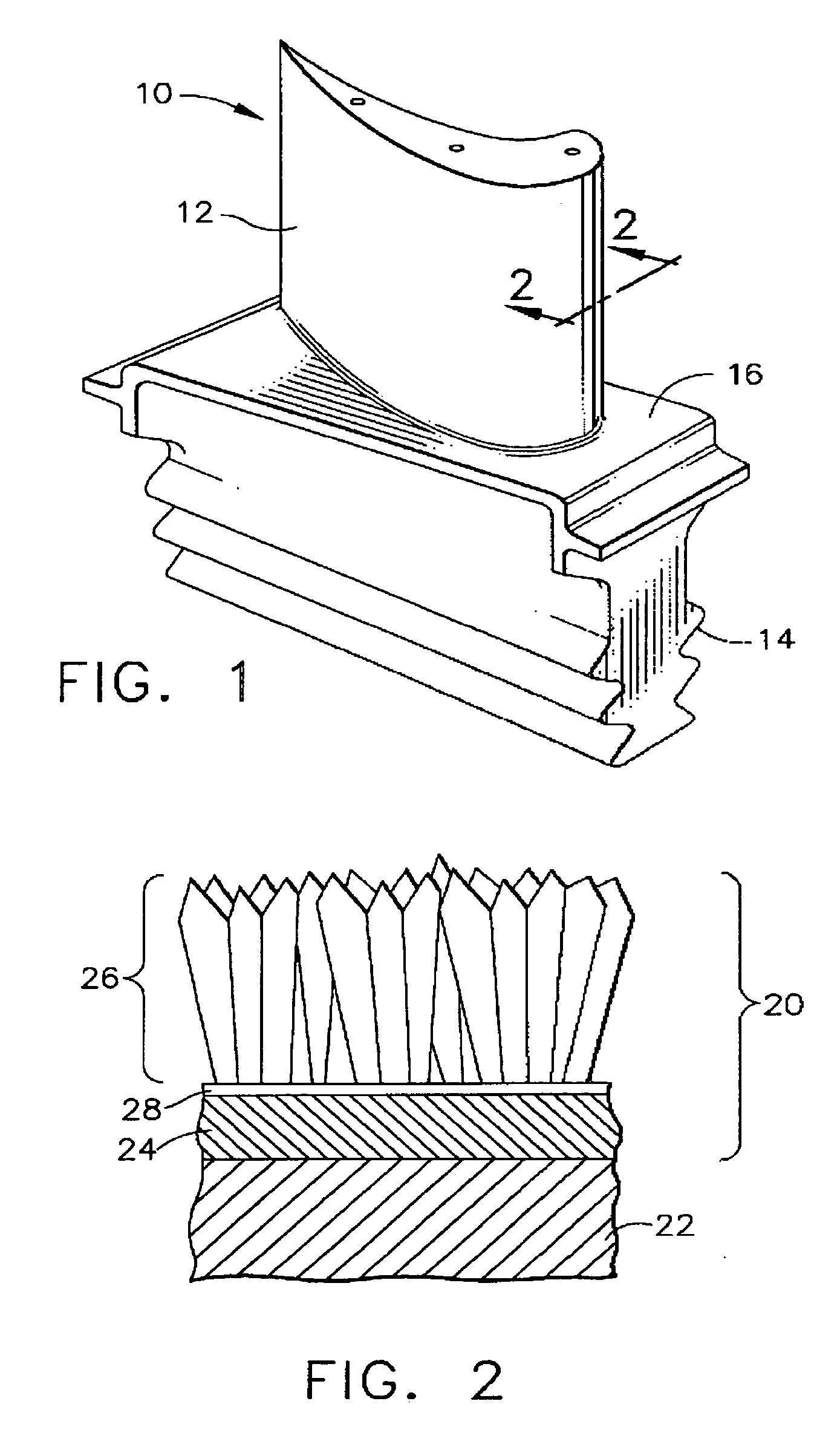
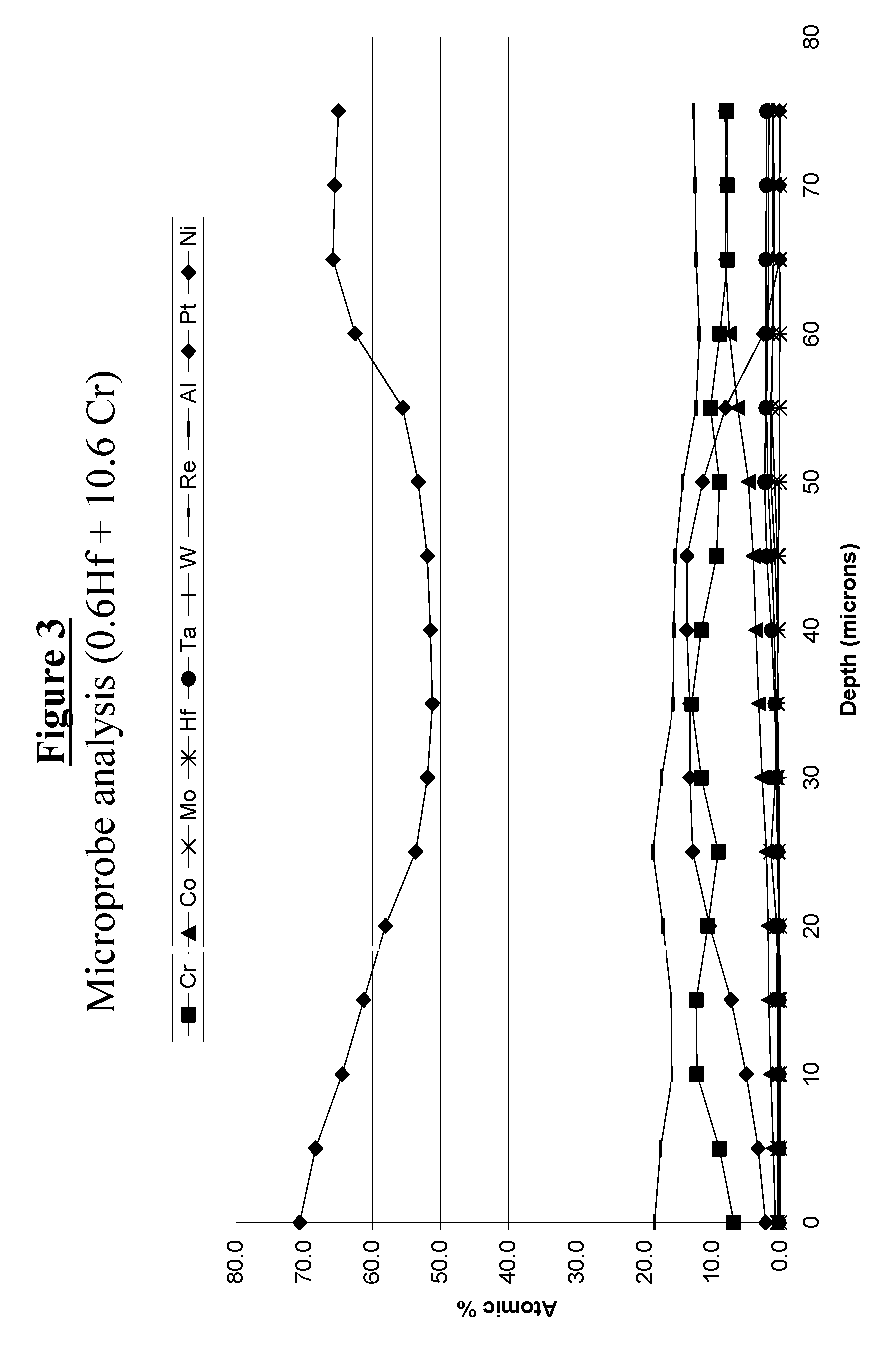
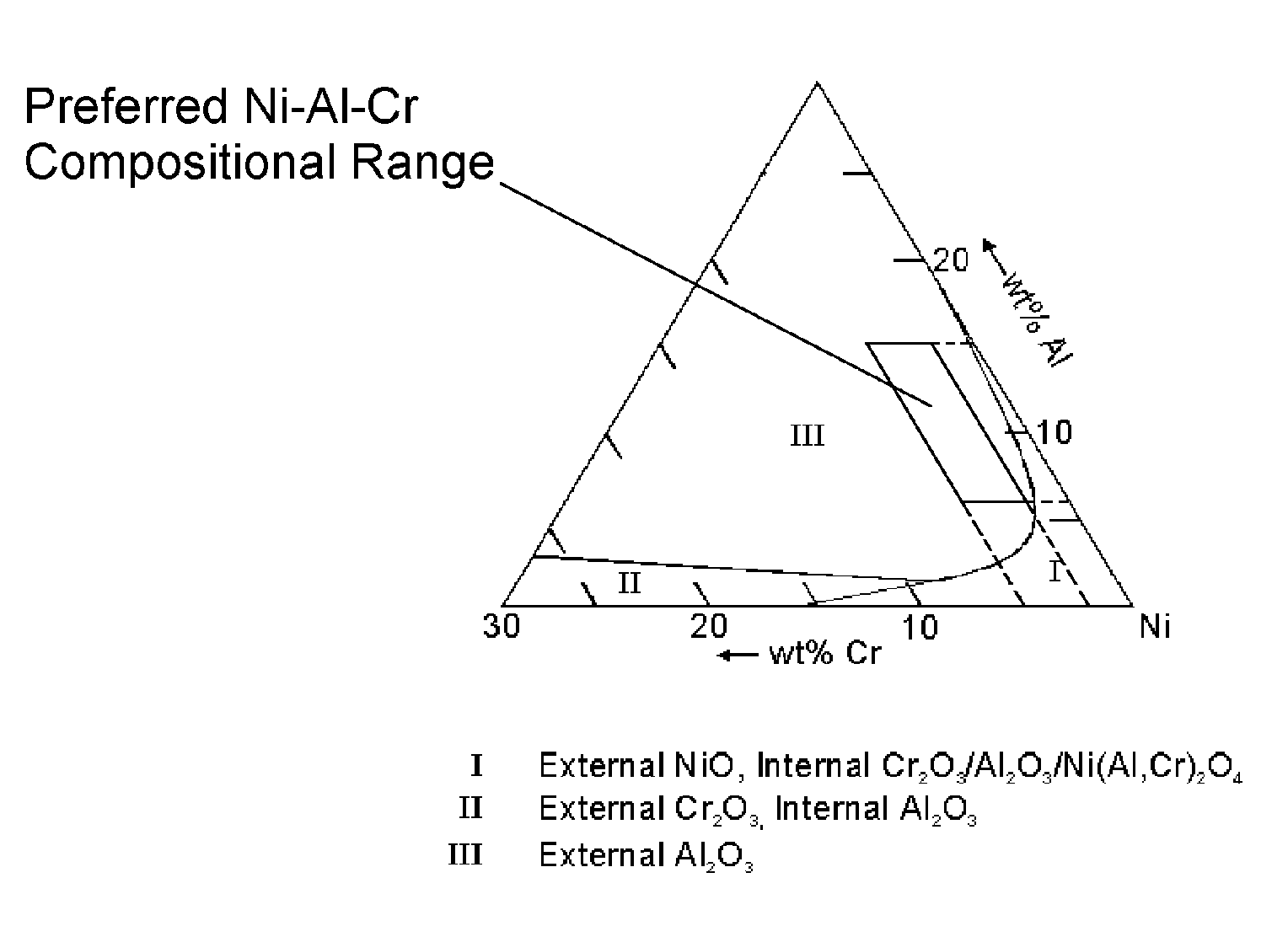
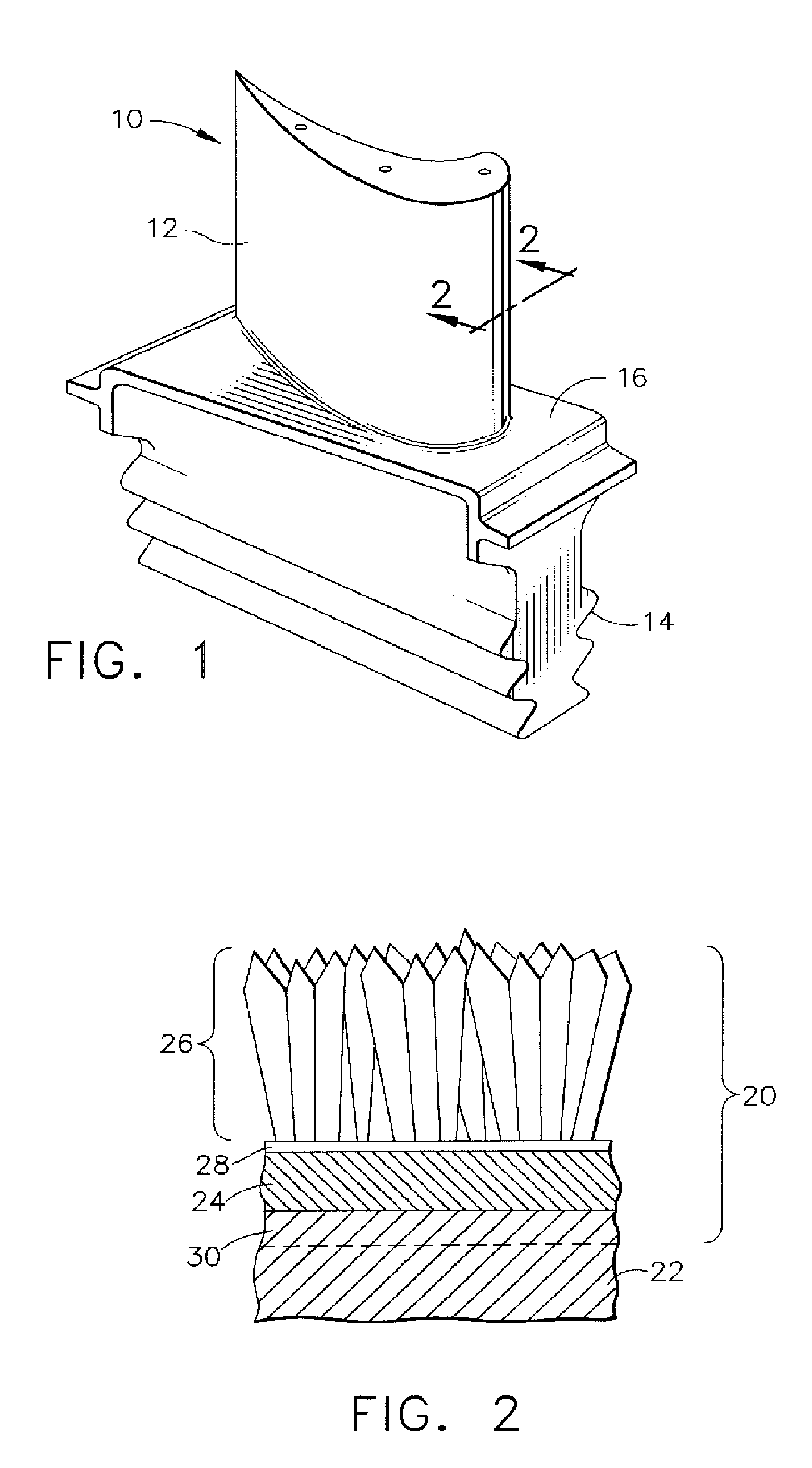
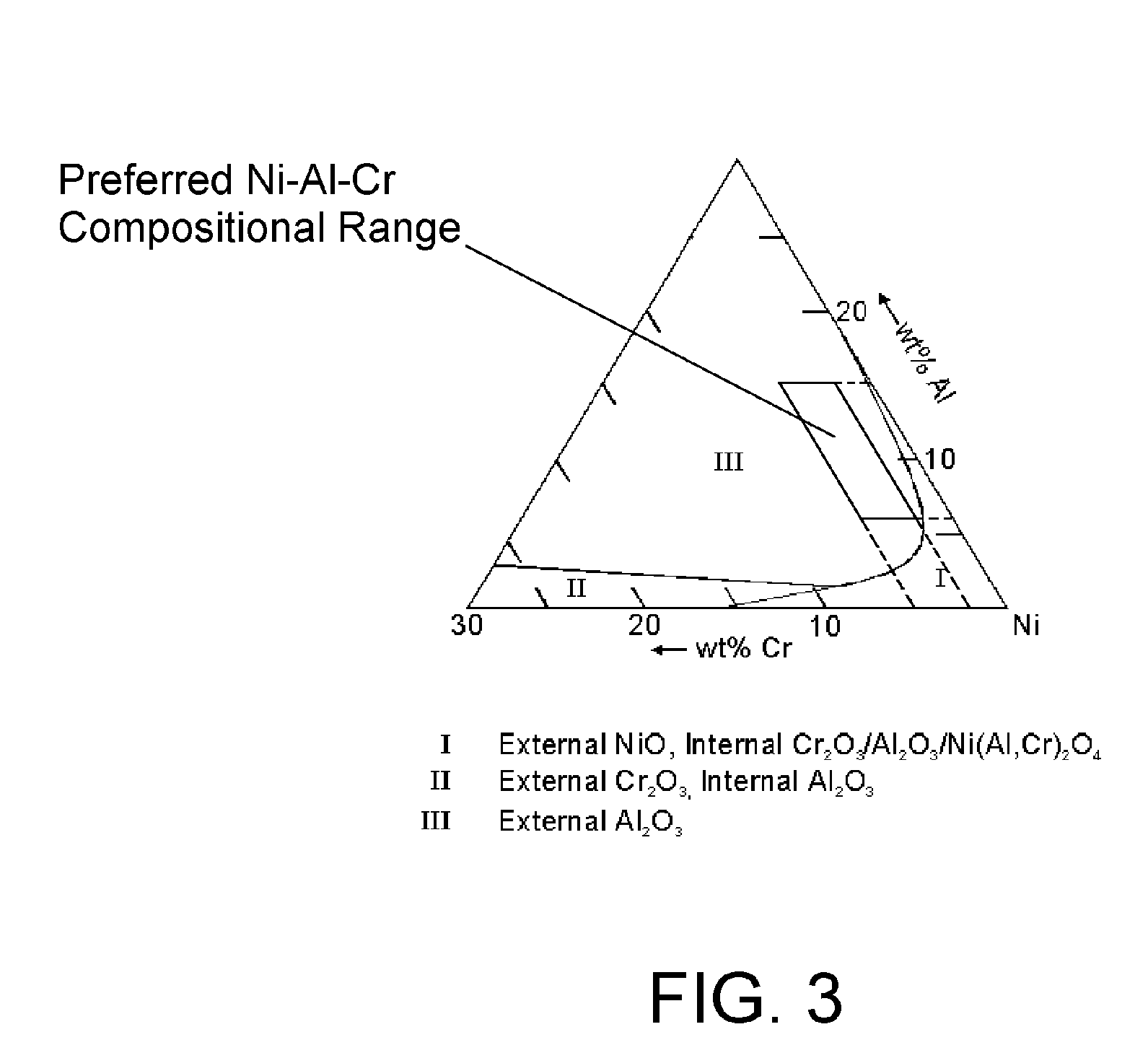
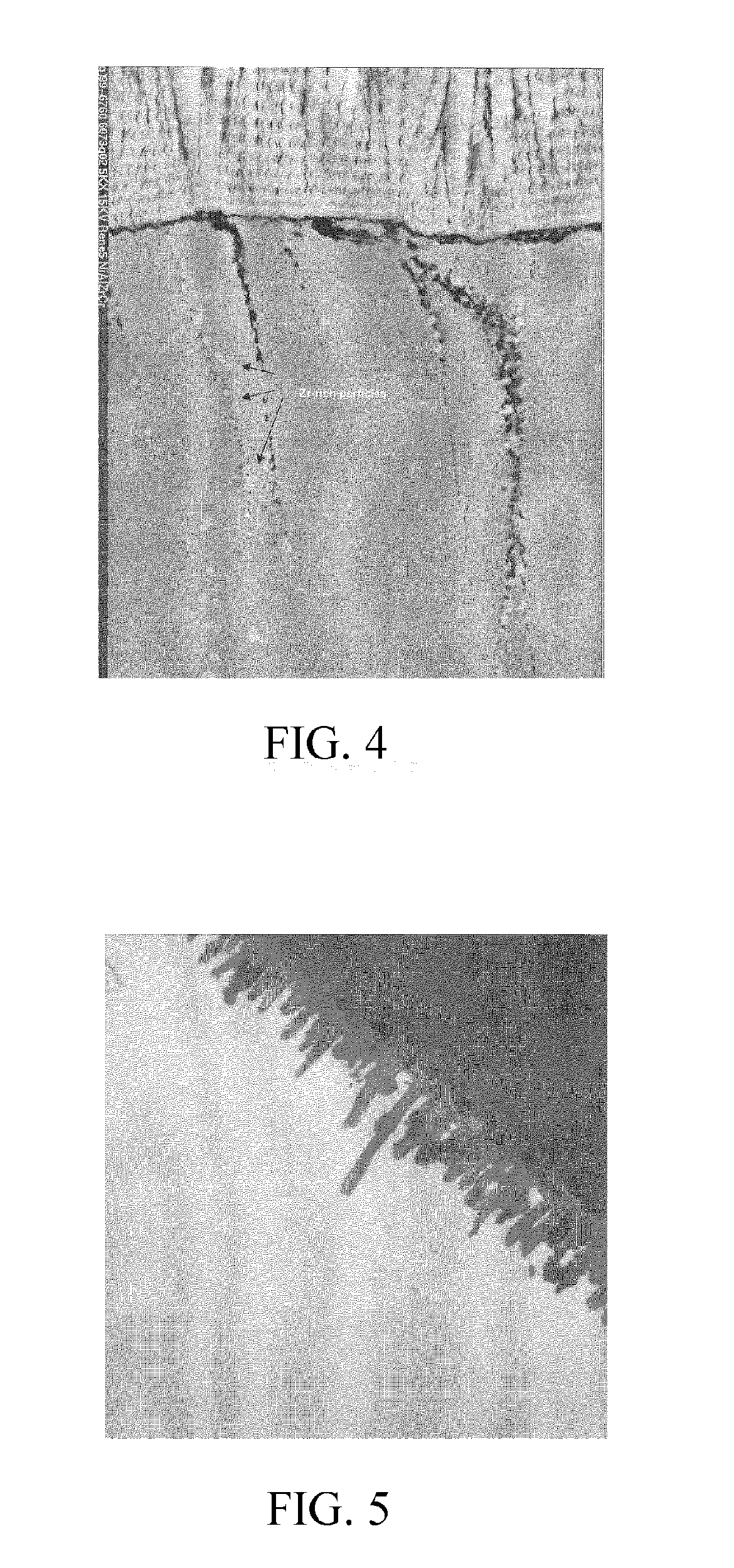
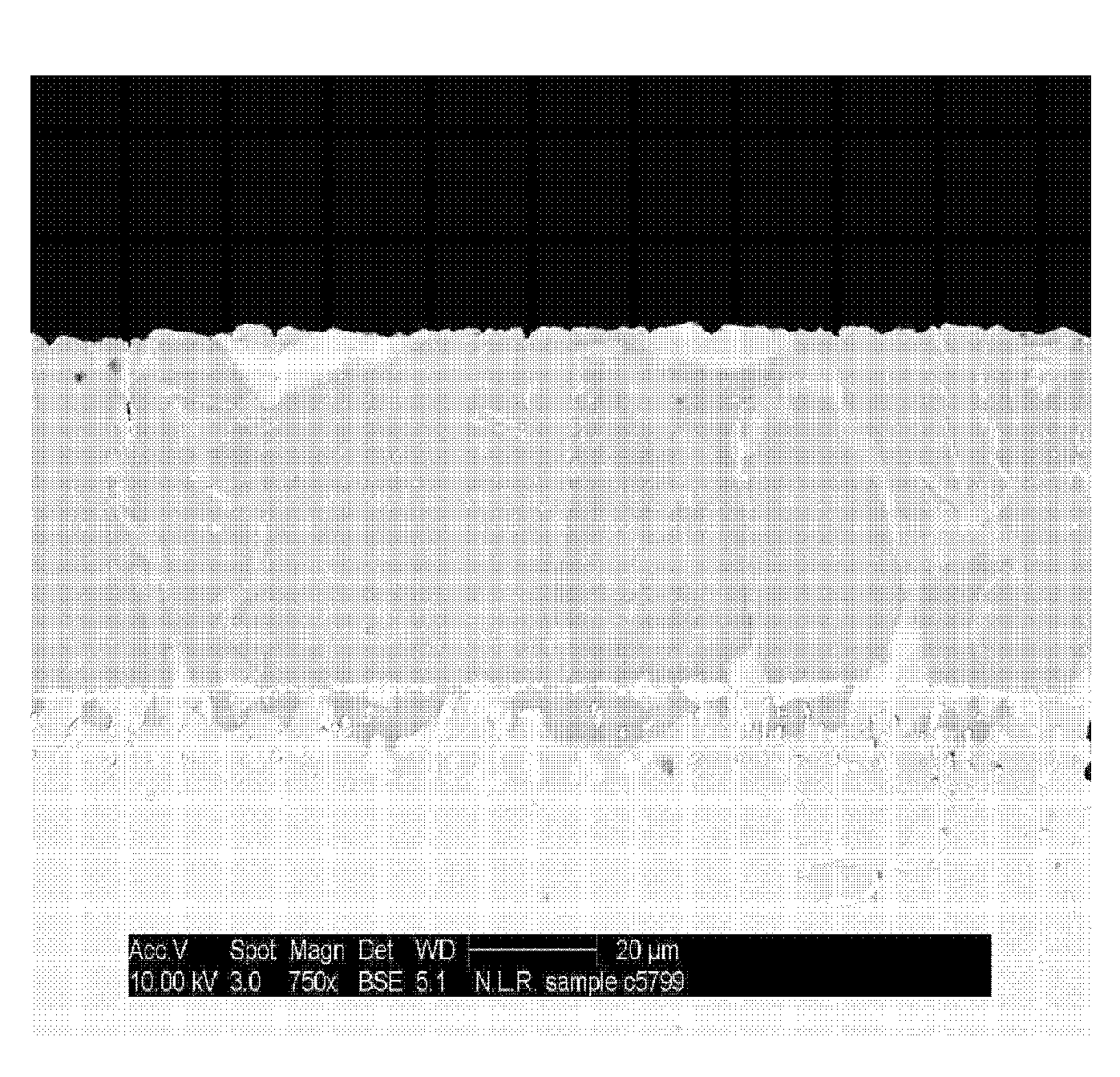
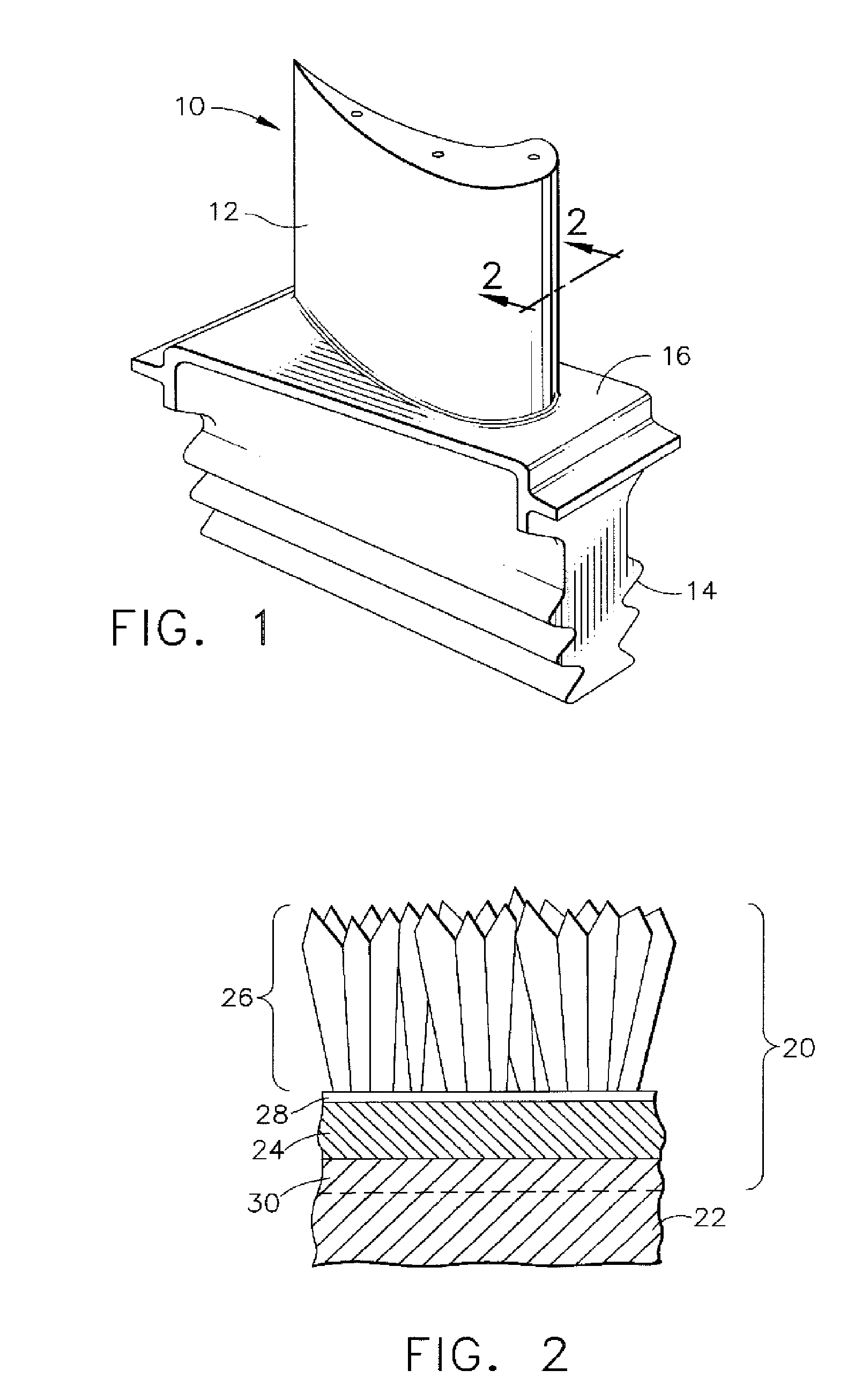
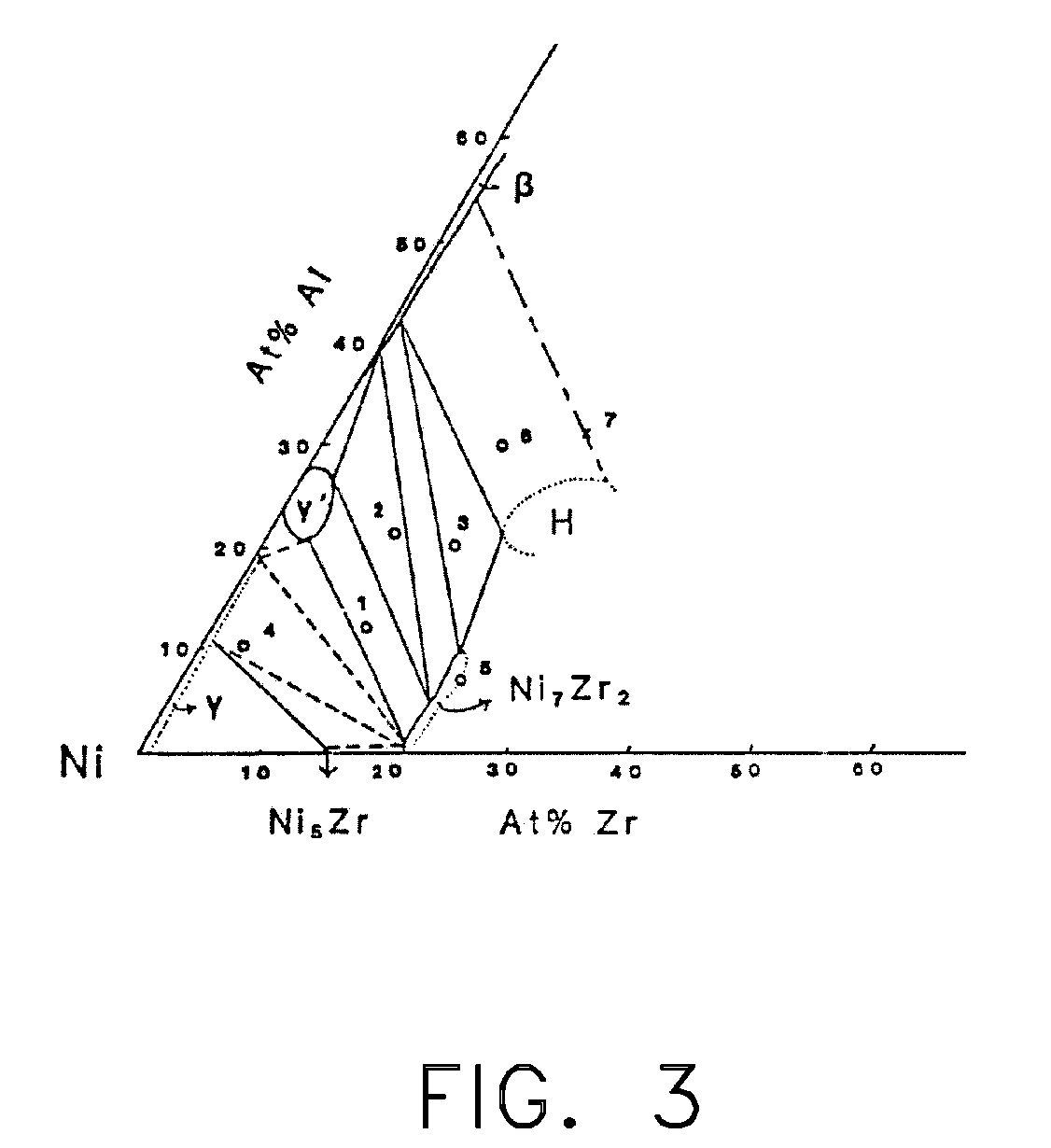
Patents
Literature
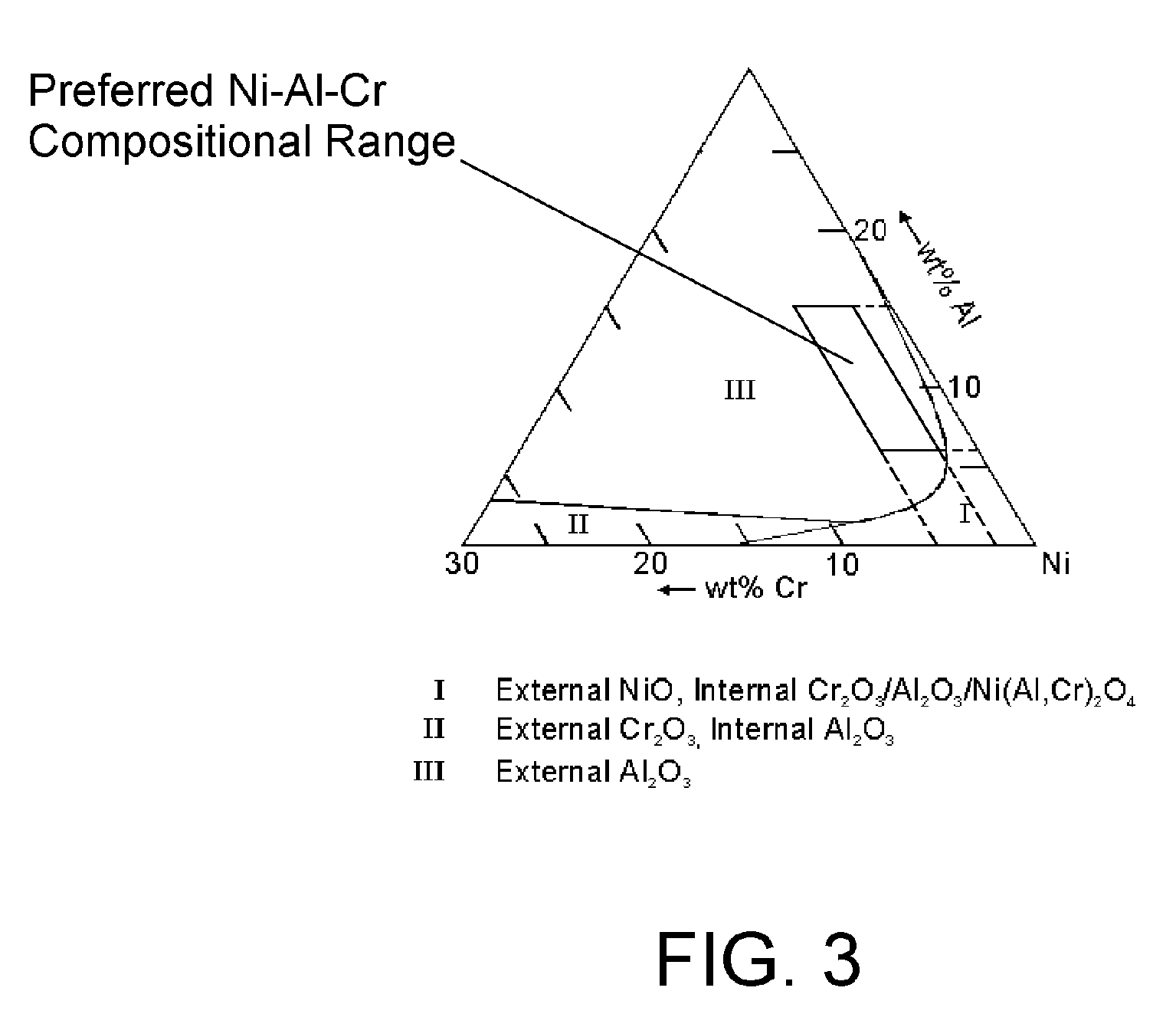
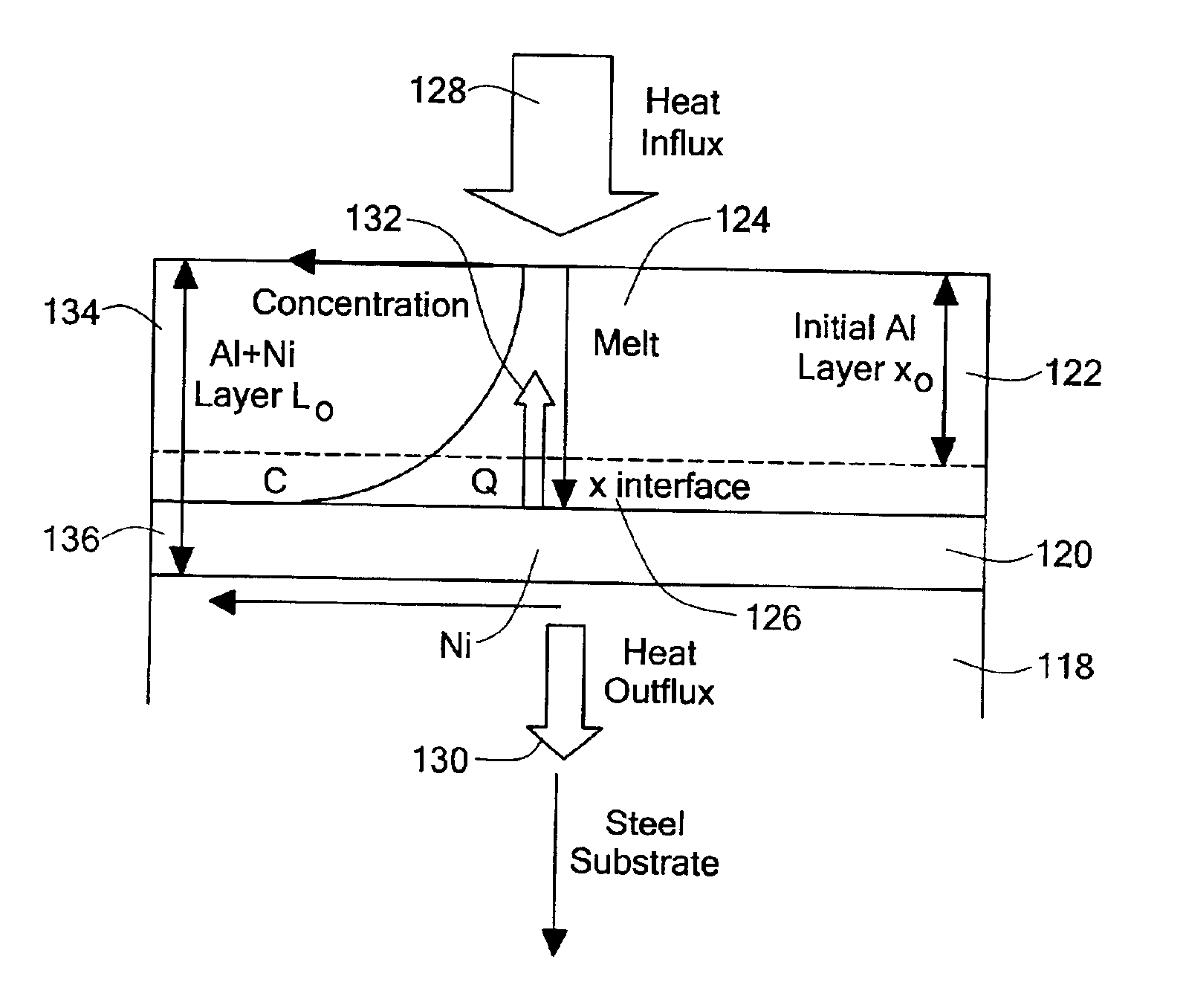
58 results about "Nickel aluminide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
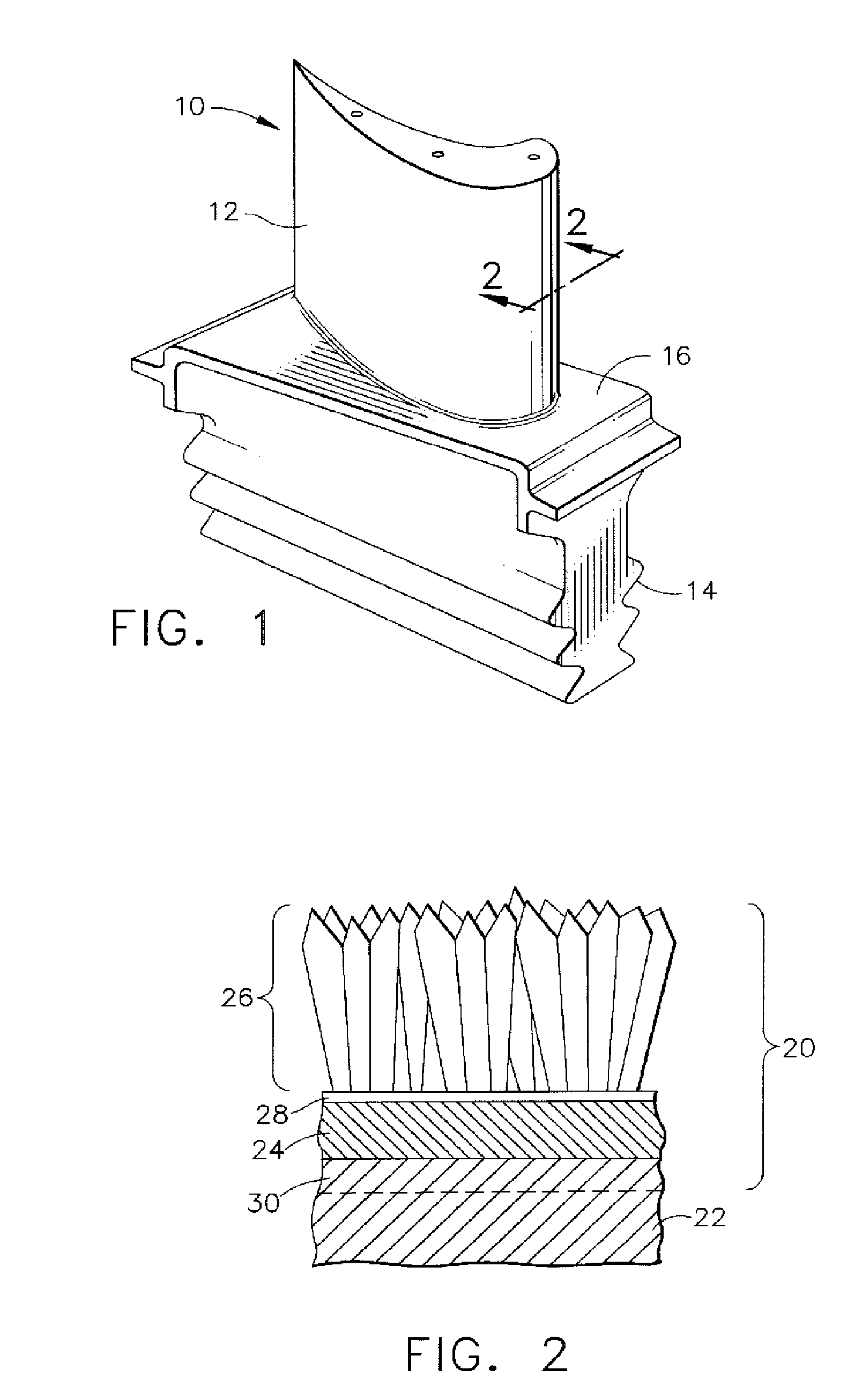
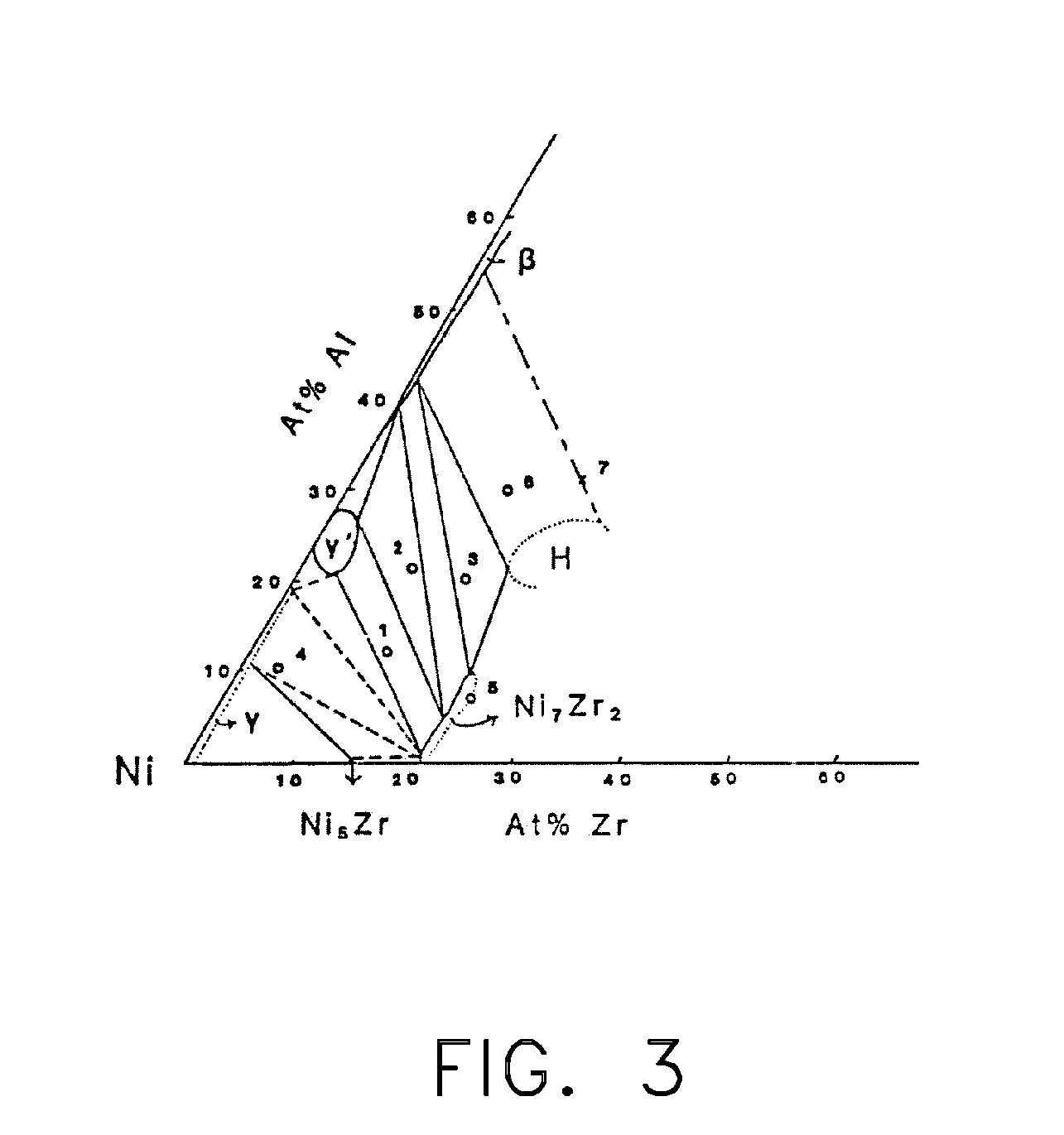
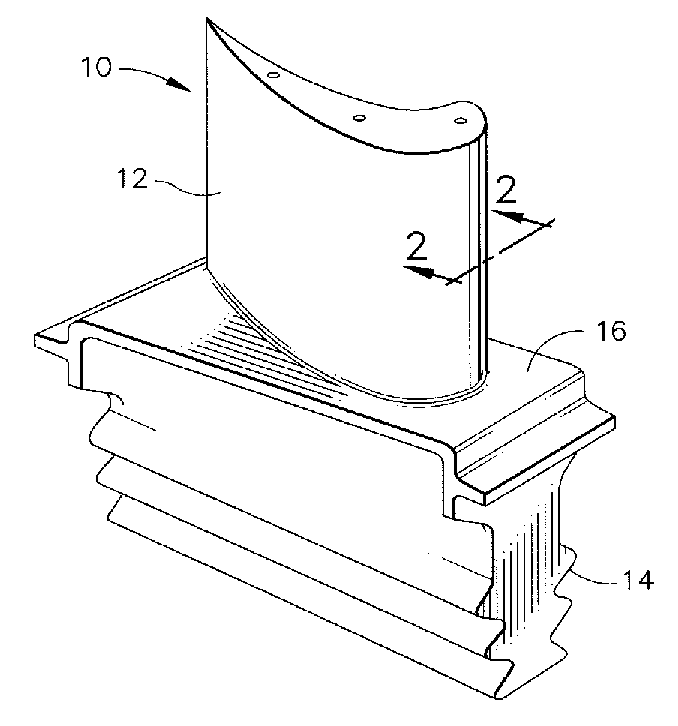
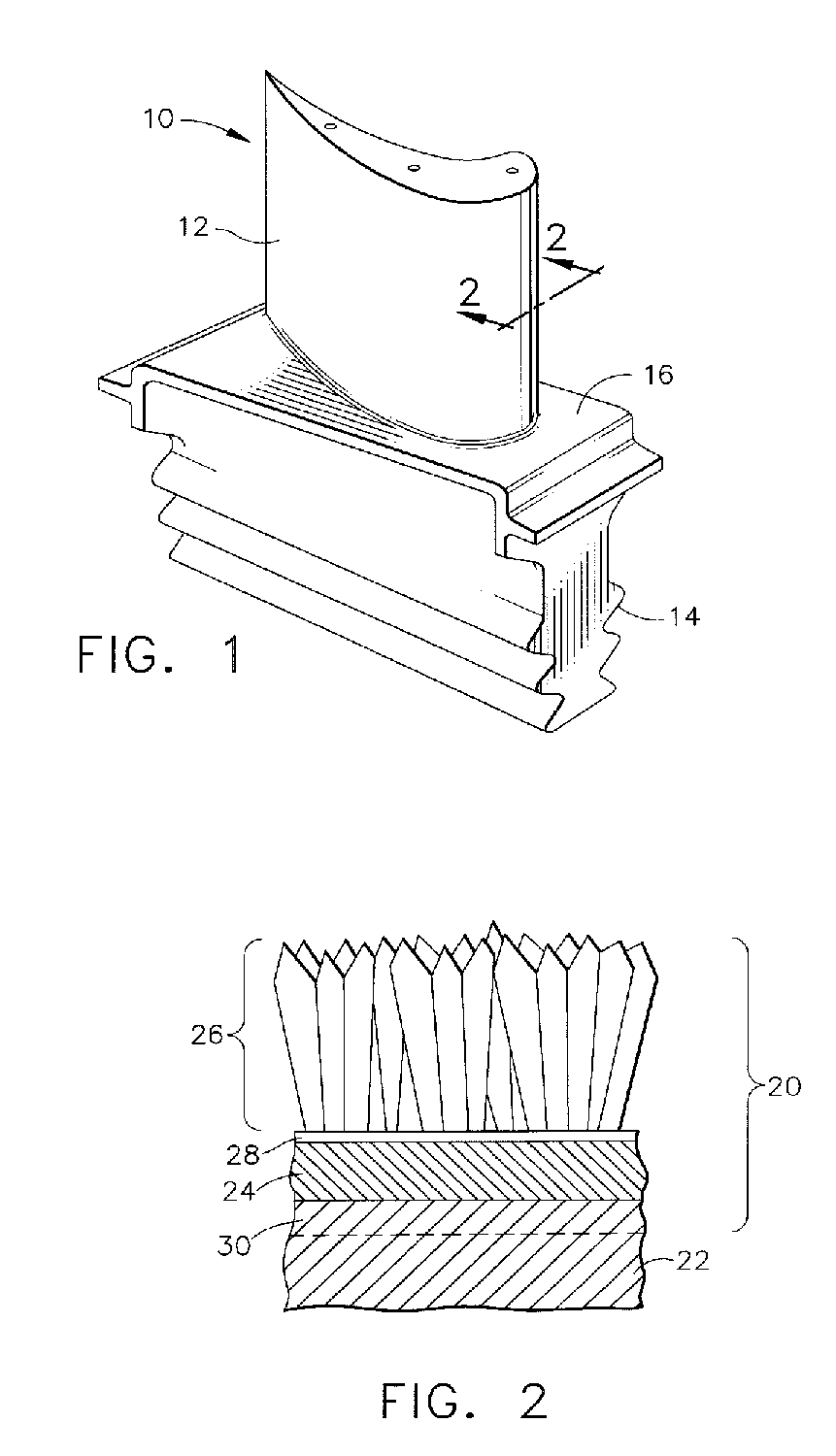
Nickel aluminide (Ni₃Al) is an intermetallic alloy of nickel and aluminium with properties similar to both a ceramic and a metal.
Superalloy article having a gamma-prime nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS20060093851A1Reduce morbidityInhibited DiffusionPropellersRotary propellersReaction zoneBond coat
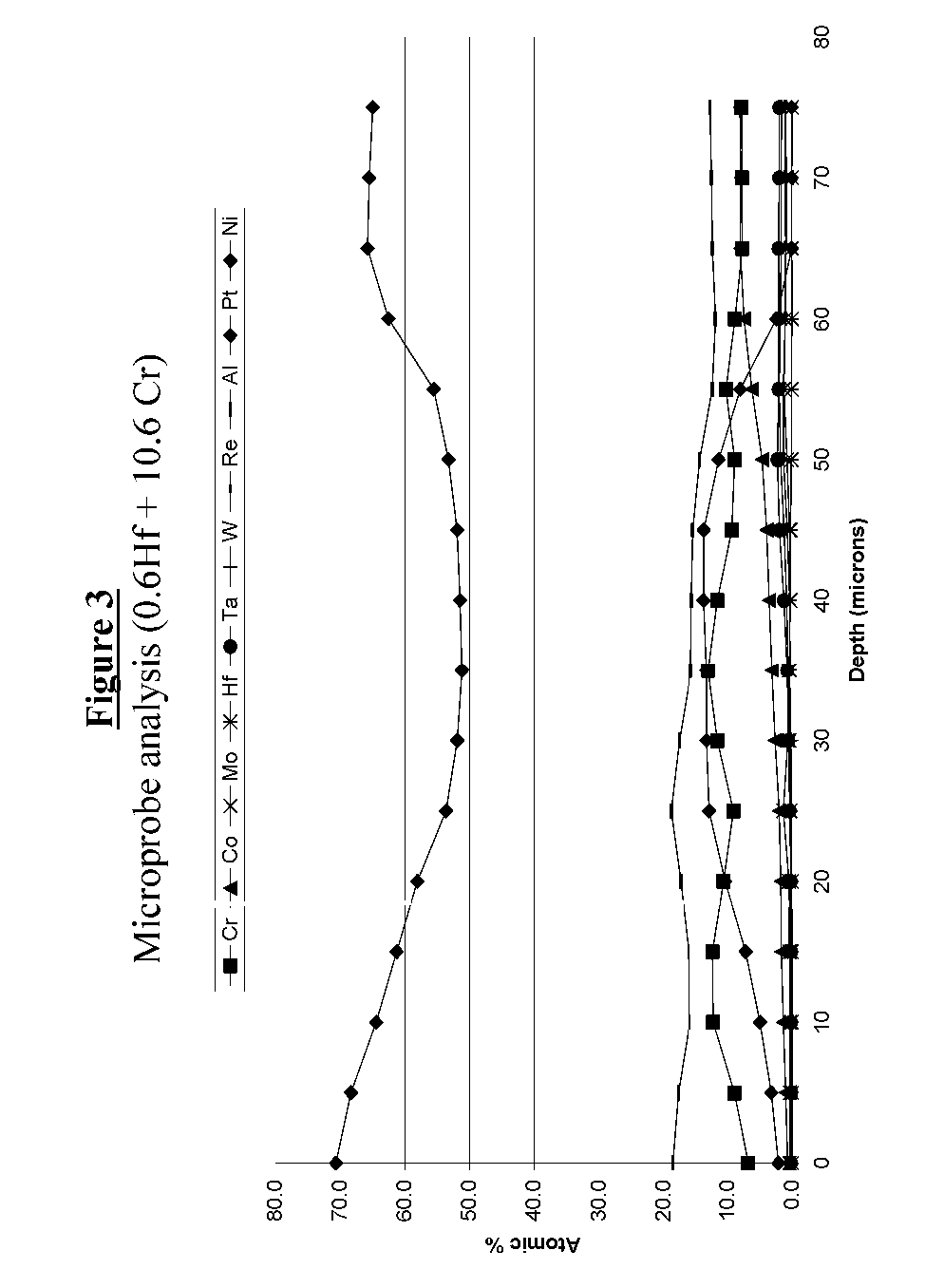
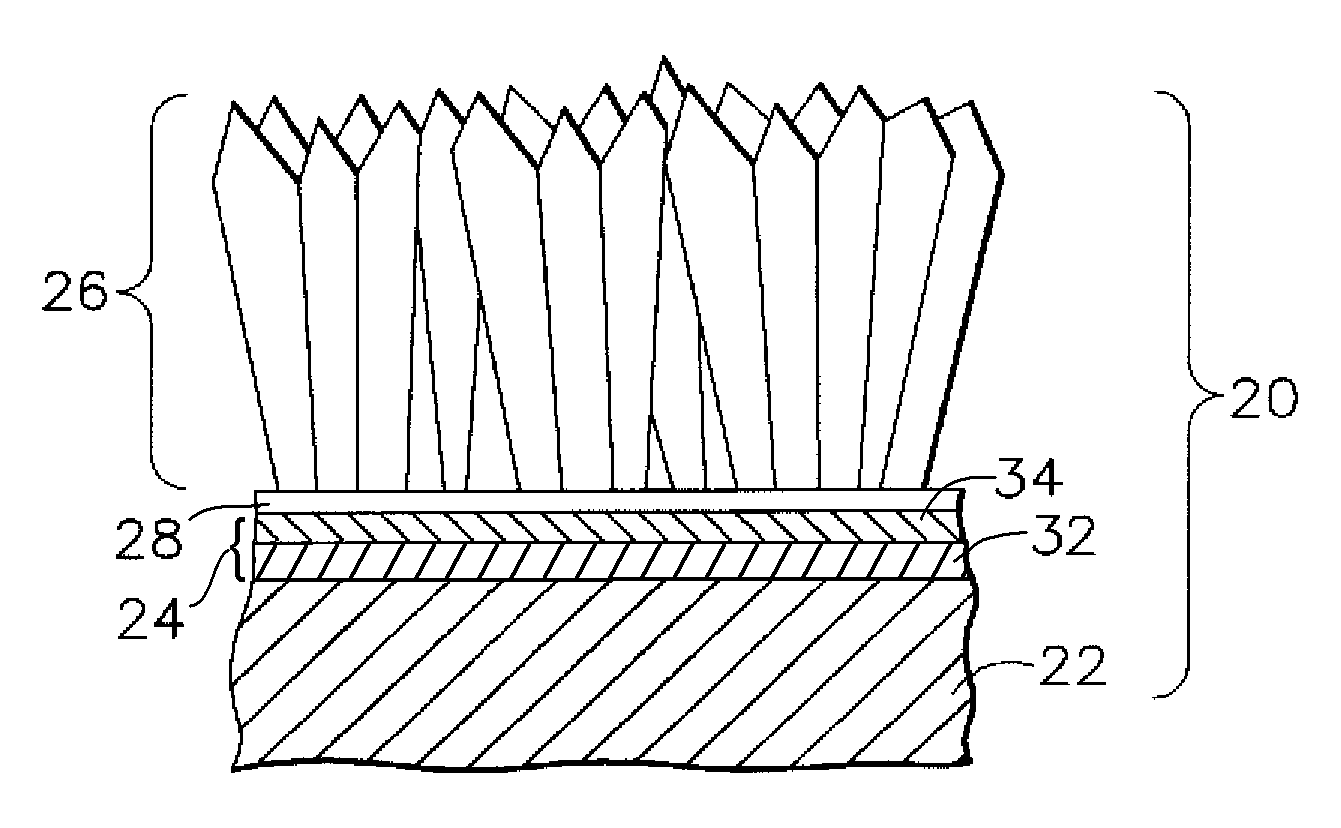
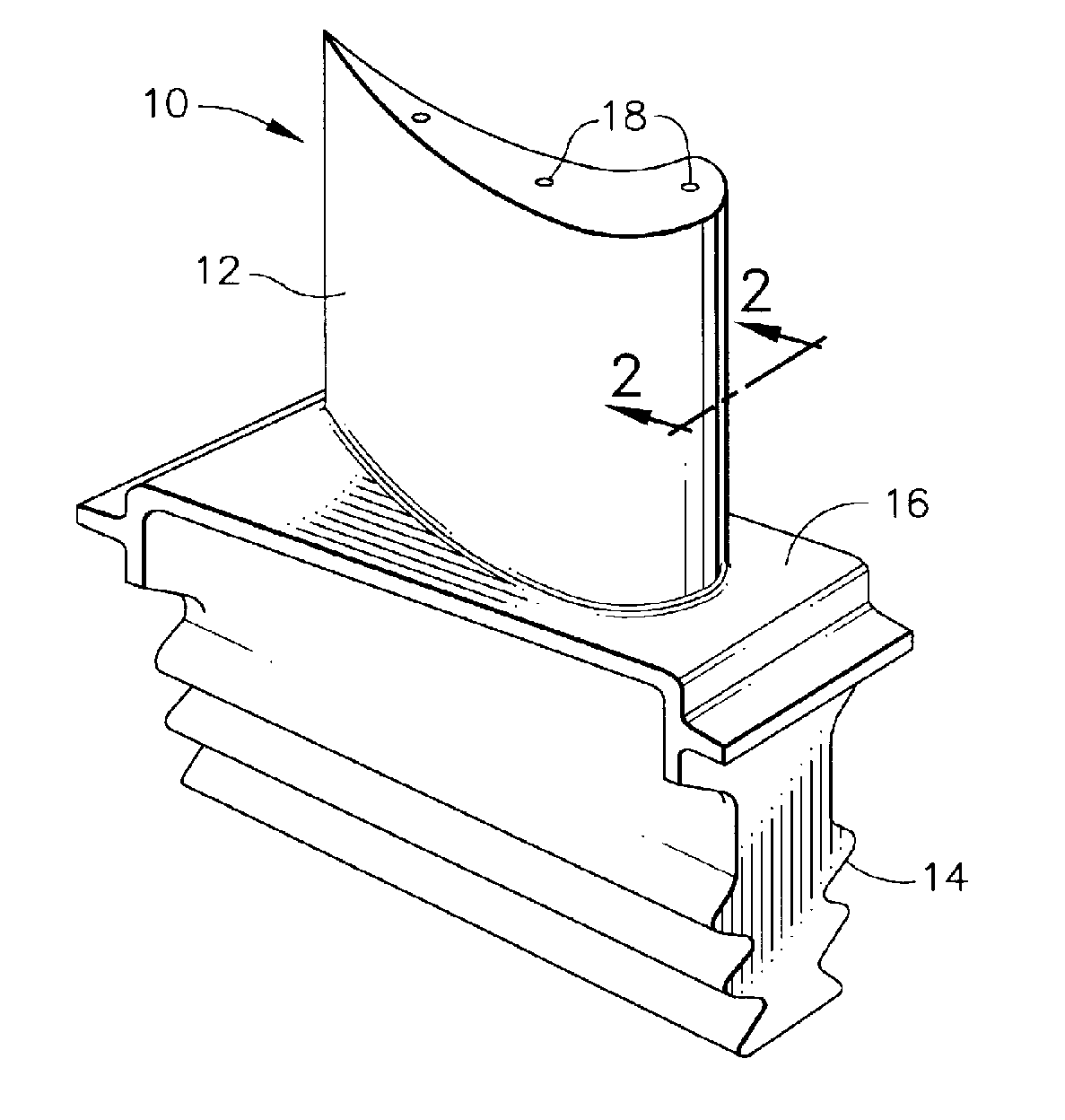
An article for use in hostile thermal environments, such as a component of a gas turbine engine. The article includes a nickel-base superalloy substrate that is prone to formation of a deleterious secondary reaction zone (SRZ), and an overlay coating having a predominantly gamma prime-phase nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) composition suitable for use as an environmental coating, including a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating. The coating comprises a chromium-containing nickel aluminide intermetallic overlay coating of predominantly the gamma prime phase, in which aluminum is present in the coating in an amount approximately equal to the aluminum content of the superalloy substrate so as to inhibit diffusion of aluminum from the overlay coating into the superalloy substrate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Coating systems containing beta phase and gamma-prime phase nickel aluminide
ActiveUS20060093801A1High solubility limitIncrease resistanceMolten spray coatingPropellersGreek letter betaBeta phase
A coating and process for depositing the coating on a substrate. The coating is a nickel aluminide overlay coating of predominantly the beta (NiAl) and gamma-prime (Ni3Al) intermetallic phases, and is suitable for use as an environmental coating and as a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating (TBC). The coating can be formed by depositing nickel and aluminum in appropriate amounts to yield the desired beta+gamma prime phase content. Alternatively, nickel and aluminum can be deposited so that the aluminum content of the coating exceeds the appropriate amount to yield the desired beta+gamma prime phase content, after which the coating is heat treated to diffuse the excess aluminum from the coating into the substrate to yield the desired beta+gamma prime phase content.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gamma prime phase-containing nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS20070071996A1Desirable environmental and mechanical propertyOxidation resistance can be improvedPropellersReaction enginesCeriumHafnium
