Patents
Literature
708 results about "Cellulose pulp" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellulose (C6H10O5)n is refined wood pulp. It is a white, free-flowing powder. Chemically, it is an inert substance, is not degraded during digestion and has no appreciable absorption. In large quantities it provides dietary bulk and may lead to a laxative effect.
Composites containing cellulosic pulp fibers and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6270883B1Reduce discolorationDiscoloration is significantly reduced or avoidedSynthetic resin layered productsNon-woven fabricsCellulose pulpPolymer chemistry
Reinforced composites containing cellulosic pulp fibers dispersed in a matrix, wherein the matrix comprises a thermoplastic polymeric material melting above 180° C. and the cellulosic pulp fibers have an alpha-cellulose purity greater than 80% by weight. Methods of making and using the reinforced composites.
Owner:RAYONIER PERFORMANCE FIBERS +1
ENHANCEd CO-FORMED MELTBLOWN FIBROUS WEB STRUCTURE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING
An enhanced, co-formed fibrous web structure is disclosed. The web structure may have a co-formed core layer sandwiched between two scrim layers. The core layer may be formed of a blend of cellulose pulp fibers and melt spun filaments. The scrim layers may be formed of melt spun filaments. Filaments of one or both of the scrim layers, and optionally the core layer, may also be meltblown filaments. The core layer may include consolidated masses of cellulose pulp fibers to, for example, enhance texture and cleaning efficacy of a wet wipe made from the structure. The material forming the consolidated masses may be selected and / or processed so as to cause the masses to have reduced visual discernibility relative the surrounding areas of the structure, when the fibrous web structure is wetted. A method for forming the structure, including formation and inclusion of the consolidated masses, is also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Technology for extracting cellulose from biomass raw materials
ActiveCN103898782AHigh purityReduce cooking timePulp bleachingPulping with acid salts/anhydridesAcetic acidOrganic acid
The invention relates to a cellulose extracting technology, and specifically relates to a technology that utilizes organic acids to extract cellulose from biomass raw materials in the presence of a hydrogen peroxide catalyst. The technology comprises the following steps: in the presence of a hydrogen peroxide catalyst, utilizing an organic acid to cook biomass raw materials, wherein the organic acid is composed of formic acid with a concentration of 70 to 95 wt% and acetic acid with a concentration of 70 to 95 wt%; extracting and screening so as to obtain screened cellulose pulp; and further bleaching the screened pulp so as to obtain the target cellulose; wherein the cellulose is dissolving pulp or industrial cellulose. The alpha-cellulose content of the cellulose obtained by the method provided by the invention is more than 90 wt%. The technology has the advantages of simple route and low energy consumption.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
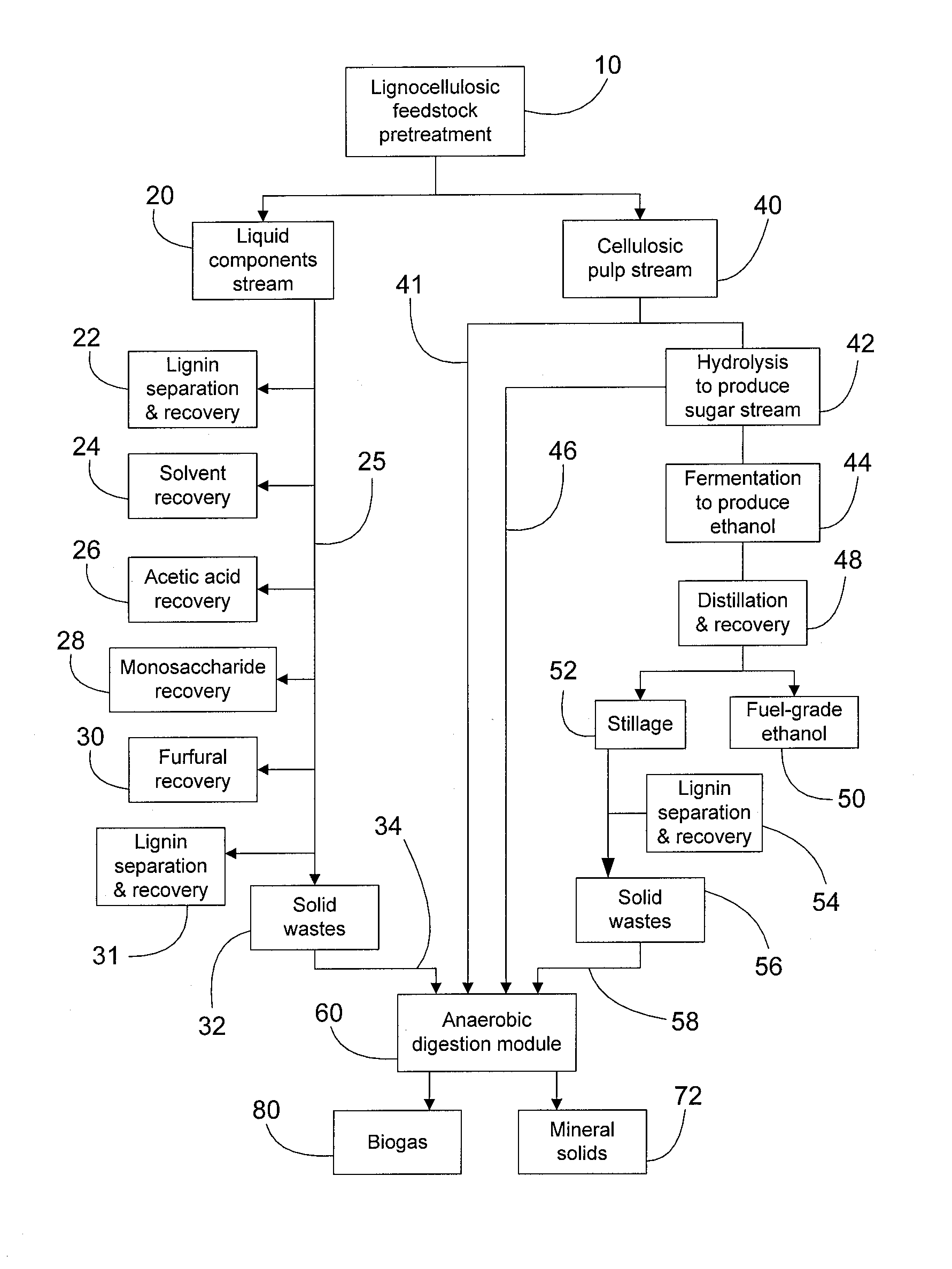
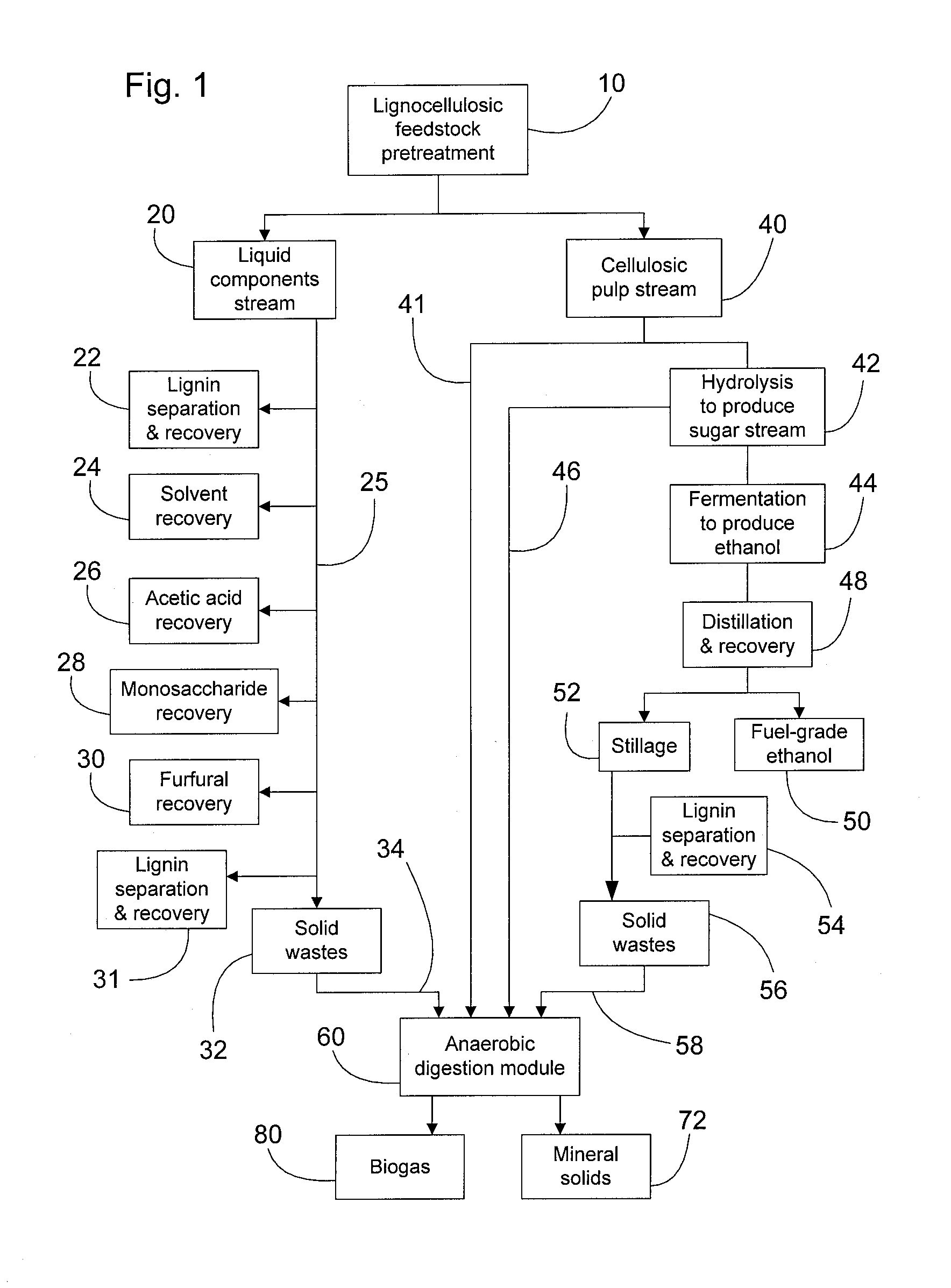
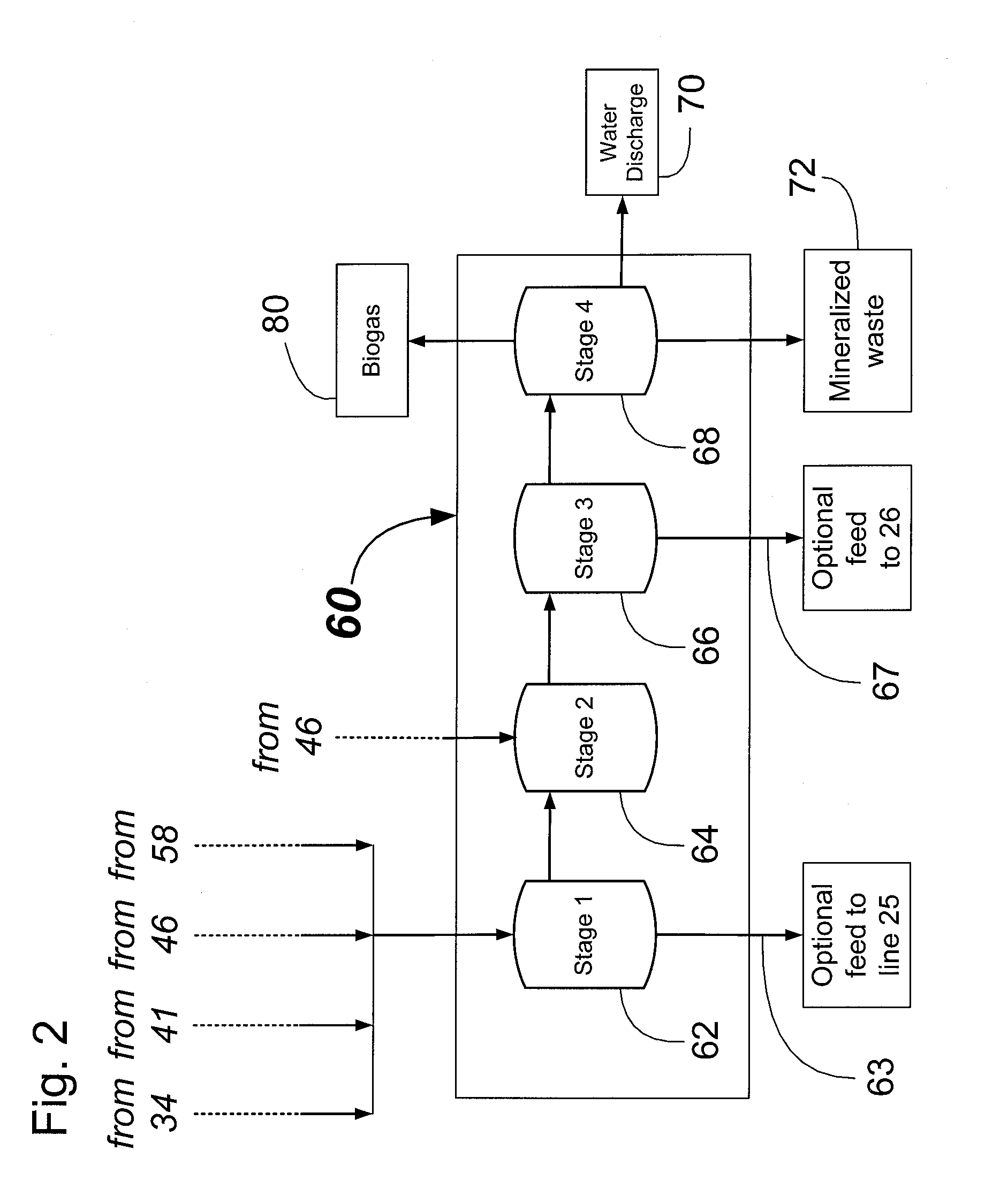
Concurrent Anaerobic Digestion and Fermentation of Lignocellulosic Feedstocks
InactiveUS20110236946A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlcoholSemi solid
A process for concurrent production of lignins, fuel alcohol, and biogas from lignocellulosic feedstocks. The process comprises: (1) pretreating a lignocellulosic feedstock to produce a solubilised liquid components stream comprising lignins, lignin-derived compounds, and a cellulosic pulp stream, (2) separating the liquid stream from the cellulosic pulp stream, (3) processing the liquid stream to separate and recover at least lignins, lignin-derived compounds, and semi-solid waste material, (b) processing the cellulosic pulp stream to saccharify and ferment the cellulose pulp to produce a beer which is then separated into fuel-grade alcohol and a waste stillage material, (4) anaerobically digesting the semi-solid waste material from the liquid stream and the waste stillage material to produce a biogas. The rate of anaerobic digestion can be manipulated by controllably supplying a portion of the monosaccharides produced from the cellulosic pulp. The cellulosic pulp stream may also be anaerobically digested.
Owner:LIGNOL INNOVATIONS
Thin, high capacity absorbent structure and method for producing same
InactiveUS7411110B2Thin and flexibleLarge capacityGarmentsSanitary towelsHigh densityAbsorbent material
