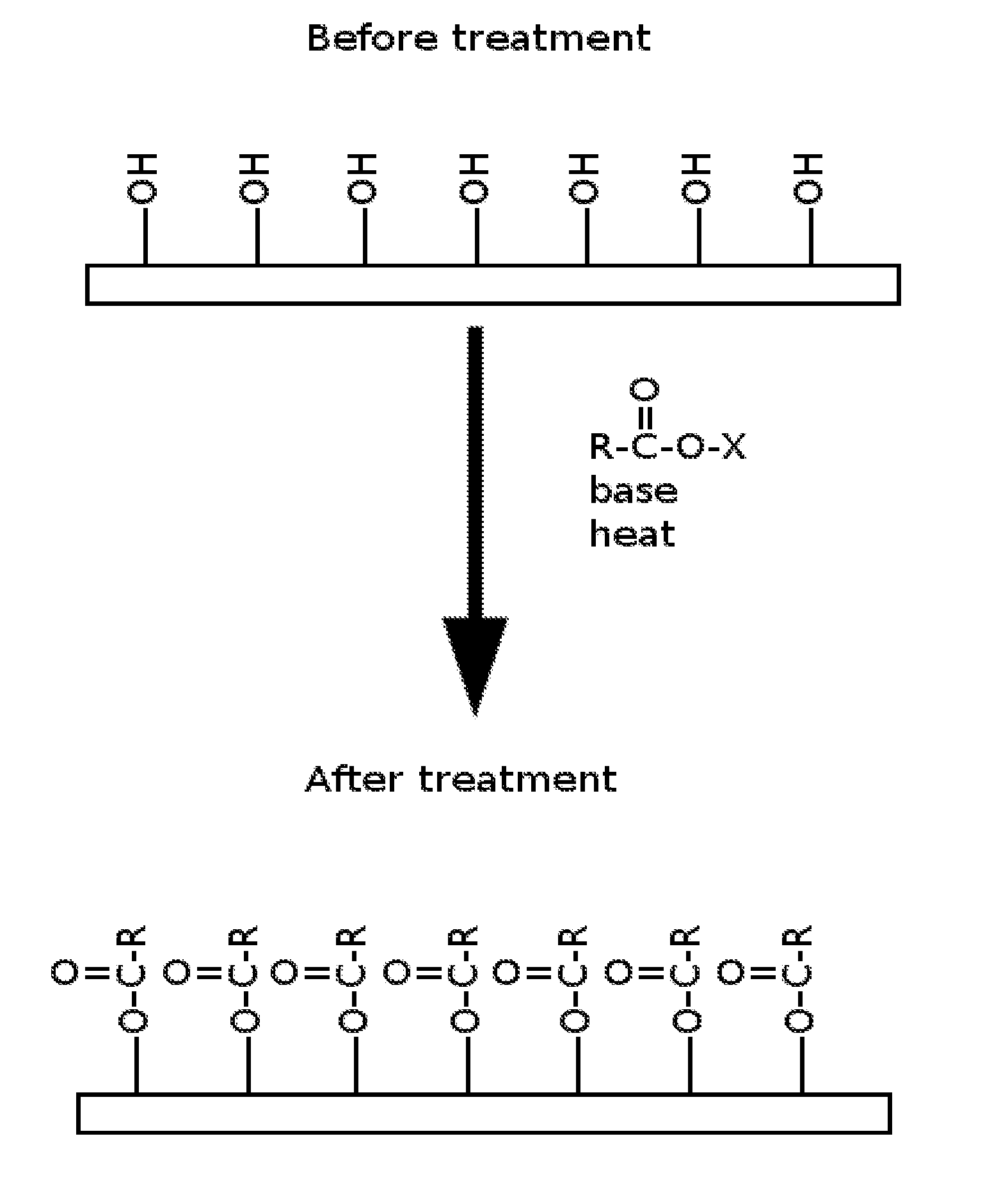
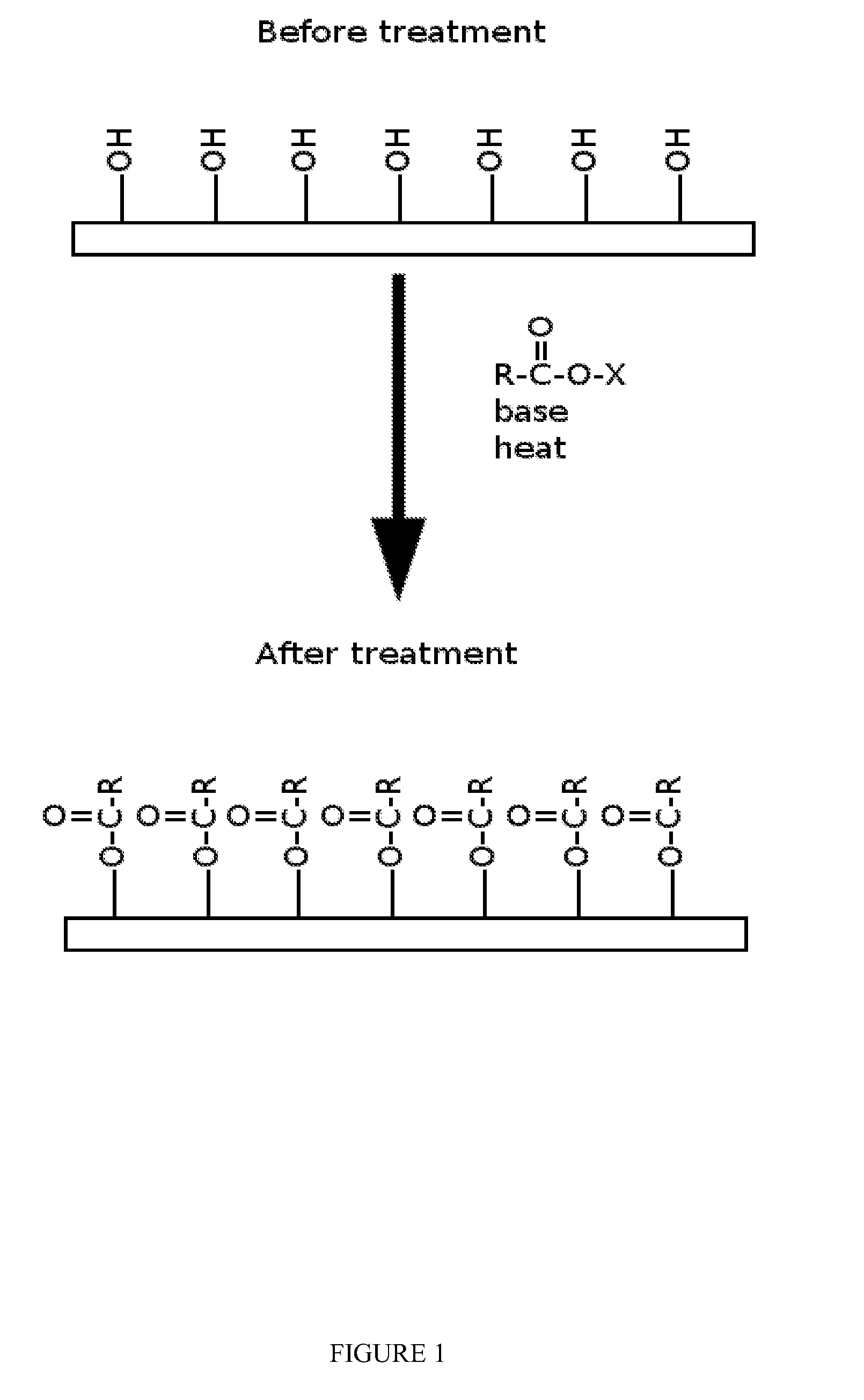
Patents
Literature
898results about "Material mixture addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellulose-reinforced high mineral content products and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20120080156A1Great filler fixationStrengthen and consolidateSpecial paperPaper after-treatmentCelluloseFiber
A method to prepare aqueous furnishes useful as feedstock in the manufacture of very high-mineral content products, particularly paper sheets having mineral filler content up to 90% that display the required physical properties for the intended applications; the furnishes comprise fibrillated long fibres / mineral fillers mixed with anionic acrylic binders and co-additives, in presence or absence of cellulose fibrils; the fibrillated long fibres and cellulose fibrils provide high surface area for greater filler fixation and the reinforcement backbone network that ties all of the product components together; the anionic binders allow rapid and strong fixation of filler particles onto the surfaces of fibrils when mixing is conducted at temperatures higher than the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the binder. The aqueous furnish provides excellent filler retention and drainage during product fabrication.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Enhanced surface sizing of paper
Size press compositions and methods for producing sized paper products, including liner board, are disclosed. The size press compositions contain at least one non-reactive cationic surface sizing agent, at least one reactive sizing agent, at least one promoter resin, at least one binder, and water. The at least one non-reactive cationic surface sizing agent may be a polymer in the form of a dispersion, an emulsion or a latex with a positive zeta potential below about pH 6. The at least one reactive sizing agent may be a dispersion, an emulsion or a latex including an alkyl ketene dimer or an alkyl succinic anhydride. The at least one promoter resin may be a polyaminoamide-epichlorohydrin resin or poly (dimethyldiallylammonium chloride).