An intermetallic composition suitable for use as an environmentally-protective coating on surfaces of components used in hostile thermal environments, including the turbine, combustor and augmentor sections of a gas turbine engine. The coating contains the gamma-prime (Ni3Al) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase and either the beta (NiAl) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase or the gamma solid solution phase. The coating has an average aluminum content of 14 to 30 atomic percent and an average platinum-group metal content of at least 1 to less than 10 atomic percent, the balance of the coating being nickel, one or more of chromium, silicon, tantalum, and cobalt, optionally one or more of hafnium, yttrium, zirconium, lanthanum, and cerium, and incidental impurities.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Intermetallic Aluminide Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC) Cutting Elements
InactiveUS20100038148A1Improve heat transfer performanceDissipate quicklyPigmenting treatmentDrill bitsPolycrystalline diamondAdamite
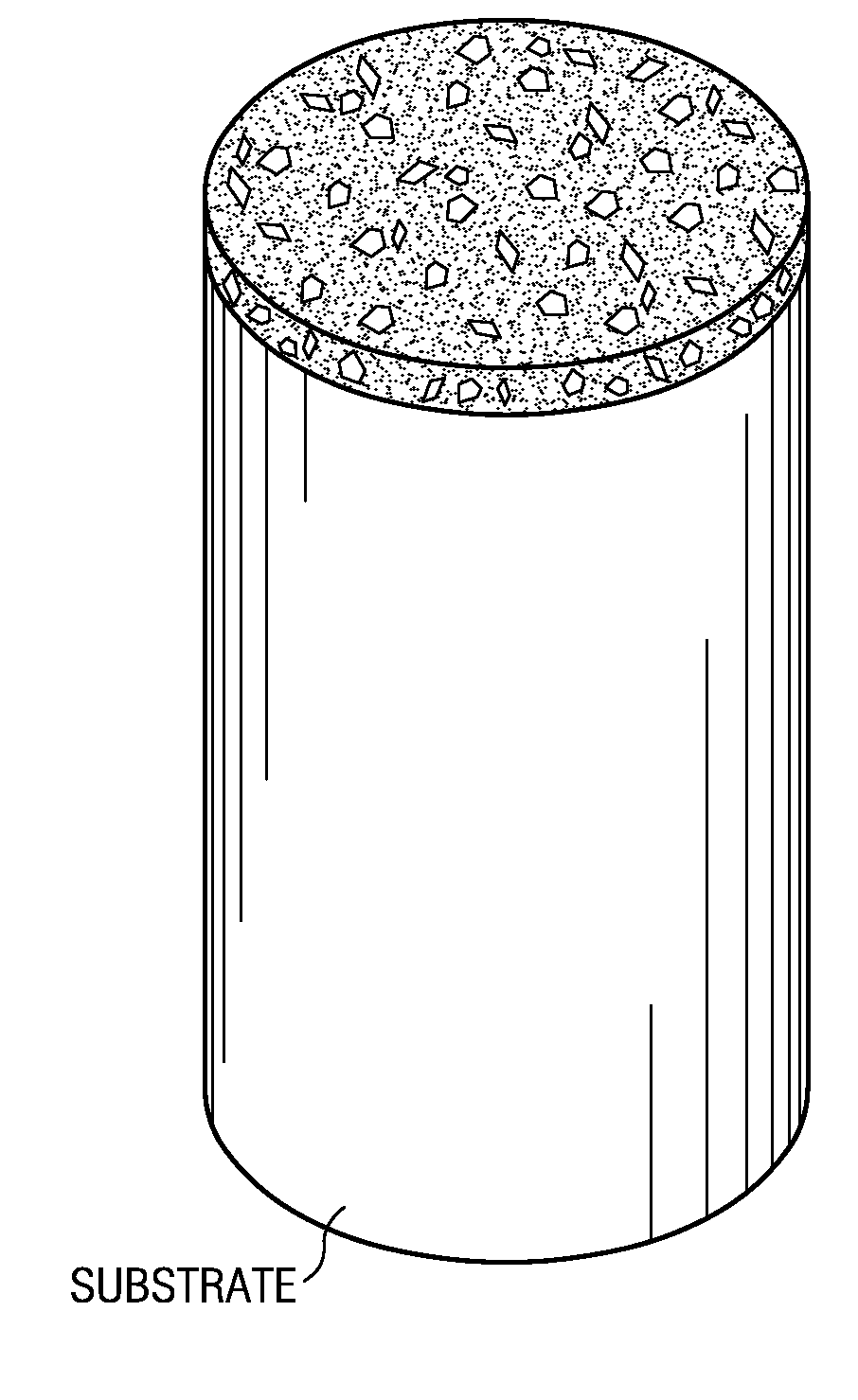
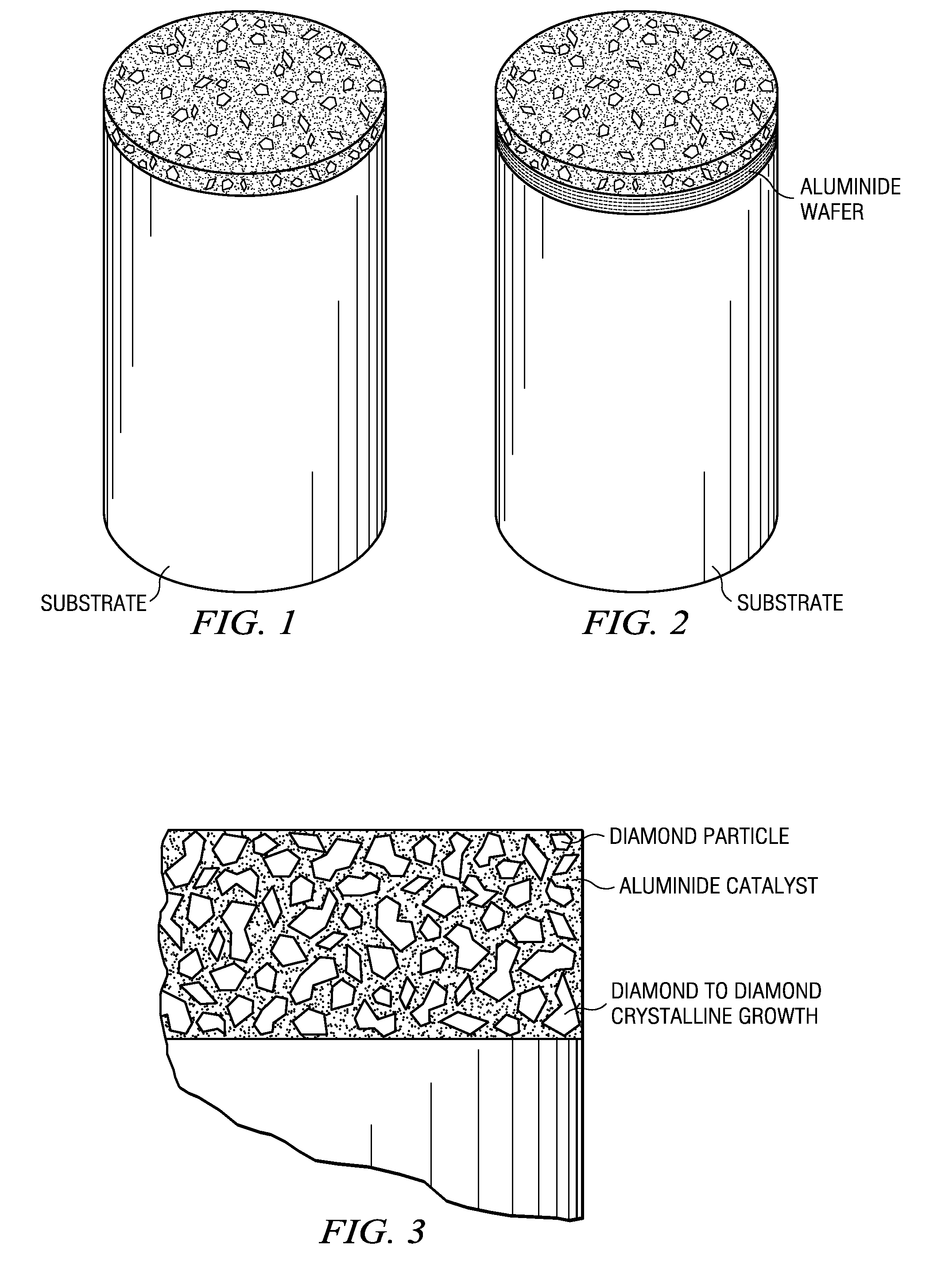
Machining and cutting tools including, but not limited to, rotary drill bits, mining tools, milling tools, wood shredders, reamers and wire dies formed with at least one substrate having a layer of polycrystalline diamond disposed thereon. The polycrystalline diamond layer may be generally described as a polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) or PDC layer. The PDC may be formed by using an intermetallic aluminide catalyst. One example of such catalyst may include nickel aluminide used to form diamond to diamond bonds between adjacent diamond particles.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Coating systems containing gamma-prime nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS7264888B2Promote formationImprove environmental resistance and strengthPropellersPump componentsBond coatSilicon
An overlay coating for articles used in hostile thermal environments. The coating has a predominantly gamma prime-phase nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) composition suitable for use as an environmental coating and as a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating. The coating has a composition of, by weight, at least 6% to about 15% aluminum, about 2% to about 5% chromium, optionally one or more reactive elements in individual or combined amounts of up to 4%, optionally up to 2% silicon, optionally up to 60% of at least one platinum group metal, and the balance essentially nickel. A thermal-insulating ceramic layer may be deposited on the coating.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Coating systems containing gamma-prime nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS20060093850A1Promote formationImprove environmental resistance and strengthBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesCoating systemBond coat
An overlay coating for articles used in hostile thermal environments. The coating has a predominantly gamma prime-phase nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) composition suitable for use as an environmental coating and as a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating. The coating has a composition of, by weight, at least 6% to about 15% aluminum, about 2% to about 5% chromium, optionally one or more reactive elements in individual or combined amounts of up to 4%, optionally up to 2% silicon, optionally up to 60% of at least one platinum group metal, and the balance essentially nickel. A thermal-insulating ceramic layer may be deposited on the coating.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Process of forming a composite coating on a substrate
InactiveUS6936118B2Easy to wearAccelerated corrosionMolten spray coatingElectric discharge heatingFiberMullite
