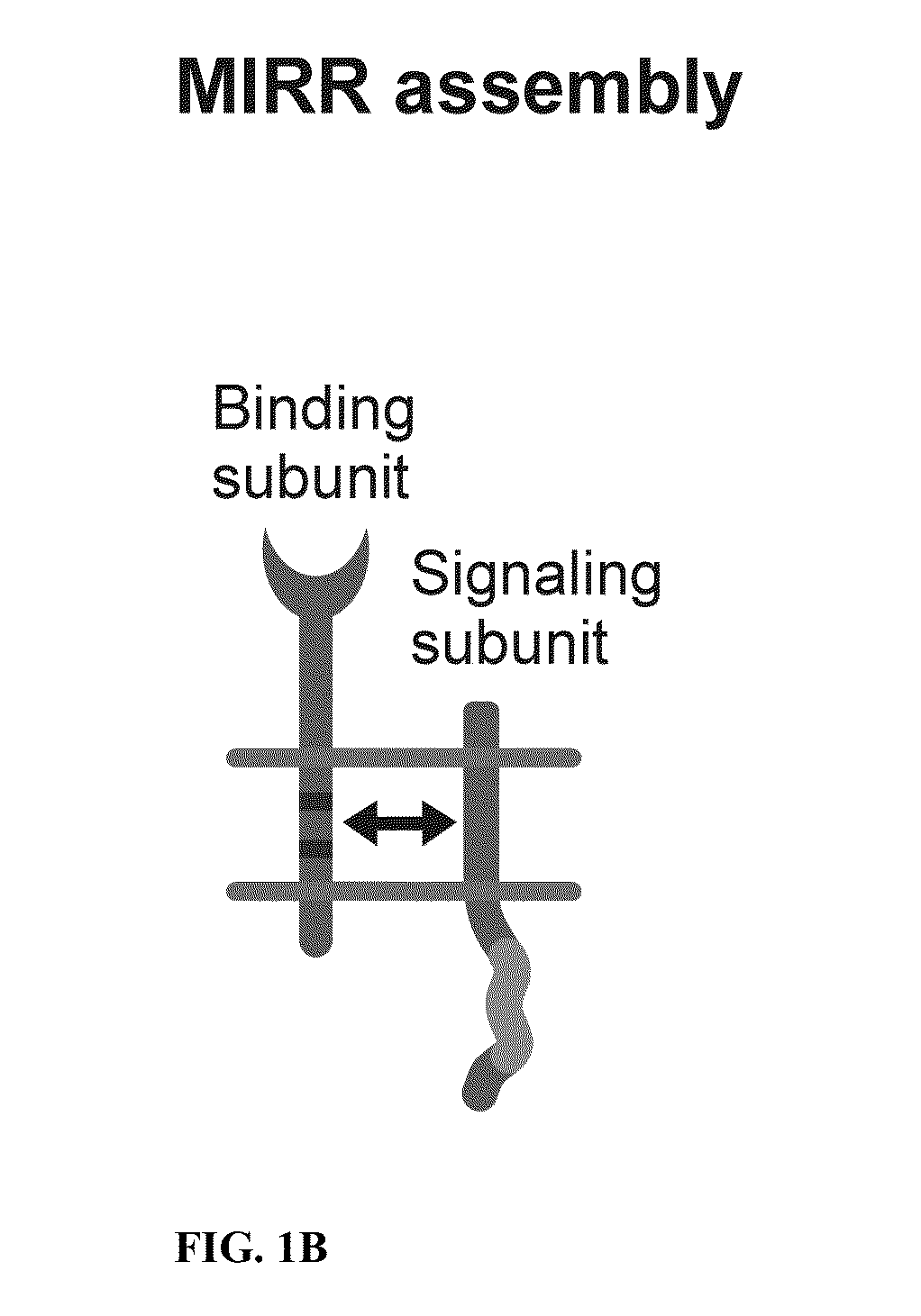
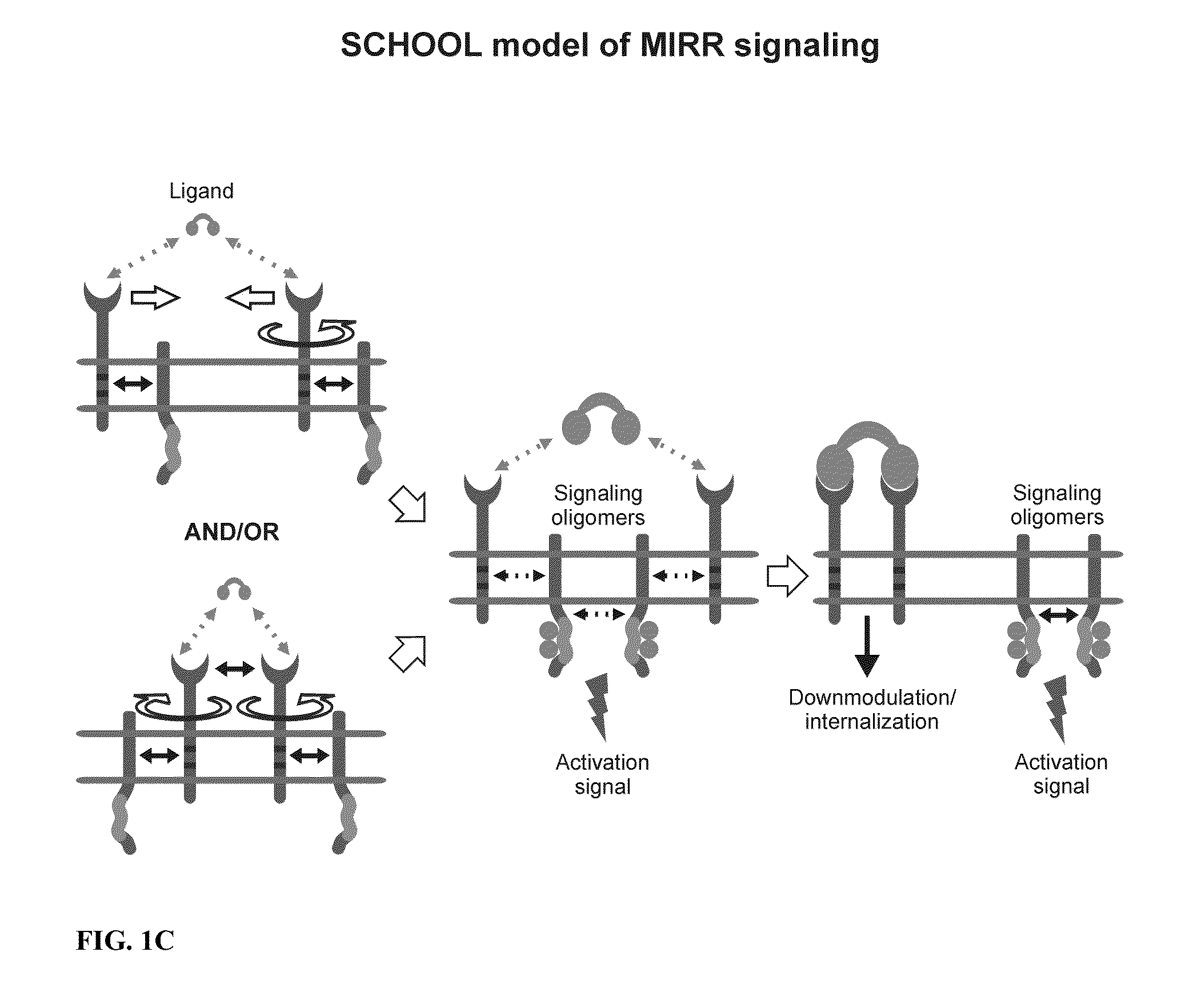
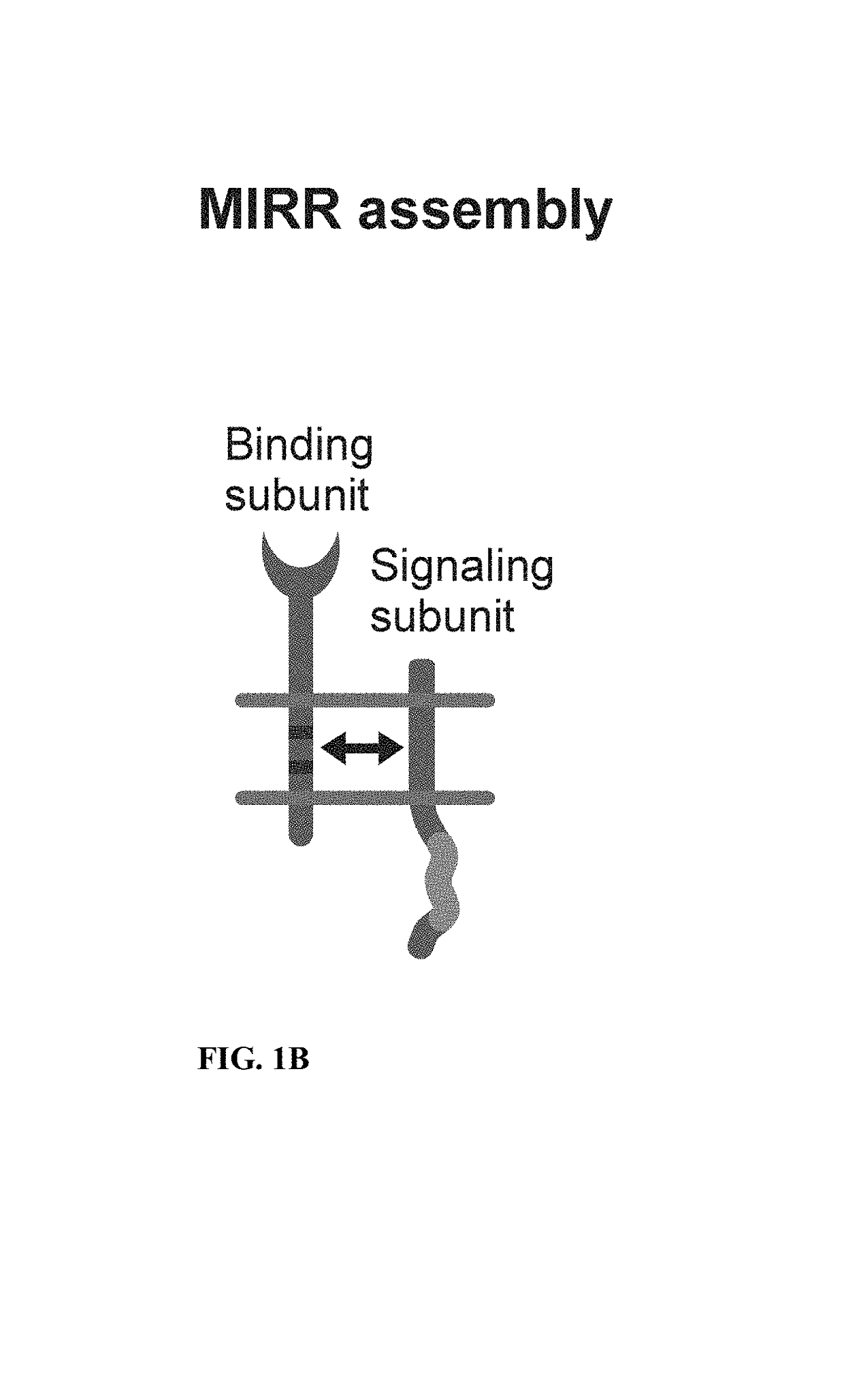
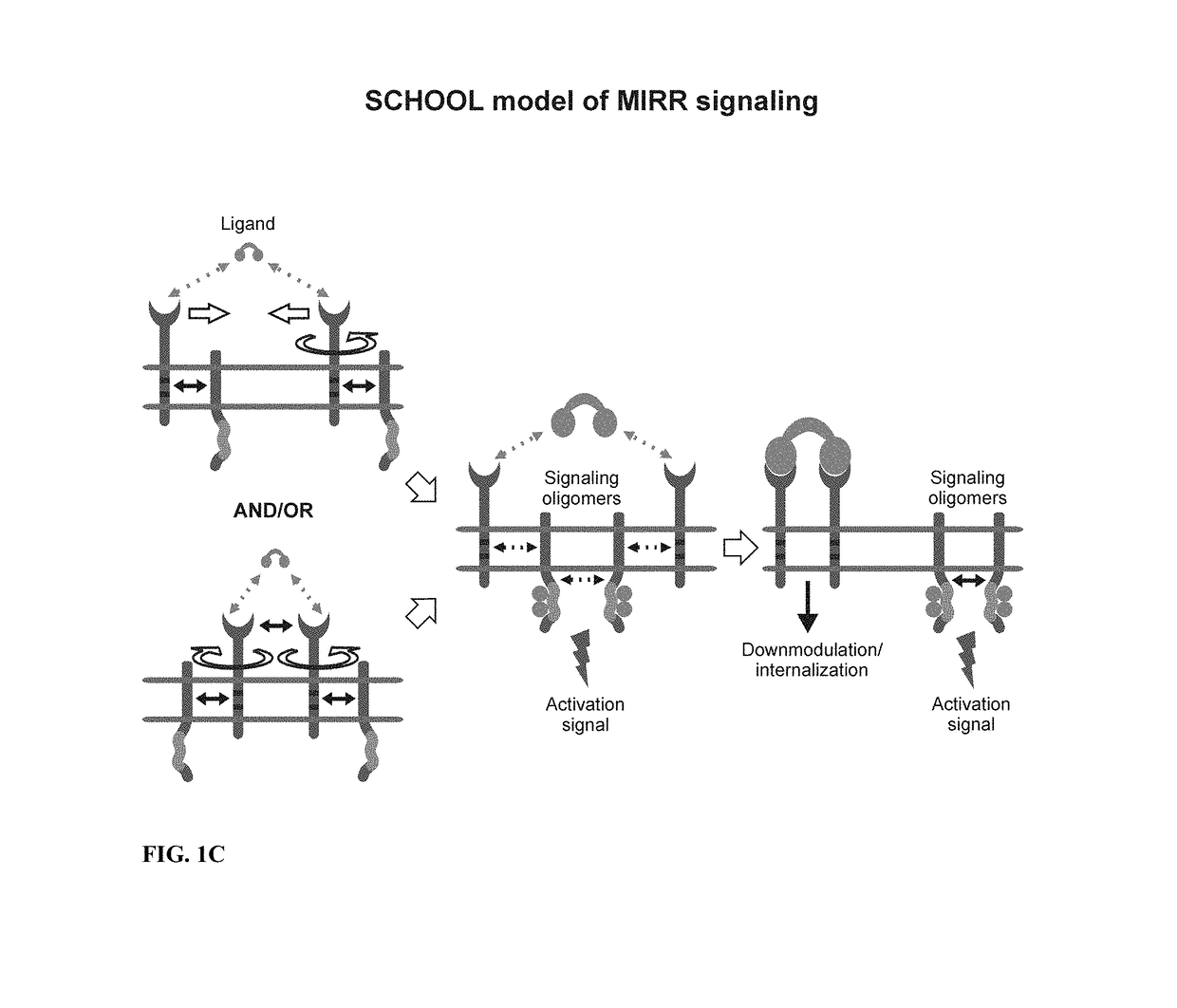
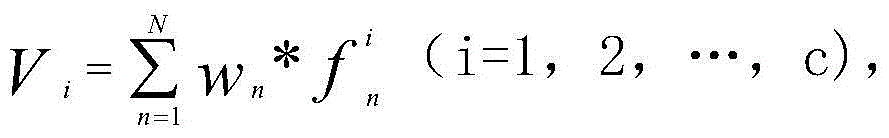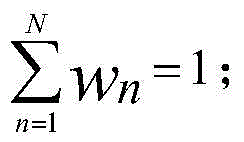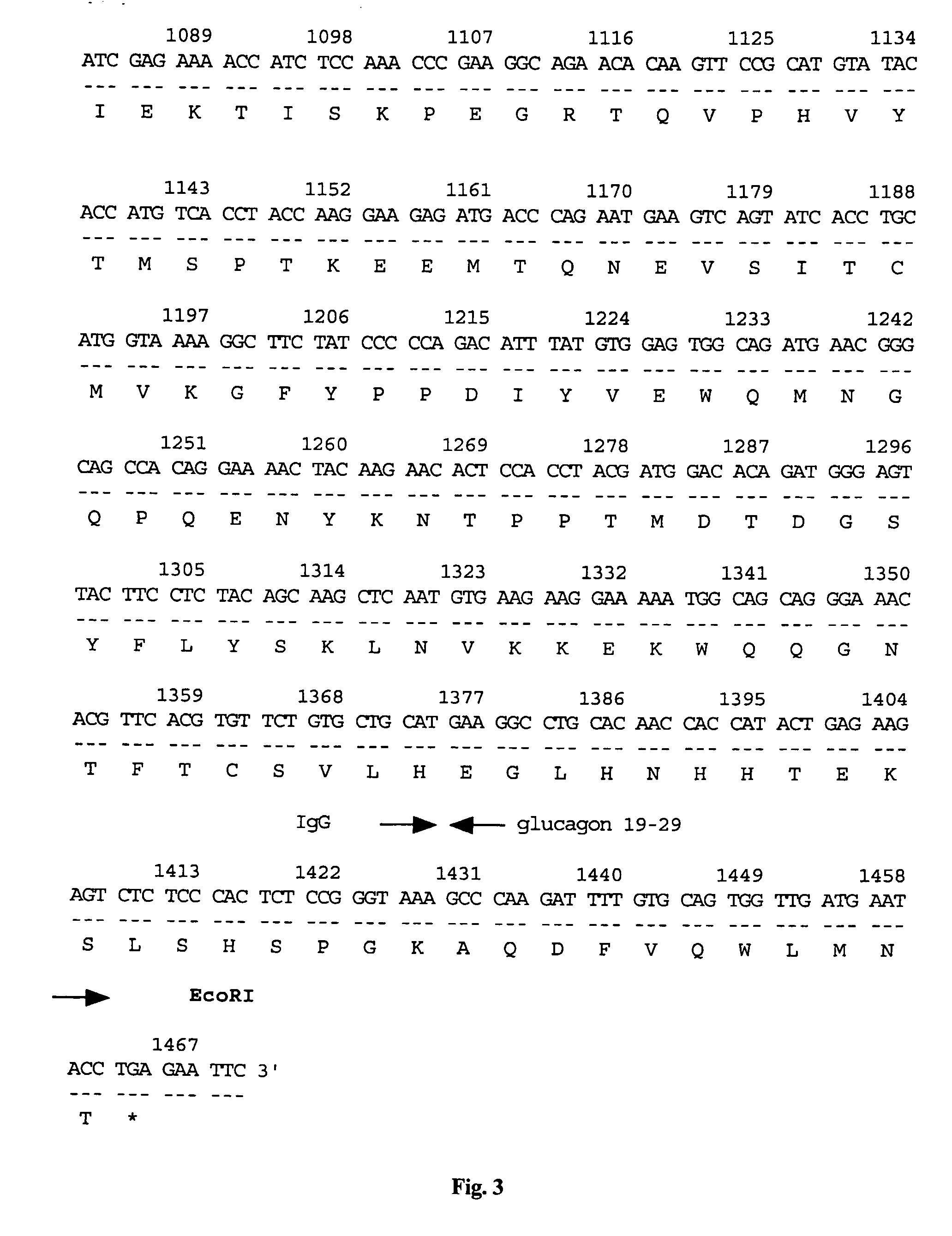Patents
Literature
41 results about "Protein Region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viral vectors and methods for producing and using the same
InactiveUS20050220766A1Improve AAV production titerReduce and even essentially eliminate contaminationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
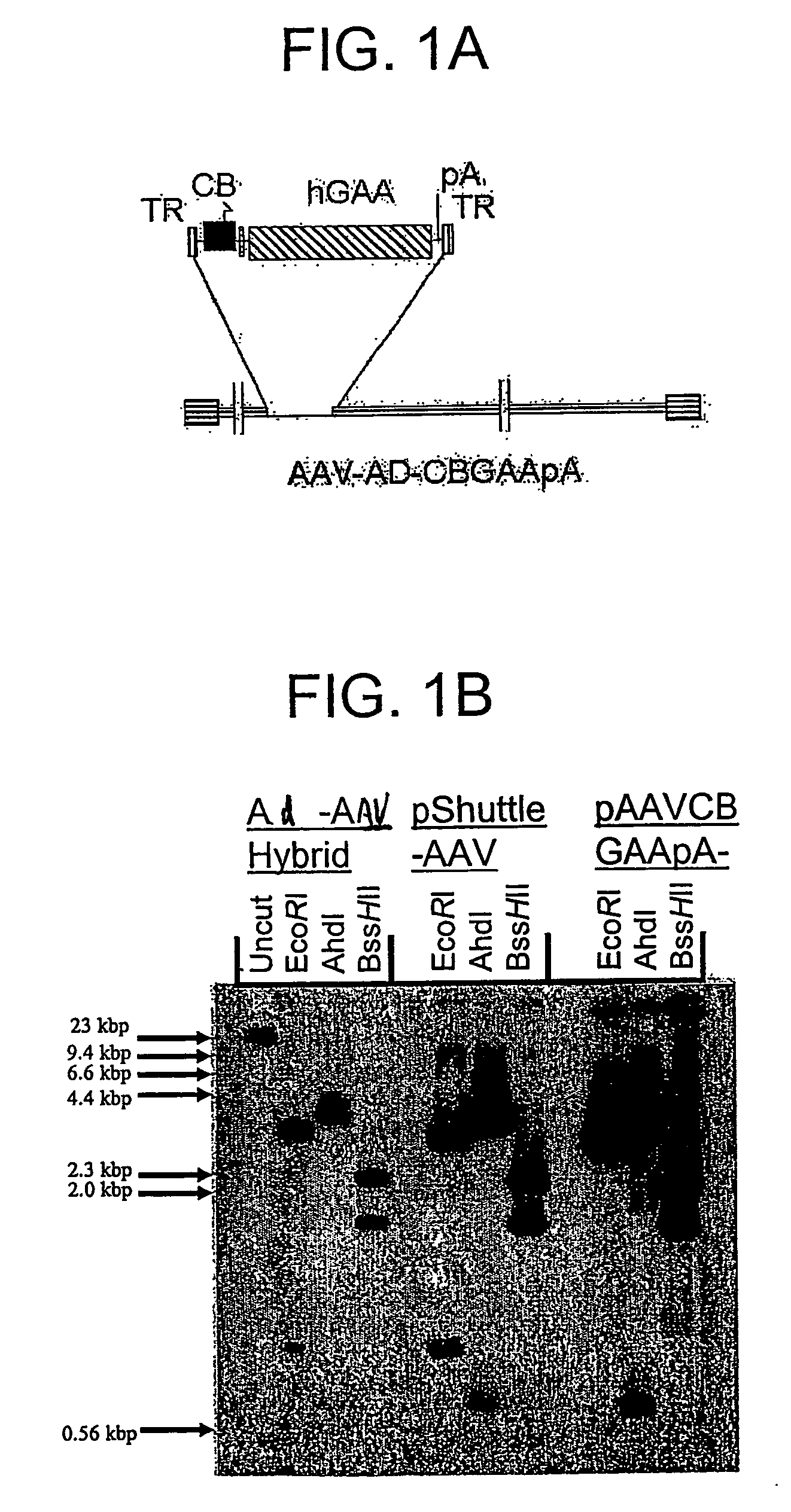
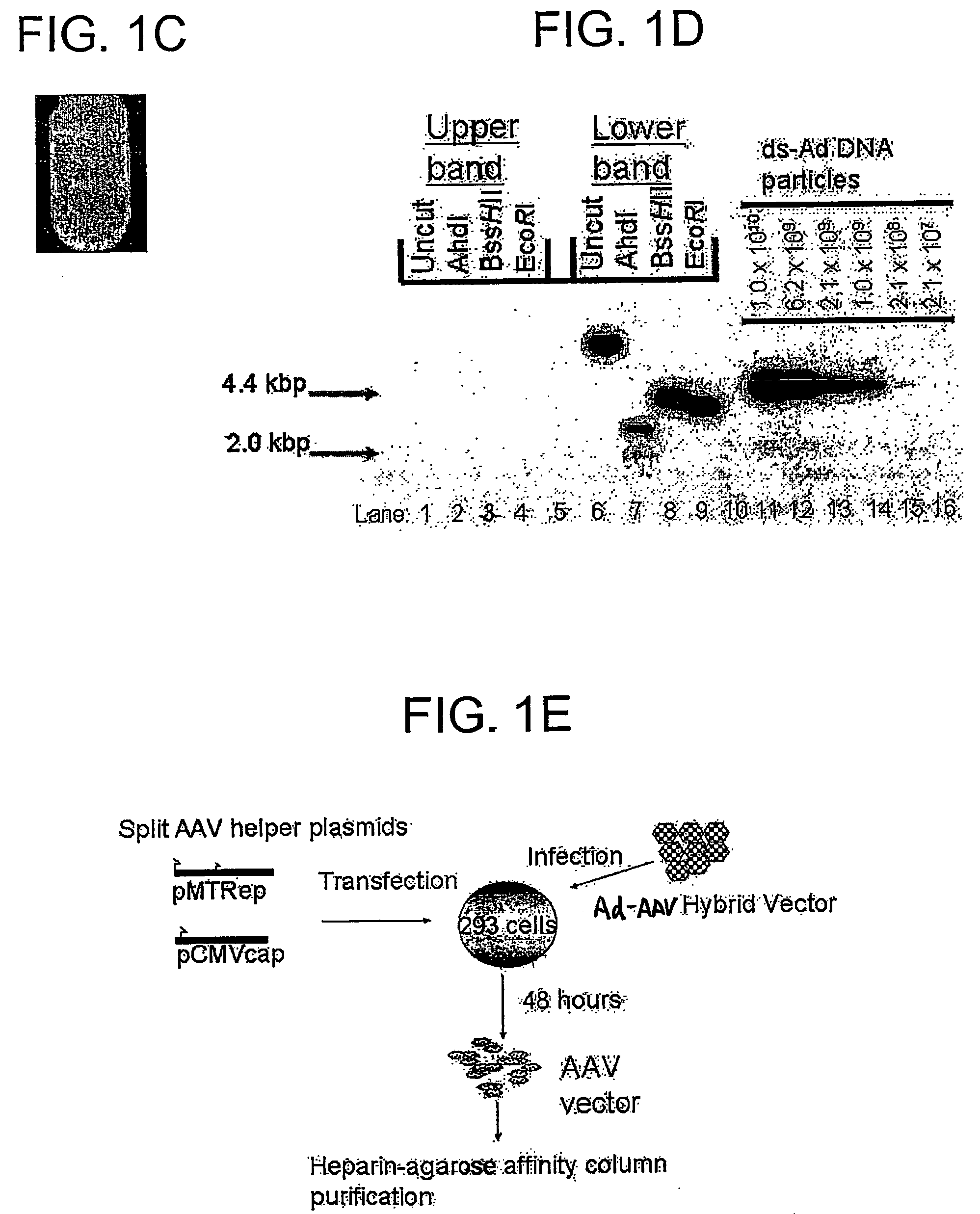
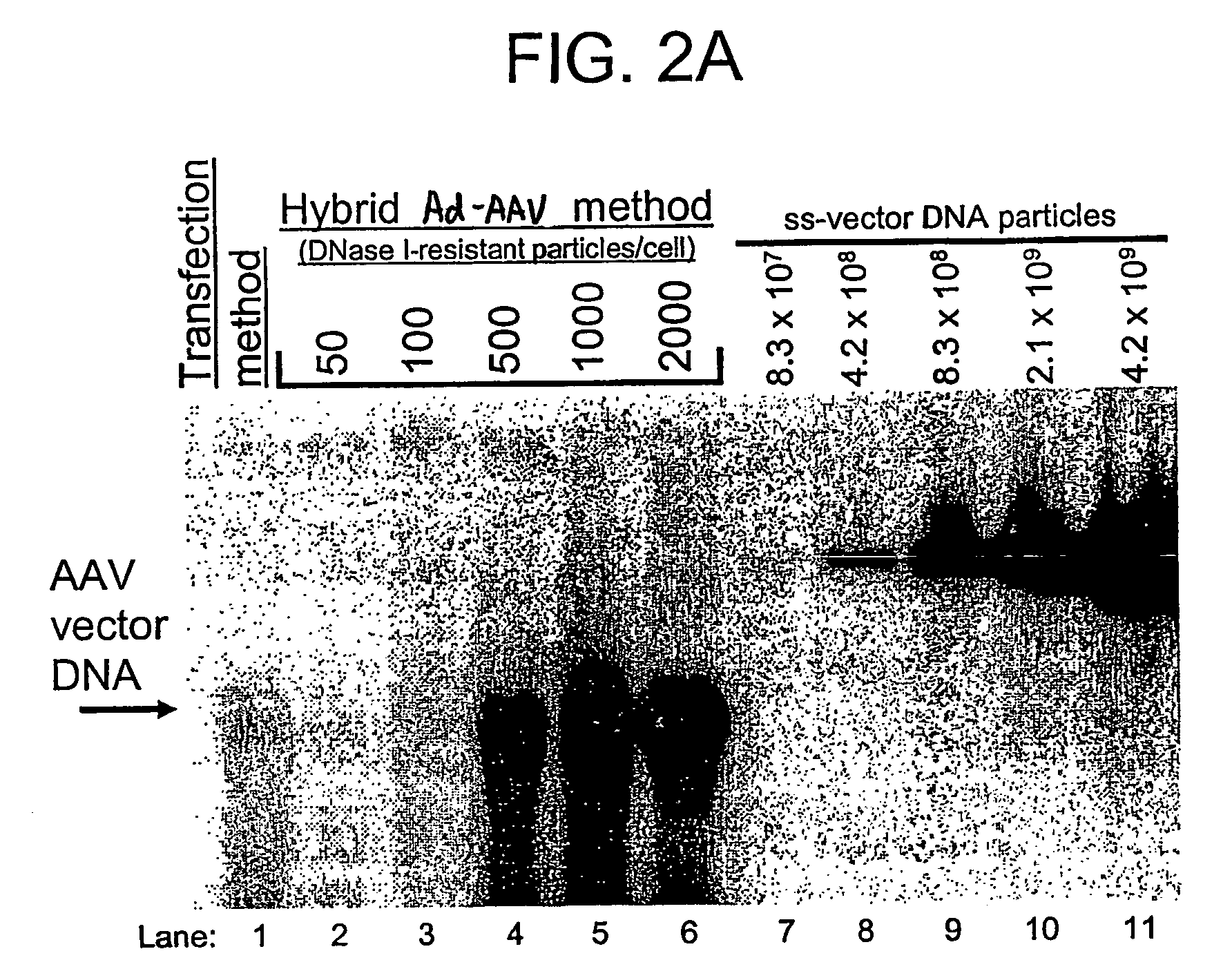
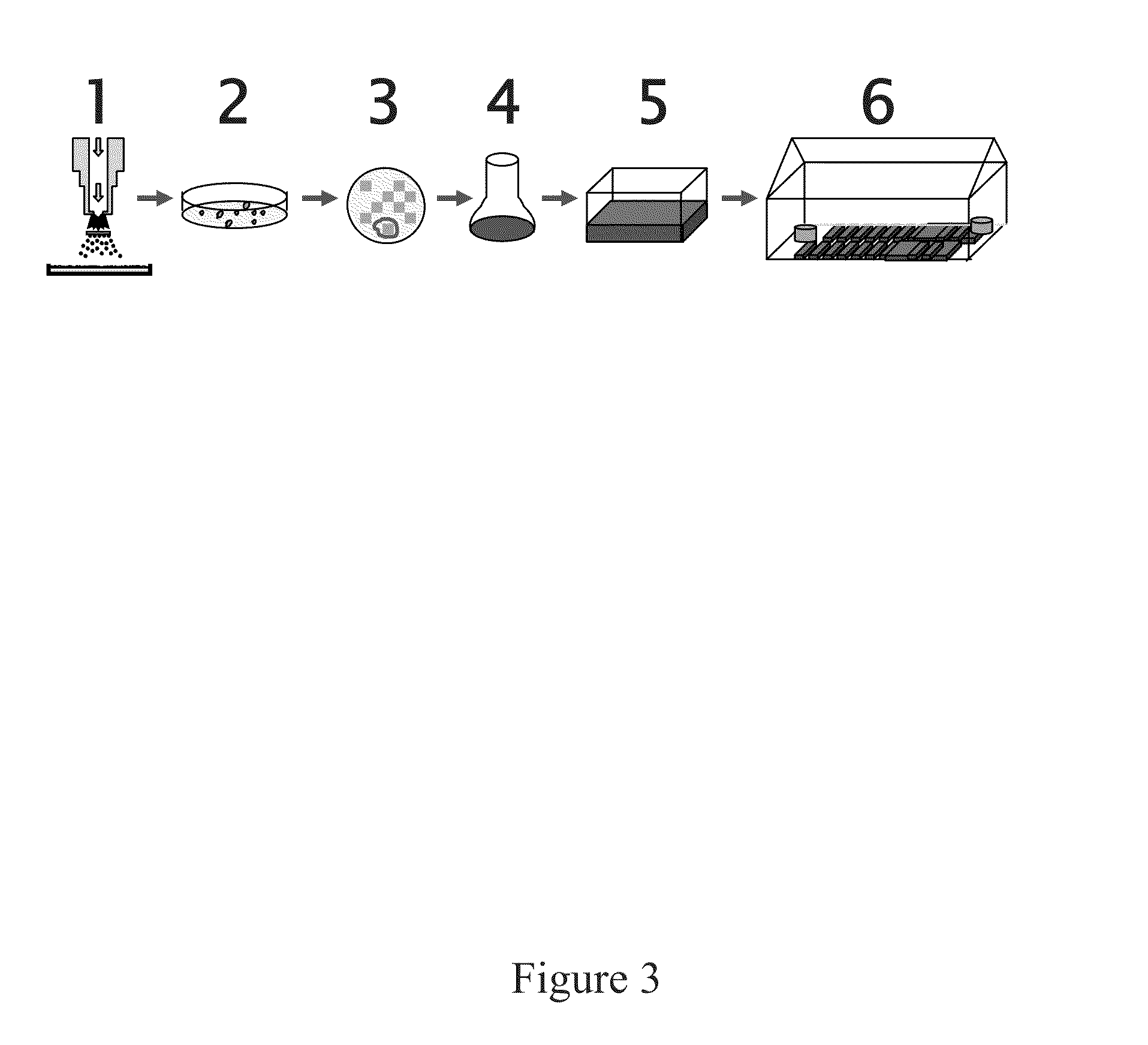
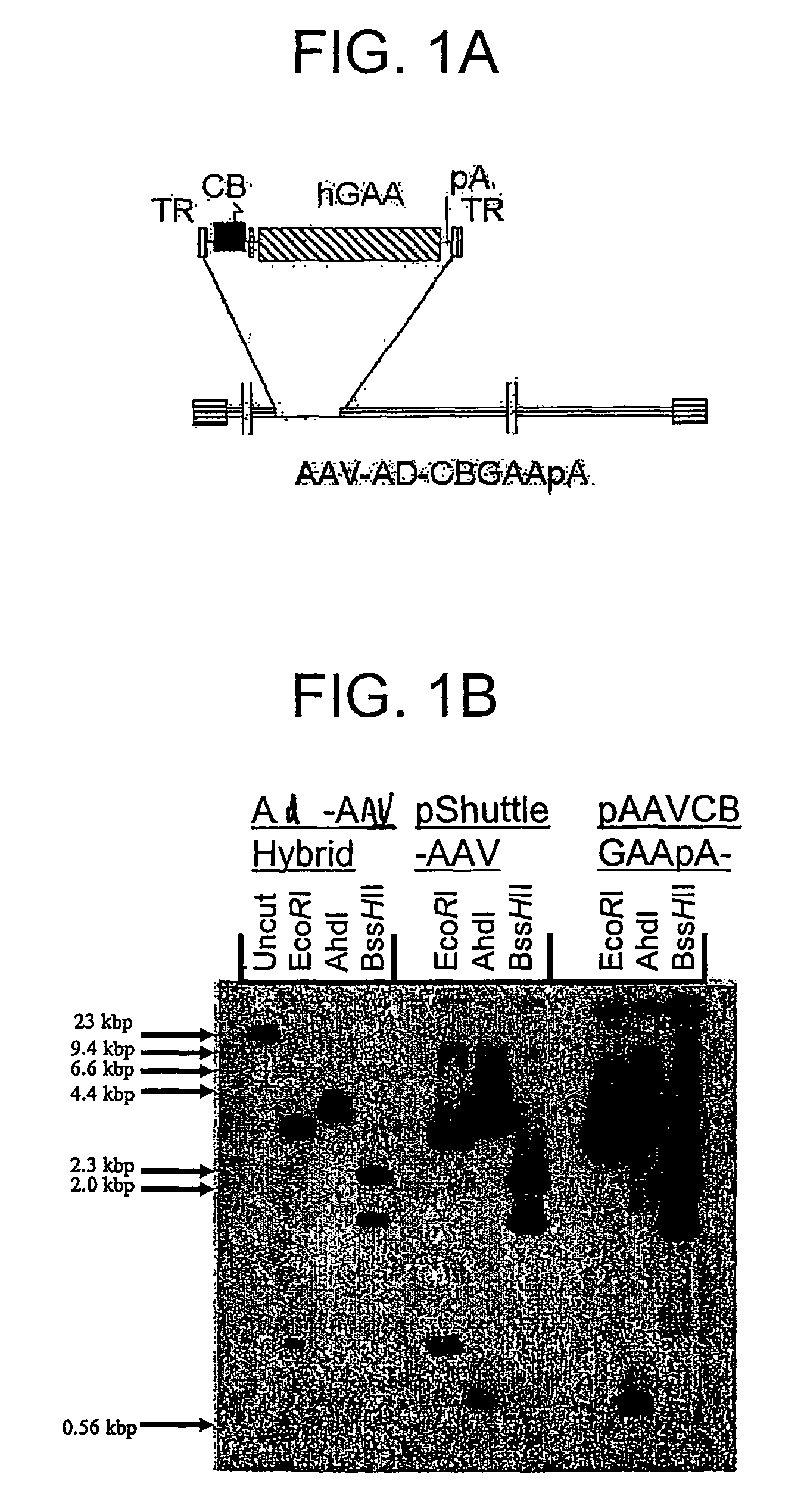
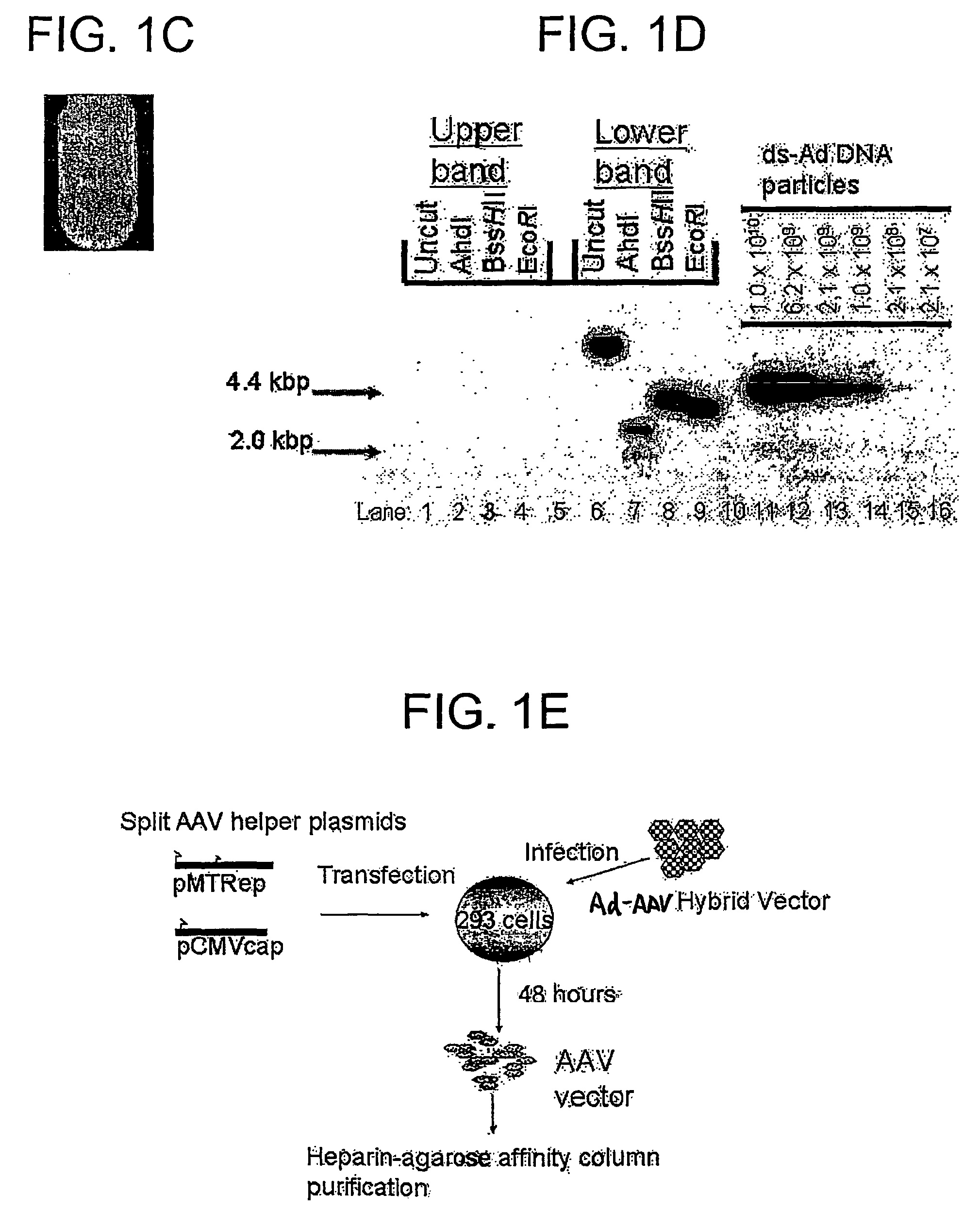
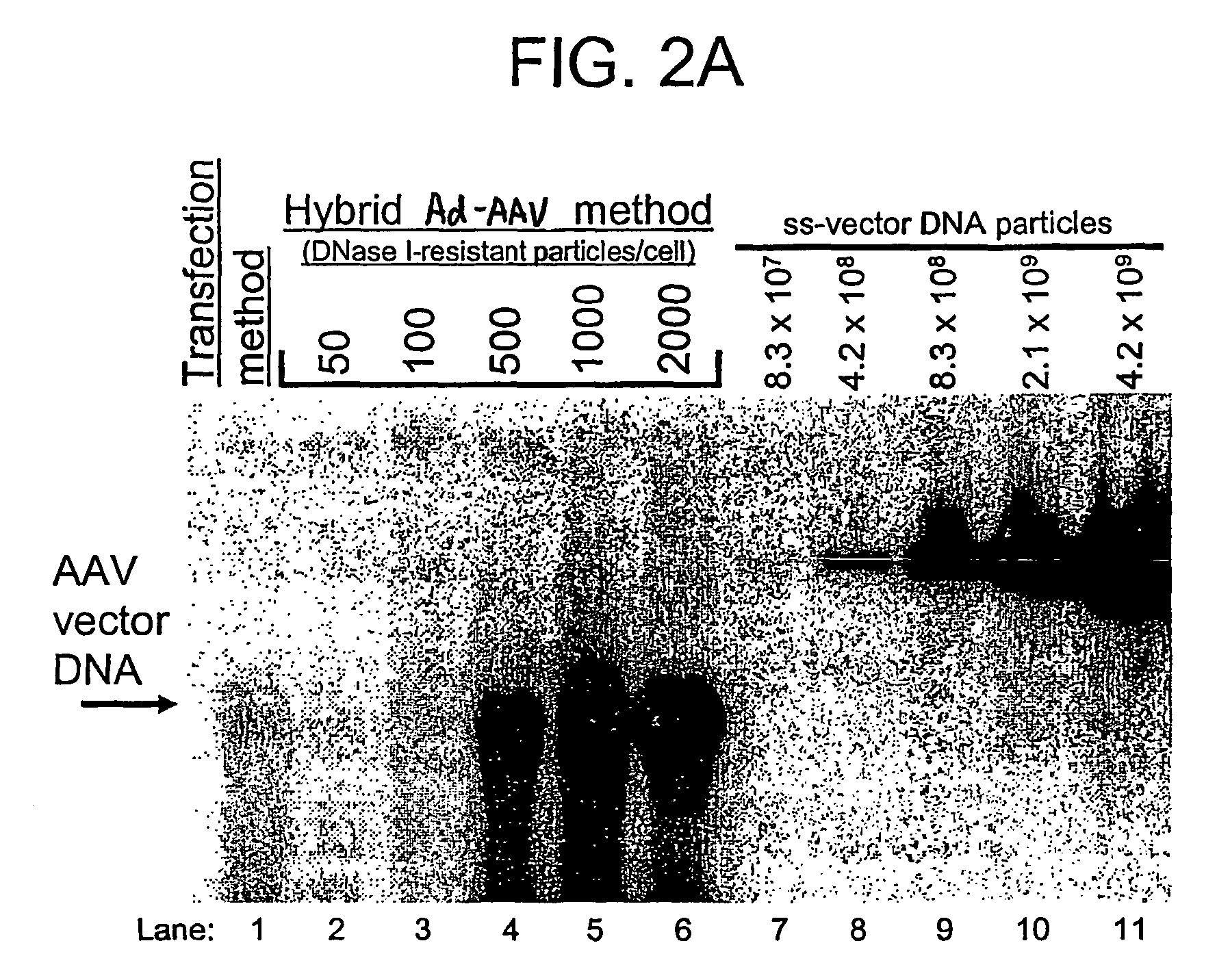
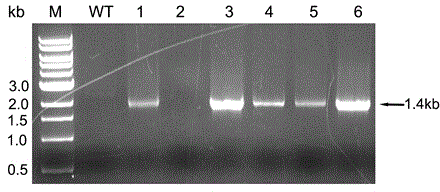
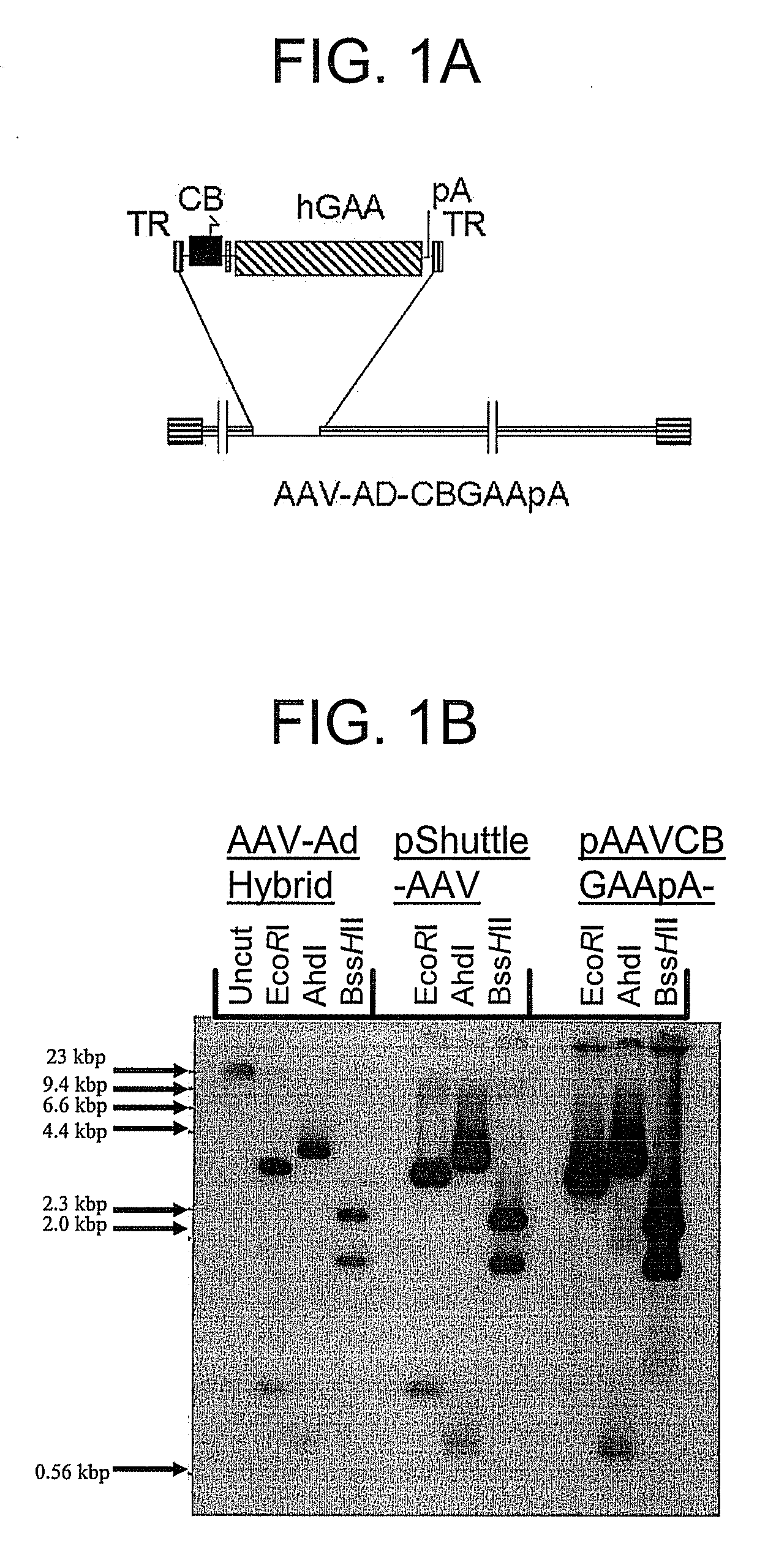
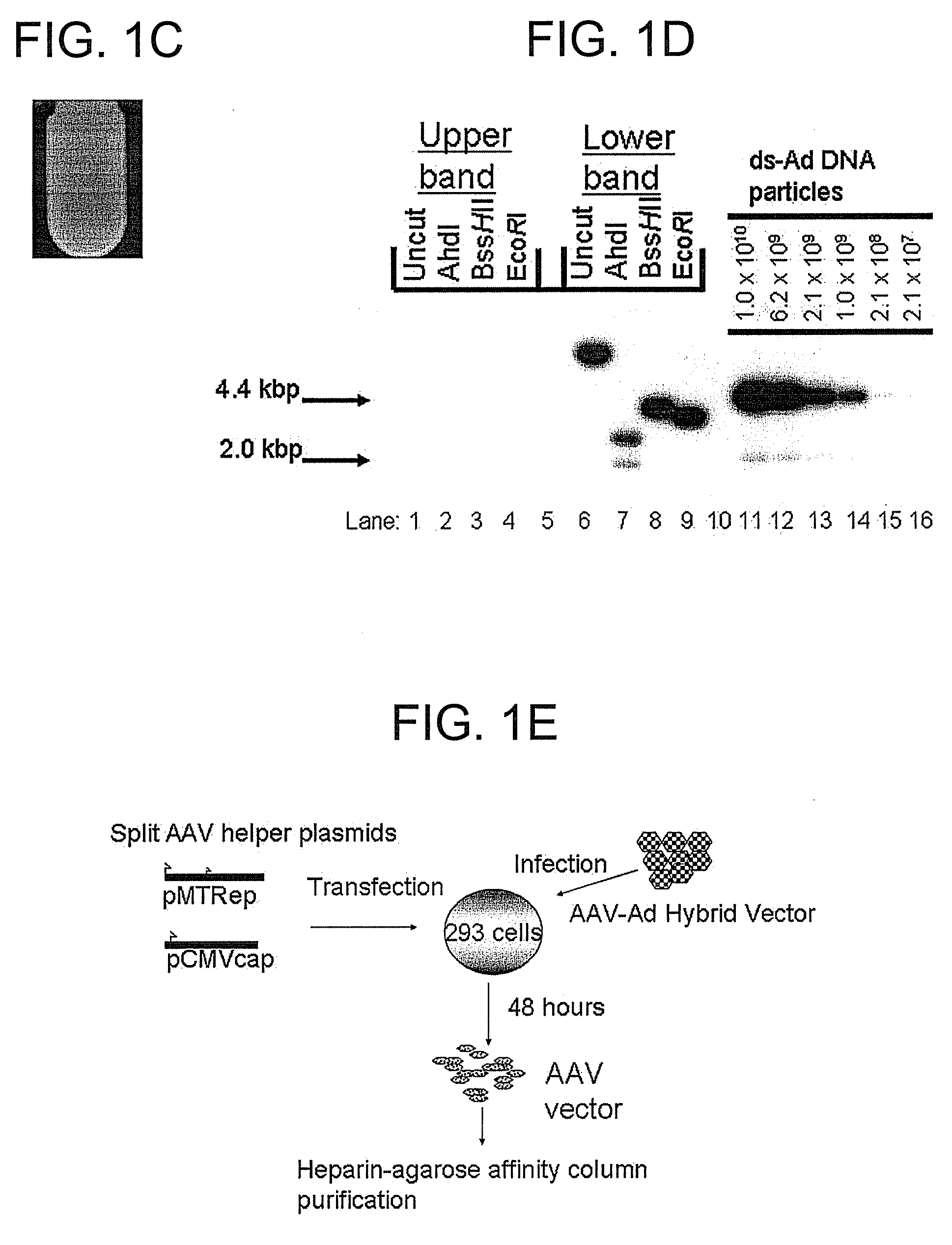
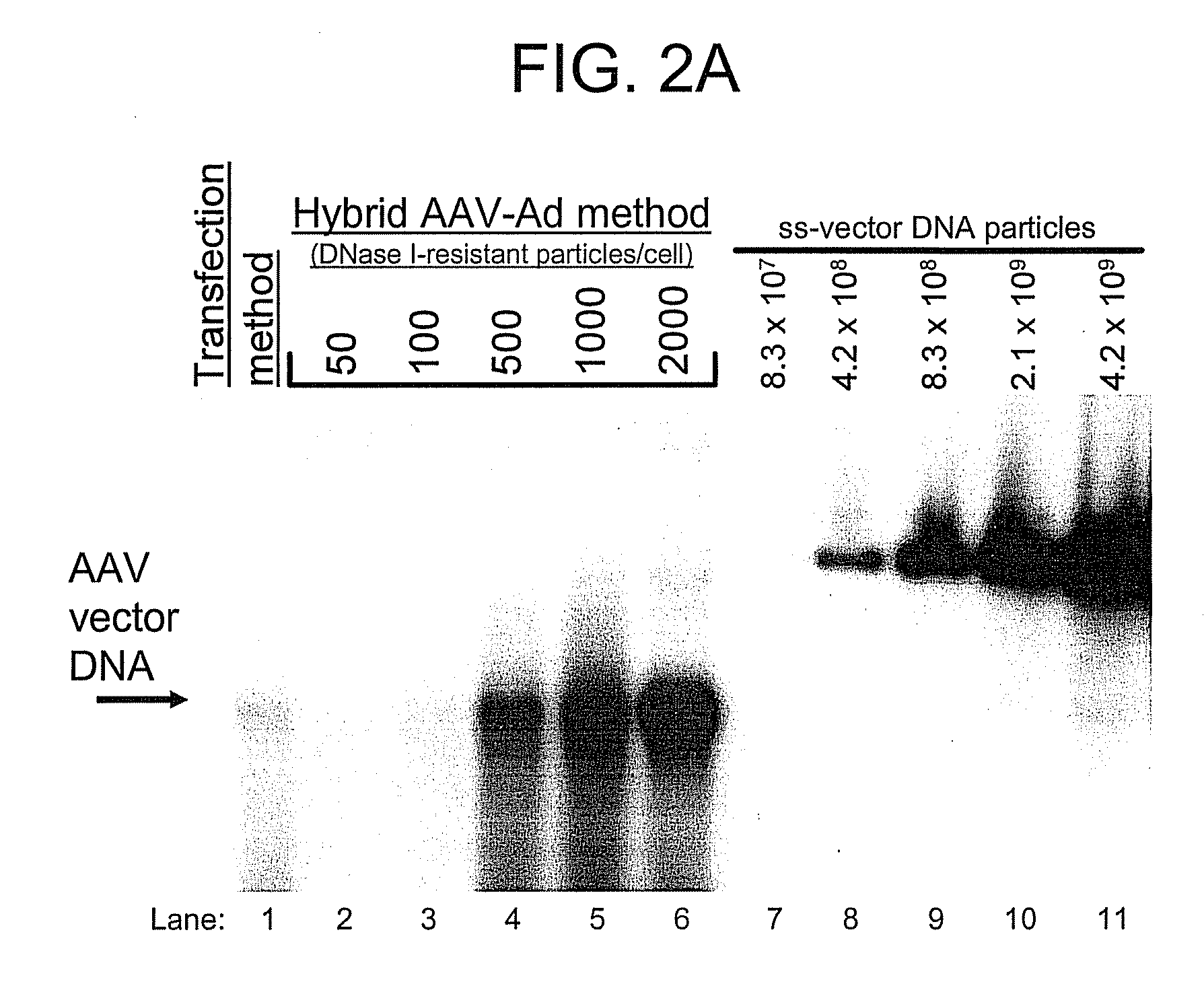
A recombinant hybrid virus, including: (a) a deleted adenovirus vector genome comprising the adenovirus 5′ and 3′ cis-elements for viral replication and encapsidation, and further comprising a deletion in an adenovirus genomic region selected from the group consisting of: (i) the polymerase region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional polymerase protein from said deleted region and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional polymerase protein, (ii) the preterminal protein region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional preterminal protein from said deleted