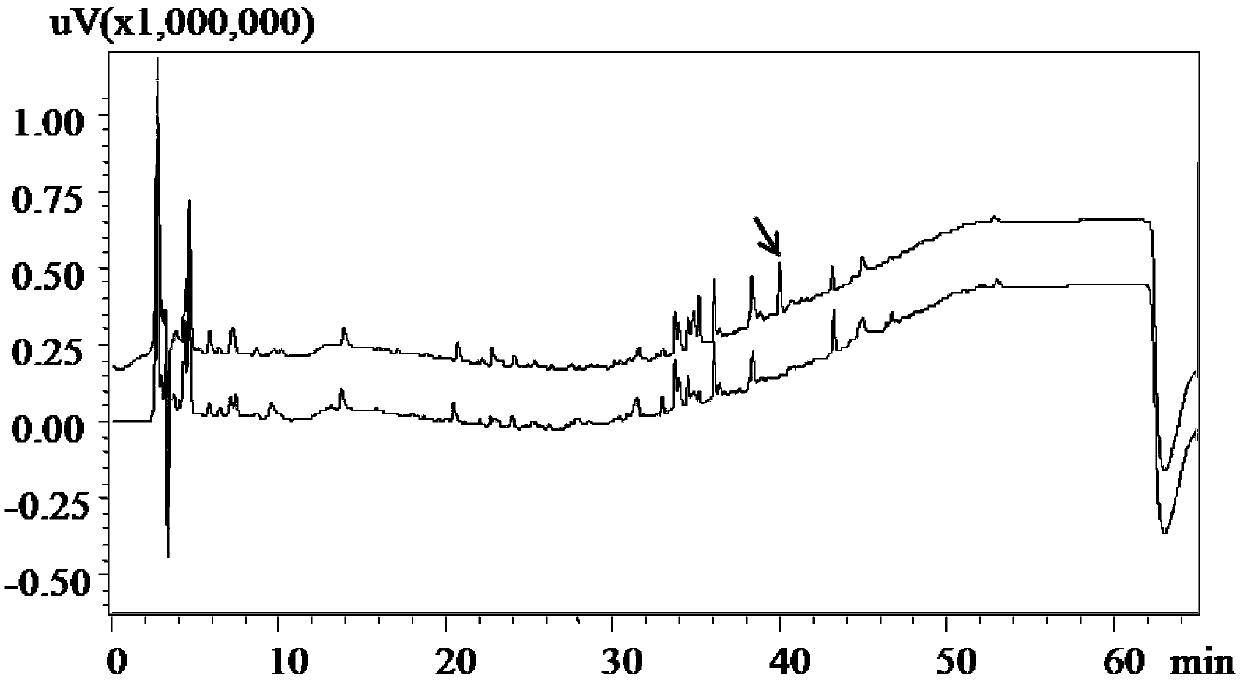
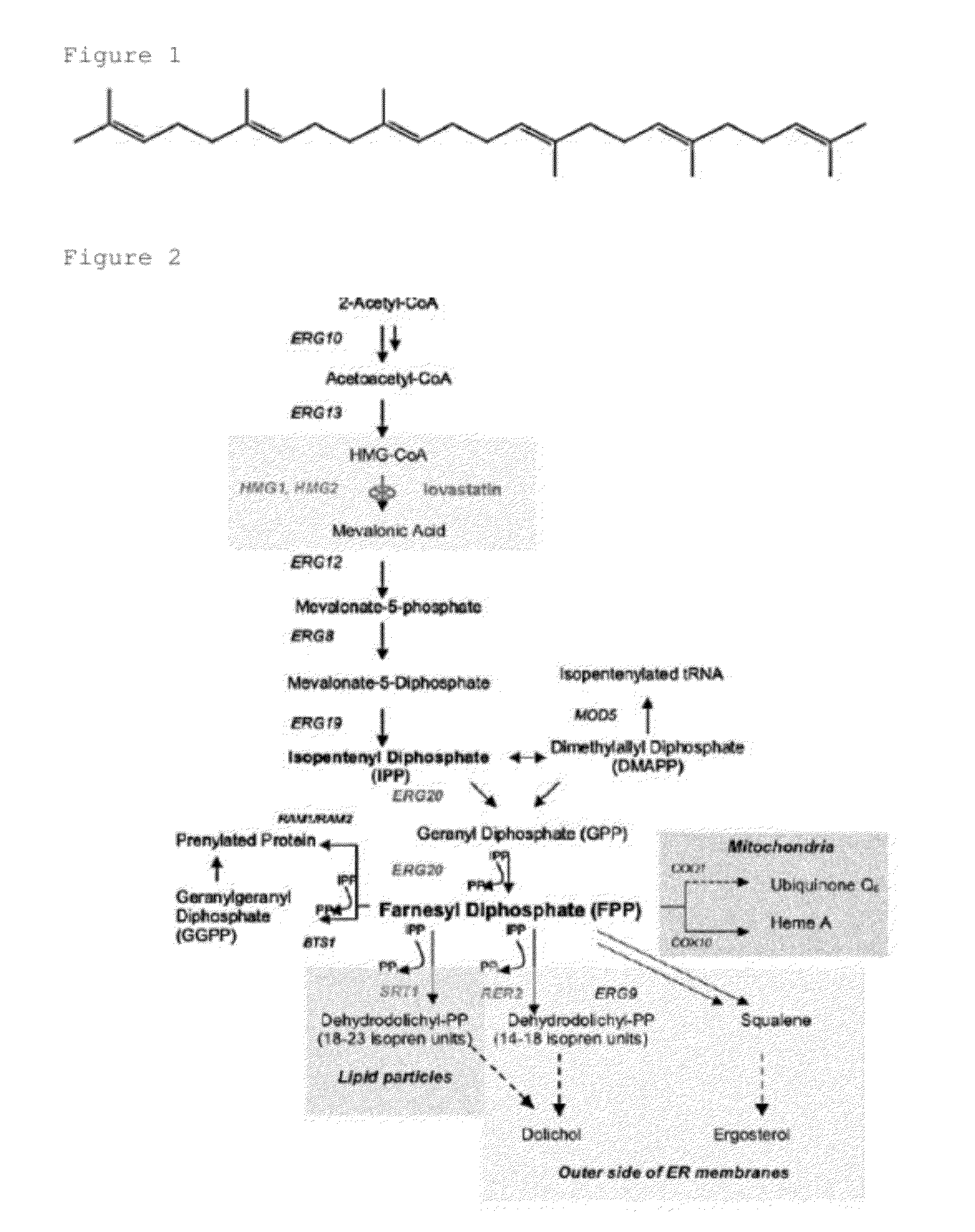
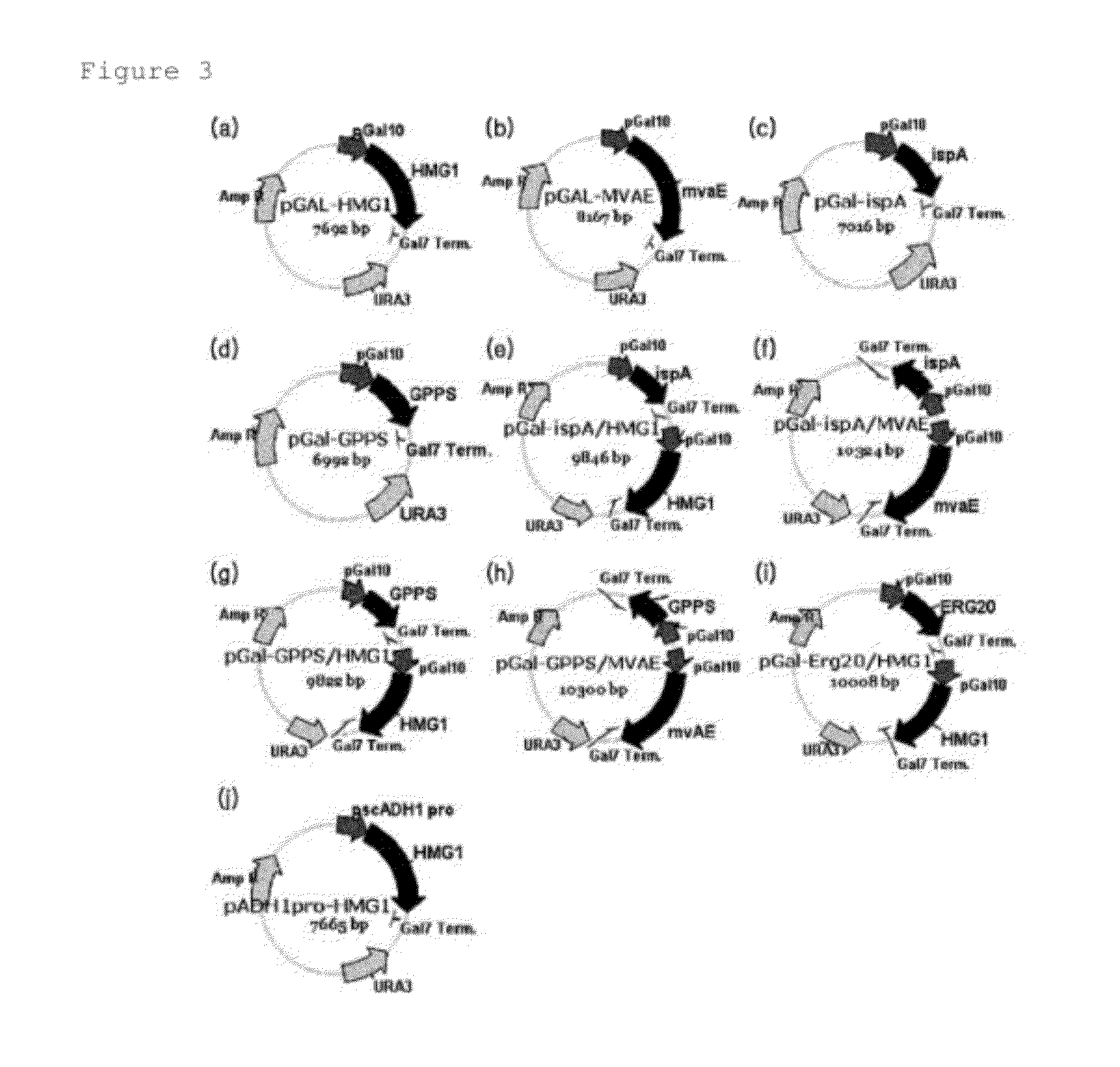
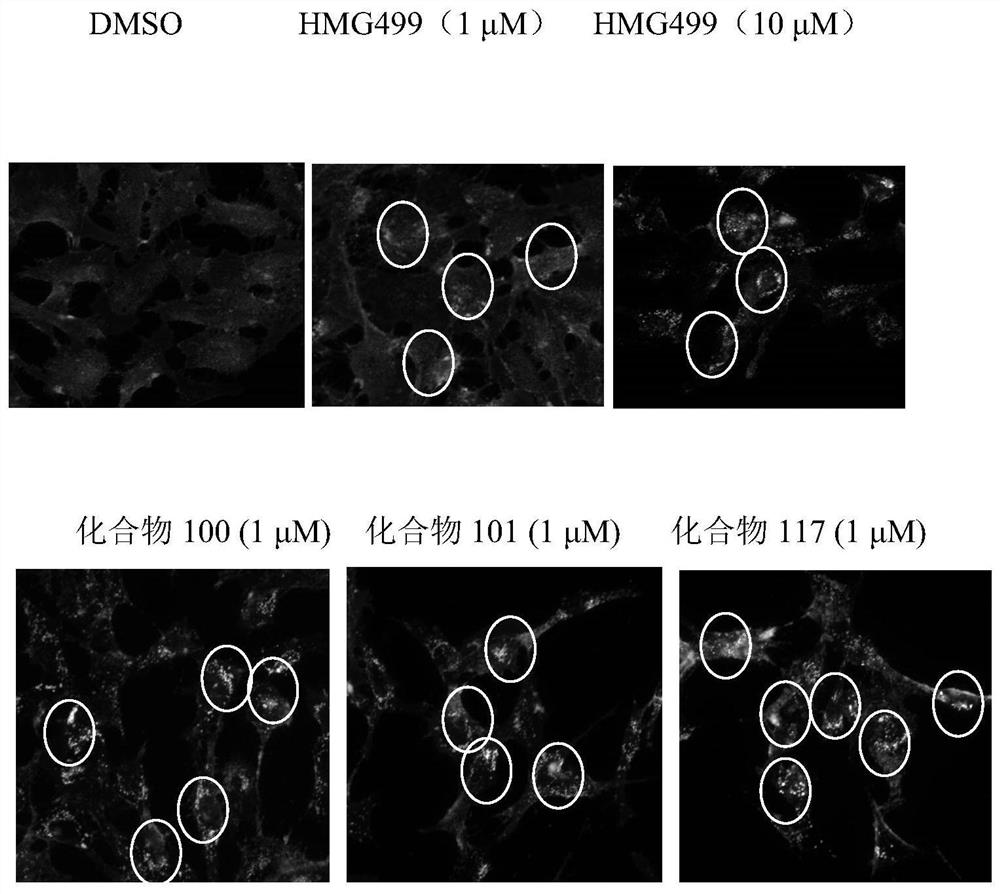
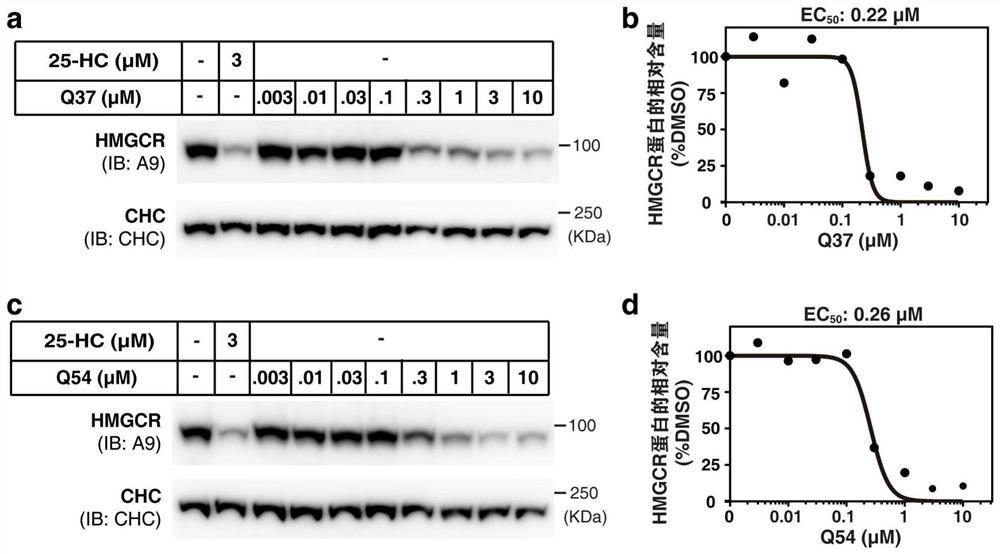
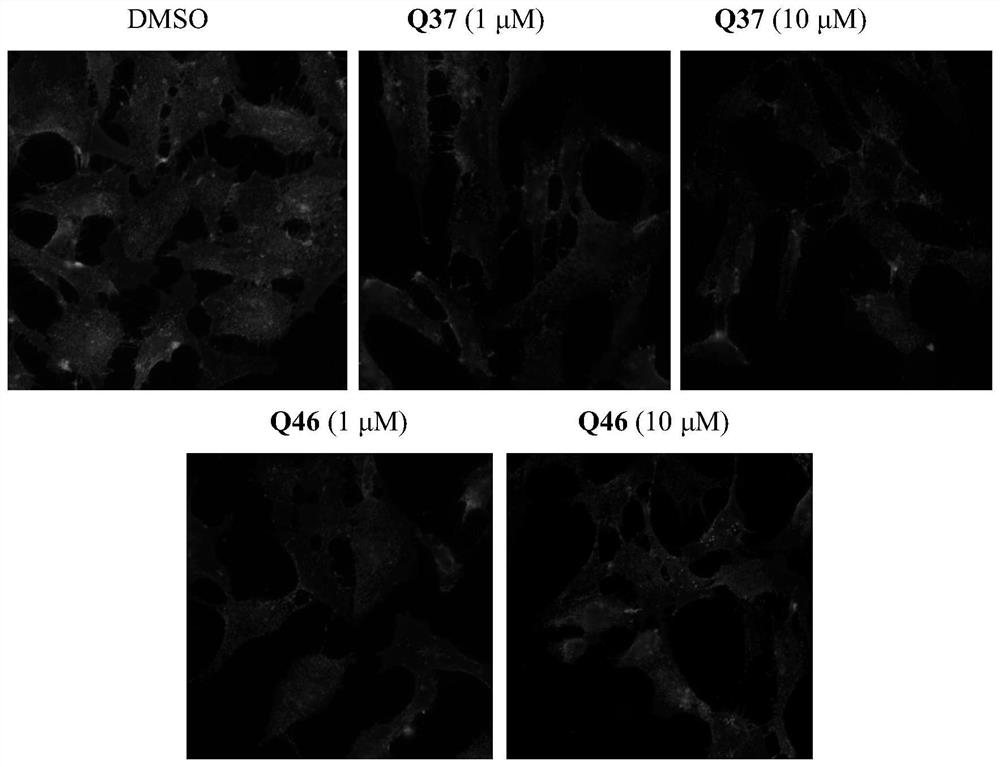
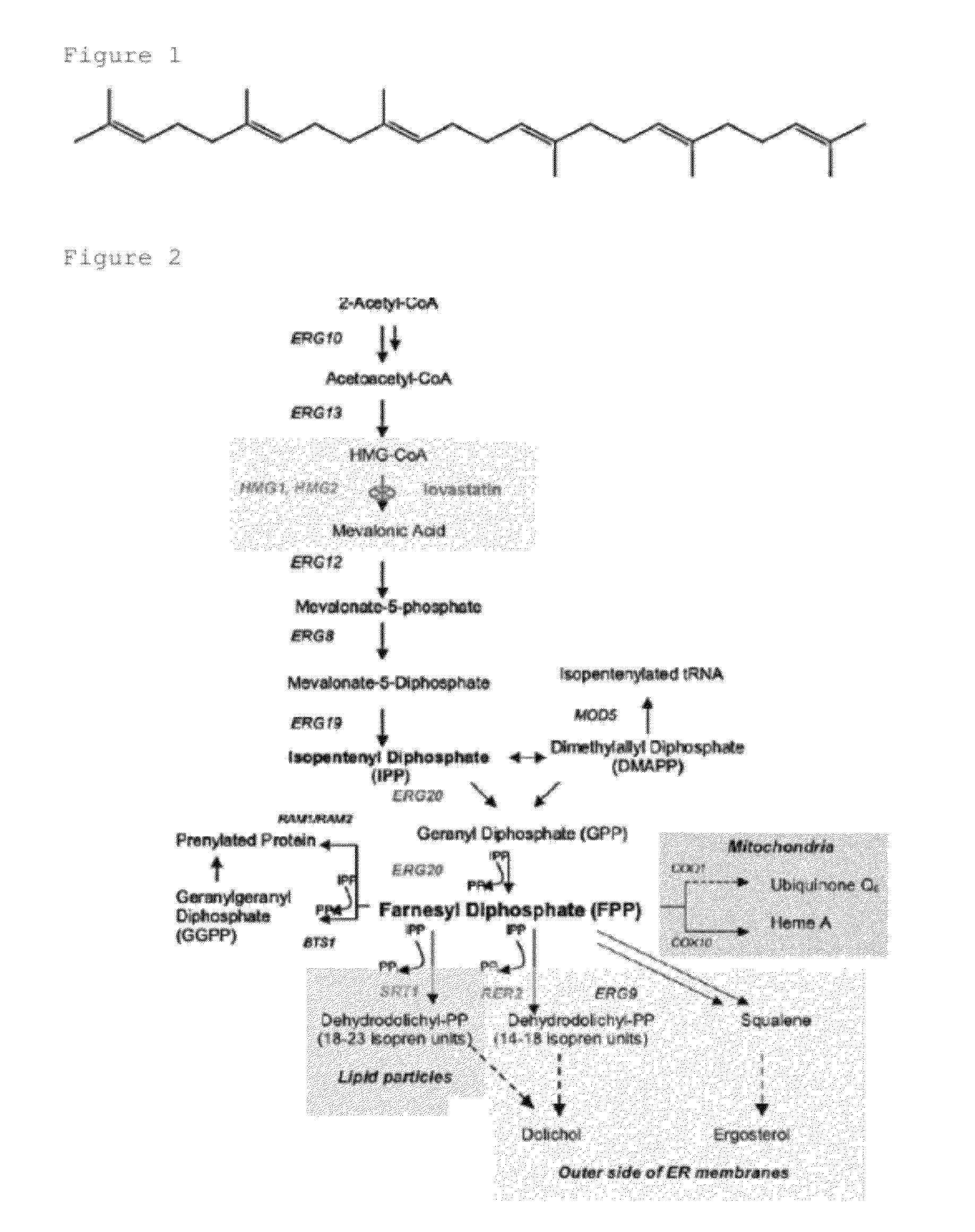
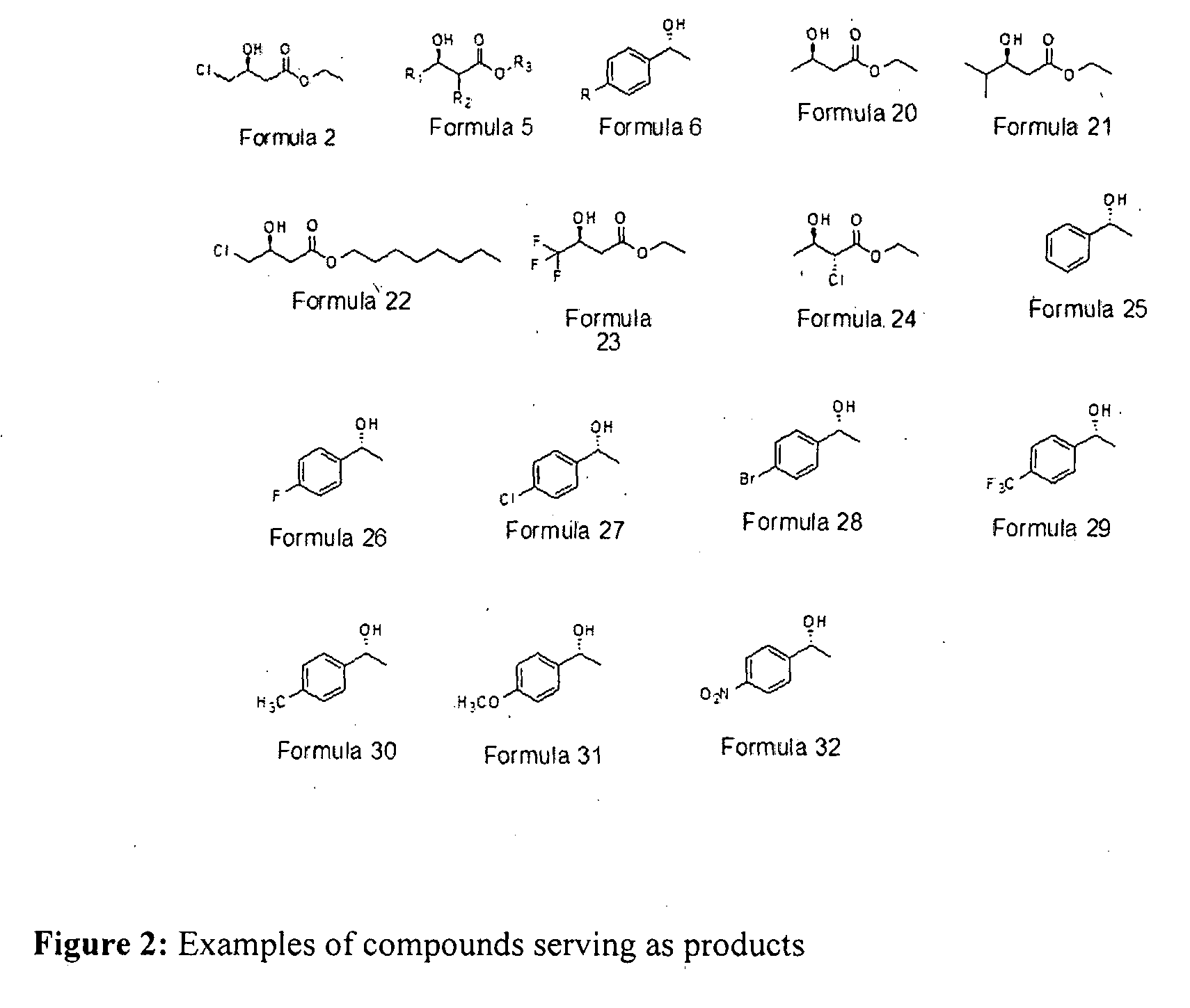
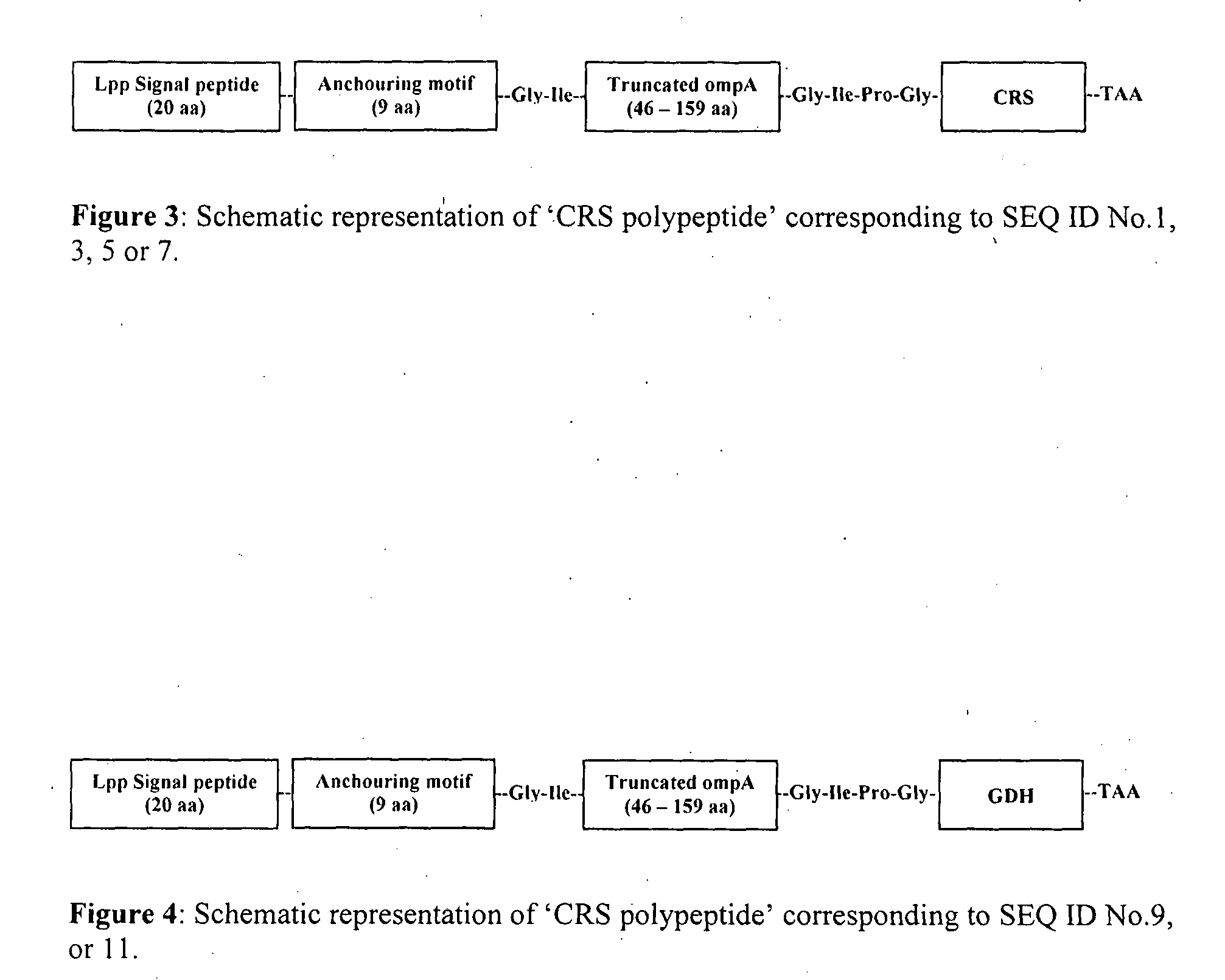
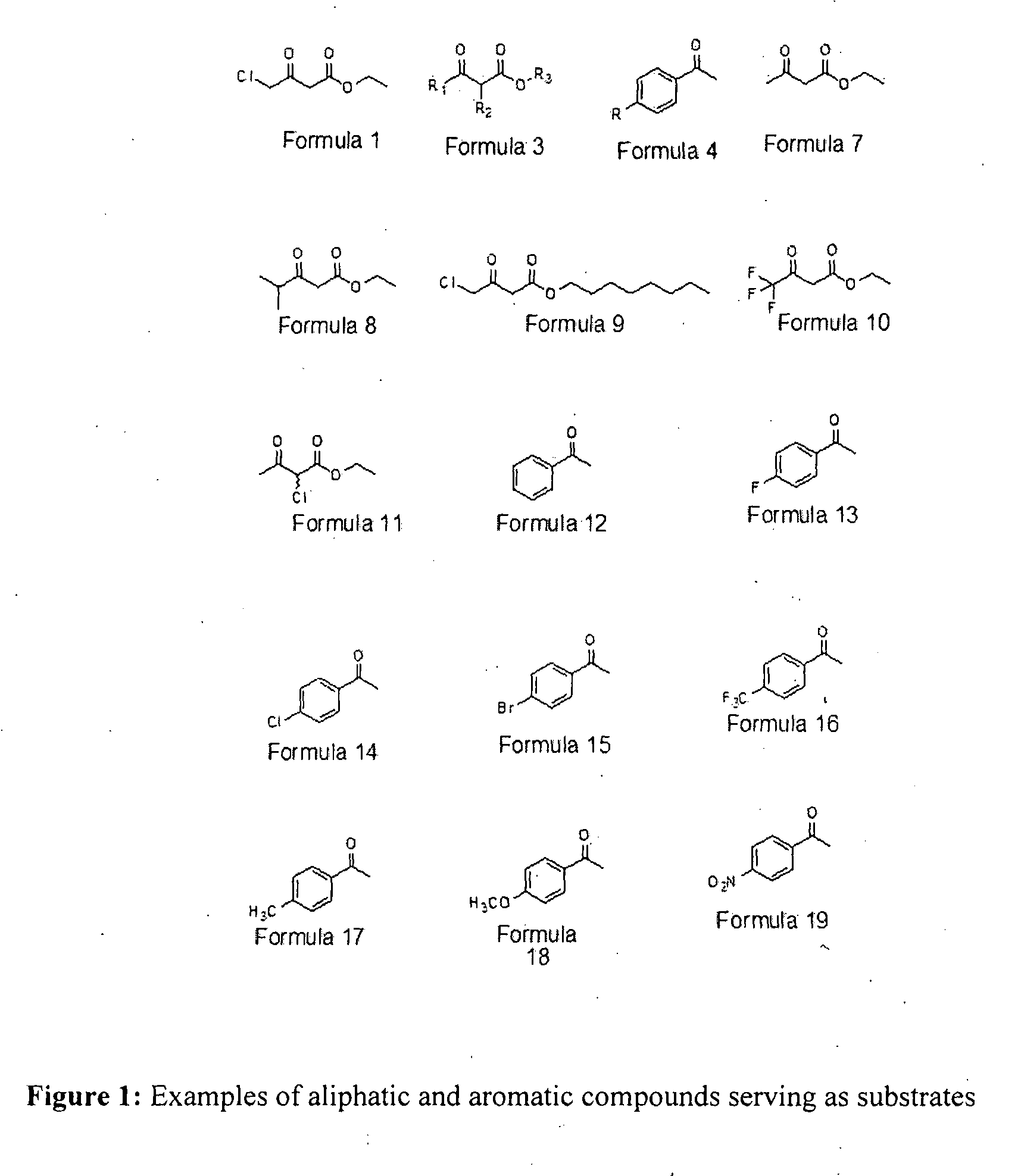Patents
Literature
40 results about "Hydroxy methyl glutaryl" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for enhancing production of isoprenoid compounds
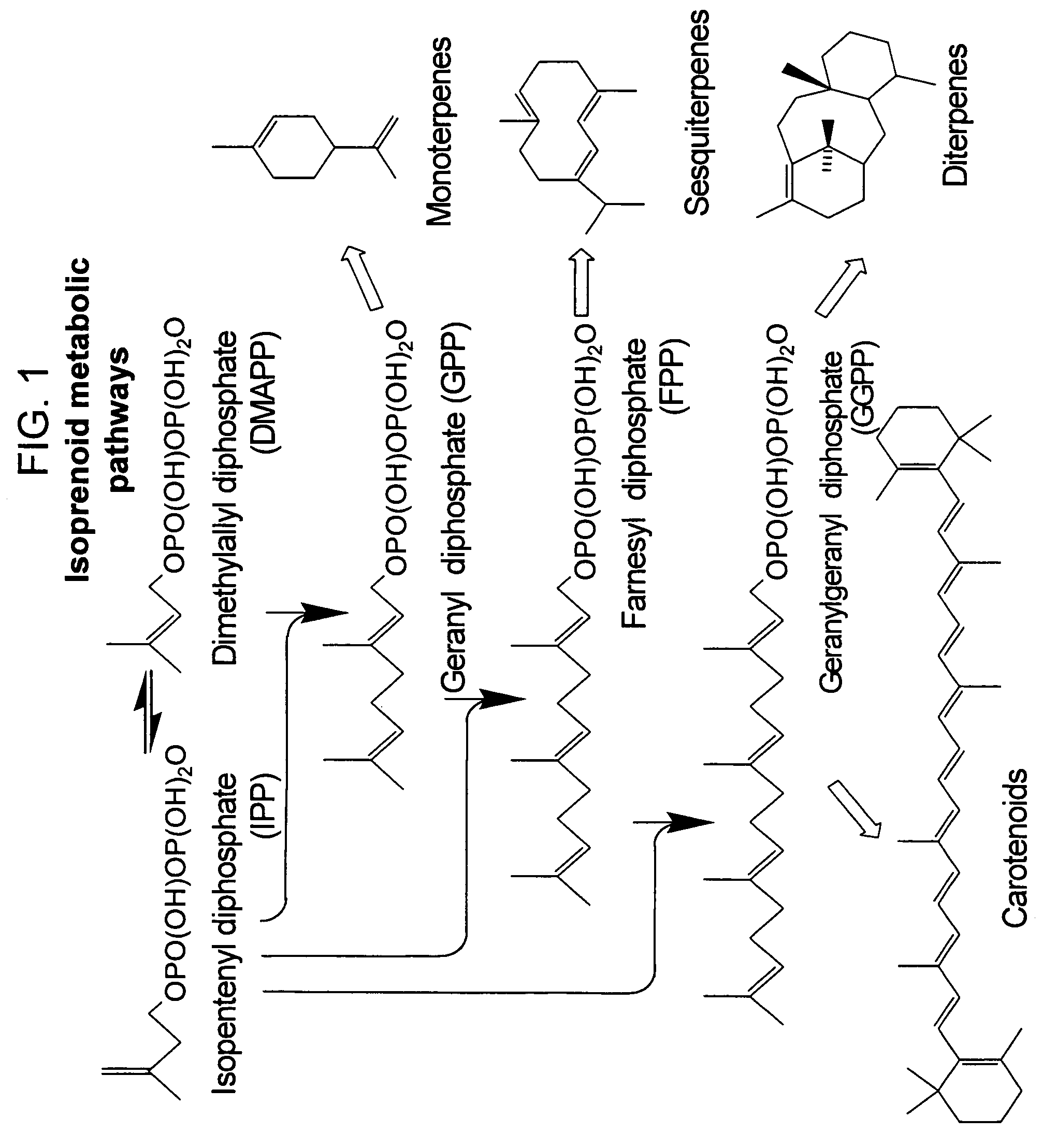
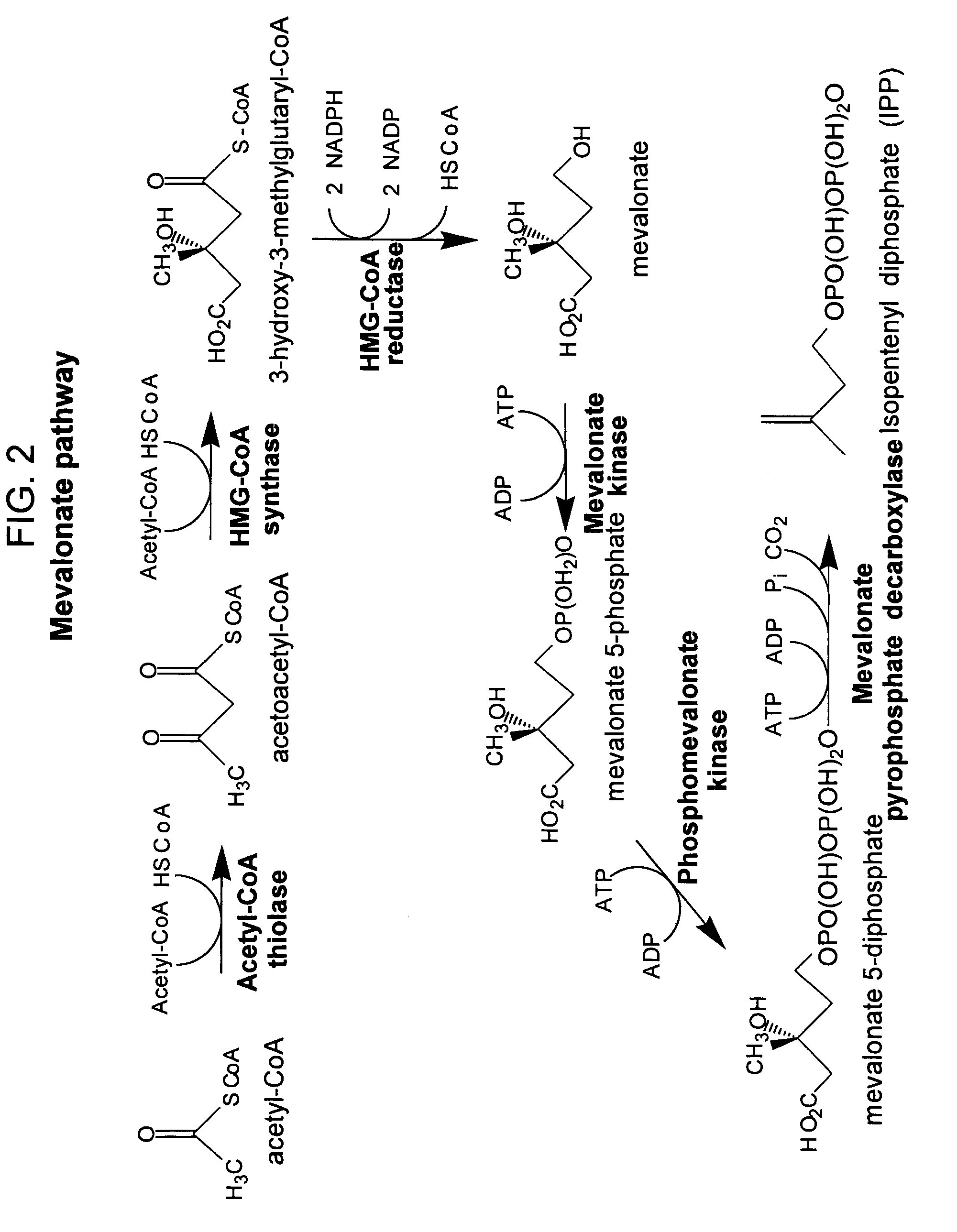
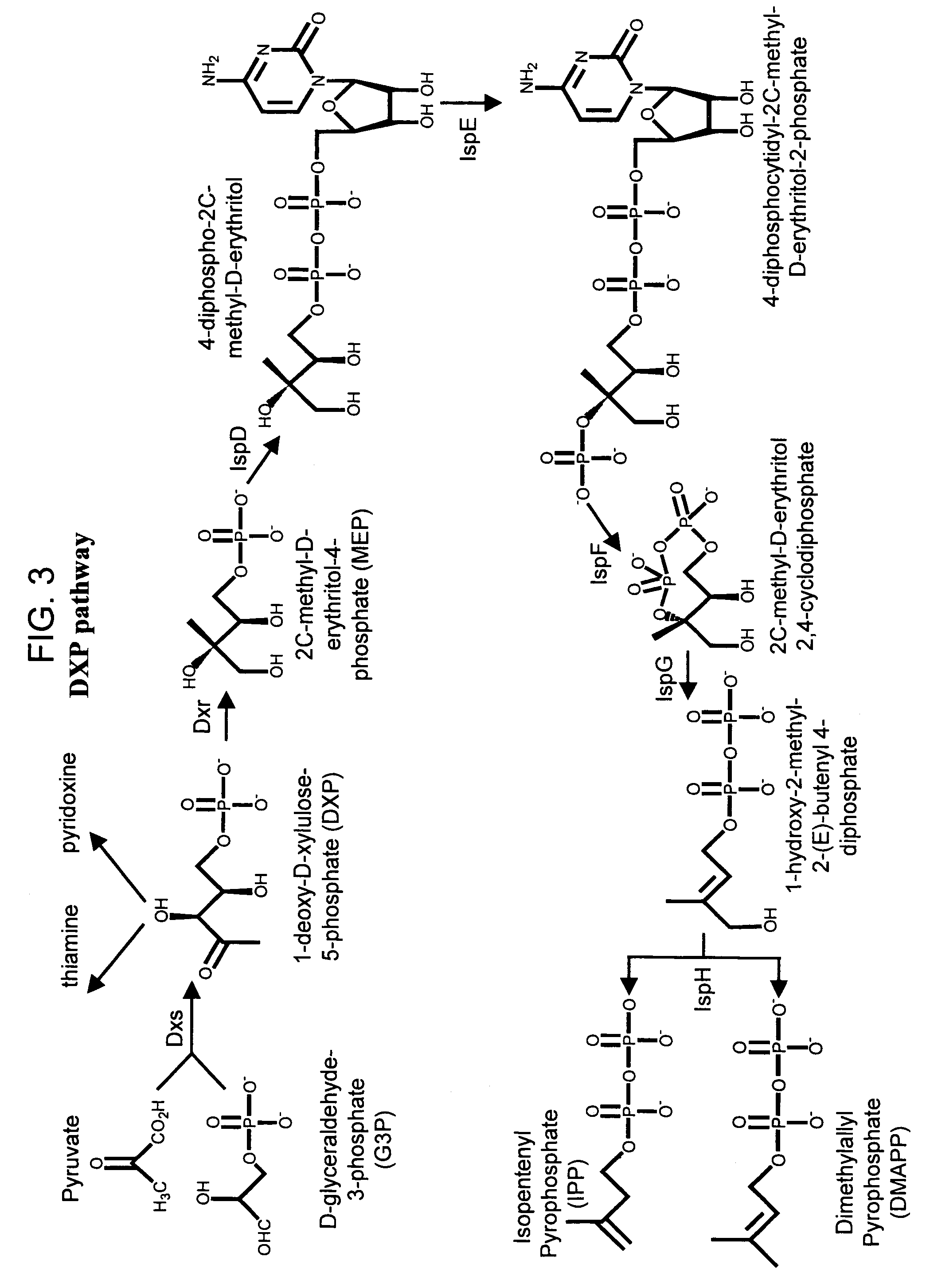
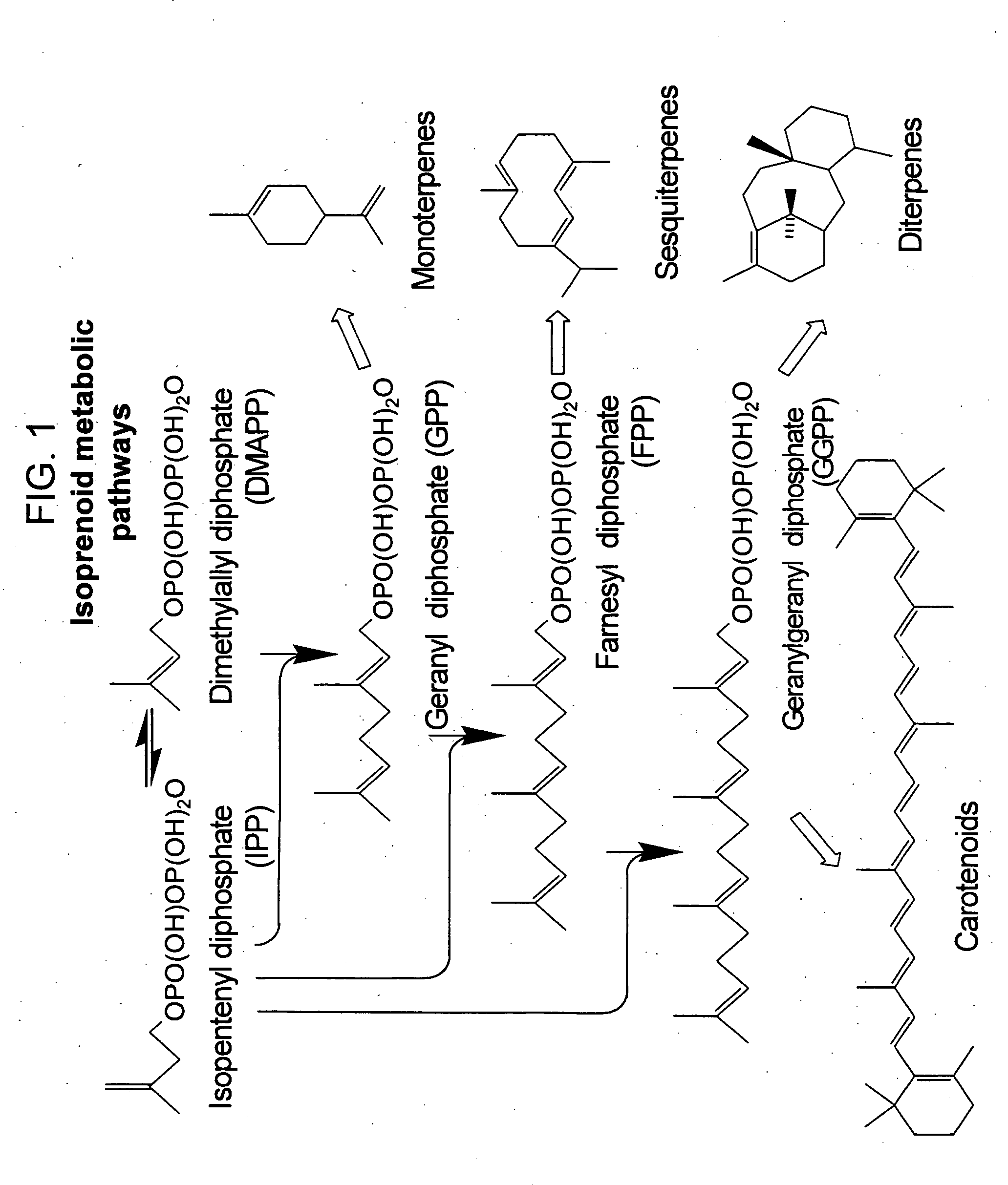
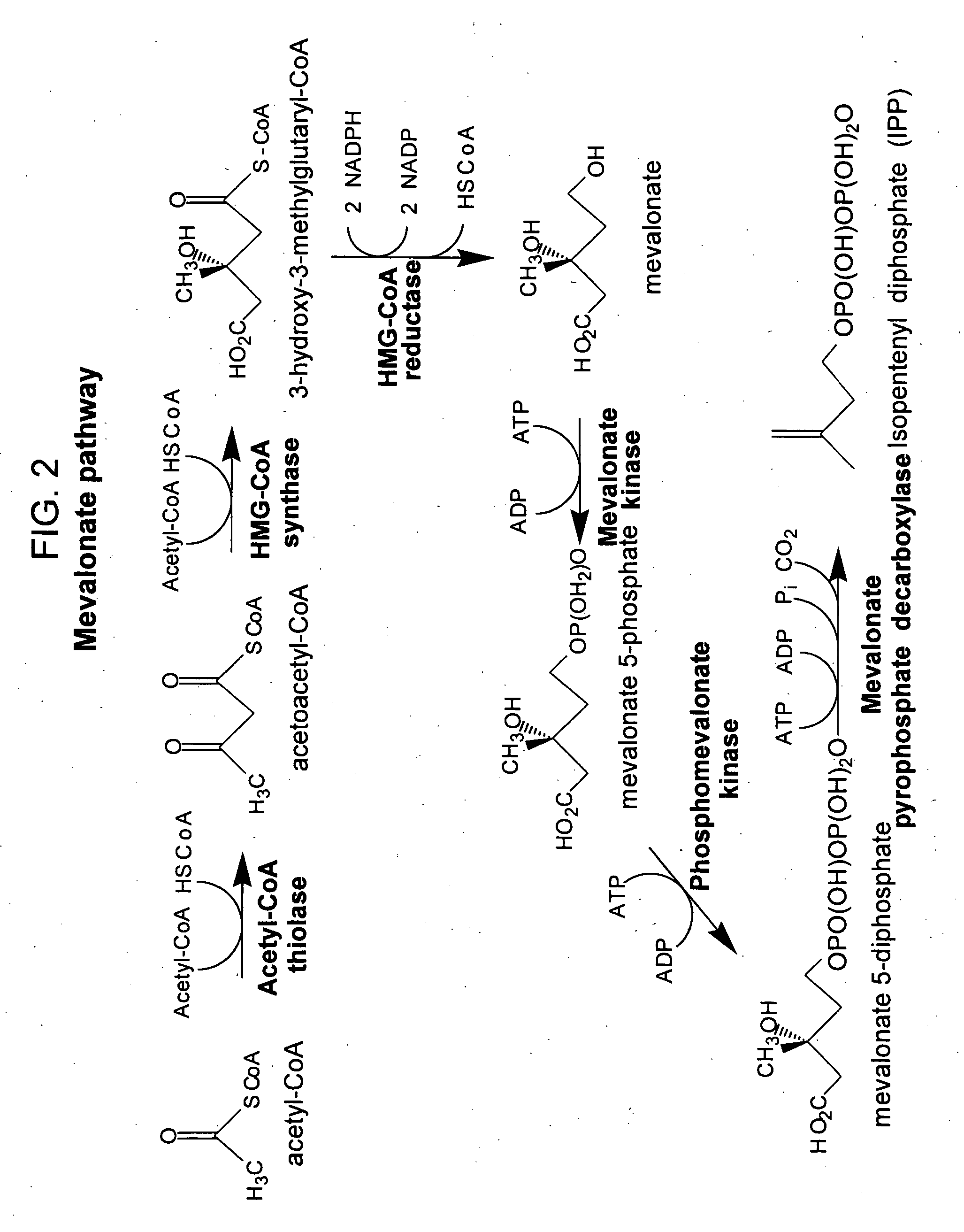
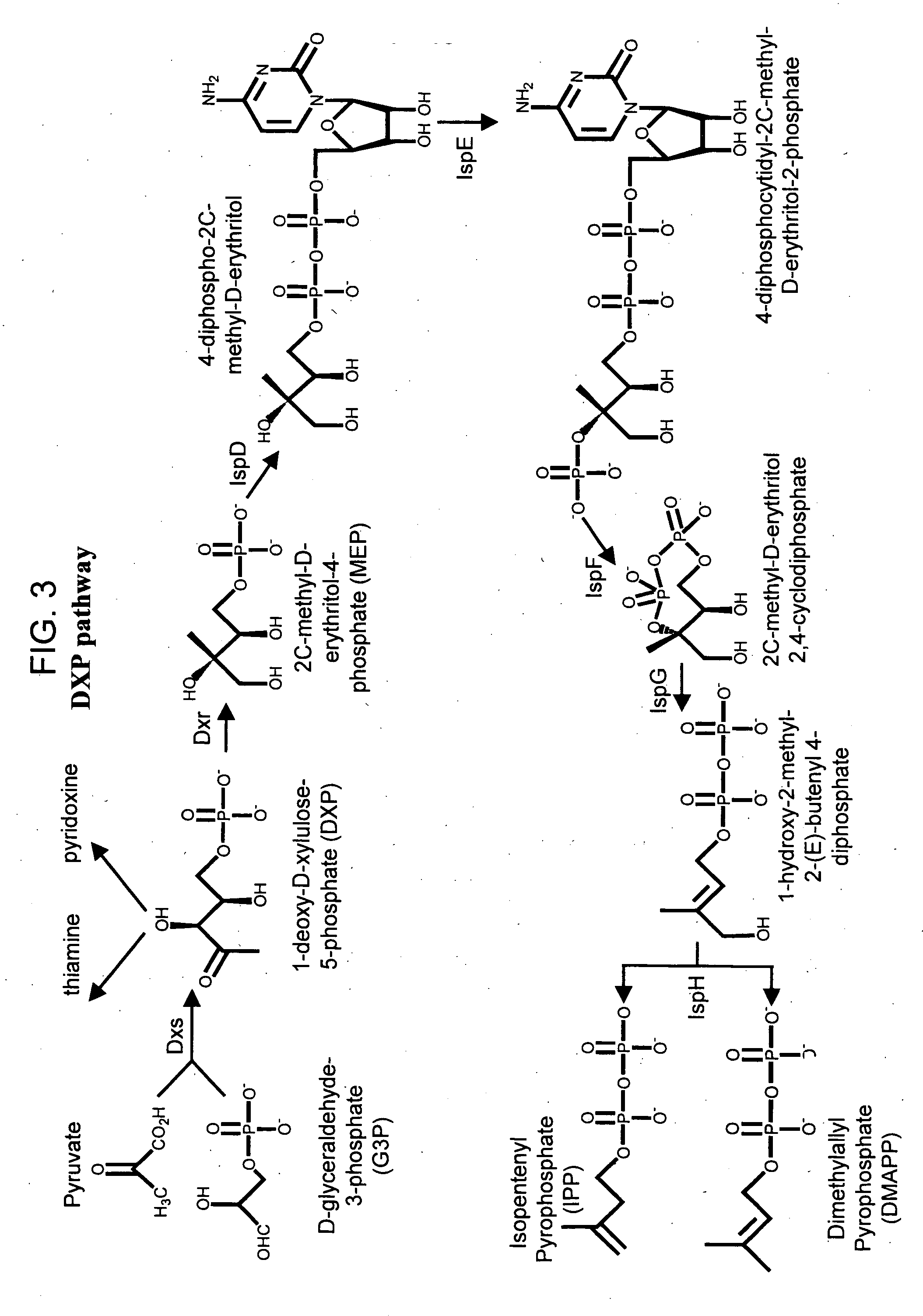
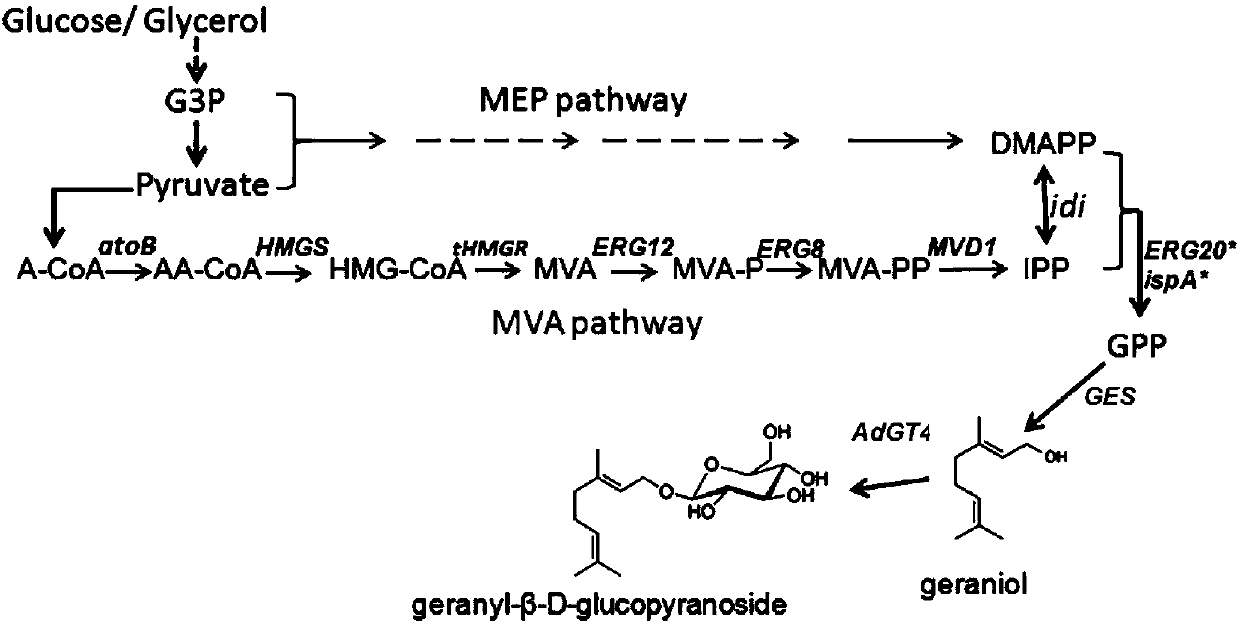
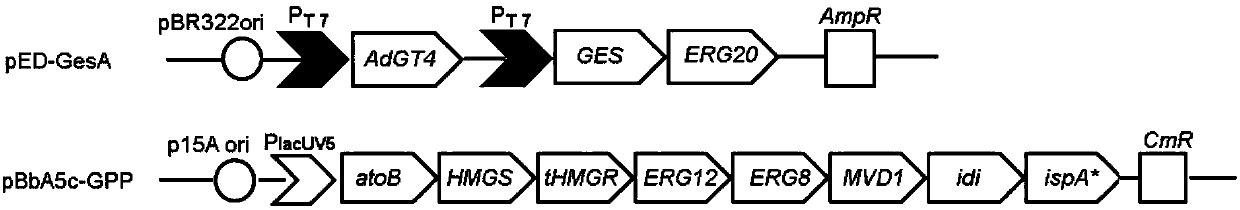
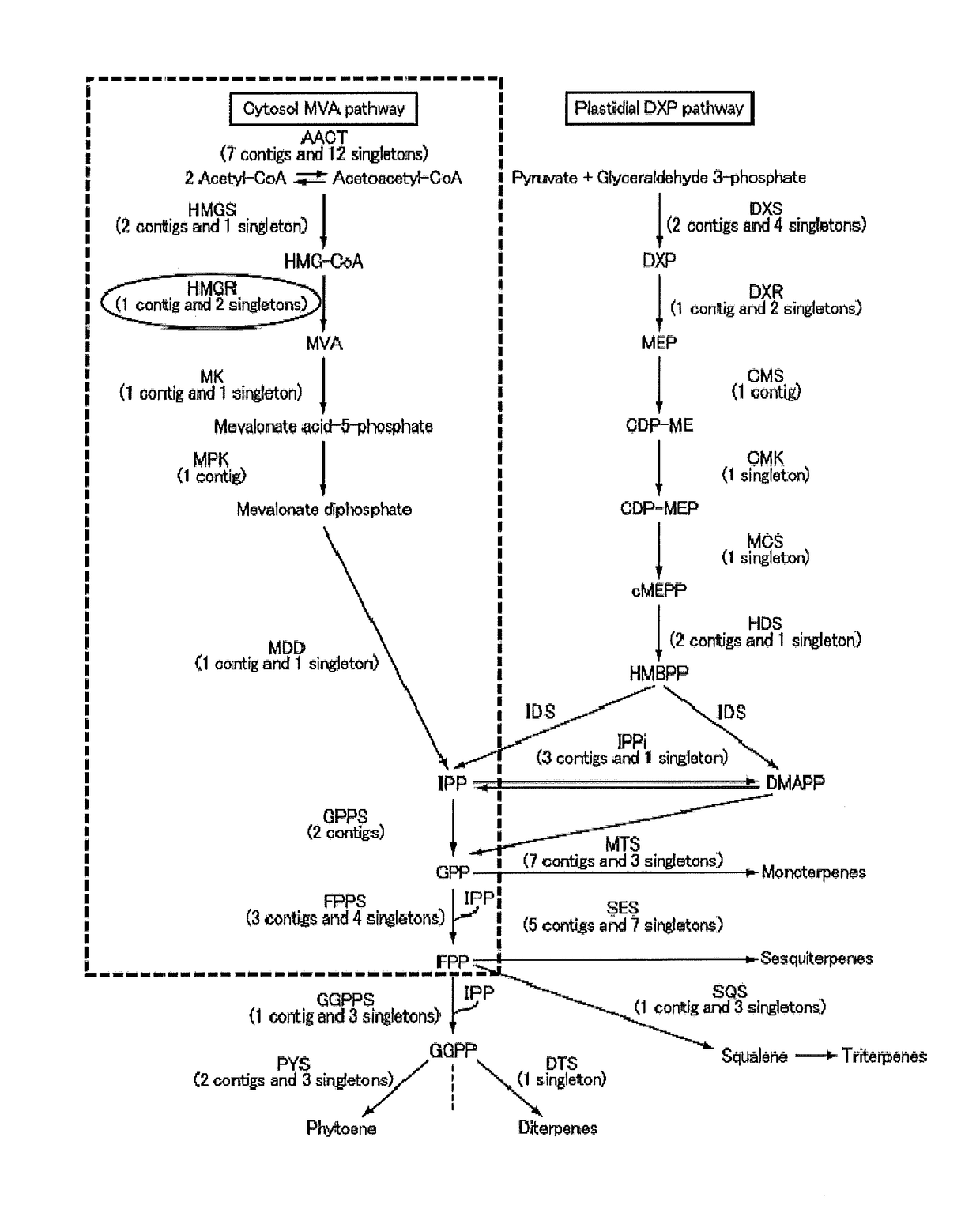
The present invention provides methods of producing an isoprenoid or an isoprenoid precursor in a genetically modified host cell. The methods generally involve modulating the level of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) in the cell, such that the level of HMG-CoA is not toxic to the cell and / or does not substantially inhibit cell growth, but is maintained at a level that provides for high-level production of mevalonate, IPP, and other downstream products of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid pathway, e.g., polyprenyl diphosphates and isoprenoid compounds. The present invention further provides genetically modified host cells that are suitable for use in a subject method. The present invention further provides recombinant nucleic acid constructs for use in generating a subject genetically modified host cell, including recombinant nucleic acid constructs comprising nucleotide sequences encoding one or more mevalonate pathway enzymes, and recombinant vectors (e.g., recombinant expression vectors) comprising same. The present invention further provides methods for identifying nucleic acids that encode HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) variants that provide for relief of HMG-CoA accumulation-induced toxicity. The present invention further provides methods for identifying agents that reduce intracellular accumulation of HMG-CoA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for enhancing production of isoprenoid compounds
ActiveUS20060079476A1Modulating levelToxic levelGenetic material ingredientsOxidoreductasesENCODEMevalonate pathway
The present invention provides methods of producing an isoprenoid or an isoprenoid precursor in a genetically modified host cell. The methods generally involve modulating the level of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) in the cell, such that the level of HMG-CoA is not toxic to the cell and / or does not substantially inhibit cell growth, but is maintained at a level that provides for high-level production of mevalonate, IPP, and other downstream products of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid pathway, e.g., polyprenyl diphosphates and isoprenoid compounds. The present invention further provides genetically modified host cells