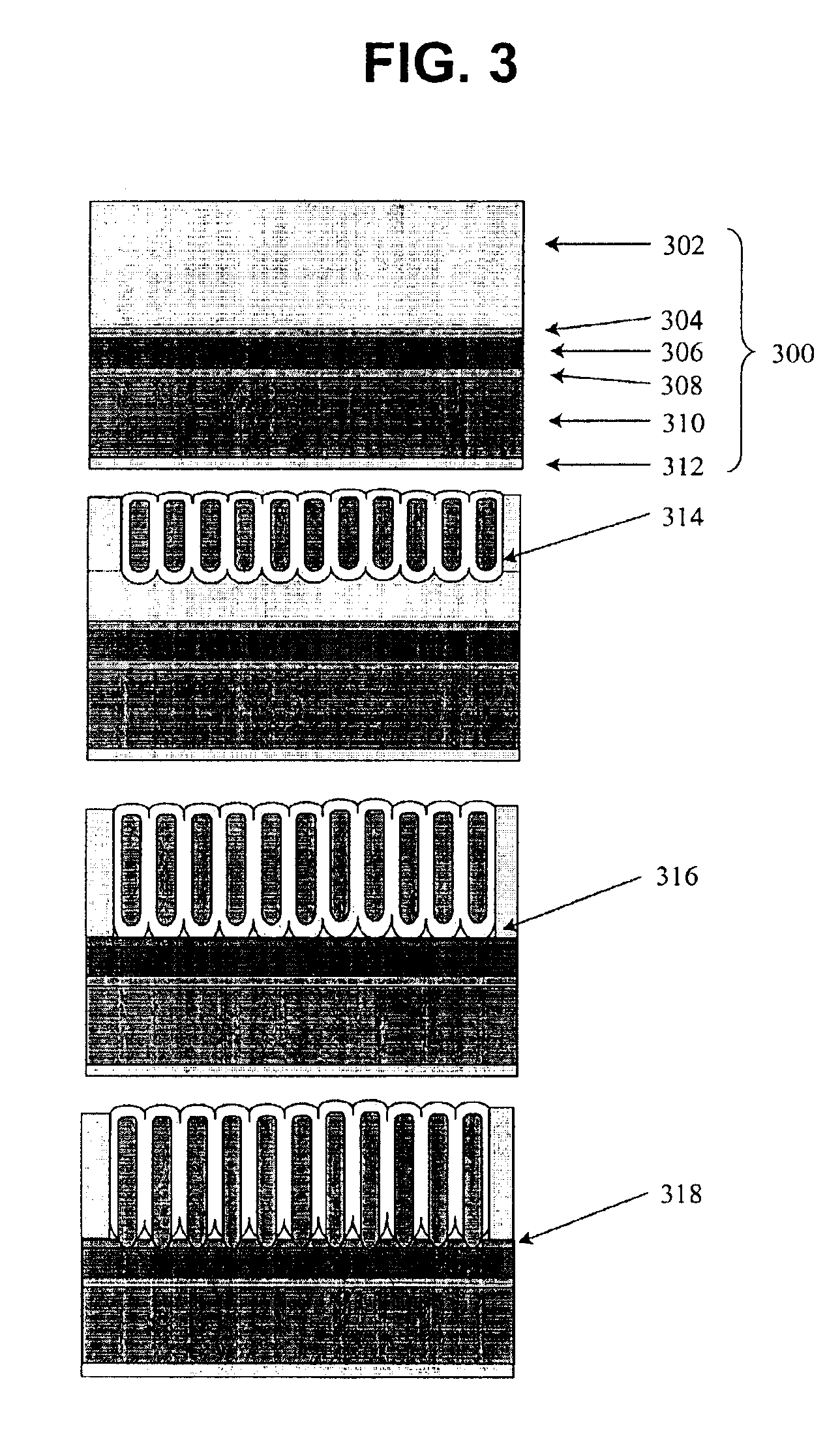
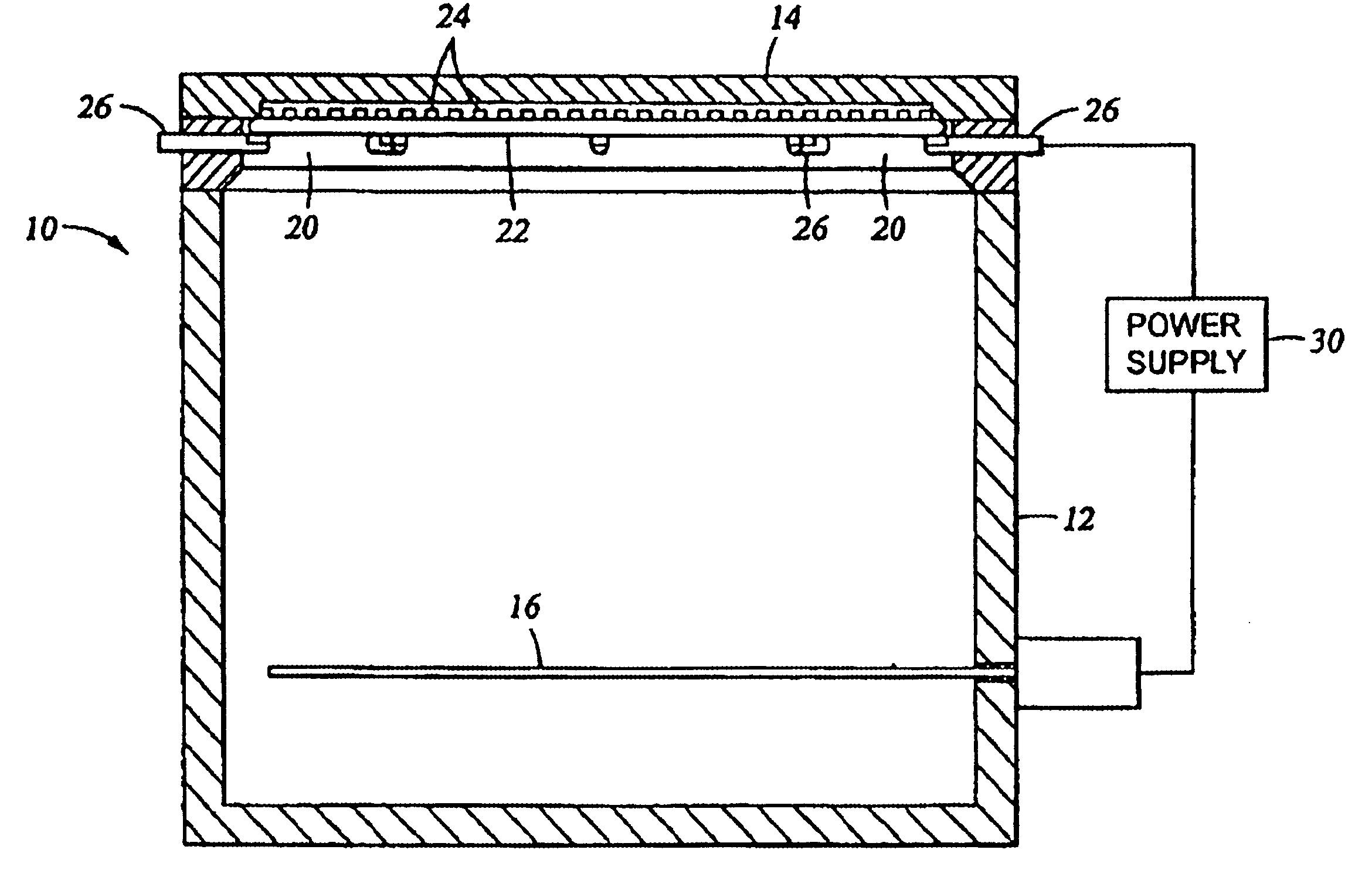
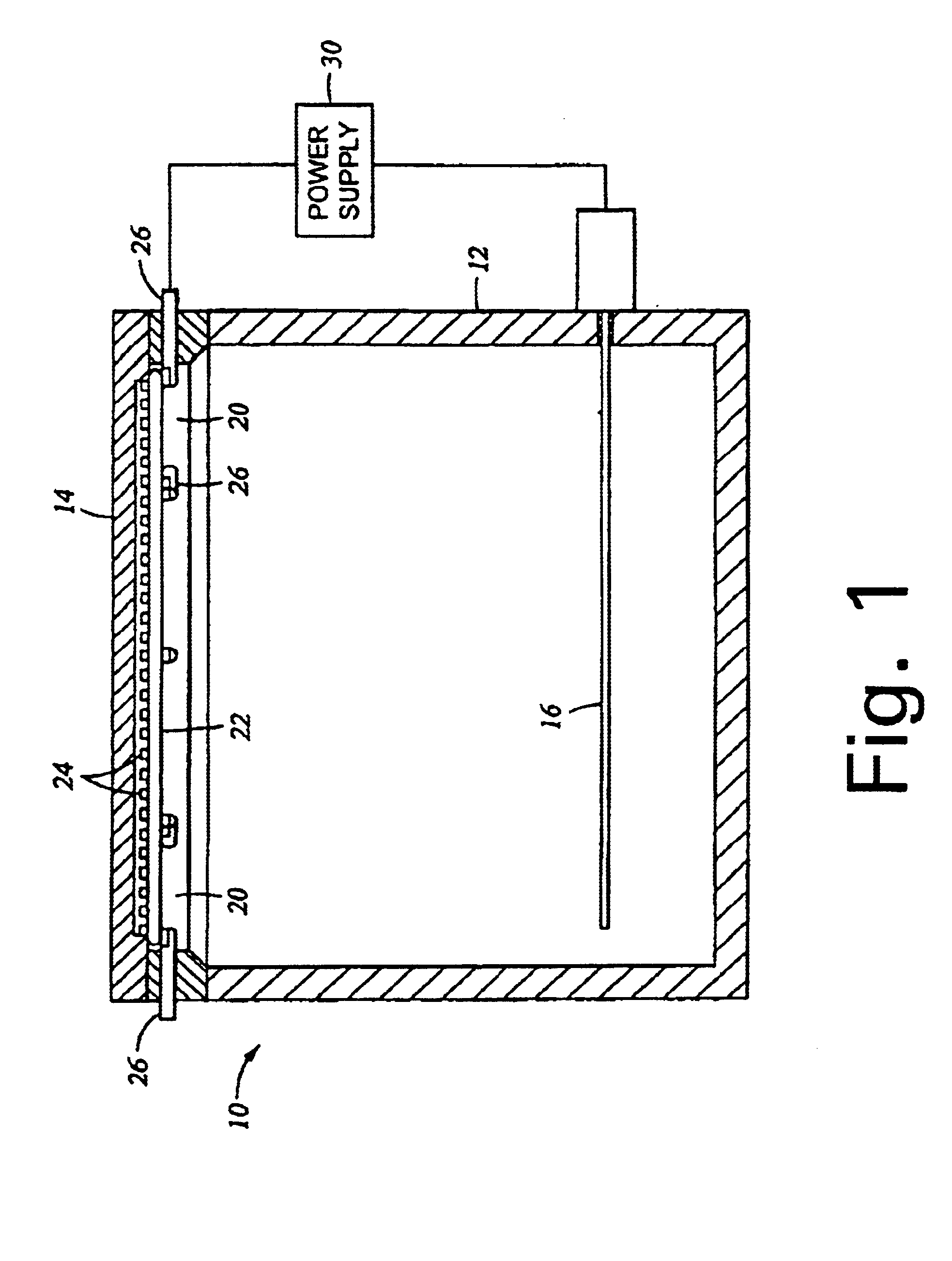
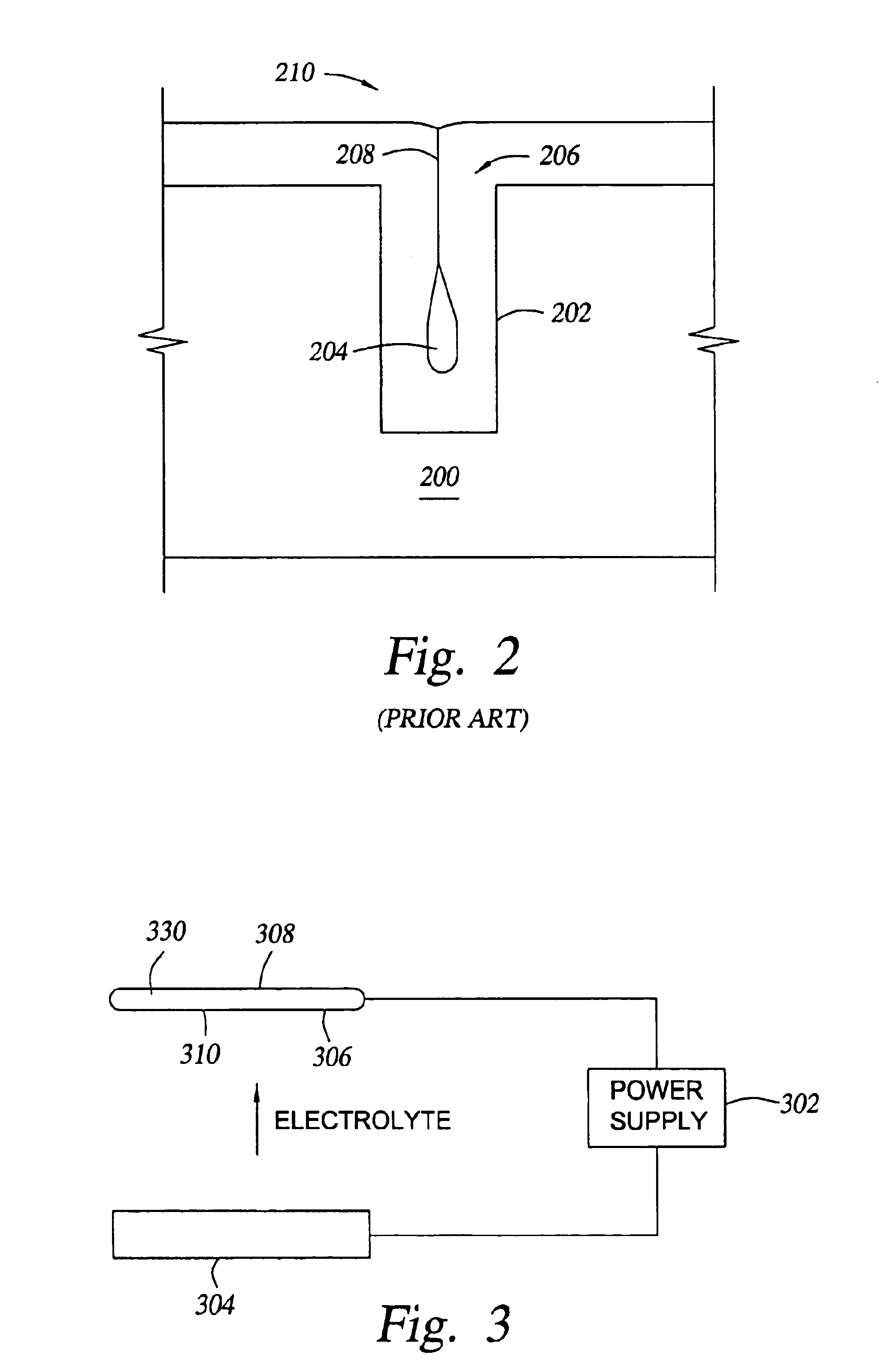
Patents
Literature
1734 results about "Galvanic deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
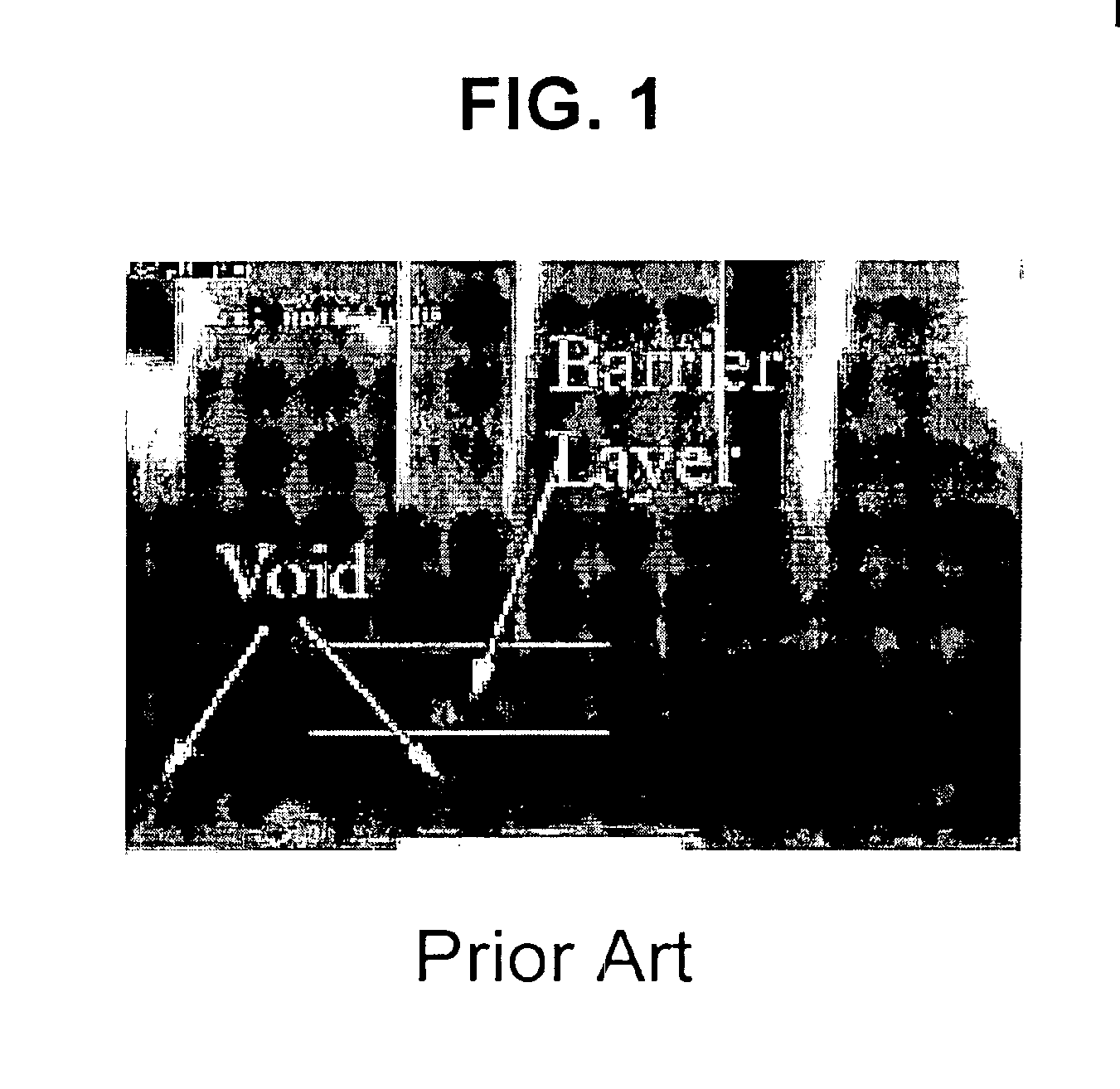
Deposition corrosion is a subtle form of galvanic cell that can produce pitting in a liquid environment when a more cathodic metal is plated out of solution onto a metal surface.