region, and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional preterminal protein, and (iii) both the regions of (i) and (ii); and (b) a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector genome flanked by the adenovirus vector genome sequences of (a), said recombinant AAV vector genome comprising (i) AAV 5′ and 3′ inverted terminal repeats, (ii) an AAV packaging sequence, and (iii) a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, wherein said heterologous nucleic acid sequence is flanked by the 5′ and the 3′ AAV inverted terminal repeats of (i). Methods of making and using the recombinant hybrid virus are also disclosed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
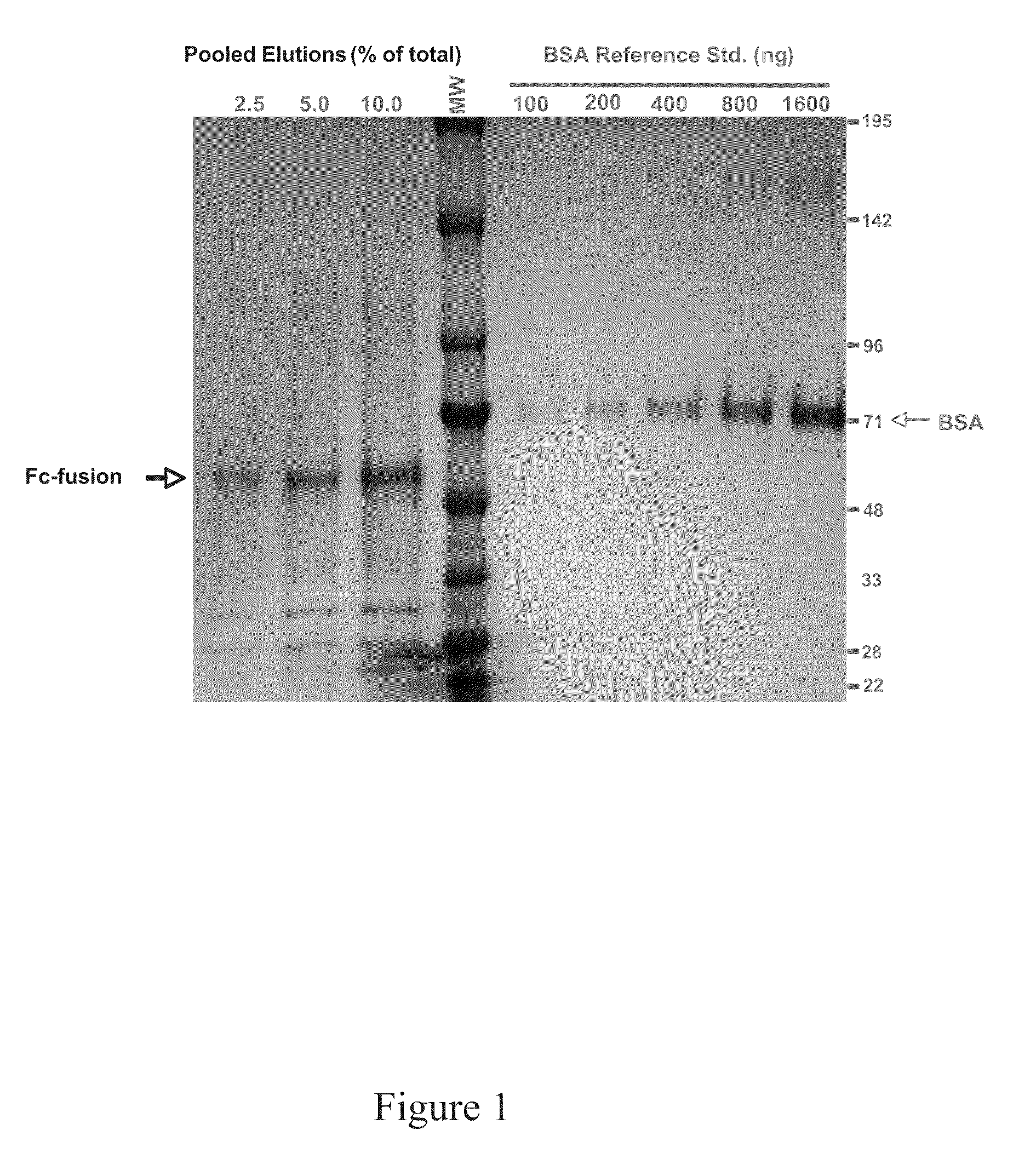
Production of fc-fusion polypeptides in eukaryotic algae
InactiveUS20110151515A1Increase serum stabilityEfficient separation and purificationUnicellular algaeVaccinesHeterologousProtein regulation
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer plastids comprising heterologous genes encoding immuno-activating domains fused to an extracellular domain (ECD) of a receptor or surface glycoprotein, a growth factor or an enzyme and produced within a subcellular organelle, such as a chloroplast. The immuno-activating domains may include those regions of a protein capable of modulating the interaction between immune effector cells via proteins containing stereoselective binding domains and specific ligands, such as the Fc regions of antibodies. The present disclosure also demonstrates the utility of plants, including green algae, for the production of complex multi-domain fusion proteins as soluble bioactive therapeutic agents.