that are suitable for use in a subject method. The present invention further provides recombinant nucleic acid constructs for use in generating a subject genetically modified host cell, including recombinant nucleic acid constructs comprising nucleotide sequences encoding one or more mevalonate pathway enzymes, and recombinant vectors (e.g., recombinant expression vectors) comprising same. The present invention further provides methods for identifying nucleic acids that encode HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) variants that provide for relief of HMG-CoA accumulation-induced toxicity. The present invention further provides methods for identifying agents that reduce intracellular accumulation of HMG-CoA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
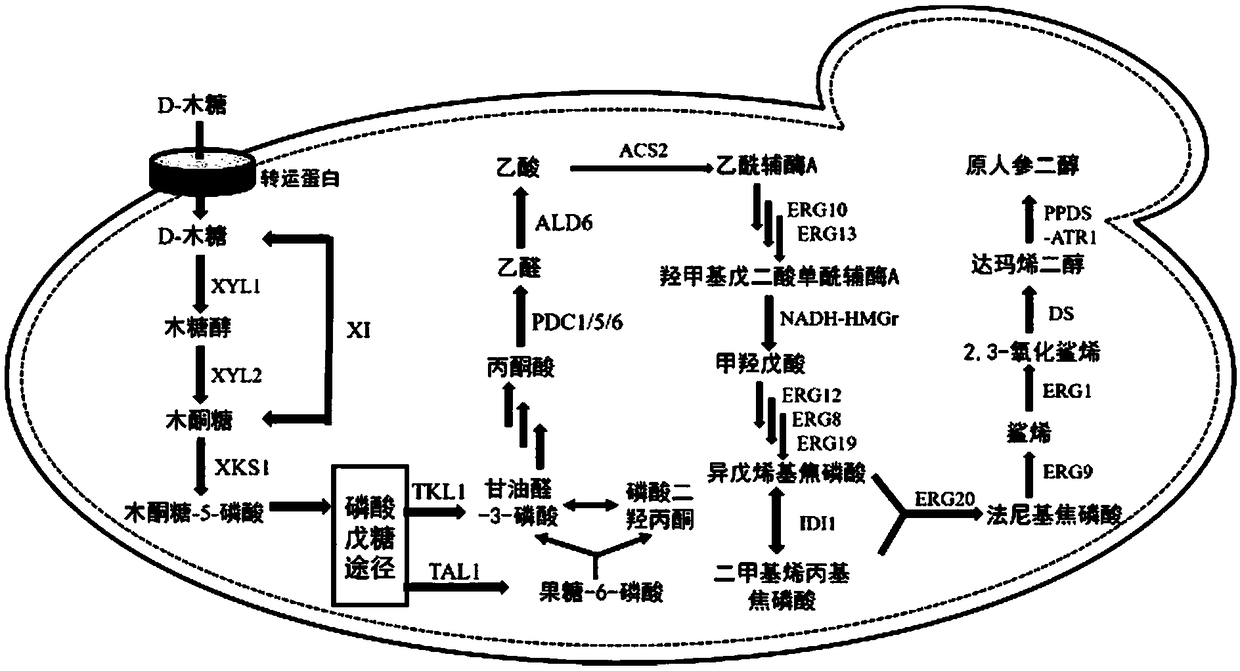
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and a construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of replacing a promoter of a saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 with a promoter PFBA1 by virtue of a homologous recombination method, introducing xylose reductase XYL1 and a xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassette, increasing the activities of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 1, introducing a farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, a squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and a dammarenediol synthase gene DS into the recombinant bacteria 1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and introducing a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl diphosphatesynthase ERG20 and a protopanoxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 into the recombinant bacteria 2, so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 3. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol can be artificially synthesized by virtue of xylose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting biological process
InactiveCN104120148AFast growthShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxy methyl glutarylGlutaryl-coenzyme A
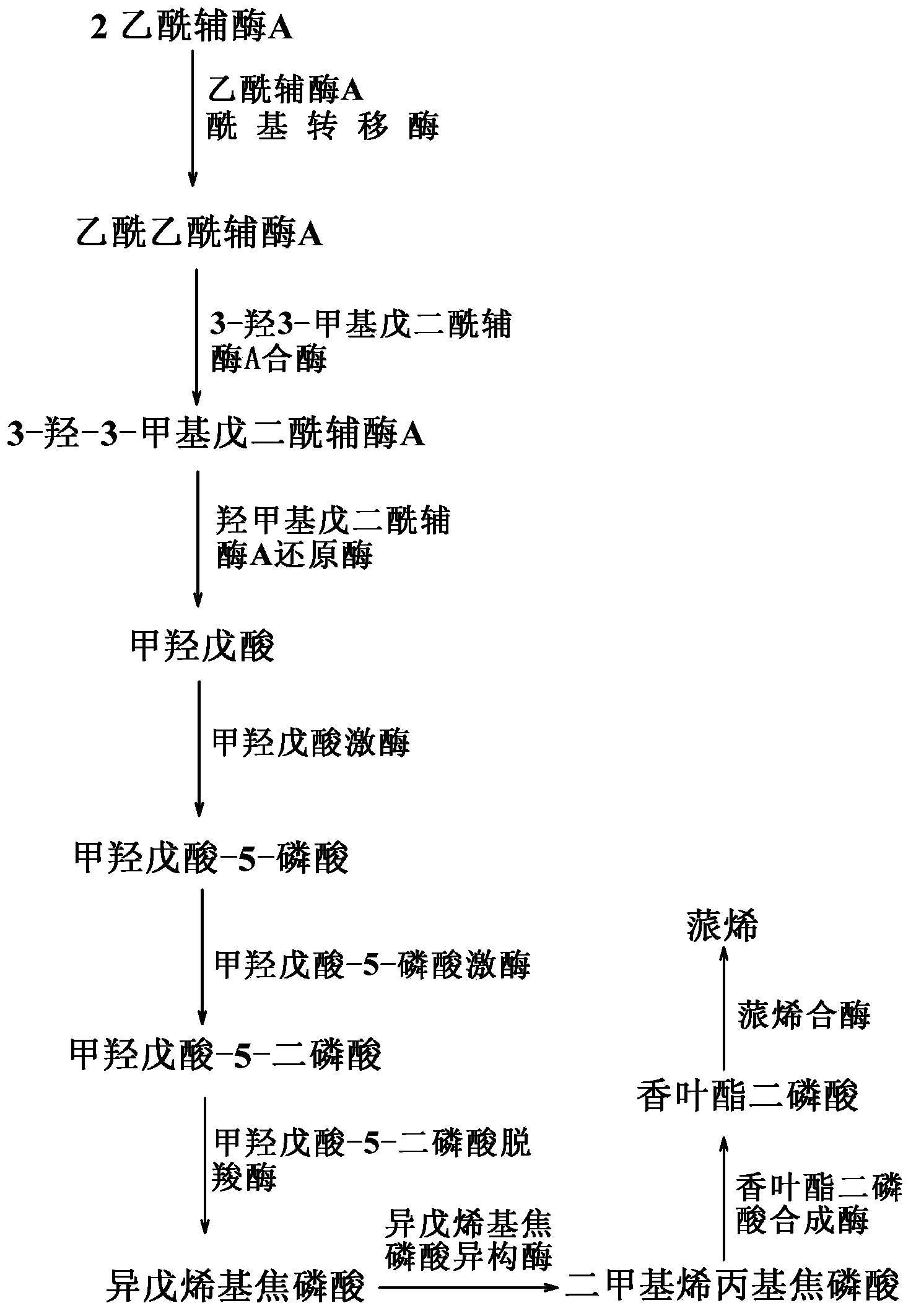
The invention provides a biological method for synthesizing alpha-pinene or beta-pinene from acetyl coenzyme A and a reconstitution cell capable of synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene, wherein the acetyl coenzyme A is obtained from a simple starting material like glucose. The method for synthesizing the alpha-pinene or beta-pinene by adopting a biological process comprises the following steps: transferring acetyl coenzyme A acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthase, hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, mevalonic acid kinase, mevalonic acid-5-phosphokinase, mevalonic acid-5-diphosphonic acid decarboxylase, isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase, geranyldiphosphate synthetase and pinene synthase into an appropriate host cell by adopting metabolic engineering technology, and culturing the obtained reconstitution cell, so that the target product, namely alpha-pinene or beta-pinene can be obtained.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacterium co-generating geraniol and nerol and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103898037AFast growthShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGenetically engineered
