Method for kinematic calibration of six-degree-of-freedom robot based on monocular vision
A robot kinematics, monocular vision technology, applied in the direction of instruments, manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve the problems of measurement result fluctuation, radial distortion, result accuracy interference, etc., to improve the accuracy of distance measurement, improve the measurement accuracy The effect of distance accuracy and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. This embodiment is carried out on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation and specific operation process are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
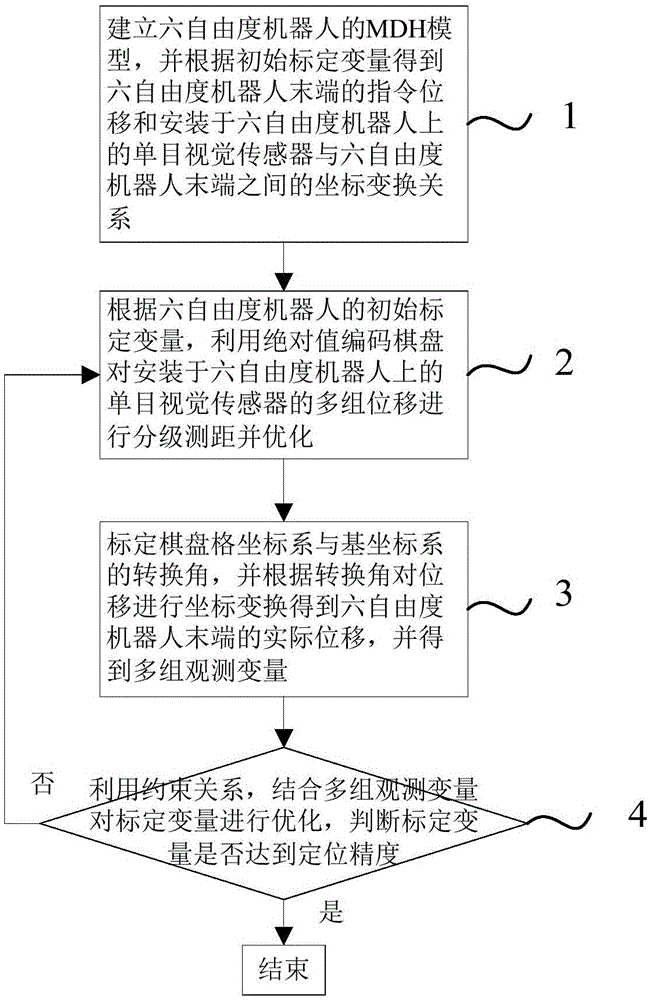
[0044]A common step in robot calibration is to construct a kinematic model based on the structural characteristics of the robot. And use the model characteristics to establish the constraint relationship between the observed variable and the variable to be calibrated; through the external sensor, the required observed variable is measured with high precision; using the constraint relationship and multiple sets of measured values, through the relevant mathematical optimization method, the optimization of the variable to be calibrated is realized; In this way, the mechanical parameters ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com