Antibody for resisting human CD79a extracellular terminal protein, coding gene and application
An antibody and coding technology, applied in anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, anti-receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant immunoglobulin, application, etc., can solve loss of CD20, recurrence, non-expression of CD20, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of high internalization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Development of ZUCH-S3 monoclonal antibody.
[0044] According to the classic method of mouse-mouse hybridoma reported by Koller and Milstein (Lin Xueyan, Zhang Ling editors. Modern Cell and Molecular Immunology. First Edition. Beijing: Science and Technology Press. 2000, p489-521.), with B cell lymphoma cell line Raji cells as immunogen, 10 7 Raji cells were injected intraperitoneally into 8-week-old female Balb / C mice, once a week, for a total of 4 times. On the 3rd day after the fourth injection, the mice were killed by dislocation, and the splenocytes were aseptically collected and kept in logarithmic The mouse myeloma cell line NS-1 cells (products of American ATCC) in the growth phase were mixed at a ratio of 6:1, and 50% polyethylene glycol (PEG, American Sigma Company, molecular weight 3350 Daltons) solution was used as the fusion medium. After fusion, selective culture was carried out in a 96-well plate (Falcon, USA). On the 9th to 20th day after fusion, the ...
Embodiment 2
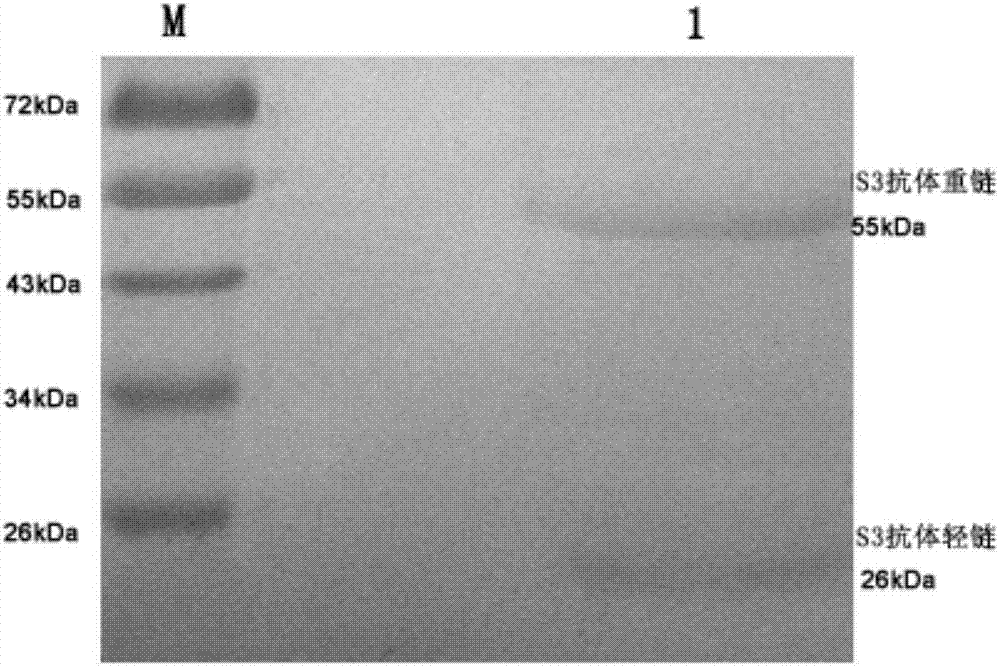
[0046] Purification and subtyping of monoclonal antibodies.
[0047] 1. Purification of monoclonal antibodies: In order to induce ascites, BALB / C mice were intraperitoneally injected with 0.5 0.5 per mouse of pristane 1 week before inoculation with hybridoma cells (hybridoma cell line ZUCH-S3 obtained in Example 1). ml, then inoculate 5.0 × 10 each 6 After 10 days, the ascites fluid was collected and centrifuged, and the antibody titer was determined. Monoclonal antibodies in ascites were purified by affinity purification (Sepharose cross-linked with Protein G). ①Ascites fluid was diluted 3 times with cold Binding Buffer, then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C to remove the precipitate. ② Thoroughly wash the affinity purification column preloaded with Sepharose-Protein G with Binding Buffer of 10 times the column bed volume. ③Put the diluted ascites into a column, and control the flow rate to 8-10 drops / min. ④ Repeat the flow of ascites on the column once. ⑤...