Precursor-based methods for the production of metal-matrix composite (MMC) coatings on steel and aluminum substrates for improved wear, corrosion and oxidation resistance have been made. Wire and surface precursors are deposited on the substrate by controlled thermal processing using plasma-arc, laser and high-density infrared radiation. The temperature distribution during the formation for coating is controlled by a real tine adaptive control method. The wire precursors produced by continuous pressure infiltration of SiC or mullite fiber with aluminum were used. Steel substrates double-layer plated with binary metals including nickel and aluminum are also thermal-processed to in-situ produce compound such as nickel aluminide coatings.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Nickel aluminide coating and coating systems formed therewith
InactiveUS6887589B2Increase resistancePromote oxidationMolten spray coatingPropellersMetallurgyCoating system
A beta-phase NiAl overlay coating containing a dispersion of ceramic particles and a process for depositing the overlay coating. If the coating is used to adhere a thermal barrier coating (TBC), the TBC exhibits improved spallation resistance as a result of the dispersion of ceramic particles having a dispersion-strengthening effect on the overlay coating. The overlay coating contains at least one reactive element and is deposited so that the some of the reactive element deposits as the ceramic particles dispersed in the overlay coating.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superalloy article having a gamma-prime nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS7288328B2Reduce morbidityInhibited DiffusionPropellersRotary propellersReaction zoneBond coat
An article for use in hostile thermal environments, such as a component of a gas turbine engine. The article includes a nickel-base superalloy substrate that is prone to formation of a deleterious secondary reaction zone (SRZ), and an overlay coating having a predominantly gamma prime-phase nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) composition suitable for use as an environmental coating, including a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating. The coating comprises a chromium-containing nickel aluminide intermetallic overlay coating of predominantly the gamma prime phase, in which aluminum is present in the coating in an amount approximately equal to the aluminum content of the superalloy substrate so as to inhibit diffusion of aluminum from the overlay coating into the superalloy substrate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of manufacture of a dual alloy impeller
InactiveUS20100215978A1Promote oxidationHigh strengthTurbinesPump componentsLow-cycle fatigueMaterials science
There is provided a method for fabricating a dual alloy structure that may in turn be machined to fabricate a rotary component for use in a gas turbine engine. The method provides a powder metal (PM) nickel based superalloy and a nickel aluminide intermetallic based alloy. The powder metal (PM) nickel based superalloy displays characteristics, such as improved strength, low cycle fatigue resistance, fracture toughness, and crack growth resistance. The nickel aluminide intermetallic based alloy displays characteristics, such as high temperature creep and oxidation resistance, suitable for use in the outer radial area of an impeller. A bore sub-element is fabricated from the powder metal (PM) nickel based superalloy. A body sub-element is fabricated from the nickel aluminide intermetallic based alloy. The bore sub-element and body sub-element are joined by inertia welding or diffusion bonding at a common mating surface.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Beta-phase nickel aluminide coating
InactiveUS6933058B2Promotes the oxidation resistance of the overlay coatingLess aluminumSuperimposed coating processThin material handlingBeta phaseBond coat
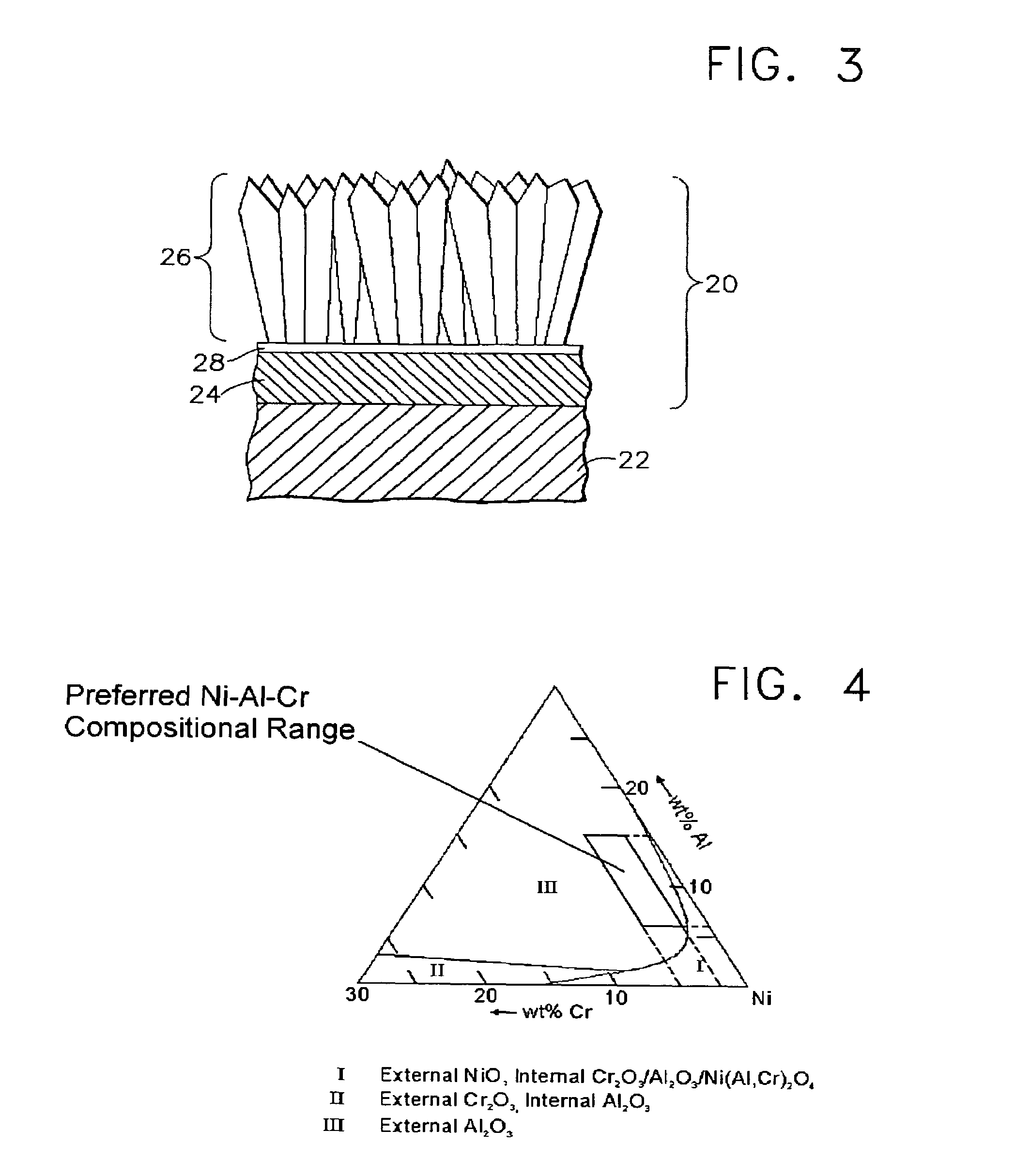
