Use of 1,3-selective lipases for pitch control in pulp and paper processes
a technology of selective lipases and pulp and paper, which is applied in the direction of non-fibrous pulp addition, cellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymes, papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of reducing paper quality, affecting the physical properties of pulp, and increasing manufacturing costs, so as to reduce the amount of fatty acid soap deposition, less deposits, and the effect of increasing the amount of pitch deposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Comparative Deposition of Selective Lipases from Different Microorganisms
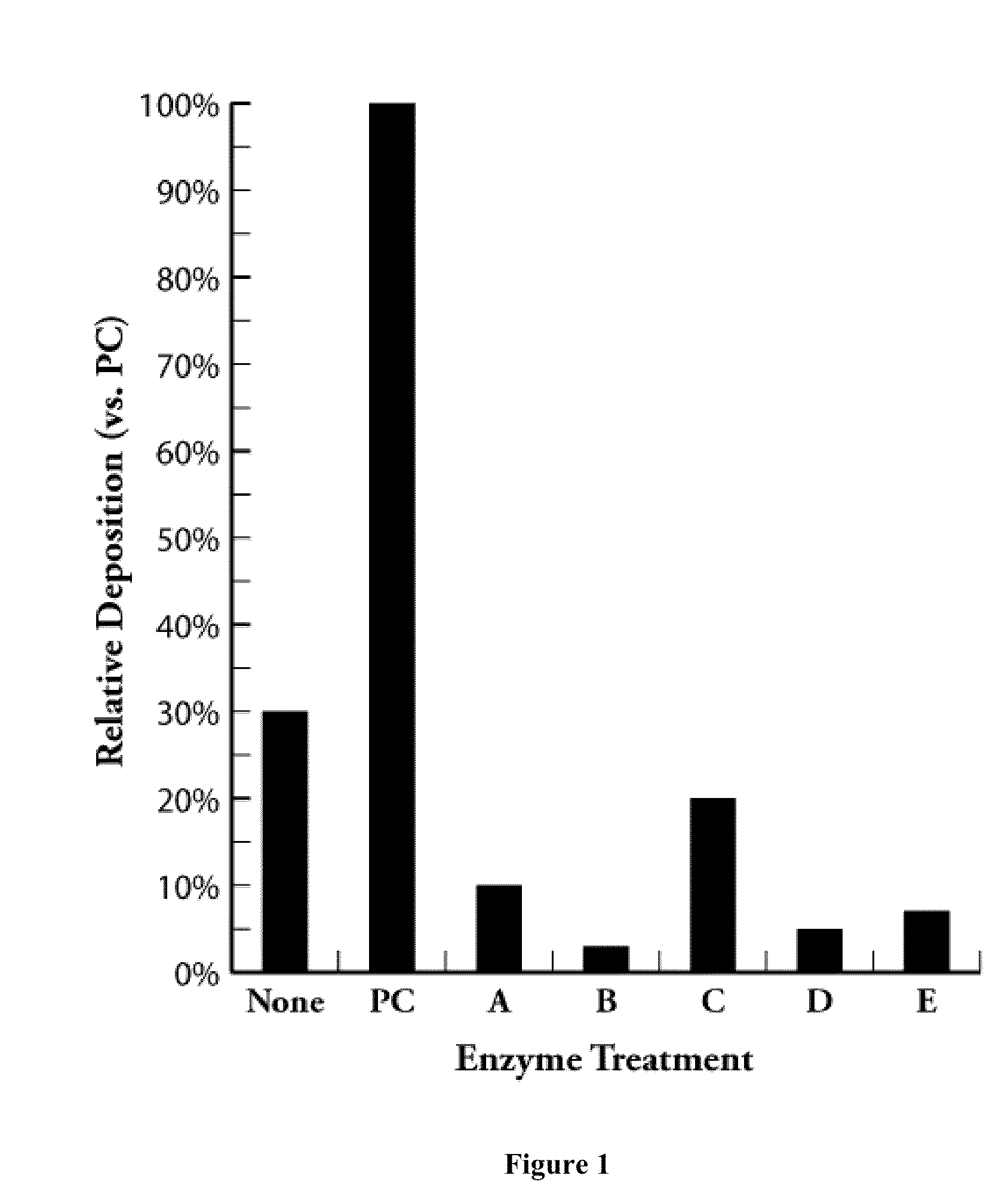
[0076]Representative stock samples of TMP secondary refiner accept with a consistency around 50% and recycled newsprint (RNP) with a consistency 3-4% were taken from a southern U.S. newsprint mill and used for the experiments. The pH of the stocks ranged from about 4.5 to 5.5, and alum and sodium aluminate solutions were used to maintain the pH at around 5.2. The experiments were performed using the procedures described above. The control was treated with 6 lbs / ton total alum equivalent and no enzyme was used.
