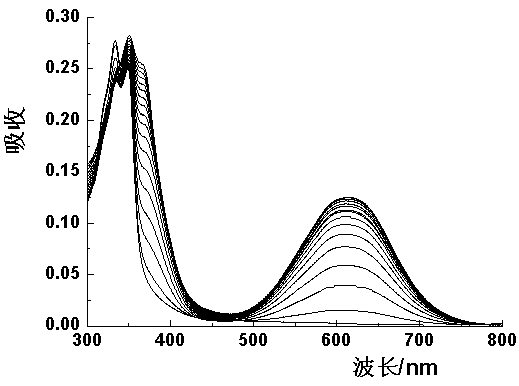
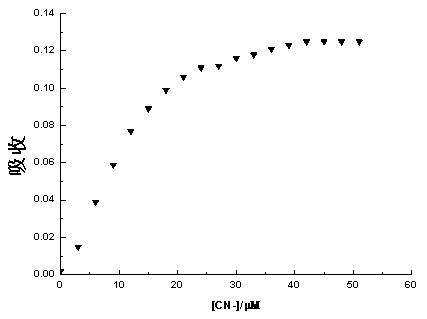
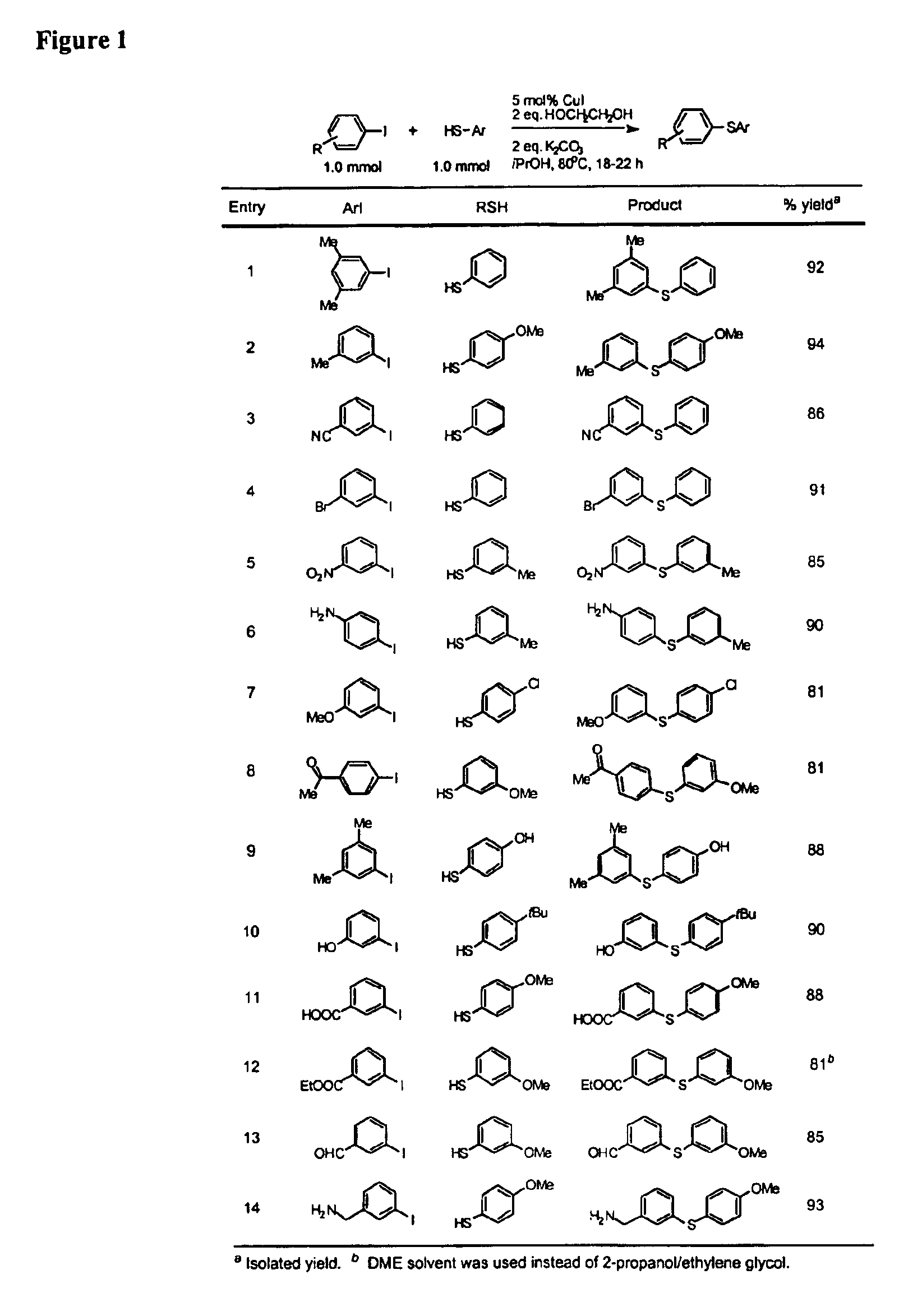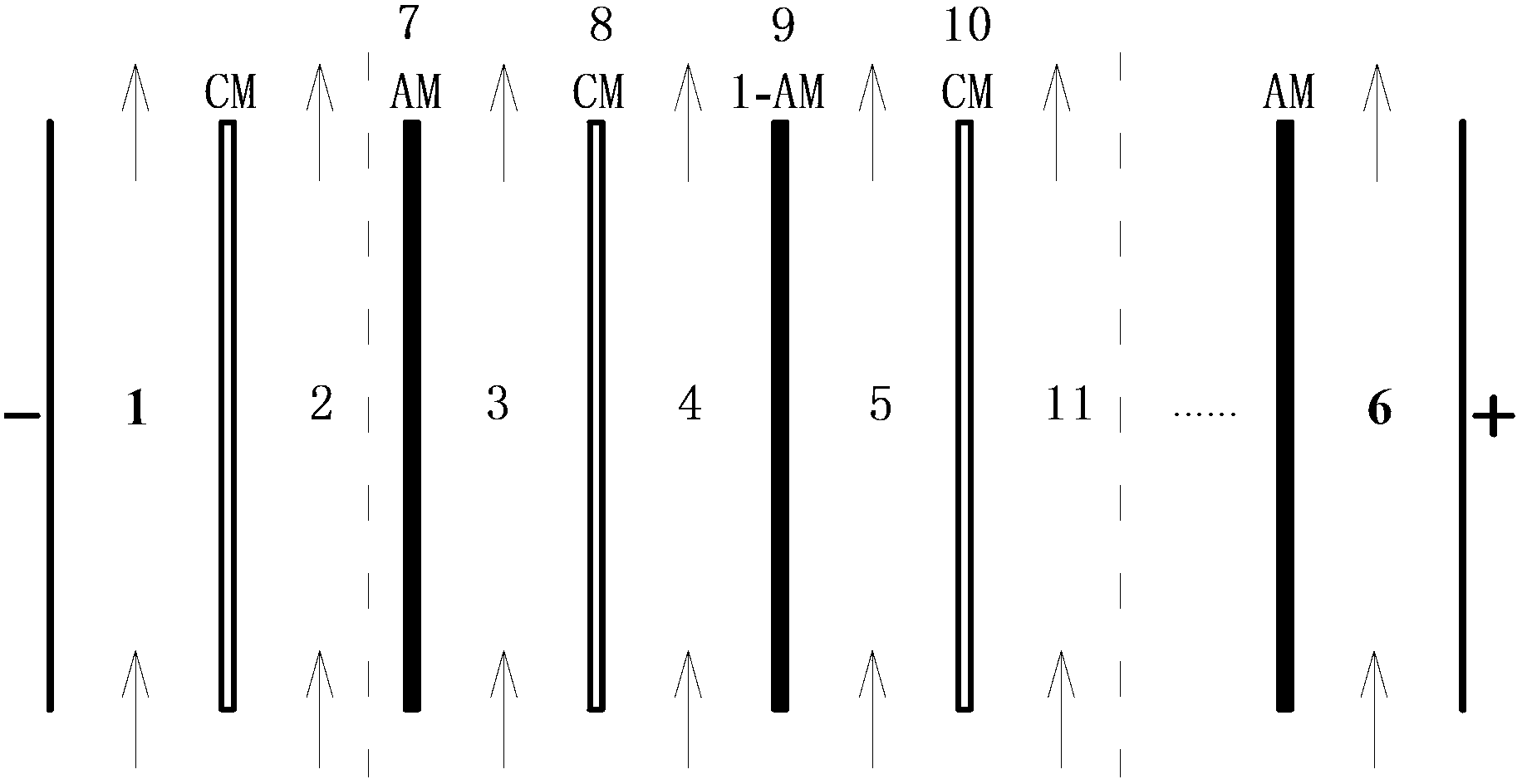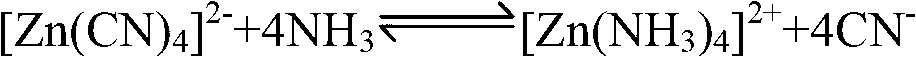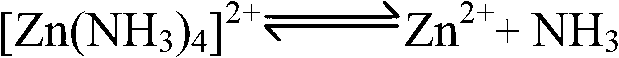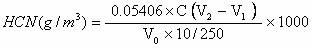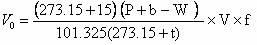Patents
Literature
267 results about "Cyanide ion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
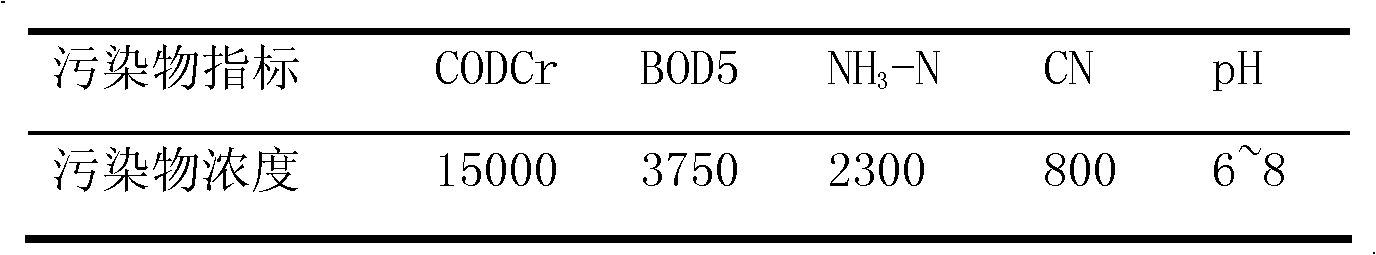
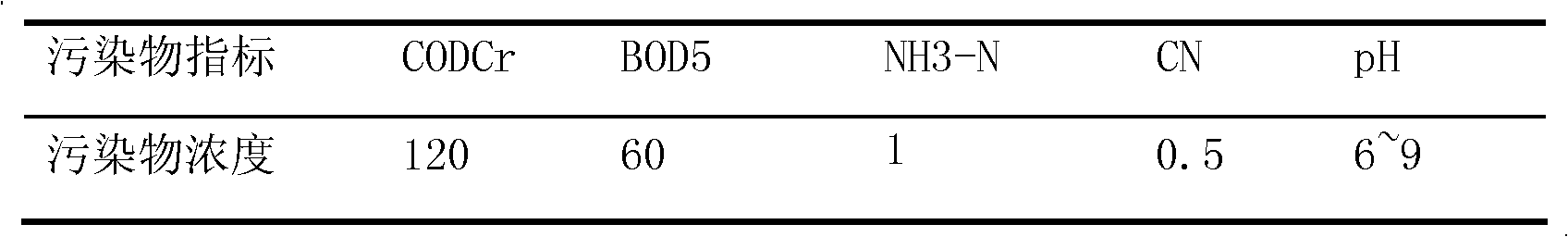
Cyanide, any compound containing the monovalent combining group CN. In inorganic cyanides, such as sodium cyanide (NaCN), this group is present as the negatively charged cyanide ion; these compounds, which are regarded as salts of hydrocyanic acid, are highly toxic.
