Patents
Literature
98 results about "Roll moment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Roll moment is a moment, which is a product of a force and a distance, that tends to cause a vehicle to roll, that is to rotate about its longitudinal axis.
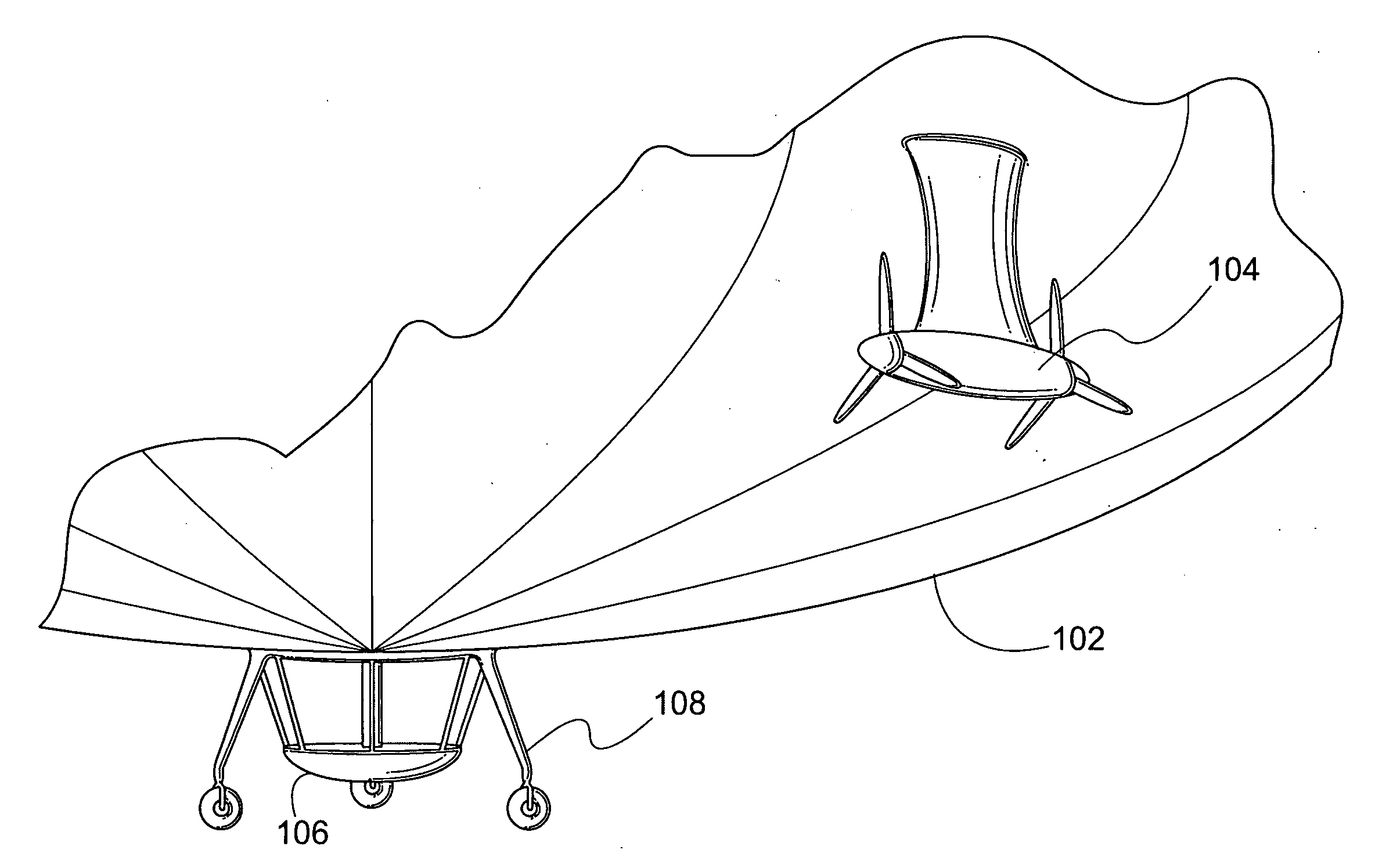
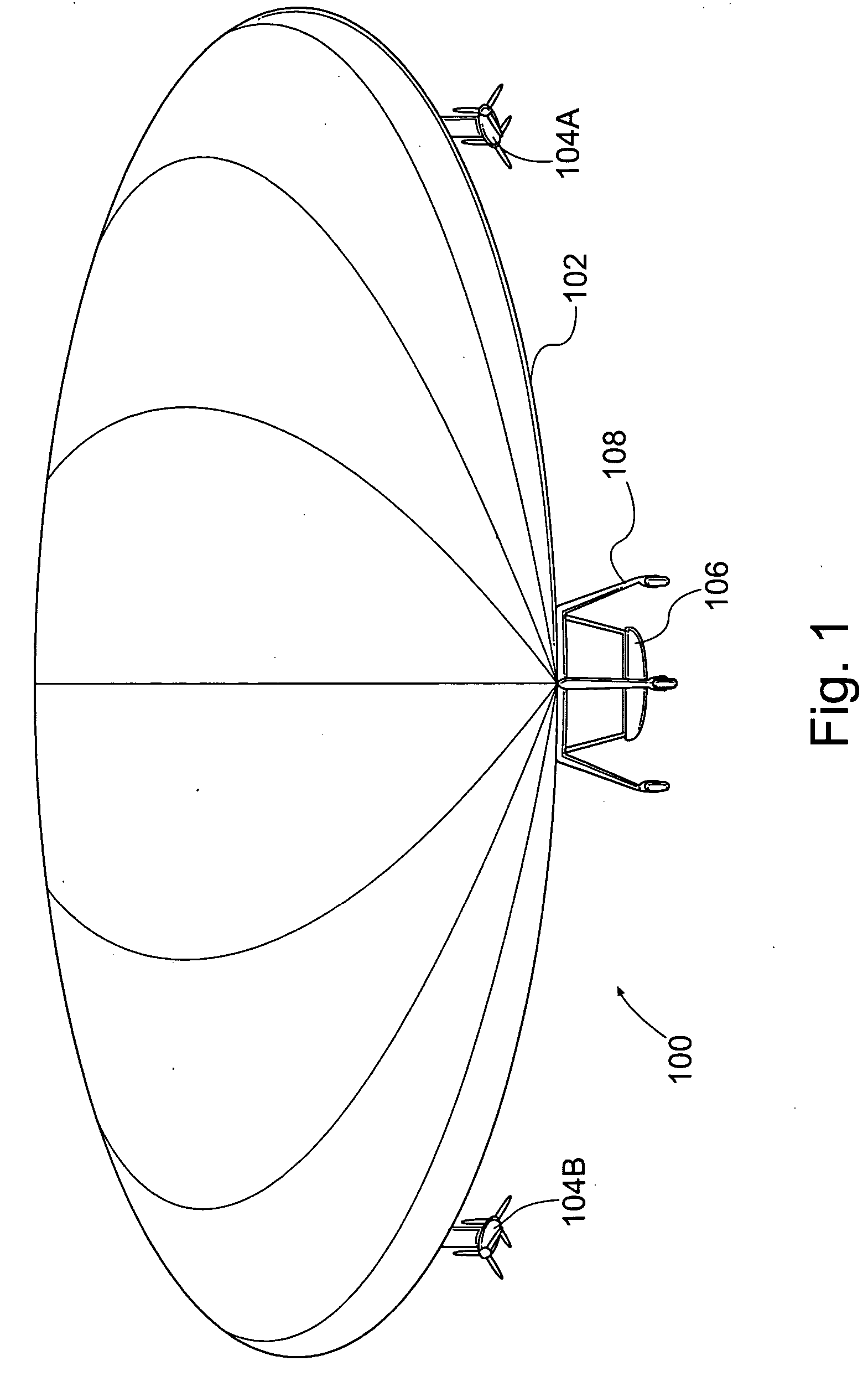
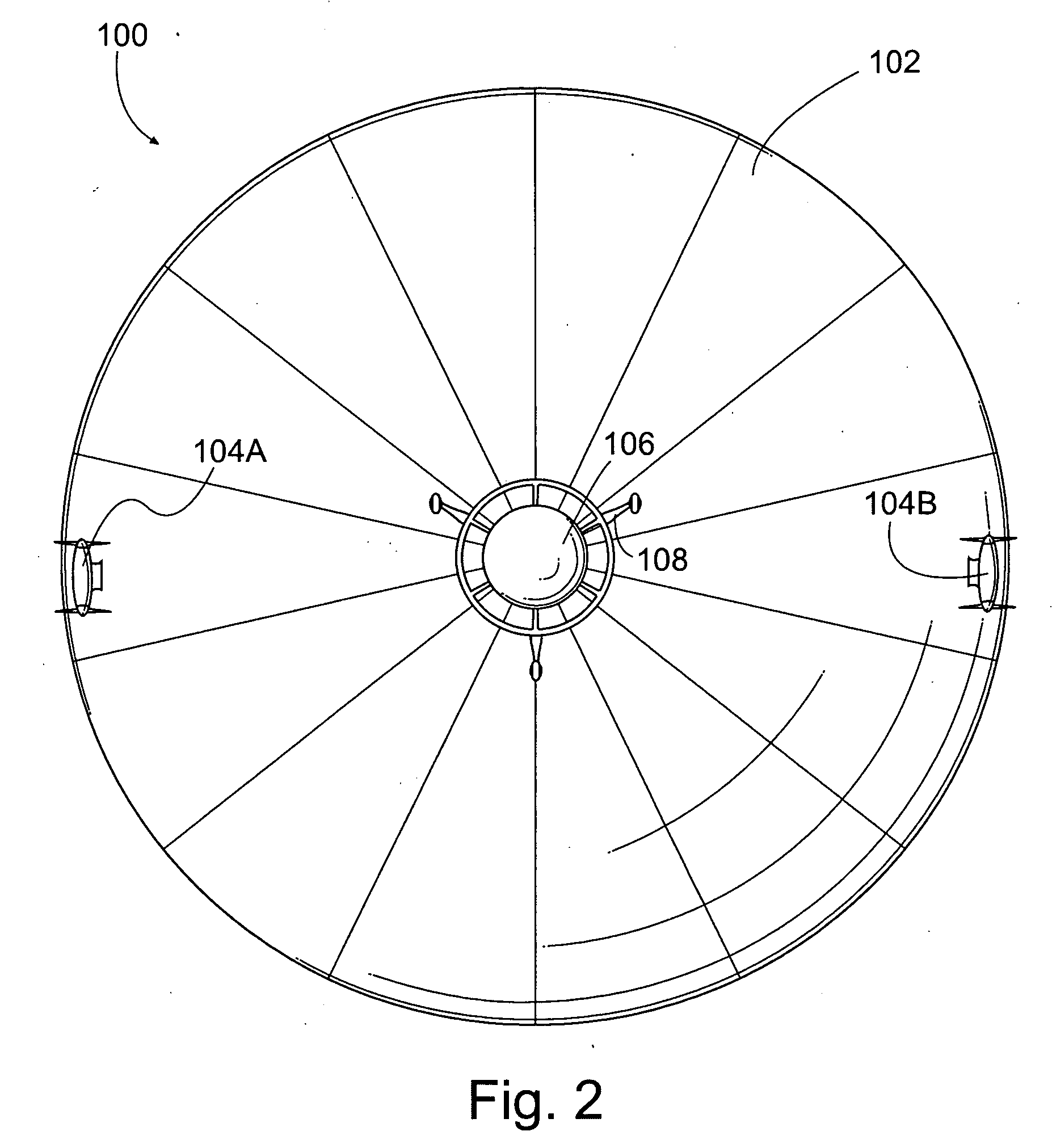
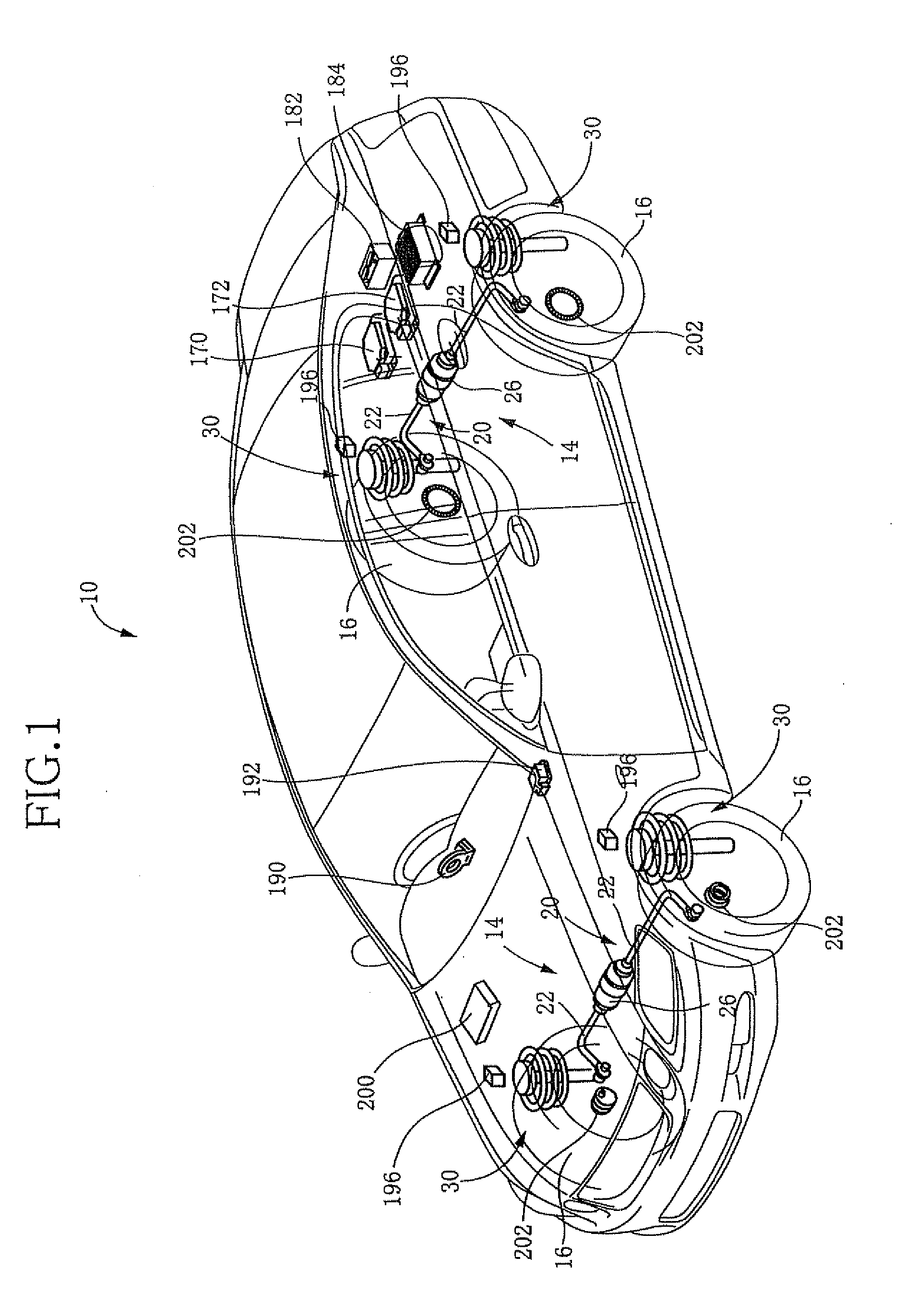
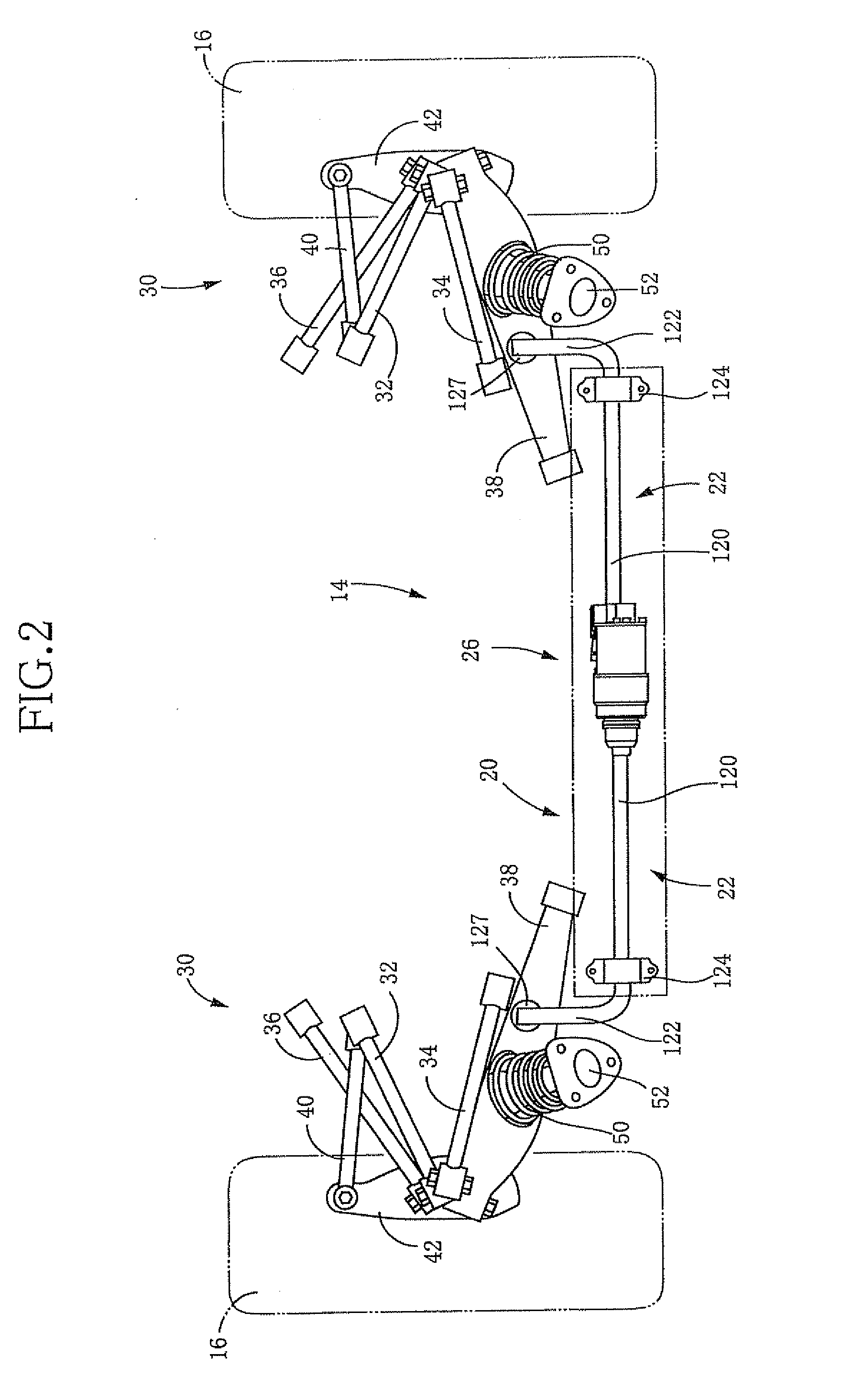
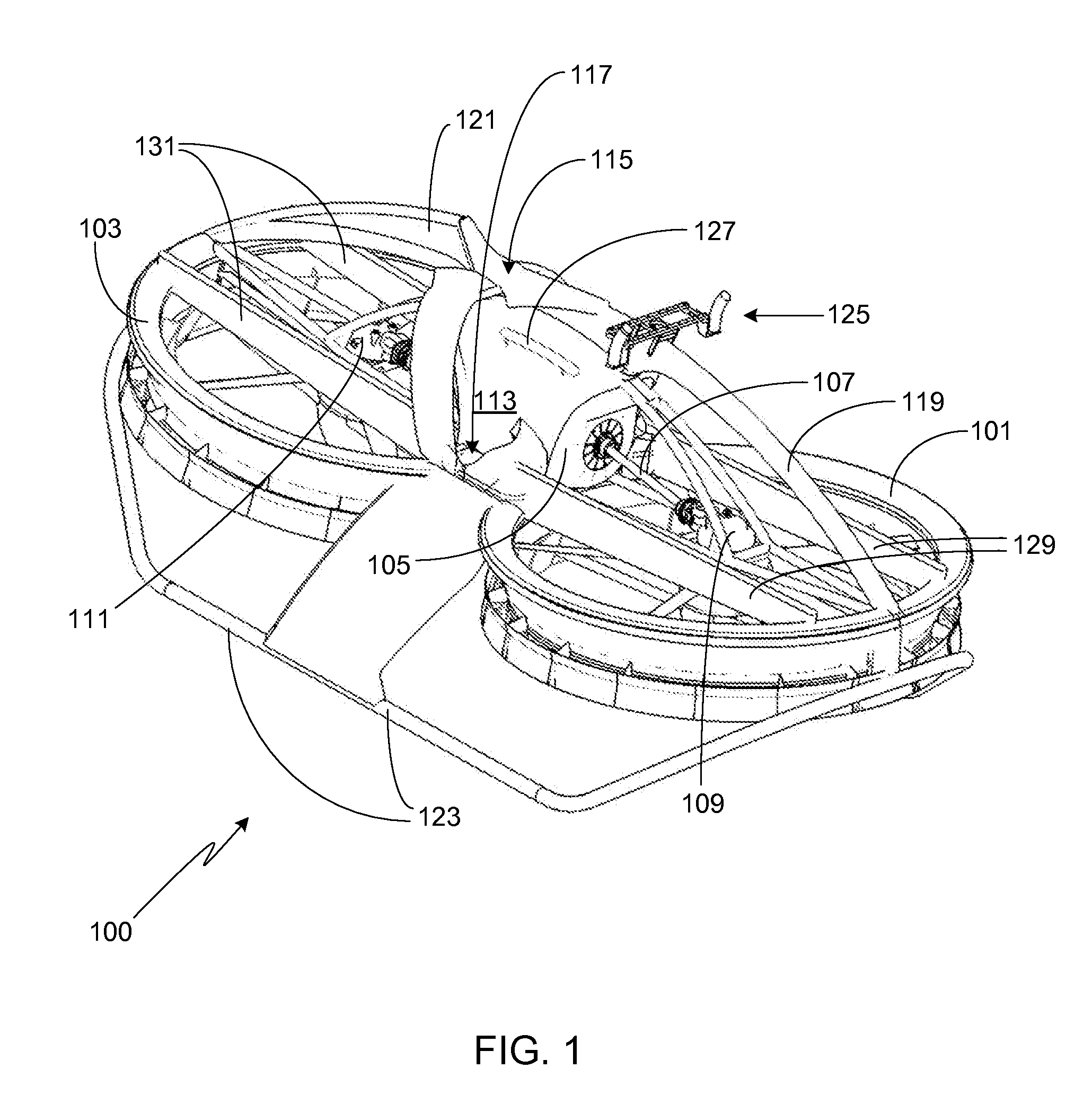
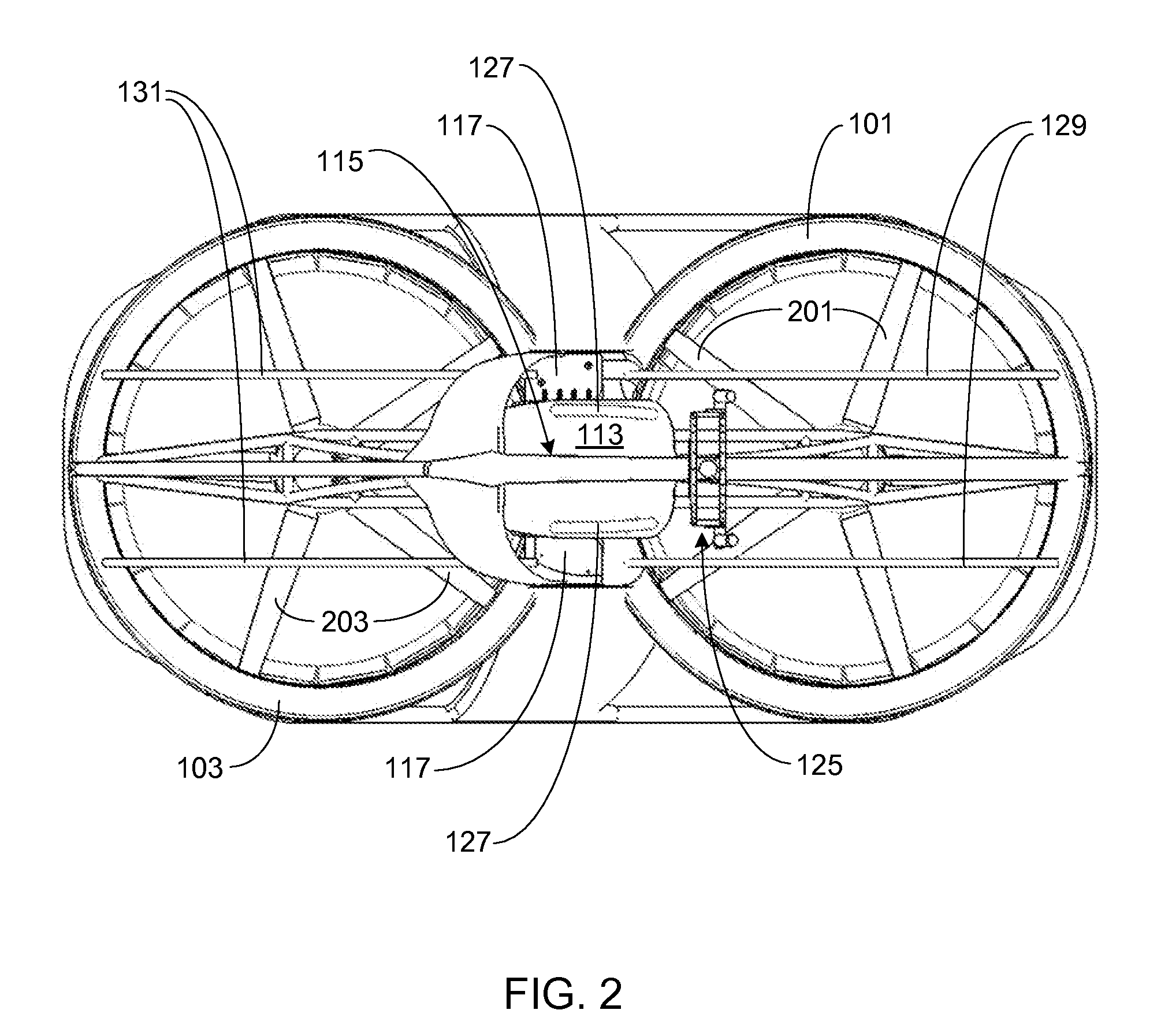
Mass transfer system for stabilizing an airship and other vehicles subject to pitch and roll moments
InactiveUS20060060695A1Process stabilityAircraft stabilisationRigid airshipsGravity centerEngineering
The invention relates to a mechanism to control the pitch and / or roll and / or center of gravity of a vehicle. The first embodiment is a track-based mass transfer system in which pathways are positioned along or radially terminate at a central horizontal plane of the vehicle to move one or more mass transfer devices to a desired location to control the pitch and / or roll and / or center of gravity of the vehicle. A second embodiment is a fluid mass distribution system in which one or more conduits selectively distribute a fluid to one or more tanks positioned near a central horizontal plane of the vehicle to control the pitch and / or roll and / or center of gravity of the vehicle.