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium co-generating geraniol and nerol and a construction method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of generic field. According to the genetically engineered bacterium disclosed by the invention, acetyl coenzyme A acyltransferase / hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, 3-hydroxyl-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthase, mevalonic acid kinase, mevalonic acid-5-phosphokinase, mevalonic acid-5-diphosphonic acid decarboxylase, isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase, geranyl diphosphonic acid synthetase and geraniol synthetase or phosphatase are expressed. The metabolic pathways of geraniol and nerol synthesized in escherichia coli are successfully constructed by genetic engineering means, and glucose is biologically converted into geraniol and nerol.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof
ActiveCN104031872AAvoid the influence of own metabolismShort reaction timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
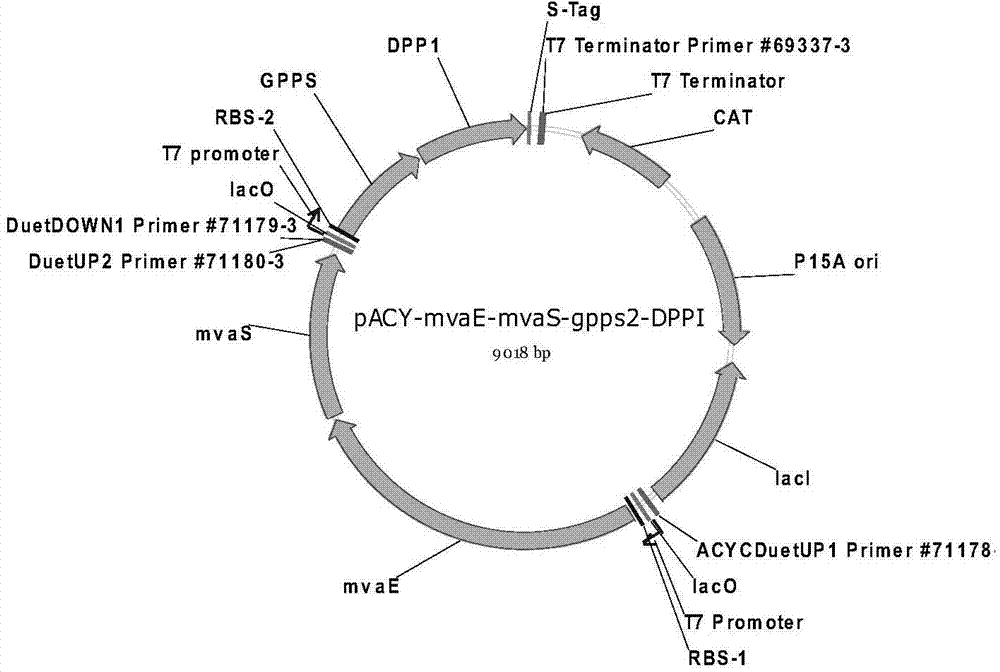
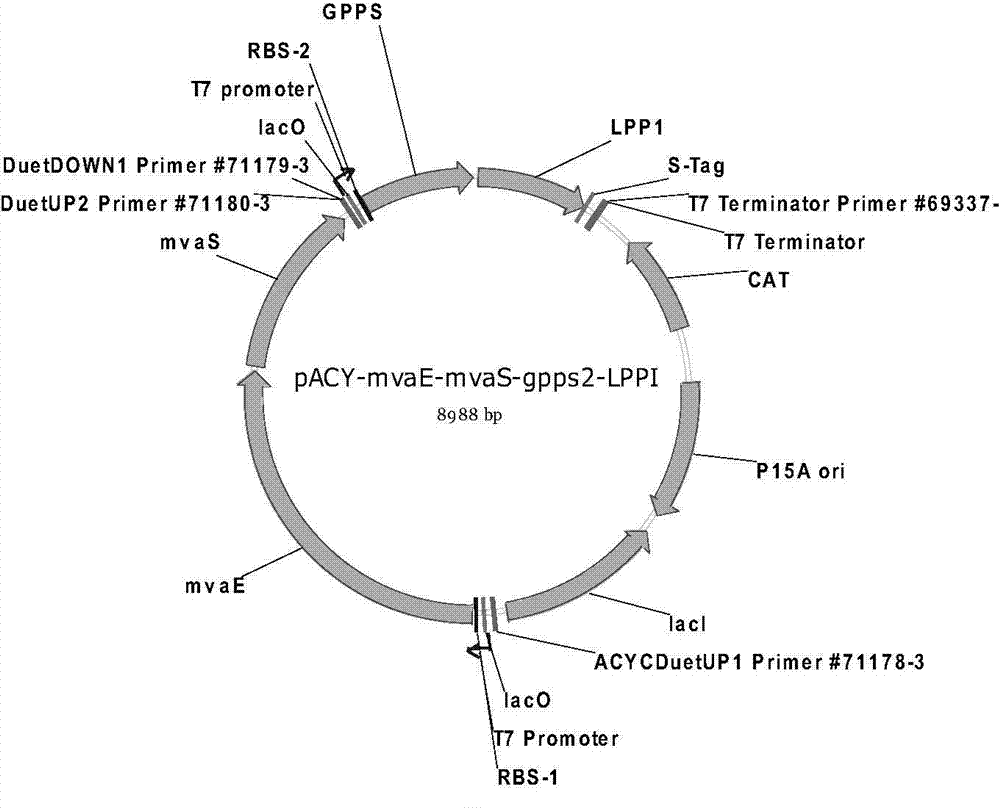
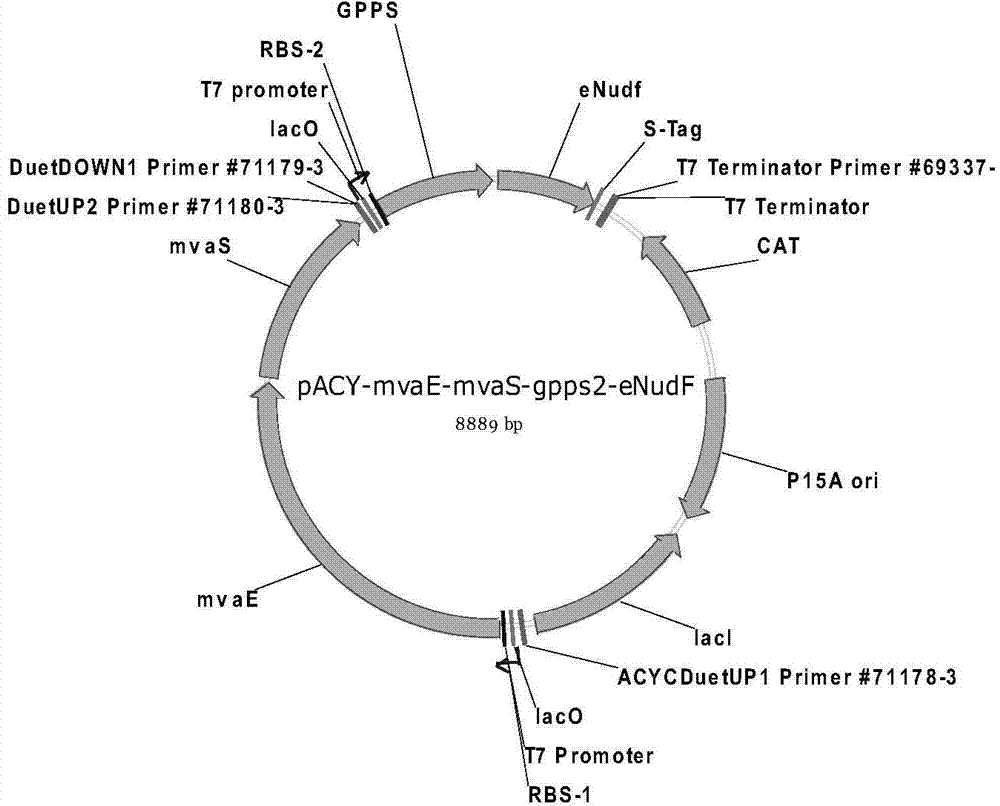
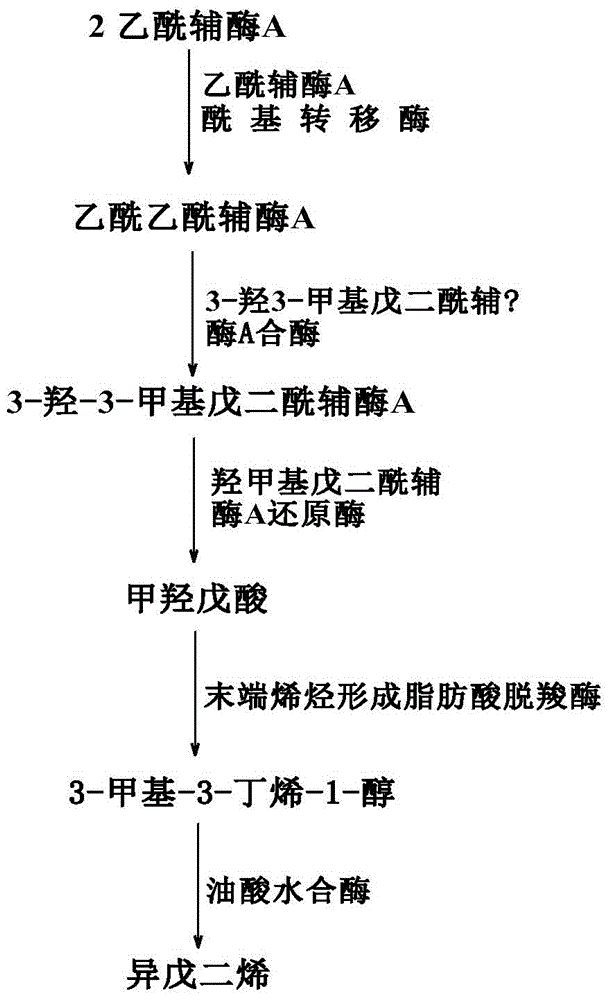
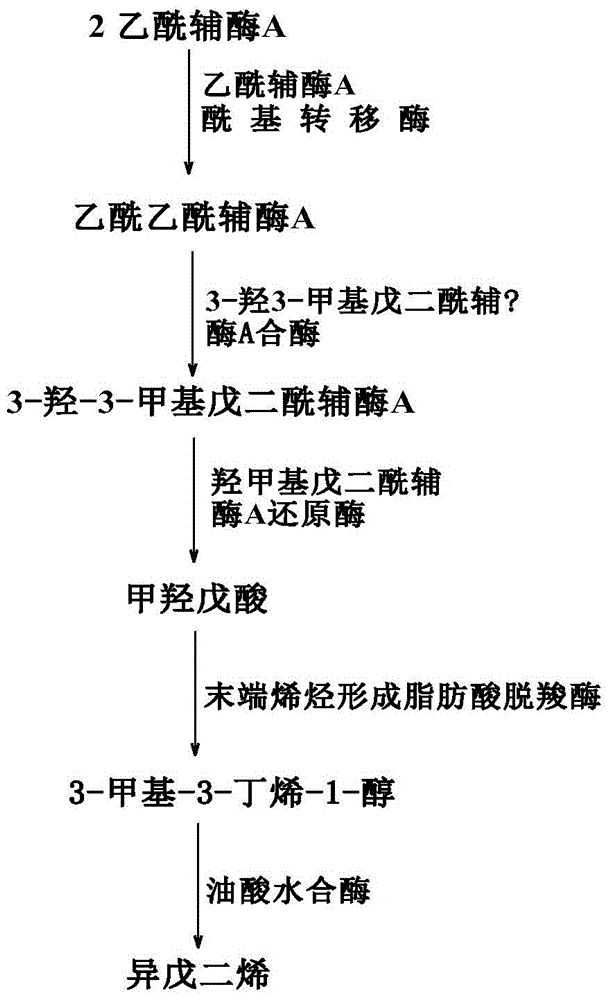
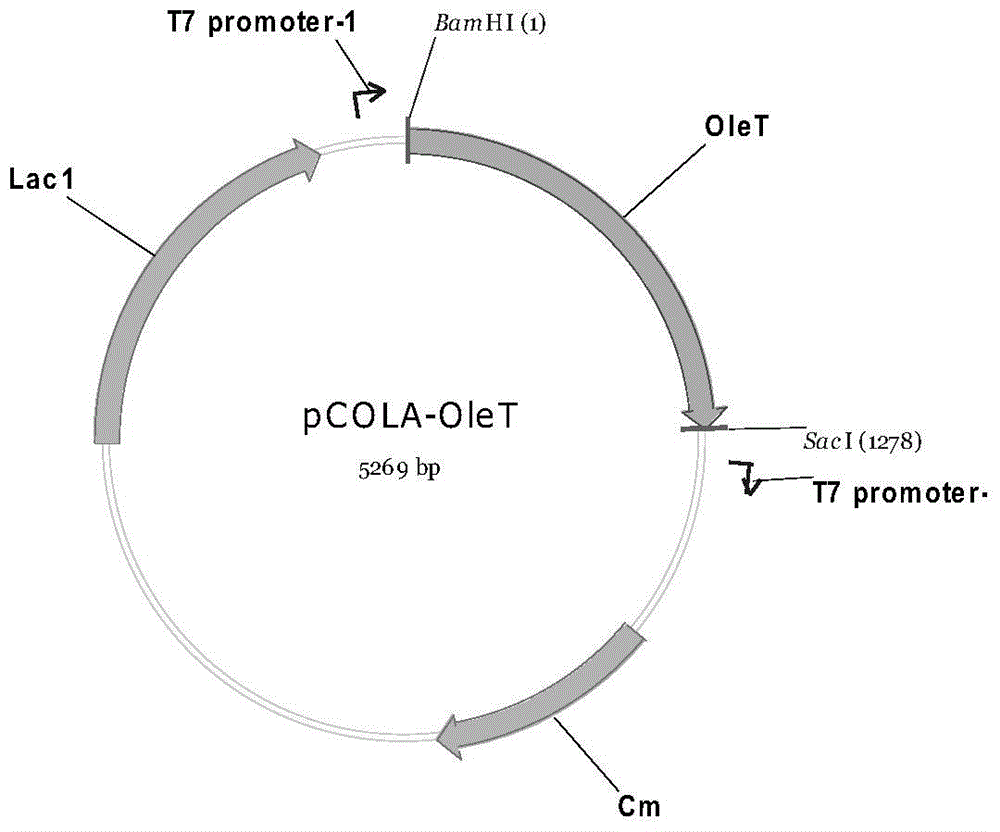
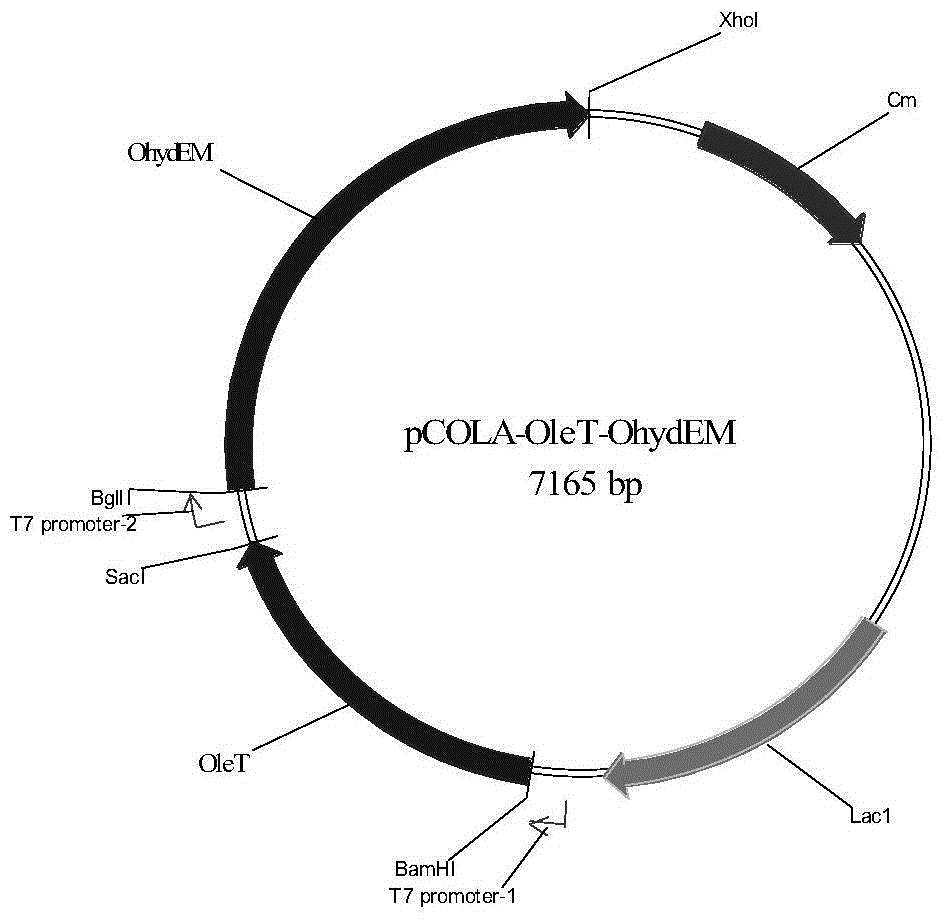
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium producing isoprene and application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering technology. According to the invention, a recombinant bacterium is obtained by transforming a gene containing acetyl-CoA acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase, terminal alkene formed fatty acid decarboxylase and oleic acid hydratase into a host bacterium, and is used for fermentation production of isoprene. Such a method substantially shortens reaction process for synthesis of isoprene through an exogenous MVA approach, only five reaction steps are needed for synthesis of isoprene of acetyl-CoA, so influence of excess exogenous gene expression on metabolism of cells is avoided. Through optimization of fermentation conditions, the yield of the fermentation product isoprene can reach 39.49 mu g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and reagent for measuring mevalonic acid, 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme a, and coenzyme a
The present invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a test solution wherein the analyte is mevalonic acid and / or 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A, comprising the following steps (p) and (q): (p) a step of allowing an enzyme that catalyzes a reaction represented by Reaction Formula 1 and an enzyme that catalyzes a reaction represented by Reaction Formula 2 to act on a test solution containing mevalonic acid and / or 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A in the presence of a hydrogen acceptor X, a hydrogen donor Y, and coenzyme A; and (q) a step of measuring an amount of: a reduced hydrogen acceptor X that is produced; or an oxidized hydrogen donor Y that is produced; or a hydrogen acceptor X that is decreased; or a hydrogen donor Y that is decreased, wherein the hydrogen donor Y and the reduced hydrogen acceptor X are not the same.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI PHARMA
