Kinematics calibration method and system for flexible robot
A technology of robot kinematics and calibration method, which is applied in the field of flexible robot kinematics calibration method and system, can solve problems affecting joint angle, error, end error, etc., and achieve the effect of improving calibration accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] A method for calibrating the kinematics of a flexible robot, comprising a linkage joint segment calibration step and a robot calibration step, wherein the linkage joint segment calibration step includes:
[0055] According to the nominal joint angle of the linkage joint segment (ie, the theoretical joint angle), the nominal pose (ie, the theoretical pose) of the linkage joint segment under zero linkage angle error is obtained. In the present invention, the terminal position and posture are referred to as pose.
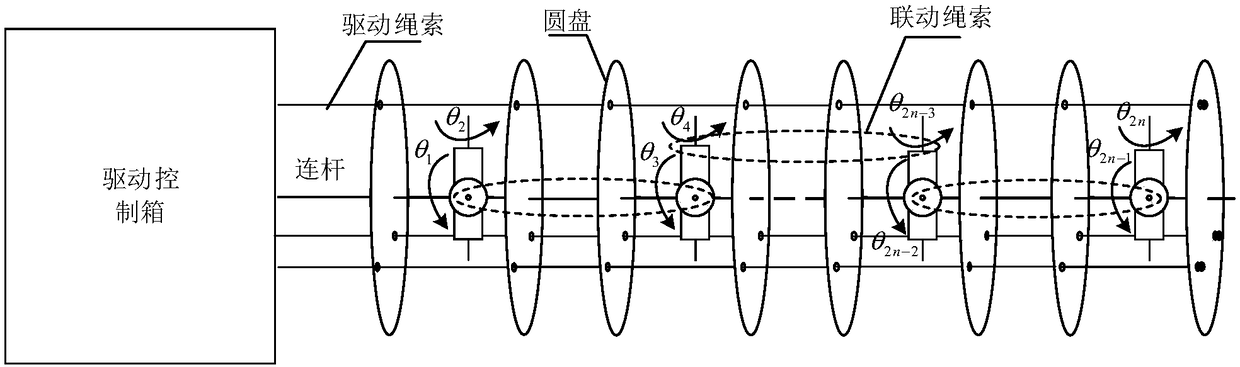
[0056] Use the parameter decoupling driving structure to drive the linkage joint segment so that the driving rope reaches the nominal length of the linkage joint segment (that is, the theoretical length of the rope), and obtain the actual pose of the linkage joint segment, where the calculation is based on the nominal joint angle of the linkage joint segment Get the nominal rope length of the linkage joint segment, refer to figure 2 , figure 2 It is a schemat...
Embodiment 1
[0064] Obtain embodiment 2 based on embodiment 1, the robot calibration step also includes:
[0065] Obtain the nominal pose of the robot under the linkage angle error of the robot according to the nominal joint angle of the robot;
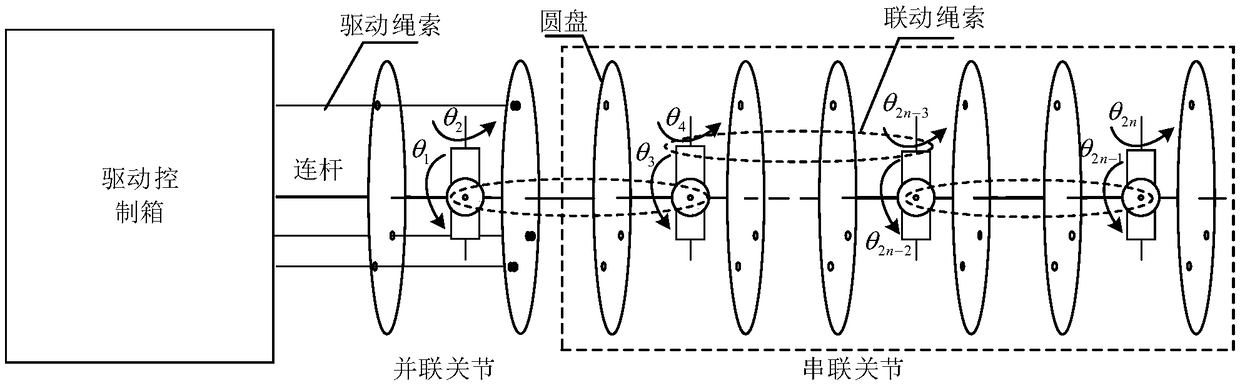
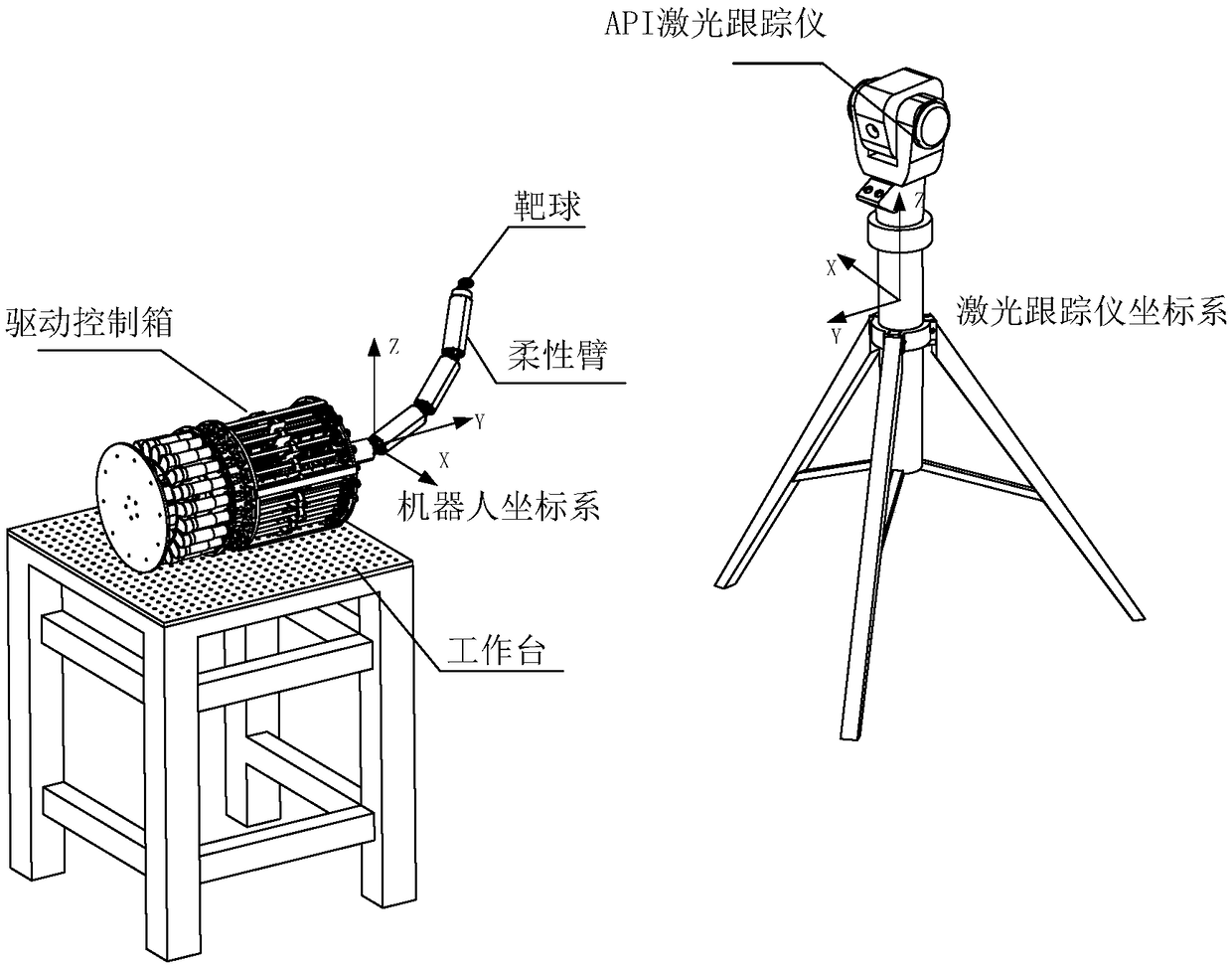
