Enhanced co-formed/meltspun fibrous web structure
a co-formed, fiber-based technology, applied in the direction of filament/thread forming, synthetic resin layered products, packaging, etc., can solve the problems of opacity, texture and feel of web material, tensile strength, drape, surface friction, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing the tensile strength, reducing the opacity of the web material, and improving the elasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Definitions
[0034]As used herein, the articles “a” and “an” when used herein, for example, “an anionic surfactant” or “a fiber” is understood to mean one or more of the material that is claimed or described.
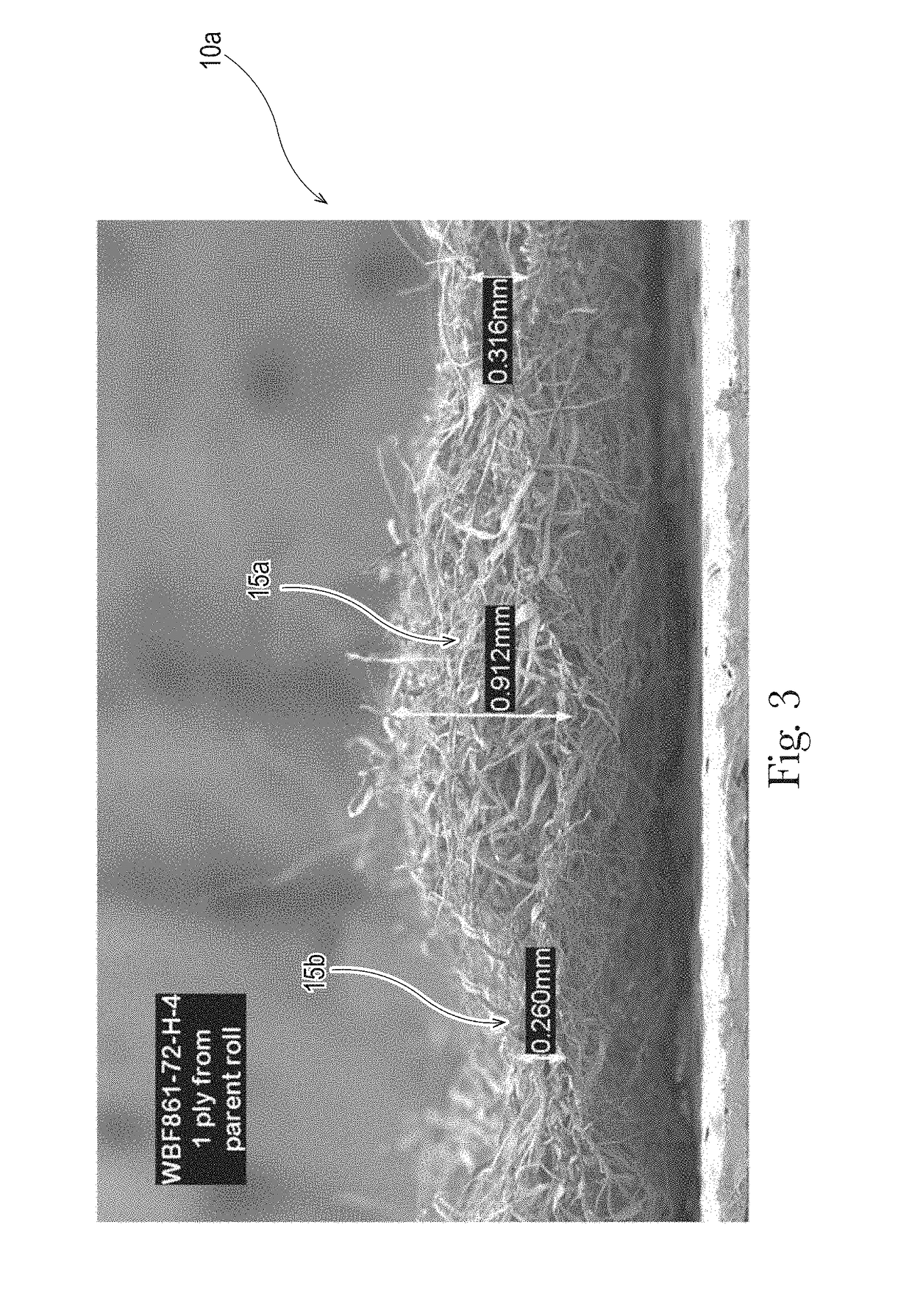
[0035]“Basis Weight” is the weight per unit surface area (in a machine-direction / cross-direction plane) of a sample of web material (on one side), expressed in grams / meter2 (gsm). Basis weight may be specified in manufacturing specifications, and also may be measured, and reflects the weight of the material prior to addition of any liquid composition.