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Swollen starch-latex compositions for use in papermaking
InactiveUS7074845B2High retention rateEasy to drainPigmenting treatmentNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaperboardPapermaking
A novel filler treatment comprising the preparation of swollen starch-latex compositions, prepared in the presence or absence of co-additives, and the addition of the said composition to a filler suspension, has been developed. Use of the treated filler during papermaking improves filler retention and produces filled papers where addition of the filler has only a minimal negative effect on strength properties. The swollen starch-latex compositions can be prepared in a batch or jet cooker, or by mixing with hot water under controlled conditions (i.e., temperature, pH, mixing, mixing time) in order to make the starch granules swell sufficiently to improve their properties as a filler additive but avoiding excess swelling leading to their rupture. The swollen starch-latex composition is then rapidly mixed with the filler slurry, preferably in a static mixer, and added to the papermaking furnish at a point prior to the headbox of the paper machine. The starch-latex composition can be used with wood-free or wood-containing furnishes. The treated filler is easily retained in the web during papermaking, improves drainage, and gives sheets having good formation. Sheets made with the treated fillers have higher bonding and tensile strengths than sheets produced using filler treated with either swollen starch alone or latex alone. Retention and drainage are further improved when conventional retention aid chemicals are added to the furnish containing the treated filler. The use of swollen starch-latex compositions could allow the papermaker to increase the filler content of the paper without sacrificing dry strength properties or increasing the amount, and hence the cost, of the retention aid added. The combination of swollen starch and latex could be used as furnish additives in the manufacture of both filled grades and grades that contain no filler such as sack papers and paperboard products.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Method for producing furnish, furnish and paper
ActiveUS20120132383A1High filler loadingHigh mechanical strengthSpecial paperPaper after-treatmentCelluloseCardboard
A method for preparing aqueous furnish to be used in paper or paper board manufacturing. Filler and / or fibers are treated with cationic polyelectrolyte and nanofibrillated cellulose. A furnish and a paper or a paper board.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Pulping processes
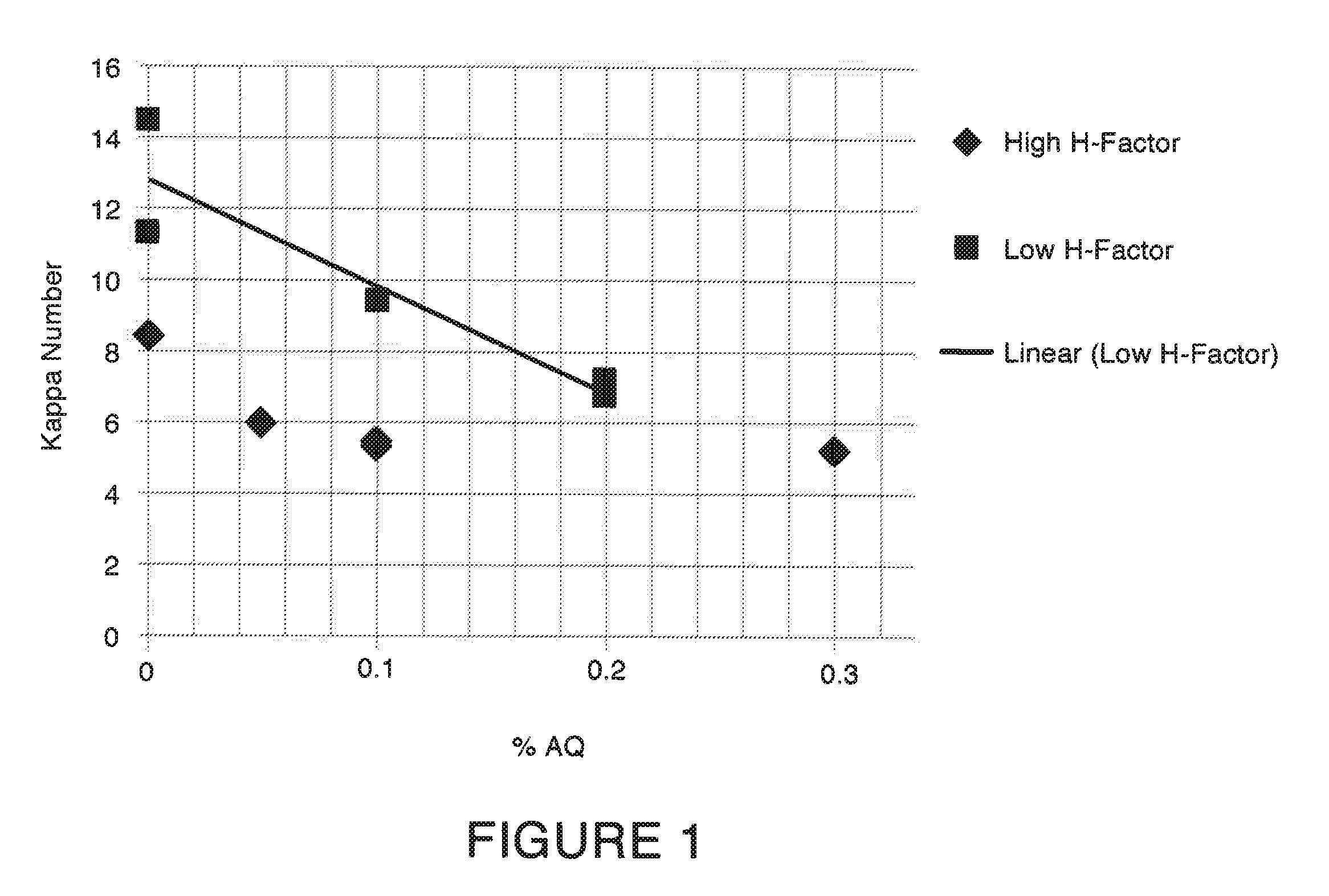
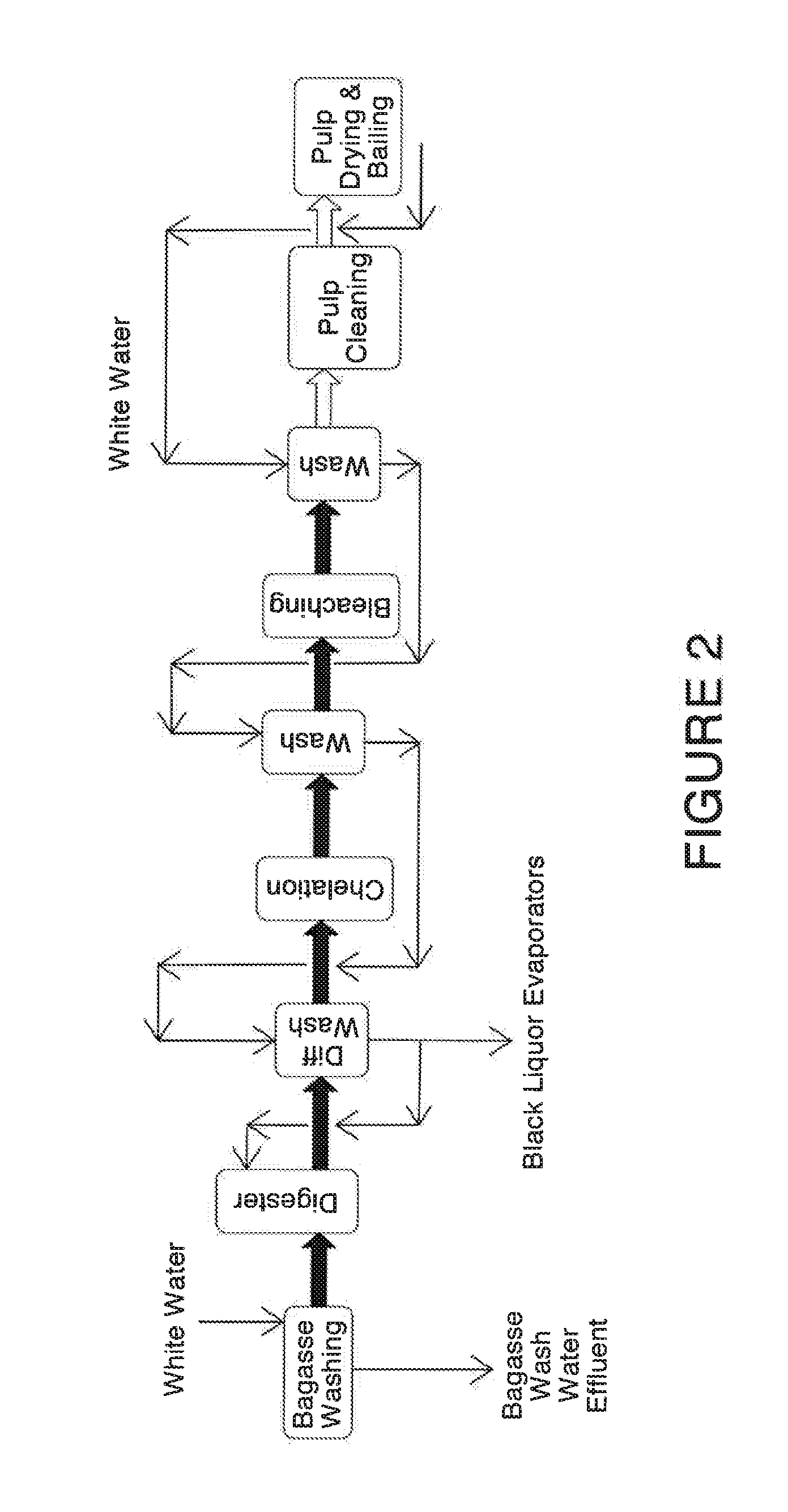
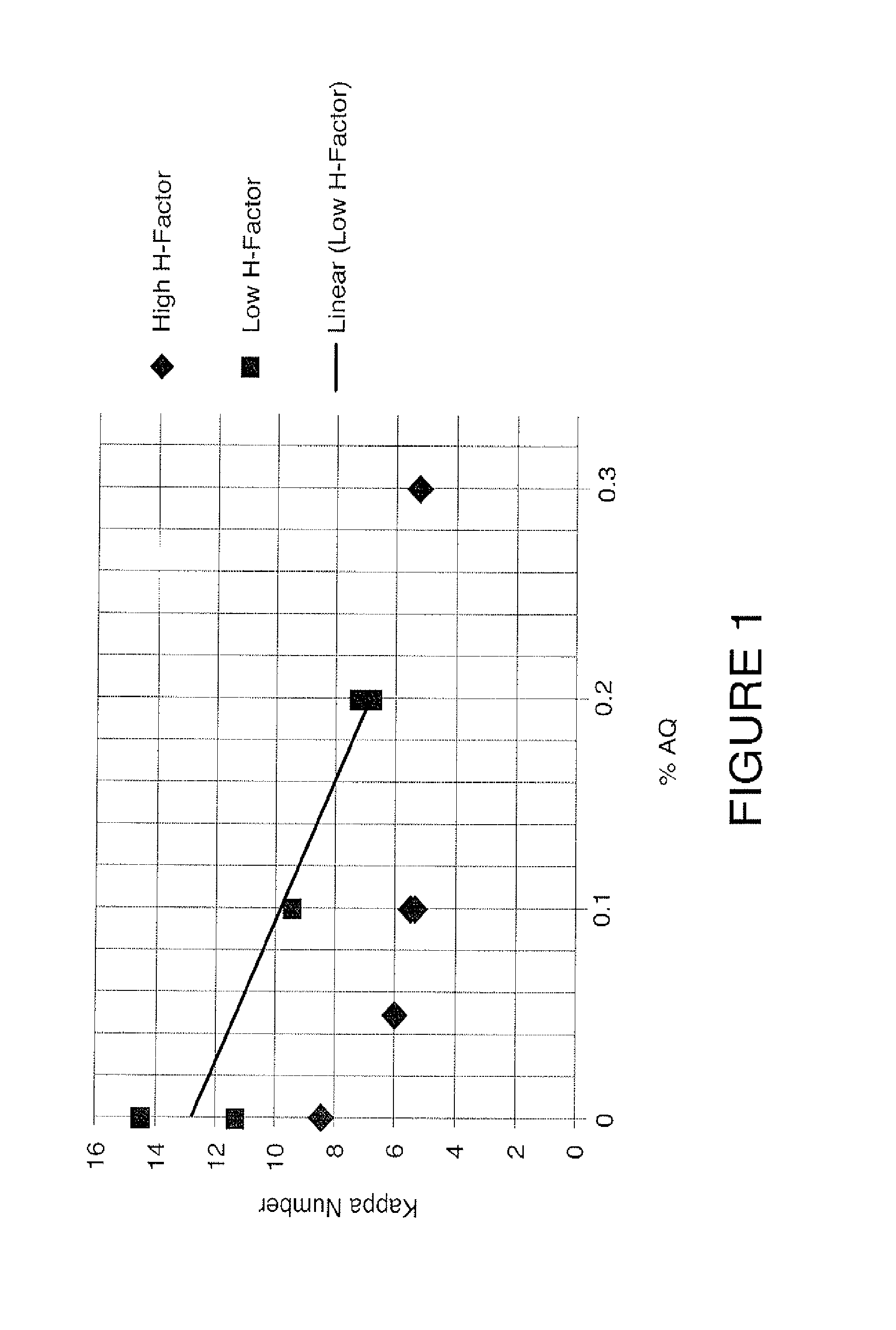
A pulping process comprises using a high concentration of anthraquinone (AQ). The pulping process is capable of providing a pulp having low Kappa number with unexpectedly high strength. The pulping process can use wood or non-wood fibers (e.g., bagasse and corn stover) to provide pulp having good papermaking quality. The method for pulping a fiber comprising cooking a first mixture comprising the fibers, water, an alkali, and a delignification selectivity enhancing chemical for a cooking time and at a cooking condition sufficient to form a first pulp having a desired Kappa number of about 15 or less, and strength parameters that are sufficient for papermaking, where the starting material prior to cooking has a Kappa number of 60 or greater.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Paper softening compositions containing low levels of high molecular weight polymers and soft tissue paper products comprising said compositions