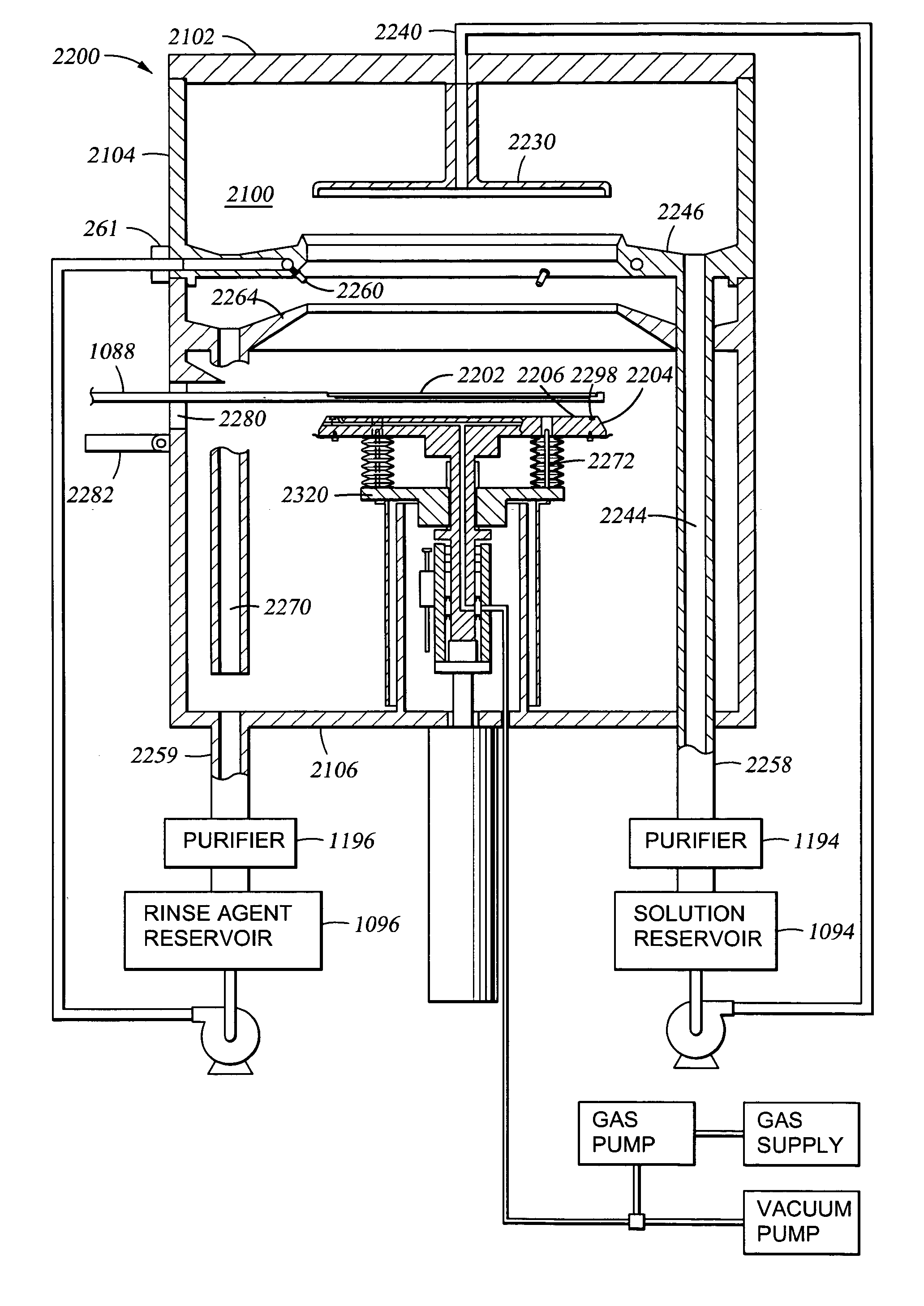
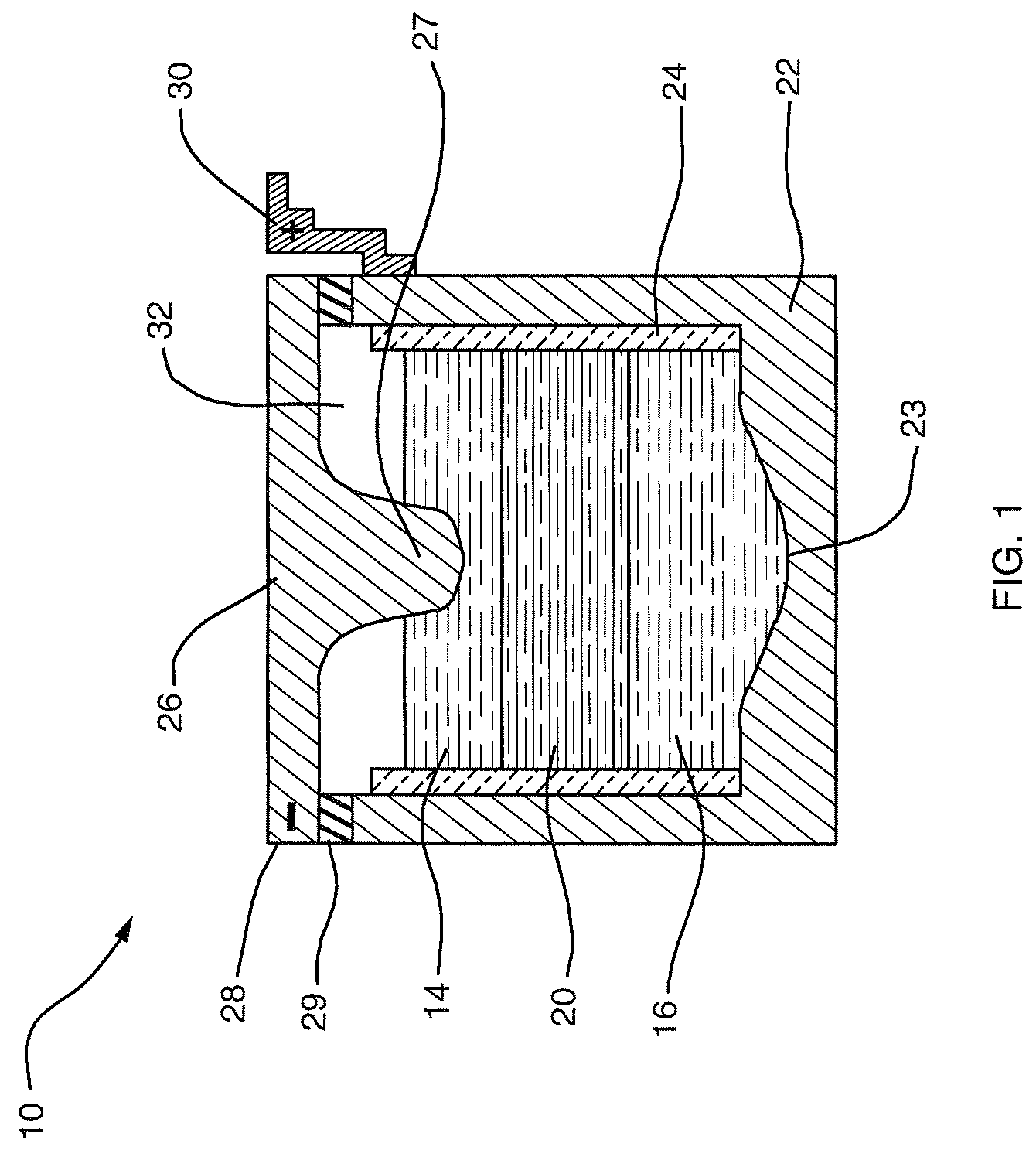
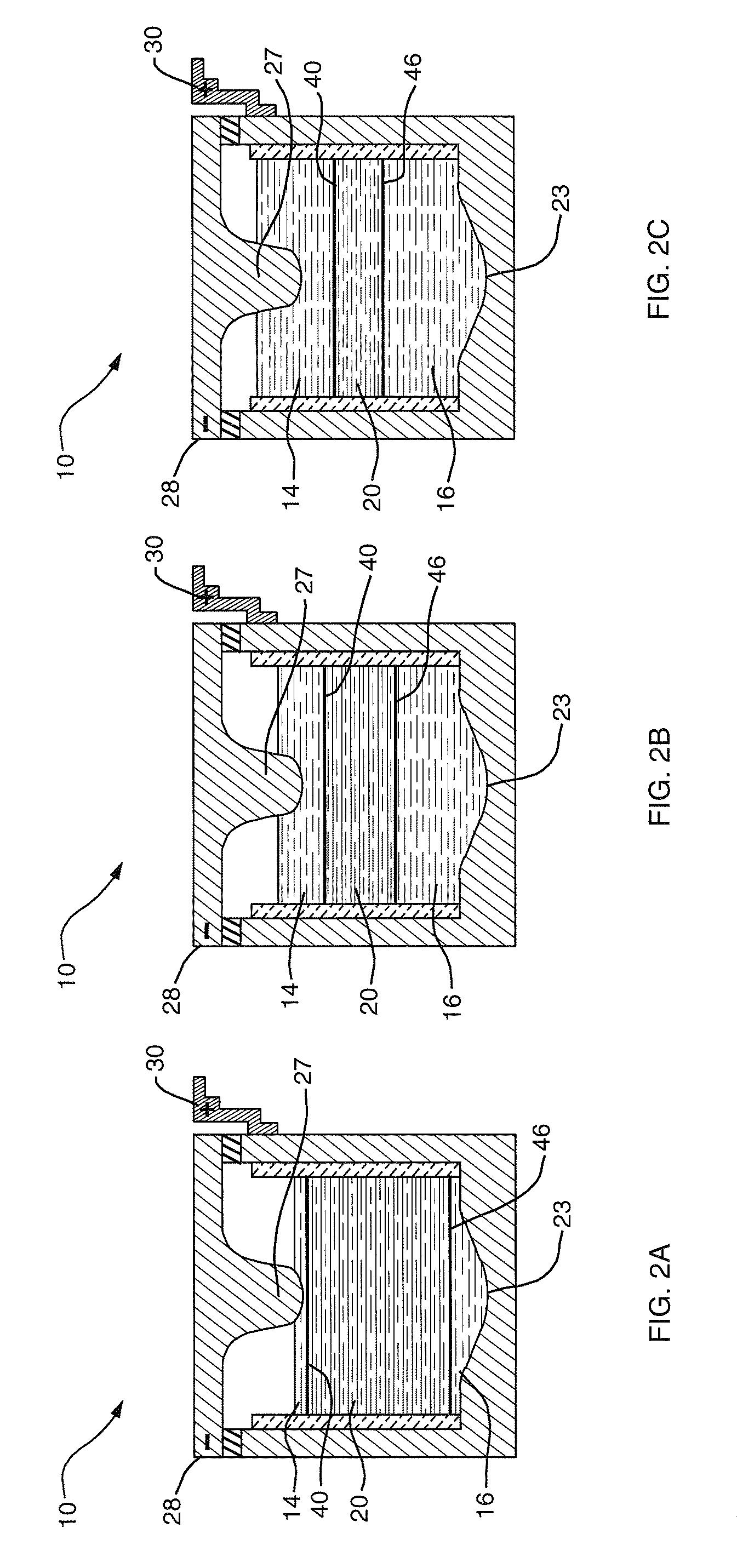
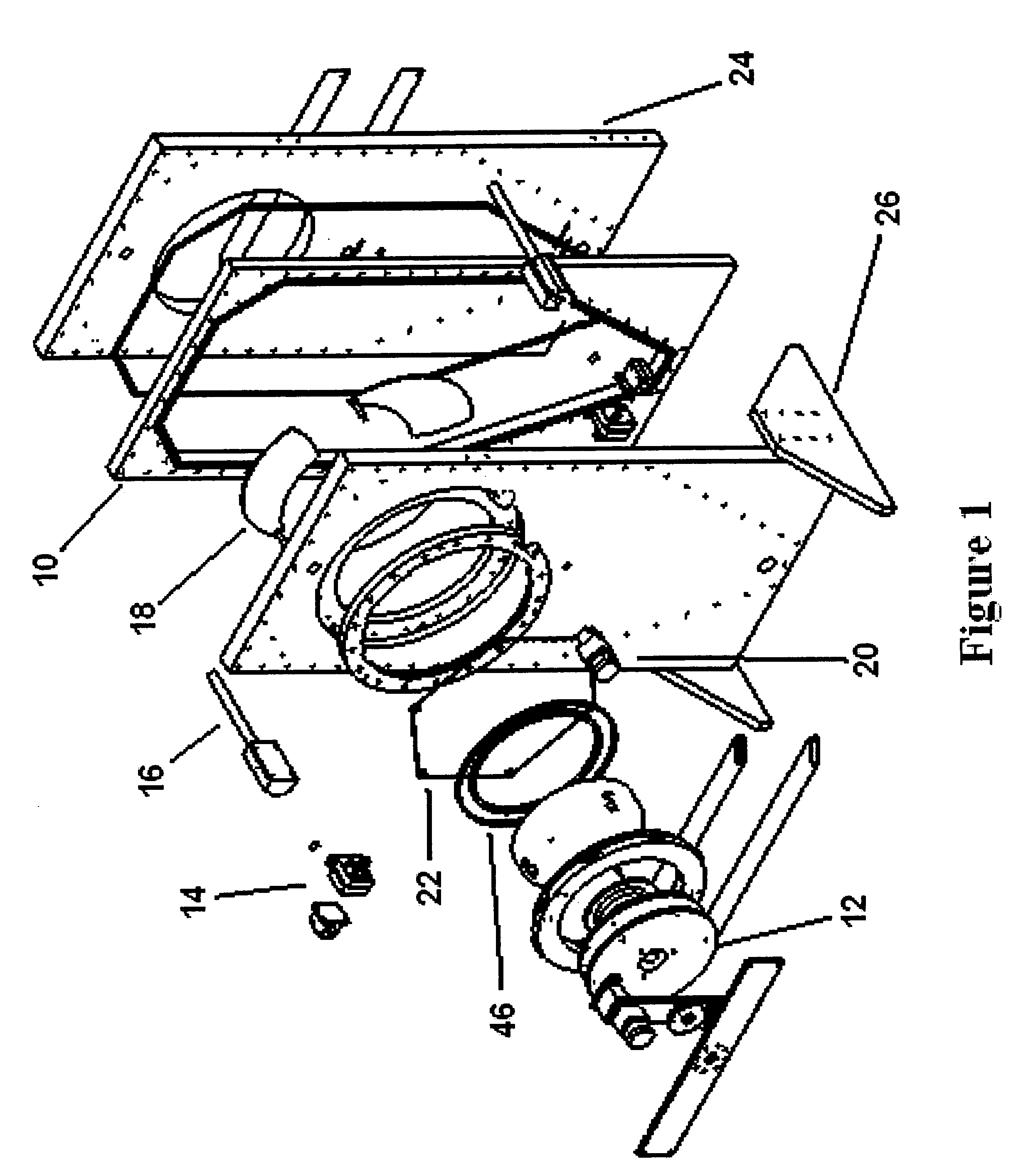
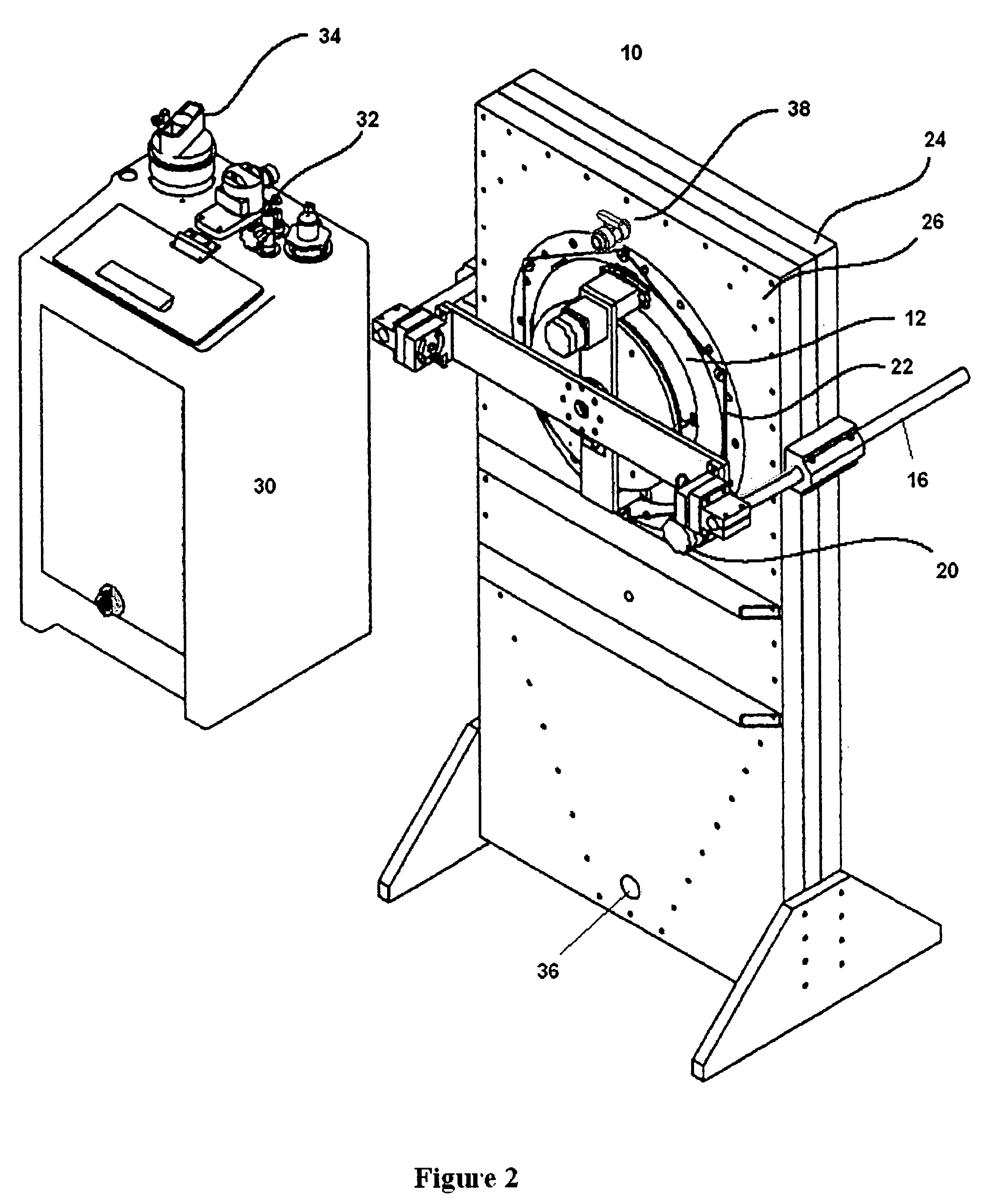
Electroless deposition apparatus
An apparatus and a method of depositing a catalytic layer comprising at least one metal selected from the group consisting of noble metals, semi-noble metals, alloys thereof, and combinations thereof in sub-micron features formed on a substrate. Examples of noble metals include palladium and platinum. Examples of semi-noble metals include cobalt, nickel, and tungsten. The catalytic layer may be deposited by electroless deposition, electroplating, or chemical vapor deposition. In one embodiment, the catalytic layer may be deposited in the feature to act as a barrier layer to a subsequently deposited conductive material. In another embodiment, the catalytic layer may be deposited over a barrier layer. In yet another embodiment, the catalytic layer may be deposited over a seed layer deposited over the barrier layer to act as a “patch” of any discontinuities in the seed layer. Once the catalytic layer has been deposited, a conductive material, such as copper, may be deposited over the catalytic layer. In one embodiment, the conductive material is deposited over the catalytic layer by electroless deposition. In another embodiment, the conductive material is deposited over the catalytic layer by electroless deposition followed by electroplating or followed by chemical vapor deposition. In still another embodiment, the conductive material is deposited over the catalytic layer by electroplating or by chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
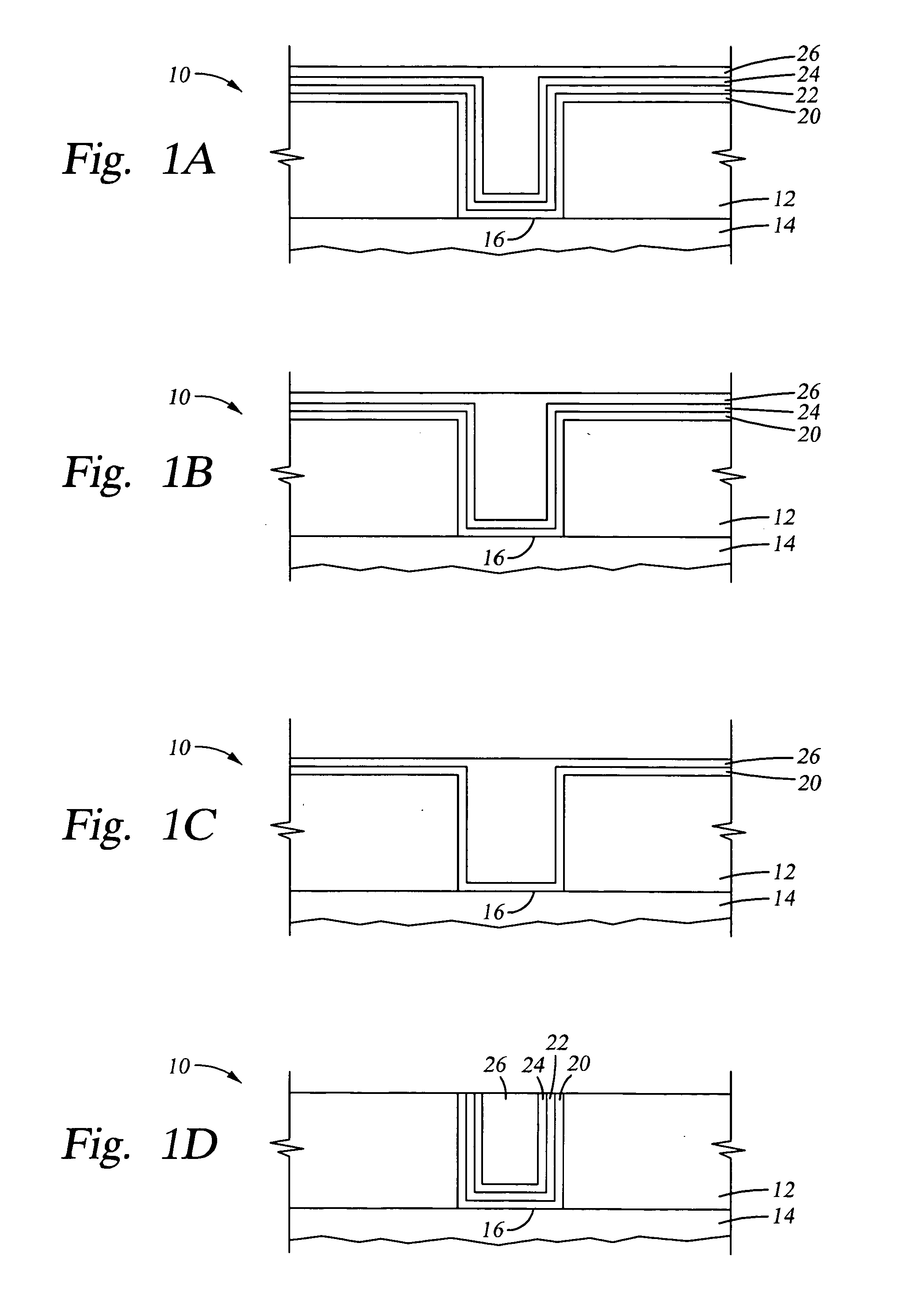
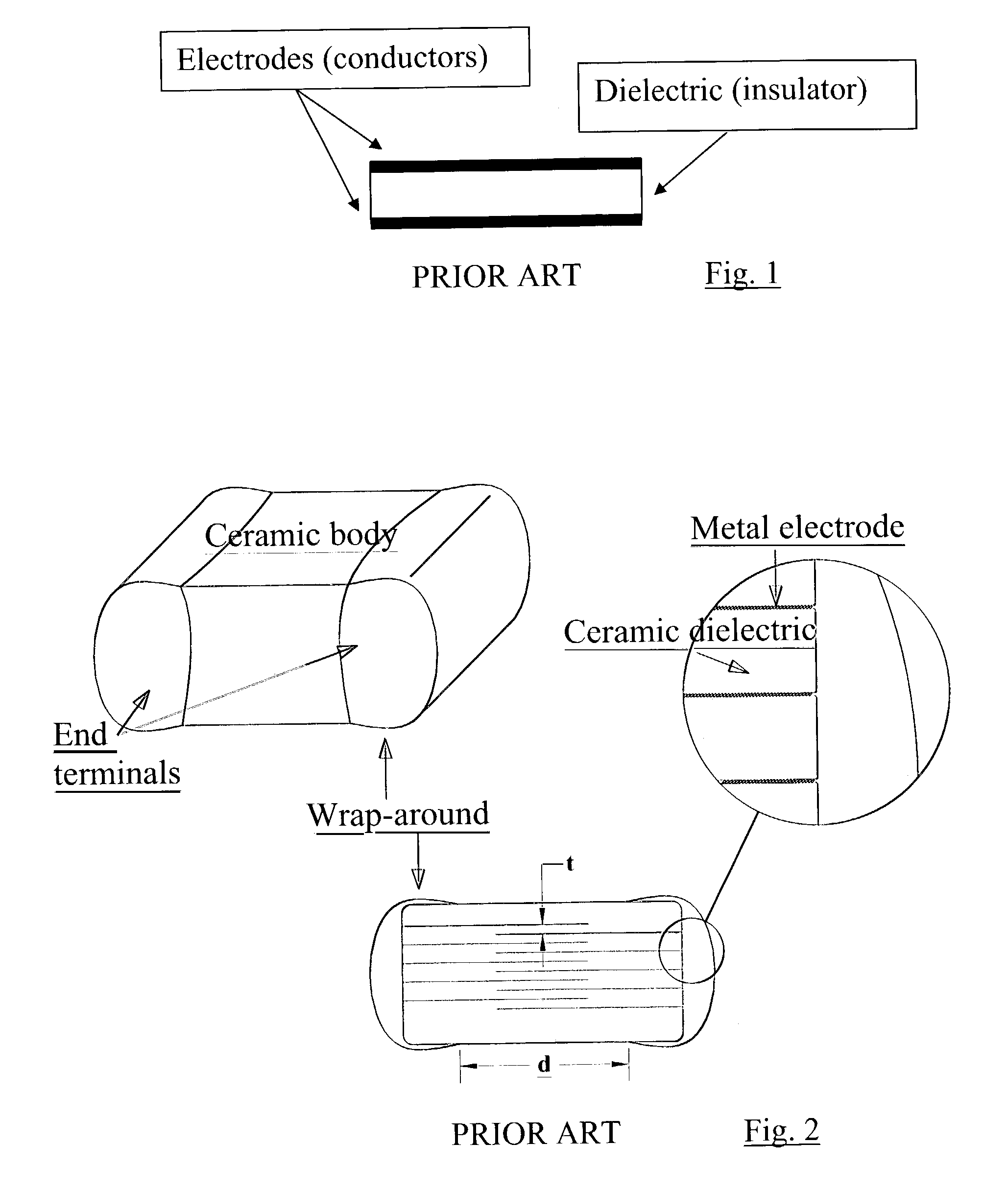
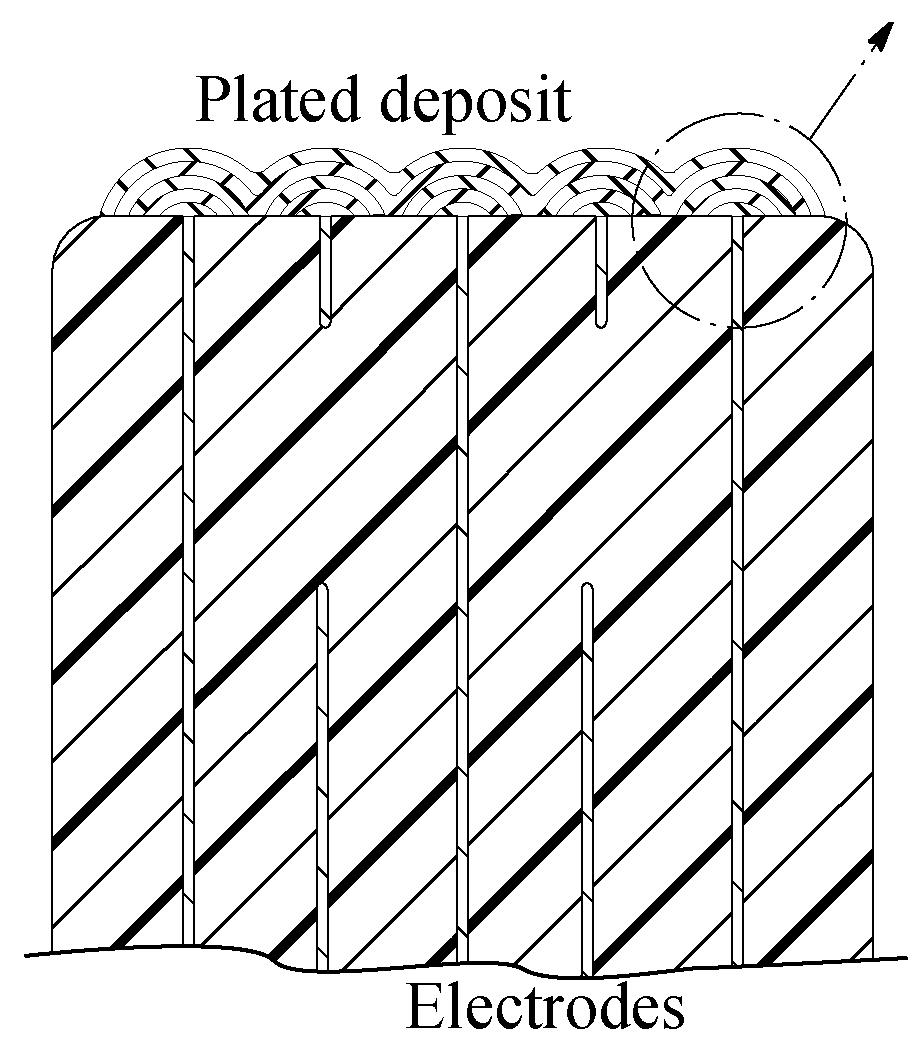
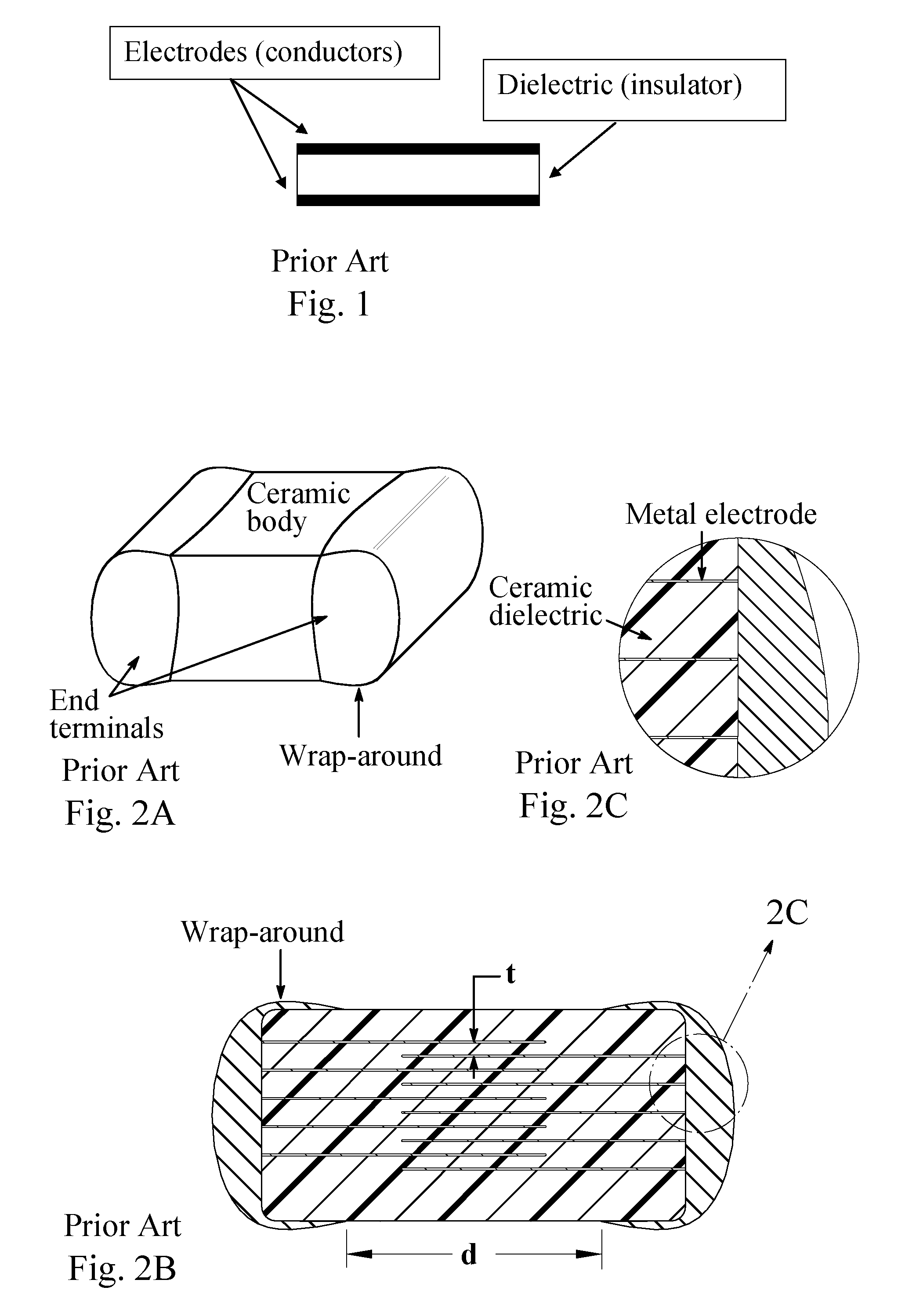
Multilayer ceramic capacitor with terminal formed by electroless plating
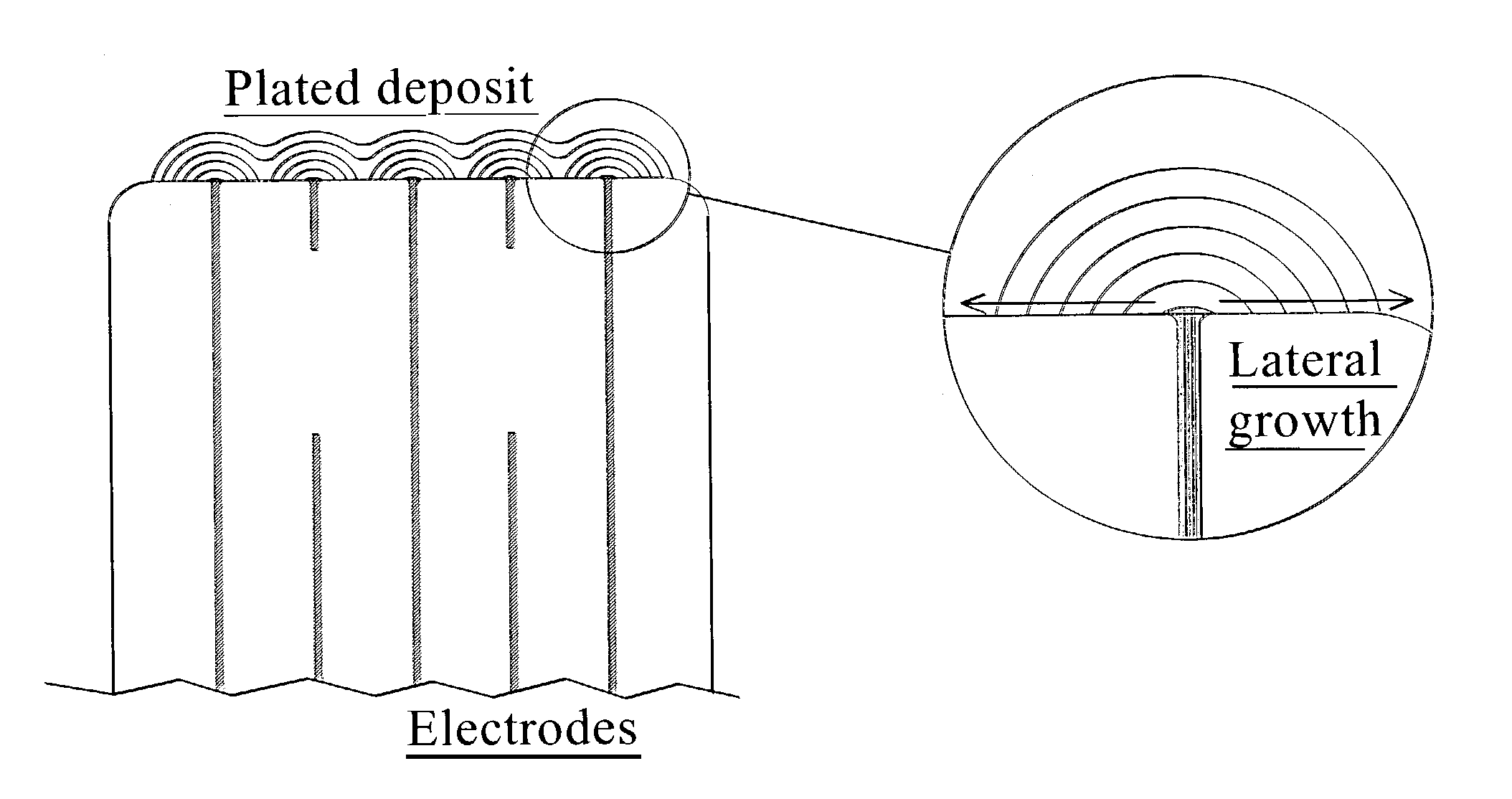
InactiveUS7345868B2High strengthFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricElectrolysisCeramic capacitor