A thin, flexible, high capacity absorbent pad and a method of making such absorbent pads. The absorbent pad contains high levels of superabsorbent material homogeneously mixed with cellulose pulp fluff. The absorbent pad is subjected to high density compaction to achieve the thinness and high absorbent capacity of the invention. The absorbent pad can be used in absorbent articles, such as diapers, training pants, feminine hygiene products, incontinence products, and swim wear.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Phase-change energy-storage fibre and method for making same
ActiveCN101041911AHigh phase change enthalpyFunction increaseConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsMelt spinning methodsCelluloseWax
The invention discloses a phase-variable energy-storage fiber and relative production, which comprises that using cellulose slurry to prepare cellulose adhesive solution, to be mixed with phase-variable wax fused solution to prepare spinning dope to obtain the phase-variable energy-saving adhesive fiber. The functional fiber is mainly formed by cellulose and wax, while the wax content is 10-40% (relative to the cellulose content). And the inventive production has simple process, significantly reduced phase-variable material loss in the process, improve the phase-variable material content and improve the phase-variable energy-saving function and mechanical function.
Owner:潍坊欣龙生物材料有限公司
Enhanced co-formed/meltblown fibrous web structure
An enhanced, co-formed fibrous web structure is disclosed. The web structure may have a co-formed core layer sandwiched between two scrim layers. The core layer may be formed of a blend of cellulose pulp fibers and melt spun filaments. The scrim layers may be formed of melt spun filaments. Filaments of one or both of the scrim layers, and optionally the core layer, may also be meltblown filaments. The fibrous web structure may have a Consumer Preference Indication (governing allocation of melt spun filaments between core layer and scrim layers) greater than 0. Alternatively, the filaments forming the scrim layers may constitute from 1 to 13 percent of the weight of the structure. Alternatively, the scrim layers may have a combined basis weight of from 0.1 gsm to less than 3.0 gsm. A method for forming the structure, including direct formation of layers, is also disclosed.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Enhanced co-formed/meltspun fibrous web structure
An enhanced, co-formed fibrous web structure is disclosed. The web structure may have a co-formed core layer sandwiched between two scrim layers. The core layer may be formed of a blend of cellulose pulp fibers and melt spun filaments. The scrim layers may be formed of melt spun filaments, and the filaments forming one or both scrim layers may have a number average diameter of 4.5 μm or less. Filaments of one or both of the scrim layers, and optionally the core layer, may also be meltblown filaments. Alternatively, the filaments forming the scrim layers may constitute from 1 to 13 percent of the weight of the structure. Alternatively, the scrim layers may have a combined basis weight of from 0.1 gsm to less than 3.0 gsm. A method for forming the structure, including direct formation of layers, is also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for manufacturing nanofibrillated cellulose pulp and use of the pulp in paper manufacturing or in nanofibrillated cellulose composites
InactiveUS20130000855A1Increase productivityPrevents hydrogen bondPulp properties modificationLuminescent/fluorescent substance additionPaper manufacturingPulp and paper industry
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Method for preparing cellulose spinning fluid
ActiveCN101240461AIncrease in sizeLow viscosityArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsHigh concentrationOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of cellulose spinning solution, including a mixed solvent with low boiling point, volatile, polar organic solvent as a promoter and the N-methylmorpholine-N oxides (NMMO) of 8-18% moisture content; the cellulose pulp is mixed with the mixed solvent forming a uniform mixed materials; the low boiling point volatile organic solvent is removed from the mixed materials and the low content is lower than 5%, the cellulose of mixed materials is dissolved in the NMMO forming the cellulose spinning solution under heating. The invention is used the promoter delaying swelling and preventing premature dissolution of cellulose to reduce the solvent viscosity, the cellulose is dissolved uniformly, completely, the advantage which the pulp is impregnated directly in the high concentration solvent, and overcomes the abuse of uneven mixed, the used promoter is easy to extract and to recycle.