[0077]The paddle and bowl deposition resulting from the treatment with 2 lbs / ton of EnzOx® PC, which is a non-selective lipase product, were normalized to 100%. The deposition of the control and other treatments were evaluated relative to EnzOx® PC treatment and deposition. The dosages of the experimental products of selective lipases A, B, C, D and E were based on equivalent protein weight.
[0078]FIG. 1 sh...
example 2
Comparative Results of Various Treatments on Paper Properties
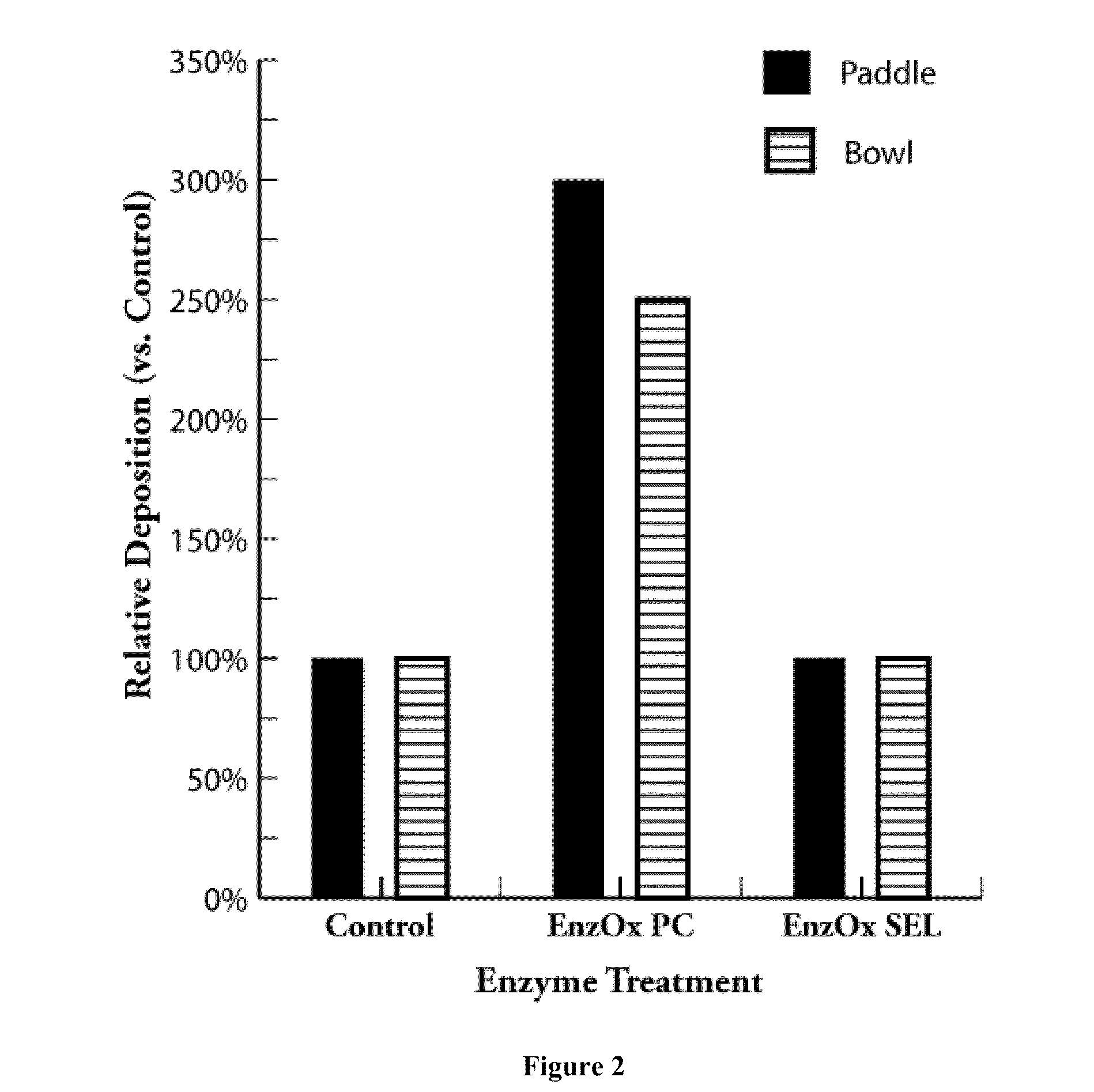
[0079]The effects of the non-selective lipase treatment and the selective lipase treatment on paper strength properties were evaluated. The testing methods and pulp stock preparation are described above. A 0.5 M acetate buffer was added to the stocks to maintain the pH in the range of 5.0-5.5. The stock was treated with 25 lbs / ton total alum equivalent. After the stock was mixed for 5 minutes, an enzyme solution (or water for the control) was added to the mixing bowl and mixed for 60 minutes. The amount of pitch deposit on the paddles and bowl surface was visually determined and compared to the control. The control was normalized to 100%, and the various enzyme treatments were evaluated relative to the control.