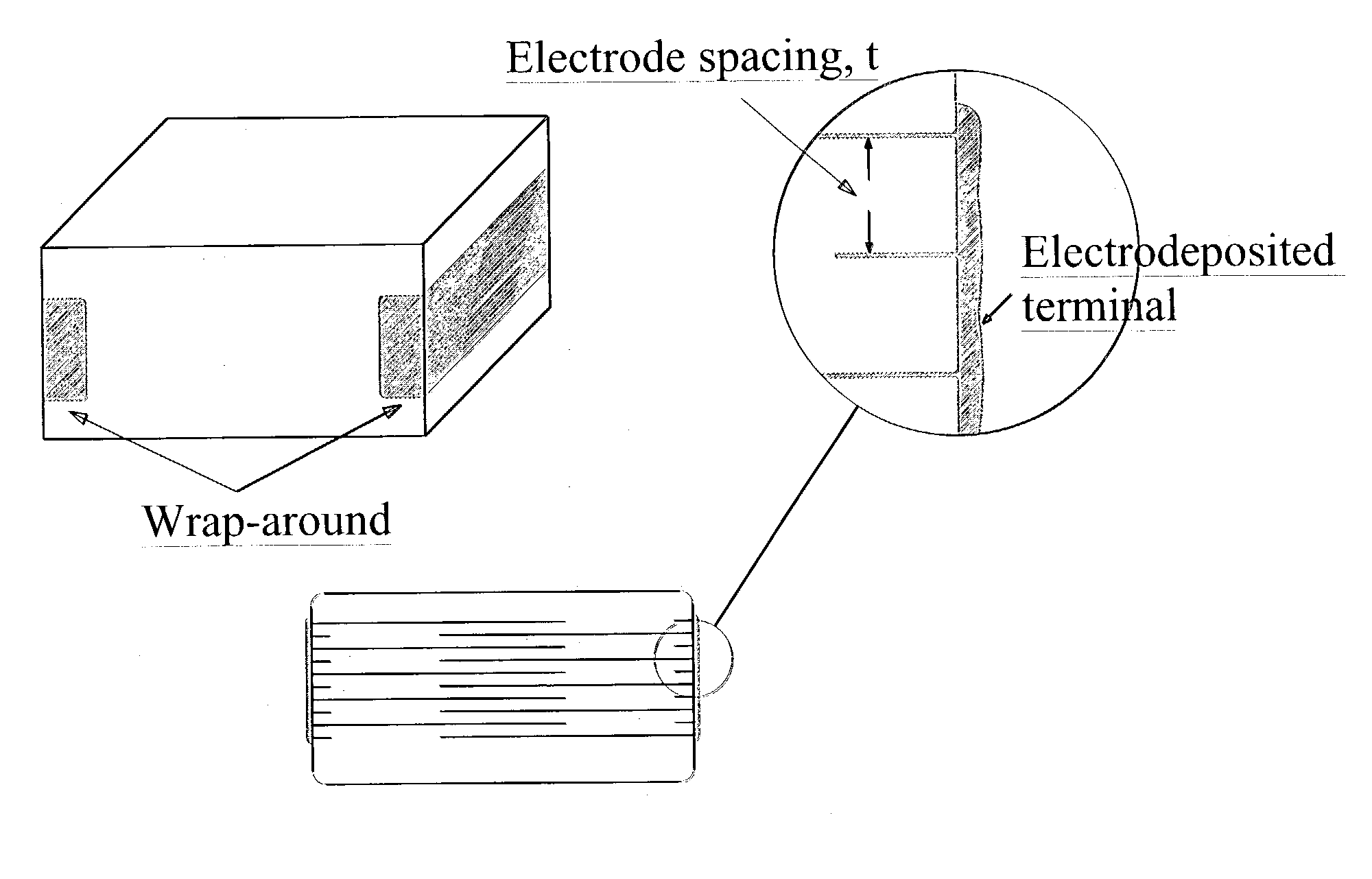
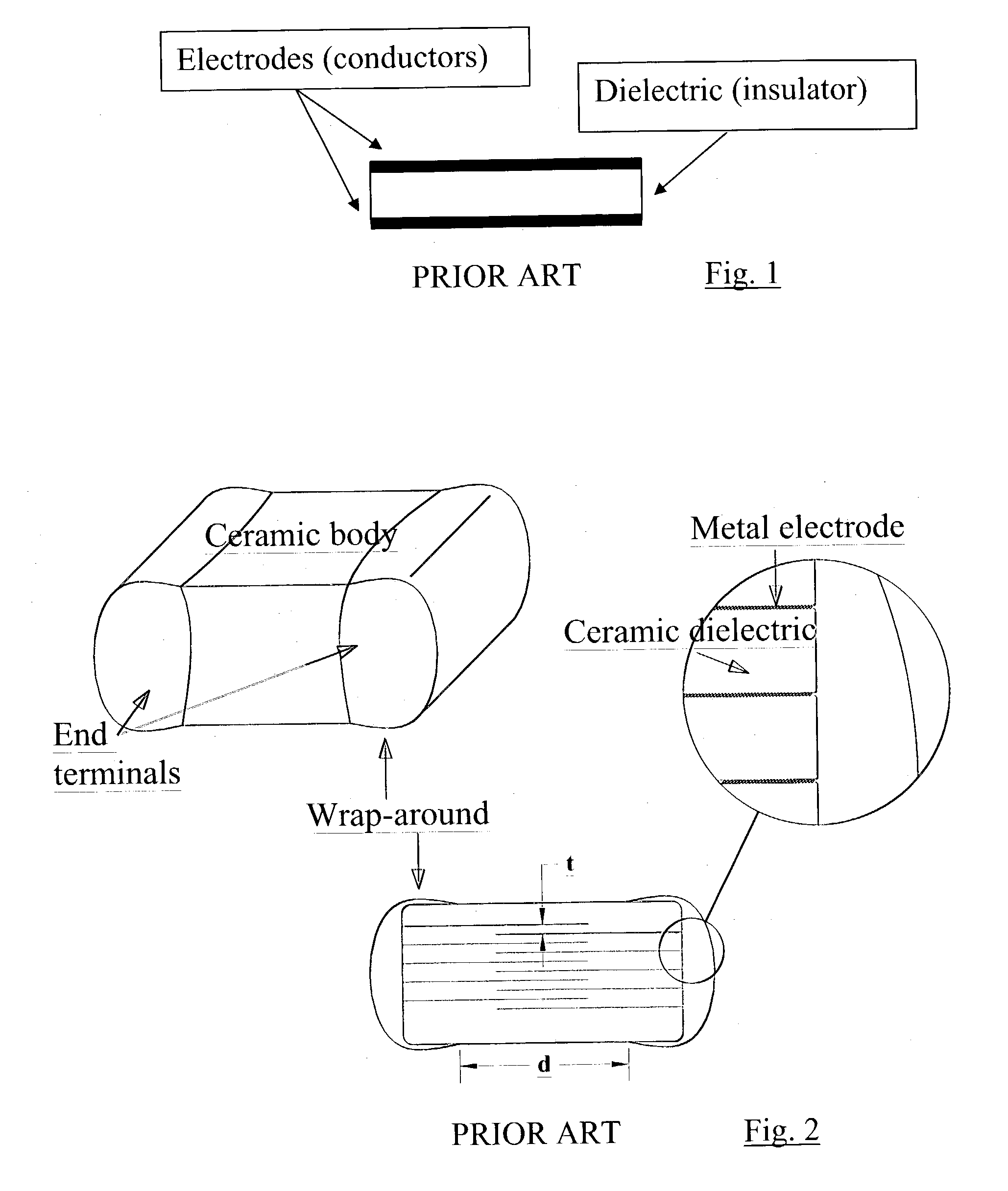
A terminal to, most commonly, a ceramic capacitor, most commonly a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC), is formed by electroless plating, also known as electroless deposition or simply as electrodeposition. In the MLCC having a multiple parallel interior plates brought to, and exposed at, at least one, first, surface, an electrically-conductive first-metal layer, preferably Cu, is electrolessly deposited upon this first surface directly in contact with, mechanically connected to, and electrically connected to, the edges of these interior plates. Lateral growth of the electrolessly-deposited first-metal is sufficient to span from exposed plate to exposed plate, electrically connecting the plates. One or more top layers, preferably one of Ni and one of Sn and Pb, are deposited, preferably by plating and more preferably by electrolytic plating, on top of the electrolessly-deposited Cu.
Owner:PRESIDIO COMPONENTS
Multilayer ceramic capacitor with terminal formed by electroless plating
InactiveUS20080158774A1High strengthFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricCeramic capacitorElectroless deposition
A terminal to, most commonly, a ceramic capacitor, most commonly a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC), is formed by electroless plating, also known as electroless deposition or simply as electrodeposition. In the MLCC having a multiple parallel interior plates brought to, and exposed at, at least one, first, surface, an electrically-conductive first-metal layer, preferably Cu, is electrolessly deposited upon this first surface directly in contact with, mechanically connected to, and electrically connected to, the edges of these interior plates. Lateral growth of the electrolessly-deposited first-metal is sufficient to span from exposed plate to exposed plate, electrically connecting the plates. One or more top layers, preferably one of Ni and one of Sn and Pb, are deposited, preferably by plating and more preferably by electrolytic plating, on top of the electrolessly-deposited Cu.