Owner:CHINESE TEXTILE ACAD
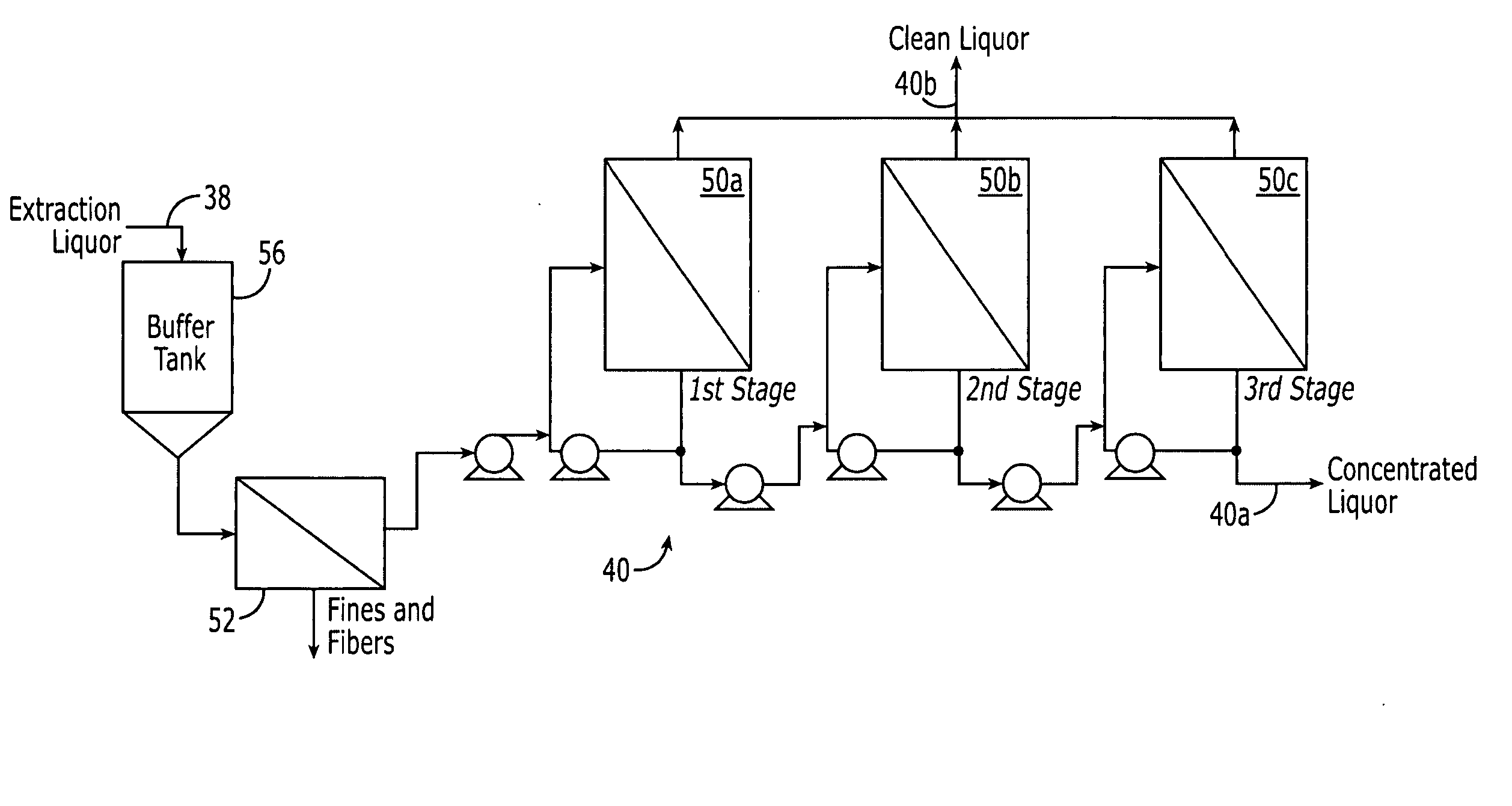
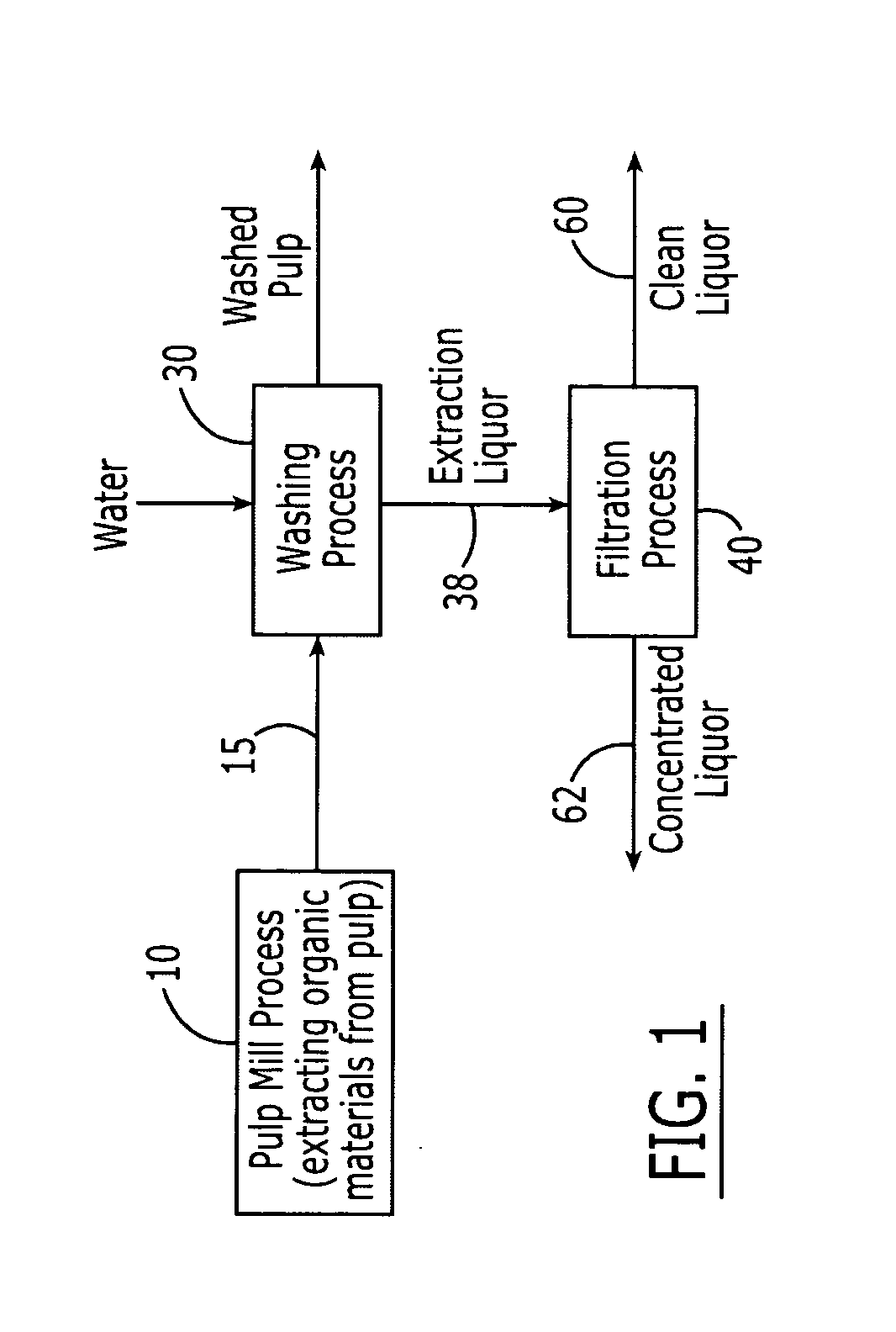
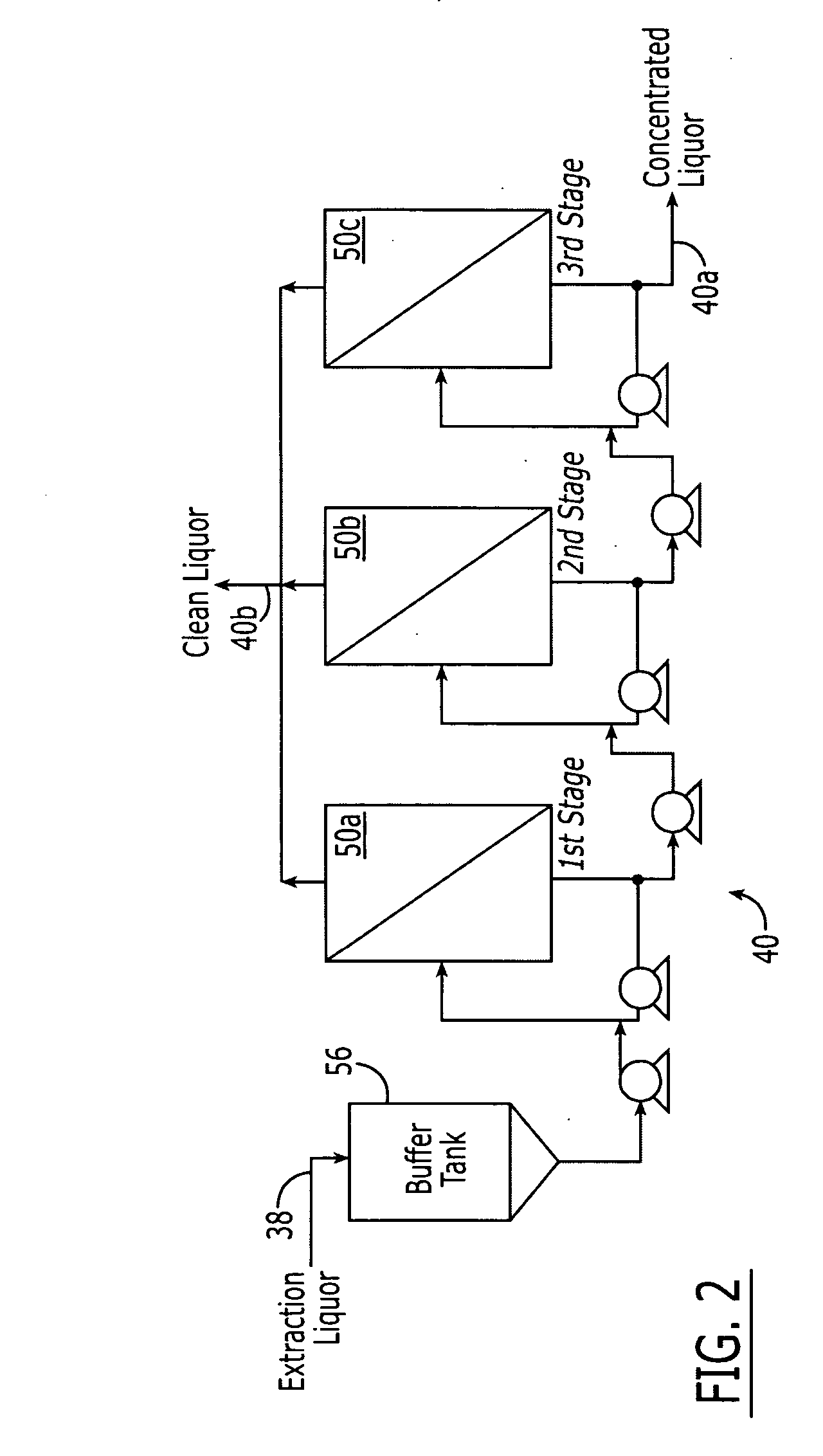
Method of concentrating pulp mill extracts
InactiveUS20060016751A1Reduce loadReduce processMembranesPulp liquors combustionWaste streamPulp mill
A process for separating organic components from a pulp mill waste stream comprising the steps of washing a cellulose pulp to obtain an aqueous extraction liquor containing organic components, and separating at least a portion of said organic components from the extraction liquor by passing the extraction liquor through at least one nanofiltration membrane. The process may be used in conjunction with a variety of pulp mill processes, including kraft cooking processes, hot caustic extraction processes, sulfite cooking processes, and bleaching processes.
Owner:RAYONIER PRODUCTS AND FINANCIAL SERVICES COMPANY
High-wetness modulus adhesive colloid fiber and preparing method
InactiveCN101024907AHigh strengthResistant to multiple deformationsArtificial filaments from viscoseBleaching apparatusFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a high-humidity modulus viscose fiber with dry strength of 3.5-6.0cN / dtex, wet elastic modulus of 0.35-0.60cN / dtex and wet strength of 2.0-4.5cN / dtex, and prepared of cellulose pulp with degree of polymerization of 500-1200 and alpha-cellulose content >=95% by the steps of dip-basifying, squeezing, ageing, yellowing, dissolving, wet spinning moulding, drafting, etc. And it has features of higher intensity and wet modulus, better loop strength performance, and lower brittleness; and the fabrics made by it has features of high intensity, multiple deformation resistance, alkali resistance, etc.
Owner:CHTC HELON
Inkjet media, recording method, recording apparatus, ink-media set, and ink recorded matter
To provide an ideal inkjet recording method capable of full-color printing and of inexpensively providing prints that have a texture similar to those of commercial prints and that offer excellent print quality, image density, image fidelity and smear resistance, by combining a specific recording media and a specific pigment-based inkjet ink. The inkjet recording method uses an ink containing particulate coloring material for printing on a media that includes a substrate composed primarily of cellulose pulp and one or more coated layers formed on at least one surface of the substrate, wherein the media has an air permeability of 0.1 ml / min to 30 ml / min as measured using a Parker Print-Surf.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for manufacturing modal fiber
ActiveCN101545150AHigh strengthBrightly dyedArtificial filaments from viscoseInternational standardDissolution
