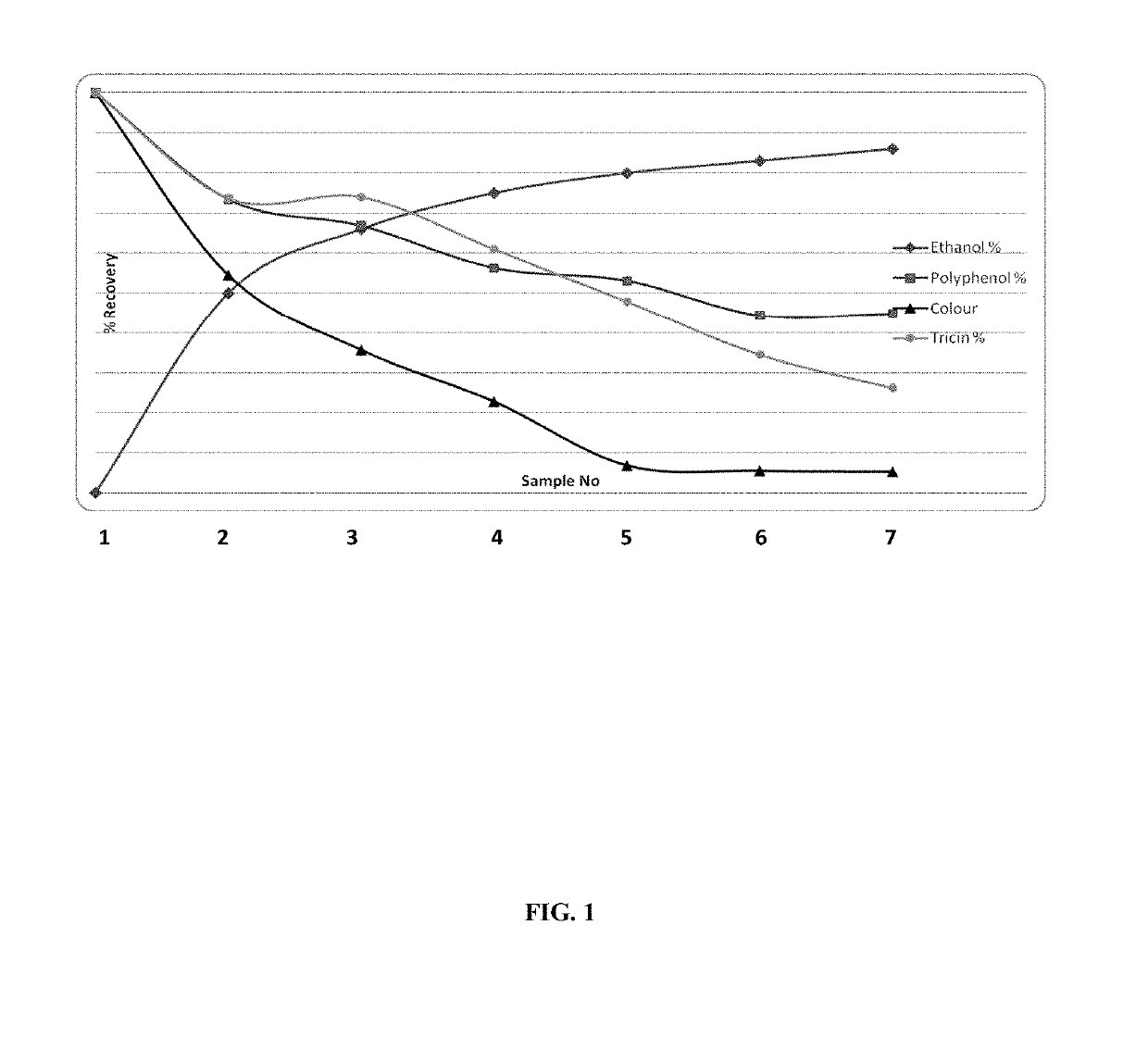
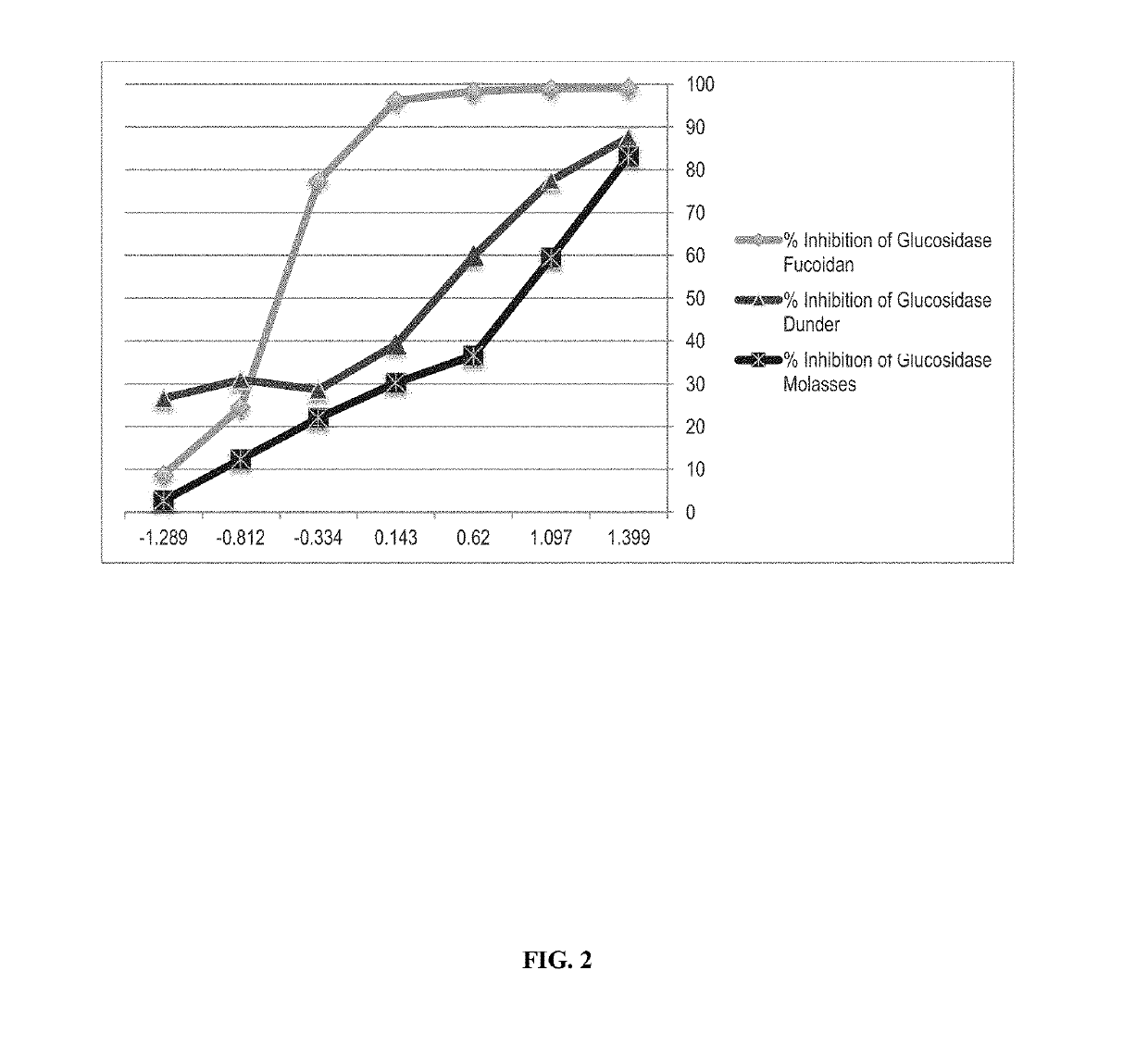
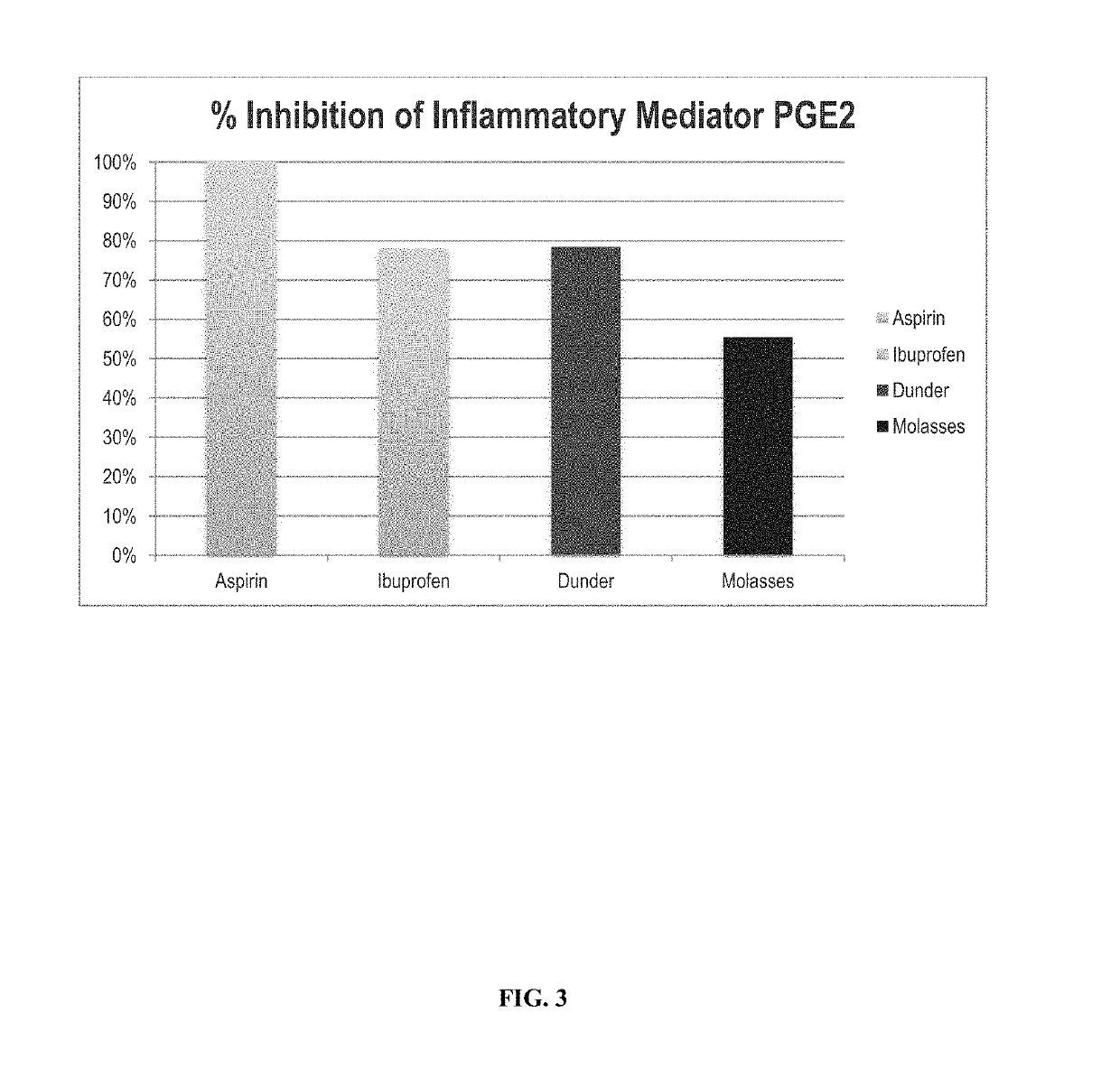
Extraction method
a technology of extracting method and extracting method, which is applied in the field of extracts, can solve the problems of unstable incorporation into other foodstuffs, difficult to refine further, and unpalatable for many people, and achieves the effects of improving taste, reducing colour and polysaccharide content, and improving functional effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Extract
Feedstock Preparation
[0143]100 ml of Mackay terminal molasses was measured into a glass beaker at room temperature (RT). The weight was 140 g. Then 100 mls of distilled water was added and stirred manually with a glass stirring rod until most of the viscous molasses was mixed with the water. The beaker was then placed on a magnetic stirrer and mixed for 10-15 minutes. The temperature was held at 26-28° C. The pH of this solution was 5.4-5.6.
[0144]The final volume was 200 ml. A 1 ml sample was removed and diluted with 1 ml water, mixed well and then a drop was placed on a Ella refractometer. The Brix reading was 48.
Treatment with AR Ethanol (100% v / v)