Owner:SAPPHIRE ENERGY
Viral vectors and methods for producing and using the same
InactiveUS7858367B2Reduce and even essentially eliminate contaminationReduce dependenceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousPolymerase L
A recombinant hybrid virus which includes: (a) a deleted adenovirus vector genome having the adenovirus 5′ and 3′ cis-elements for viral replication and encapsidation and a deletion in an adenovirus genomic region selected from the polymerase region and / or the preterminal protein region, wherein the deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional polymerase and / or preterminal protein from the deleted region and the hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional polymerase protein; and (b) a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector genome flanked by the adenovirus vector genome sequences of (a), wherein the recombinant AAV vector genome includes an AAV packaging sequence and a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, wherein the heterologous nucleic acid sequence is flanked by 5′ and 3′ AAV inverted terminal repeats.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Polypeptide for inhibiting novel coronavirus infection and screening method thereof
PendingCN111560054APrevent intrusionSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid compositionGlutamic acid
The invention discloses a polypeptide for inhibiting novel coronavirus infection and a screening method thereof, which belong to the technical field of biological medicine. The screening method comprises the following steps: obtaining an S protein gene sequence of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2; determining an HR1 region and an HR2 region of an S protein region of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2; selecting a natural peptide fragment consisting of 30-36 amino acids in the HR2 region as a polypeptide for inhibiting novel coronavirus infection; on the basis of the natural peptide fragment, glutamic acid-lysine or glutamic acid-arginine pairs are designed through site-specific mutagenesis to form a polypeptide chain inner salt bridge. Compared with the prior art, the polypeptide for inhibiting the novel coronavirus infection has the beneficial effects that the polypeptide for inhibiting the novel coronavirus infection can form a stable 6-HB spiral structure with HR1P and has the capability of inhibiting the novel coronavirus infection from invading cells.
Owner:哈尔滨吉象隆生物技术有限公司
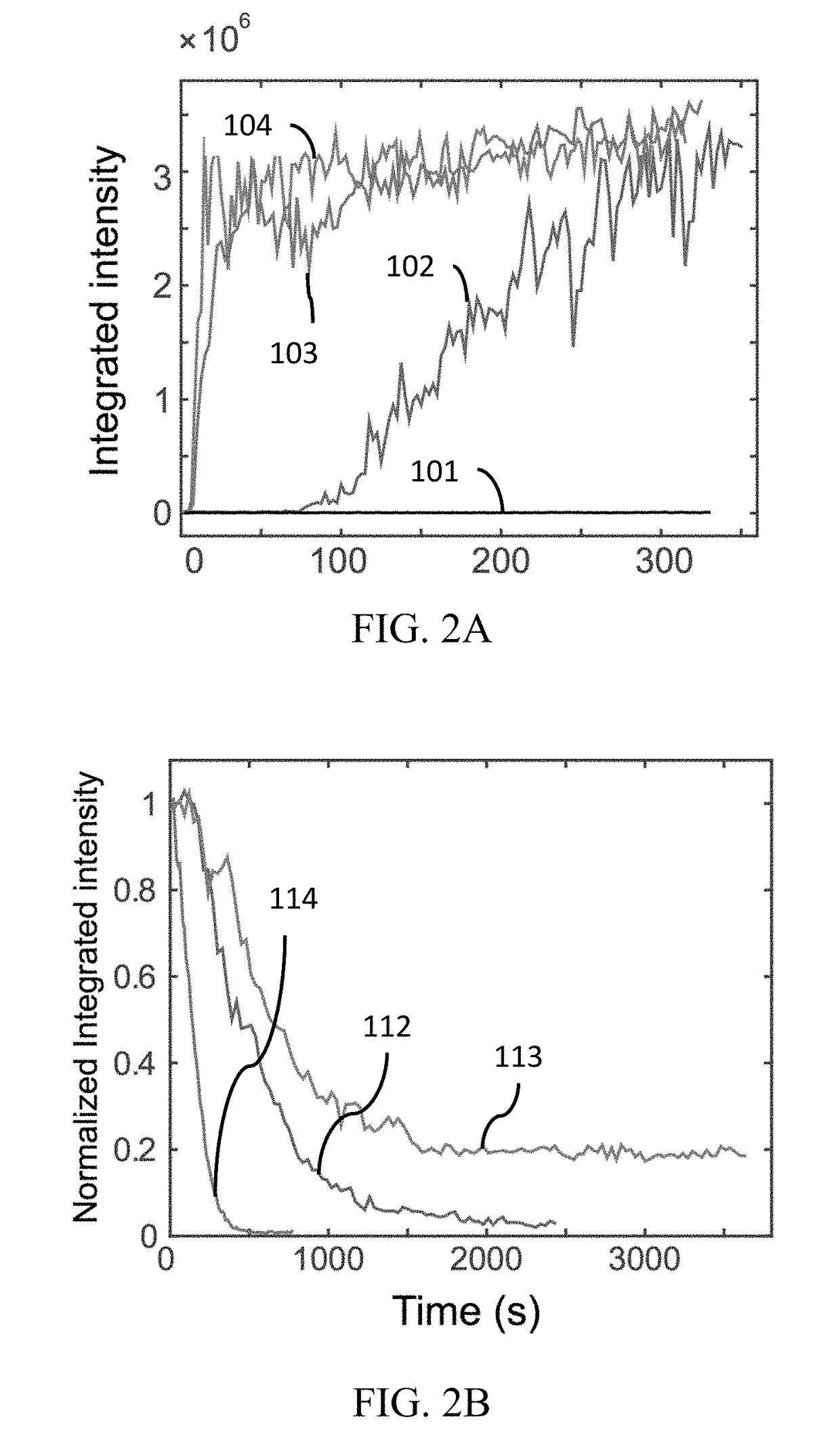
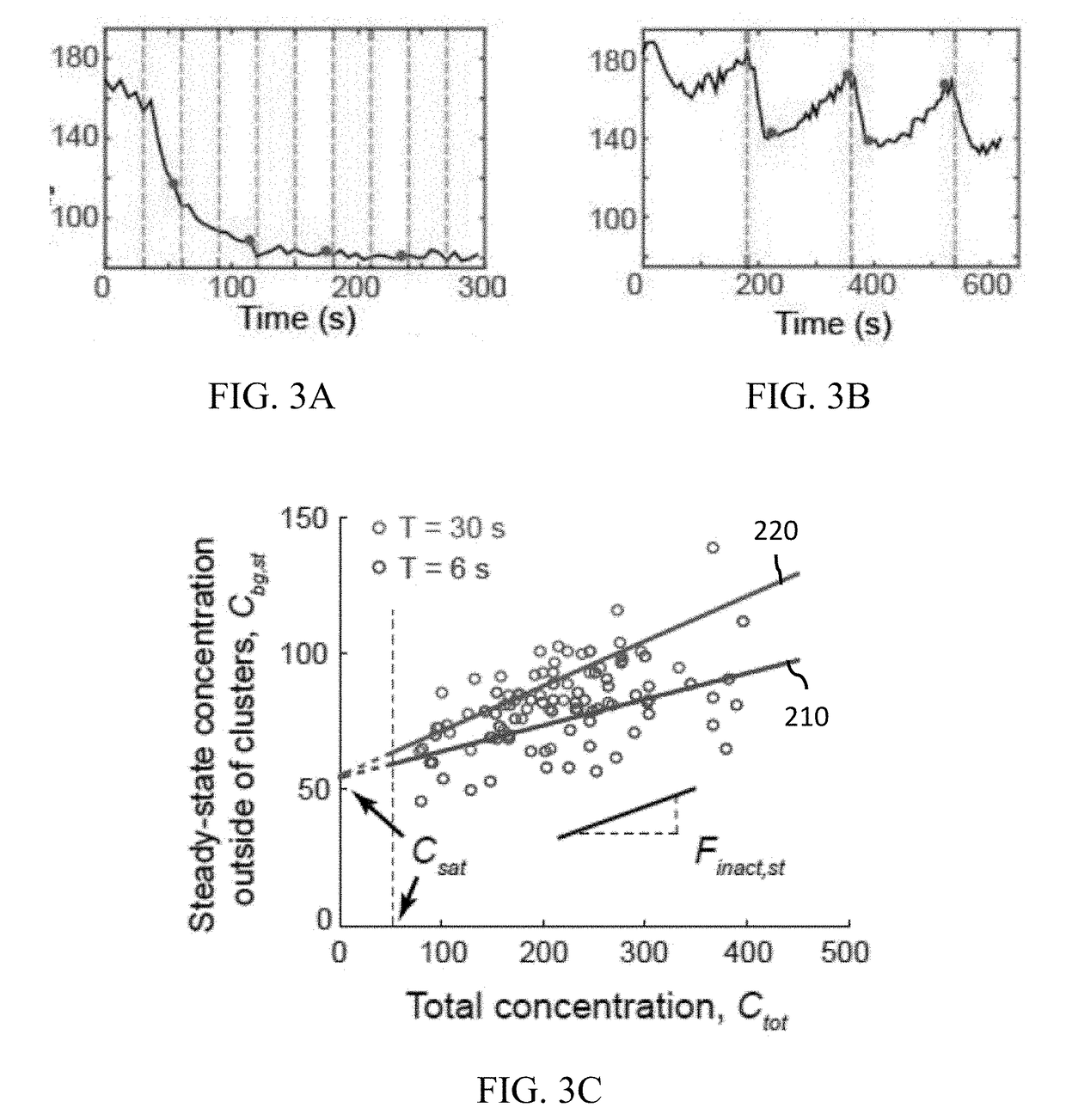
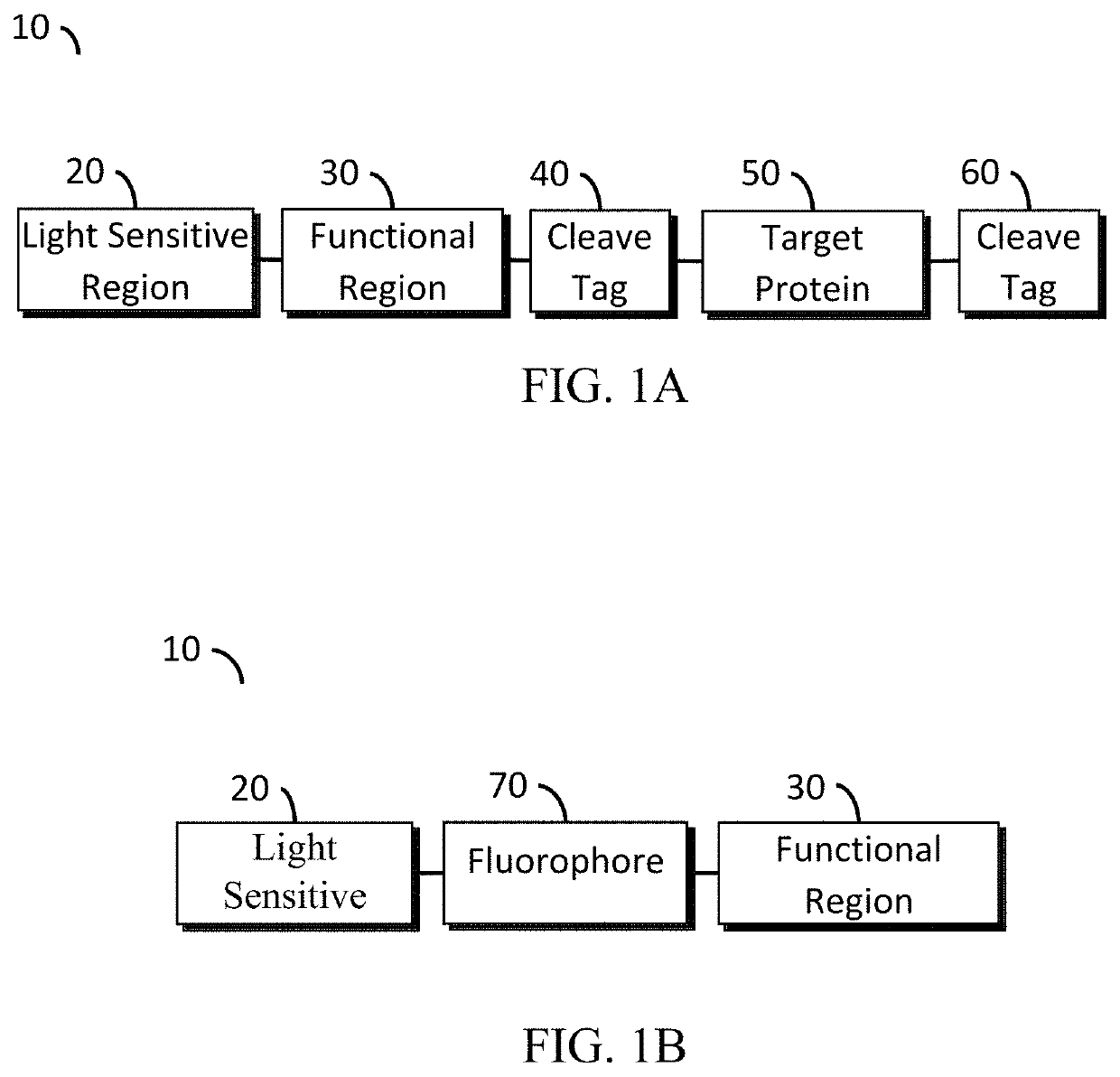
Optogenetic tool for rapid and reversible clustering of proteins
ActiveUS20170355977A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptogeneticsProtein target
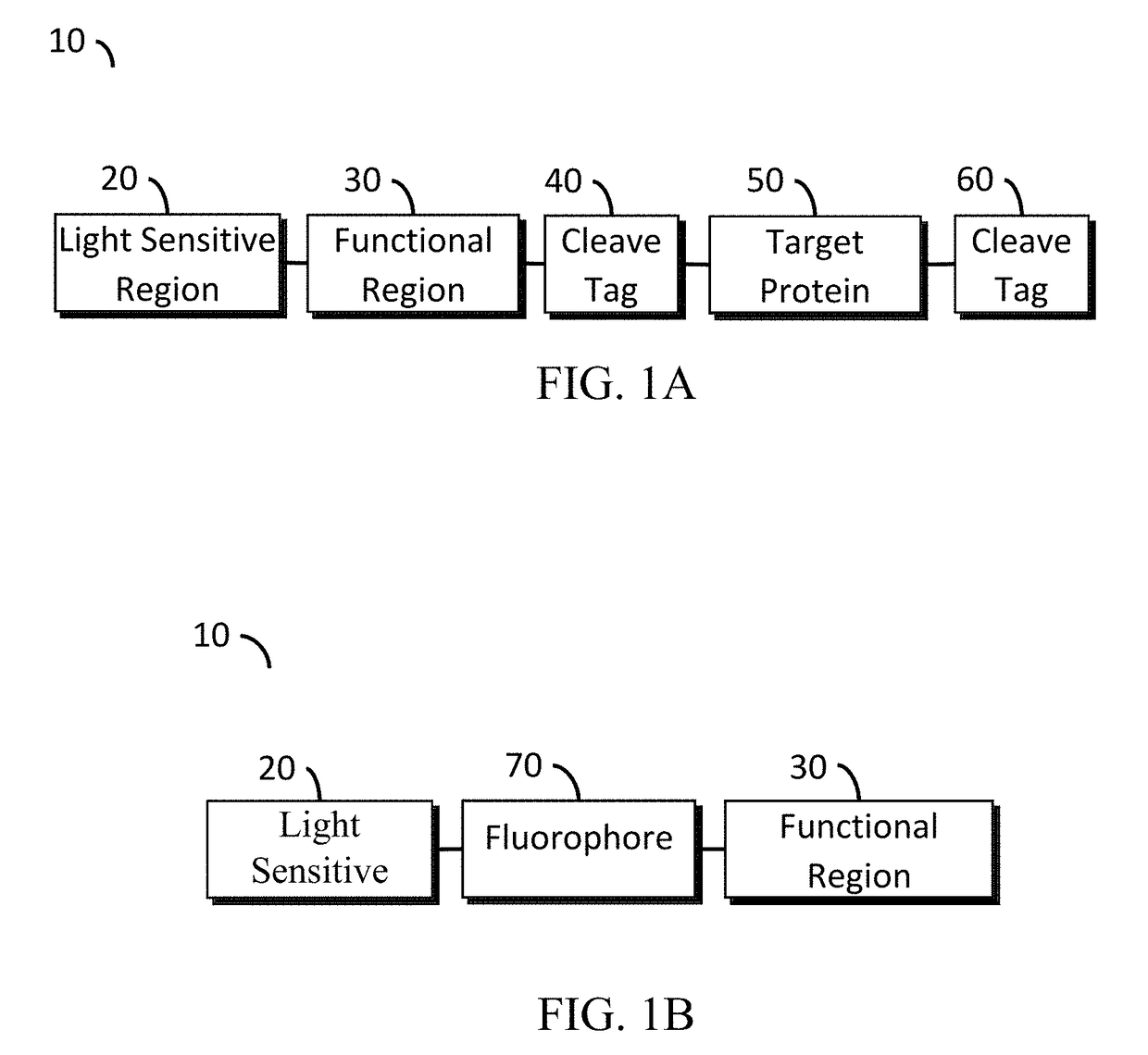
A protein construct including a gene encoding a light-sensitive protein fused to at least one of either a low complexity sequence, an intrinsically disordered protein region (IDR), or a repeating sequence of a linker and another gene encoding a light-sensitive protein. Among the many different possibilities contemplated, the protein construct may also advantageously include cleavage tags. This protein construct may be utilized for a variety of functions, including a method for protein purification, which requires introducing the protein construct into a living cell, and inducing the formation of clusters by irradiating the construct with light. The method may also advantageously include cleaving a target protein from an IDR, and separating the clusters via centrifuge. A kit for practicing in vivo aggregation or liquid-liquid phase separation is also included, the kit including the protein construct and a light source capable of producing a wavelength that the light-sensitive protein will respond to.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
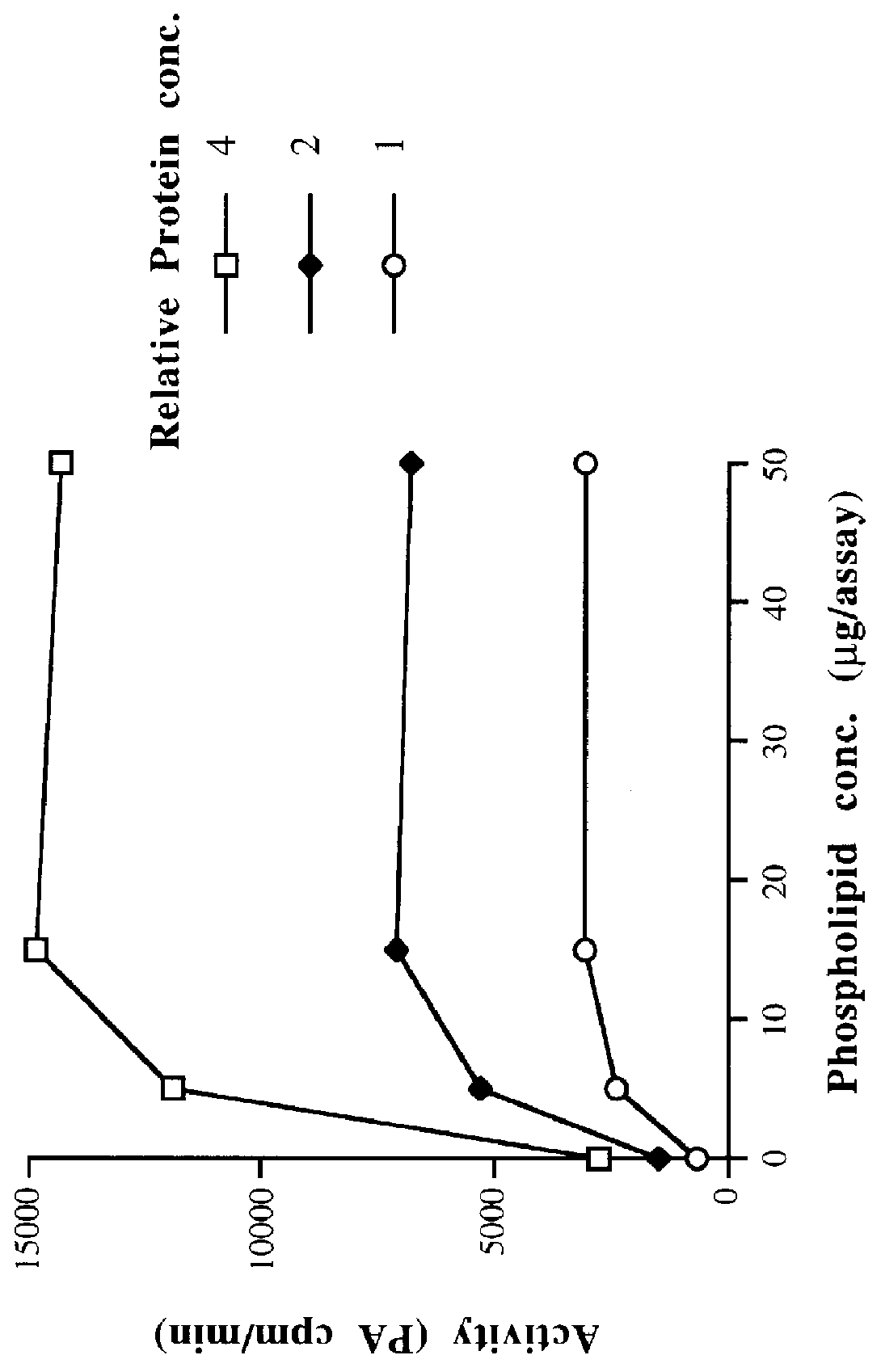
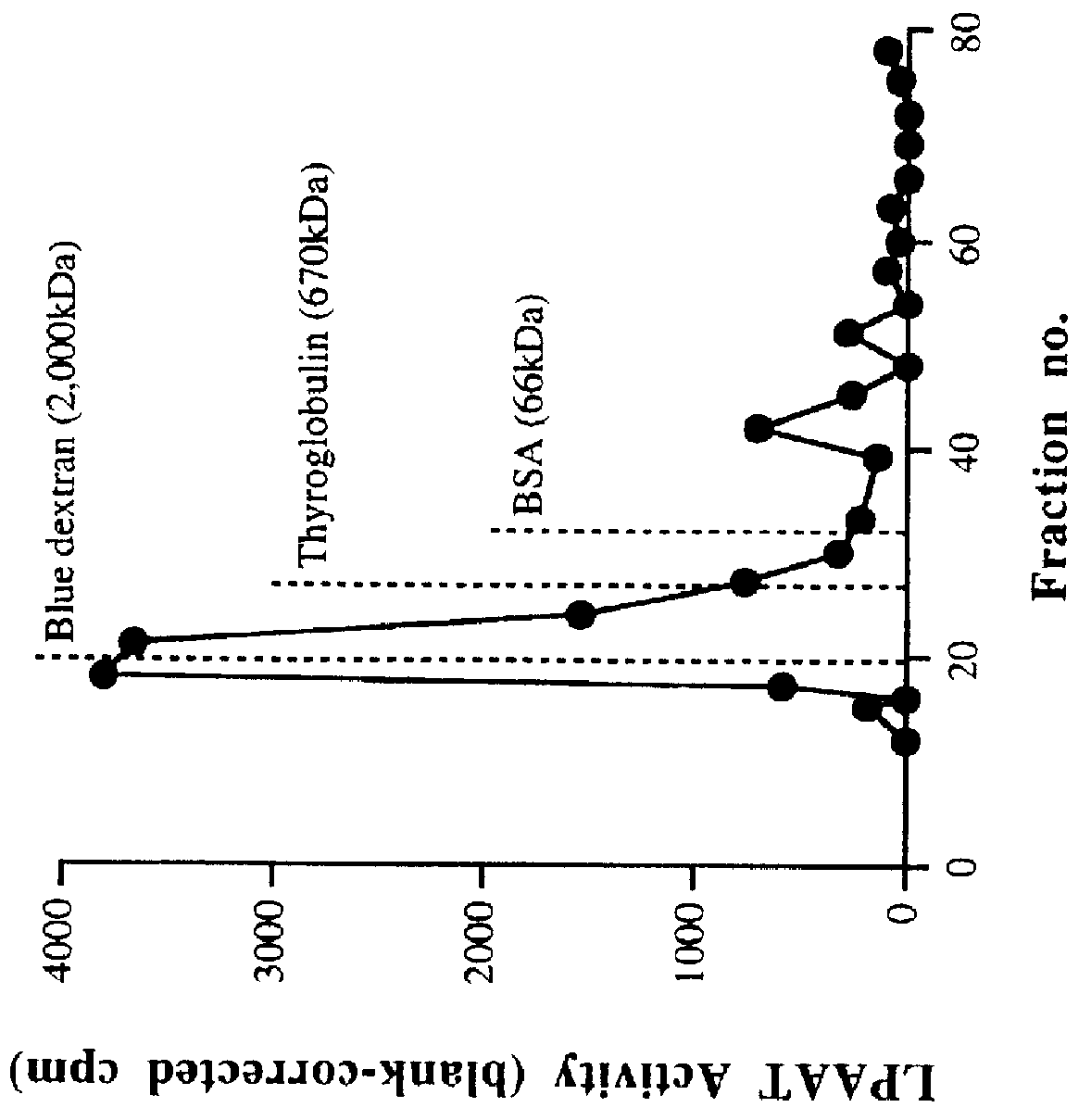
Plant lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferases
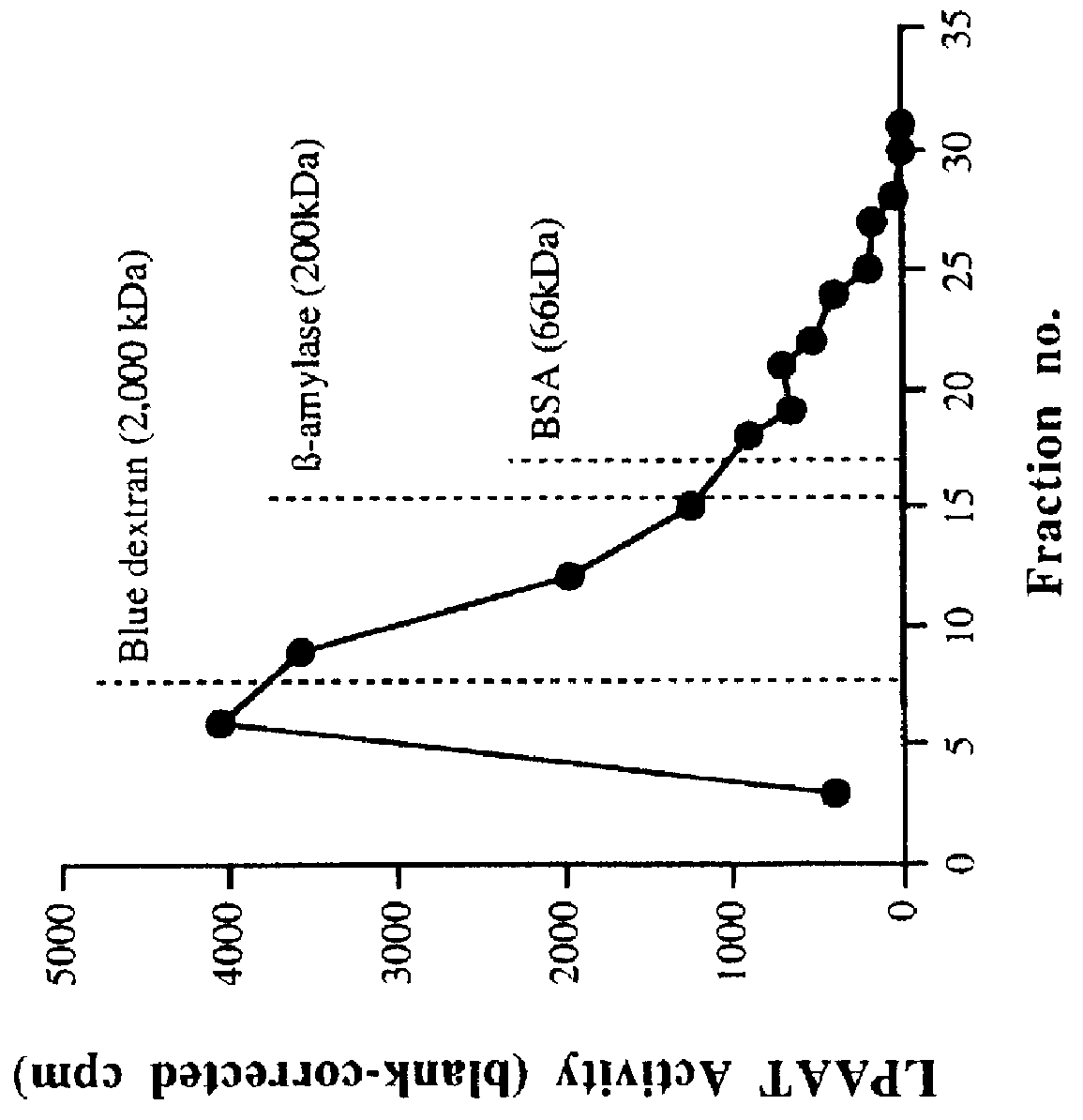
This invention relates to plant LPAATs, means to identify such proteins, amino acid and nucleic acid sequences associated with such protein, and methods to obtain, make and / or use such plant LPAATs. Purification, especially the removal of plant membranes and the substantial separation away from other plant proteins, and use of the plant LPAAT is provided, including the use of the protein as a tool in gene isolation for biotechnological applications. In addition, nucleic acid sequences encoding LPAAT protein regions are provided, and uses of such sequences for isolation of LPAAT genes from plants are considered.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY)
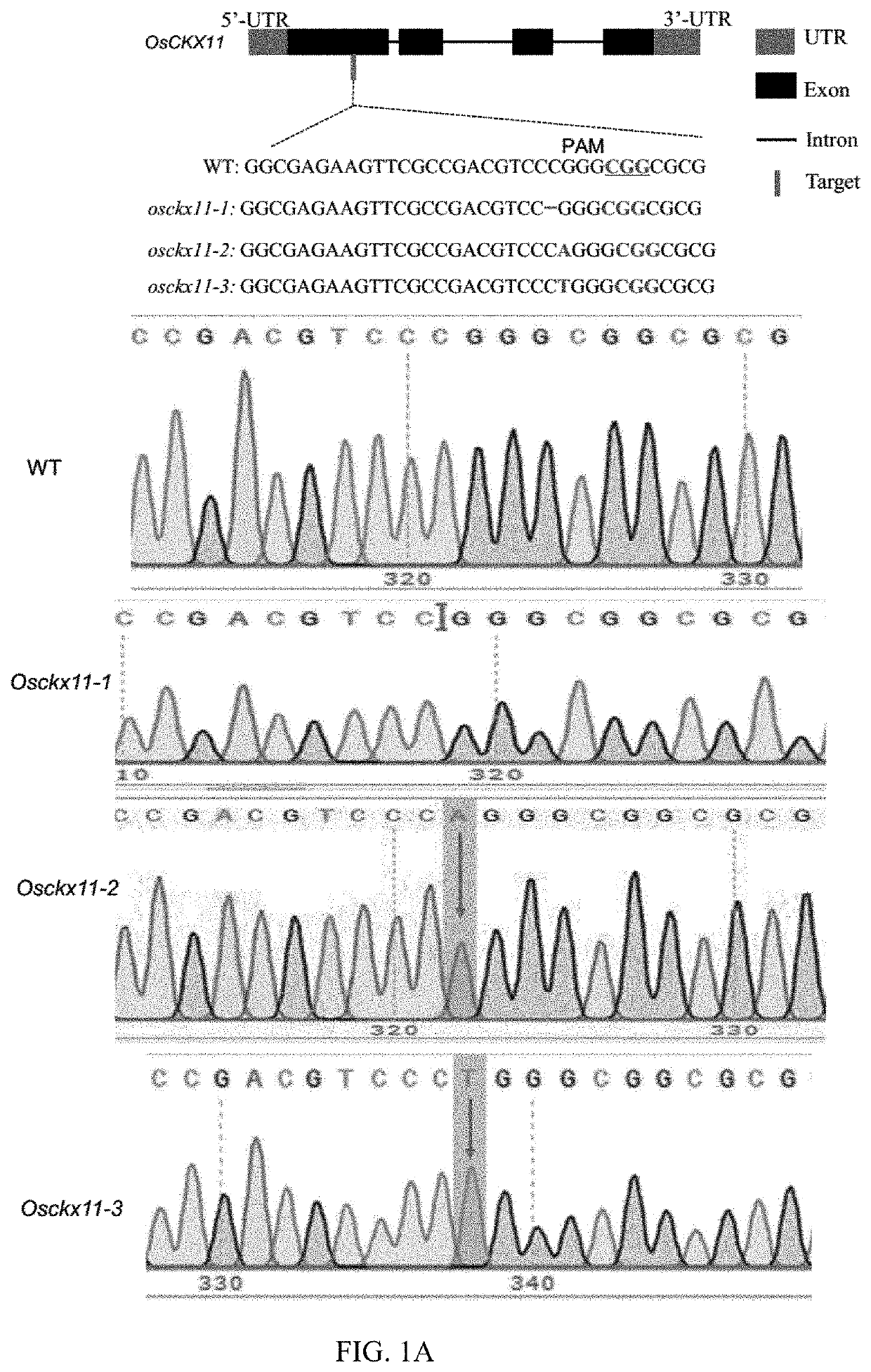
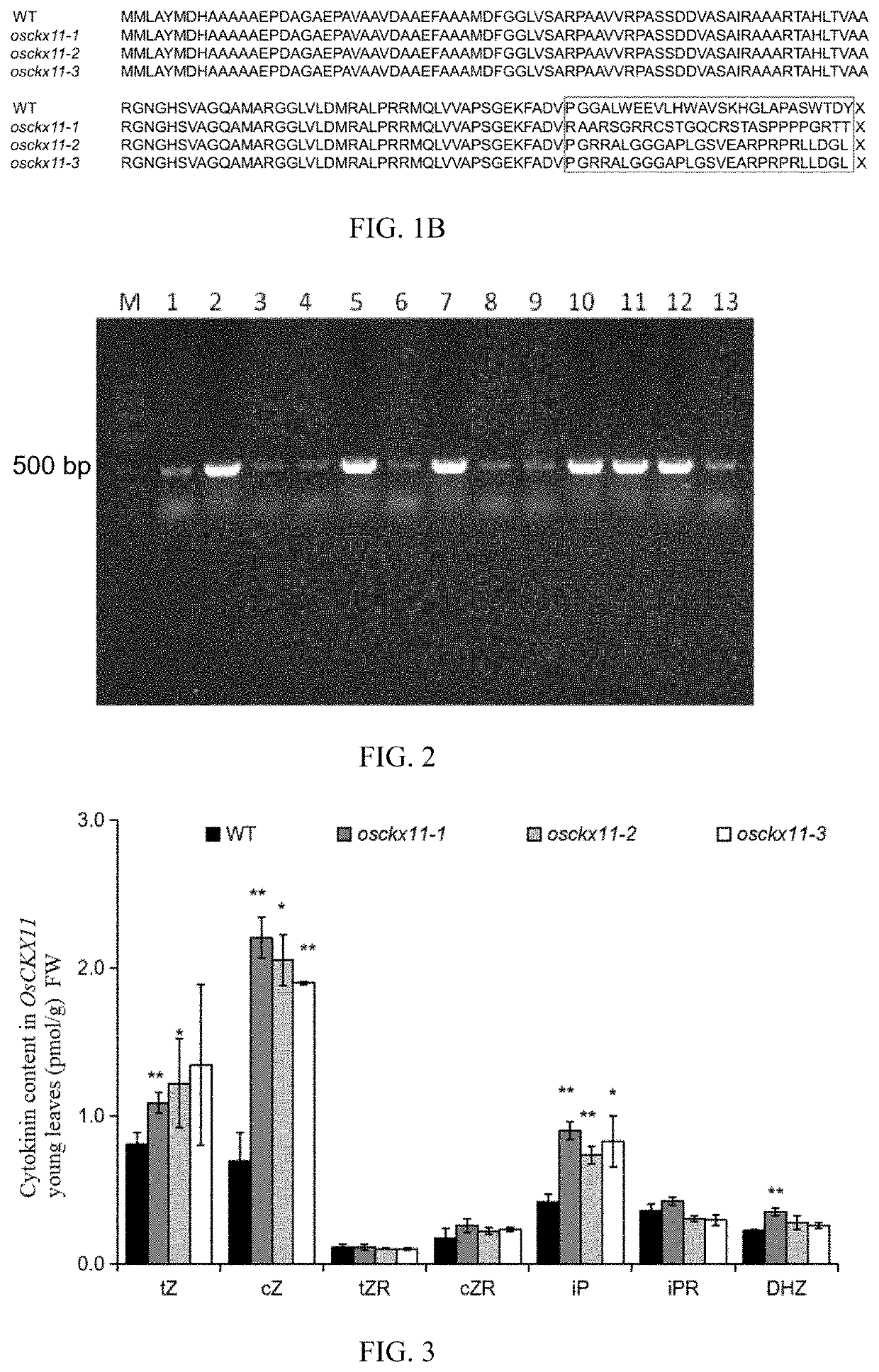
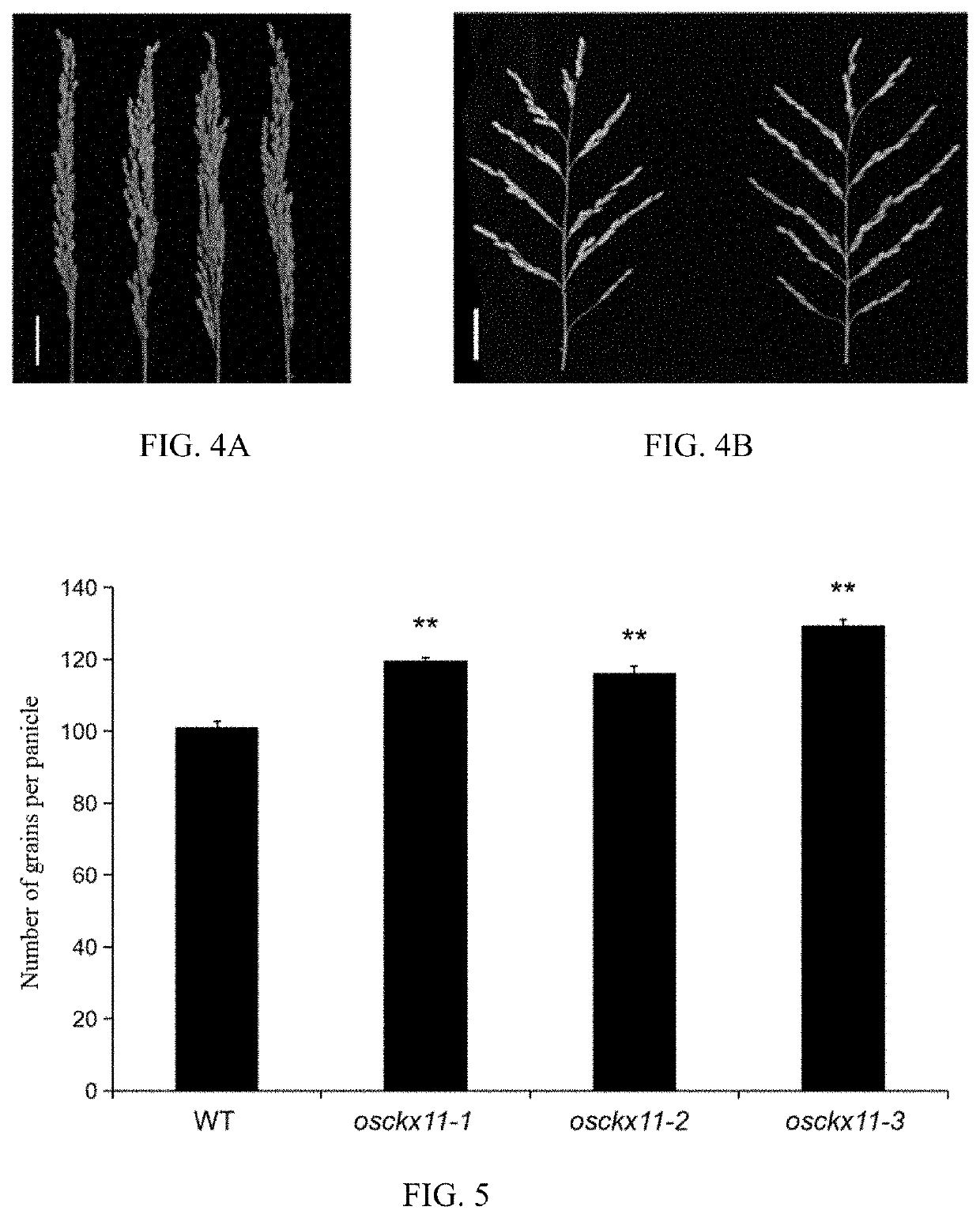
A gene osckx11 for controlling rice grain number and use thereof
PendingUS20210324397A1Reduce expressionSignificant positive effectOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePlant genetic engineering
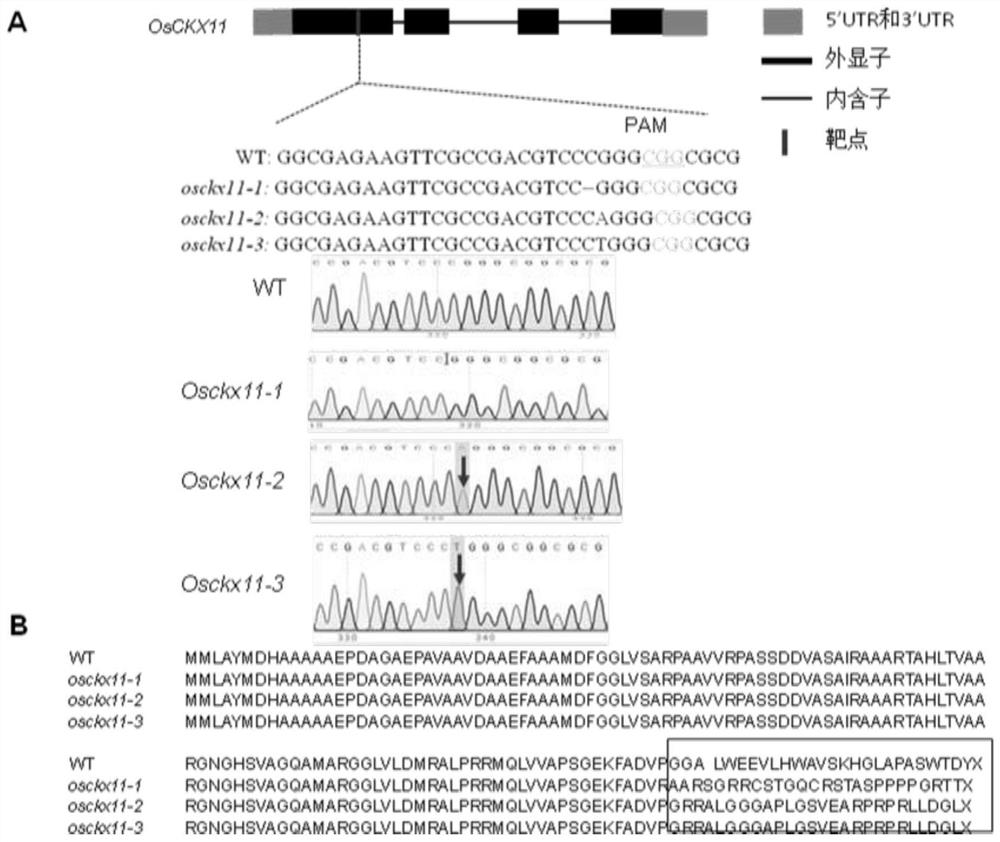
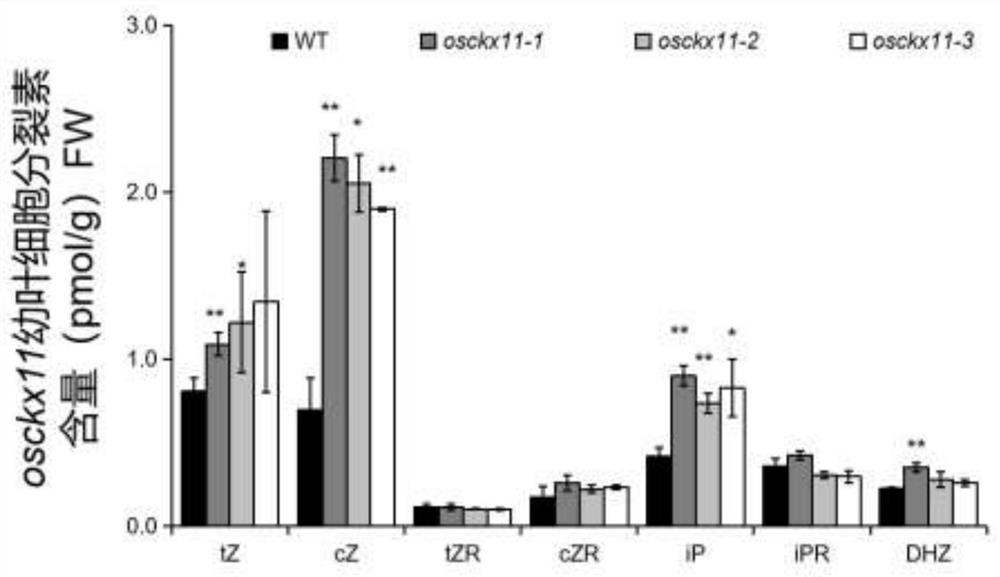
