Patents
Literature
120 results about "Stabilator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
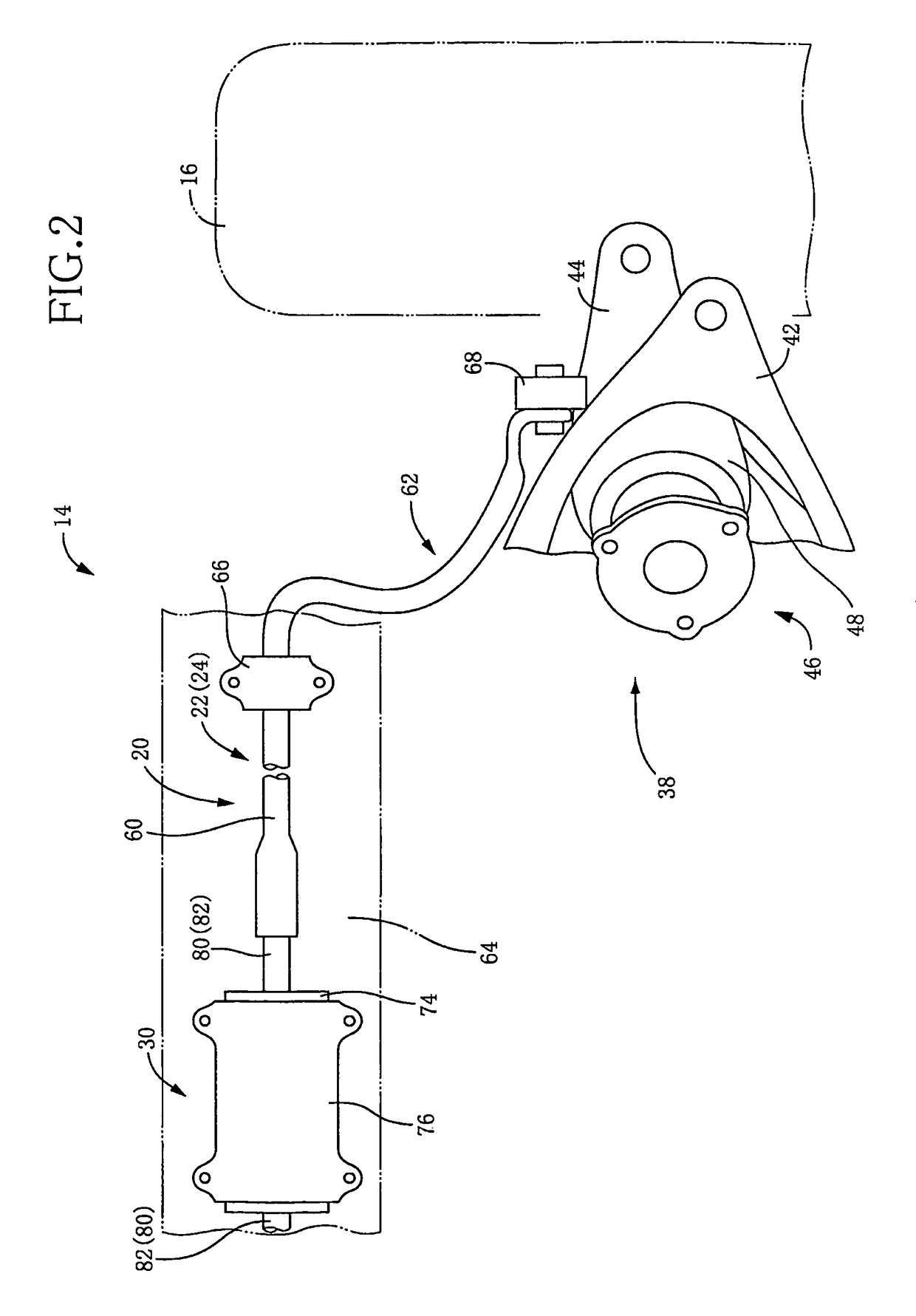
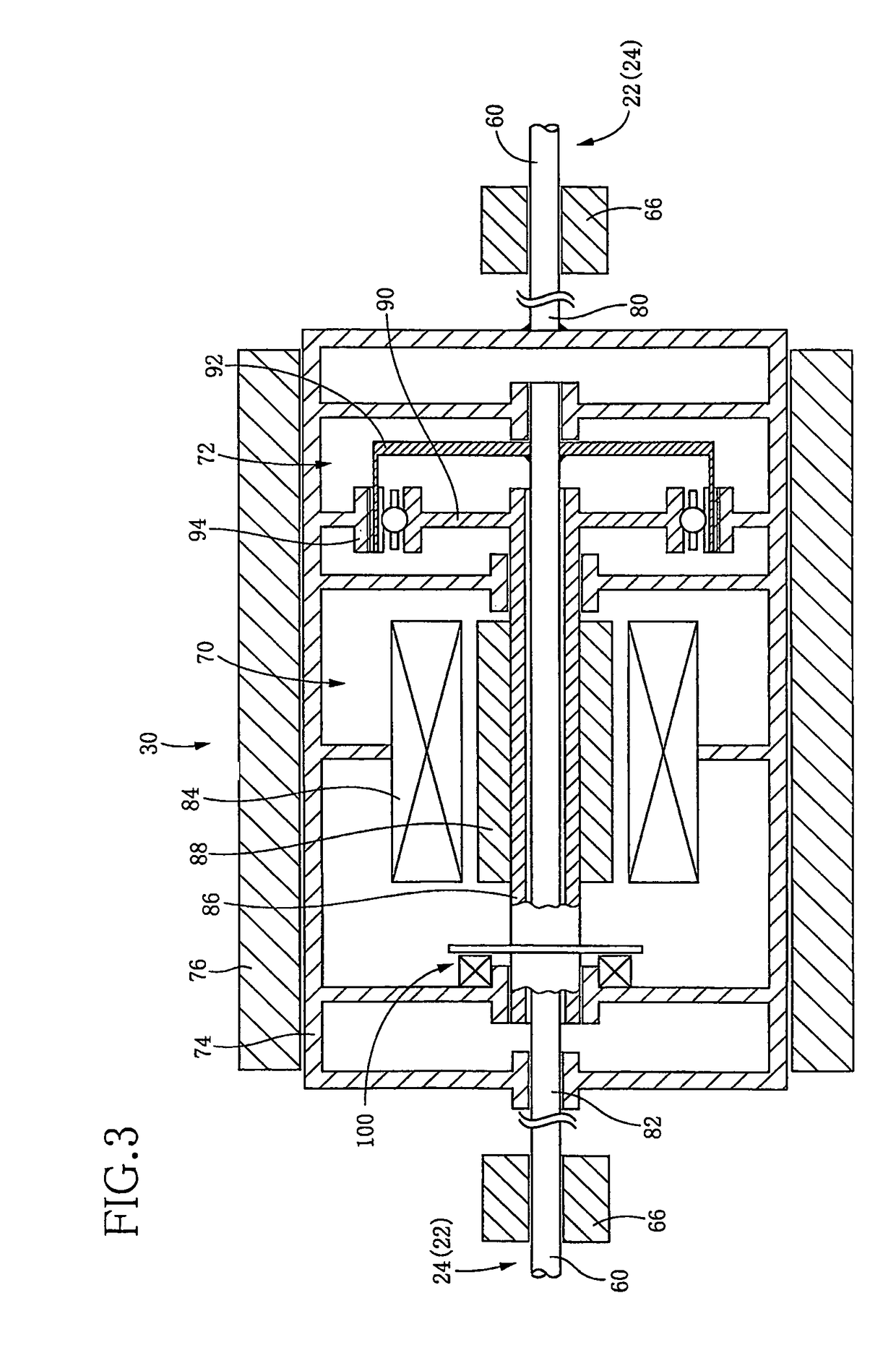
A stabilator, more frequently all-moving tail or all-flying tail, is a fully movable aircraft stabilizer. It serves the usual functions of longitudinal stability, control and stick force requirements otherwise performed by the separate parts of a conventional horizontal stabilizer and elevator. Apart from a higher efficiency at high Mach number, it is a useful device for changing the aircraft balance within wide limits, and for mastering the stick forces.
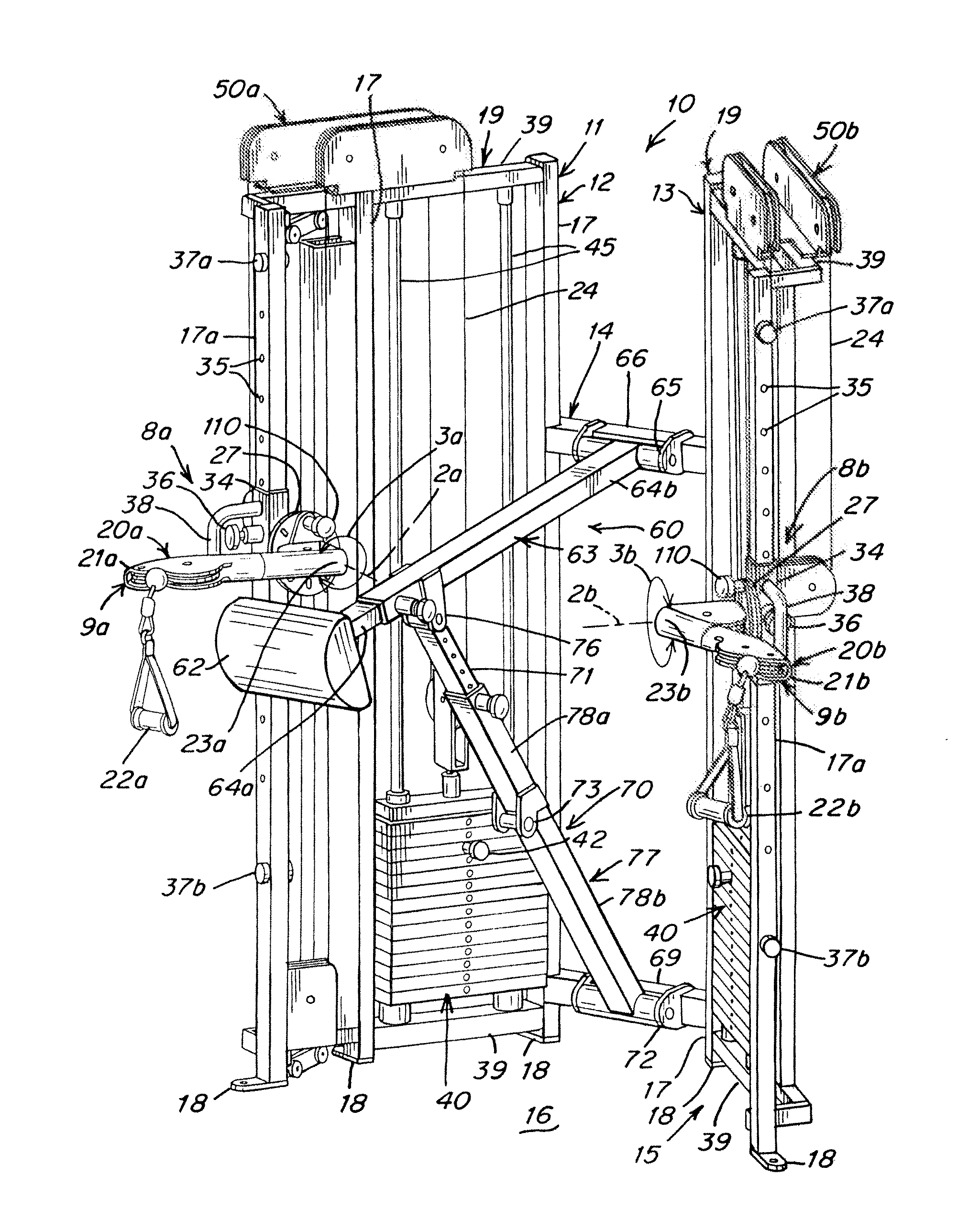
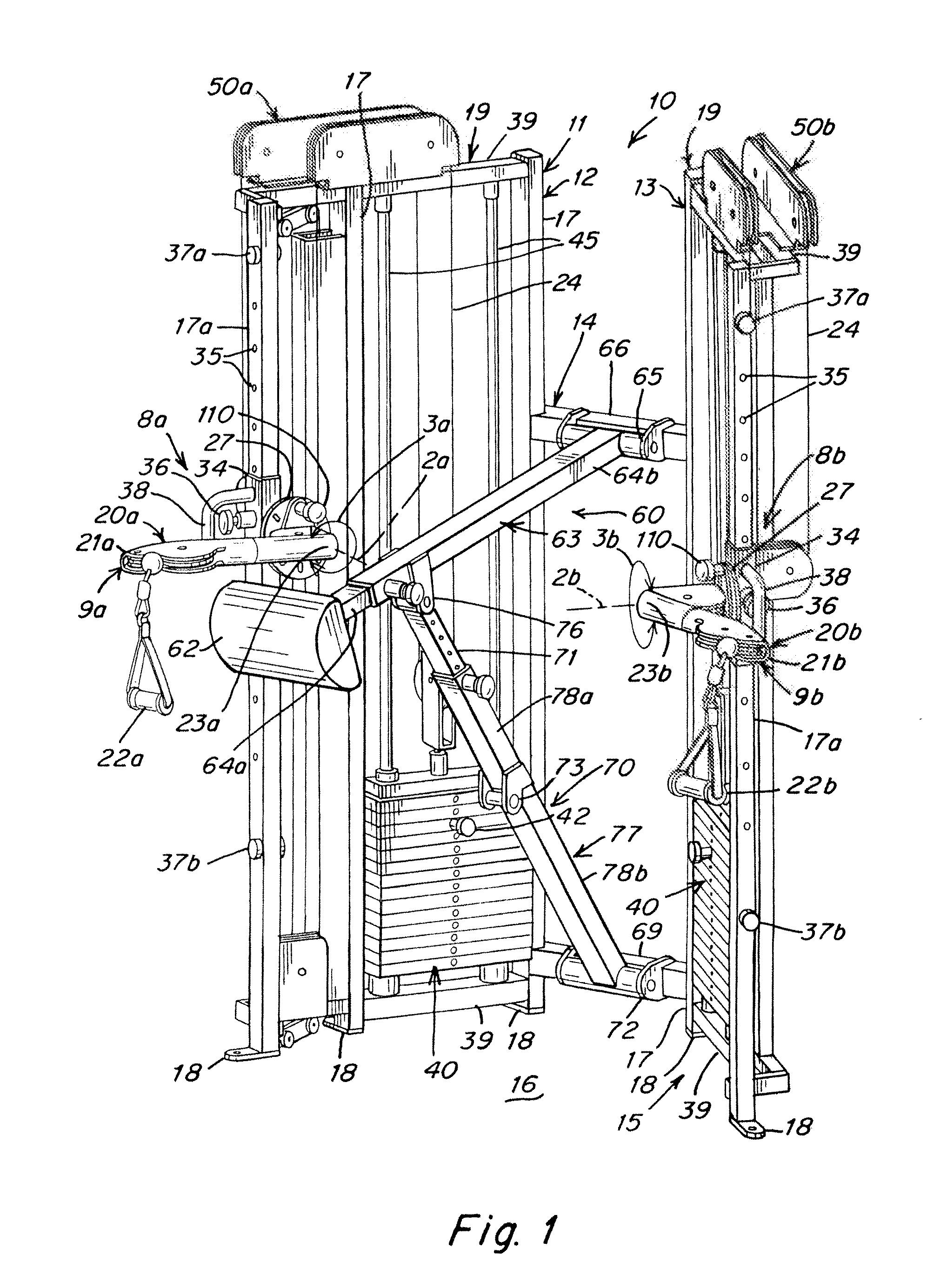
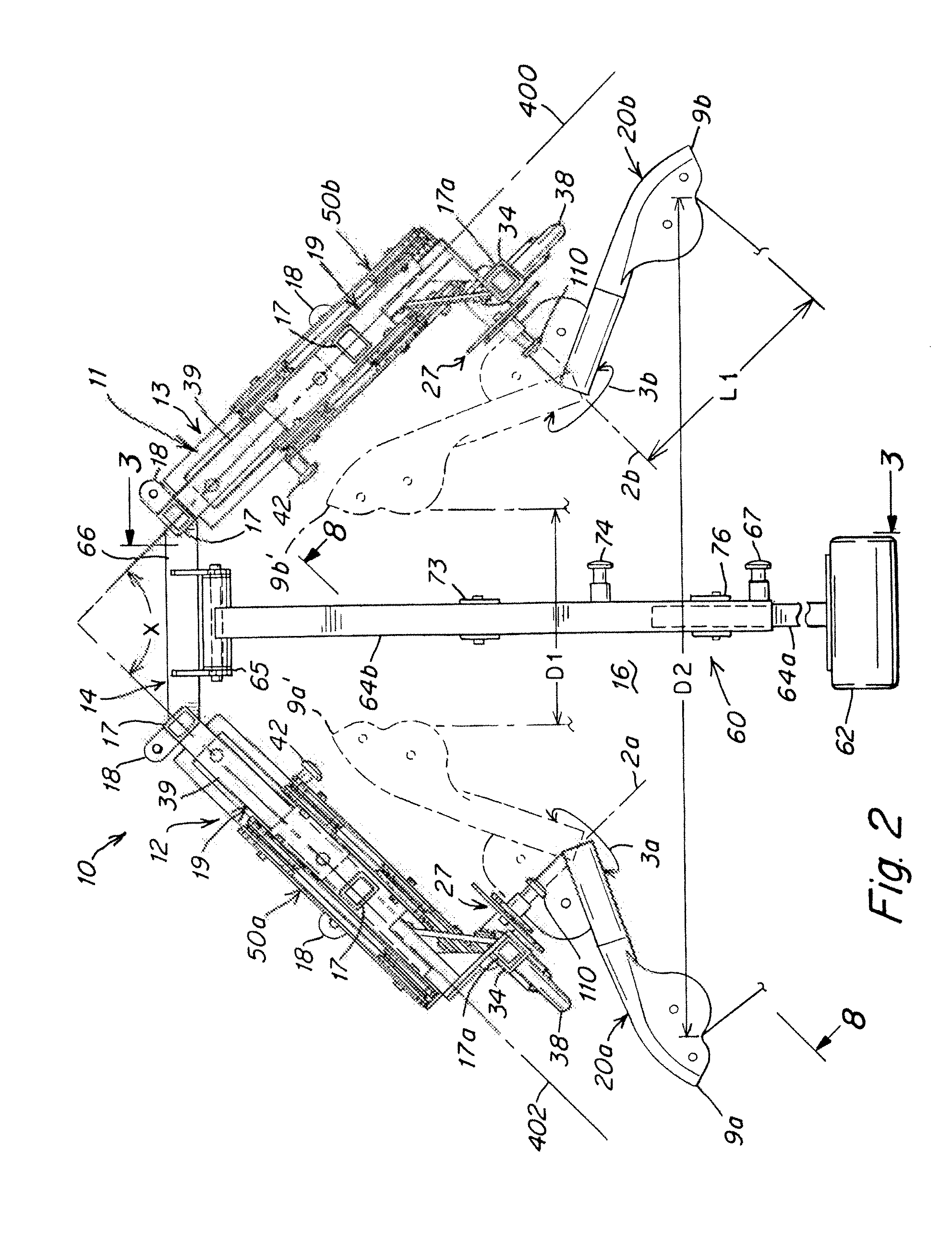
Exercise apparatus and method with selectively variable stabilization
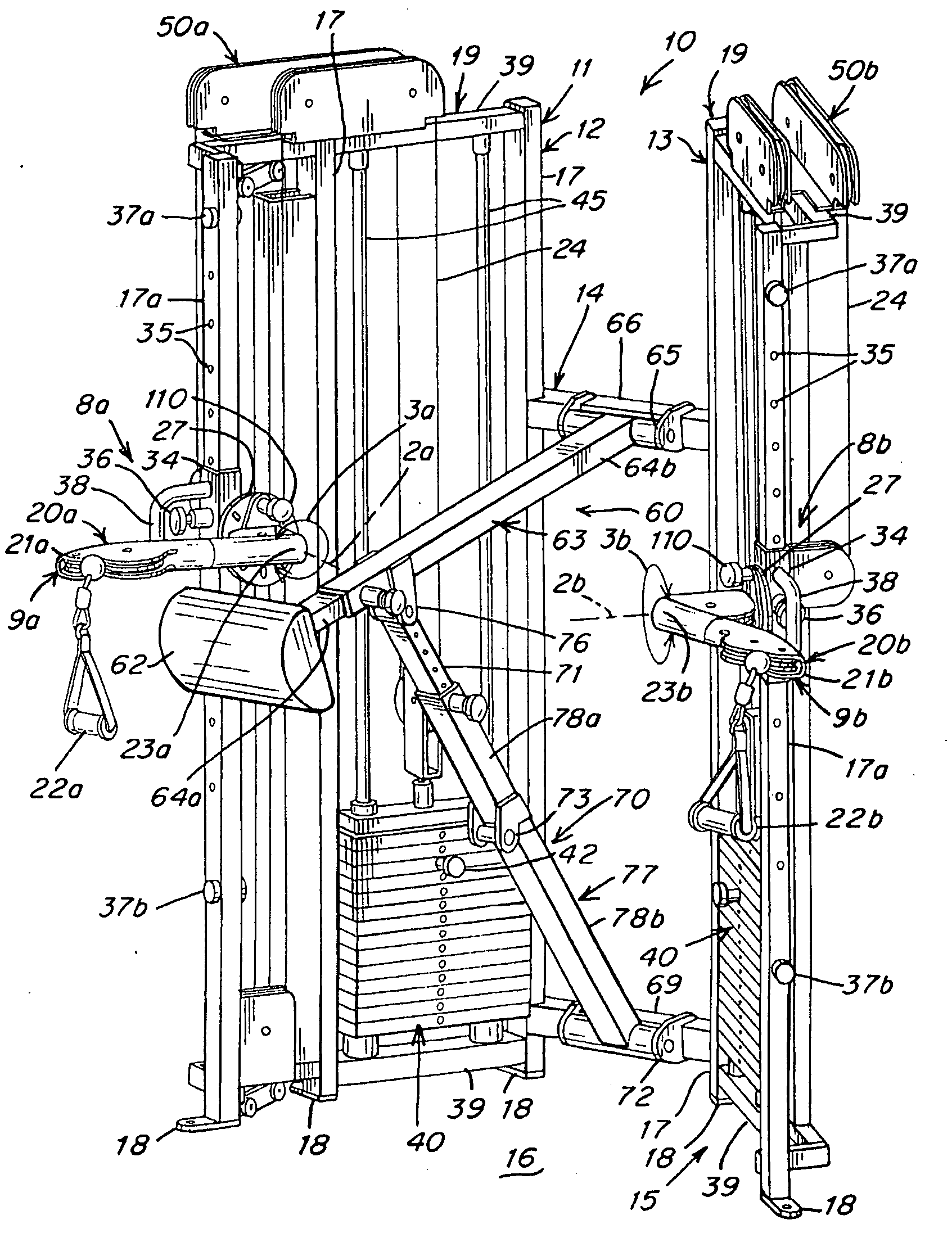
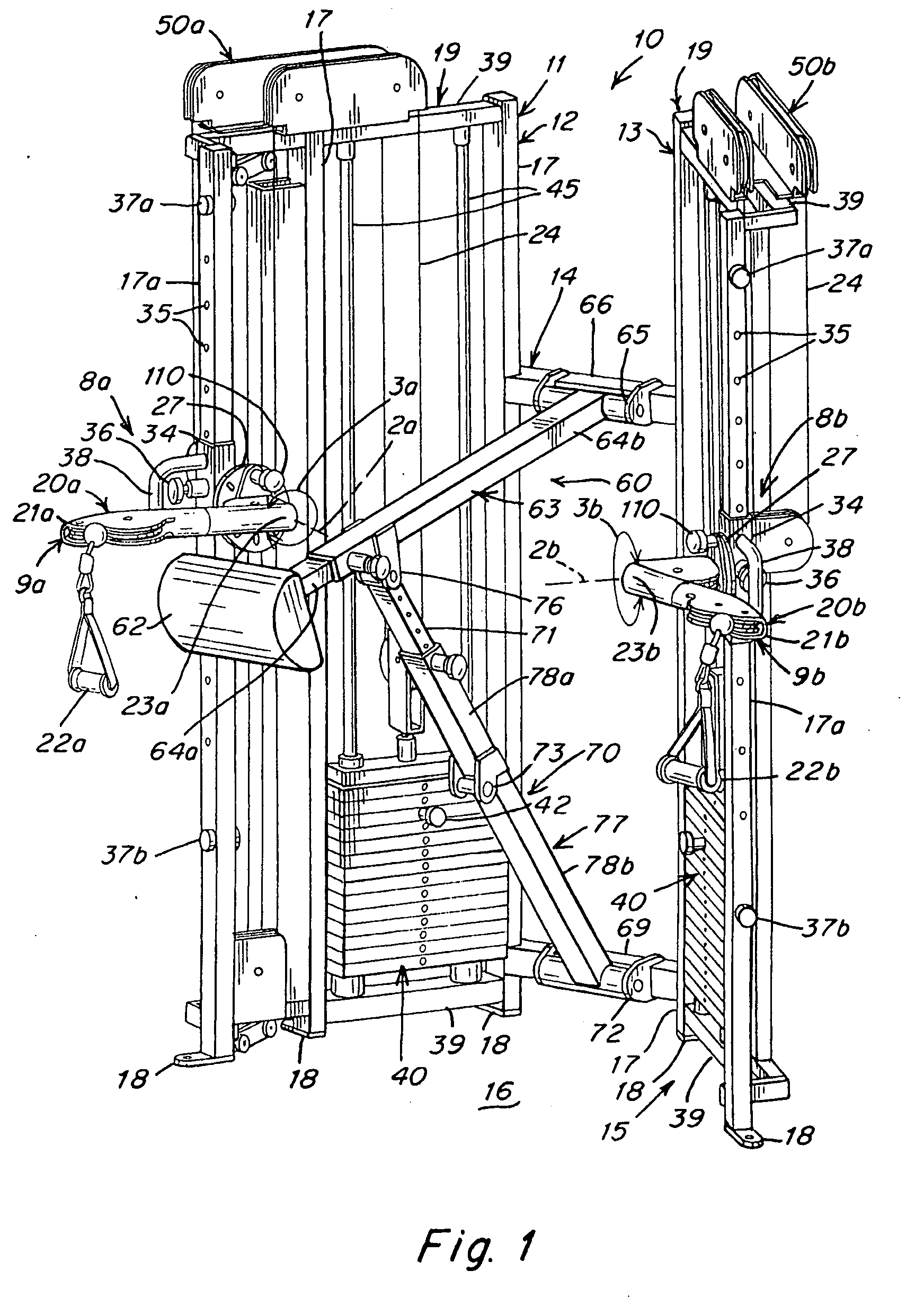
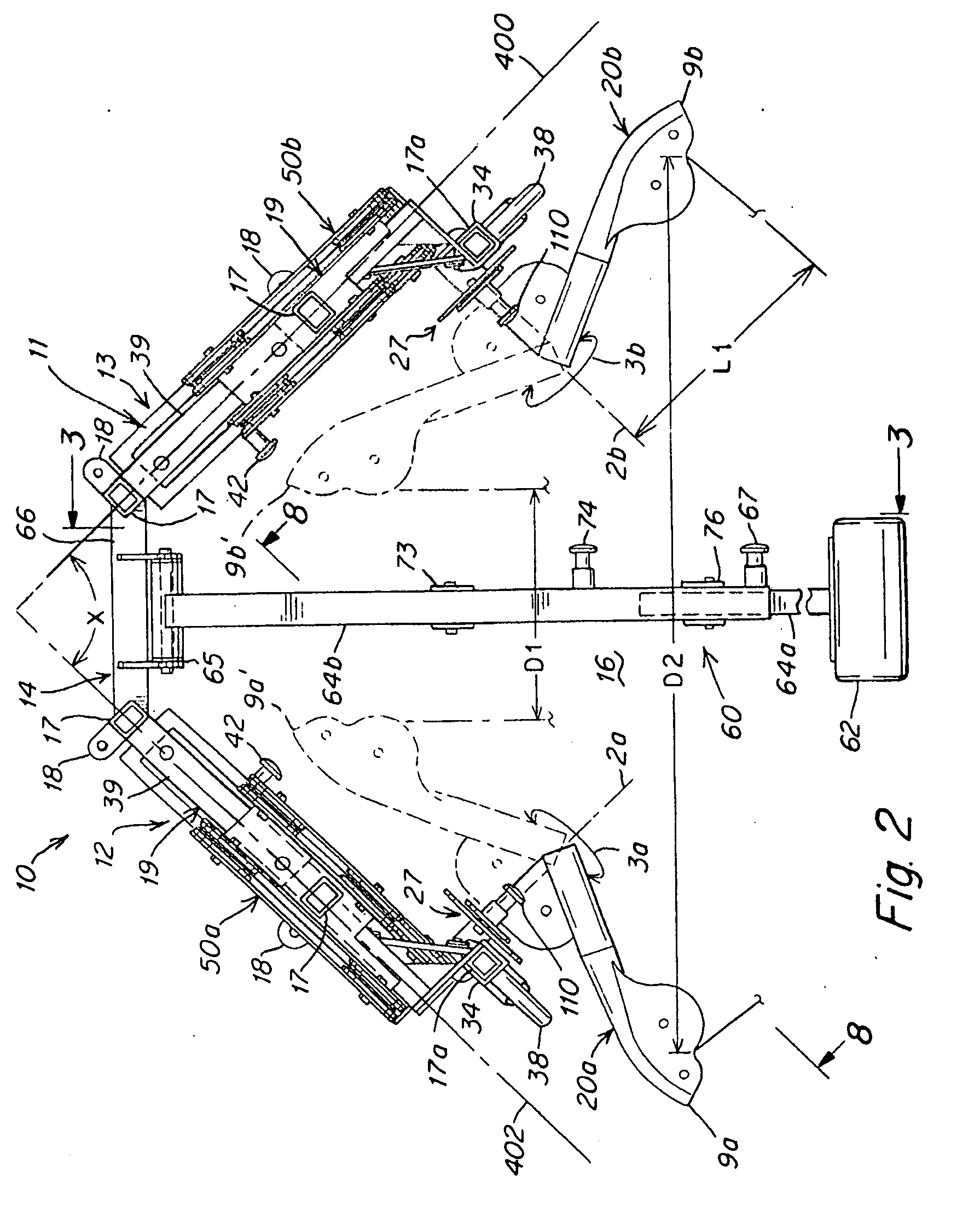
ActiveUS20090170675A1Offsetting weightHigh strengthMuscle exercising devicesMuscle strengthSmall footprint
Exercise apparatus and method with selectively variable stabilization enabling a user to progressively increase his / her core body muscular strength. In various embodiments, the exercise apparatus includes a resistance cabling system providing a user defined line of motion, and a partial stabilizer pad being adjustably positionable offset from the line of motion, wherein the user's core body is positionable against the pad and required to resist the torque created by the offset. The user can progressively increase the distance between the line of motion and partial stabilizer pad, in order to progressively increase the force which the user's core body must resist to maintain an upright stature. In this way, the user can progressively, over time, increase his or her core body strength. A vertically and rotatably adjustable handle / arm assembly, resistance cabling and pulley assembly, and an overall exercise apparatus having a relatively small footprint but allowing multiple variable exercise routines, are also provided.