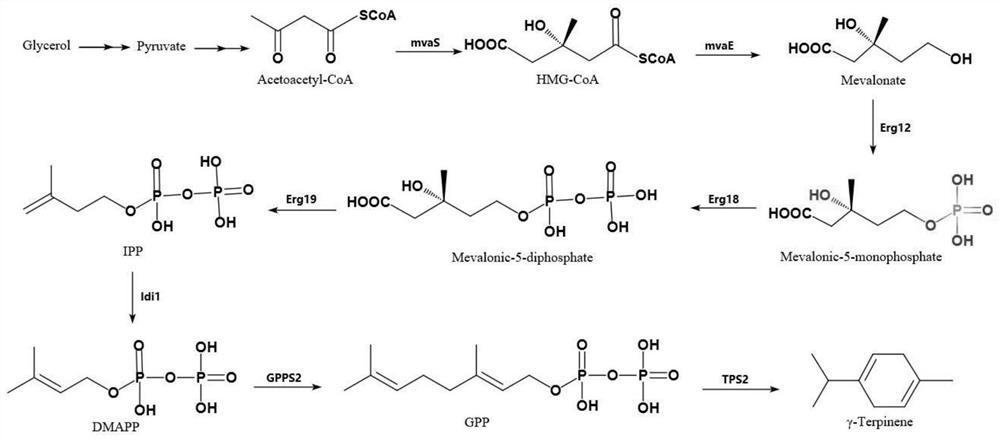
Genetically engineered bacterium with gamma-terpinene synthesis capacity and constructing method and application thereof
ActiveCN107354118AEfficient fermentation productionIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
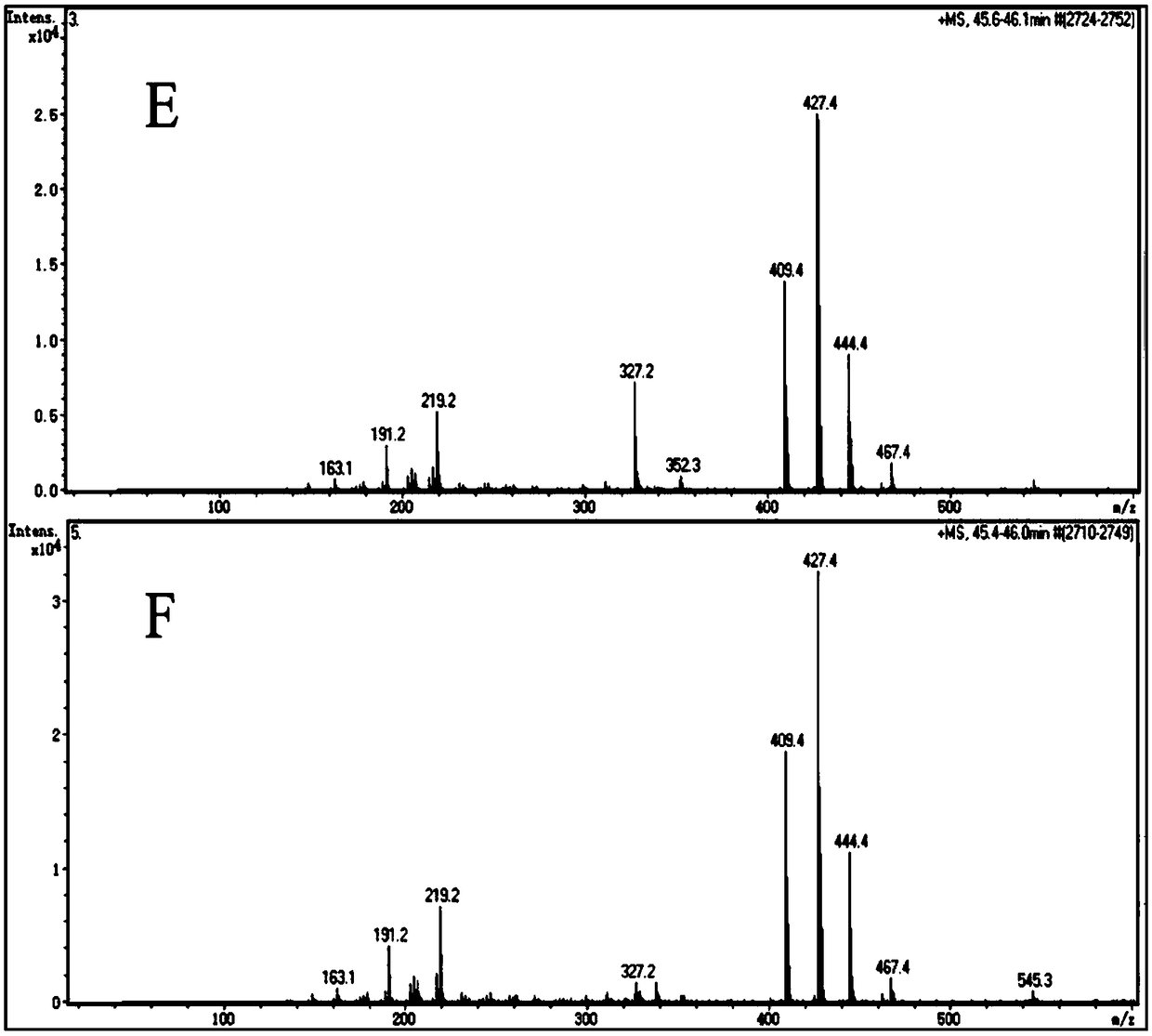
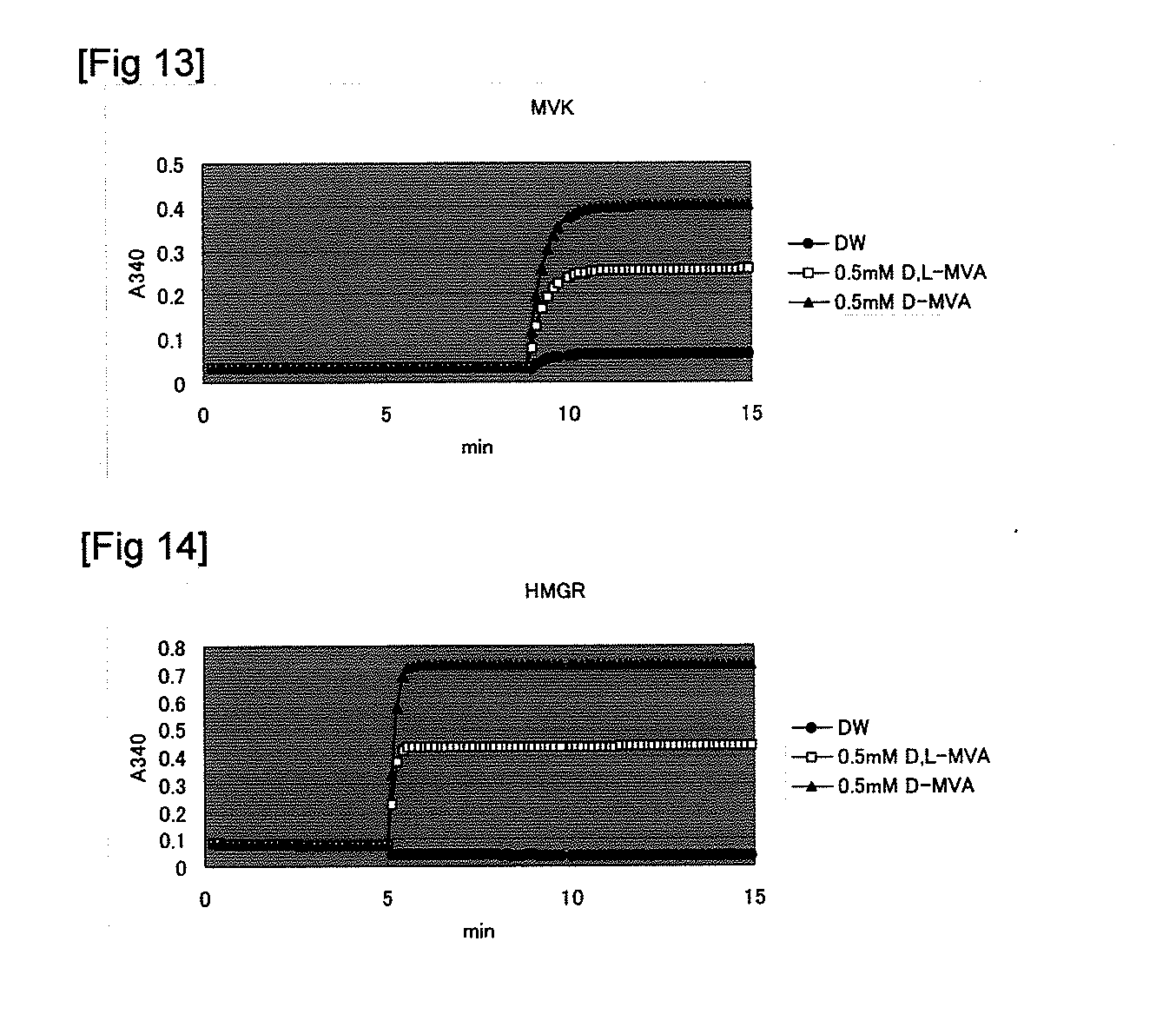
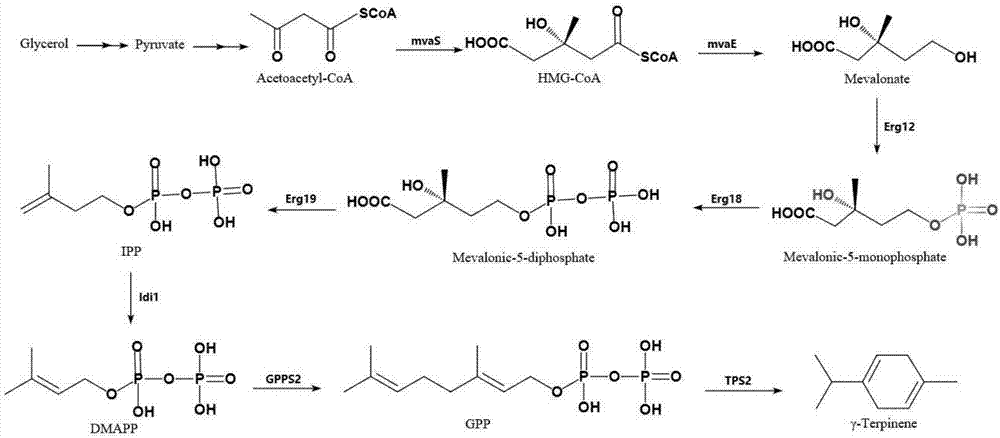
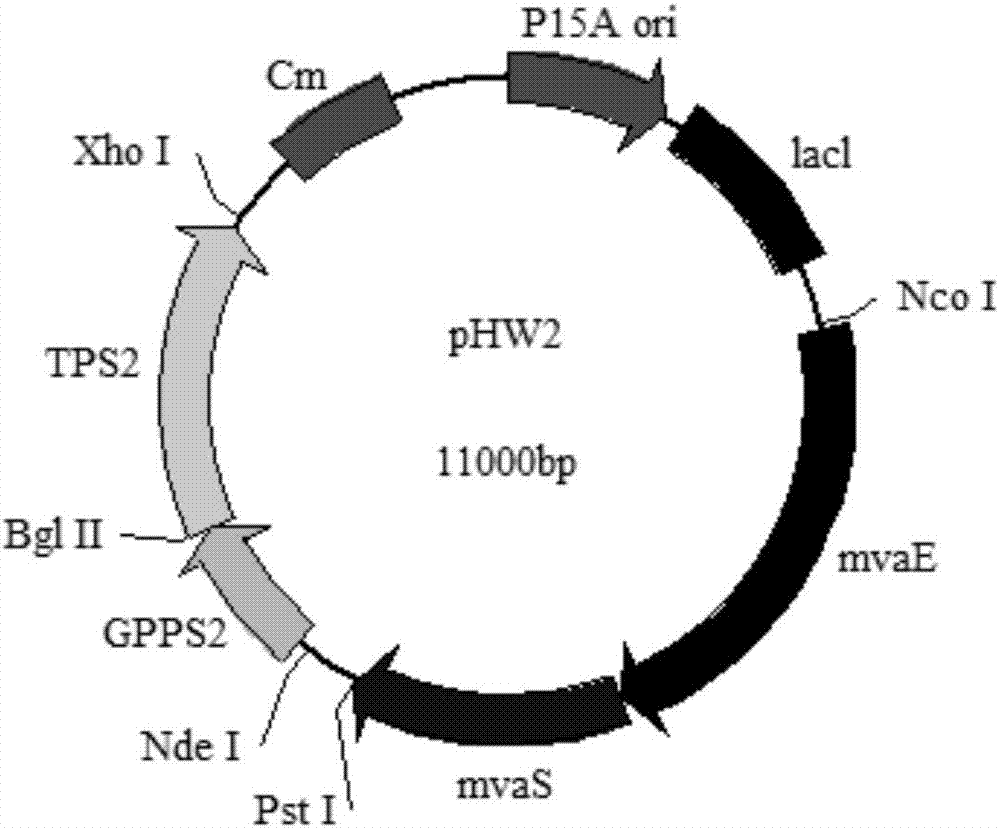
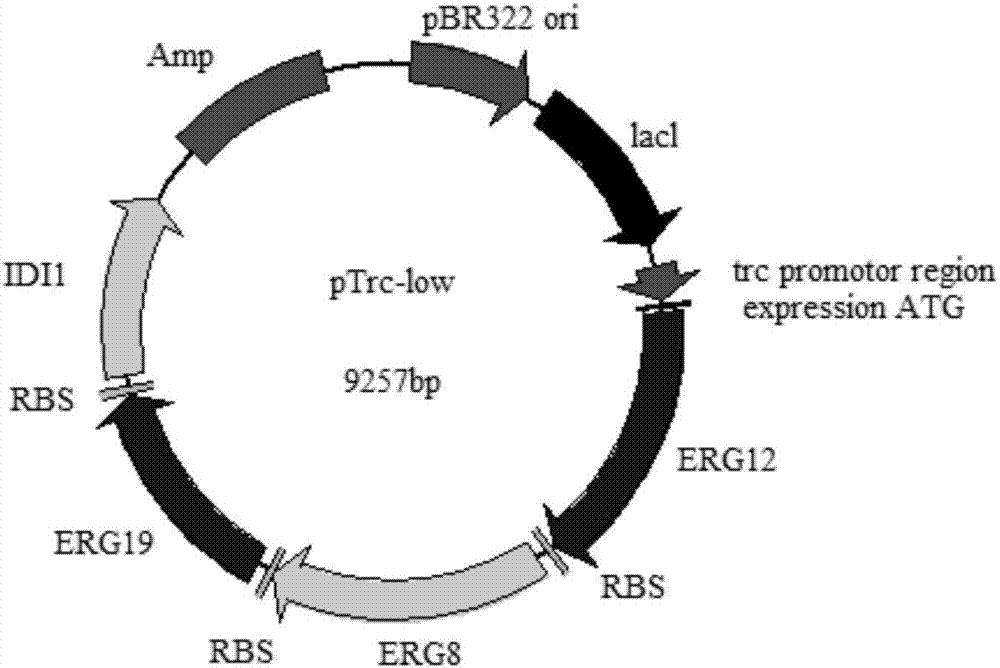
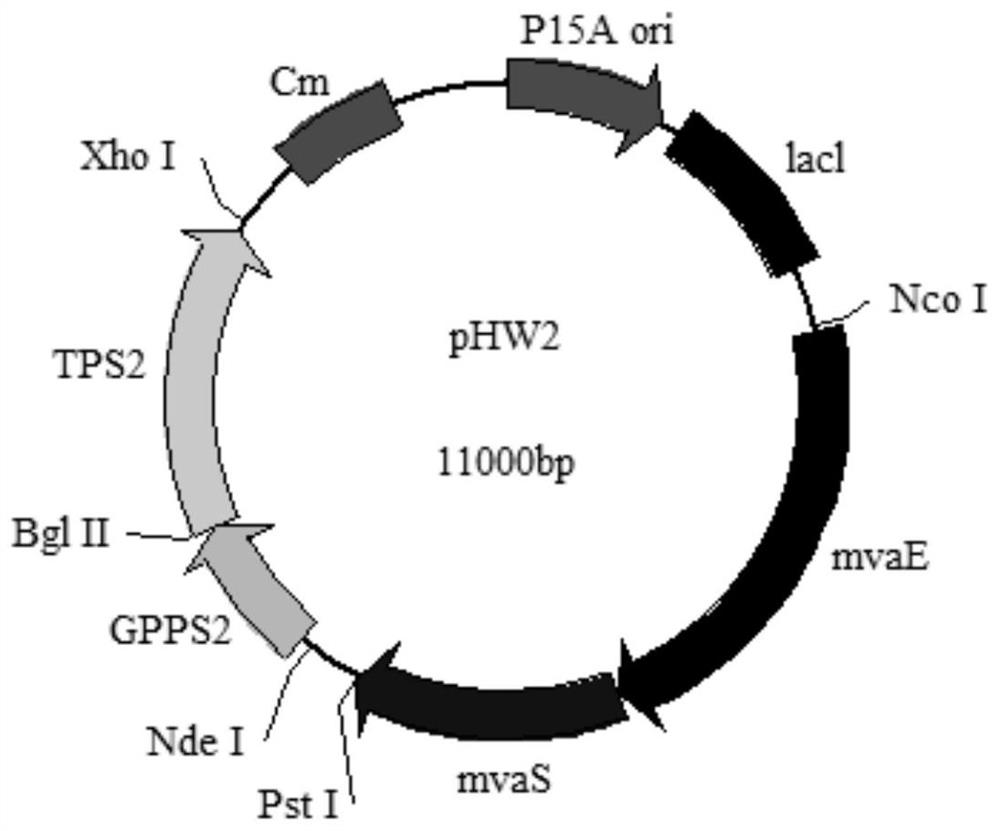
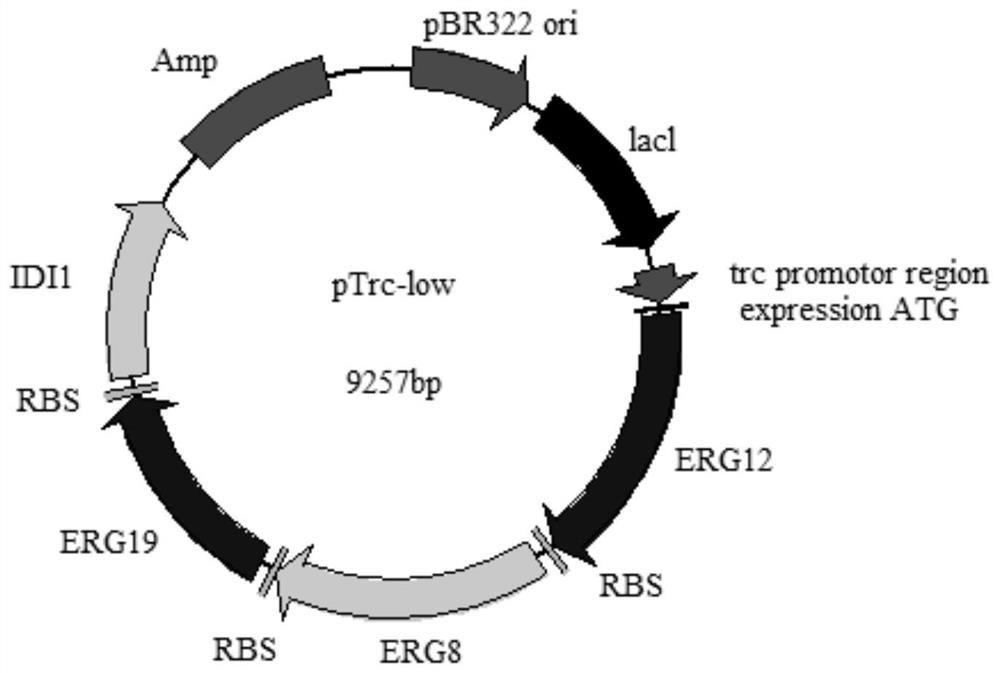
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium with gamma-terpinene synthesis capacity and a constructing method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to engineered escherichia coli, a path for synthesizing MVA from mevalonic acid is reconstructed by heterogeneous expression of hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A synthetase mvaS, hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase mvaE, mevalonate kinase Erg12, phosphomevalonate kinase Erg8, mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase Erg19 and Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase Idi1, meanwhile, geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase GPPS2 and gamma-terpinene TPS2 are led into a bacterium body, and by utilizing the biotransformation capacity of the genetically engineered bacterium, gamma-terpinene can be efficiently produced in an environment-friendly mode. Through fermentation with the genetically engineered bacterium, the output of gamma-terpinene can reach 80 mg / L. The genetically engineered bacterium and the gamma-terpinene synthesis method are suitable for practical industrial production.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
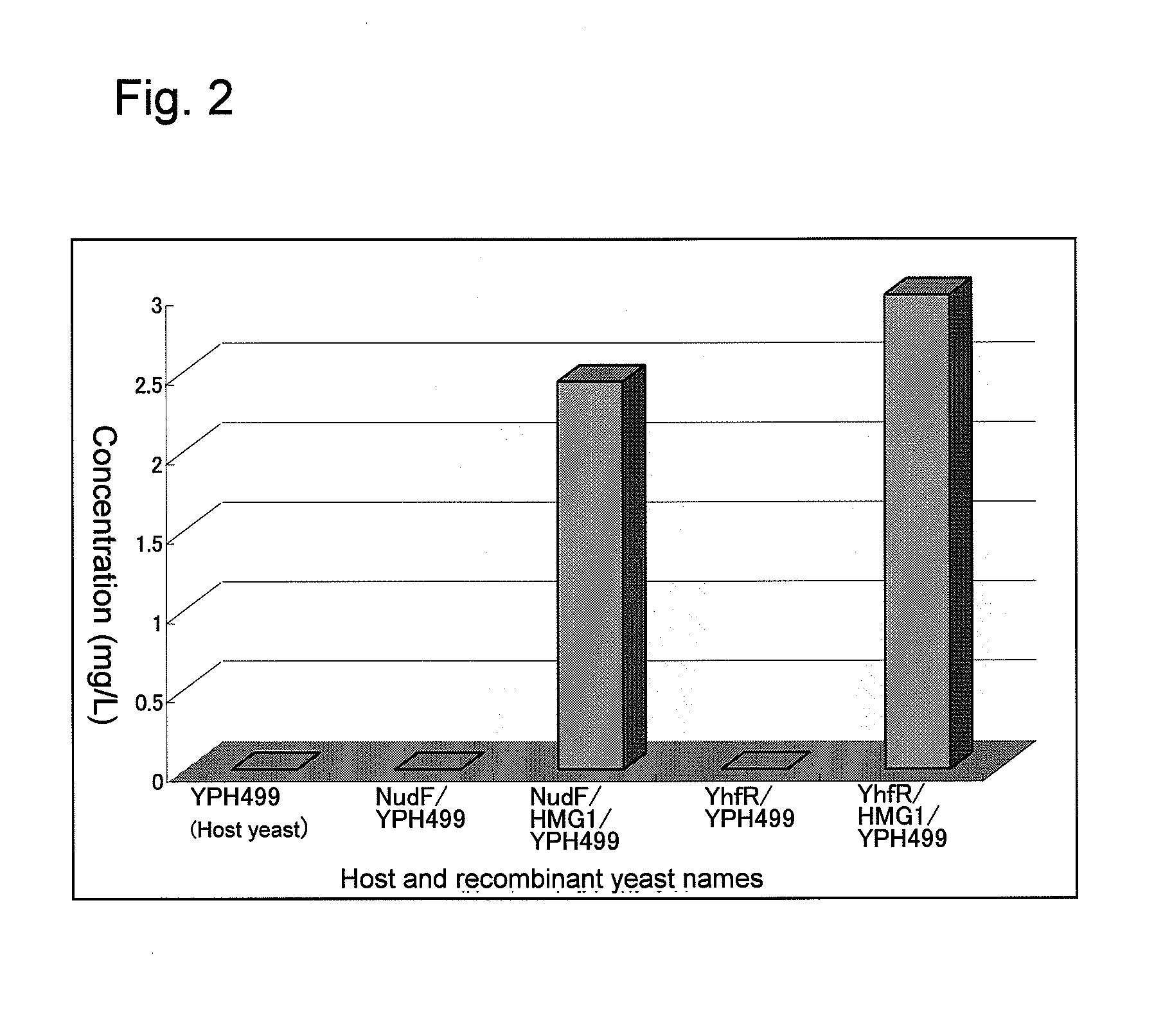
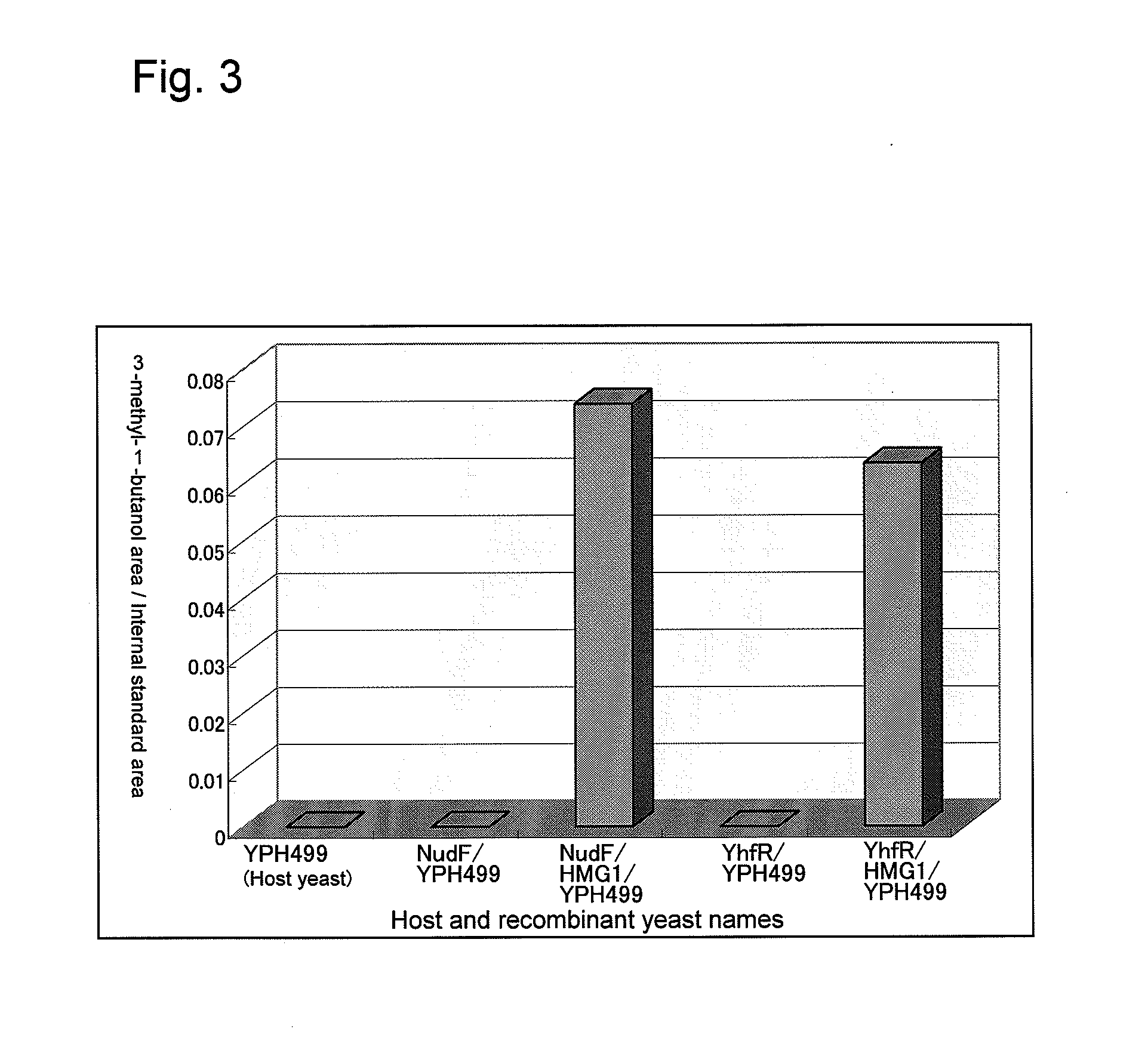
Recombinant yeast and branched alcohol production method using recombinant yeast
This invention provides a recombinant yeast that can produce branched alcohol appropriate for automotive fuel and the like and a branched alcohol production method whereby branched alcohol can be produced at low cost with the use of the recombinant yeast.A recombinant yeast in which a hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase gene has been expressed to a high degree and the ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase gene and / or the yhfR gene are introduced so as to be expressed therein is provided.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Composition and methods used during Anti-hiv treatment
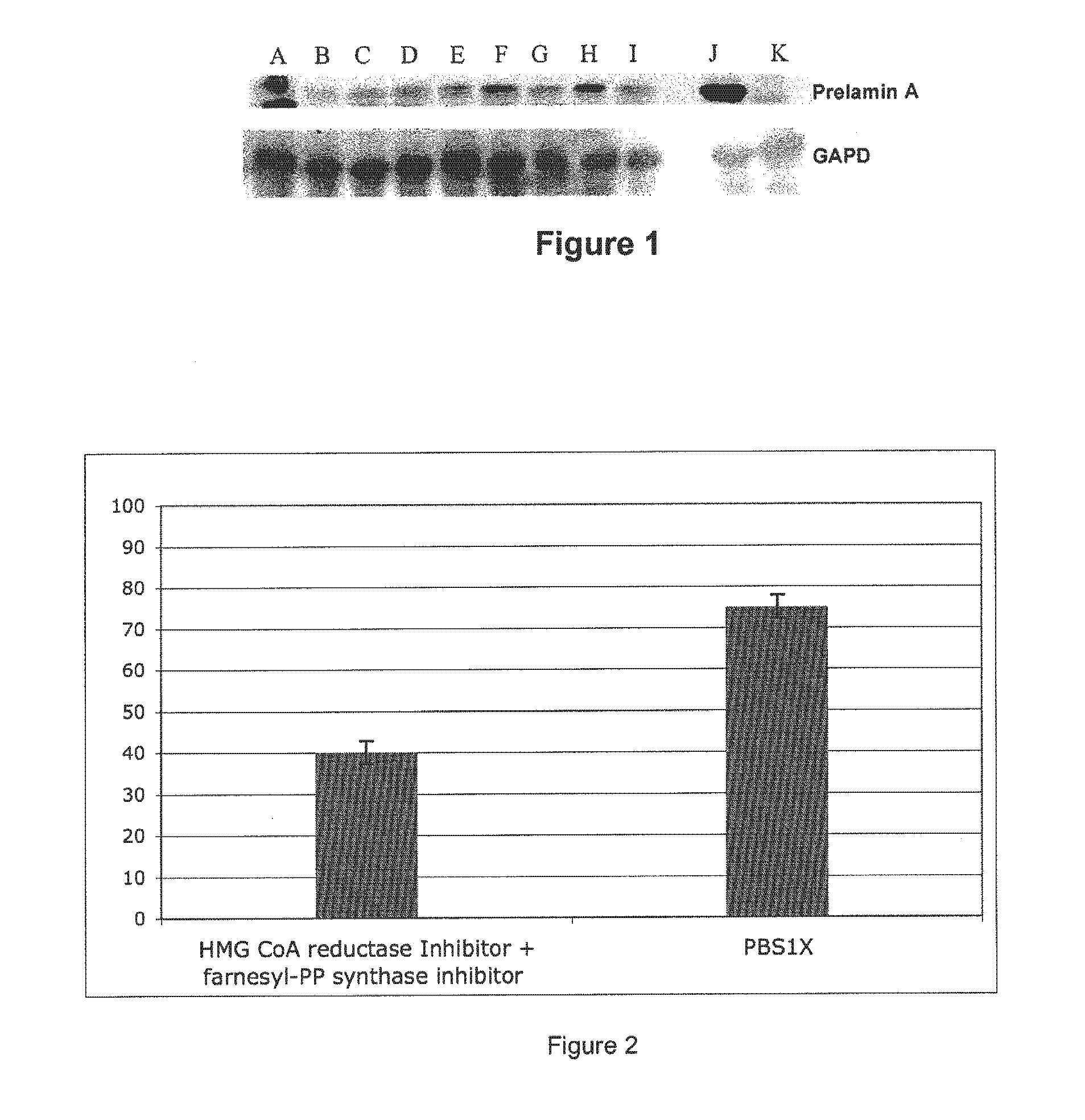
InactiveUS20110046091A1Restoration of the normal phenotypeSymptoms improvedBiocideMetabolism disorderPremature agingSide effect