Disclosed is a composition suitable for atomizing without excessive aerosolization in the form of an oil-in-water emulsion comprising: a) a continuous aqueous phase, and b) a discontinuous oil phase wherein the rheology of the aqueous phase is modified by the addition of a water-in-oil emulsion comprising: i) a high molecular weight polymer in a discontinuous aqueous phase, and ii) a continuous organic solvent phase. Preferred embodiments of the present invention relate to compositions for softening an absorbent paper tissue comprising a) a quaternary ammonium softening active ingredient; b) an electrolyte; c) a high molecular weight polymer emulsion comprising: i) from about 20% to about 40% by weight of the premix of a high molecular weight polymer; ii) from about 40% to about 60% of water; and iii) from about 20% to about 40% of an organic solvent; and d) a vehicle in which said softening active ingredient is dispersed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Methods and agents for improving paper printability and strength
InactiveUS20010051687A1Improving printability strengthLess viscousNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCardboardSizing
Compositions containing hydrophilic polyacrylamide and hydrophobic surface size agents and the use of such compositions in paper and board to improve printability, sizing and strength are provided in the instant invention.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Method of increasing filler content in papermaking
ActiveUS20100126684A1Avoid problemsNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingCellulose fiber
The invention provides a method of producing paper with a higher proportion of mineral filler particles than is otherwise be possible without the expected loss in paper strength. The method allows for the use of the greater amount of filler particles by coating at least some of the filler particles with a material that prevents the filler materials form adhering to a strength additive. The strength additive holds the cellulose fibers together tightly and is not wasted on the filler particles. The method is particularly effective when the filler particles are a PCC-GCC blend and when the GCC particles are coated with the adherence preventing coating.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Hydrophobically modified cationic acrylate copolymer/polysiloxane blends and use in tissue
InactiveUS6951598B2Simple structureLow levelNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationFiberVitrification
The present invention is a soft tissue sheet. The tissue sheet comprises papermaking fibers and a polysiloxane composition. The polysiloxane composition comprises a polysiloxane and a compatible synthetic resin binder having a glass transition temperature of about 100° C. or less.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Anionic-cationic polymer blend for surface size
InactiveUS20050022956A1Acceptable resistanceSufficient surface smoothnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCellulosePolymer science
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
Bicomponent strengthening system for paper
InactiveUS20060065380A1Reduce the amount requiredNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperGramPolysaccharide
The present invention is directed to a bicomponent strengthening system and the paper webs produced with the bicomponent strengthening system. Through use of the strengthening system, paper webs may be produced in which the strength characteristics of the web may be specifically tailored. The first component of the system comprises a polymer having at least about 1.5 m-eq primary amine functionality per gram of polymer and a molecular weight of at least about 10,000 Daltons. The second component may be either a polymeric anionic compound or a polymeric aldehyde functional compound. For example, the polyamine polymer component may be a polyvinylamine or polysaccharide having primary amine functionality. In one embodiment, the second component may be a cationic polymeric aldehyde functional compound. For example, the second component may be a cationic glyoxylated polyacrylamide. In another embodiment, the second component may be a polymeric anionic compound comprising carboxy functionality.