Embodiment 3
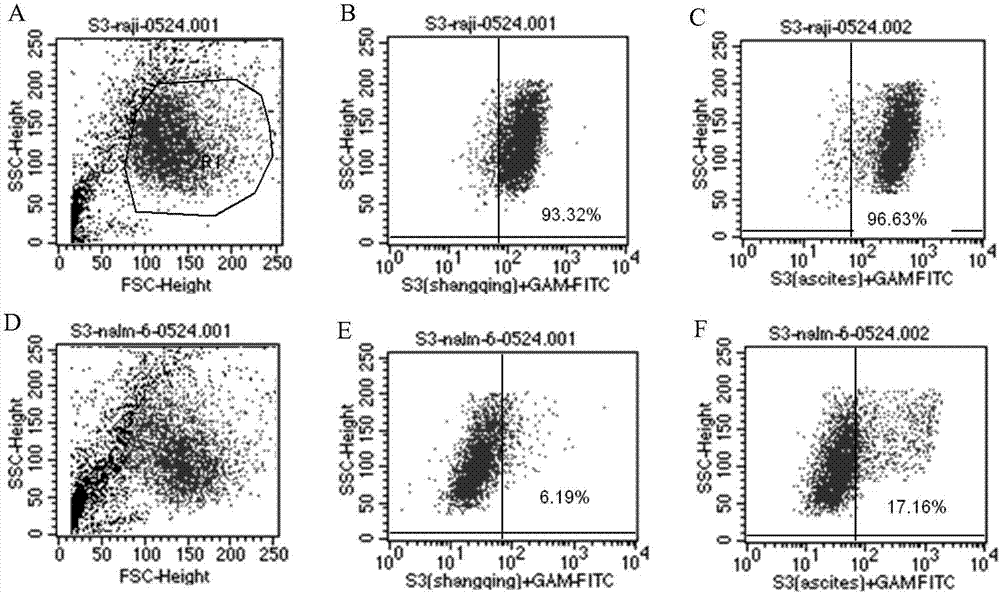
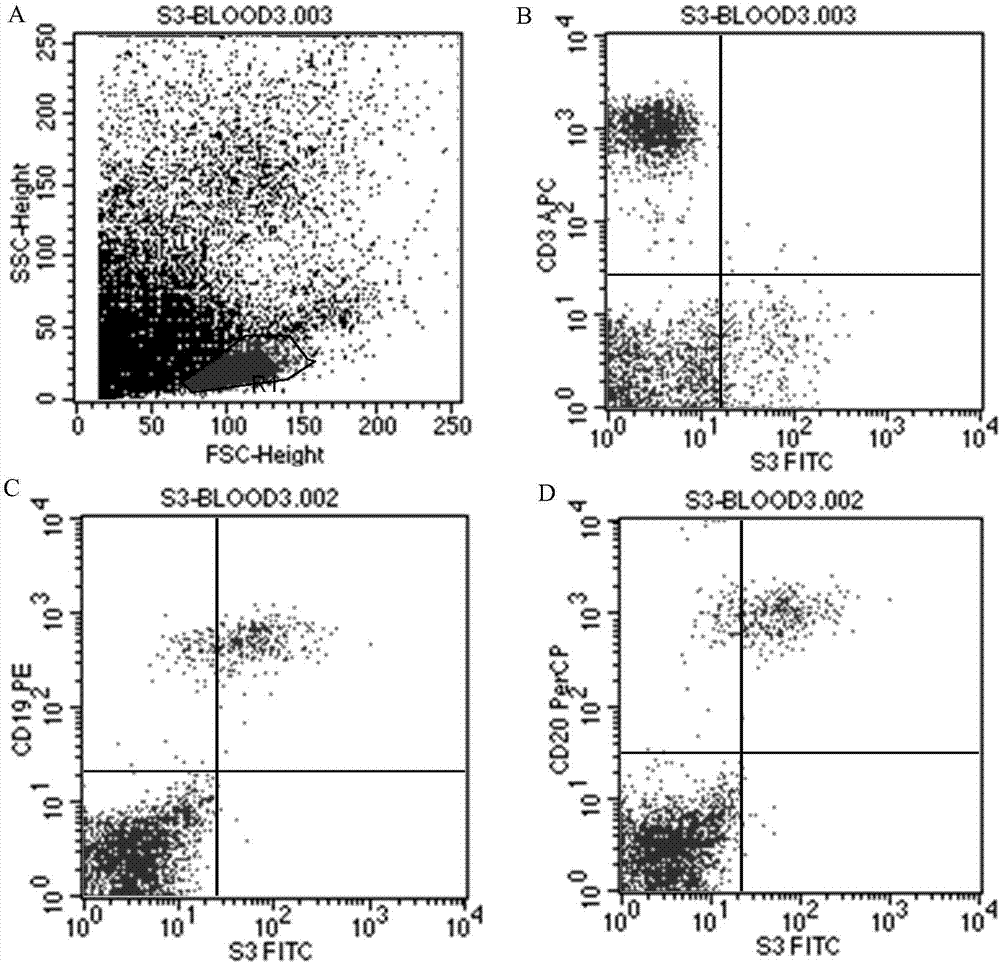
[0050] The ability of S3 monoclonal antibody to recognize antigen was detected by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscope.
[0051] The steps are as follows: ① Count Raji cells, Nmlm-6 cells, normal peripheral blood cells, B-cell lymphoma patient cells and B-cell acute leukemia cells (B-ALL), block Fc receptors with bovine serum albumin, wash with PBS, and adjust them respectively. Concentration to 1×10 7 / ml, take 100μl of cell suspension from each tube; ②Add 50μl of S3 monoclonal antibody culture supernatant or 10μl of purified antibody to each tube, incubate at 4°C for 30min; ③Add PBS and centrifuge at 1000g for 10 minutes to wash away unbound S3; ④Add 5 μl of FITC-labeled goat anti-mouse monoclonal antibody (GAM-FITC) respectively, incubate at 4°C for 30min; ⑤Add PBS respectively, centrifuge at 1000g for 10min, remove the supernatant; ⑥Detect and analyze by flow cytometry or fluorescence microscope. ⑦ The results are shown in Figure 2 to Figure 6 :
[0052] like f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com