A protective overlay coating for articles used in hostile thermal environments, and more particularly a predominantly beta-phase NiAl intermetallic overlay coating for use as an environmental coating or as a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating deposited on the overlay coating. The overlay coating has inner and outer regions, with the inner region containing more chromium than the outer region. The lower chromium content of the outer region promotes the oxidation resistance of the overlay coating, while the higher chromium content of the inner region promotes the hot corrosion resistance of the coating interior. Under hot corrosion conditions, hot corrosion may attack the outer region, but further hot corrosion attack will substantially cease once the relatively high-chromium inner region of the overlay coating is encountered.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Beta-phase nickel aluminide coating
InactiveUS20050118453A1Promotes the oxidation resistance of the overlay coatingLess aluminumPropellersPump componentsBeta phaseBond coat
A protective overlay coating for articles used in hostile thermal environments, and more particularly a predominantly beta-phase NiAl intermetallic overlay coating for use as an environmental coating or as a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating deposited on the overlay coating. The overlay coating has inner and outer regions, with the inner region containing more chromium than the outer region. The lower chromium content of the outer region promotes the oxidation resistance of the overlay coating, while the higher chromium content of the inner region promotes the hot corrosion resistance of the coating interior. Under hot corrosion conditions, hot corrosion may attack the outer region, but further hot corrosion attack will substantially cease once the relatively high-chromium inner region of the overlay coating is encountered.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gamma prime phase-containing nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS20070071995A1Improve oxidation resistanceImprove corrosion resistancePropellersRotary propellersGreek letter betaCombustor
An intermetallic composition suitable for use as an environmentally-protective coating on surfaces of components used in hostile thermal environments, including the turbine, combustor and augmentor sections of a gas turbine engine. The coating contains the gamma-prime (Ni3Al) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase and either the beta (NiAl) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase or the gamma solid solution phase. The coating has an average aluminum content of 14 to 30 atomic percent and an average platinum-group metal content of at least 1 to less than 10 atomic percent, the balance of the coating being nickel, incidental impurities, and optionally hafnium.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Al-steel weld joint
ActiveUS20170291247A1Sheet joiningWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNickel aluminideMaterials science
A weld joint is disclosed that weld bonds together an aluminum workpiece and a steel workpiece. The weld joint includes an aluminum weld nugget, an intermetallic layer, and an annular ring of aluminide particles that is selected from the group consisting of nickel aluminide particles, iron aluminide particles, and a combination thereof. The annular ring of aluminide particles extends upwards from a weld bond surface of the weld joint such that the annular ring of aluminide particles extends radially inwardly into the aluminum weld nugget and protects the weld bond surface of the weld joint against crack propagation that may originate from a notch root of the weld joint.