Owner:LTAS HLDG
Method for shaping wing velocity profiles for control of flapping wing micro air vehicles
ActiveUS8700233B1Reduce weightReduce complexityUnmanned aerial vehiclesDigital data processing detailsFlapping wingGravity center
A method of controlling wing position and velocity for a flapping wing air vehicle provides six-degrees-of-freedom movement for the aircraft through a split-cycle constant-period frequency modulation with wing bias method that generates time-varying upstroke and downstroke wing position commands for wing planforms to produce nonharmonic wing flapping trajectories that generate non-zero, cycle averaged wing drag and alter the location of the cycle-averaged center of pressure of the wings relative to the center of gravity of the aircraft to cause horizontal translation forces, rolling moments and pitching moments of the aircraft.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICAS AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE THE
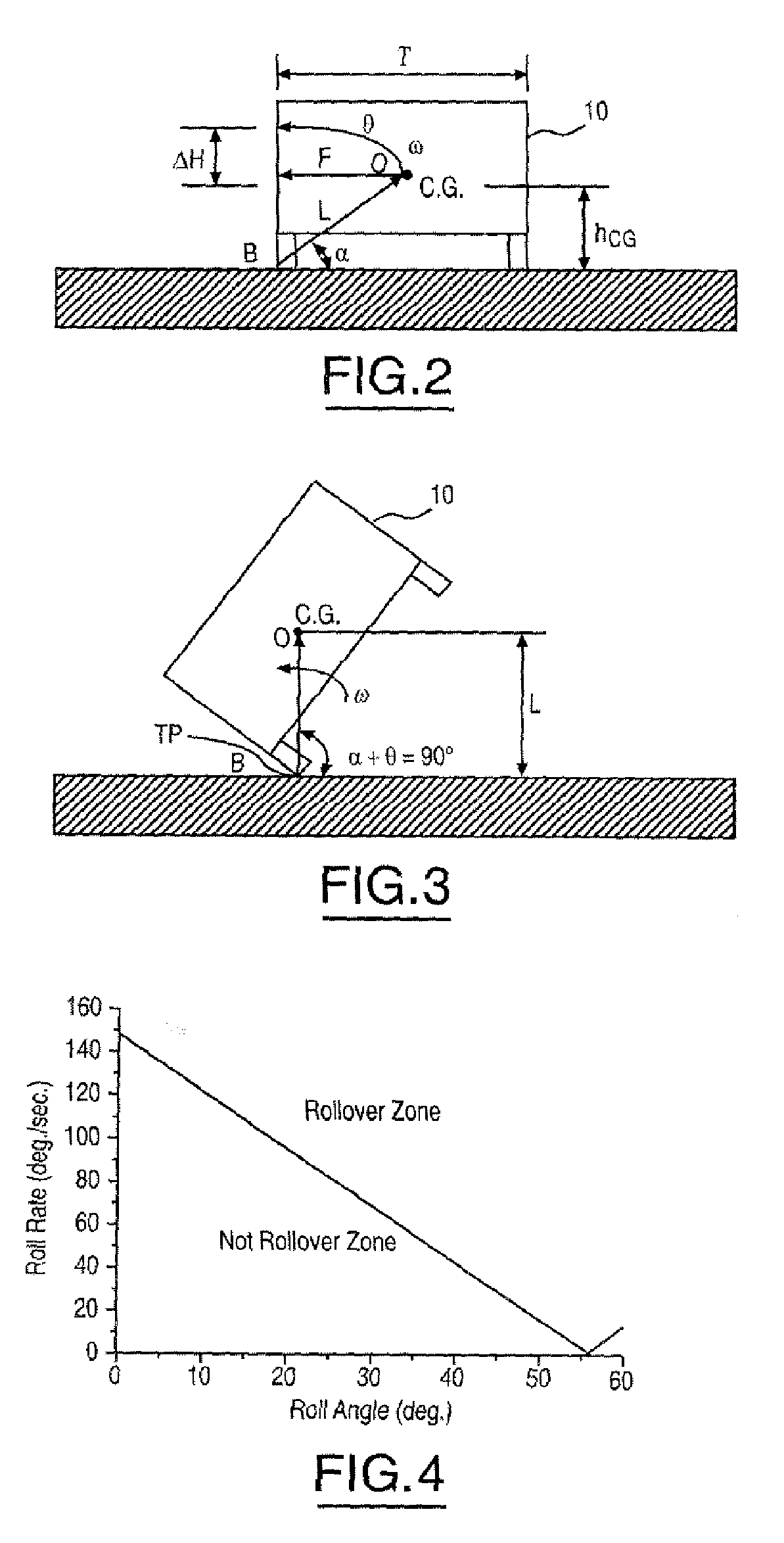
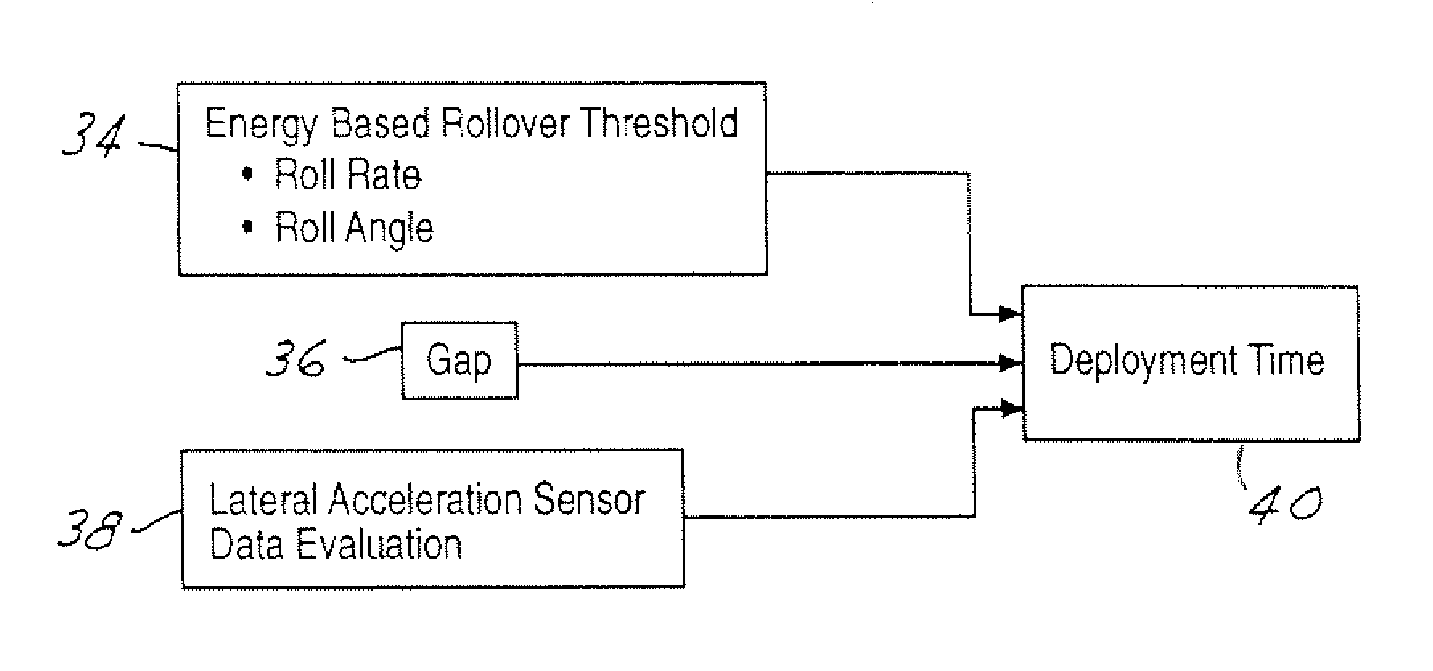
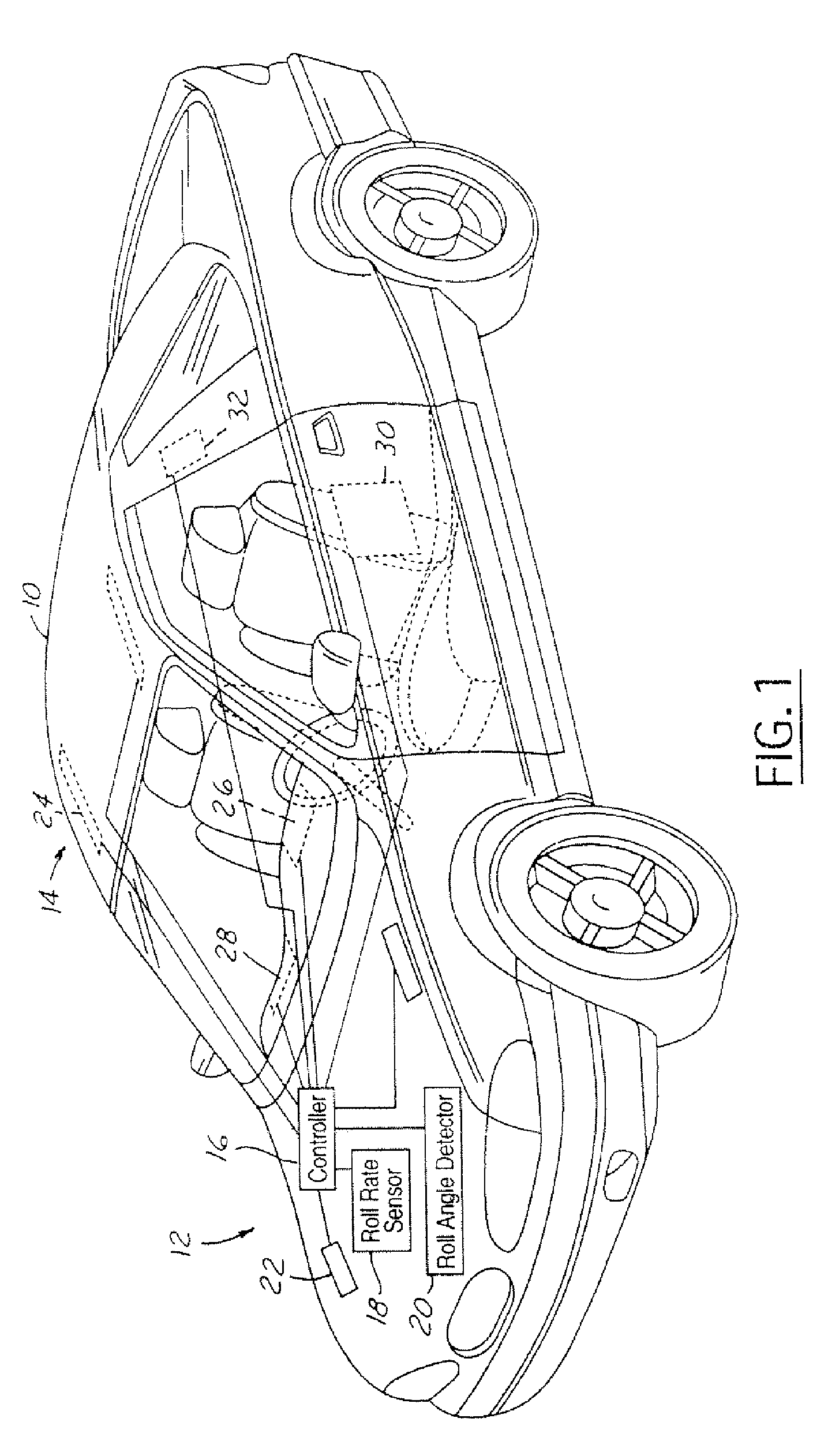
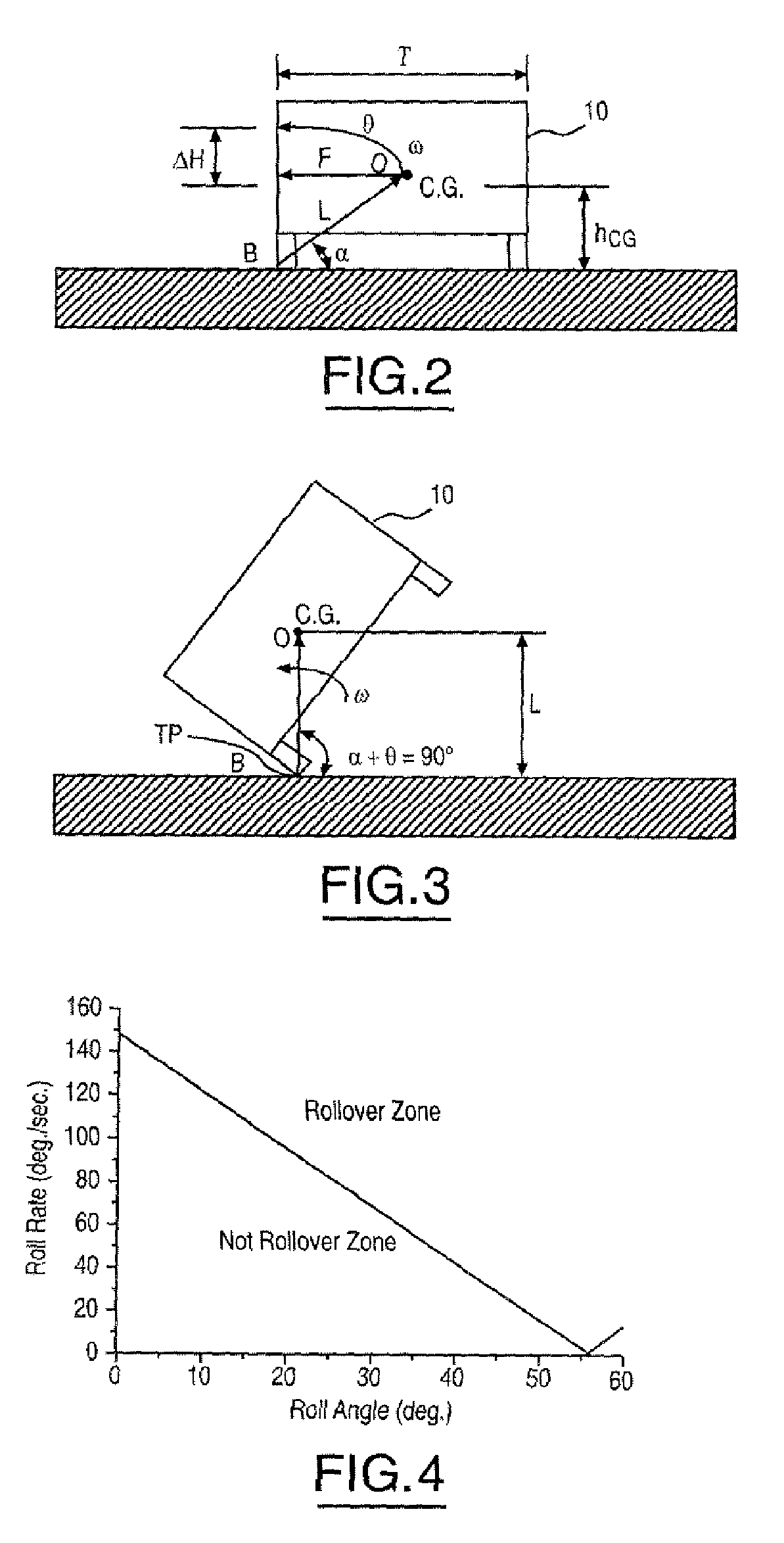
Method and apparatus for detecting rollover of an automotive vehicle based on a lateral kinetic energy rate threshold
InactiveUS20060178808A1Less timeLess man-hoursDigital data processing detailsStatic/dynamic balance measurementRolloverControl signal
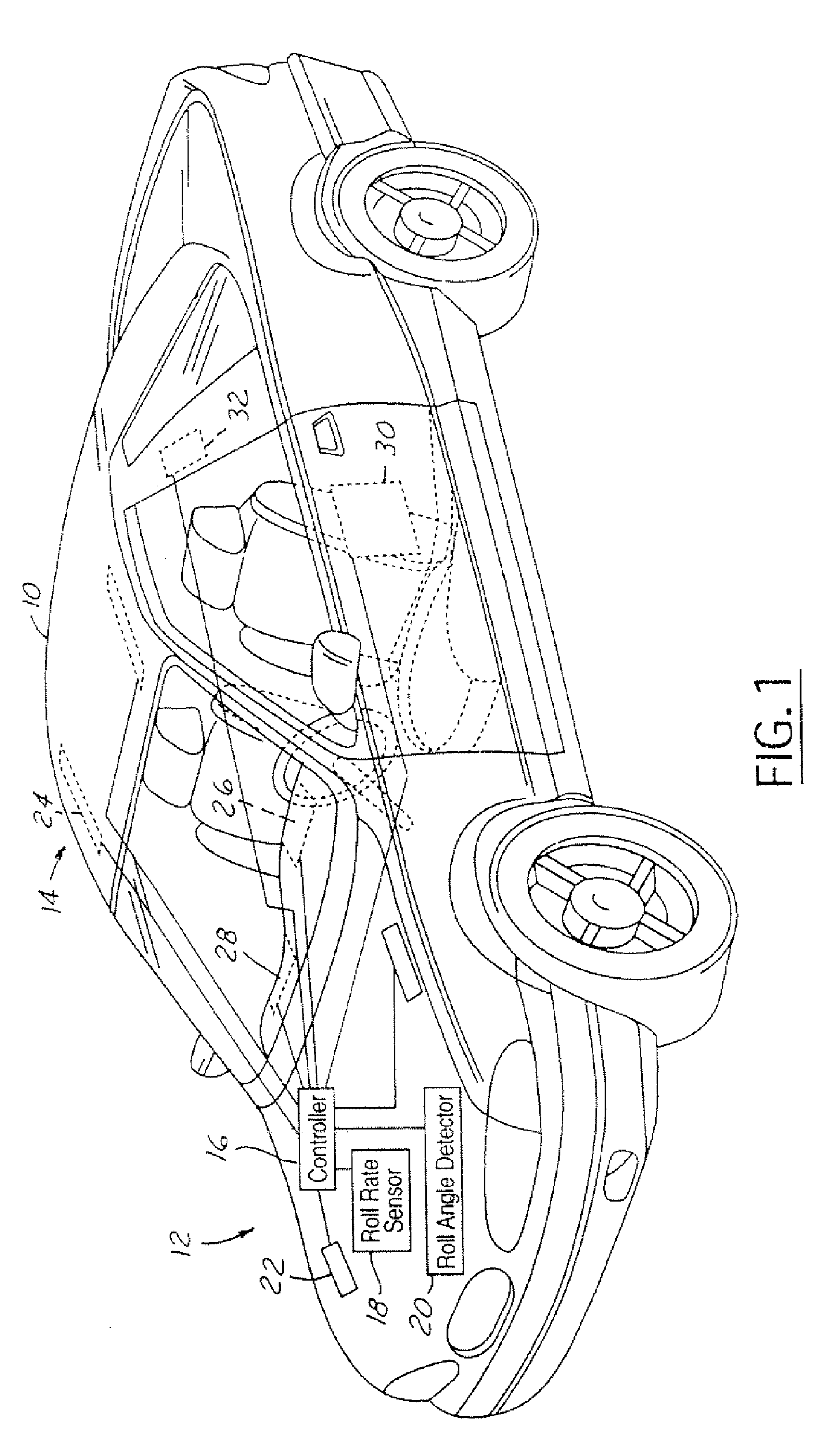
A rollover sensing system (12) that may be used in the determination of when to deploy restraints in the vehicle. The rollover sensing system (12) may include lateral acceleration sensors (32), a roll rate sensor (18), and a roll angle detector (20). A control circuit (16) determines a roll moment of inertia as a function of the lateral acceleration, a trip point length as a function of the lateral acceleration and a trip point angle as a function of the lateral acceleration. The control circuit (16) determines a rollover threshold in response to the roll rate signal, the roll angle signal, the trip point length, the roll moment of inertia, and the trip point length. The control circuit generates a control signal for the deployment circuit in response to the rollover threshold.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Full suspension footwear
ActiveUS20060021262A1Maximize operating efficiencyMinimal torqueSolesUpperGround contactAnkle foot joint
A method and apparatus for enhancing the ability of a human to run and jump with comfort comparable to running barefoot on a trampoline and with control comparable to that of the unaided human form, yet with freedom from ankle-turning roll moments associated with substantial ground contact member (GCM) extension downwardly away from the sole of the foot including, a resiliently urged GCM constrained to two degrees of freedom: translation away from the sole of the user's foot and rotation about a longitudinal axis at ground level. The apparatus relates flexure of a GCM toe pressure member to comparable flexure of user's toes at the metatarsal joints. The apparatus also incorporates lower leg to ankle pivot bracing, and extends the GCM in downward direction parallel to the lower leg while mimicking user ankle articulation with parallelism-maintaining rotation about a downwardly resiliently urged transverse pivot axis similar to the user's own ankle joint for extended travel.
