Cellulose degrading bacterium n3 for producing IAA and application thereof
A technology of cellulose-degrading bacteria and bacterial suspensions, applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms, to achieve the effects of accelerating cellulose degradation, promoting the efficiency of straw returning to the field, and increasing crop yields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] 1. Reagent preparation:
[0055] LB medium: peptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, sodium chloride 10g, distilled water 1000mL, adjust the pH to 7.0-7.2, and sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes (the solid medium adds 20g agar to this formula).
[0056] Inorganic salt culture medium: ammonium sulfate 2.0g, sodium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2g, calcium dichloride 0.1g, distilled water 1000mL, adjust pH to 7.0~7.2, and kill at 121℃ Bacteria for 20 minutes.
[0057] Liquid fermentation medium: 6g sodium chloride, 0.1g magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.1g calcium chloride, 0.5g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 10g yeast extract, 20g straw, 1000mL distilled water, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0058] Enrichment medium: 20g sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 5g microcrystalline cellulose, 5g cellulose powder, 1g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 1g nitric acid, 0.2g magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.1g copper chloride dihydr...
Embodiment 2
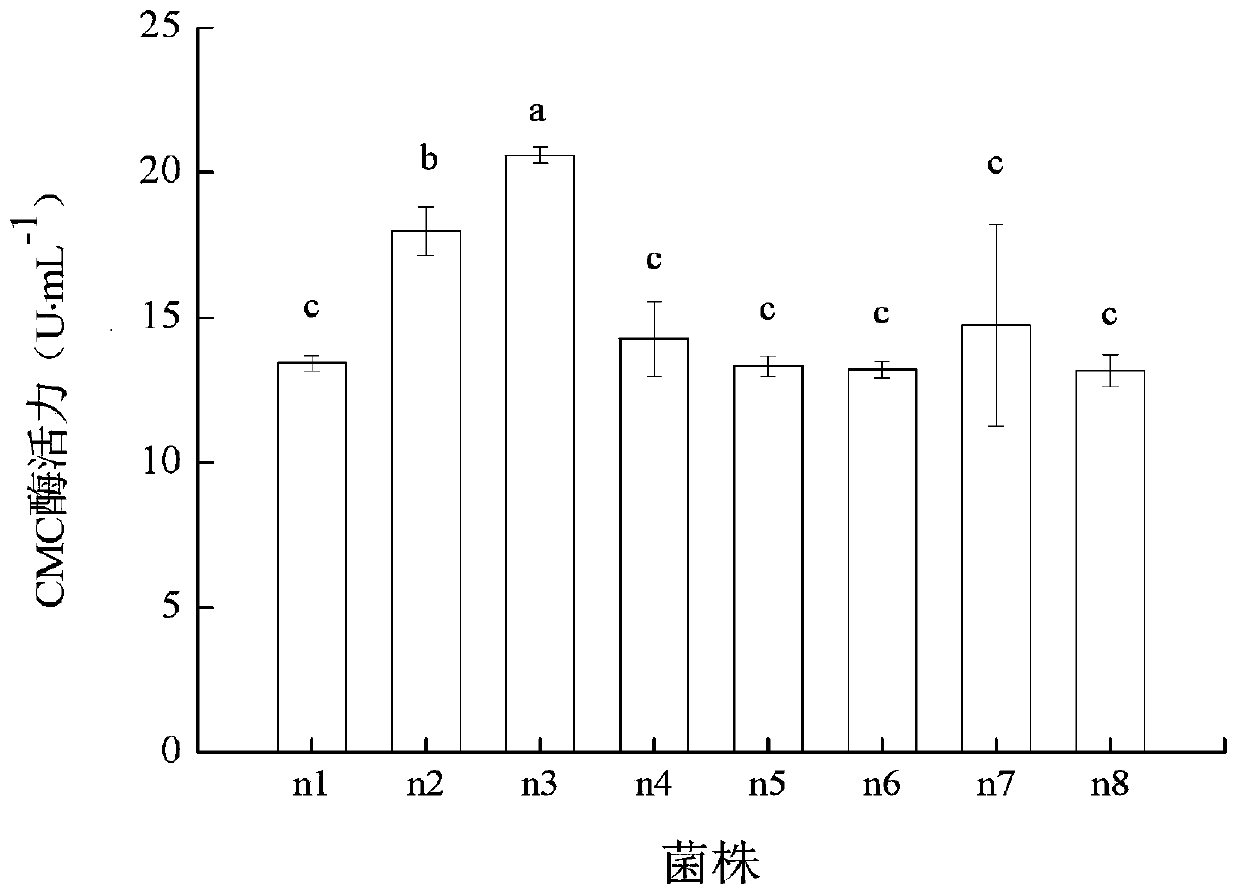
[0082] The effects of different pH, ventilation, and nitrogen sources on the ability of strains to produce CMC enzymes
[0083] 1. The influence of the initial pH of the medium on the ability of CMC enzyme production
[0084] The strain was inoculated into a liquid fermentation medium with wheat straw powder as the sole carbon source, cultured in a liquid shake flask at 37°C for 60 hours, and its OD was measured with a spectrophotometer 520 value. The initial pH was set to 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and after 60 hours of cultivation, the content of CMC enzyme produced was measured with a spectrophotometer.