Owner:HUAMI INC +1
Gamma prime phase-containing nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS7247393B2Desirable environmental and mechanical propertyOxidation resistance can be improvedPropellersReaction enginesCeriumHafnium
An intermetallic composition suitable for use as an environmentally-protective coating on surfaces of components used in hostile thermal environments, including the turbine, combustor and augmentor sections of a gas turbine engine. The coating contains the gamma-prime (Ni3Al) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase and either the beta (NiAl) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase or the gamma solid solution phase. The coating has an average aluminum content of 14 to 30 atomic percent and an average platinum-group metal content of at least 1 to less than 10 atomic percent, the balance of the coating being nickel, one or more of chromium, silicon, tantalum, and cobalt, optionally one or more of hafnium, yttrium, zirconium, lanthanum, and cerium, and incidental impurities.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods for depositing gamma-prime nickel aluminide coatings
ActiveUS7357958B2Reduce the possibilityTrend downBlade accessoriesVacuum evaporation coatingBond coatSilicon
Methods for depositing an overlay coating on articles intended for use in hostile thermal environments. The coating has a predominantly gamma prime-phase nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) composition suitable for use as an environmental coating and as a bond coat of a thermal barrier coating system. The coating further contains at least one platinum group metal, preferably chromium, optionally one or more reactive elements, and optionally silicon. The coating is deposited by a process that entails forming a platinum group metal layer and at least one separate layer of other constituents of the coating, and then performing a diffusion heat treatment to yield the coating.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Physical vapor deposition apparatus and process
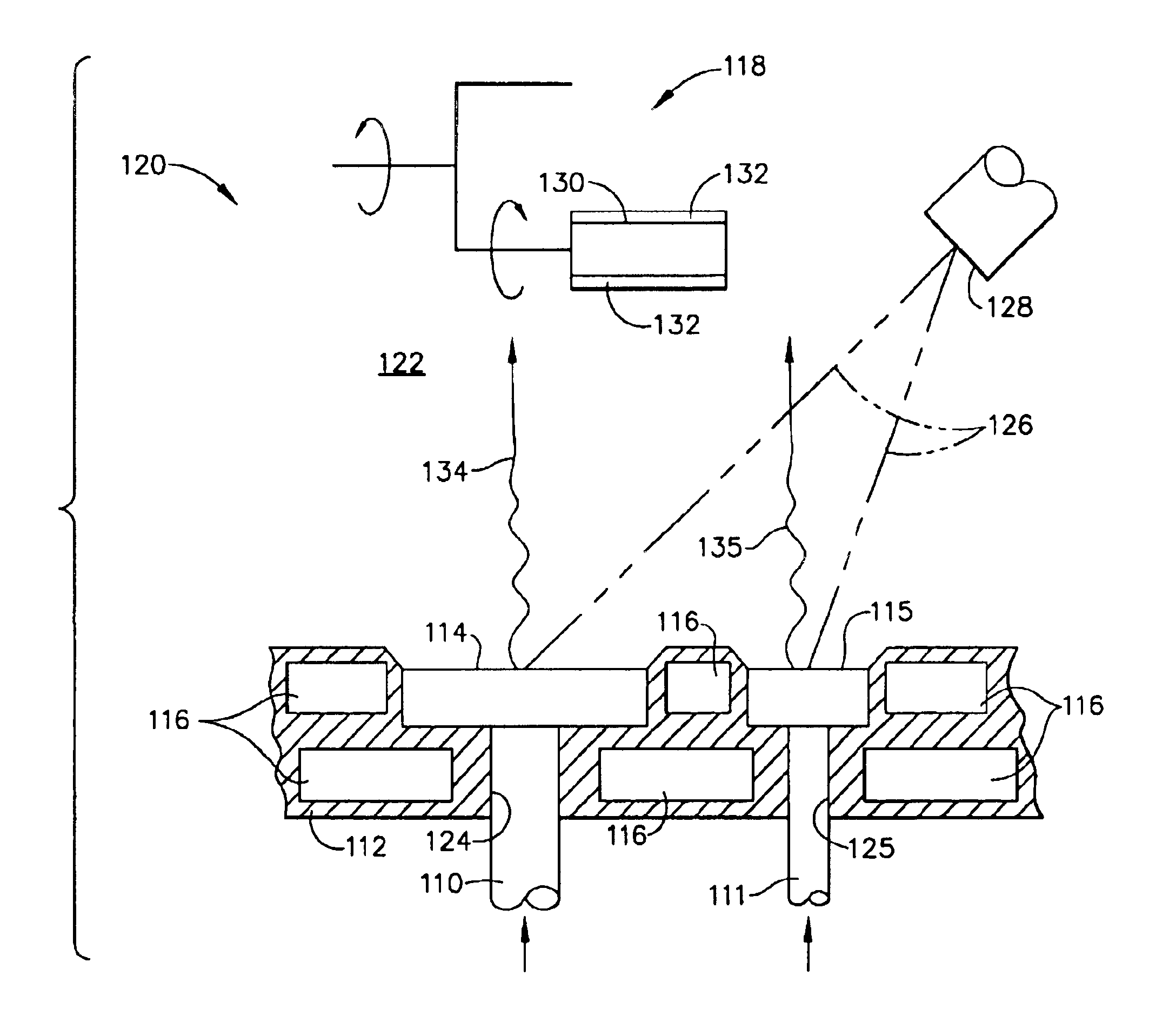
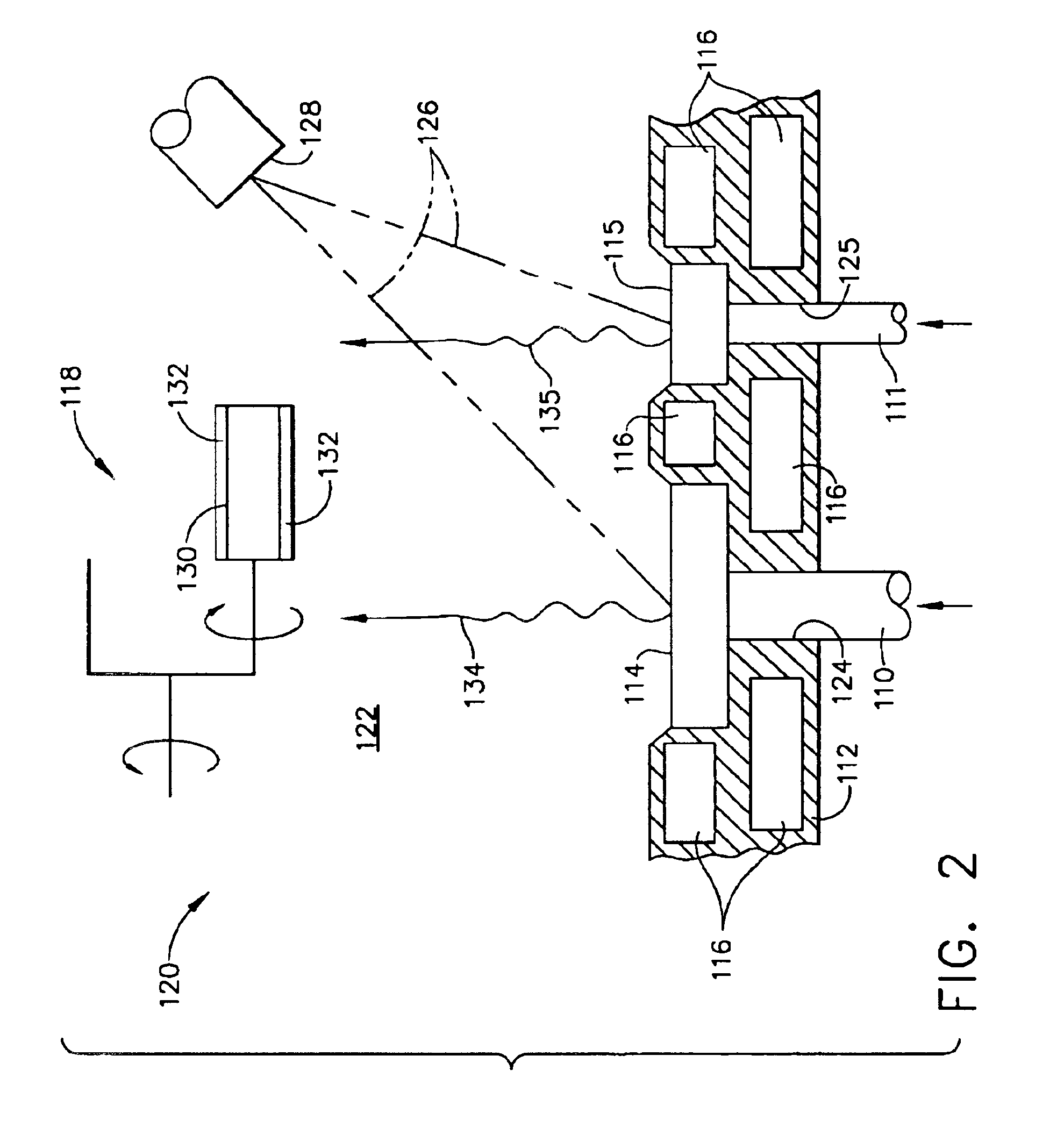
InactiveUS6869508B2Increase vapor pressureCellsElectric discharge heatingGreek letter betaNickel aluminide
A PVD process and apparatus (120) for depositing a coating (132) from multiple sources (110, 111) of different materials. The process and apparatus (120) are particulaity intended to deposit a beta-nickel aluminide coating (132) containing one or more elements whose vapor pressures are lower than NiAl. The PVD process and apparatus (120) entail feeding at least two materials (110, 111) into a coating chamber (122) and evaporating the materials (110, 111) at different rates from separate molten pools (114, 115) thereof. Articles (130) to be coated are suspended within the coating chamber (122), and transported with a support apparatus (118) relative to the two molten pools (114, 115) so as to deposit a coating (132) with a controlled composition that is a mixture of the first and second materials (110, 111).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for post deposition of beta phase nickel aluminide coatings
InactiveUS20050053800A1High densityAccelerated corrosionMolten spray coatingPretreated surfacesSurface finishBeta phase
A method for producing an article such as a turbine component that is coated with a β-phase, high aluminum content coating, such as substantially stoichiometric NiAl, and which has a surface finish suitable for application of a ceramic topcoat. The method involves heating the coated article to near the brittle-ductile transition temperature of the coating and impacting the coating with particles of a preselected size so that the brittle coating is not adversely affected by chipping or breakage. The impacting produces a surface finish of 120 micro-inches or finer so that a ceramic thermal barrier layer can be applied over the coating. The preferred method of improving the surface finish utilizes heated peening media to impact the heated coated article, thus allowing use of a broader selection of peening media.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