The present disclosure belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses a gene for controlling the rice grain number per panicle and its use. Nucleotide sequence of OsCKX11 is SEQ ID NO. 1, nucleotide sequence for coding protein region is SEQ ID NO. 2, amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is SEQ ID NO. 3. The disclosure constructs an OsCKX11-knocked-out vector using CRISPR / Cas9, and identifies multiple independent homozygous lines through PCR amplification and sequencing methods, and provides a mutant in which specific knockout of gene OsCKX11 of the rice leads to an increase in cytokinin levels and an increase in grain number per panicle. Based on the biological function of OsCKX11 to increase the rice grain number per panicle, methods such as gene editing, natural allele replacement, RNA interference, or molecular assisted breeding can be used to improve existing rice varieties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Gene OsCKX11 for controlling number of rice grains per spike and application of gene OsCKX11 for controlling number of rice grains per spike
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Inhibition of TCR Signaling with Peptide Variants
ActiveUS20130039948A1Current is limitedIn-vivo radioactive preparationsVirus peptidesADAMTS ProteinsT cell
The present invention provides compositions comprising peptides derived from amino acid sequences (or from combinations thereof) of fusion and other protein regions of various viruses, including but not limited to, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, herpesvirus saimiri, human herpesvirus 6, Lassa virus, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, Mopeia virus, Tacaribe virus, Friend murine leukemia virus; human T lymphotropic virus type 1; herpesvirus ateles; Marburg virus; Sudan Ebola virus; Zaire Ebola virus, and comprising L- and / or D-amino acids and combinations thereof, which affect T cells by acting on the T cell antigen receptor (TCR). More specifically, the peptides act on the TCRαβ-CD3δε-CD3γε-ζζ signaling complex. Yet more specifically, the peptides act on the TCRα / CD3δε / ζζ signaling module of TCR. The present invention further relates to the prevention and therapy of various T cell-related disease states involving the use of these compositions. Specifically, the compositions are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of a disease or condition where T cells are involved or recruited. The compositions of the present invention also are useful in the production of medical devices comprising peptide matrices (for example, medical implants and implantable devices).
Owner:SIGNABLOK
Recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase and fungal expression vector as well as fungal insecticide thereof
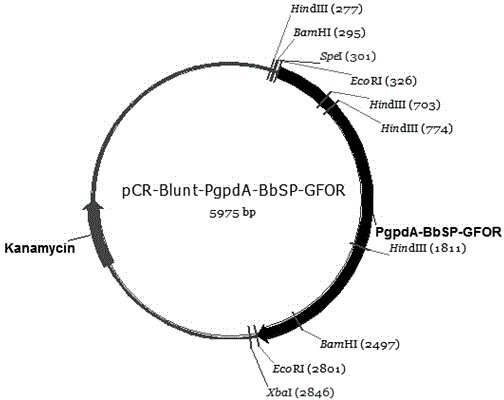
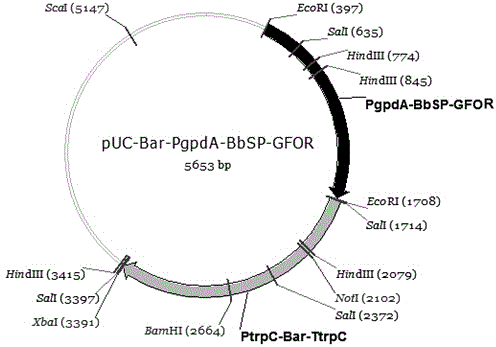
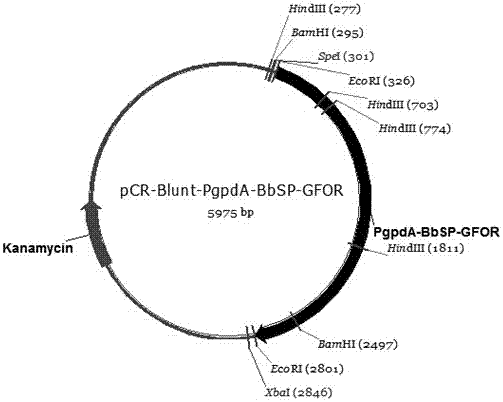
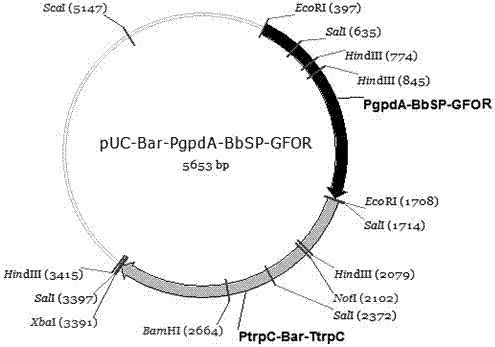
The invention provides a recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase and a fungal expression vector as well as a fungal insecticide thereof. A recombinant nucleotide sequence, which comprises a signal peptide sequence for coding the chitinase of beauveria bassiana and a mature protein region sequence for coding the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase of zymonomas mobilis, is constructed by use of the molecular biological technique. According to the recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase, the PgpdA-BbSP-GFOR segment is cloned into a pUC-Bar vector to obtain the fungal expression vector; the fungal expression vector is imported into the wild-type beauveria bassiana Bb0062 strain to obtain the beauveria bassiana transformant of BbSP-GFOR. The recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase effectively blocks the activity of the GNBPs in a host; the time that the fungi knock down insect pests is shortened by 48 hours and the insecticidal efficacy is remarkably improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Viral vectors and methods for producing and using the same
InactiveUS20110294193A1Reduce and even essentially eliminate contaminationReduce dependencePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
A recombinant hybrid virus, including: (a) a deleted adenovirus vector genome comprising the adenovirus 5′ and 3′ cis-elements for viral replication and encapsidation, and further comprising a deletion in an adenovirus genomic region selected from the group consisting of: (i) the polymerase region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional polymerase protein from said deleted region and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional polymerase protein, (ii) the preterminal protein region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional preterminal protein from said deleted region, and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional preterminal protein, and (iii) both the regions of (i) and (ii); and (b) a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector genome flanked by the adenovirus vector genome sequences of (a), said recombinant AAV vector genome comprising (i) AAV 5′ and 3′ inverted terminal repeats, (ii) an AAV packaging sequence, and (iii) a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, wherein said heterologous nucleic acid sequence is flanked by the 5′ and 3′ AAV inverted terminal repeats of (i). Methods of making and using the recombinant hybrid virus are also disclosed.
