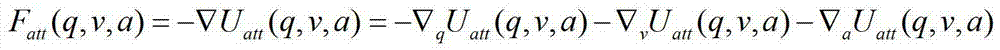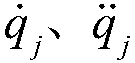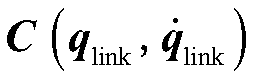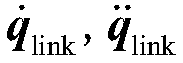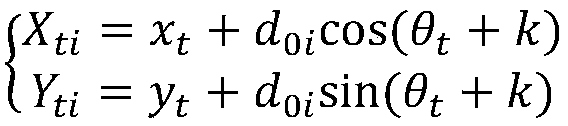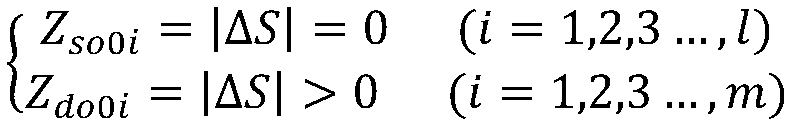Patents
Literature
291 results about "Robot dynamic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
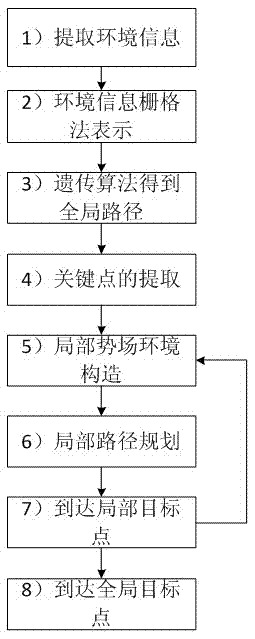
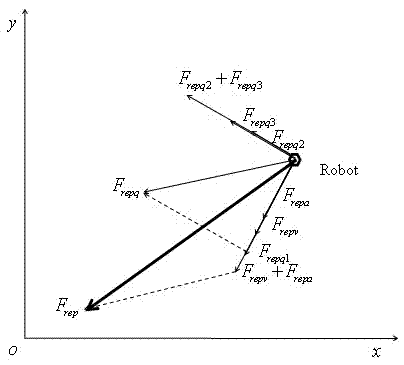
Mixed robot dynamic path planning method
InactiveCN103092204AIncrease flexibilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsGlobal planningProcess dynamics
The invention discloses a mixed robot dynamic path planning method which is capable of being applied on the condition that a part of environment information is known, and unknown dynamic and static obstacles exist at the same time. Aiming at the conditions, the mixed robot dynamic path planning method comprises the following steps: utilizing a genetic algorithm (GA) as a global planning method to obtain global paths, and then conducting local planning by means of an improved artificial potential field method. According to the mixed robot dynamic path planning method, in local planning, speed and acceleration information of a robot and a barrier is considered, and therefore the mixed robot dynamic path planning method has better effects on processing dynamic path planning. In addition, effects of global planning path for local planning are also considered. The mixed robot dynamic path planning method is ease to achieve, robot paths obtained are more optimized, and meanwhile good flexibility is shown in the application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
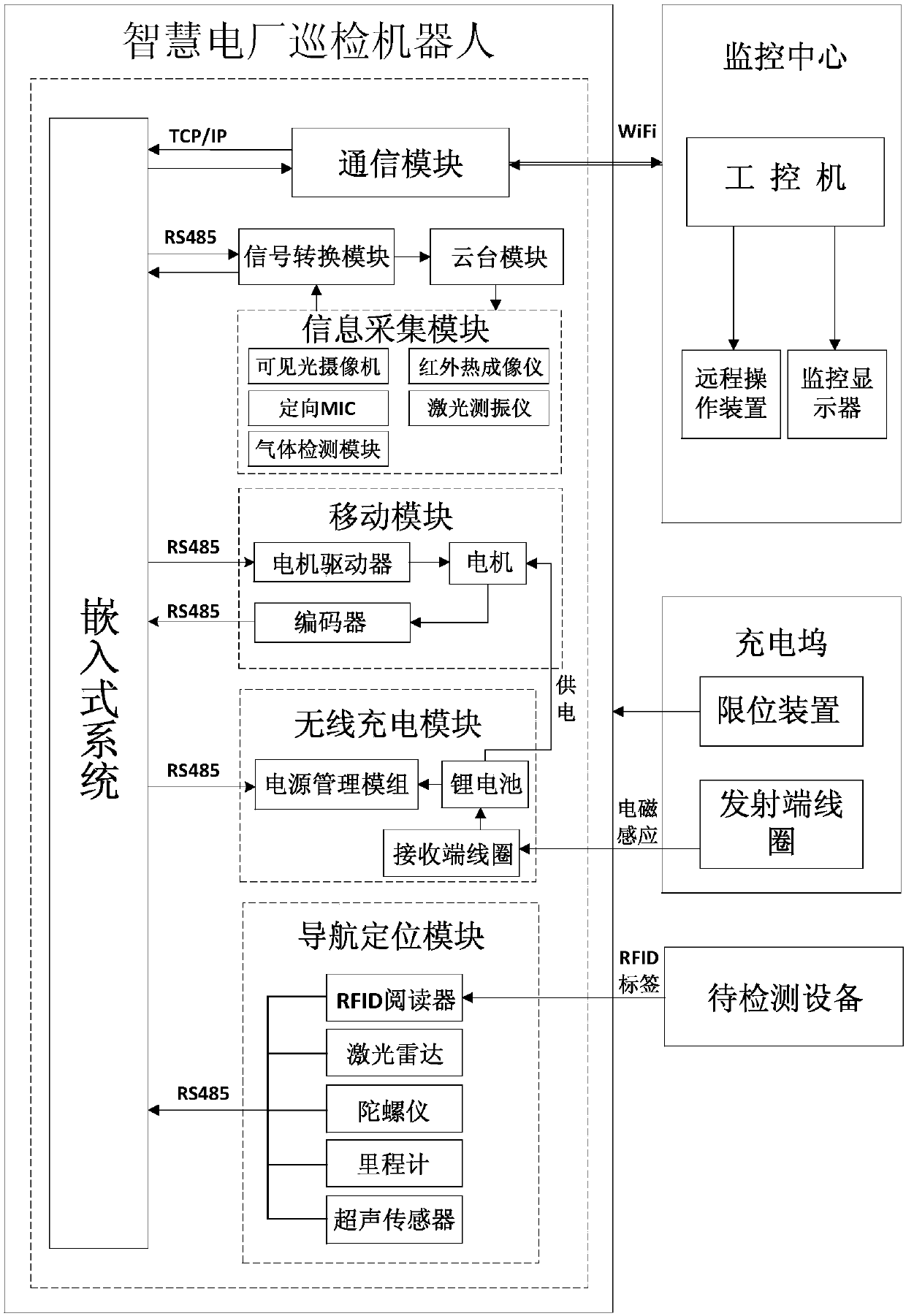
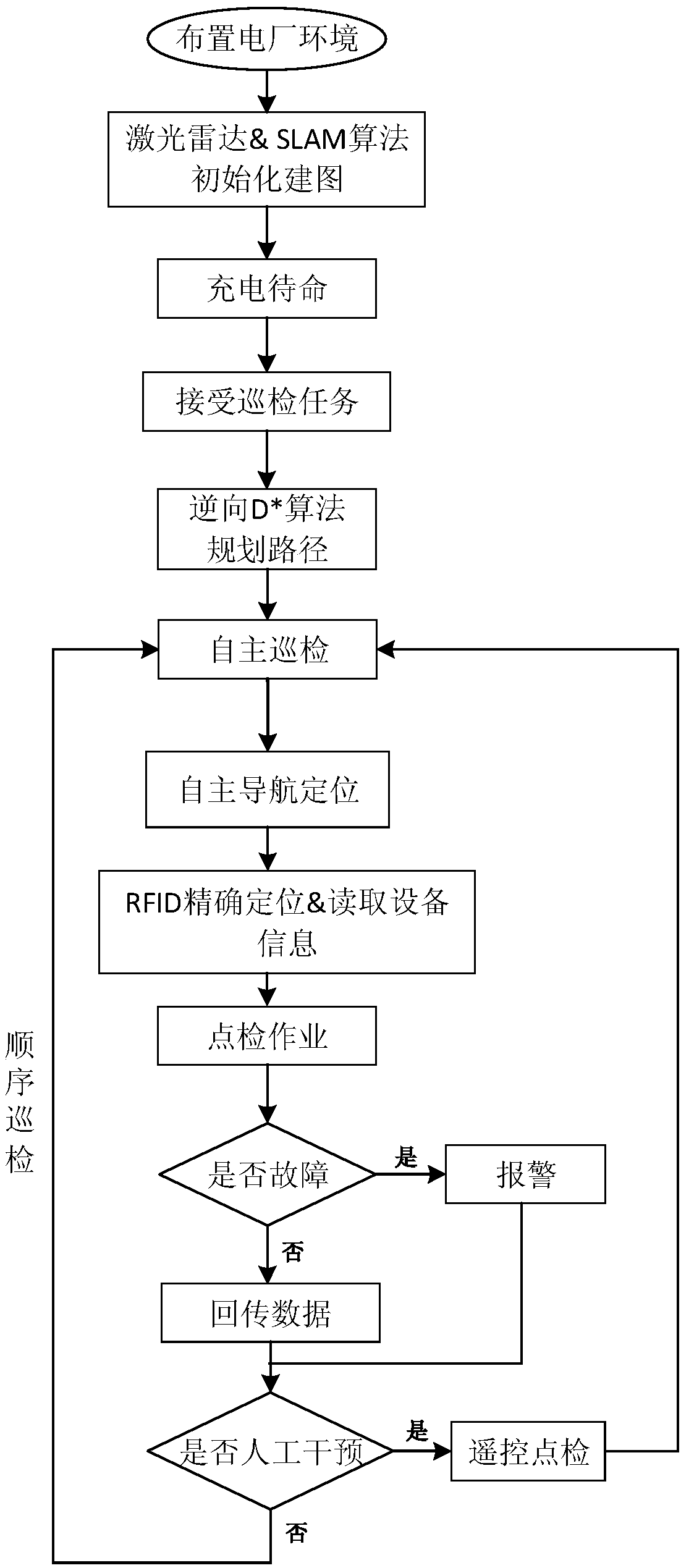
Intelligent power plant autonomous polling robot polling system and method
InactiveCN109599945AFast and convenient autonomous cruiseLow costBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerUltrasonic sensorGyroscope
The invention discloses an intelligent power plant autonomous polling robot polling system and method. The method comprises the following steps: integrating a laser radar and a gyroscope, incrementally a raster map by using the laser radar through a SLAM algorithm; searching a middle target location with the minimum target cost estimation by using a reverse D* algorithm, thereby realizing robot dynamic path planning and positioning; reading a label through a RFID reader to acquire information needing to detect in the equipment; detecting an obstacle by using an ultrasonic sensor in the robot running process, and autonomously eluding environment obstacle in the path by combining the SLAM algorithm, thereby realizing autonomous navigation and movement in the complex power plant environment.Multiple non-contact sensors satisfy spot check demands of various sets of equipment. The polling system can automatically poll in the plant, the artificial control is unnecessary, the polling data istransmitted to a control center in real time, and the polling system can give an alarm when abnormity occurs; the polling system can replace the artificial polling, improve the polling efficiency, and improve the security of the power plant equipment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
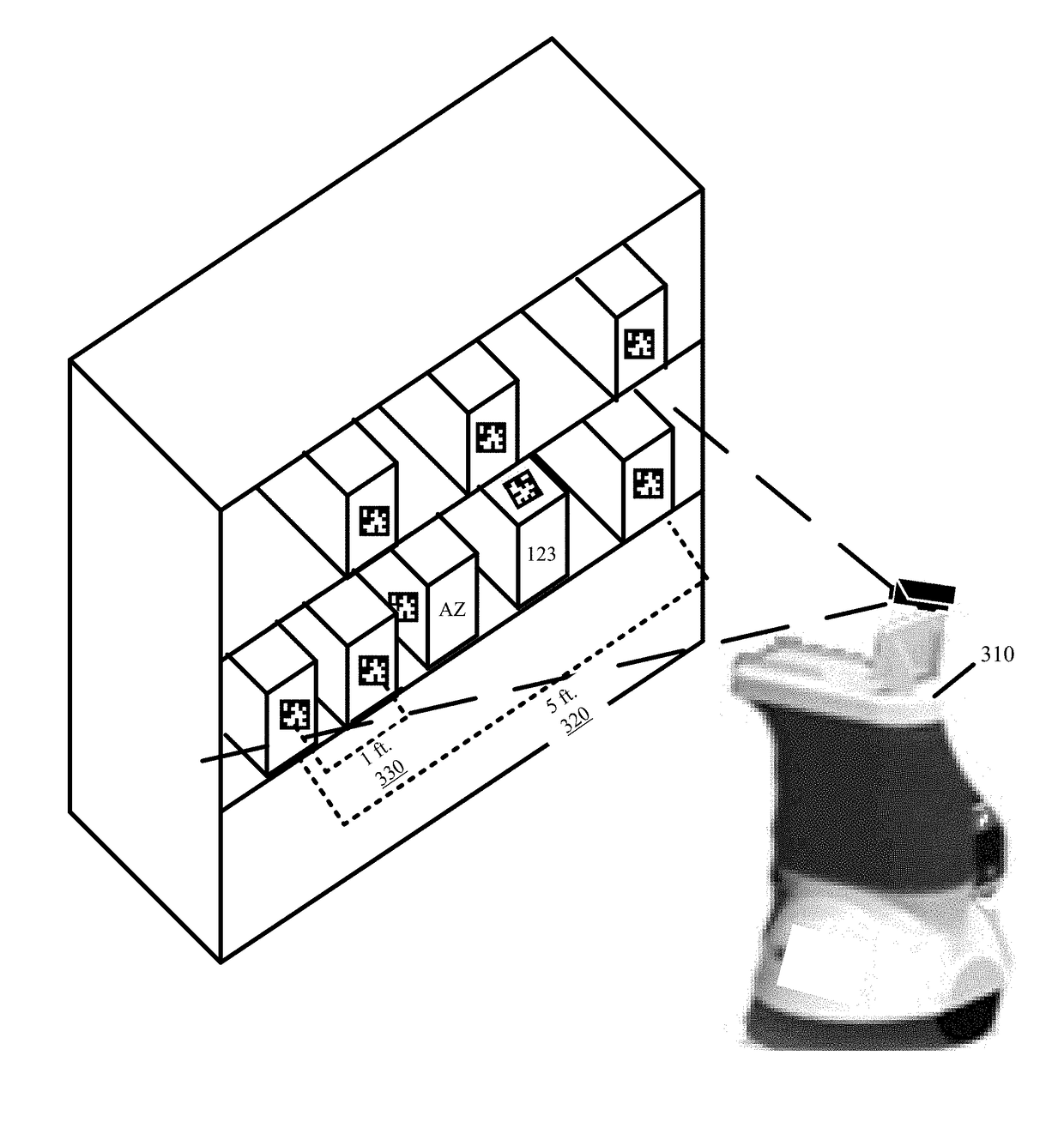
Inventory Management Robots
Provided are robots for managing inventory of arbitrary size, shape, weighted, or other distinct featured items. The robots dynamically and adaptively manage inventory for items stacked atop one another, items stacked behind one another, items that are horizontally arranged, items that are dispensed from a gravity flow dispenser, items that are dispensed from a back-to-front push dispenser, and items that are loosely contained within a bin. The robots have a sensory array from which dimensions of a particular arrangement and dimensions of a particular item in the particular arrangement can be calculated. The calculated dimensions can include length, width, or height of a particular arrangement and a particular item or force imposed by the particular arrangement and mass of the particular item. Based on these dimensions, the robots can dynamically track different item inventories without counting each individual item.
