Inclination-angle-constraint-based kinematic calibration method for Stewart parallel robot
A technology of robot kinematics and robot movement, applied in the field of automation, can solve the problems of destroying passive joint hinges, limited selection space, and affecting the accuracy of calibration results, etc., to avoid dependence on accurate measurement, high degree of automation, and improve pose The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention is described in further detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
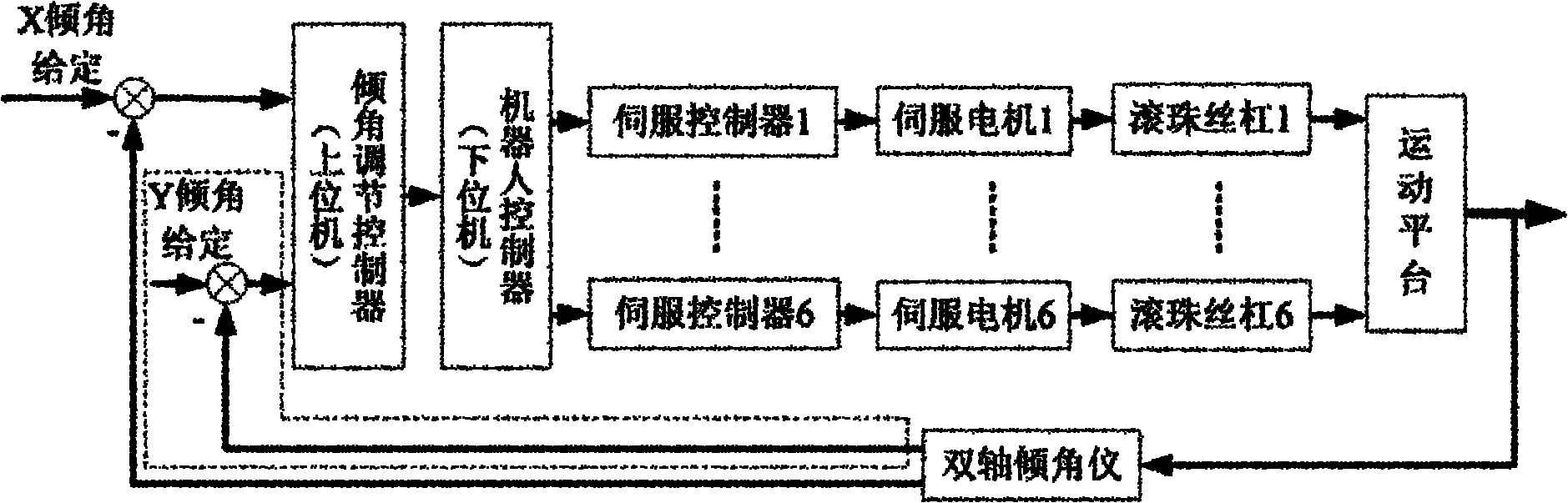
[0025] see Figure 1-5 , a Stewart parallel robot kinematics calibration method based on inclination constraints, including the following steps:
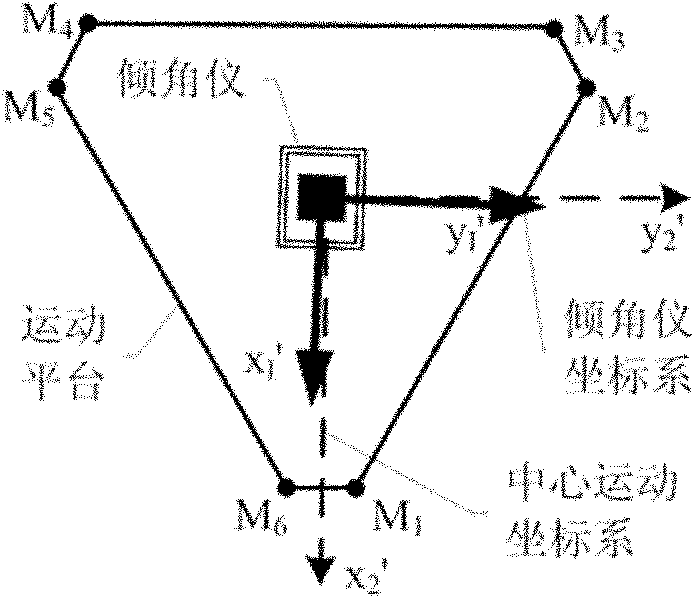
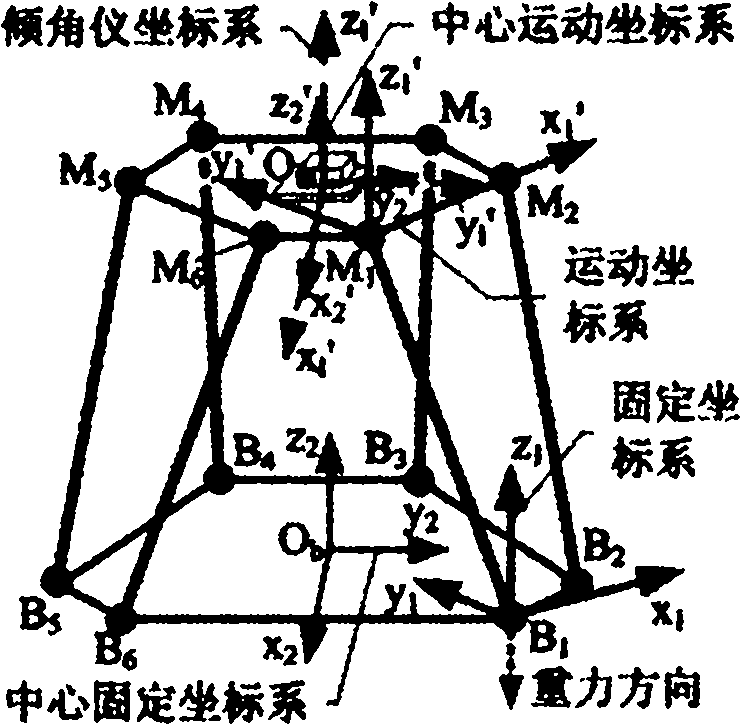
[0026] First, specify how to establish the calibration coordinate system, such as image 3 shown, where:
[0027] Motion coordinate system M 1 -x 1 'y 1 'z 1 ′——take the joint hinge point M on the motion platform 1 as the origin of the coordinate system; x 1 ' axis passes through M 2 point, and along direction; x 1 'y 1 ' plane by M 1 , M 2 and M 6 Three points are determined, and the motion coordinate system is established according to the principle of the right-hand system;
[0028] Center motion coordinate system O m -x 2 'y 2 'z 2 ′—— general M 1 -x 1 'y 1 'z 1 ' around itself z 1 ′ axis rotates 5π / 6 clockwise, and then translates to the nominal geometric center O of the motion platform m get li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com