This invention relates to a composition comprising an anti-HIV treatment and a treatment for side effects of said anti-HIV treatment in an HIV-infected patient. This invention is, for example, very useful in the treatment of side effects caused by certain anti-HIV treatments, for example premature aging and lipodystrophy, which can be caused by protease inhibitors or reverse transcriptase inhibitors. The composition of this invention includes at least one hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor, at least one farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitor, and at least one anti-HIV agent. One of the processes for treating an HIV-infected patient includes, in any order, the following steps: (i) administration of a mixture including at least one hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor and at least one farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitor and (ii) administration of an anti-HIV agent, in which the administrations are concomitant, successive or alternative.
Owner:UNIV DAIX MARSEILLE
Cosmetic and/or dermatological composition
InactiveUS20110165092A1Effective treatmentRestoration of the normal phenotypeBiocideCosmetic preparationsAgeingSubject matter
The subject matter of the invention is a cosmetic and / or dermatological composition for use in the treatment of skin and / or hair disorders. More particularly, the invention relates to a cosmetic and / or dermatological composition comprising an inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, an inhibitor of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, or an inhibitor of one of the physiologically acceptable salts thereof and a cosmetic and / or dermatological product. The present invention finds, for example, a very advantageous use in the treatment of the effects of early ageing, in particular in terms of the skin and the hair system.
Owner:UNIV DE PROVENCE D AIX MARSEILLE I
Method of reducing the risk of adverse cardiovascular (CV) events associated with the administration of pharmaceutical agents which favor CV events
Owner:HELLSTROM HAROLD RICHARD
Pharmaceutical preparation for treating cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS20110052683A1Maximize the effect of treatmentImprovement of side effectsBiocideGranular deliverySide effectMyopathy
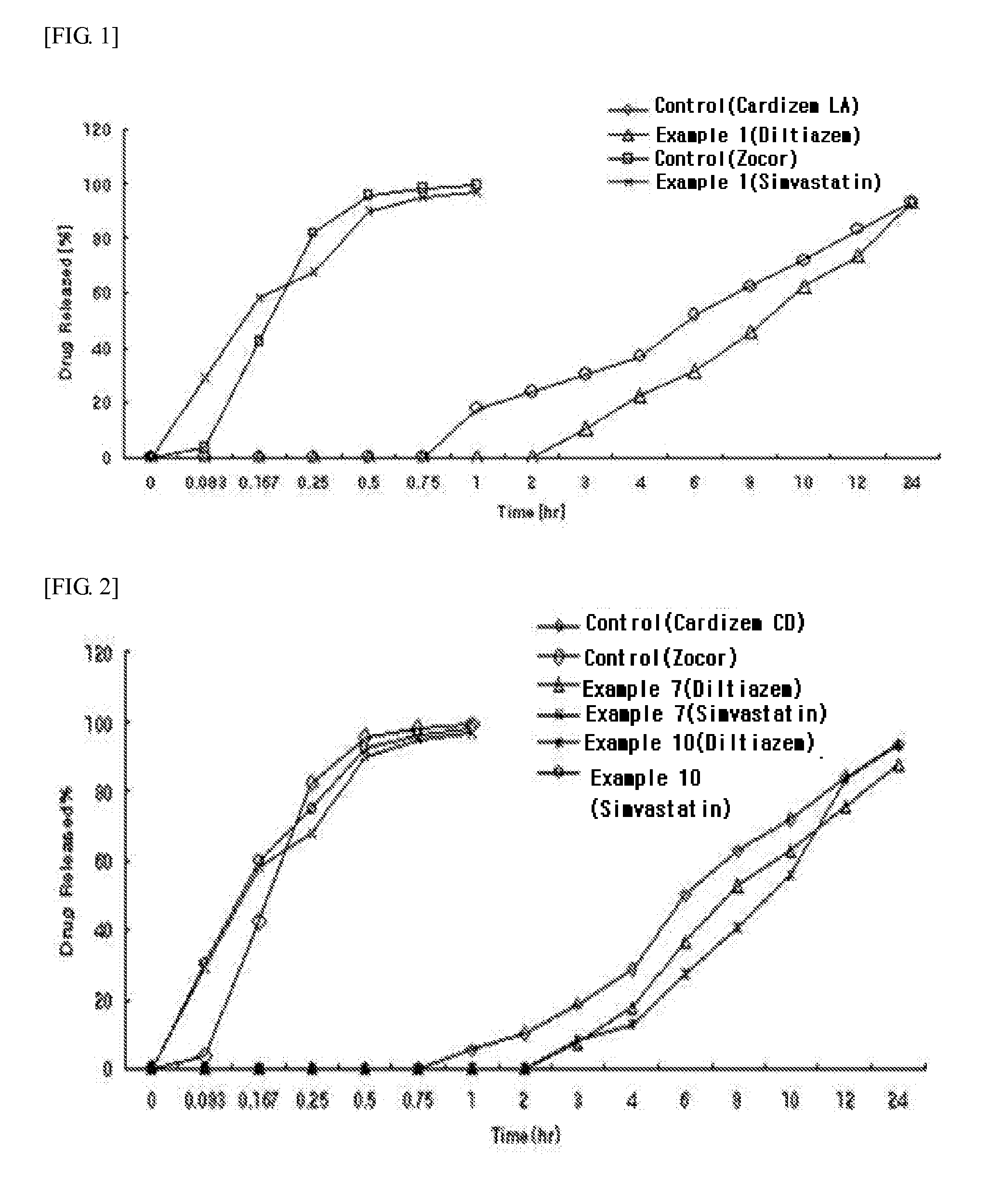
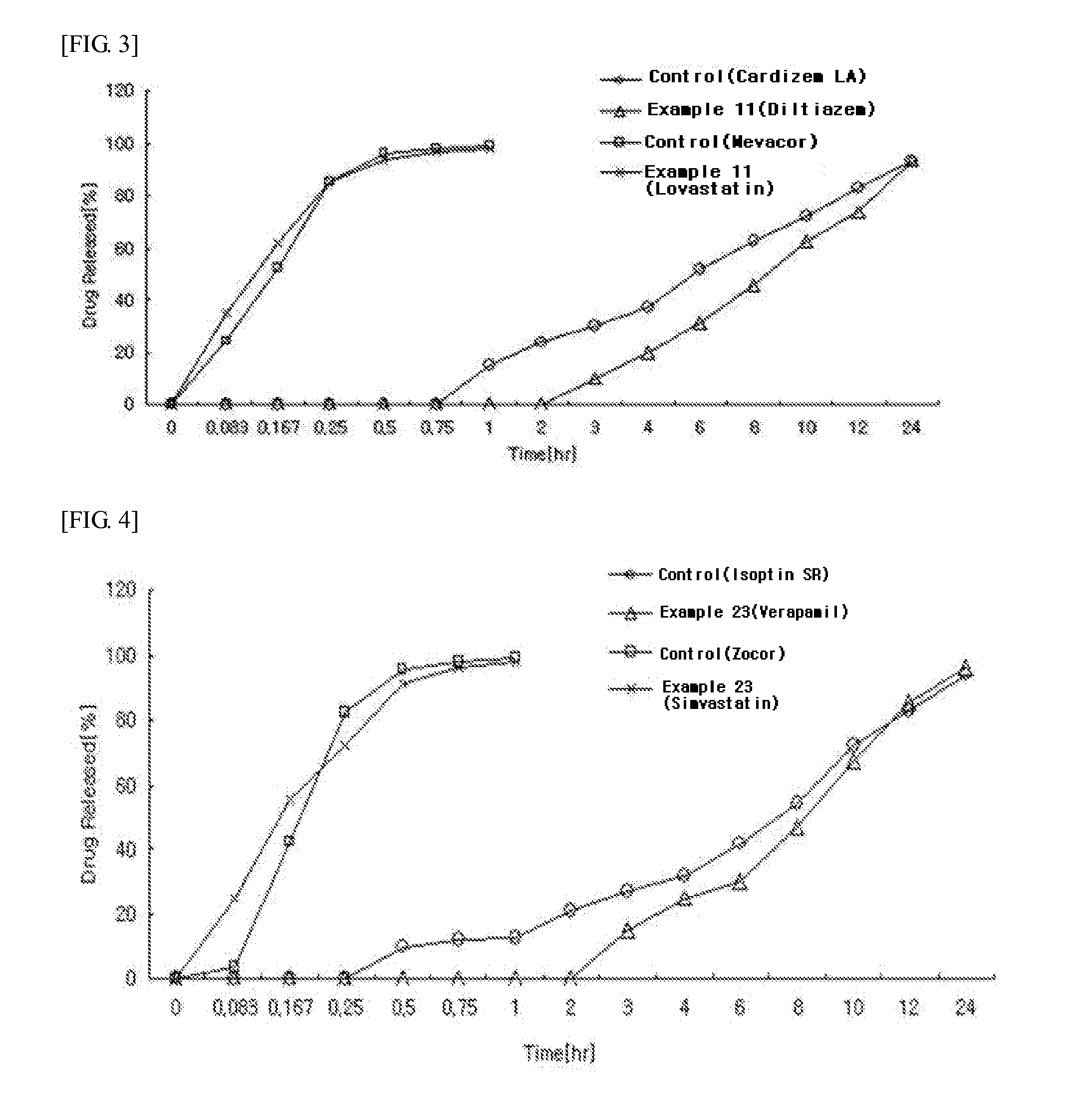
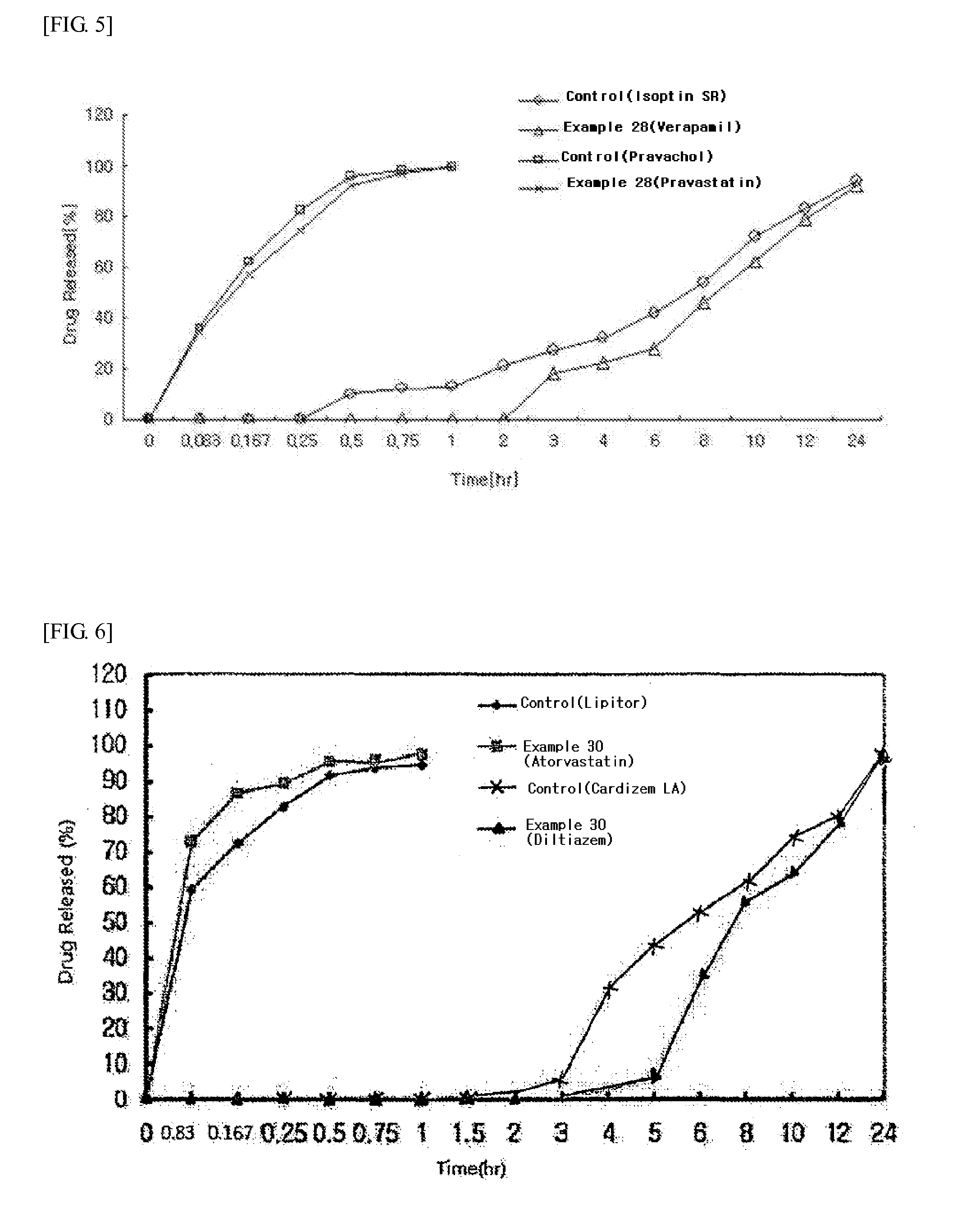
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical preparation comprising a prior-release compartment containing a hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor as a pharmacologically active ingredient, and a delayed-release compartment containing a non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker as a pharmacologically active ingredient. The preparation of the present invention provides synergistic effects through combined administration of the non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker and the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, and induces the time-dependent absorption, metabolism and action mechanism of individual drugs through the controlled release thereof to avoid competitive antagonism between drugs, thus maximizing the effects of each pharmacologically active ingredient while minimizing side effects, for example, the risk of myopathy, and substantially increasing the compliance of patients by taking one tablet once a day.