Owner:INVIA ROBOTICS INC
Automatic obstacle avoidance method for intelligent underwater robots
ActiveCN102999050AImprove survivabilityAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsTask completionSurvivability
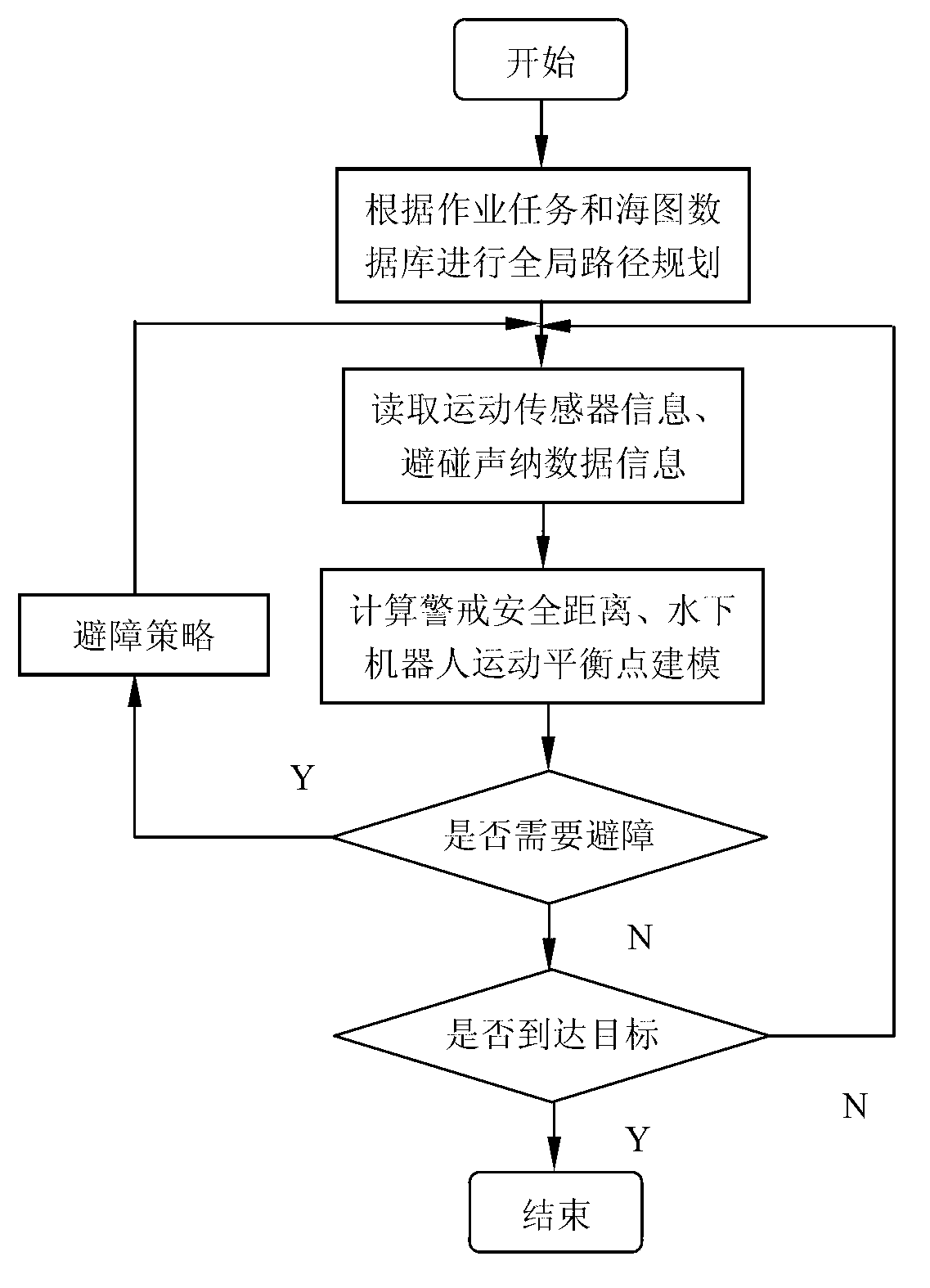
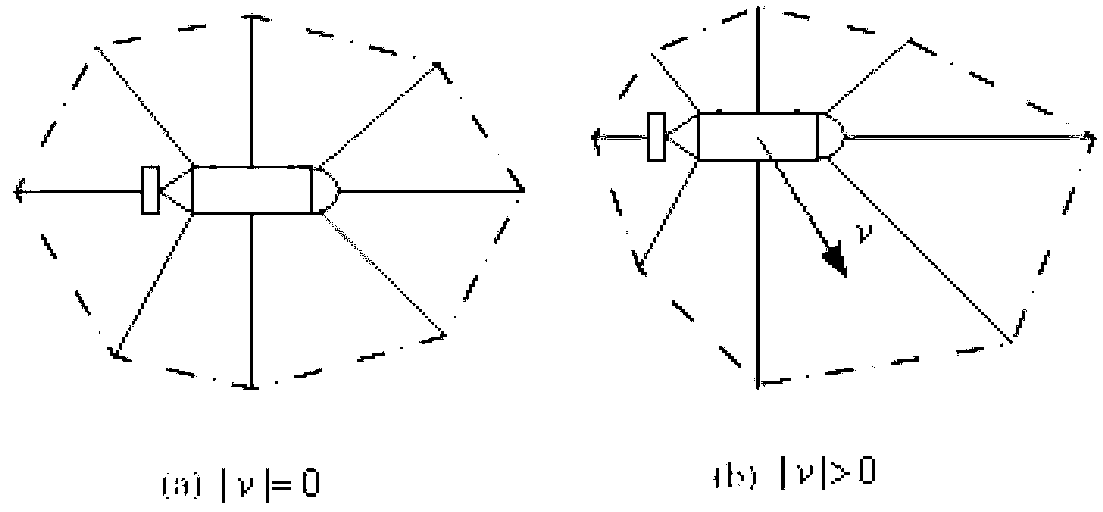
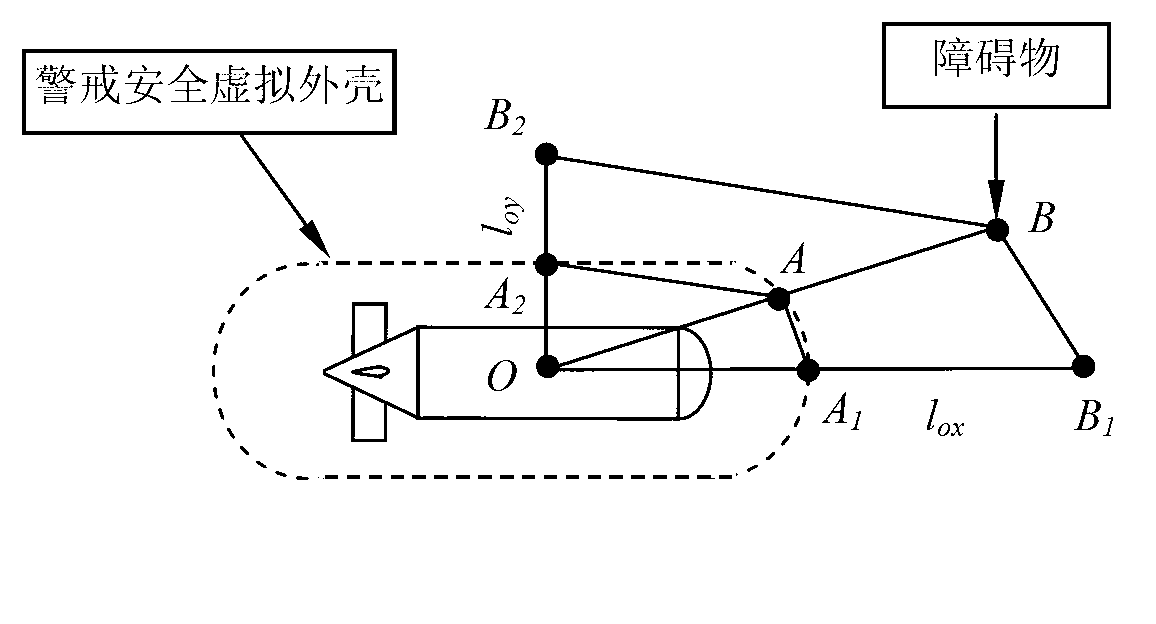
The invention relates to an automatic obstacle avoidance method for intelligent underwater robots, in particular to a method for considering underwater robot moving objects and obstacles and underwater robot control performances integrally to achieve obstacle avoidance. The method comprises performing global path planning according to job tasks and chart database information; reading underwater robot motion sensor information and obstacle avoidance sonar information; calculating underwater robot safety alerting distances, and establishing a safe virtual outer casing of an underwater robot; determining whether obstacle avoidance is needed; and determining whether an object is reached, and the task is completed if the object is reached. According to the automatic obstacle avoidance method, effects of speed information of underwater robots are introduced in robot obstacle avoidance strategies, local obstacle avoidance planning and control and hydrodynamic performances of underwater robots are combined, established obstacle avoidance strategies can reflect dynamic obstacle avoidance capacities of underwater robots, and underwater robot survival capabilities are improved.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船特装科技发展有限公司
Feedforward control method for flexible torque of robot based on flexible kinetic model
InactiveCN108714896AImprove accuracyIn line with the actual workProgramme-controlled manipulatorEstimation methodsRobot dynamic
The invention discloses a feedforward control method for a flexible torque of a robot based on a flexible kinetic model. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a cognizable minimuminertial parameter model of a flexible joint of the robot; S2, carrying out data sampling and pretreatment on joint movement parameters in the moving process of the flexible joint of the robot in real time periodically; S3, substituting the pre-treated joint movement parameters into the cognizable minimum inertial parameter model, recognizing flexible kinetic parameters by means of the least square estimation method, and substituting the parameters back to calculate a torque value needed by the flexible joint; S4, sending the torque value as a feedforward amount to a bottom layer of a servo driver periodically; and S5, overlaying the feedforward amount and an output amount of an electric current loop in a form of compensation to achieve flexible control of the robot. By establishing the kinetic model of the flexible joint of the robot and recognizing the torque rigidity parameter of the flexible joint and the minimum inertial parameter to obtain the torque value as the feedforward amount, dynamic response and positioning precision of the robot are improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
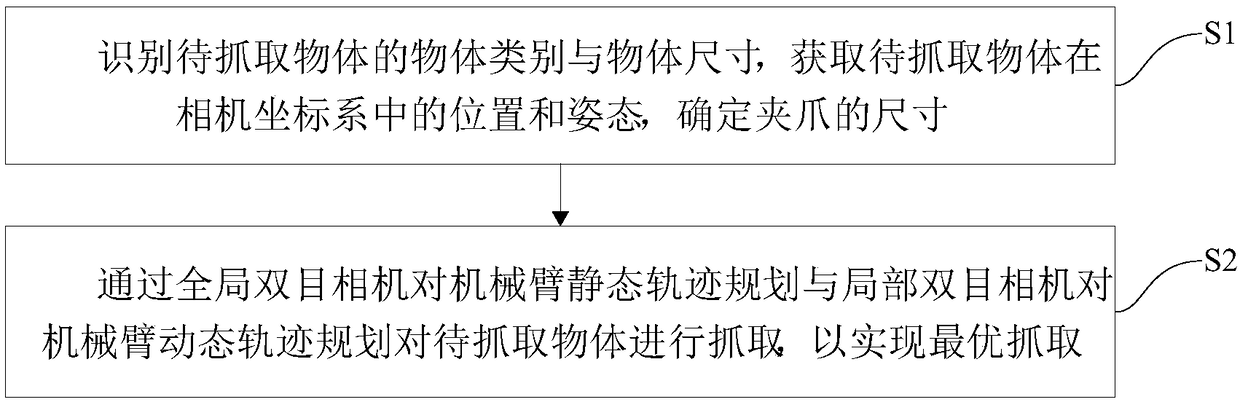
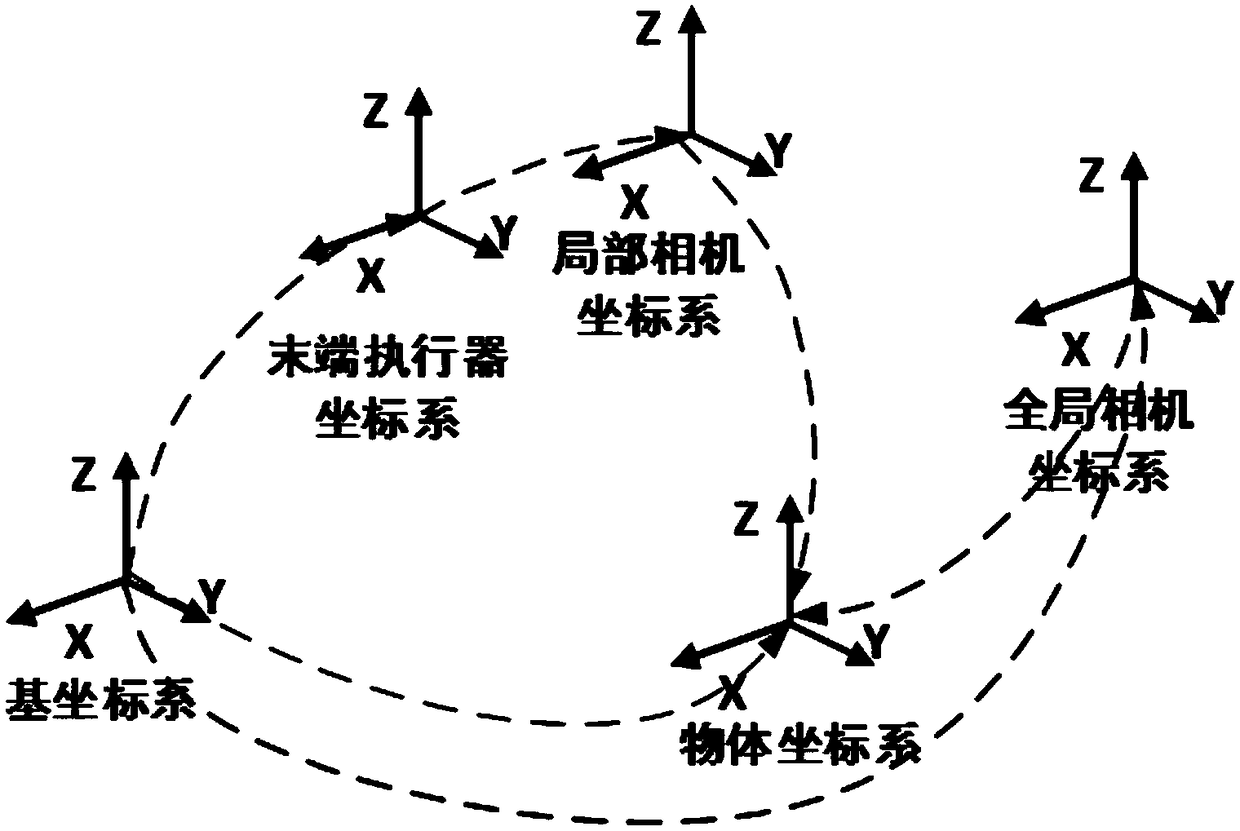
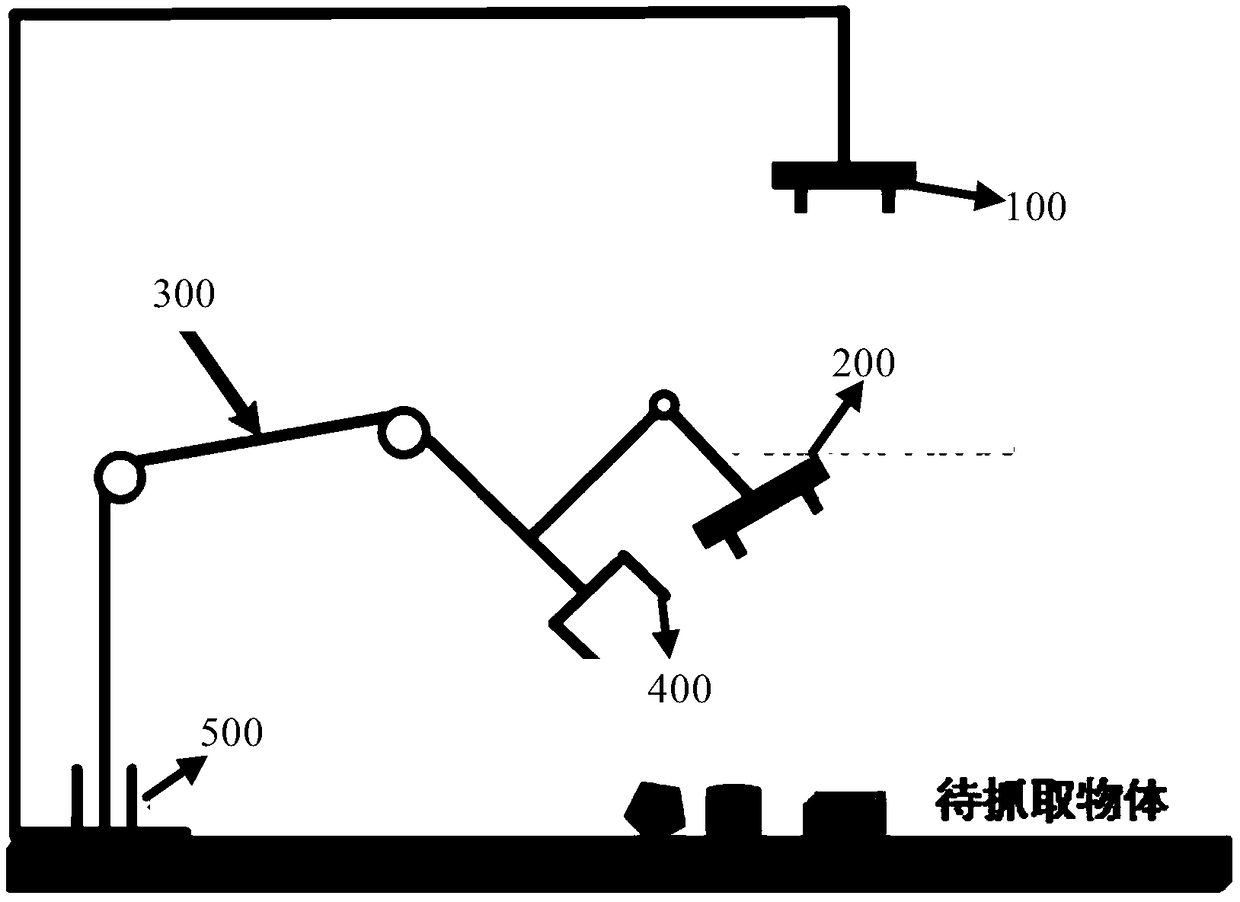
Robot dynamic grabbing method and system based on global and local visual semantics
ActiveCN109483554AThe recognition algorithm is simpleImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorRecognition algorithmSemantics
The invention discloses a robot dynamic grabbing method and system based on global and local visual semantics. The method comprises the following steps of identifying the object category and object size of a to-be-grabbed object, acquiring the position and posture of the to-be-grabbed object in a camera coordinate system, and determining the size of a gripper; and planning a static trajectory of amechanical arm through a global binocular camera and planning a the dynamic trajectory of the mechanical arm through a local binocular camera for grabbing the to-be-grabbed object, and achieving optimal grabbing. Through the method, the positioning precision of the position and posture of the grasped object is improved, the strength and size of the gripper are adaptively adjusted, dynamical planning and disturbance response are achieved, meanwhile, an object identifying algorithm is simplified, and the object identifying precision is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
RBF-based mobile manipulator self-adaptive control method
InactiveCN109176525AControl movementImprove robustnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic modelsClosed loop
The invention discloses an RBF neural network based mobile manipulator self-adaptive control method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, establishing a standard mobile manipulator dynamical model; S2, constructing an RBF neural network of the robot dynamic model; S3, designing a mobile manipulator trajectory tracking method with the adaptive capability through the constructed neural network; S4, automatically identifying unknown mobile platform and manipulator dynamic parameters through online learning, and conducting closed-loop identification and compensation on the unknown dynamic parameters, wherein the parameters of the RBF neural network can be updated on line, and finally, the feasibility and effectiveness of the simulation verification control method are verified. Through the method, output errors caused by the unknown dynamic parameters and external disturbance can be eliminated completely without an accurate robot dynamic model; the deficiency that a model-based robot control scheme cannot be implemented without the accurate dynamic model is made up; and the dynamic performance of a mobile manipulator and the trajectory tracking precision of a joint space areimproved.