Owner:KILLION DAVID L +1
Air-Vehicle Integrated Kinesthetic Control System
ActiveUS20120032032A1Actuated personallyVertical landing/take-off aircraftsControl systemFlight vehicle
A lift platform with a kinesthetic control system that is coupled to means for altering air flow through the first and second longitudinally-spaced ducts comprising the lift platform is provided. The control system includes a control handle bar with left and right hand grips, and first and second control roll bars located on either side of the lift platform's central cowling. Forward / rearward movement of the control handle bar from a neutral position generates nose-down / nose-up pitching moments, respectively; counterclockwise / clockwise movement of the control handle bar from the neutral position generates counterclockwise rotation / clockwise rotation of the lift platform about a lift platform vertical centerline; and left movement / right movement of the control roll bars generates left roll / right roll moments about the lift platform roll axis.
Owner:AEROFEX
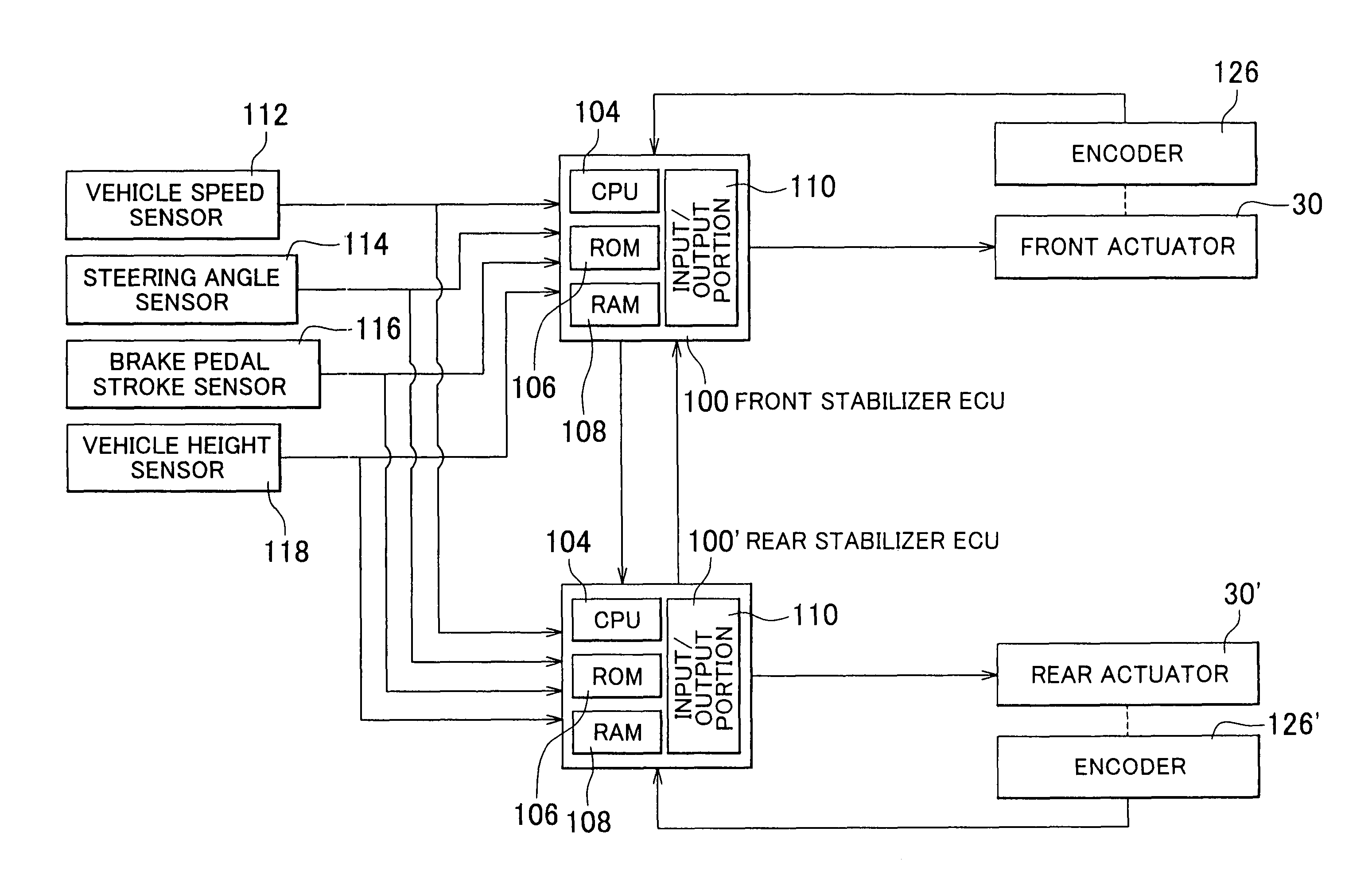
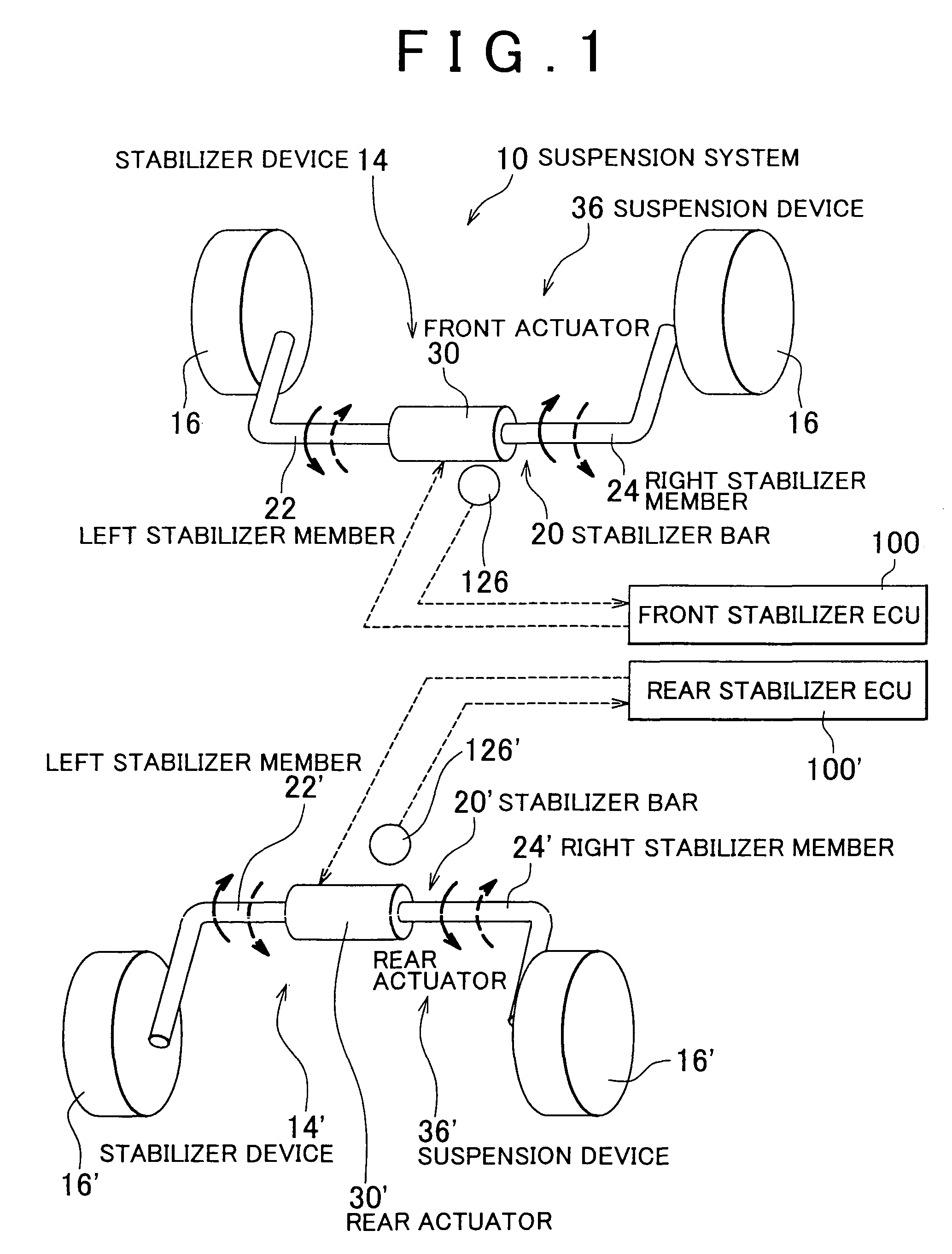
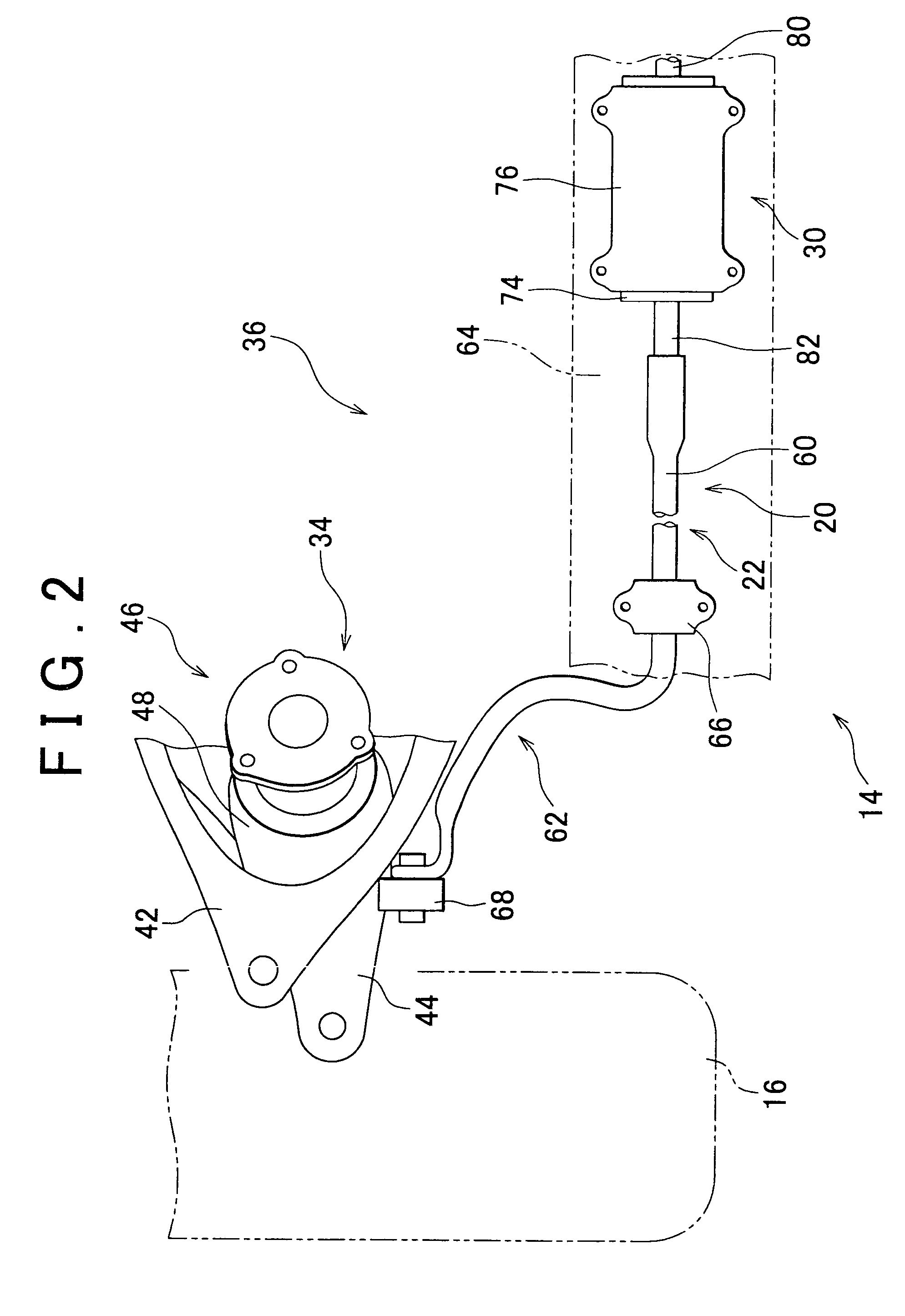
Vehicle stabilizer system
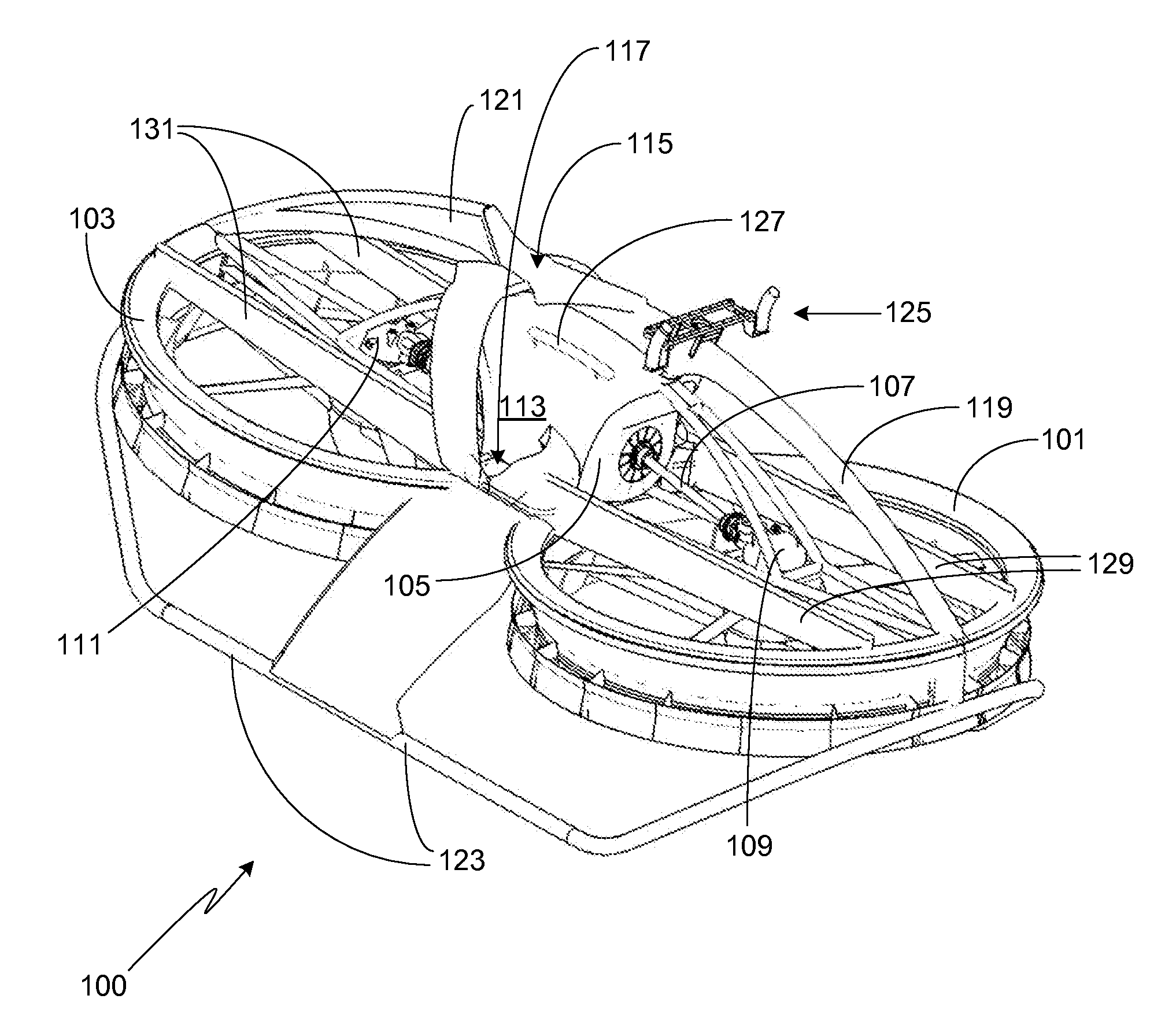
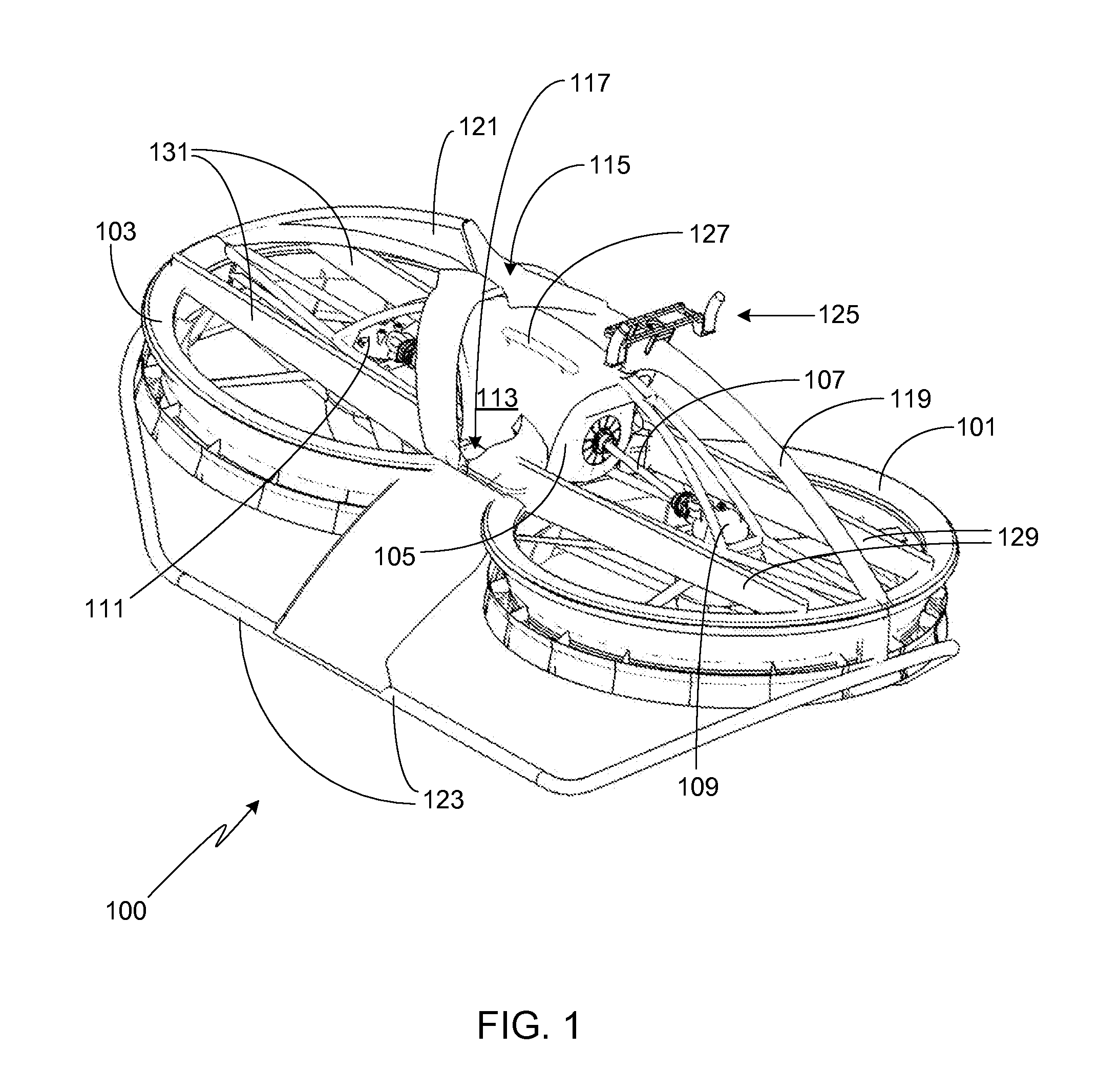
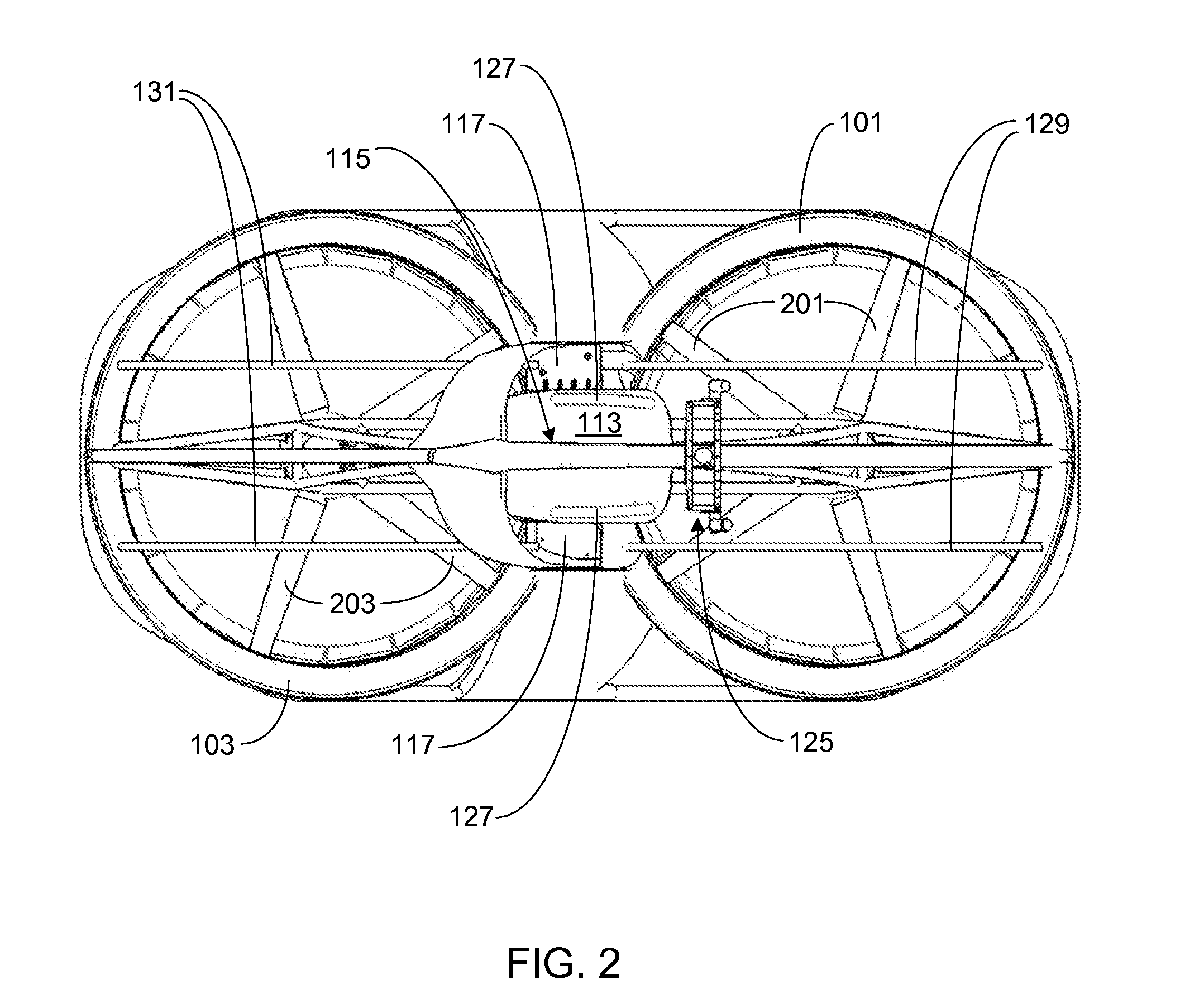
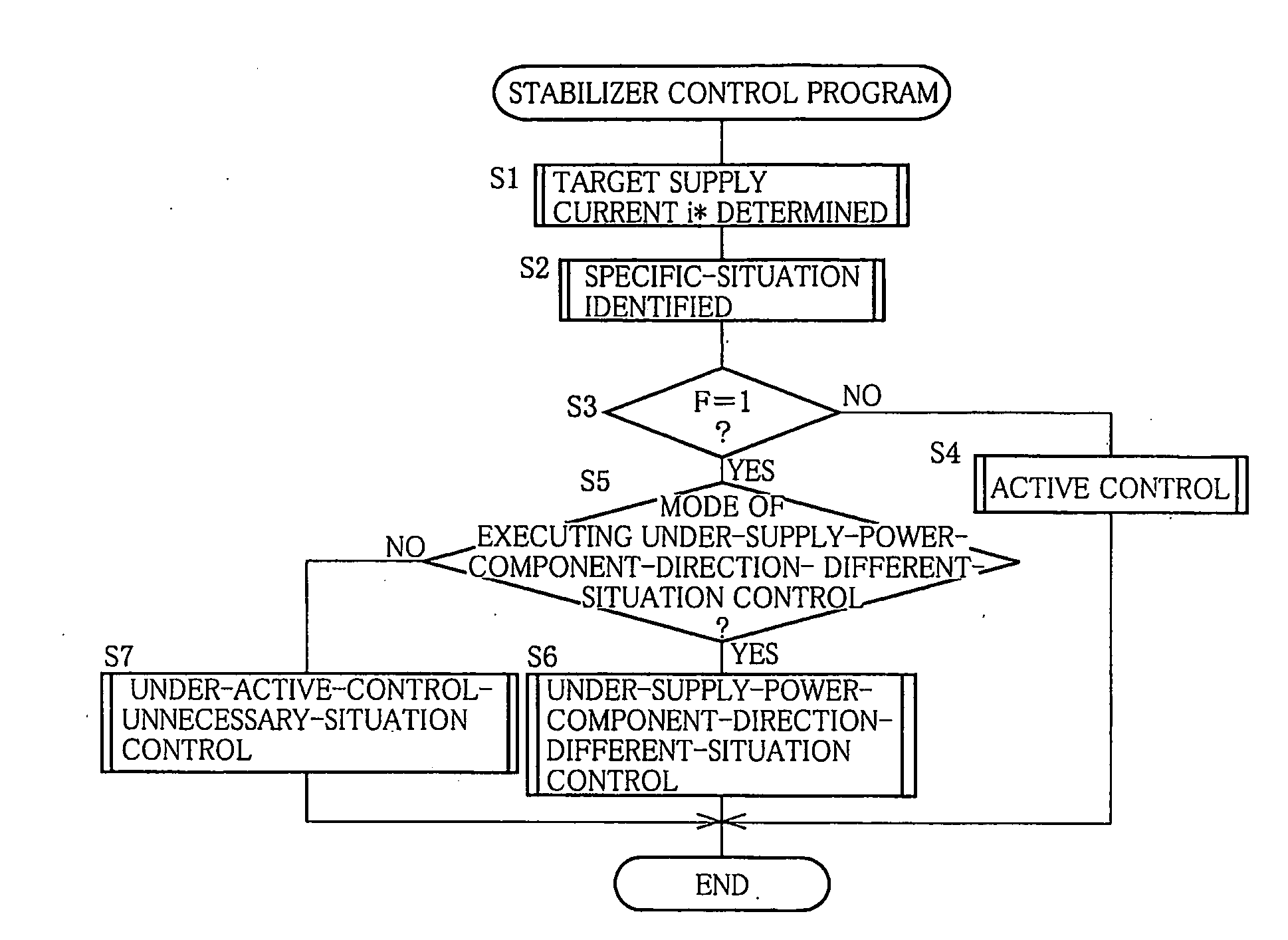
InactiveUS20090224493A1Increase profitSmall resistanceDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesElectric machineryActuator
A stabilizer system for a vehicle includes a stabilizer bar and an actuator and that executes a control actively changing stiffness of the stabilizer bar in accordance with roll moment acting on a body of the vehicle. Each of a situation in which the vehicle is running straightforward and a situation in which a torque generating direction of a motor of the actuator changes in opposite direction plural times is identified as a specific situation. In the