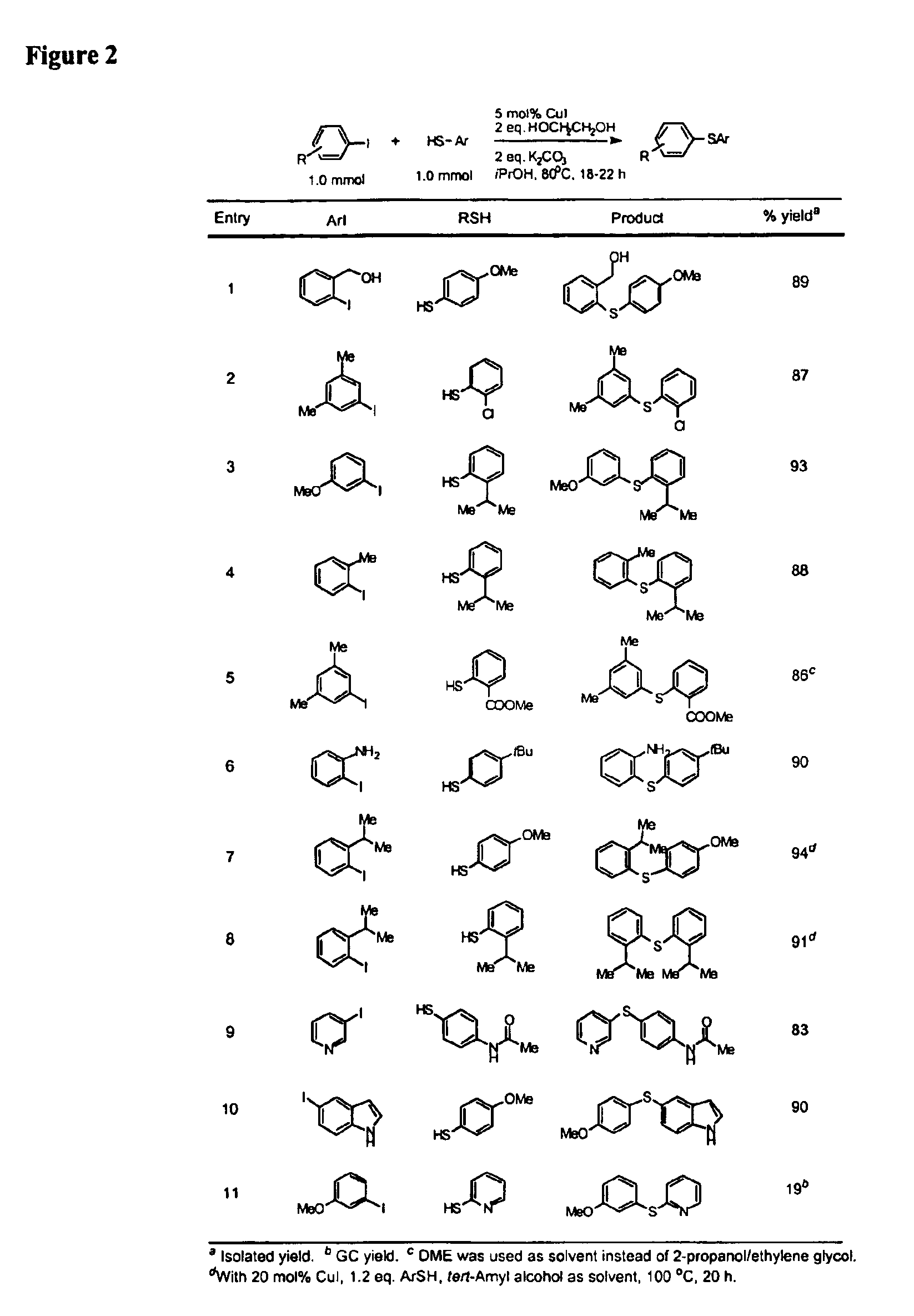
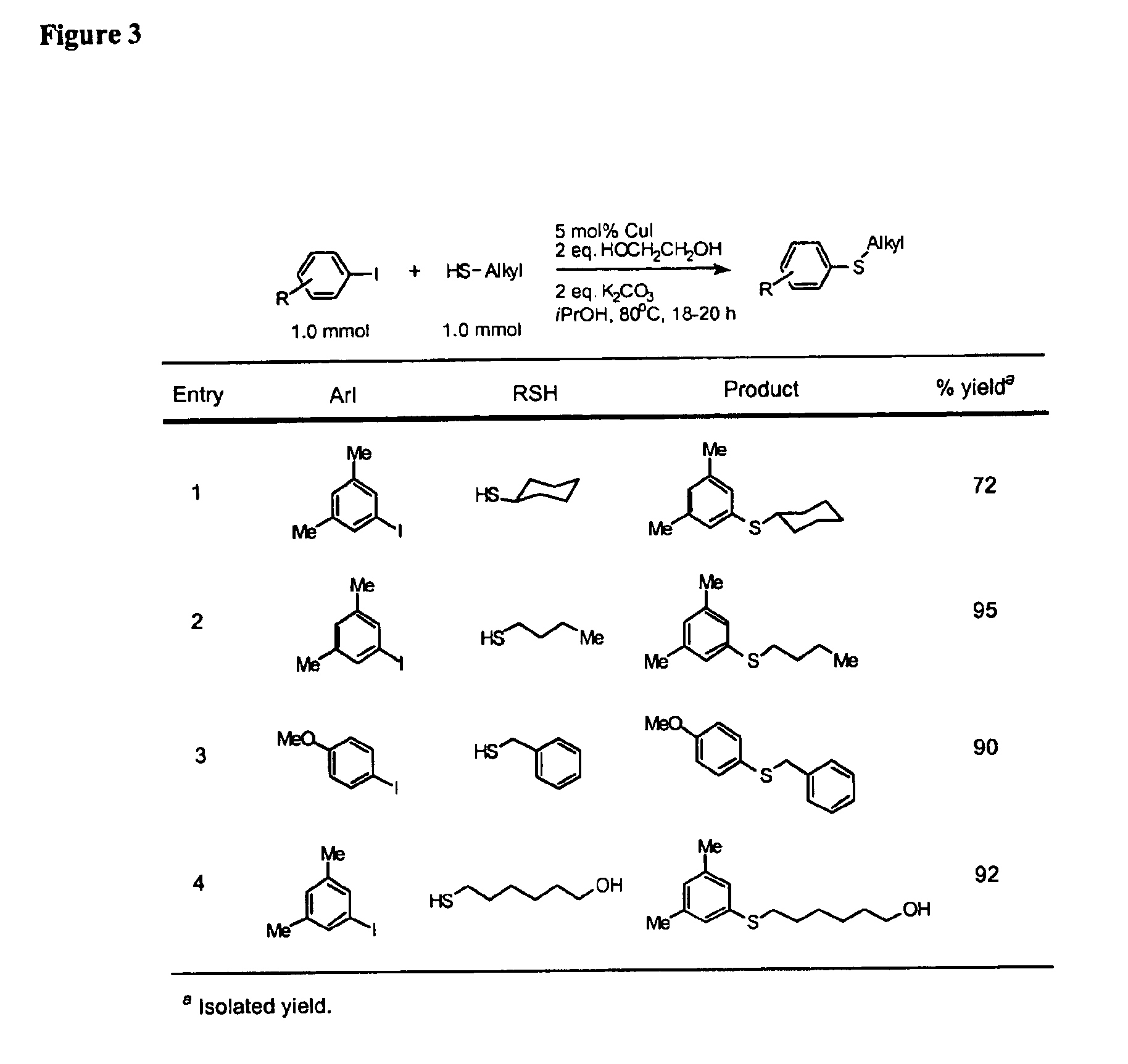
Copper-catalyzed formation of carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bonds
InactiveUS6888032B2Cheap and practicalLow costOrganic compound preparationThiol preparationCarbon–carbon bondSulfide
One aspect of the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming methods. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-sulfur bond between the sulfur atom of a thiol moiety and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In other embodiments, the present invention relates to copper(II)-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of an amide and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-carbon bond between the carbon atom of cyanide ion and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In another embodiment, the present invention relates to a copper-catalyzed method of transforming an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl chloride or bromide into the corresponding aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl iodide. Yet another embodient of the present invention relates to a tandem method, which may be practiced in a single reaction vessel, wherein the first step of the method involves the copper-catalyzed formation of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl iodide from the corresponding aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl chloride or bromide; and the second step of the method involves the copper-catalyzed formation of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl nitrile, amide or sulfide from the aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl iodide formed in the first step.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
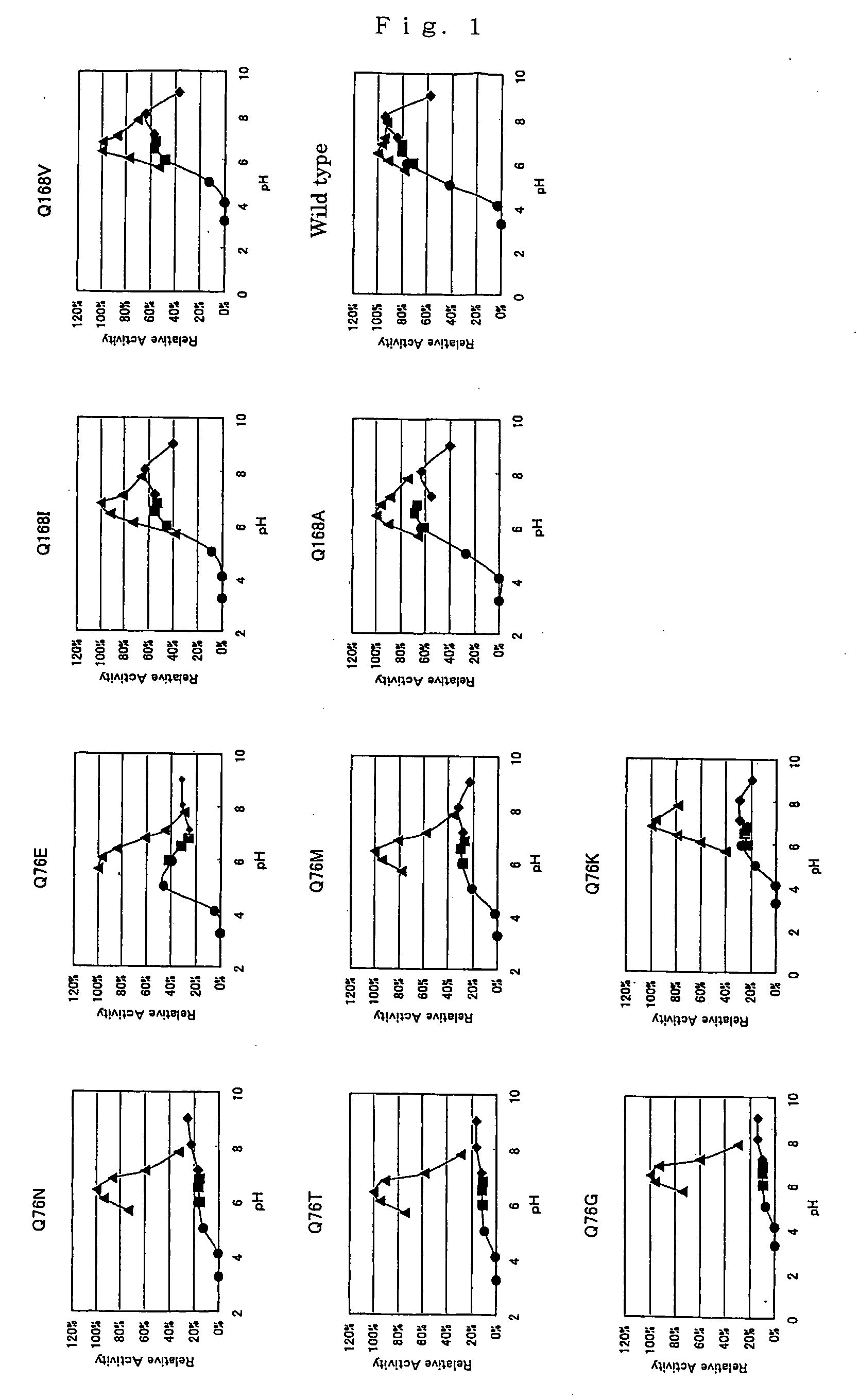
Modified pyrroloquinoline quinone (pqq) dependent glucose dehydrogenase excellent in substrate specificity
InactiveUS20070105173A1Action propertyProcess stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiWild typePyrroloquinoline quinone
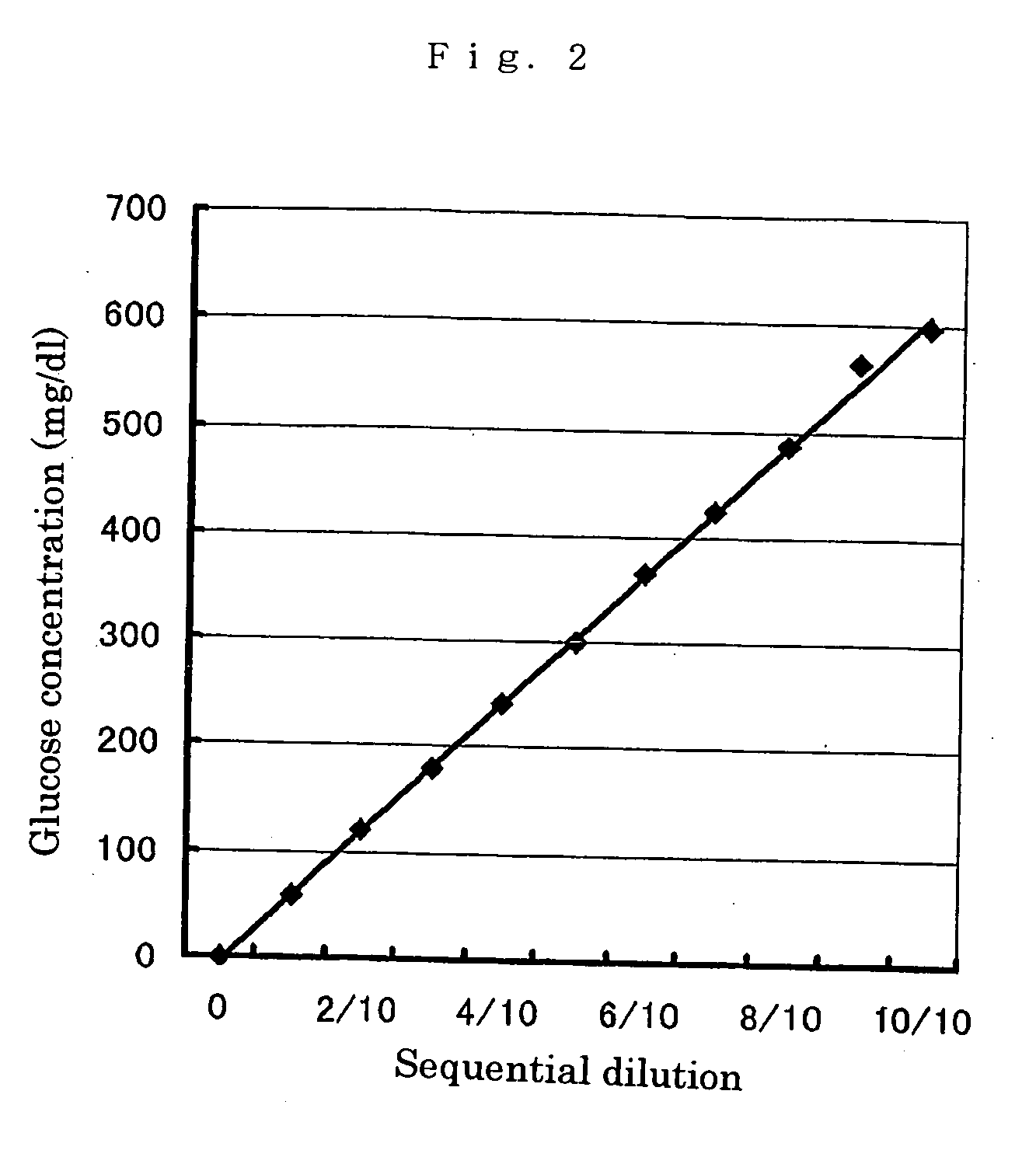
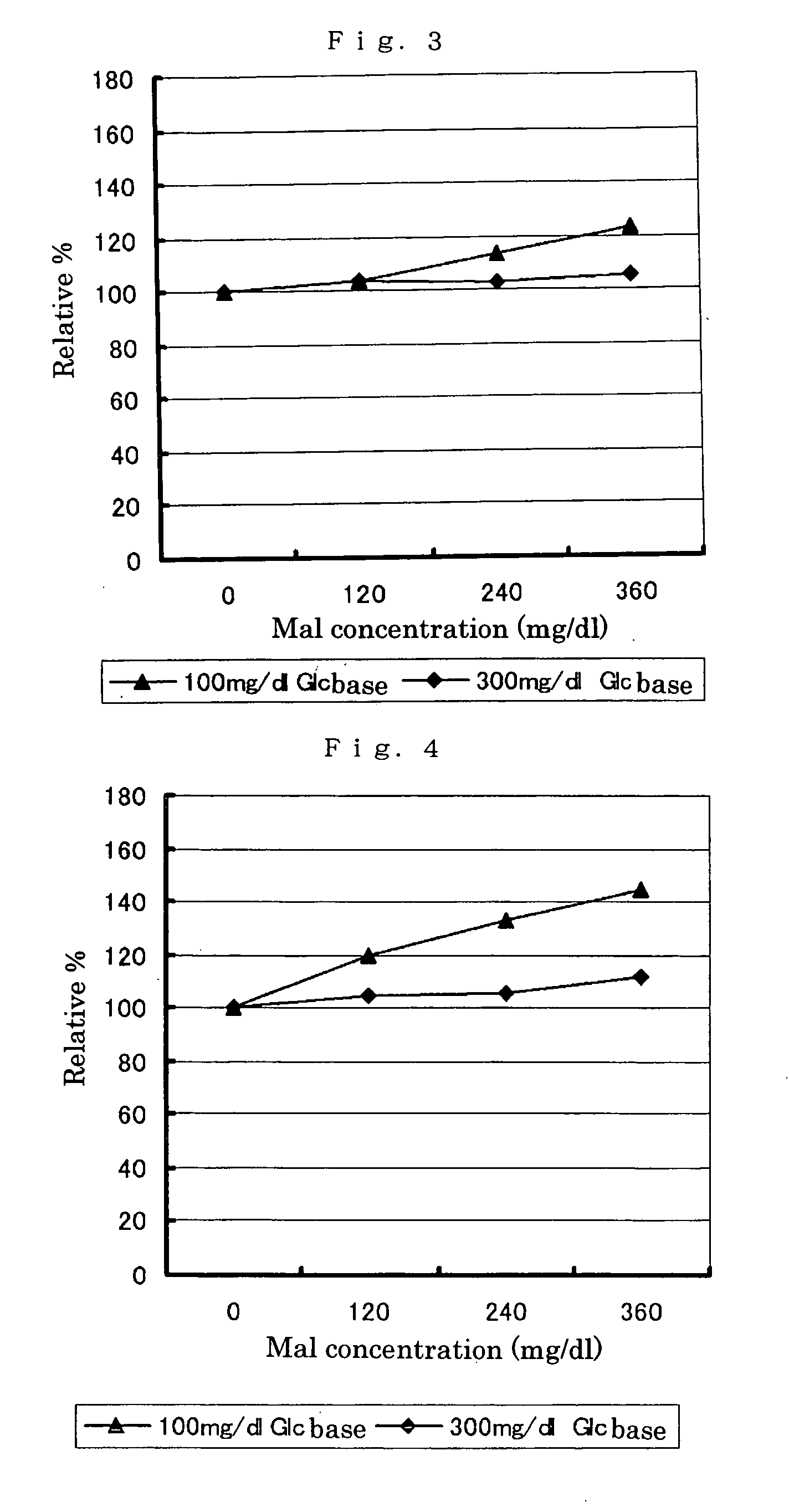
PQQGDH having an improved substrate specificity or having an improved specific activity in an assay system using ferricyanide ion as a mediator is provided. Modified PQQGDH having the enhanced substrate specificity by introducing an amino acid mutation in a particular region of PQQGDH, and a method of enhancing the specific activity compared with a wild type in the assay system using the ferricyanide ion as the mediator by deleting, substituting, or adding one or more amino acids in an amino acid sequence of the wild type pyrroloquinoline quinone dependent glucose dehydrogenase.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Gold-core silver-shell nanoprobe, preparation method thereof and application thereof in cyanide ion colorimetric detection
InactiveCN104096849AStable in natureEvenly dispersedMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNanotechnologyNanoparticleRoom temperature
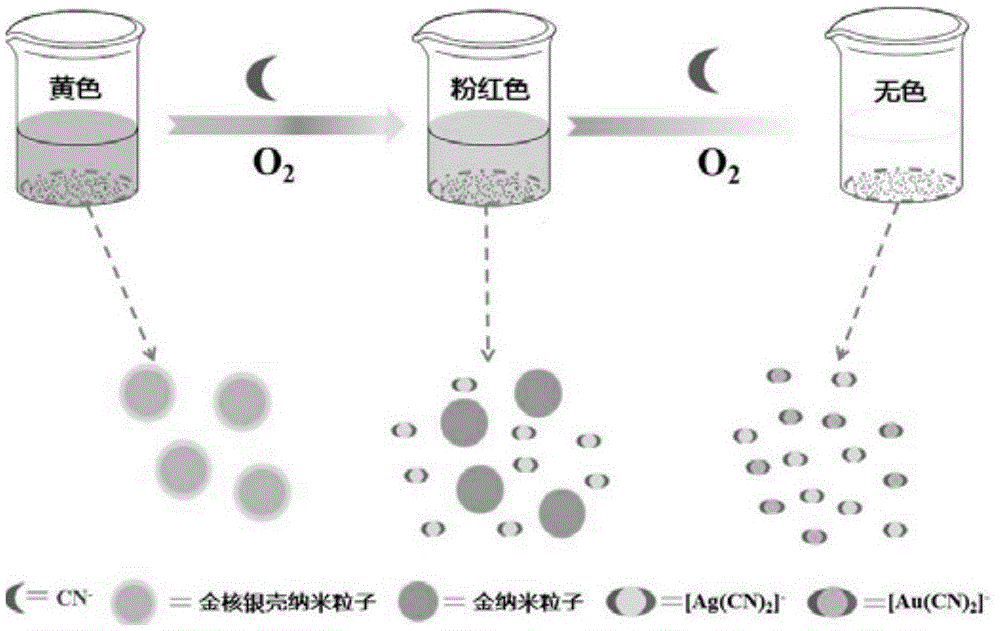
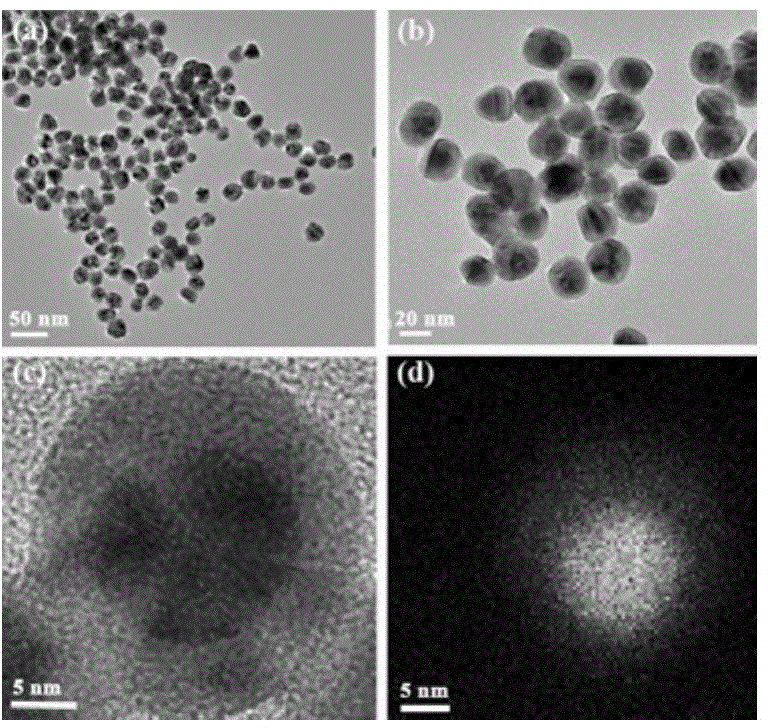
The invention relates to a gold-core silver-shell nanoprobe, in particular to a gold-core silver-shell nanoprobe, a preparation method thereof and application thereof in cyanide ion colorimetric detection. The gold-core silver-shell nanoprobe is a spherical nanoparticle of a core-shell structure, a core is made of gold and 11-14nm in diameter, a shell is made of silver and 1.3-7.4nm in thickness, and stabilizers are citrate ions absorbed on the surface of the silver shell. The particle size of the gold-core silver-shell nanoprobe is 13.6-28.8nm. The preparation method includes: dissolving HAuCl4 in water to prepare an HAuCl4 solution, and heating the HAuCl4 solution to boiling to obtain a solution A; additionally dissolving sodium citrate in water, and heating the solution to boiling to obtain a solution B; mixing the solution A and the solution B, enabling the mixed solution to change from light yellow to wine red after heating, and cooling the mixed solution to room temperature so as to obtain a gold nanoparticle solution; dissolving the gold nanoparticle solution in water, sequentially adding a Tollens' reagent and formaldehyde, and making the solution to change to yellow after reaction so as to obtain the gold-core silver-shell nanoprobe.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104357044AEasy to synthesizeFew synthetic stepsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesFluorescence
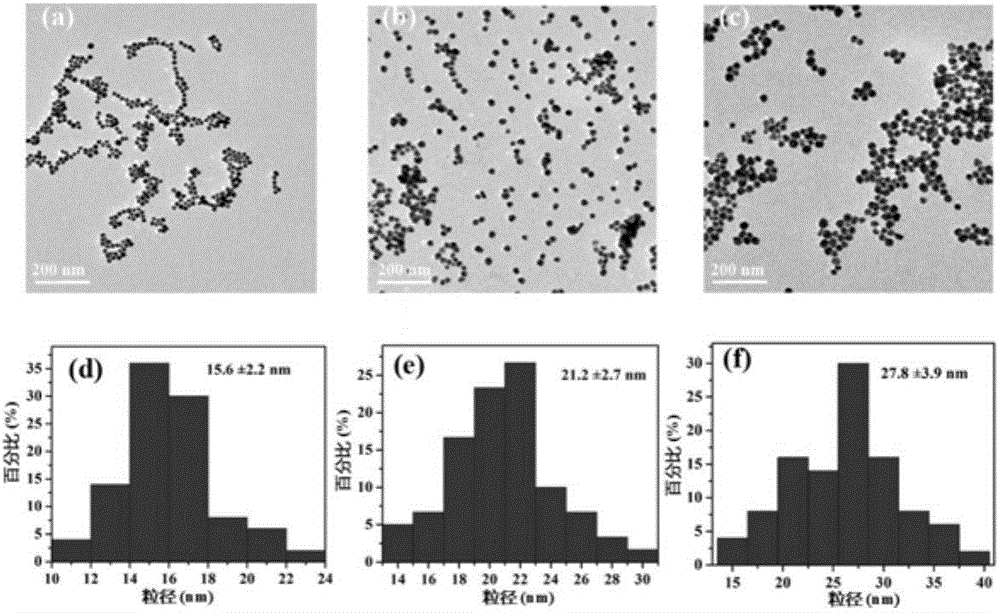
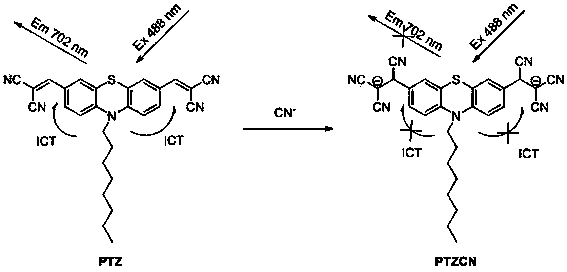
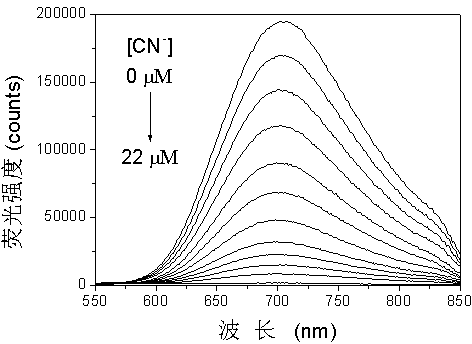
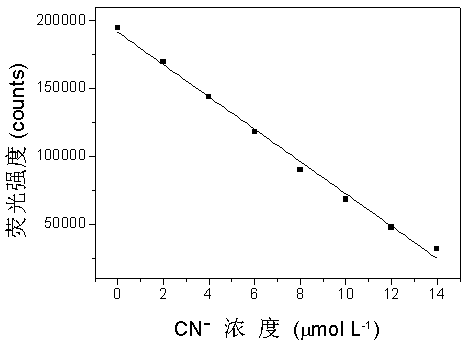
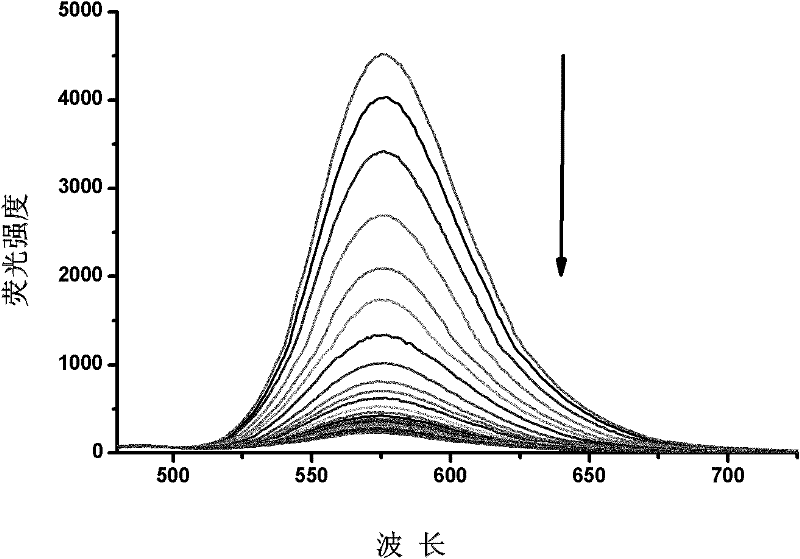
The invention provides a fluorescent probe. The structural formula of the fluorescent probe is represented by general formula I shown in the specification, wherein R is one of C7-C12 alkyl groups. The invention further provides a preparation method of the fluorescent probe and an application of the fluorescent probe to detection of cyanide ions. A phenothiazine derivative is used as a fluorescent parent, a malononitrile structure is introduced as an active center reacting with the cyanide ions, and selective detection of the cyanide ions is realized by the aid of fluorescent differences between reactants and products. The prepared fluorescent probe PTZ is excited at 488 nm and emitted at 702 nm, has very high selectivity and sensitivity for the cyanide ions and is high in response speed, the lowest concentration of the cyanide ions is detected to be 67 nmol / L<-1>, the cyanide ions can be detected quantitatively, and the fluorescent probe can be applied to detection of the cyanide ions in water bodies, soil and organisms.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Fluorescent probe for detecting cyanide ion and synthesis and application method thereof
ActiveCN107082785AThe synthesis method is simpleLow costGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceIodideRelative standard deviation
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting a cyanide ion and a synthesis and application method thereof. A cyanide ion fluorescent probe takes boron fluoride dipyrrole (BODIPY) as a fluorescent signal group and hemicyanine as a recognition site, and the probe is obtained by carrying out Knoevenagel condensation reaction on 1,3,5,6-tetramethyl 8-(4(formylphenyl)) boron fluoride dipyrrole and 1,2,3,3-tetramethyl-3H-indolium iodide. Ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence emission spectroscopy research finds that the probe can solely identify the cyanide ion, the lowest detection limit can reach 59 nM, the identification process is not interfered by other negative ions, and response speed is high. The fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention can be used for detection of the actual water sample, and relative standard deviation is less than 5%. Besides, the fluorescent probe is simple in synthesis method and relatively low in cost and has a good application prospect in cyanide ion detection.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
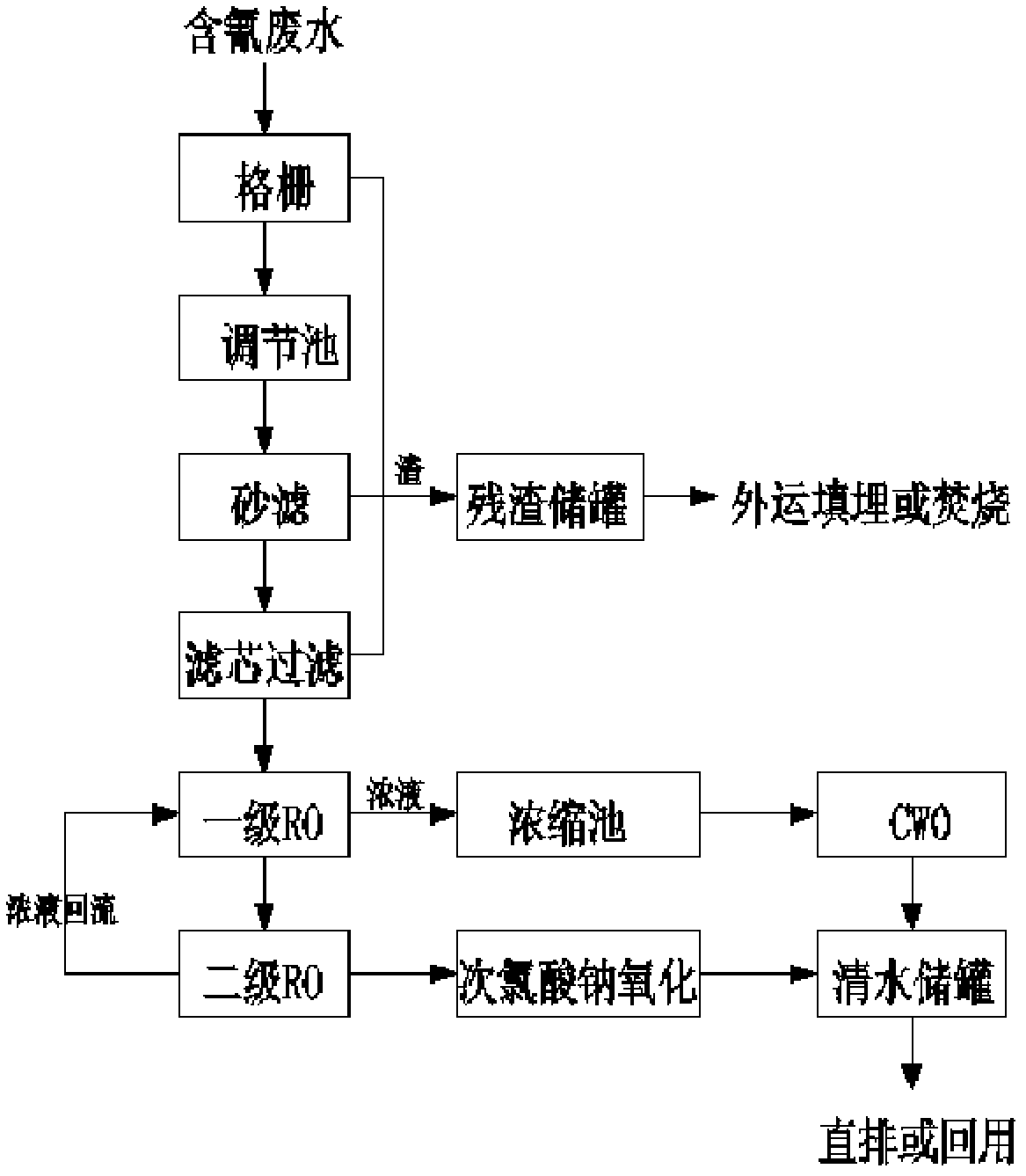
Method and system for treating cyanide-containing wastewater at low concentration
ActiveCN102502994AHarmlessRealize resource processingWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentGratingAfter treatment
The invention discloses a system and a method for treating cyanide-containing wastewater at low concentration. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: pre-treating the cyanide-containing wastewater at low concentration to remove large solid pollutant particles from the cyanide-containing wastewater at low concentration; performing membrane treatment to remove most cyanide ions, treating effluent obtained after treatment by the conventional NaClO oxidation method and other methods, and then discharging effluent which reaches the standard; and performing catalytic wet oxidation on concentrated liquor produced after the membrane treatment, and discharging the treated concentrated liquor which reaches the standard. The system mainly comprises a grating, a membrane treatment system, and catalytic wet oxidation treatment equipment. The invention has the advantages that: the cyanide-containing wastewater at low concentration is subjected to membrane treatment and then is treated by the conventional NaClO oxidation method, and effluent which reaches the standard is discharged, so the treatment difficulty and cost of a discharge and treatment system are reduced; and the concentrated liquor is subjected to catalytic wet oxidation, and the effluent obtained after treatment can reach the direct discharging standard, or can be recycled as clear water.
