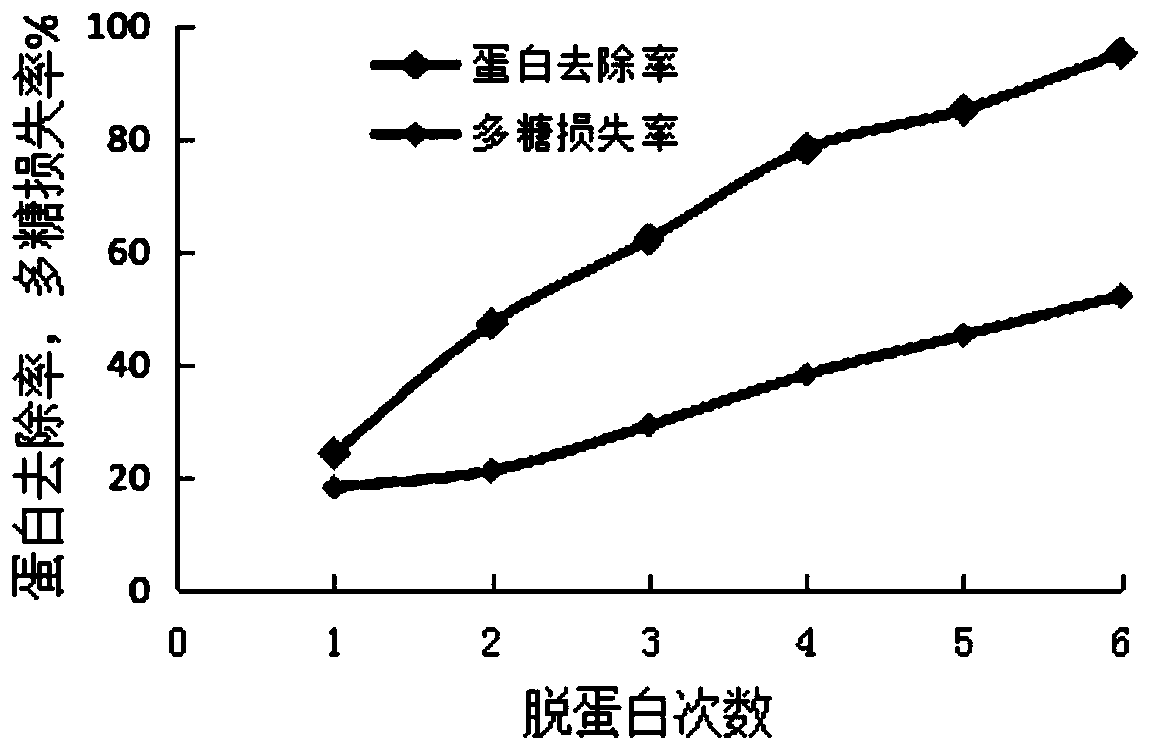
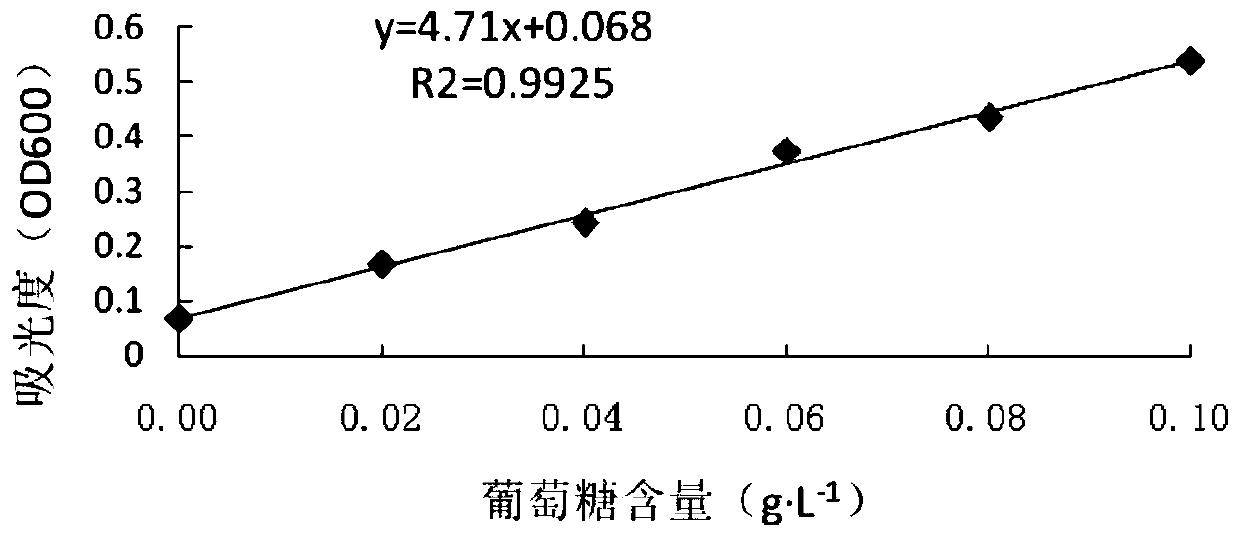
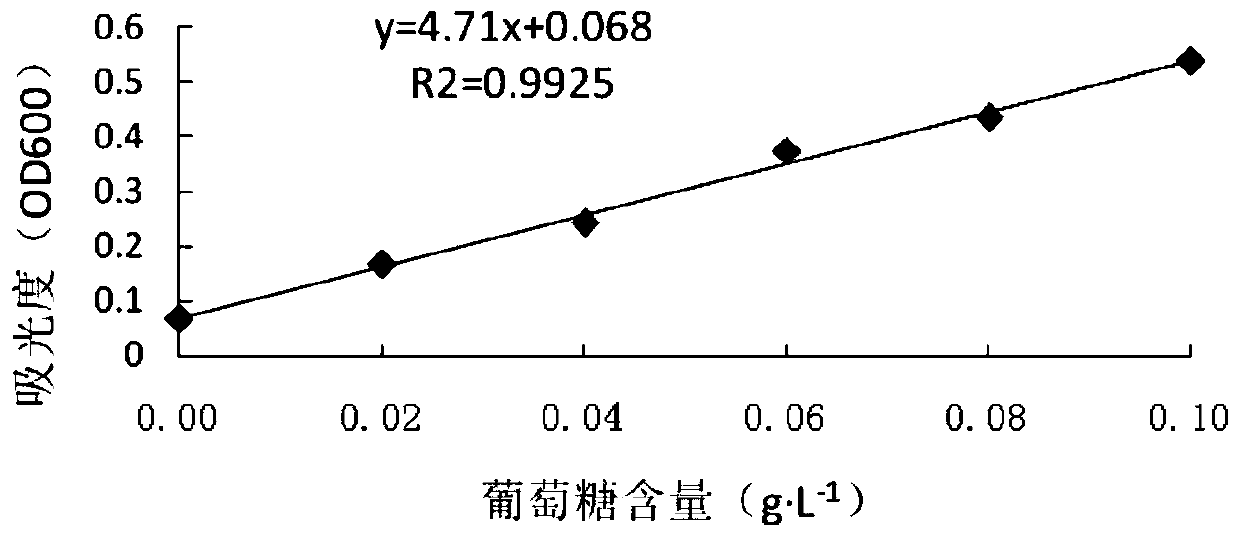
Method for extracting rhizobium japonicum exopolysaccharides
A soybean rhizobia and extraction method technology, applied in the field of soybean rhizobia exopolysaccharide extraction, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory protein removal effect, and achieve the effect of enhancing protein removal rate and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: in the present embodiment, the soybean rhizobium exopolysaccharide extraction method is carried out according to the following steps:
[0026] Step 1. Inoculate the soybean rhizobia HH103 stored at -80°C on a TY plate, put it into a 28°C incubator and incubate it upside down for 3 days, pick a ring of plate seeds and inoculate it into a 10mL test tube of TY liquid medium, 140rpm Shake culture at 28°C for 2 days, and inoculate 5mL of seed liquid into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask with a 1% inoculum amount, and inoculate it in a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask with a liquid volume of 100mL, and shake at 28°C for 2 days at 140rpm to obtain a soybean rhizobium fermentation broth;
[0027] Centrifuge the soybean rhizobium fermentation broth at a rate of 8000rpm for 5min, take the supernatant, add trichloroacetic acid with a mass concentration of 80% to a final concentration of 4%, let it stand at 4°C for 16h, and then centrifuge at a rate of 8000rpm for 5min , take the super...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com