Owner:HANALL PHARMA CO LTD
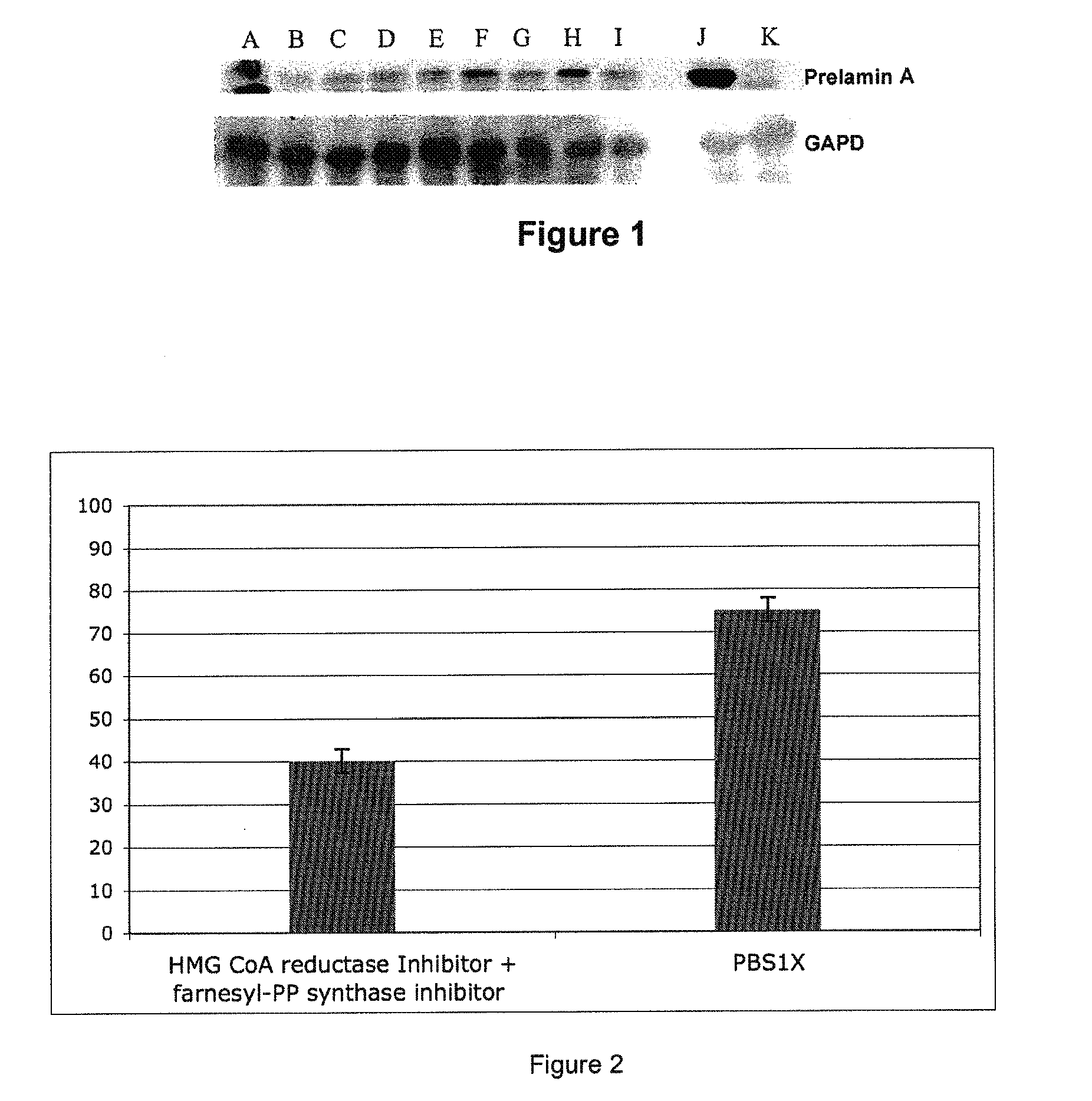
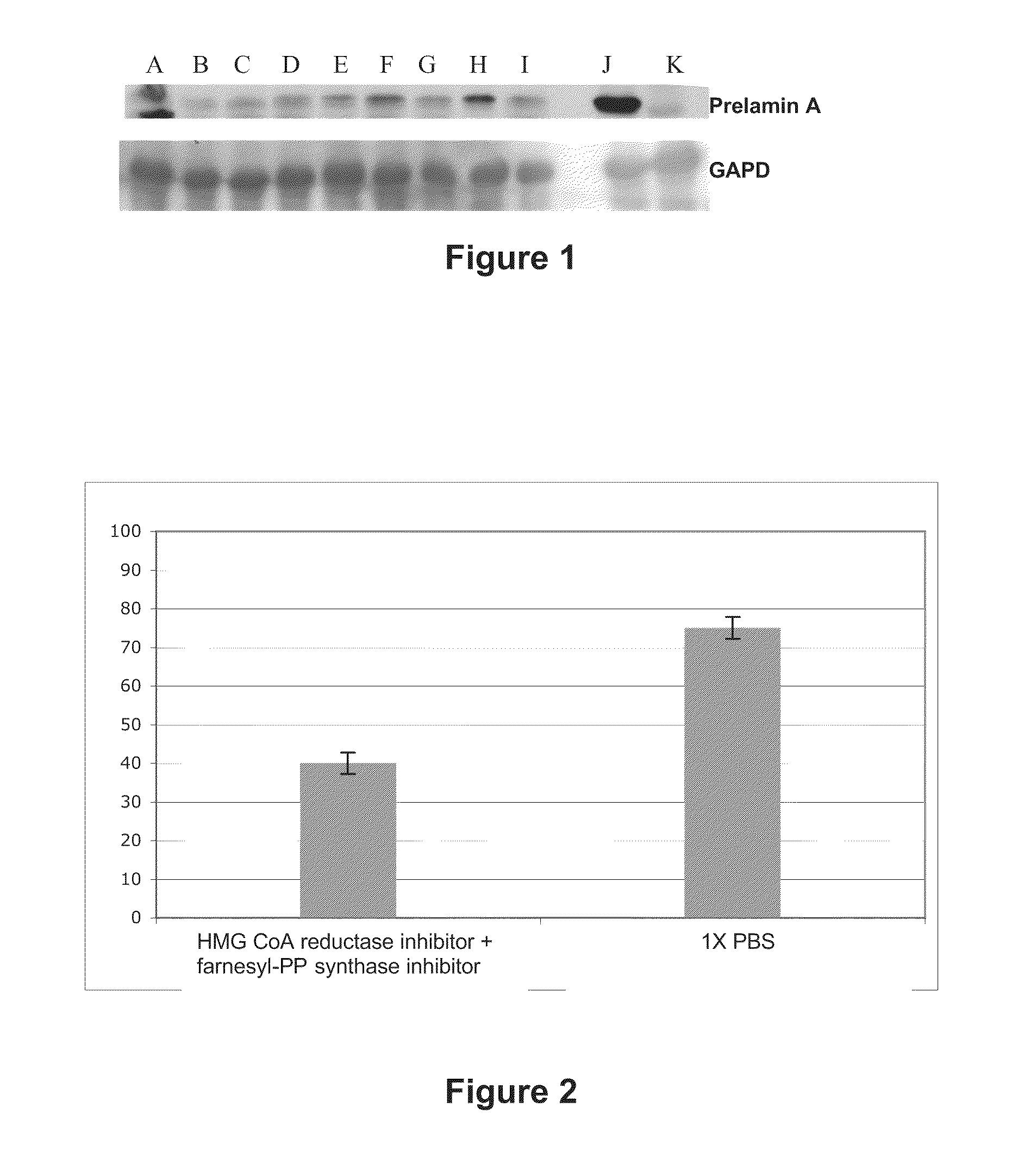
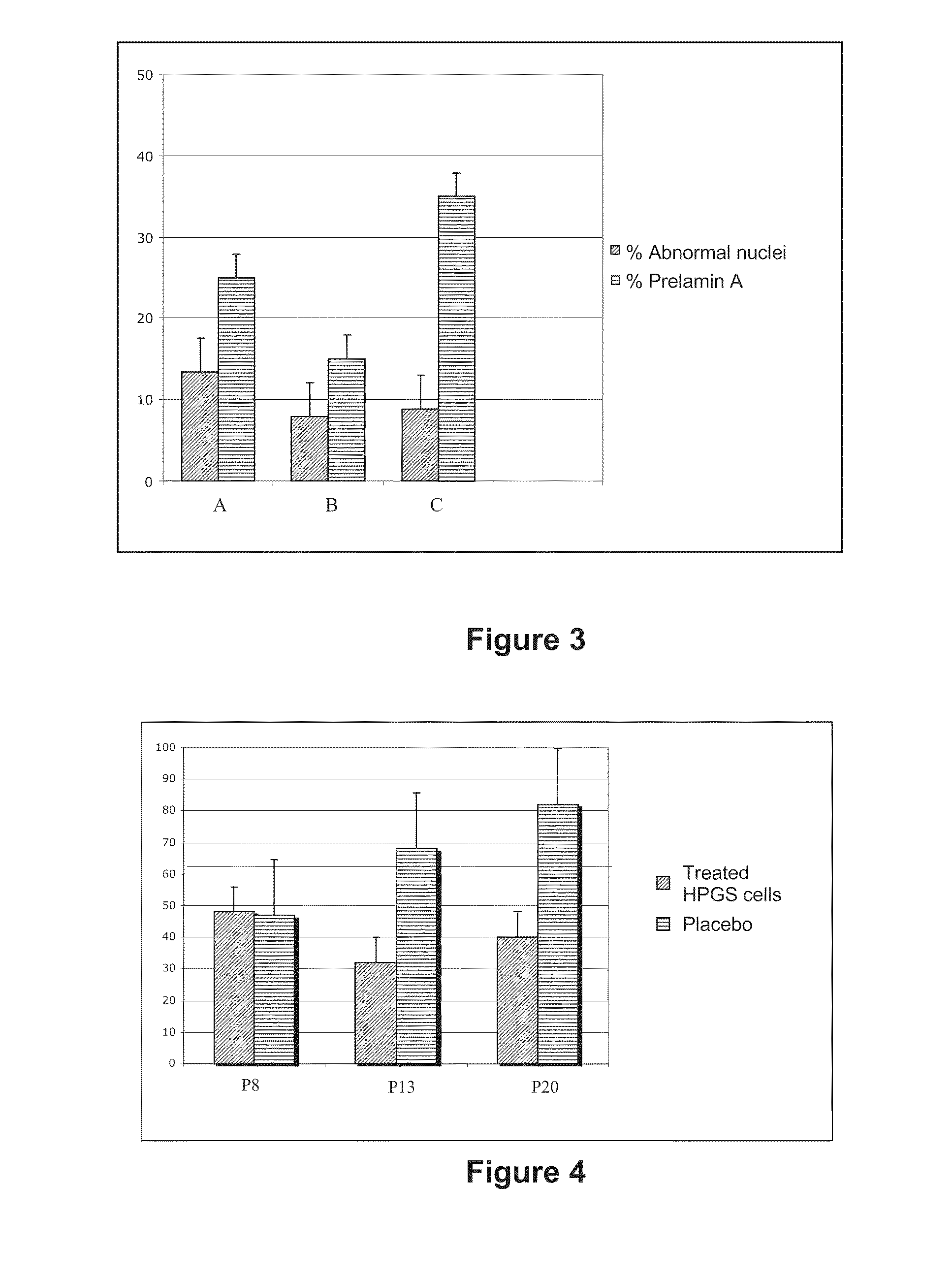
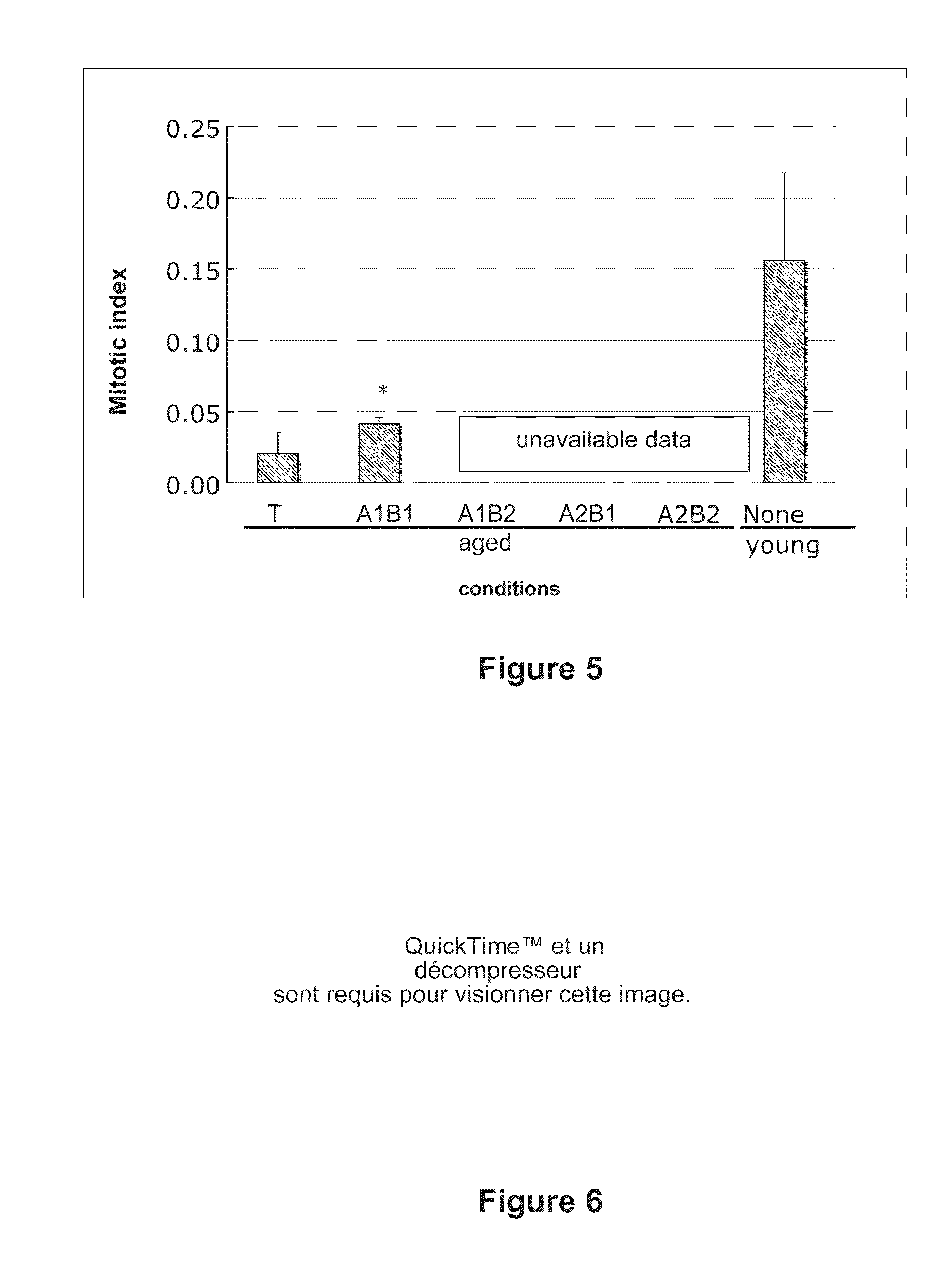
HMG-CoA reductase and farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitors for the treatment of conditions related to prenylated proteins in cells
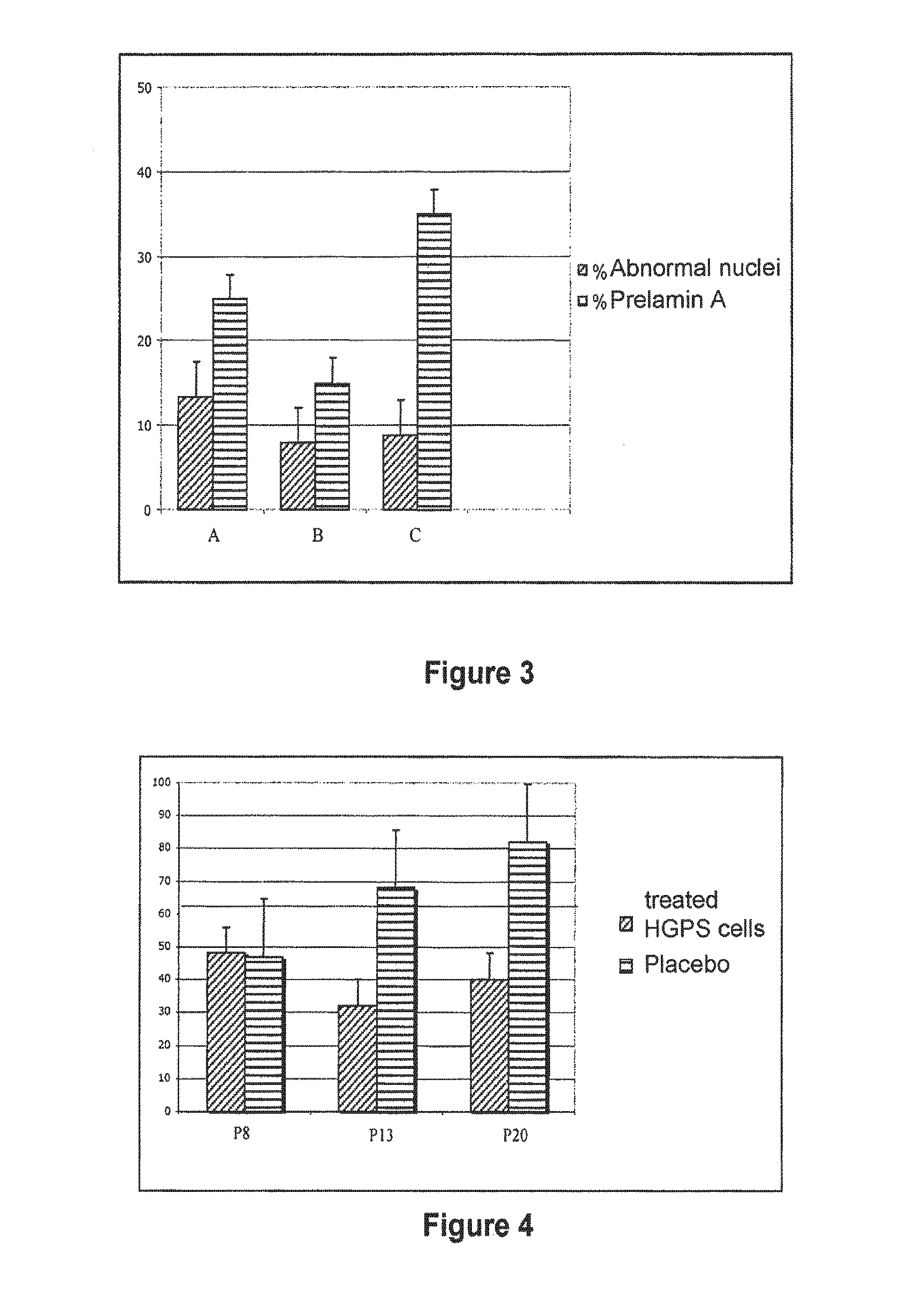
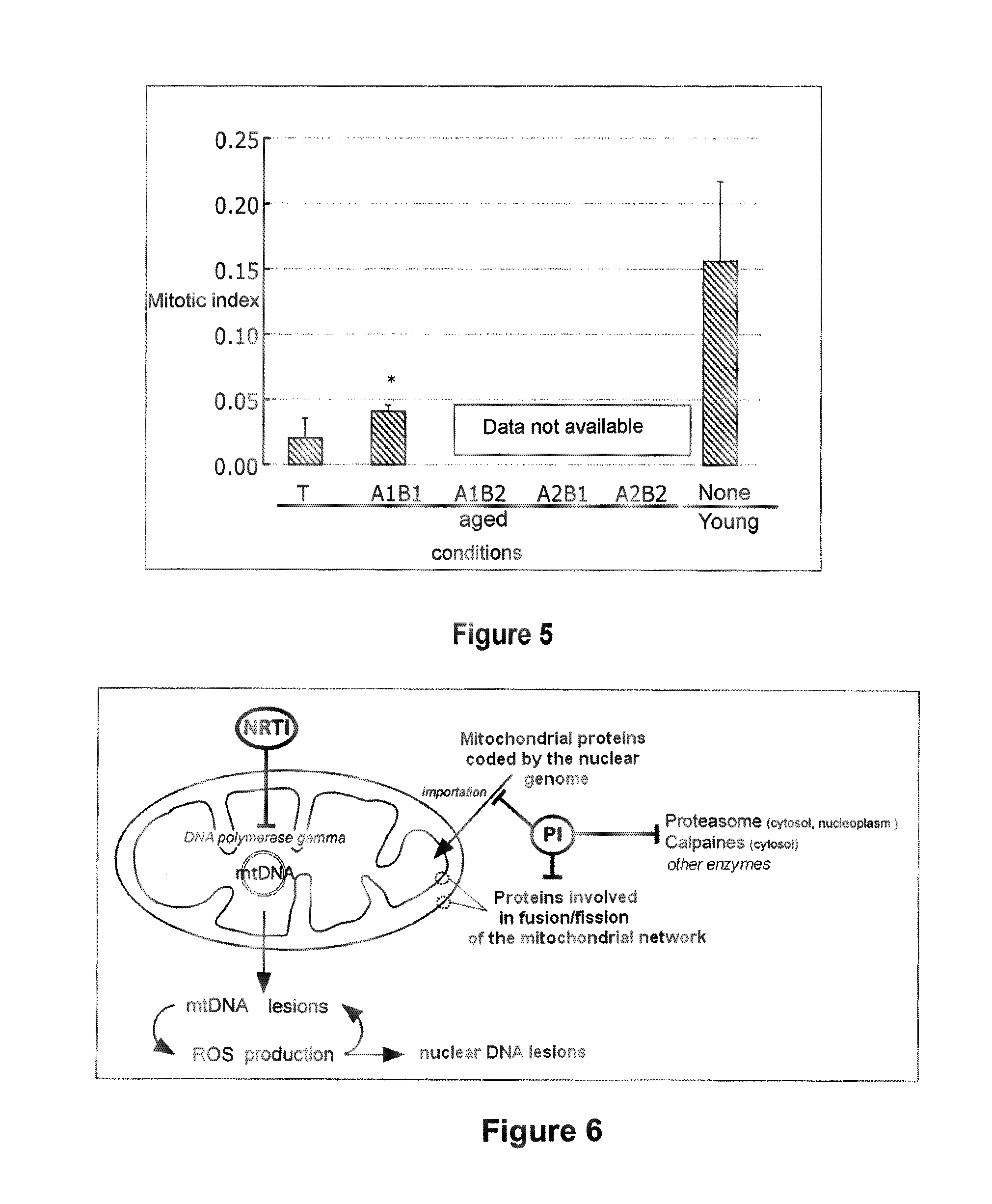
InactiveUS8518914B2Restoration of the normal phenotypeGood effectCosmetic preparationsBiocidePrenylationPhysiology
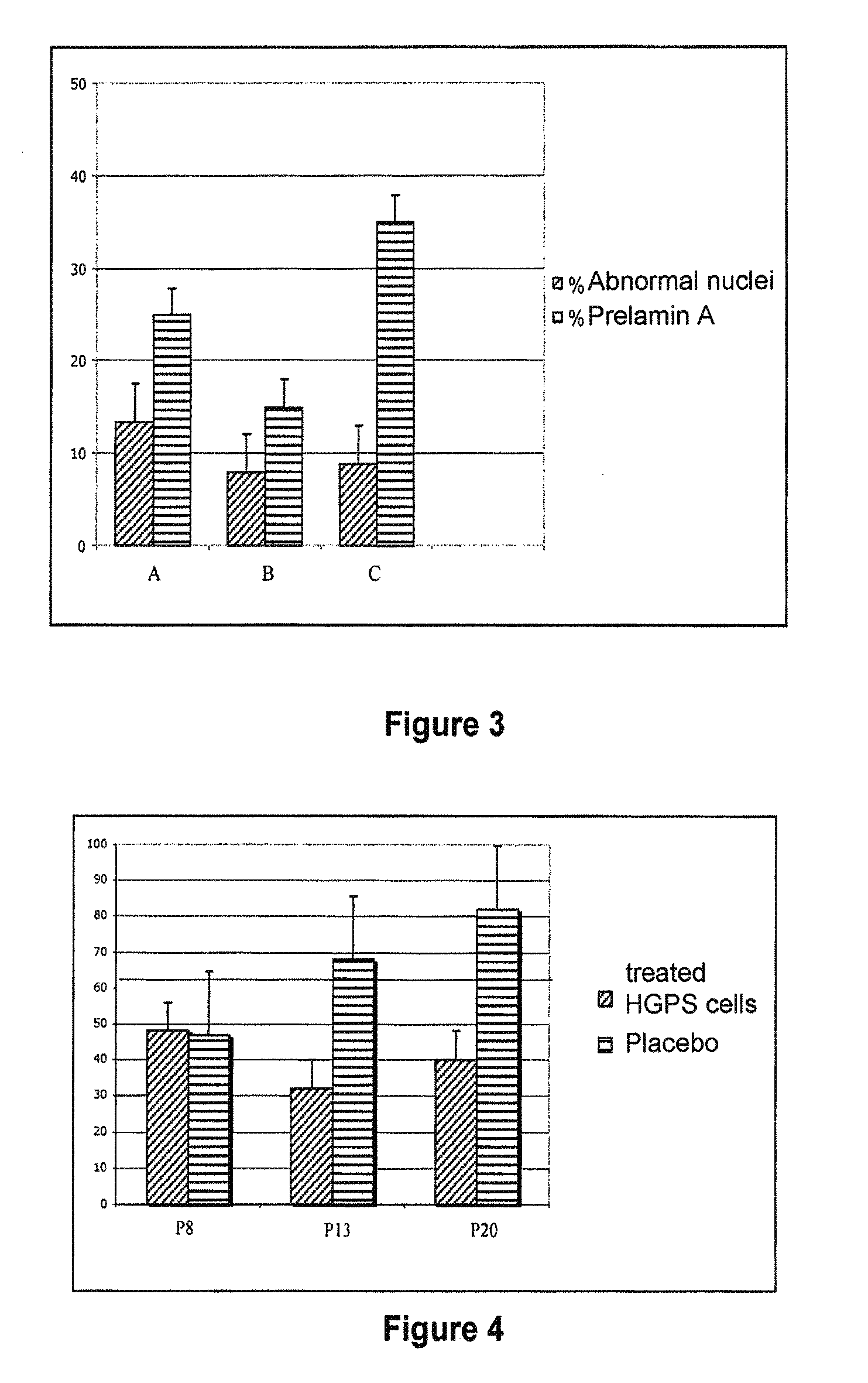
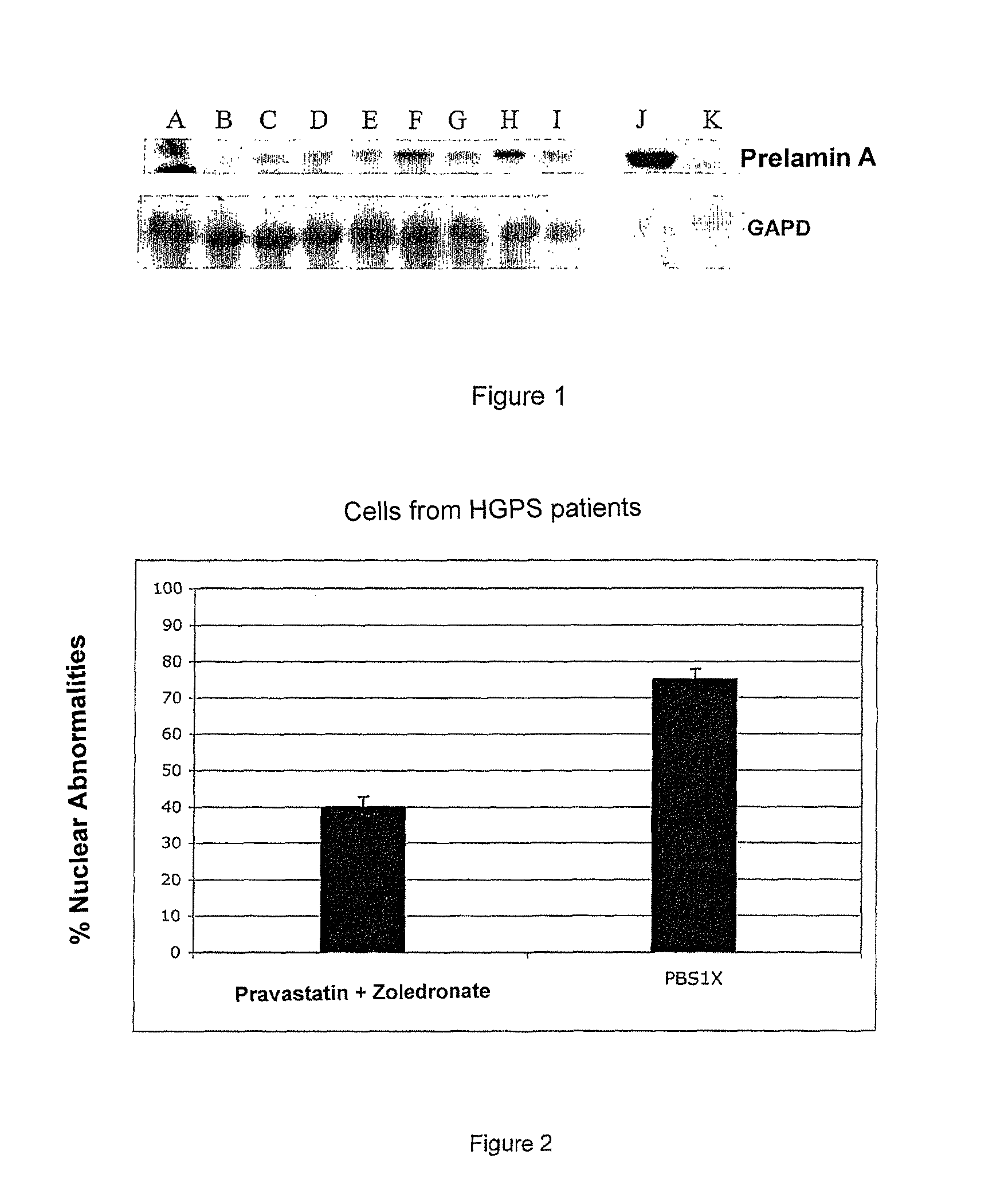
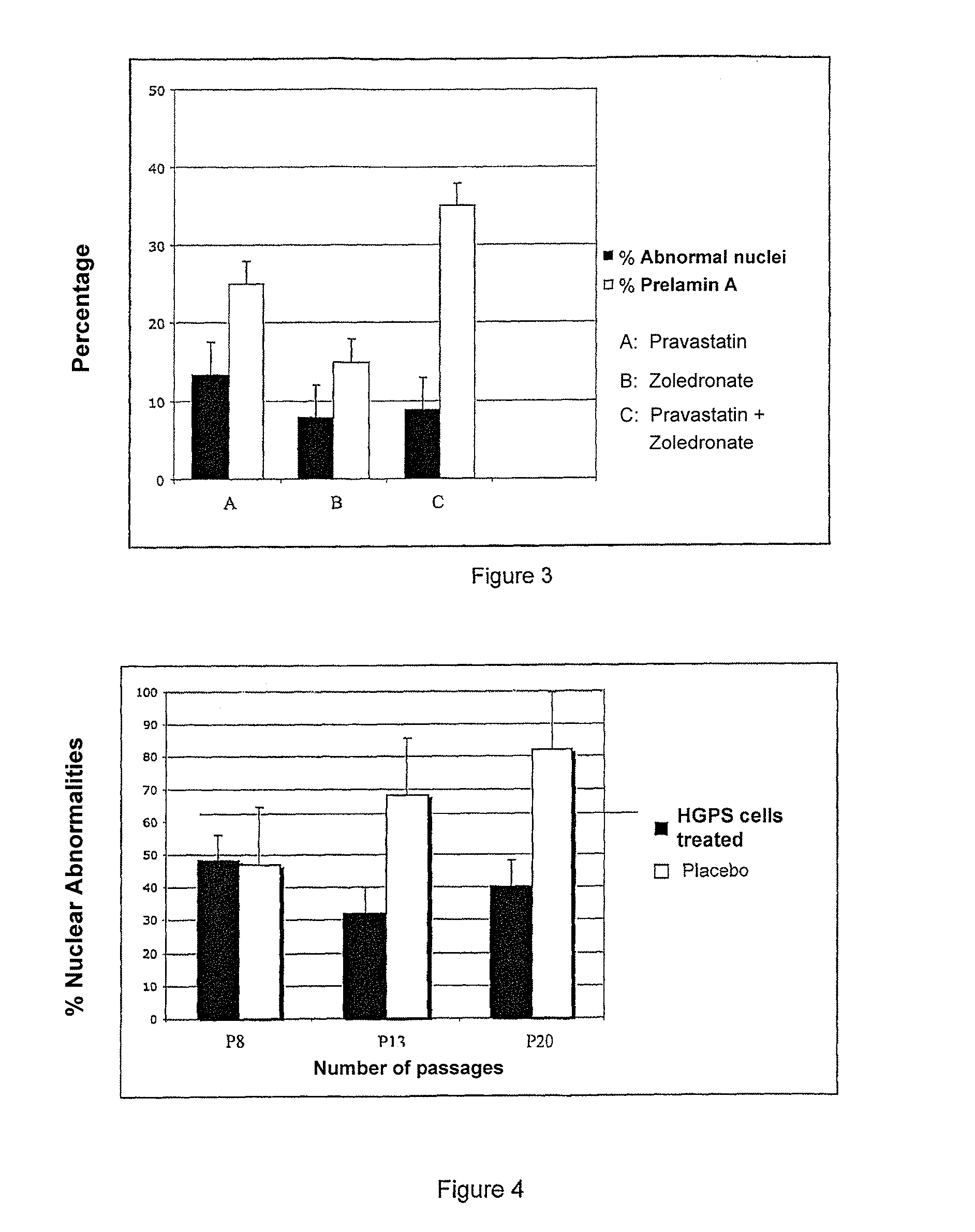
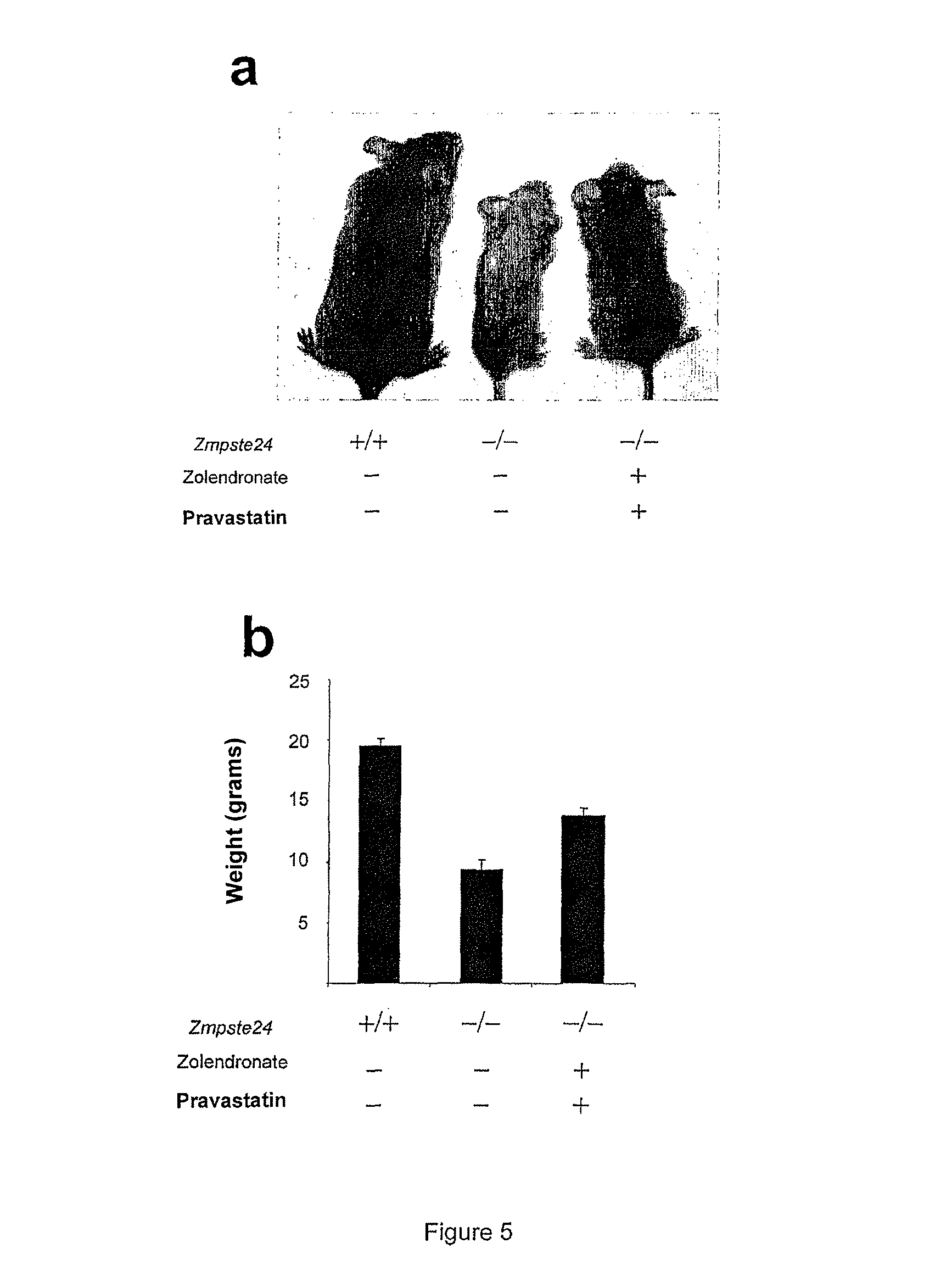
The invention relates to the use of a hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor and of a farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitor, or of one of their associated physiologically acceptable salts, in the preparation of a composition, particularly a pharmaceutical composition, for use in the treatment of human or animal, pathological or nonpathological situations related to the accumulation and / or the persistence of prenylated proteins in cells, such as during progeria (Hutchinson-Gilford syndrome), restrictive dermopathy or physiological aging.
Owner:ASSOC FRE CONTRE LES MYOPATHIES +3
Escherichia coli expression strain for high yield of geraniol glucoside and application thereof
ActiveCN110317765AEasy to synthesizeEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGeranyl pyrophosphate
The invention provides an Escherichia coli expression strain for high yield of geraniol glucoside, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The Escherichia coli expression strain jointly expresses an acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase gene, a methyl glutaryl coenzyme A synthetase gene, a HMG-CoA reductase gene, a mevalonate kinase gene, phosphomevalonate kinase gene, a pyrophosphate mevalonate decarboxylase gene, an isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase gene, a geranyl pyrophosphate GPP synthetase ispA*, a geraniol synthetase gene, a geranyl pyrophosphate GPP synthetase ERG20* and a glycosyltransferase gene. The yield of geraniol glucoside produced from the Escherichia coli expression strain is high, reliable in mass and good in application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Modified yeast strain and a method for producing squalene using the same
InactiveUS20120322129A1High priceImprove efficiencyFungiOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyHydroxy methyl glutaryl
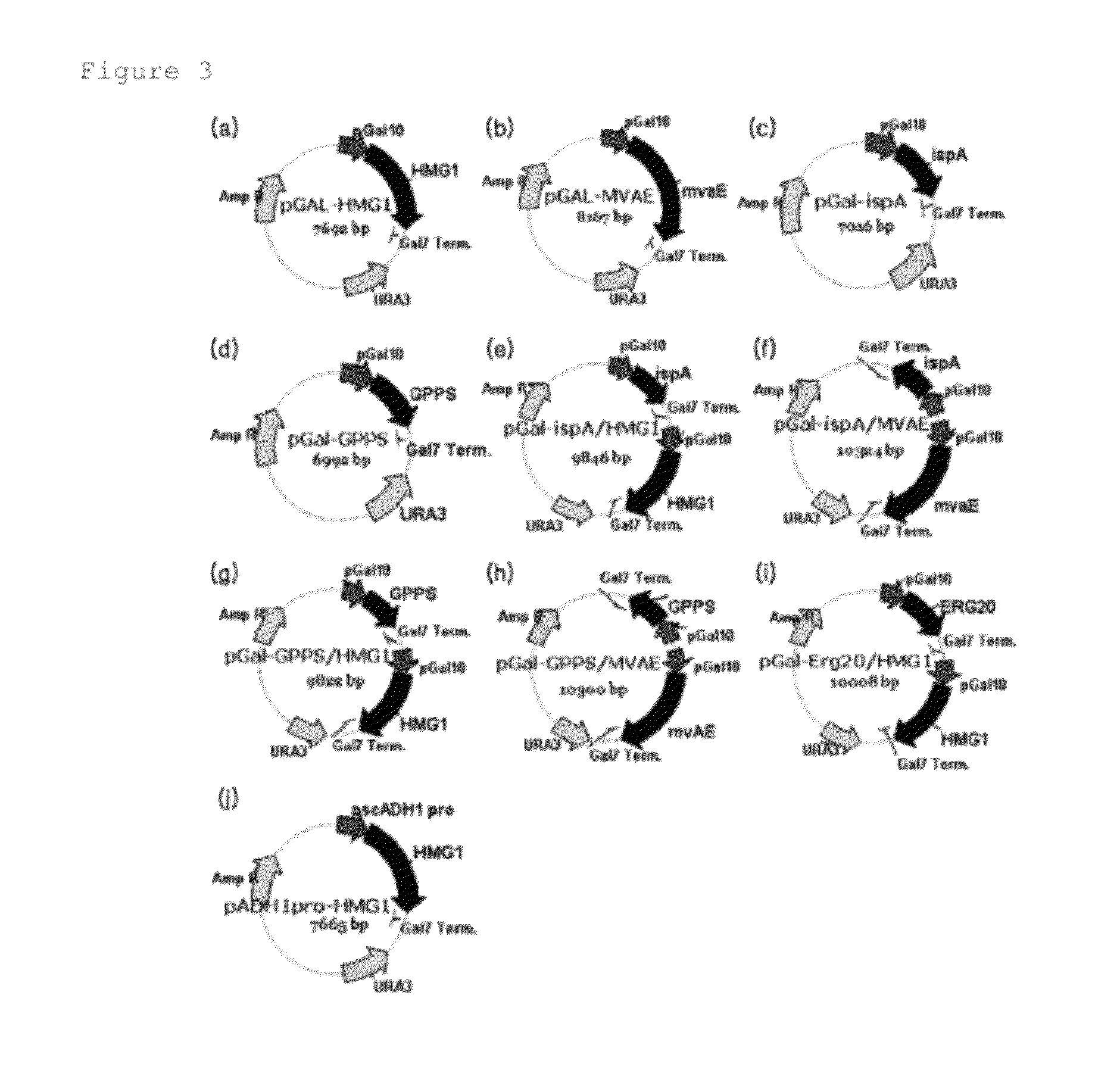
The present invention relates to a modified yeast strain which is prepared by introducing a vector that expresses HMG-CoA reductase (hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase) and farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, and a method for producing squalene using the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y2805 modified yeast strain that is transformed with a vector including the HMG1 gene, and ispA or Erg20 gene, and a method for producing squalene with high efficiency by culturing the modified yeast strain.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Polymorphs of a 1-pyrrole derivative, intermediate for the preparation of atorvastatin
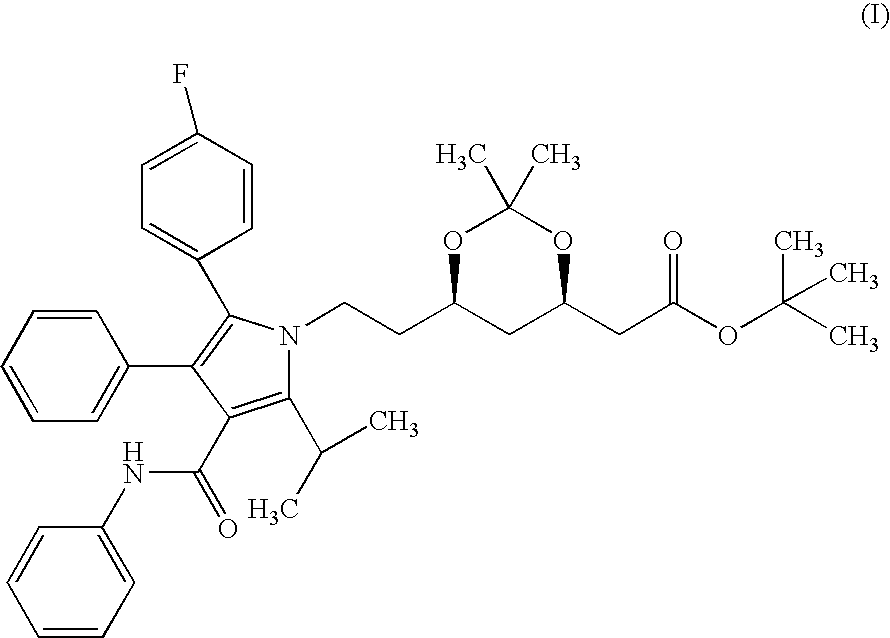
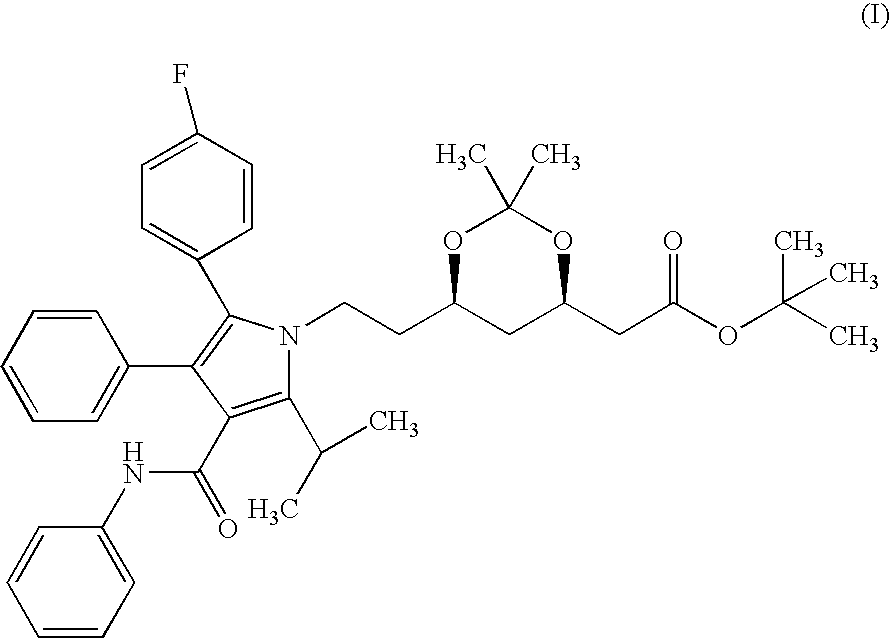
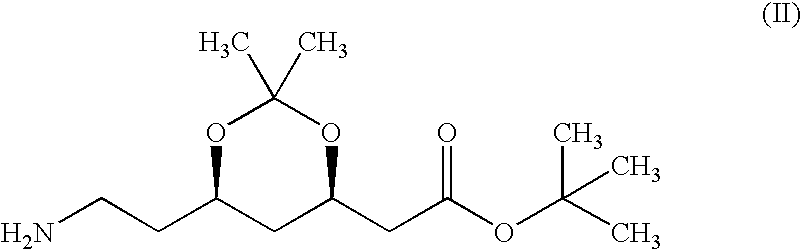
The invention relates to new crystalline forms I and II of (4R-cis)-6-[2-[3-phenyl-4-(phenyl-carbamoyl)-2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-5-(1-methyl-ethyl)-pyrrol-1-yl]-ethyl]-2,2-dimethyl-[1,3]dioxane-4-yl-acetic acid-tertiary butyl ester of the Formula (I) and a process for the preparation thereof. The new polymorphs of the present invention are useful pharmaceutical intermediates which can be used in the preparation of the hydroxymethyl-glutaryl coenzyme (HMG-COA) reducing enzyme inhibitor having the INN (International Non-proprietory Name) atorvastatin.