specific situation, a control of changing an operation mode of the motor such that presence or absence of occurrence of resistance of the actuator against its operation by external input force is changeable, and a control of limiting a supply current to the motor such that the torque generating direction of the motor is inhibited from coinciding with a direction away from a neutral position are executed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
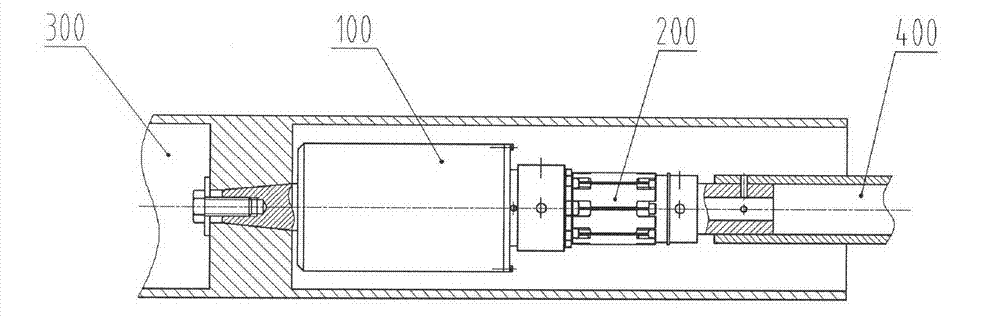
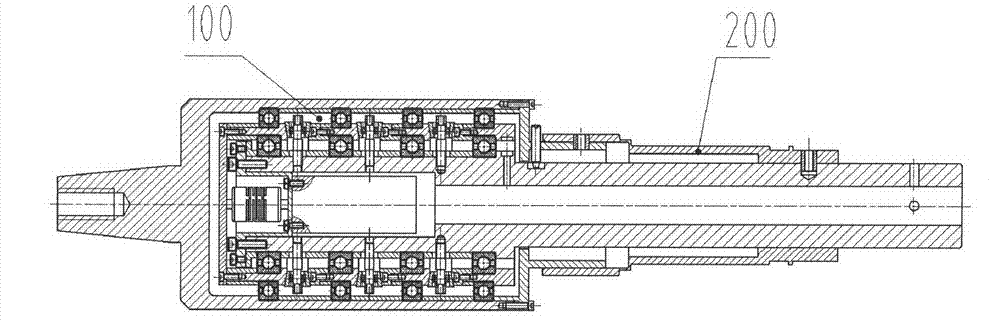
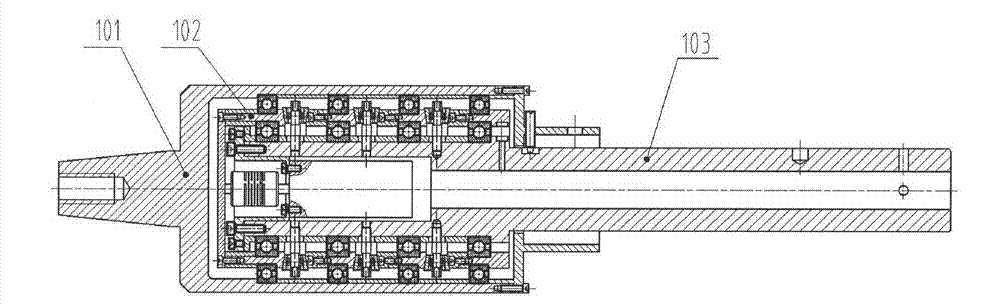
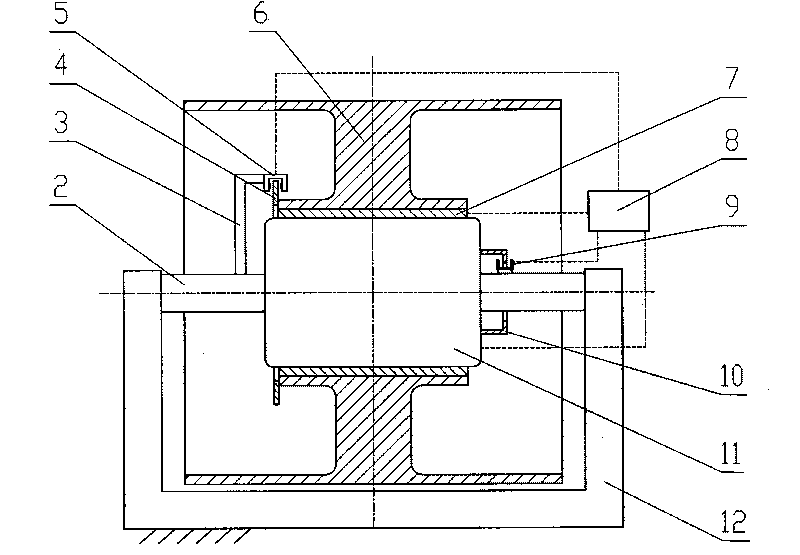
High-precision device for measuring rolling moment based on mechanical bearing support
ActiveCN102889973AImprove rigidityEliminate measurement effectsAerodynamic testingMeasurement deviceSimple component
The invention discloses a high-precision device for measuring a rolling moment based on a mechanical bearing support, which is lower in researching and testing costs, higher in precision as comparison with the conversional high-precision rolling moment strain gauge balance and capable of meeting the requirement for small rolling moment wind channel measurement of a wind channel model in various attack angle states. The high-precision device comprises a simple component rolling moment balance (200) and a mechanical bearing support (100), wherein the mechanical bearing support (100) comprises a shell assembly (101), a rotary inner sleeve assembly (102) and a central shaft assembly (103); the rotary inner sleeve assembly (102) is arranged inside the shell assembly (101) by using an outer ring bearing and arranged on the central shaft assembly (103) by using an inner ring bearing; the front end of the shell assembly (101) is fixedly provided with a measured wind channel model (300); and the central shaft assembly (103) is provided with the simple component rolling moment balance (200) and fixed on a model supporting rod (400).