Owner:上海神添实业有限公司
Robot dynamic obstacle avoidance method based on artificial potential field and rolling window
ActiveCN108762264AImprove convenienceMake up for local optimNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsPotential fieldOdometer
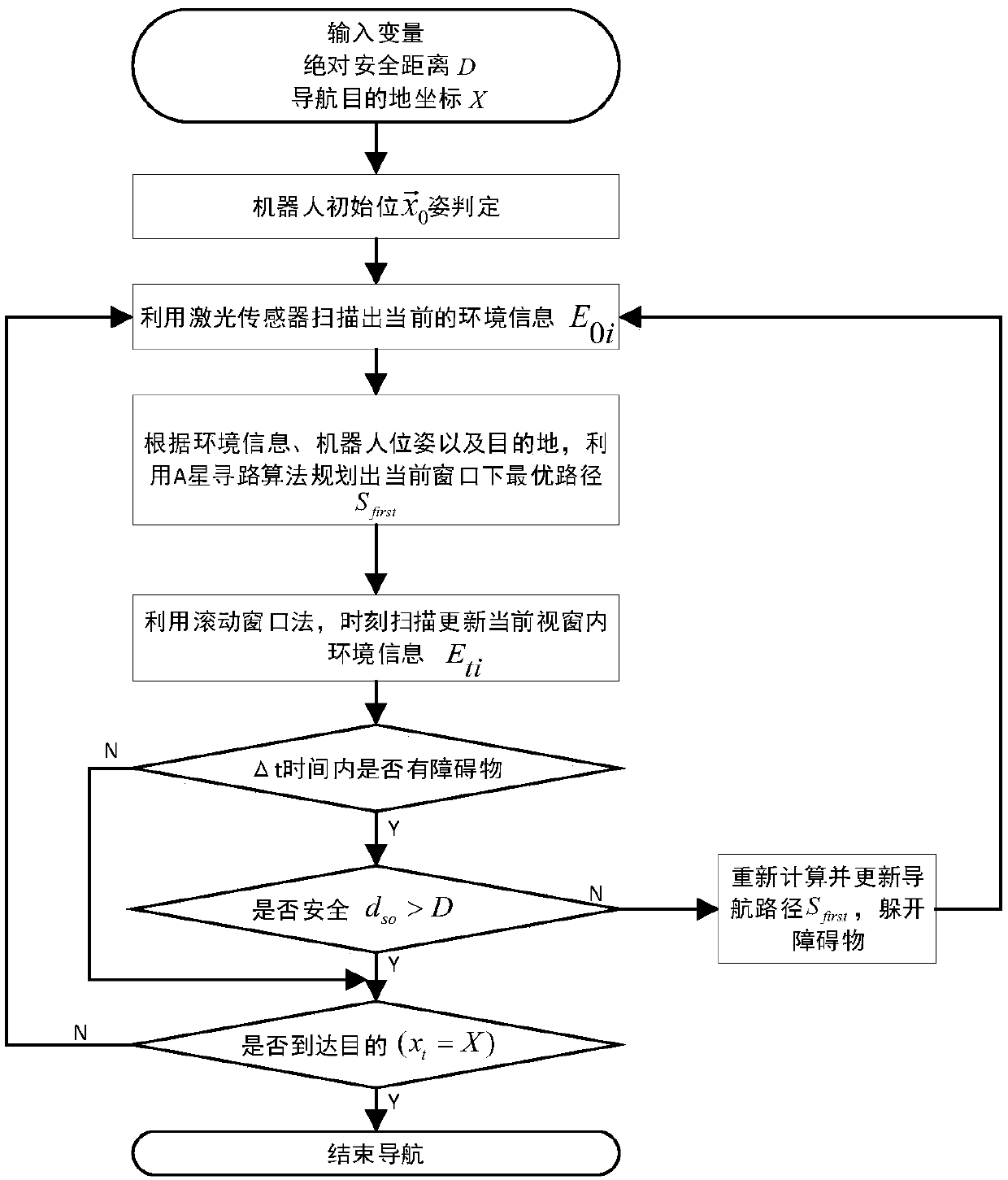
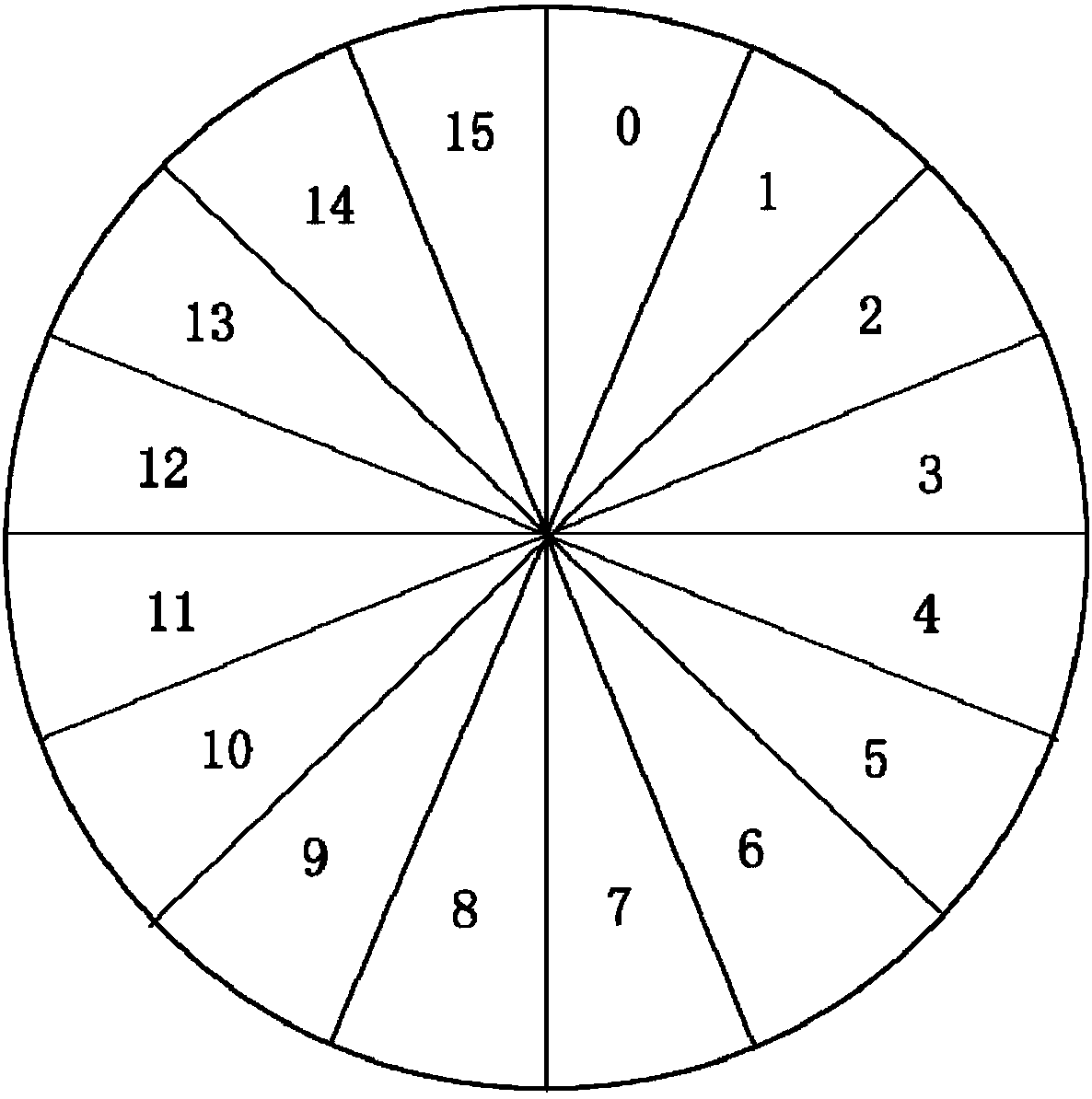
The invention relates to a robot dynamic obstacle avoidance method based on an artificial potential field and a rolling window, and belongs to the technical field of robot path planning. The method comprises the following steps: S1, setting the absolute safety distance D of a moving robot to an obstacle and the position coordinate information X(x, y) of a destination; S2, determining the pose X0 of the current robot in a global coordinate system according to the historical odometer data of the robot and the current environmental information E0i; S3, initially planning an optimal path Sfirst under a current window by using an A-star path finding algorithm and starting to execution; S4, scanning and updating the real-time environment information E1i under the current window by using a rolling window method, and calculating whether there is an obstacle in the environment within the [delta]t time window; S5, determining whether the distance to the obstacle is within the set absolute safetydistance; and S6, determining whether the robot reaches the coordinate position X (x, y) of the destination, and ending the navigation if so. The method of the invention effectively improves the optimality of the dynamic global path planning.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
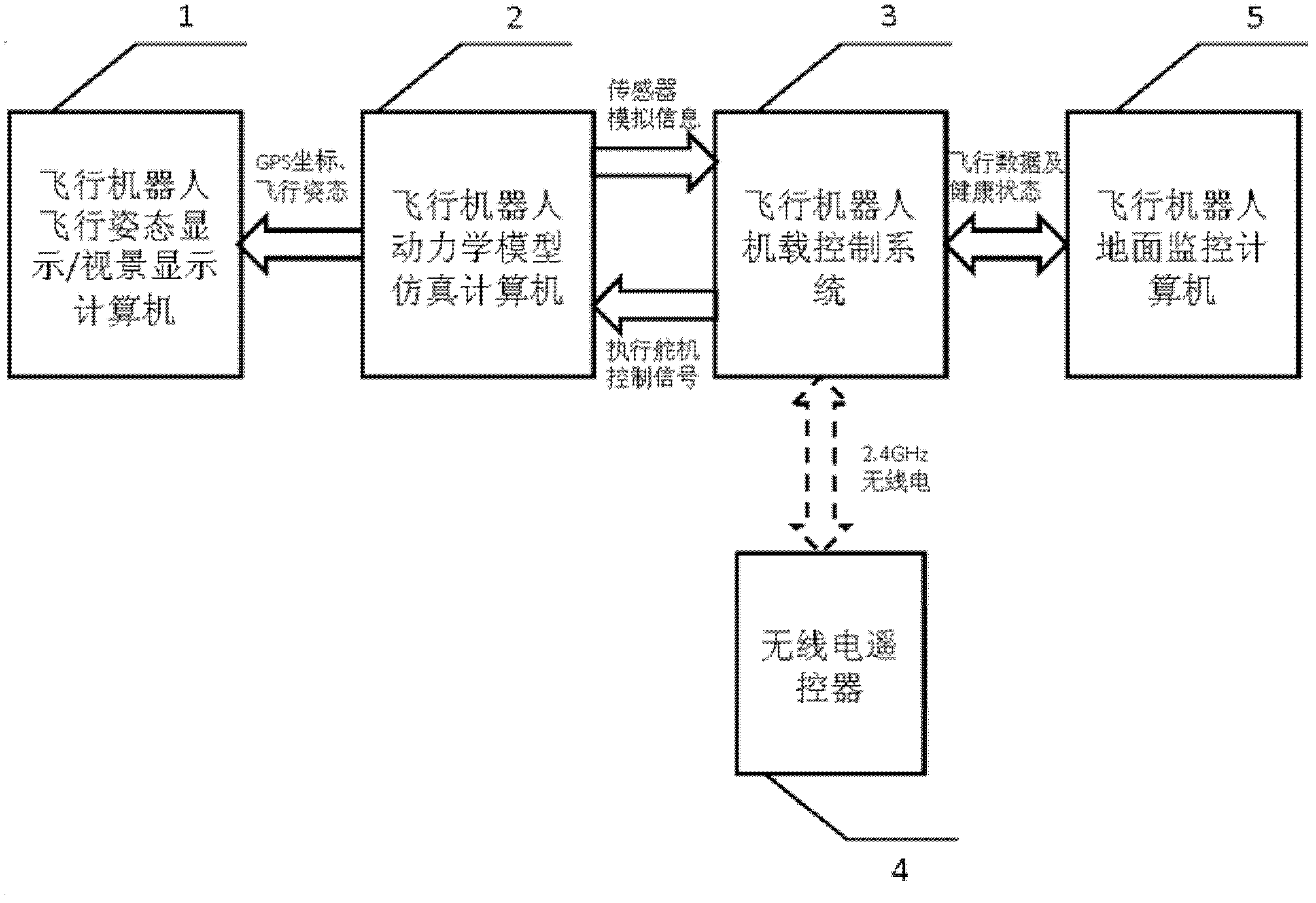
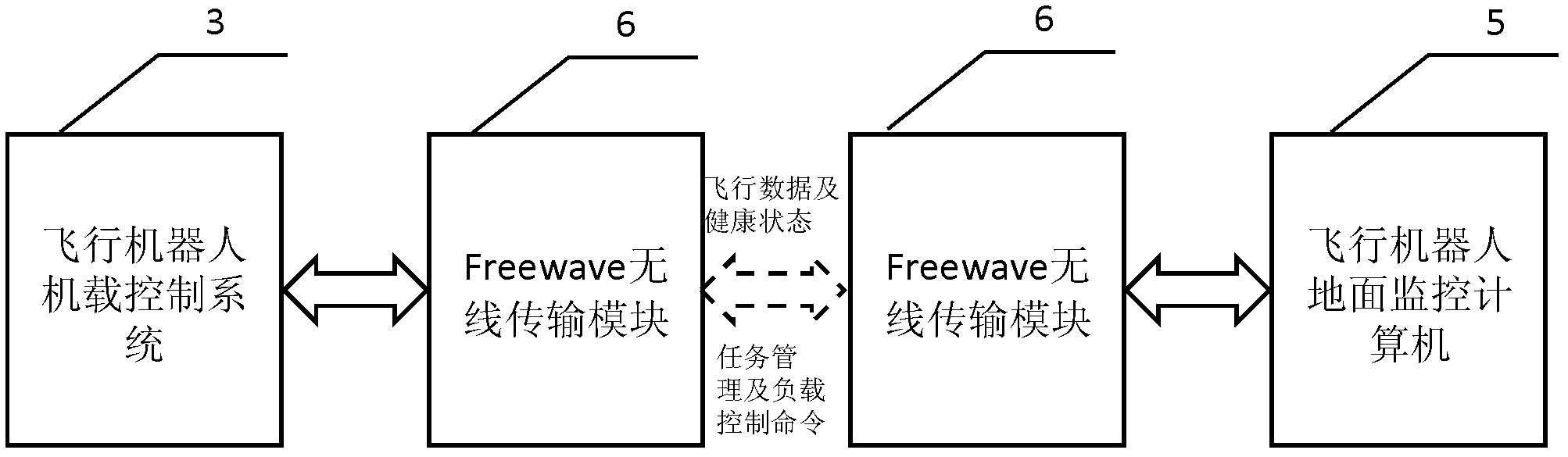
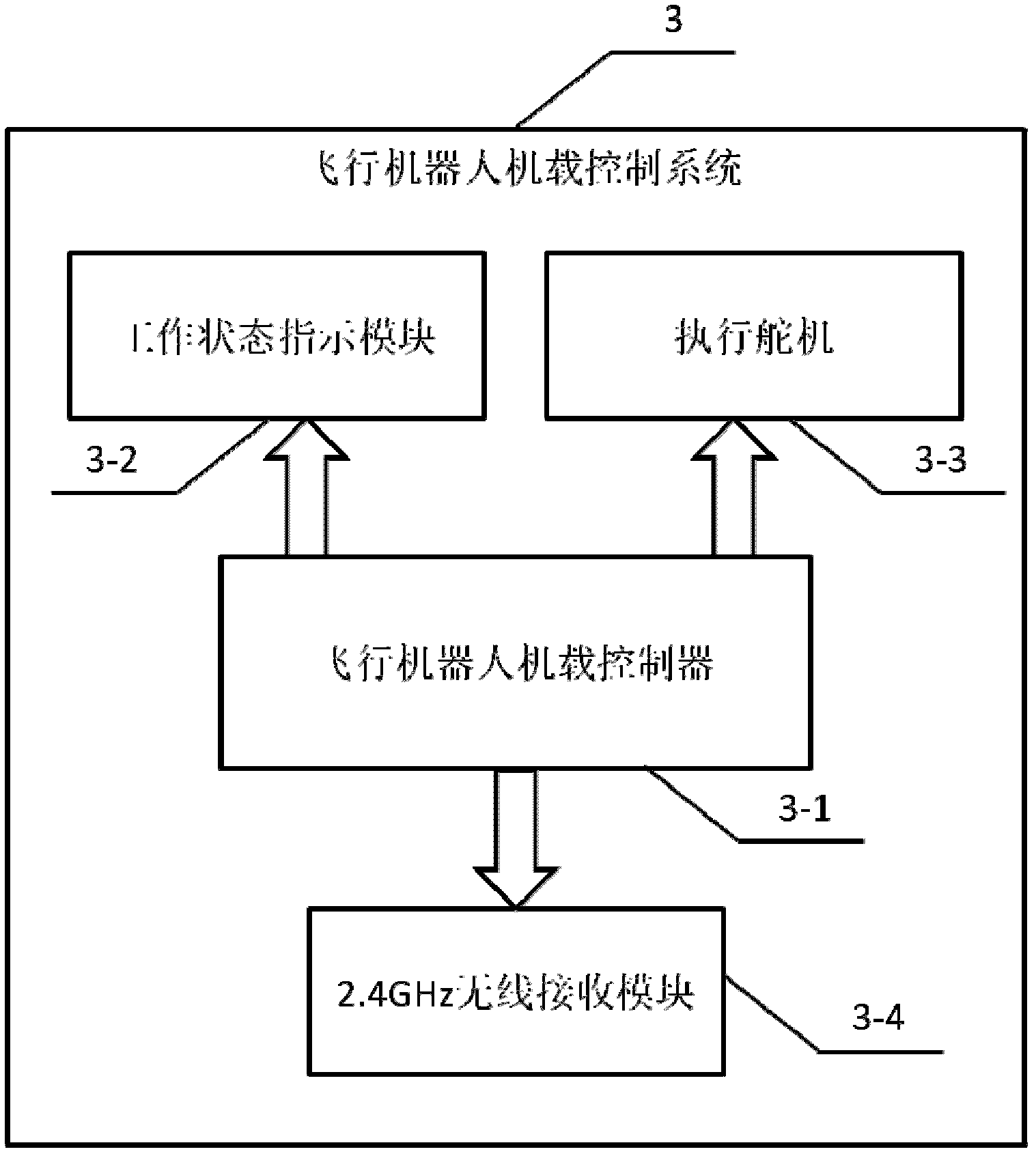
Flying robot control system semi-physical simulation platform
InactiveCN103149846AVerify correctnessImprove general performanceSimulator controlControl signalSoftware system
The invention relates to a flying robot control system semi-physical simulation platform which comprises a flying robot flight posture display / visual scene display computer, a flying robot dynamic model simulation computer, a flying robot airborne control system, a radio remote controller and a flying robot ground monitoring computer. The flying robot control system semi-physical simulation platform can simultaneously on-line debug a software system, a hardware system and a control algorithm of a flying robot and draws near an actual working condition of the flying robot to the maximum degree. A simulation experiment can directly verify the correctness of control signals through an executing steering gear of the flying robot airborne control system. The flying robot flight posture display / visual scene display computer can assist in verifying the actual working condition of the flying robot and the correctness of the control signals. The flying robot control system semi-physical simulation platform has stronger generality, stronger systematicness, stronger operability and stronger displaying performance and can be conveniently used in semi-physical simulation experiments of various flying robots. Repeated design of the flying robot control system is avoided, and test work of new function extension of the flying robot control system is greatly simplified.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
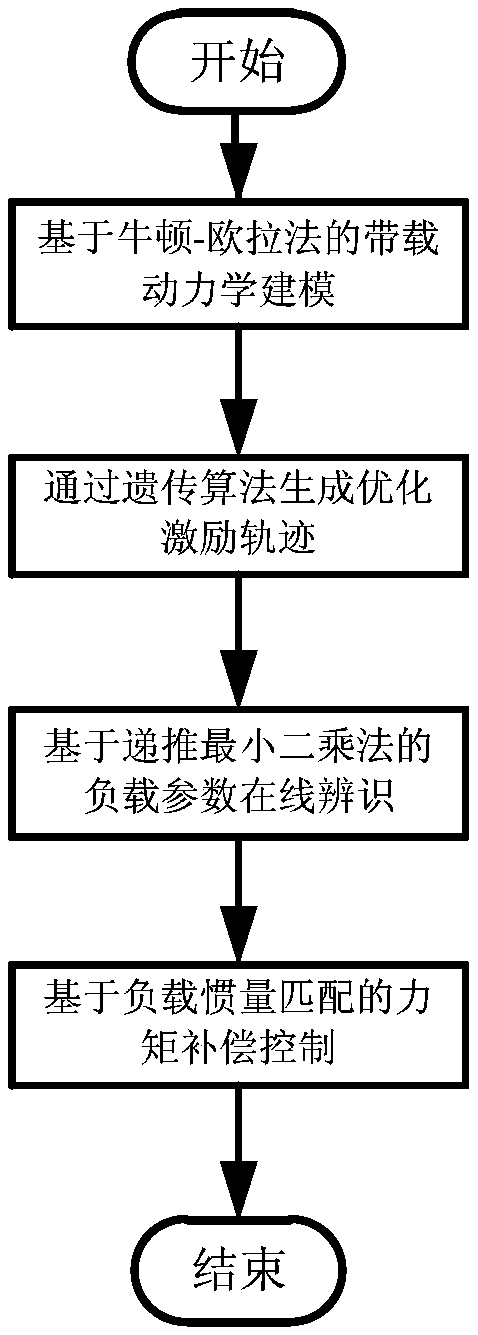
Industrial robot torque compensation control method based on load adaptive identification
ActiveCN109514602ASolve the problem of reduced control accuracyHigh control precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive identificationRobot dynamic
The invention discloses an industrial robot torque compensation control method based on load adaptive identification. The industrial robot torque compensation control method comprises the steps that according to robot overall stress balance analysis, a robot dynamics model under the load working condition is established in a deduced mode through a Newton-Euler method on the basis of considering friction; the optimal excitation trajectory of robot load identification is solved; load inertial parameters are calculated; and on the basis of load inertia matching, joint driving torque consumed by the load when a robot moves under the load working condition is compensated, and further verification and optimization are conducted through experiments. According to the industrial robot torque compensation control method, the influences of the load on operation performance of the robot are considered, under the premise that no any external sensor is needed, adaptive identification of any load andtorque compensation control are completed through easy operation easy to achieve, the control precision of the robot under the load working condition is effectively improved, and very important significance for processes such as carrying and friction stir welding of the industrial robot under high-speed and large-load movement is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Industrial robot obstacle avoidance track planning method based on torque control
ActiveCN107139171ACollision prediction worksObstacle avoidanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic modelsCollision detection
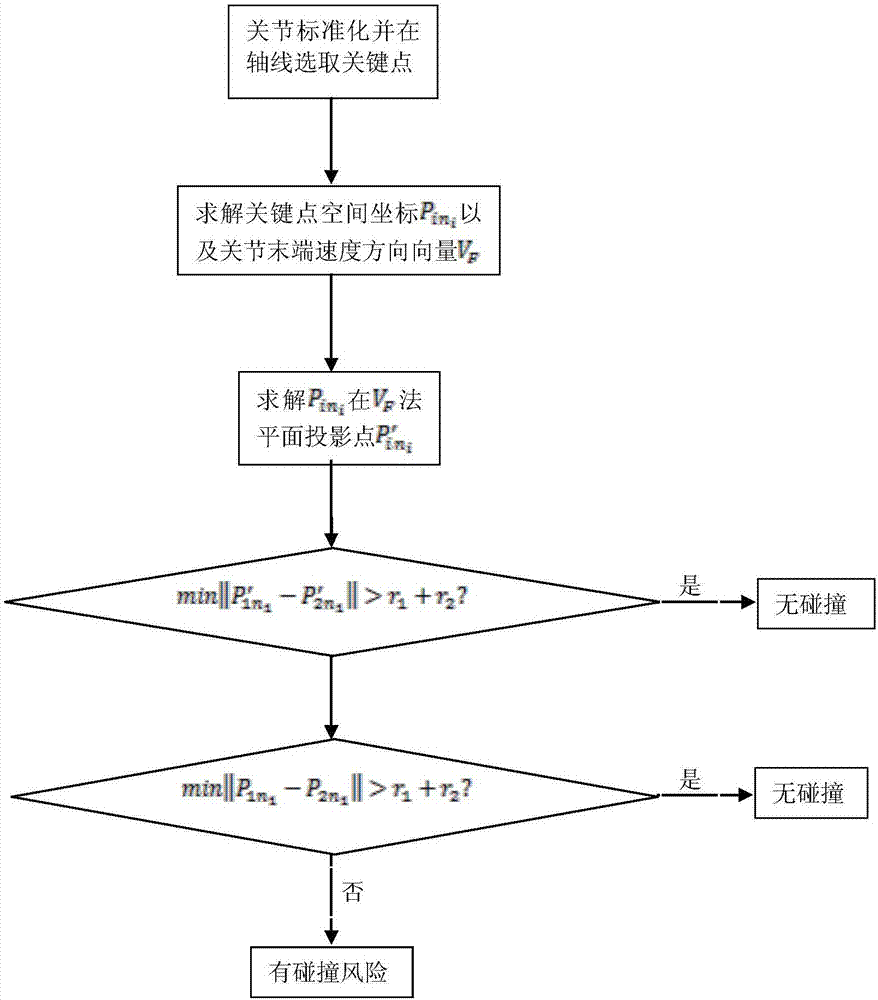
The invention discloses an industrial robot high-speed high-precision obstacle avoidance track planning method based on torque control. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a robot dynamics model is established by identifying kinematics and inertial parameters of all joints; 2, displacements of all joint angles are obtained through inverse kinematics solution when a robot moves to an end point; 3, the displacements of the joint angles are adopted as motion tracks, speeds and accelerated speeds of all joints are planned through a sine jerk planning method, the speeds and the accelerated speeds are substituted into the dynamics model so as to solve control torque in the motion tracks; 4, collision detection is carried out by adopting a method of judging the distance between key points after detecting the interference conditions of joint projections; and 5, when it is detected that the collision may occur, an impedance accelerated speed is applied to the dangerous joints to reduce the motion speed of the joints so as to achieve the obstacle avoidance. The industrial robot obstacle avoidance track planning method based on the torque control has the advantages that the control precision is high, the obstacle avoidance is effectively realized, and the safety is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Dynamic path planning method of robot by combining A* algorithm and VFH obstacle avoiding algorithm