Owner:EGIS GYOGYSZERGYAR NYILVANOSAN MUKODO RESZVENY TARSASAG
Medicament composition for treating diabetes and application of medicament composition
ActiveCN102526739AGood effectSignificant progressOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTHydroxymethyl
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to a medicament composition for treating diabetes and application of the medicament composition, in particular to application of the medicament composition in treatment of diabetic nephropathy and diabetic merged hyperlipidemia. For better treating the diabetes and complications thereof, the invention provides the medicament composition. The medicament composition contains hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, glycosaminoglycan and insulin sensitizer serving as active ingredients, and particularly contains low molecular weight heparin, pioglitazone and rosuvastatin.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Gliclazide sustained release tablet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109758429AGood hypoglycemic effectGood lipid-lowering effectMetabolism disorderSulfonylurea active ingredientsVitamin CAdhesive
The invention discloses a gliclazide sustained release tablet and a preparation method thereof. The tablet is composed of a sustained release layer and an auxiliary layer with the weight ratio of 1-2:0.6-1.2. The sustained release layer comprises, by weight, 88-132 parts of gliclazide, 220-330 parts of skeleton material, 120-180 parts of sustained release layer filler, 4-6 parts of sustained release layer adhesive and 3-4.5 parts of slow release layer lubricant. The auxiliary layer comprises, by weight, 28-42 parts of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, 27-40.5 parts of montmorillonite, 20-30 parts of fruit and vegetable powder, 24-36 parts of auxiliary layer adhesive, 3.5-5.25 parts of vitamin C, 1.6-2.4 parts of deionized water and 2-3 parts of auxiliary layer lubricant. The gliclazide is combined with a drug for lowering blood lipids, a drug for treating diarrhea and a nutrient substance used by diabetic patients to make the tablet to significantly increase the hypoglycemic effect of the gliclazide, and adverse reactions such as hypoglycemia and diarrhea are not easy to cause.
Owner:ANHUI LIANYI PHARMA
Composition and methods used during Anti-hiv treatment
InactiveUS20150342970A1Restoration of the normal phenotypeSymptoms improvedBiocideMetabolism disorderPremature agingSide effect
This invention relates to a composition comprising an anti-HIV treatment and a treatment for side effects of said anti-HIV treatment in an HIV-infected patient. This invention is, for example, very useful in the treatment of side effects caused by certain anti-HIV treatments, for example premature aging and lipodystrophy, which can be caused by protease inhibitors or reverse transcriptase inhibitors. The composition of this invention includes at least one hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor, at least one farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitor, and at least one anti-HIV agent. One of the processes for treating an HIV-infected patient includes, in any order, the following steps: (i) administration of a mixture including at least one hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor and at least one farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase inhibitor and (ii) administration of an anti-HIV agent, in which the administrations are concomitant, successive or alternative.
Owner:UNIV DAIX MARSEILLE
A kind of isoprene-producing genetically engineered bacteria and its application
ActiveCN104031872BAvoid the influence of own metabolismShort reaction timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses an isoprene-producing genetic engineering bacterium and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The present invention comprises acetyl-CoA acyltransferase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase, terminal alkene-forming fatty acid decarboxylase and oleic acid hydratase. The gene is transformed into the host bacteria to obtain recombinant bacteria, and the recombinant bacteria are used for fermentation to produce isoprene. The method provided by the invention greatly shortens the reaction process of Escherichia coli synthesizing isoprene by using the exogenous MVA pathway, and the isoprene can be synthesized from acetyl-CoA in only 5 steps, avoiding the need for excessive exogenous genes. effects on the cell's own metabolism. At the same time, by optimizing the fermentation conditions, the yield of fermentation product isoprene can reach 39.49 μg / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for adjusting expression of hydroxymethylglutaryl coa reductase using BZIP-type transcription factor, isoprenoid-producing plant into which gene encoded for BZIP-type transcription factor is introduced, and method for manufacturing polyisoprenoid in which said plant is used
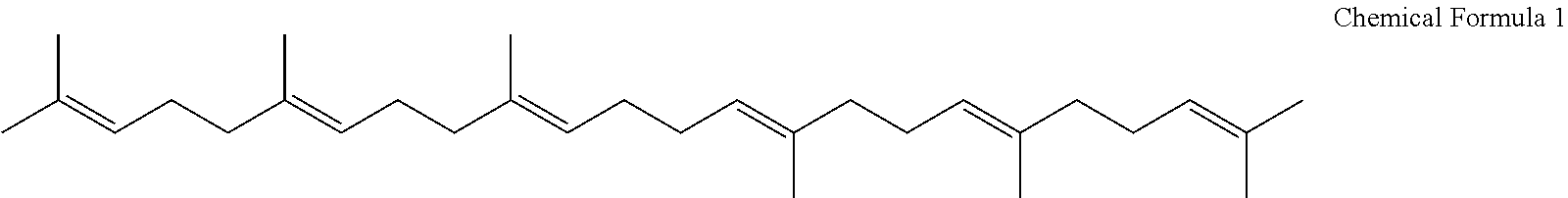
ActiveUS20160251632A1Increase polyisoprenoid productionEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyHydroxy methyl glutaryl
The present invention provides a method enhancing the polyisoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. Also provided are an isoprenoid-producing plant having an overall enhanced pathway of polyisoprenoid biosynthesis, and a method of producing a polyisoprenoid using the isoprenoid-producing plant. The present invention relates to a method of regulating the expression of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase by a bZIP transcription factor.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Cholic acid derivative and application thereof in lowering cholesterol
ActiveCN113563405APromote degradationDecrease increaseMetabolism disorderDigestive systemCholic acidTG - Triglyceride
The invention discloses a cholic acid derivative as shown in a formula (I) and a preparation method thereof, and the target product cholic acid derivative is prepared through reactions such as TBS protection, 4, 4-dimethylation, deprotection, oxidation, Witting reaction, reduction, hydrolysis, acylation and deprotection. The invention further provides an application of the cholic acid derivative in preparation of drugs for preventing and / or treating hypercholesteremia and hypertriglyceridemia, resisting atherosclerosis and resisting non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, the cholic acid derivative can effectively promote degradation of hydroxymethyl glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, HMGCR), and reduce HMGCR protein increase caused by statins, so that the endogenous cholesterol level is reduced, a beneficial reference is provided for research and development of new cholesterol-reducing medicines, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Modified yeast strain and a method for producing squalene using the same
InactiveUS8679804B2High priceImprove efficiencyFungiOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyHydroxy methyl glutaryl
The present invention relates to a modified yeast strain which is prepared by introducing a vector that expresses HMG-CoA reductase (hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase) and farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, and a method for producing squalene using the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y2805 modified yeast strain that is transformed with a vector including the HMG1 gene, and ispA or Erg20 gene, and a method for producing squalene with high efficiency by culturing the modified yeast strain.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Cholesterol metabolism regulating and controlling medicament sifting motion system and method with hydroxymethyl glutaryl cozymase A reductase as target point
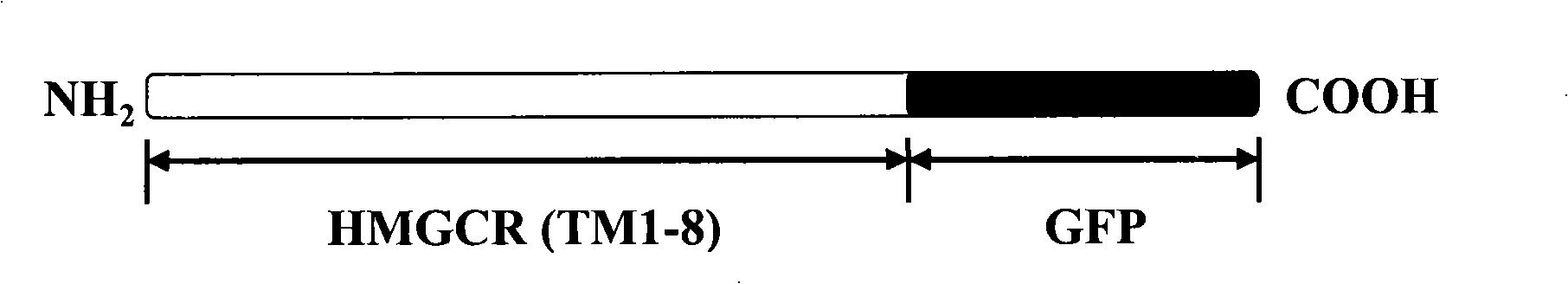
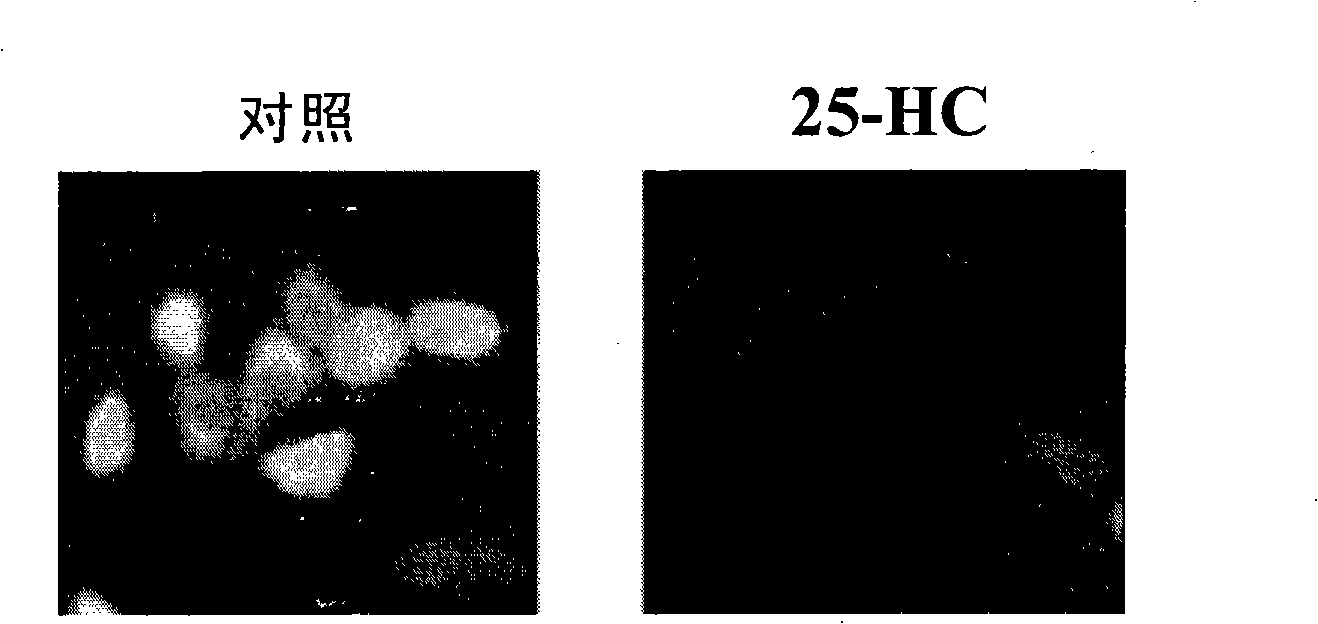
ActiveCN101343326AReserved functionRetain activityBiological testingHybrid peptidesHydroxy methyl glutarylCholesterol metabolism
The invention discloses a screening system which takes HMG-CoA reductase A as a target spot to regulate cholesterol drug. The screening system adopts a cell system which is formed through connecting N-terminal protein fragment of HMG-CoA reductase A with a detectable signal element and guiding the N-terminal protein fragment into cells, to ensure cells to express fusion protein. The screening system can be used for screening substances which takes HMG-CoA reductase A as the target spot for regulating cholesterin.
Owner:CHOLESGEN (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Designer cells for enantioselective reduction of ketones and use thereof in efficient production of enantioenriched alcohols
ActiveUS9790524B2Improve conversion rateImprove efficiencyBacteriaOxidoreductasesHydroxy methyl glutarylCarbonyl reductase activity
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for adjusting expression of hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA reductase using bZIP-type transcription factor, isoprenoid-producing plant into which gene encoded for bZIP-type transcription factor is introduced, and method for manufacturing polyisoprenoid in which said plant is used
ActiveUS10087424B2Easy accessEasy to operateOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyHydroxy methyl glutaryl
The present invention provides a method enhancing the polyisoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. Also provided are an isoprenoid-producing plant having an overall enhanced pathway of polyisoprenoid biosynthesis, and a method of producing a polyisoprenoid using the isoprenoid-producing plant. The present invention relates to a method of regulating the expression of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase by a bZIP transcription factor.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
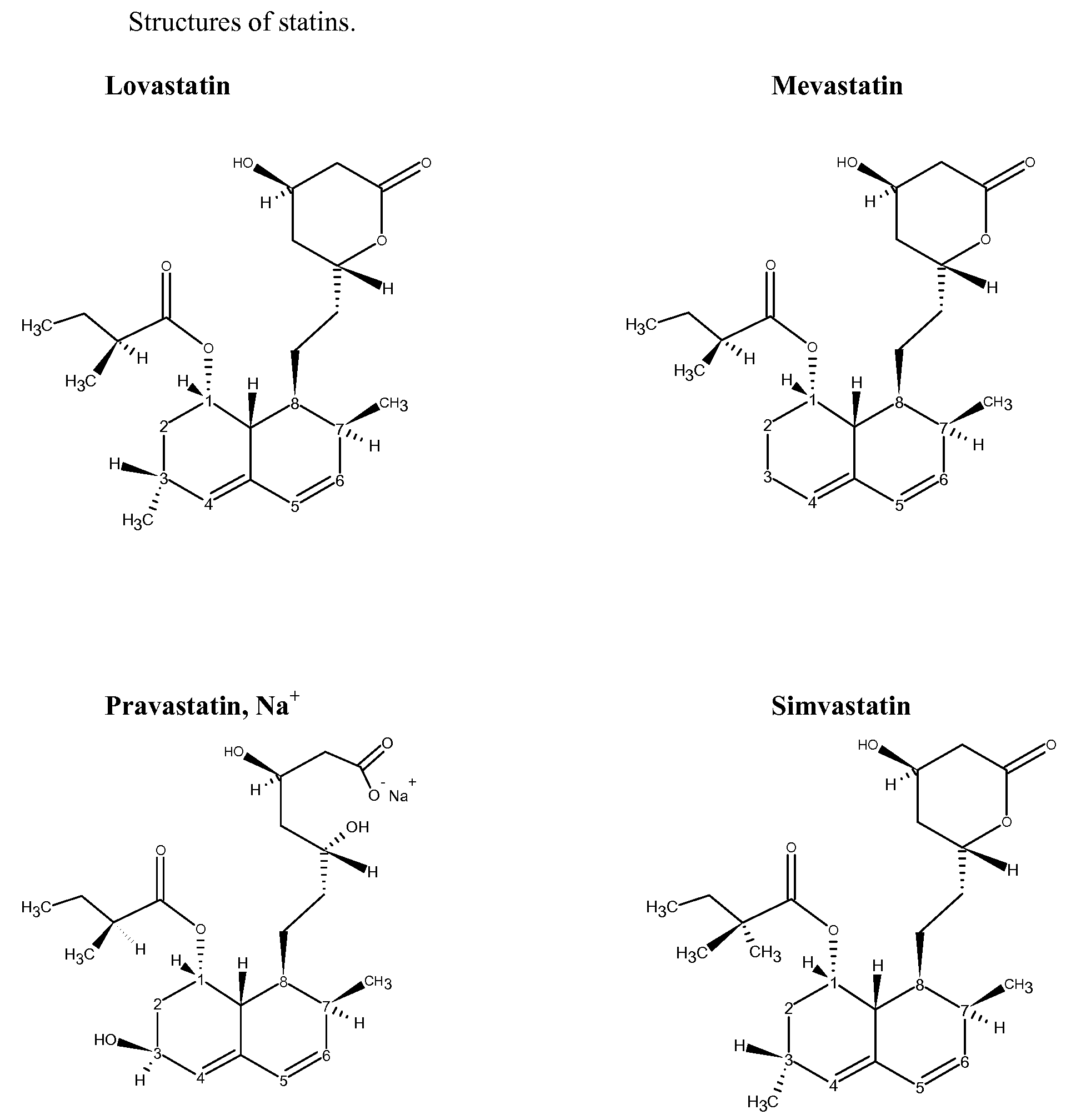
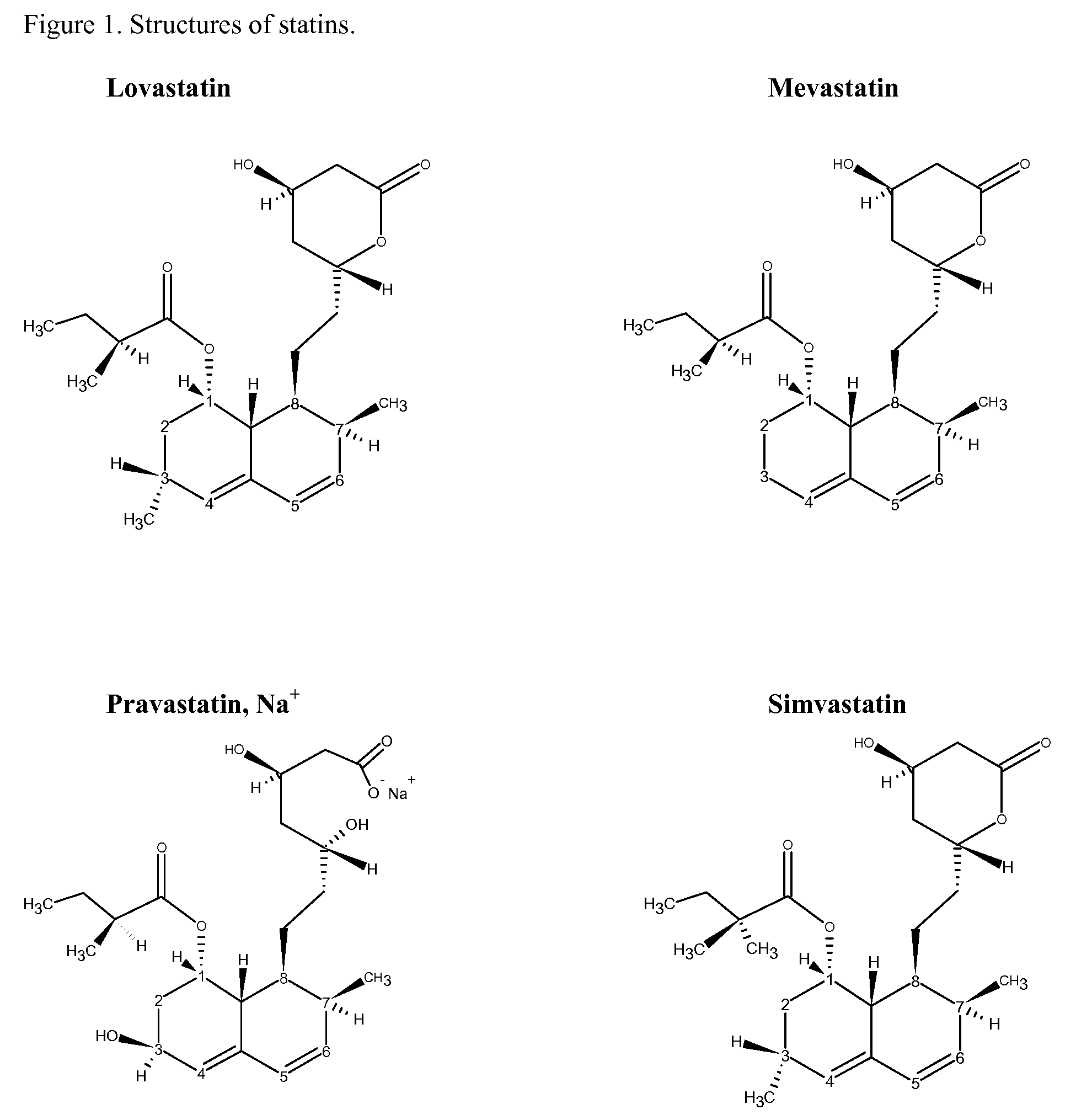
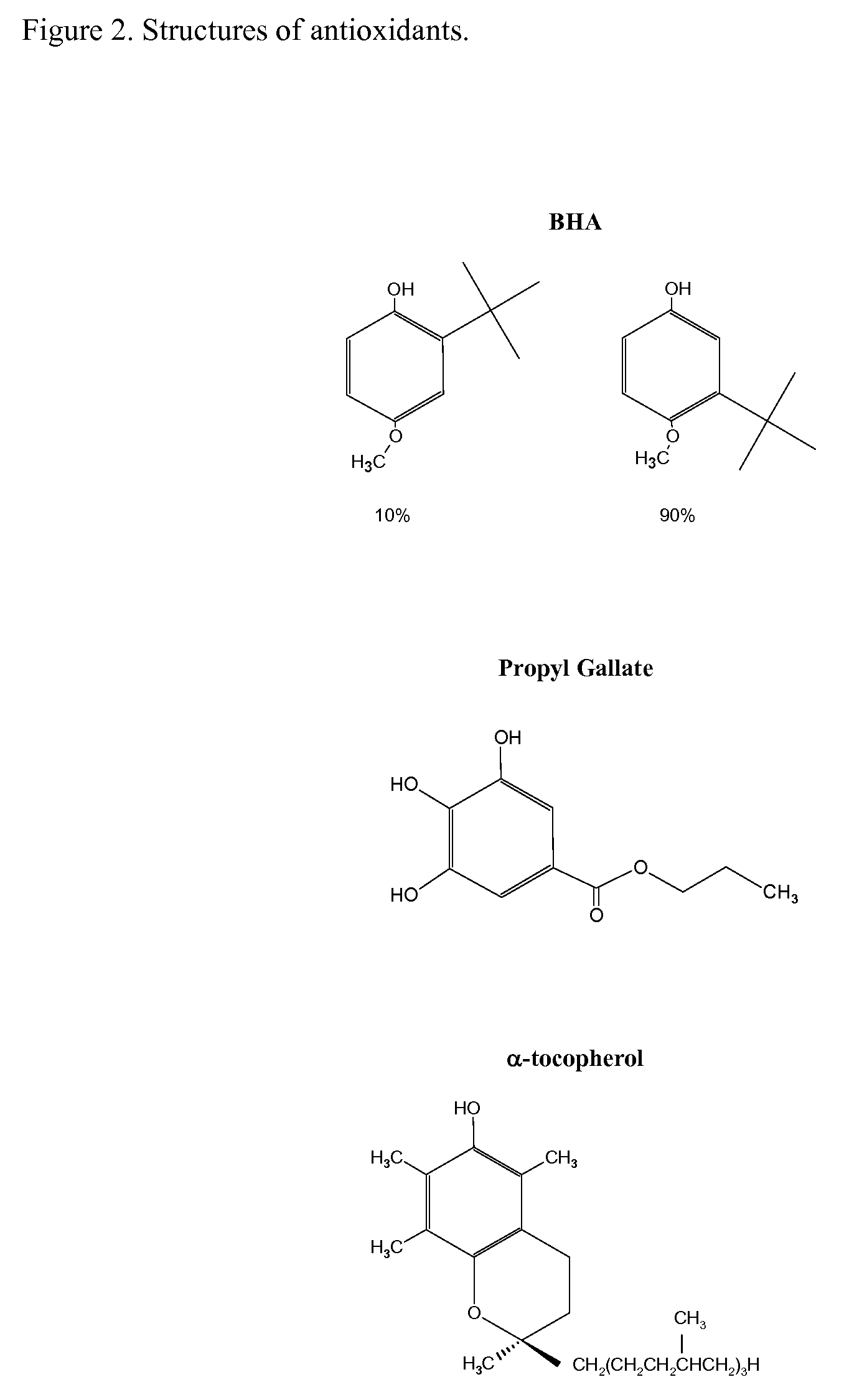
Reactivity of Hydroxymethylglutaryl Coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) Reductase Inhibitors Containing Conjugated Dienes with Phenolic Antioxidants in the Solid-State
InactiveUS20080312458A1Reduce oxidative degradationOxidative degradationOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPhenolic antioxidantHydroxy methyl glutaryl
The object of this invention was to probe the reactivity of lovastatin, simvastatin, pravastatin, and mevastatin in the solid-state without radical initiators in order to determine the antioxidant that provided the best stability for the statin. Phenolic antioxidants were evaluated.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Designer cells for enantioselective reduction of ketones and use thereof in efficient production of enantioenriched alcohols
ActiveUS20160289713A1Improve productivityImprove conversion rateOxidoreductasesFermentationAlcoholEnantiomer
The present invention is to provide a preparation of variant recombinant whole cell biocatalysts, referred herein as “designer cells” having significantly enhanced carbonyl reductase activity for use in the efficient production of variant industrially important enantiomerically enriched alcohols. More specifically, the alcohol is optically pure ethyl (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate, which is useful as chiral building block and an intermediate for the production of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
A genetically engineered bacterium with γ-terpinene synthesis ability and its construction method and application
ActiveCN107354118BEfficient fermentation productionIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium with gamma-terpinene synthesis capacity and a constructing method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to engineered escherichia coli, a path for synthesizing MVA from mevalonic acid is reconstructed by heterogeneous expression of hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A synthetase mvaS, hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase mvaE, mevalonate kinase Erg12, phosphomevalonate kinase Erg8, mevalonate pyrophosphate decarboxylase Erg19 and Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase Idi1, meanwhile, geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase GPPS2 and gamma-terpinene TPS2 are led into a bacterium body, and by utilizing the biotransformation capacity of the genetically engineered bacterium, gamma-terpinene can be efficiently produced in an environment-friendly mode. Through fermentation with the genetically engineered bacterium, the output of gamma-terpinene can reach 80 mg / L. The genetically engineered bacterium and the gamma-terpinene synthesis method are suitable for practical industrial production.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com