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
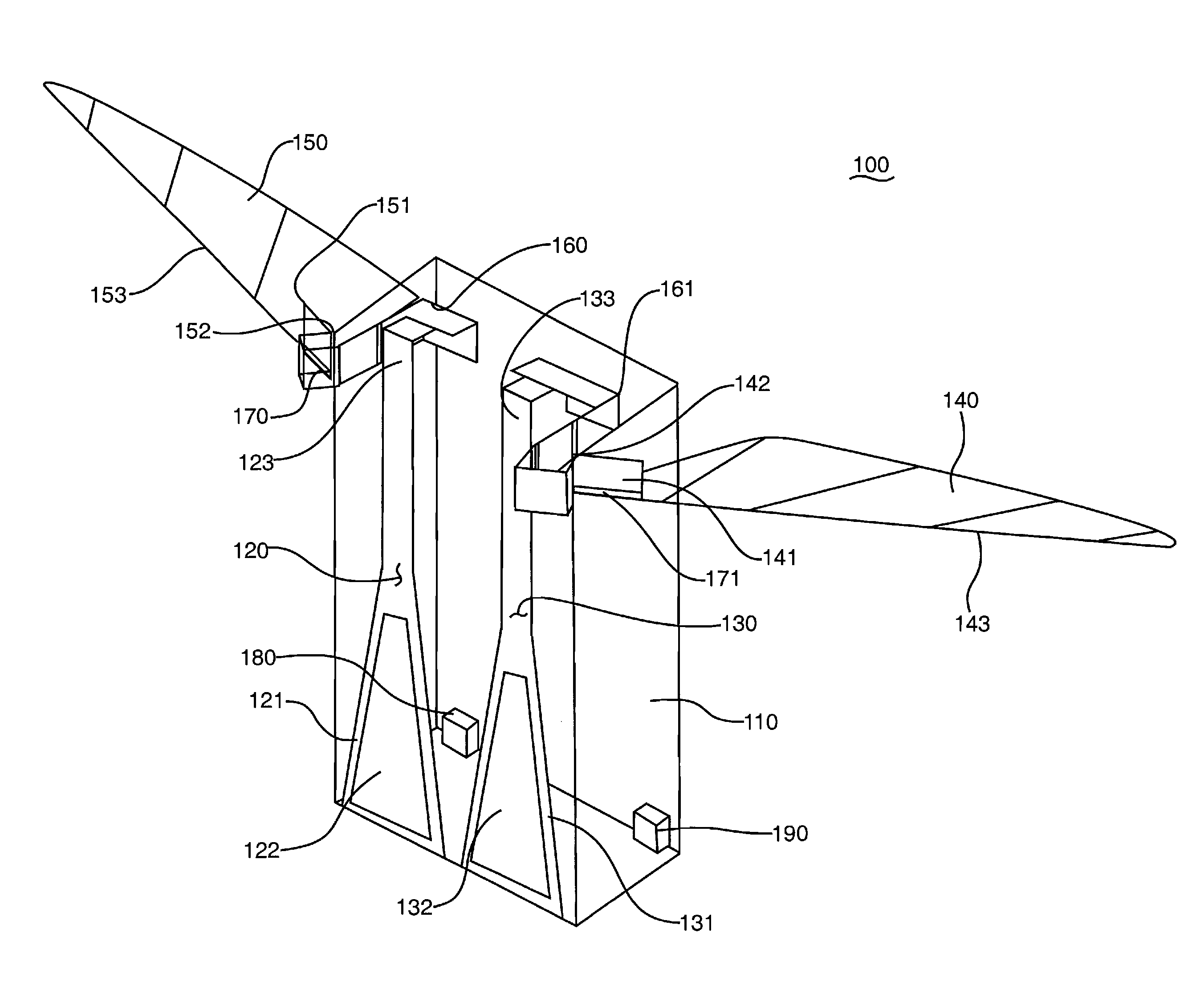
Apparatus and method for twisting a wing to increase lift on aircraft and other vehicles
A method and apparatus for varying the twist of a wing such that induced drag is minimized or reduced during cruise and lift is maximized or increased at least during takeoff and landings. In addition, variations in the twist may produce yawing and rolling moments. The twist amount is varied pursuant to the operating conditions, including those parameters used to determine the lift coefficient. The twist for reducing induced drag and / or improving lift may be employed by geometric or aerodynamic twist, including full span control surfaces used to provide roll control, high-lift and reduced induced drag. The twist may also be employed by twisting just a portion of the wing or the entire wing, either geometrically or aerodynamically.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
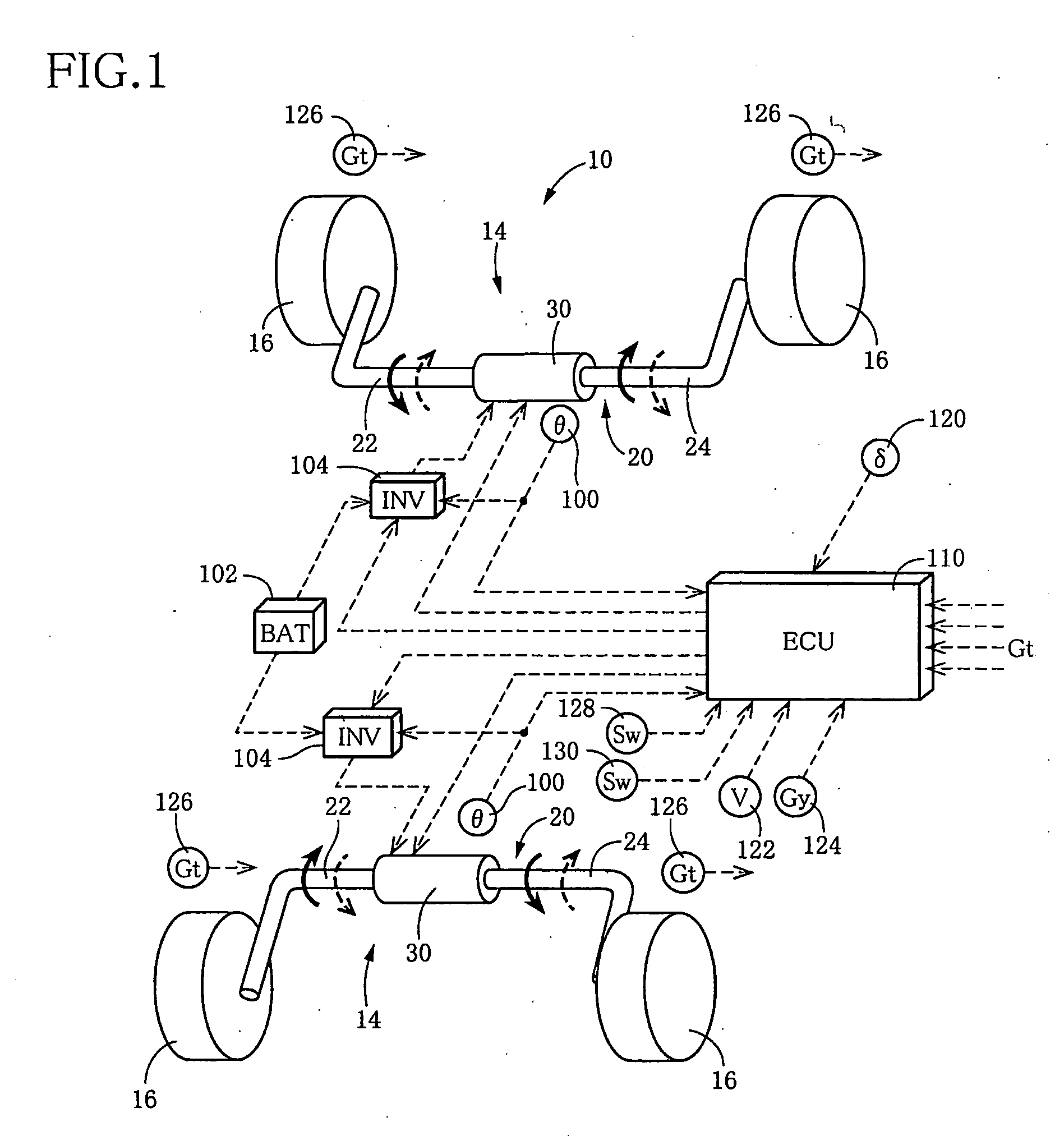
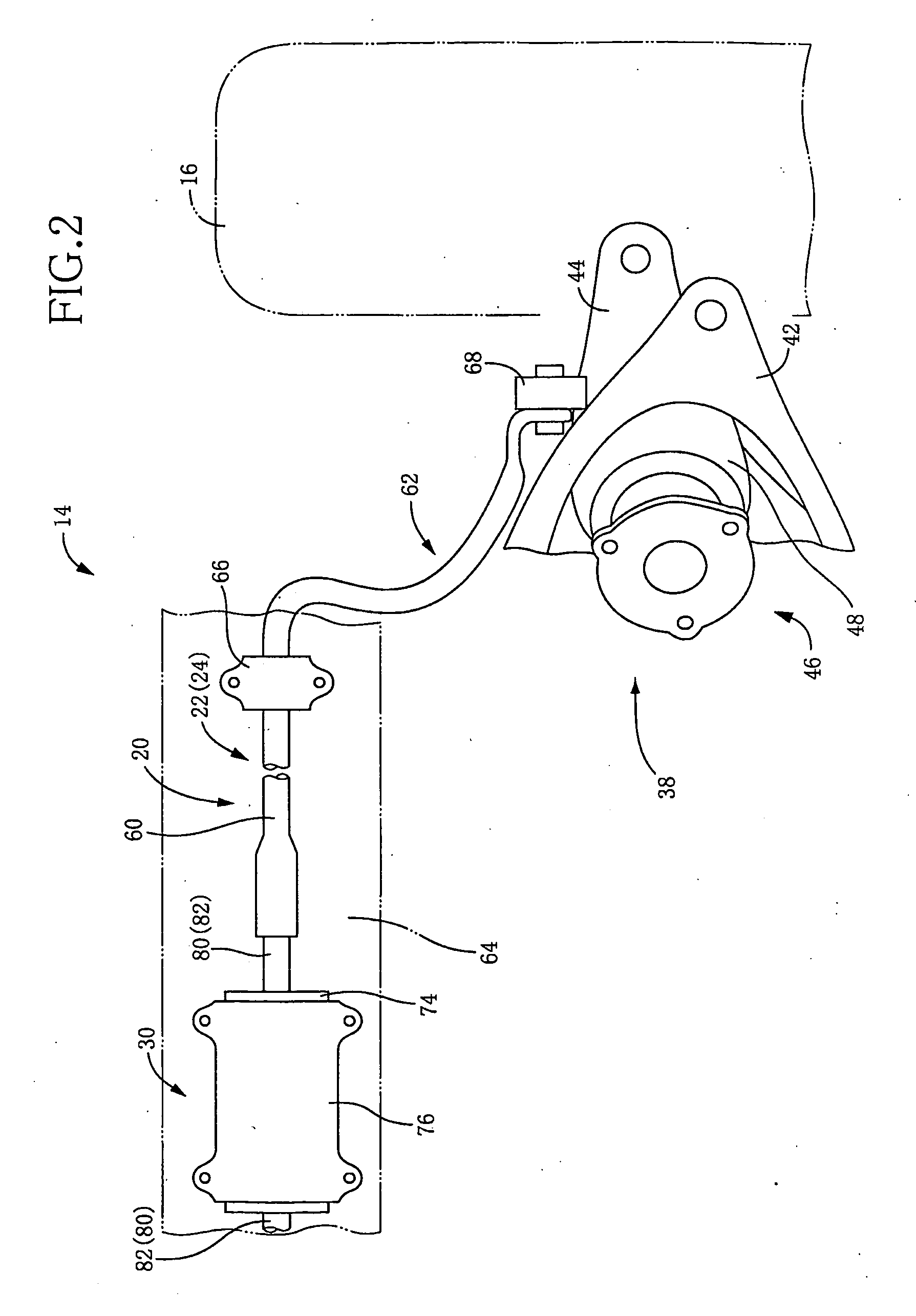
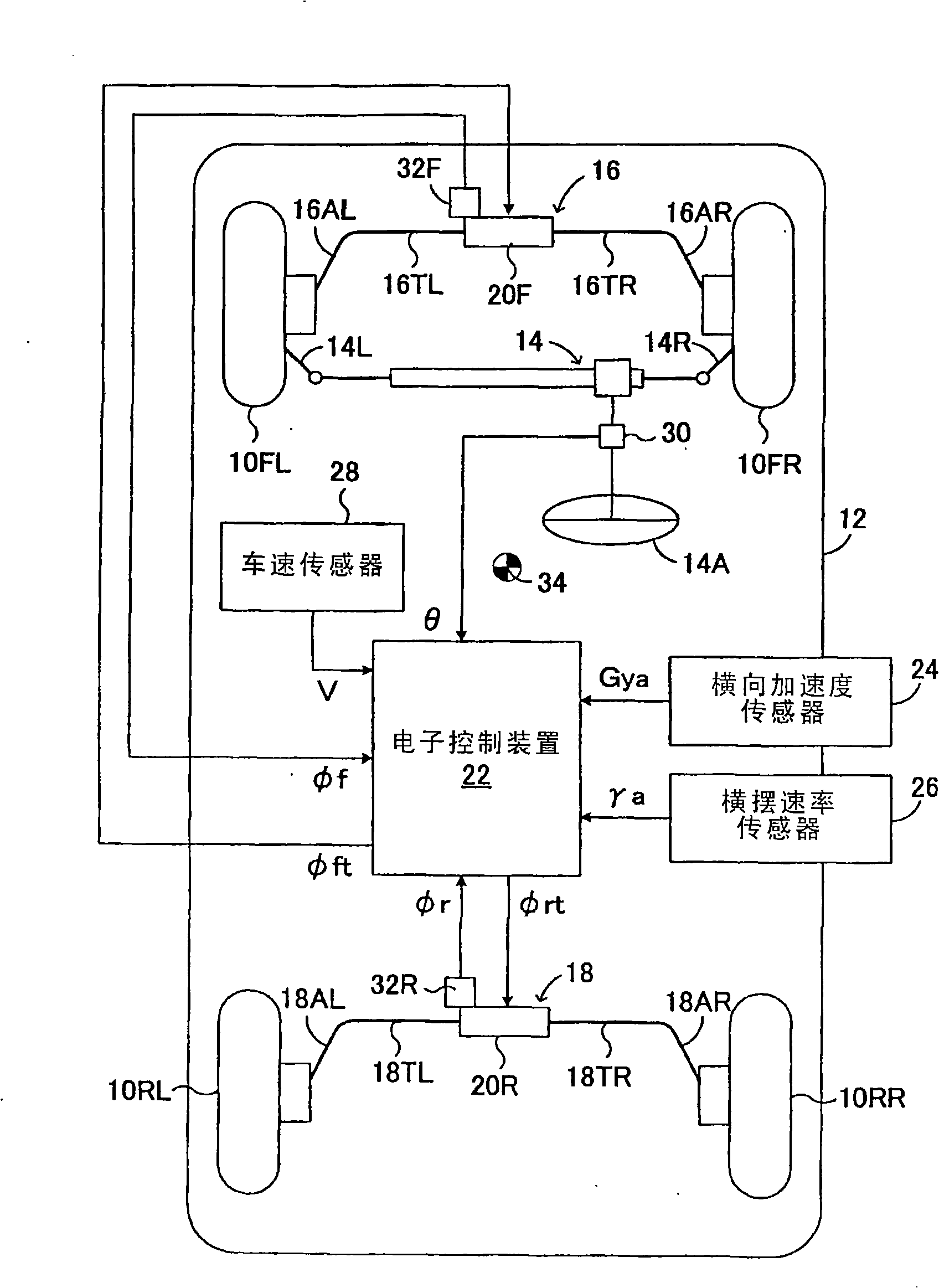
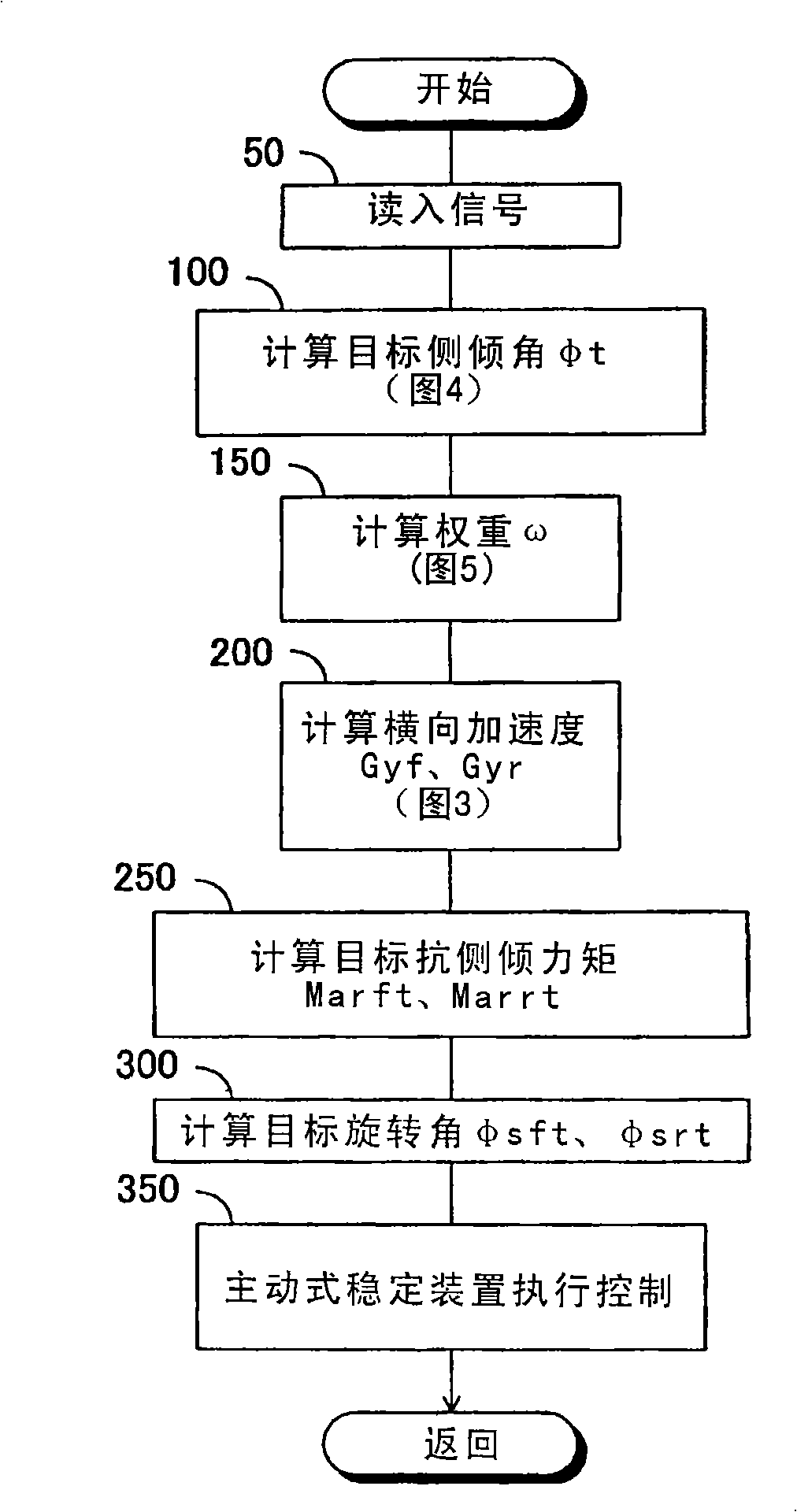
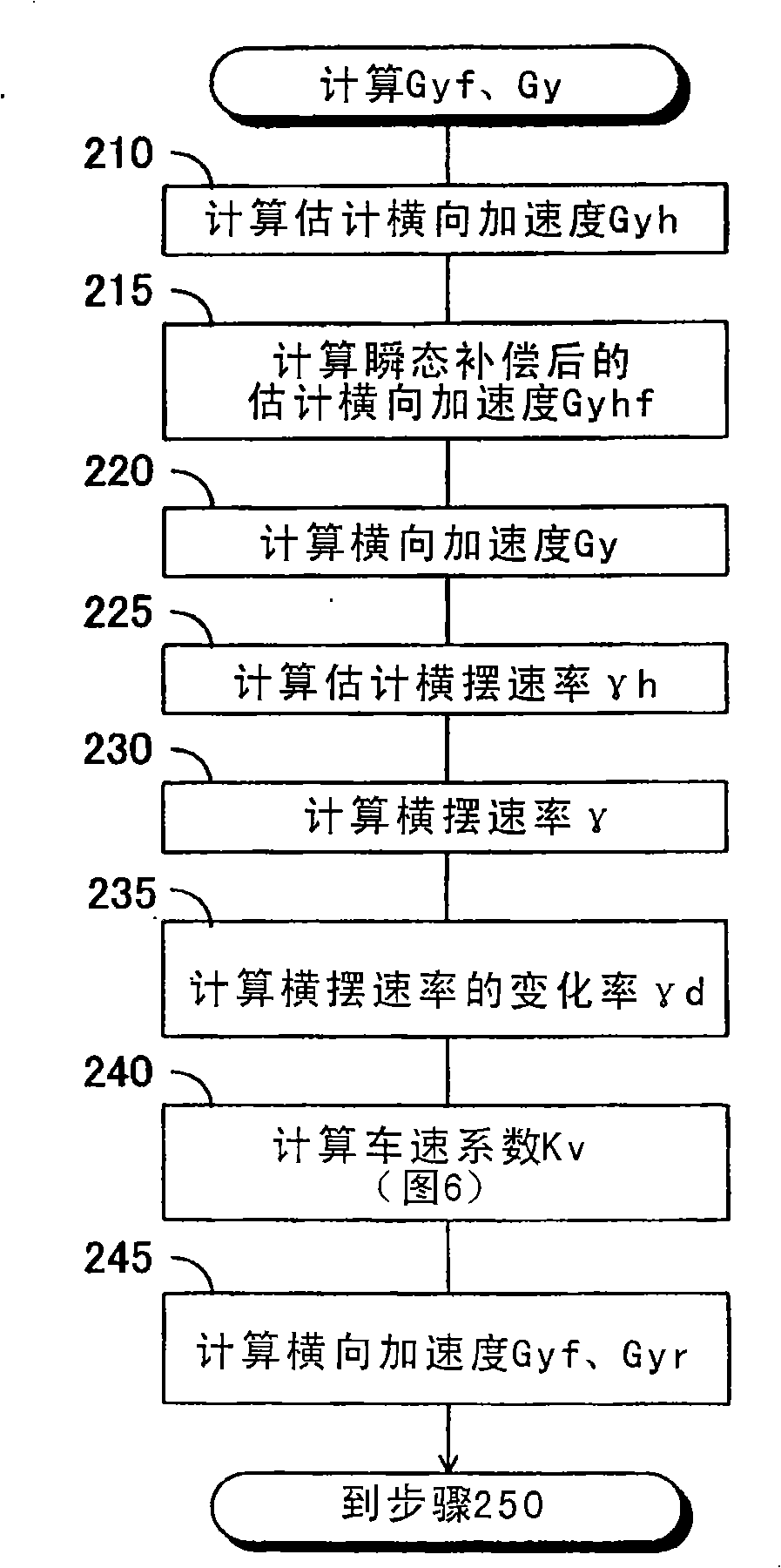
Roll rigidity controller of vehicle
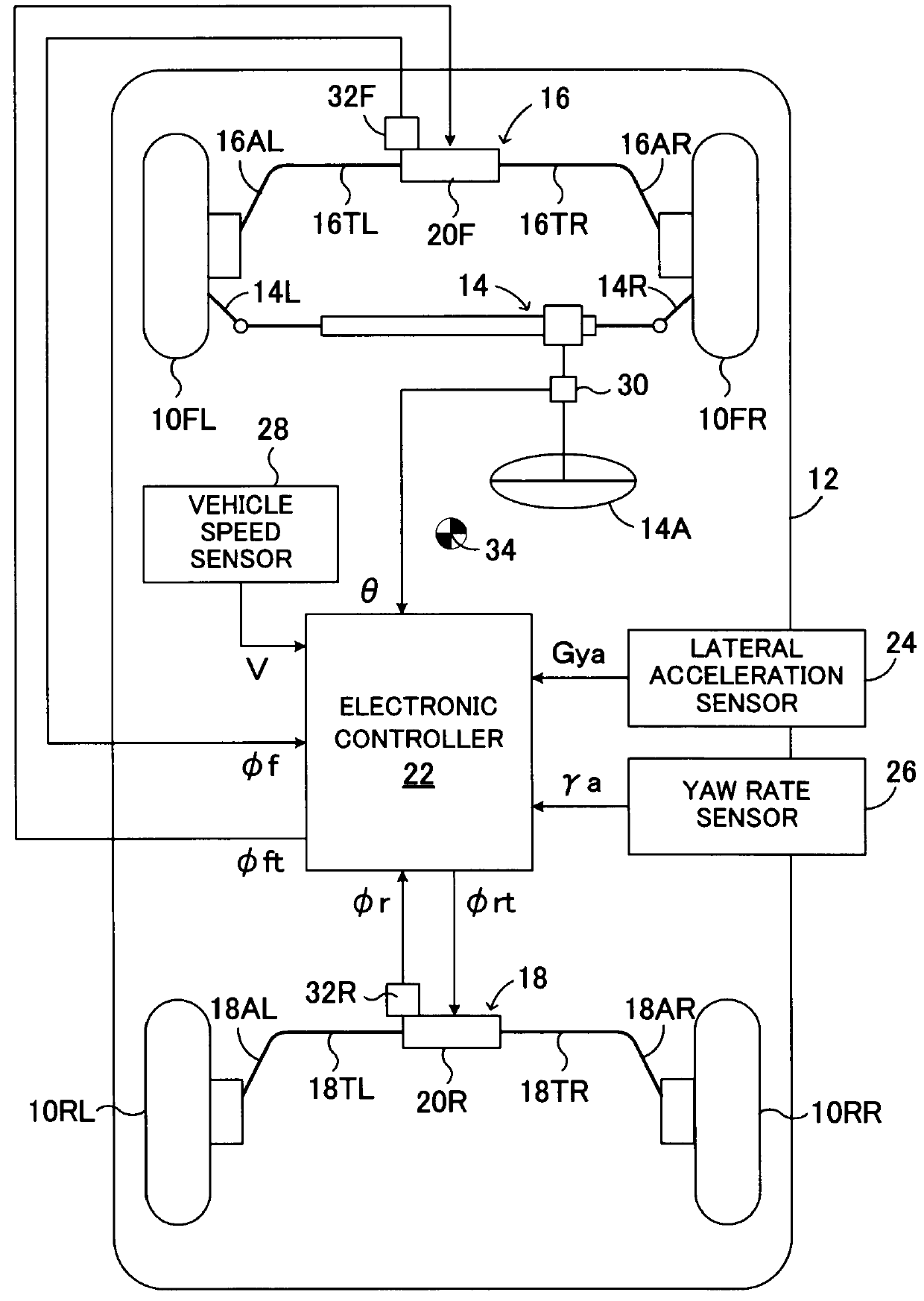
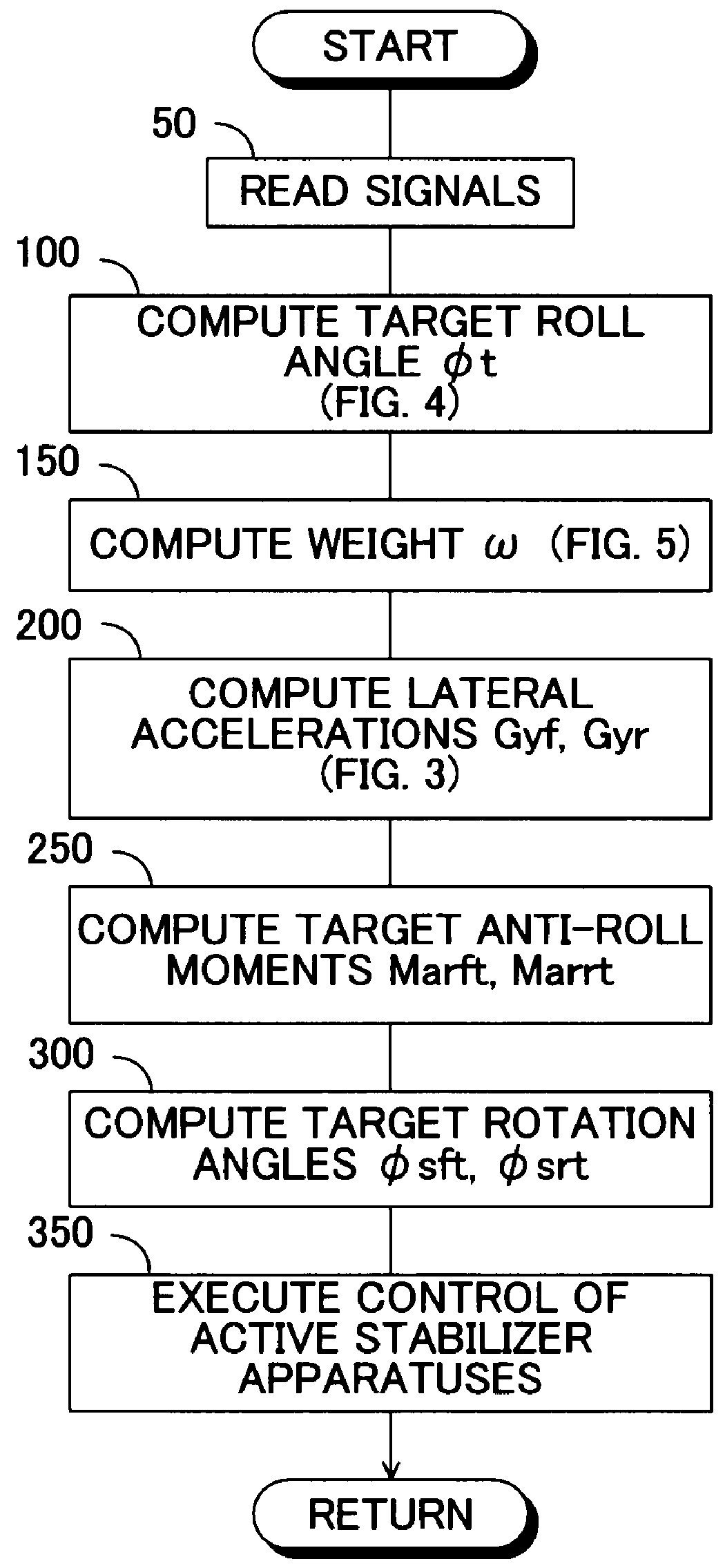
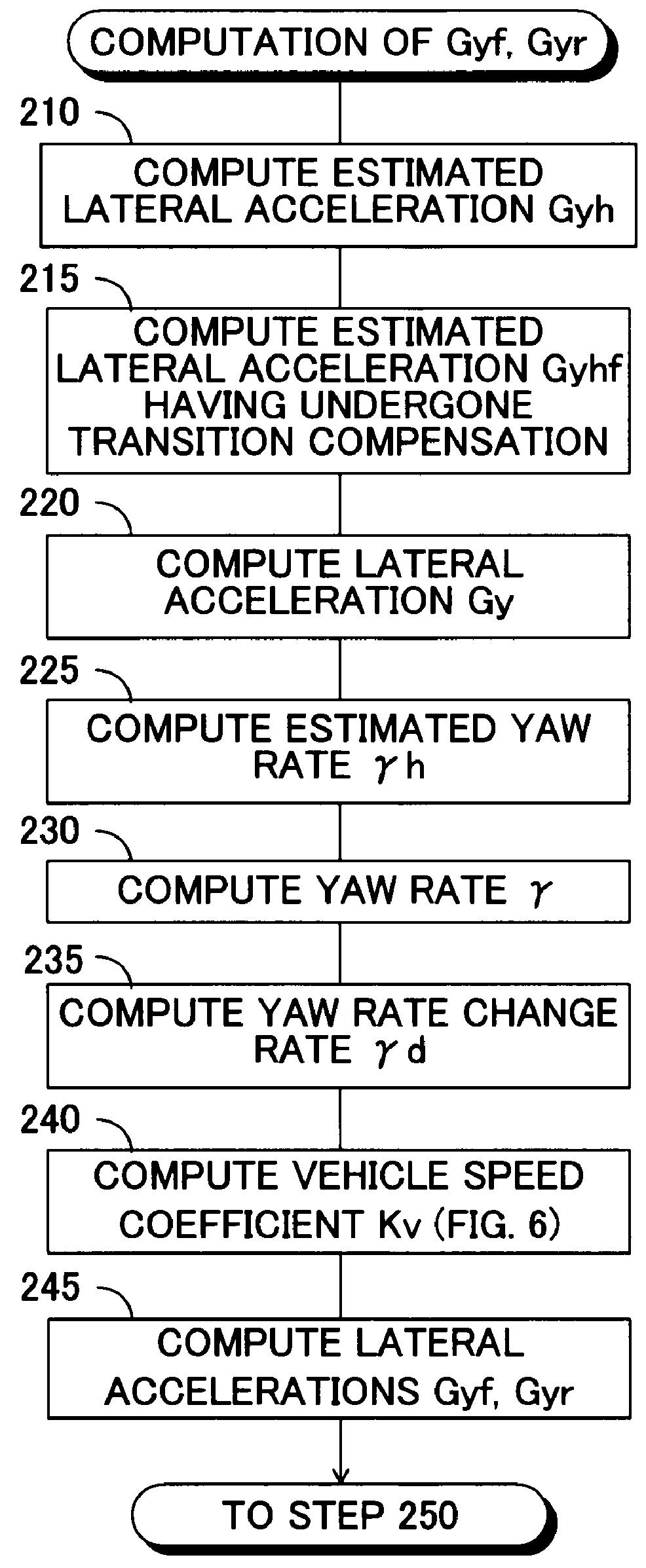
InactiveUS8170749B2Increase and decrease supportIncrease and decrease roll rigidityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesRolling momentRolling angle
A target roll angle of the vehicle is computed based on an actual lateral acceleration at the centroid of the vehicle, and the lateral acceleration of the vehicle at the centroid is corrected by use of lateral acceleration correction amounts based on a yaw rate of the vehicle, whereby the lateral accelerations of the vehicle at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position are computed. Subsequently, target anti-roll moments at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position are computed based on the target roll angle and the accelerations of the vehicle at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position, and active stabilizer apparatuses of the front and rear wheels are controlled based on these target anti-roll moments.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Suspension system for vehicle