Owner:PRESIDIO COMPONENTS
Miniature RF and microwave components and methods for fabricating such components
InactiveUS7259640B2Small sizeReduce manufacturing costAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhysical chemistrySelective deposition
Owner:MEMGEN CORP
Method for fabricating a self-aligned nanocolumnar airbridge and structure produced thereby
ActiveUS20050208752A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPorosityElectrical conductor
A method for fabricating a low k, ultra-low k, and extreme-low k multilayer interconnect structure on a substrate in which the interconnect line features are separated laterally by a dielectric with vertically oriented nano-scale voids formed by perforating it using sub-optical lithography patterning and etching techniques and closing off the tops of the perforations by a dielectric deposition step. The lines are supported either by solid or patterned dielectric features underneath. The method avoids the issues associated with the formation of air gaps after the fabrication of conductor patterns and those associated with the integration of conventional low k, ultra-low k and extreme low k dielectrics which have porosity present before the formation of the interconnect patterns.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Abrasive tool with metal binder phase
InactiveUS6419574B1Sufficient sharpnessImprove discharge performanceRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding drivesWear particleMetal
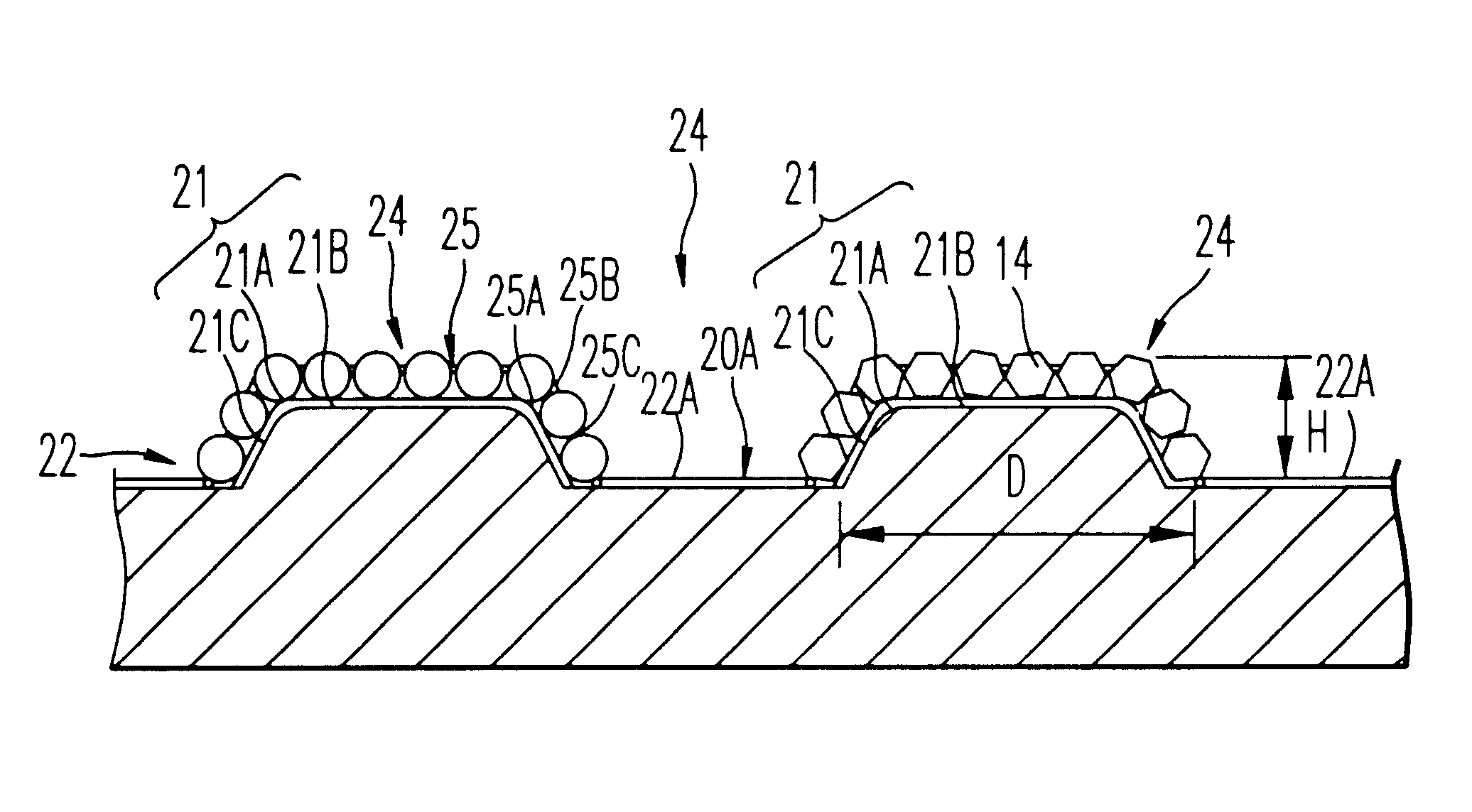
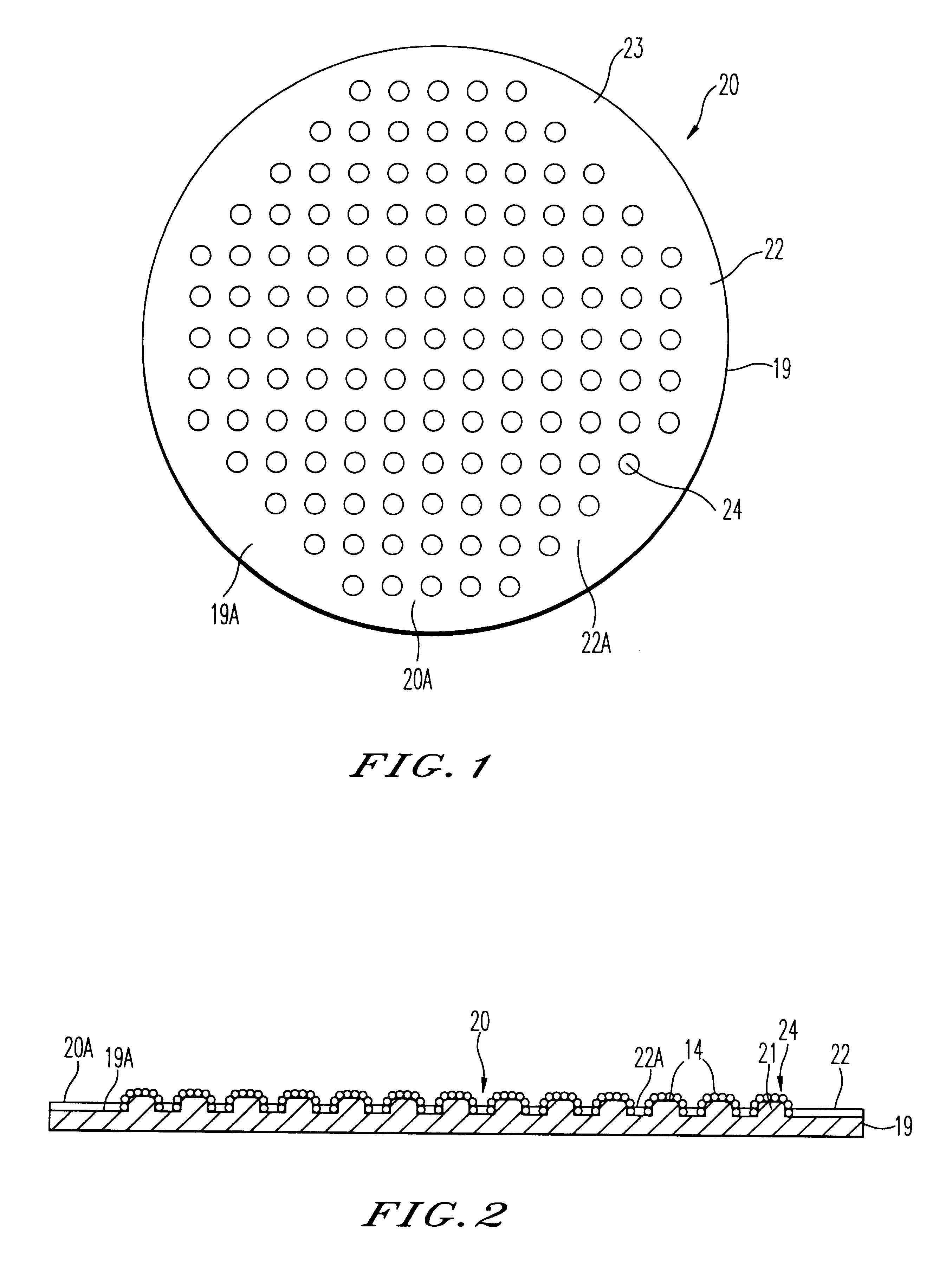
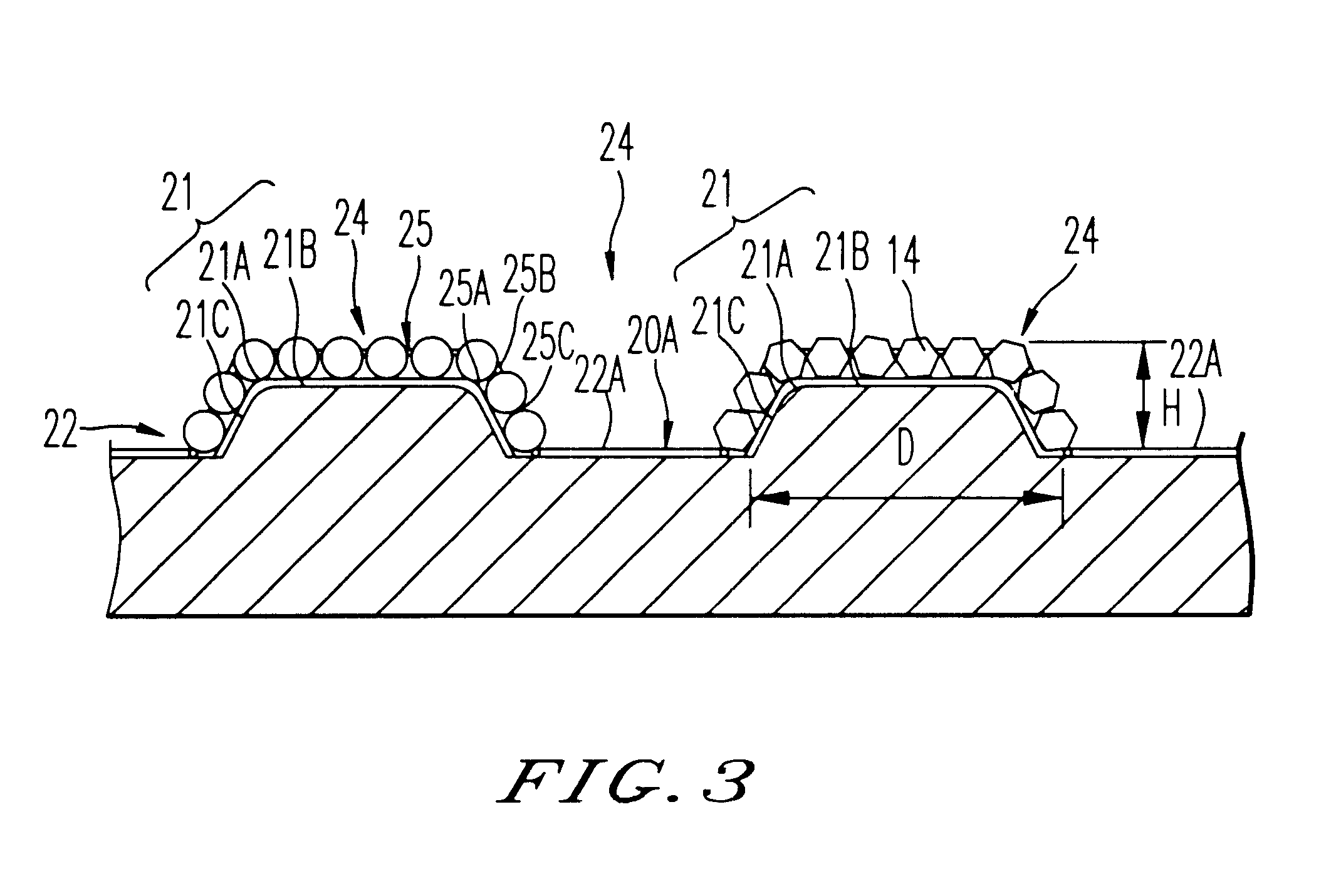
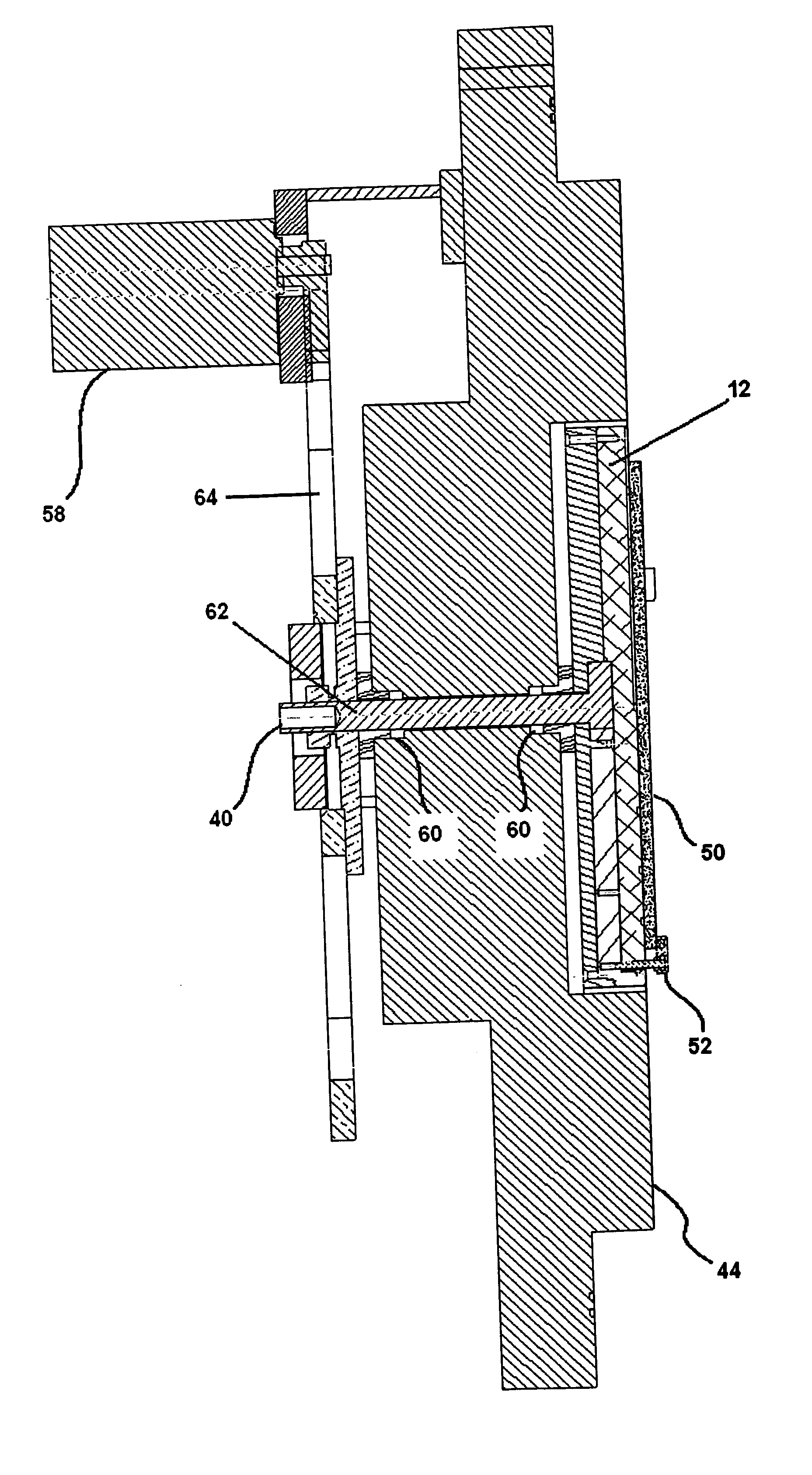
In the electrodeposited abrasive wheel 20 of the abrasive tool according to the present invention, plural mound parts 21, which are upheaved at the central domain of base metal 19 in almost columnar shape, are arranged mostly in the shape of lattice. An abrasive grain layer 22 is formed on a base metal 19, and plural ultra abrasive grains 14 are adhered only to each mound parts 21 by electrodeposited metal phase 25, and referred as the small abrasive-grain-layer parts 24, respectively. Ultra abrasive grains are laid out at corner R part 21a and top 21b of the mound parts 21 at the small abrasive-grain-layer parts 24. Ultra abrasive grains at each small abrasive-grain-layer parts are set as 11-500 pieces, and the rate which ultra abrasive grains occupy to the whole area of abrasive grain layer accounted by plane projection is set as 20%-80% of the range. At the time of grinding, only ultra abrasive grains contact to grinding work piece, then high abutment pressure is maintained, and sharpness and the discharge performance of ground wastes are good.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Vapochromic led
InactiveUS6160267ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumLight-emitting diode
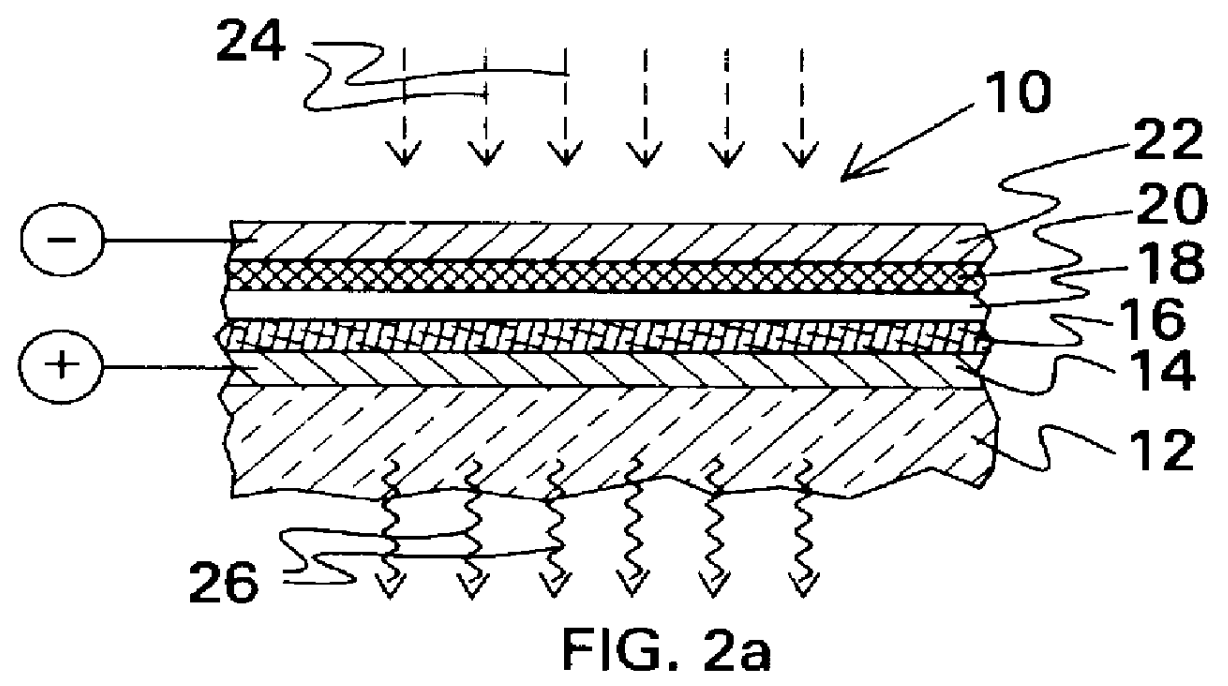
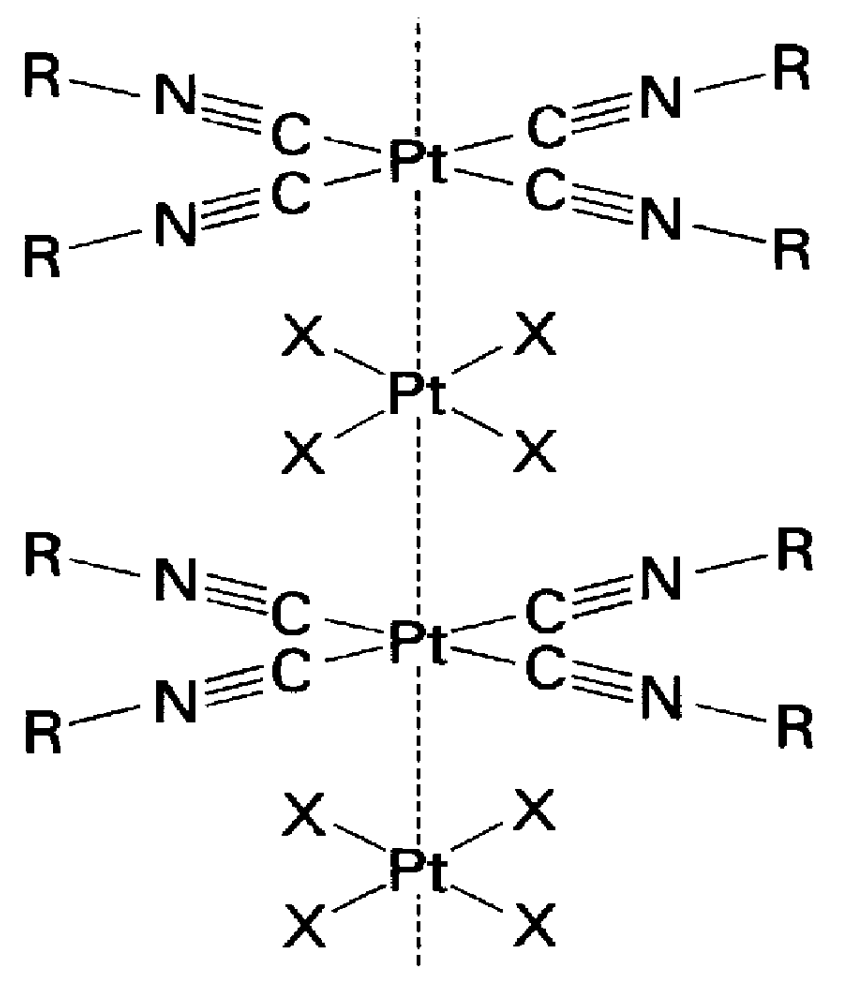
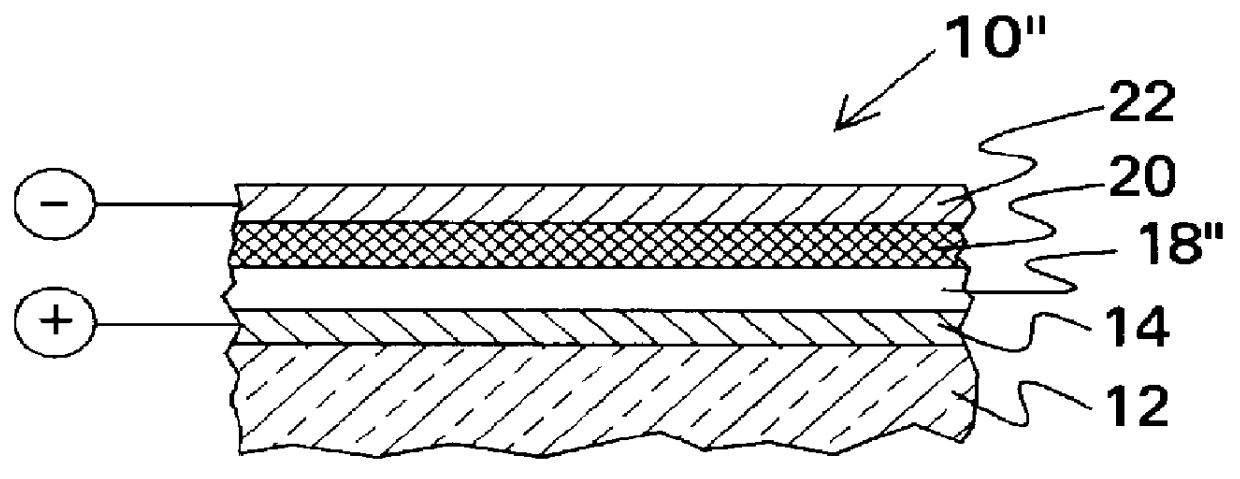
A sandwich device was prepared by electrodeposition of an insoluble layer of oligomerized tris(4-(2-thienyl)phenyl)amine onto conducting indium-tin oxide coated glass, spin coating the stacked platinum compound, tetrakis(p-decylphenylisocyano)platinum tetranitroplatinate, from toluene onto the oligomer layer, and then coating the platinum complex with aluminum by vapor deposition. This device showed rectification of current and gave electroluminescence. The electroluminescence spectrum ( lambda max=545 nm) corresponded to the photoluminescence spectrum of the platinum complex. Exposure of the device to acetone vapor caused the electroemission to shift to 575 nm. Exposure to toluene vapor caused a return to the original spectrum. These results demonstrate a new type of sensor that reports the arrival of organic vapors with an electroluminescent signal. The sensor comprises (a) a first electrode; (b) a hole transport layer formed on the first electrode; (c) a sensing / emitting layer formed on the hole transport layer, the sensing / emitting layer comprising a material that changes color upon exposure to the analyte vapors; (d) an electron conductor layer formed on the sensing layer; and (e) a second electrode formed on the electron conductor layer. The hole transport layer emits light at a shorter wavelength than the sensing / emitting layer and at least the first electrode comprises an optically transparent material.