Owner:CYBEX INTERNATIONAL
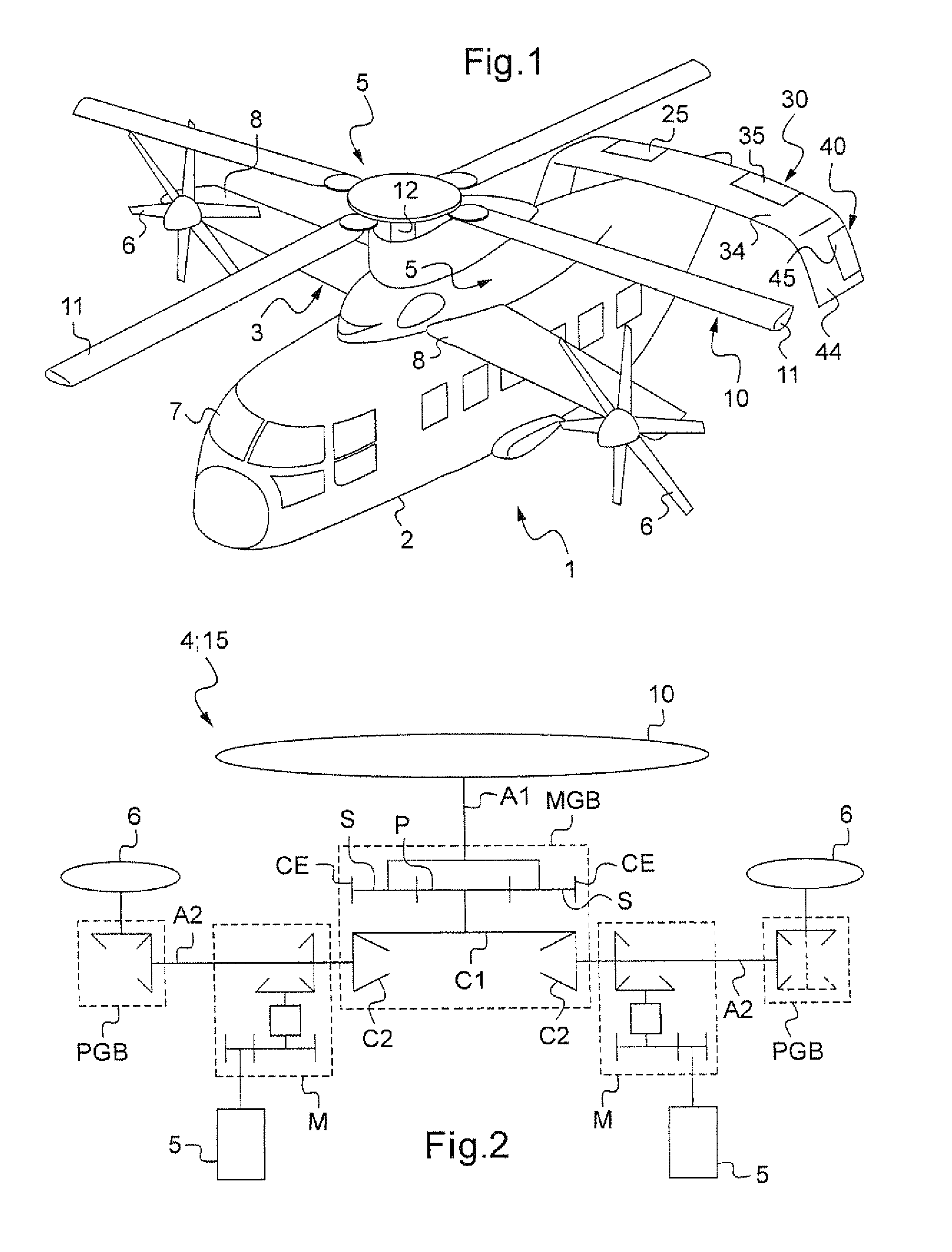
Fast hybrid helicopter with long range with longitudinal trim control
ActiveUS8052094B2Drag minimizationCompensate relative offsetPropellersAircraft controlInterconnectionBlade pitch
Owner:AEROPORT INT MARSEILLE PROVENCE
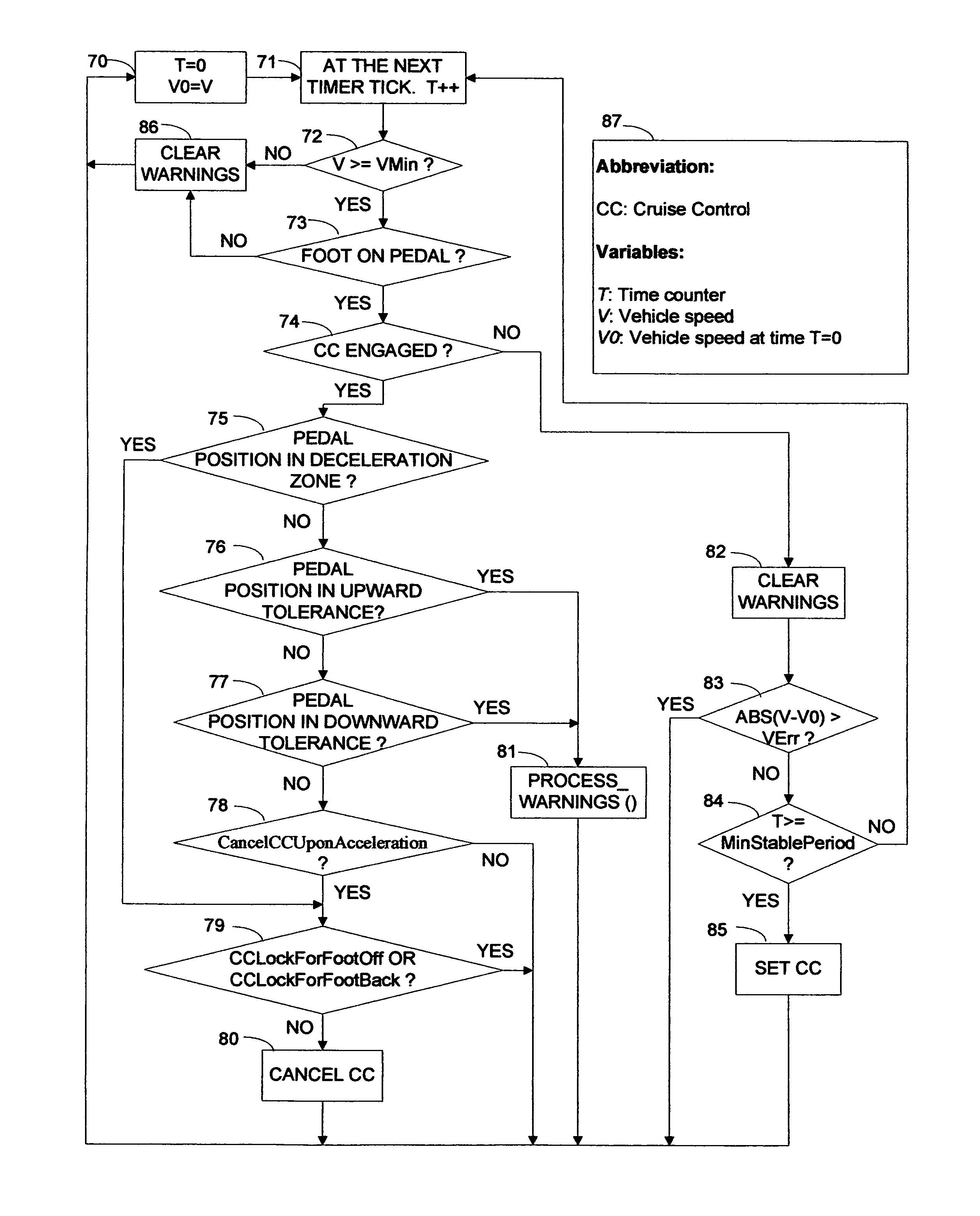
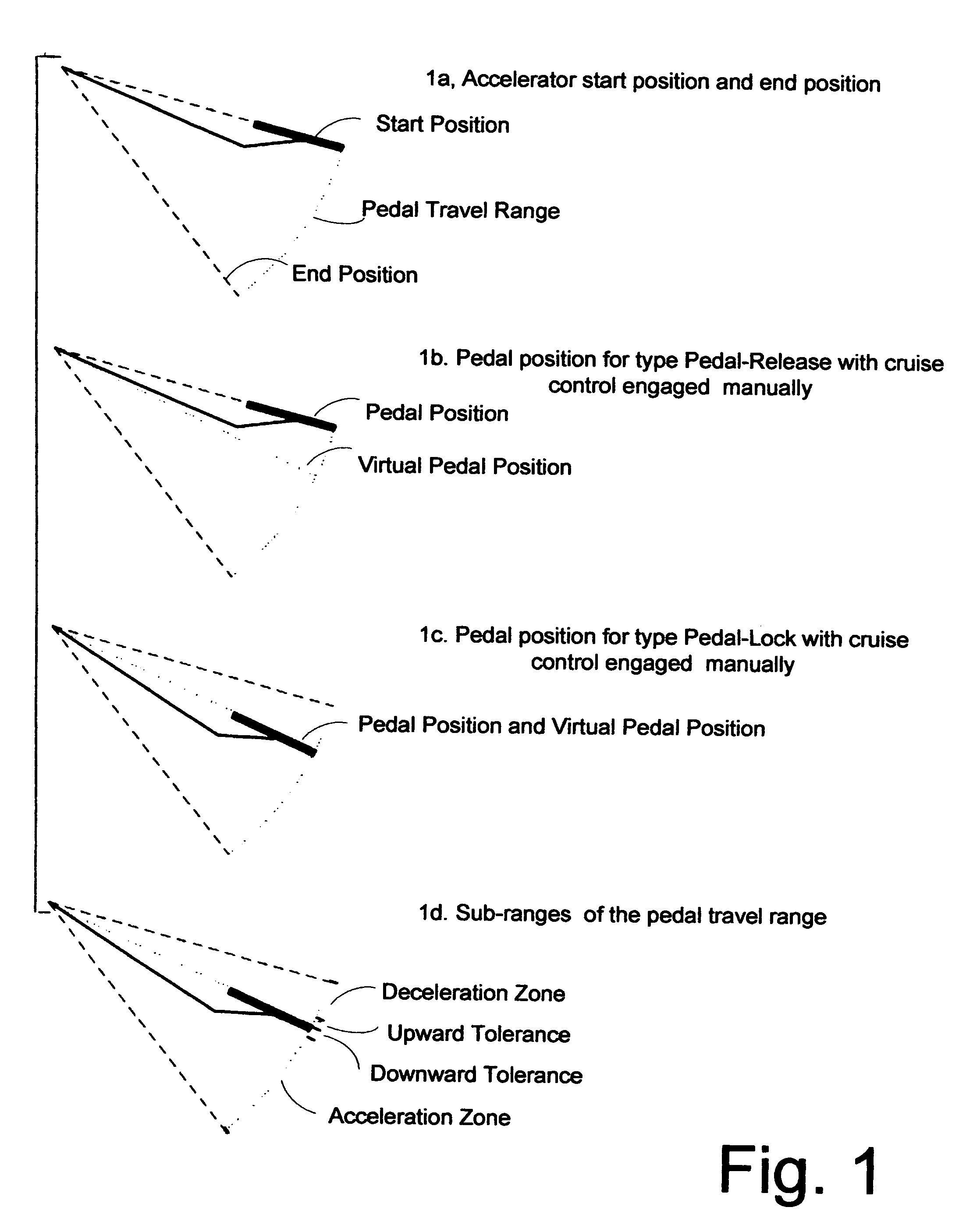
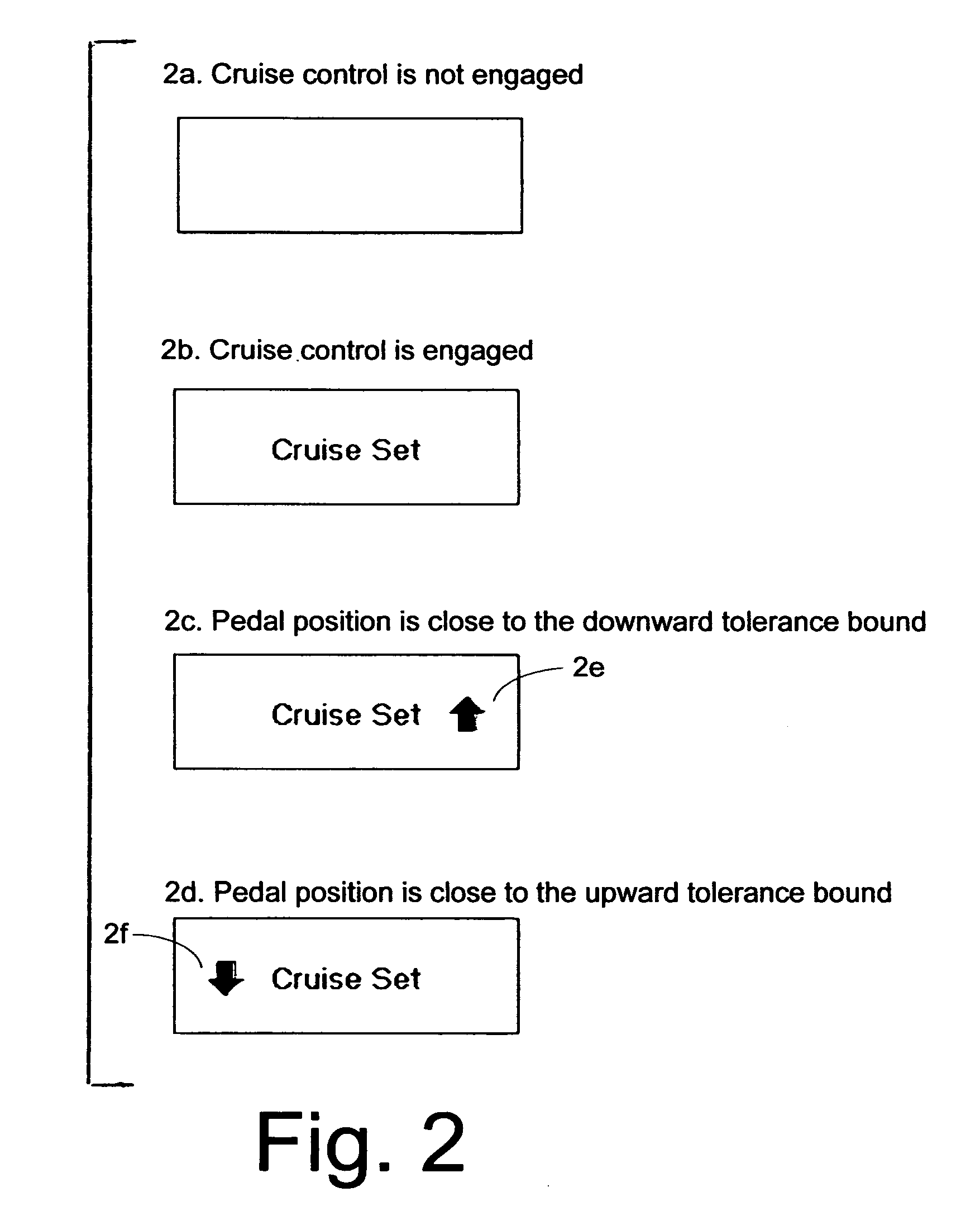
Speed stabilizer for automatically turning conventional cruise controls on/off in dense low speed traffic to save fuel
InactiveUS7706953B1Filter out instabilityMaximizing periodControlling membersVehicle fittingsDriver/operatorLED display
The stabilizer works with any conventional cruise control (CC) and permits automatic CC in slower heavy traffic as it eliminates laborious frequent manual actuation of CC control buttons otherwise needed in such heavy traffic. More frequent automatic CC operation at slower speeds increases fuel efficiency. When the vehicle maintains a speed above a minimum speed and exceeds a brief preset period, the speed stabilizer sets the cruise control at that speed. When the cruise control is thus engaged, the driver's foot can move the accelerator pedal within a small tolerance range without canceling the cruise control. When the pedal is close to the bounds of the tolerance range, a warning signal such as a flashing LED display, is generated by the speed stabilizer to inform the driver that further movement of the pedal will cause acceleration / deceleration, automatically canceling cruise control. Actuation of conventional CC control buttons restores conventional CC.
Owner:SUN JUN SHI
Exercise apparatus and method with selectively variable stabilization
Exercise apparatus and method with selectively variable stabilization enabling a user to progressively increase his / her core body muscular strength. In various embodiments, the exercise apparatus includes a resistance cabling system providing a user defined line of motion, and a partial stabilizer pad being adjustably positionable offset from the line of motion, wherein the user's core body is positionable against the pad and required to resist the torque created by the offset. The user can progressively increase the distance between the line of motion and partial stabilizer pad, in order to progressively increase the force which the user's core body must resist to maintain an upright stature. In this way, the user can progressively, over time, increase his or her core body strength. A vertically and rotatably adjustable handle / arm assembly, resistance cabling and pulley assembly, and an overall exercise apparatus having a relatively small footprint but allowing multiple variable exercise routines, are also provided.
Owner:CYBEX INTERNATIONAL
Convertible airplane with exposable rotors
ActiveUS20180141652A1Reduce noiseSolve excessive vibrationWing adjustmentsCanard-type aircraftJet aeroplaneJet engine
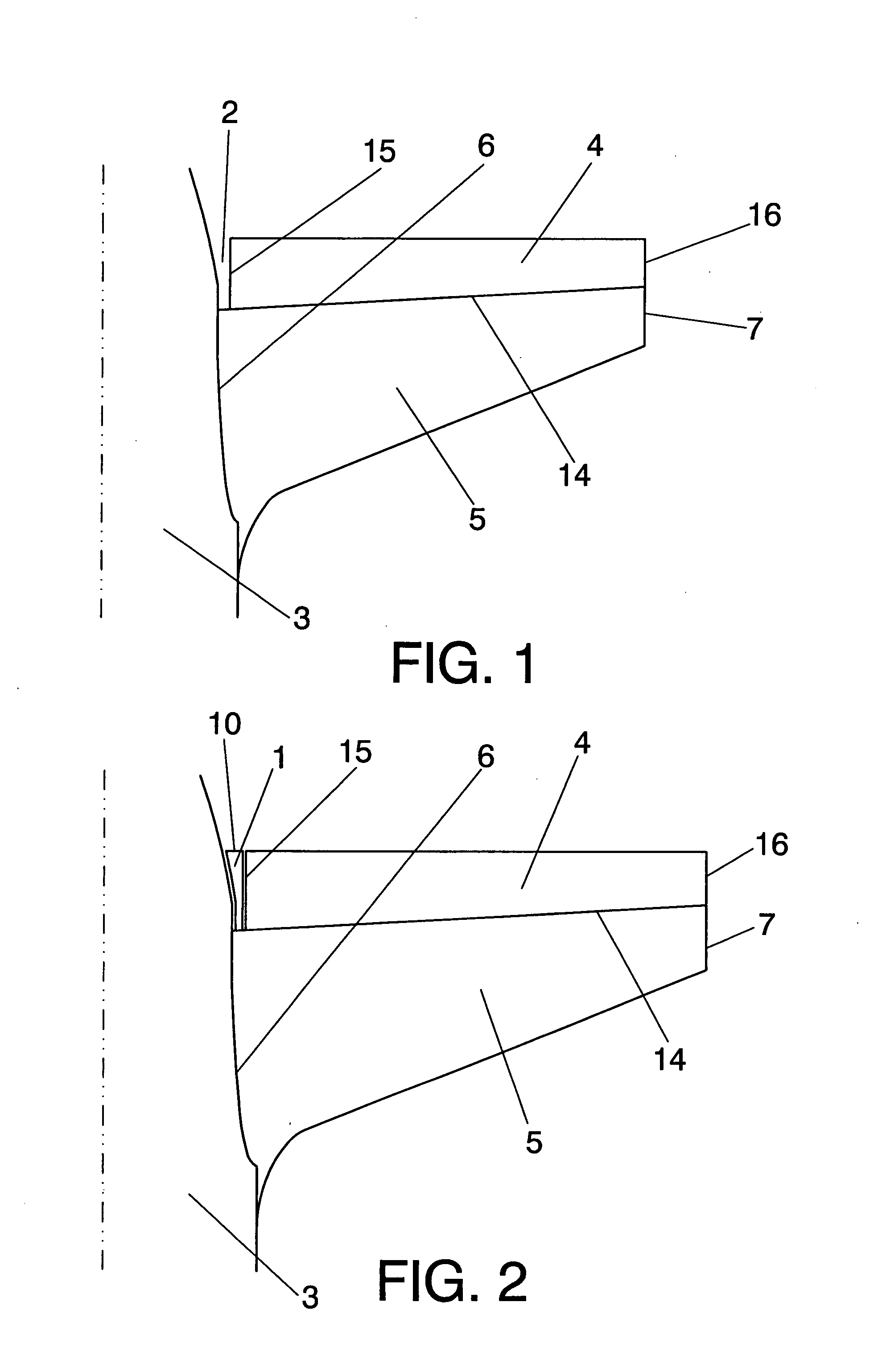
Convertible-type aircraft, able to fly with the speed and the reduced operating costs of a fixed-wing aircraft and also to take-off / land vertically and hover / manoeuvre like an helicopter.The aircraft object of the invention comes in the form of a classical plane, with a fuselage (1), a fixed wing (2), an horizontal stabilizer (3) and a vertical fin (4), as well as one or several jet engines or turboprops (5) for propulsion and it comprises exposable rotors (6 and 7) installed inside the wing and possibly inside the horizontal stabilizer or the fuselage for lifting the aircraft for vertical take-off / landing and stationary flight.For the flight and the horizontal take-off / landing, the rotors are completely enclosed inside the wing and possibly inside the horizontal stabilizer or the fuselage.