ActiveCN108549385AGuaranteed Autopilot MissionIncrease flexibilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsAlgorithmRobot dynamic
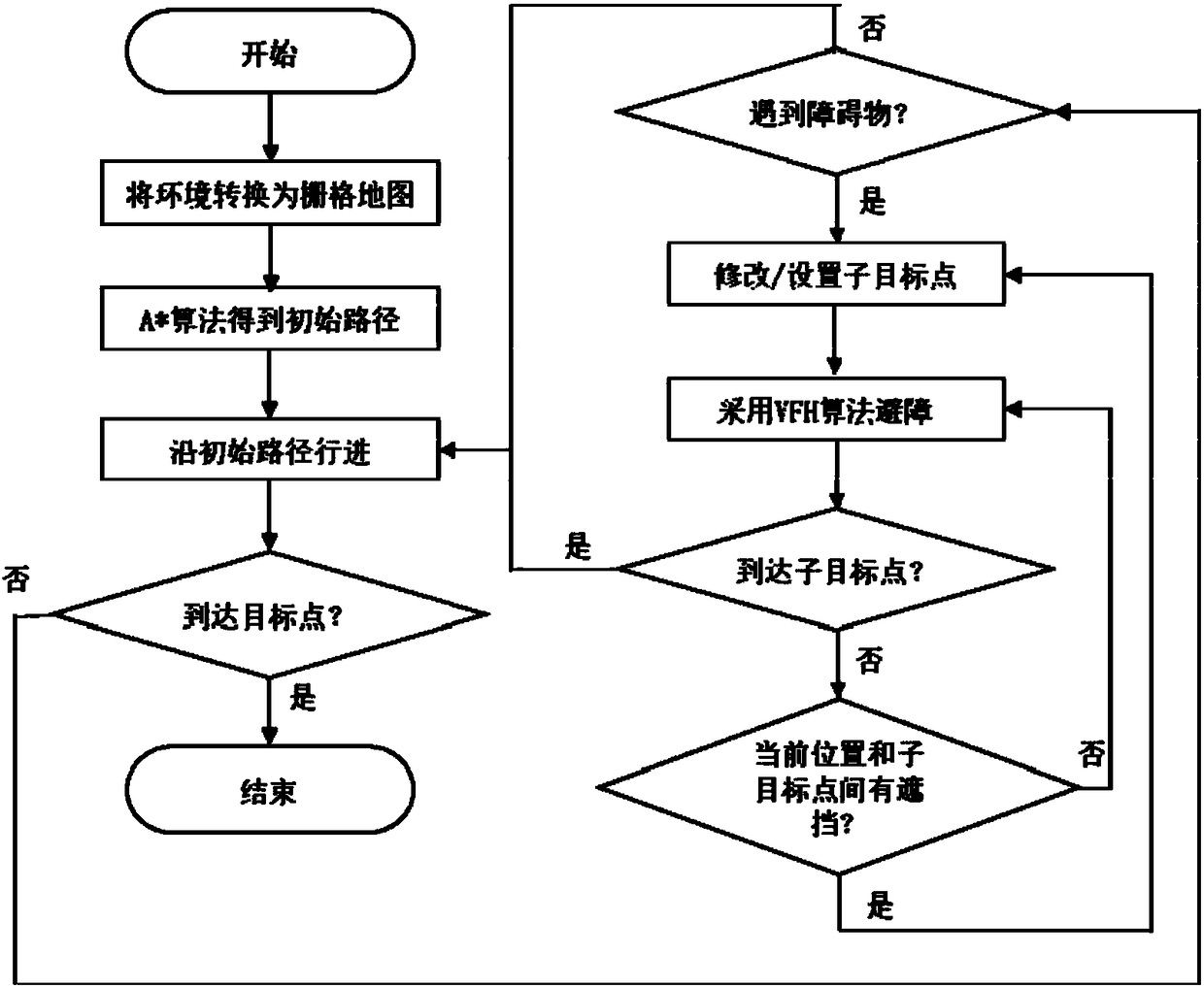
The invention discloses a dynamic path planning method of a robot by combining an A* algorithm and a VFH obstacle avoiding algorithm. The method comprises steps of representing the environment where the robot is located into a grid map and searching a global initial path in a grid map by use of the A* algorithm; when the robot moves towards a target point along the initial path, judging whether the robot comes across an obstacle, if yes, using the VFH algorithm to carry out obstacle avoidance, or else allowing the robot to move towards the target point; during obstacle avoidance, firstly, setting a stage target point in the initial path, generating an obstacle avoiding path between the current position and the stage target point, moving for one step forwards, updating the current position,judging whether the space between the current position of the robot and the stage target point is shielded, if yes, re-calculating the obstacle avoiding path, or else, allowing the robot to move forone step forwards towards the stage target point along the obstacle avoiding path; and carrying out circulation until the robot reaches the stage target point, returns back to the initial path and continues to move towards a destination. By combining the two algorithms, efficiency of path planning of the robot is improved; and the autonomous navigation ability of the robot in the indoor dynamic environment is ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
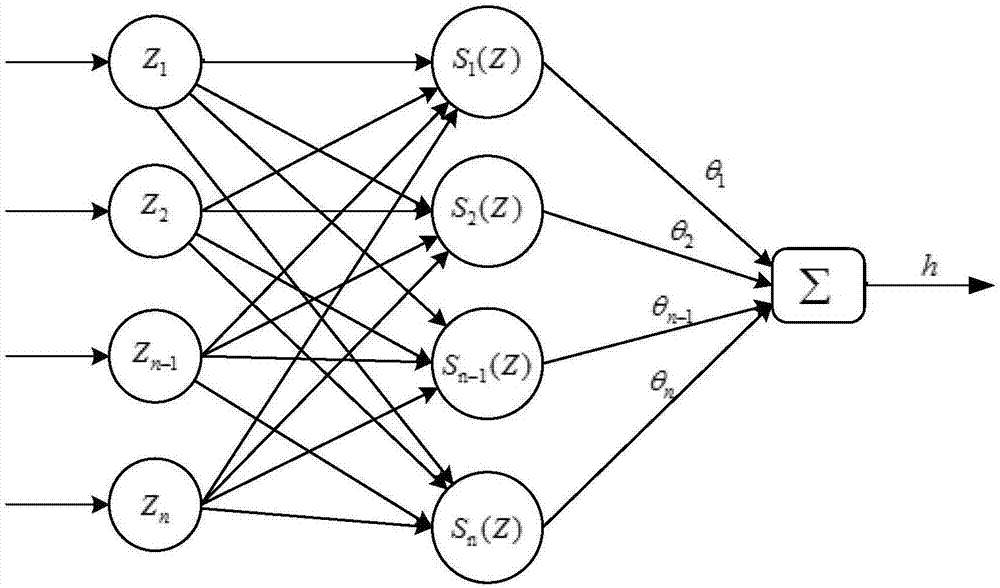
Robot dynamics modeling method based on deep learning
ActiveCN108621159ASimulation is accurateHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorHidden layerData set
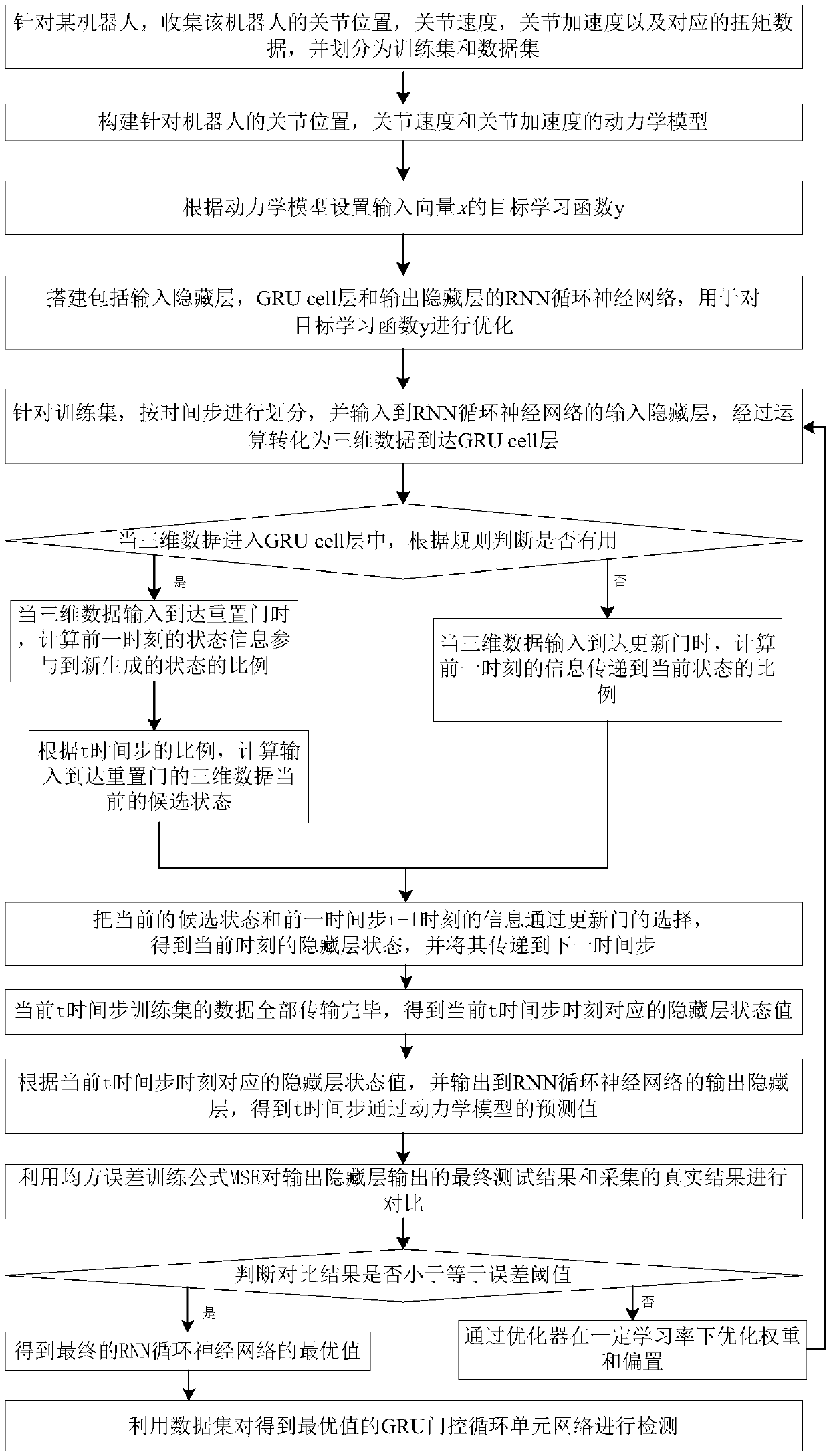
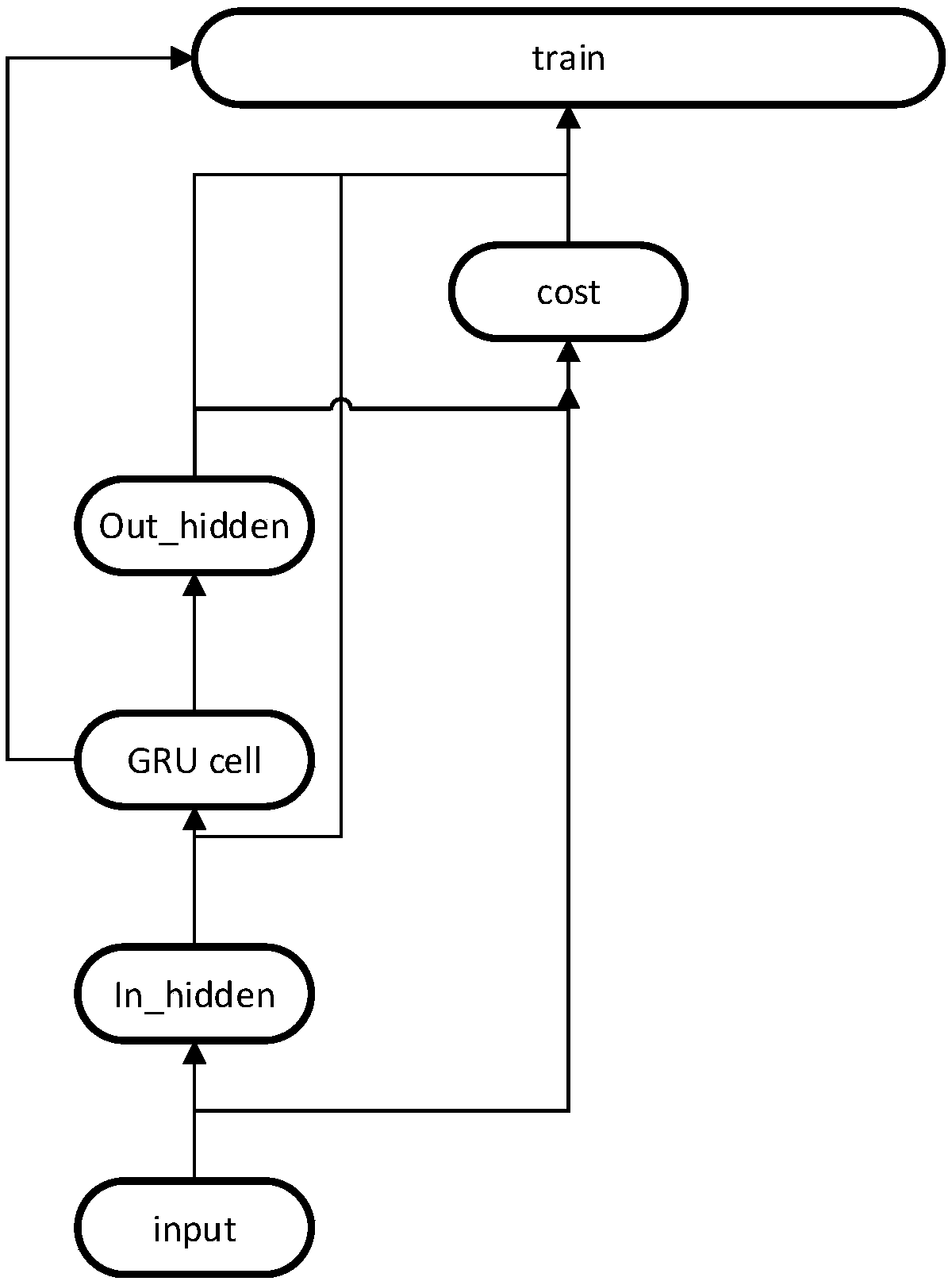
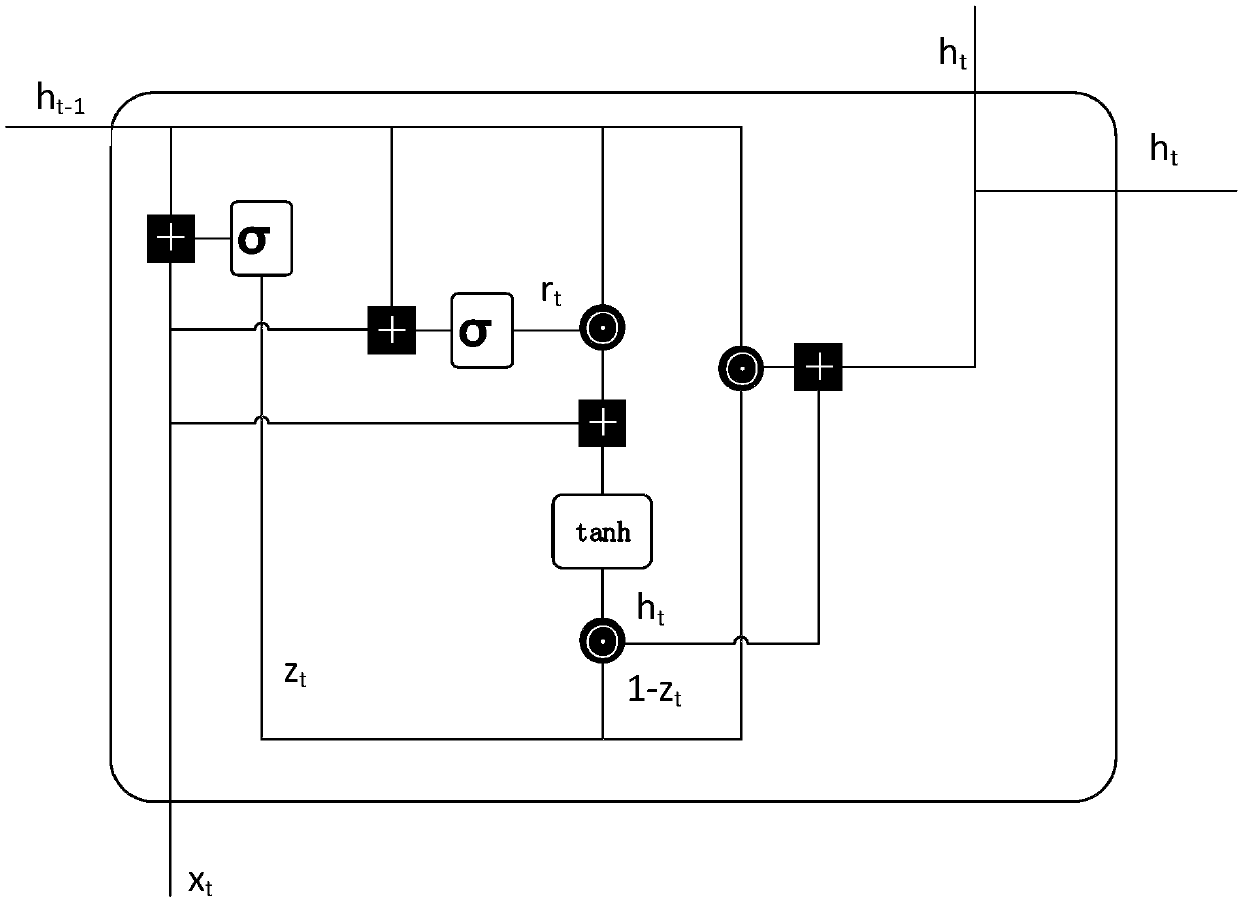
The invention discloses a robot dynamics modeling method based on deep learning and belongs to the field of intelligent robots. Data are acquired and divided into a training set and a data set, and adynamics model is a built, and a recurrent neural network (RNN) is constructed; the training set is divided according to the time step and is input into an input hidden layer, and is converted into three-dimensional data to reach a GRU cell layer, currently input information is combined with previous information, and the proportion of state information, participated into a newly generated state, at the previous moment is calculated; and then a current candidate state obtained due to calculation and information of the previous time step moment are selected through an updating gate, a hidden layer state at the current moment is obtained, transmitted to a next time step, and output to an output hidden layer, and an acquired real result with a predicted value smaller than or equal to an errorthreshold is obtained and is an optimal value. Finally, the data set is utilized for detecting a gated recurrent unit (GRU) network. According to the method, the torque detecting precision is improved, the training time of an input signal is greatly shortened, and the gradient error of traditional counterpropagation is reduced.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Parallel robot indirect self-adaptive fuzzy control parameter determining method
ActiveCN106527129AGuaranteed stabilityCompensation for UncertaintyAdaptive controlControl objectiveControl system
The invention belongs to the technical field of parallel robot fuzzy control, and provides a parallel robot indirect self-adaptive fuzzy control parameter determining method. The method comprises the steps that a parallel robot dynamic model is established; a parallel robot control target is determined; a parallel robot fuzzy controller is determined according to the parallel robot dynamic model; and according to the parallel robot control target and the parallel robot fuzzy controller, the self-adaptive control rate of the control target is determined. The method can self-adaptively adjust the parameters of a fuzzy control system to acquire a given tracking error performance indicator to realize high quality control requirements.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method and module for distinguishing load of six-axis robot
ActiveCN106346477ASimple installation and debuggingImprove working precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorLoad generationComputer module
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of robot control, and discloses a method and a module for distinguishing a load of a six-axis robot. The method for distinguishing the load of the six-axis robot comprises the following steps: according to a preset parameter limiting value of each joint, generating an excitation track of the six-axis robot; when the six-axis robot carrying the load is controlled to run along the excitation track, collecting a parameter running value of each joint; according to the parameter running value of each joint and a preset robot dynamics model, calculating a torque predicting value of each joint; calculating a difference between the torque running value and the torque predicting value, the difference serving as torque produced by the load, and according to preset relationship of the torque produced by the load and a load inertia parameter, calculating the load inertia parameter. The embodiment of the invention also provides the module for distinguishing the load of the six-axis robot. The module for distinguishing the load of the six-axis robot disclosed by the embodiment has the advantage that compared with the prior art, the parameter running value of the robot is collected on line, and the load inertia parameter of the robot is distinguished; because a six-dimensional force sensor is not used, the cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI STEP ELECTRIC +1
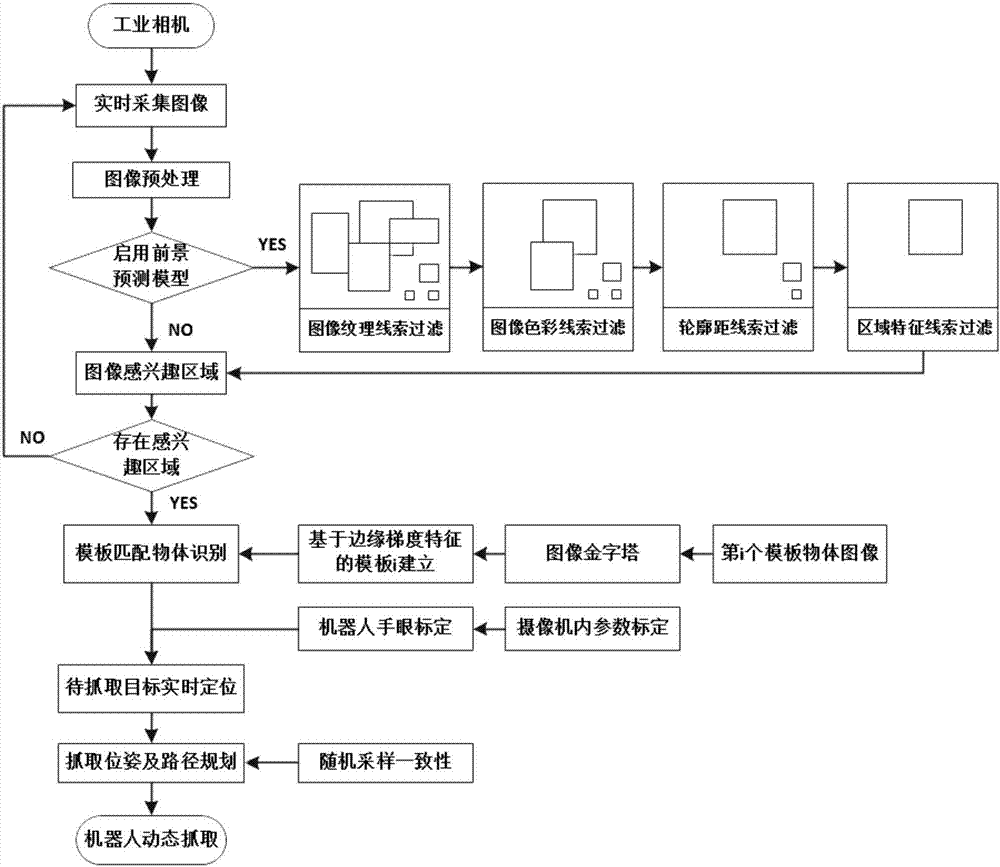