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing modal fiber, which comprises basification reaction, ageing reaction, yellowing reaction, dissolution of viscose glue, filter of the viscose glue, defoaming of the viscose glue, ripening of the viscose glue, wet spinning, drawing and other related process steps. The method adopts cellulose pulp with alpha cellulose content of less than 95 percent as a raw material, uses common equipment for producing common viscose glue short fiber, and adopts the technology to control a simple and practical special process formulation and a spinning drawing mode to manufacture the modal fiber capable of reaching international standards. The method has the advantages of little investment, easily obtained and low-cost raw materials, high productivity and simple process operation; and the manufactured modal fiber has good quality and stable performance.
Owner:杭州奥通新材料智能科技有限公司
Methods of making composites containing cellulosic pulp fibers
InactiveUS20020000683A1Reduce discolorationDiscoloration is significantly reduced or avoidedSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationFiber-reinforced compositeCellulose pulp
Reinforced composites containing cellulosic pulp fibers dispersed in a matrix, wherein the matrix comprises a thermoplastic polymeric material melting above 180° C. and the cellulosic pulp fibers have an alpha-cellulose purity greater than 80% by weight. Methods of making and using the reinforced composites.
Owner:RAYONIER PERFORMANCE FIBERS
Ink-jet recording method, ink, ink cartridge, recording apparatus, and recorded matter
ActiveUS20100245416A1Quality improvementLow costDuplicating/marking methodsInksParticulatesPolymer science
An ink-jet recording method including: printing on a medium by ejecting thereon ink having a pH value of 8 or more and containing at least a particulate colorant, emulsion resin and surfactant, the medium prepared by providing at least a coat layer containing a pigment on at least one surface of a substrate containing cellulose pulp as a main component, wherein printing is performed at a deposited ink amount of 15 g / m2 or less, and wherein the medium has a pH value of 8 or more at a paper surface, and the amount of pure water transferring onto a surface of the medium having the coat layer after a contact time of 100 ms measured with a dynamic scanning absorptometer is 30 mL / m2 or less and the amount of pure water transferring onto the surface of the medium after a contact time of 400 ms is 35 mL / m2 or less.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image forming method