[0145]The feedstock (200 ml) was placed in a glass beaker on a magnetic stirrer and adjusted so that a clear vortex was formed, ethanol was slowly added into the vortex to ensure rapid mixing of the feedstock with the ethanol. Over a period of about 30 minutes, 950 ml of ethanol was added. The temperature was mainta...
example 2
Preparation of Extract
Preparation of Feedstock
[0149]200 ml of feedstock was prepared from Mackay terminal molasses as previously described in Example 1. The Brix level was 48.
Addition of AR Ethanol (100%)
[0150]1000 ml of ethanol was added in 200 ml increments so the formation, colour and appearance of the precipitate could be observed as the percentage of ethanol increased. Observations were made at 50, 66, 75, 80 and 83% ethanol (v / v), but no samples were collected. The final mixture volume (83% ethanol, v / v) was 1200 ml and this was left standing at 20-25° C. overnight (approximately 18 hours). As before, the ethanol was slowly added into a stirring vortex created by rapid magnetic stirring of the mixture.
Recovery of the 83% Supernatant
[0151]The supernatant was recovered in the same way as described in Example 1. The volume was 1050 ml.
Removal of Ethanol
[0152]Ethanol was removed at 45° C. under vacuum as described in Example 1. The final syrup volume was 78 ml and the Brix level w...
example 3
Preparation of Extract
Preparation of Feedstock
[0156]100 ml of molasses from a primary sugar mill was used. The crude molasses had a Brix of 78 using an Atago-Pal 2 digital refractometer. The weight of the material was 145 g. As described in the previous experiments, 100 ml of distilled water was added to the 100 ml of molasses, mixed and stirred for 15 minutes to ensure a homogeneous feedstock. The final feedstock had a Brix of 49-50.
Effect of Adding Increasing Amounts of Ethanol (100% v / v)
[0157]Two separate lots of 7 centrifuge tubes were used and 10 ml of feedstock was added to each. To the first 7 tubes, distilled water was added as follows: 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60 ml. To the second 7 tubes, 100% v / v ethanol was added as follows: 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60 ml. All tubes were mixed and shaken 3 times during standing at room temperature (25° C.) for 90 minutes.
Removal of Precipitates
[0158]All tubes were centrifuged as described previously. Supernatants were recovered and mea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com