Owner:GARNIER GIL B D +6
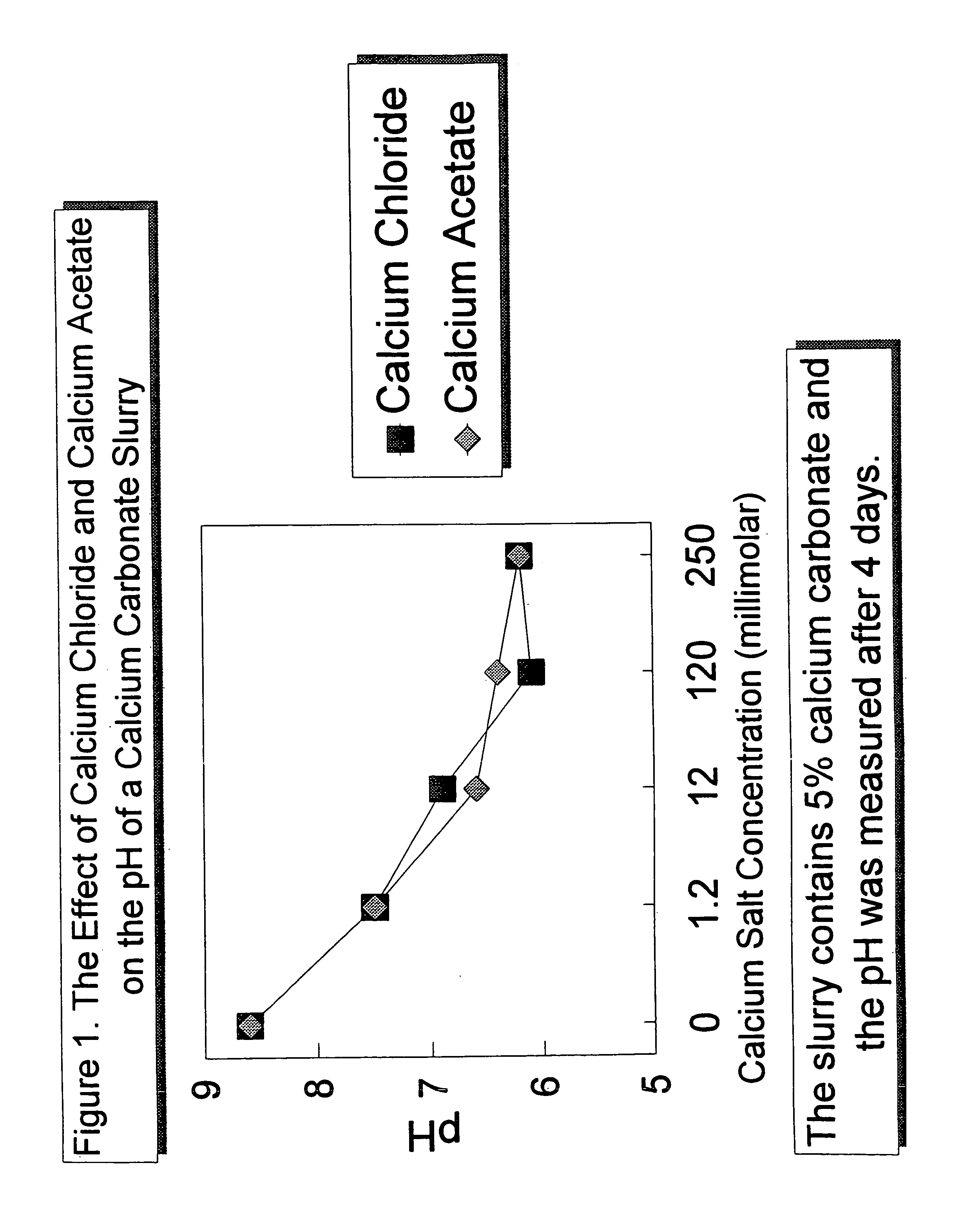
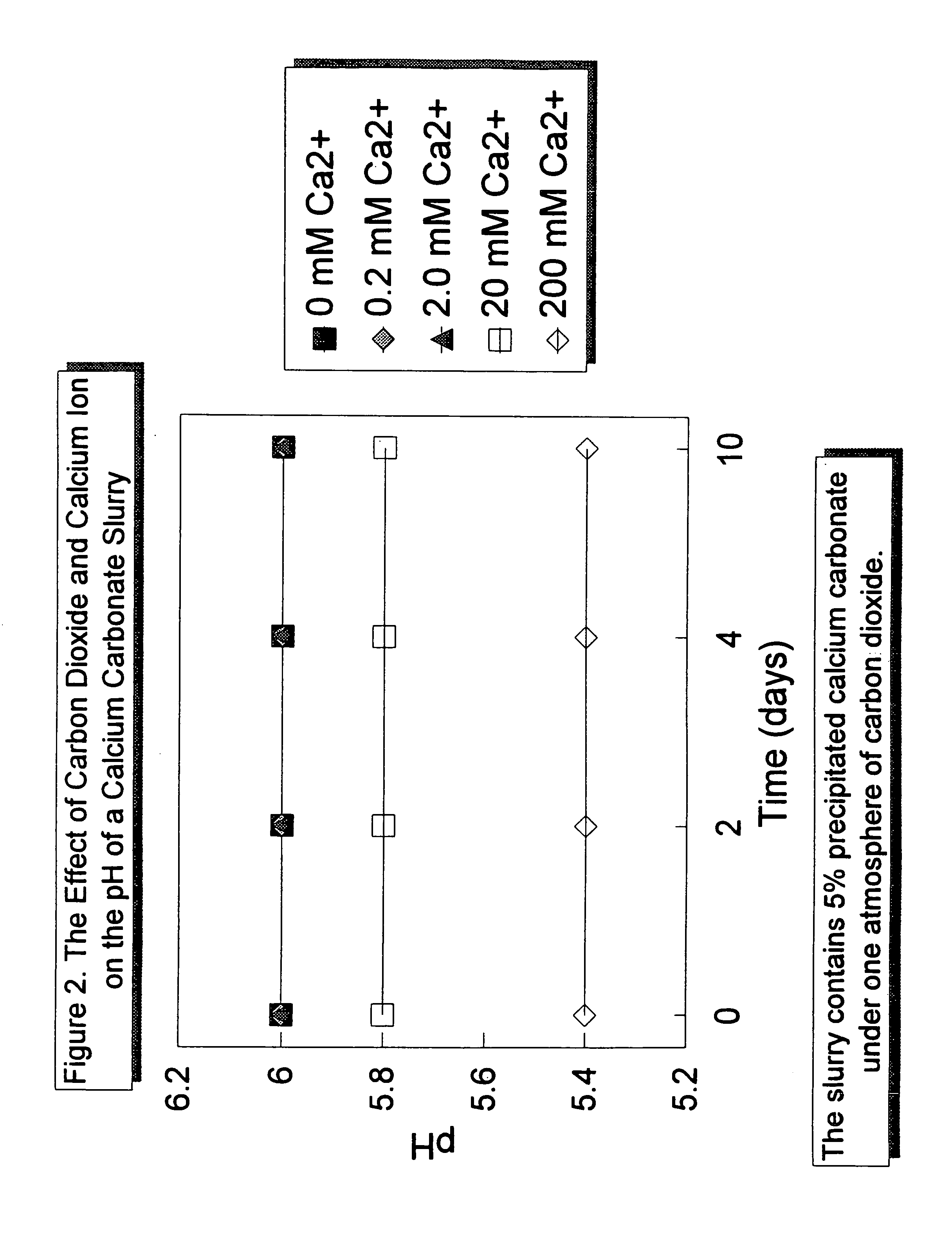
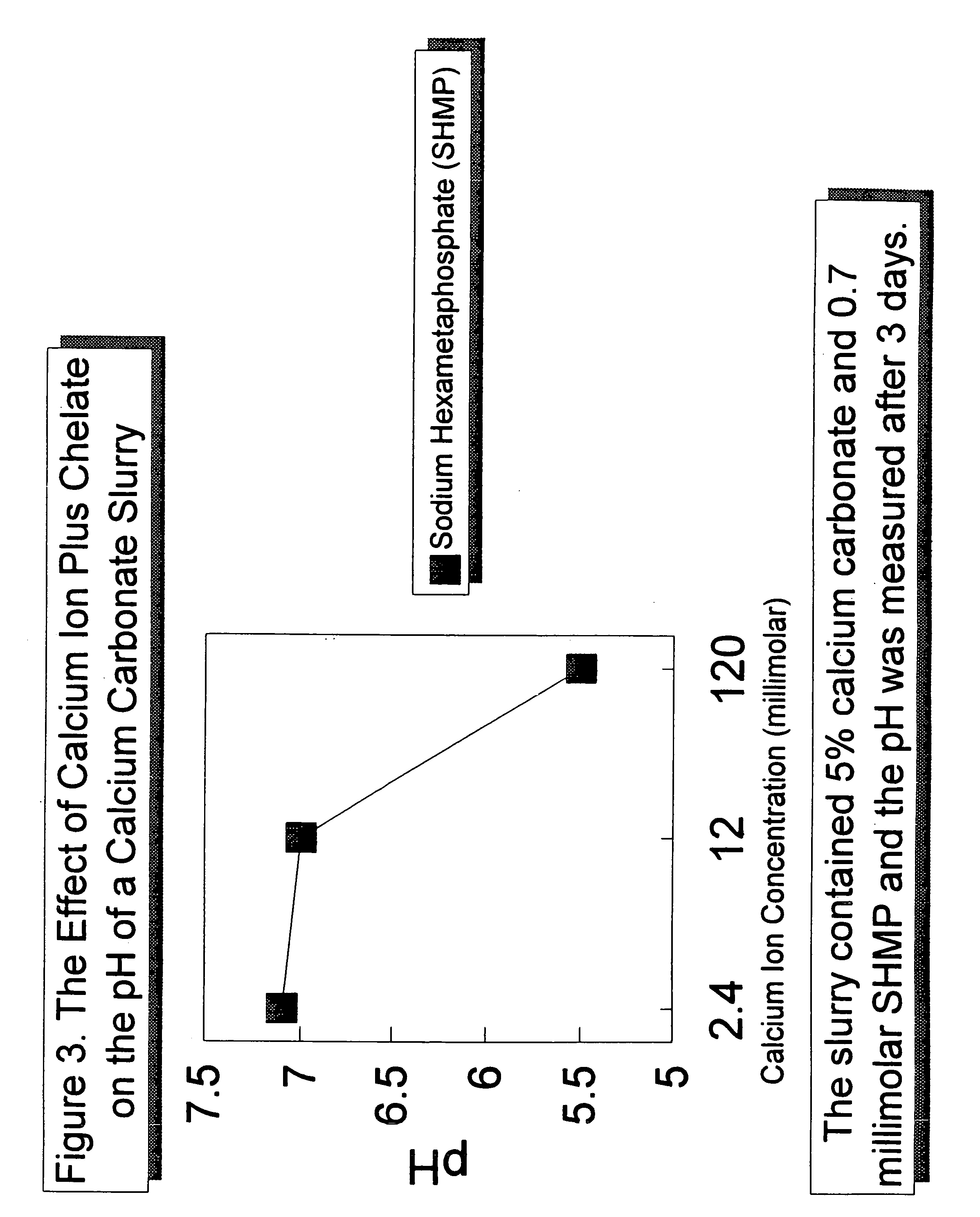
Acid stabilized calcium carbonate an method of making it
InactiveUS7033428B2Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentPrecipitated calcium carbonateWater soluble
The present invention relates to an acid-stabilized calcium carbonate slurry having a pH of less than 7, preferably between about 6 and about 7, containing water, calcium carbonate, preferably precipitated calcium carbonate, and an acid-stabilizer of a water soluble calcium salt, a weak acid, a chelating agent, a weak acid capable of chelating calcium ion, or a mixture thereof. The acid-stabilizer is present in an amount sufficient to provide an aqueous calcium carbonate slurry having an increased calcium ion concentration and an acidic pH. In a typical acid-stabilized calcium carbonate slurry of the invention, the acid-stabilizer is present in an amount sufficient to provide a calcium ion concentration of about 1 millimolar to about 5 molar, preferably from about 1 to about 120 millimolar. The invention also relates to a method of making the acid-stabilized calcium carbonate slurry of the invention, to a method of forming a filled paper, that includes the step of adding the acid-stabilized calcium carbonate slurry of the invention to a papermaking pulp in a process for making acid paper, and to a filled paper produced according to the method of the invention.
Owner:MINERALS TECH
Paper substrates useful in wallboard tape applications