[0080]The results are shown in FIG. 2. EnzOx® PC, the non-selective lipase treatment, produced about 250%-300% more deposits compared to the Control. In contrast, EnzOx® SEL, the selective lipase treatment, gave abou...
example 3
Quantification of Triglyceride Hydrolysis and Fatty Acid Release
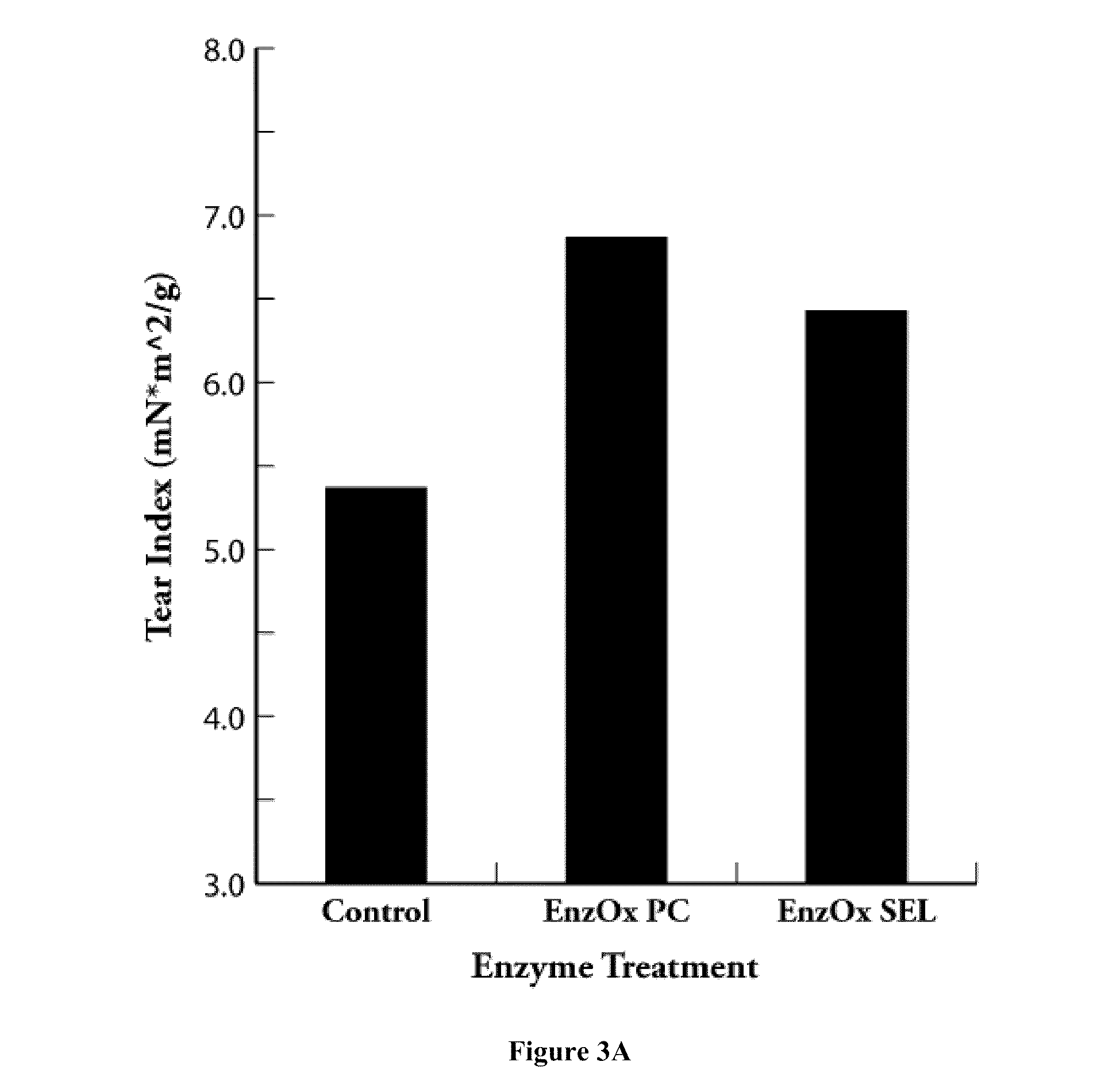
[0082]In the non-selective lipase treatment, the enzymes hydrolyze triglycerides to glycerol and fatty acids. For each mole of triglyceride, three moles of fatty acids and one mole of glycerol are produced. In contrast, selective lipases hydrolyze triglycerides into monoglycerides, with reduced production of fatty acids and no formation of glycerol. Thus, for each mole of triglyceride, only two moles of fatty acids are generated. Therefore, the selective lipase treatment produces smaller amounts of fatty acids and poses less risk of fatty soap deposition in paper mills.
[0083]FIG. 4 compares the total amounts of free fatty acid released by the two different lipase enzyme treatments without the addition of alum. The results demonstrate that the amount of the free fatty acids generated by the non-selective lipase product is much greater than that of the selective lipase product under the same dosage conditions.
[0084]FIG. 5...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com