The present invention provides an image forming method at least including: applying, by an inkjet method, an ink composition containing at least one pigment as a coloring material, at least one kind of resin particles, at least one fluorine-based surfactant and water, on a recording medium which has a single pigment layer or multiple pigment layers on or above at least one surface of a support containing a cellulose pulp as a main component, and has an amount of transfer of purified water to a medium, when measured with a dynamic scanning absorptometer, of from 1 ml / m2 to 15 ml / m2 for a contact time of 100 ms, and of from 2 ml / m2 to 20 ml / m2 for a contact time of 400 ms; and applying a treatment liquid containing at least one aggregating agent that aggregates components in the ink composition.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Technical method for separating organic constituent of biomass
ActiveCN101092435ATake advantage ofEasy to separateSugar derivativesLignin derivativesReaction temperatureHigh pressure
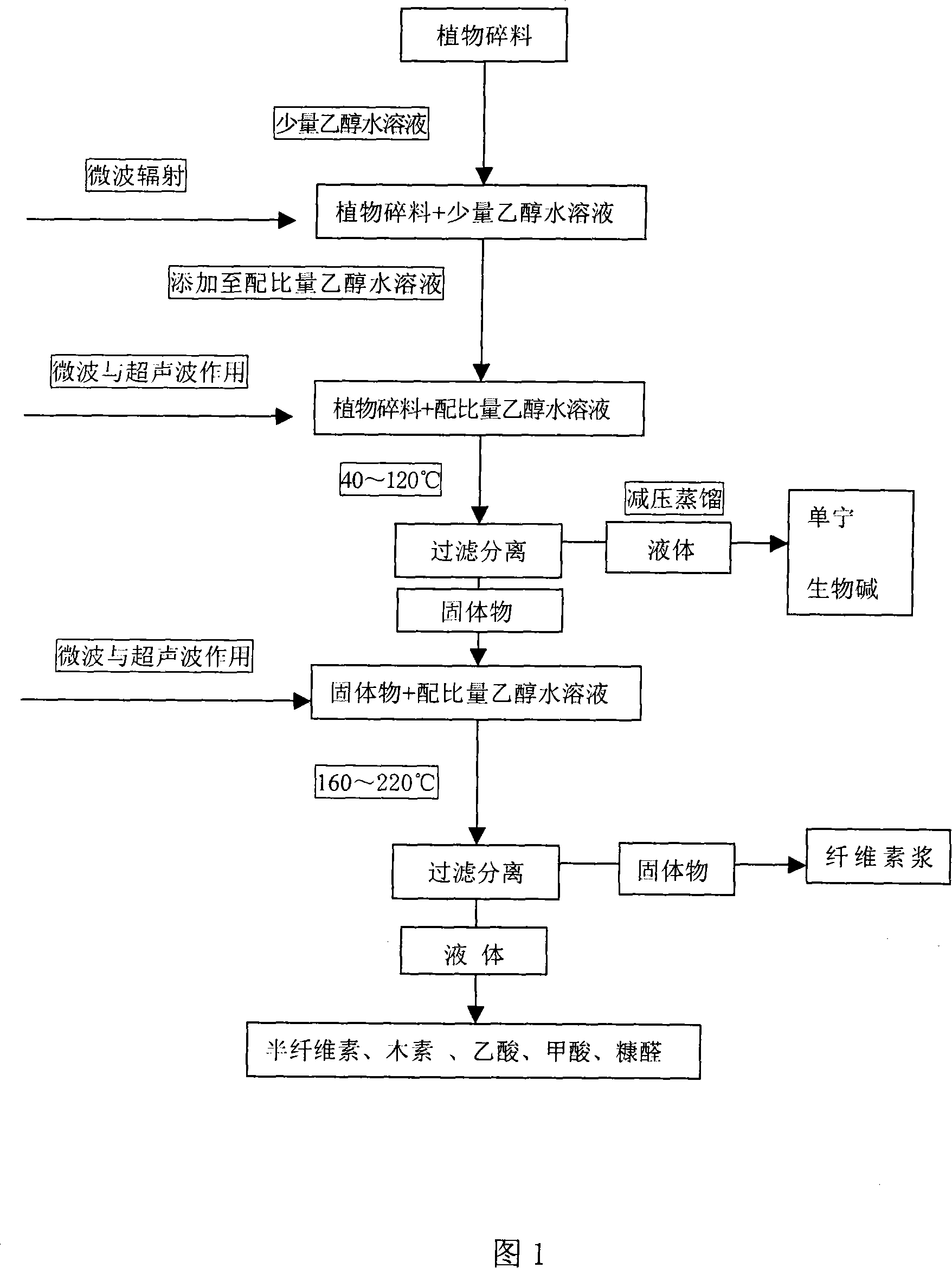
This invention discloses a method for separating biomass organic components. The method comprises: washing classified raw materials, decomposing in a high-pressure reactor under the actions of microwave and ultrasonic wave, and extracting organic components from biomass with 20-70 vol. % aqueous solution of an organic solvent. The separation process comprises: (1) extracting low-temperature-soluble organic component from biomass at 40-120 deg.C under 0.4-0.6 MPa; (2) separating cellulose pulp at 160-220 deg.C; (3) separating acetic acid, lignin and furfural from the liquid (separated by solid-liquid separation) by centrifuge and precipitation. According to different plants, the powers and frequencies of microwave and ultrasonic wave, as well as the reaction temperature and time can be adjusted. The method has such advantages as low organic molecule loss, little change, no harm of the products, high cellulose purity (higher than 95%), low lignin residue (not higher than 2%), and no environmental pollution.
Owner:贾海涛
Cellulose solution and preparation thereof thereof
A cellulose solution containing components as follow: cellulose, which is 7.0%-30.0% of weight of cellulose solution, other components of are imidazolium ionic liquid which can dissolve cellulose and organic solvent mutual soluble with the imidazolium ionic liquid, with a weight ratio ranging from 1:9 to 24:1. The aforementioned cellulose solution is prepared by: mixing cellulose pulp with other components, preparing uniform cellulose solution by steps of heating, stirring, kneading, and vacuumizing. The cellulose solution prepared by aforementioned method can reduce hardness in process, relieving abrasion of apparatus, and the prepared solution is high in concentration, stable and hard to degrade. And cost can be reduced, suitable for industrialization.