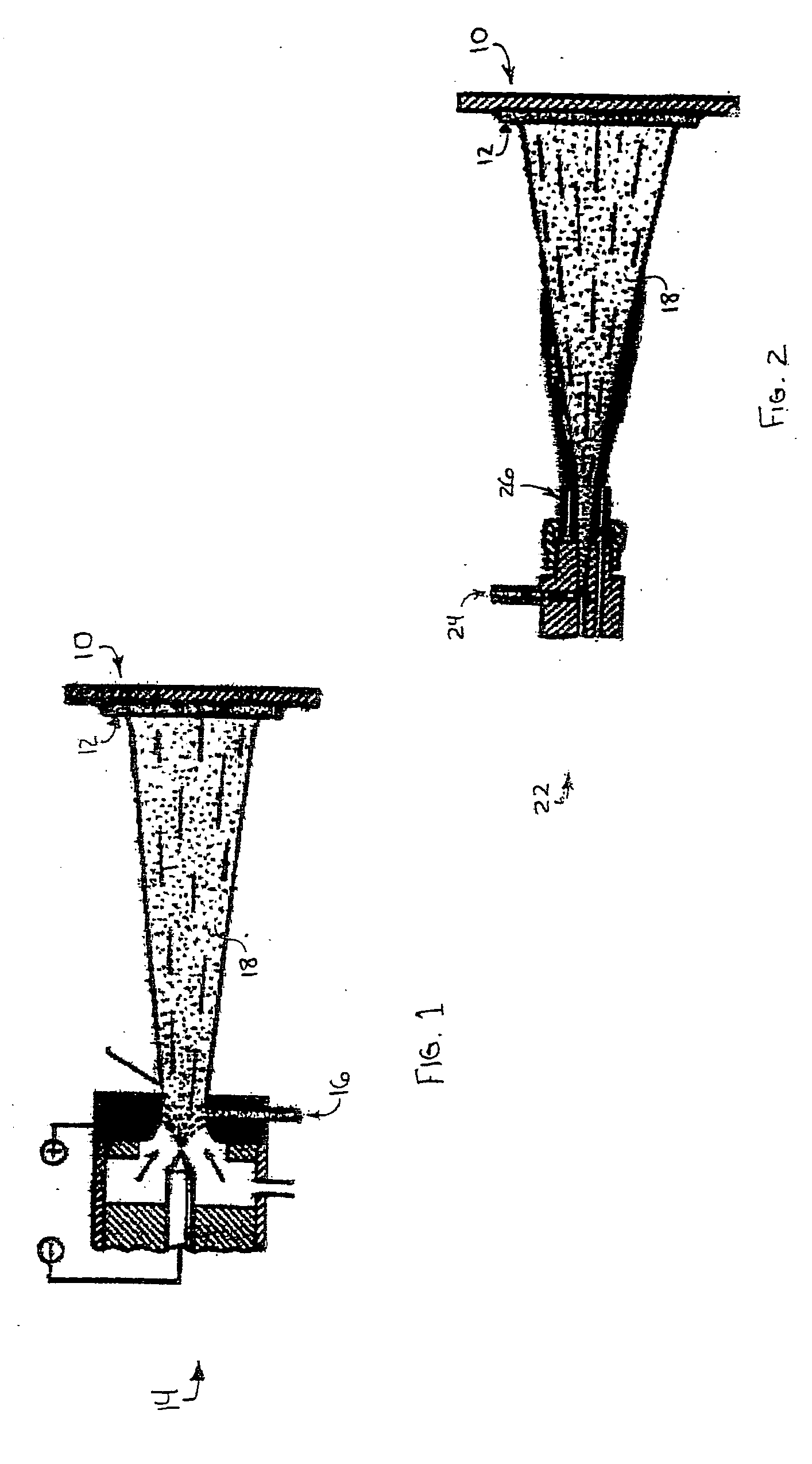
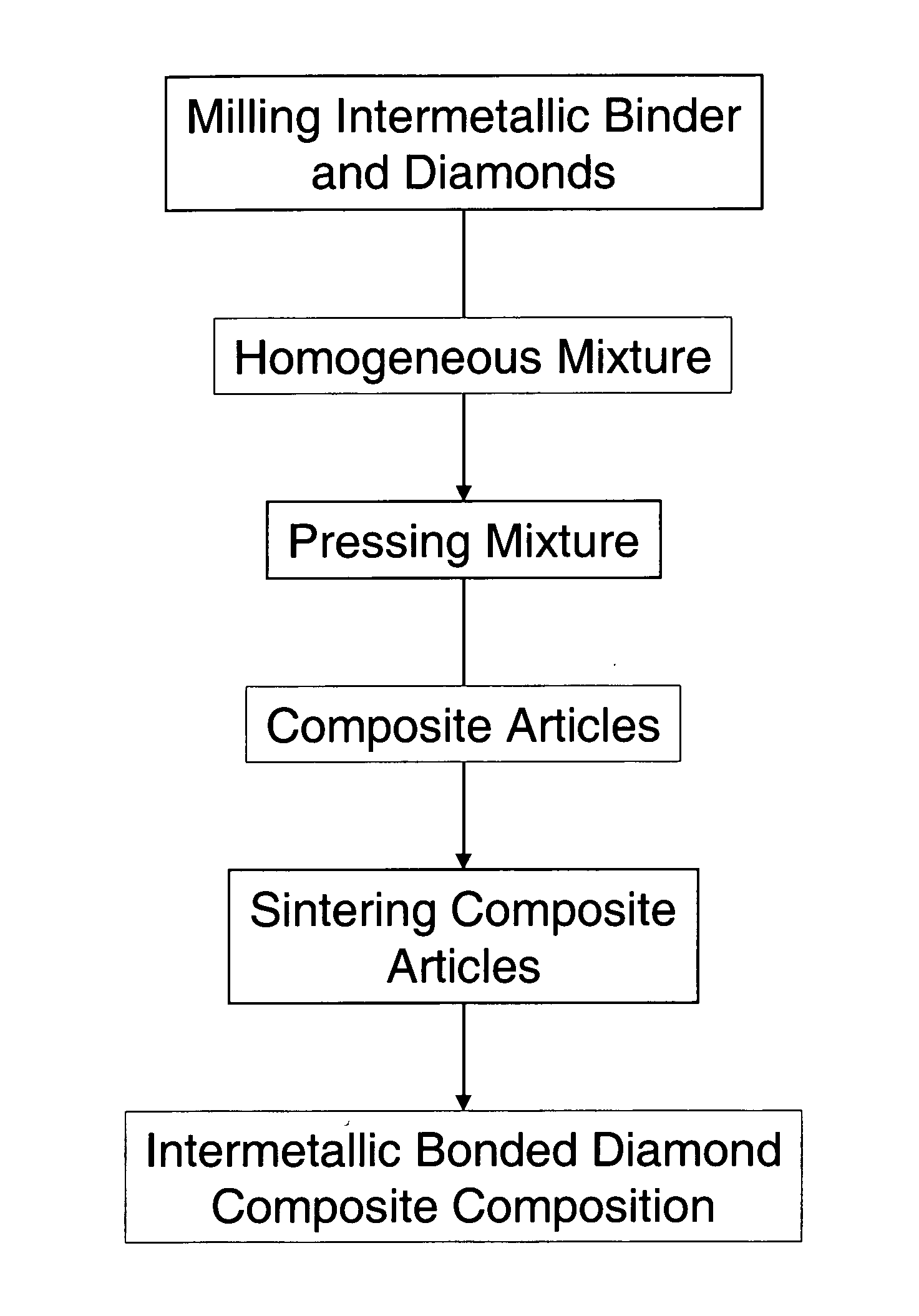
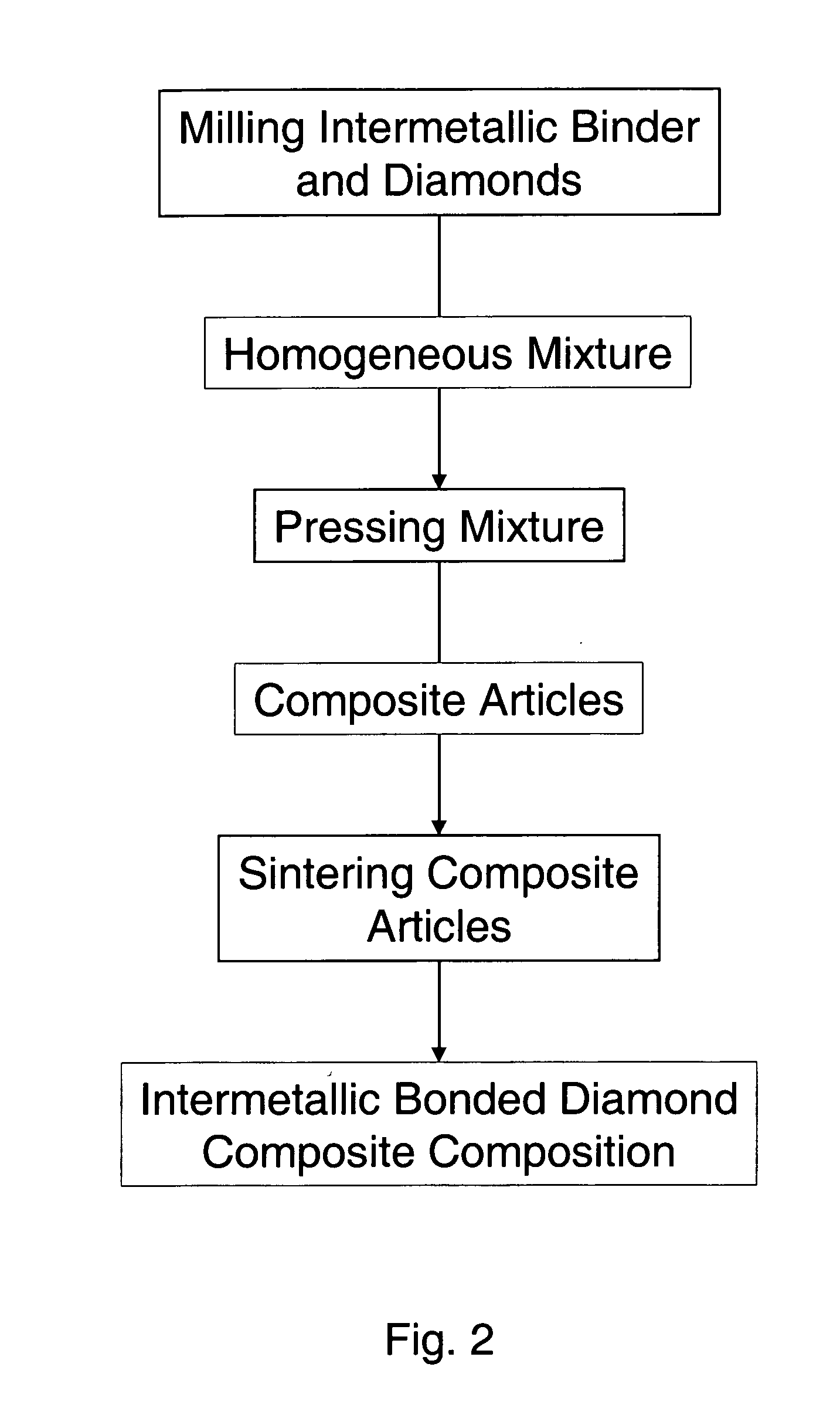
Intermetallic bonded diamond composite composition and methods of forming articles from same
ActiveUS20060280638A1Improve oxidation resistanceImproved of diamond retentionOther manufacturing equipments/toolsGraphiteIntermetallic
An intermetallic bonded diamond composite composition and methods of processing such a composition are provided by the present invention. The intermetallic bonded diamond composite composition preferably comprises a nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) binder and diamond particles dispersed within the nickel aluminide (Ni3Al) binder. Additionally, the composite composition has a processing temperature of at least about 1,200° C. and is processed such that the diamond particles remain intact and are not converted to graphite or vaporized by the high-temperature process. Methods of forming the composite composition are also provided that generally comprise the steps of milling, pressing, and sintering the high-temperature intermetallic binder and diamond particles.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Gamma prime phase-containing nickel aluminide coating
ActiveUS7250225B2Desirable environmental and mechanical propertyOxidation resistance can be improvedPropellersRotary propellersCombustorHafnium
An intermetallic composition suitable for use as an environmentally-protective coating on surfaces of components used in hostile thermal environments, including the turbine, combustor and augmentor sections of a gas turbine engine. The coating contains the gamma-prime (Ni3Al) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase and either the beta (NiAl) nickel aluminide intermetallic phase or the gamma solid solution phase. The coating has an average aluminum content of 14 to 30 atomic percent and an average platinum-group metal content of at least 1 to less than 10 atomic percent, the balance of the coating being nickel, incidental impurities, and optionally hafnium.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Catalytic combustors
InactiveUS20050066663A1Enhances subsequent chemical bondingGood adhesionContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsPtru catalystEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Beta-phase nickel aluminide overlay coating and process therefor
InactiveUS20050019491A1Enhances spallation resistanceAvoid insufficient temperatureMolten spray coatingPretreated surfacesChemical compositionBeta phase
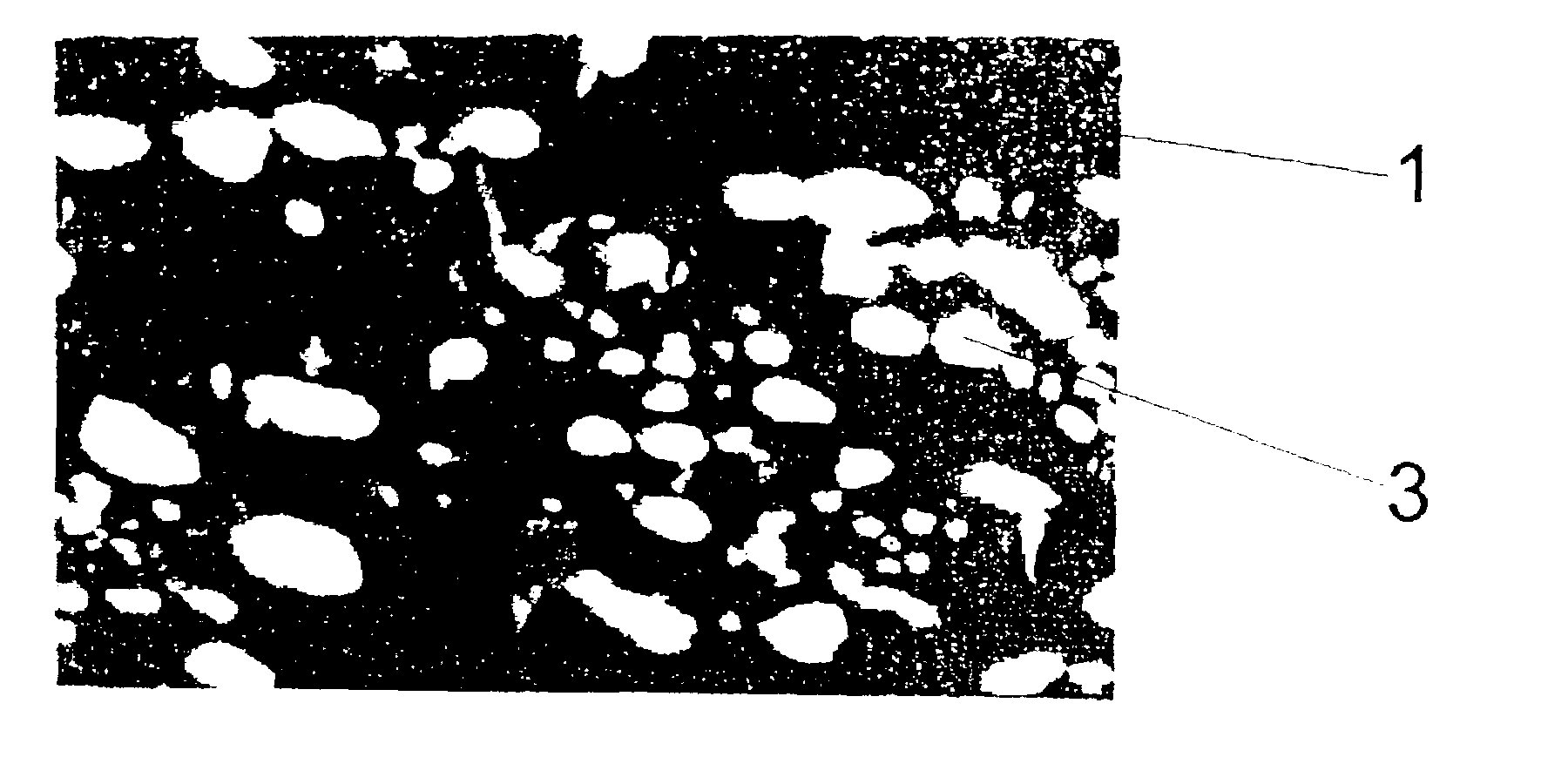
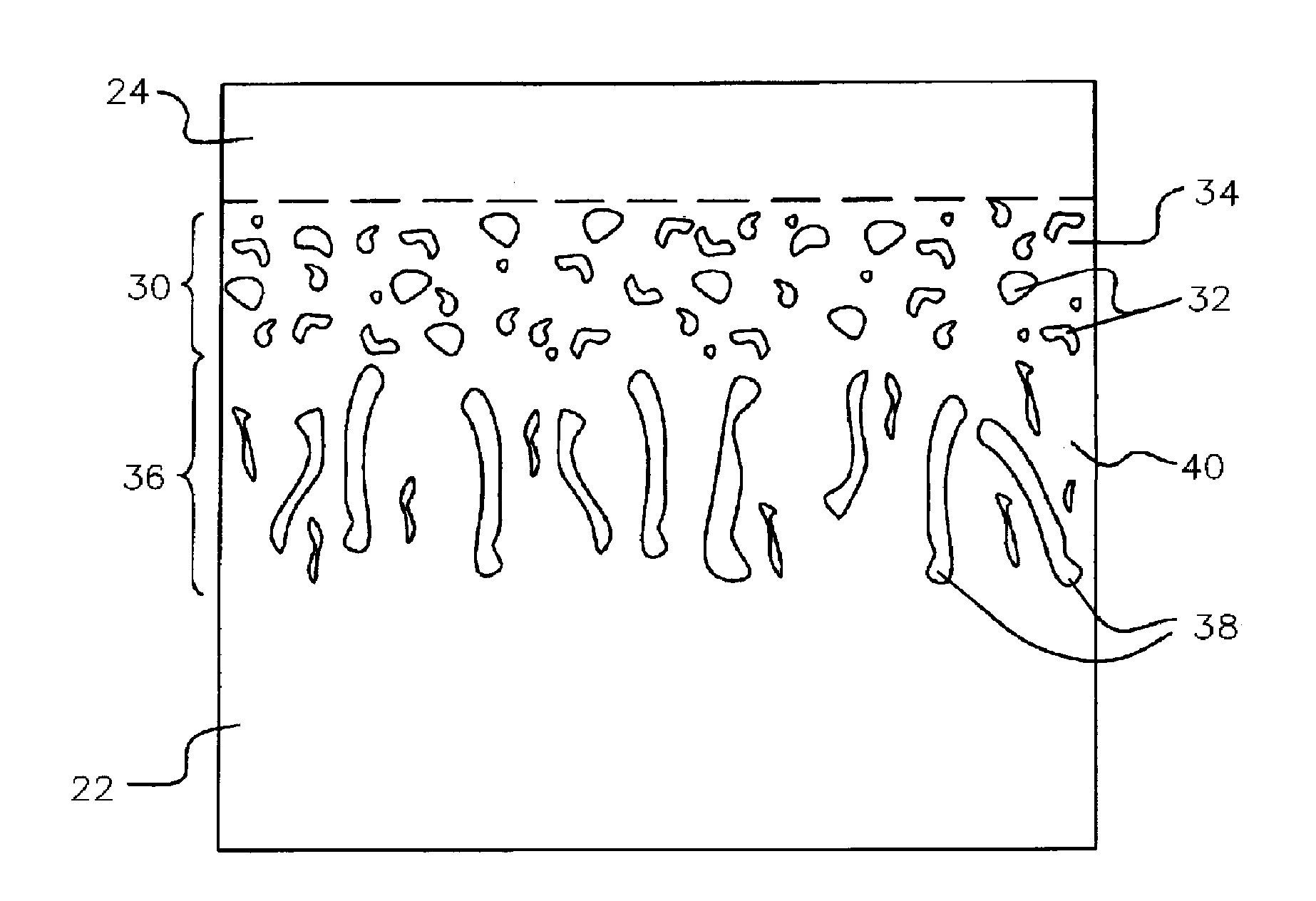
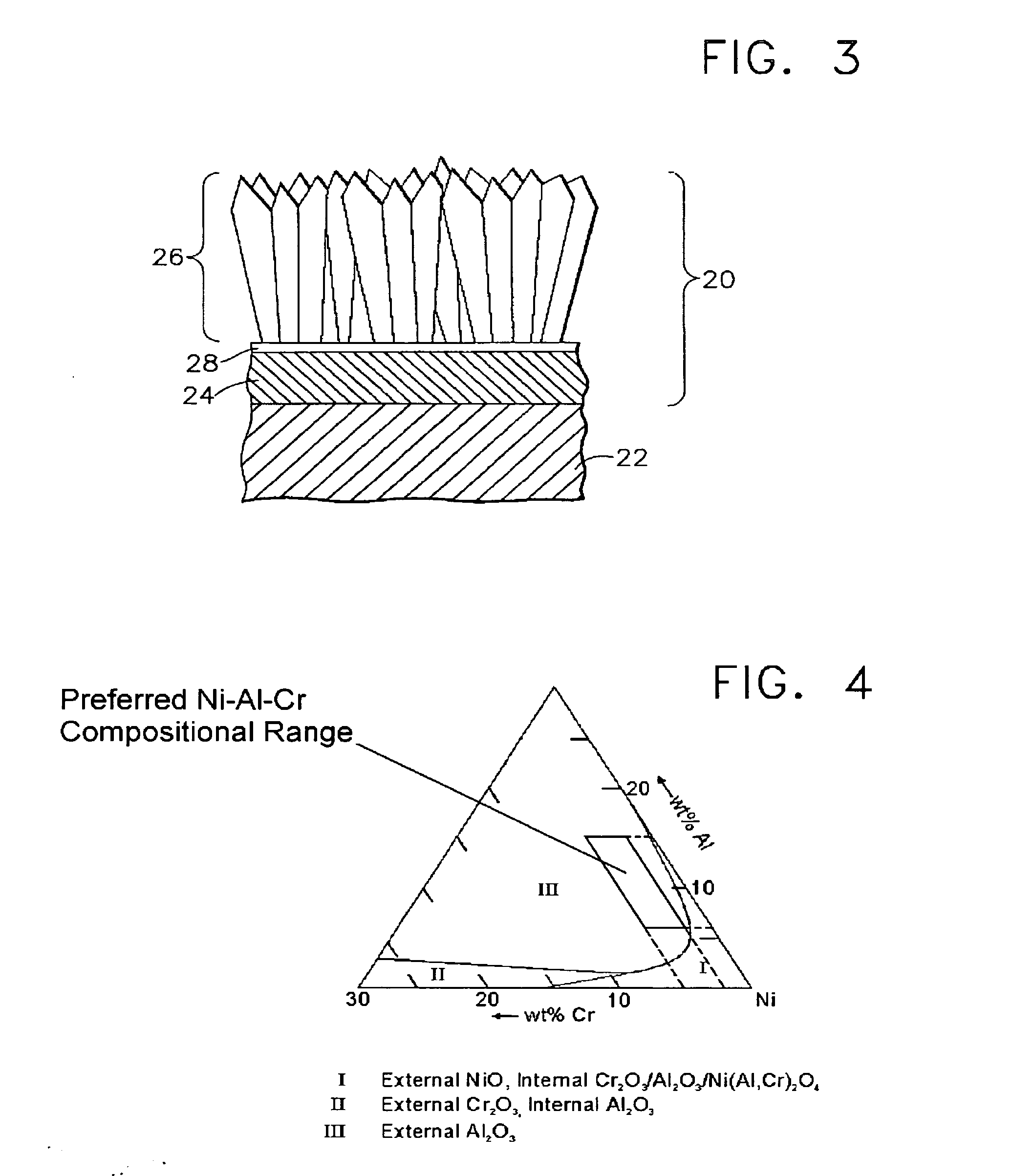
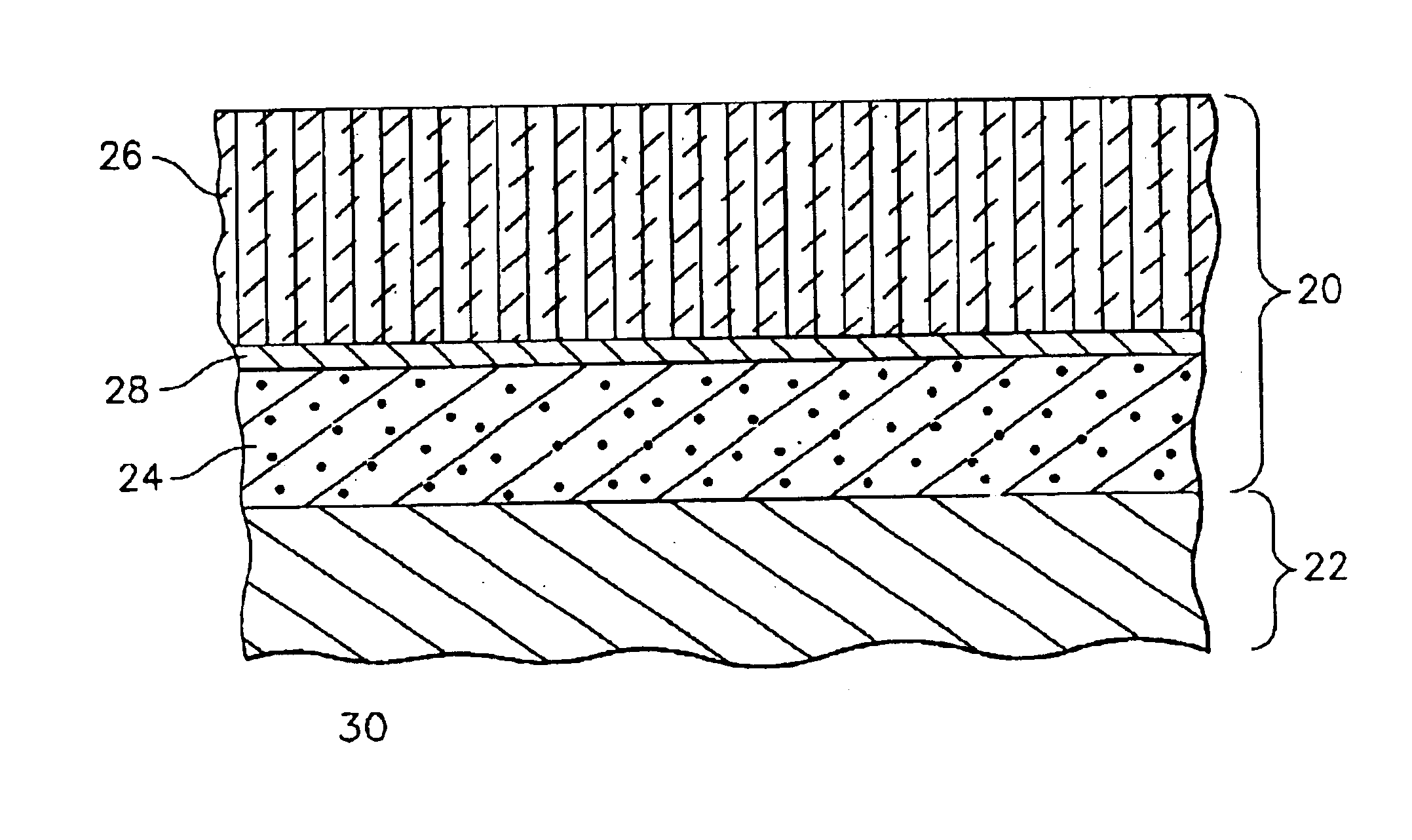
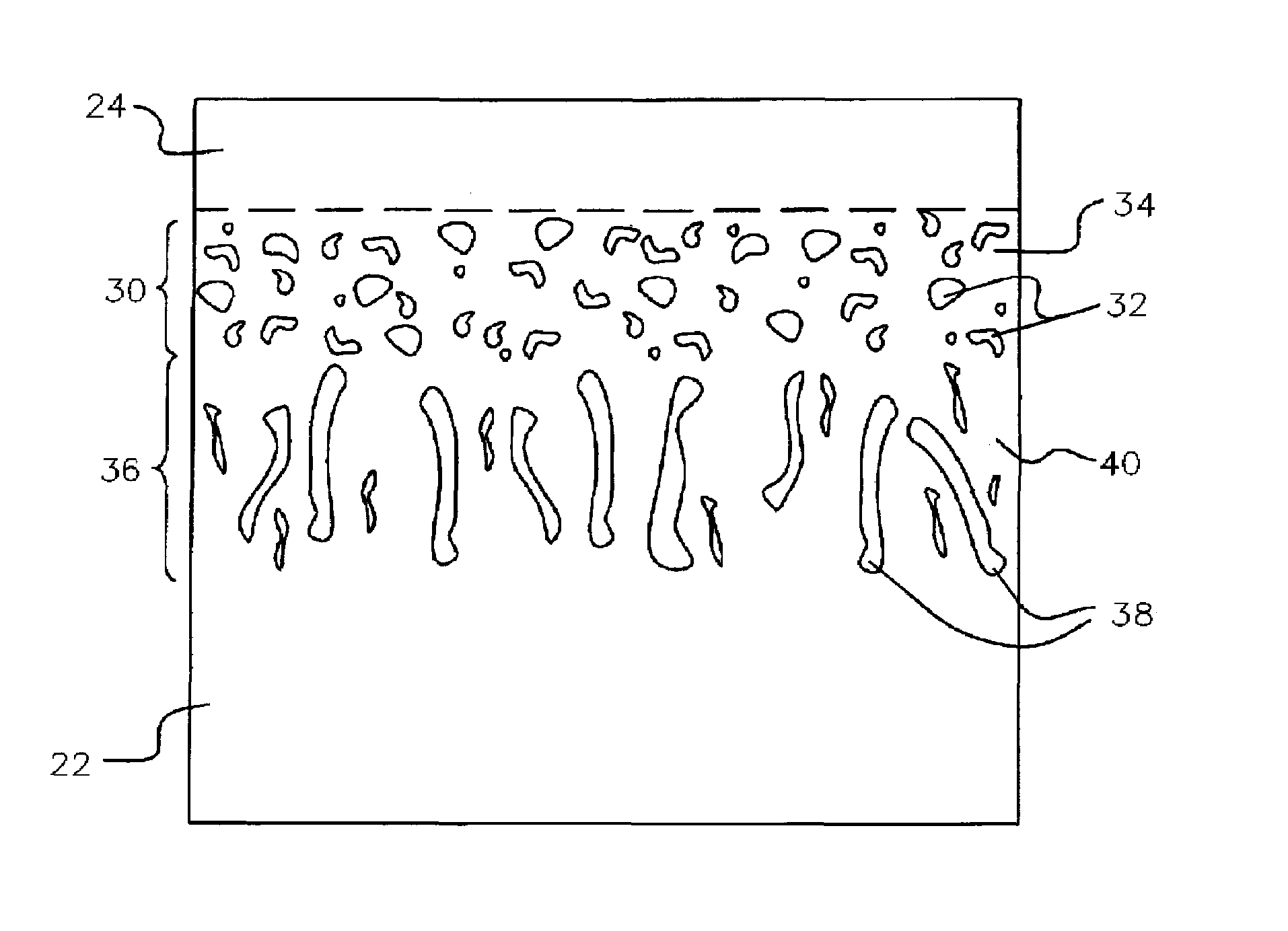
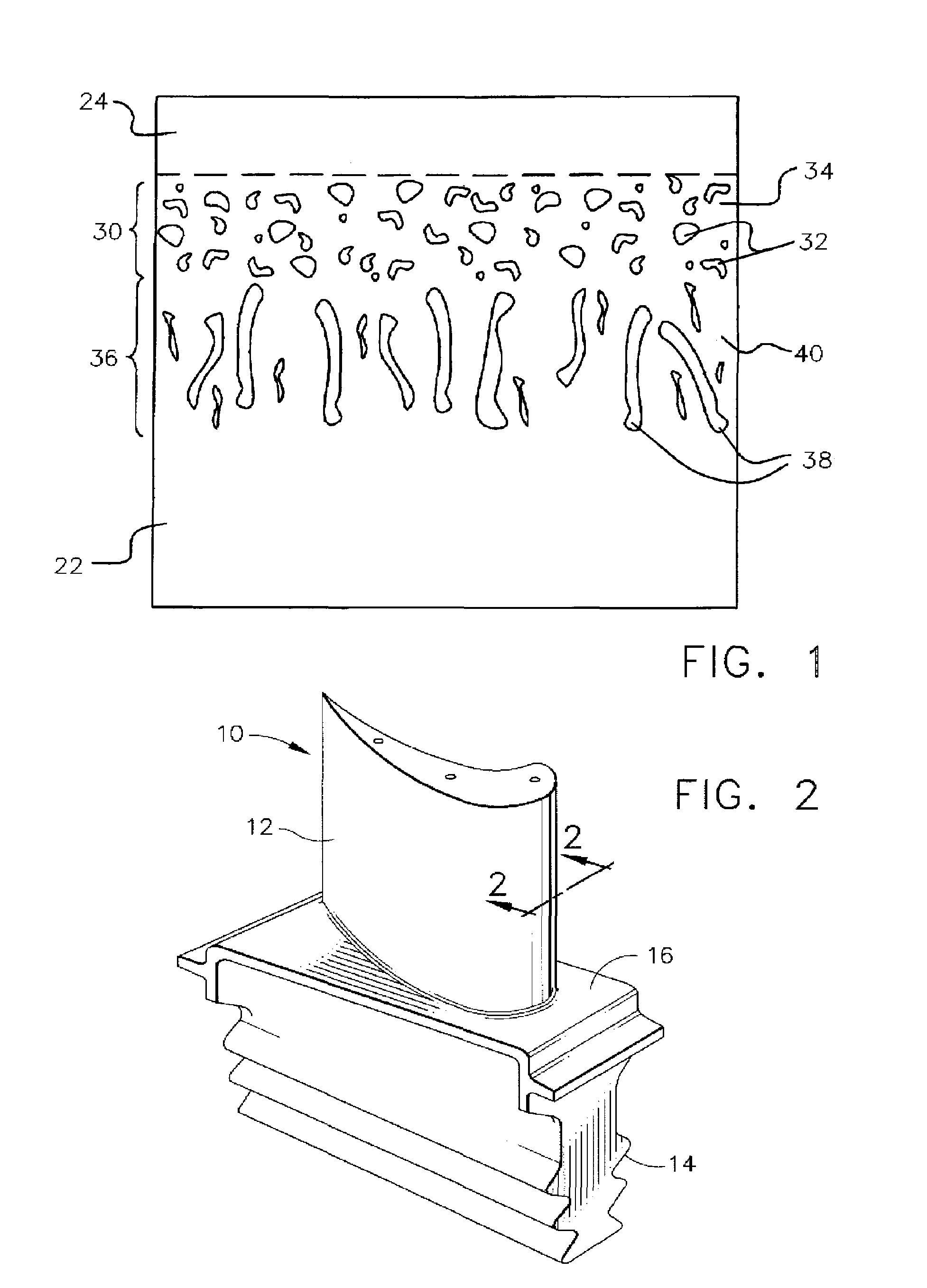
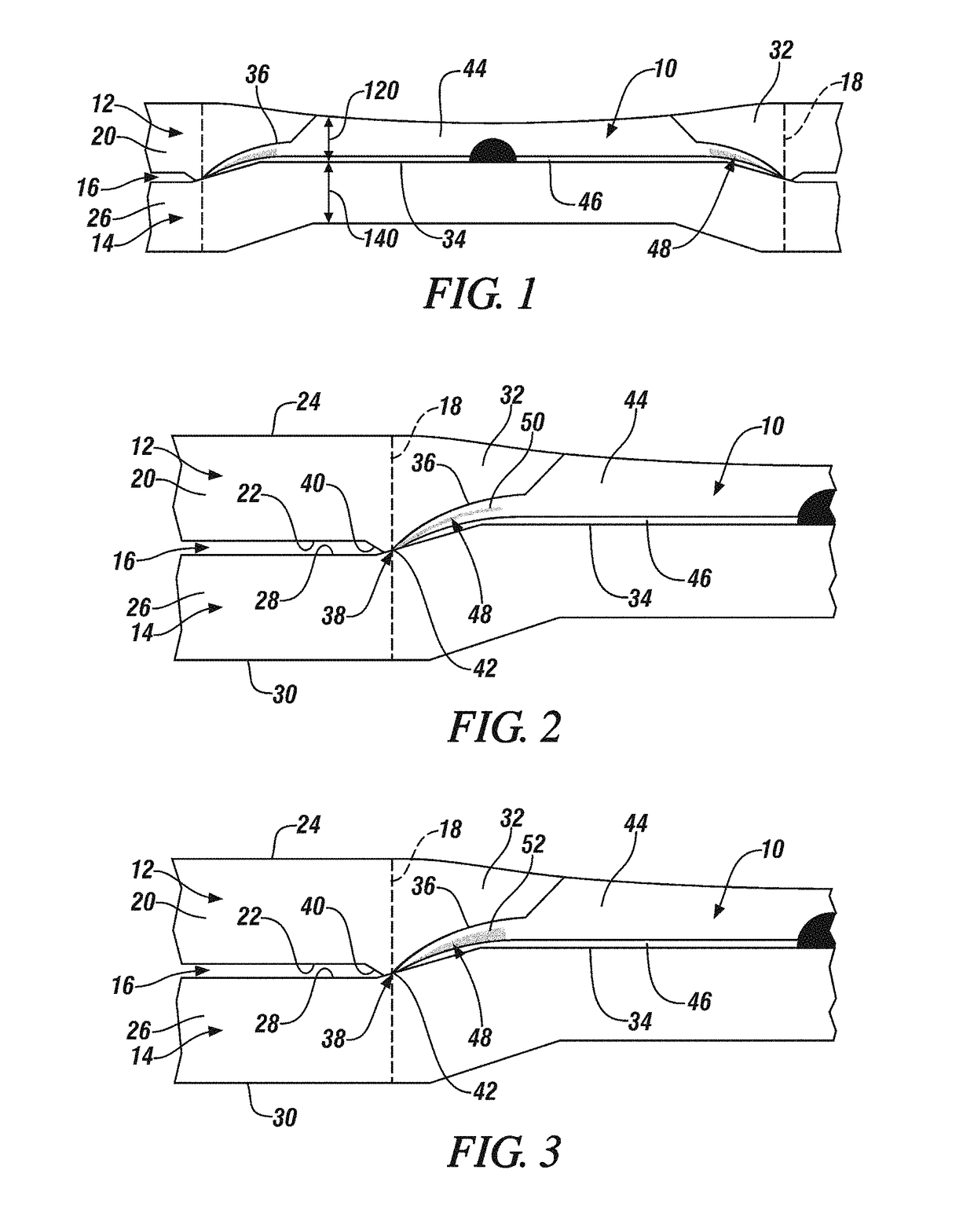
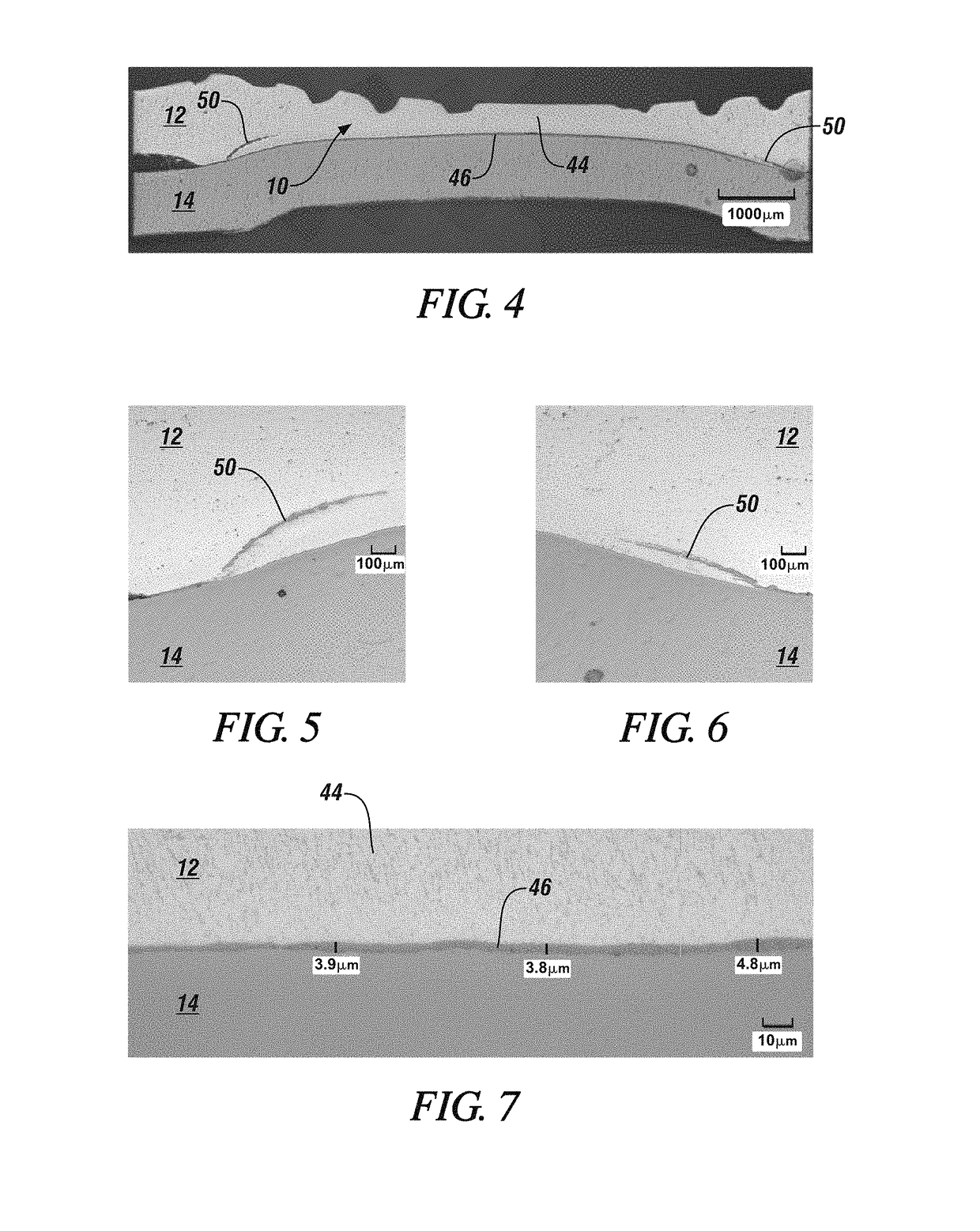
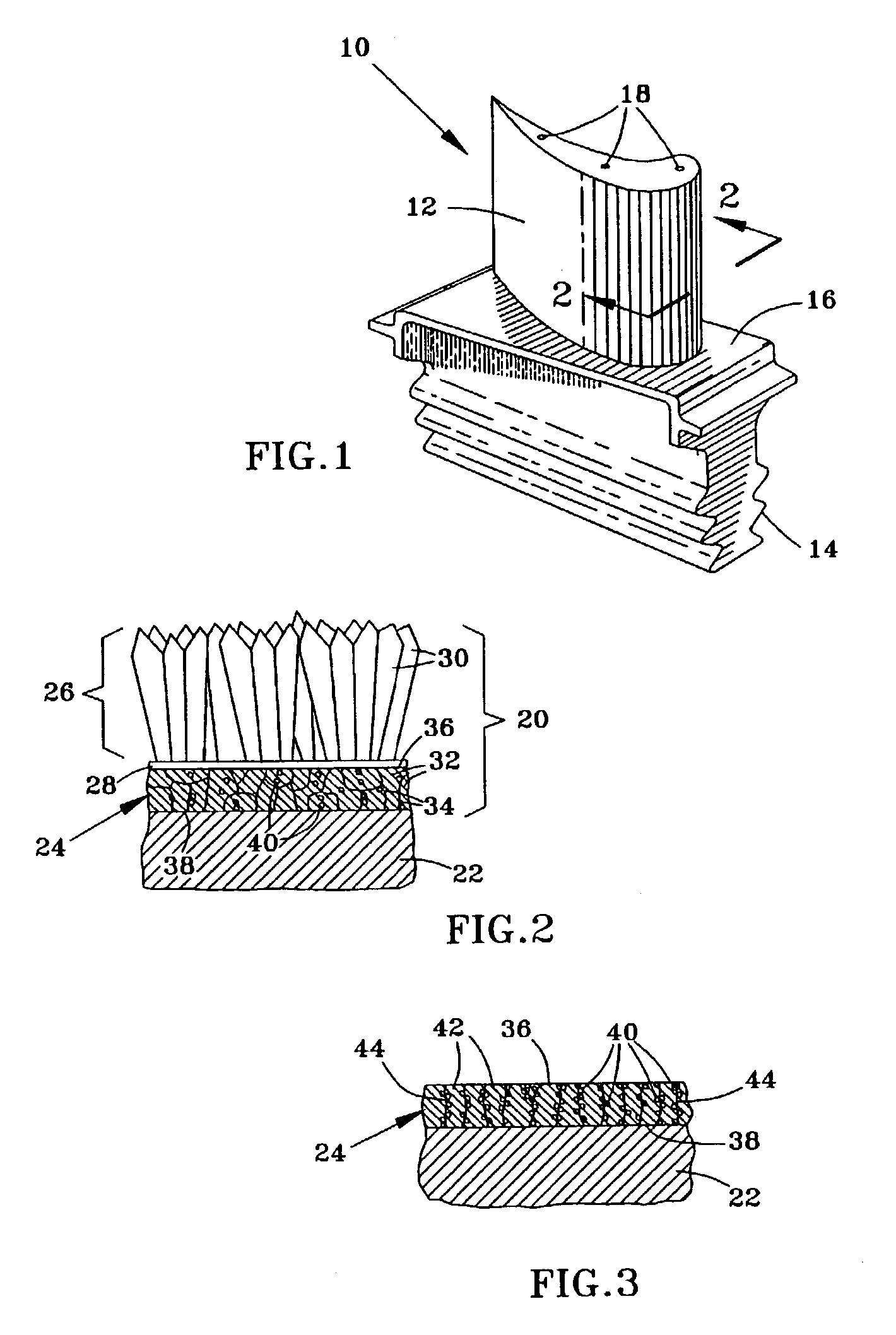
A beta-phase nickel aluminide (NiAl) overlay coating (24) and method for modifying the grain structure of the coating (24) to improve its oxidation resistance. The coating (24) is deposited by a method that produces a grain structure characterized by grain boundaries (44) exposed at the outer coating surface (36). The grain boundaries (44) may also contain precipitates (40) as a result of the alloyed chemistry of the coating (24). During or after deposition, the overlay coating (24) is caused to form new grain boundaries (34) that, though open to the outer surface (36) of the coating (24), are free of precipitates or contain fewer precipitates (40) than the as-deposited grain boundaries (44). New grain boundaries (34) are preferably produced by causing the overlay coating (24) to recrystallize during coating deposition or after deposition as a result of a surface treatment followed by heat treatment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Coating systems containing beta phase and gamma-prime phase nickel aluminide
ActiveUS7326441B2Improve solubilityHigher reactive element contentMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesGreek letter betaBeta phase