Owner:KMD BEIJING ENERGY & ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
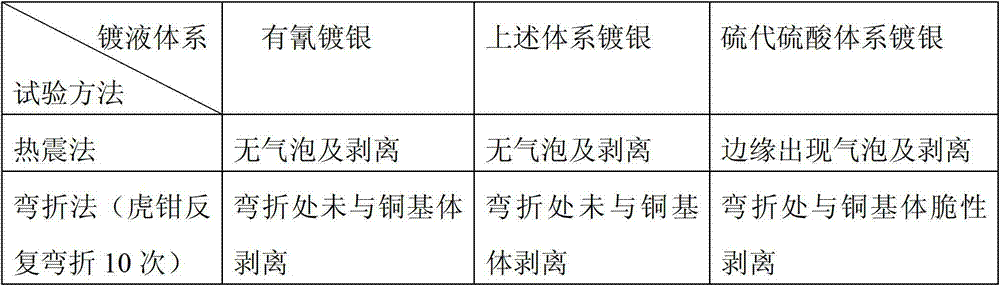
Plating solution and plating method of cyanide-free plating silver
The invention discloses a plating solution and a plating method of cyanide-free plating silver. 20-60g silver nitrate, 70-90g ammonium acetate, 70-110g nicotinic acid, 60-90g potassium carbonate, 40-70g potassium hydroxide, 0.2-1.2g o-benzoyl sulfimide sodium and 0.16-0.64g polyethylene glycol are contained in 1L of the plating solution with a pH value of 9-10. According to the plating solution and the plating method of the cyanide-free plating silver, the plating solution does not contain cyanide ions; the pollution of wastewater treatment is reduced; the injury to a human body due to precious metal plating is reduced; a formula of the plating solution is simple, and easy to control; compared with other cyanide-free plating, the current density is higher; and the deposition efficiency of a silver coating can be improved. With the adoption of pulse plating, a coating that is small in coating stress and good in compactness and brightness, and combines with a matrix well can be obtained.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Molecular probe for detecting cyanide ions and synthesis and application method thereof
InactiveCN103772280ARaw materials are easy to getHigh synthetic yieldOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorImideChromogenic
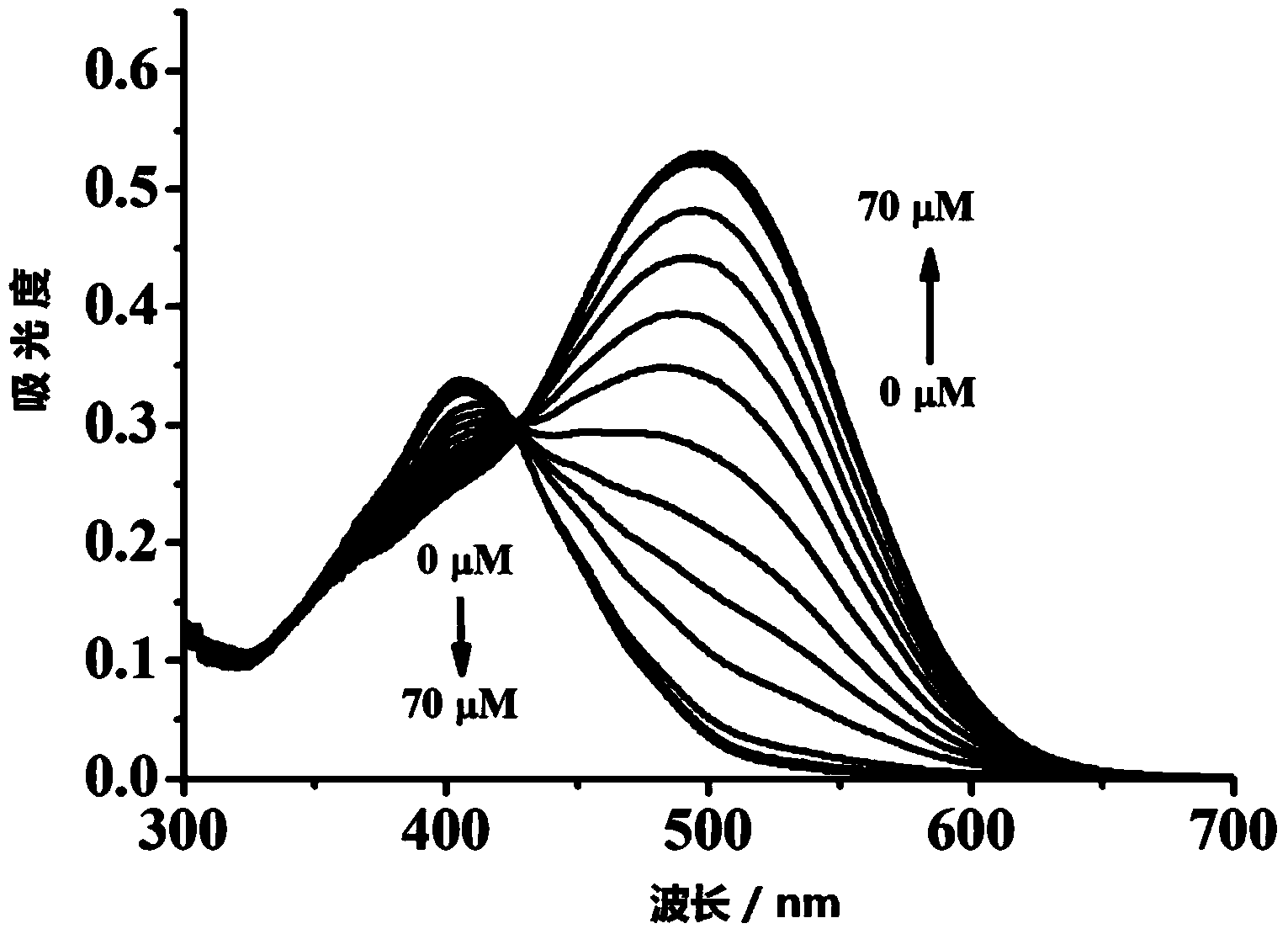
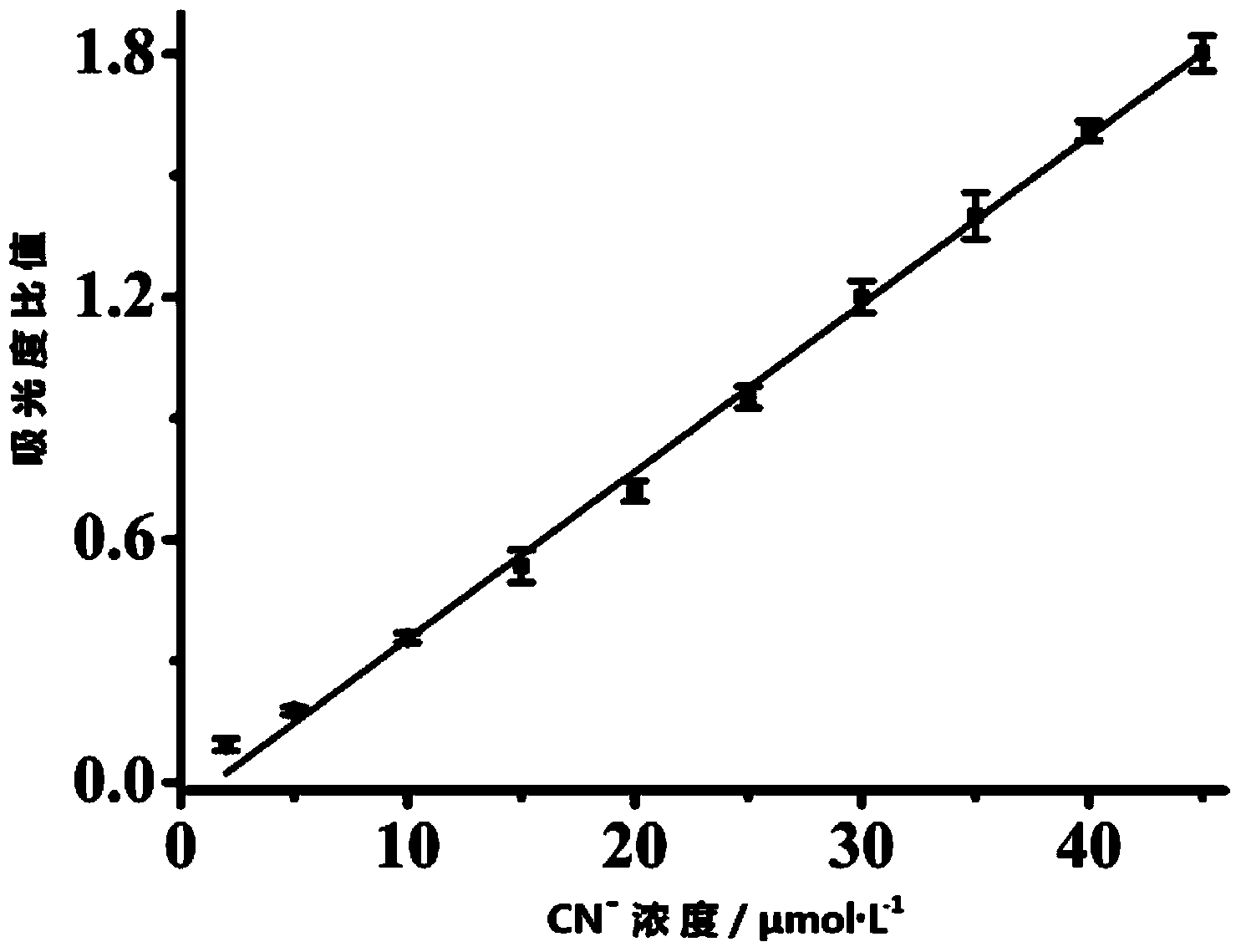
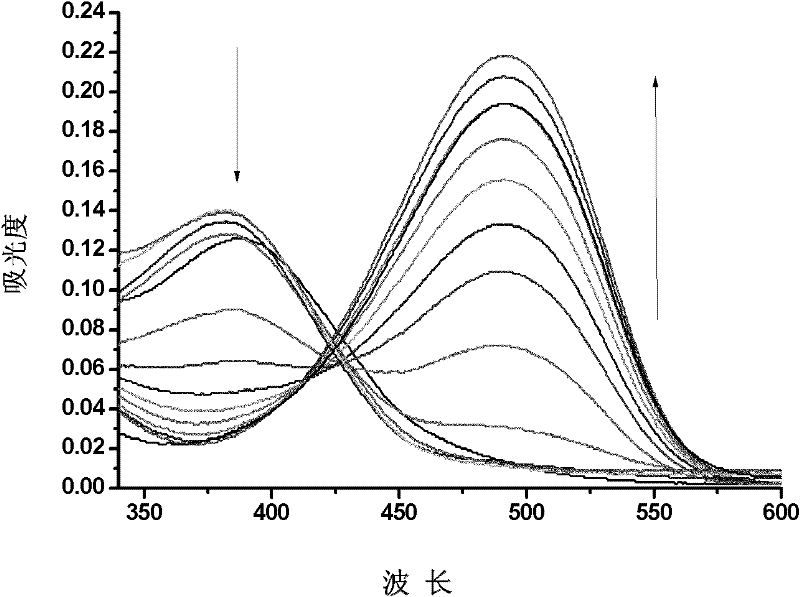
The invention discloses a molecular probe for detecting cyanide ions and a synthesis and application method thereof. The probe disclosed by the invention is obtained by performing condensation on 4-amino-1,-8-naphthalimide framework which is diazotized and salicylaldehyde or a derivative of the salicylaldehyde. Chromophore of the probe adopts a naphthalene imide azobenzene structure; a response group to the cyanide ions is a salicylaldehyde unit; an absorption peak of the independent probe in the solution is positioned at 407nm, and the solution is yellow; along with the adding of the cyanide ions, the absorbency at the 407nm wavelength is continuously decreased, the absorbency at the 497nm wavelength is continuously increased, and the color of the solution turns from yellow into red. Molecules of the probe are high in selectivity and sensitivity to the cyanide ions and high in response speed; the response range is 2-45mu mol.L<-1>; the detection limit is 0.4mu mol.L<-1>. The probe can be used for detecting the cyanide ions in water, soil and organisms.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for decyanating coking wastewater
InactiveCN102030401AEfficient removalEasy to operateWater/sewage treatmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentFlocculationFERRIC FERROCYANIDE
The invention relates to a method for decyanating coking wastewater, comprising the following steps of: decyanating by using ferrous sulfate to complex; reacting cyanide ions with ferrous irons and iron ions to generate ferric ferrocyanide which is insoluble in water and is called as Prussian blue precipitation; and then separating the precipitation from water to remove cyanide in the water and controlling the total cyanide in the wastewater entering a biochemical system below 15mg / l and the cyanide below 8mg / l. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the benefits that: in the method, the decyanating is carried out by using ferrous sulfate to complex; the operation method is simple and requires less investment, and the cyanide in the ammonia-evaporating wastewater can be removed effectively and the smooth operation of the subsequent biological treatment of the coking wastewater can be ensured; meanwhile, by using the flocculation action of the ferrous sulfate, oil and suspension in the coking wastewater and Prussian blue can be flocculated and precipitated together, thereby achieving the functions of removing the oil and the suspension by flocculation, creating the beneficial microorganism environment for biochemical treatment and reducing the biochemical treatment load.