[0066] refer to figure 1 , use the normal driving structure to drive the robot so that the driving rope reaches the nominal rope length of the robot, and obtain the actual pose of the robot, calculate the nominal rope length of the robot according to the nominal joint angle of the robot, and use different normal drive for different linkage joint segments Structural drive, each linkage joint segment is driven by a normal drive structure. In this embodiment, the normal driving structure uses three driving ropes to drive the linkage joint segment, and is provided with a motor position sensor and a rope tension sensor. When driving the whole arm of the robot, among the three motors of the three driving ropes in each linkage joint segment, one motor ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3 is a concrete description of the specific implementation process of the flexible robot kinematics calibration method:
[0071] First, the kinematics analysis of the rope-driven manipulator is carried out. The kinematics analysis of the rope-driven super-redundant manipulator includes not only the mapping relationship between the joint space and the operation space, but also the mapping relationship between the rope driving space and the joint space. Therefore, its kinematic analysis can be divided into two steps: first, deduce the mapping relationship between the joint space and the operation space, that is, the relationship between the pose of the robot end coordinate system and the joint variables ψ, α; then deduce the mapping between the rope drive space and the joint space The relationship, that is, the relationship between the joint variables ψ, α and the change in the length of the driving rope Δli, such as Figure 4 shown.
[0072] First, the mappin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com