Owner:AMALFITANO ANDREA +2
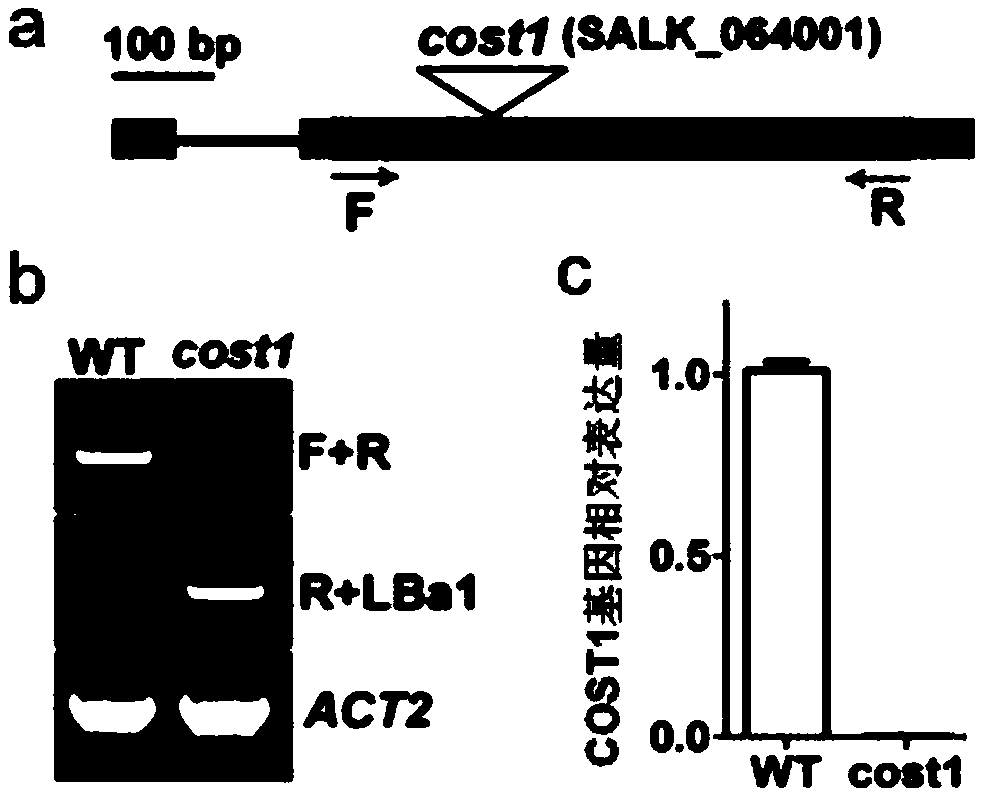
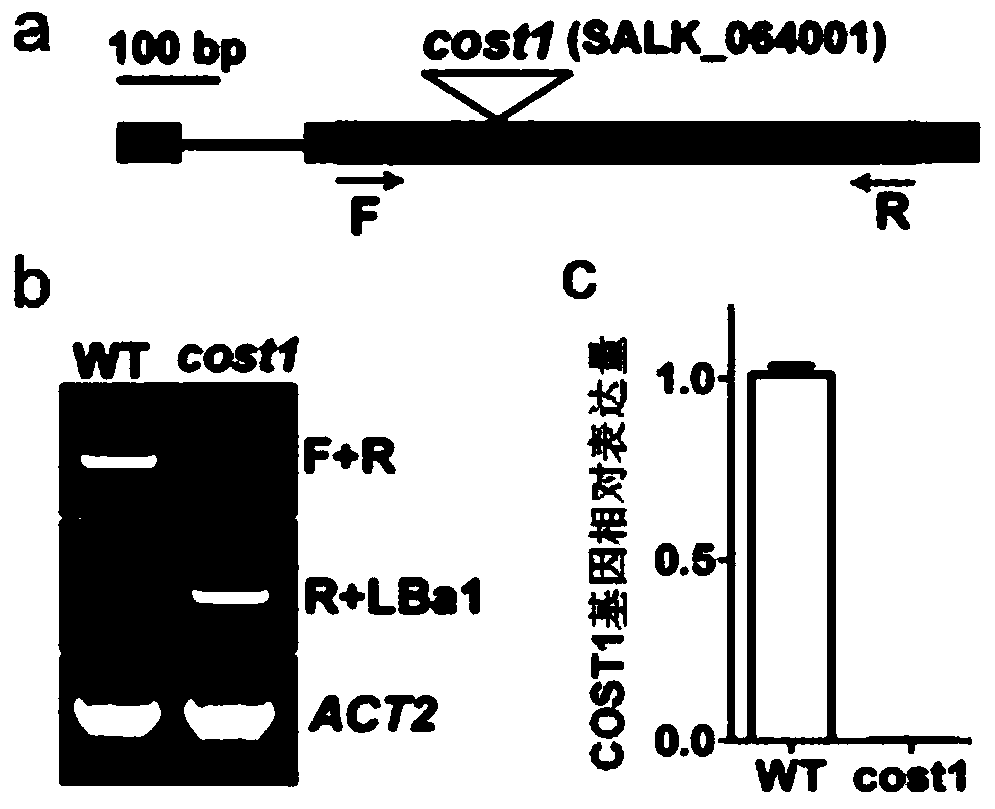
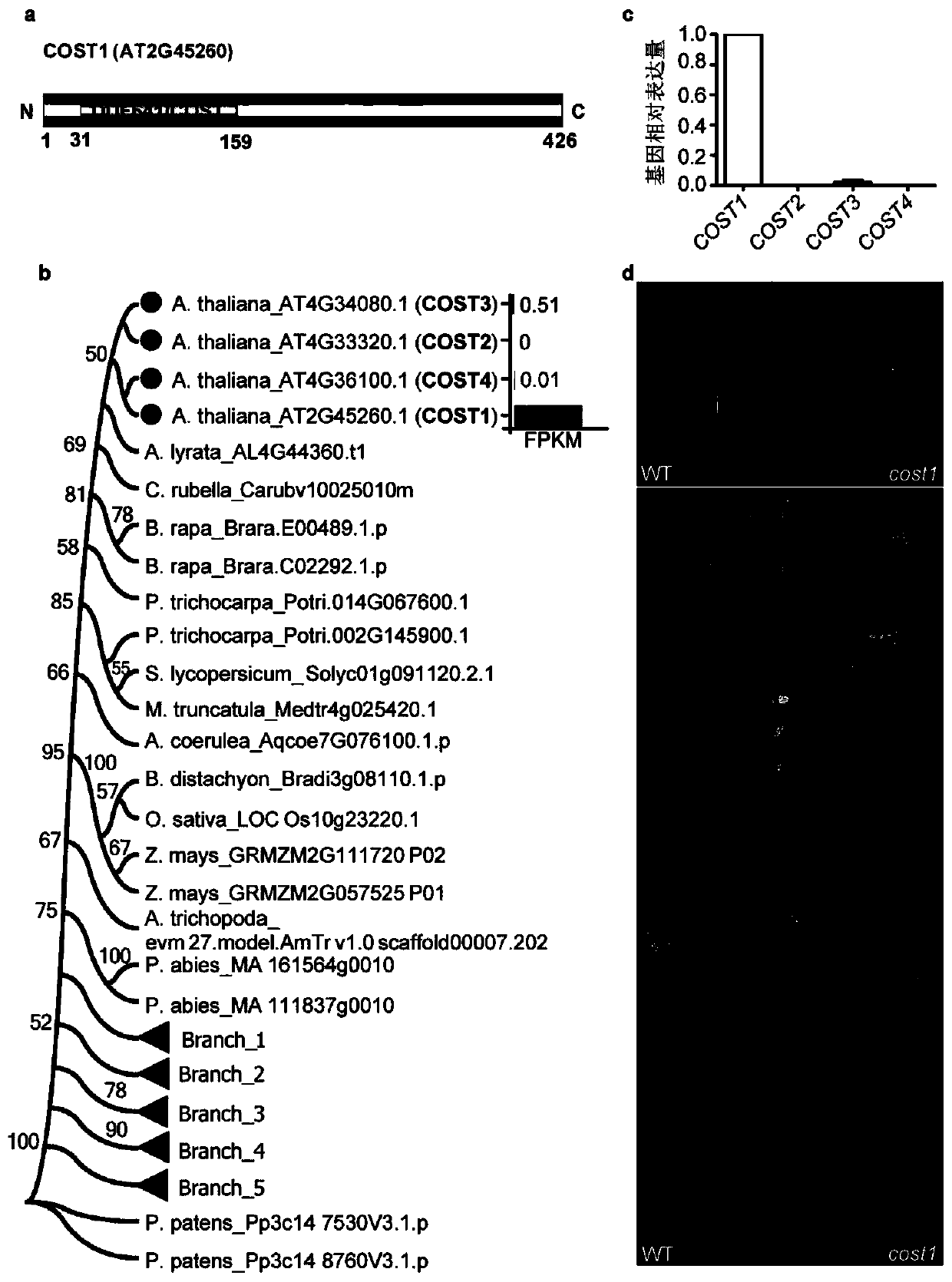
Method for improving plant drought resistance by inhibiting expression of COST1 genes
ActiveCN108949821AImprove drought resistanceGenetic improvementPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a method for improving plant drought resistance by inhibiting expression of COST1 genes. The nucleotide sequence of the COST1 genes is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and the protein sequence coded by the COST1 genes is an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2. Homologous genes of the COST1 genes include tomato SlCOST1 genes, rice OsCOST1 genes, poplar PtCOST1 and PtCOST2 genes and other genes having the homology degree of more than 40% with fragments in any nucleotide or protein region of COST1 in other species. A foundation is laid for cultivating more drought resistant transgenic plants. The method can be applied to plant genetic improvement.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Optogenetic tool for rapid and reversible clustering of proteins
ActiveUS10533167B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsMaterial analysis by optical meansProtein targetOptogenetics
A protein construct including a gene encoding a light-sensitive protein fused to at least one of either a low complexity sequence, an intrinsically disordered protein region (IDR), or a repeating sequence of a linker and another gene encoding a light-sensitive protein. Among the many different possibilities contemplated, the protein construct may also advantageously include cleavage tags. This protein construct may be utilized for a variety of functions, including a method for protein purification, which requires introducing the protein construct into a living cell, and inducing the formation of clusters by irradiating the construct with light. The method may also advantageously include cleaving a target protein from an IDR, and separating the clusters via centrifuge. A kit for practicing in vivo aggregation or liquid-liquid phase separation is also included, the kit including the protein construct and a light source capable of producing a wavelength that the light-sensitive protein will respond to.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
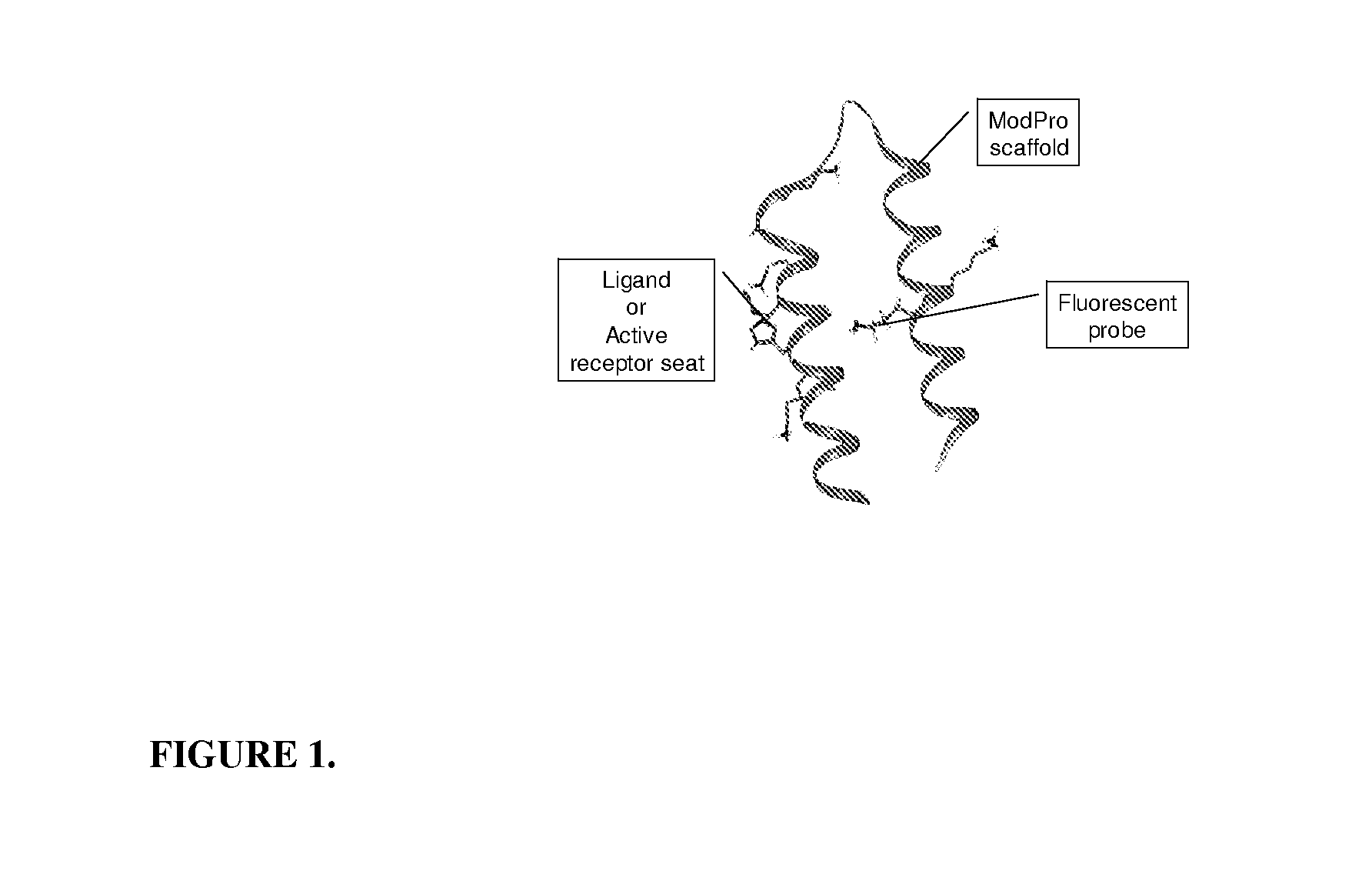
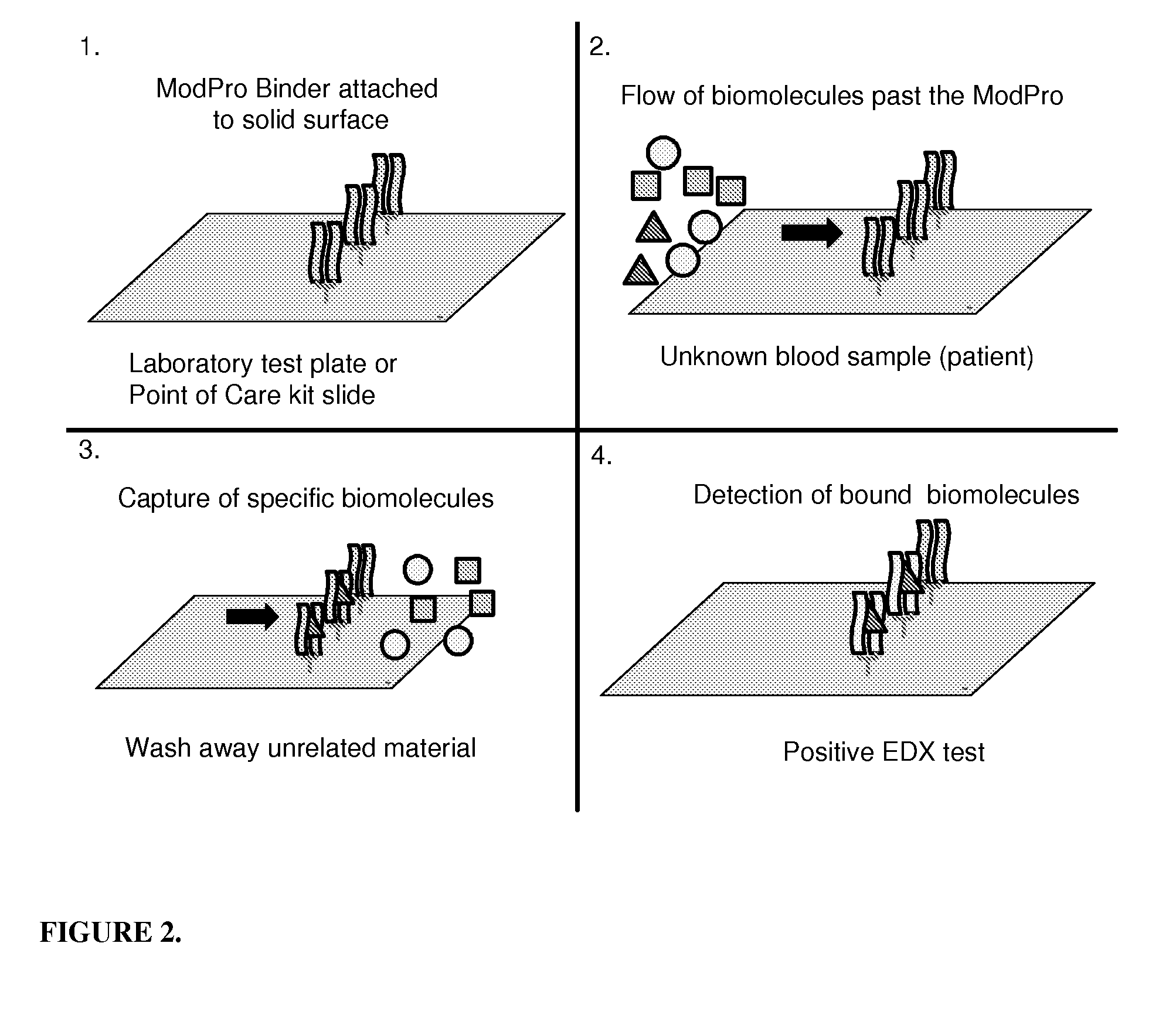
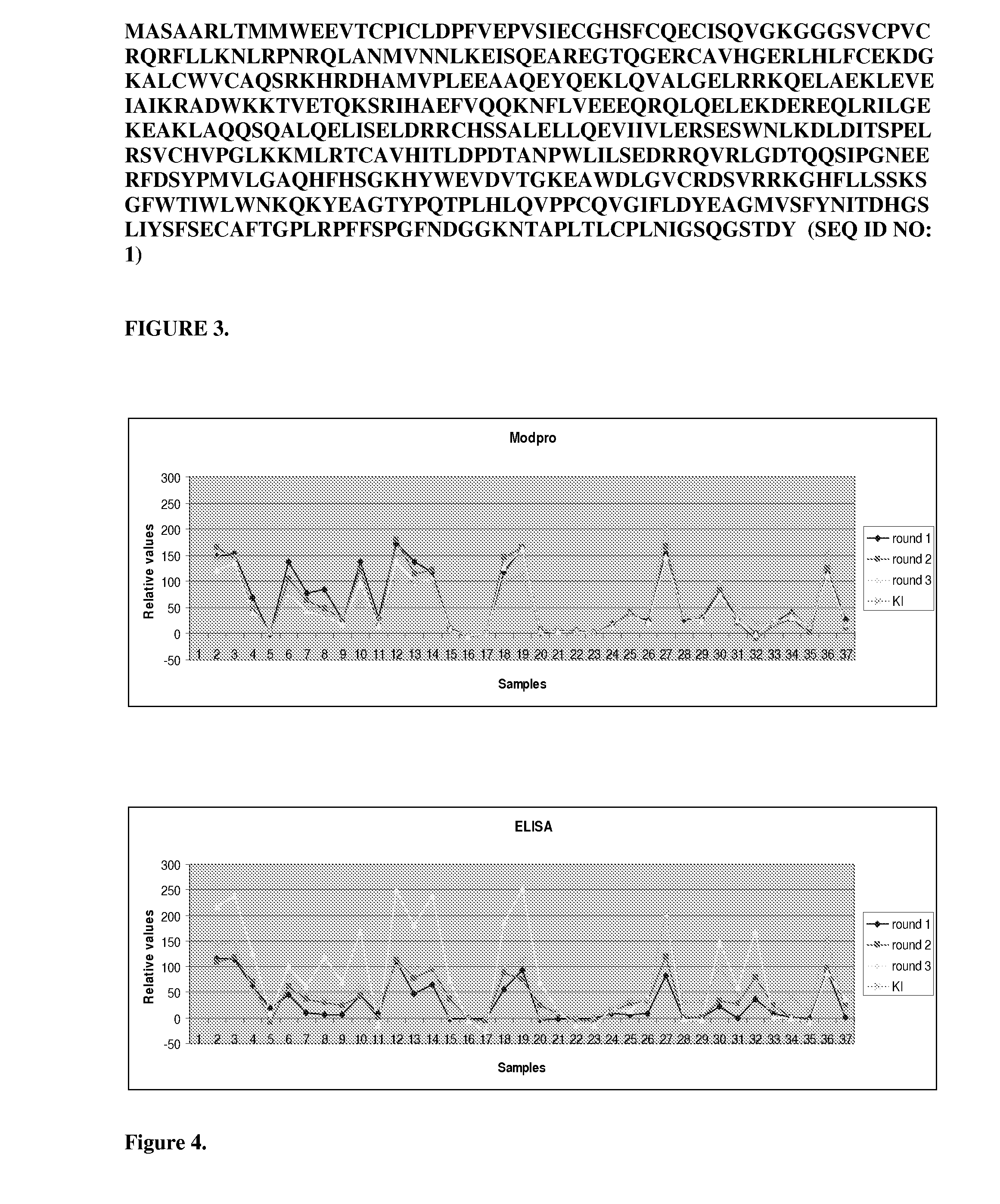
Novel diagnostic sensor for rapid and reproducible ro52 protein domain detection
The present invention relates to the use of specific synthetic sensor molecules for the discrimination of proteins and protein domains involved in autoimmunity. More specifically, in one embodiment, the invention relates to the detection of antibodies which bind to specific domains of the Ro52 protein. In another embodiment, the invention relates to the use of specific synthetic sensor molecules to identify domains of the Ro52 protein with different antibody specificities. The invention also includes a method for assessing the risk that a fetus will develop congenital heart block. The invention enables the evaluation and differential diagnosis of a range of autoimmune disorders, allowing appropriate treatment or more generally medical intervention decisions to be made.
Owner:MEADOWLAND BUSINESS PARTNERS
Conserved neisserial antigens
InactiveUS20080132448A1Reduce complexityShorter hybridizationAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntigenSalmonella serotype typhi
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
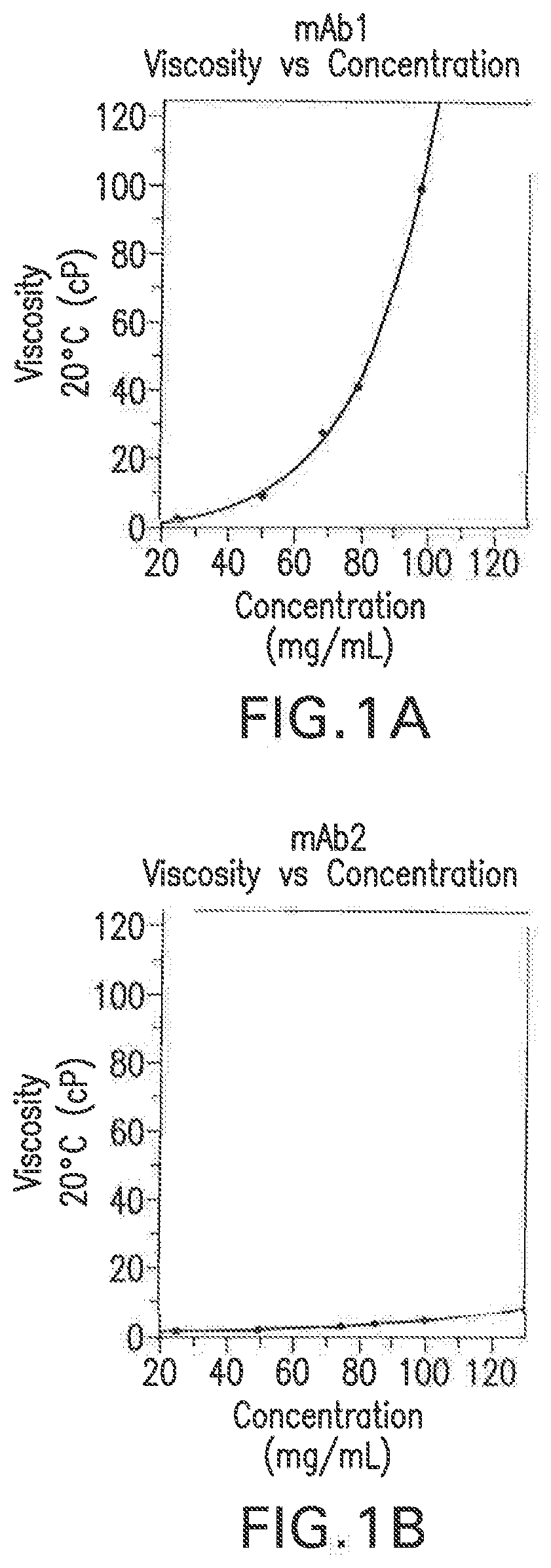
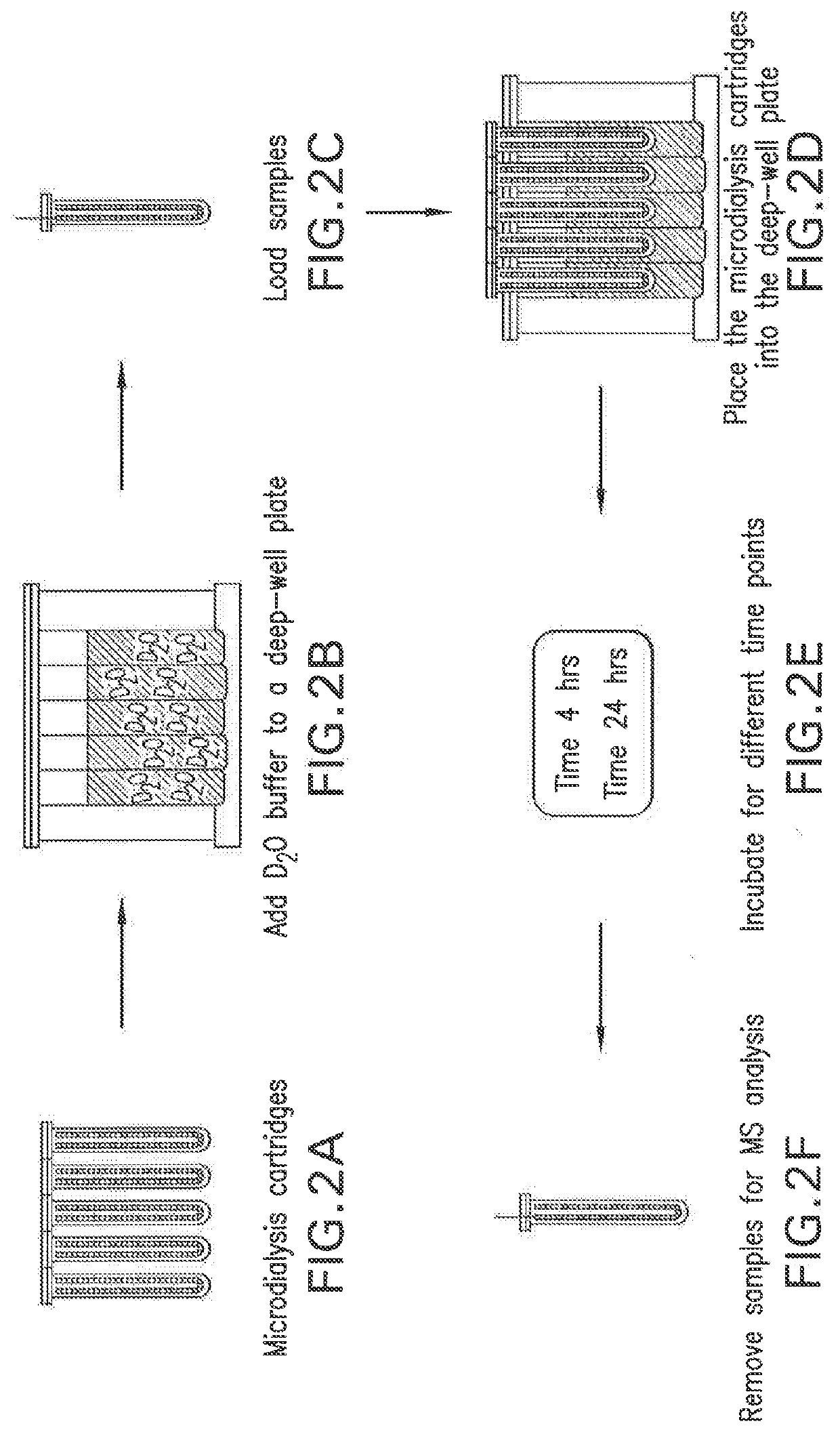
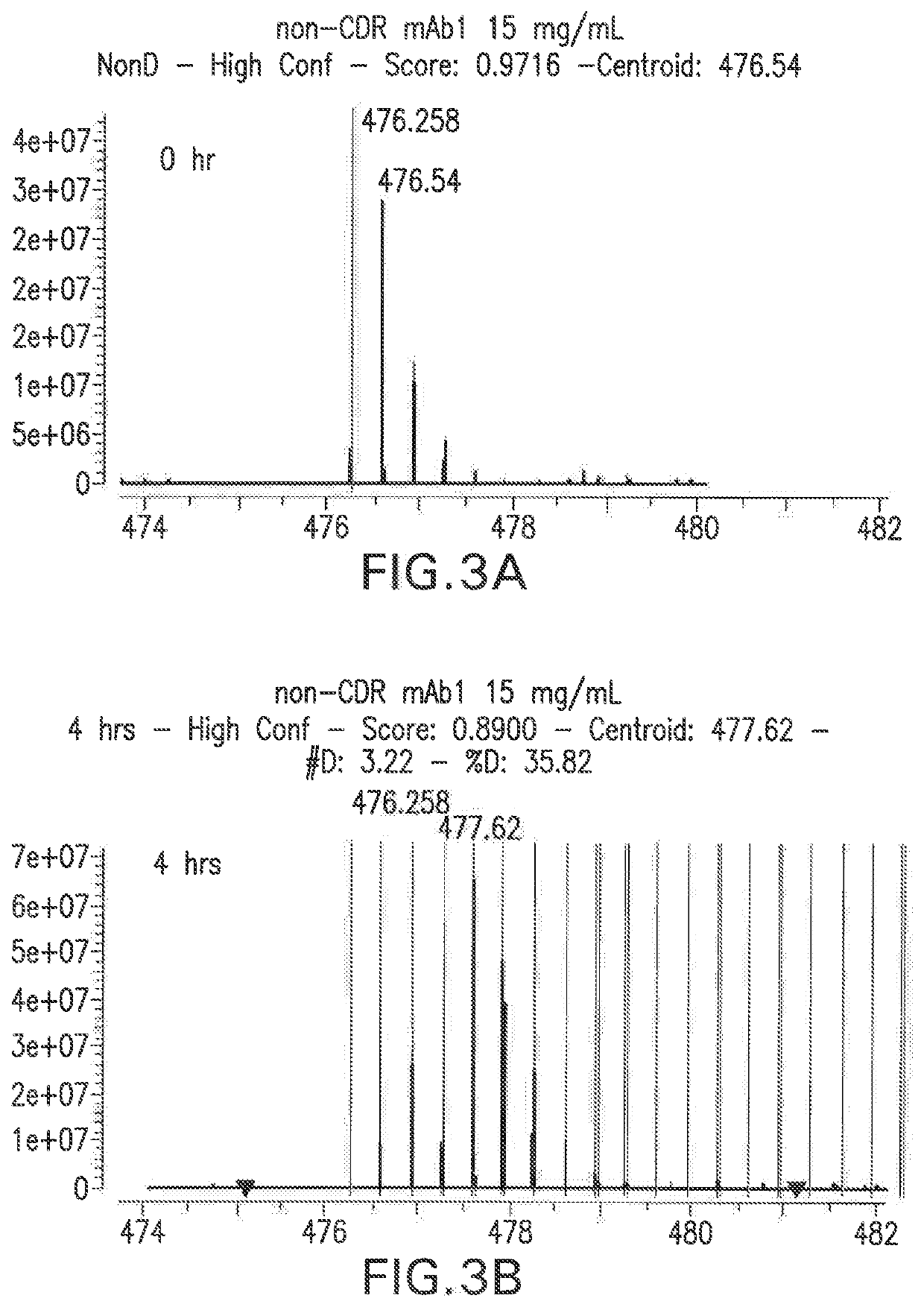
Systems and methods for quantifying and modifying protein viscosity
PendingUS20190345196A1Modifying the viscosity of a protein drugModify the viscosity of the protein drugPreparing sample for investigationMutant preparationCrystallographyViscosity
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Method for improving plant drought resistance by inhibiting expression of cost1 gene
ActiveCN108949821BImprove drought resistanceGenetic improvementPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