Owner:CHINESE TEXTILE ACAD
Recording media, recording media-ink set, inkjet recording method and inkjet recording apparatus
ActiveUS20090291213A1Excellent in density and gloss and image reliabilityClose to commercial printed matterMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsRefractive indexCellulose pulp
To provide an inkjet recording method including: flying ink by application of stimulation to the ink to form an image on a recording media, wherein the recording media has at least one barrier layer of 10 m or less in thickness on at least one surface of a substrate comprising a cellulose pulp, the barrier layer contains 30% by mass or more of an inorganic pigment with a refraction index of 1.5 or less other than alumina, and the content of pigment with a refraction index of less than 1.5 in the barrier layer is 10% by mass or less, wherein the ink contains either a pigment or colored fine particle as coloring material, and a coloring material fixing constituent, and the surface tension of the ink is 25 mN / m or less, and the total amount of the ink on the recording media is 15 g / m2 or less.
Owner:RICOH KK
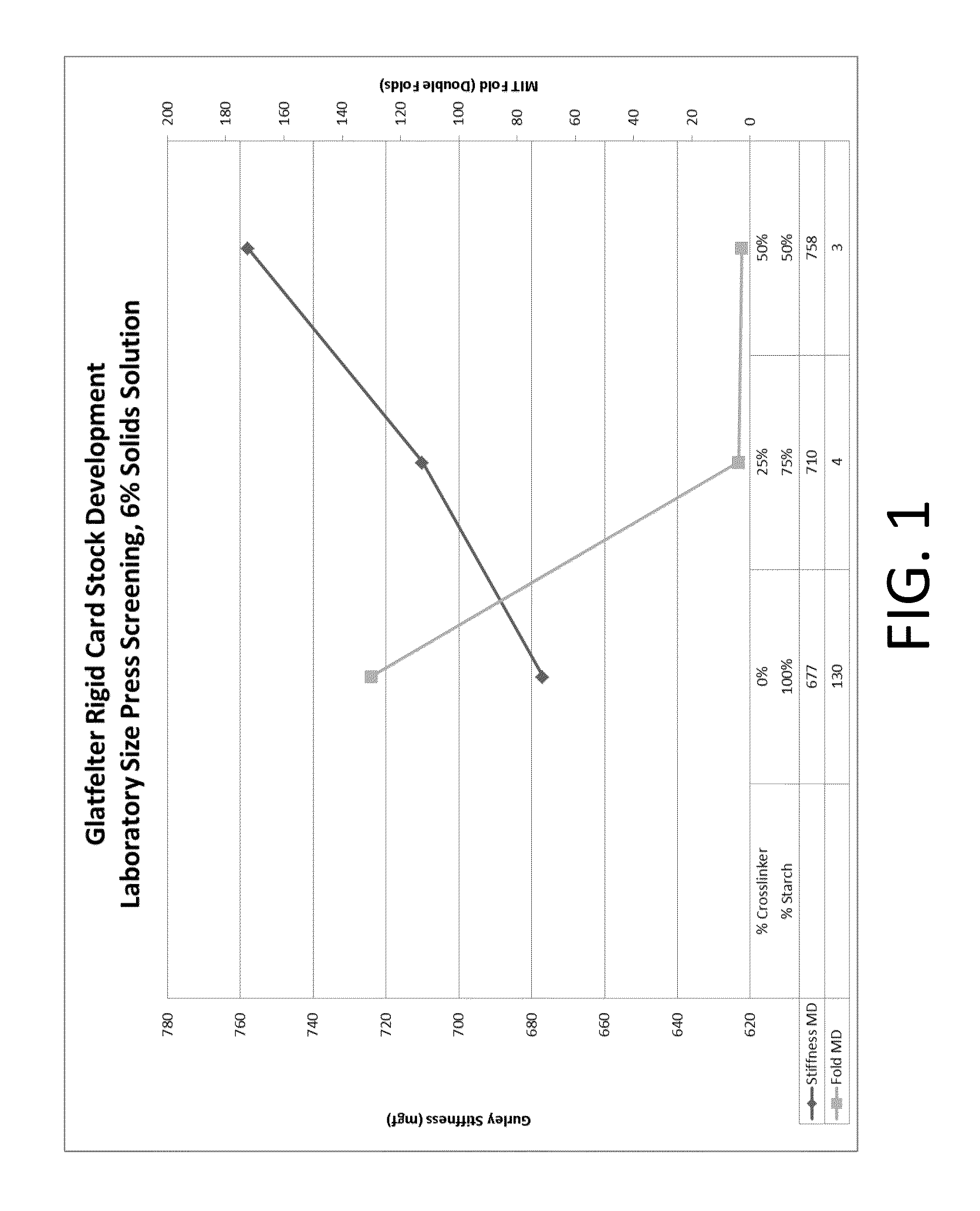
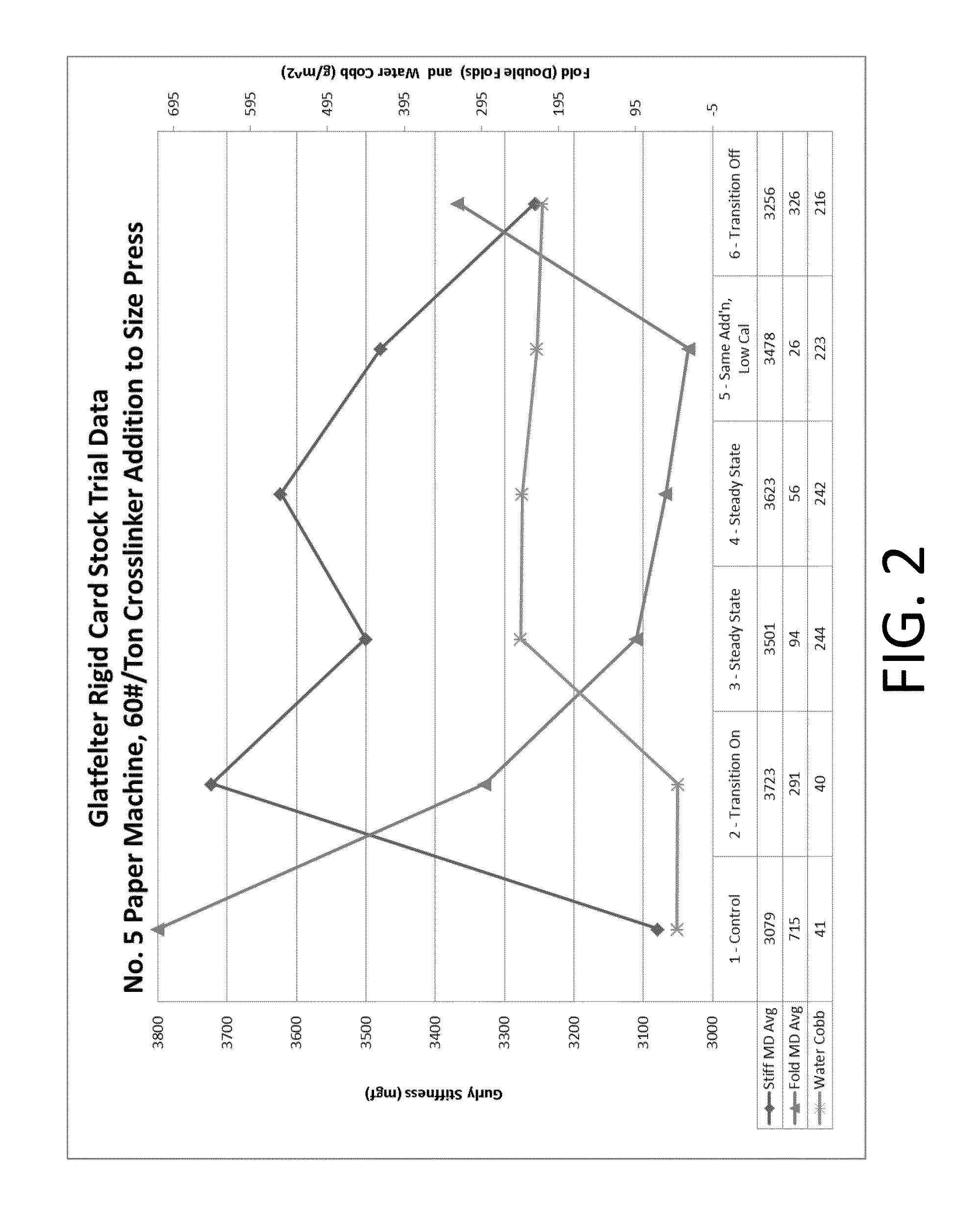
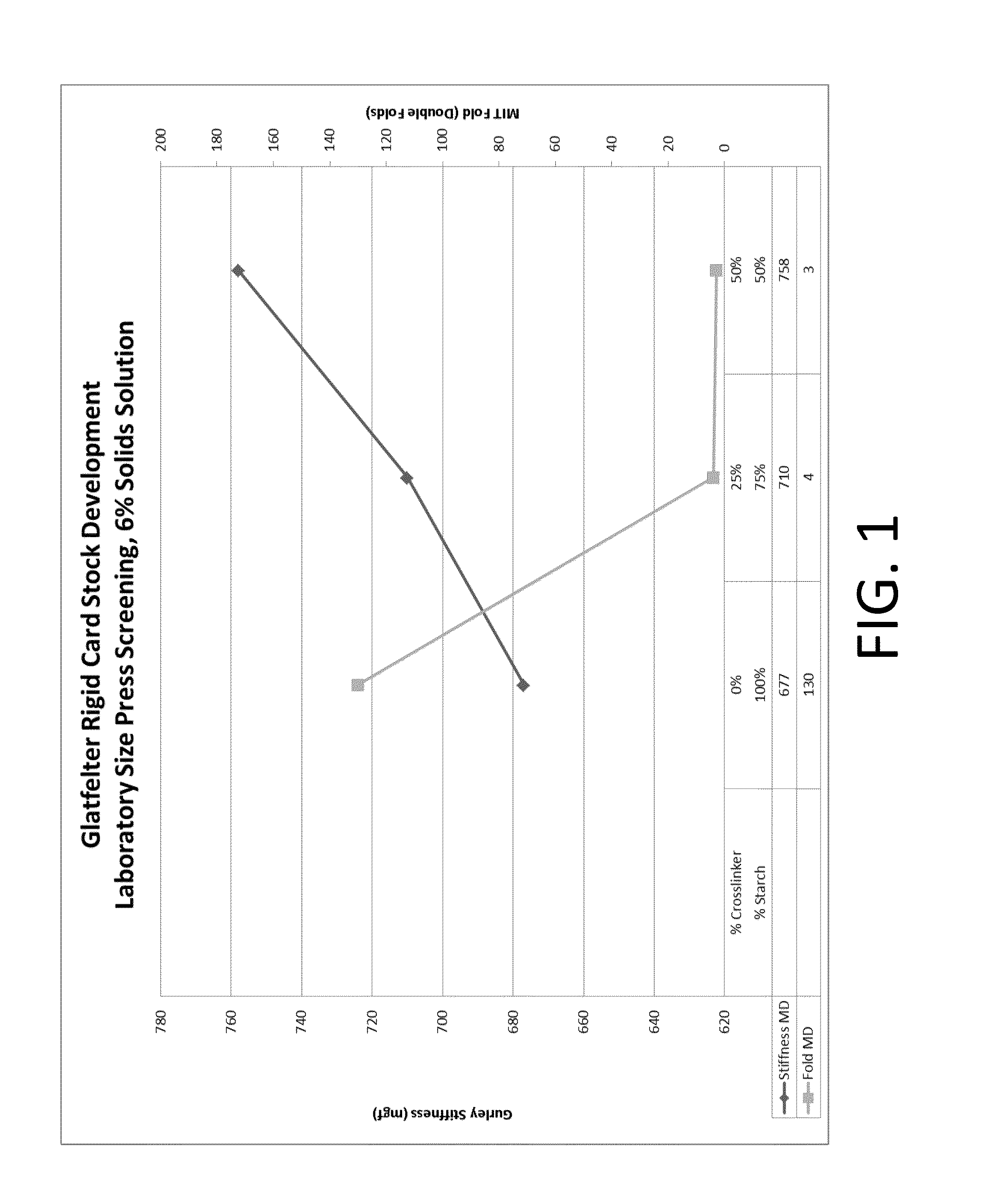
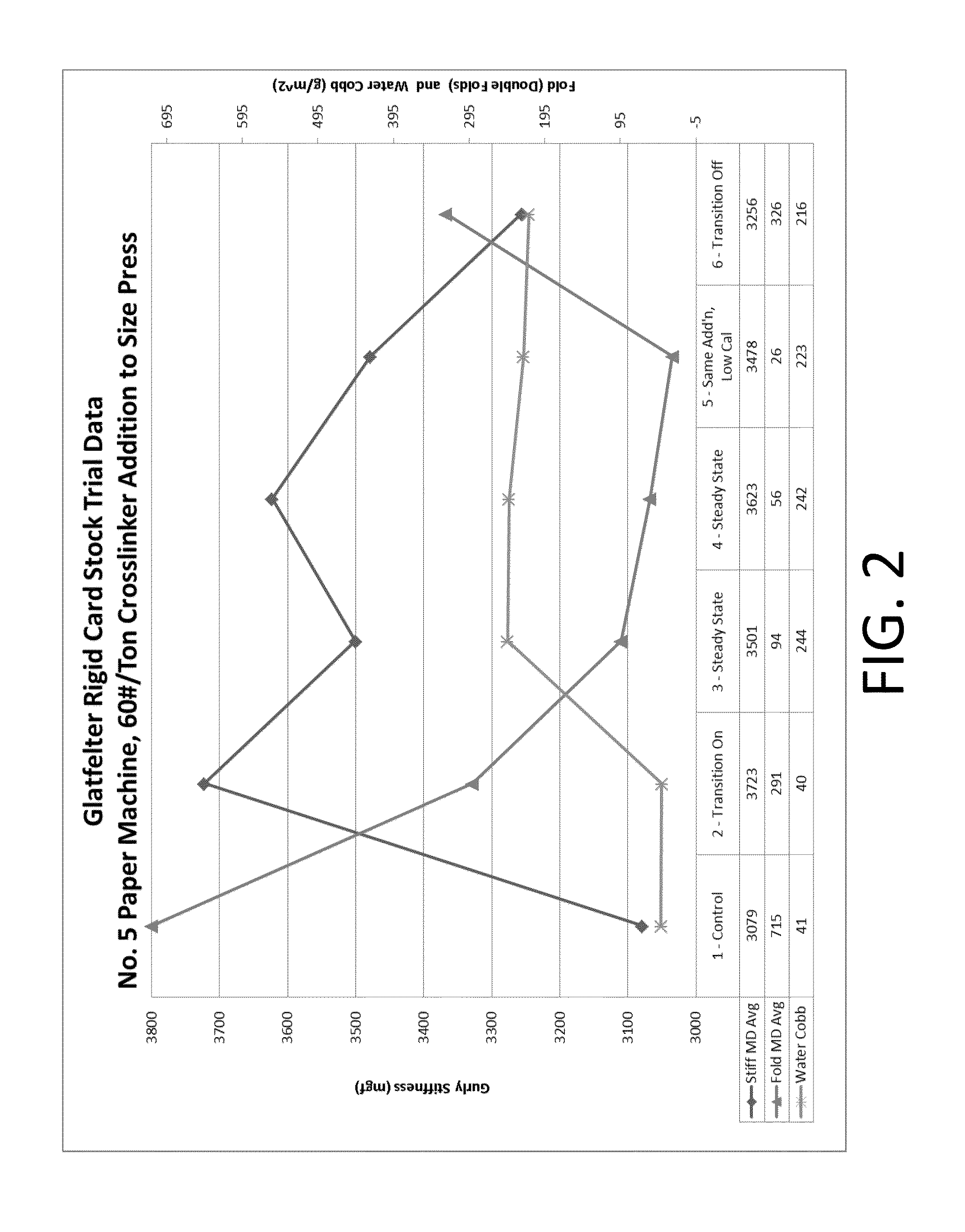
Process for making a stiffened paper
ActiveUS9133583B2Improve mechanical propertiesIncreased stiffness and rigidityNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingSlurry
Owner:PIXELLE SPECIALTY SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Process for making a stiffened paper
ActiveUS20130284388A1Improve mechanical propertiesIncrease stiffnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingSlurry
A process for making a stiffened and rigid paper includes preparing a pulp slurry consisting essentially of water, a cellulosic pulp, a crosslinker, and a starch, and optionally a binder; draining the liquid from the pulp slurry to form a web; and drying the web. Alternatively, a process for making a stiffened and rigid paper includes the step of adding at least one crosslinker at one or more locations, such as at the wet-end, dry-end, or at both ends of the papermaking process. Suitable crosslinkers include a glyoxal-containing crosslinker, a gluteraldehyde, a polyfunctional aziridine, a zirconium-containing crosslinker, a titanium-containing crosslinker, and an epichlorohydrin, and mixtures thereof. When a binder is employed, it can be added either in the dry or wet form. Provided is a neutral or alkaline process to produce a paper product having the improved mechanical properties of a laminated product in the Z-direction, without a lamination step.