Owner:ACRE COKING & REFRACTORY ENG CONSULTING CORP DALIAN MCC +1
Receptor compound for detecting CN- by colorimetry-fluorescence two channels, synthesis thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102863406AOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorReceptorChemical compound
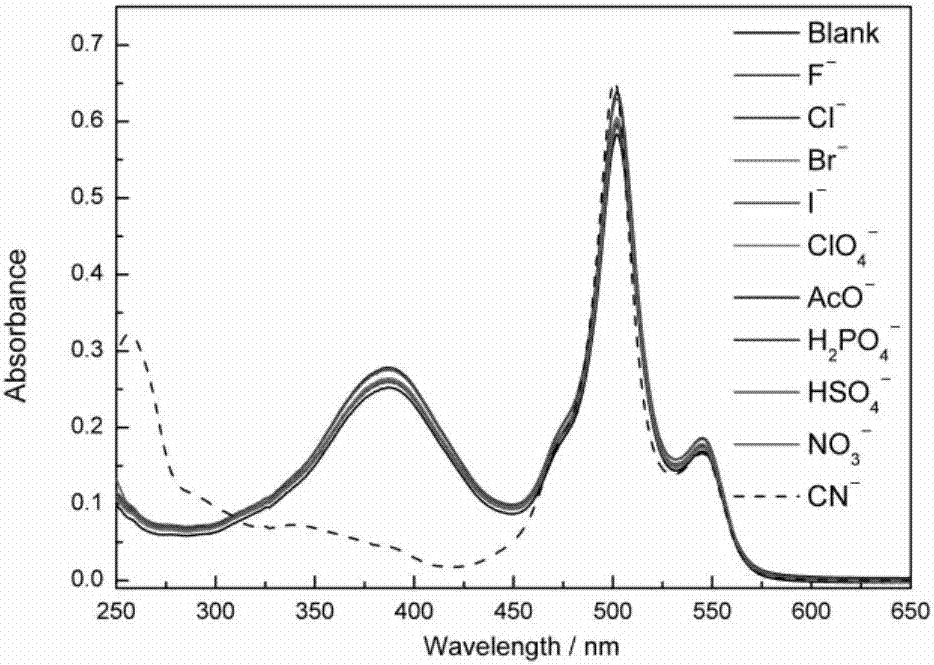
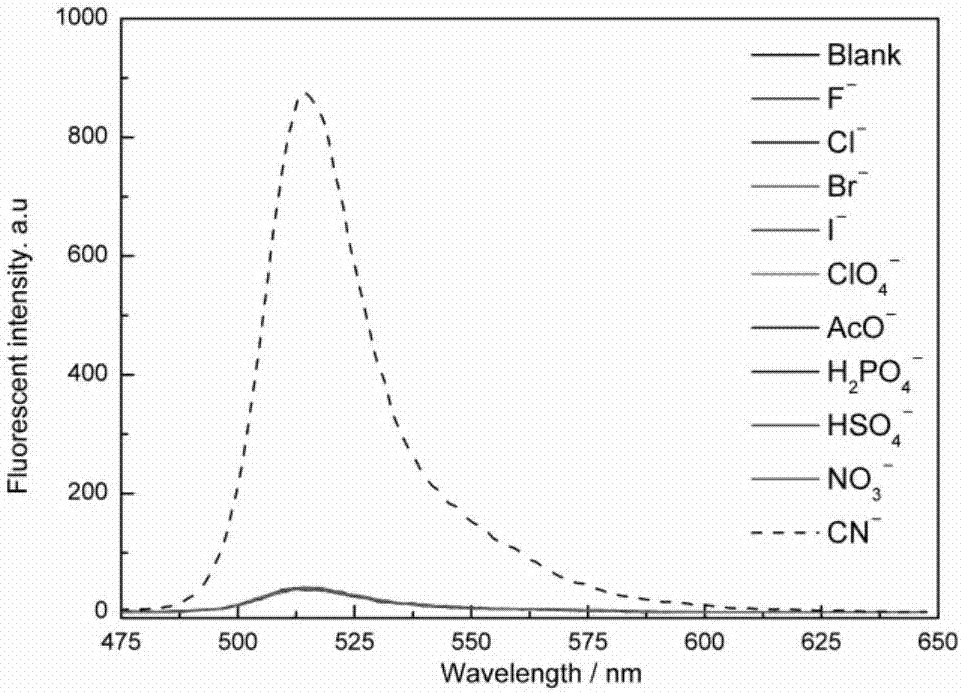
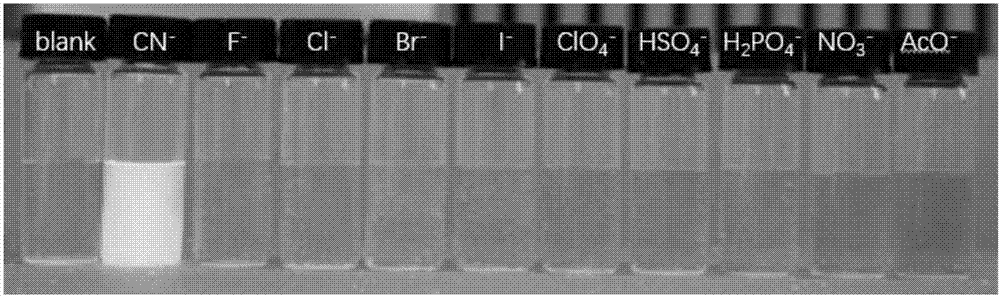
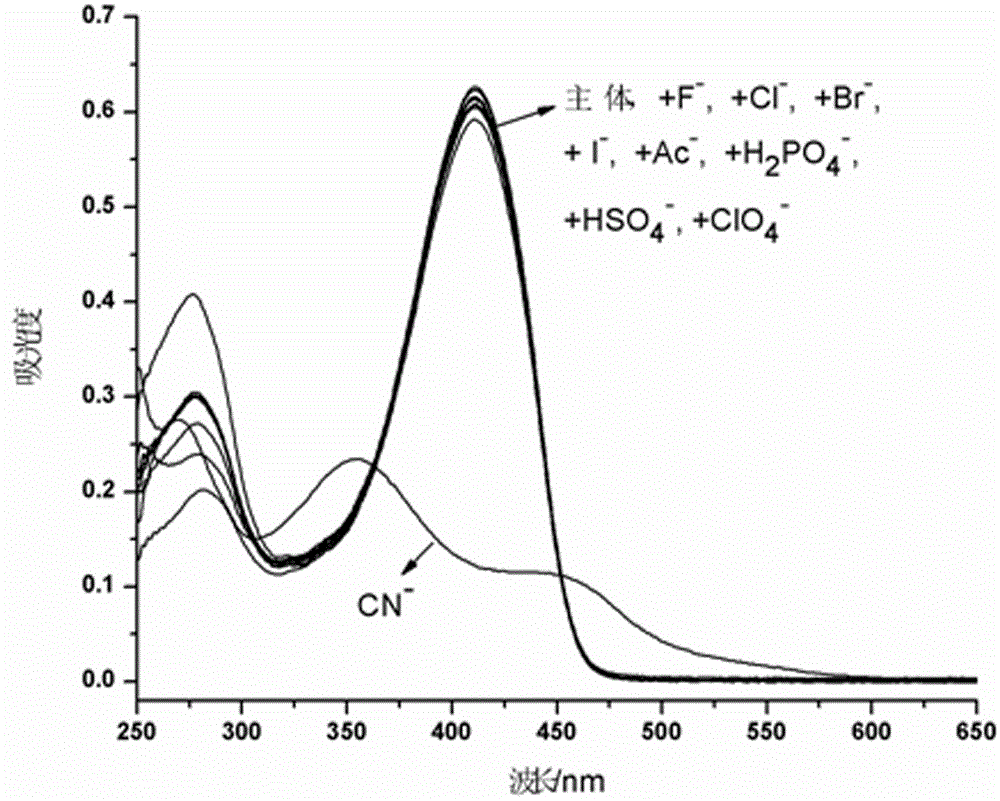
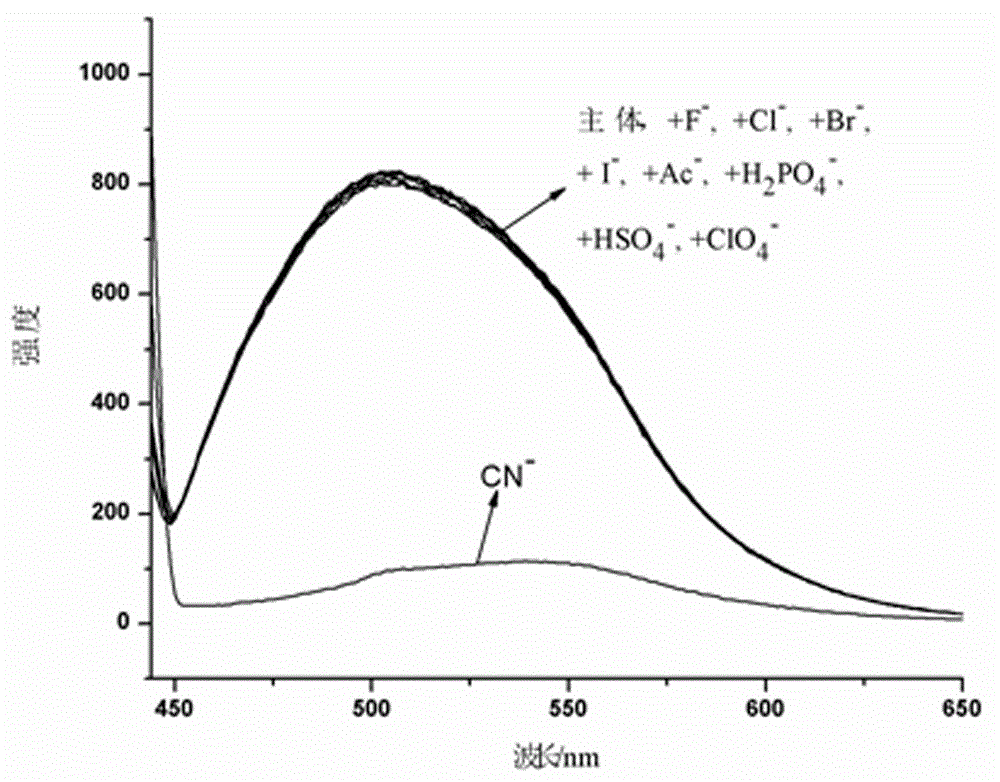
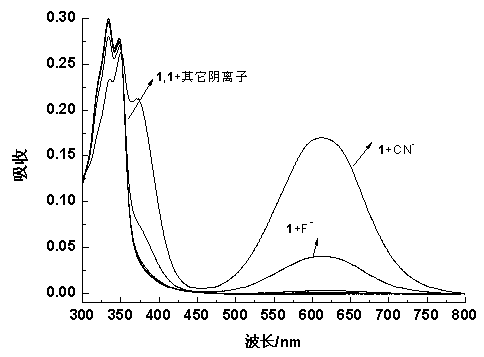
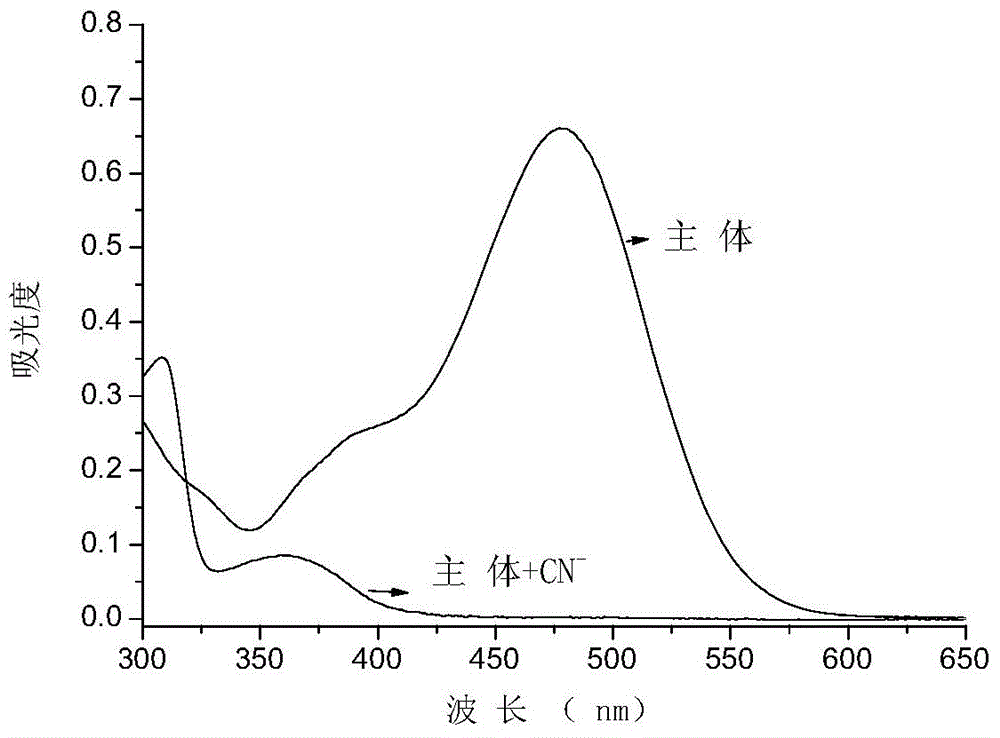
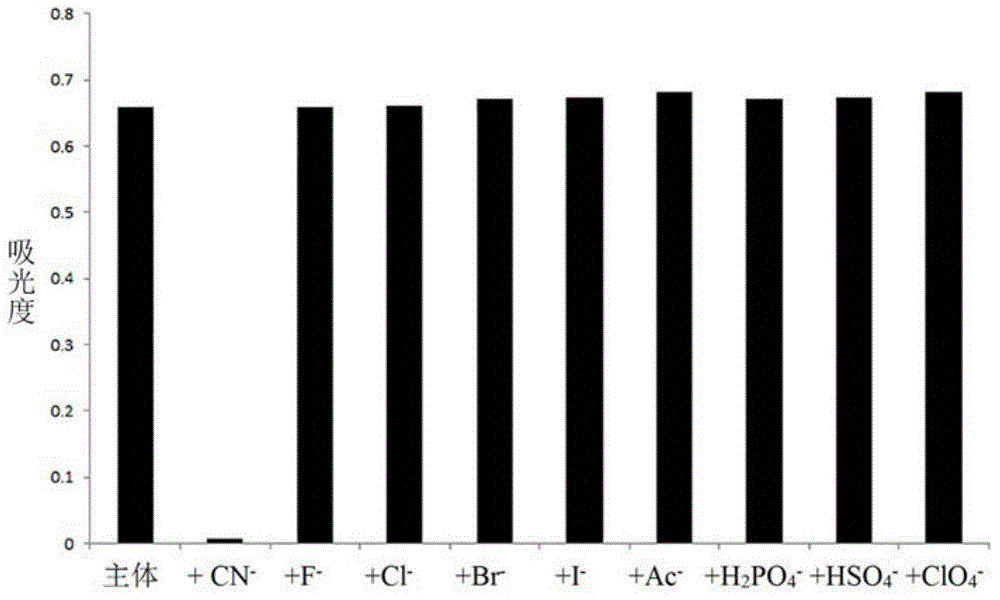
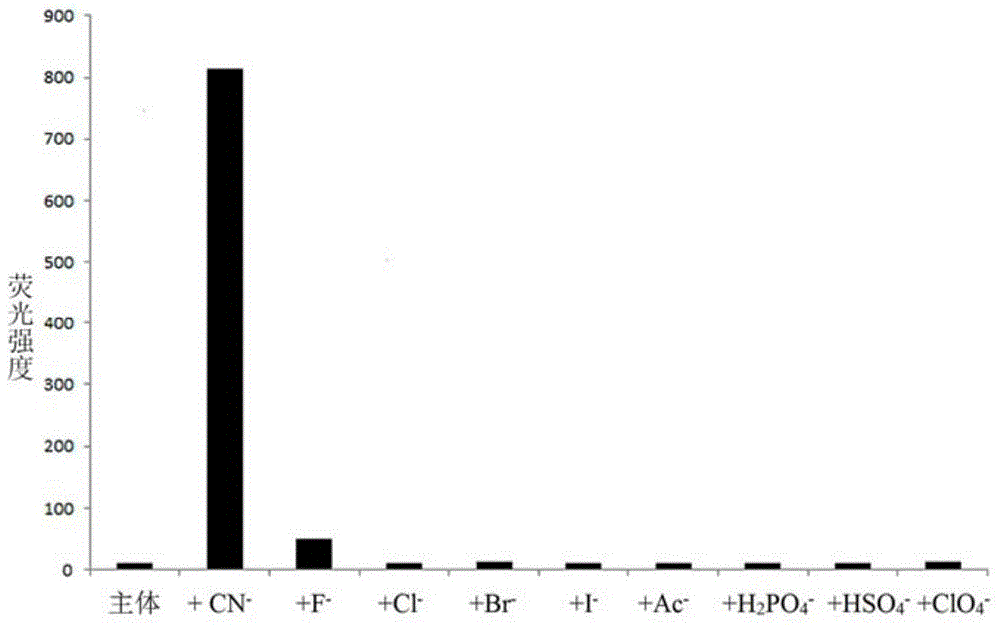
The invention provides a receptor compound--2-cyanogroup-3-(5-(4-nitrobenzophenone)-2-furyl) acrylonitrile for detecting CN- by colorimetry-fluorescence two channels. The recognition effect of the receptor compound to nine anions such as F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, Ac-, H2PO4-, HSO4-, ClO4-, Cn-and the like is researched by the colorimetric method, the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy and the fluorescent spectrometry. The result shows that the receptor compound can independently select the colorimetry-fluorescence two channels in DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide)-H2O to identify the cyanide ion, and is very high in the detection sensitivity of CN-, wherein the lowest detection limit can reach to 1*10<-8> mol. L<-1>. Furthermore, the invention further prepares a receptor-based cyanogen detection test paper, so that the cyanide ion in the DMSO-H2O can be conveniently and quickly detected by means of colorimetry-fluorescence.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
4-aroyl-1,8-naphthalimide compound and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN104003935AReduce manufacturing costNovel synthetic routeOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAcyl groupOrganosolv
The invention discloses a 4-aroyl-1,8-naphthalimide compound and a preparation method and use thereof, wherein the 4-aroyl-1,8-naphthalimide compound has a structural formula as shown in the specification, R1 is C1-C10 straight chain or branched chain alkyl; and R2 is phenyl, naphthyl, biphenylyl, substituted phenyl, quinary or senary heteroaryl or benzo quinary or senary heteroaryl. The preparation method is as follows: a 4 bromo-1,8-naphthalimide compound is used as a raw material to react with substituted phenylacetonitrile or aromatic ring acetonitrile in an organic solvent in the presence of an alkali catalyst to obtain a 4-aryl acetonitrile-1,8-naphthalimide compound, and then the 4-aroyl-1,8-naphthalimide compound is obtained in the effects of fluoride ions or cyanide ions. The 4-aryl acetonitrile-1, 8-naphthalimide compound is used as a color or fluorescence sensor for detection of the fluoride ions or cyanide ions, and has high sensitivity and high selectivity during identifying of the cyanide ions in a mixed solvent.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Measuring method for cyanides in cyanide-containing wastewater of gold mine
InactiveCN104833674AAccurate measurementGood effectMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhosphoric acidWastewater
The invention discloses a measuring method for cyanides in cyanide-containing wastewater of a gold mine. In order to solve the problem that a great number of foams are produced by heating and distilling under an acidic condition, a defoaming agent GC-1 is added into a cyanide-containing wastewater sample to inhibit activities of a surfactant in wastewater, so that the water sample does not produce foams in a distilling process; phosphoric acid and Na2-EDTA are added into the water sample, and heated and distilled in a medium with pH lower than 2, so that cyanide ions are separated from complex cyanide by utilizing the characteristic that the complexing capacity between the metal ions and the EDTA is higher than that between the metal ions and the cyanide ions, the cyanide ions are distilled in the form of hydrogen cyanide, and the content of the cyanide ions is titrated by silver nitrate after the cyanide ions are absorbed by a sodium hydroxide solution. Under an alkaline condition, the cyanide ions act with the silver nitrate to form soluble sliver-cyanogen complex irons (Ag(CN)2<->), and the excessive sliver ions react with 5-(4-dimethylaminobenzylidene)rhodanine indicator liquor, so that the solution is changed into orange red from yellow, thereby ending the measurement. The method has the advantages of obvious effect and accurate measured result, and is simple to operate and easy to grasp.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST
Recovery processing method of cyanide barren solution
InactiveCN102701339AHigh purityAvoid enteringAlkali metal cyanidesDispersed particle separationCyanide ionSodium cyanide
The invention relates to a recovery processing method of cyanide barren solution, which comprises the following steps: at first, ammonia water is added in the cyanide barren solution, the mass ratio of the ammonia water and the cyanide barren solution is 0.5% to 2%; then the cyanide barren solution in which the ammonia water is added is pumped into an electrodialysis device, CN<-> in the cyanide barren solution passes through an anion-exchange membrane and enters a sodium cyanide recovery chamber under the action of a direct-current electric filed, metal cations such as Cu<2+> and Zn<2+> pass through a cation-exchange membrane and enter a metal ion recovery chamber, CN<-> is continuously released from a cyano complex in the cyanide barren solution along with the continuous decrease of CN<-> and heavy metal cations such as Cu<2+> and Zn<2+>, metal ions such as Cu<2+> and Zn<2+> and NH3 are continuously released from a copper-zinc metal ammino complex, so that cyanide ion CN<-> in the cyano complex is promoted to be released, and sodium cyanide and metal ions are recovered. The method can reduce the treatment cost of the cyanide barren solution, remarkably improves the recovery rate and the purity of cyanide ions in the cyanide barren solution, and removes the copper, zinc and other heavy metal ions in the cyanide barren solution.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method and application of cyclic mercaptan-modified activated carbon
ActiveCN109589952AImprove adsorption capacityEasy to makeIon-exchange process apparatusCarbon compoundsActivated carbonPrussian blue
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of cyclic mercaptan-modified activated carbon and belongs to the technical field of precious metal recovery. According to the method disclosed by the invention, cyclic mercaptan is adopted as an activated carbon modifier and the activated carbon is modified by using an impregnation method to adsorb Au(S2O3)2<3-> in a solution. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the problem of cyanide pollution of a conventional method of adsorbing and recovering the Au(S2O3)2<3-> by using copper cyanide ion (Cu(CN)4<2->)-supported activated carbon, complicated modification process of a method of adsorbing and recovering the Au(S2O3)2<3-> by using prussian blue-supported activated carbon and difficulty in continuous adsorption and the like are solved; the modified activated carbon prepared by adopting the method disclosed by the invention can effectively adsorb gold in thiosulfate gold leaching; and the activated carbon has the advantages of multilevel adsorption capacity and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Derivative electrocatalyst for growing Prussian blue or Prussian blue analogues in situ on metal substrate and preparation method of derivative electrocatalyst
