Dynamic path planning method for mobile robot
A mobile robot, dynamic path technology, applied in the directions of instruments, motor vehicles, road network navigators, etc., can solve the problems of low complexity of A* algorithm, large amount of calculation, small amount of calculation, etc., to achieve high planning efficiency and reduce calculation. The effect of reducing quantity and number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
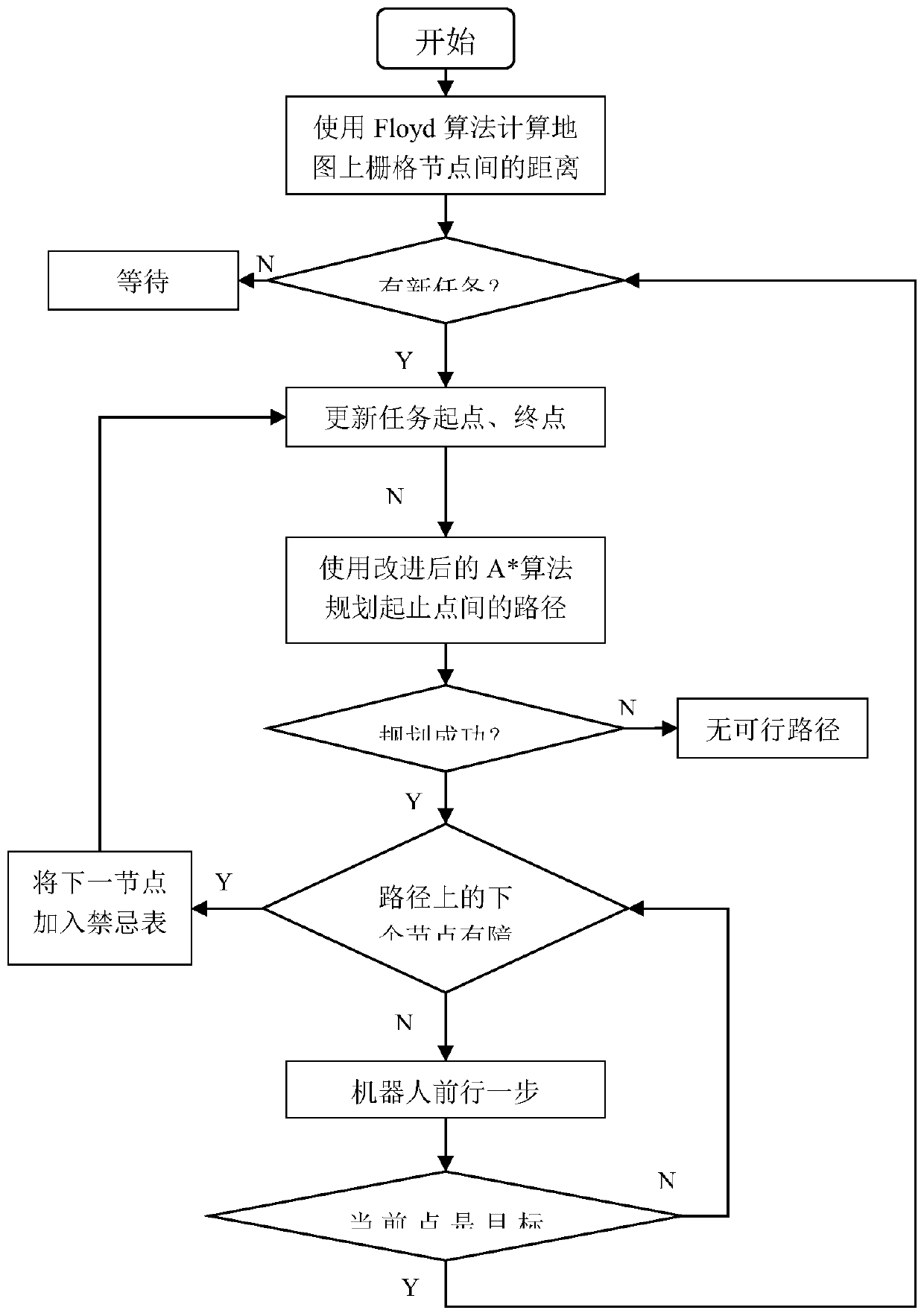
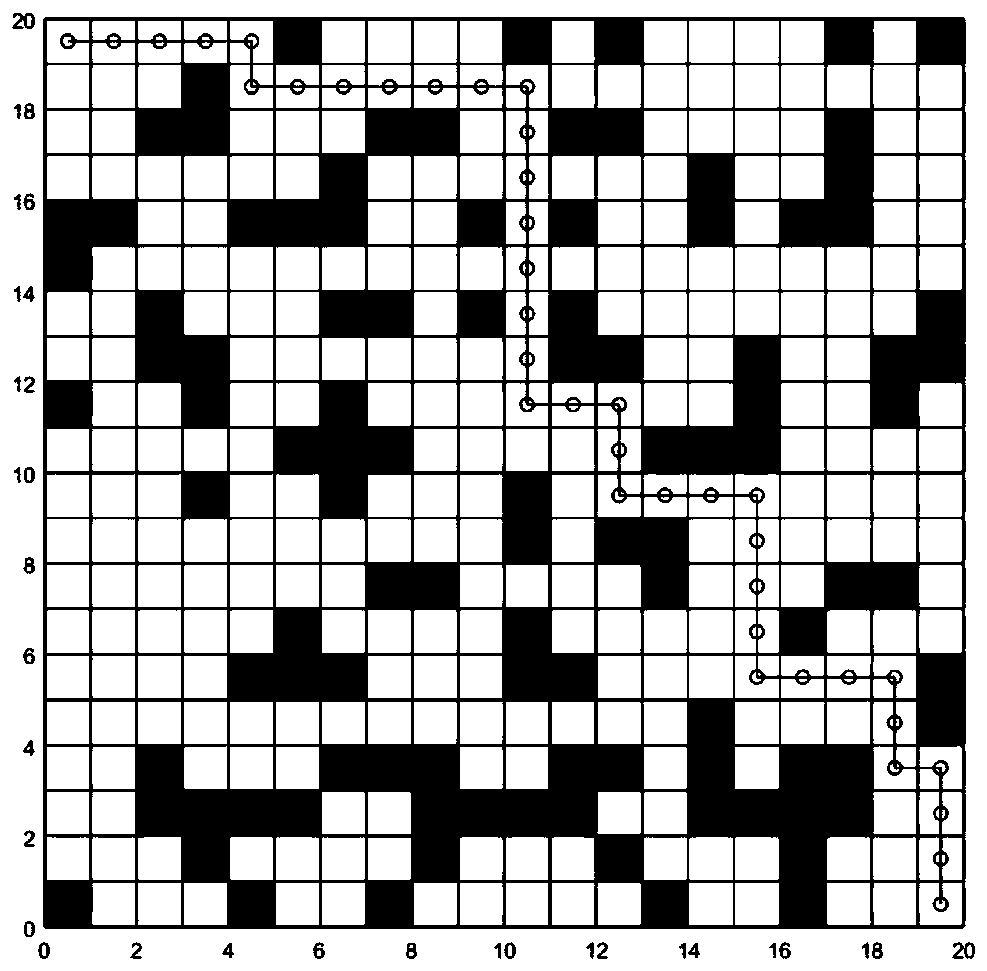
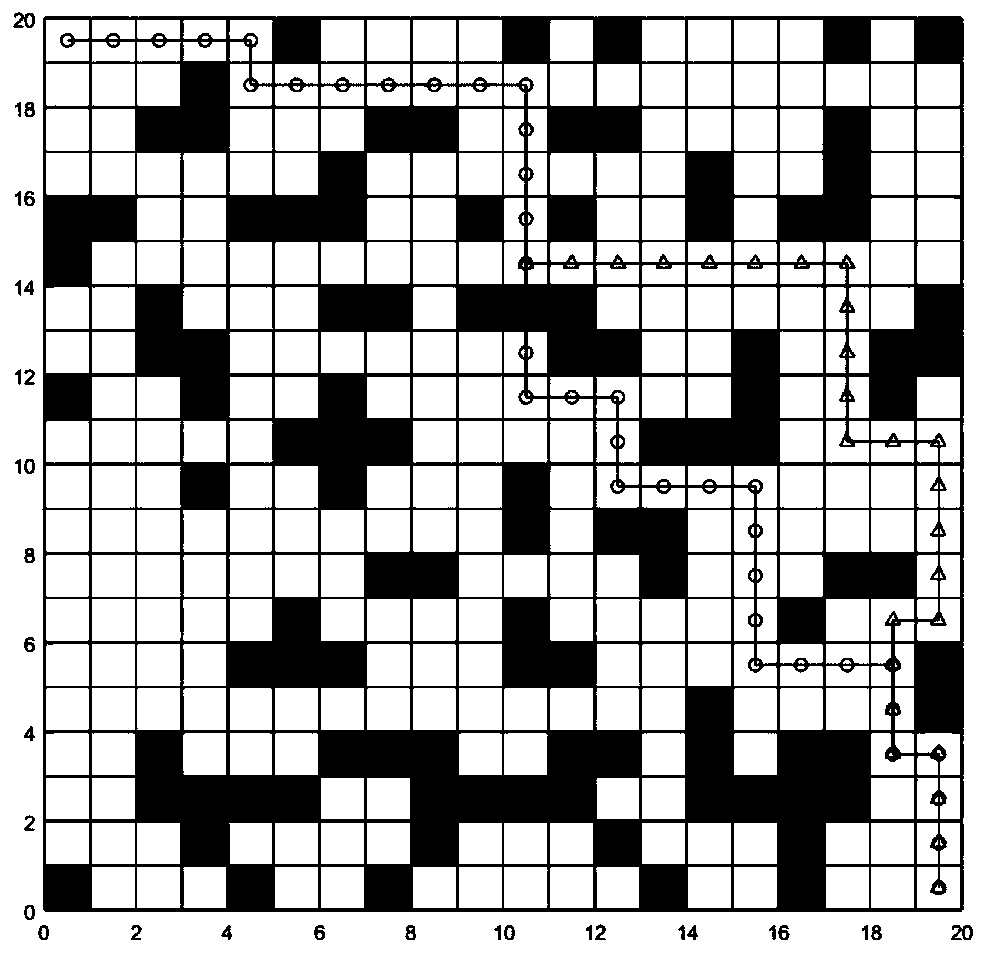
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a kind of dynamic path planning method of mobile robot, and it comprises the following steps:
[0032] (1) The process of using the Floyd algorithm to calculate the distance between all node pairs on the static grid map is:
[0033] (11) Use D[v][w] to record the shortest distance between each pair of nodes, that is, the distance between node v and node w;
[0034] (12) Scan each point in turn, and use it as the base point to traverse all the values of each pair of nodes D[v][w]. When node v to node w passes through the base point, D[v][w] is smaller , update the value of D[v][w] with a smaller distance value.
[0035] (2) The robot detects whether there is a new task to be issued at present, and if there is no one, the process of waiting in place is as follows: Whenever the robot completes the curre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com