Owner:DESLYPPER CHRISTIAN ROGER RENE
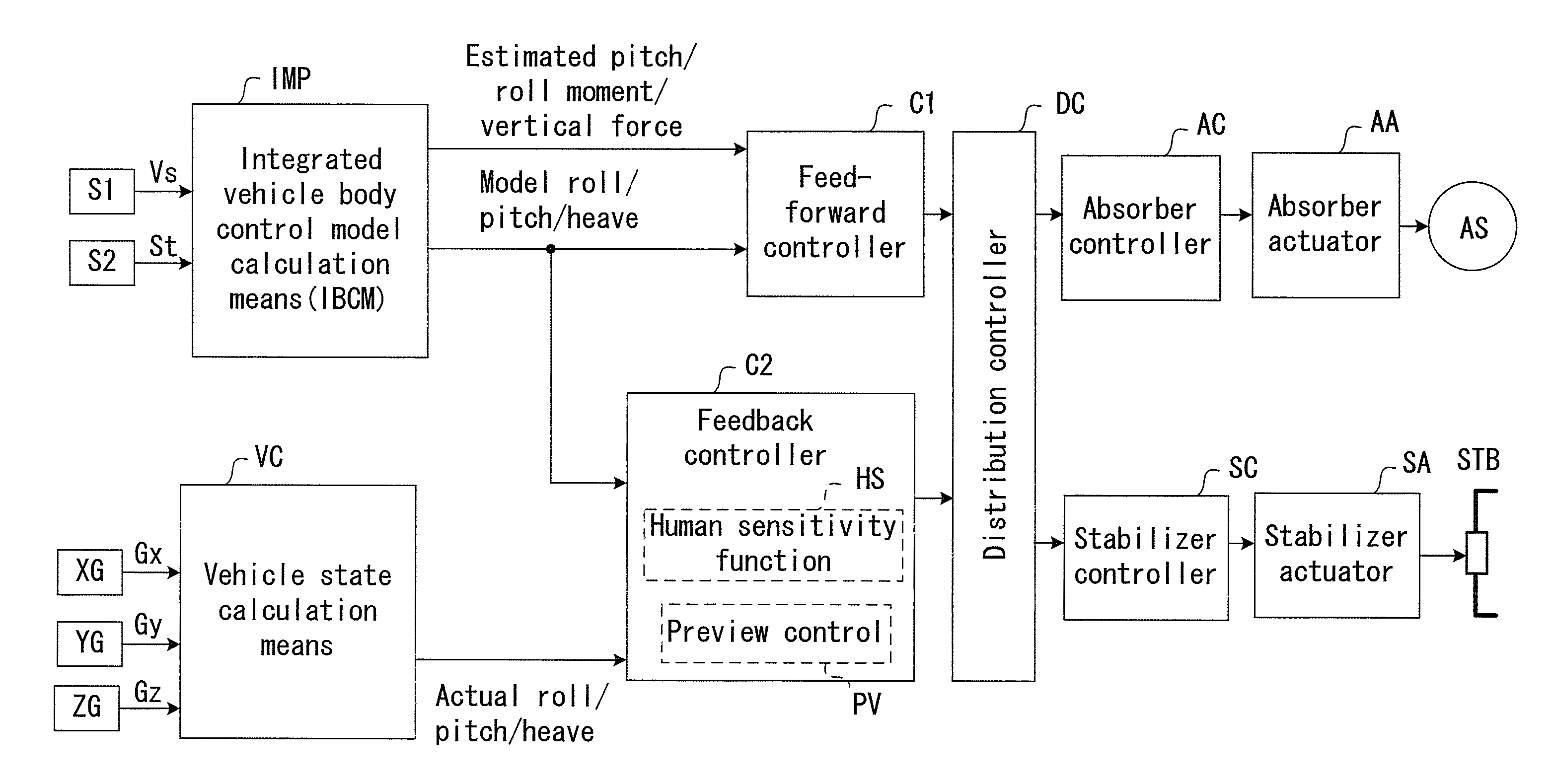
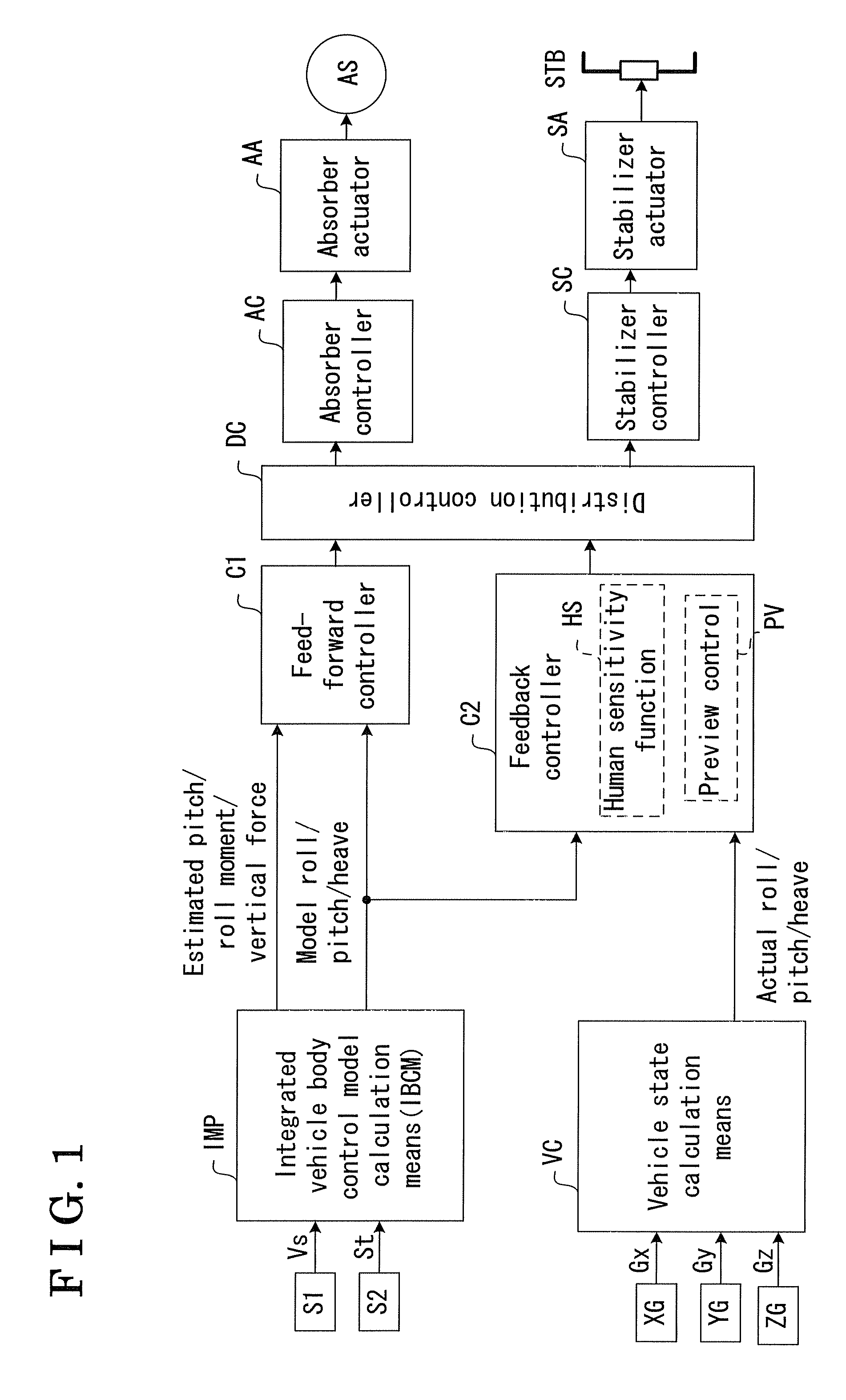
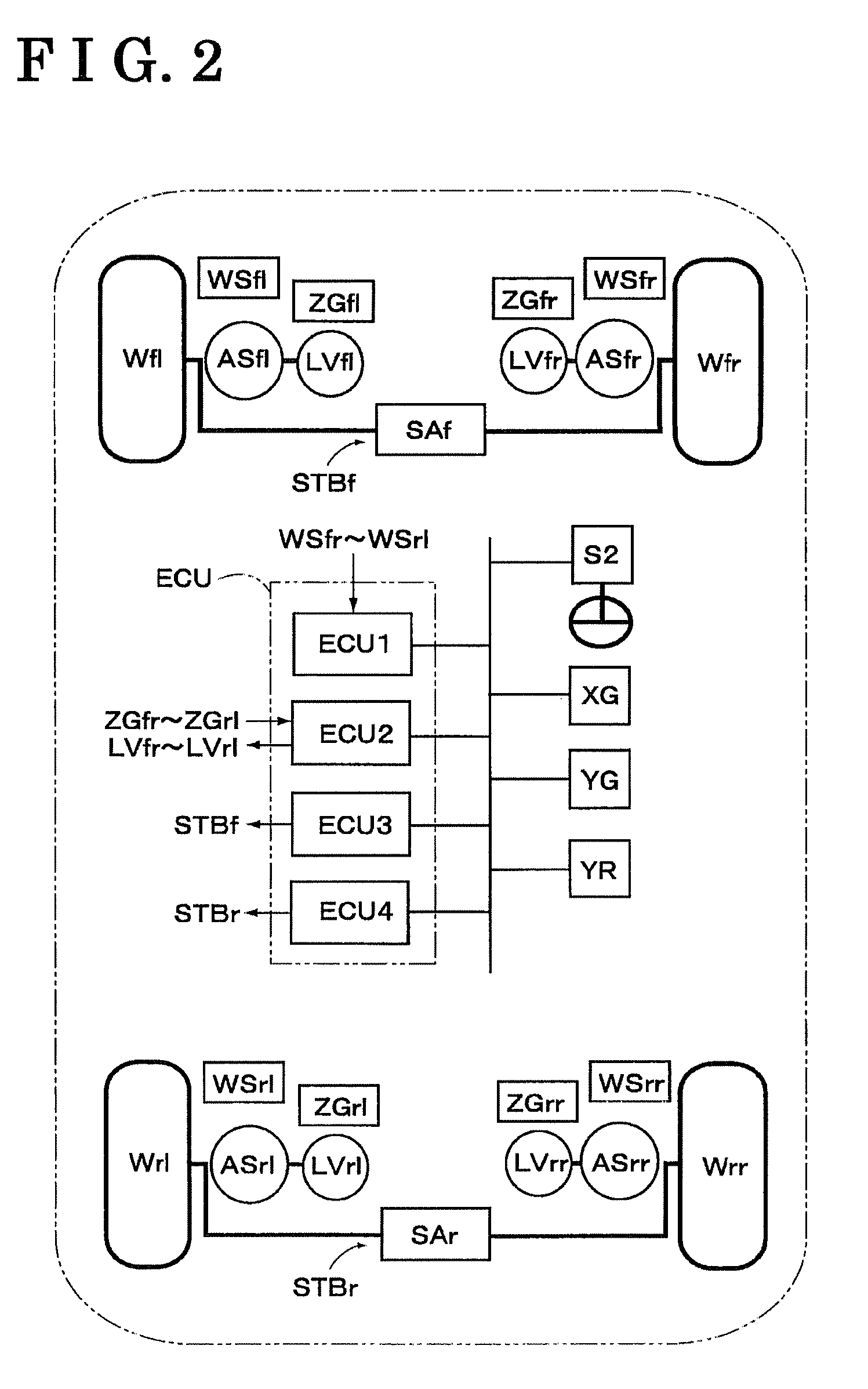
Integrated Vehicle Body Attitude Control Apparatus
InactiveUS20080262690A1Analogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsAttitude controlEngineering
An integrated vehicle body attitude control apparatus includes a detecting portion detecting a vehicle state including a vehicle speed and a steering state, an integrated vehicle body control model calculation portion setting a model rotation axis of a vehicle body and calculating an integrated vehicle body control model including a model value, a distribution controller combining pitch components, heave components and roll components calculated by a first calculator and a second calculator, distributing a combined resultant of the pitch components and the heave components for controlling damping force by the shock absorber controller and distributing a combined resultant of the roll components for controlling the torsional force by the stabilizer controller, and an actuation controller controlling actuation of a shock absorber and a stabilizer in response to a distribution result by the distribution controller.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
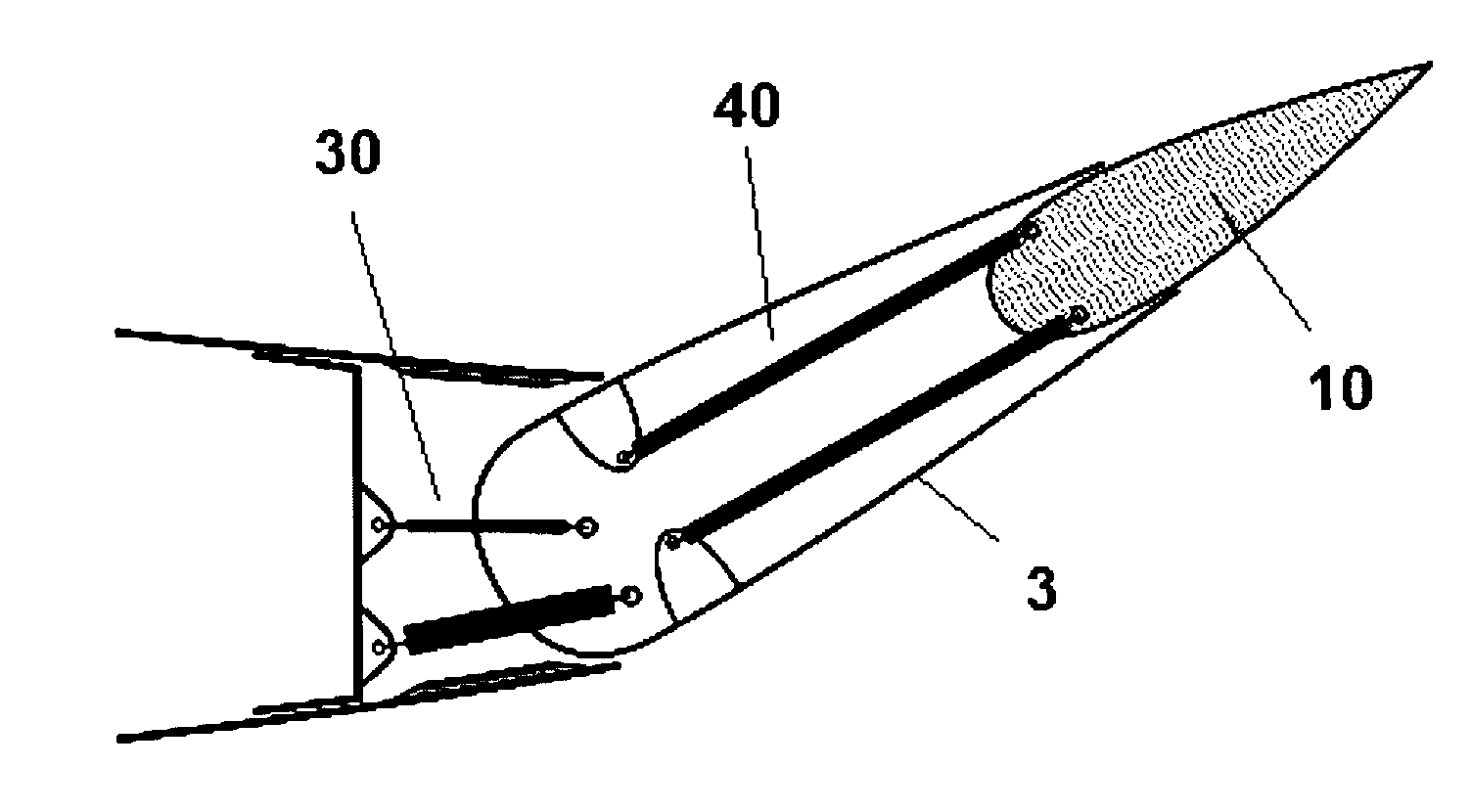
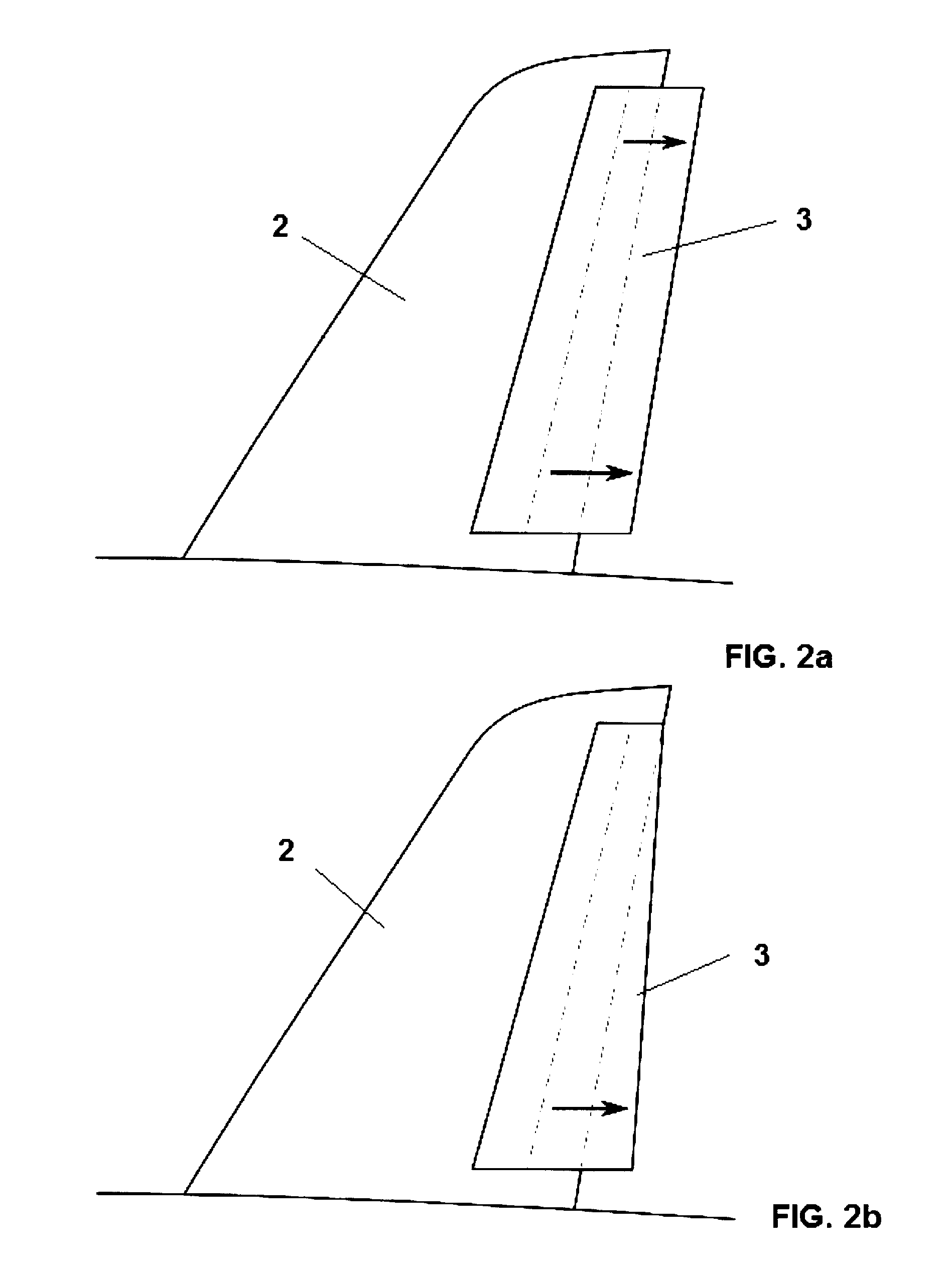
Stabilizing and directional-control surface of aircraft
InactiveUS20090256025A1Increases weight of unitLow energy efficiencyAircraft stabilisationWing lift eficiencyLow speedControllability
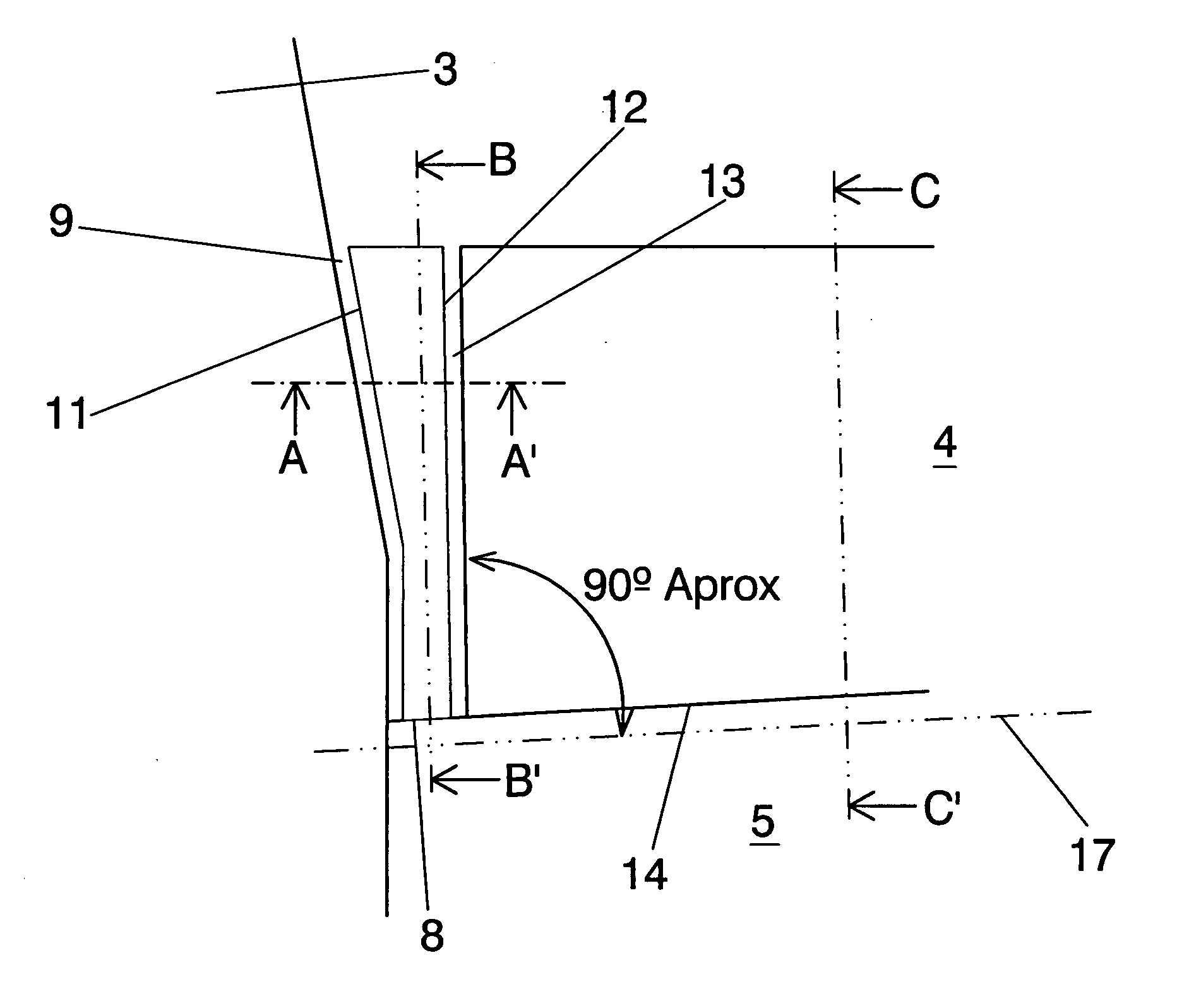
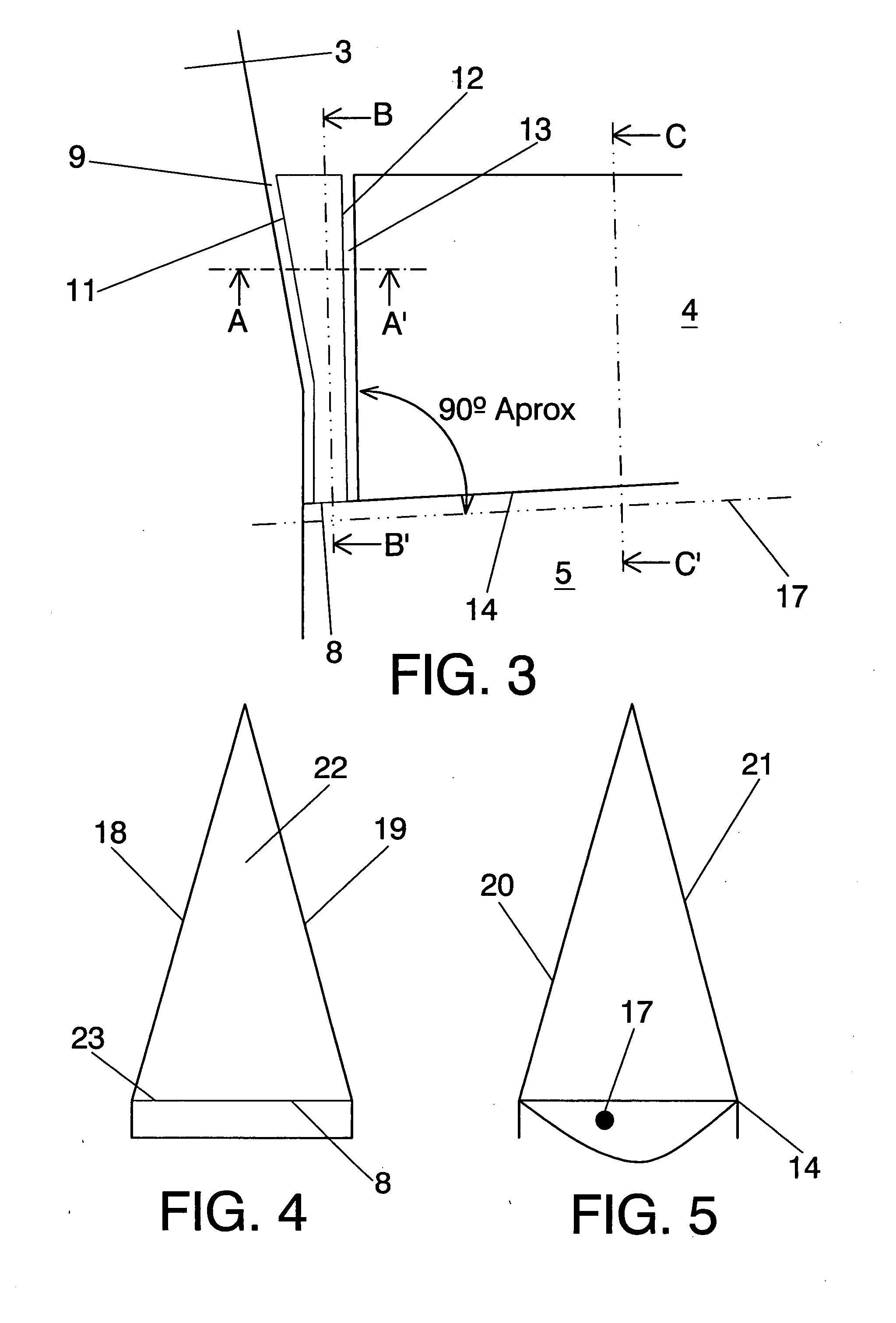
Stabilizing and directional-control surface of an aircraft, said surface comprising a vertical stabilizer (2) and a rudder (3), it being possible for said rudder (3) to be deflected relative to the vertical stabilizer (2), and moreover the rudder (3) comprises an internal profile (10) that can be extended and retracted by means of an actuating system (40) relative to the rest of the structure of the rudder (3), so that the stabilizing and control surface, in the retracted position of the internal profile (10) of the rudder (3), is an excellent aerodynamic surface in normal flying conditions, and at the same time increase of the aerodynamic control surface of the vertical stabilizer (2) is achieved for requirements of controllability of the aircraft at low speeds of said aircraft and against strong yawing moments acting thereon, in the position in which the internal profile (10) of the rudder (3) is extended, and moreover the structure of the rudder (3) can be opened, to permit extension of the internal profile (10), and said structure closes once the internal profile (10) is fully extended, so that the rudder (3) forms, with the extended internal profile (10), a structure that preserves its properties of aerodynamic surface and continuity of flow.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