Owner:CALMEC +1
Dynamic pulse plating for high aspect ratio features
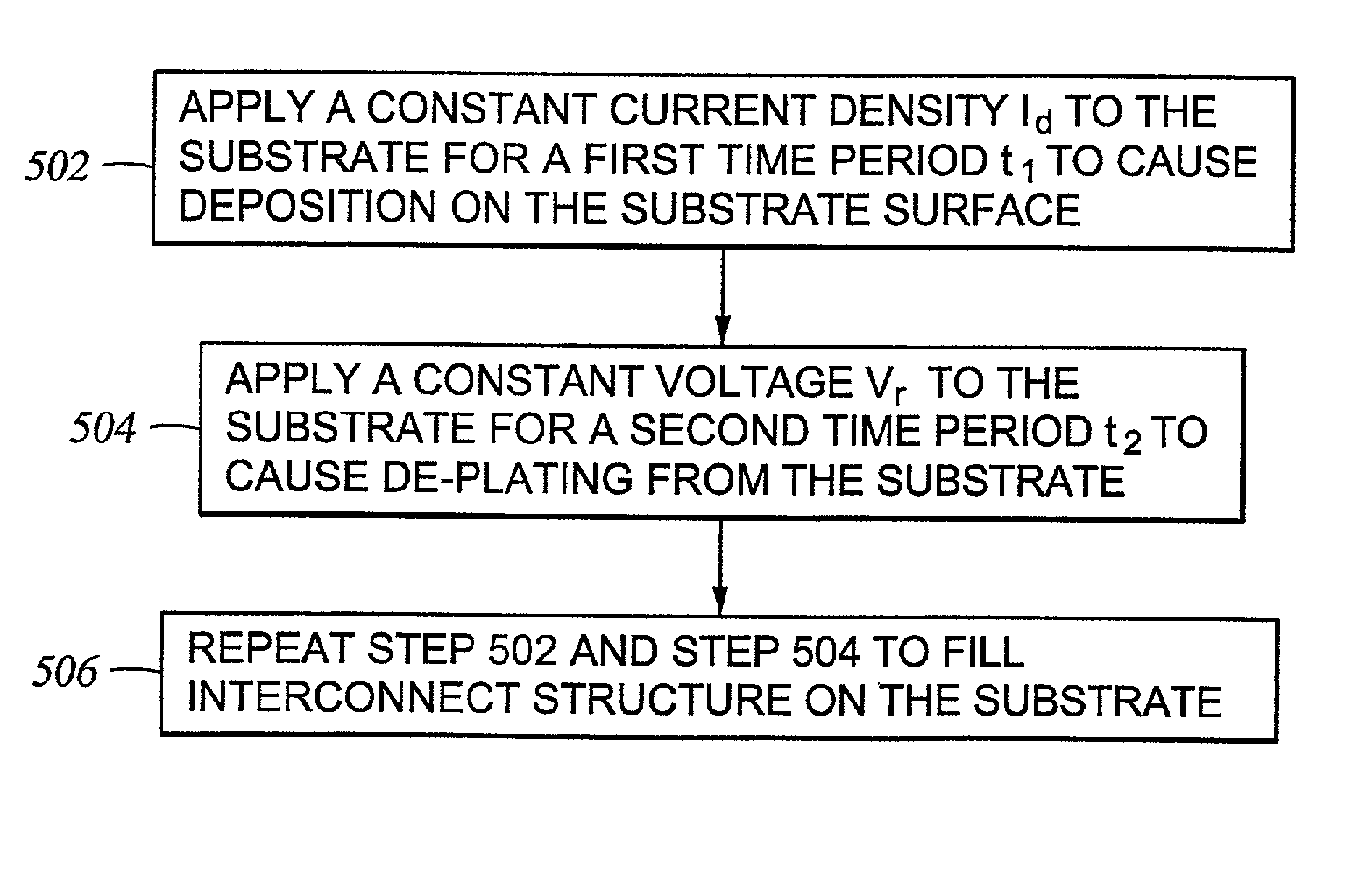
A method for depositing a metal on a substrate is provided. The metal is deposited by sequentially applying a electrodeposition pulse followed by an electrodissolution pulse to the substrate. After each electrodissolution pulse an before the next electrodeposition pulse there is provided at least one time interval of zero electrical voltage or current, also known as an "off-time", between the pulses. The first two electrodeposition pulses should preferably have the same time durations. Thereafter, the time durations of subsequent electrodeposition pulses are gradually decreased to provide a void-free and seam-free deposition of metal in high aspect ratio features.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High-amperage energy storage device with liquid metal negative electrode and methods
ActiveUS8268471B2Improve ionic conductivityIncrease response ratePrimary cell to battery groupingCell electrodesElectrolysisEngineering
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Preparation method of neodymium iron boron magnet
ActiveCN102103916AReduce usageUniformity controllableInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare earthImpurity
A preparation method of neodymium iron boron magnet is disclosed. The composition general formula of the magnet provided by the invention is R1R2FeMB, wherein R1 is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Nd, Pr, La, Ce, Sm, Sc, Y and Eu, having a content of 23 to 35 wt%; R2 is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Tb, Dy, Gd, and Ho, having a content of 0.1 to 5 wt%; M represents transition group metal with the exception of Fe, having the content of 0.01 to 5 wt%; B represents simple substance boron, having the content of 0.8 to 1.2 wt%; the balance isFe and the other inevitable impurities. The preparation method of neodymium iron boron magnet provided by the invention works in such a manner that: one or more elements in the R2 are plated to the surface of the magnet, the metal R2 is diffused into the interior of the magnet by primary high temperature heat treatment, and imbalance organization and internal stress brought by the high temperature treatment are eliminated through secondary low temperature tempering. Low temperature molten salt electrodeposition method is employed to plate films. The present invention is advantageous in greatly improving the production efficiency, reducing the dosage of the heavy rare earth during preparation process of magnet, saving rare earth resource, and obtaining high coercivity without reducing remanent magnetism and magnetic energy product of a magnet.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Load-type monoatomic catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109225257AIncrease profitReduce dosageMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectricityPhysical field
The invention provides a load-type monoatomic catalyst. The catalyst is formed by uniformly loading monodispersed metal atoms on the surface of a nano substrate material. A preparation method thereofcomprises the following steps: in an electrolyte solution containing metal salt, performing electrochemical deposition by using a three-electrode system, using a glassy carbon electrode loaded with the nano substrate material as a working electrode, using a graphite rod as a counter electrode, using a silver / silver chloride electrode as a reference electrode, performing linear volt-ampere scanning, enabling the metal atoms to be monodispersely and uniformly deposited on the nano substrate material, to obtain the load-type monoatomic catalyst. The load-type monoatomic catalyst is capable of, based on electro-deposition, constructing a monoatomic structure, through an electro-deposition method, rapidly, efficiently, and controllably depositing single atoms, and realizing deposition of positive and negative electrodes, and the obtained load-type monoatomic catalyst has important significance to a general application in the catalytic and particle physical field.
Owner:INST OF ADVANCED TECH UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
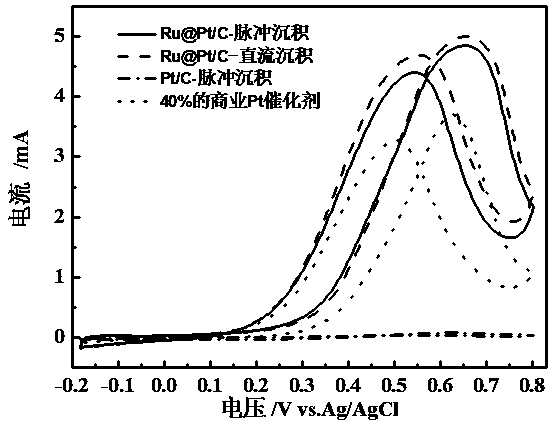
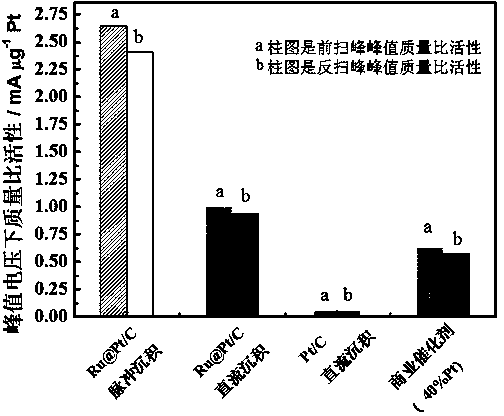
Core-shell structure catalyst for fuel cells and its pulse electrodeposition preparation method
ActiveCN103638925AIncrease profitReduce usageCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPlatinumPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a core-shell structure catalyst for fuel cells and its pulse electrodeposition preparation method. The active component of the catalyst is a nanoparticle with a core-shell structure, and an active metal is cladded in the form of an ultrathin shell on the surface of a carbon carrier loaded metal or alloy nanoparticle serving as a core. The catalyst takes a non-platinum noble metal or transition metal as the core, and adopts more than one of Pt, Ir or Au as the shell. The preparation method includes: preparation of the nanoparticle serving as the core, making of a working electrode for pulse electrodeposition, and preparation of the catalyst by pulse electrodeposition. The catalyst can be used as an anode or cathode catalyst of a low temperature fuel cell. The obtained catalyst has very high stability. Compared with underpotential deposition, the method is simple to operate, has no need for inert atmosphere protection, and is more suitable for large-scale industrial production, also can greatly reduce the noble metal consumption of fuel cells, and greatly reduce the cost of fuel cells, thus having great significance in promoting the commercialization process of fuel cells.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
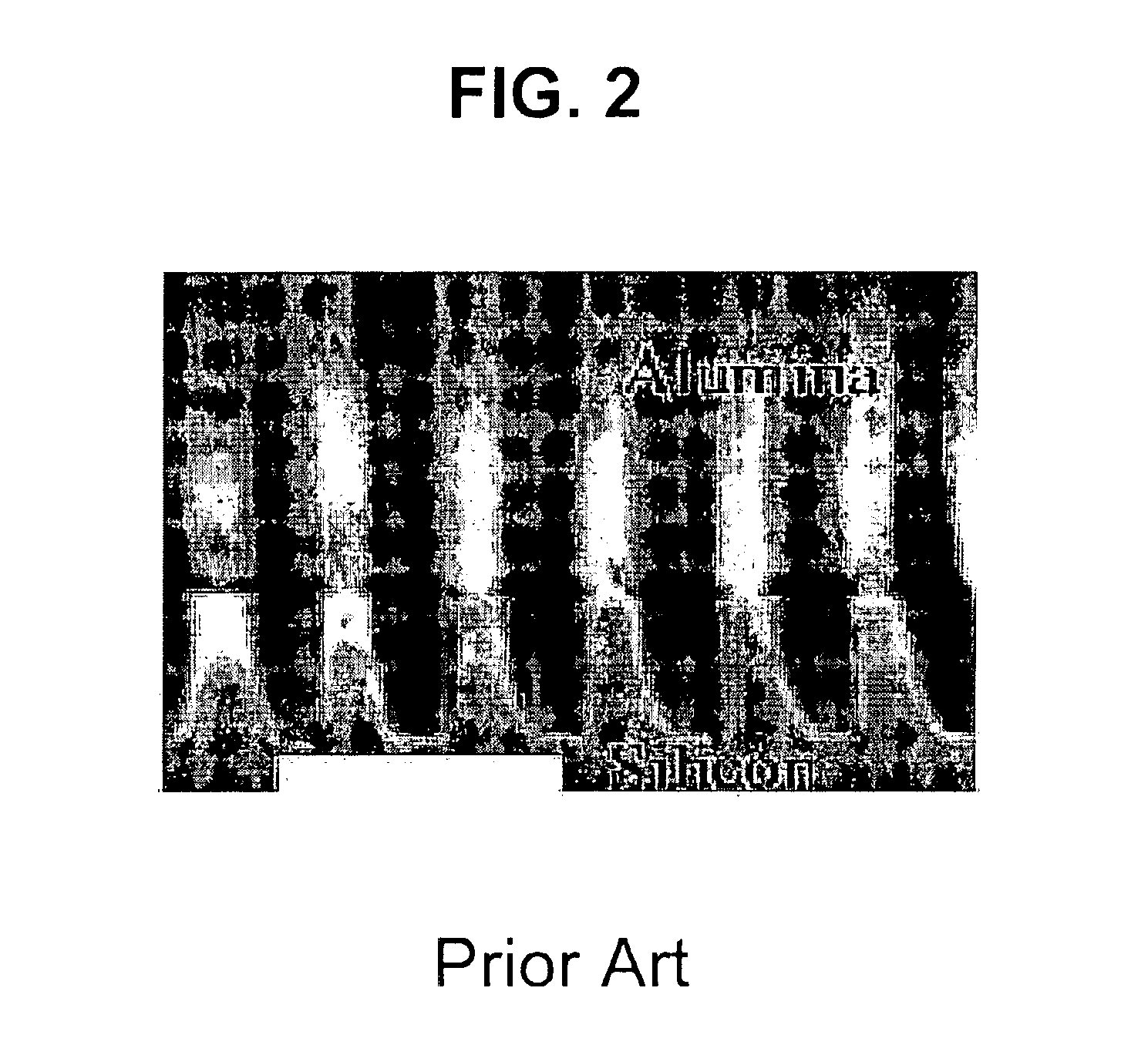
Enabling nanostructured materials via multilayer thin film precursor and applications to biosensors
A thin film based nanoporous alumina template has been developed which allows the in situ removal of an electrically insulating alumina barrier layer at the pore bases. This barrier free nanoporous system has great utility for electrodeposition of a wide variety of nanowire materials. An exemplary multilayer thin film precursor is provided comprising Al (anodization layer), Ti (diffusion barrier) and Pt (active electrode) on a Si substrate. Aluminum anodization in sulfuric acid with a subsequent applied voltage ramping program produces a Pt electrode at the base of the nanopores without the additional steps of alumina removal, barrier layer dissolution, and metal deposition onto the pore bottoms.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Mickel coated steel strap for deep drawing and preparation method
This invention provides a method for processing nickel-plated deep shocked steel band. The processing procedures are: (1). low carbon band is proceeded continuous electro-deposition of nickel; (2) under the protective atmosphere (H2 75%, N2 25%), proceeding continuous annealing, then continuous laser thermal shock treatment; (3). cold-rolling. This invention also provides the nickel-plated, deep-shocked steel band produced by above-said method. This inventive steel band has advantages of: tensile strength=270-420 MPa, the ductility ratio being not less than 30%, hardness=120-200, thickness of nickel=2-3 micrometer, porosity ratio being less than 4 holes / sq cm, extension ratio being not less than 8%, corrosion property reaching grade 8. It is can be used for the shell of cells with high performance.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Dynamic pulse plating for high aspect ratio features
A method for depositing a metal on a substrate is provided. The metal is deposited by sequentially applying a electrodeposition pulse followed by an electrodissolution pulse to the substrate. After each electrodissolution pulse an before the next electrodeposition pulse there is provided at least one time interval of zero electrical voltage or current, also known as an “off-time”, between the pulses. The first two electrodeposition pulses should preferably have the same time durations. Thereafter, the time durations of subsequent electrodeposition pulses are gradually decreased to provide a void-free and seam-free deposition of metal in high aspect ratio features.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
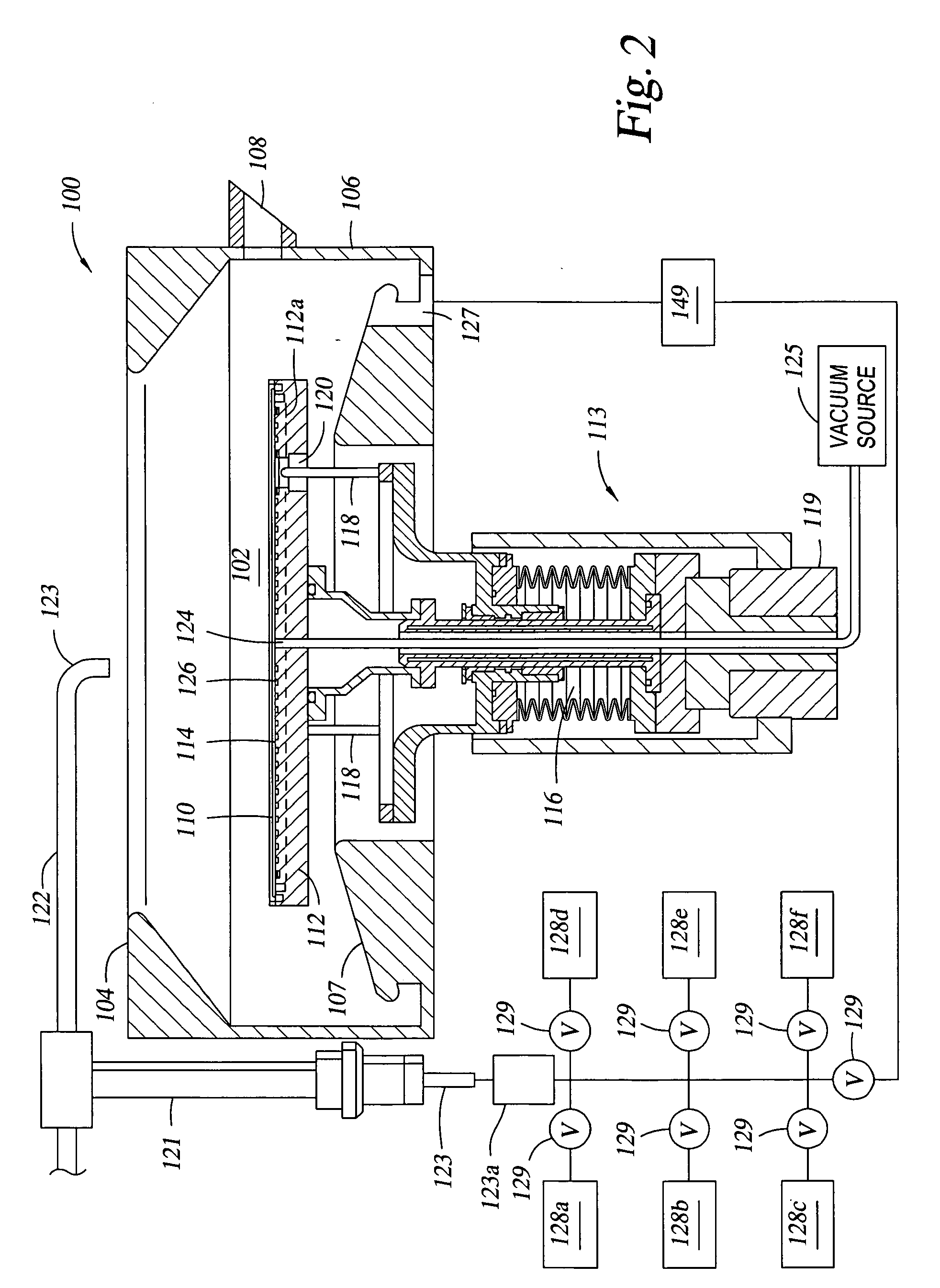
Dynamic profile anode
InactiveUS20060049038A1Minimize contaminationConstant surface profileCellsMachining electric circuitsPower flowCurrent distribution
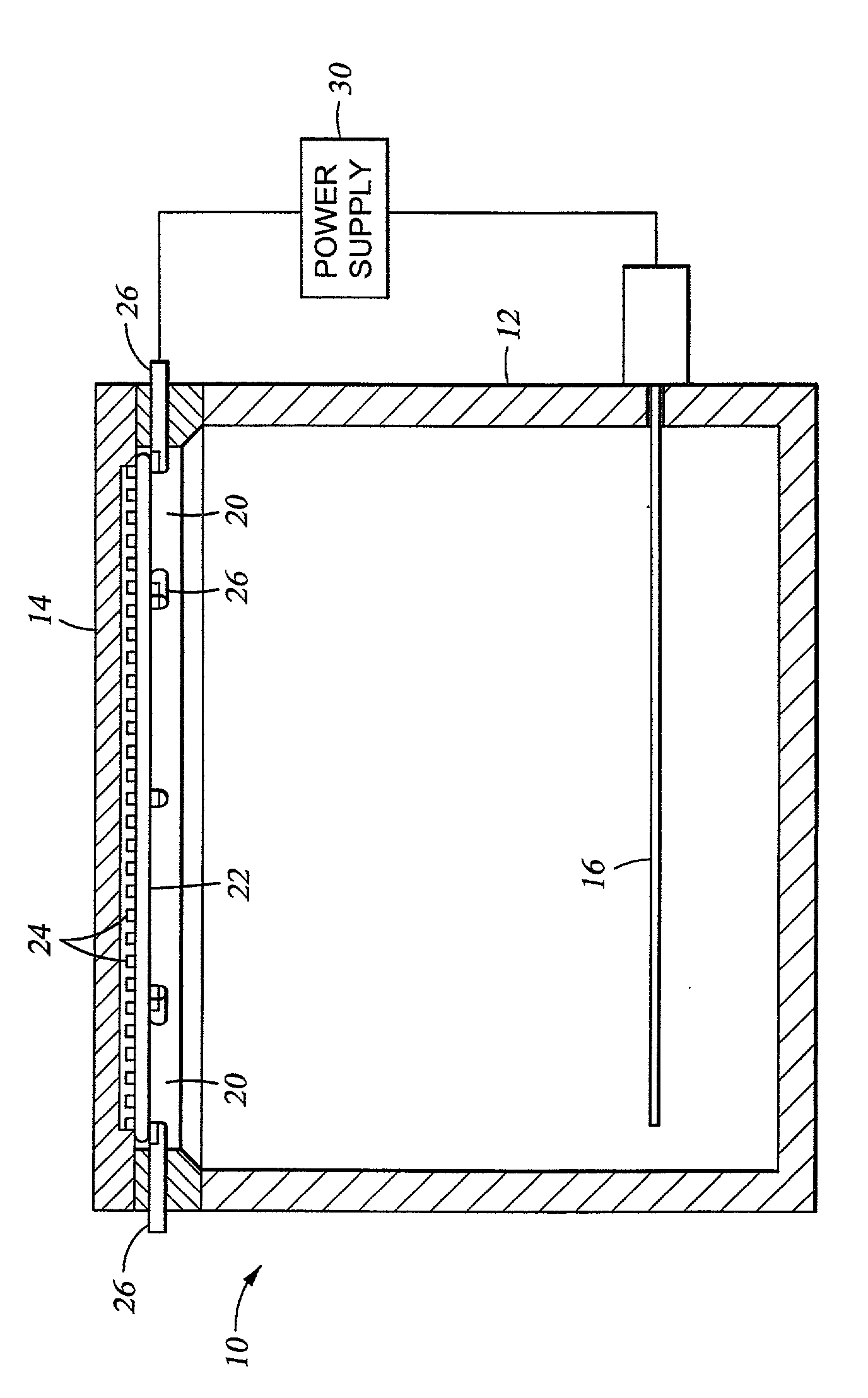
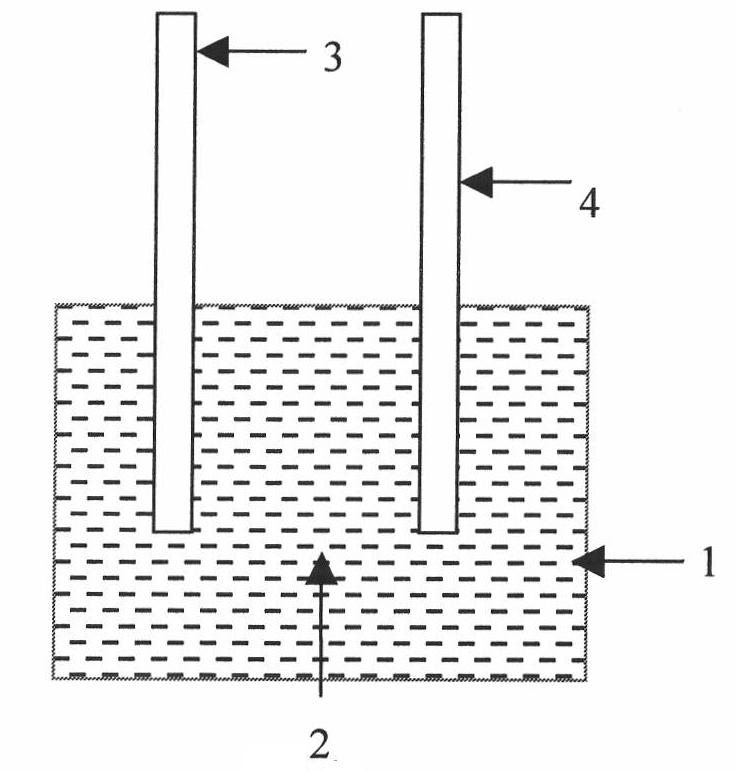
A dynamic profile anode whose shape can be varied to optimize the current distribution to a substrate during highly controlled electrodeposition. Enhanced control of the process provides for a more uniform deposit thickness over the entire substrate, and permits reliable plating of submicron features. The anode is particularly useful for electroplating submicron structures. The anode is advantageously able to use metallic ion sources and may be placed close to the cathode thus minimizing contamination of the substrate. The anode profile may be varied during the deposition process. The anode may consist of multiple concentric regions, each of which may be operated at independent voltages and currents.