ActiveUS20060191656A1Natural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPulp and paper industryCellulose fiber
This invention relates to paper products and / or substrates suitable for being made and / or converted into wallboard tape; which also may be known as joint tape and / or drywall tape, having a pH of at least 7.0 and containing a plurality of cellulose fibers, a wet strength additive, an alkaline sizing agent, and an anionic promoter, as well as methods of making and using the same.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Paper or board treating composition of carboxylated surface size and polyacrylamide
InactiveUS6034181ALess viscousEasy to handleWater-repelling agents additionDuplicating/marking methodsCardboardMeth-
A composition used in paper and board making comprises a carboxylated surface size containing at least 40 mole percent of hydrophobic groups such as styrene / (meth)acrylic acid copolymers or styrene / maleic acid (anhydride or salt) copolymers, and a hydophilic polyacrylamide.
Owner:CYTEC +2
Paper articles exhibiting water resistance and method for making same
This invention relates to a process for preparing sized paper and paperboard which incorporates in the paper and paperboard at the size press size a composition comprising one or more “hydrophobic polymers” wherein hydrophobic polymers, the amount of such polymers and the weight ratio of starch to such polymer in the composition are selected such that the paper and paper board exhibits a Cobb Value equal to or less than about 25 and to a sized paper or paperboard web formed by the process.