A coating and process for depositing the coating on a substrate. The coating is a nickel aluminide overlay coating of predominantly the beta (NiAl) and gamma-prime (Ni3Al) intermetallic phases, and is suitable for use as an environmental coating and as a bond coat for a thermal barrier coating (TBC). The coating can be formed by depositing nickel and aluminum in appropriate amounts to yield the desired beta+gamma prime phase content. Alternatively, nickel and aluminum can be deposited so that the aluminum content of the coating exceeds the appropriate amount to yield the desired beta+gamma prime phase content, after which the coating is heat treated to diffuse the excess aluminum from the coating into the substrate to yield the desired beta+gamma prime phase content.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of welding nickel-aluminide
ActiveUS20120175355A1Increase deposition rateArc welding apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesGas tungsten arc weldingNickel aluminide
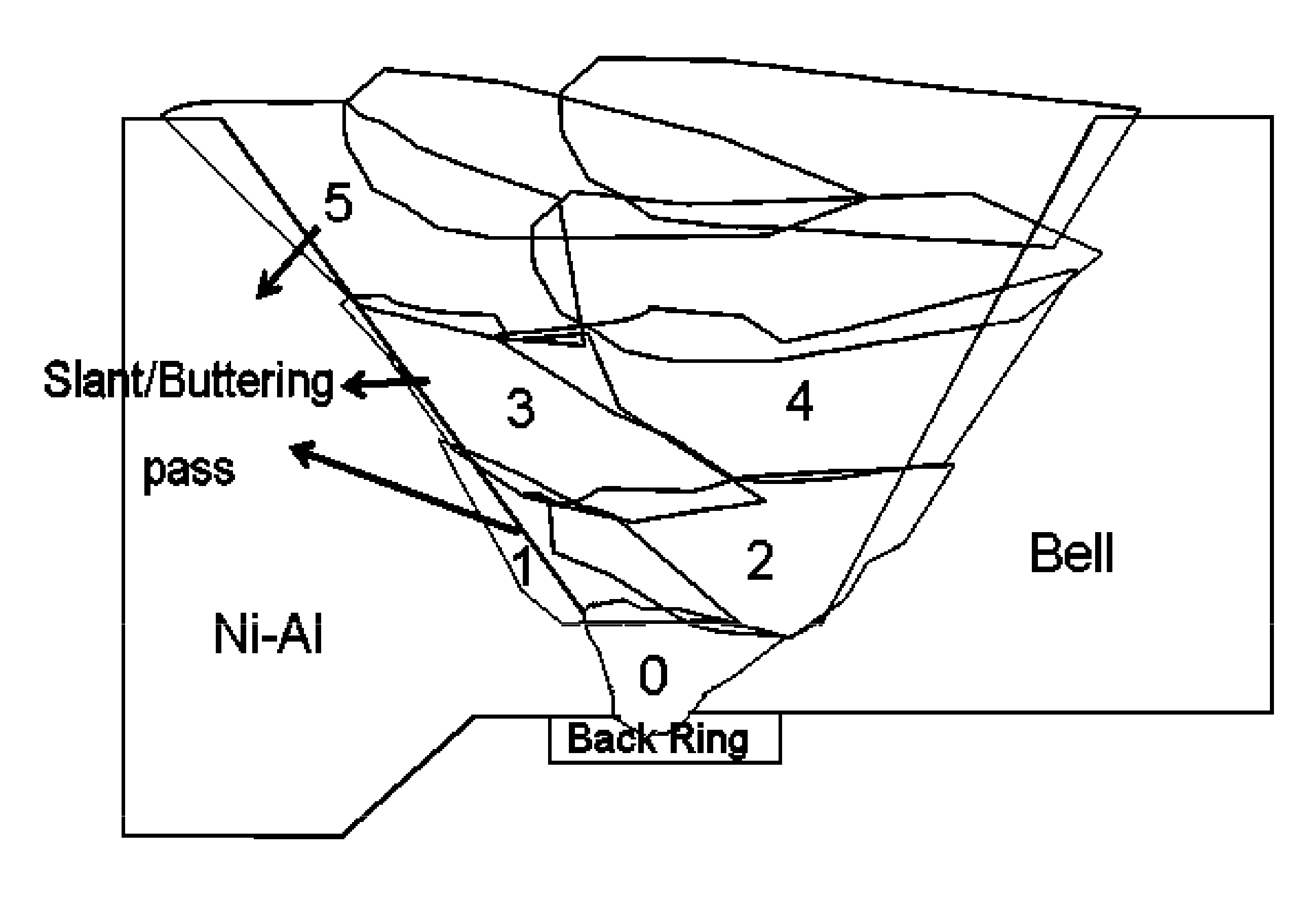
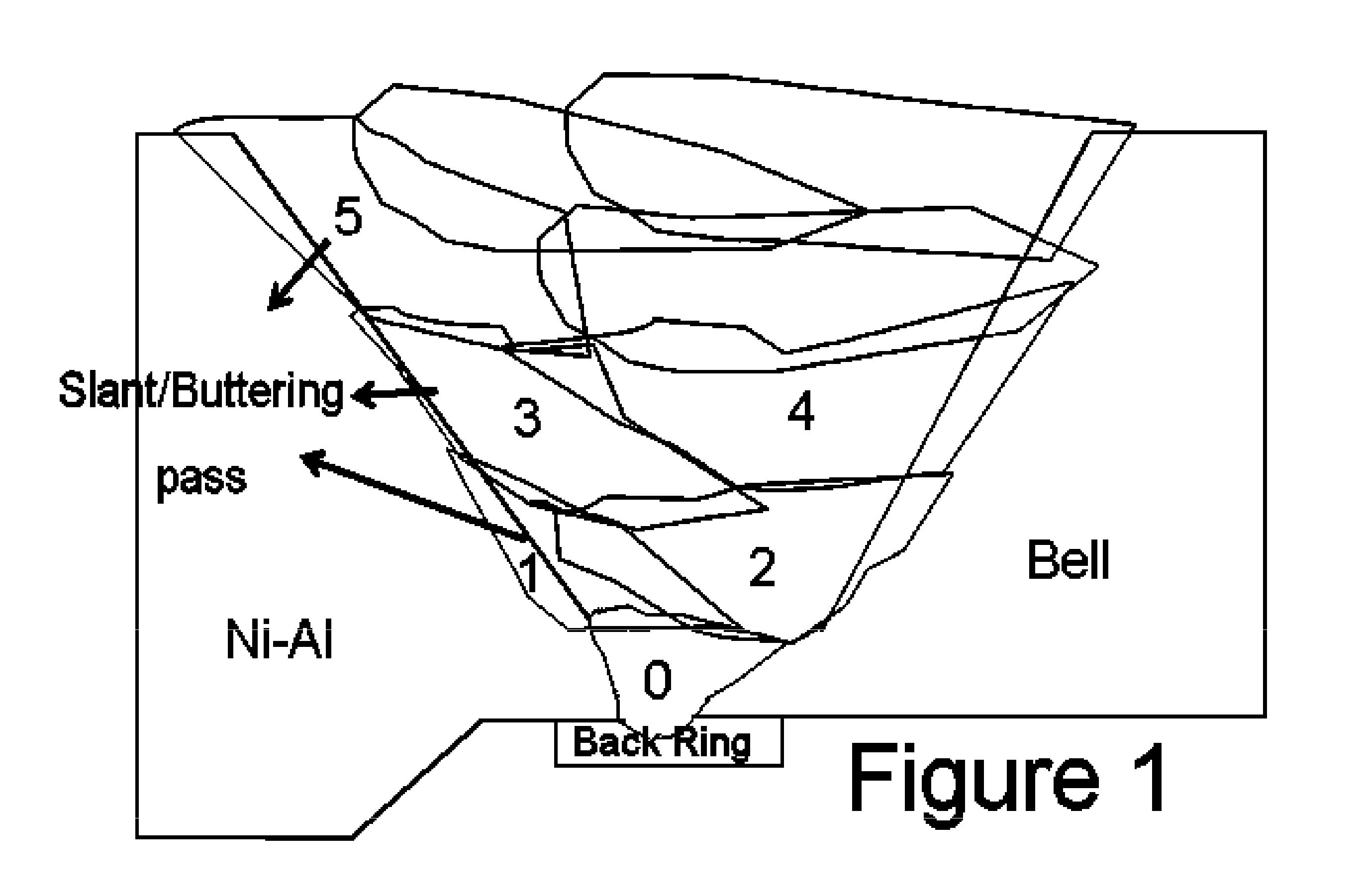
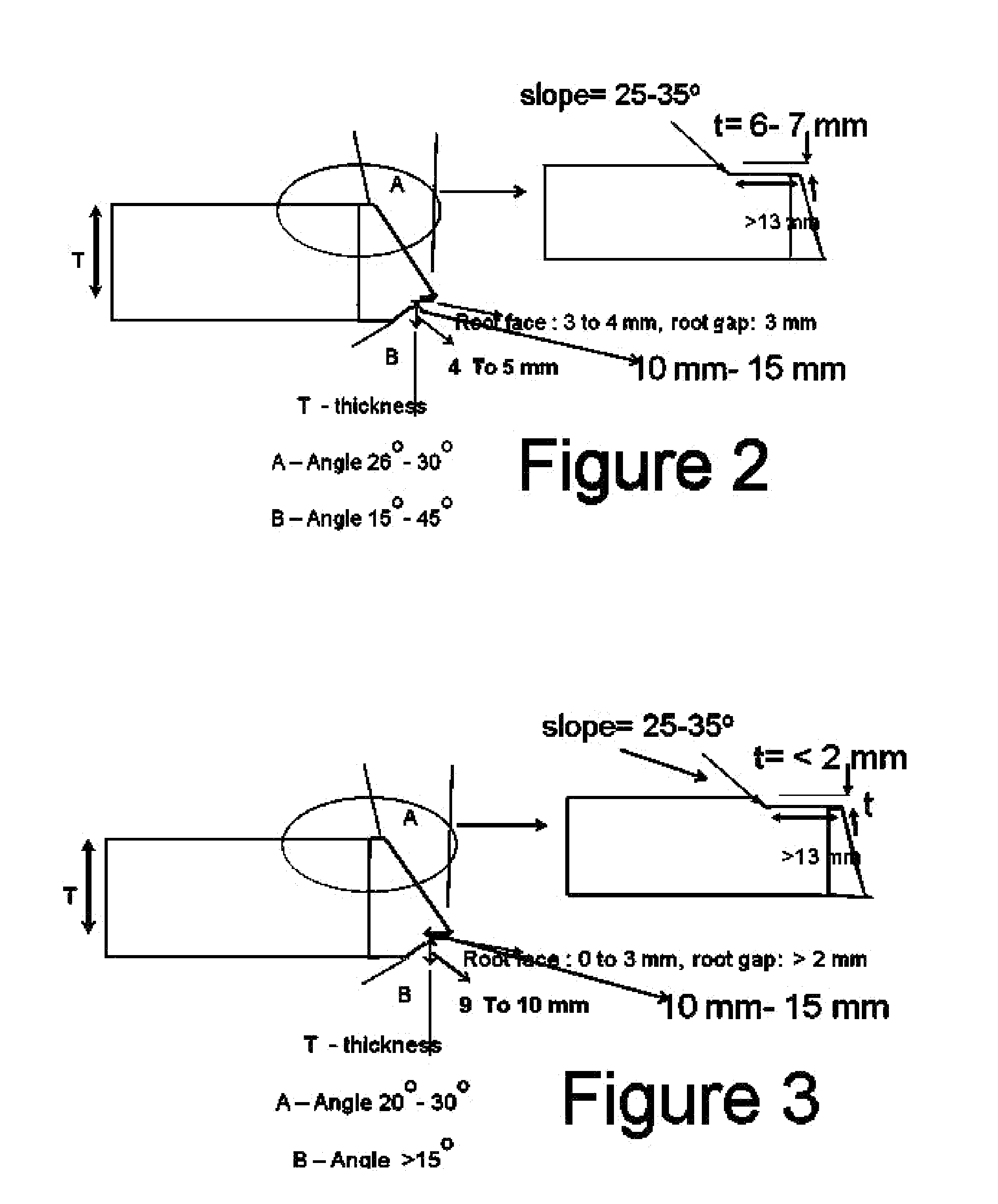
A method for gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) of nickel-aluminide to itself or other nickel-based alloys using a filler wire. Method limitations: I) outer surface of weld groove has 1-2 mm machining, weld groove angle <30°; and root face <3 mm; II) measured temperature 30 cm (12″) from weld torch and 3 mm from groove edge <200° C.; and interpass temperature <85° C. at 3 mm from weld groove edge; III) except for root pass, all filler and cap pass layering should start from nickel-aluminide edge; each bead should be peened; and weld cap pass should overlap nickel-aluminide edge by 3 mm; IV) weld bead layout at the nickel-aluminide edge should be laid at torch angle <30°; V) weld heat input should be 17-23 kJ / in; and VI) linear welding speed is >8.6 cm / min; and deposition rate should be >3.0 cm3 / min.
Owner:ARCELORMITTAL INVESTIGACION Y DESARROLLO SL
Nickel-aluminide based wear resistant material for piston rings
InactiveUS20040076851A1Easy to wearImproves wear resistance and ability to resistPiston ringsBraking action transmissionWear resistantPiston ring
A piston ring comprises a coating of a wear-resistant composite composition, particularly intended for high temperature applications. The wear-resistant composite composition comprises a ceramic compound and at least 50 volume %, based on the total volume of the wear-resistant composition, of an intermetallic nickel-aluminide chosen from the group consisting of NiAl and Ni3Al. A piston ring comprises a wear-resistant composite composition, particularly intended for high temperature applications. The wear-resistant composite composition comprises a ceramic compound and at least an intermetallic nickel-aluminide chosen from the group consisting of NiAl and Ni3Al.
Owner:KONCENTRA MARINE & POWER
Ductile environmental coating and coated article having fatigue and corrosion resistance
A ductile corrosion and oxidation resistant coating, being predominately of gamma-prime nickel aluminide intermetallic includes 15-30 atomic % aluminum, up to atomic % chromium, optionally, up to 30 atomic % of a platinum group metal, optionally, up to 4 atomic % of a reactive element, and optionally, up to 15 atomic % of at least one strengthening element, and a balance being essentially nickel or nickel and at least one of cobalt, iron, or cobalt and iron. A coated article includes the ductile corrosion and oxidation resistant coating on a superalloy substrate such as a turbine disk, turbine seal, a turbine blade, a turbine nozzle, a turbine shroud, or a turbine frame or case having an under platform or non-gas path region.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Beta-phase nickel aluminide overlay coatings and process therefor
InactiveUS7150922B2Improve the oxidation resistance of the overlay coatingIncrease resistancePropellersMolten spray coatingBeta phaseGrain structure