Disclosed is a method for improving plant drought resistance by inhibiting expression of COST1 genes. The nucleotide sequence of the COST1 genes is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the protein sequence coded by the COST1 genes is an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. Homologous genes of the COST1 genes comprise tomato SlCOST1 genes, rice OsCOST1 genes, poplar PtCOST1 and PtCOST2 genes, and other genes in other species having a homology degree of more than 40% with fragments in any nucleotide or protein region of COST1.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
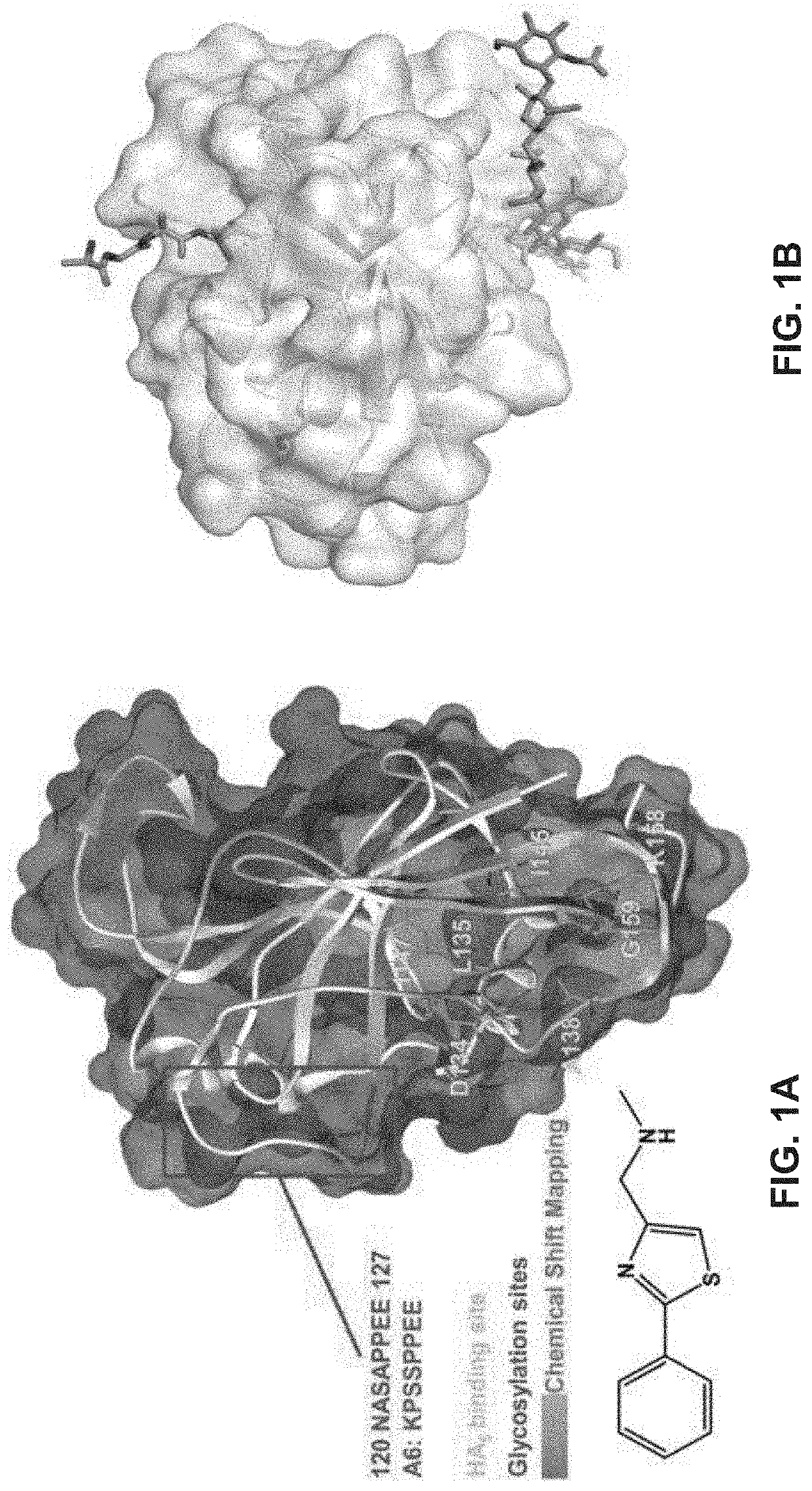
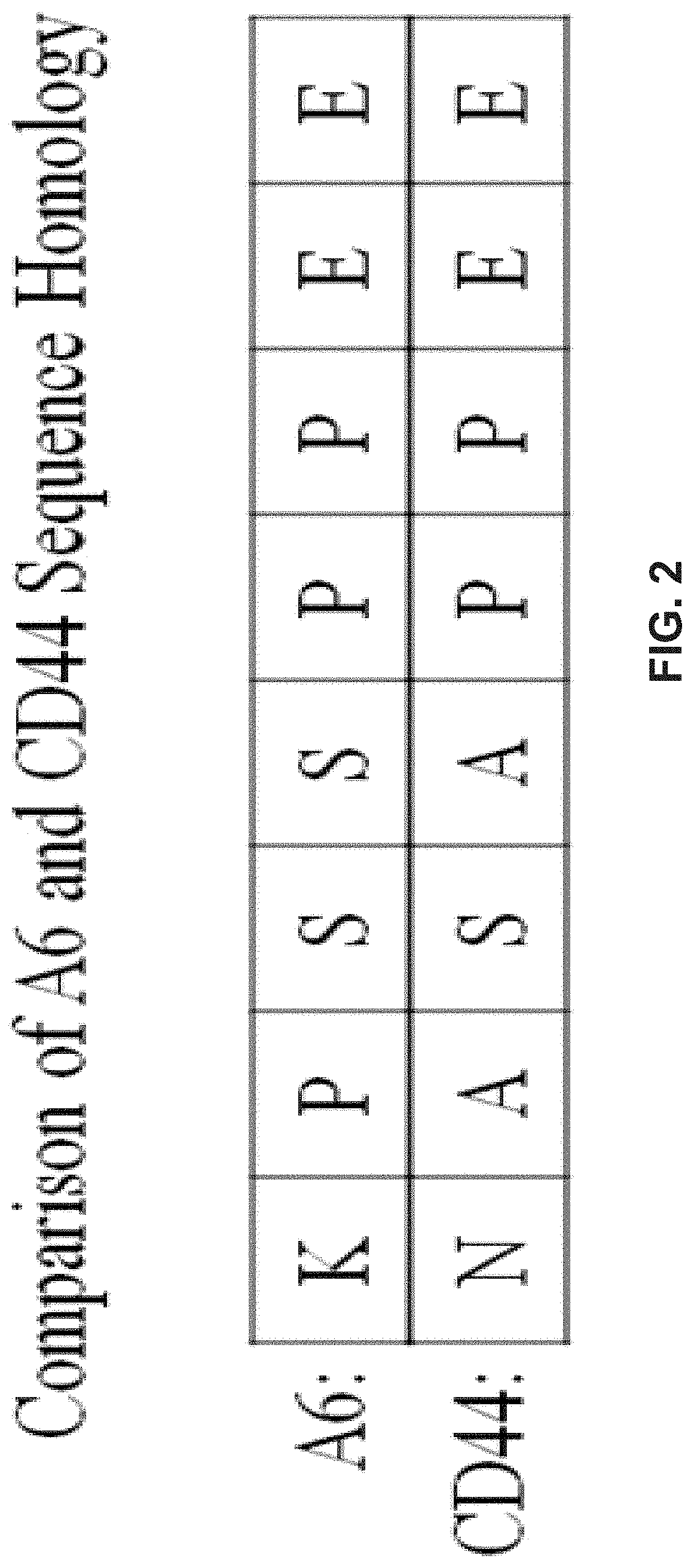
Methods for diagnosing and treating diseases based on modulating drug efflux by binding to cryptic region of cd44
InactiveUS20200299355A1Preventing cellular effluxEffective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to methods for modulating efflux of drugs based on binding to a protein region of CD44 in part comprising the amino acid sequence specified in the provisional application referenced above, and incorporated in its entirety by reference herein (“PROV”). In some aspects, the present invention relates to methods for treatment of cancer by preventing the cellular efflux of therapeutic drugs; for example, preventing the cellular efflux of anti-cancer agents, for example a taxane, by contacting a CD44-modulating peptide, comprising the amino acid sequence specified in the provisional application referenced above, and incorporated in its entirety by reference herein (“PROV”).
Owner:SPLASH PHARMA INC
Automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method
ActiveCN104699997AFix time saverEasy to fixSpecial data processing applicationsImaging processingNetwork model
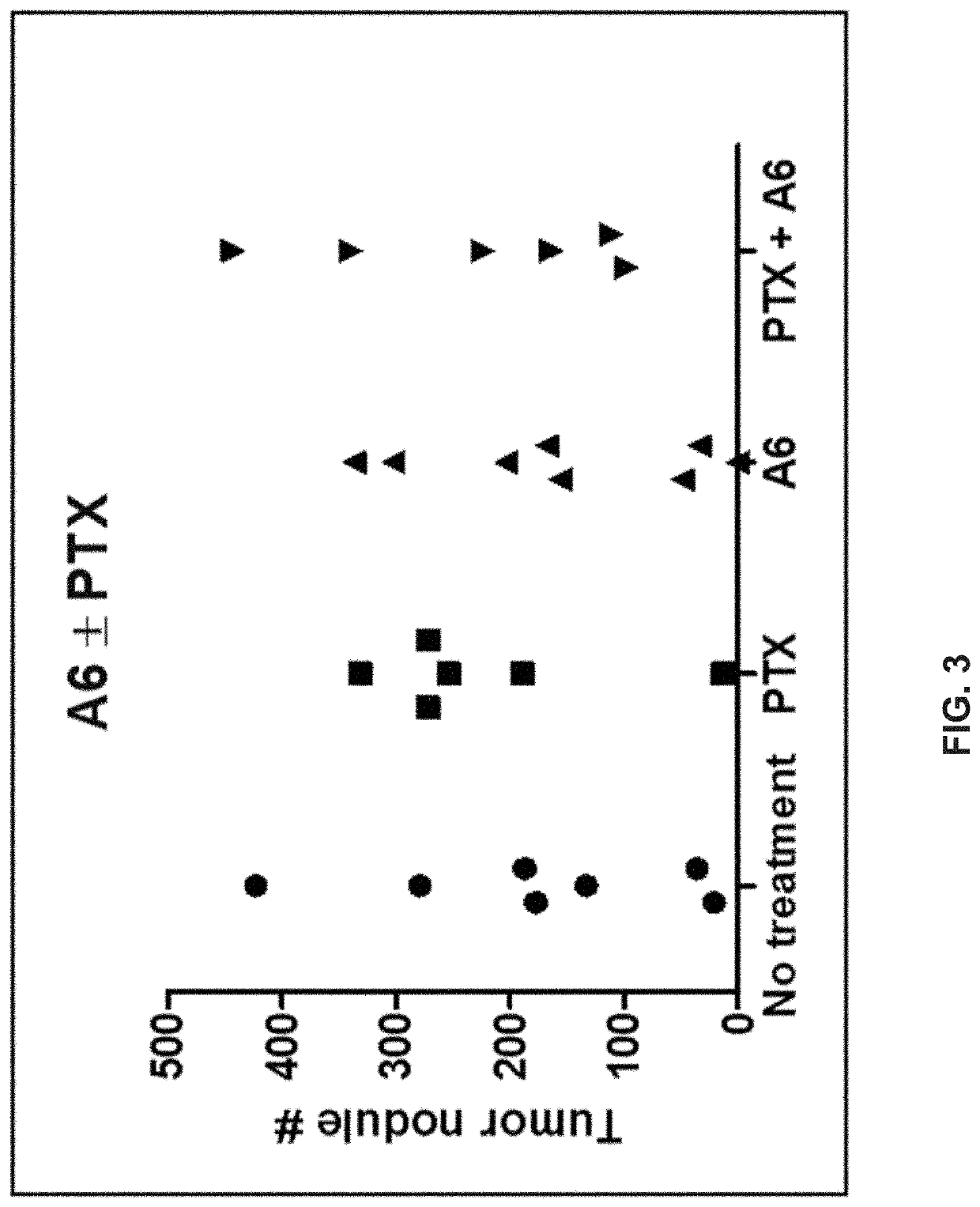
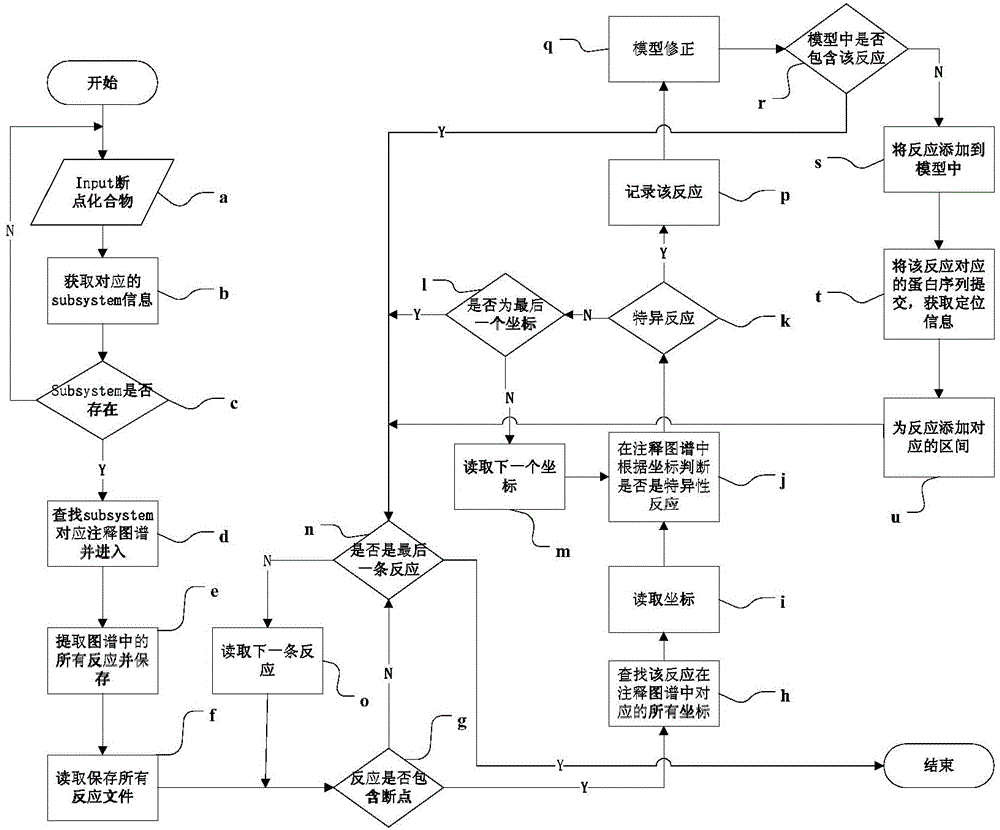
The invention discloses an automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method. According to the automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method, website script semanteme can be submitted and analyzed automatically by combining a hypertext transfer protocol with a Java control HttpClient and utilizing an image processing algorithm; a genomic metabolic network model is subjected to automatic breakpoint supplementing on the basis of online databases including a KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database, a MetaCyc database, a MetRxn database and a plurality of protein region positioning and predicting websites; specific reactions high in reliability can be determined according to a protein region predicting result and a weight rating mechanism, and accordingly, an automatic modifying process of a rough metabolic network model is completed. The automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method has the advantages of time saving and convenience, and an obtained modified model is more comprehensive and more accurate.
Owner:广州市康伦生物技术有限公司
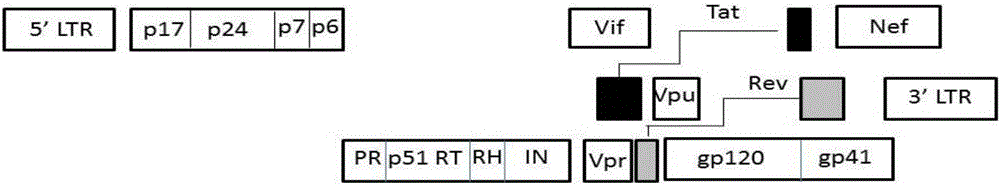
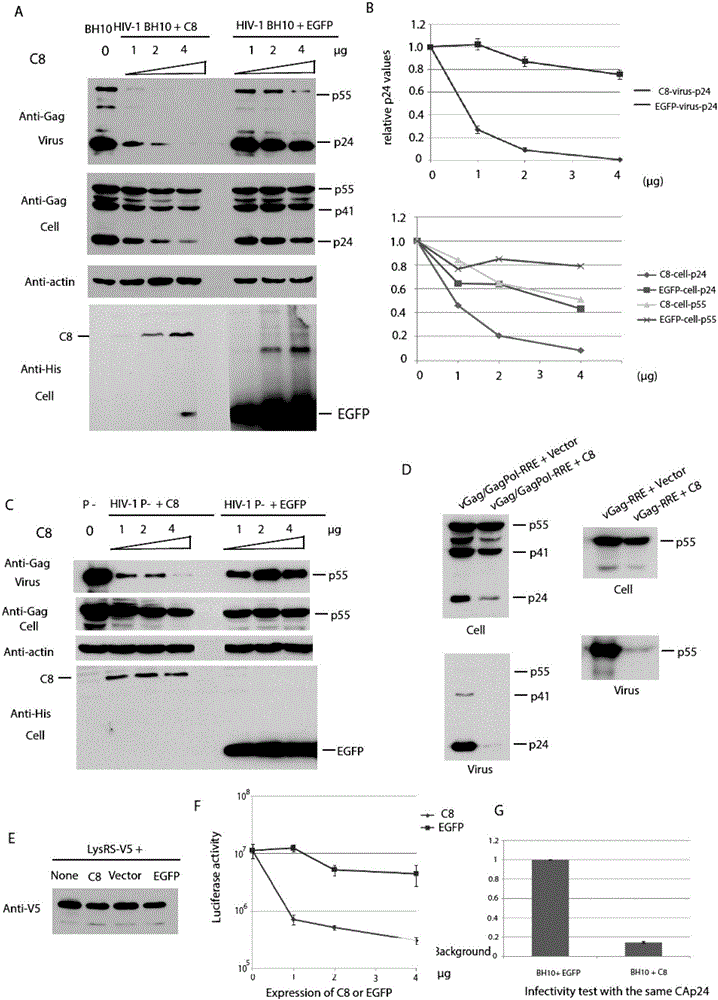
Coiled-coil structure protein 8 capable of inhibiting HIV-1 and its application
ActiveCN105039348BBlock assemblyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsImmunodeficiency virusUbiquitin ligase
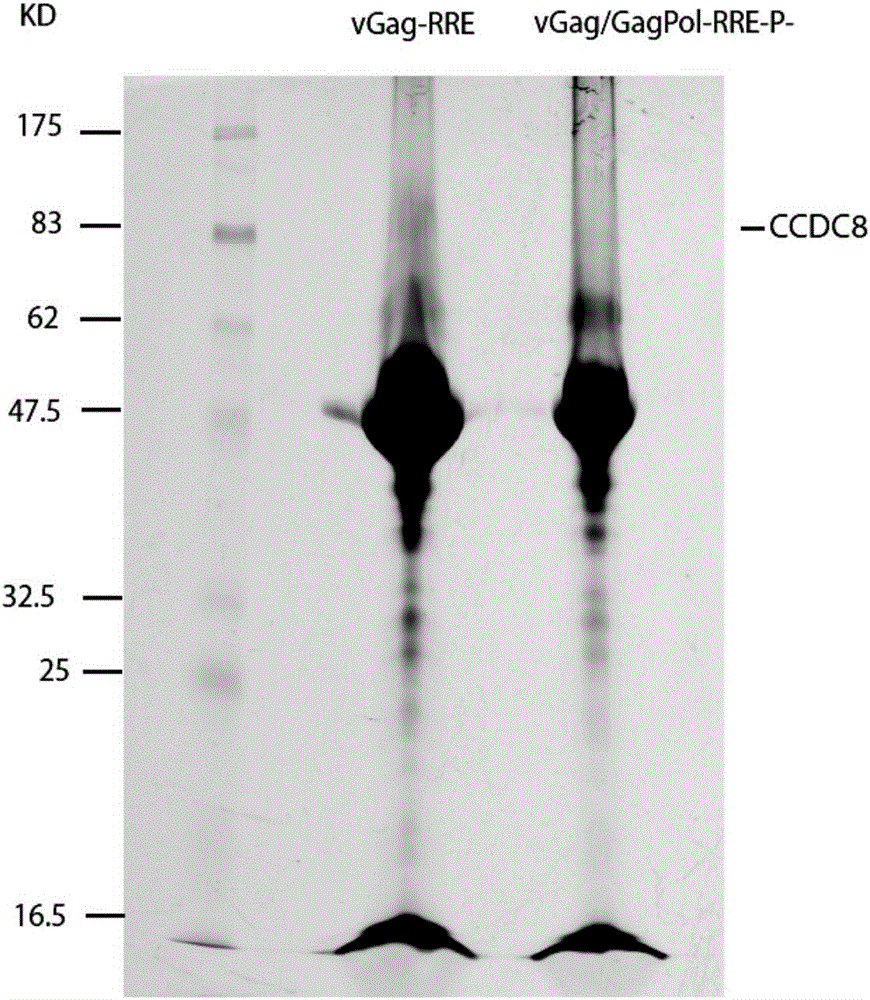
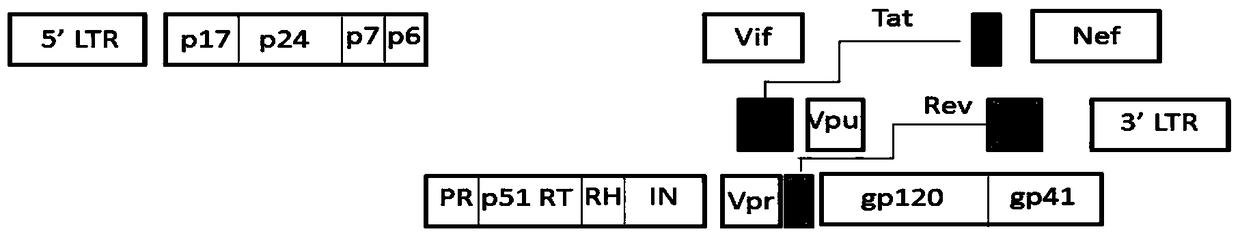
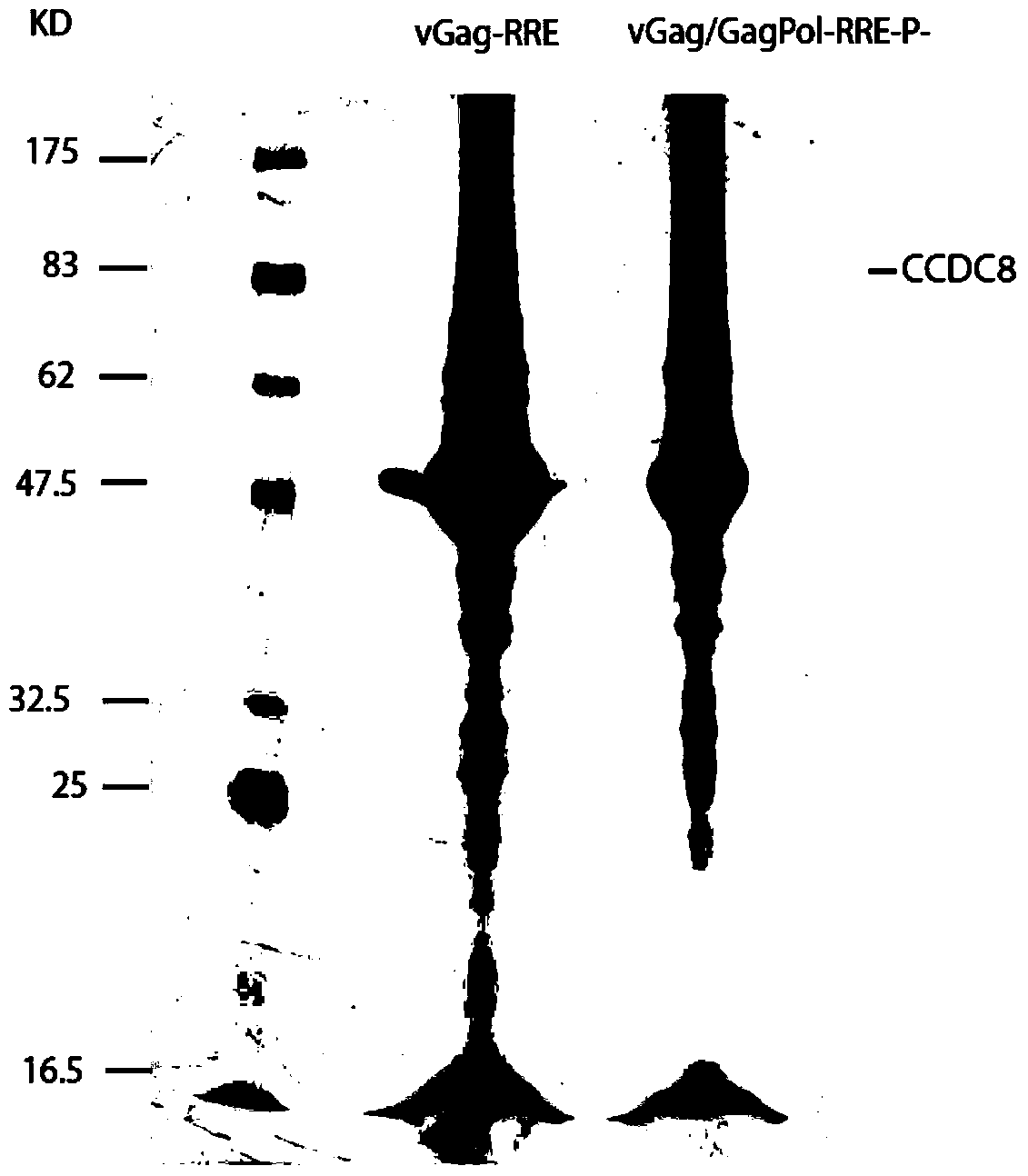
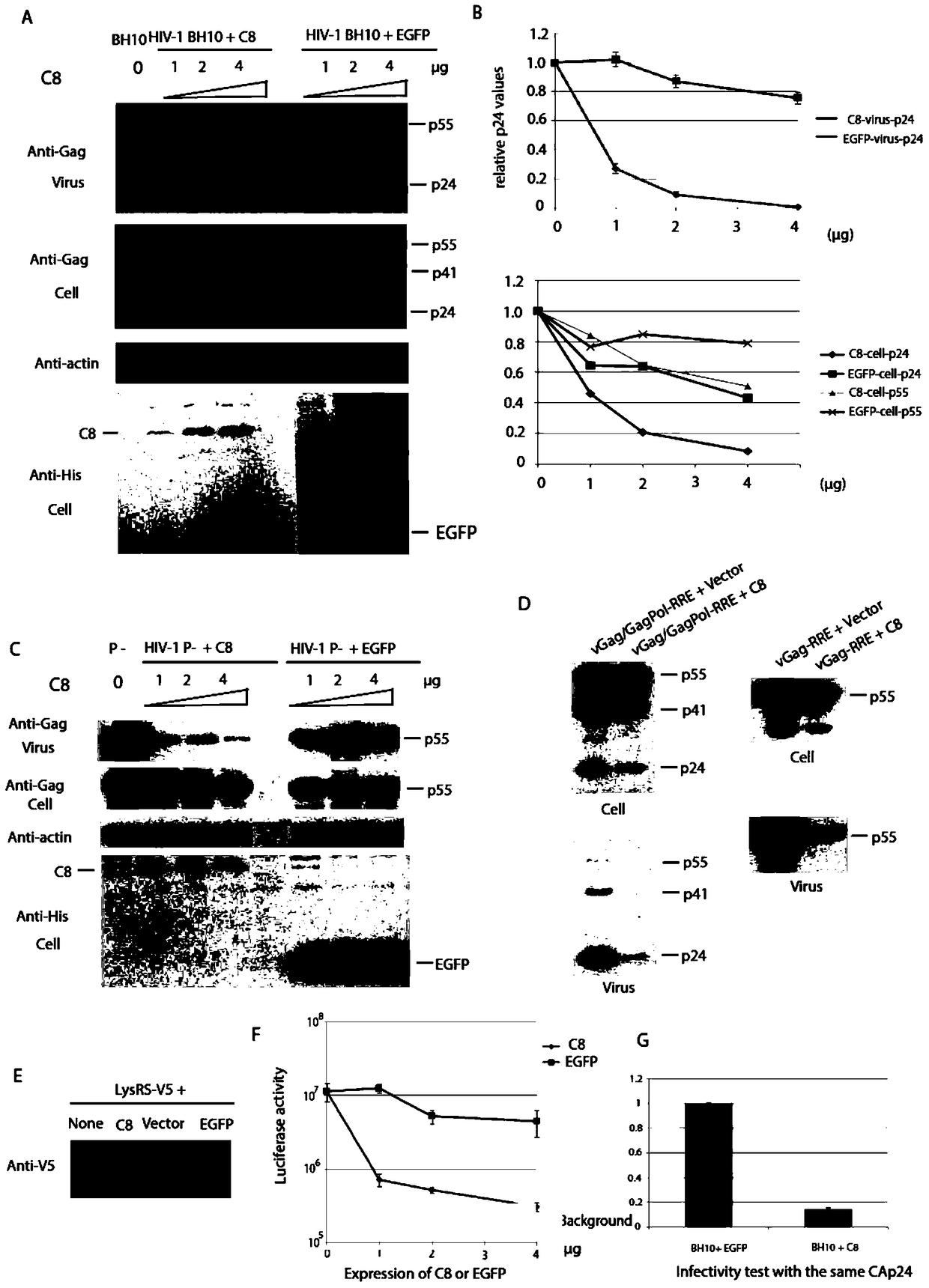
The invention relates to new coiled-coil domain containing protein 8 (CCDC8) having inhibition on HIV-1 and an application thereof. The CCDC8, which is generated by human cells, in the invention has a strong anti-HIV-1 effect. By means of combination of the CCDC8 with matrix protein region of HIV-1Gag, assembly of the Gag protein on cytomembrane is inhibited. The CCDC8, OBSL1, and E3 ubiquitin ligase Cul7 cause internalization, multi-ubiquitination and degradation of the HIV-1Gag. According to the invention, on the basis of the CCDC8, a new plasmid is established and can be used for express new proteins, namely, the protein composed of 274 amino acids at the N-terminal of the CCDC8, thereby degrading HIV-1.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
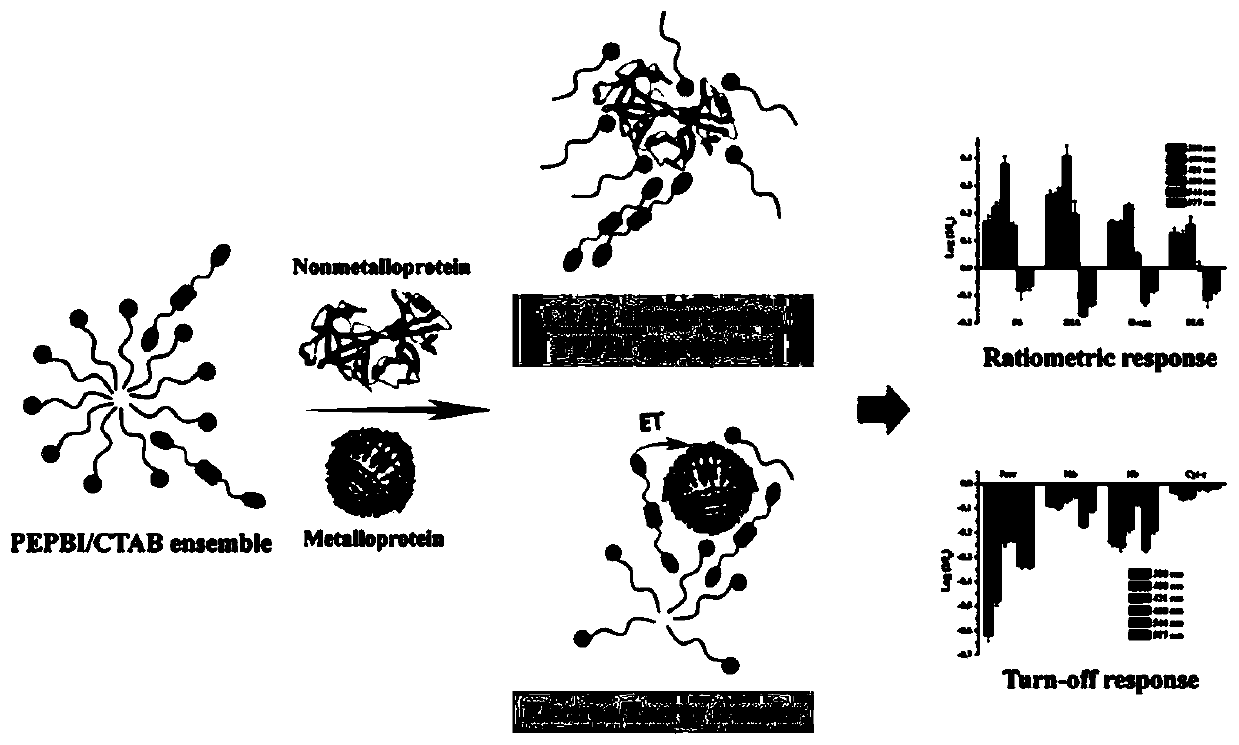
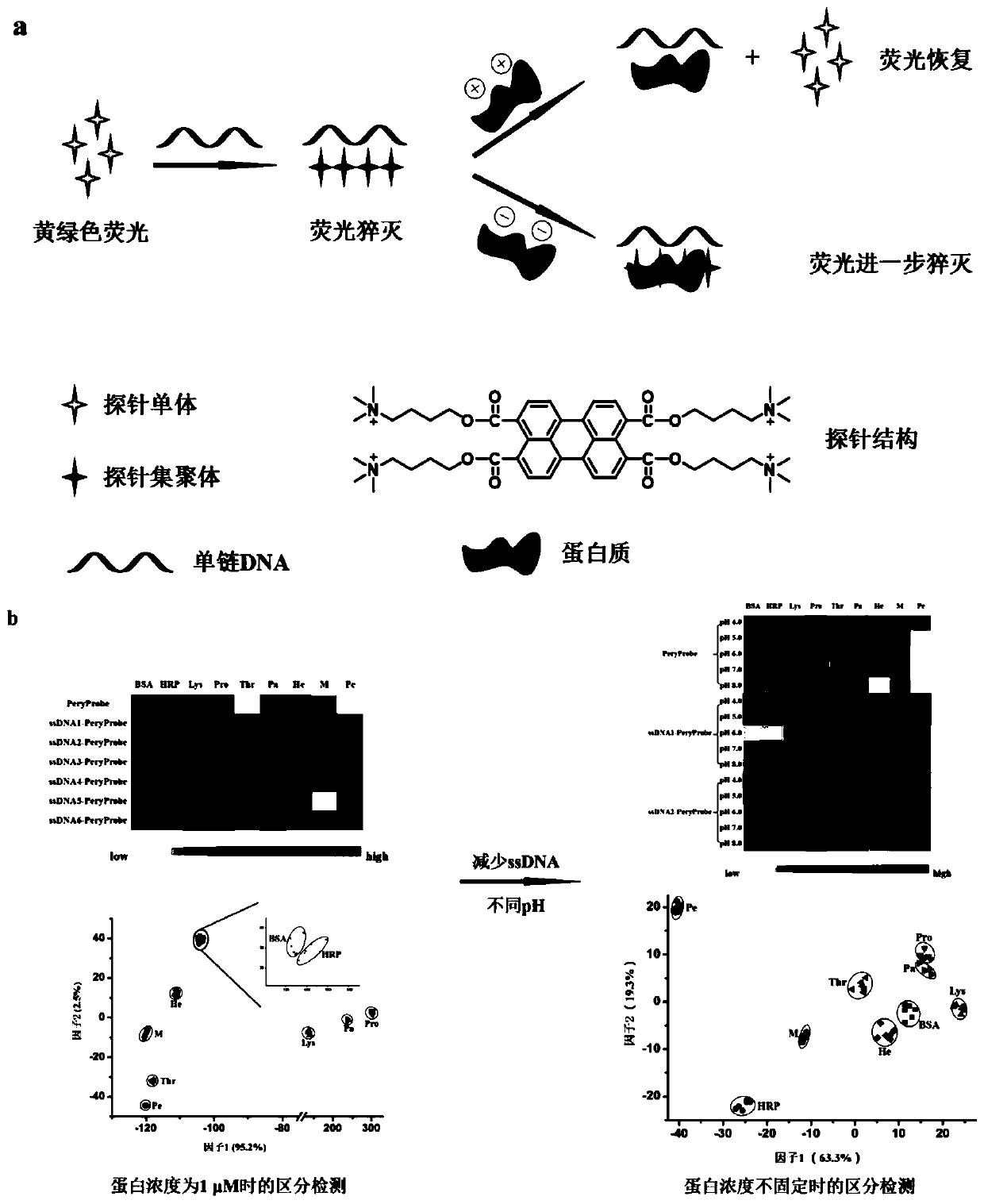
Perylene derivative probe self-assembled fluorescent sensor array for protein distinguishing detection
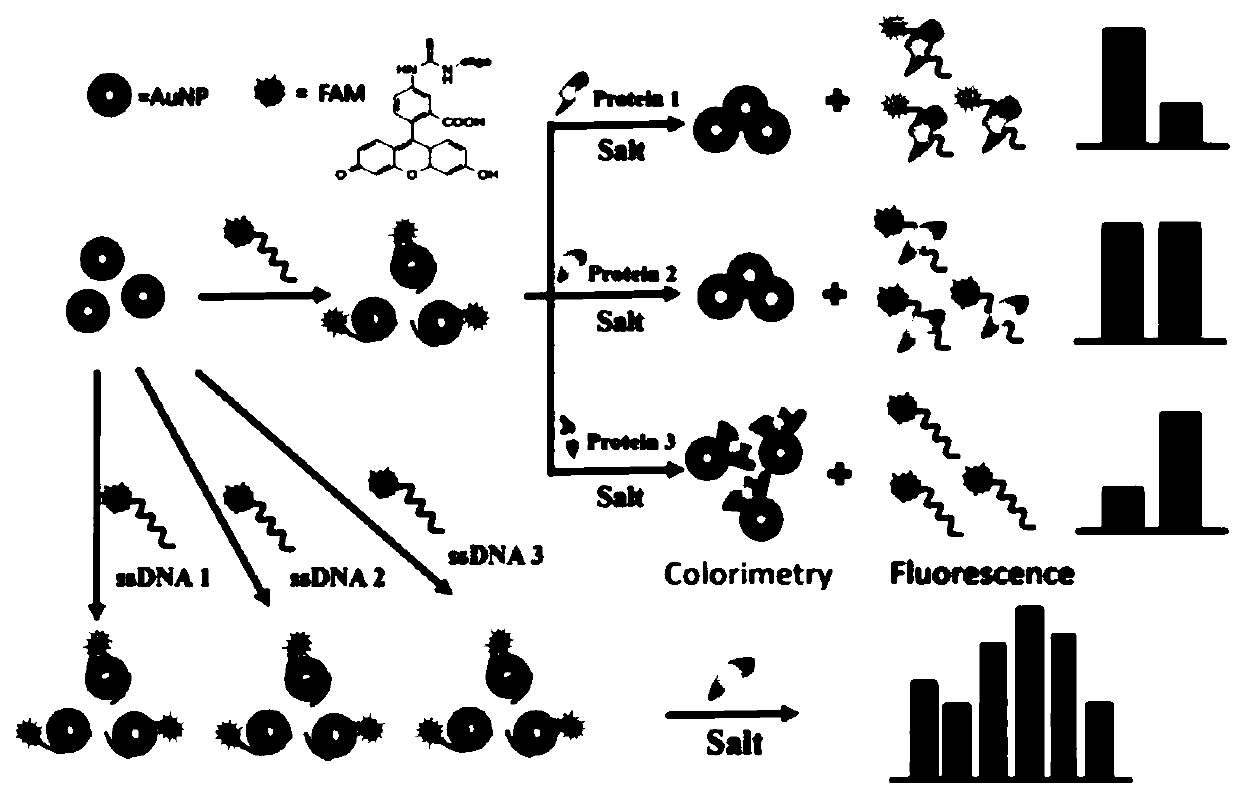
ActiveCN110907651ALow costEasy to buildBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein solutionSingle strand