Owner:INT PAPER CO +1
Paper or board with surface of carboxylated surface size and polyacrylamide
InactiveUS6494990B2Improving printability strengthLess viscousNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCardboardPolymer science
A paper or board is coated with a composition comprising from 30-95 parts by weight of a synthetic, carboxylated surface size containing at least about 40 mole percent of hydrophobic groups and at least about 25 mole percent of carboxylated groups such as styrene / acrylic acid copolymer, and from 5-70 parts by weight of a substantially hydrophilic polyacrylamide such as a cationic or anionic polyacrylamide.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Filler for papermaking process
The present invention relates to a filler comprising calcium salt and cellulose derivative having a degree of substitution of net ionic groups up to about 0.65, wherein the filler is substantially free from fibres or fibrils of cellulose or lignocellulose. The invention also relates to a filler comprising calcium salt and a cellulose derivative having a degree of substitution of net ionic groups up to about 0.65, wherein the cellulose derivative contains cationic groups.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL PULP & PERFORMANCE CHEM
Articles of manufacture made from pulp composition
InactiveUS20140205777A1Strength parameter sufficientSynthetic resin layered productsPulp bleachingFiberKappa number
One aspect of the invention relates to an article of manufacture made from a pulp composition comprising an ARF pulp. In one embodiment, the pulp composition made from agricultural renewable fibers (ARF) having low Kappa number with unexpected quality sufficient for papermaking (e.g., high strength parameters and high freeness). In another embodiment, the ARF pulp has ISO brightness of 60% or higher, and unexpected quality sufficient for papermaking (e.g. high strength.parameters and high freeness). In another embodiment, the ARF pulp is made from a pulping process comprising using a high concentration of anthraquinone (AQ).
Owner:CARGILL INC
Gypsum board suitable for wet or humid areas
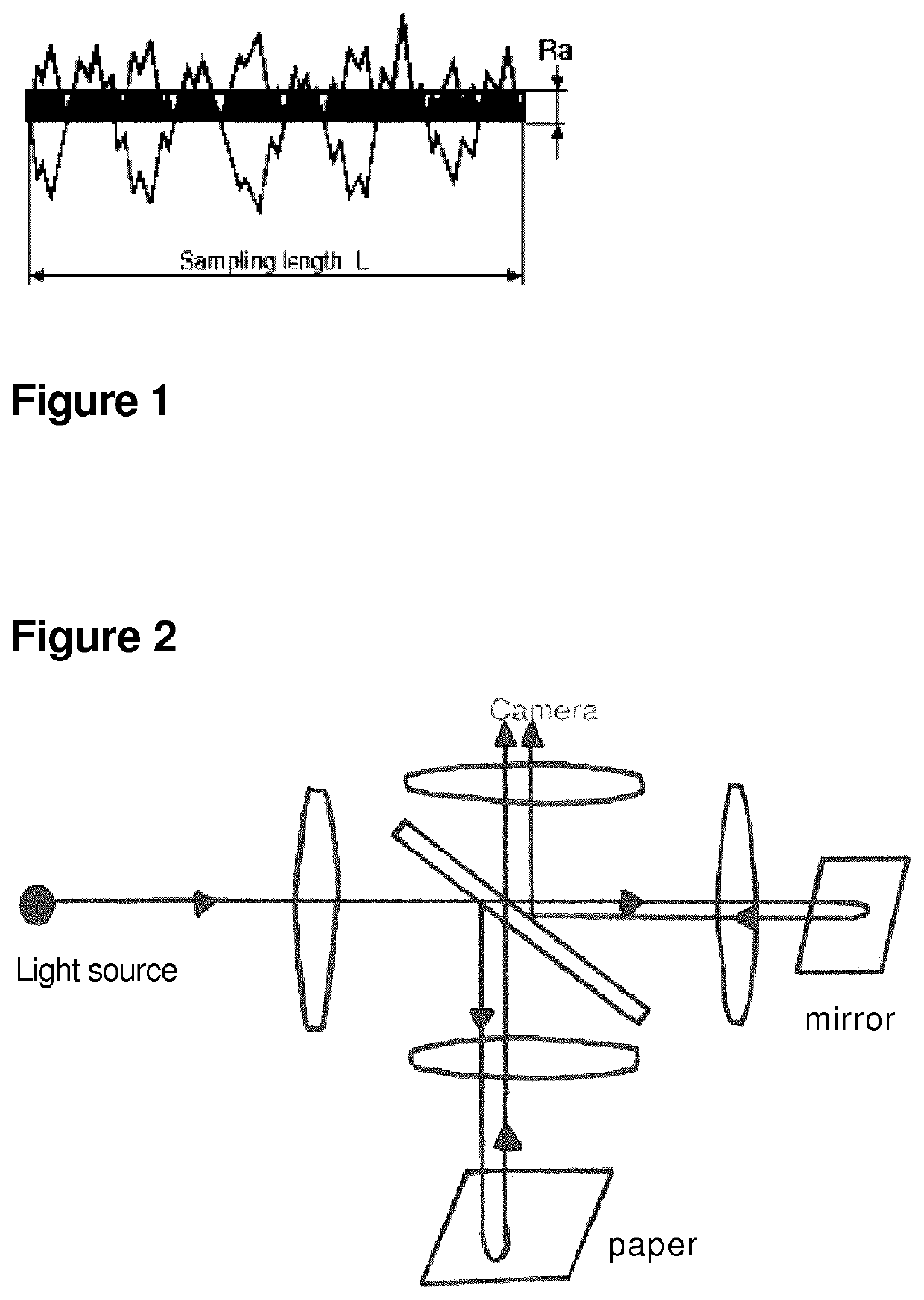
ActiveUS10662648B2High leveling propertyConstruction materialWater-repelling agents additionSurface roughnessEngineering
Gypsum board having a core, said core having at least one side covered with a non-woven fabric; characterized in that the inner side of the non-woven fabric, which is in contact with the core of the gypsum board, has a surface roughness Ra of from 25 to 60 micrometers, preferably from 25 to 50 micrometers, advantageously from 25 to 40 micrometers.
Owner:AHLSTROM MUNKSJO OYJ
Methods for biobased derivatization of cellulosic surfaces
ActiveUS20180066073A1Generate/increase wet strengthHigh strengthFlexible coversWrappersCelluloseDerivatization
The present invention describes tunable methods of treating cellulosic materials with a composition that provides increased hydrophobicity and / or lipophobicity to such materials without sacrificing the biodegradability thereof. The methods as disclosed provide for binding of saccharide fatty acid esters on cellulosic materials, including that the disclosure provides products made by such methods. The materials thus treated display higher hydrophobicity, lipophobicity, barrier function, and mechanical properties, and may be used in any application where such features are desired.