[0085] The result is figure 2 Shown: when the pH value is 5.0, the CMC enzyme activity is the highest, reaching 24.96U·mL -1 , When the pH value is 4.0, the enzyme activity is the second, 24.85U·mL -1 , Indicating that the n3 strain has strong acid tolerance, and the CMC enzyme activity at pH 4.0 and 5.0 is significantly higher than that under other pH conditions.
[0086] 2. The effe...
Embodiment 3
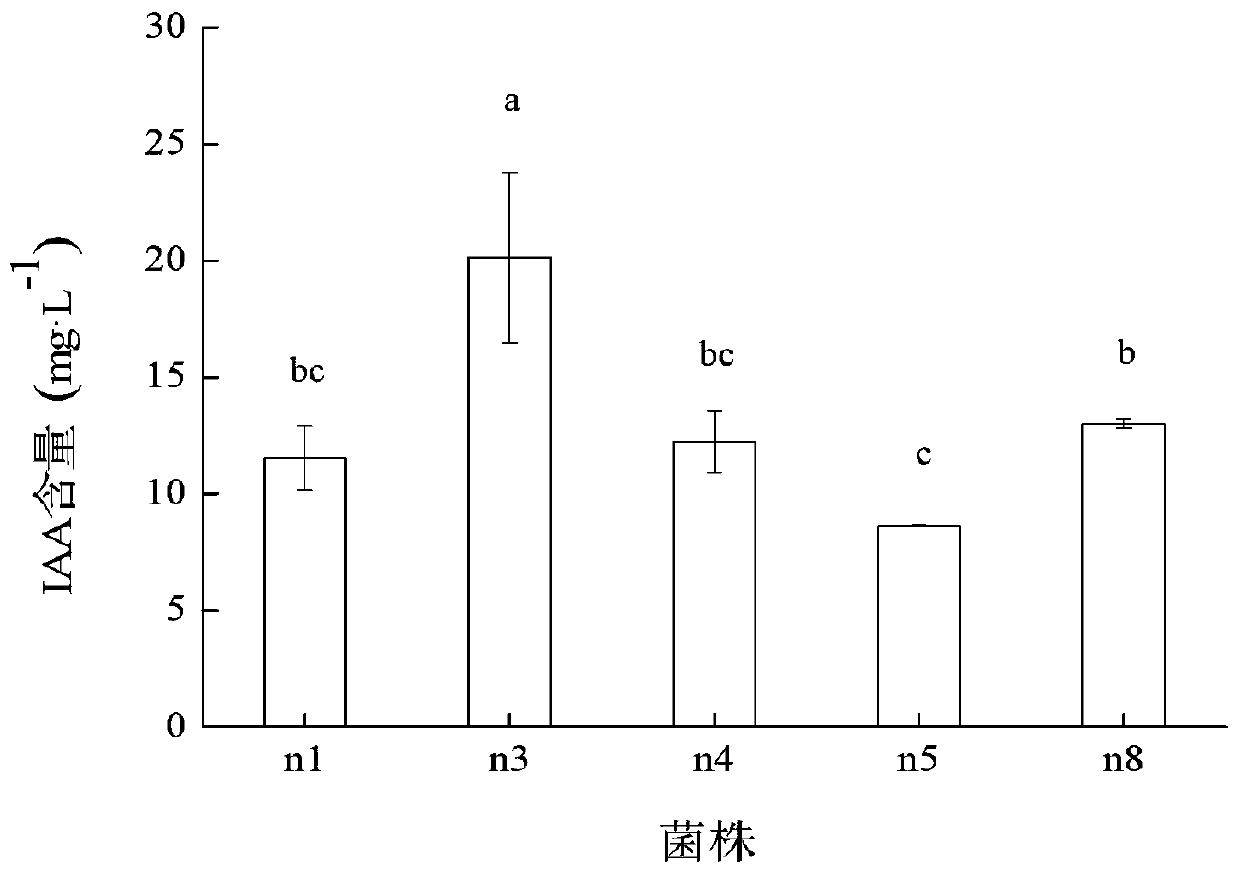
[0093] Test the effects of different pH, ventilation, different time, different carbon sources, and different nitrogen sources on the yield of strain IAA and growth of strain
[0094] 1. The influence of fermentation time on strain IAA yield and strain growth
[0095] Will contain 100mg·L -1 50mL LB liquid medium (IAA detection medium) of L-tryptophan is placed in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, and a bacterial suspension with an OD value of about 1 is inoculated according to the inoculum amount of 1% (V / V), 30℃, 180rpm Shaker culture, dynamic sampling at 10, 15, 20, 32, 44, and 56h respectively to determine the growth of strains (OD 600 ) And IAA capacity (OD 530 ), three repetitions for each treatment.
[0096] The result is Figure 5 Shown: OD at 20h 600 After 20h, the growth of the strain appears to decline. The content of IAA produced is basically the same as the growth of the strain. At 10-15h, the content of IAA produced by the strain increases logarithmically, and the IAA content r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| bleeding rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com