Robot dynamic capture method and system
PendingCN107992881AEfficient extractionAccurate extractionProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage enhancementTemplate matchingHigh frame rate
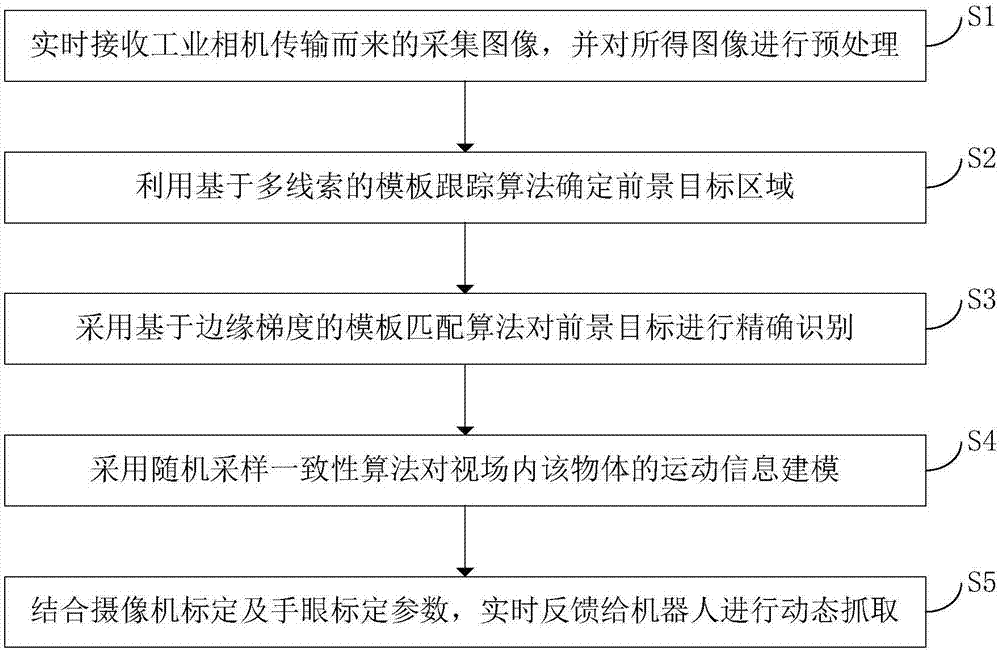
The invention discloses a robot dynamic capture method and system. The method comprises the steps that S1, a collected image transmitted from an industrial camera is received in real time, and the obtained image is preprocessed; S2, a template tracking algorithm based on multiple clues is utilized to determine a foreground target region; S3, a template matching algorithm based on an edge gradientis adopted to precisely recognize a foreground target; S4, a random sampling consensus algorithm is adopted to perform modeling on motion information of an object in a view field; and S5, the information is fed back to a robot in real time for dynamic capture in combination with camera calibration and hand-eye calibration parameters. According to the robot dynamic capture method and system, by theadoption of a target tracking algorithm based on multiple clues, the motion target foreground region can be extracted efficiently and accurately; and under the application scene of robot sorting, therunning speed of a visual motion target tracking algorithm can be effectively increased, high-frame-rate real-time recognition is realized, and therefore the precision of visual servo is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CAS DERUI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
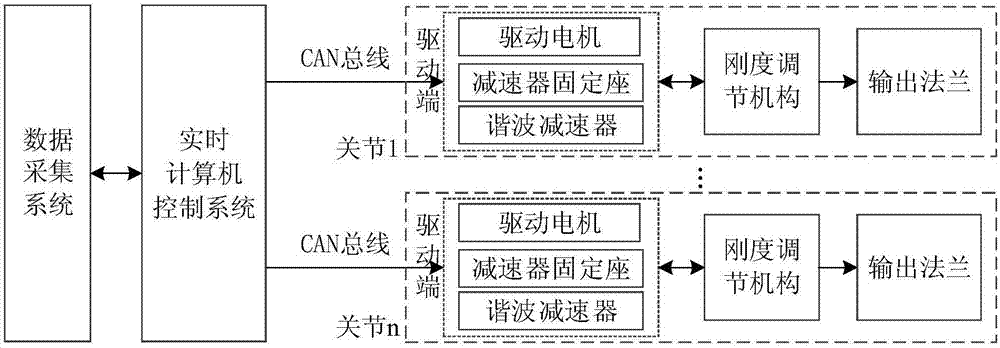
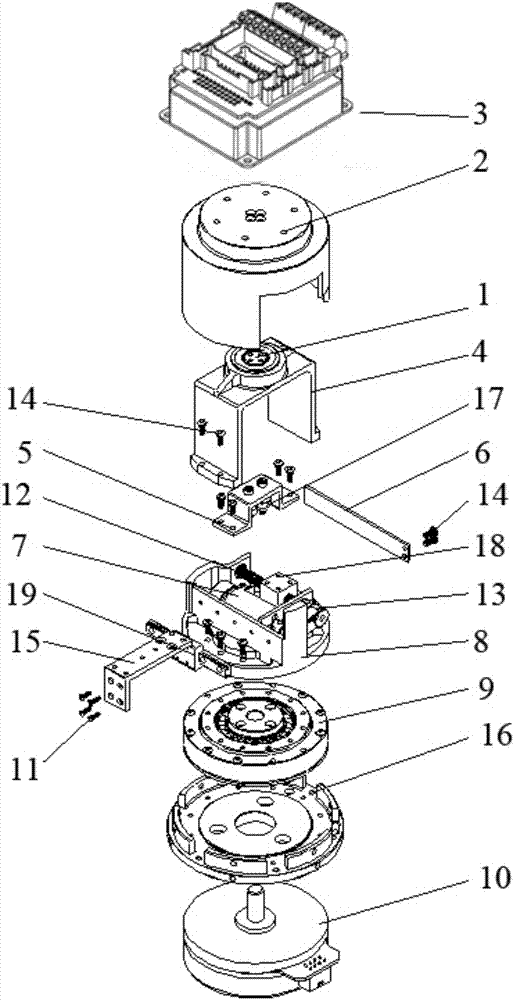
Mechanical arm control system based on variable-stiffness elastic driver and control method of mechanical arm control system
PendingCN106945046AImprove securityQuick calculationProgramme-controlled manipulatorVariable stiffnessComputer control system
The invention discloses a mechanical arm control system based on a variable-stiffness elastic driver. The mechanical arm control system comprises a real-time computer control system, a data acquisition system, a driving end, a stiffness adjusting mechanism and an output flange. The invention further discloses a mechanical arm control method based on the variable-stiffness elastic driver. According to the mechanical arm control system disclosed by the invention, the structure is compact, the universality is high, the stiffness is continuous and adjustable, and the external impact fore can be effectively reduced; by utilization of the own smooth feature of the mechanical arm control system, a joint connection rod is protected, and then all parts of a whole robot are well protected; in a control process, the nonlinear problem caused by an elastic element in the elastic driver, namely the influence, caused by the variable stiffness, on the performance, as well as the robot dynamics and the driver dynamics are considered; through the construction of a novel high-dimensional integral Lyapunov-Krasovskii functional on a closed-loop system, the controller design procedure is simplified, and the overall stability of the closed-loop system is guaranteed; and the mechanical arm control system has the characteristics of being high in stability and strong in interference-resistant capability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
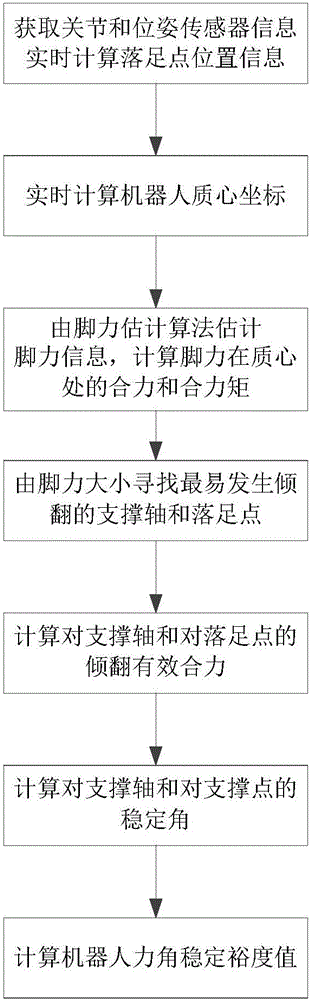
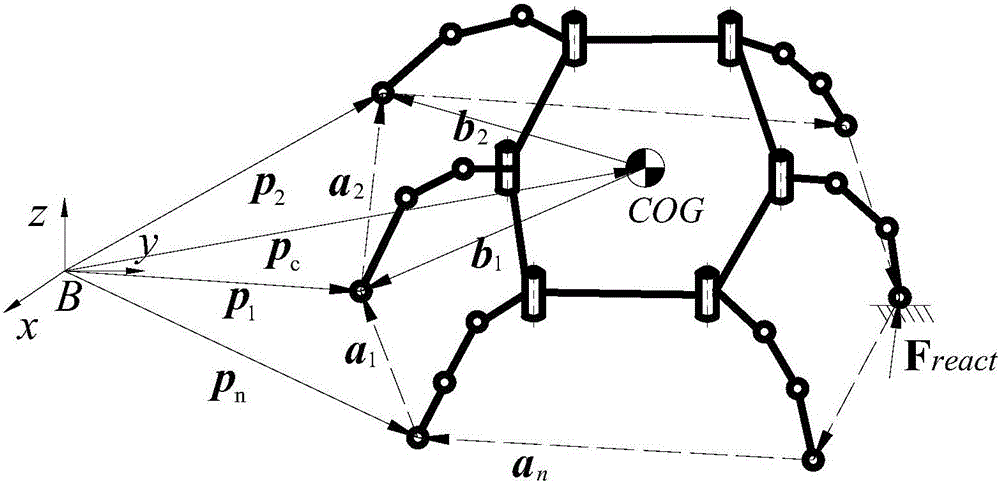
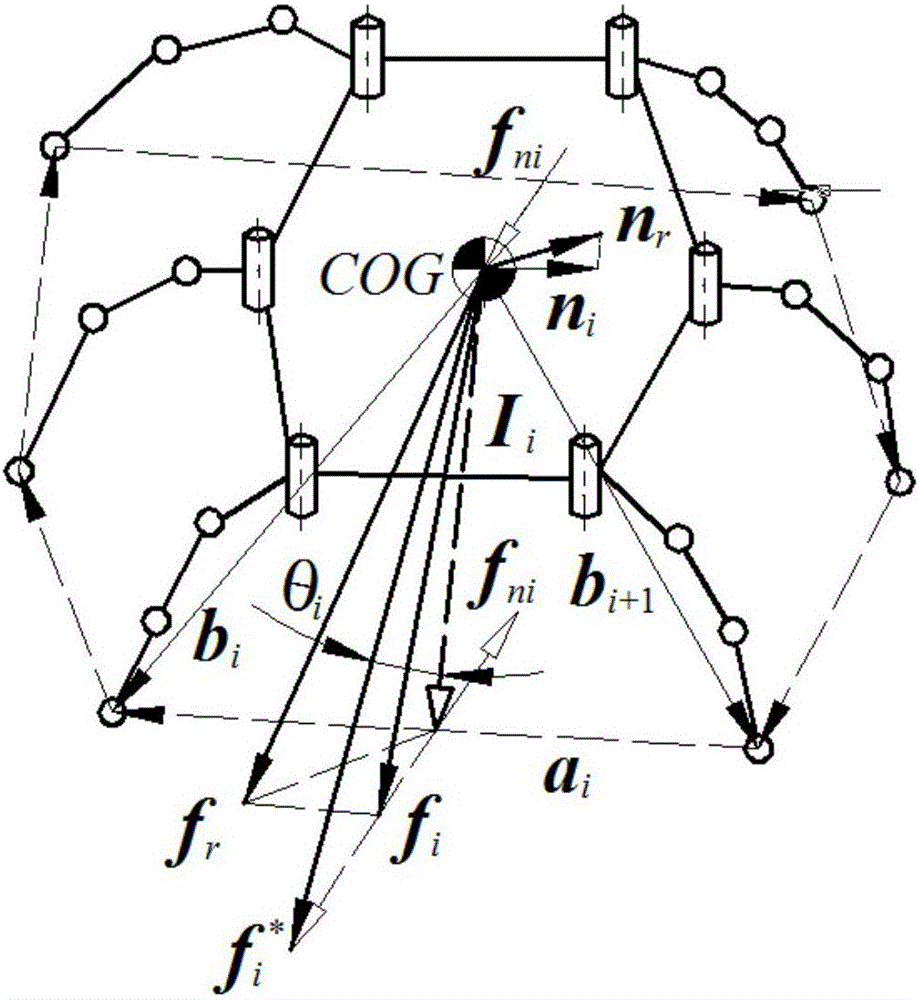
Quantitative determination method for dynamic stability of multi-legged robot based on leg force estimation algorithm
InactiveCN106547206AReduce angleThe judgment method is concise and clearAdaptive controlVehiclesRolloverEngineering
The invention provides a quantitative determination method for the dynamic stability of a multi-legged robot based on a leg force estimation algorithm, which is applicable to real-time detection for the stability of the robot when walking in an unstructured environment. The quantitative determination method is characterized in that motion states of joints and the robot body are acquired by a sensor, and variable values required by calculating the stability margin is solved through obverse and inverse kinematics; then the leg force of each supporting leg is estimated through the leg force estimation algorithm, and a supporting shaft and a landing point at which rollover occurs most easily are acquired according to the leg forces; a resultant force which is effective to rollover of the supporting shaft and the landing point is calculated according to a resultant force of the leg forces at the mass center and the moment of the resultant force, thus stability angles of the supporting shaft and the landing point can be acquired according to a formula, and a minimum stability angle is selected so as to calculate to acquire a normalized force angle stability margin value of the robot according to a formula. The advantages lie in that the method provided by the invention directly judges the stability margin for the supporting shaft and the landing point; stability variations brought about by the height of the mass center can be represented; and a vulnerable multi-dimensional force sensor is not required to be adopted to measure the leg force.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
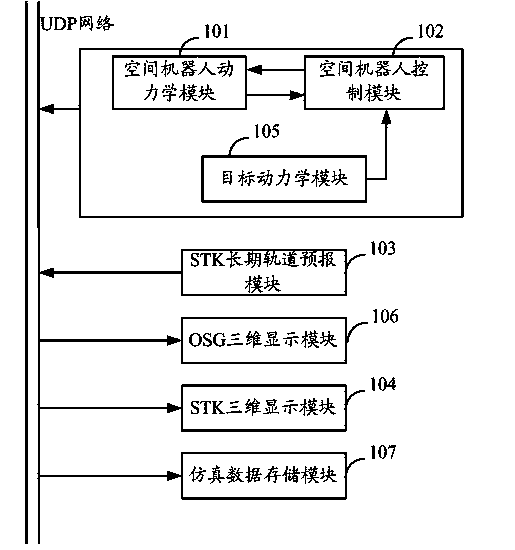
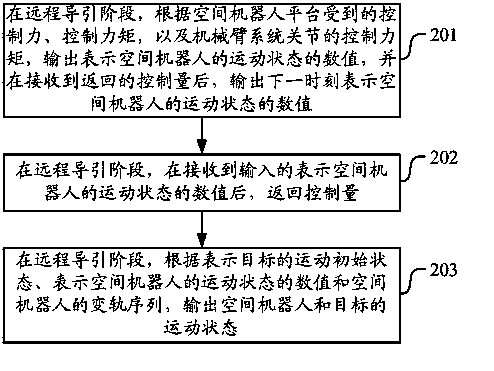
System and method for dynamics simulation of space robot
The invention discloses a system and method for dynamics simulation of a space robot. The method for dynamics simulation of the space robot comprises the steps that a space robot dynamics module outputs a value representing the motion state of the space robot in the remote guiding stage according to the control force and the control moment which are received by a space robot platform and the control moment of a mechanical arm system joint and after the returned control amount is received, a value representing the motion state of the space robot at the next moment is output; after a space robot control module receives the value which is input by the space robot dynamics module and represents the motion state of the space robot in the remote guiding stage, the control amount is returned to the space robot dynamics module by the space robot control module; an STK long-term orbit prediction module outputs the motion state of the space robot and the motion state of a target in the remote guiding stage according to a value representing the motion initial state of the target, the value representing the motion state of the space robot and the orbital transfer sequence of the space robot. According to the system and method for dynamics simulation of the space robot, complete simulation of the whole task stage of the space robot can be provided.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
