Method for detecting analytes by means of an analyte/polymeric activator bilayer arrangement
An analyte and activator technology, applied in the field of analytical sensors, can solve problems such as difficult detection, high background signal, and low sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] Embodiment 1: the detection of nucleic acid
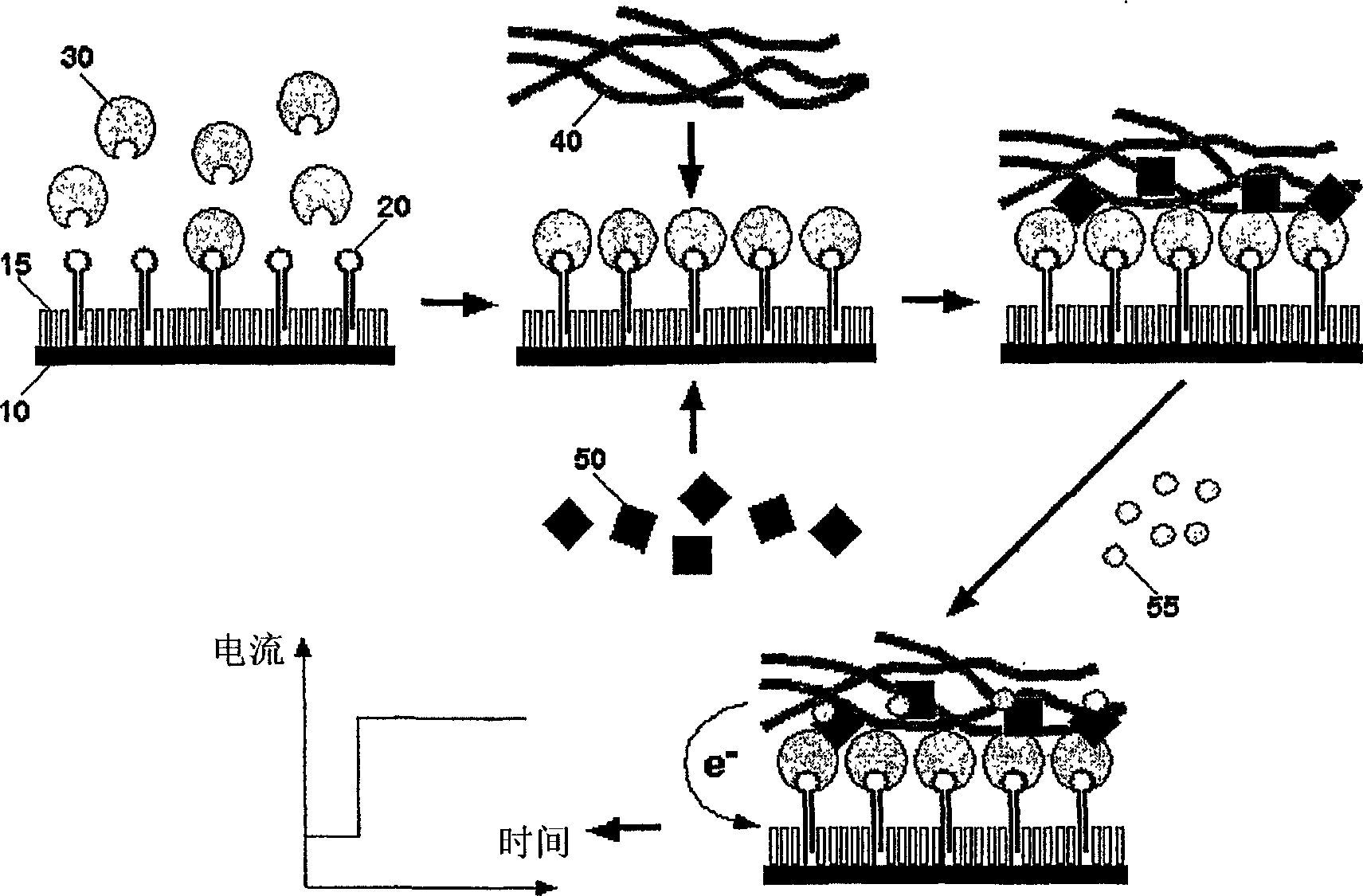
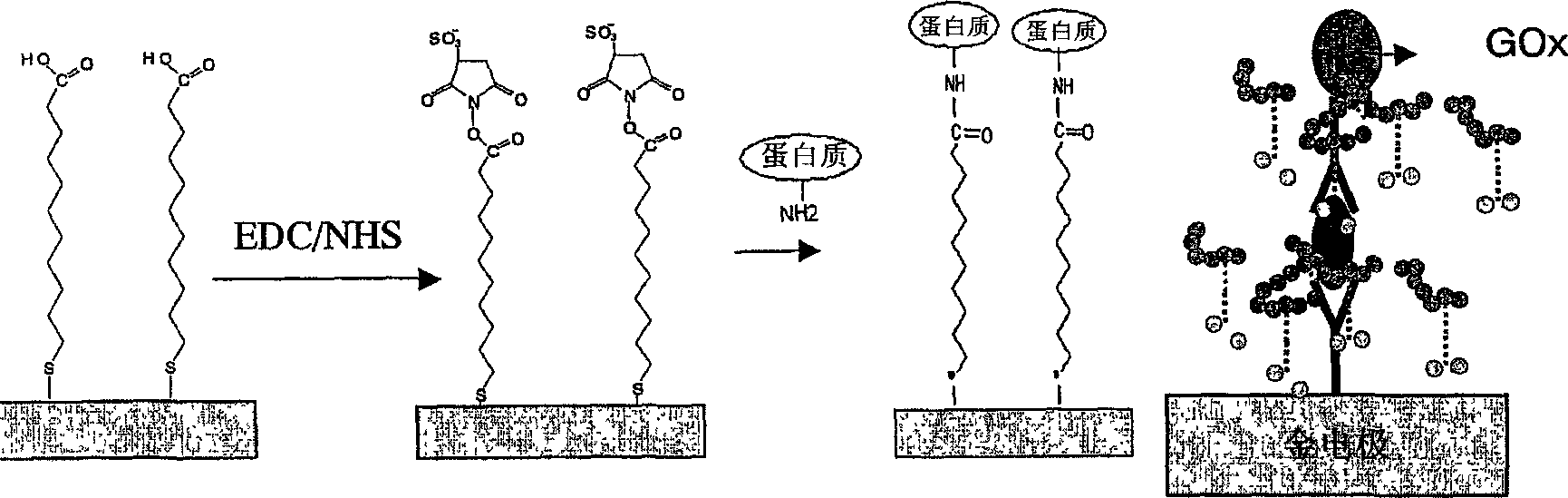
[0117]Generally, nucleic acid detection according to the present invention is performed as shown in FIG. 1 . First, a mixture of thiolated oligonucleotides (also carrying biotin modifications as labels) used as capture molecules (20) and thiol molecules used as blocking agents (15) to reduce background was immobilized on the surface of a gold electrode ( 10) on. The electrodes are then exposed to a solution supposedly containing the analyte of interest (30). After hybridization to its complementary biotinylated target DNA (ie, capture molecule), the enzyme conjugate is bound via an avidin-biotin interaction (50). Finally, the redox polymer (40) is brought onto the electrode surface by layer-layer electrostatic self-assembly. The redox polymer layer electrochemically activates the enzymatic label bound to the target DNA. The current generated by the catalytic oxidation of the substrate in the presence of the substrate mol...
Embodiment 11
[0118] Example 1.1: Extraction of mRNA from Rat Tissue and Synthesis of Biotinylated cDNA
[0119] Using Dynabeads® mRNA DIRECT TM Kit (Dynal ASA, Oslo, Norway), rat liver mRNA extraction was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions. For reverse transcription (RT), 10 ng of this mRNA was used in a total volume of 20 μl containing Sigma-Aldrich's 1×eAMV buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.3, 40 mM KCl, 8.0 mM MgCl 2 , 1 mM DTT), 500 μM of each dNTP, 1.0 μM antisense primer, 20 U RNase inhibitor and 20 U enhanced avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase (eAMV). The samples were incubated in a DNA thermal cycler (Gene Amp PCR System 9700, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) at 56°C for 50 min, and the obtained cDNA was directly used as a template for PCR amplification.
[0120] PCR was performed using 2.0 μl RT-reaction mix in a total volume of 50 μl containing Sigma-Aldrich's 1×AccuTaq buffer (5 mM Tris-HCl, 15 mM ammonium sulfate, pH 9.3, 2.5 mM MgCl 2 ...