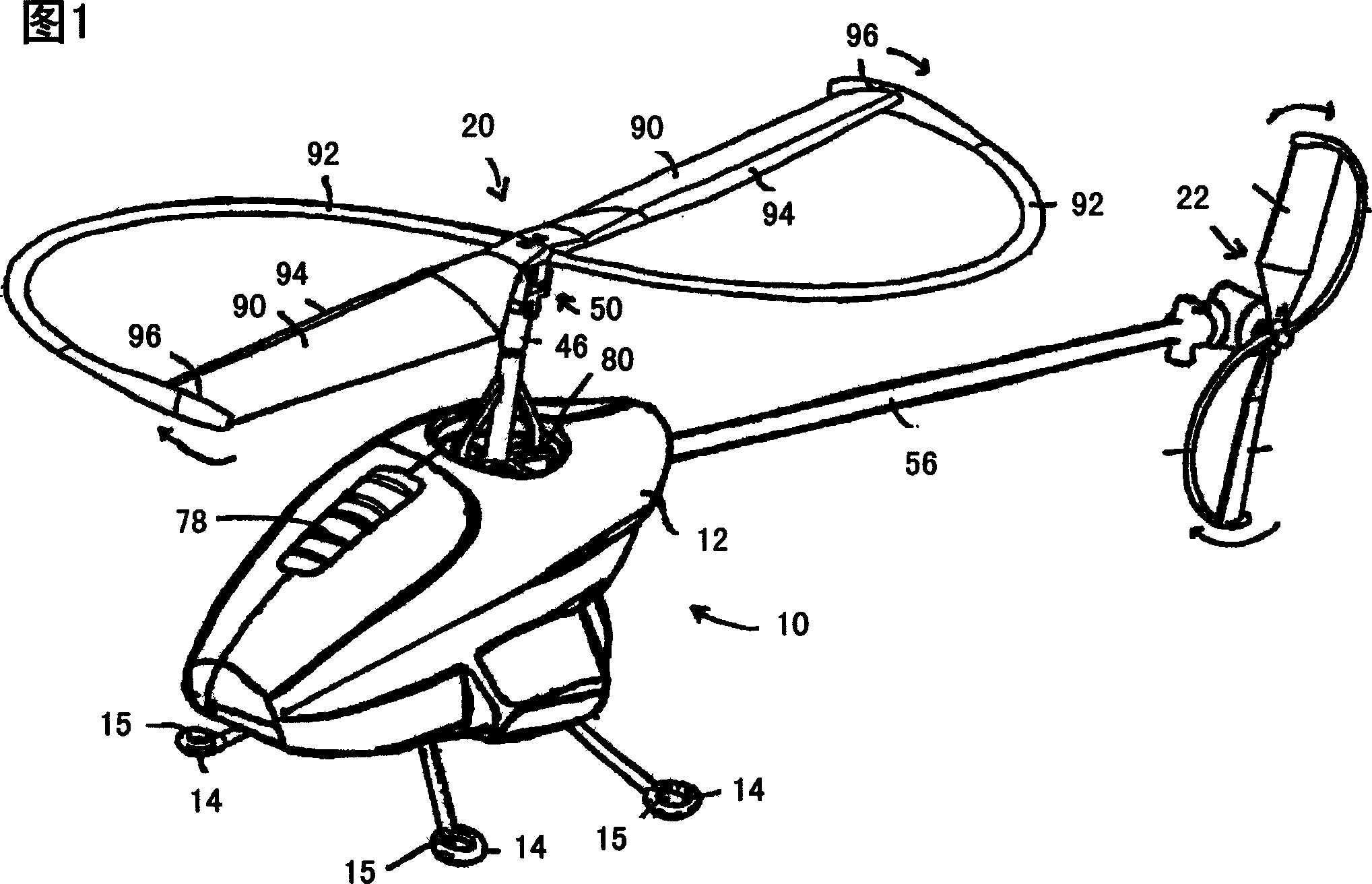
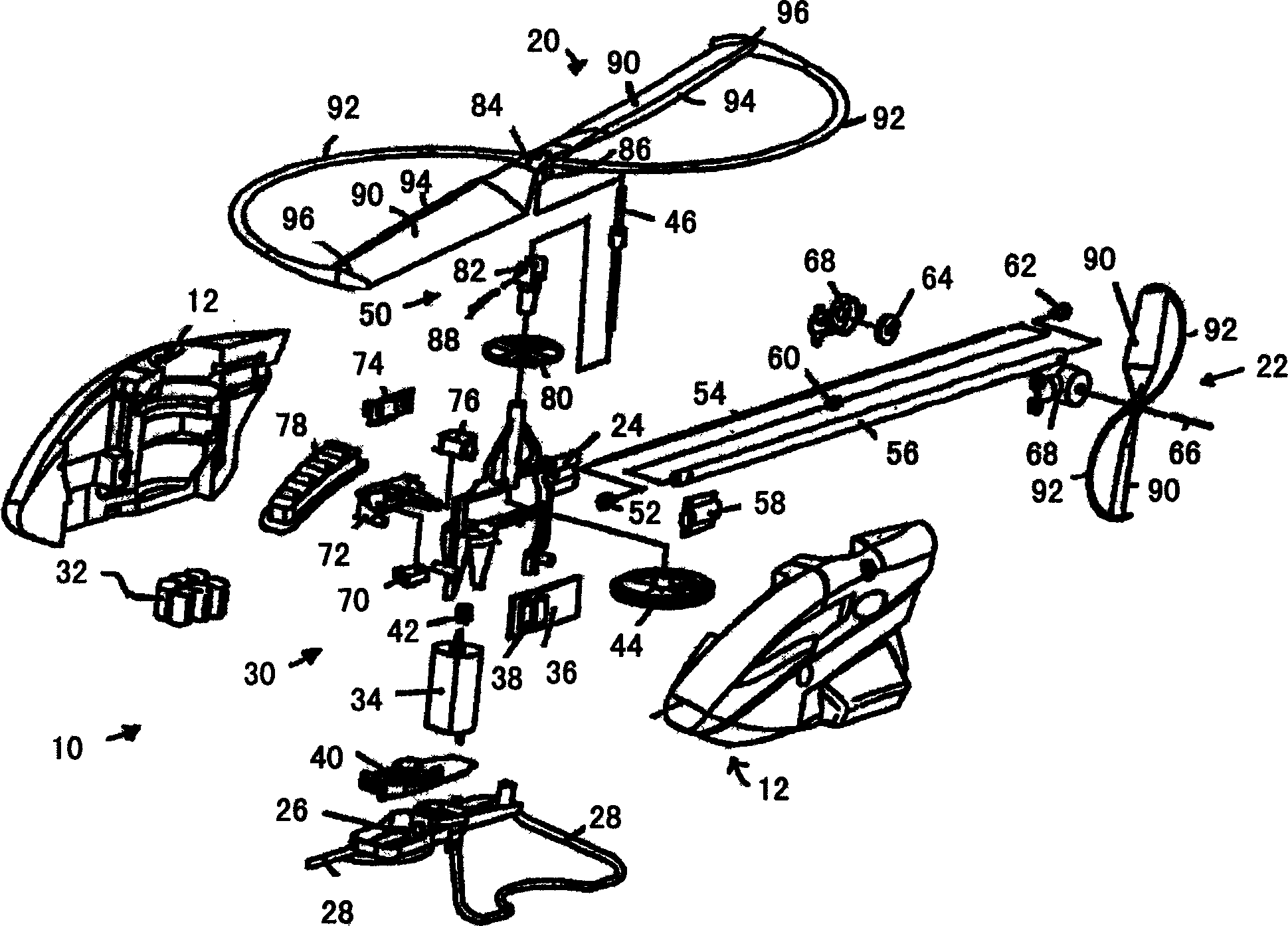
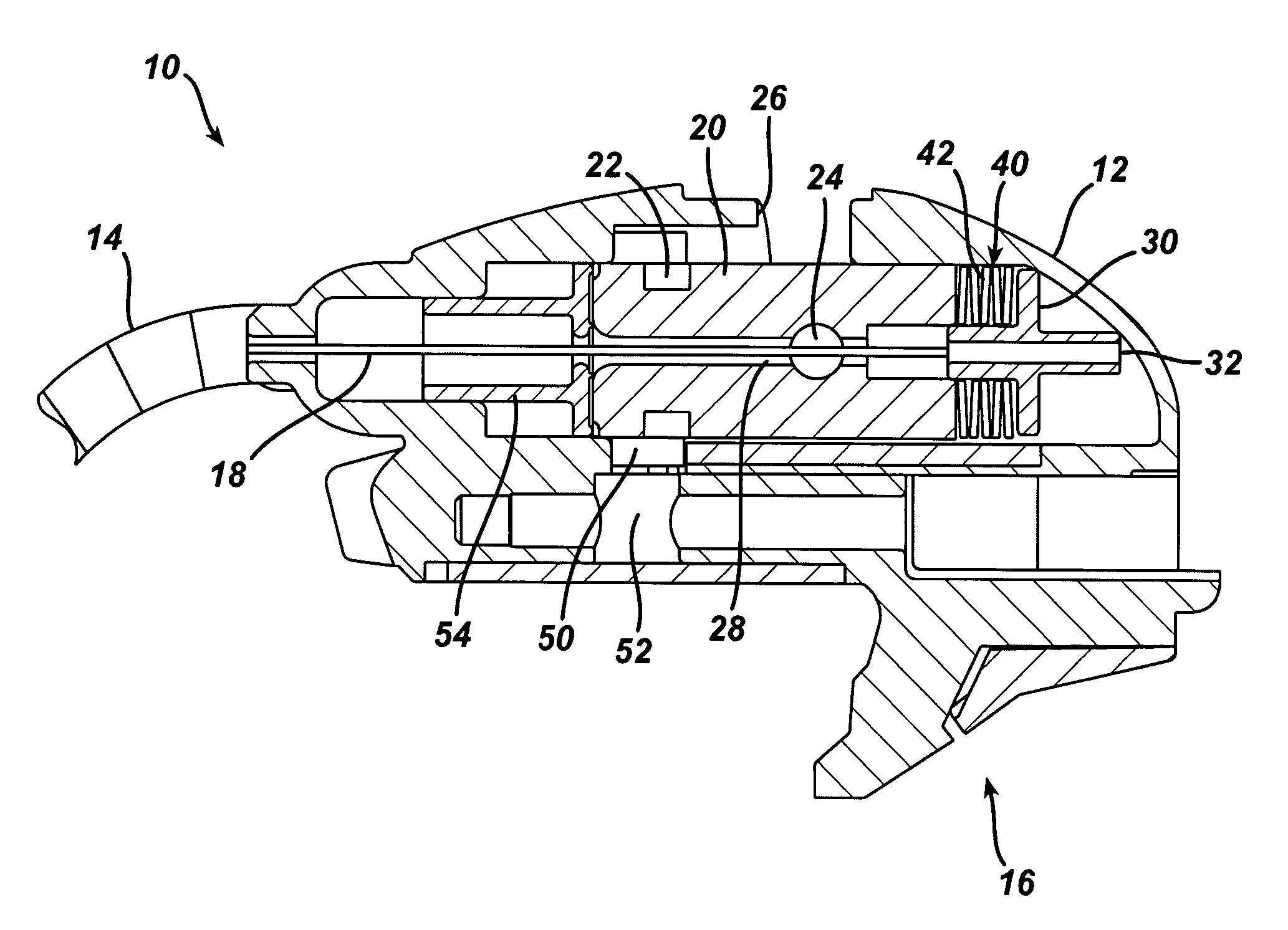
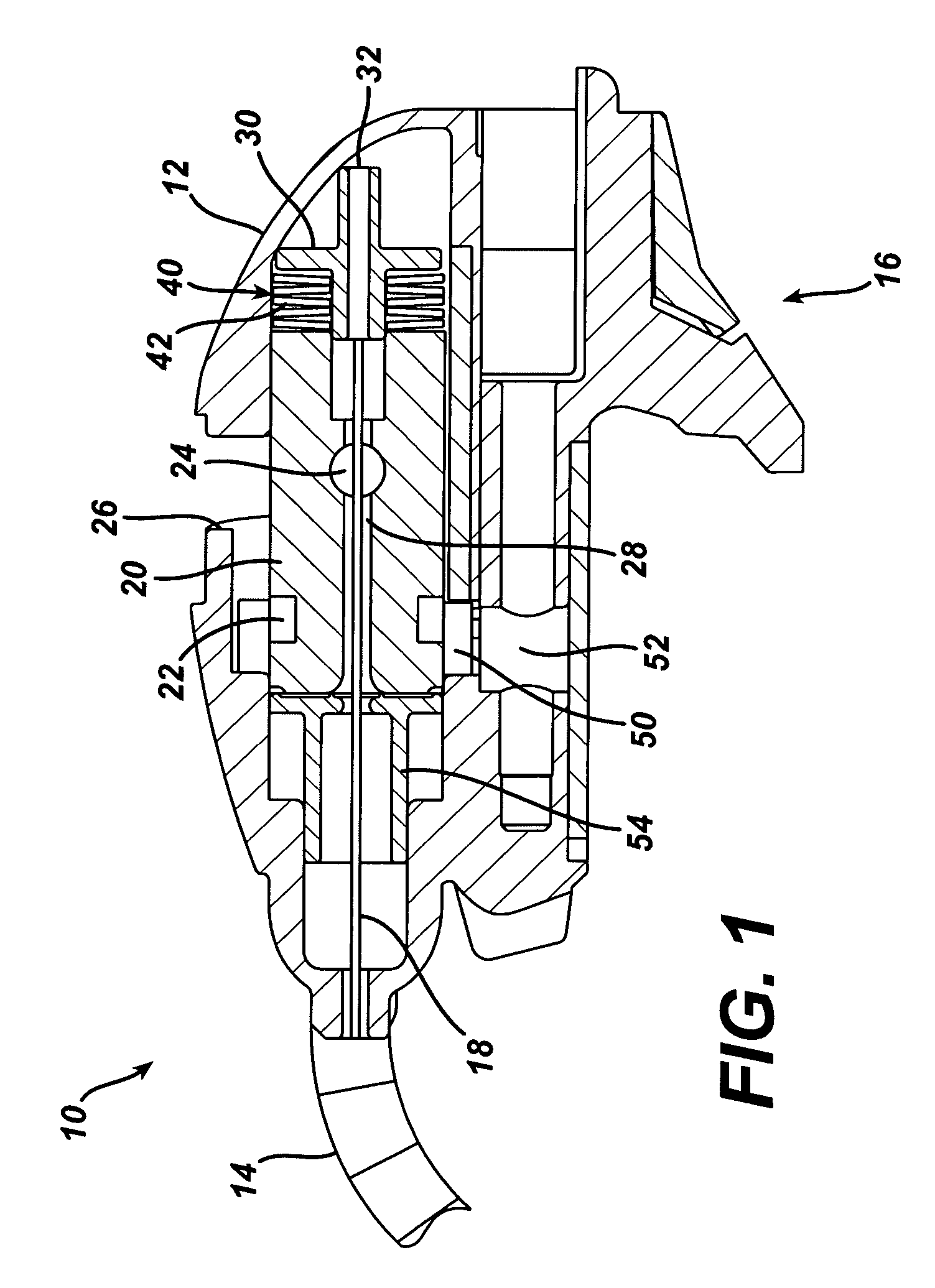
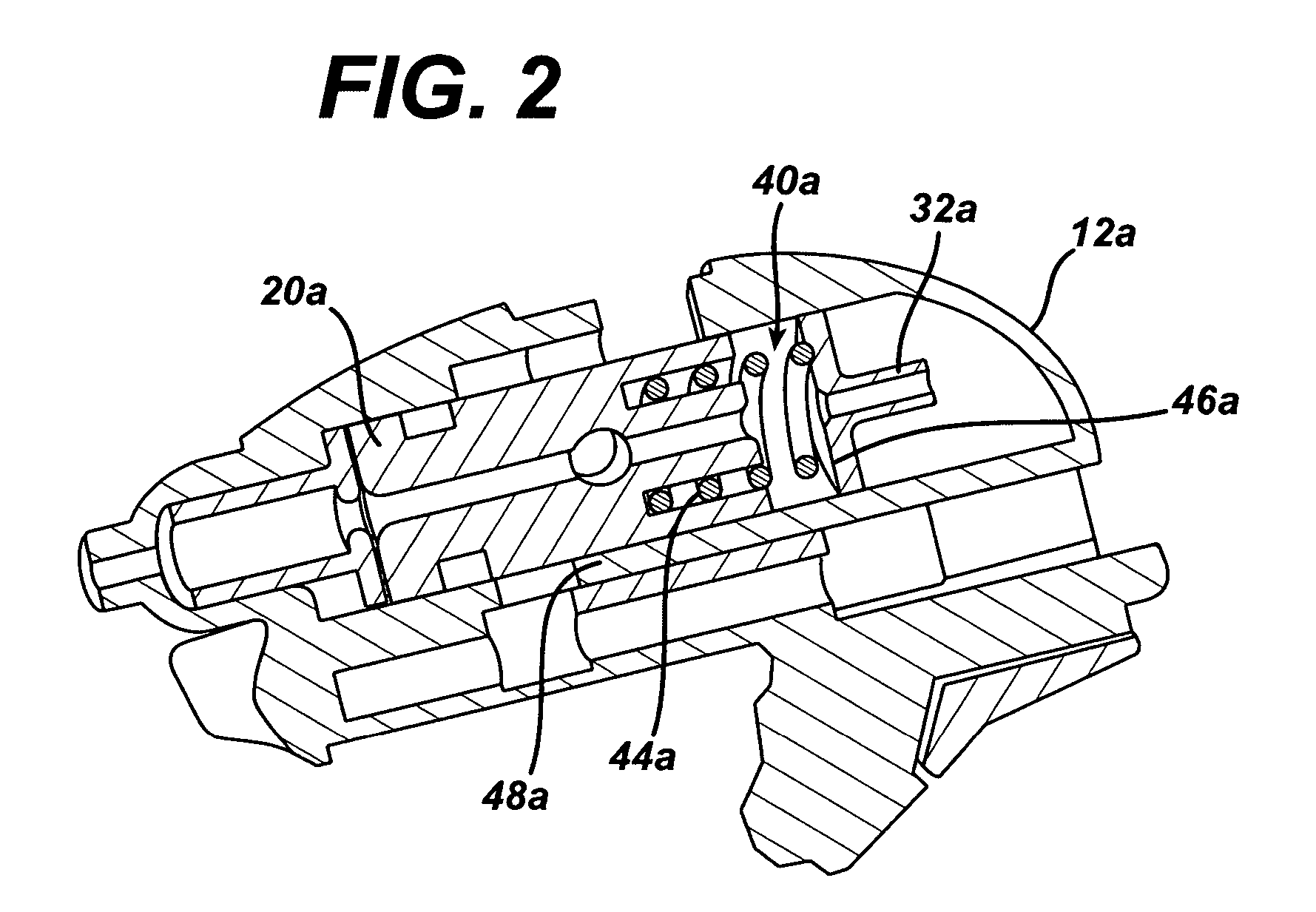
Propellers, propeller stabilizers, and propeller related vehicles
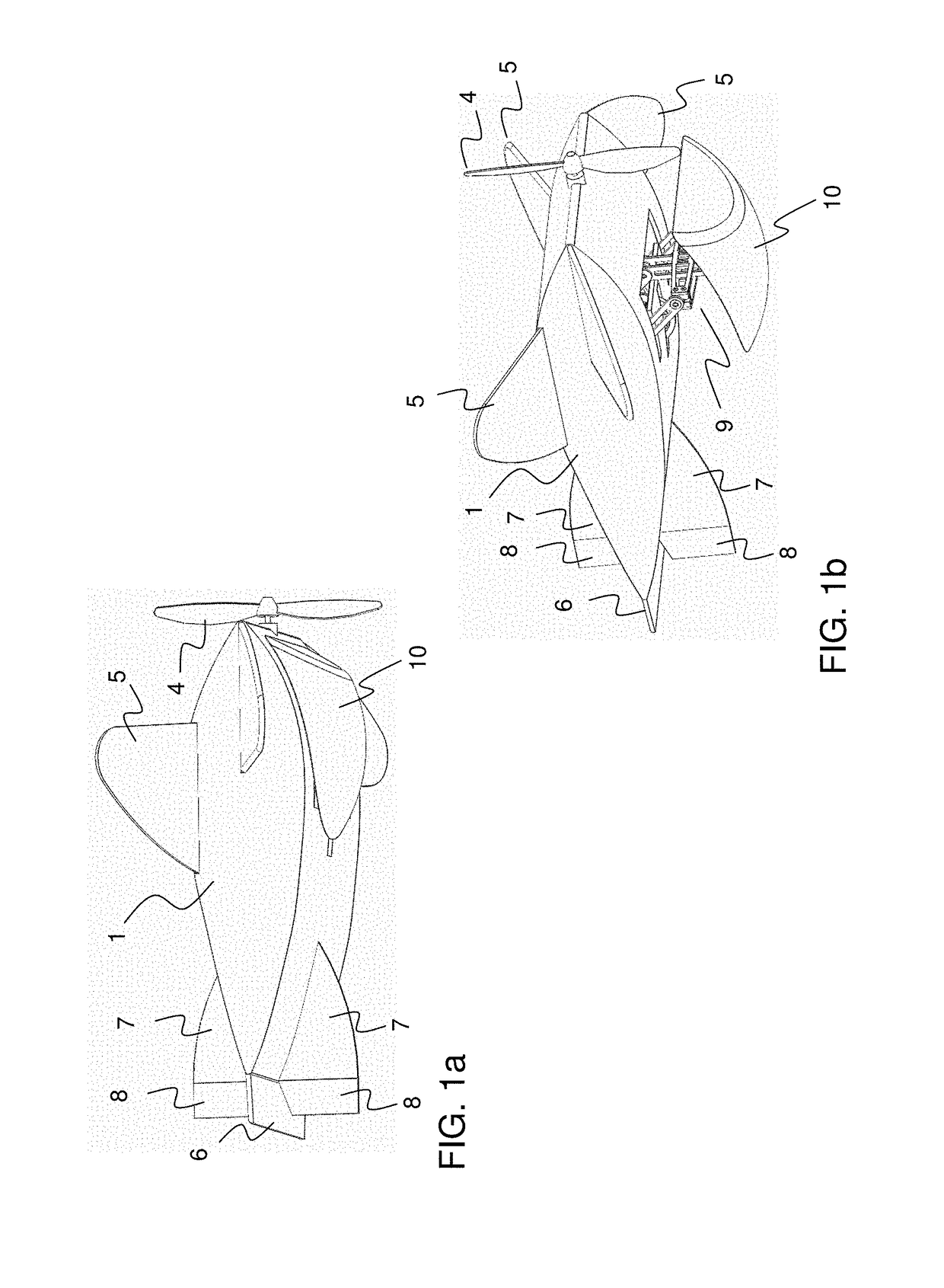
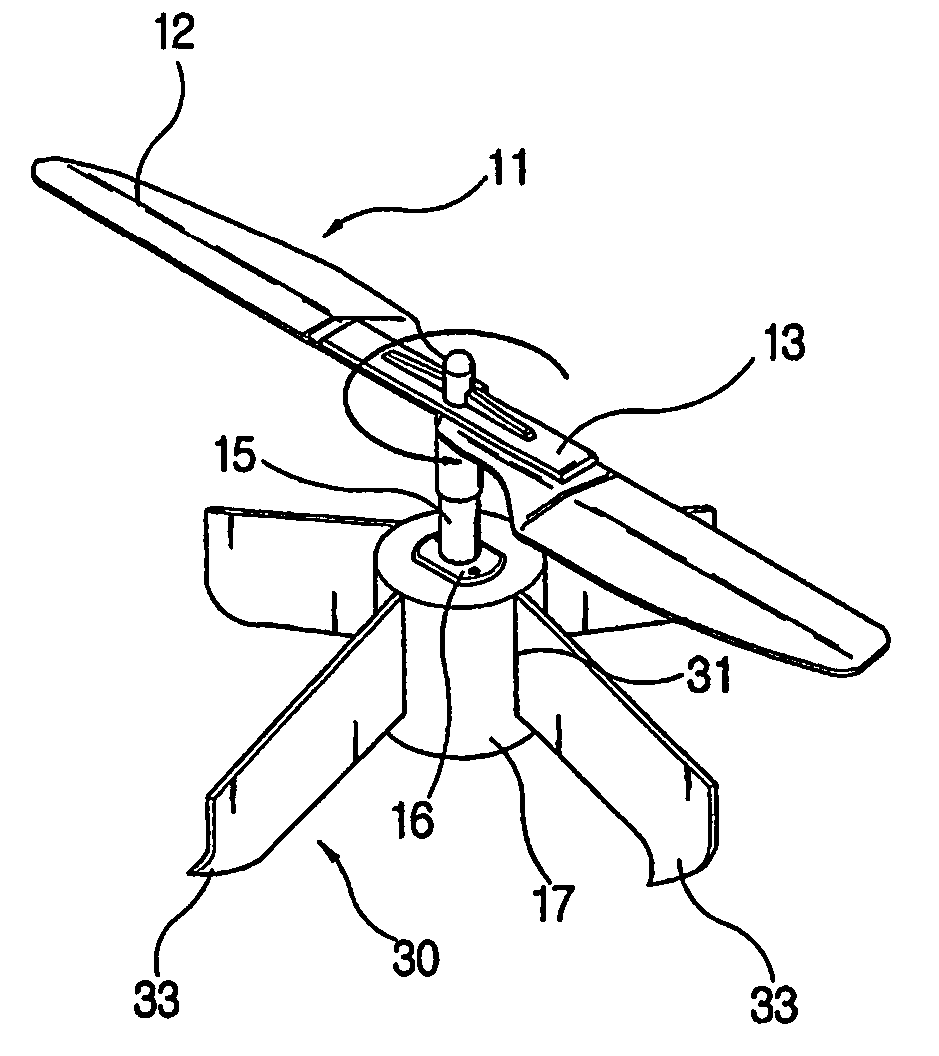
A propeller related vehicle in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention is described as a helicopter having an airframe housing a motor mechanism for powering a main propeller attached to a main drive shaft that extends vertically through the airframe and for powering a tail rotor. The helicopter further includes a horizontal stabilizing mechanism attached between the main propeller and the main drive shaft, which permits the main propeller to freely pivot about the main drive shaft independently from the airframe. As such when the main propeller is rotating and the main propeller begins to pitch, the rotating main propeller has a centrifugal force created by the rotation thereof and will tend to pivot about the horizontal stabilizing mechanism in a manner that offsets the pitch such that the helicopter remains in a substantially horizontal position. In addition various main propeller configurations may be employed that provide additional self-stabilization.
Owner:REHCO LLC
Flexible shaft stabilizing devices with improved actuation
ActiveUS7497823B2Good repeatabilityIncrease flexibilityDiagnosticsSurgical instrument supportEngineeringCam
A stabilizing device having a flexible shaft with a terminal connector and surgical tools used therewith. The flexible shaft is responsive to a tension element connected to a distal end of the shaft and in communication with a proximal end of the shaft. An elastic means interfacing between the proximal end of the tension element and an actuating cam cause the shaft to adapt for differences in activating tension between straight and curved positions. Accordingly, stretching and deformation of the tensioning element is reduced and shaft stiffness upon activation of the tensioning element is repeatable. The terminal connector includes a ball-and-socket arrangement adapted to resiliently absorb movement of an organ during surgery. A bendable suction stabilizer foot adaptable to contours of an organ is also provided as an attachment to the stabilizer device.