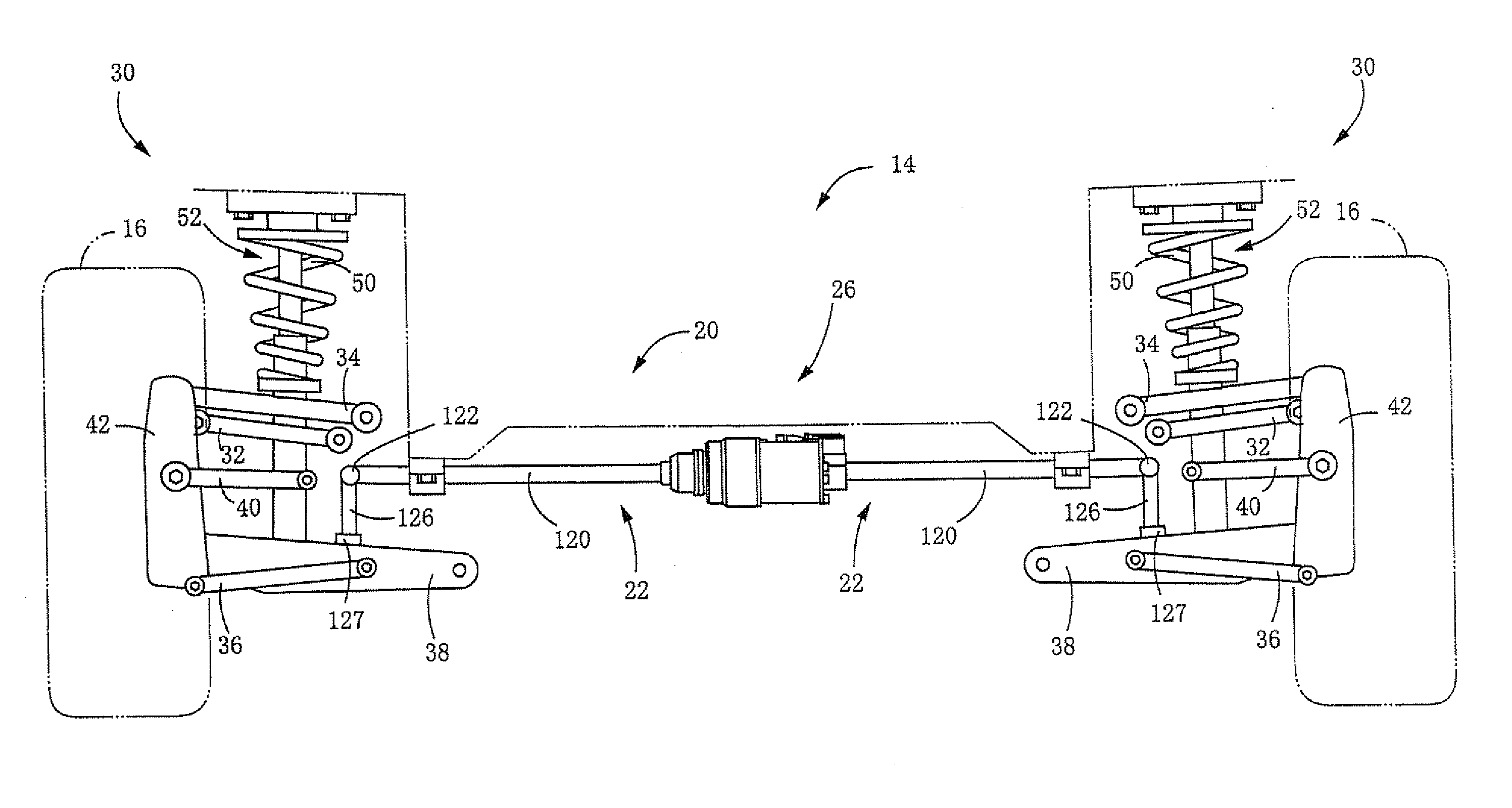
InactiveUS20100207343A1Improve overall utilizationIncrease profitInterconnection systemsResilient suspensionsDamping factorRolling moment
A suspension system for a vehicle, including: a stabilizer apparatus configured to change a stabilizer force by an operation of an actuator; a pair of absorbers of a hydraulic type each configured to change a damping coefficient thereof: a control device which includes (a) a stabilizer-force control portion configured to control the stabilizer force in accordance with roll moment acting on a body of the vehicle and (b) a damping-coefficient control portion configured to control the damping coefficient of each of the absorbers, wherein the damping-coefficient control portion is configured to execute a damping-coefficient reduction control for reducing the damping coefficient of each of the absorbers when a prescribed condition is satisfied and wherein the stabilizer-force control portion is configured to increase the stabilizer force in an instance where the damping-coefficient reduction control is under execution, as compared with an instance where the damping-coefficient reduction control is not under execution.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
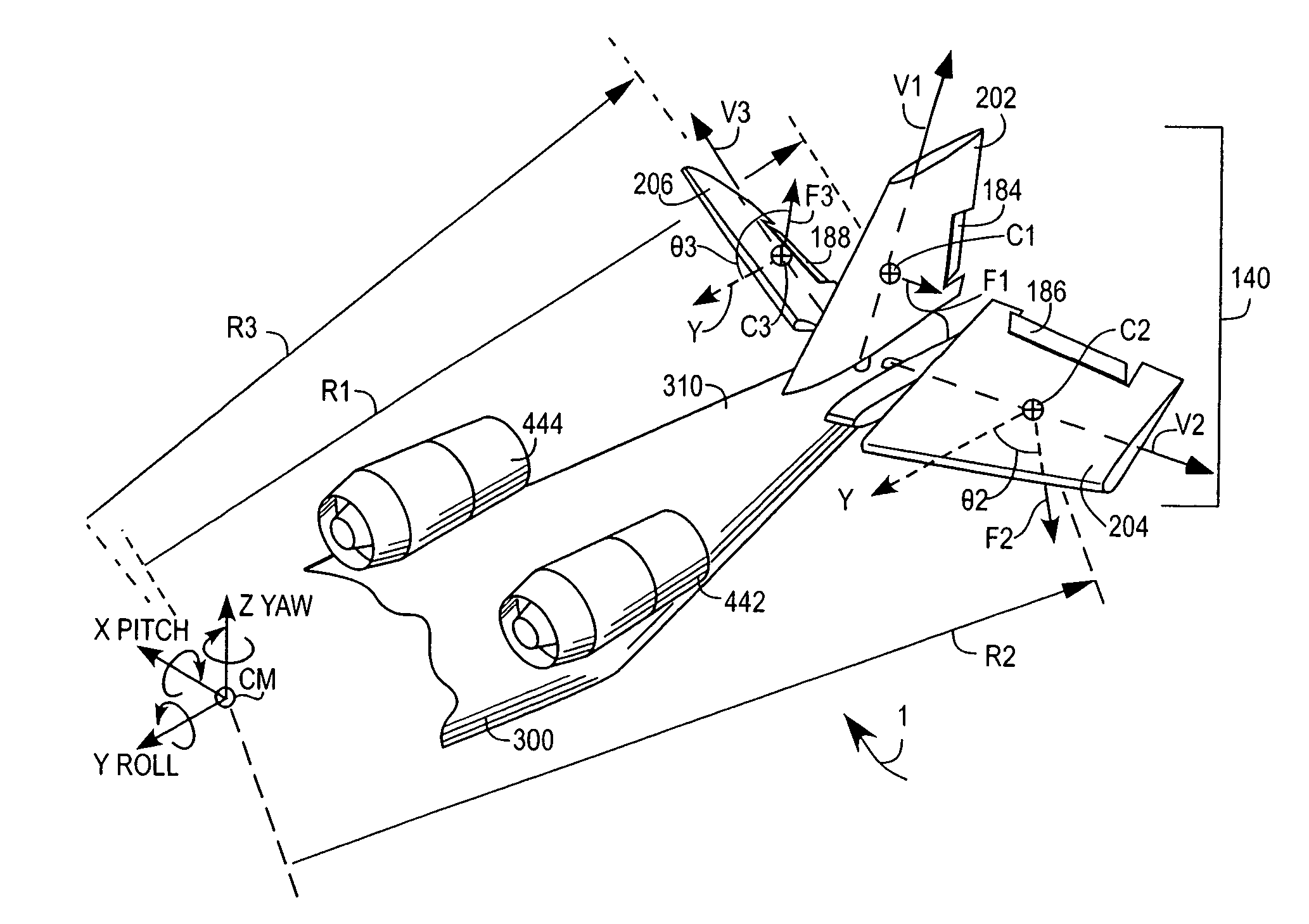
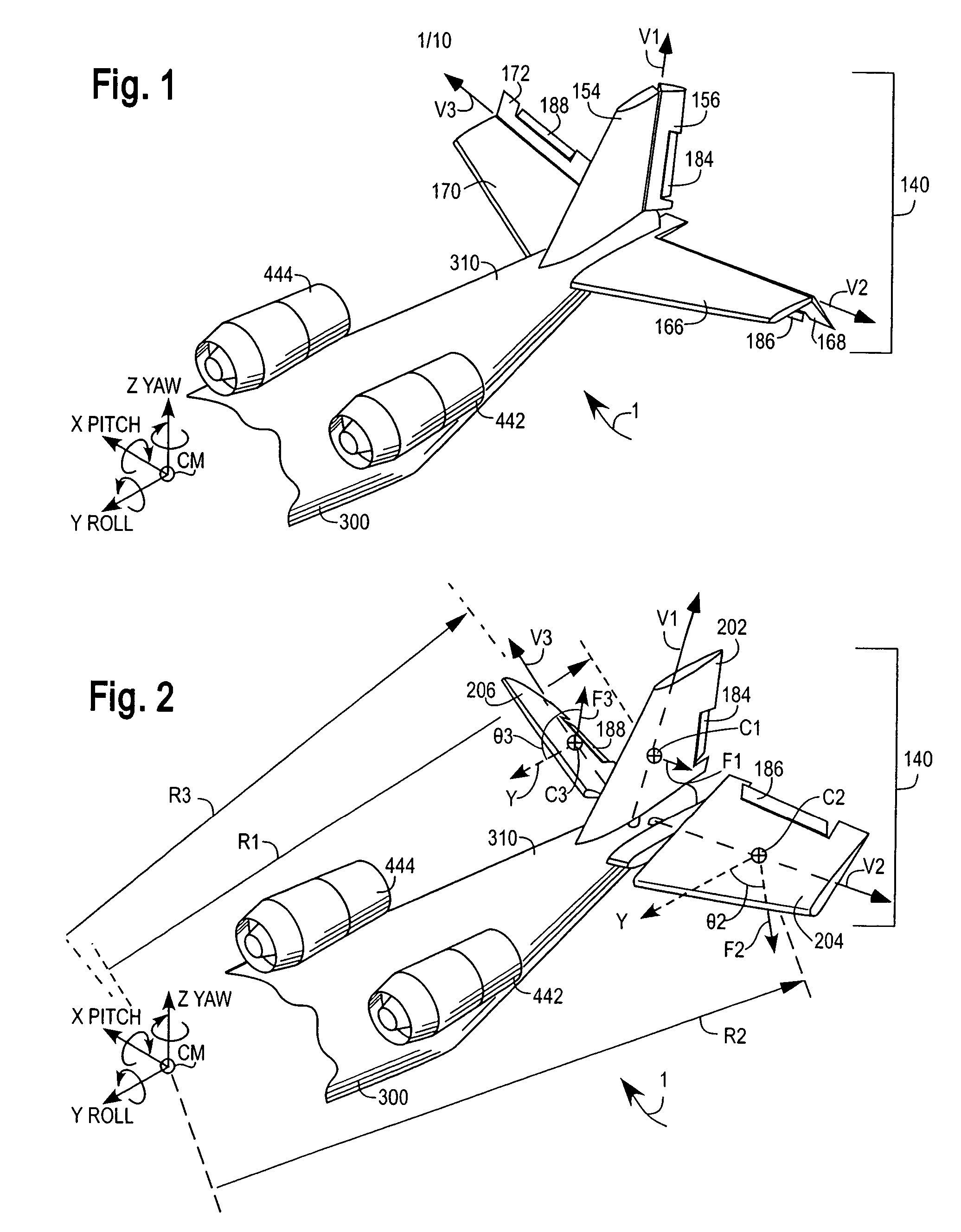
Aircraft attitude control configuration
An aircraft attitude control configuration enables control surfaces to provide attitude control for an aircraft at hover or low air speed conditions. The aircraft attitude control configuration includes a thruster mounted to an aircraft for thrusting air, a first control surface kinematically coupled to the aircraft at a position downstream of the thruster, and a second control surface kinematically coupled to the aircraft at a position downstream of the thruster, the second control surface being differentially movable with respect to the first control surface such that a portion of the thrusted air from the thruster generates a first vector force on the first control surface and another portion of the thrusted air generates a second vector force on the second control surface, so that the first and the second vector forces provide a net roll moment about the Y-Roll axis.