ActiveCN110449156AGood shape flexibilityImprove electrocatalytic performanceMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesMetal ions in aqueous solutionAdhesive
The invention relates to a derivative electrocatalyst for growing Prussian blue or Prussian blue analogues in situ on a metal substrate and a preparation method of the derivative electrocatalyst. Themethod comprises the following steps: pre-treating the metal substrate, immersing the metal substrate into a metal cyanate aqueous solution or a metal cyanate alcoholic solution, and adding an acid into the system so as to obtain a substrate on which Prussian blue or Prussian blue analogues grow; and calcining the substrate so as to obtain the derivative electrocatalyst for growing Prussian blue or Prussian blue analogues in situ on the metal substrate. According to the method disclosed by the invention, in-situ growth of derivatives of the Prussian blue or Prussian blue analogues can be realized on multiple metal substrates, varieties of metal cyanide ions are regulated, products of different morphologies, compositions and physicochemical properties can be obtained, the prepared electrocatalyst can directly serve as an electrode, use of an adhesive is avoided, the preparation process is simplified, the resistance is reduced, and rapid electron transfer and effective mass transfer processes can be ensured, so that the catalytic activity is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for detecting cyanide ions based on gold nanorods
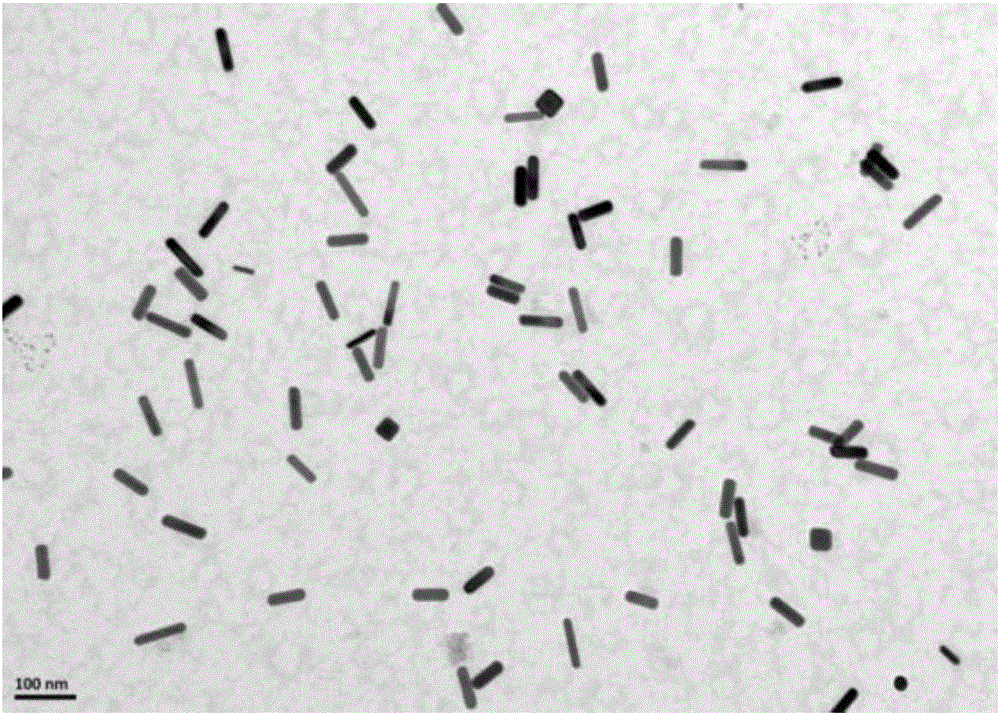
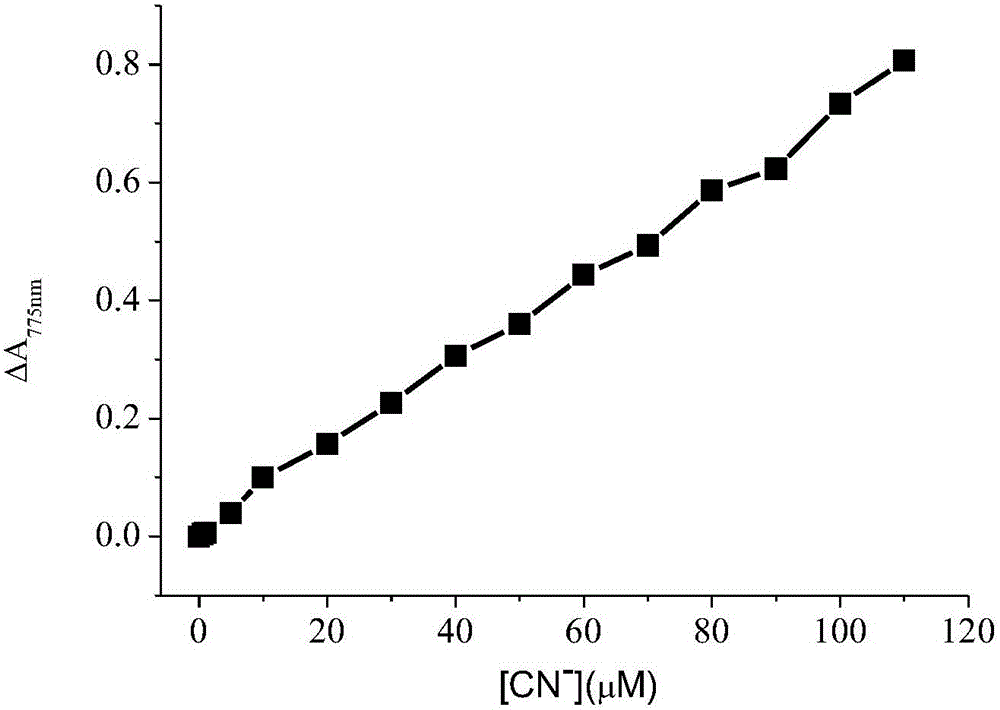
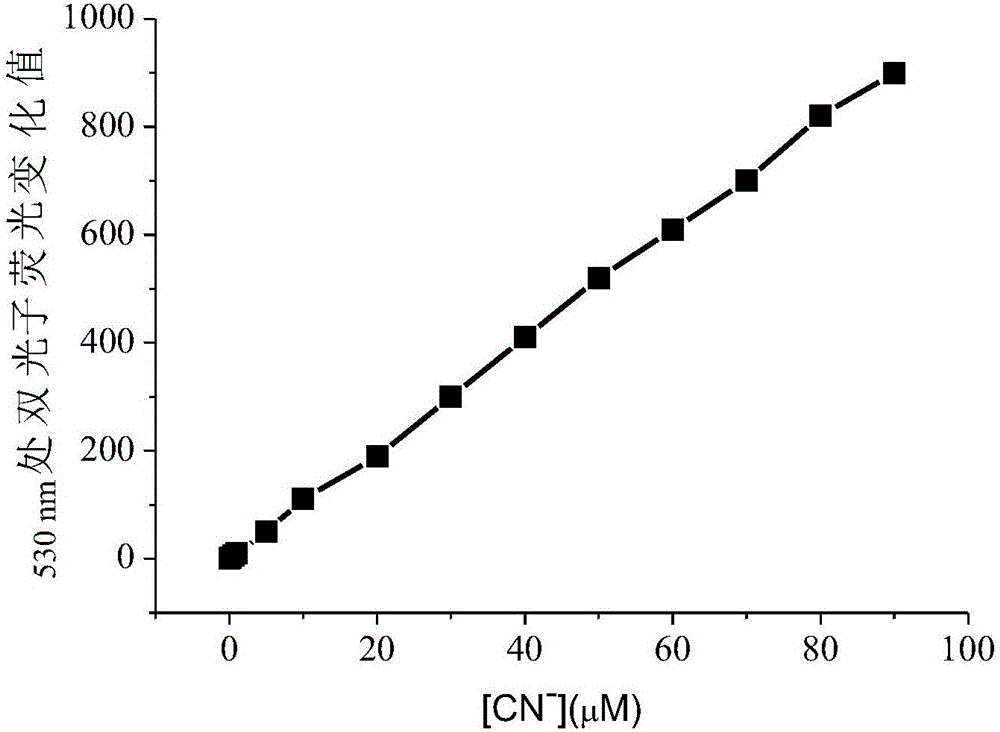
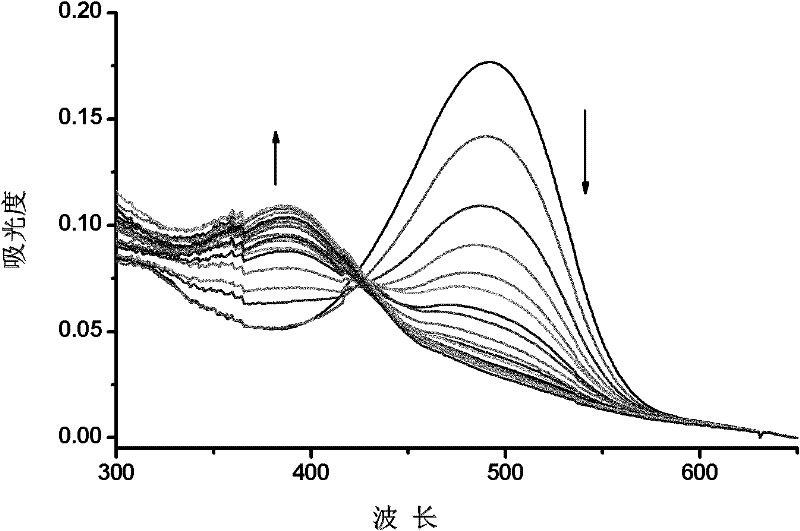
ActiveCN105842181AEasy to prepareUniform sizePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsCyanide compoundGold nanorod
The invention discloses a method for detecting cyanide ions based on gold nanorods, comprising the following steps: preparing gold nanorod solution, reacting the gold nanorod solution with a series of cyanide ion standard solutions, drawing a working curve through linear variations of ultraviolet absorption spectrum and / or two-photon excited fluorescent spectrum to obtain a linear equation with one unknown, measuring a sample by a corresponding scanning method, and taking a spectral value of the sample to the linear equation with one unknown for the standard working curve to calculate a sample concentration value. The preparation process of the gold nanorods is simple and convenient and is nontoxic and environment-friendly, the synthesized gold nanorods are uniform in size and good in stability and can react sensitively and quickly with cyanide ions in a water environment, cyanide ions in the water environment can be detected quickly and sensitively by using both ultraviolet spectrophotometry and two-photon excited fluorescence method, and lowest detection limit of ultraviolet spectrophotometry is up to 0.5 MuM, with lowest detection limit of the two-photon excited fluorescence method up to 0.01 MuM.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Fluorescence chemical sensor and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102190670AGood water solubilityObvious color changeChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCopper organic compoundsFluorescenceBenzaldehyde
The invention provides a fluorescence chemical sensor and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the fluorescence chemical sensor is shown as the formula (I), wherein R1 refers to sulfur or oxygen; and R2 refers to sulphonate, iodate, fluorphosphate or fluoborate. The preparation method for the fluorescence chemical sensor comprises the following steps of: (1) performing oxidation reaction on 4'-(N,N-dimethyl pyridyl amido)benzene under the action of an oxidant to obtain 4'-(N,N-dimethyl pyridyl amido)benzaldehyde; (2) reacting the 4'-(N,N-dimethyl pyridyl amido)benzaldehyde with a compound in a formula (III) to obtain a compound in a formula (II); and (3) reacting the compound in the formula (II) with copper ion-containing inorganic salt to obtain the fluorescence chemical sensor, wherein in the formulas (II) and (III), R1 refers to sulfur or oxygen; and R2 refers to sulphonate, iodate, fluorphosphate or fluoborate. The fluorescence chemical sensor can specifically, efficiently, timely and easily detect cyanide ions in aqueous solution.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for testing content of hydrogen cyanide in gas
InactiveCN102636616ARapid determinationAccurate measurementChemical analysis using titrationPotassium hydroxideSulfide
The invention provides a method for testing content of hydrogen cyanide in gas. The method comprises the following steps of: absorbing the hydrogen cyanide in the gas by adopting a potassium hydroxide solution, transferring the absorption solution to a volumetric flask with a certain volume, taking a certain amount of absorption solution, adding a cadmium acetate solution to make sulfide in the absorption solution to form indissolvable cadmium sulfide to sediment, filtering and sintering the absorption solution to eliminate the sediments, taking Dabr as an indicator of the solution, taking a standard silver nitrate solution to titrate, making cyanide ions react with silver nitrateto form soluble cyanide complex ion (Ag(CN)2), making excessive silver ions react with the Dabar indicator so as to make the color of the solution change from yellow to orange to the end, and calculating the content of the hydrogen cyanide according to the volume of the consumed standard silver nitrate solution. The method provided by the invention solves the problems that various kinds of reagents used in the prior art are poisonous and harmful, and moreover the reagents have the disadvantages of complex analysis step, long elapsed time and the like, have potential safety hazards existing in the testing process, and enhance the sewage treatment load of the back section. The method can rapidly and accurately test the content of the hydrogen cyanide in coke oven coal.
Owner:云南昆钢煤焦化有限公司
Preparation method of cage-shaped ferronickel bimetallic phosphide loaded nitrogen-doped porous carbon material
PendingCN111889128AEasy to retouchImprove electrocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionEtchingPorous carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cage-shaped nickel-iron bimetallic phosphide loaded nitrogen-doped porous carbon material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cyanide ions are used as organic ligands, nickel ions and iron ions are used as metal sources; a ferronickel bimetallic Prussian blue compound growing on melamine is prepared through a coprecipitation method, the precursor is etched into a cage-shaped cube through one-step ammonia water, the cage-shaped cube and sodium hypophosphite are calcined at the temperature of 350 DEG C in an Ar atmosphere, andthe cage-shaped ferronickel bimetallic phosphide loaded nitrogen-doped porous carbon material is obtained. The PBA nano hollow cage-shaped particle group obtained by an ammonia water etching method can expose more active sites in the reaction process; the sintered and roughened porous carbon substrate with the melamine sponge three-dimensional structure not only can fix active sites to prevent agglomeration, but also can increase conductivity to accelerate charge transfer; metal phosphide is effectively formed through doping of phosphorus, the electronic structure around nickel and iron can beadjusted, and the charge transfer process can be accelerated.