Embodiment 12
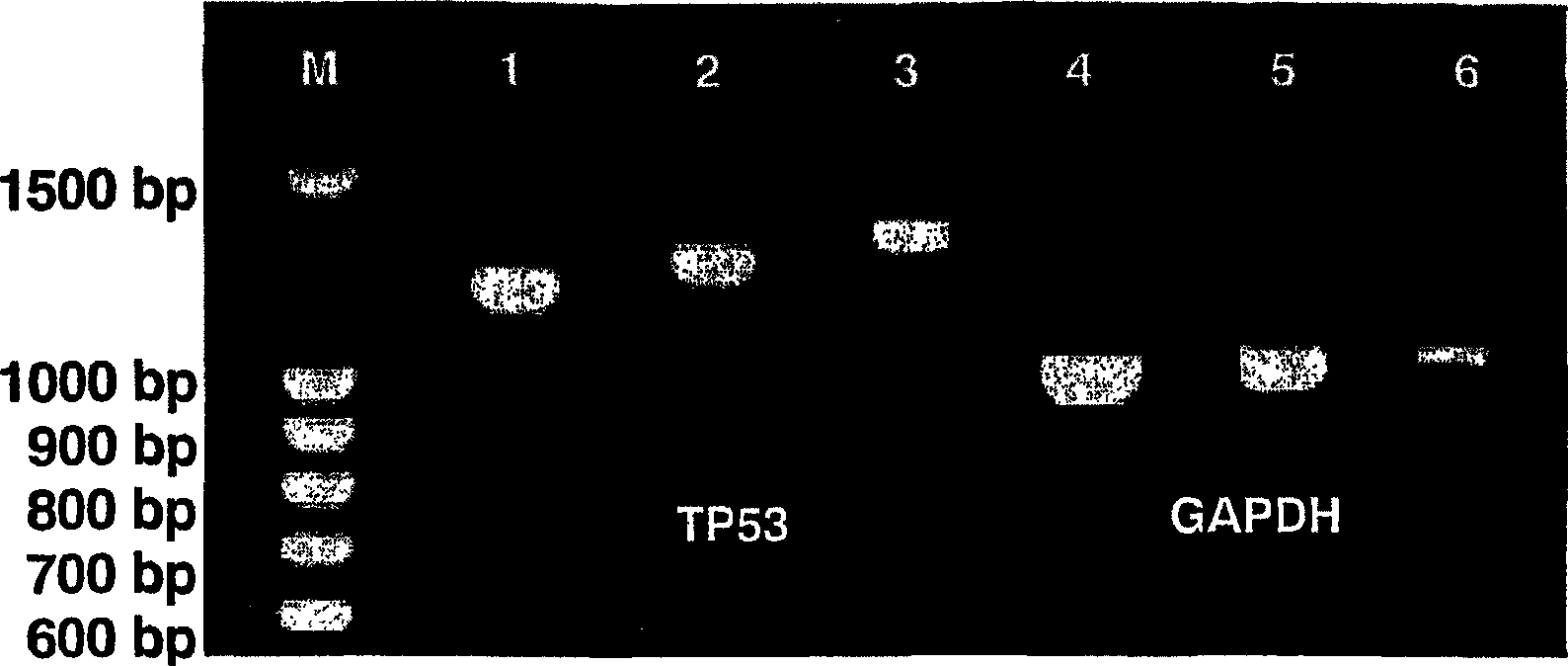
[0124] Example 1.2: Capture probe immobilization and evaluation of monolayer quality
[0125] Prior to the detection of DNA analytes, a mixture of thiolated oligonucleotides and thiol molecules used as capture probes was immobilized on the gold electrode surface by self-assembly. To minimize absorption associated with non-hybridization of target DNA, anionic thiol molecules are used to form a mixed monolayer of blocking components. Use the following capture probes: for GAPDH detection, 5′-T 12 TTACTCCTTGGAGGCCATGTAGG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5); and 5'-T 12 ATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTCAACGG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 6); for TP53 detection, 5'-T 12 ATGGAGGATTCACAGTCGGA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 7) and 5'-T 12 TCAGTCTGAGTCAGGCCCCA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 8); and as a control, 5'-T 12 CCTCTCGCGAGTCAACAGAAACG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 9). Oligonucleotides were thiolated using 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid according to routine procedures and assembled onto gold electrodes by exposing the cleaned electrodes to a 50 μM oligonucleotide solutio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com