Owner:HS MFG GRP LLC
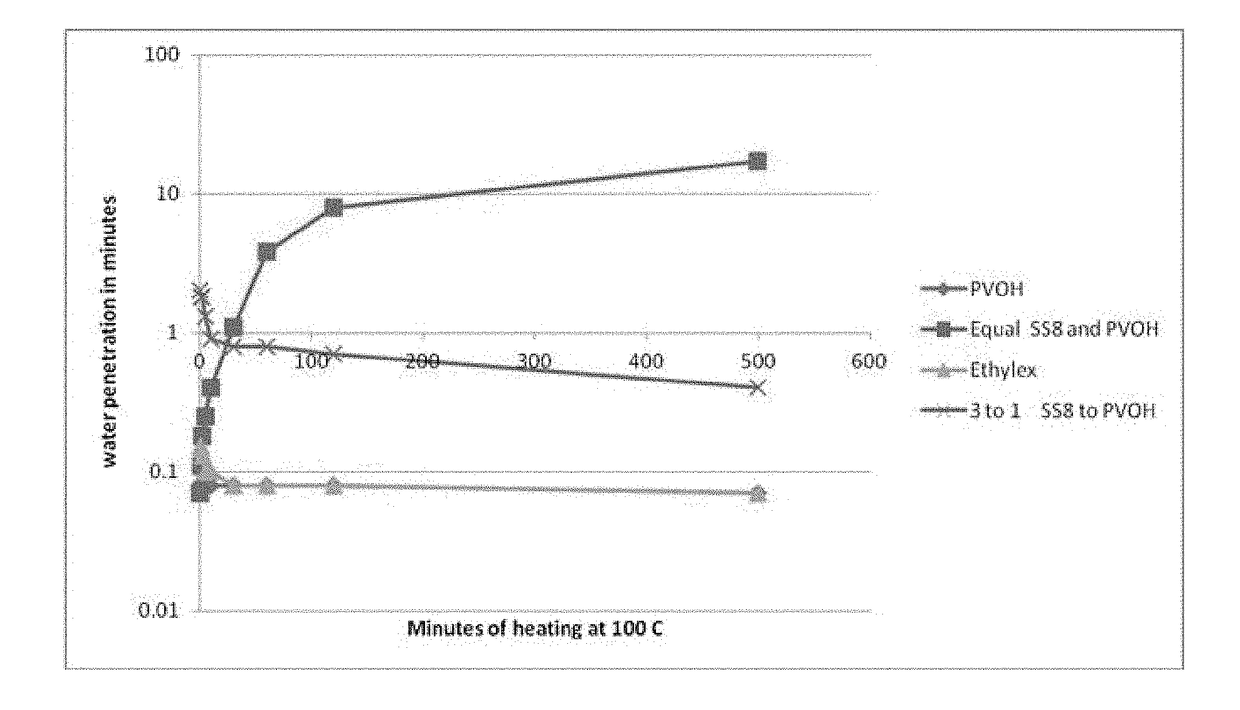
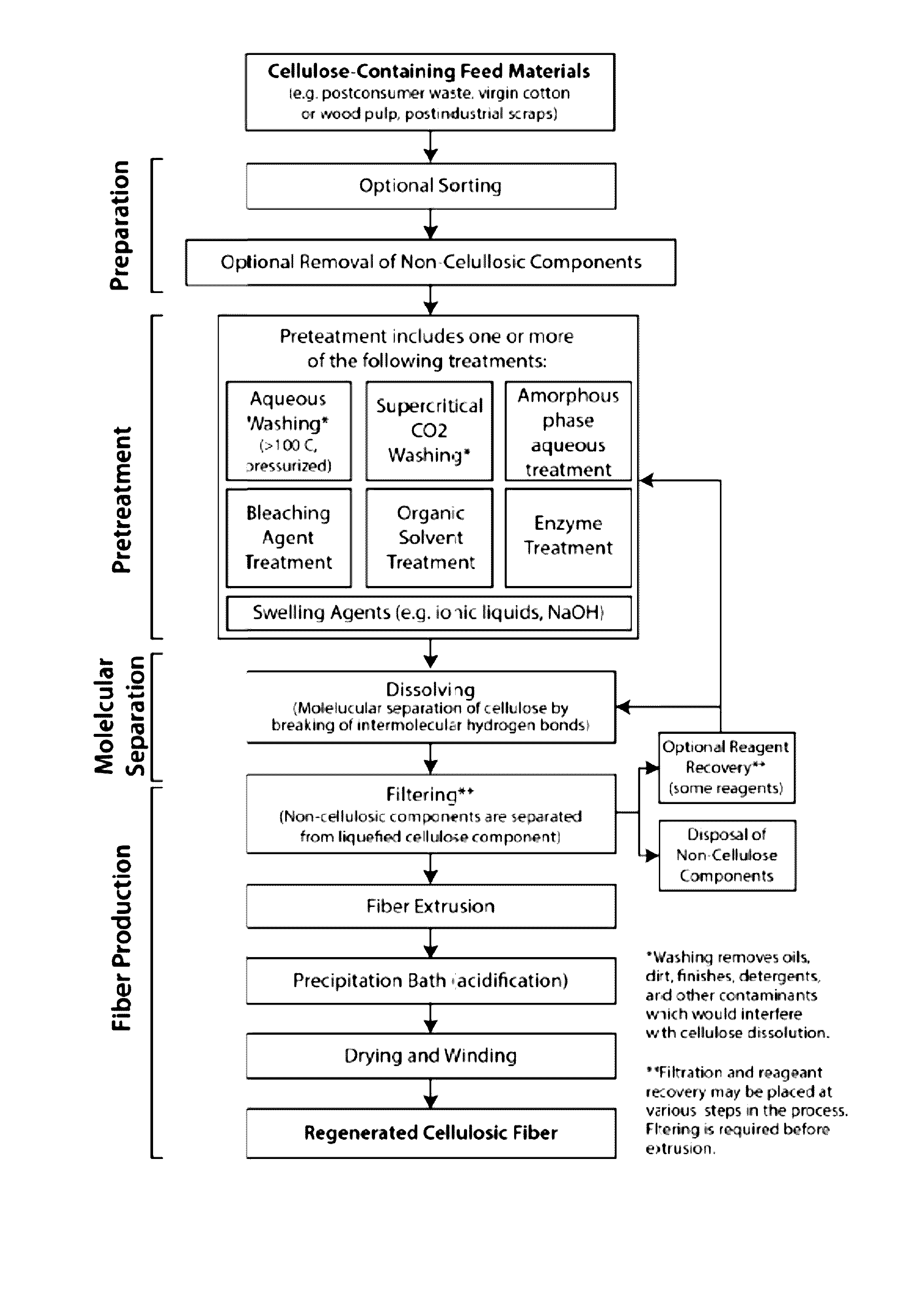
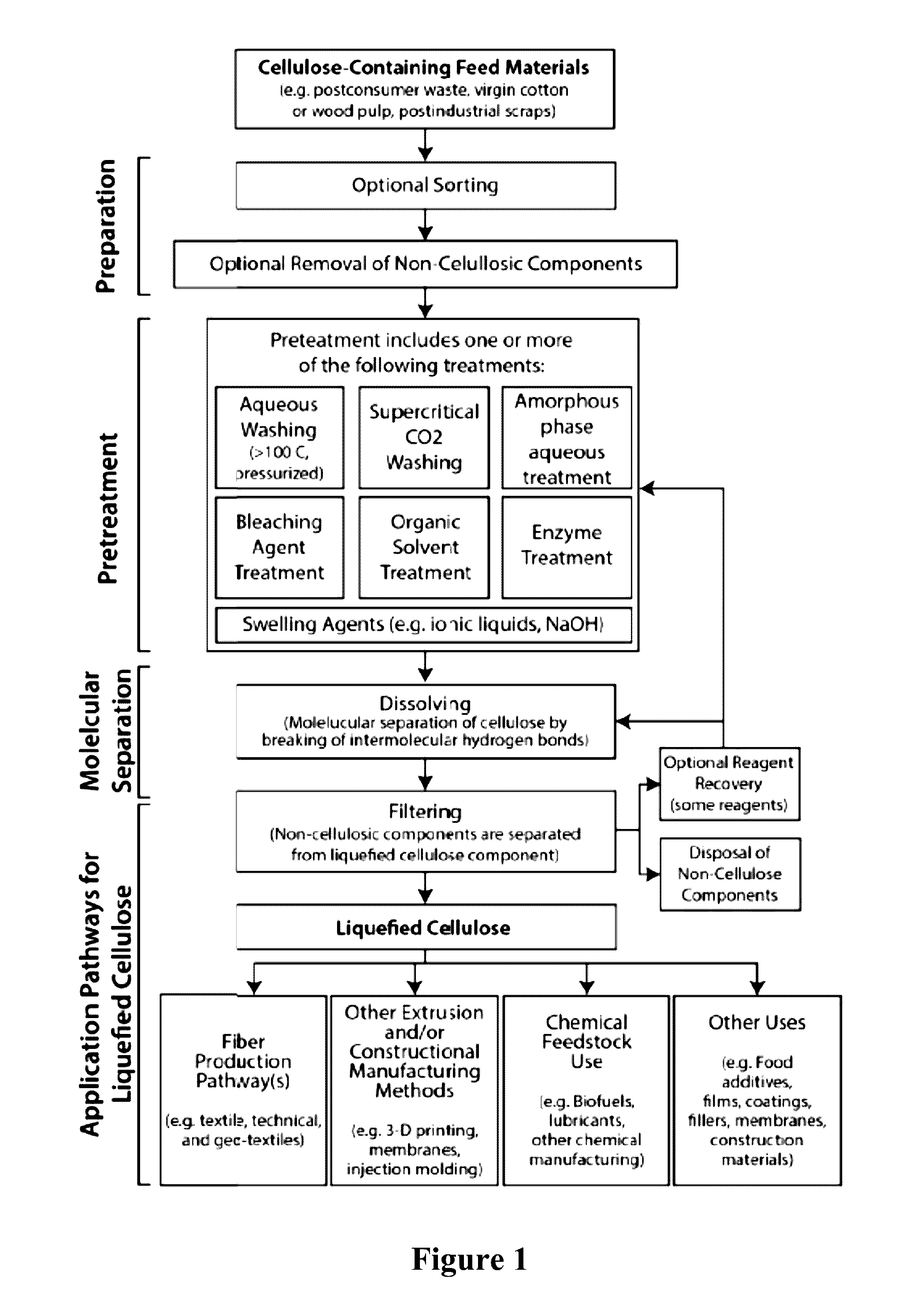
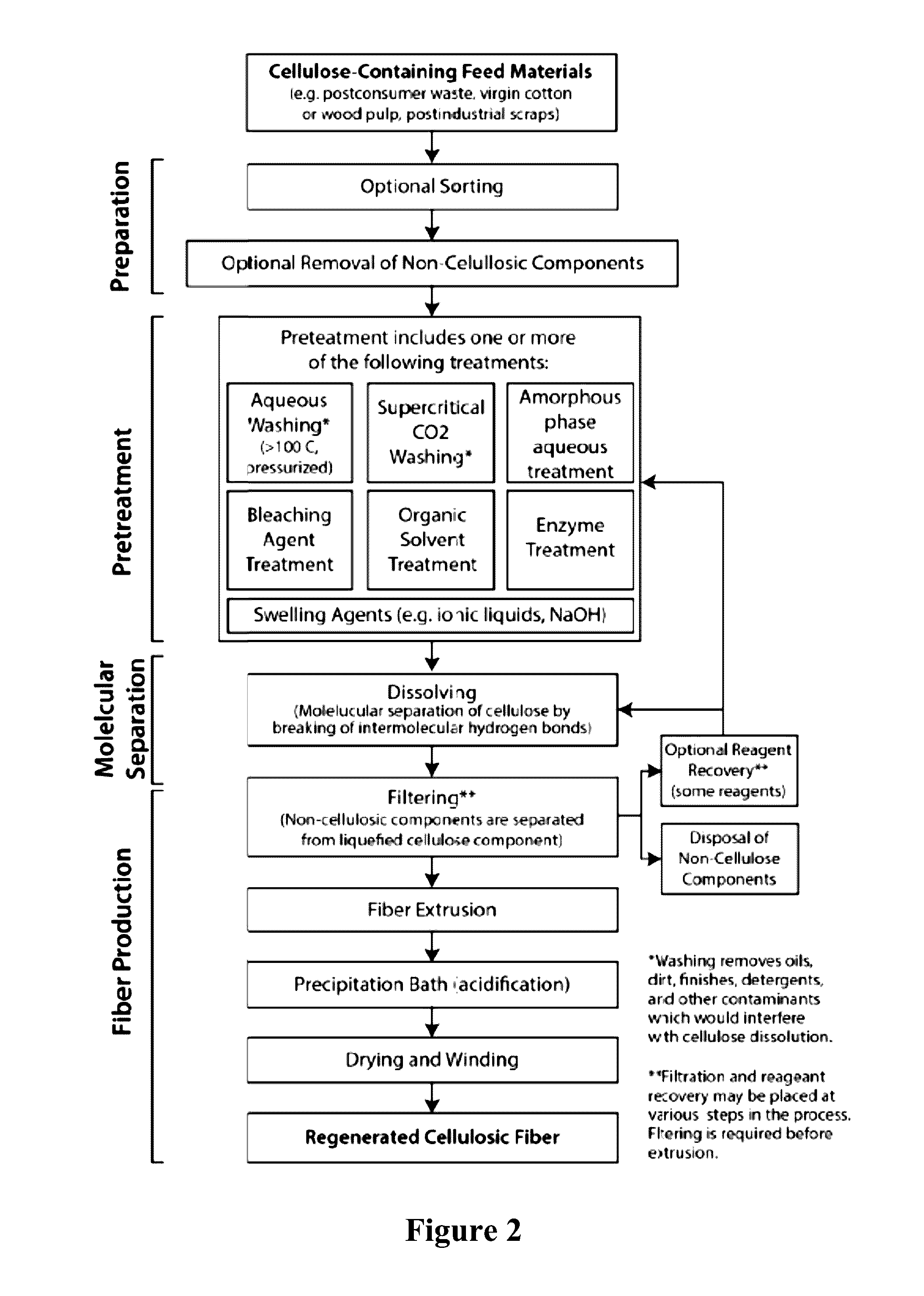
Methods and systems for processing cellulose-containing materials and isolating cellulose molecules; methods for regenerating cellulosic fibers
InactiveUS20160369456A1Reduce environmental impactPretreatment with water/steamPulp properties modificationPost-consumer wastePre treatment
Methods and systems of the present invention use cellulose-containing materials, which may include post-consumer waste garments, scrap fabric and / or various biomass materials as a raw feed material to produce isolated cellulose molecules having desirable properties that can be used in the textile and apparel industries, and in other industries. A multi-stage process is provided, in which cellulose-containing feed material is subjected to one or more pretreatment stages, followed by a pulping treatment, to isolate cellulose molecules. The isolated cellulose molecules may be used in a variety of downstream applications. In one application, isolated cellulose molecules are extruded to provide regenerated cellulose fibers having desirable (and selectable) properties that are usable in various industrial applications, including textile production.
Owner:EVRNU SPC
Paper or board treating composition of carboxylated surface size, polyacrylamide and crosslinker
InactiveUS6281291B1Less viscousEasy to handleNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCardboardMeth-
A composition useful in paper and board making comprises a carboxylated surface size containing at least 40 mole percent of hydrophobic groups and at least about 25 mole percent of carboxylated groups such as styrene-(meth)acrylic aicd copolymers or styrene-maleic acid (anhydride or salt) copolymers, a hydrophilic polyacrylamide and a crosslinking agent such as glyoxylated vinylamide polymers, formaldehyde, melamine-formaldehyde condensates and glyoxyl-extended materials.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Method for increasing the advantages of starch in pulped cellulosic material in the production of paper and paperboard
ActiveUS8758562B2Avoid degradationPrevent degradationNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCellulosePaperboard
The invention relates to a method for increasing the benefit from starch in pulped, preferably repulped cellulosic material at paper or paperboard manufacturing comprising the steps of (a) pulping a cellulosic material containing a starch; (b) treating the cellulosic material containing the starch with one or more biocides, preferably in the thick stock area; and (h) adding an ionic polymer and preferably, an auxiliary ionic polymer to the cellulosic material; wherein the ionic polymer and the optionally added auxiliary ionic polymer preferably have a different average molecular weight and preferably a different ionicity, wherein the ionicity is the molar content of ionic monomer units relative to the total amount of monomer units.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Crepe facilitating composition