Owner:淮安新能源材料技术研究院
Monomolecular-layer probe for detecting cyanide ion and preparation and application methods thereof
ActiveCN105181684ALess quantityNo interferenceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElectron donorCyanide ion
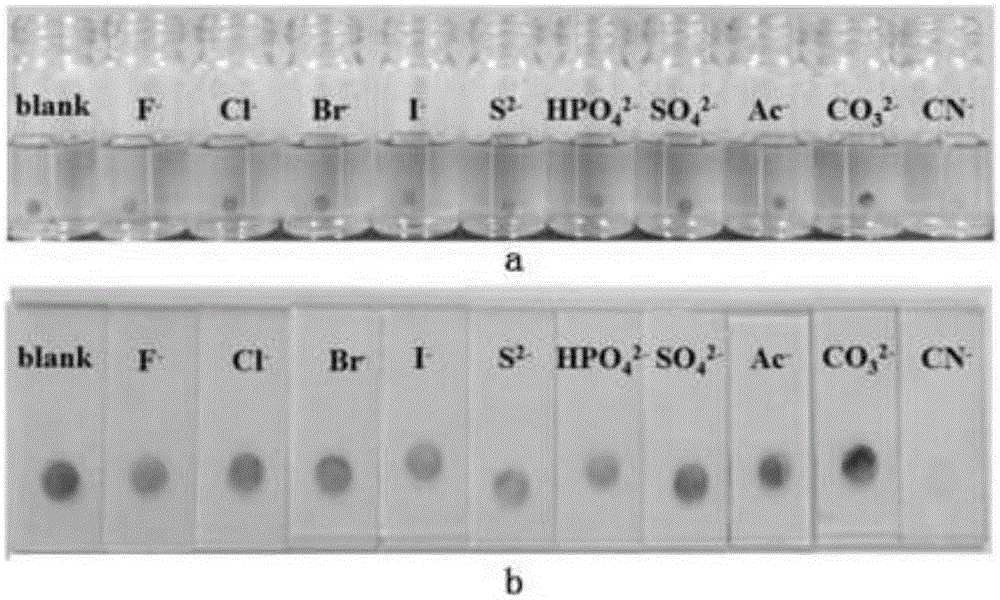
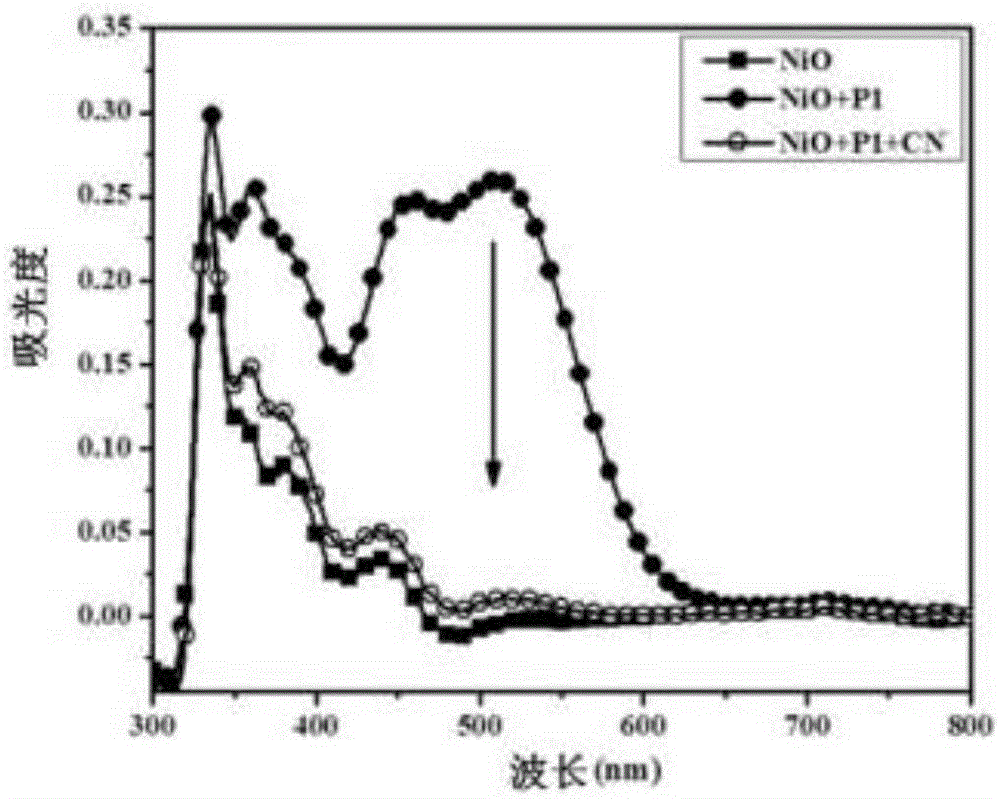
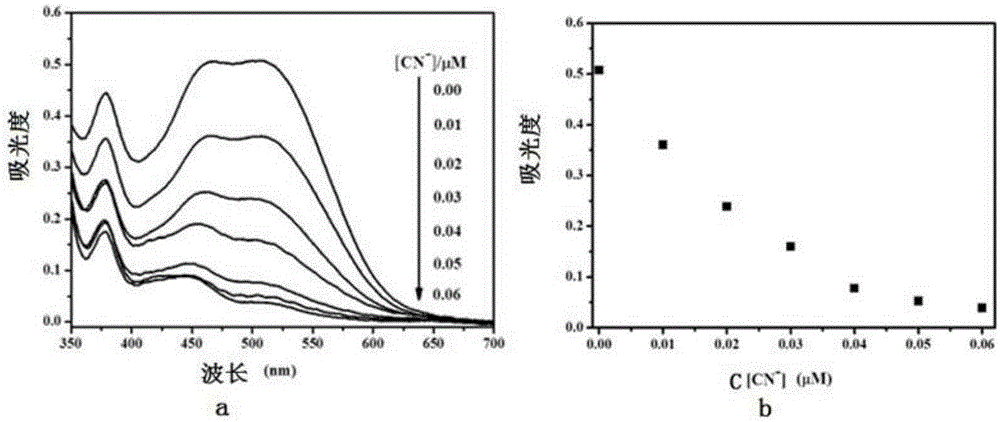
The invention relates to a monomolecular-layer probe for detecting cyanide ion and preparation and application methods thereof. The probe of the invention is P1 for adsorbing a monomolecular layer onto the surface of a metallic oxide thin film. P1 is a conjugated molecule based on triphenylamine and a dicyanovinyl group. Triphenylamine is used as an electron donor unit, and the dicyanovinyl group is used as an electron acceptor unit and simultaneously is a detection group. In addition, triphenylamine is also connected to a carboxyl group used for adsorbing P1 onto the metallic oxide thin film. As P1 is adsorbed on the metallic oxide thin film, the thin film is dark red. The probe is used to detect trace amount of cyanide ion in an aqueous solution, and the detection group reacts with cyanide ion such that dark red of the thin film remarkably fades. The detection method has high specificity and can rapidly respond to cyanide ion (10<8> mol / L) in an extremely dilute solution. Limit of detection (LOD) of cyanide ion by the monomolecular-layer probe is 2.99nmol / L. Thus, the monomolecular-layer probe is fast and convenient and has high sensitivity in detection of a solution phase in comparison with a conventional probe molecule.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method and device for purifying hydrogen cyanide industrial waste gas by electrodialysis
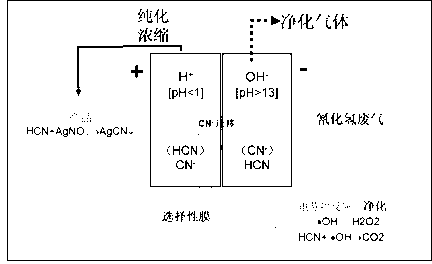
ActiveCN103071370AHigh selectivityIncrease added valueDispersed particle separationCyanide ionCobalt
The invention discloses a method and a device for purifying hydrogen cyanide industrial waste gas by electrodialysis. The method comprises the steps as follows: filling the hydrogen cyanide waste gas into a cathode, and purifying the hydrogen cyanide waste gas by utilizing free radicals with strong oxidizing property generated by electro-fenton reaction at the cathode; purifying and concentrating part of cyanide ions which are not fully oxidized by utilizing the selective permeability of a cobalt-containing perfluoro-sulfonate ion exchange membrane at an anode; and adding hydrocyanic acid purified and concentrated at the anode with different types of salts to prepare cyanide which is low in toxicity and easy to store and transport. According to the method, the liquid phase adsorption capacity is increased, the harmful gas purifying capacity can be increased by utilizing the liquid phase adsorption, electrodialysis and ion exchange principles while higher gas purifying rate is obtained, the generated gas such as NH3, H2, O2 or the like can serve as a raw material for other industrial production, high-toxicity high-risk byproducts are prevented being generated in the purifying process, and byproducts with higher added values can be obtained by an enriching and depositing method.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sensor molecules for identifying cyanide ion and hydrogen sulfate ion in relayed manner, synthesis and application thereof
InactiveCN105859722AOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHydrogen SulfateFluorescence
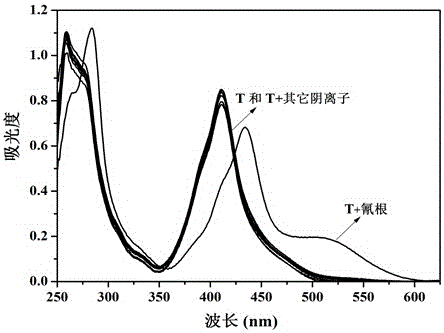
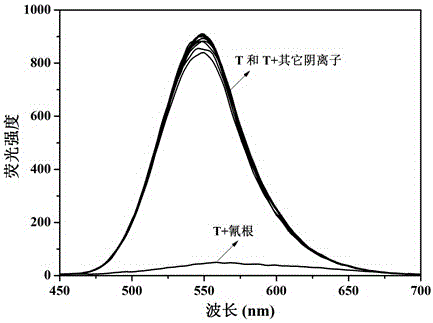
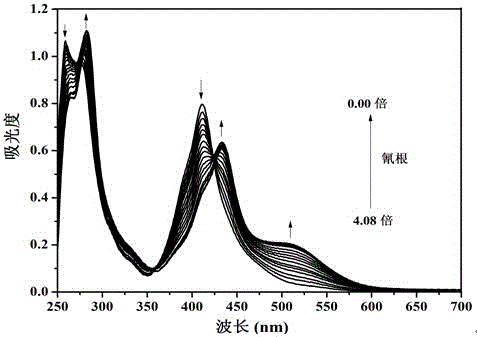
The invention provides sensor molecules T for identifying a cyanide ion and a hydrogen sulfate ion in the relayed manner through colorimetric fluorescence. The phenazine of the molecules serves as a stable system of a rigid structure, so that the solution of host molecules emits the strong fluorescence. The host molecules are combined with the cyanide ion to cause the color of the solution to change from yellow to saffron yellow. Meanwhile, the fluorescence quenching phenomenon occurs, and is represented as "ON-OFF" in spectral change. Meanwhile, a complex T-CN can further identify the hydrogen sulfate ion in the relayed manner, so as to cause the color recovery of the solution of the host molecules of the sensor and the fluorescence recovery. In spectral change, the above change is represented as "OFF-ON". The synthesis of the "ON-OFF-ON" type sensor molecules realizes the multi-functional operation of the sensor, so as to make a good contribution to the development of environment-friendly materials. At the same time, test paper loaded with the above sensor molecules is prepared, which has the advantages of convenient carrying, obvious phenomenon, rapid detection and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Waste water integrated treatment method of paraquat produced by cyanamideprocess
ActiveCN101628767ARealize resource utilizationReduce pollutantsOrganic chemistryChemical industryTreatment effectParaquat
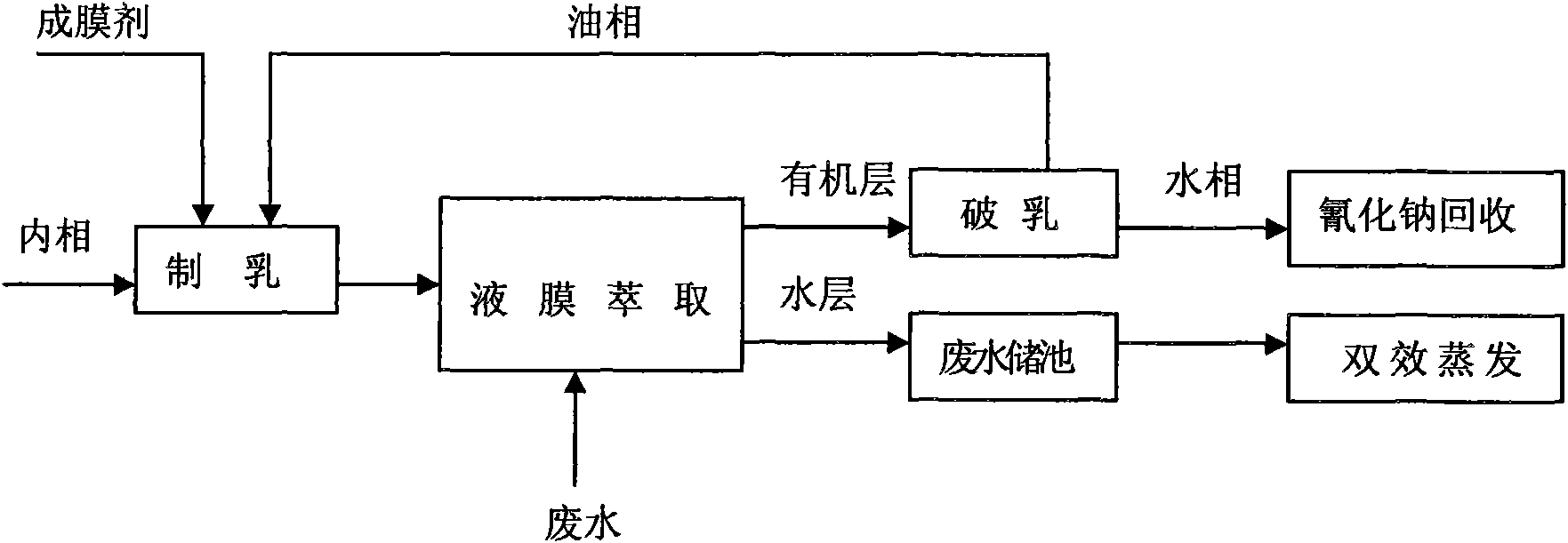
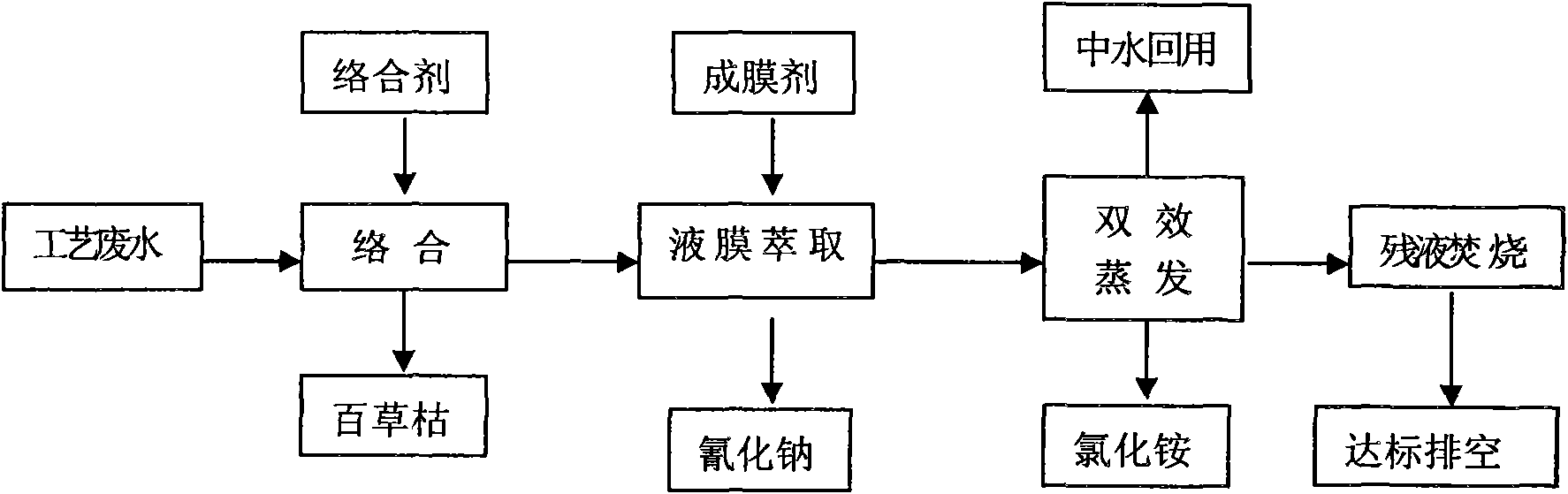
The invention discloses a waste water integrated treatment method of paraquat produced by cyanamideprocess, belonging to the technical field of waste water treatment. In the method, complexing agent is used for coordinately separating and recovering paraquat in waste water, a liquid membrane extraction method is used for recovering cyanide ions, double-effect distillation is used for recovering salt in the waste water, an incinerator is used for incinerating residual liquid, etc. The method has good treatment effect, high recovery rate, and can realize recycling usage of paraquat waste water resource of cyanamideprocess technique, lower pollutant in the waste water, reduce environmental pollution and lower the waste water treatment cost for paraquat manufacturing enterprises.