Owner:SURFECT TECH
Preparation method of foam electrode for water electrolysis
InactiveCN101748426AReduce precipitation overpotentialReduce energy consumptionElectrode shape/formsHigh activityEnergy consumption
The invention discloses a preparation method of a foam electrode for water electrolysis, which belongs to the technical field of water electrolysis. Foam nickel is selected as the base material of the electrode material; oil stains on the surface of the foam nickel are removed so that the surface is clean; the foam nickel is soaked in diluted acid solution, and the surface of the foam nickel is activated; pure water is used to flush the activated foam nickel, and the foam nickel is quickly soaked into an electrodeposition tank as a cathode for electrodeposition; the active surface is prepared; the foam electrode with the active surface is thoroughly cleaned, dried and thermally treated; and the thermally treated foam material is cut to prepare the electrode material. The high-activity foam electrode material prepared through the method provided by the invention can be used for the electrode material in the electrolysis hydrogen production industry, can reduce hydrogen precipitation overpotential in the electrolysis process, reduce energy consumption, and improve the production efficiency.
Owner:GRIPM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for highly controlled electrodeposition
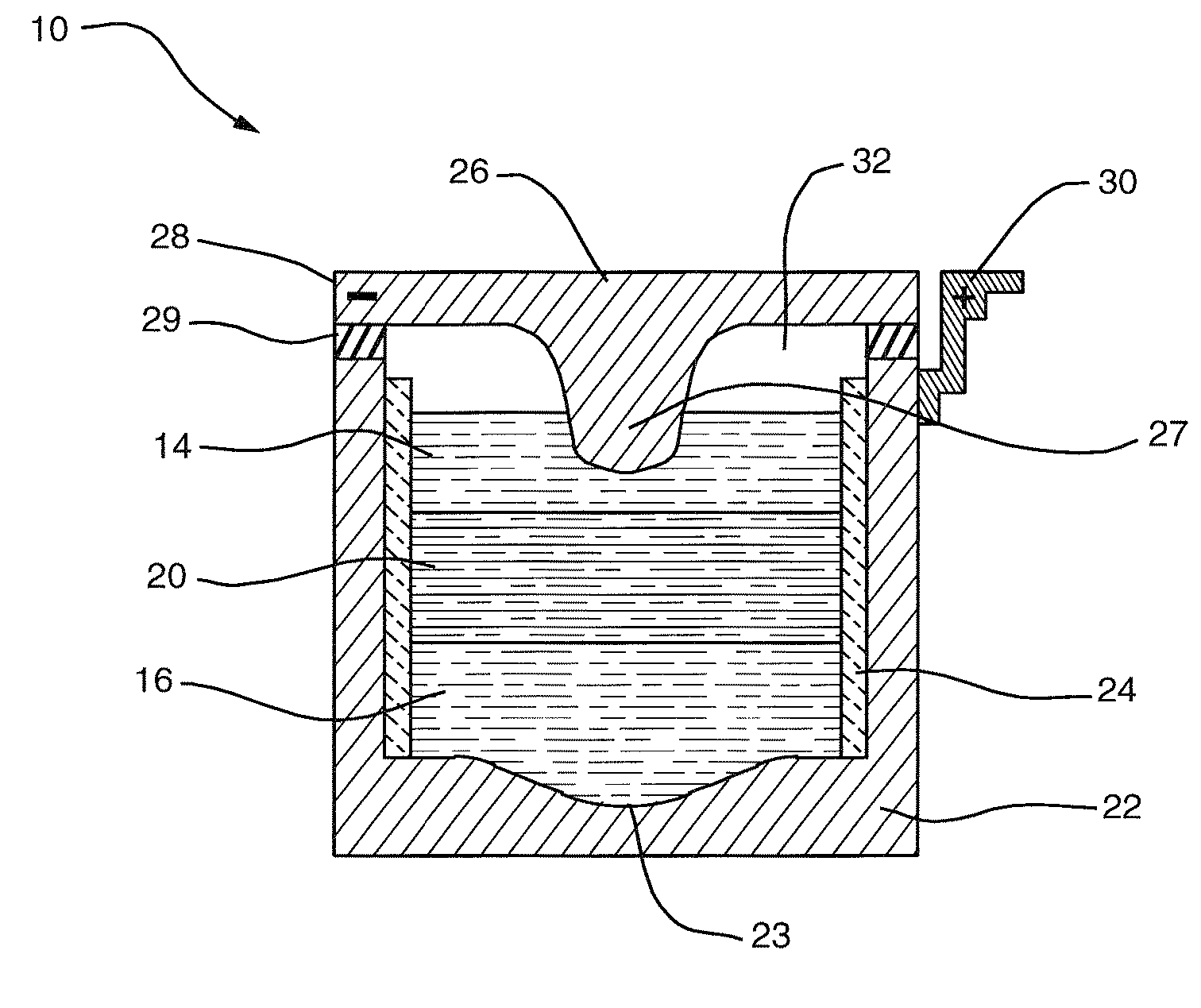
An apparatus and method for highly controlled electrodeposition, particularly useful for electroplating submicron structures. Enhanced control of the process provides for a more uniform deposit thickness over the entire substrate, and permits reliable plating of submicron features. The apparatus includes a pressurized electrochemical cell to improve plating efficiency and reduce defects, vertical laminar flow of the electrolyte solution to remove surface gases from the vertically arranged substrate, a rotating wafer chuck to eliminate edge plating effects, and a variable aperture to control the current distribution and ensure deposit uniformity across the entire substrate. Also a dynamic profile anode whose shape can be varied to optimize the current distribution to the substrate. The anode is advantageously able to use metallic ion sources and may be placed close to the cathode thus minimizing contamination of the substrate.
Owner:COOK BIOTECH +1
Solution composition and method for electroless deposition of coatings free of alkali metals
InactiveUS6911067B2Low costImprove anti-corrosion performanceAnti-corrosive paintsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless depositionMaterials science
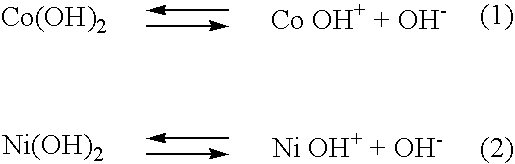
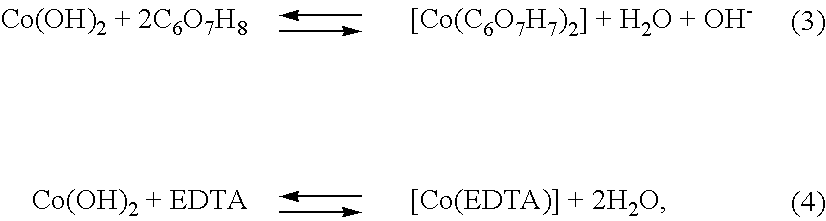
An electroless deposition solution of the invention for forming an alkali-metal-free coating on a substrate comprises a first-metal ion source for producing first-metal ions, a pH adjuster in the form of a hydroxide for adjusting the pH of the solution, a reducing agent, which reduces the first-metal ions into the first metal on the substrate, a complexing agent for keeping the first-metal ions in the solution, and a source of ions of a second element for generation of second-metal ions that improve the corrosion resistance of the aforementioned coating. The method of the invention consists of the following steps: preparing hydroxides of a metal such as Ni and Co by means of a complexing reaction, in which solutions of hydroxides of Ni and Co are obtained by displacing hydroxyl ions OH− beyond the external boundary of ligands of mono- or polydental complexants; preparing a complex composition based on a tungsten oxide WO3 or a phosphorous tungstic acid, such as H3[P(W3O10)4], as well as on the use of tungsten compounds for improving anti-corrosive properties of the deposited films; mixing the aforementioned solutions of salts of Co, Ni, or W and maintaining under a temperatures within the range of 20° C. to 100° C.; and carrying out deposition from the obtained mixed solution.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Loaded multifunctional catalysis composite material, preparation method thereof and application of composite material to catalytic removal of water pollutants
ActiveUS20190329236A1Promote full accessReduce recombination rateMaterial nanotechnologyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhoto catalysisNickel
The invention discloses a loaded multifunctional catalysis composite material, a preparation method thereof and an application of the composite material to catalytic removal of water pollutants. The preparation method includes the steps: preparing a zinc oxide nano-sheet loaded nickel foam (Ni@ZnO) composite material by an electro-deposition method; compounding molybdenum disulfide micro-nano particles on ZnO porous nano-sheets by an electro-deposition method to obtain Ni@ZnO / MoS2. The composite material Ni@ZnO / MoS2 combines the advantages of components such as nickel foam, the zinc oxide nano-sheets and molybdenum disulfide from the point of material performances, high catalytic degradation activity and recycled performances are achieved, photo-catalysis and electro-catalysis are combined from the point of material application, and the catalytic activity of the composite material is improved by the aid of synergistic effects of photo-catalysis and electro-catalysis.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
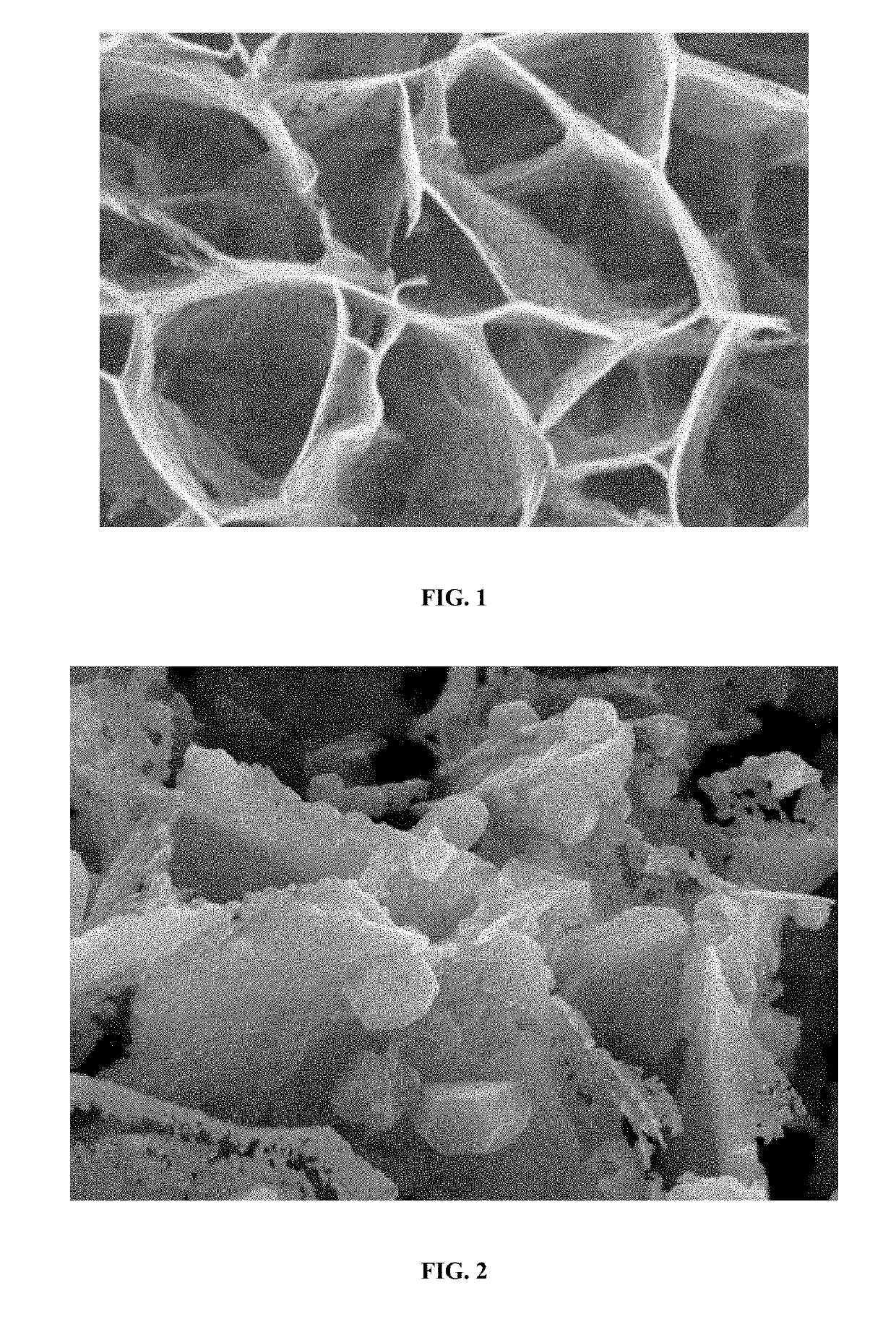
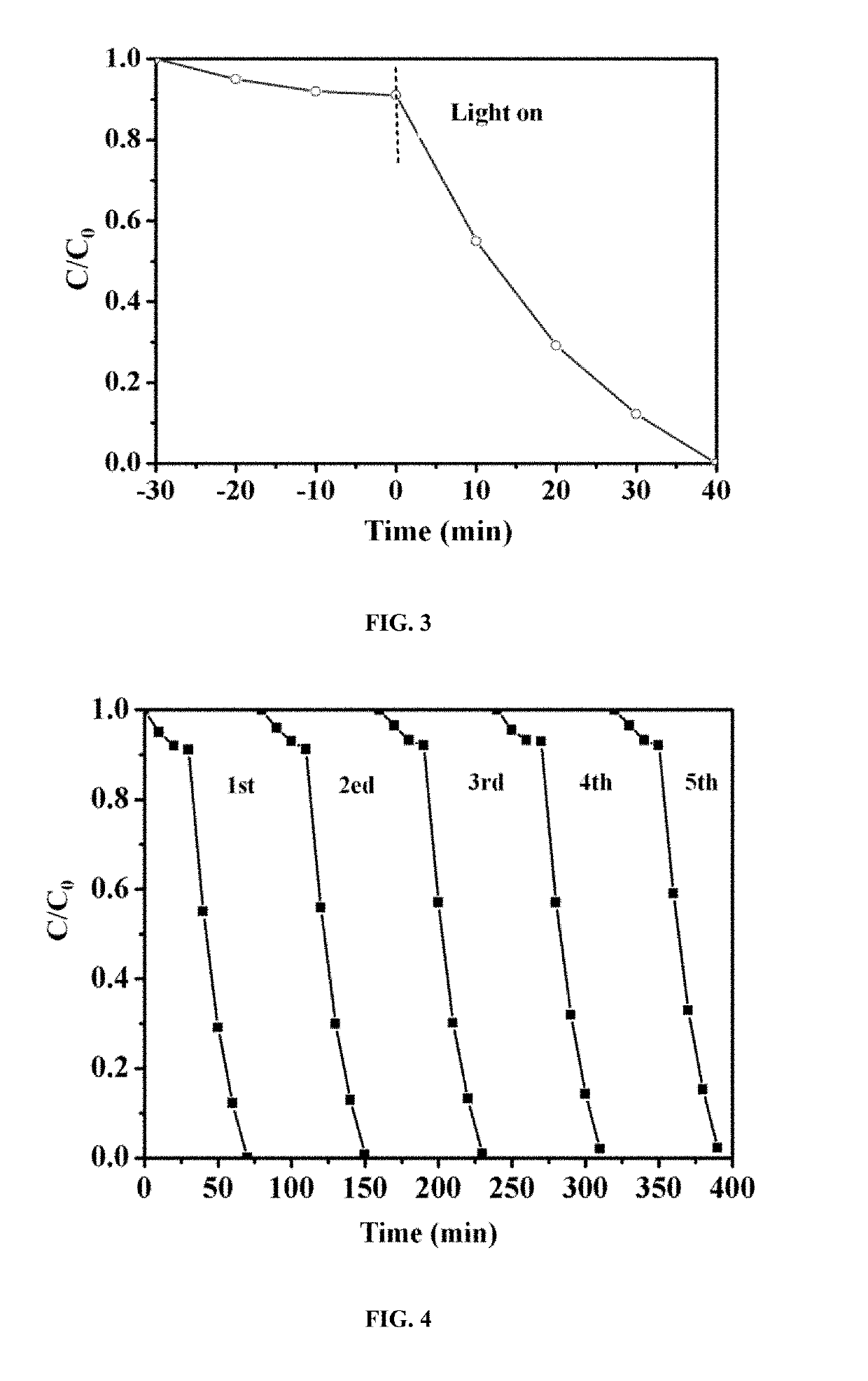
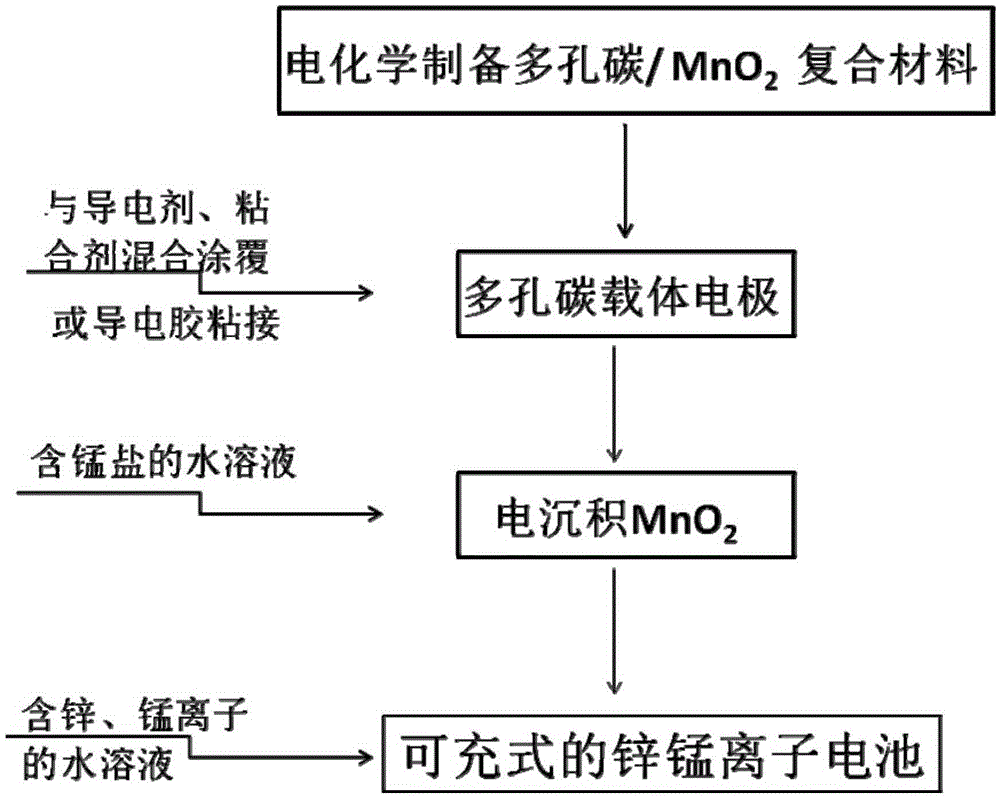
Porous carbon/manganese dioxide composite electrode, preparation method of porous carbon/manganese dioxide composite electrode and rechargeable zinc-manganese ion battery
ActiveCN105390697AControl particle sizeControl distribution densityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureSupporting electrolyteElectrolytic agent
The invention relates to a porous carbon / manganese dioxide composite electrode, a preparation method of the porous carbon / manganese dioxide composite electrode and a rechargeable zinc-manganese ion battery, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemistry. Porous carbon with high specific surface area and favorable electric conductivity is taken as a carrier electrode; the carrier electrode is electrolyzed in flowing water solution which contains a manganous salt precursor and a supporting electrolyte; and manganese dioxide is deposited on the surface of the porous carbon. Through selecting the concentration of the manganous salt as well as the concentration, pH value, current, temperature and time of the supporting electrolyte in the electric deposition process, a porous carbon / manganese dioxide composite is prepared, so that the regulation and control of the particle size and distribution density of the manganese dioxide are realized, and the active substance utilization rate of the manganese dioxide is improved. By taking the obtained porous carbon / manganese dioxide composite as the electrode, and by using the water solution containing zinc and manganese ions as electrolyte to assemble secondary batteries, the specific capacity of the electrode is above 200mAh / g and the electrode has the characteristics of being high in capacity and long in service life. The preparation method is easy to operate, green and environmental.