A beta-phase nickel aluminide (NiAl) overlay coating (24) and method for modifying the grain structure of the coating (24) to improve its oxidation resistance. The coating (24) is deposited by a method that produces a grain structure characterized by grain boundaries (44) exposed at the outer coating surface (36). The grain boundaries (44) may also contain precipitates (40) as a result of the alloyed chemistry of the coating (24). During or after deposition, the overlay coating (24) is caused to form new grain boundaries (34) that, though open to the outer surface (36) of the coating (24), are free of precipitates or contain fewer precipitates (40) than the as-deposited grain boundaries (44). New grain boundaries (34) are preferably produced by causing the overlay coating (24) to recrystallize during coating deposition or after deposition as a result of a surface treatment followed by heat treatment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nickel aluminide intermetal compound-carbon nanotube composite material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101550523AImprove flexural strengthImprove fracture toughnessCarbon nanotubeMaterials science
The invention discloses a nickel aluminide intermetal compound-carbon nanotube composite material which comprises, based on the weight percentage, 2 percent to 9 percent of nickel-plated carbon nanotube, and the balance of nickel aluminide intermetal compound. The preparation method of the composite material comprises the following steps: a mechanical alloying method is used for preparing Ni3Al nano powder; a chemical nickel-plating method is used for plating nickel on the surface of the carbon nanotubes; a mechanical ball milling method is used for the synthesis of Ni3Al-carbon nanotube composite powder which is obtained by cold pressing, premolding, hot pressing and sintering. The composite material has higher compressive strength and fracture toughness and good corrosion resistance, thus being applicable to turbine blades of aeroengines and having potential application prospect in the nuclear industry, the catalyst industry, the electronic technology and other fields.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Aluminum-based material and a method for manufacturing products from aluminum-based material
An aluminum-based material and method of manufacturing products from the aluminum-based material formed by a solid solution of zinc, magnesium and copper in aluminum with dispersed phase particles of aluminum, zinc, magnesium and copper essentially evenly distributed in the solution and particles of nickel aluminide being essentially evenly distributed in the matrix of the aluminum-based material that contains particles, essentially evenly distributed in the matrix, of at least one of the aluminides group such as chromium aluminide and zirconium aluminide, with a total content of 0.1–0.5% of the volume with the maximum amount of nickel aluminide particles being 3 μm and the proportion between the maximum and minimum amount of nickel aluminide particles of no more than 2 and with the maximum amount of chromium aluminide and zirconium aluminide particles is 0.05 μm, resulting in the aluminum-based material having a microhardness of no less than 170 HV, a tensile strength of no less than 530 MPa and elongation of no less than 2%.
Owner:AXENOV ANDREI ANATOLYEVICH +2
Nickel aluminide coating and coating systems formed therewith
InactiveUS20050069650A1Increase resistancePromote oxidationLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingMetallurgyCoating system
A beta-phase NiAl overlay coating containing a dispersion of ceramic particles and a process for depositing the overlay coating. If the coating is used to adhere a thermal barrier coating (TBC), the TBC exhibits improved spallation resistance as a result of the dispersion of ceramic particles having a dispersion-strengthening effect on the overlay coating. The overlay coating contains at least one reactive element and is deposited so that the some of the reactive element deposits as the ceramic particles dispersed in the overlay coating.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com