Owner:PIXELLE SPECIALTY SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Manufacture of cellulosic pulp sheets
InactiveUS20150027651A1Natural cellulose pulp/paperPulp properties modificationEthylene HomopolymersWater soluble
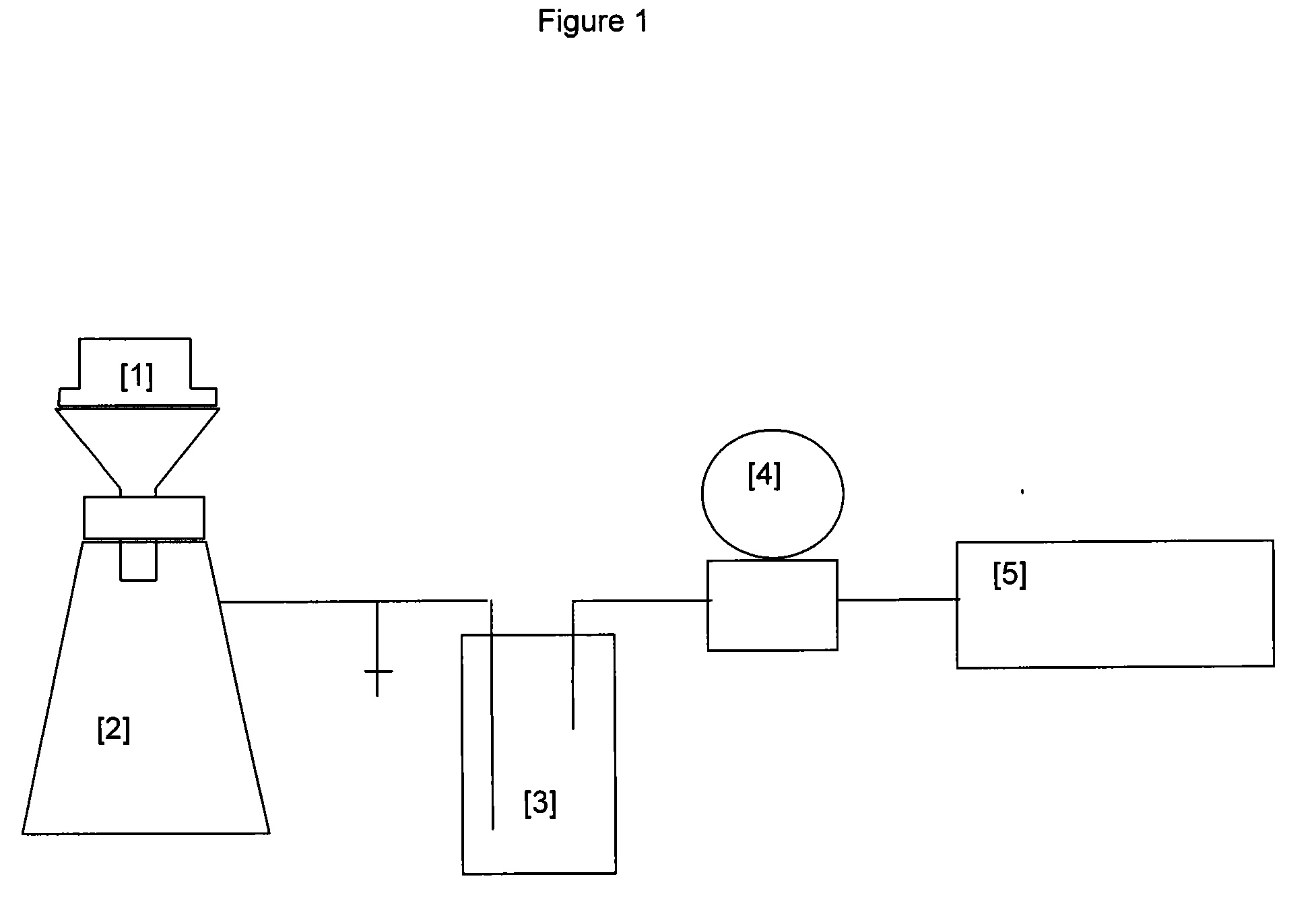
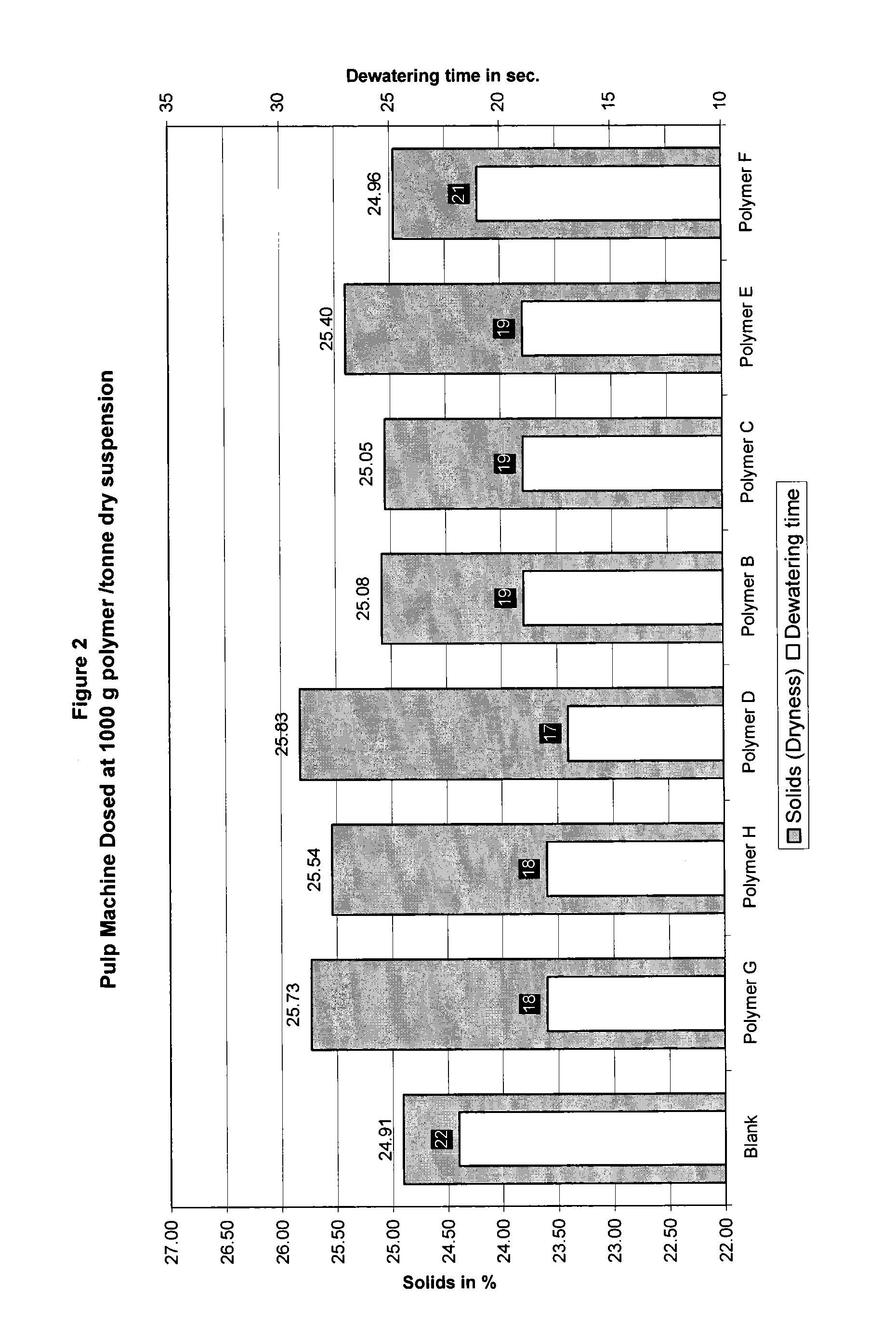
A pulp making process in which fibrous cellulosic material is pulped to form an aqueous suspension of cellulosic material, the suspension is drained through a screen to form a pulp sheet and that the pulp sheet is dried to form a dry market pulp, in which a water soluble cationic polymer is added to the suspension as the sole drainage aid wherein the water-soluble cationic polymer is either,i) a copolymer comprising (a) between 1 and 70 mole % (meth) acrylamide and (b) between 30 and 99 mole % (meth) acryloyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride with an intrinsic viscosity between 5 and 9 dl / g; orii) a hydrolysed homopolymer of vinylformamide comprising between 1 and 100 mole % vinyl amine units and having a K value of between 45 and 240.The process of the invention provides improved drainage time and solids content of the dewatered pulp.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Recording paper and method for recording images using the same
InactiveUS20050107254A1Shrinking and dimensional changeTransmissibilityWater-repelling agents additionDecorative surface effectsCellulose pulpSizing
A recording paper including a substrate which includes cellulose pulp and has a surface treated with a surface sizing solution, wherein the surface sizing solution contains a surface sizing agent and a nonionic surfactant having an HLB in a range of 6 to 13, a content of the nonionic surfactant is in a range of 1 to 100 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the surface sizing agent, and the surface sizing agent has a contact angle with water in a range of 40 to 75°.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Inkjet recording method, inkjet recording medium, and aqueous ink
ActiveUS20100209611A1Easy to printHigh grade printingMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsEmulsionPolymer science
An inkjet recording method including printing an image on a recording medium using an aqueous ink, wherein the recording medium includes a support containing a cellulose pulp, and a coat layer containing a pigment and a binder, and optionally containing a cationic additive in an amount of 0.1% or less in the total amount of the coat layer, which is formed in one or more layers on at least one surface of the support, wherein the recording medium has an outermost layer of the coat layer having a gloss at an angle of 60 degrees in accordance with JIS-ZS-8741 of 13 or less, and a centerline average roughness Ra of 0.2 μm to 2.5 μm at a cut-off value of 0.8 and the aqueous ink contains coloring particles, a resin emulsion, water, and a wetting agent, the aqueous ink has a solid content of 3% by mass or more.
Owner:RICOH KK
Technological process of producing fire retardant antiflux fiber
ActiveCN1847476AHigh strengthGuaranteed alkali resistanceFlame-proof filament manufactureMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCellulose pulpFire retardant
The present invention discloses technological process of producing fire retardant antiflux fiber. The fire retardant antiflux fiber is produced with cellulose pulp as material, and the production process includes the steps of: dipping, squeezing, crushing, ageing, sulfidizing, maturating, spinning, refining and stoving. The refining step includes washing, cross-liking and dewatering and oiling; and in the sulfidizing step, the silicon fire retardant is compounded into solution added into the alkali cellulose through stirring for dissolving and mixing to produce viscose of fire retardant fiber. The fire retardant antiflux fiber of the present invention has high fire retardant antiflux effect, high fiber strength and excellent filtering performance.
Owner:潍坊欣龙生物材料有限公司
Method for dissolving cellulose
The invention discloses a method for dissolving cellulose, characterized by: using at least one from the group consisting of wood pulp, cotton pulp, hemp pulp, bamboo pulp, bagasse pulp, grass fibered pulp, cellulose non-woven fabric or steam exploded cellulose pulp as cellulose raw material, uniformly stirring the cellulose raw material, NaOH and water at a temperature of -15-50 DEG C to obtain a cellulose solution. The prepared cellulose concentrated solution has good spinnability and film forming property. The method breaks through a dissolution method of traditional gluing technology, does not relate to carbon disulfide and other substance causing serious environmental pollution, and is green and environmentally friendly. According to the invention, the cellulose raw material can be directly rapidly dissolved at room temperature, without heating or precooling a solvent. The method has the advantages of saving energy, and reducing energy consumption. By using raw materials having low cost, the method has the advantages of simple operation, small investment, high productivity, and is easy to realize large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Preparation method of bacterial cellulose/polyaniline/graphene film material and application thereof
