Application of transport assistance factor GmPHF1b of phosphate transporter
A technology of transporter and phosphate, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing plant biomass and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
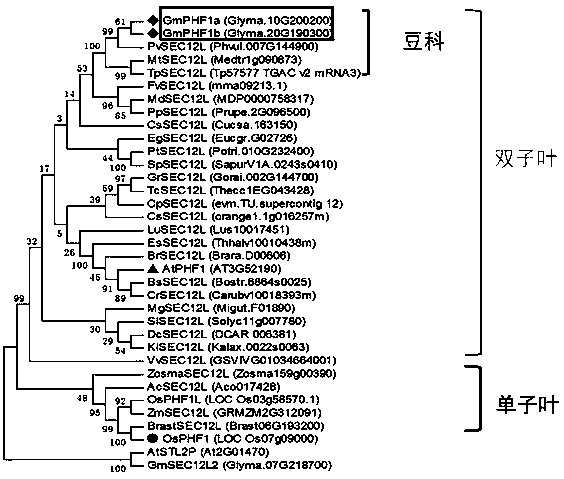
[0030] Phylogenetic tree analysis of embodiment 1, PHF1
[0031] Multiple sequence alignment of PHF1 protein
[0032] According to the sequence information of Arabidopsis thaliana and rice PHF1 gene, the candidate gene was screened by Blast in the soybean genome database Phytozome (http: / / www.phytozome.net / soybean), and the obtained gene sequence was carried out in the Arabidopsis thaliana database (TAIR) Blast was used to determine their possible functions, and Phytozome provided information about genes to determine their chromosomal location, and named them according to the Arabidopsis nomenclature (Bucher, 2007). The amino acid sequence of soybean PHF protein was compared with the amino acid sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana and rice PHF1 protein using GENEDOC software for multiple sequence alignment.
[0033] In the published soybean genome database, through homologous comparison, it is predicted that the soybean PHF1 phosphorus transporter family has two members, named Gm...
Embodiment 2
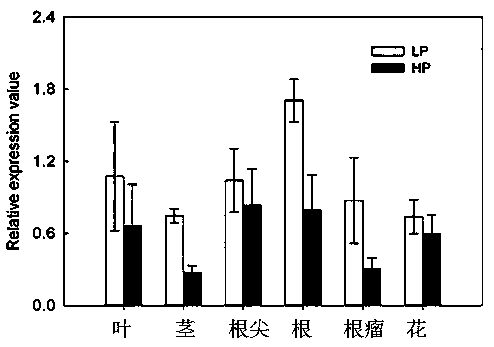
[0035] Embodiment 2, GmPHF1b gene expression pattern
[0036]The nutrient solution cultivation method was adopted for planting. One week after the seedlings were raised, the seedlings with uniform growth were selected and soaked in fresh rhizobia bacteria solution for 30 minutes, and then the seedlings were transferred into the bread boxes with different nutrient solutions. The experiment was a single factor, including two phosphorus levels: low phosphorus (LP: 5 μmol / L) and normal phosphorus (HP: 250 μmol / L); all were low nitrogen (100 μmol / L) and inoculated with rhizobia. 4 repetitions. Leaves, stems, root tips, roots, nodules, and flowers were harvested 55 days after transplanting; samples were stored at -80°C for RNA extraction. soybean PHF1a Gene quantitative PCR primer sequences are:
[0037] GmPHF1b-F: TGGGTCGTGGATTCGGAGGC;
[0038] GmPHF1b-R: CCCCACTTGGGTGGACTGCAA;
[0039] The quantitative PCR procedure was as follows: the cDNA obtained by reverse transcription...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3. Subcellular localization of GmPHF1b
[0044] 1 Vector construction
[0045] according to GmPHF1b Design primers from the full-length cDNA sequence, and add the upstream and downstream primers of the vector respectively Bam HI restriction site, primers are as follows:
[0046] PHF1b-F: GTggatccATGGGGAATGATGCAGGGTC;
[0047] PHF1b-R: GTggatccTCagTCACATATCTACTGGCCCCCAA;
[0048] Using the cDNA of wild-type soybean root as a template, it was amplified by Ex Taq (TAKALA, Japan). GmPHF1b Gene fragment, the PCR product was recovered and then linked to the pBI121-GFP vector digested with the corresponding enzyme, and the clone was picked, detected and sequenced, and the correctly fused clone was saved for future use. After obtaining the desired recombinant vector, the plasmid was transformed into Agrobacterium GV3101 competent cells, and the bacteria were shaken for later use.
[0049] 2 Tobacco transformation
[0050] The GV3101 positive clones containing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com