Owner:SHANDONG KEXIN BIOCHEM
Nano-silver fluorescent probe for detection of cyanide ion
InactiveCN102627966AHigh detection sensitivityLow detection concentrationFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceRoom temperature
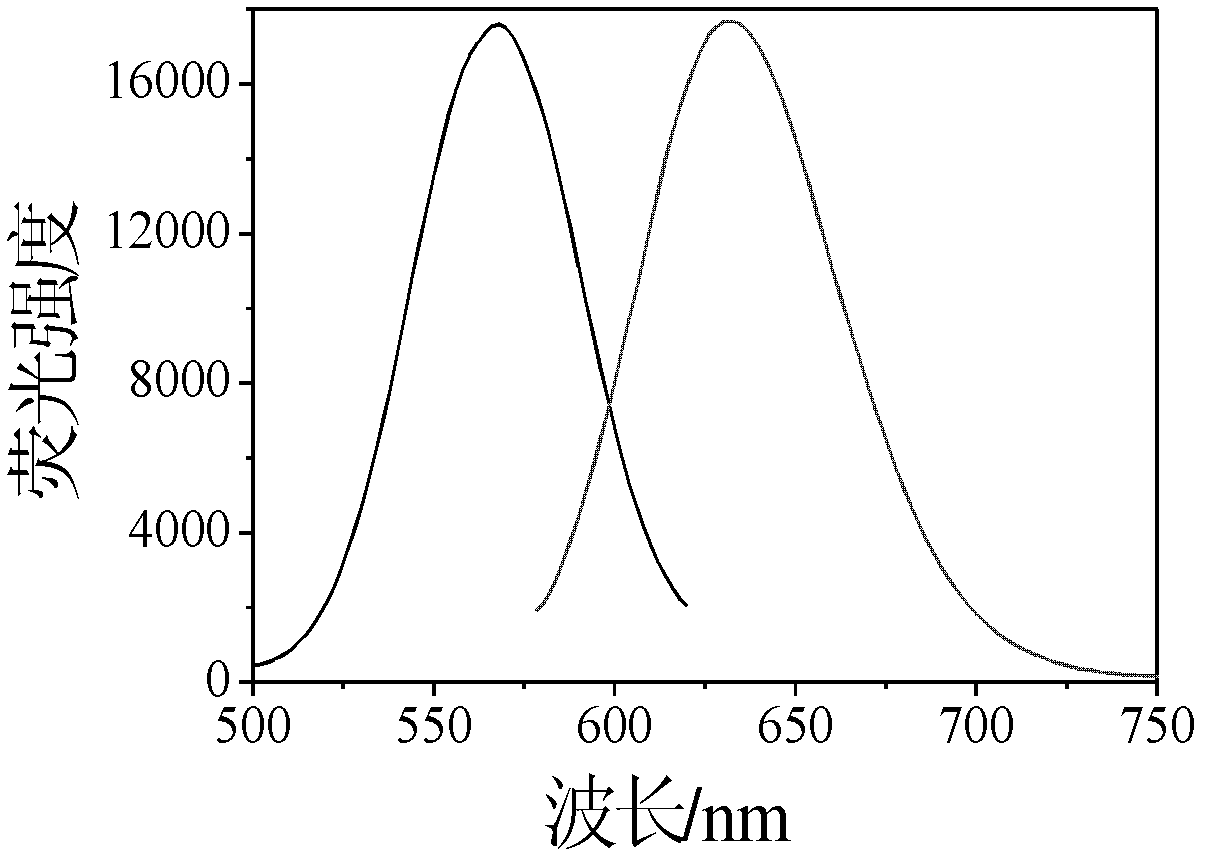
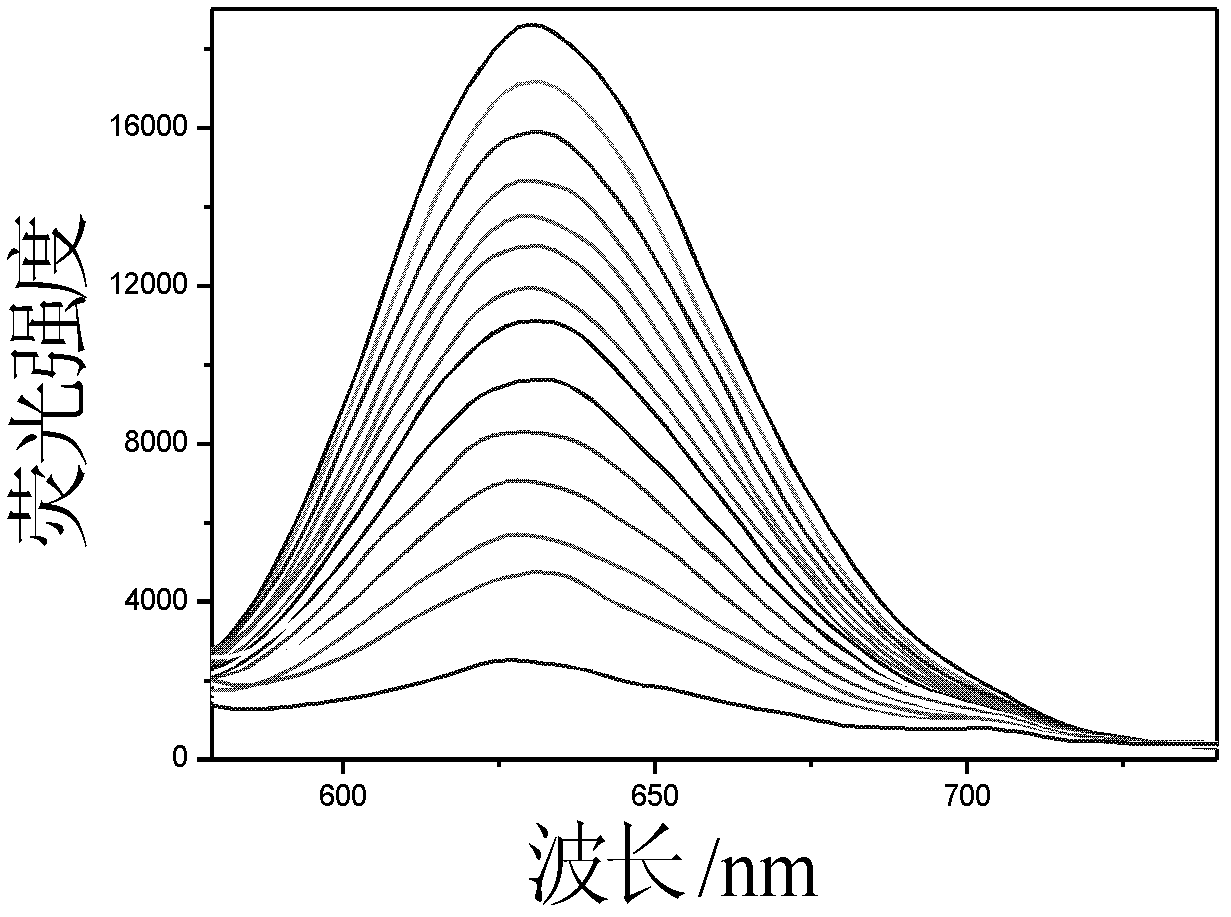
The invention provides a nano-silver fluorescent probe for detection of cyanide ion. The nano-silver fluorescent probe is prepared through the following step: oligonucleotide is use as a template to react for at room temperature for 4 hours under the effect of a reducing agent sodium borohydride, so as to obtain a water-soluble nano-silver fluorescent probe. The prepared nano-silver fluorescent probe is excitated at 568nm and emits at 632nm, the fluorescent probe has sensitive selectivity to cyanide ion and can detect a minimum cyanide concentration of 2.5nM.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Reducing electroless silver plating solution and reducing electroless silver plating method
InactiveUS20140242288A1Solve reductionAvoid decompositionLiquid surface applicatorsAnti-corrosive paintsDecompositionWater soluble
Provided are a reducing electroless silver plating solution and a reducing electroless silver plating method using the silver plating solution, the reducing electroless silver plating solution being capable of preventing decomposition of silver in the plating solution thereby to maintain stability of the solution and also being capable of preventing excessive roughening of an underlying metal or the like thereby to form a plating film having good film characteristics and a good appearance. The reducing electroless silver plating solution according to the present invention comprises a water-soluble silver salt and a reducing agent, wherein cyanide ions in a concentration of 0.006×10−3 mol / L to 12.5×10−3 mol / L are contained.
Owner:C UYEMURA & CO LTD
Application method of ratio-type cyanide ion fluorescent probe molecule
InactiveCN103134787ATo achieve specific identificationHigh electron deficiencyFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesFluorescence
The invention relates to an application method of a ratio-type cyanide ion fluorescent probe molecule. The invention belongs to the technical field of anion detection. The method is characterized in that the method is an application of a ratio fluorescent probe molecule, which is 1,2,2,3-tetramethyl-4,5-benzoindoline, used in cyanide ion detection. The probe molecule is obtained by a one-step process of periodic methane alkylation of 2,3,3-trimethyl-4,5-benzindole. In a system where DMF:H2O=1:1 (V / V), the probe molecule is excited by using 320nm light, and emission occurs at 461nm. When cyanide ion is added, intra-molecular charge transfer (ICT) process is broken, emission peak at 461nm is reduced, and new emission peak occurs at 425nm. Therefore, solution fluorescence is turned from bluish green to deep blue. In a system wherein cyanide ion coexists with other anions, the probe molecule shows high interference resistance, high specificity, and high sensitivity.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Cyanide receptor compound based on 2-cyano-3-(6-N, N-dimethylamino-2-naphthyl) acrylonitrile, preparation method and application
ActiveCN105037202AEasy to synthesizeRaw materials are easy to getCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationBinding siteAcrylonitrile
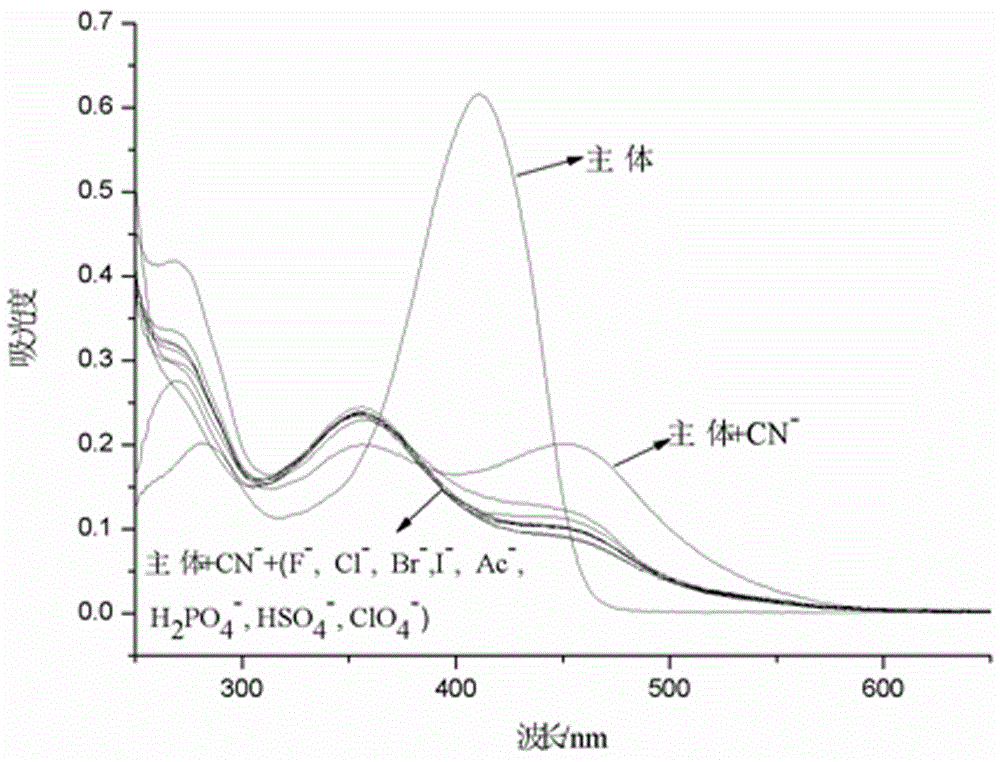
The invention discloses a cyanide receptor compound based on 2-cyano-3-(6-N, N-dimethylamino-2-naphthyl) acrylonitrile, a preparation method and application thereof. The compound takes a C=C double bond as a reactive binding site and takes 6-N, N-dimethylamino-2-naphthaldehyde as a fluorescence signal reporter group. When a receptor encounters cyanide ions, the cyanide ions and the C=C double bond of the receptor can carry out addition reaction so as to cause proton transfer and charge transfer in receptor molecules, so that the receptor molecules have color and fluorescence changes. The invention respectively researches the identification effects of the compound to F<->, Cl<->, Br<->, I<->, Ac<->, H2PO4<->, HSO4<->, ClO4<-> and CN<-> through colorimetry, ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy and fluorescent spectrometry. The results show that the receptor compound can singly and selectively identify cyanide ions in an HEPES-DMSO-H2O system and has very high sensitivity to detection of CN<->.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bimetallic organic gel and preparation and application thereof in detection of cyanide ions
InactiveCN104447886AEasy to storeEasy to carryOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceHexadecaneHydrazone
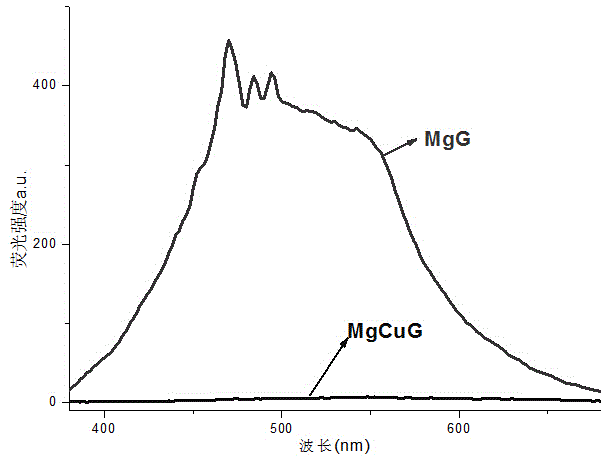
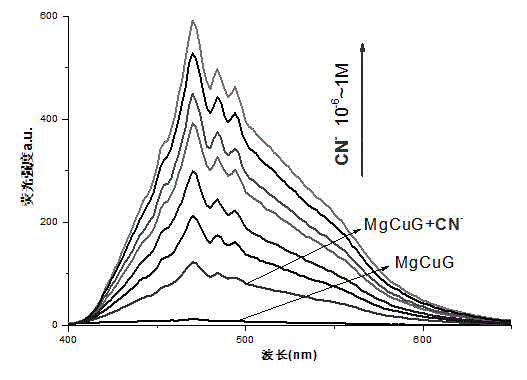
The invention provides organic metal gel for detecting CN<->. The organic metal gel is metal organic gel MgCuG which is prepared from 1-naphthyl-3,4,5-tri(hexadecyloxy)benzoyl hydrazone as a gelator matched with metal ions Mg<2+> and Cu<2+>. When a water solution of CN<-> is added to the bimetallic organic gel, the organic gel generates relatively strong light blue fluorescence, and a similar fluorescence change phenomenon cannot be generated by addition of other anions, and therefore, the bimetallic organic gel can achieve the single selective response on the CN<->, can be used as a solid soft material of an intelligent sensor of the CN<->, and is used for detecting the CN<->; the defects in identification of the CN<-> in the solution are overcome; and the bimetallic organic gel is easy to store and carry, and convenient to use, and has the certain potential application value.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Benzothiazole 2-acetonitrile dye and application thereof
The invention relates to benzothiazole 2-acetonitrile dye. A chemical structure of the benzothiazole 2-acetonitrile dye is shown as a formula (I) in the specification. The benzothiazole 2-acetonitrile dye is prepared from 4-(diphenylamine) benzaldehyde and benzothiazole 2-acetonitrile-2-acetonitrile through a reaction. The benzothiazole 2-acetonitrile dye can be used for detecting cyanide ions.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Coumarin derivative and preparation method and application in detecting cyanide ion
ActiveCN103044406AEnhanced nucleophilicityObvious color changeOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWastewaterStructural formula
The invention discloses a ratio-type coumarin derivative which can be used for detecting cyanide ions. The structural formula (I) of the coumarin derivative is described in the specification, wherein R is shown in the specification. The coumarin derivative is used for detecting cyanide ions; the process of detecting the cyanide ion is carried out in a buffer solution of Na2CO3-NaHCO3; and the pH value of the buffer solution is 9.4. The coumarin derivative provided by the invention can be used for uniquely, efficiently and simply detecting the cyanide ions, is applicable to detection on cyanide ions in wastewater generated in industrial processes such as electroplating, chemical engineering, metallurgy, mineral separation and surface treatment, and is high in detection sensitivity and good in selectivity.
Owner:山西永津集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com