Owner:中国人民解放军军事科学院防化研究院
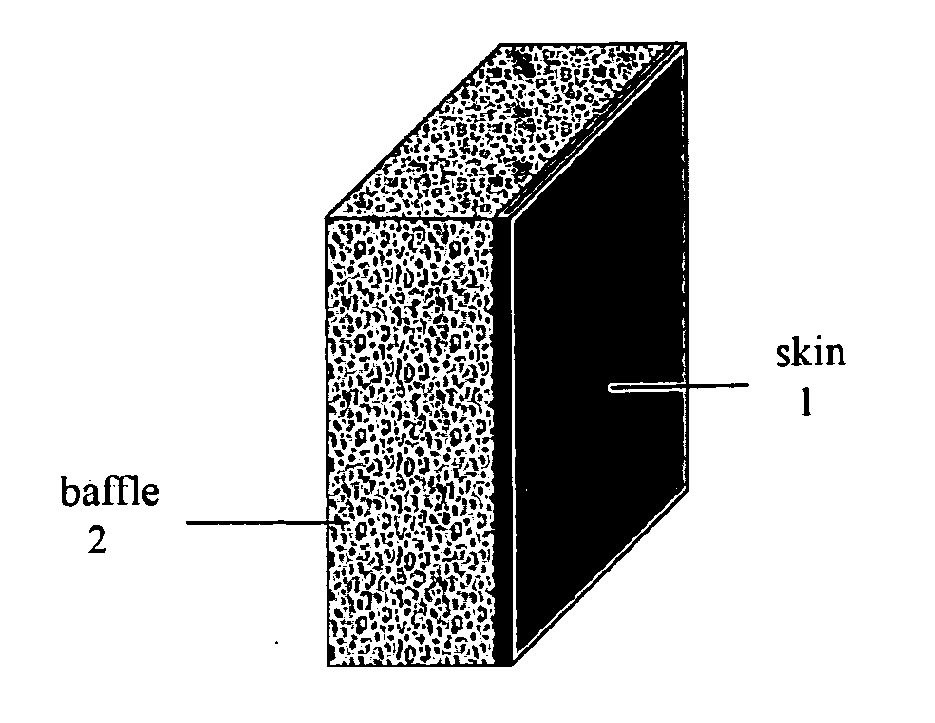
Nanolaminate-reinforced metal composite tank material and design for storage of flammable and combustible fluids
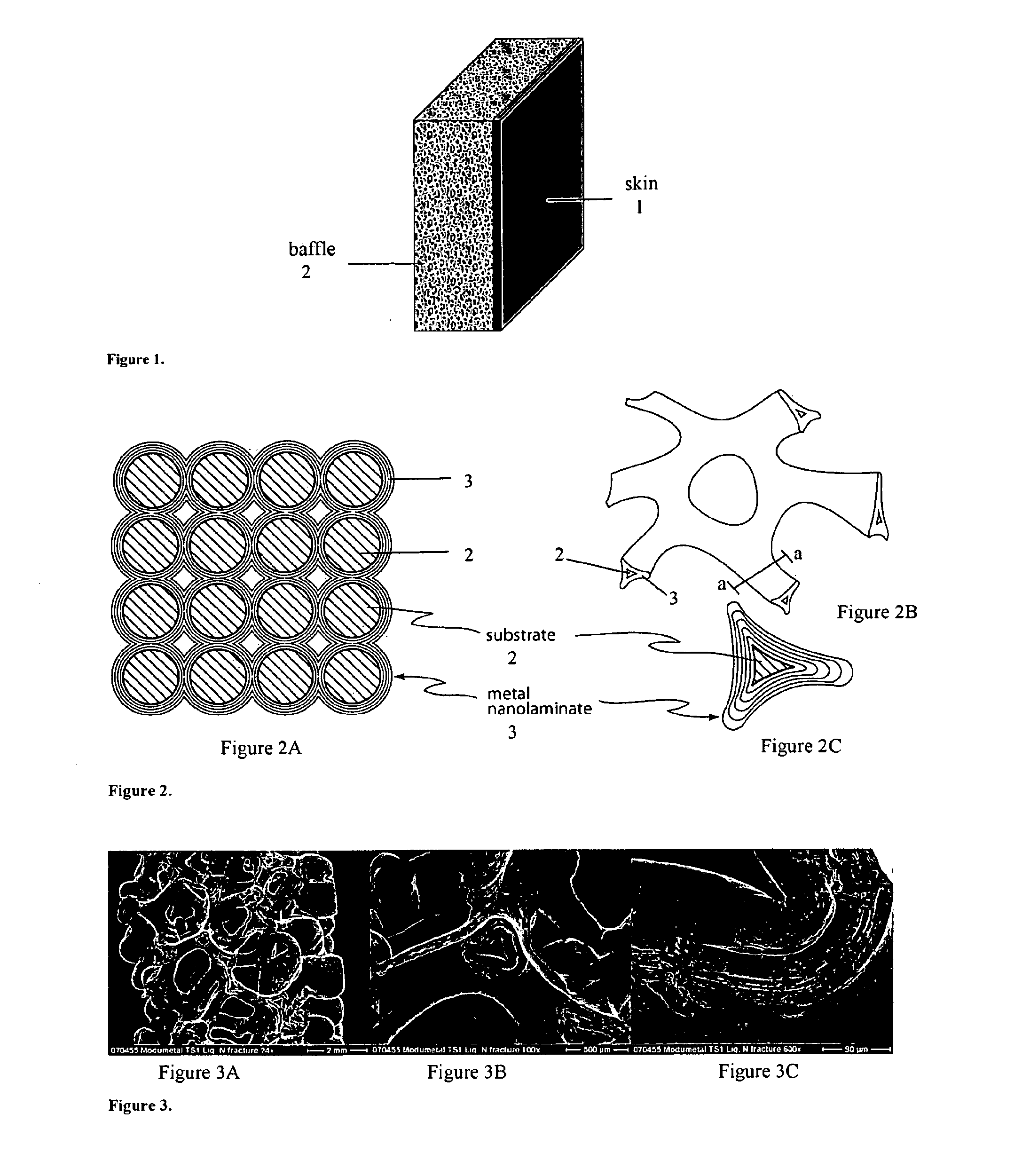
ActiveUS20110186582A1Raise the ratioGreat vehicle traveling distanceElectrolytic coatingsLarge containersFuel tankVoid space
An improved fuel tank and method of forming a fuel tank utilize reinforced porous metal composite materials. In one embodiment, the composite material includes a fully dense, fluid-impermeable skin (1) combined with a porous metal baffle (2). The skin (1) and baffle (2) may be formed as a single monolithic system via electrodeposition of a nanolaminate material into at least a portion of open, accessible void space within a porous preform (e.g., a metal foam preform) and on the exterior surface of the preform to form the fluid-impermeable skin (1).
Owner:MODUMETAL LLC
Electrolyte for the galvanic deposition of low-stress, crack-resistant ruthenium layers
InactiveUS6117301AAnti-corrosive paintsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPyridiniumRuthenium
An electrolyte for the galvanic deposition of stress-relieved, crack-resistant ruthenium layers containing ruthenium in complexed form. The additive for the electrolyte is pyridine or an N-alkylated pyridinium salts of formula I wherein R(-) is -(CH2)3-SO3(-), -CH2-CHOH-CH2-SO3(-), or R' and H is, alkyl with 1-6 C atoms, -CH=CH2, or -CO2Na.
Owner:DEGUSSA GALVANOTECHN
Multilayer ceramic capacitor with terminal formed by electroless plating
ActiveUS20040066605A1Little effect on capacitanceIncrease capacitanceFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricMetallurgyCeramic capacitor
A terminal to, most commonly, a ceramic capacitor, most commonly a multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC), is formed by electroless plating, also known as electroless deposition or simply as electrodeposition. In the MLCC having a multiple parallel interior plates brought to, and exposed at, at least one, first, surface, an electrically-conductive first-metal layer, preferably Cu, is electrolessly deposited upon this first surface directly in contact with, mechanically connected to, and electrically connected to, the edges of these interior plates. Lateral growth of the electrolessly-deposited first-metal is sufficient to span from exposed plate to exposed plate, electrically connecting the plates. One or more top layers, preferably one of Ni and one of Sn and Pb, are deposited, preferably by plating and more preferably by electrolytic plating, on top of the electrolessly-deposited Cu.
Owner:PRESIDIO COMPONENTS
Diesel soot filter
InactiveUS6991668B2High porosityImprove removal efficiencyCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentEngineeringSoot
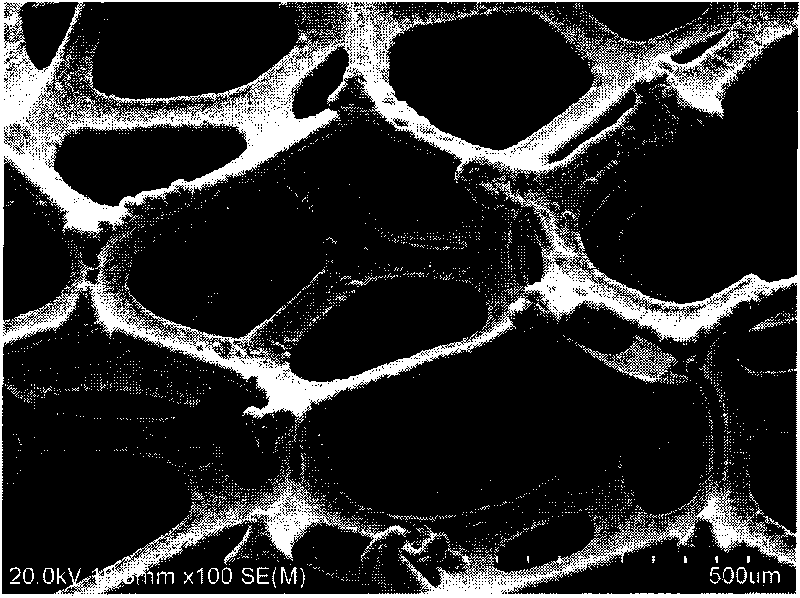
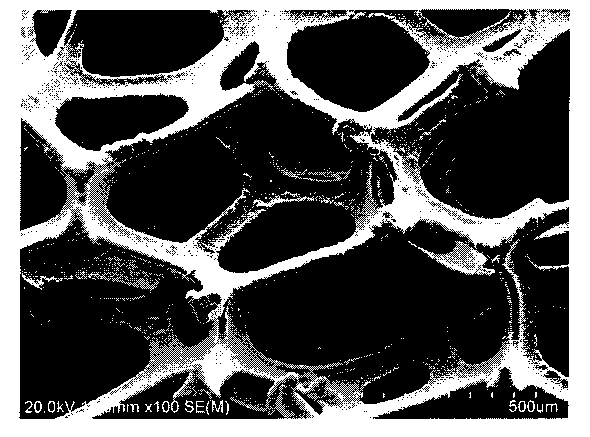
A filter for removing soot from the exhaust gases from a diesel engine. The filter incorporates two elements. The first element is a flow-through filter element incorporating a porous metal substrate formed by electrodepositing a metal such as nickel in the interstitial spaces of a packed array of electrically nonconductive particles of a material and then removing the material of the particles to produce the porous metal substrate. The second element is a hollow body having an inlet port and an outlet port, the filter element being positioned in and sealed to the hollow body so that diesel exhaust gases directed into the inlet port of the hollow body flow through the porous metal substrate from the inlet side of the porous metal substrate to the outlet side of the porous metal substrate and then out the outlet port of the hollow body. The bulk density of the porous metal substrate is less than 40% of the density of the metal of the substrate. The average pore diameter of the pores at the inlet side of the porous metal substrate is greater than one micrometer. The area of the pores of the inlet side of the porous metal substrate is greater than about 35% the area of the inlet side of the porous metal substrate.
Owner:TOWSLEY FR E
Preparation method of high-hardness Cu-SiC nanometer compound plating layer and special device thereof
InactiveCN101717977AHigh content of nanoparticlesEvenly distributedElectrolytic coatingsNanoparticleCrystal structure
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-hardness Cu-SiC nanometer compound plating layer and a special device thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: pretreating nanometer SiC particles, preparing an electrolytic solution containing the nanometer SiC particles, primarily treating a cathode plate and carrying out electrolytic deposition for preparing the high hardness Cu-SiC nanometer compound plating layer. In the preparation method of a high-hardness Cu-SiC nanometer compound plating layer, secondary reunion of the nanometer particles can be effectively avoided, the electrolytic solution spray deposition process can be higher than the cathode current density of the common electrodeposition processes for carrying out electrolytic deposition, and therefore, high speed electrolytic deposition on unit area of the cathode surface can be realized. The nanometer composite plate prepared by the invention has the advantages of high content of nanometer particles, uniform distribution of nanometer particles, high hardness, compact crystal structure, good surface quality, and the like.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Multi-parameter water quality monitoring integrated microarray electrodes and preparation method