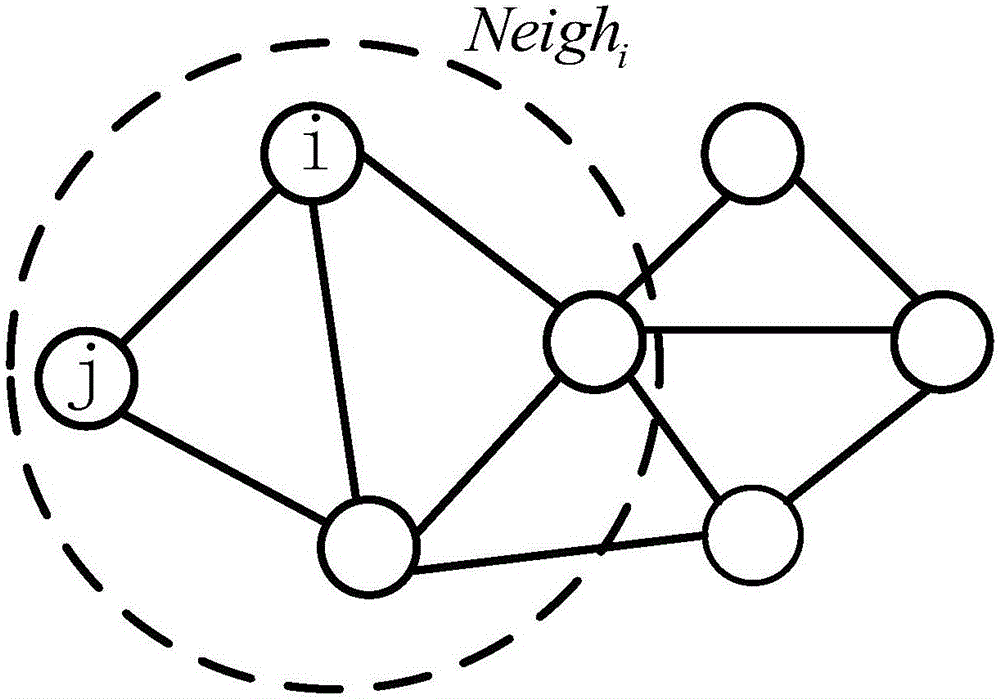
Distributed multi-robot dynamic network connectivity control method
ActiveCN106054875ASolve problemsImprove connectivityPosition/course control in two dimensionsTelecommunications linkDynamic network topology
The invention discloses a distributed multi-robot dynamic network connectivity control method, and belongs to the technical field of multi-robot dynamic network control. The method comprises minimum spanning tree distributed dynamic network topology control based on event drive and optimal neighbor communication link connectivity maintaining motion control based on a local artificial potential field. Each robot node periodically broadcasts the location thereof and updates neighbor information, the local minimum spanning trees of the neighbor networks of the nodes are established in a distributed manner, an optimal neighbor is selected, and the communication link with the optimal neighbor is maintained through a local artificial potential field method, so that global information connectivity is optimized and optimal network communication cost is achieved on the basis of maintaining the connectivity of the multi-robot dynamic network. There is no need for a center node to perform calculation in a centralized way, and distributed and parallel implementation can be carried out, so that the communication load is reduced, and the scalability and robustness of the multi-robot network are enhanced. The problem of communication link interrupt caused by robot motion can be overcome.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Legged robot stability control method and system with environmental adaptation
ActiveCN102736628AReduce equivalent errorMeet real-time control requirementsPosition/course control in two dimensionsControl systemLegged robot
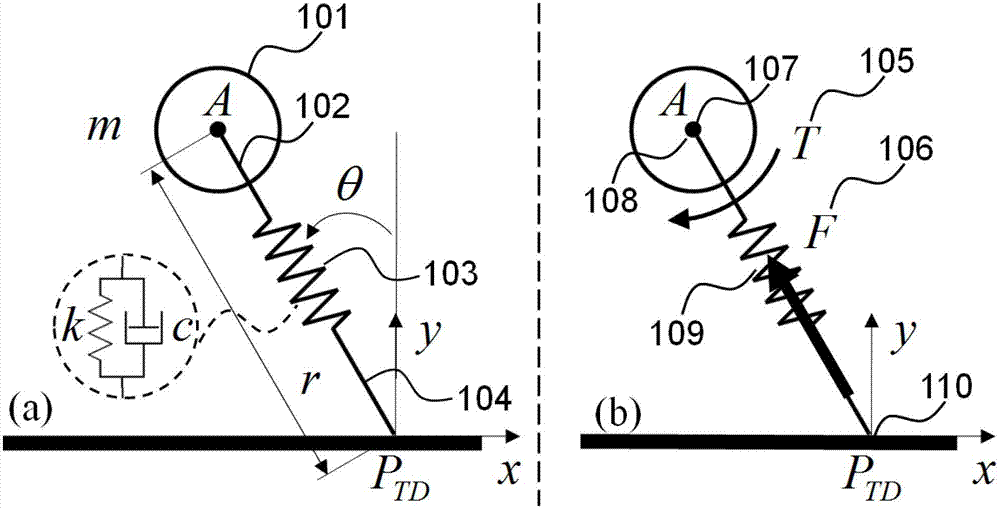
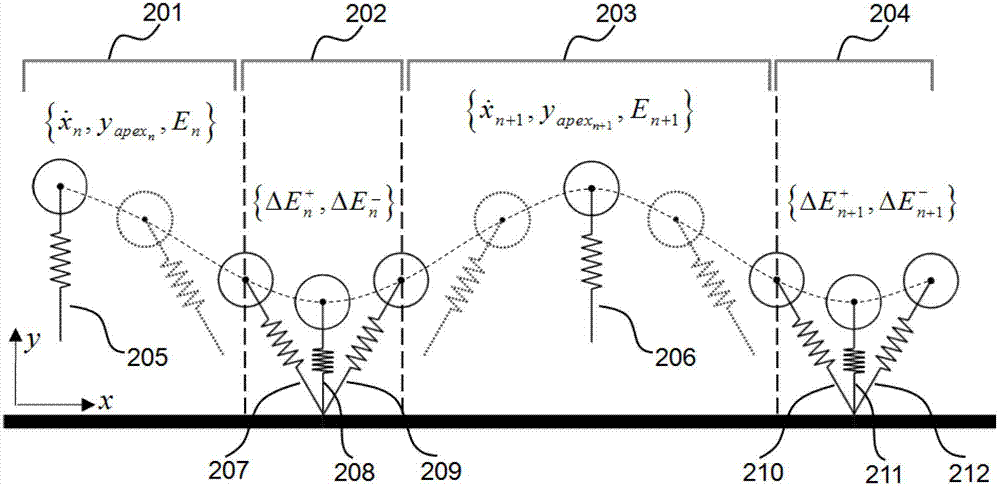
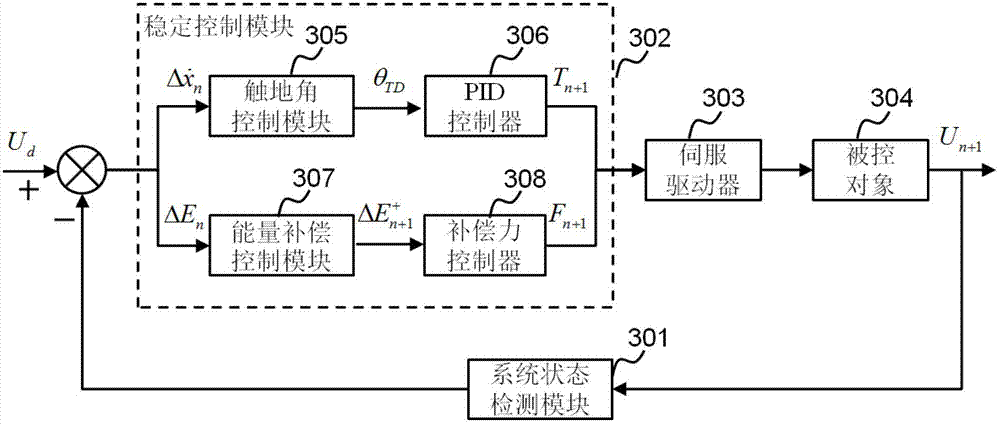
The invention discloses a legged robot stability control method and system with the environmental adaptation. The control method comprises the following steps of: comparing the relevant parameter information of a previous earth contact process with a control target expected to reach; carrying out feedback control to the horizontal kinematic velocity of a flight phase and total system energy; predicting and controlling the earth contact angle, and carrying out system energy compensation control; and finally, realizing the expected stable periodic motion of a legged robot serial line internet protocol (SLIP) equivalent model under different ground environments. The system comprises a system status detection module and a stable control module. According to the legged robot stability control method and system with the environmental adaptation, a specific robot dynamics model does not need to be built, an accurate fixed-point earth contact angle does not need to be calculated, and dominated convergence is realized by feedback control. The control method is simple and is quick in calculating, and the problems of insufficient control instantaneity, insufficient adaptability and the like in the traditional method can be better solved. In addition, the control system has a better unknown environment adaptability, and a better solution is provided for the legged robot stability control.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
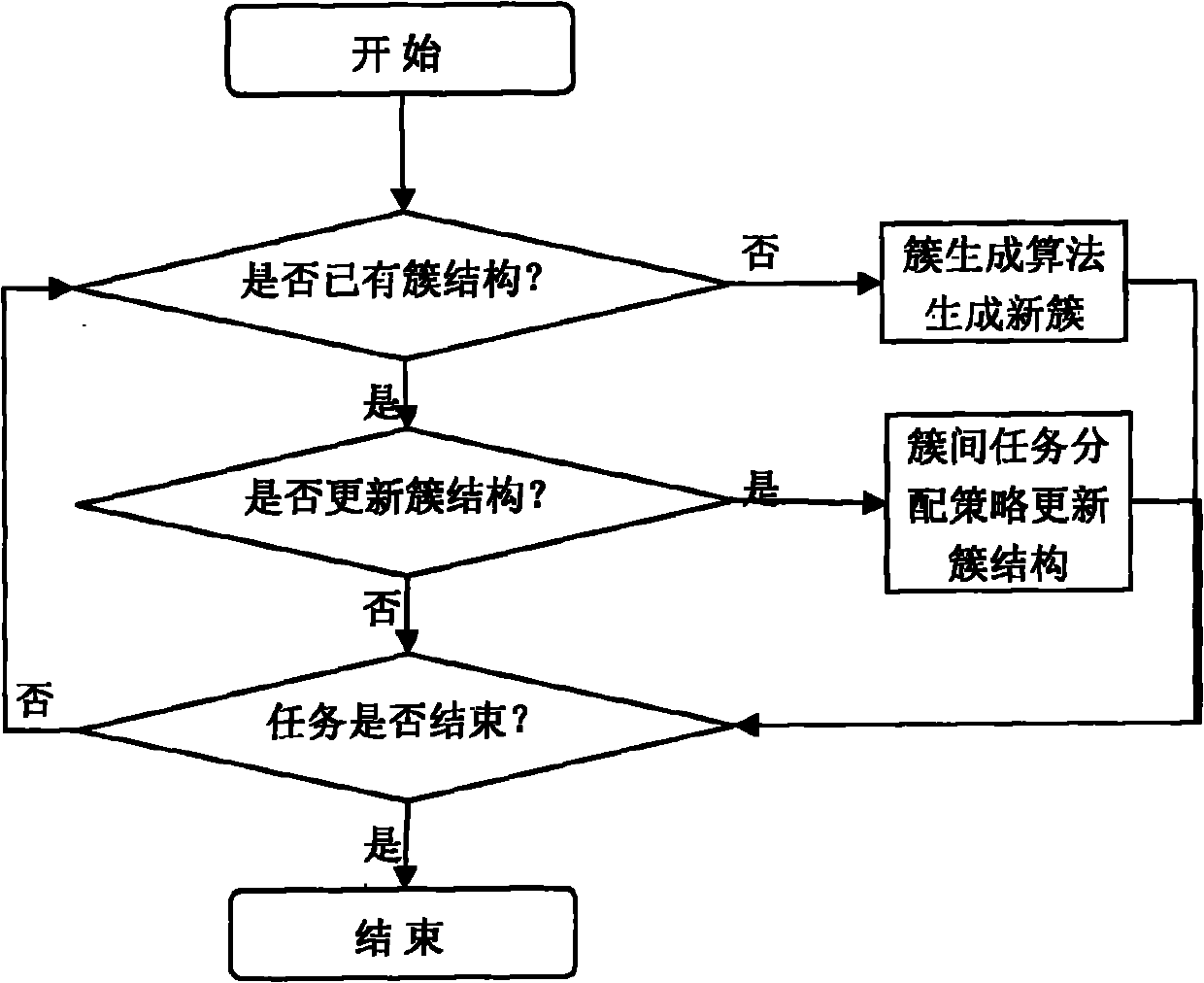
Clustering-based multi-robot task distributing method for use in exploiting tasks
The invention discloses a clustering-based multi-robot task distributing method for use in exploiting tasks, which comprises a clustering structure generating process and an inter-cluster robot dynamic task distributing process, wherein the tree topology-based clustering structure generating process comprises the steps of: (1) judging a cluster structure, (2) determining conditions for forming a dynamic cluster structure according to an initial task and information acquired by a robot, and (3) setting task dynamic change-oriented cluster updating rules; and the biologically started inter-cluster robot task distribution process comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing the functions of the robot in the clustering cooperation research according to different task types, and (2) establishing an interaction mechanism in a multi-robot clustering mode to realize the inter-cluster task distribution of the robot. The method has the advantages that: the robot has high flexibility in a cooperation process; the design of a single robot is simplified, and the robustness of the system can be improved; and the distribution result can flexibly adapt to the change of environment.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
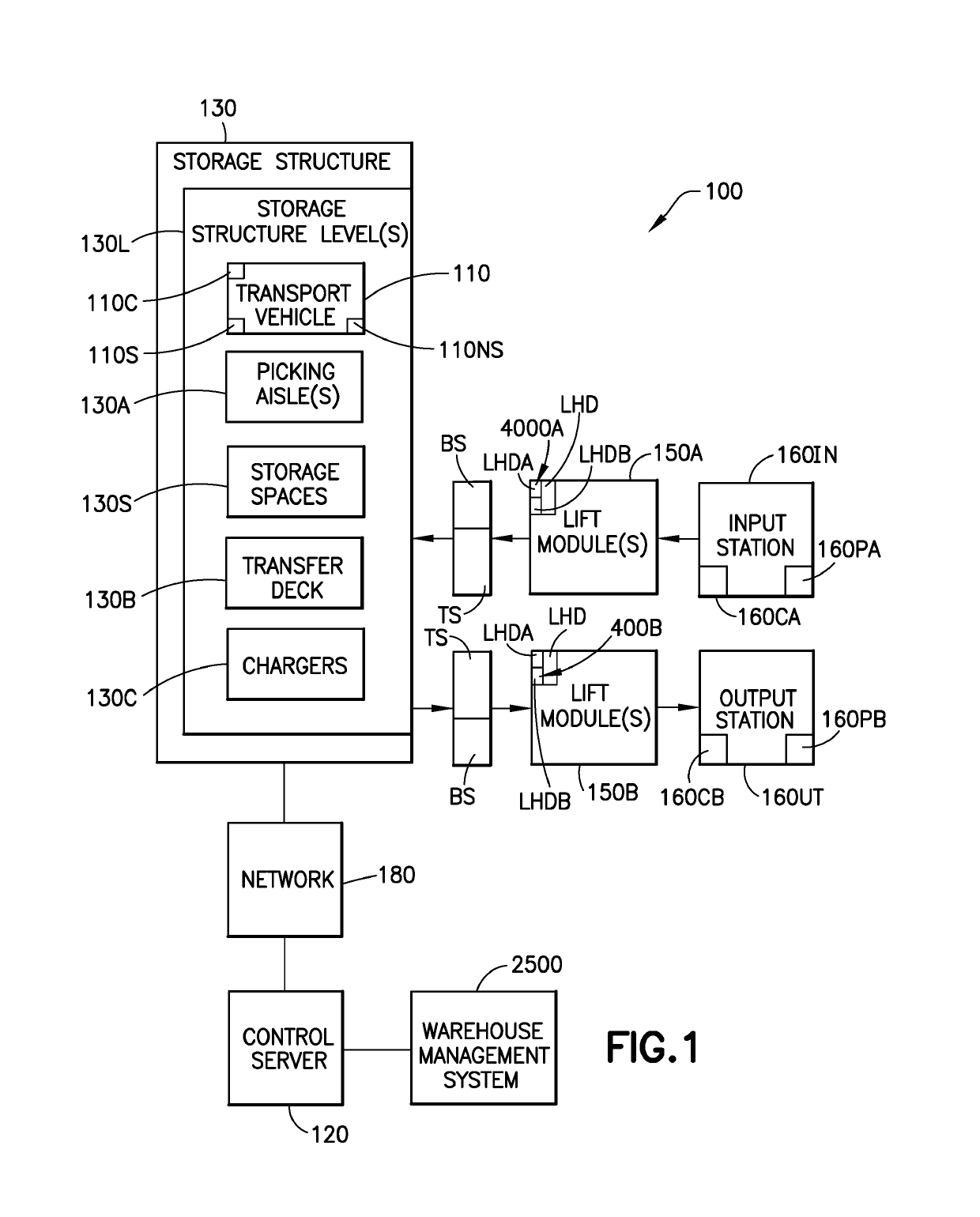
Storage and retrieval system
ActiveUS20190092570A1Reduce travel timeProgramme controlMathematical modelsDynamic modelsRobot dynamic
A storage array system including an open undeterministic transport surface, a navigation array disposed in connection with the transport surface, the navigation array includes a distributed feature, a first waypoint at a first position of the distributed feature, a second waypoint displaced from the first waypoint along the distributed feature and offset with respect to the first waypoint in a direction angled to the distributed feature, and a guided bot, arranged to traverse the transport surface, with a non-holonomic steering system, the guided bot having a bot pose determination system employing sensor data detecting the distributed feature, wherein the guided bot includes a controller configured to generate a substantially smooth curved bot traverse path on the transport surface connecting the first and second waypoints with a predetermined optimal trajectory of the guided bot along the traverse path determined based on a bot dynamic model.