Owner:ETHICON INC
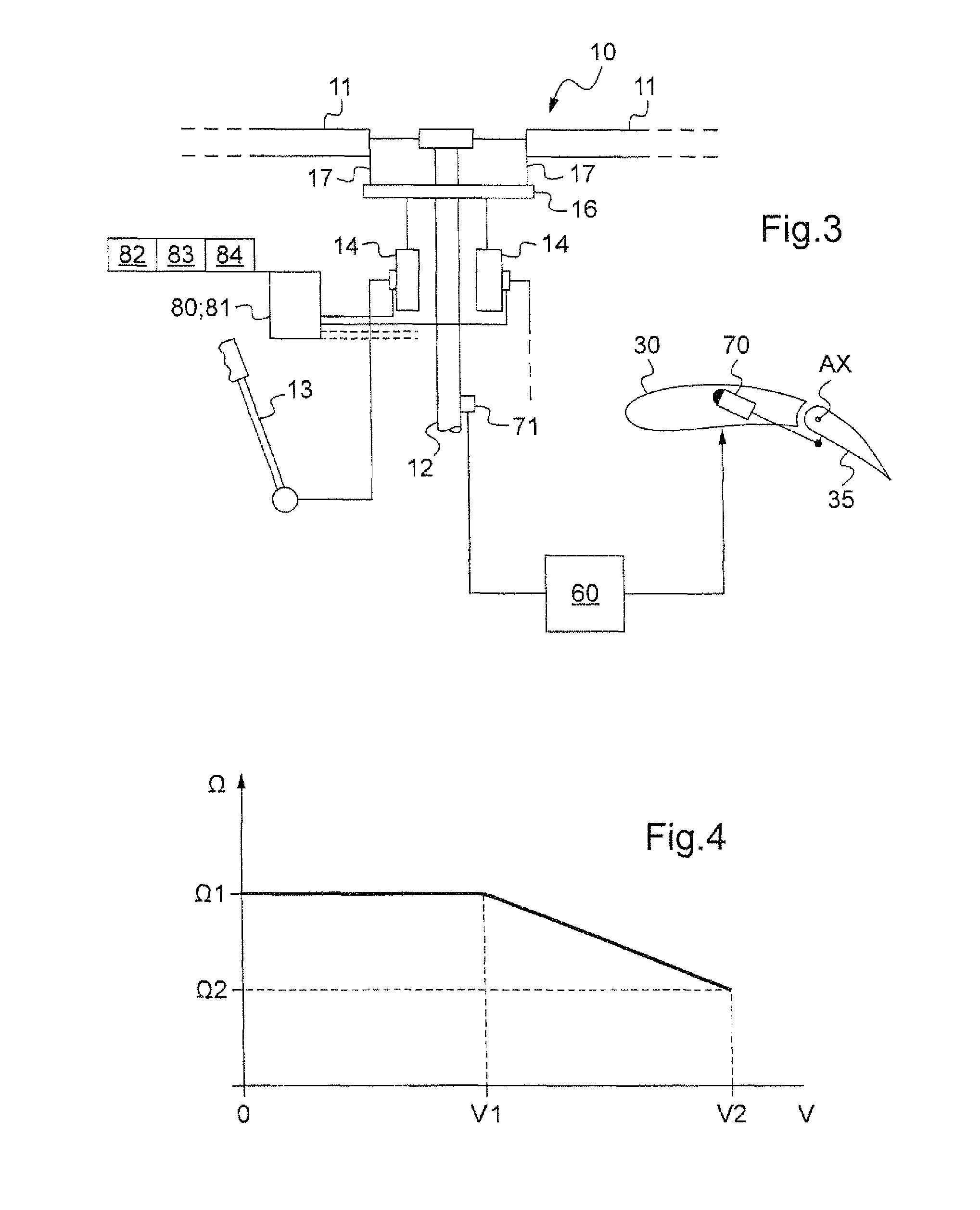
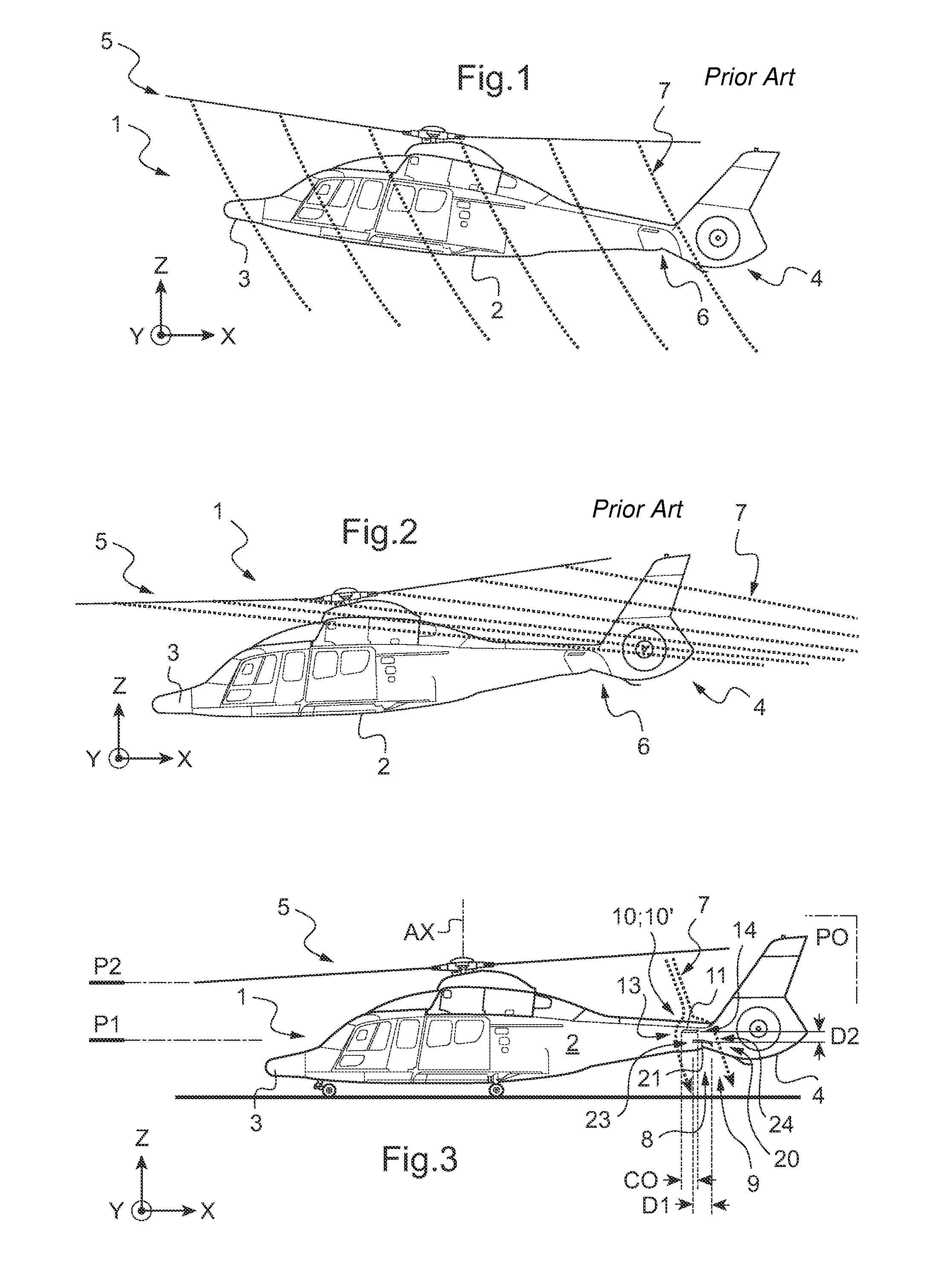
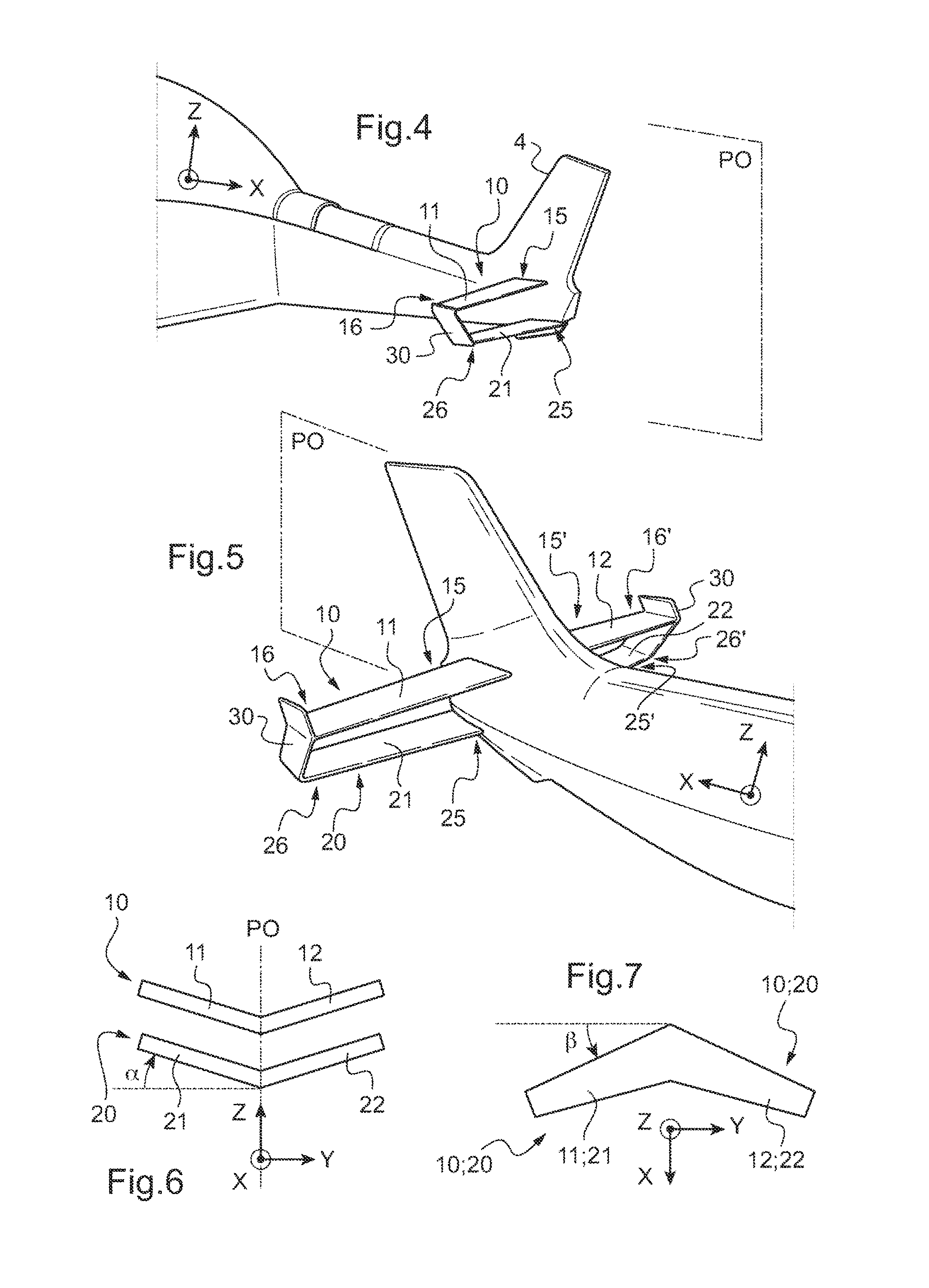
Method of minimizing the attitude hump phenomenon and a rotary wing aircraft provided with stabilizer means therefor
A system and method of minimizing the attitude hump phenomenon of a rotary wing aircraft is provided. The rotary wing aircraft includes upper pitching-stabilizer and at least one lower pitching-stabilizer. The lower stabilizer is positioned in a wake of the upper stabilizer generated by a stream of air passing through the rotary wing and impacting against the upper surface of the upper stabilizer.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Multi-mode mobility micro air vehicle
A multi-mode mobility micro air vehicle (MAV) accomplishes ground locomotion by hopping on a retractable leg. The hopping is translated into forward locomotion when aided by the forward thrust of propellers, and the orientation of locomotion is directed by aerodynamic controls like ailerons, rudders, stabilators, or plasma actuators. The foot of the leg is convexly curved so as to produce hopping that is statically and passively dynamically stable. The MAV is also equipped for vertical takeoff so that it may conduct multiple idling missions in sequence and may return home for recovery and reuse. Structural integration of power storage and photovoltaic generation systems into the aerodynamic surface of the MAV lightens the weight of the MAV while also providing a strong structure and permitting the MAV to harvest its own energy. The MAV may autonomously conduct surveillance missions and / or serve as a flying platform for self-healing sensor or communications networks, especially when multiple MAVs are used in concert.
Owner:ORBITAL RES
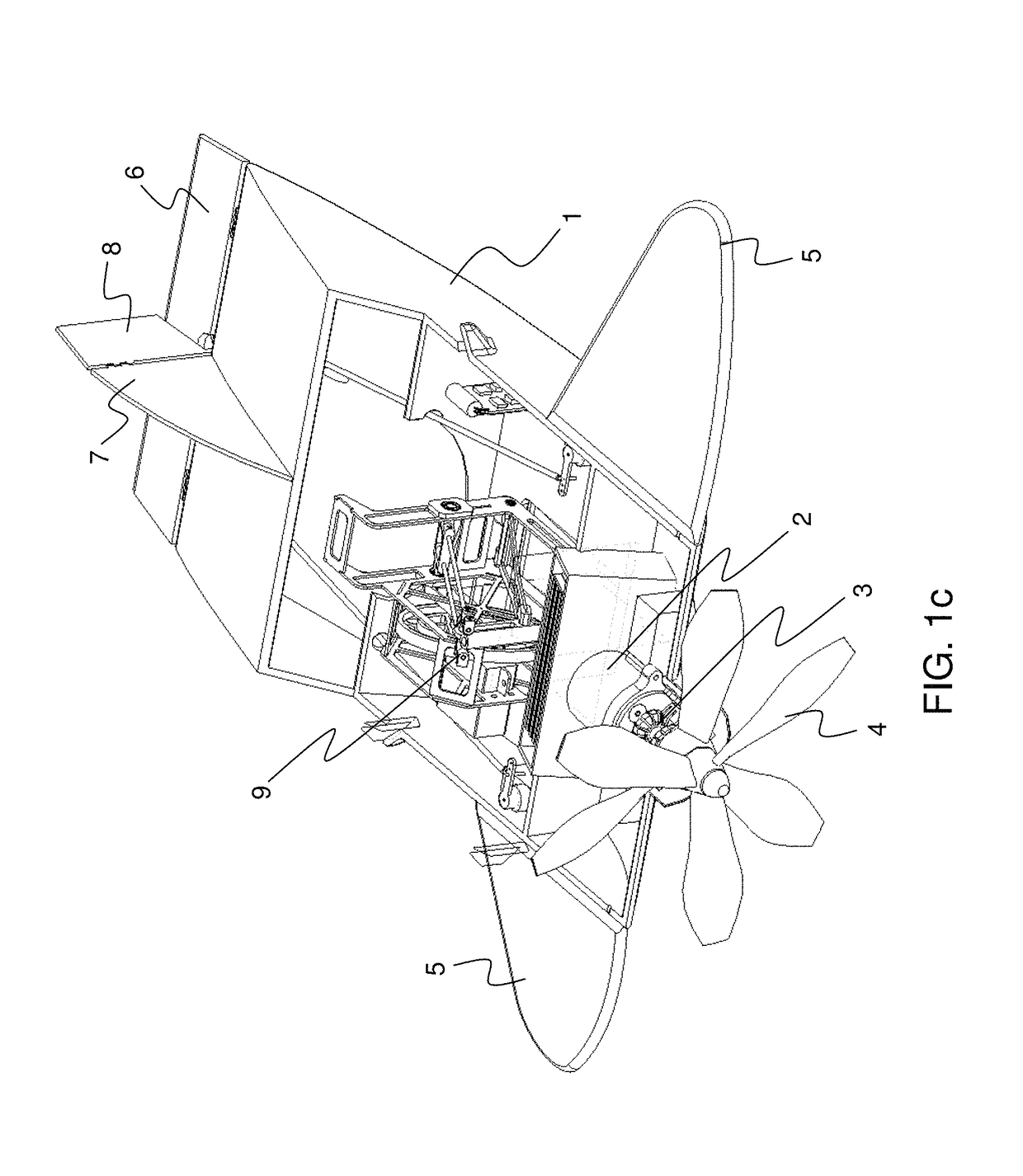
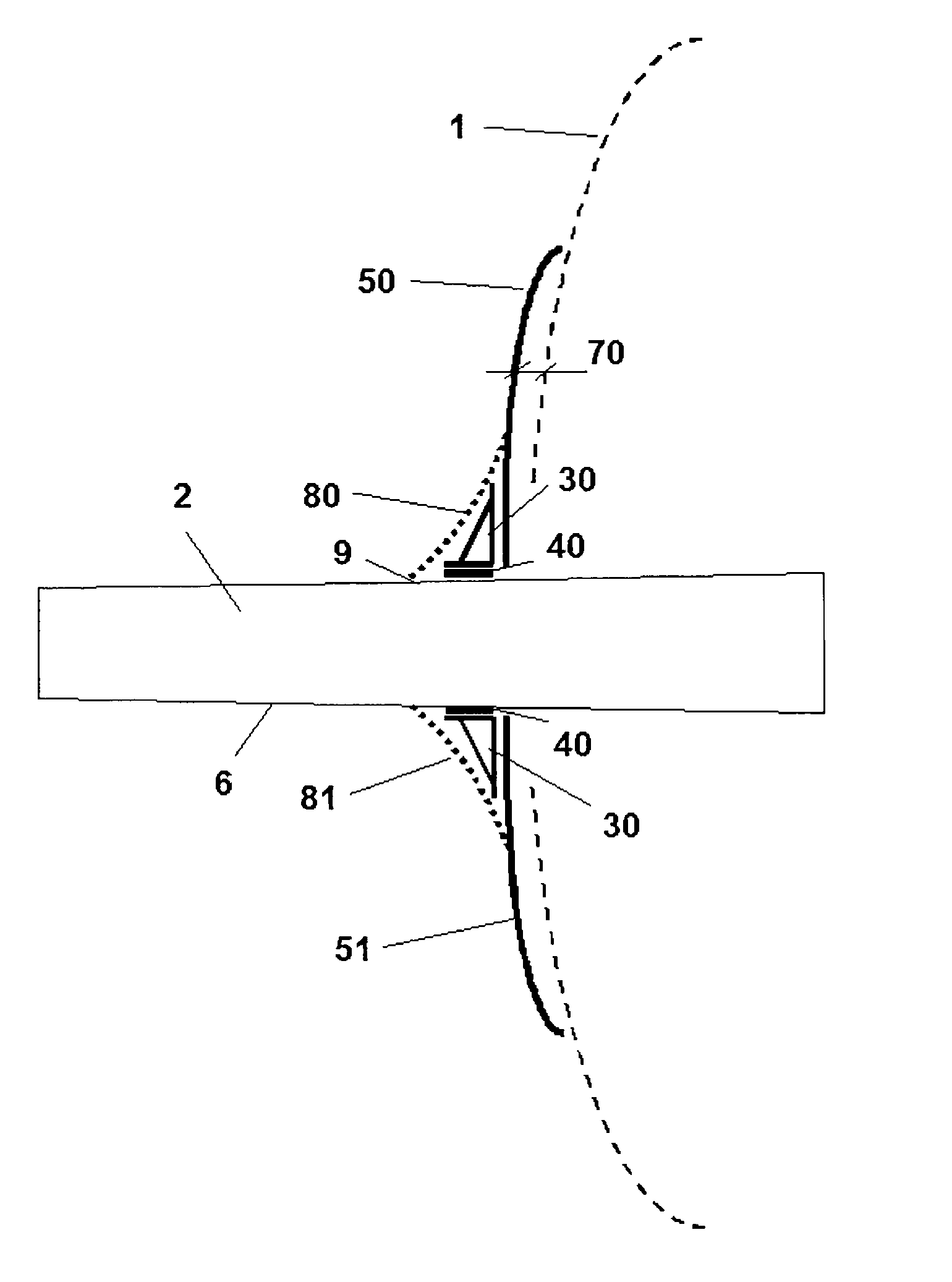
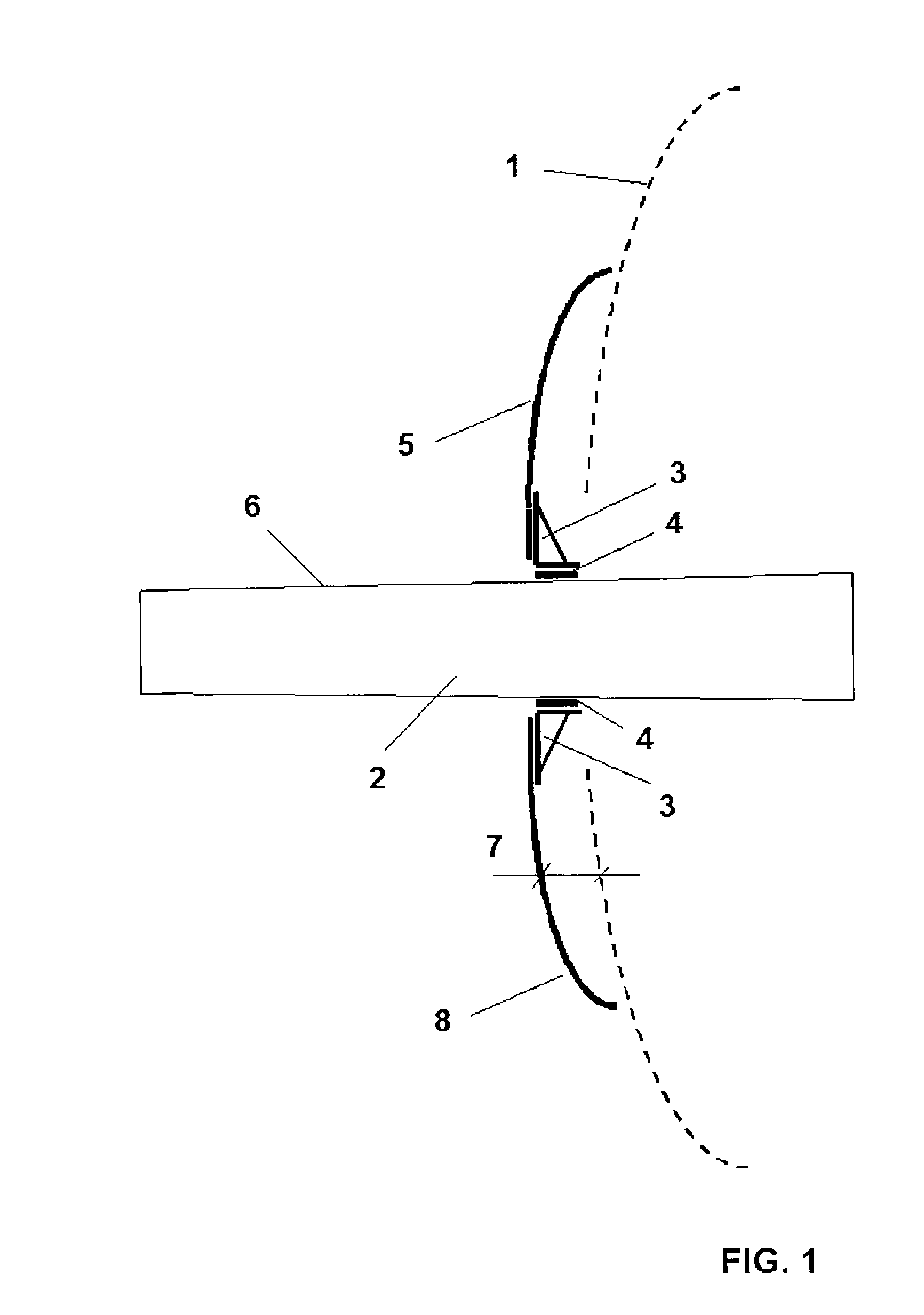
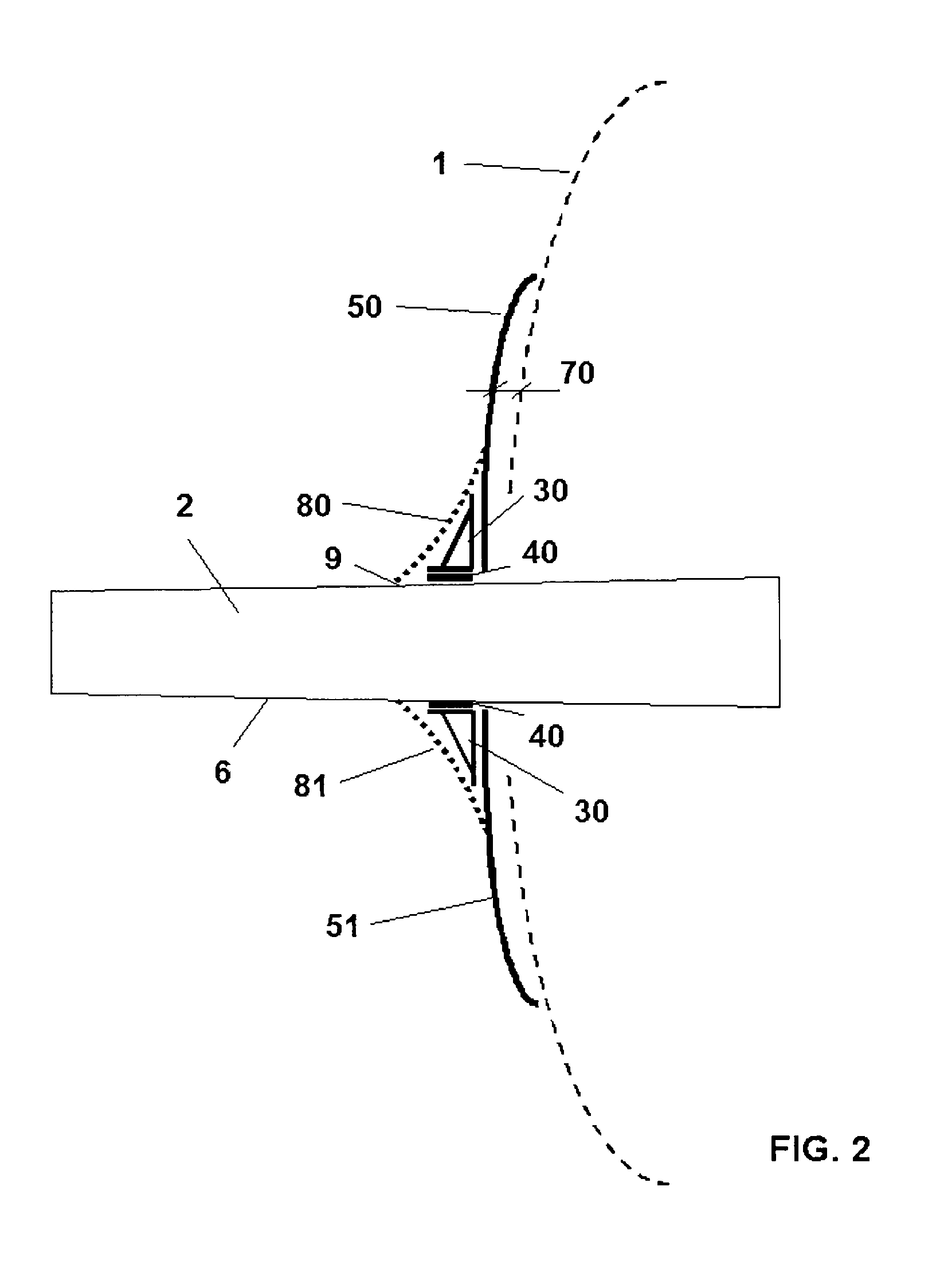
Fairing system for a horizontal stabiliser of an aircraft and process for installing said system
InactiveUS20100163672A1Avoid improper sealingEasy to adjustAircraft stabilisationMetal working apparatusFuselageCowling
The invention relates to a fairing system for a horizontal stabiliser of an aircraft and to a process for installing said system, such that the fairing system for the sealing of the horizontal stabiliser (2) and the fuselage (1) of the aircraft comprises a primary fairing (50, 51) arranged on the horizontal stabiliser (2) of the aircraft, the mentioned primary fairing (50, 51) being solidly connected to the mentioned horizontal stabiliser (2) which is in turn trimmable with respect to the fuselage (1), the fairing system in turn comprising a secondary fairing (80, 81) such that the primary fairing (50, 51) is coupled to the horizontal stabiliser (2) through supports (30) arranged in the direction of the chord of the primary fairing (50, 51), said supports (30) being located in the outer part of said primary fairing (50, 51) with respect to the fuselage (1), the secondary fairing (80, 81) being arranged in the outer part of the supports (30), the purpose of said secondary fairing (80, 81) being to cover the mentioned supports (30) and offer a good aerodynamic performance of the assembly. The invention also relates to a process for installing such a fairing system on the horizontal stabiliser (2) of an aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
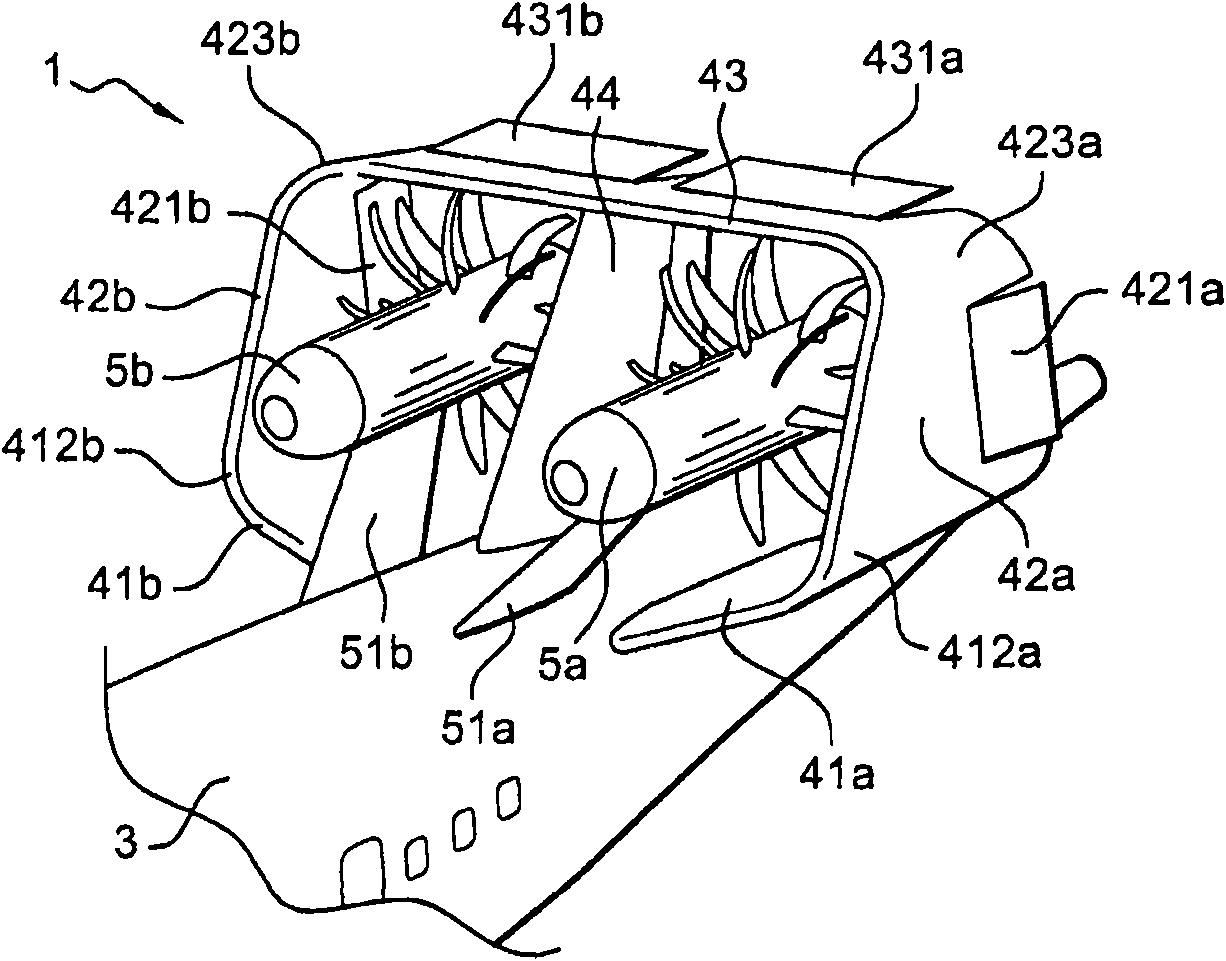
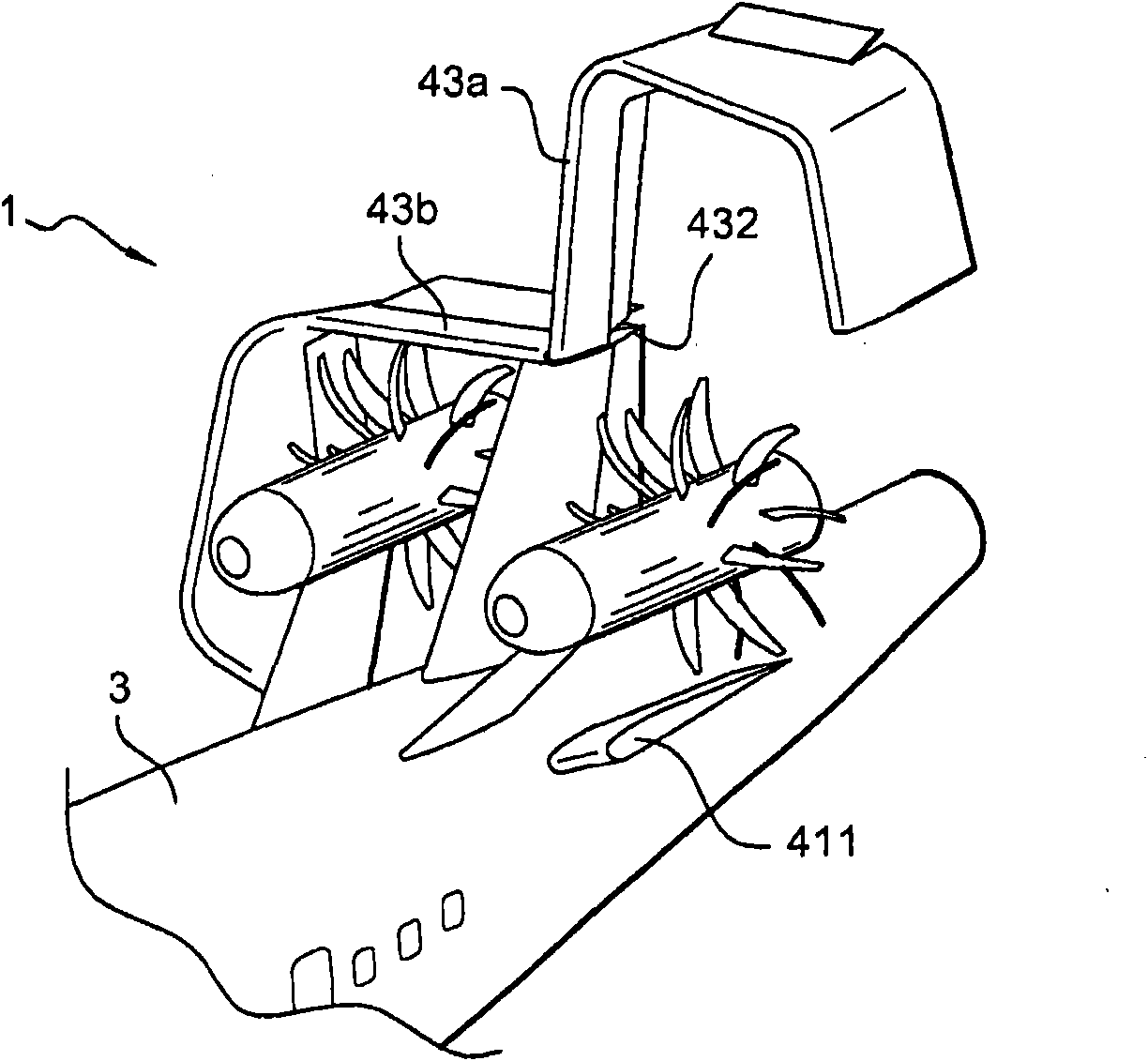
Pneumatic layout of dual flying wings of UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)
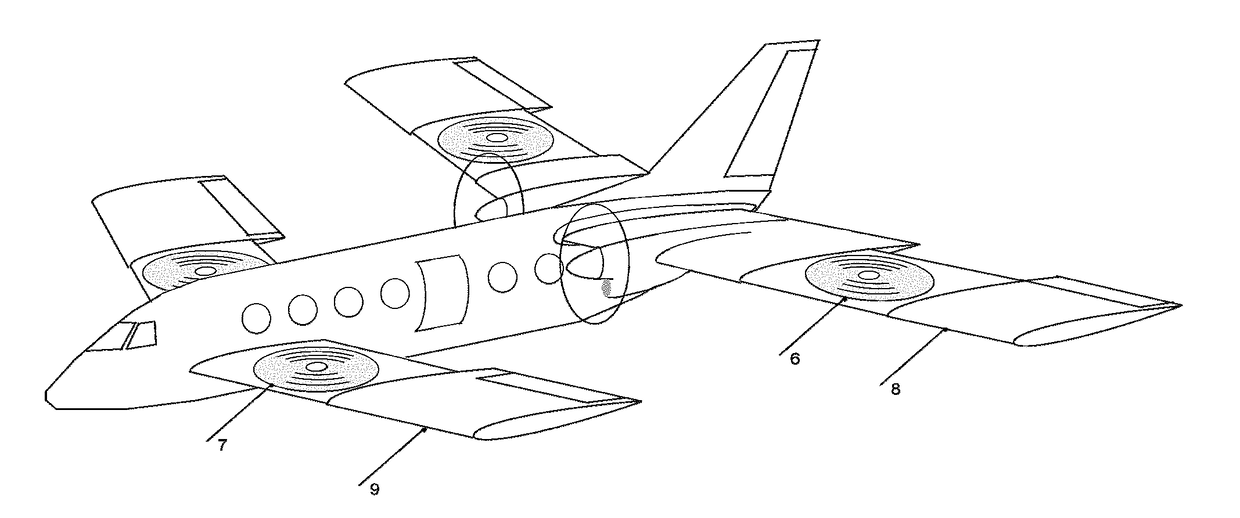
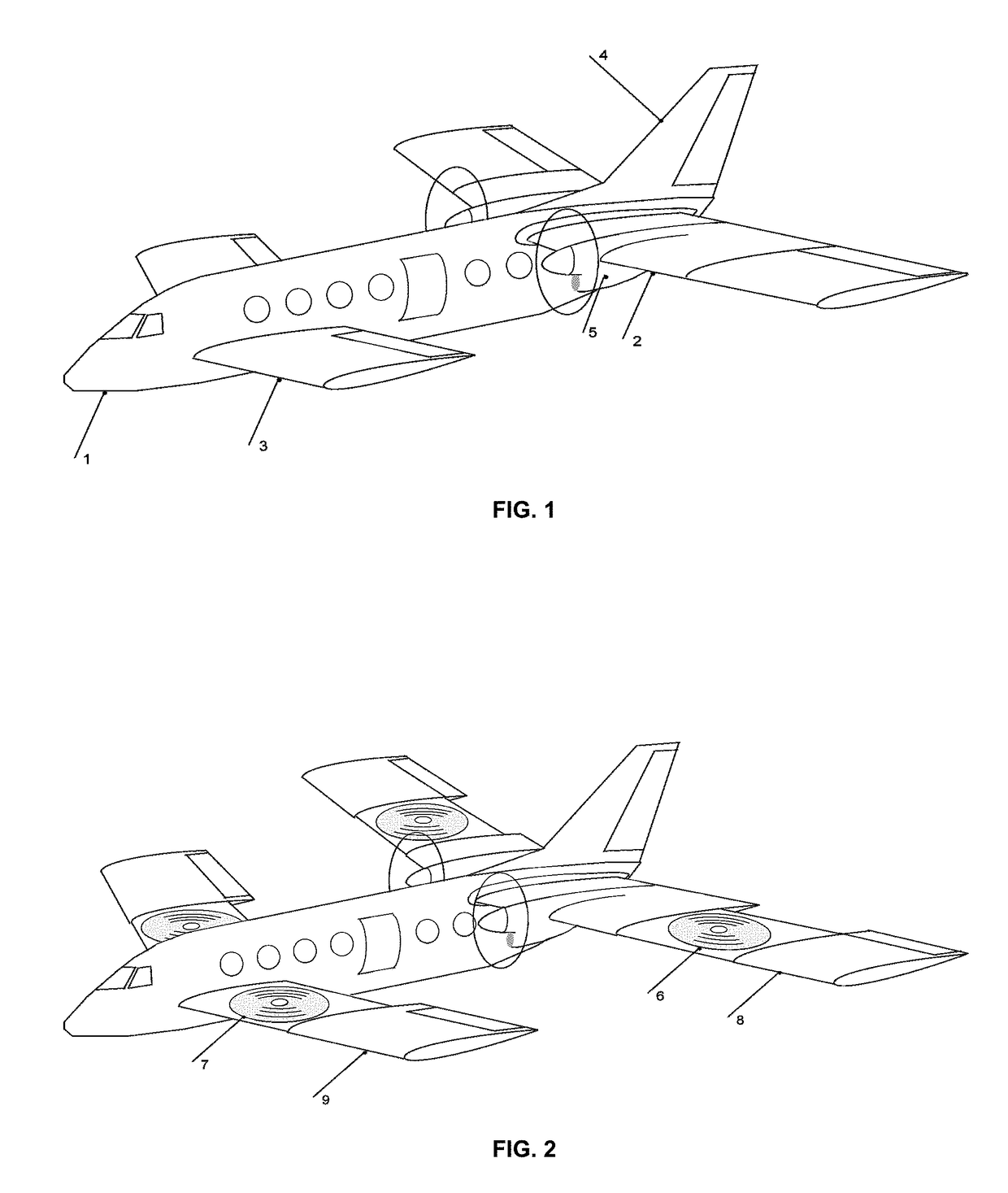
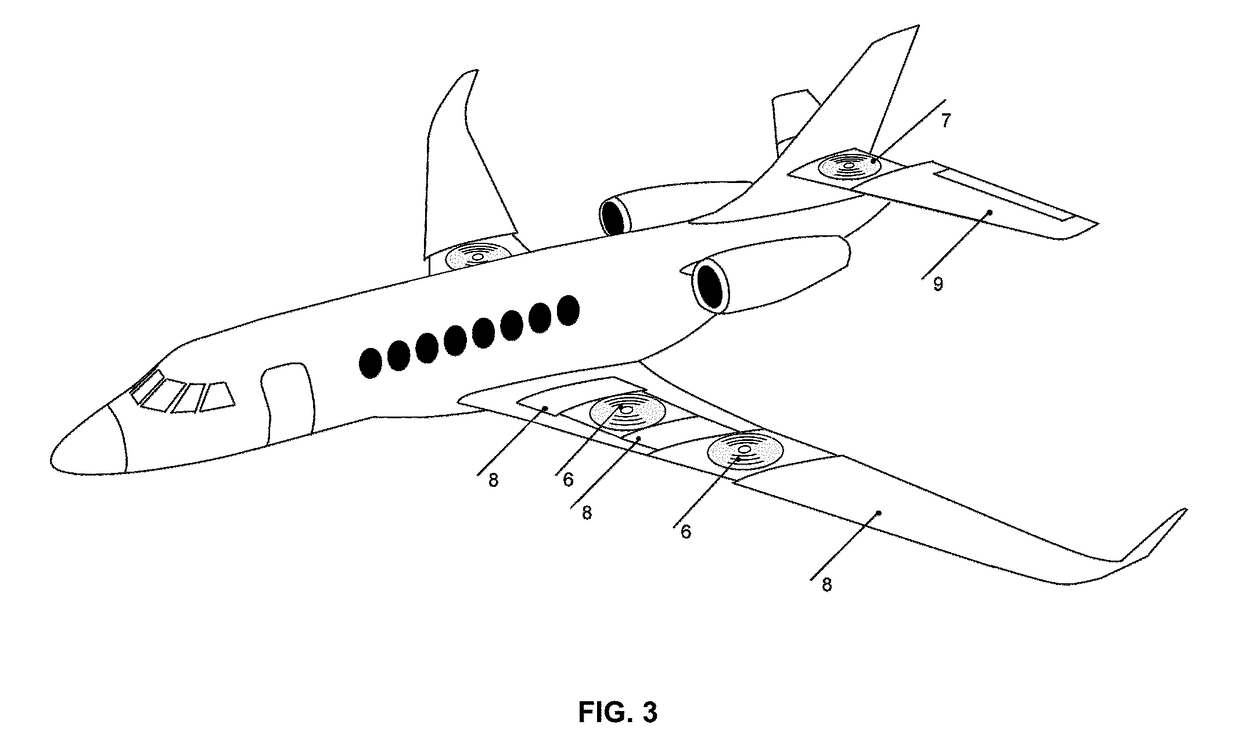
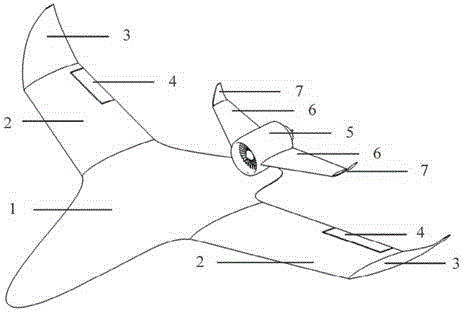
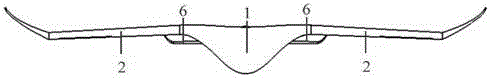
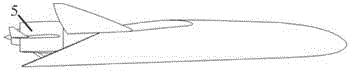
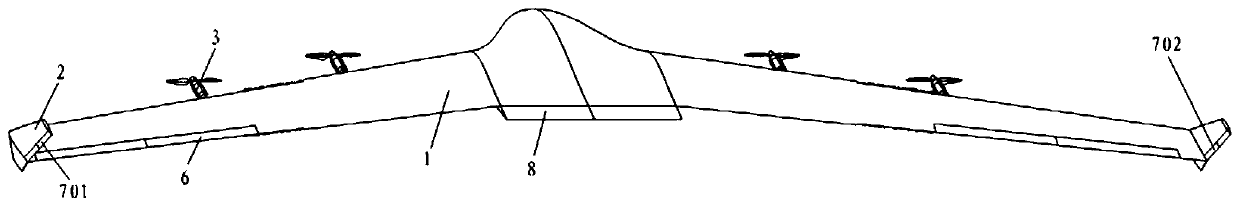
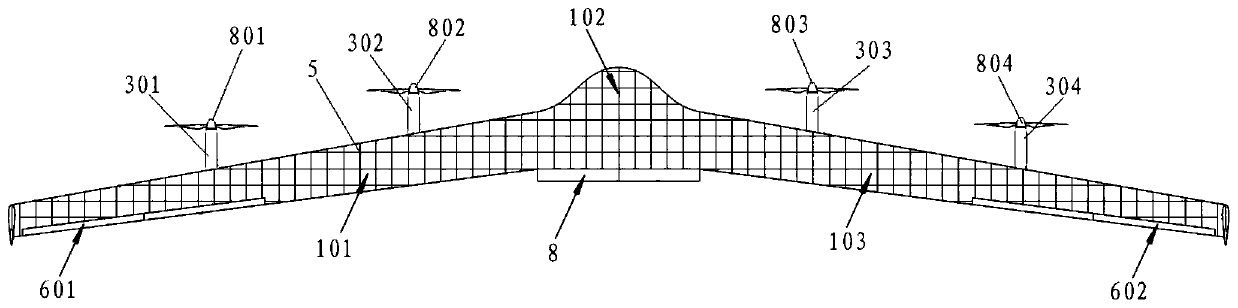
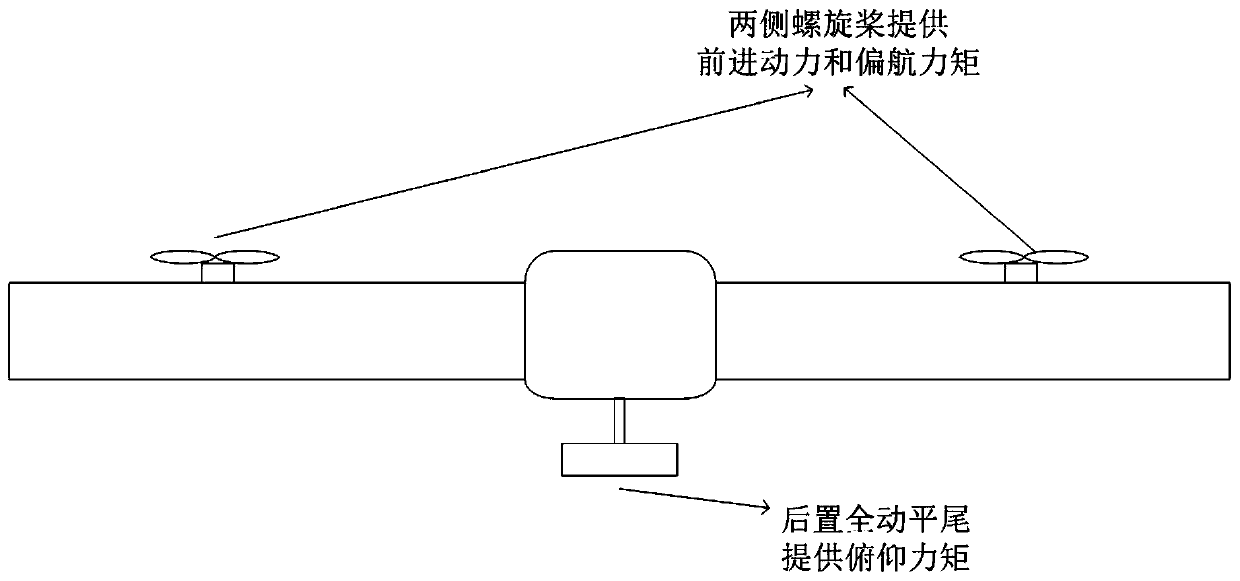
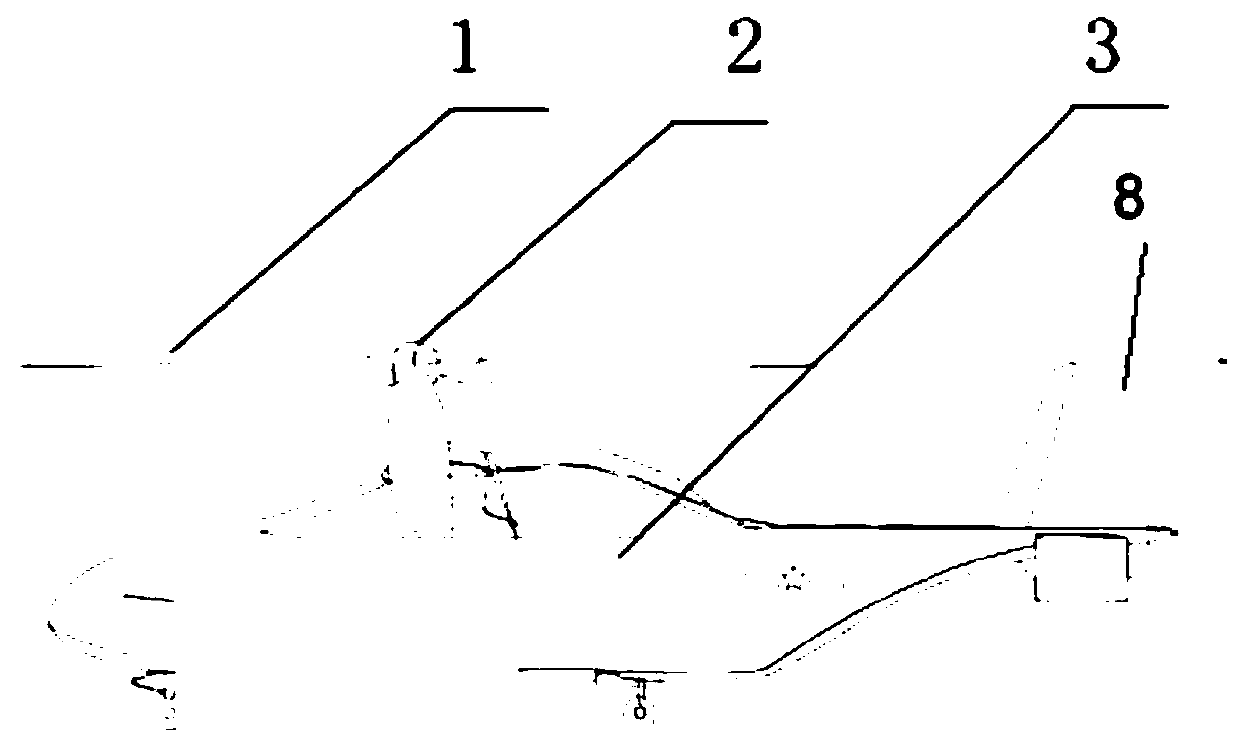
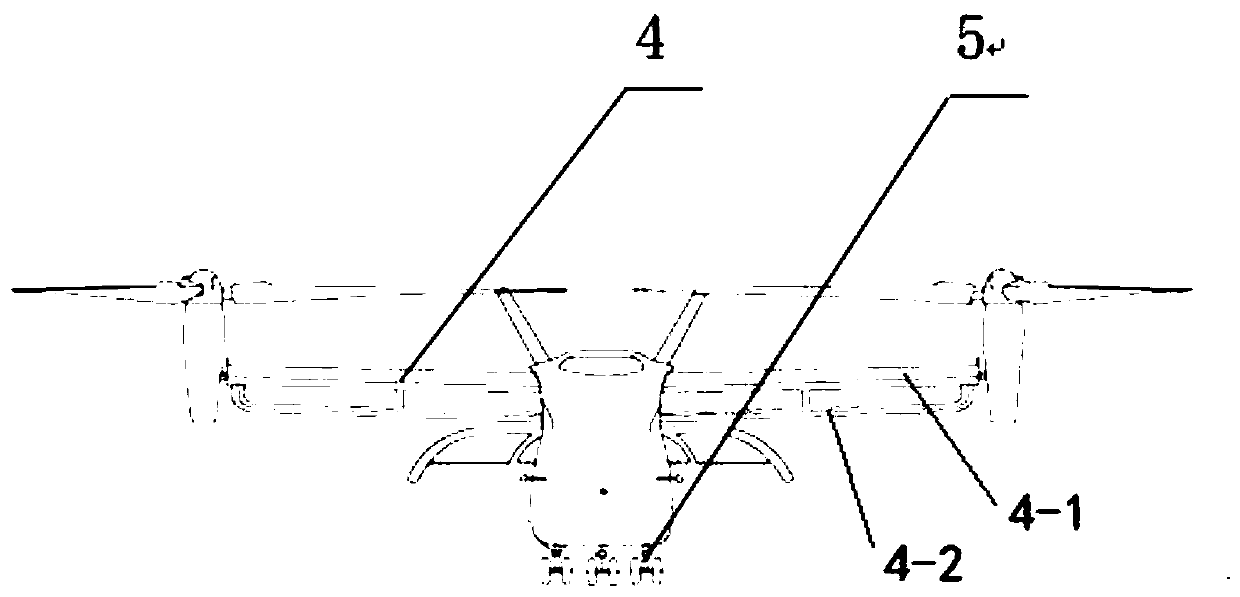