The invention relates to a perylene derivative probe self-assembled fluorescent sensor array for protein distinguishing detection, and belongs to the technical field of sensor arrays. The problems that an existing sensor array for protein distinguishing is complex in construction, and the concentration of protein to be detected needs to be known are solved. According to the invention, single-stranded DNA is utilized to induce aggregation of the perylene probe so as to quench fluorescence of the perylene probe, and protein can interact with a single-stranded DNA / probe compound to cause fluorescence change of the probe; through different changes of fluorescence intensity after different protein solutions are added, a novel fluorescence sensor array based on perylene derivative probe self-assembly is constructed, and nine proteins are successfully distinguished. The construction method disclosed by the invention is simple and rapid in reaction, and can distinguish the protein at a relatively low concentration without knowing the concentration of the protein to be detected.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coiled-coil domain containing protein 8 (CCDC8) having inhibition on HIV-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105039348ABlock assemblyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsImmunodeficiency virusCell membrane
The invention relates to new coiled-coil domain containing protein 8 (CCDC8) having inhibition on HIV-1 and an application thereof. The CCDC8, which is generated by human cells, in the invention has a strong anti-HIV-1 effect. By means of combination of the CCDC8 with matrix protein region of HIV-1Gag, assembly of the Gag protein on cytomembrane is inhibited. The CCDC8, OBSL1, and E3 ubiquitin ligase Cul7 cause internalization, multi-ubiquitination and degradation of the HIV-1Gag. According to the invention, on the basis of the CCDC8, a new plasmid is established and can be used for express new proteins, namely, the protein composed of 274 amino acids at the N-terminal of the CCDC8, thereby degrading HIV-1.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
A low-complexity prediction method for naturally disordered proteins
ActiveCN107169312BIncrease computing speedImprove robustnessBiostatisticsProteomicsComputation complexityTheoretical computer science
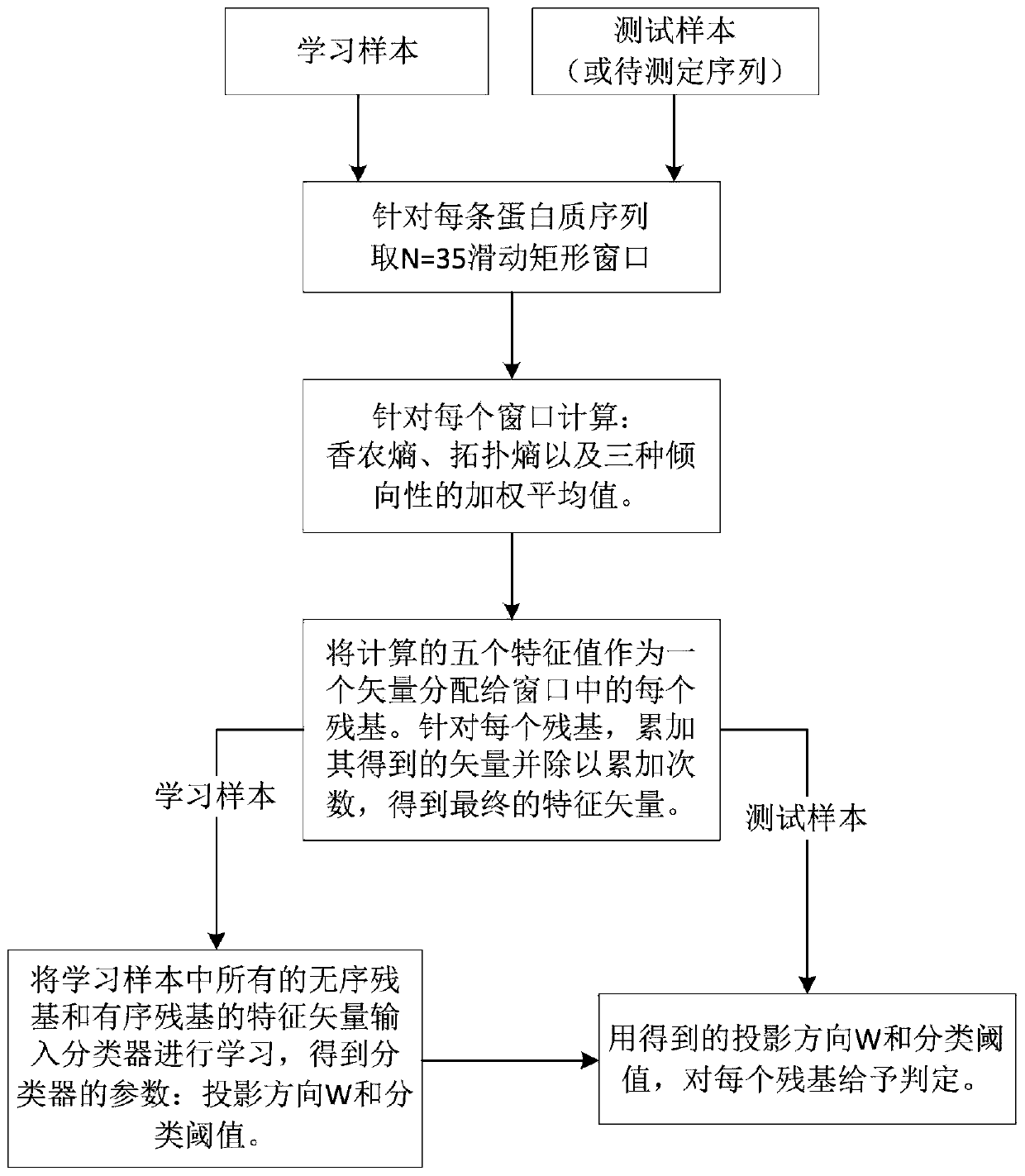
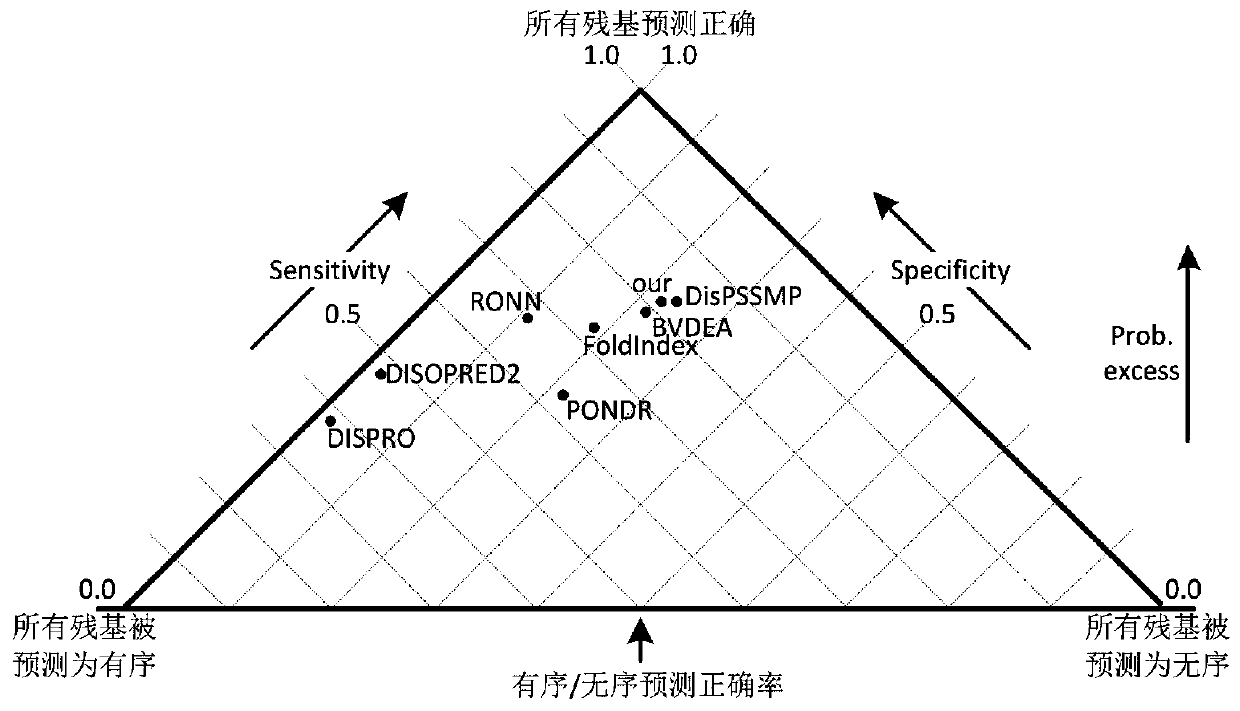
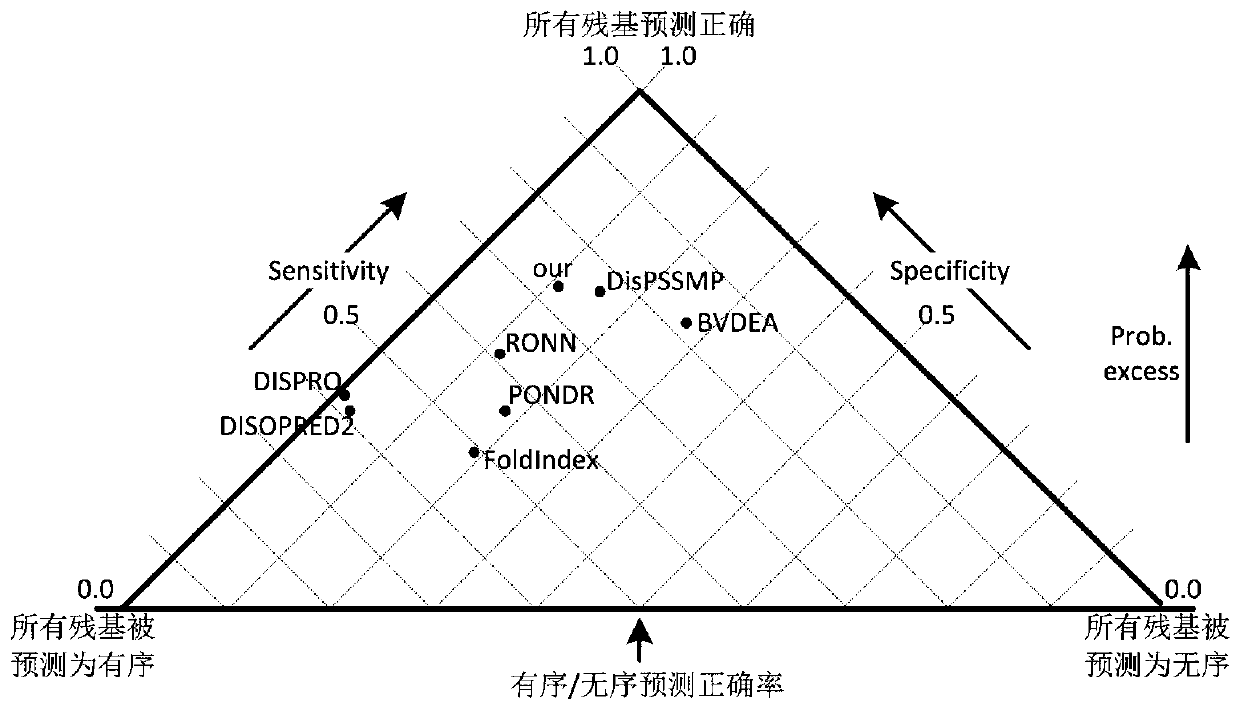
The invention provides a low computational complexity prediction method for natural disordered proteins. In the method, aimed at each residue of a protein sequence, Shannon entropy, topological entropy, and weighted average of tendency of three kinds of amino acids are calculated, and using Rayleigh-entropy maximization, a natural disordered protein region is predicted. The scheme just uses five characteristic and a linear classifier, and the method has relatively high computation speed and robustness. A simulation result shows that under similar predicted accuracy degree, compared with an existing prediction scheme in the same type, the designed natural disordered protein prediction scheme greatly reduces characteristic number and computational complexity.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
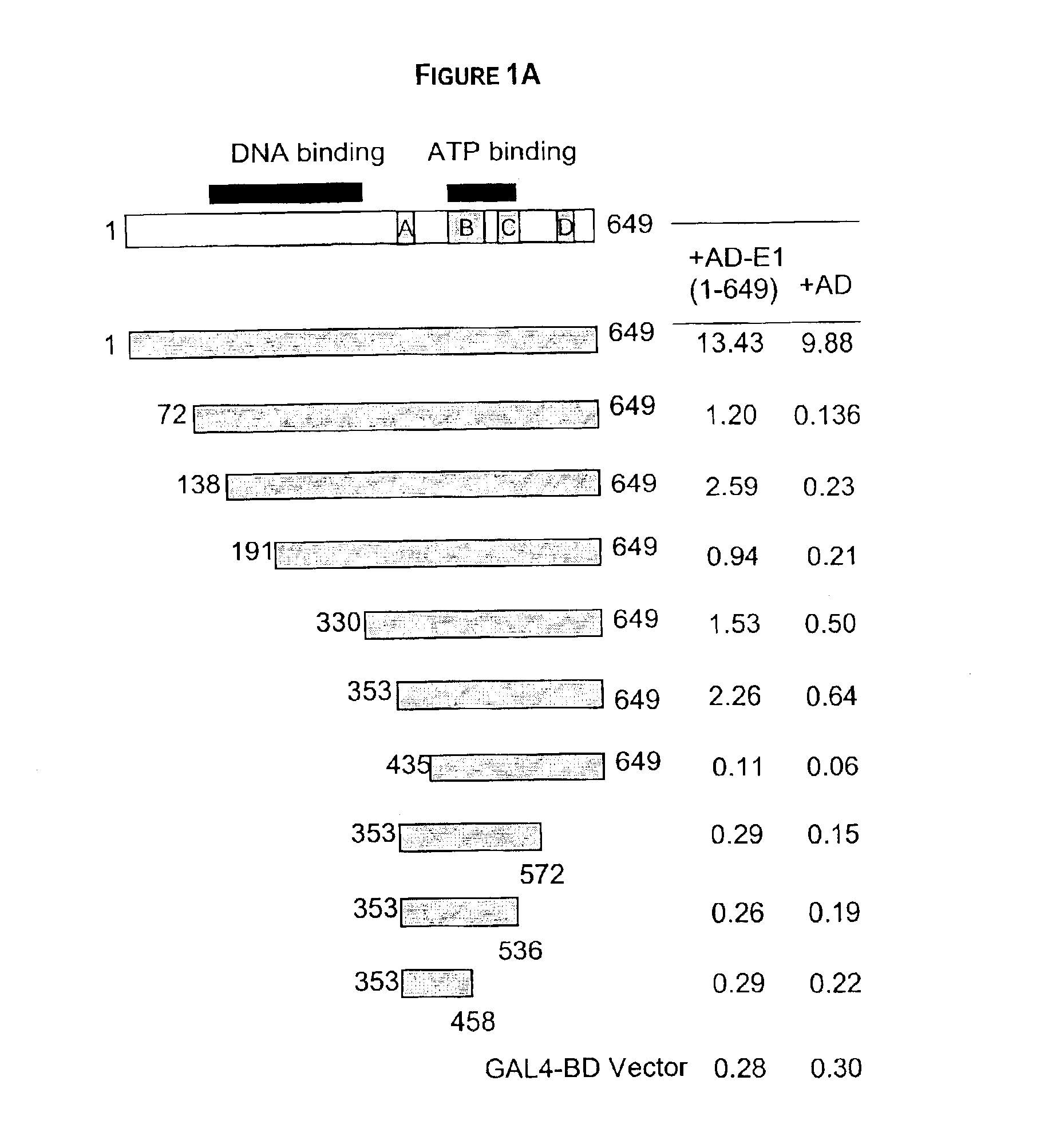
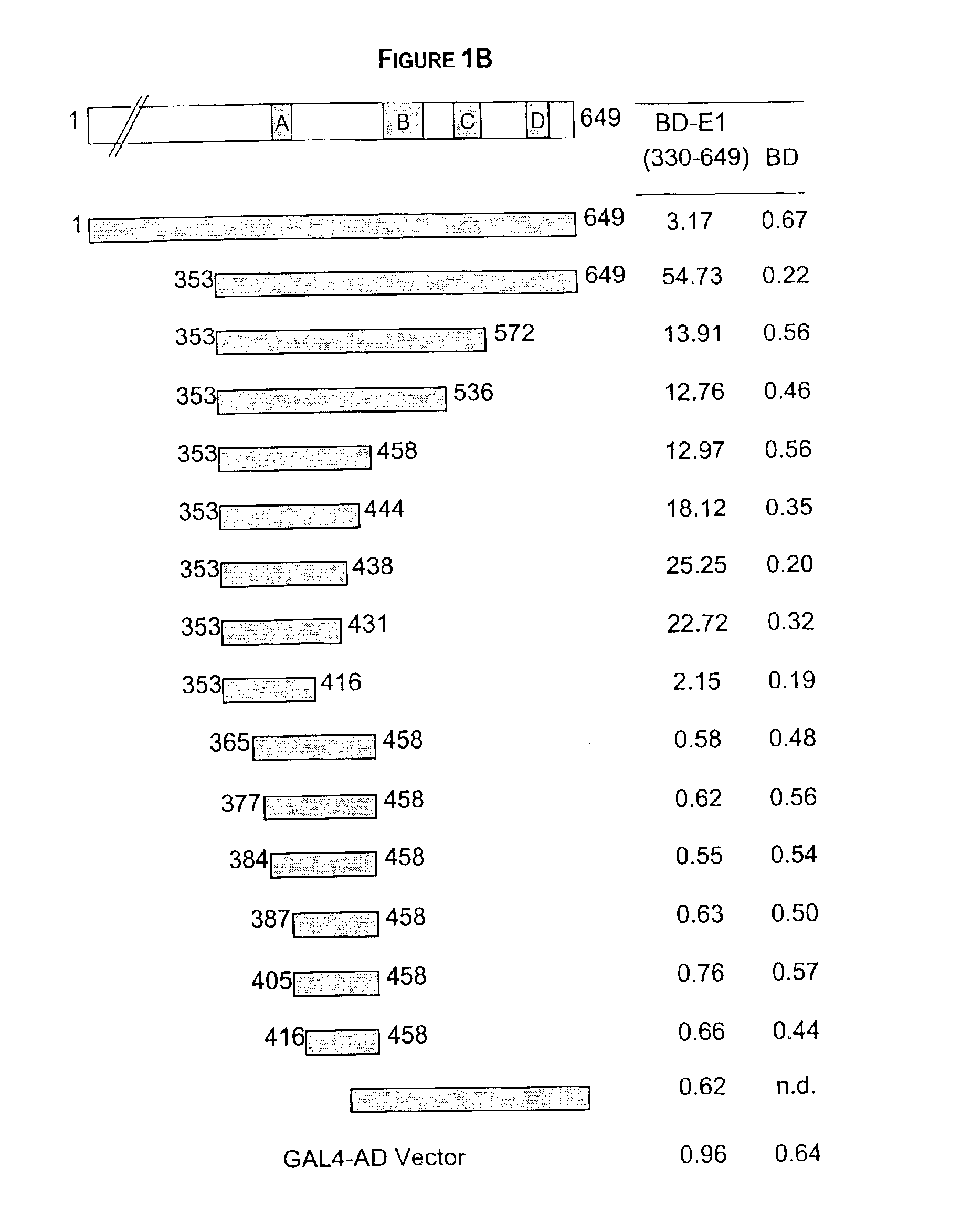
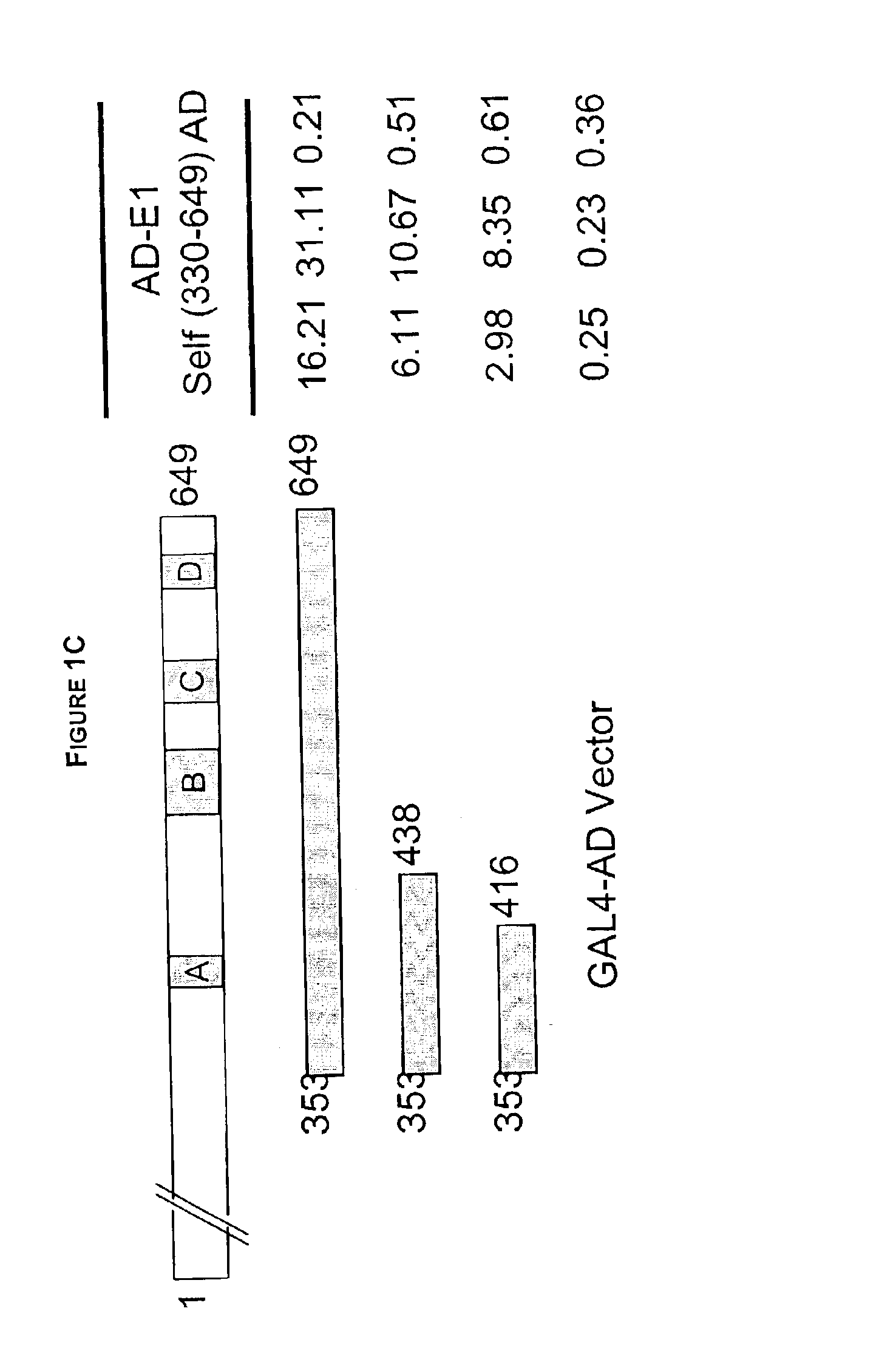
Regions of papilloma virus E1 helicase involved in E1 oligomerization
There is provided an amino acid sequence comprised within the PV E1 protein region A delineated by amino acids 352 and 439, and any derivative variant or fragment thereof, necessary for the oligomerization of the E1 protein. This amino acid sequence is capable of self-association and of associating with the full length E1 protein and any derivative, variant or fragment thereof comprising the sequence of this invention. A specific aspect of this first embodiment, the amino acid domain of this invention delimited by amino acids 353 to 438 of the PV E1 protein. More particularly, the amino acid domain of this invention is as defined by SEQ ID NO. 2. There is also provided a cross-linking assay to directly measure the level of oligomerization (or inhibition thereof) of the E1 protein. In accordance with a fourth embodiment of this invention, there is provided a N-terminally truncated E1 protein. More particularly, one aspect of this fourth embodiment encompasses the E1 protein delimited by amino acid 72 to 649 (SEQ ID NO. 78).