InactiveCN102495119ARich sourcesMature processing technologyDecorative surface effectsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsInsulation layerWater quality
The invention relates to multi-parameter water quality monitoring integrated microarray electrodes and a preparation method. The invention is characterized in that the microarray electrodes are fabricated on an oxidized wafer. According to the invention, a Pt thin film is used as a substrate of the microarray electrodes, photosensitive polyimide is used as an insulation layer, electrode sites are exposed by using photoetching, and other parts of the microarray electrodes are insulated; an electrochemical modification method is used for electrodeposition of Ag / AgCl and IrOx films on bare electrodes so as to respectively form reference electrodes and pH test electrodes, thereby realizing determination of temperature, oxidation reduction potentials, conductivity and pH values. The preparation method comprises production of the micro-array electrodes, preparation of the Ag / AgCl reference electrodes and preparation of the pH electrodes. Integration and miniaturization of the microarray electrodes provided in the invention are convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metal surface coating method and application thereof
ActiveCN102321900AImprove the protective effectZero pollutionElectrolytic inorganic material coatingSilanesHigh surface
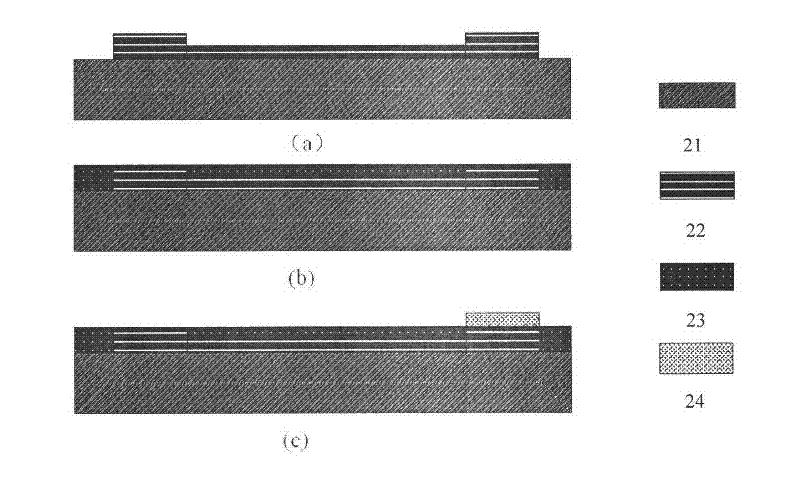
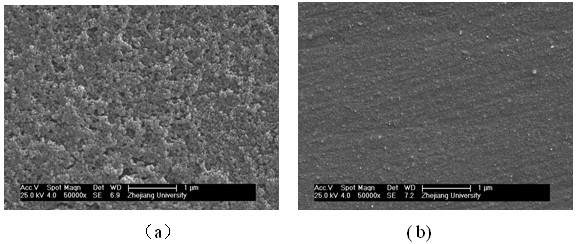
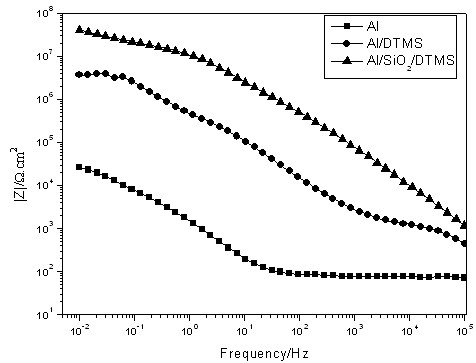
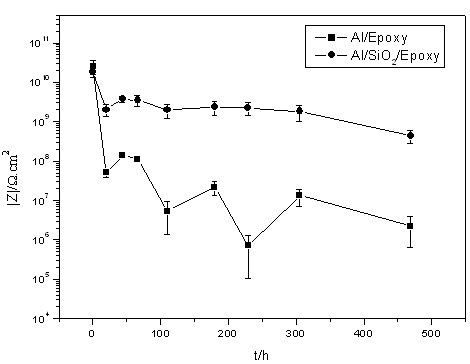
The invention discloses a metal surface coating method and an application thereof. An inert, porous nano-oxide film is deposited firstly on a metal substrate by an electrodeposition method, and then a protective layer is covered on the surface. The nano-oxide film is prepared on a metal surface by precursor aqueous solutions of SiO2, TiO2 or ZrO2 through an electrodeposition method. The protective layer used for covering is a commonly-used organosilane film, inorganic / organic hybridized silane film or common organic coating. The metal surface coating and protecting technology provided by the invention has a simple process, low cost, is especially green and environment-friendly, has wide adaptability, and almost has no selectivity for the types of the metal substrate or subsequent protective layers. The nano-oxide film pretreatment layer prepared by electrodeposition has good bonding force with the metal substrate, high surface energy, a rough and porous surface, and large specific surface area, and thus can tightly bond with the subsequent covering layer, which greatly improves the corrosion resistance of the whole protective layer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
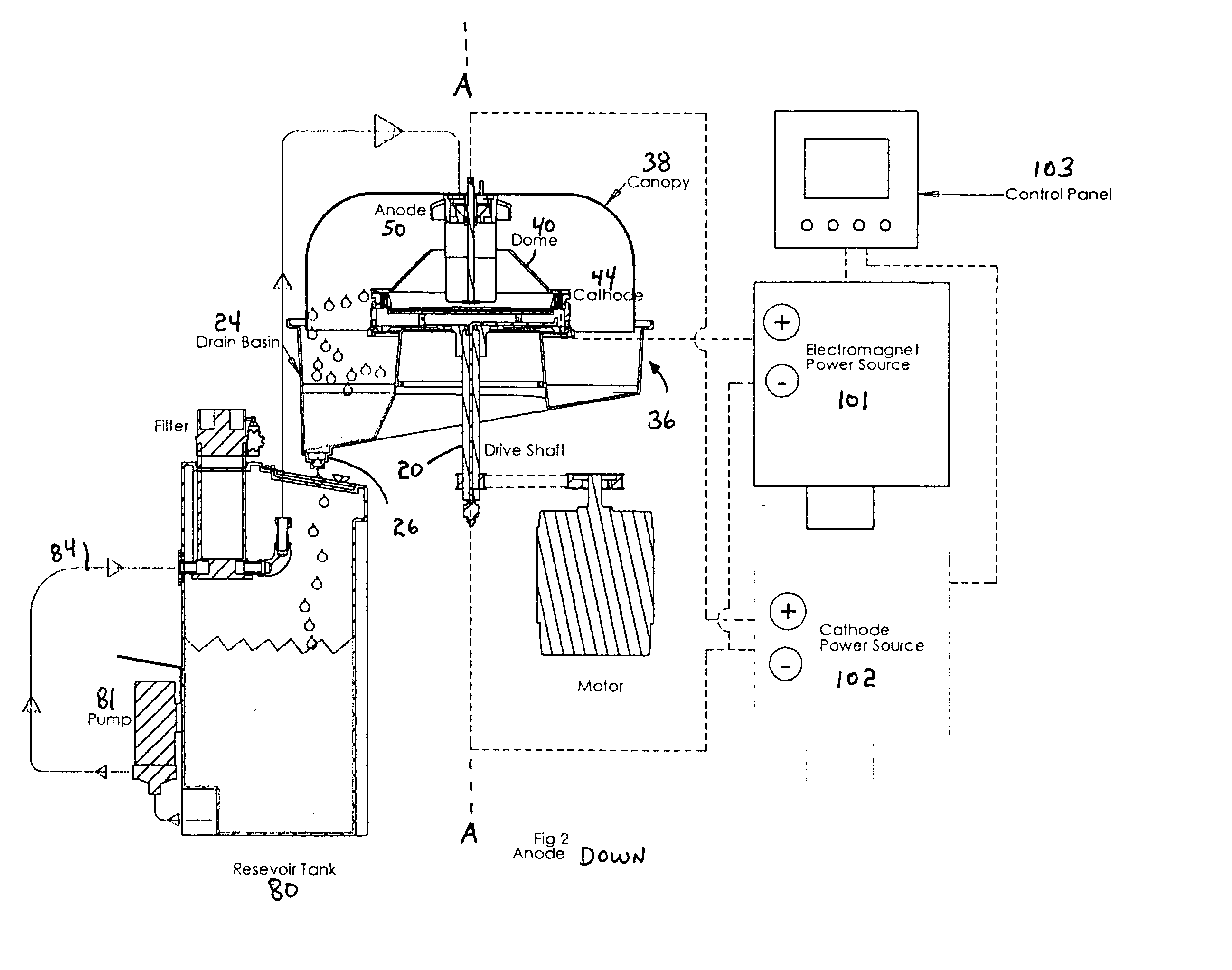
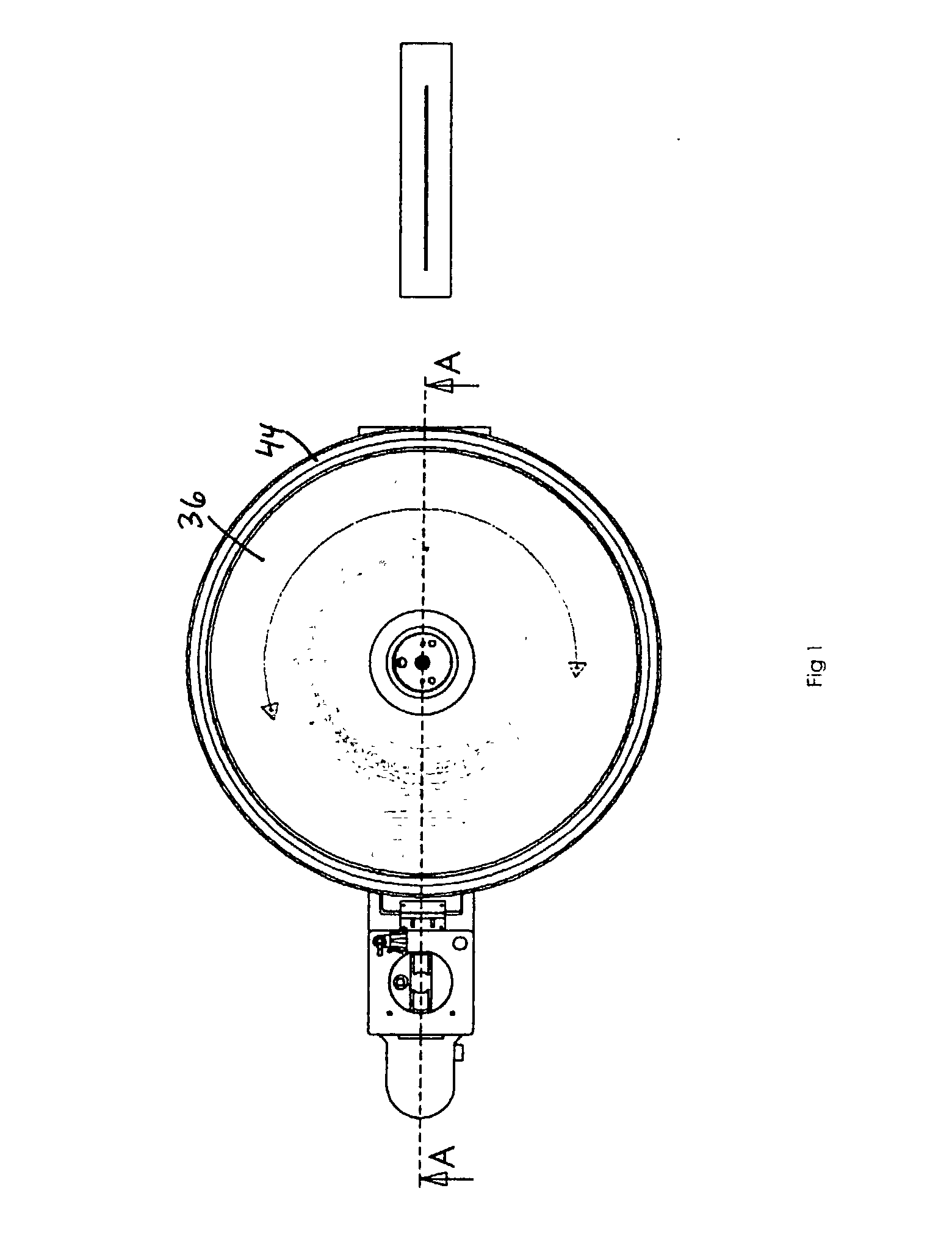
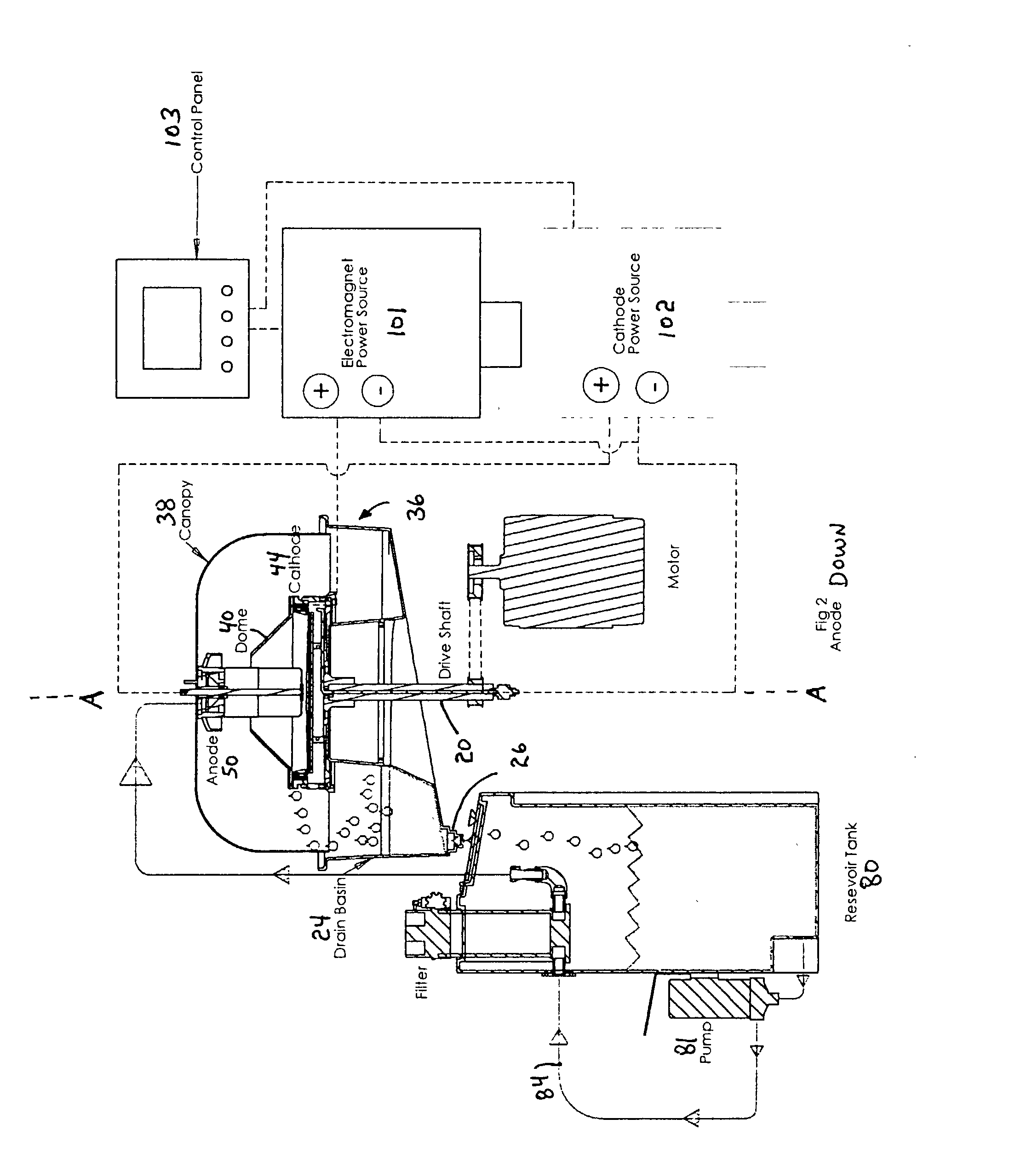
Electrodeposition apparatus and method using magnetic assistance and rotary cathode for ferrous and magnetic particles
A method and apparatus for microencapsulating or electrodeposited coating of ferromagnetic and soft-magnetic sub-micron or nano sized powderized material comprising use of a rotary flow-through device assisted by an electromagnet within the electrode ring to alternately position the powder at the face of the cathode ring and electroplate the powder and reorient it prior to another repositioning. The invention is also of a process and apparatus for forming a strip, mesh, or film from magnetic powderized material in an organized bipolar arrangement, which is particularly useful for electroforming foils with the magnetic particles positioned in a monolayer within a multilayer metallic foil.
Owner:SURFECT TECH
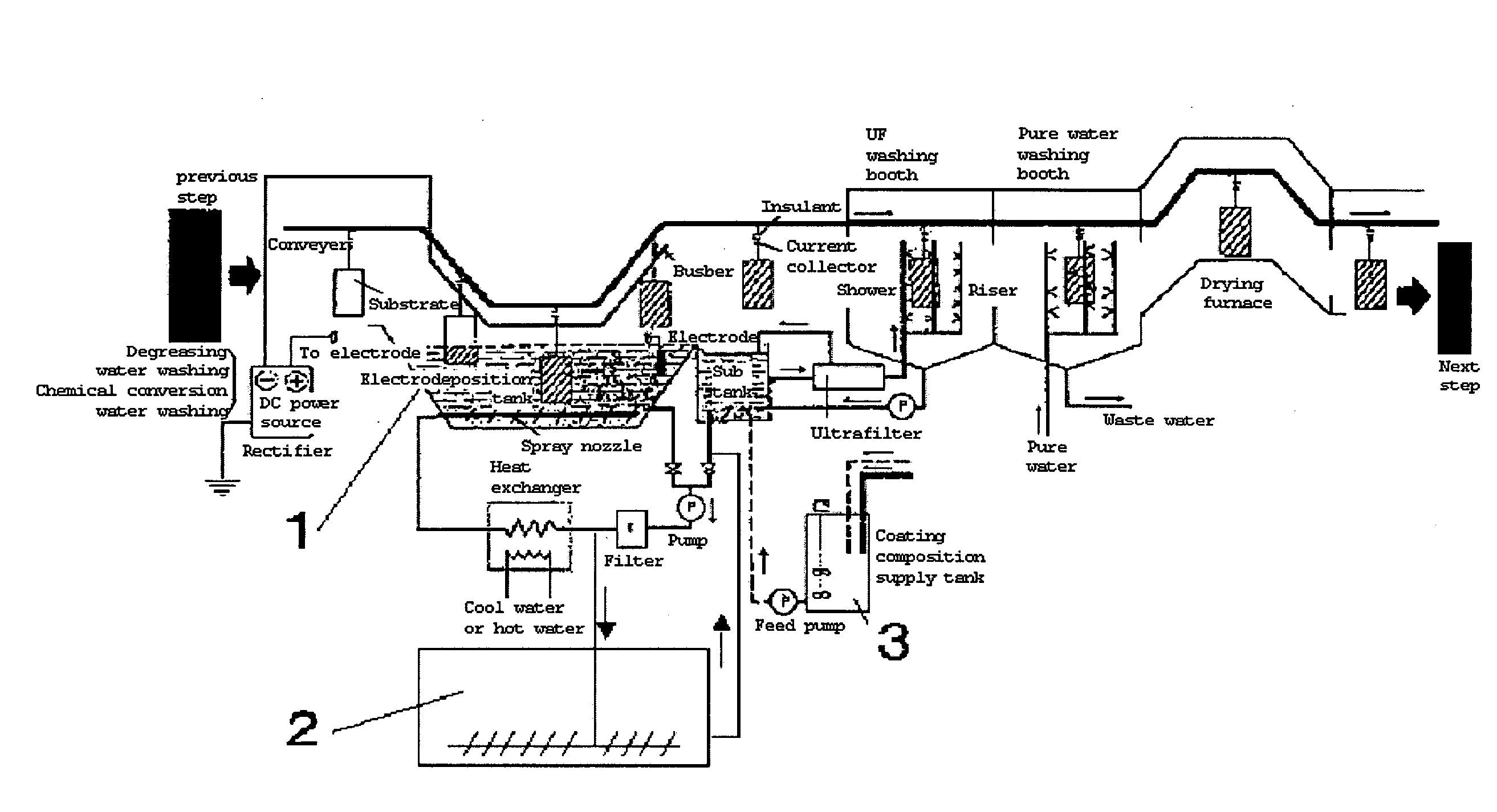
Method for forming multilayer coating film and coated article
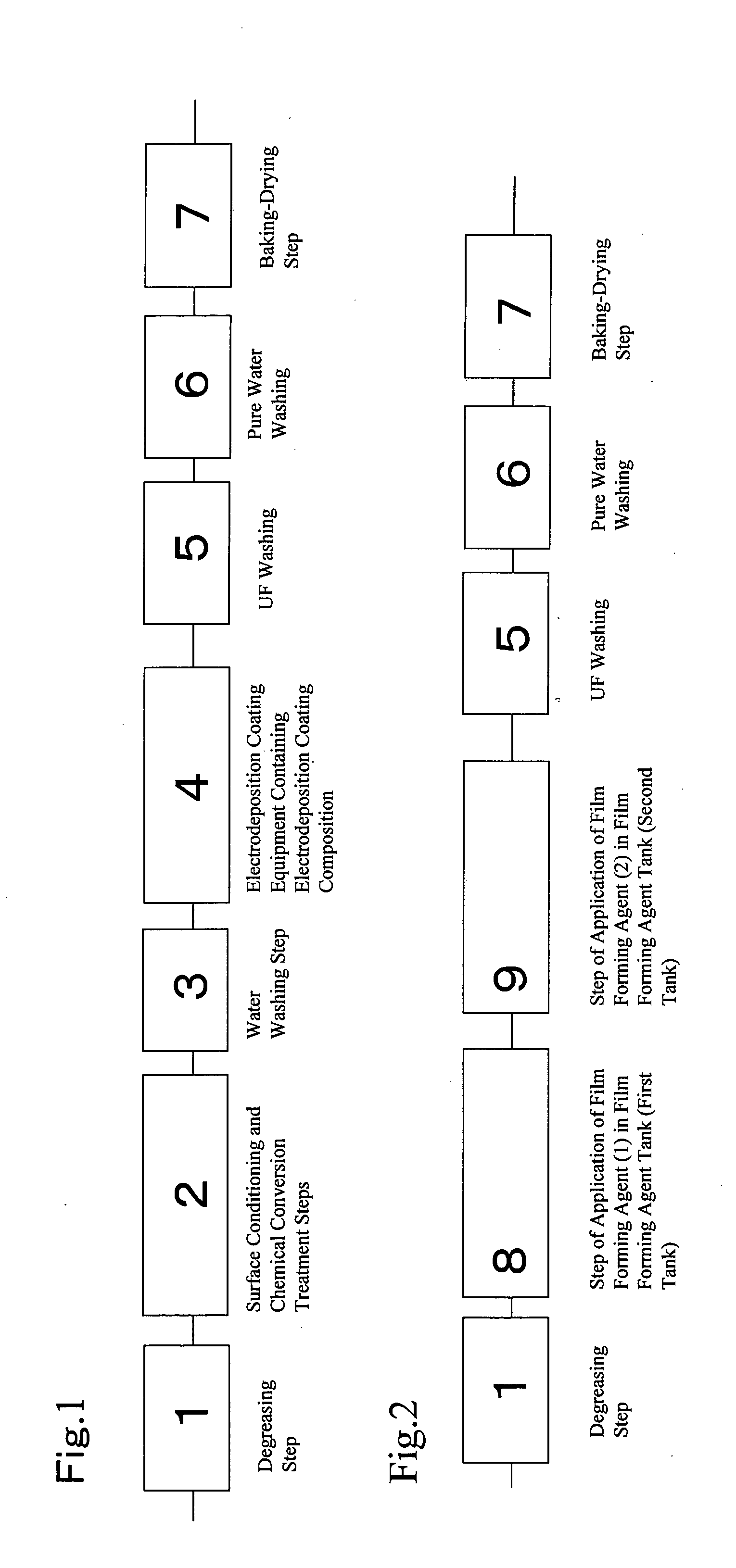
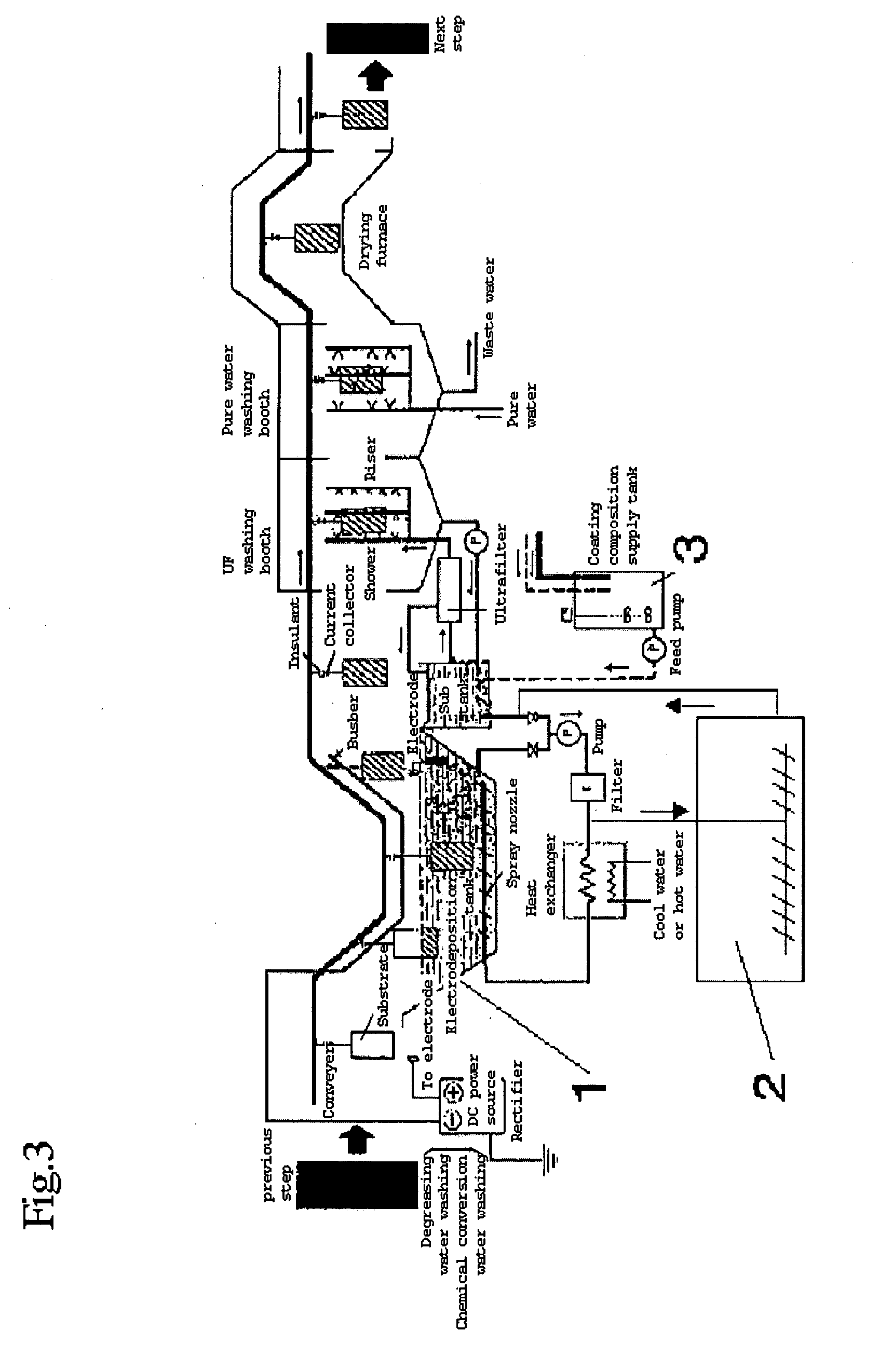
ActiveUS20090101512A1Raise the gradeCorrosion resistanceSurface reaction electrolytic coatingElectrophoretic coatingsPhysical chemistryFilm-forming agent
An object of the present invention is to provide a coated article having excellent finish and corrosion resistance unaffected by a chemical conversion coating solution even if water washing after a pretreatment step is omitted and a pretreatment solution is carried as a contaminant into an electrodeposition coating composition.The present invention provides a method for forming a multilayer coating film comprising a chemical conversion coating film (F1) and an electrodeposition coating film (F2); the method comprising the following steps.Step 1: immersing a metal substrate in a coating film forming agent (1) as a chemical conversion coating solution to form a chemical conversion coating film (F1); andStep 2: without water washing, subjecting the metal substrate to electrodeposition coating using a coating film forming agent (2) as a cationic electrodeposition coating composition (I) to form an electrodeposition coating film (F2).
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com