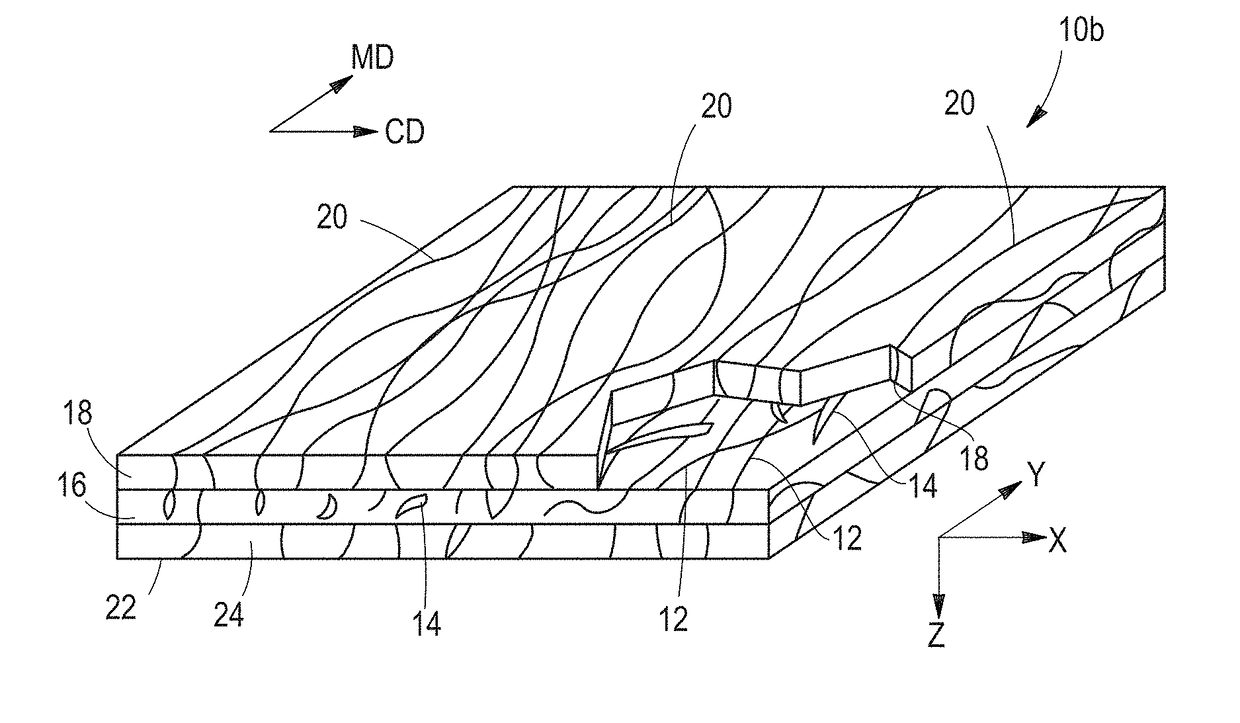
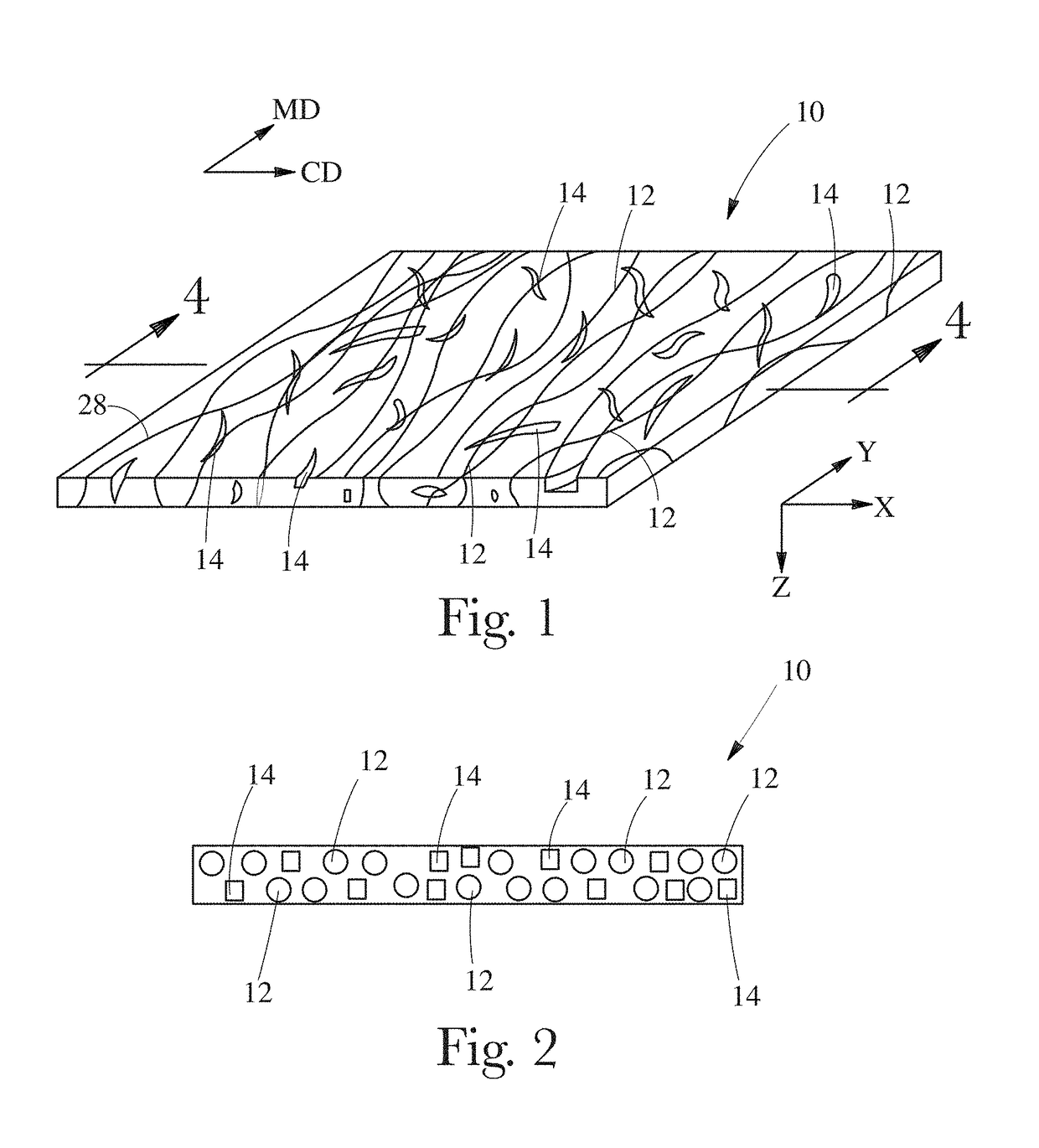
[0036]“Co-formed fibrous web structure” as used herein means that the fibrous web structure comprises an intermixed and / or entangled blend of at least two different materials wherein at least one of the materials comprises filaments, such as spun polymer filament (e.g., filaments spun from polypropylene resin), and at least one other material, different from the first material, comprises fibers. In one example, a co-formed fibrous web...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com