Owner:SYMBOTIC LLC
Control method for tracking motion speed and motion track of rehabilitation training robot at the same time
InactiveCN105320138ACreate a decoupled state equationAsymptotically track motion trajectoriesChiropractic devicesPosition/course control in two dimensionsDrive wheelDynamic models
The invention belongs to the field of control of wheel type rehabilitation robots, and particularly relates to a control method for tracking the motion speed and motion track of a rehabilitation training robot at the same time, and the control method can effectively improve safety and rehabilitation effects of a trainee. According to control method provided by the invention, based on a kinematics model and a dynamics model of a rehabilitation walking training robot, a redundant freedom degree characteristic, and a nonlinear input-output linearization theory, an equation of a decoupling state between rotating speed and driving force of each driving wheel is established; a driving force controller is designed, and based on the decoupling state equation, asymptotic tracking of the motion speed of the rehabilitation walking training robot is realized; and further, based on the driving force controller together with a nonlinear feedback control law, and based on a rehabilitation walking training robot dynamics model, asymptotic tracking of the motion track is realized.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
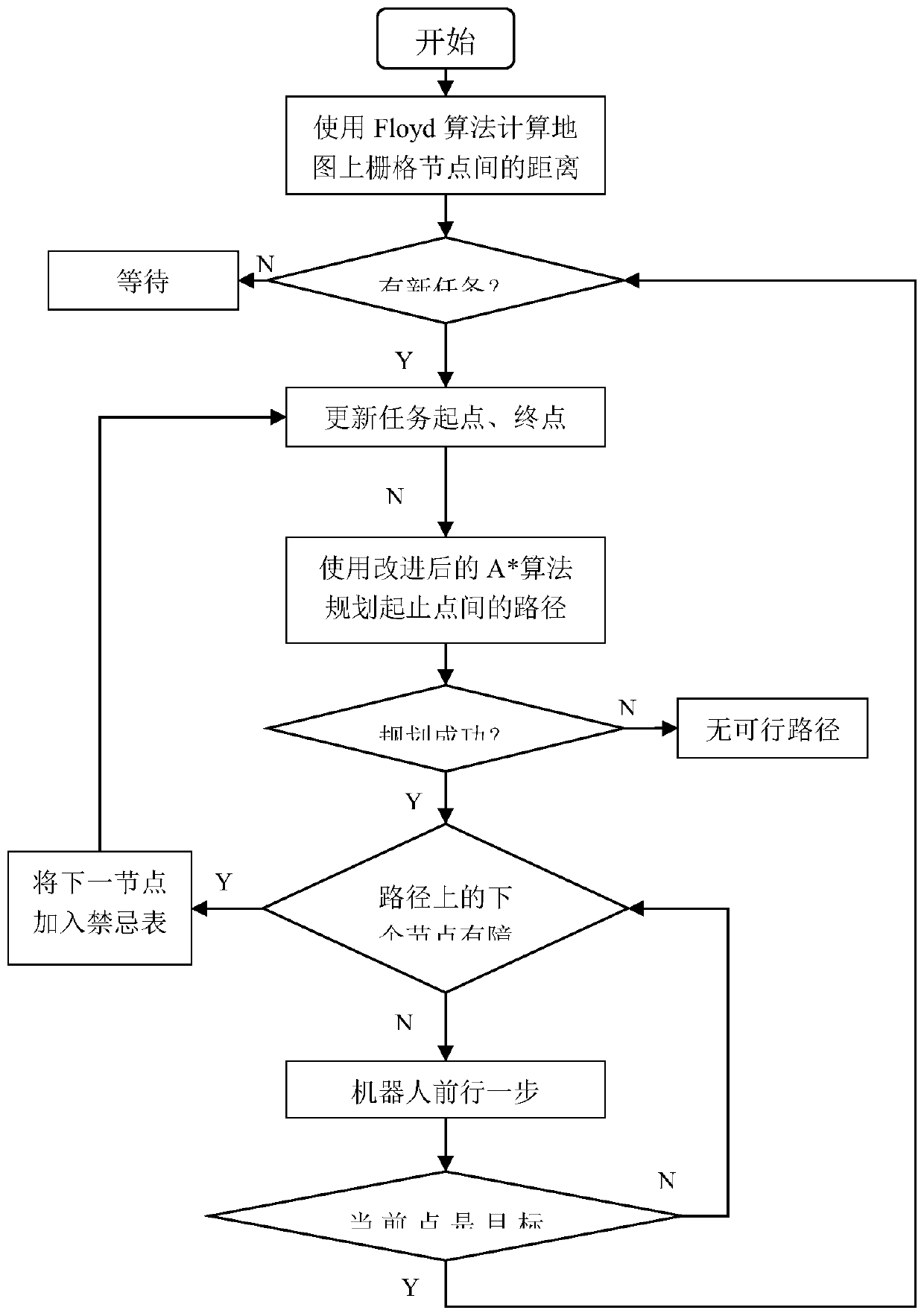
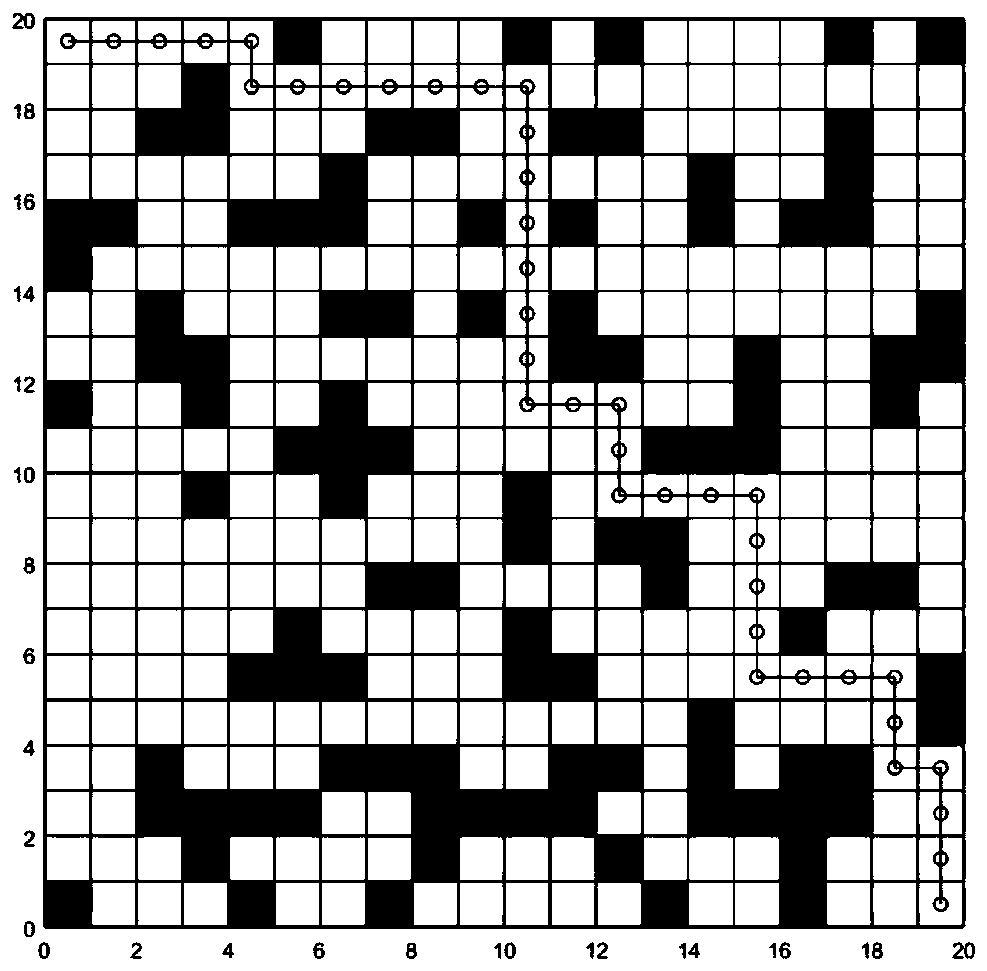
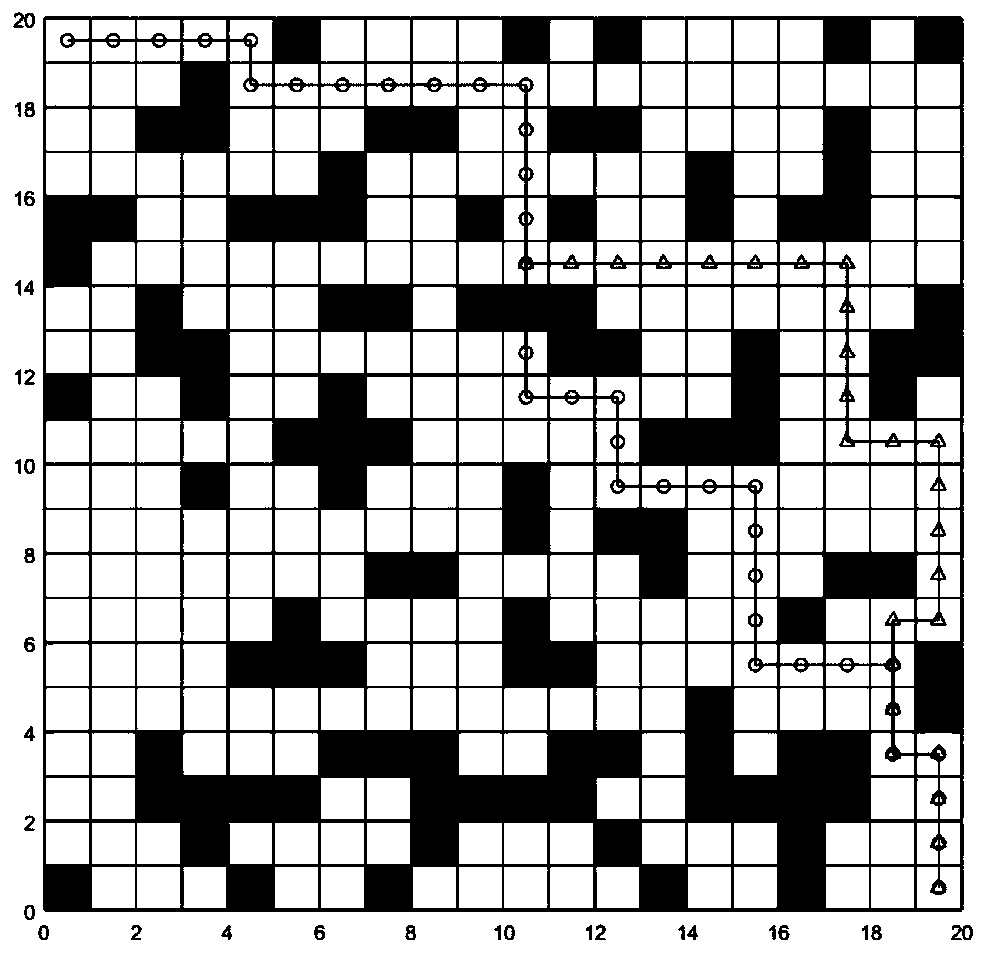
Dynamic path planning method for mobile robot
InactiveCN110442125ASmall amount of calculationReduce the numberInstruments for road network navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsAutomatic controlSimulation
The invention is applicable to the technical field of automatic control, and provides a dynamic path planning method for a mobile robot, comprising the following steps: calculating a distance betweenall the node pairs on a grid map by a Floyd algorithm; when a new issued task is detected, planning a path of the task by an improved A* algorithm; checking whether there is an obstacle on a next nodeof the path when the robot walks along the planned path, if not, making a step forward, if any, adding the next node in a close table, and rapidly planning a path from the current node to a target point by the improved A* algorithm; repeating the previous step until the robot reaches the target point. Based on a calculation result from the Floyd algorithm, the dynamic path planning method of theinvention improves a heuristic function of the A* algorithm, and applies the A* algorithm in the dynamic path planning scene of a continuous task of the mobile robot. By using the improved A* algorithm, the path is re-planned only when a dynamic obstacle appears on the path, thereby greatly reducing computational cost and greatly improving real-time of the robot in operation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
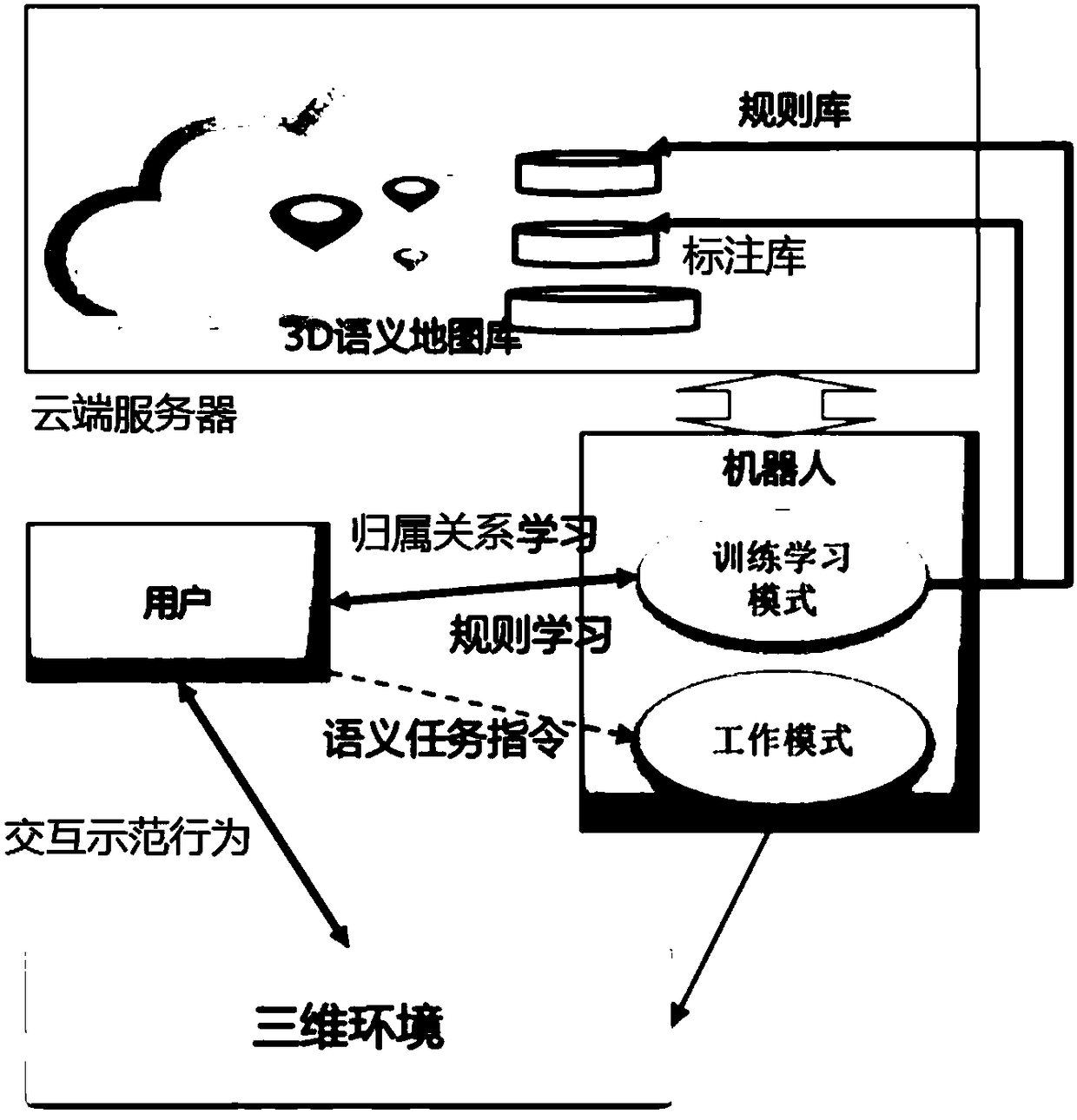
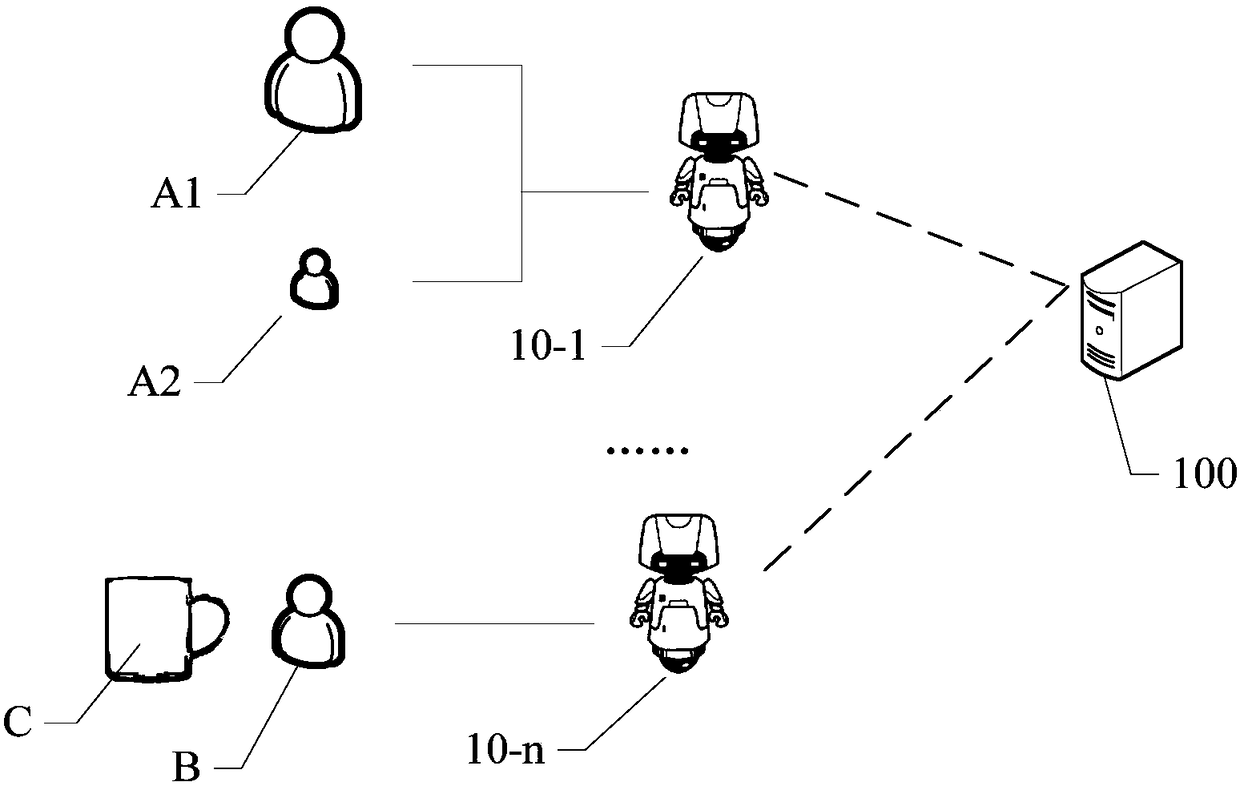
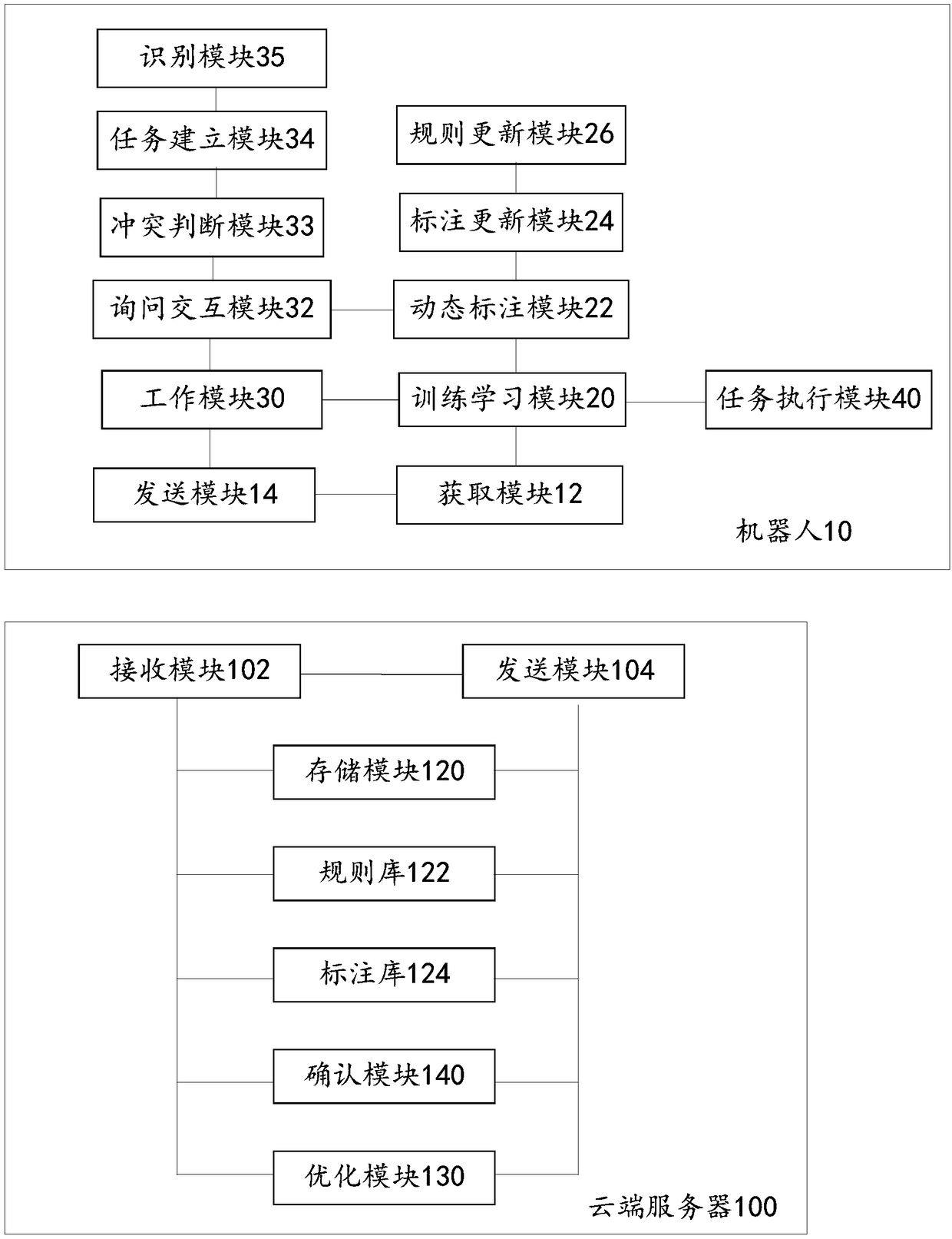
Dynamic learning method and system for robot, robot and cloud server
A dynamic learning method for a robot, comprising a training learning mode, the training learning mode comprising the following steps: dynamically annotating an attribute relationship between an object and a person in a three-dimensional environment to form an annotation library; acquiring a rule base, and passing the rule base and the annotation library The interactive demonstration behavior establishes a new rule and a new annotation; when it is confirmed that the established new rule has no conflict with the rule in the rule base, the new rule is updated to the rule base and the new annotation is updated to the annotation library.