Owner:MORGAN AIRCRAFT LLC
Apparatus and method for twisting a wing to increase lift on aircraft and other vehicles
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Active rollover protection
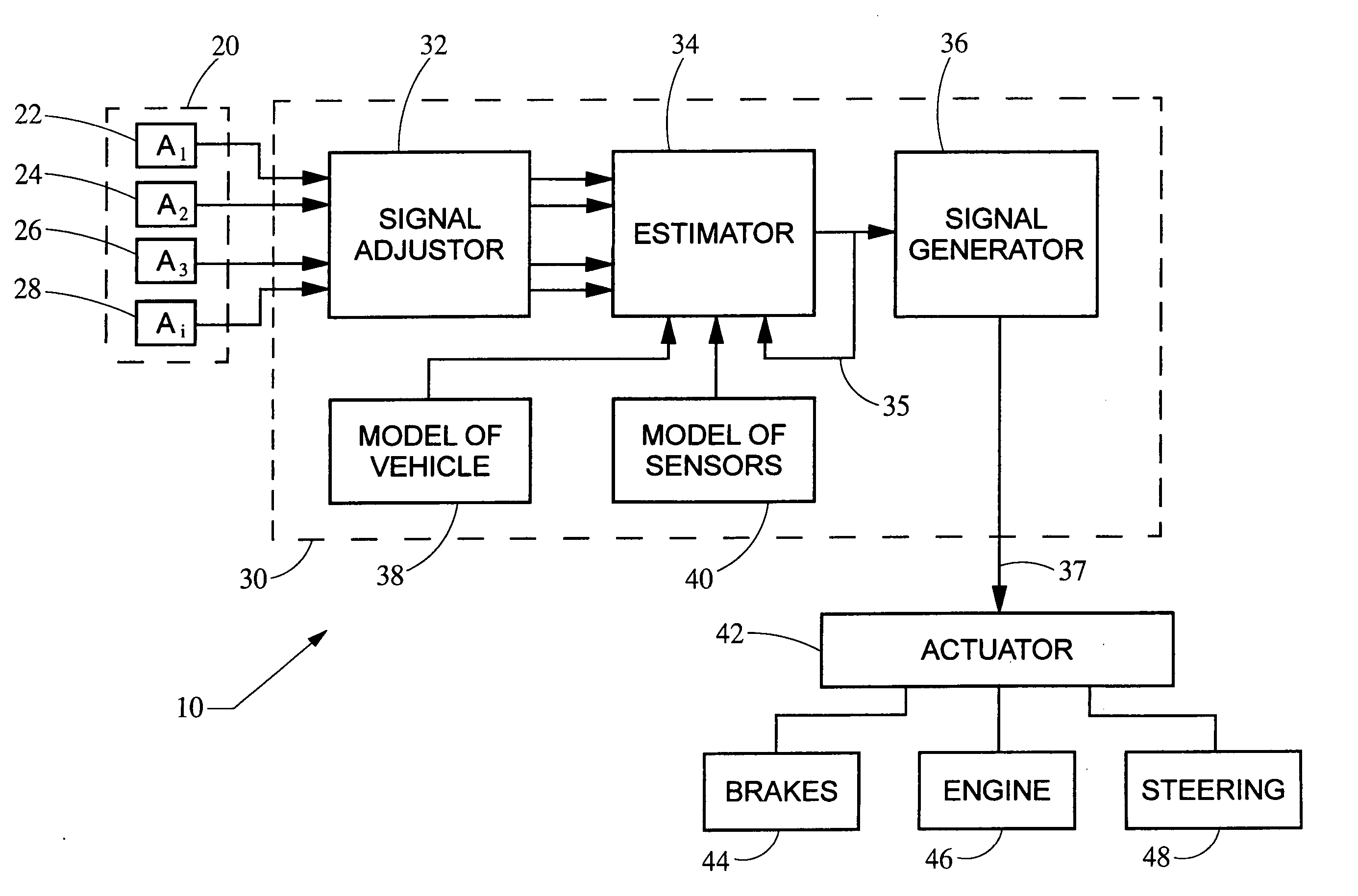
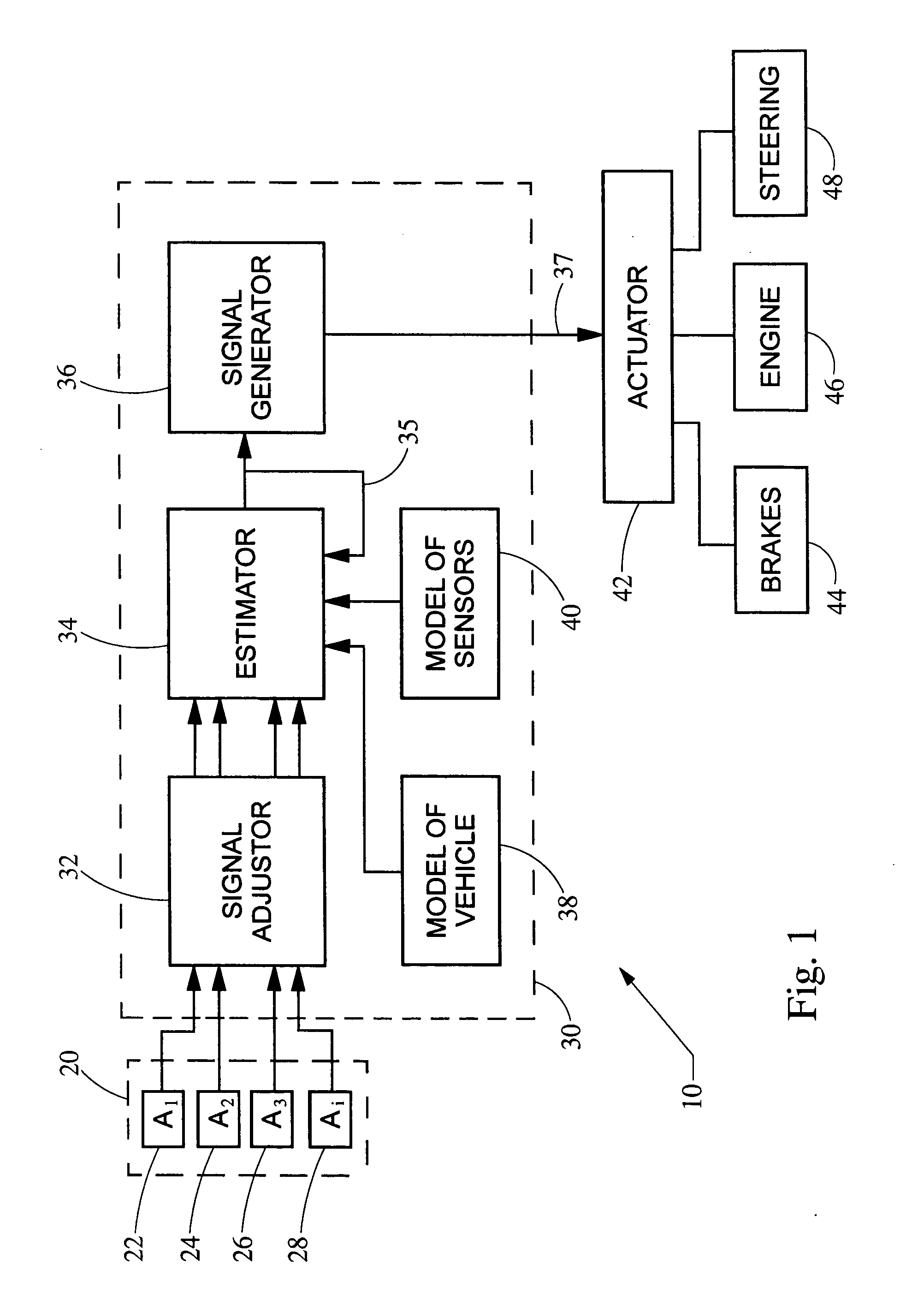
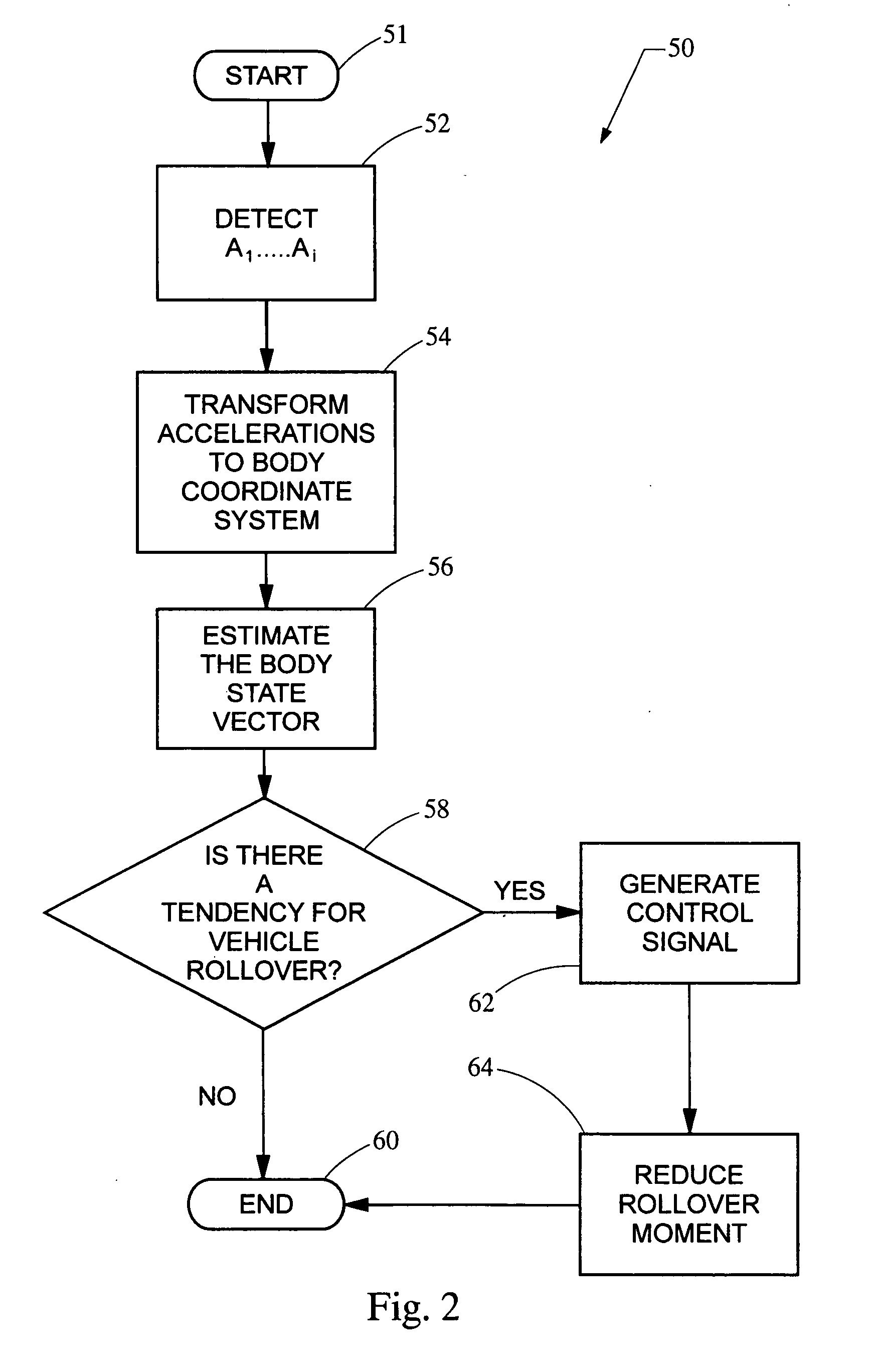
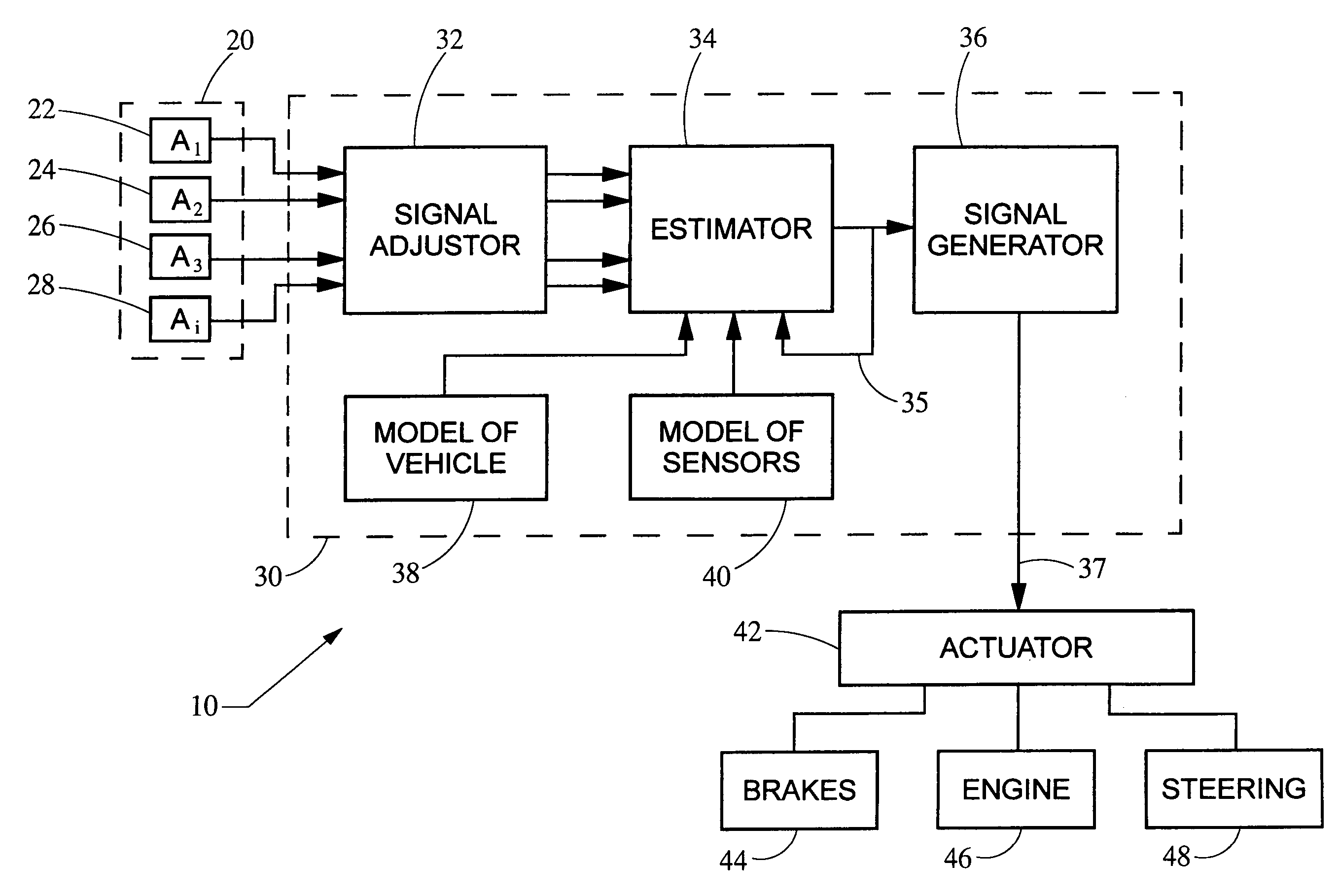
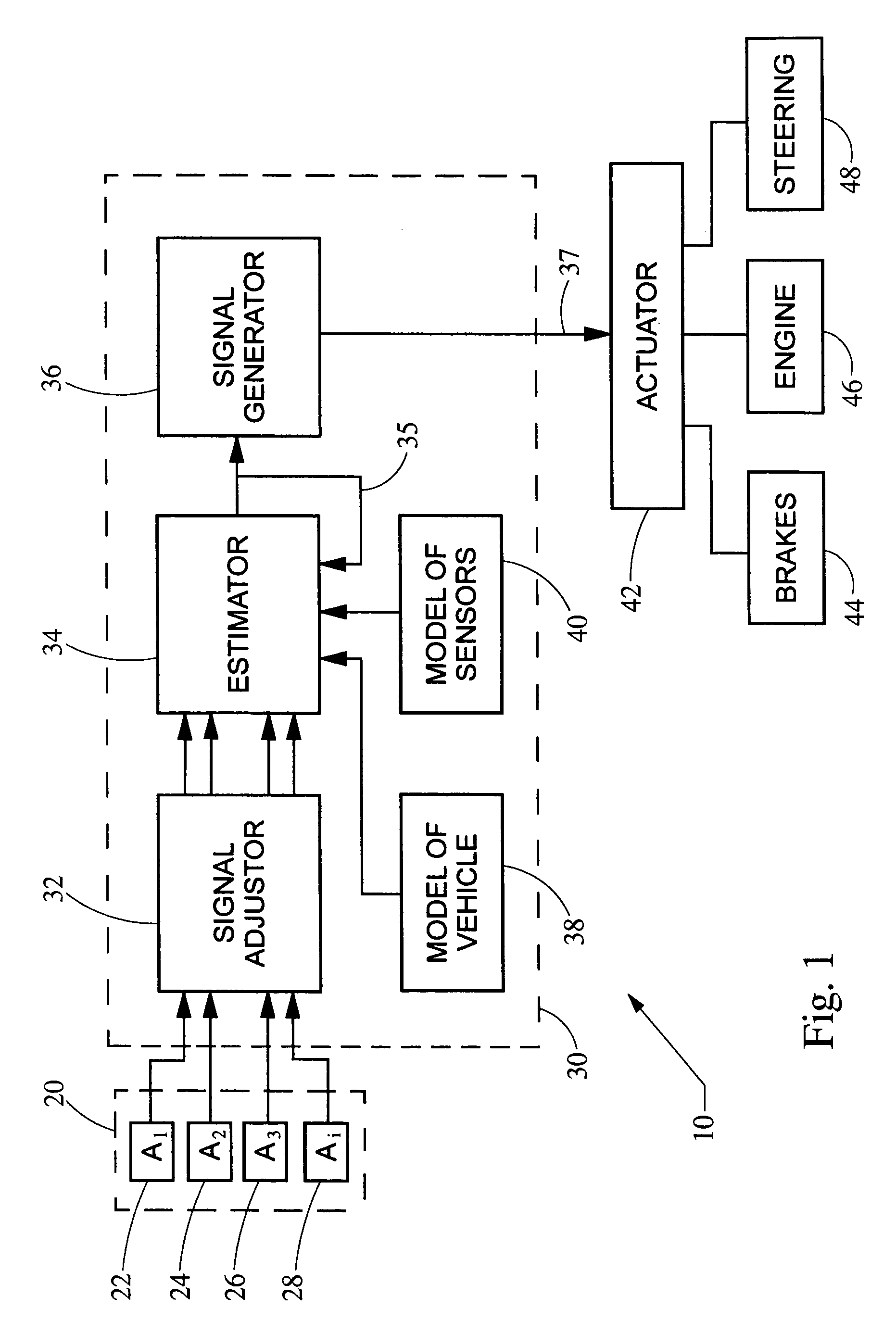
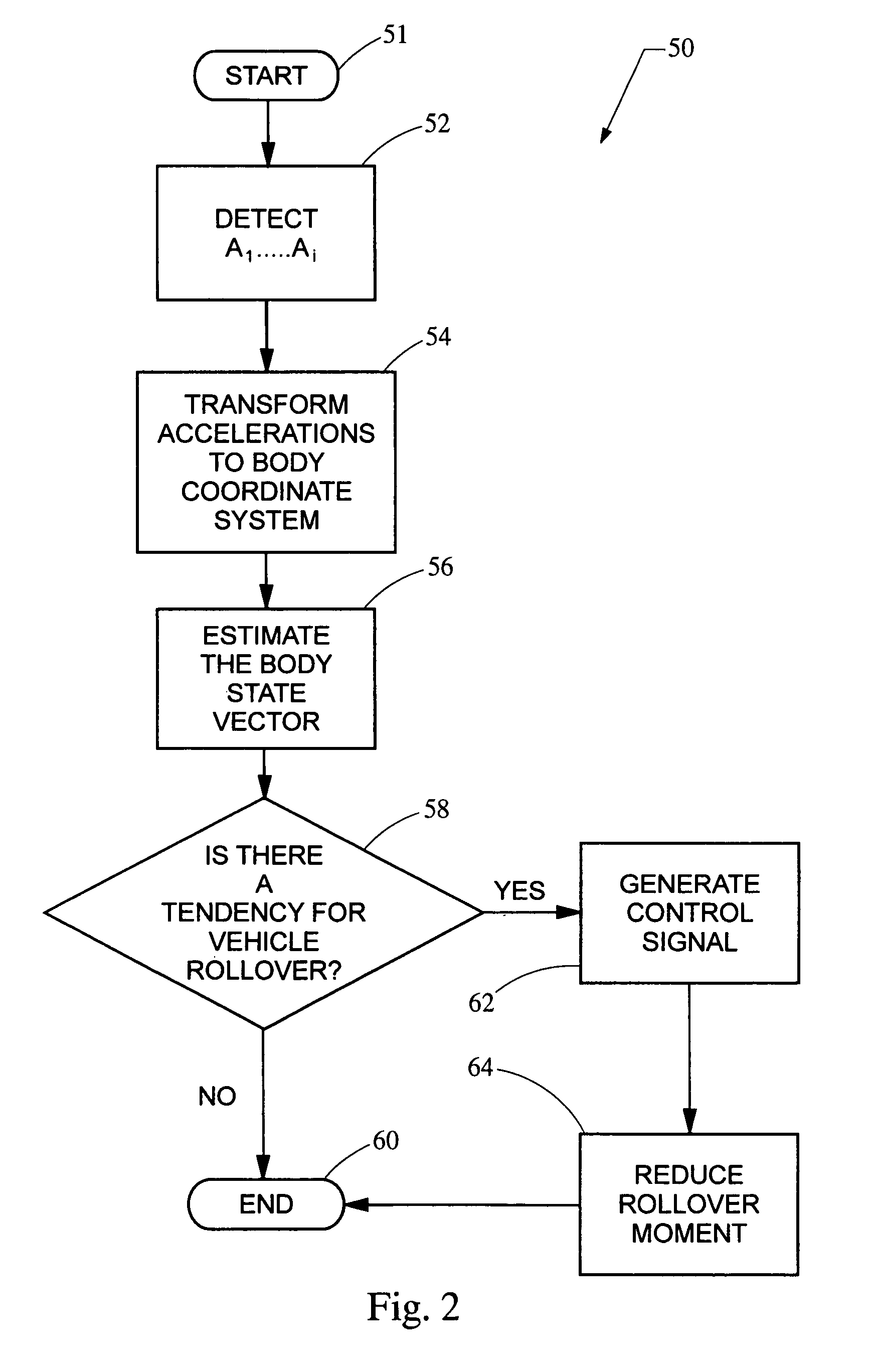
ActiveUS20050216154A1Reduces roll momentHigh precisionElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsVehicle dynamicsSensor array
A system and method protects against rollover in a vehicle by employing an array of linear acceleration sensors. A control module includes, among other things, a model of the vehicle dynamics and a model of the array of sensors. A state vector is estimated based on the detected accelerations, the model of the vehicle dynamics and the model of the sensors. A control signal is generated based on the state vector, and the roll moment of the vehicle is reduced based on the control signal.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
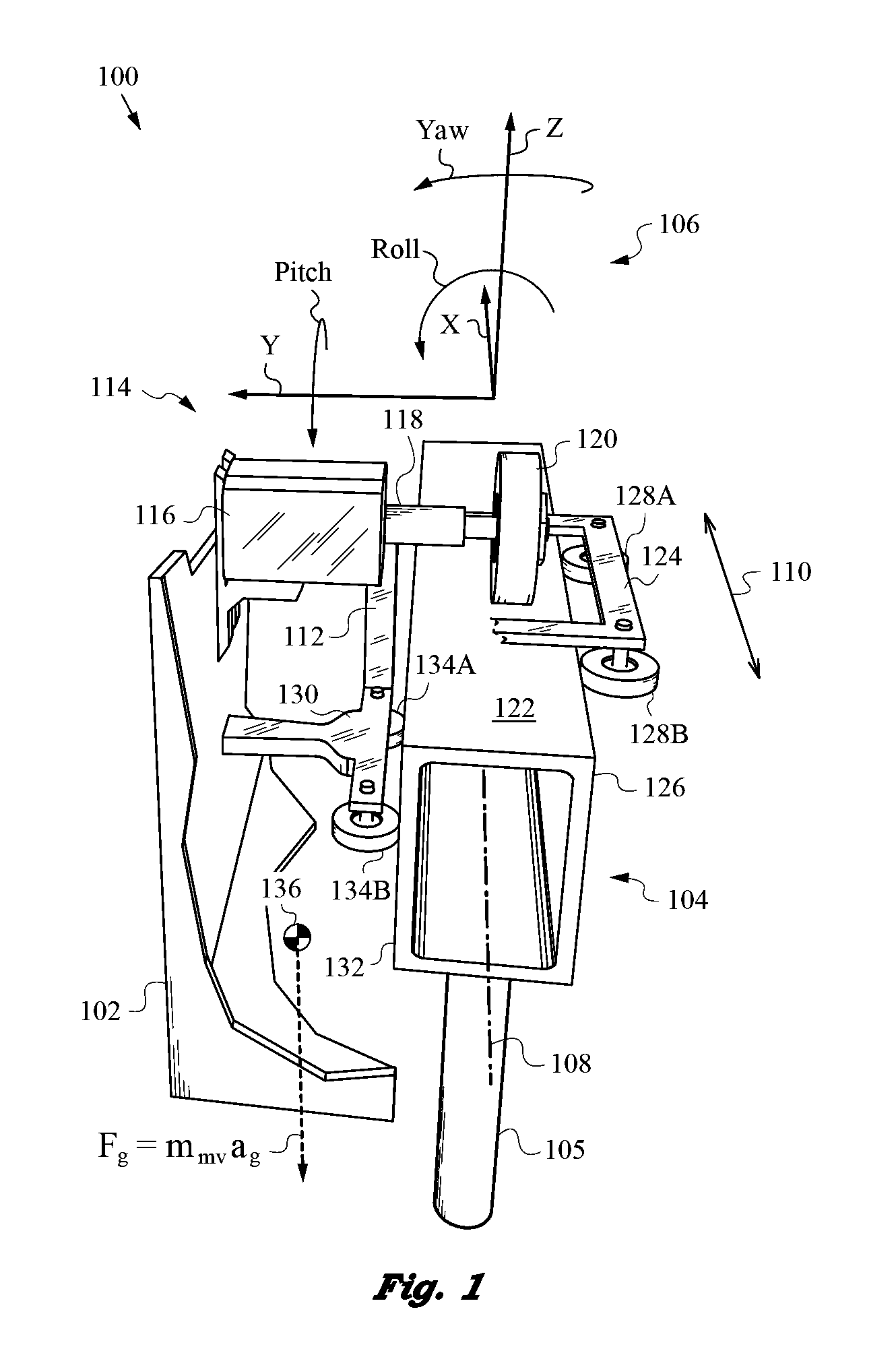
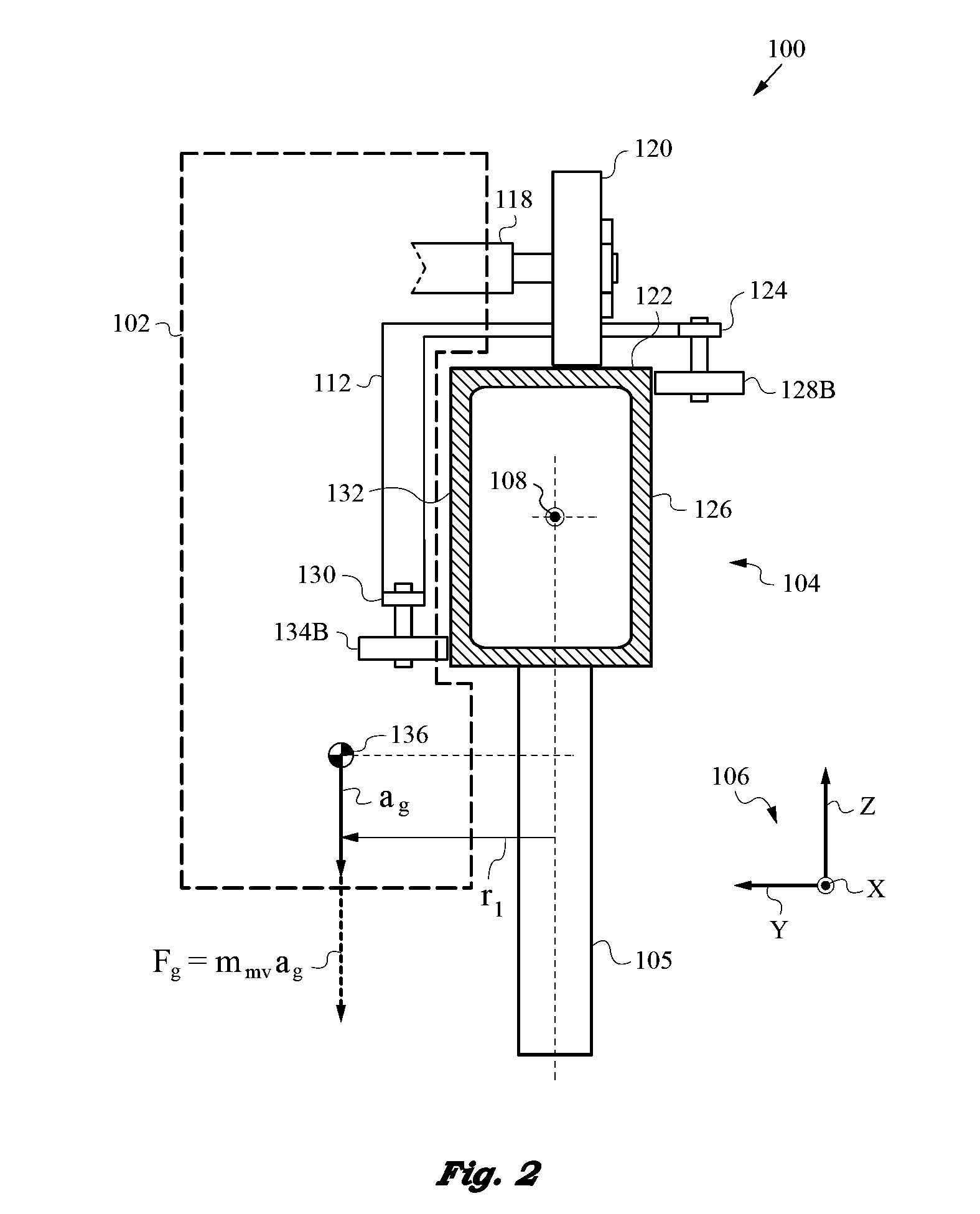
Monorail Vehicle Apparatus with Gravity-Controlled Roll Attitude and Loading
InactiveUS20140174315A1Significant changeConstant contact forceMonorailsRailway componentsBogieRolling moment
Monorail vehicle that travels on a non-featured rail with substantial profile variation and controls roll attitude, lateral location, and loading through judicious placement of the vehicle's center of gravity without using springs or suspensions. The vehicle has a bogie for engaging the non-featured rail so the center of gravity has a lateral offset r1 from the rail centerline to produce a roll moment Nr determined by vehicle's mass and value of r1. The center of gravity also has a vertical offset r2. The bogie uses first and second assemblies for engaging the rail to produce a pair of surface normal reaction forces to thus control roll attitude and loading by the placement of the center of gravity, thereby enabling accurate alignment of the monorail vehicle.