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM CANADA LTD
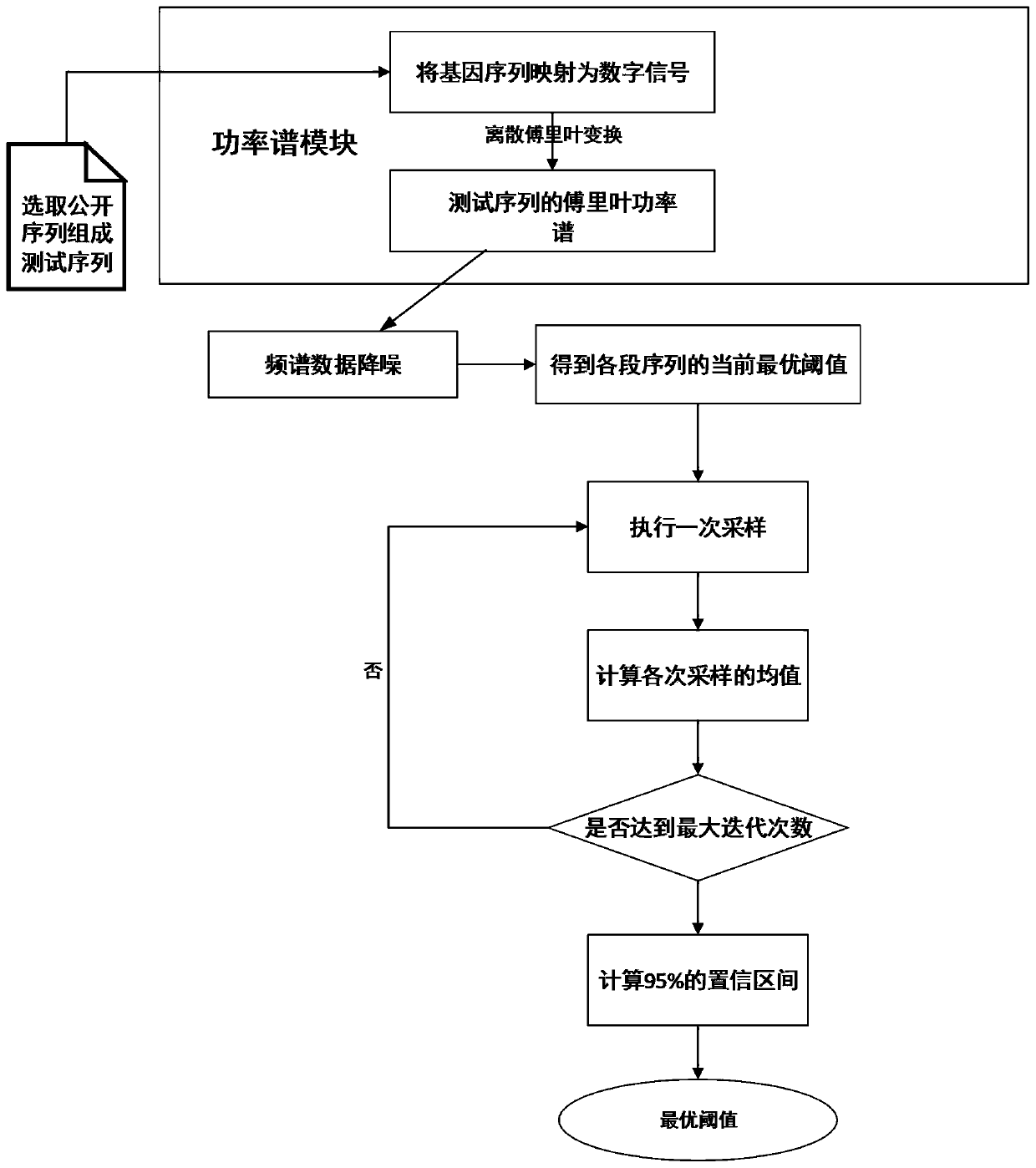
Method for predicting threshold of phellinus igniarius protein region based on power spectrum
PendingCN109859802AGuaranteed accuracyReduce the impact of errorsBiostatisticsInstrumentsFrequency spectrumConfidence interval
The invention provides a method for predicting threshold of a phellinus igniarius protein region based on power spectrum. The method includes the following steps: inserting n nucleotide sequences corresponding to the published phellinus igniarius and its homologous protein acquired from a database into a background sequence to generate a gene sequence; performing spectral prediction on the gene sequence to obtain a Fourier power spectrum; performing denoising processing on the spectrum by a low-frequency filter; obtaining the current optimal threshold of each section of sequence by comparing the spectral values; performing multiple times of iterative sampling on the sequence; and calculating the confidence interval to obtain an optimal threshold. The algorithm for predicting threshold of aphellinus igniarius protein region based on power spectrum ensures the accuracy of threshold selection, reduces the error impact of random sequence interception, and improves the accuracy of phellinus igniarius gene prediction.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Inhibition of TCR signaling with peptide variants
The present invention provides compositions comprising peptides derived from amino acid sequences (or from combinations thereof) of fusion and other protein regions of various viruses, including but not limited to, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, herpesvirus saimiri, human herpesvirus 6, Lassa virus, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, Mopeia virus, Tacaribe virus, Friend murine leukemia virus; human T lymphotropic virus type 1; herpesvirus ateles; Marburg virus; Sudan Ebola virus; Zaire Ebola virus, and comprising L- and / or D-amino acids and combinations thereof, which affect T cells by acting on the T cell antigen receptor (TCR). More specifically, the peptides act on the TCRαβ-CD3δε-CD3γε-ζζ signaling complex. Yet more specifically, the peptides act on the TCRα / CD3δε / ζζ signaling module of TCR. The present invention further relates to the prevention and therapy of various T cell-related disease states involving the use of these compositions. Specifically, the compositions are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of a disease or condition where T cells are involved or recruited. The compositions of the present invention also are useful in the production of medical devices comprising peptide matrices (for example, medical implants and implantable devices).
Owner:SIGNABLOK
Method for testing ion transmission condition of peptide fragment in simulated environment
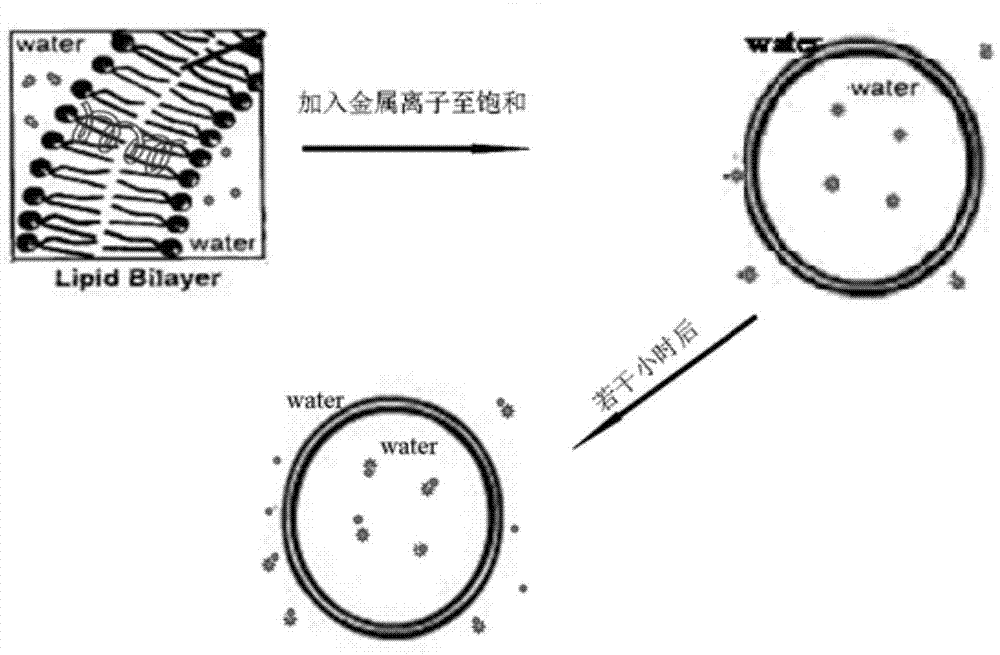
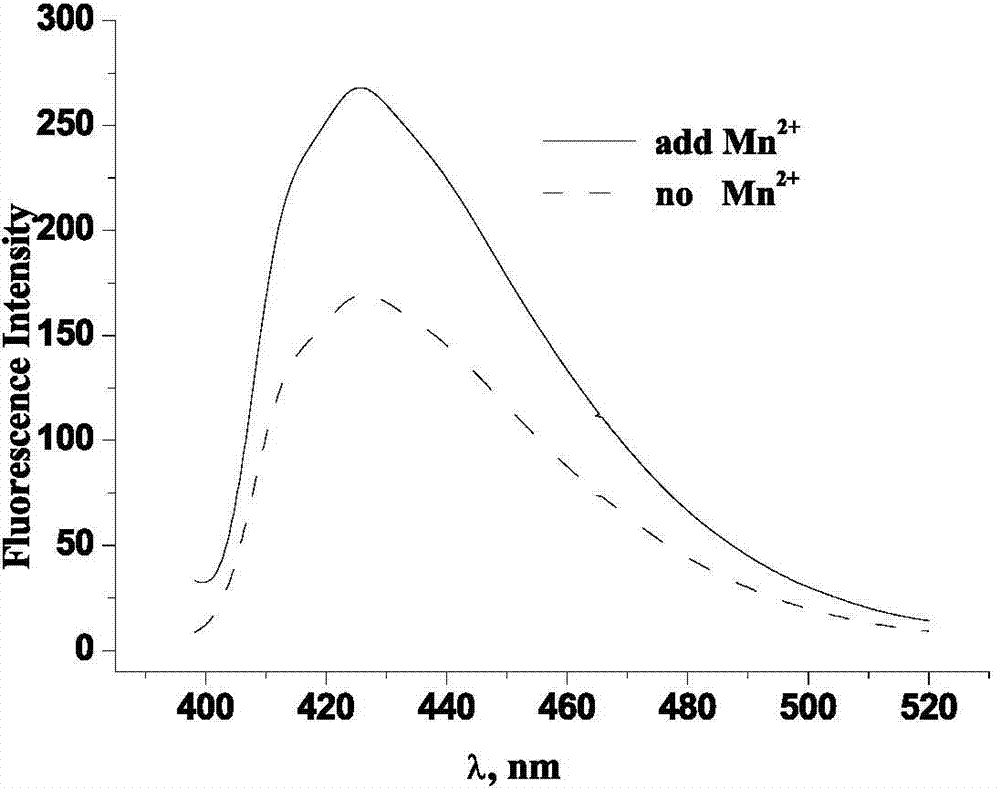
ActiveCN104730049AEasy to operateIntuitive test resultsFluorescence/phosphorescenceStock solutionStandard samples
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a method for testing an ion transmission condition of a peptide fragment in a simulated environment. The testing method is a fluorescent spectrometry; and ions are metal ions. The testing method comprises the following six steps: preparing a buffering solution; preparing a standard sample stock solution of aureomycin, preparing a phospholipid monolayer vesicle without the peptide fragment, carrying out fluorescence detection on the phospholipid monolayer vesicle without the peptide fragment, preparing a phospholipid monolayer vesicle with the peptide fragment, and carrying out the fluorescence detection on the phospholipid monolayer vesicle with the peptide fragment. Aiming at the peptide fragment of a fourth membrane-spanning protein region, a testing method and a testing condition are further improved; by virtue of the testing method, the defects that the operation is complicated, the specialty is high, the cost is high and the requirements on instruments and operators are relatively high in the prior art are overcome; and the ion transmission condition of the fourth membrane-spanning protein region can be relatively conveniently researched, and a transmission function of a whole solute transportprotein transmission body is achieved.
Owner:宁波市博坤生物科技有限公司
Protein structural biomarkers to guide targeted chemotherapies
ActiveUS9341627B2Quick measurementReadily tested and interpreted and usedCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsGenomicsProtein structure
Owner:KIM SUNYOUNG
Vector for gene therapy and method of quantifying target protein in mammal or cultured cells with the administration of the vector for gene therapy
InactiveUS20060223767A1High sensitivityUndesired physiological actionOrganic active ingredientsVectorsProtein targetMammal
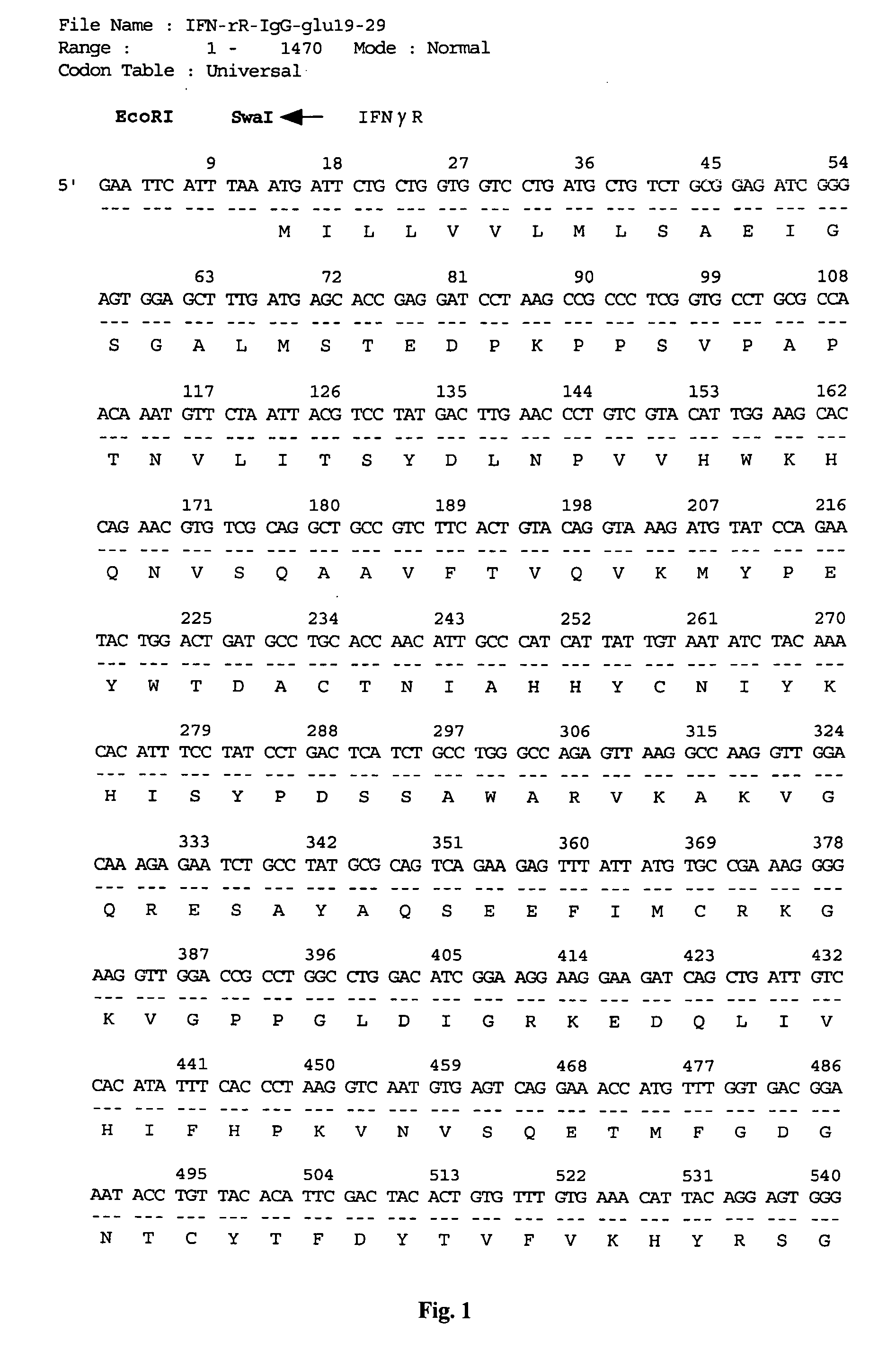
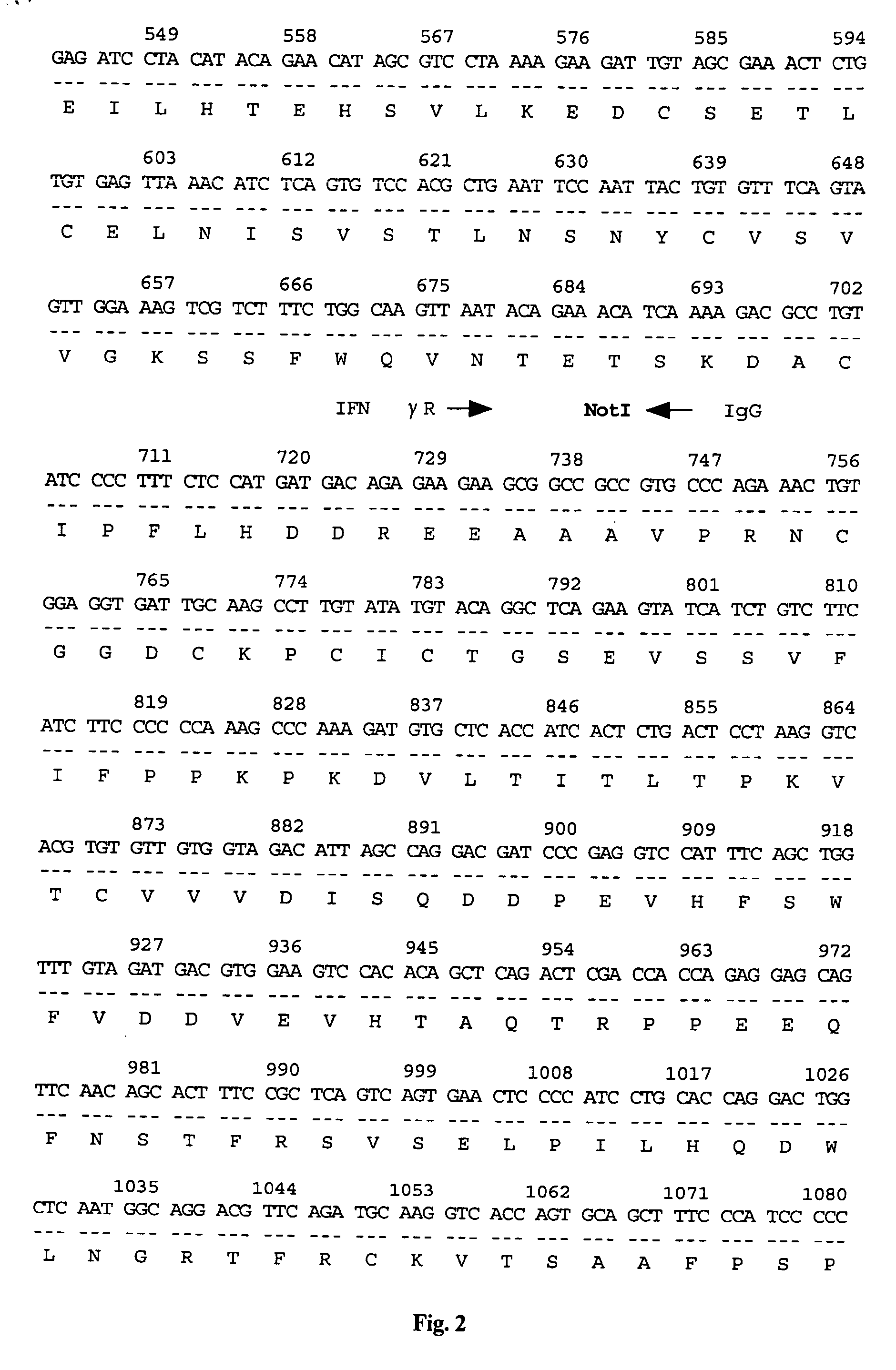
Disclosed is a vector for gene therapy, by which the blood level of a desired protein can be monitored at high sensitivity when a gene therapy is conducted, wherein the label peptide does not have a physiological activity and has no immunogenicity in many mammals. The vector for gene therapy comprises a nucleic acid coding for a fusion protein of glucagon C-terminal side 19-29 amino acid peptide region and a desired protein region which should be produced in the body, which nucleic acid is incorporated into an expression vector for mammalian cells.
Owner:NLLGATA TLO LNC
A kind of recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase and its fungal expression vector and fungal insecticide
The invention provides a recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase and a fungal expression vector as well as a fungal insecticide thereof. A recombinant nucleotide sequence, which comprises a signal peptide sequence for coding the chitinase of beauveria bassiana and a mature protein region sequence for coding the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase of zymonomas mobilis, is constructed by use of the molecular biological technique. According to the recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase, the PgpdA-BbSP-GFOR segment is cloned into a pUC-Bar vector to obtain the fungal expression vector; the fungal expression vector is imported into the wild-type beauveria bassiana Bb0062 strain to obtain the beauveria bassiana transformant of BbSP-GFOR. The recombinant glucose-fructose oxidoreductase effectively blocks the activity of the GNBPs in a host; the time that the fungi knock down insect pests is shortened by 48 hours and the insecticidal efficacy is remarkably improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com