InactiveCN105175761AImprove stabilityImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesFiltrationFilm material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bacterial cellulose / polyaniline / graphene film material and application thereof and relates to the preparation method of the film material and application thereof. The invention aims at solving the problems of complex preparation process, high cost and poor stability and mechanical property of an existing flexible electrode material. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: preparing bacterial cellulose pulp; preparing a polyaniline-graphene compound material solution, carrying out vacuum filtration on the bacterial cellulose to form a film, then adding the polyaniline-graphene compound material solution, continuously carrying out filtration and drying, and preparing the bacterial cellulose / polyaniline / graphene film material for the application in a supercapacitor. The bacterial cellulose / polyaniline / graphene film material has the advantages that large-scale production can be achieved; the preparation process is simple; the cost is low; the stability and the mechanical property of the conducting film material are good, and the prepared supercapacitor has good capacitive character. The invention belongs to the technical field of nano materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing luminous Lyocell fibre
InactiveCN101298705AHigh recovery rateNo pollutionArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsLuminescent compositionsNon toxicityAntioxidant
The invention relates to a luminescent Lyocell fiber preparation method. The method includes the following steps: a rare-earth luminescent material and micro antioxidants occupying 1 to 20 percent of a fibrin pulp weight are added into NMMO water solution, and suspension is obtained after ultrasonic dispersing and mechanical stirring; the suspension and fibrin pulp occupying 5 to 15 percent of the NMMO weight are arranged into a reaction kettle, the mixture is swelled for 0.5 to 5 hours under temperature of 90 to 120 DEG C and a vacuum degree of minus 0.1 to minus 0.06 MPa, and then the mixture is stirred mechanically for dissolving to obtain a spinning stock-solution; then the spinning stock-solution is delivered to a spinning machine to obtain the required fiber through a dry-wet spinning process. The prepared fiber takes the fibrin fiber as a basic material and the fibrin is provided with hydrophilic hydroxide radical which can integrate with the rare-earth luminescent material in the fiber, and the fiber cannot be dropped off after washing with long service life. The solvent of the invention has the advantages to of non-toxicity and high-recycling rate and the fibrin fiber can be degraded without contamination to environment.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Cellulosic fibre composition
InactiveCN102971462AEasy to prepareWithout significant loss of qualityWood working apparatusPaper/cardboardChemical treatmentNitroxyl radicals
The invention relates to a composition comprising cellulosic fibres having an average degree of substitution of anionic groups of from 0.001 to 0.25, and DEG a length weighted mean fibre length up to 1,100 [mu]m and a length weighted mean fibre width over 10 [mu]m, or DEG a length weighted mean fibre length up to 1,100 [mu]m, and wherein at least 50 % by weight of the cellulosic material is insoluble in water, or DEG a length weighted mean fibre length / width ratio up to 30, or DEG a length weighted mean fibre width over 35 [mu]m. The invention also relates to a composition comprising cellulosic fibres having a specific surface area of at least 1.5 m2 / g, a length weighted mean fibre length / width ratio up to 30, and a dry solids content of at least 5 % by weight, based on the weight of the composition, or up to 30 % by weight, based on the total weight of the cellulosic fibres, of cellulosic fibres with a length weighted mean fibre length up to 100 [mu]m. Method of producing a composition comprising cellulosic fibres which comprises subjecting cellulosic fibres to chemical treatment and mechanical treatment, wherein the chemical treatment comprises treating cellulosic fibres with (i) at least one agent containing a carboxyl group, optionally substituted, (ii) at least one oxidant and at least one transition metal, or (iii) at least one nitroxyl radical, and the mechanical treatment comprises subjecting cellulosic fibres to extrusion with a twin-screw extruder or a planetary roller extruder. The invention also relates to a method of producing a composition comprising cellulosic fibres which comprises subjecting cellulosic fibres having an average degree of substitution of anionic groups of from 0.001 to 0.25 to extrusion. The invention also relates to a composition comprising cellulosic fibres obtainable by the methods, a process for producing a cellulosic pulp mixture which comprises mixing the composition with cellulosic pulp, a cellulosic pulp mixture obtainable by the process, and the use of the composition and cellulosic pulp mixture as an additive in the production of paper and board, processes for producing paper and board in which the composition or cellulosic pulp mixture is used, paper and board obtainable by the processes, and various uses of the paper and board.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com