InactiveUS20070000630A1Improve stress distributionGood flexibilityMechanical working/deformationSpecial paperFiberWater insoluble
The invention relates to a crepe facilitating aqueous composition comprising at least one water-insoluble, non-surface active thermoplastic material having a softening or melting point within the range of from 40° C. to 100° C., and at least one water-soluble polymer, preferably a cationic water-soluble polymer. As the composition is comprised in a wet fibre web during creping thereof, a more uniform creping is obtained while the integrity of the web is preserved and dust formation is reduced, and a tissue product having improved properties is provided.
Owner:BIM KEMI
Stable and Aqueous Compositions of Polyvinylamines with Cationic Starch, and Utility for Papermaking
ActiveUS20110247775A1Improved dry strength performanceIncreased machine productivityNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperUltimate tensile strengthChemistry
A stable aqueous composition comprising polyvinylamine and liquid cationic starch in a ratio of from 90 to 55 parts of polyvinylamine on active basis to 10 to 45 parts of liquid cationic starch on active basis is disclosed. The composition can be used in papermaking as a strength or as a drainage aid.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Method of increasing filler content in papermaking
The invention provides a method of producing paper with a higher proportion of mineral filler particles than is otherwise be possible without the expected loss in paper strength. The method allows for the use of the greater amount of filler particles by coating at least some of the filler particles with a material that prevents the filler materials form adhering to a strength additive. The strength additive holds the cellulose fibers together tightly and is not wasted on the filler particles. The method is particularly effective when the filler particles are a PCC-GCC blend and when the GCC particles are coated with the adherence preventing coating.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Methods for biocompatible derivitization of cellulosic surfaces
The present invention describes methods of treating cellulosic materials with a composition that provides increased hydrophobicity to such materials without sacrificing the biodegradability thereof. The methods as disclosed provide for esterification of available hydroxyl groups on cellulosic materials, where such hydroxyl groups are “masked” by bulky organic chains, including that the disclosure provides products made by such methods. The materials thus treated display higher hydrophobicity, barrier function, and mechanical properties, and may be used in any application where such features are desired.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com