The invention relates to a pneumatic layout of dual flying wings of a UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle). The pneumatic layout is characterized by comprising a pneumatic layout of a blended wing body flying wing, a layout of installing a turbofan engine above the rear section of the blended wing body flying wing and a pneumatic layout of installing a stabilator at two sides of a nacelle on the outer wall of the turbofan engine, wherein the blended wing body flying wing with a high lift-to-drag ratio is formed by a fuselage, wings, wingtip winglets and direction ailerons together; the stabilator which is used for providing a positive lifting force during flight trimming of the UAV is formed by horizontal tails and horizontal tail winglets, and the dual flying wings are formed by the blended wing body flying wing and the stabilator together. According to the pneumatic layout of the dual flying wings of the UAV, disclosed by the invention, the UAV has high lift-to-drag ratio, good operability and high stability, and the pneumatic layout has the advantage of good stealth performance.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Micro aerial vehicle
InactiveUS7445536B2Counterbalances the reaction torquePrevent excessive expansionUnmanned aerial vehiclesMicro-sized aircraftMicro air vehicleFlight vehicle
The purpose of this invention is to provide an ultra-miniature aircraft which is able to perform ‘Vertical Take-off and Landing (VTOL)’ and maintaining altitude when the vehicle is moving or when the horizontal velocity of a vehicle is at 0 by getting life only from a single rotor's rotation, and without using separate stabilizers such as a tail-rotor or a gyro. To fulfill the above purpose, this invention comprises: several blades in airfoil shape that are places in calculated angle and space; hubs that connect the blade to with a body of a vehicle; a rotor which gives lifting force with its spin; a spin-able axle which its vertical hem is bound to the hubs; a rotor drive that is needed to spin the rotor; a vehicle body that is placed right under the rotor in order to fly from the lift that is obtained by revolutions of the rotor; fixed-wings that are placed in certain angle and space around the outside of the vehicle body in order to reduce a reaction torque, which affects the body to turn the opposite direction of the rotor, from the rotor's movement; and a reaction-torque-counterbalancing-system on each of the above fixed-wings that offsets the reaction torque aggressively.
Owner:AIRROBOT
Unstable rowing simulator
InactiveUS20150258366A1Ensure balanceMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesEngineeringStabilator
Lever-type rowing machine, whose main rigging dimensions meet the corresponding parameters of sweep rowing or sculling boat is mounted to the base frame by using front and rear elastic suspension so that the simulator makes it possible to rotate (tilt) about its transverse and longitudinal axes and move vertically, thus making it possible to simulate the boat swings on the transverse and longitudinal axes and movement in the vertical direction. In addition, the simulator has passive and active stabilization systems, enabling the athlete to maintain a balance, and stiffness of its front and rear suspension and stabilizer system can be adjusted depending on the weight and balancing ability of user. There is also a possibility to constraint the suspension thus ensuring full stability of the simulator and exercise regime, corresponding to the exercising on common rowing machines.
Owner:KAUNO TECHNOLOGIJOS UNIVTAS
Unstable rowing simulator
Lever-type rowing machine, whose main rigging dimensions meet the corresponding parameters of sweep rowing or sculling boat is mounted to the base frame by using front and rear elastic suspension so that the simulator makes it possible to rotate (tilt) about its transverse and longitudinal axes and move vertically, thus making it possible to simulate the boat swings on the transverse and longitudinal axes and movement in the vertical direction. In addition, the simulator has passive and active stabilization systems, enabling the athlete to maintain a balance, and stiffness of its front and rear suspension and stabilizer system can be adjusted depending on the weight and balancing ability of user. There is also a possibility to constraint the suspension thus ensuring full stability of the simulator and exercise regime, corresponding to the exercising on common rowing machines.