Owner:CLOUDMINDS SHANGHAI ROBOTICS CO LTD
Robust control method based on reinforcement learning and Lyapunov function
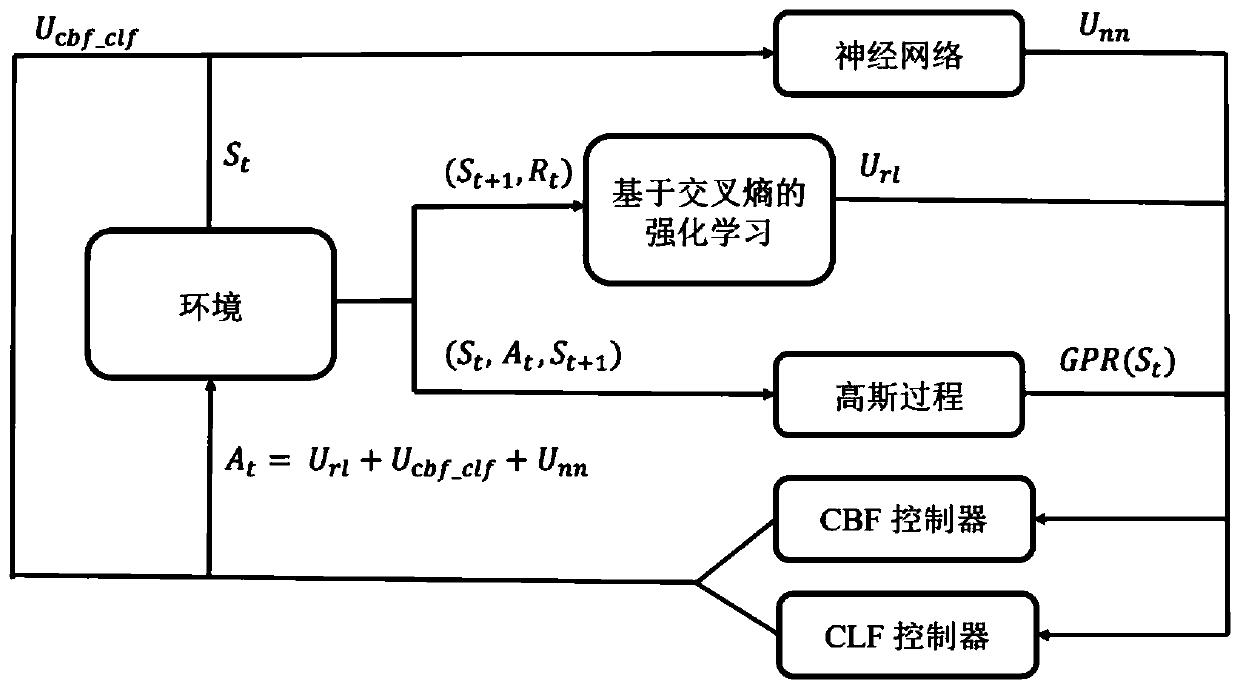
ActiveCN110928189ASolve the difficult problem of settingGuaranteed freedom to exploreAdaptive controlRobotic systemsSimulation
The invention relates to a robust control method based on reinforcement learning and a Lyapunov function. Modeling is conducted on robot dynamics through self-adaptive online Bayesian reasoning, a constrained reinforcement learning problem is constructed based on Lyapunov, and efficient learning, stable work and safe exploration of the robot are achieved by constructing a Lyapunov function controlstrategy and a barrier function control strategy. The technical problems of insecurity, instability and inefficiency of a nonlinear hybrid dynamic safety-critical robot system facing system uncertainty and external environment uncertainty in a task scene with limited state and action space are solved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Multi-axis robot dynamics modeling method based on shaft invariant
ActiveCN108972558AImprove computing efficiencyImprove stabilityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSymbolic SystemsSimulation
The invention provides a multi-axis system dynamics modeling and resolving principle based on a shaft invariant. Iterative explicit dynamics modeling of a tree chain, a closed chain, a joint providedwith friction and viscous and a multi-axis system of a movable base is realized, an established model has an elegant chain symbol system and has the function of pseudo codes, so that complete parameterization including topology, coordinate systems, polarity, structural parameters, mass inertia and the like is achieved. The principle may be set as a circuit or codes to be executed directly or indirectly and partially or entirely within a multi-axis machine system; and in addition, the invention also comprises an analysis and verification system constructed on the principles and used for designing and verifying a multi-axis machine system.
Owner:居鹤华
Space robot arresting control system, reinforce learning method and dynamics modeling method
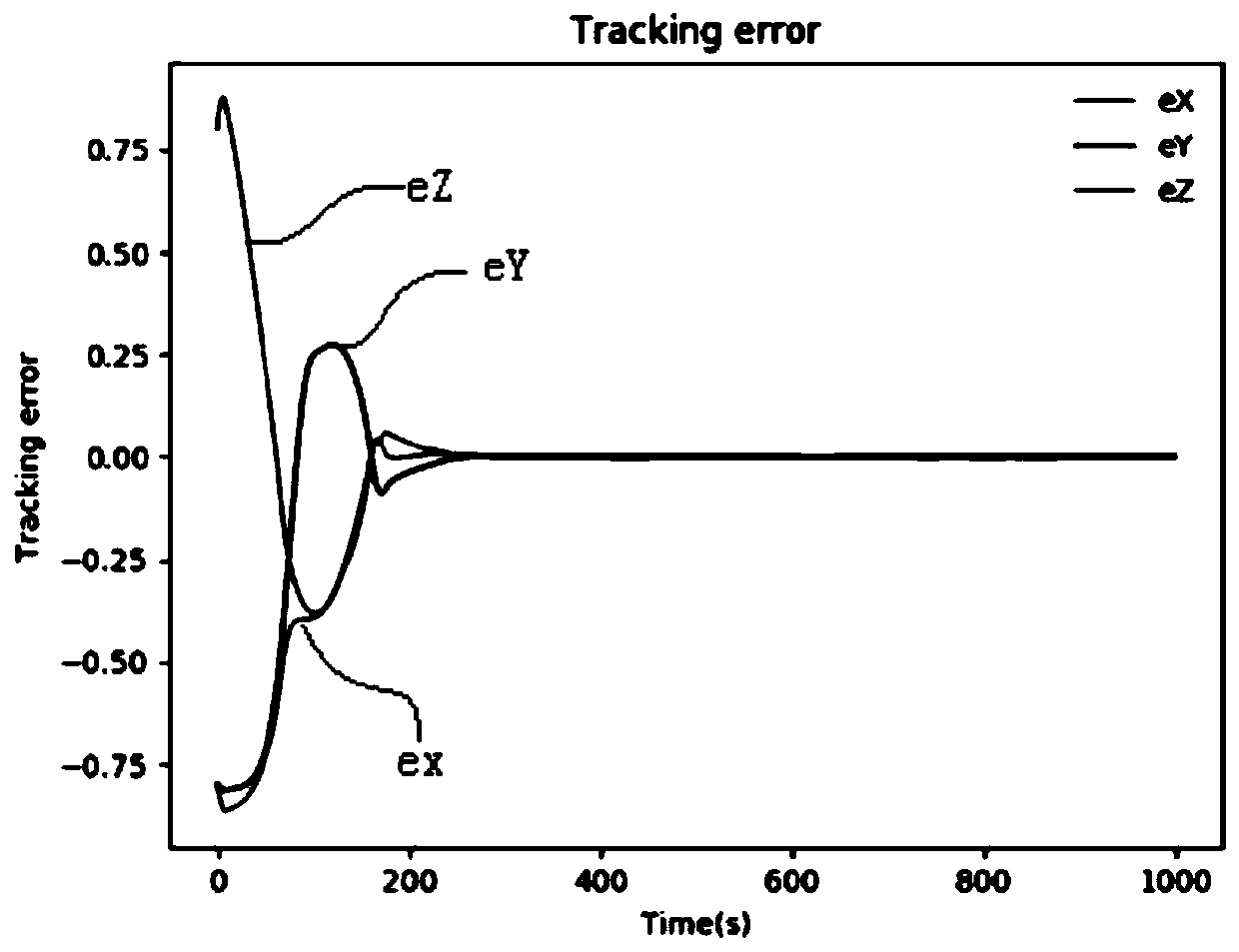
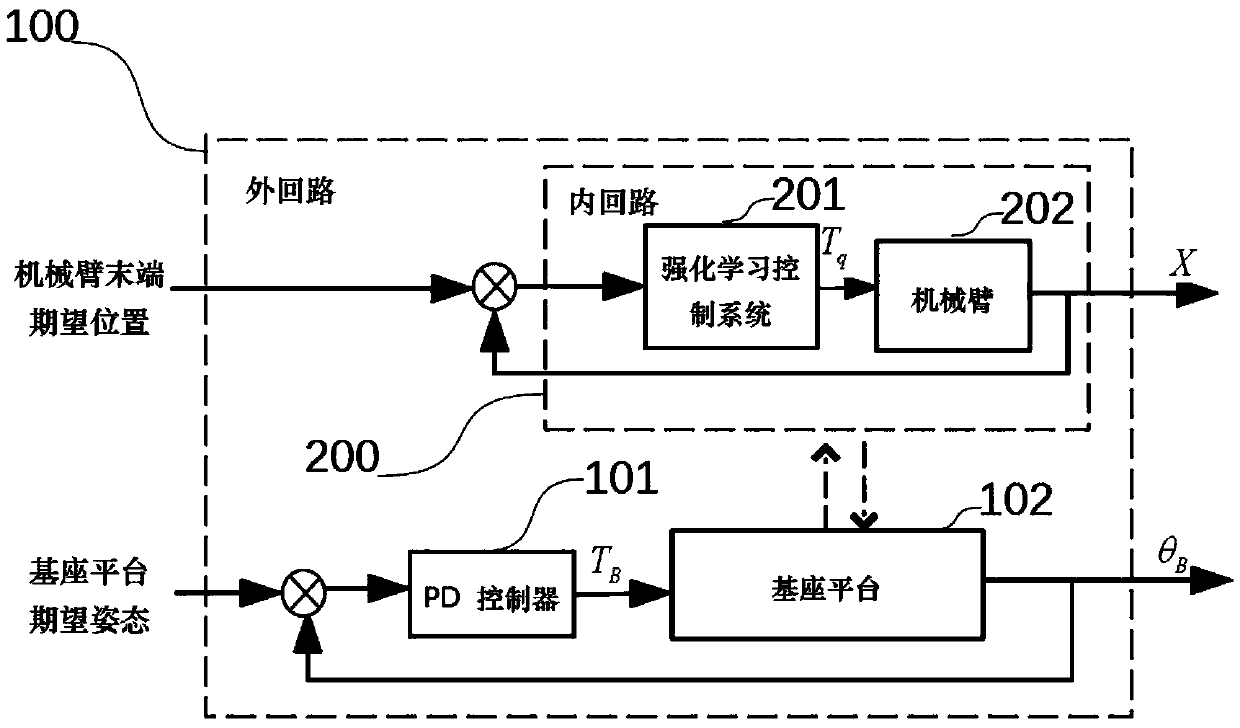
InactiveCN109605365AReduce disturbanceSmooth terminal movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorInner loopControl system
The invention discloses a space robot mechanical arm arresting control system. The space robot mechanical arm arresting control system comprises two loops, namely, an inner loop and an outer loop, inthe outer loop, the system achieves the attitude stability of a space robot mechanical arm base platform in the arresting process through a PD controller, and in the inner loop, the system controls amechanical arm to achieve arresting maneuvering on a non-cooperative target through a reinforce learning control system based on reinforce learning. The invention further discloses a reinforce learning method for controlling the reinforce learning control system of the mechanical arm in the inner loop of the system and a space robot dynamics modeling method of the space robot mechanical arm arresting control system. According to the space robot arresting control system, the reinforce learning method and the dynamics modeling method, compared with PD control, the posture disturbance of the baseplatform under reinforce learning RL control is smaller, the movement process of the tail end of the mechanical arm is more stable, the control precision is higher, moreover, the motion flexibility of the mechanical arm under the reinforce learning RL control is good, and the autonomous intelligence is achieved to the greater extent.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Robot hand-eye calibration method and device based on novel three-dimensional (3D) calibration block
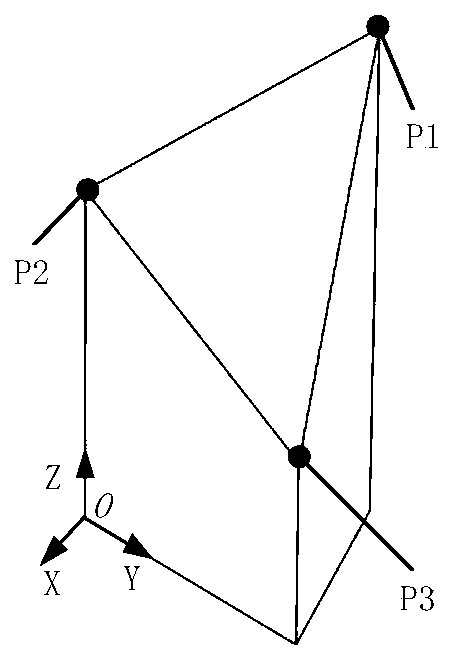
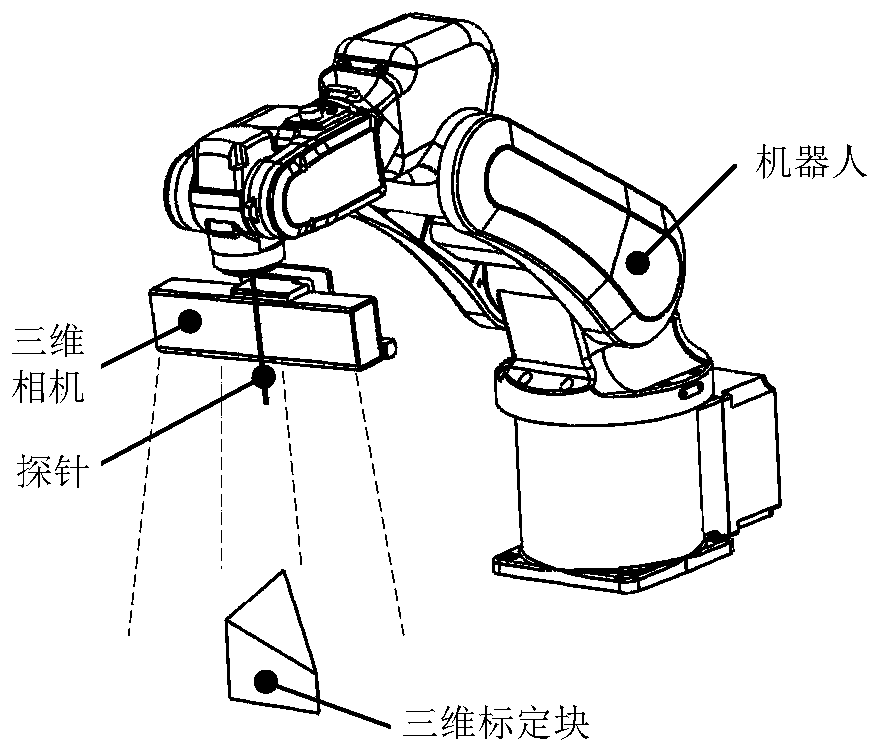
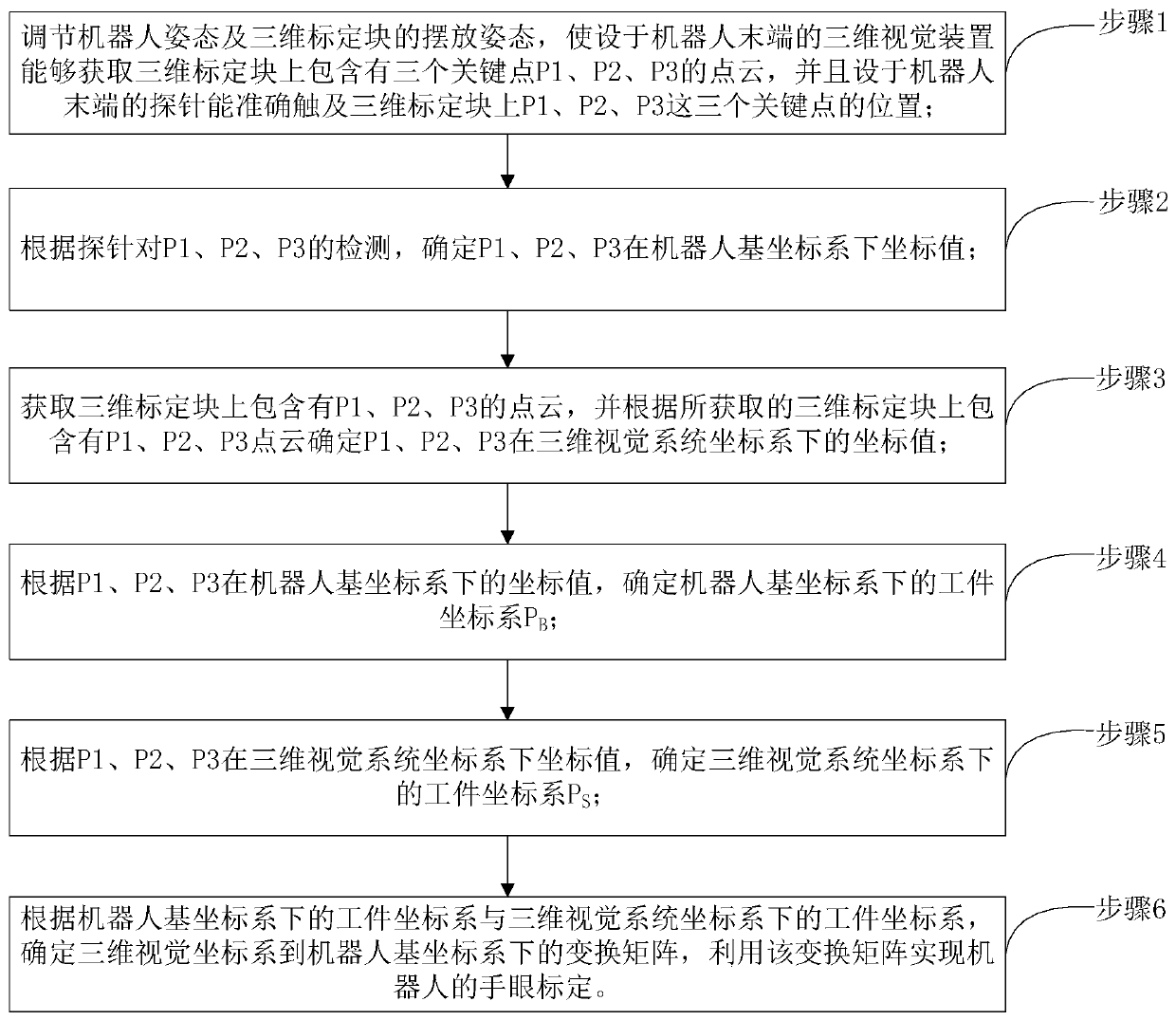
The invention provides a robot hand-eye calibration method and device based on a novel three-dimensional (3D) calibration block. The robot hand-eye calibration method based on the novel 3D calibrationblock includes the steps of enabling a 3D vision device to acquire a point cloud, containing three key points, on the 3D calibration block, by adjusting postures of a robot and placing postures of the 3D calibration block, and enabling a probe to accurately touch positions of the three key points on the 3D calibration block; confirming coordinate values of the three key points under a robot basecoordinate system; confirming coordinate values of the three key points under a 3D vision system coordinate system according to the acquired point cloud, containing the three key points, on the 3D calibration block; confirming a workpiece coordinate system PB under the robot base coordinate system; confirming a workpiece coordinate system PS under the 3D vision system coordinate system; and confirming a transformation matrix from the 3D vision system coordinate system to the robot base coordinate system according to the PB and the PS, and using the transformation matrix to realize hand-eye calibration of the robot. The robot hand-eye calibration method and device based on the novel 3D calibration block can perform the hand-eye calibration low in cost, convenient and quick, and high in accuracy in the robot dynamic 3D vision system, and is wide in application.
Owner:佛山金洽智能装备有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com