Owner:KAUNO TECHNOLOGIJOS UNIVTAS
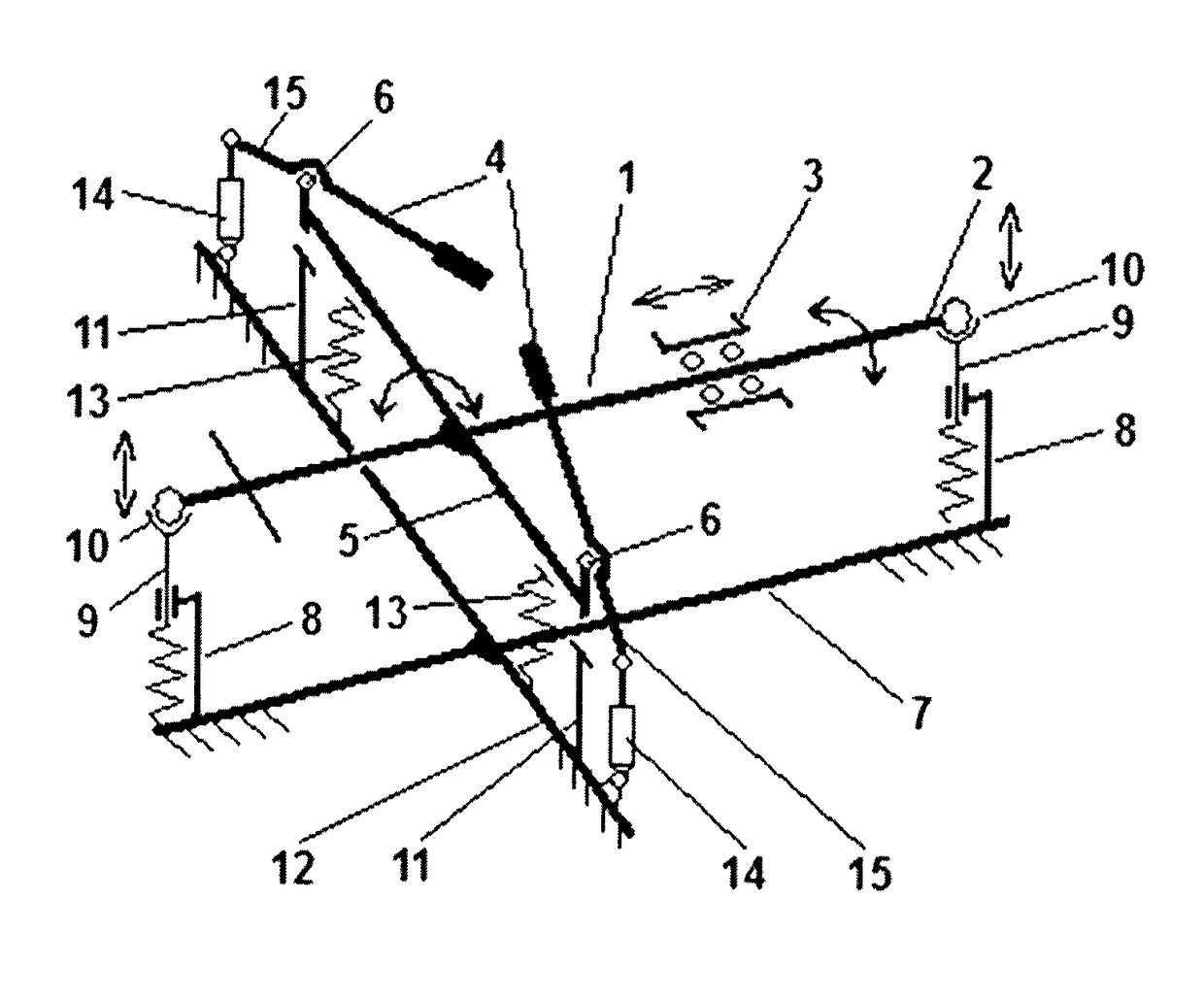
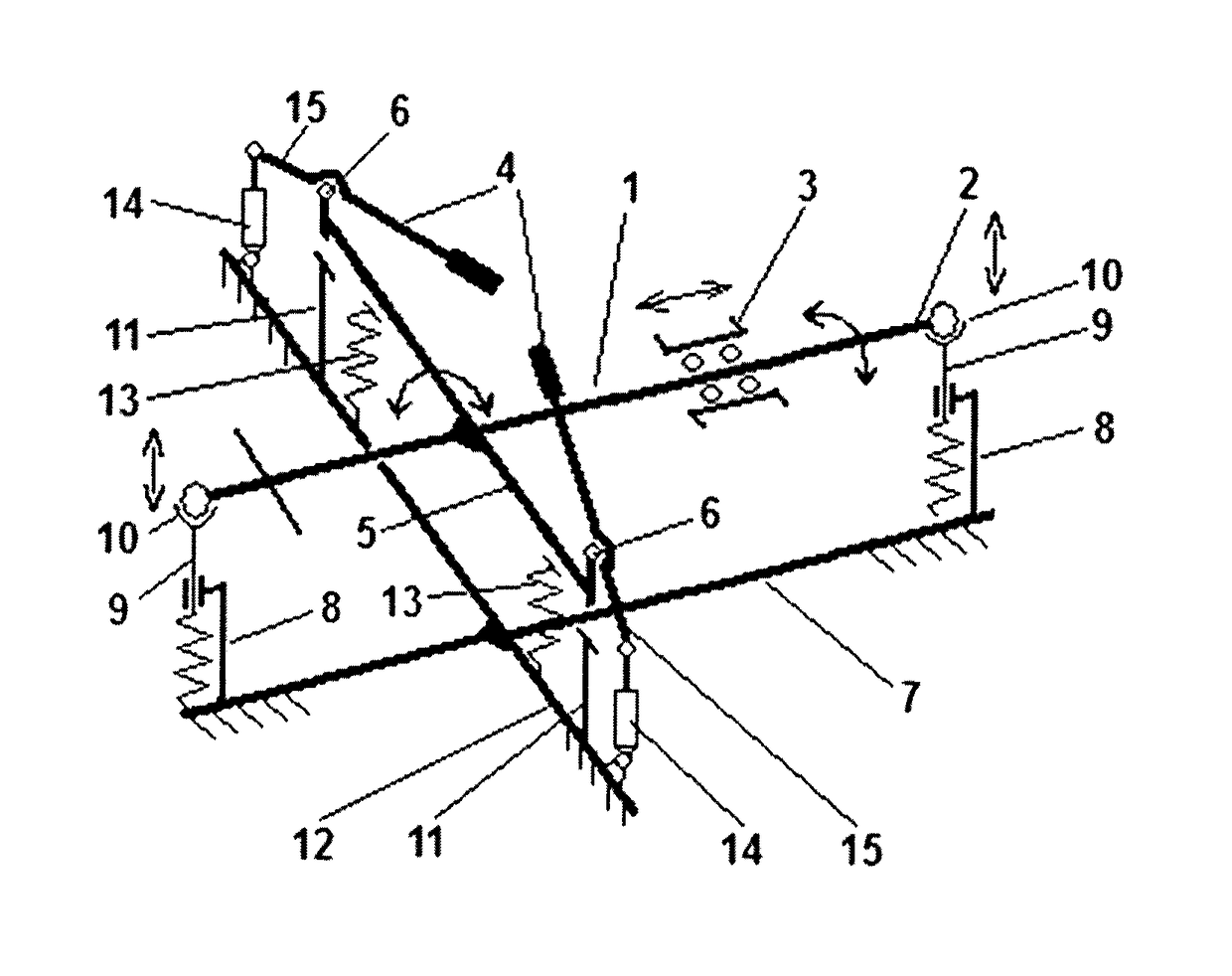
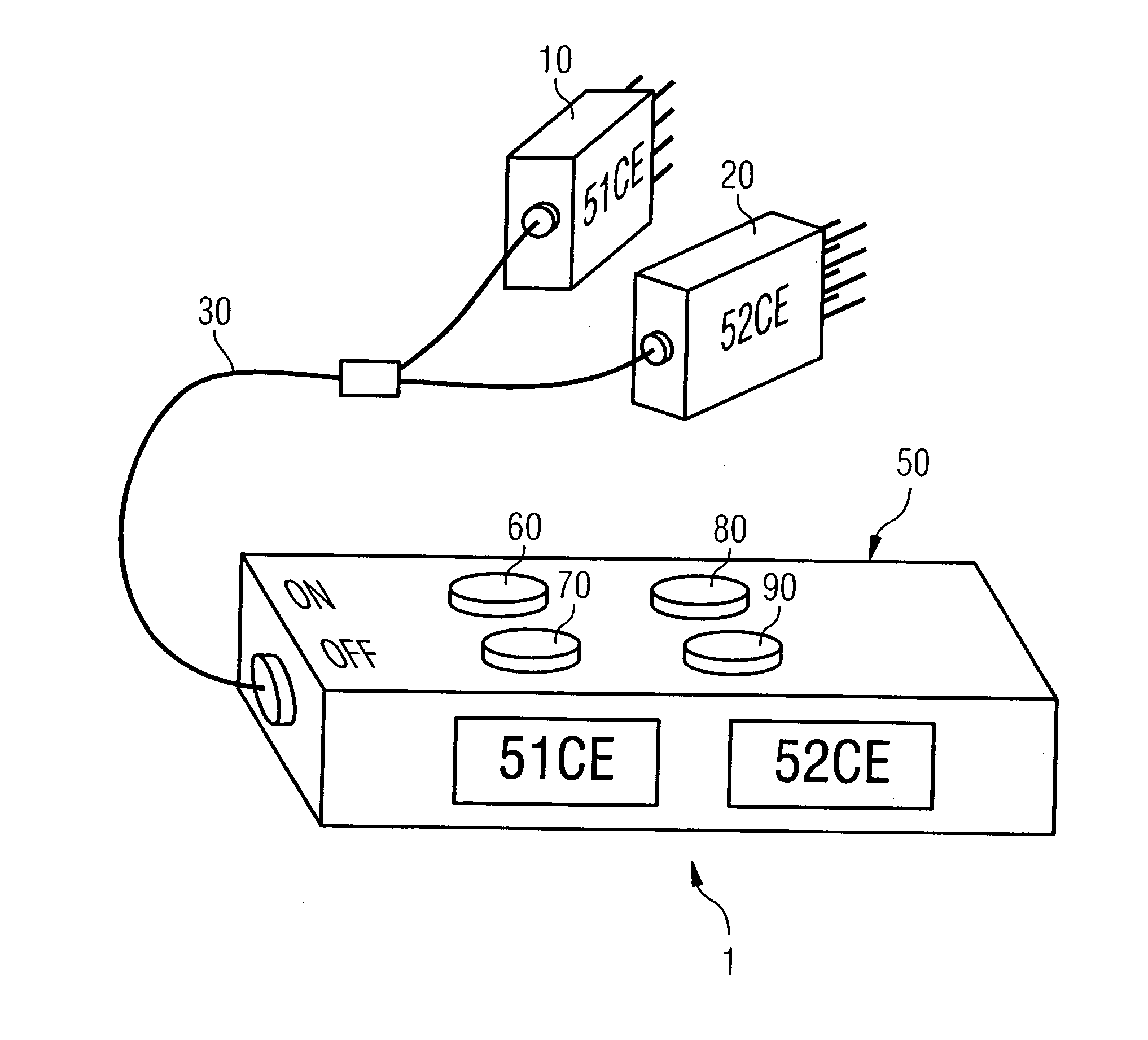
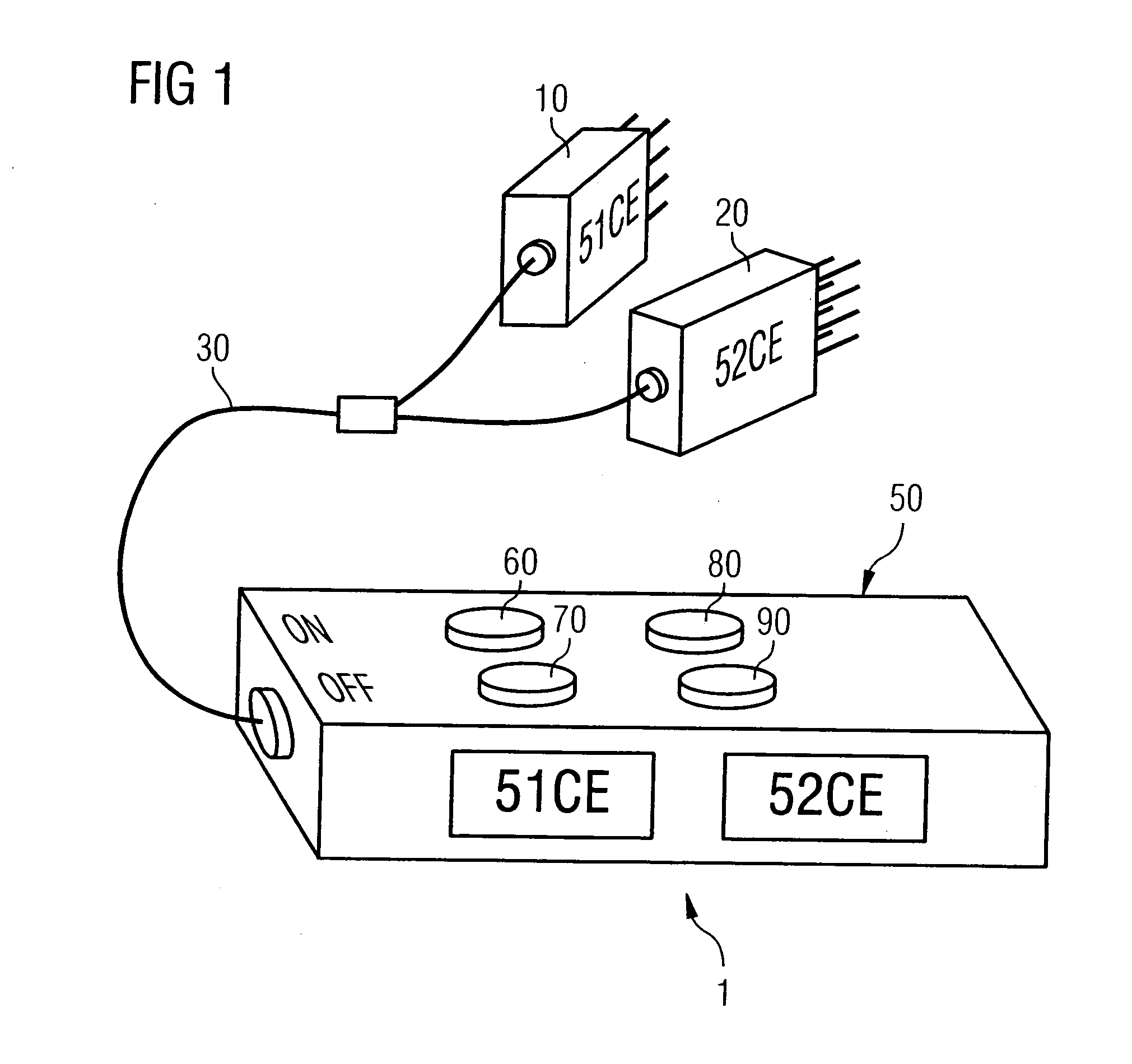
Tester for testing signal lines of a flight control system for a ths motor of an aircraft
InactiveUS20110043369A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsDigital data processing detailsFlight vehicleTester device
The present invention relates to a tester, its use and a method for testing signal lines of a flight control system for a trimmable horizontal stabilizer (THS) motor of an aircraft. The tester comprises at least one test-relay (52, 54) to be connected with a relay socket of the flight control system, when the signal lines of the flight control system are to be tested, and at least one indicator (60, 70, 80, 90) being electrically connected with the at least one test-relay (52, 54) for indicating whether a voltage being applied to the test-relay (52, 54) is equal to or larger than a predetermined voltage. The method according to the invention comprises the steps of connecting at least one test-relay (52, 54) of a tester (1), in place of the original relay, with the relay socket of the flight control system, applying a voltage to the at least one test-relay (52, 54) and determining whether a voltage being applied to the at least one test-relay (52, 54) is equal to or larger than a predetermined voltage.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Structural dynamic stability for an aircraft
ActiveUS8074926B2Improvement in structural dynamic stabilityReduce generationAircraft stabilisationStructural dynamicsEngineering
An improvement and method for improved structural dynamic stability for 20 and 30 Series Learjets are disclosed. The improvement includes a redistribution of the elevator mass balance to uncouple the elevator rotational motion from the stabilizer translation motion for the higher order horizontal frequencies having node lines in the proximity of the mass outboard counterbalance weights. The original tail section includes a rudder, and a horizontal stabilizer supporting an elevator mounted adjacent the rudder. The elevator includes a proximal end adjacent the rudder and a distal end that includes a counterbalance portion. The improvement includes replacement of an original mass counterbalance weight from within the counterbalance portion with a new mass counterbalance weight of less mass, and the inclusion of additional mass counterbalance weights disposed within the elevator and interposed between the proximal end and the counterbalance portion.
Owner:BURGESS CALVIN
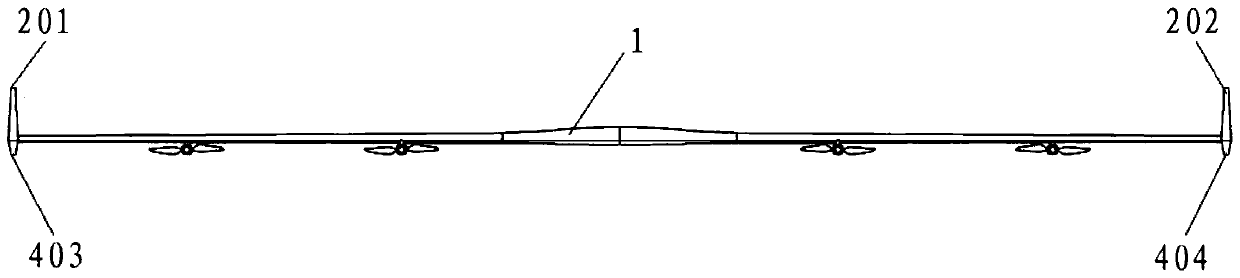
Flying wing layout solar unmanned aerial vehicle
PendingCN110254720AImprove the lift-to-drag ratioClean appearanceAircraft power plant componentsAll-wing aircraftUncrewed vehicleEngineering
The invention discloses a flying wing layout solar unmanned aerial vehicle. The flying wing layout solar unmanned aerial vehicle comprises wings, vertical fins, power pods, non-retractable landing gears, a control surface and a solar cell array, wherein the control surface comprises ailerons, rudders and stabilators; the vertical tails adopt a trapezoidal shape and are arranged at wing tips on the two sides of the wings, the stabilators adopt a rectangular shape and are arranged at the tail parts of the middle sections of the wings, the ailerons are arranged at the trailing edges of the wings, the rudders are arranged at the trailing edges of the vertical fins; the power pods are hung below the wings, the solar cell array is laid on the upper surfaces of the wings, the non-retractable landing gears are arranged below the whole flying wing layout solar unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the unmanned aerial automobile, the scale of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be reduced by virtue of a high pneumatic lift-drag ratio and a light structural weight, and the wind resistance capability of the unmanned aerial vehicle is enhanced through the high flight speed.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
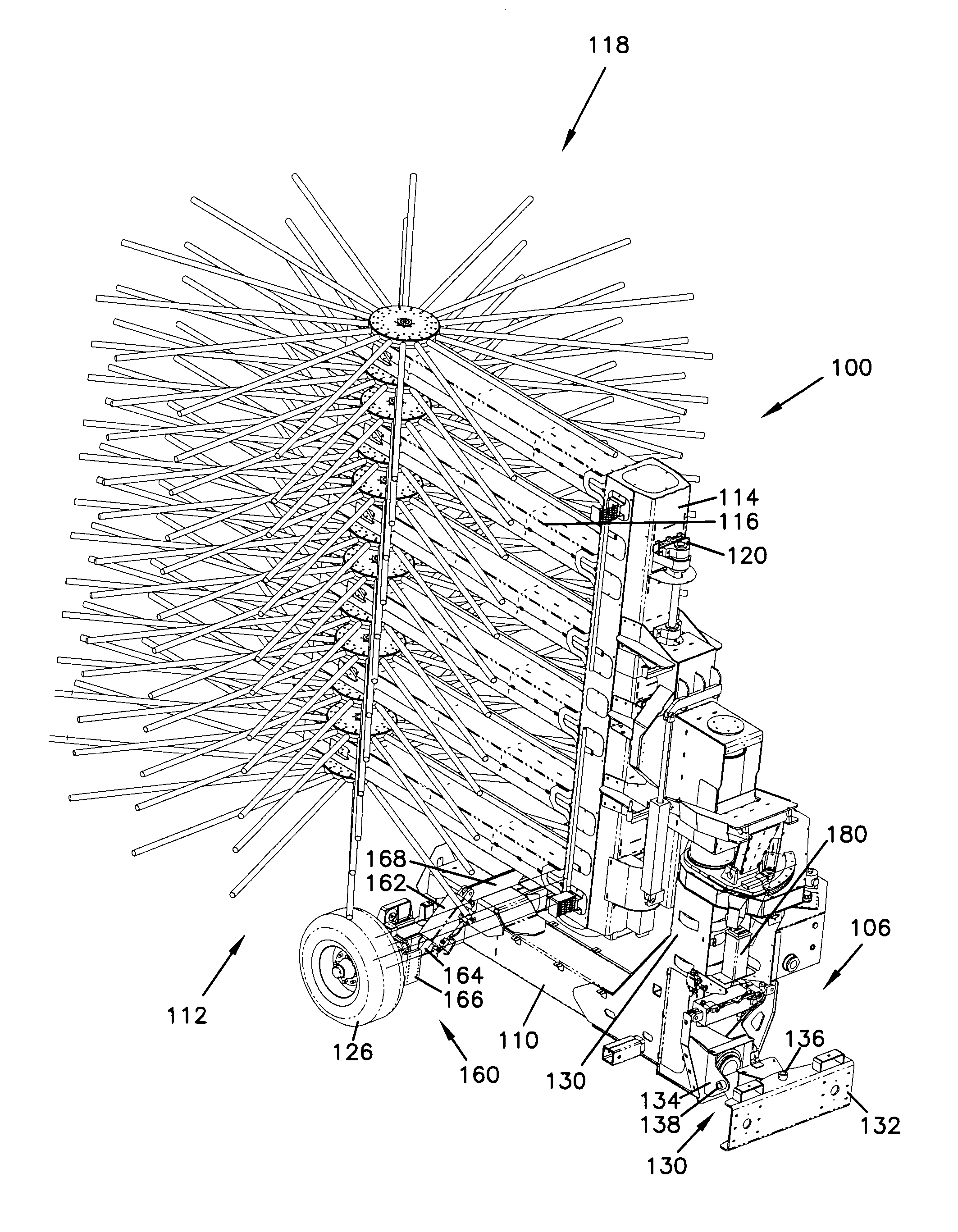
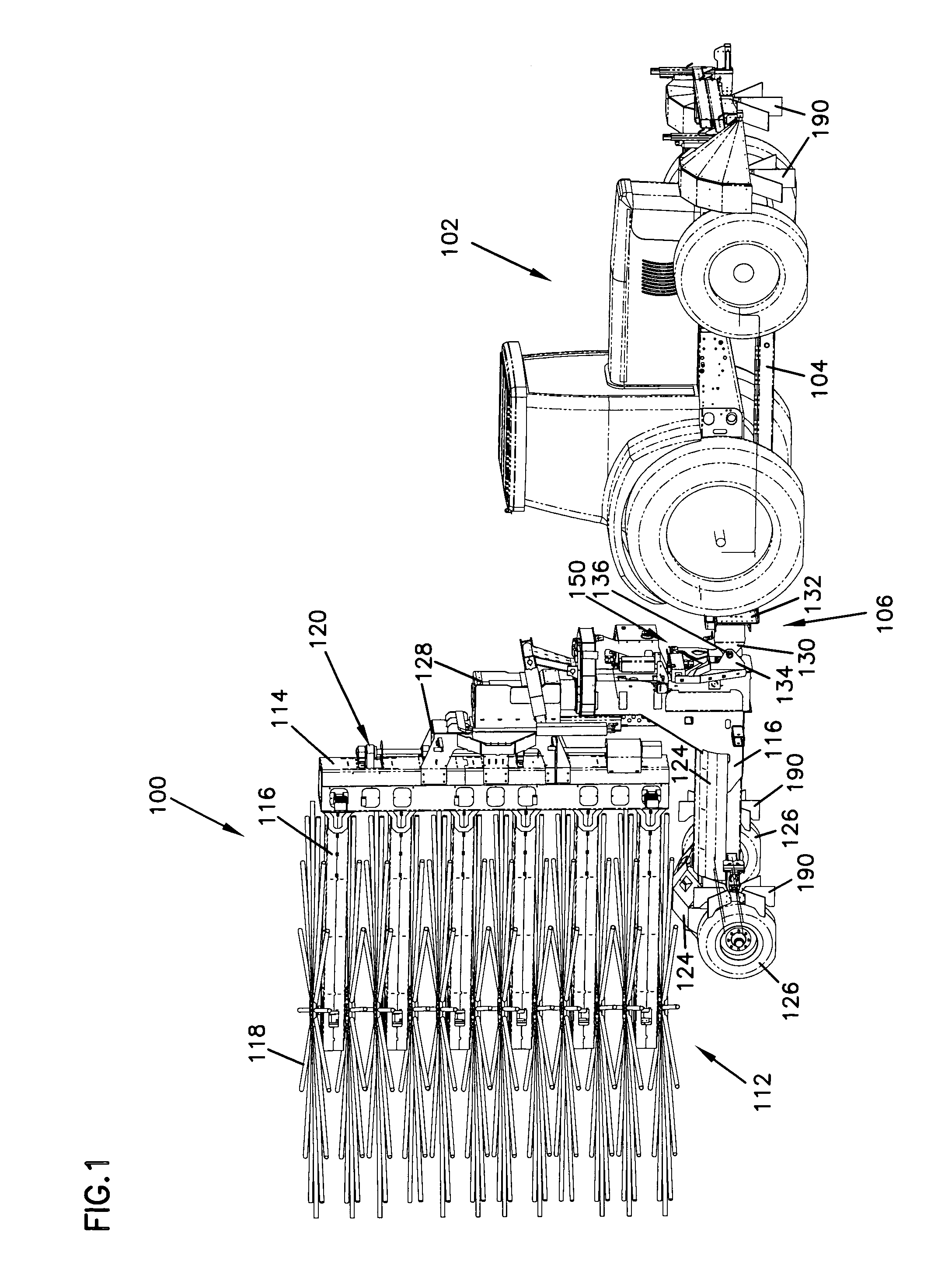
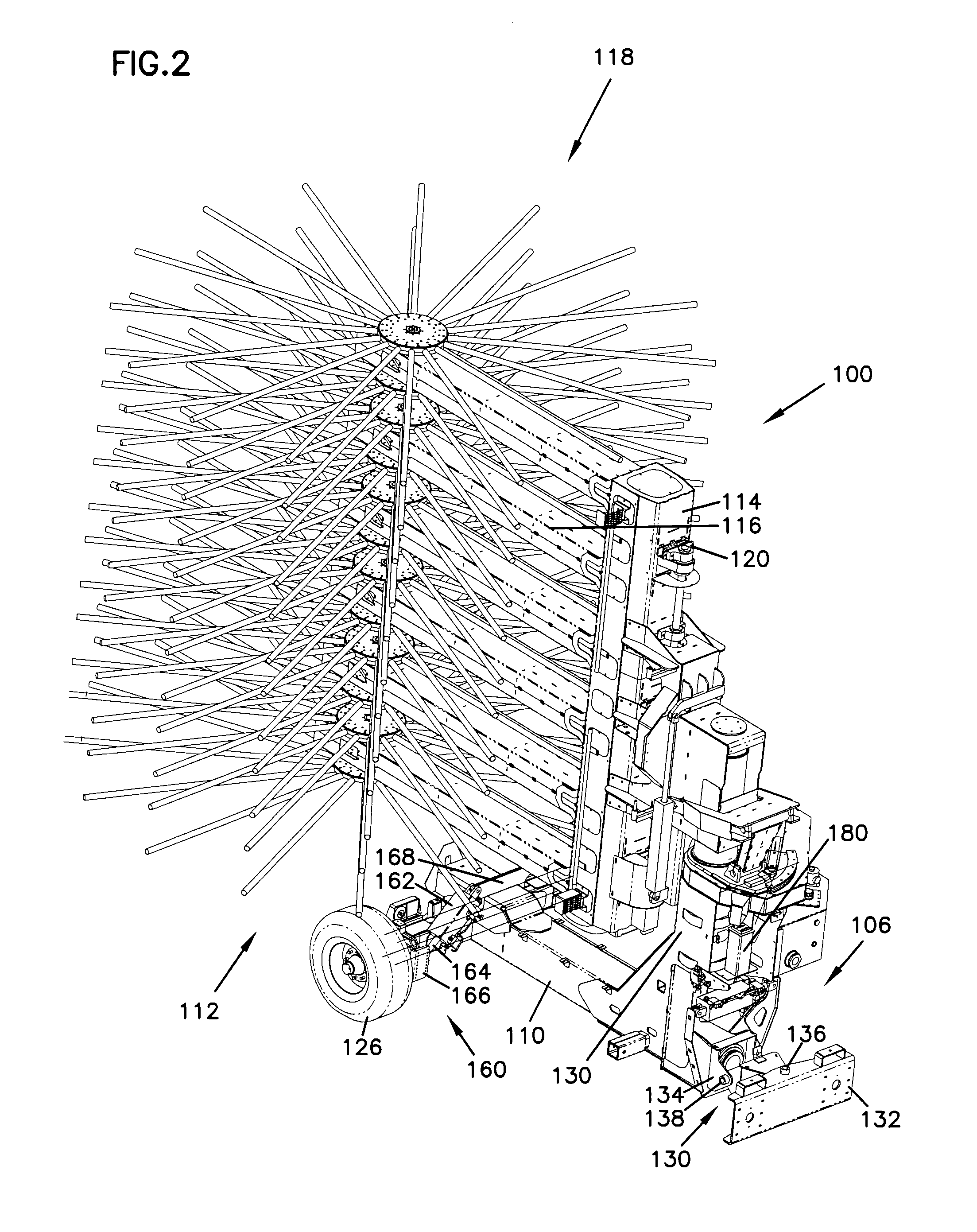
Vehicle stabilizer system
A stabilizer system provides leveling for a towed harvester vehicle. The harvester includes a hitch having a gimbal mounting to the tractor. The subframe is utilized to accommodate the gimbal and provides for utilizing the mass of the tractor to react to the stabilizer system leveling forces. The harvester utilizes telescoping assemblies that are placed intermediate the hitch and the frame as well as between the axle and the frame. The telescoping assemblies retract and extend to varied positions and provide correction. Flow to extend and retract the telescoping assemblies is provided through a proportional pendulum type valve that increases flow as needed when tilted from horizontal. The flow is increased and decreased in proportion to the amount of tilting from the home vertical position.
Owner:OXBO INT CORP
Flying wing configuration drone aircraft invisibility control surface mounting structure
PendingCN111380409AReduce reflective areaTo achieve the effect of stealthAircraft controlMovable targetsSurface mountingWing configuration
The invention provides a flying wing configuration drone aircraft invisibility control surface mounting structure. The flying wing configuration drone aircraft invisibility control surface mounting structure comprises an auxiliary wing unit and a resistance direction rudder unit, the auxiliary wing unit comprises an auxiliary wing steering engine, a first steering engine rocker arm, a first steering engine connecting rod, an inclined rib, a right side supporting base, a control surface and a left side connecting base, the resistance direction rudder unit comprises two resistance direction rudder steering engines, a second steering engine rocker arm, a second steering engine connecting rod, a resistance direction rudder upper control surface, a resistance direction rudder lower control surface, a right side mounting base, a left side mounting base, a transverse shaft, a resistance direction rudder pull base and a stabilizing plane rear beam, and the flying wing configuration drone aircraft invisibility control surface mounting structure is reasonable in design, capable of enabling the lower surface of an aircraft to be free of convex objects, small in reflection area during radar irradiation, capable of achieving the invisibility function and in addition capable of enabling the control surface to be detachable and convenient to maintain.
Owner:AEROSPACE SHENZHOU AIRCRAFT
Supercooled large drop icing condition detection system
The invention provides a supercooled large drop icing condition detection system. The method and apparatus for an ice detection system (806). The ice detection system (806) comprises a first sensor (400) located on a leading edge (412) of a vertical stabilizer (120) on an aircraft (100), a second sensor (402) located on a first side (414) of the vertical stabilizer (120), and a third sensor (404) located on a second side (416) of the vertical stabilizer (120). The first sensor (400) is configured to detect a first type of icing condition (860) for the aircraft (100). The second sensor (402) is configured to detect a second type of icing condition (860) for the aircraft (100). The third sensor (404) is configured to detect the second type of icing condition (860) for the aircraft (100).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Sealing system for the gap existing between the fuselage and the elevator of an aircraft with orientable horizontal stabiliser
InactiveUS20080169382A1Low costLow maintenanceFuselage framesAircraft stabilisationClassical mechanicsElevator
Sealing system for the gap (2) existing between the fuselage (3) and the elevator (4) of the orientable horizontal stabiliser (5) of an aircraft which comprises a main body (1) formed by an upper surface (18) and a lower surface (19) and at least one longitudinal vertical element (22) arranged between the two surfaces (18,19) which grants rigidity to the main body (1), and a plurality of first elastic sealing profiles (9) between the first surface (11) of the main body (1) and the outer surface of the fuselage (3) and making contact with them, and a plurality of second elastic sealing profiles (13) between the second surface (12) of the main body (1) and the first end of the elevator (15) and making contact with them, in such a way that the sealing of the gap (2) takes place and an aerodynamic continuity is produced between the fuselage (3) and the elevator (4) when the elevator (4) is at rest in the plane of the orientable horizontal stabiliser (5) for any of the orientation positions of the orientable horizontal stabiliser (5).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
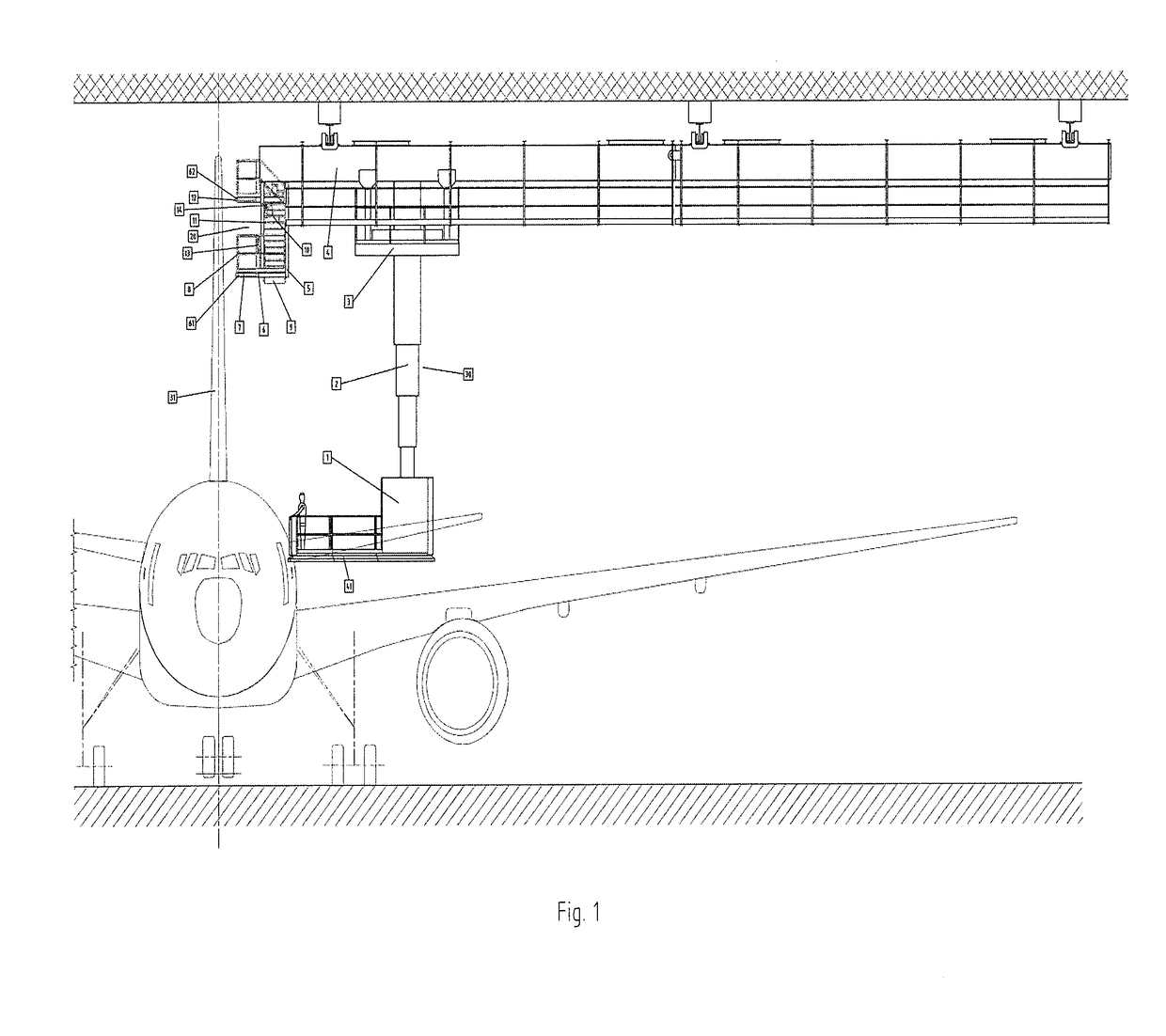
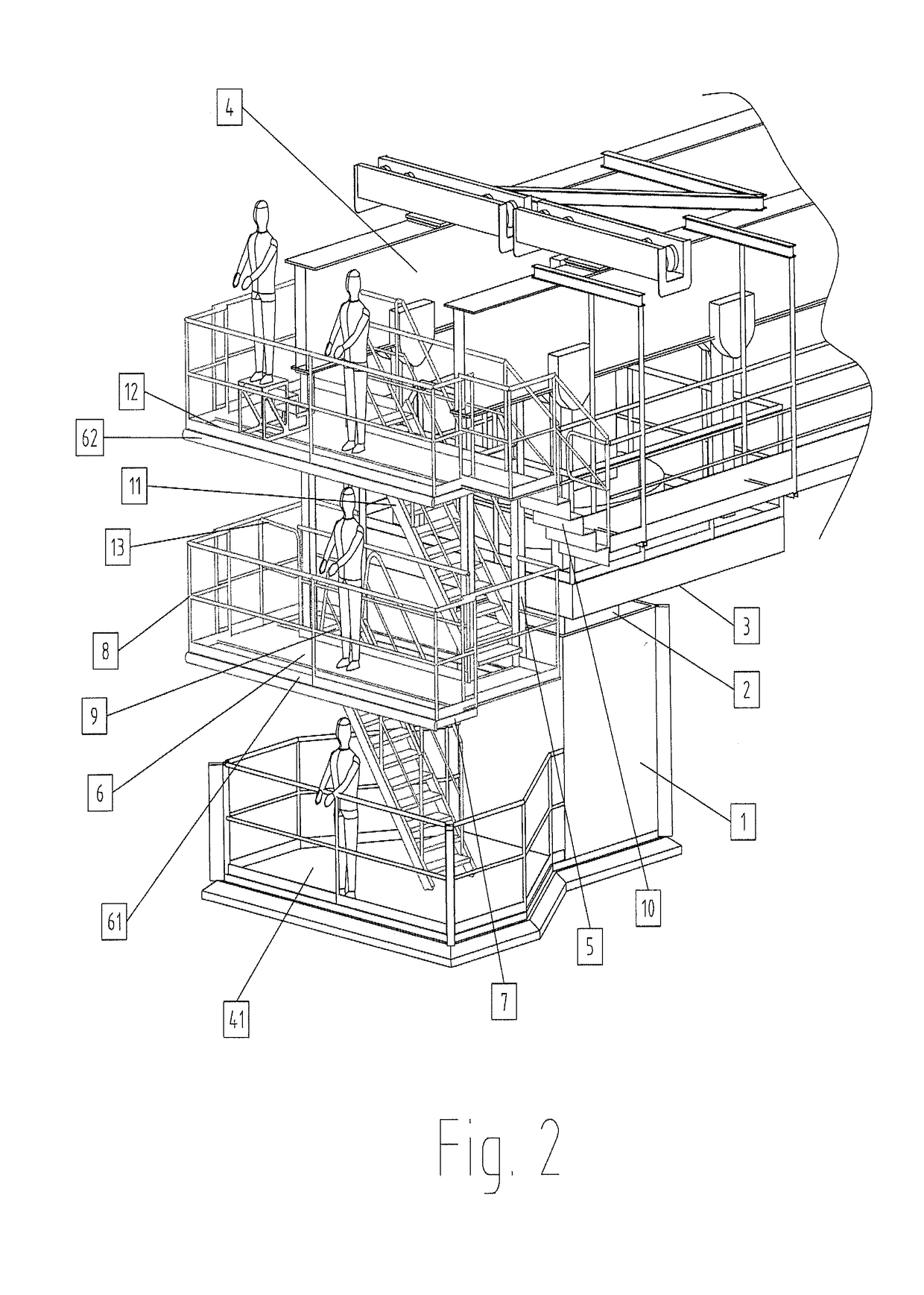
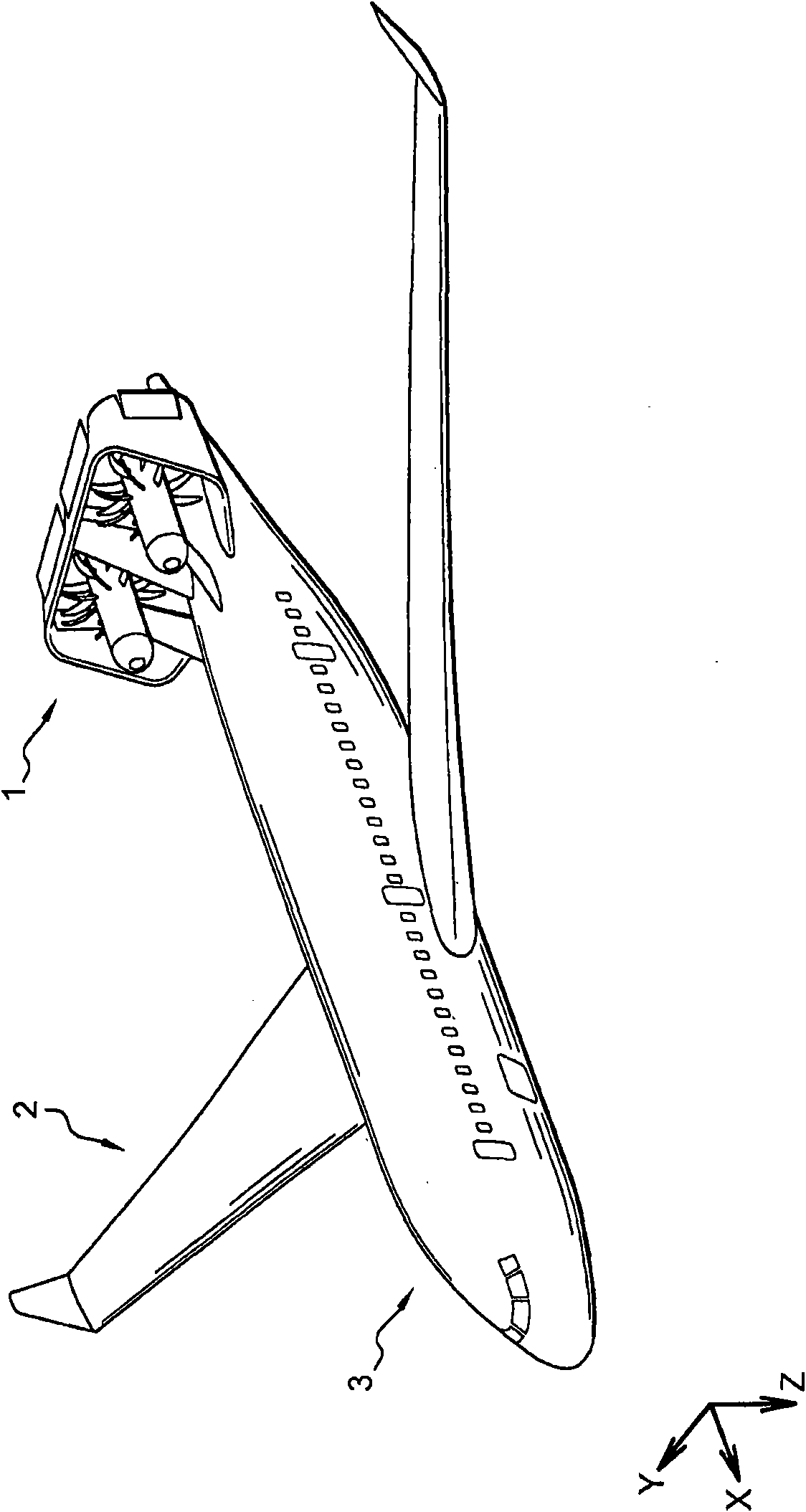
Apparatus for treating the surface or carrying out maintenance and/or inspection tasks of a vertical stabilizer of an aerial vehicle in a low interior height hangar
InactiveUS20180194603A1Effectively and safely reachImprove securityLifting devicesTravelling cranesMarine engineeringOverhead crane
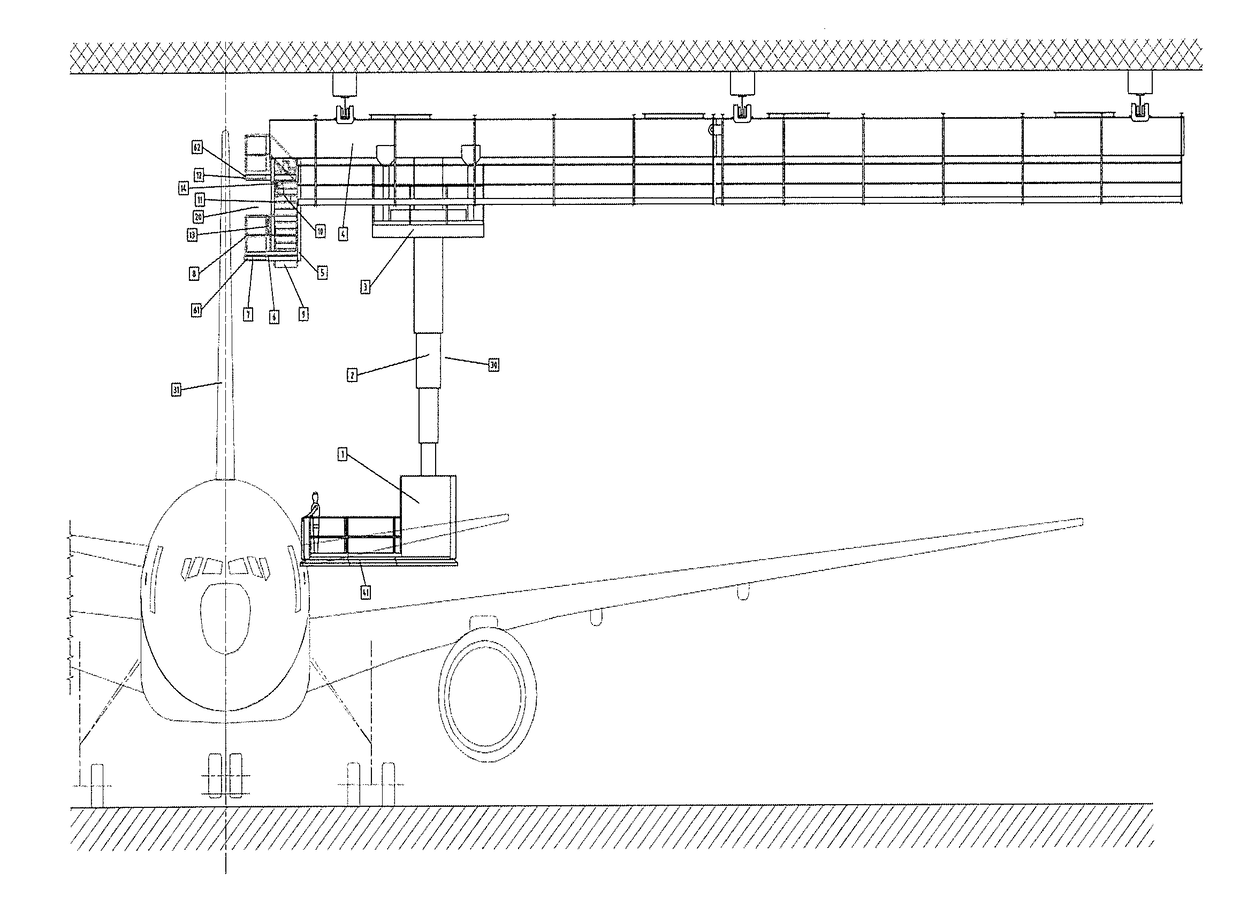
The present invention concerns an apparatus for treating surfaces or carrying out maintenance / inspection tasks of the top of a vertical stabilizer (31) of an aerial vehicle by at least one technician comprising:a single overhead crane (4) hanged on a roof (100) of a hangar building,a single suspended vertically movable lateral teleplatform unit (30) comprising a telescopic mast (2) connected to the single overhead crane (4),a suspended staging structure (20) firmly connected to the overhead crane (4) by a supporting structure (5), the suspended staging structure (20) comprising at least one working platform (61,62) for treating or carrying out maintenance / inspection tasks of the vertical stabilizer (31) of the aerial vehicle at different heights by at least one technician,the length of the overhead crane (4) does not extend beyond the vertical axis (A) of the vertical stabilizer (31), characterized in that the suspended staging structure (20) is not vertically movable and is independent from the vertically movable lateral teleplatform unit (30) permitting to reach the suspended staging structure (20).
Owner:AMOVA S A R L
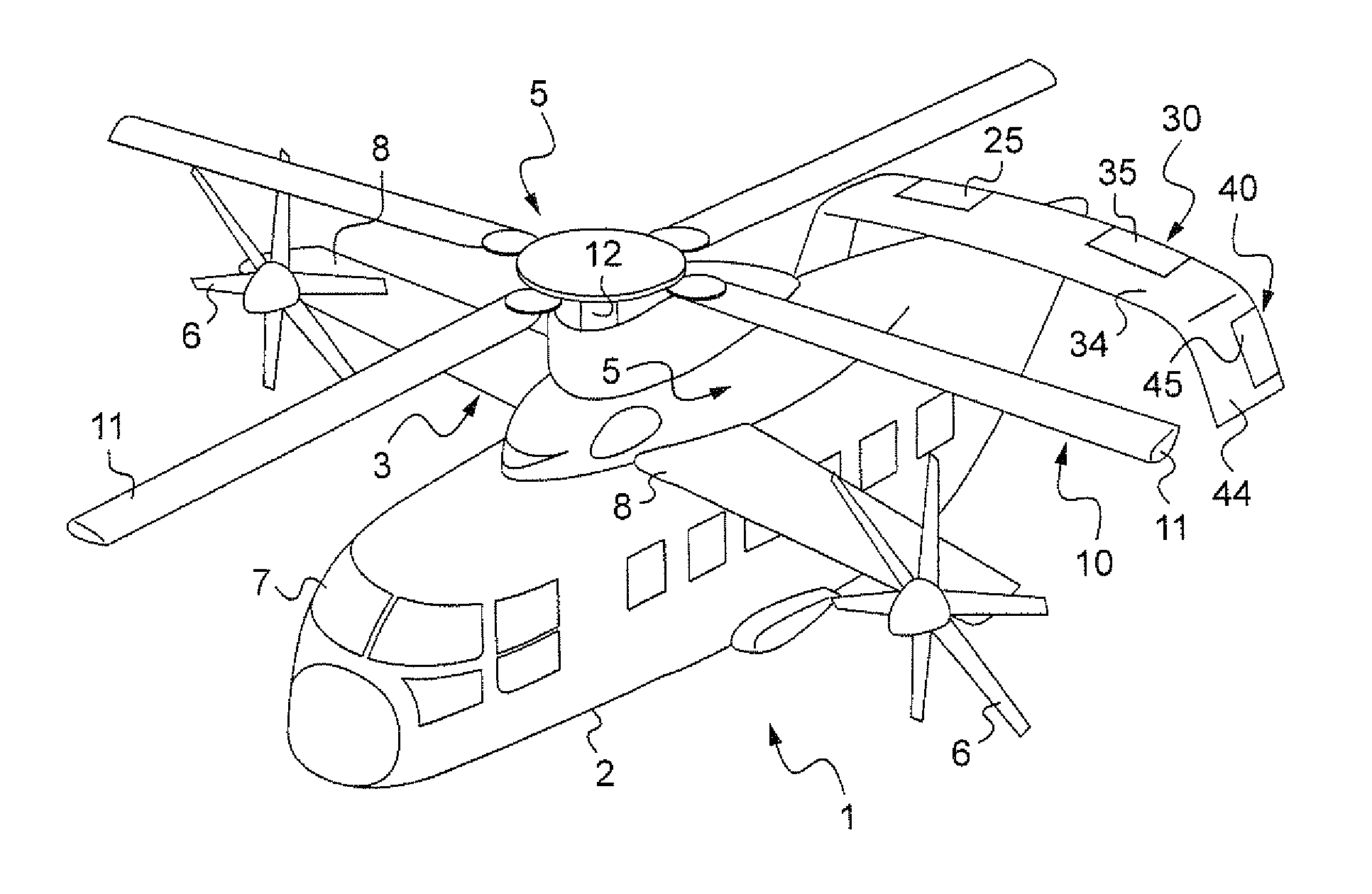
Aircraft with rear annular tail
The aircraft (1) has a wing and a horizontal upper aerodynamic surface (73), where the surface is situated at the rear of an aircraft. A jet engine (8a) is fixed under the horizontal upper aerodynamic surface by a pylon (9a), where the pylon has an upper part fixed to the surface and a lower part for maintaining the engine. A horizontal tail unit is fixed on a cylindrical shaped fuselage (2) in the rear of the wing. The tail unit is fixed to an upper part of a drift above the fuselage.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Hydraulic vehicle stabilizer system with two-stage bi-rotational hydraulic pump system
A stabilizer system and method that can provide high speed, relatively low force extension and retraction of a stabilizer leg during a first portion of a stroke, and low speed, relatively high force extension and retraction during a second portion of the stroke. Accordingly, the stabilizer system and method takes less time to deploy than conventional stabilizer systems but without sacrificing performance.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Vehicle stabilizer system
InactiveUS7905499B2Increase profitSmall resistanceDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesPower flowOperation mode
A stabilizer system for a vehicle includes a stabilizer bar and an actuator and that executes a control actively changing stiffness of the stabilizer bar in accordance with roll moment acting on a body of the vehicle. Each of a situation in which the vehicle is running straightforward and a situation in which a torque generating direction of a motor of the actuator changes in opposite direction plural times is identified as a specific situation. In the specific situation, a control of changing an operation mode of the motor such that presence or absence of occurrence of resistance of the actuator against its operation by external input force is changeable, and a control of limiting a supply current to the motor such that the torque generating direction of the motor is inhibited from coinciding with a direction away from a neutral position are executed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
UAV layout with least control surface configurations and control method for same
ActiveCN110576965AReduce in quantityReduce control consumptionActuated personallyFlight vehicleFlight control modes
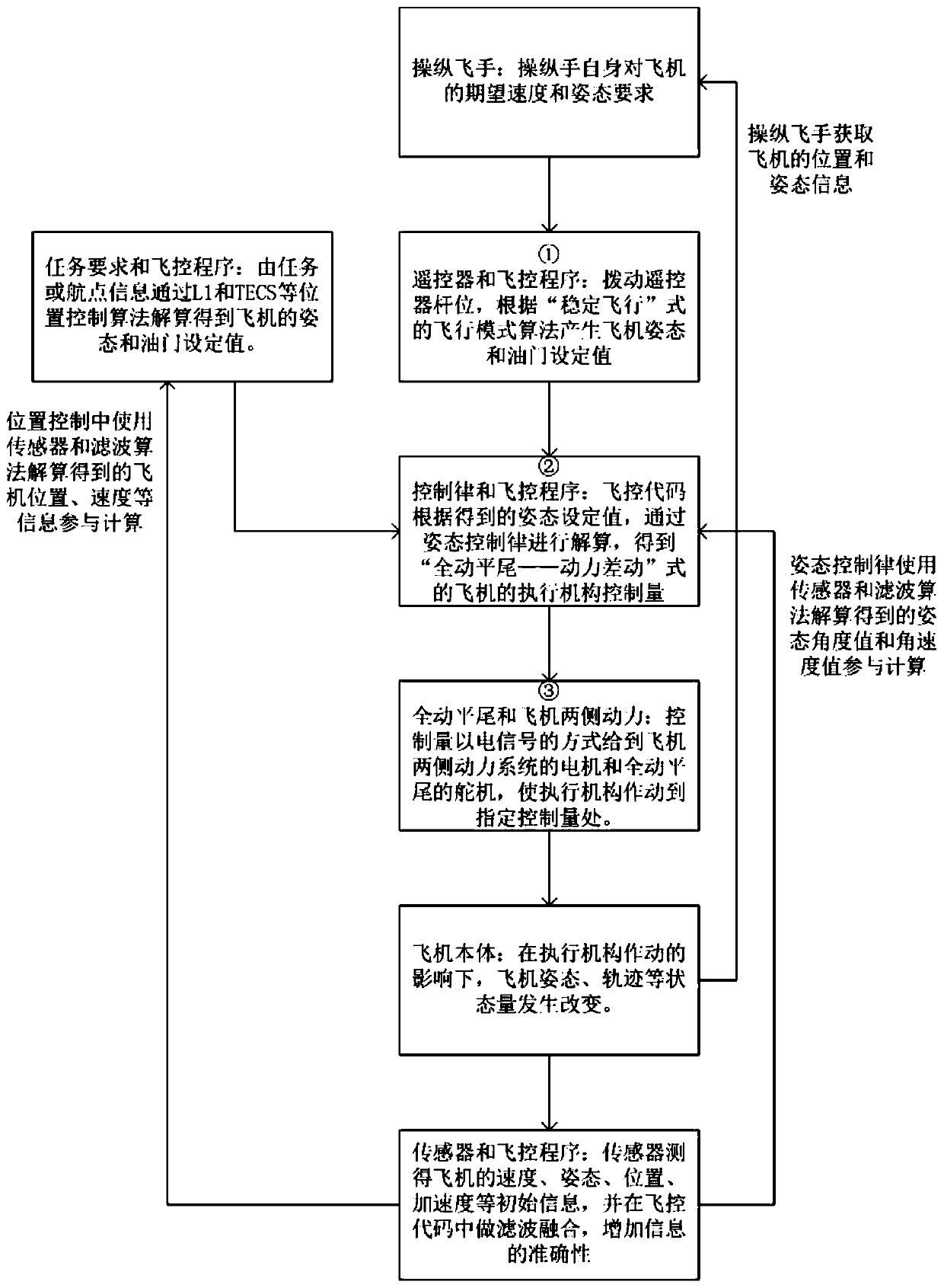
The invention provides a UAV layout with the least control configurations and belongs to the technical field of flight vehicle design and flight control. A UAV comprises a plane body, wings on both sides, engines on both sides and a stabilator, wherein the engines on the both sides are fixed under the wings on the both sides respectively, and the stabilator is fixed on the tail part of the plane body; and horizontal course control of the UAV is realized by the engines on the both sides of the plane body, and longitudinal control of the UAV is realized by deflection of the stabilator. The UAV layout provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that only one stabilator is disposed on a control pneumatic control surface of the UAV, so a resistance generation face is greatly reduced during UAV design and flight resistance is reduced without addition of an extra control execution mechanism; the least control surface is used for control, and the quantity of the control execution mechanism is minimized, so energy consumption generated from control can be reduced to a certain extent; and overall deflection of the stabilator is used, so steerage effects of control are increased as much as possible on the premise that a horizontal tail area is reduced and thus UAV control is more sensitive and effective.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method and apparatus to control aircraft horizontal stabilizer
ActiveCN105584627AFunction increaseImprove reliabilityAircraft stabilisationWith power amplificationStabilatorAerospace engineering
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Ship-borne heat power electric drive tilt rotor wing craft
ActiveCN109866919AAddressing Structural ComplexitySolve the failure rateSandwich constructionsAir-flow influencersShortest distanceEngineering
The invention discloses a ship-borne heat power electric drive tilt rotor wing craft which comprises a tilt rotor wing system, a modularized fuselage structure, box-type double-layer wings, a double-layer box type stabilator, a vertical fin, a power assembly and energy management integration system and a flight control system. The tilt rotor wing system comprises rotor wings and propeller hubs arranged at the tail ends of the box-type double-layer wings. The box-type double-layer wings are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the modularized fuselage structure. The power assembly and energy management integration system comprises a heat power direct drive power generation system, a power generator and a motor. The heat power direct drive power generation system is connected with thepower generator. Electric energy sent by the power generator can be divided into two ways, one way of the energy enters a dual-redundancy 1100V energy management system, and the other way of the energy enters a dual-redundancy 270V energy management system. According to the craft, by means of structure design of the modularized fuselage structure, the box-type double-layer wings and the double-layer box-type stabilator, the pneumatic efficiency can be improved, the rotor wings can be folded conveniently, short-distance vertical lifting can be achieved, and the craft is particularly suitable for ship-borne use.
Owner:南京乐飞航空技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com