Owner:SOLARCITY
Ducted fan for VTOL vehicles with system and method to reduce roll moments
ActiveUS8876038B2Reducing the roll momentUniform pressurePump componentsReaction enginesEngineeringRolling moment
A ducted fan for a VTOL vehicle includes a substantially cylindrical duct having an inlet at an upper end and an outlet at a lower end, and an air mover unit located within the substantially cylindrical duct. The duct also includes inner and outer wall portions and a substantially annular upper lip connecting the inner and outer wall portions, thus defining the inlet. The substantially annular upper lip has opposed fore and aft portions and opposed side portions and is provided with at least first and second openings, respectively, at each of the opposed side portions. The first and second arrays of openings permit flow of air into at least first and second respective chambers formed within the duct, the first and second chambers connected by at least one passageway to thereby enable substantial equalization of surface pressure at the opposed side portions of the substantially annular upper lip.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
Active rollover protection
ActiveUS7031816B2Reduces roll momentHigh precisionElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsSensor arrayVehicle dynamics
A system and method protects against rollover in a vehicle by employing an array of linear acceleration sensors. A control module includes, among other things, a model of the vehicle dynamics and a model of the array of sensors. A state vector is estimated based on the detected accelerations, the model of the vehicle dynamics and the model of the sensors. A control signal is generated based on the state vector, and the roll moment of the vehicle is reduced based on the control signal.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
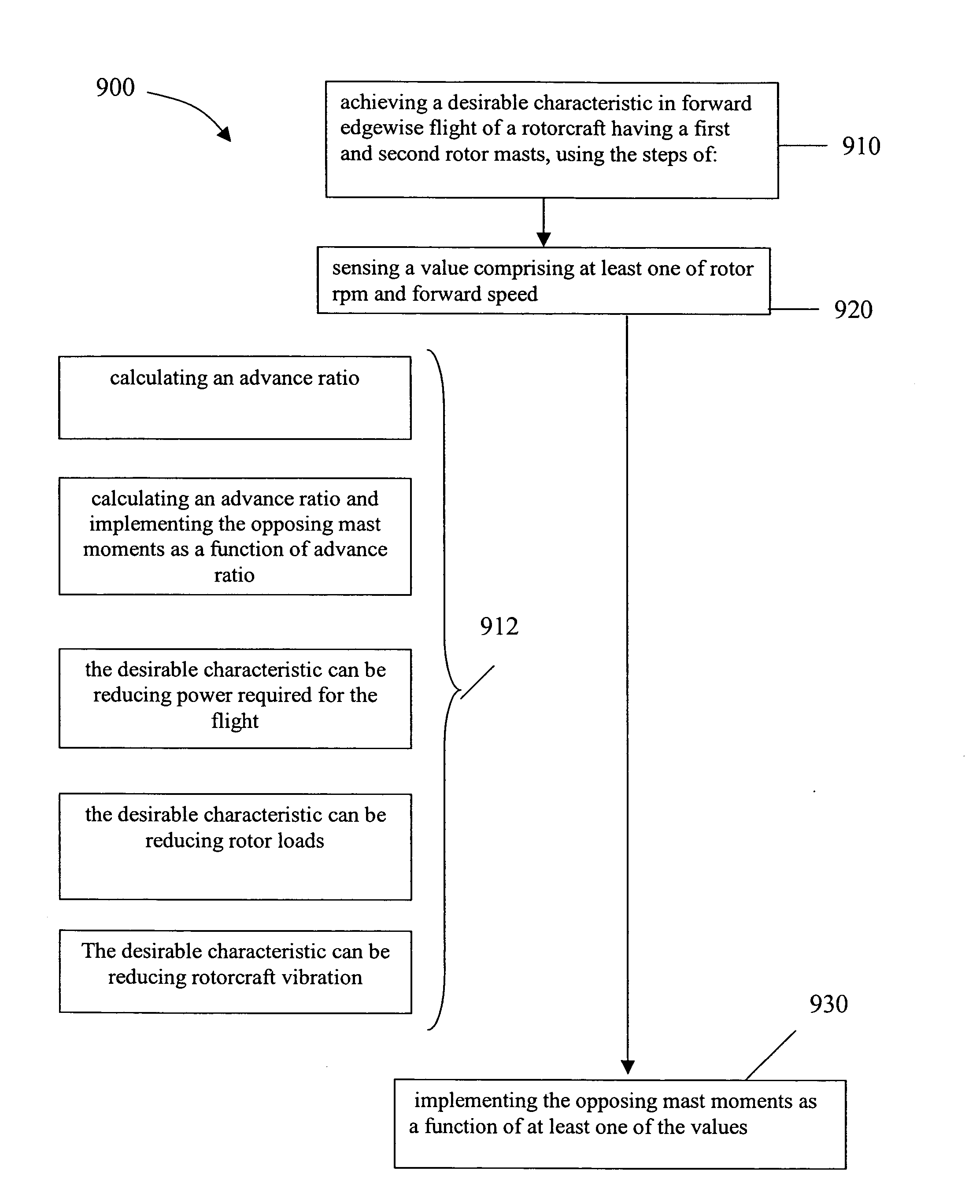
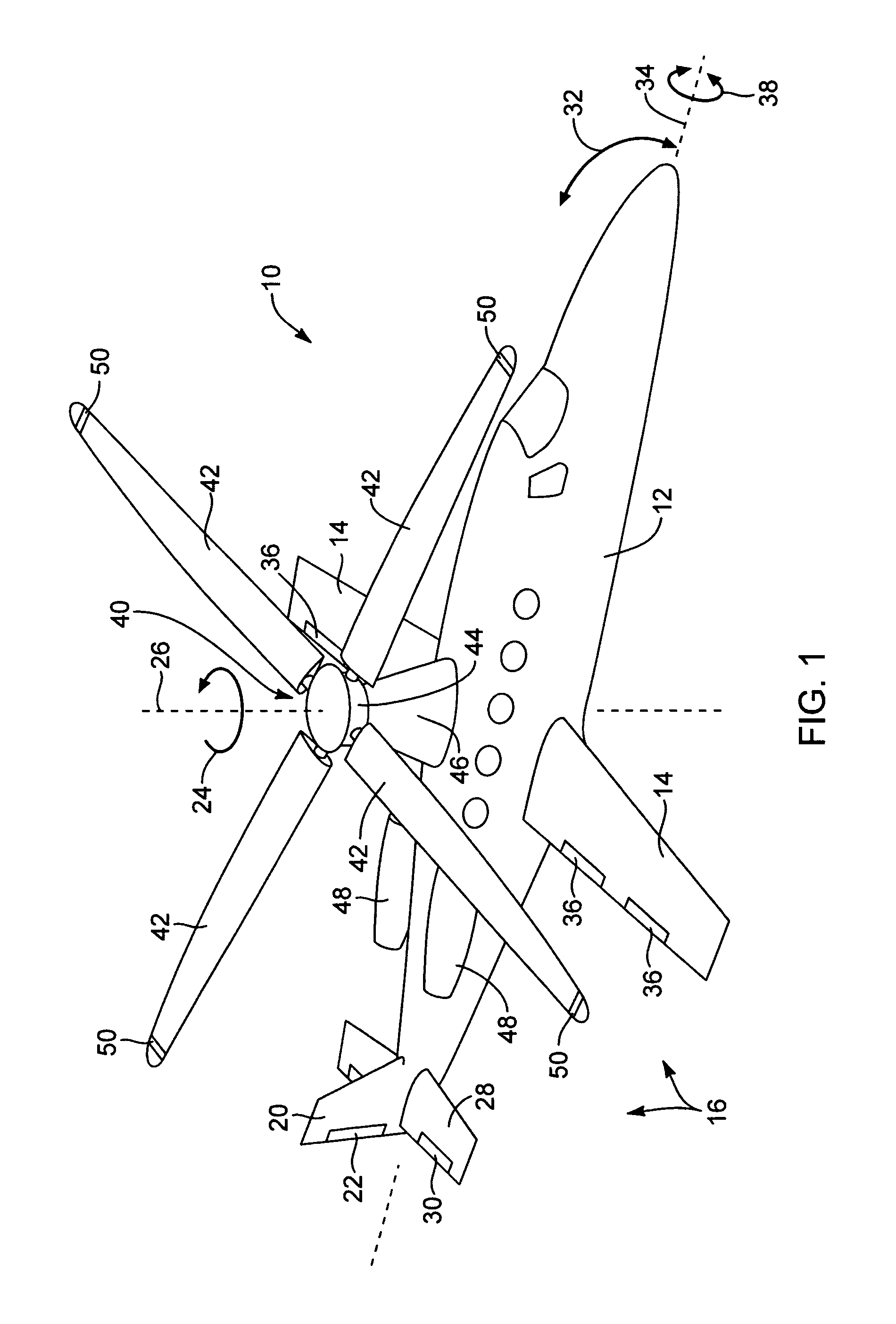
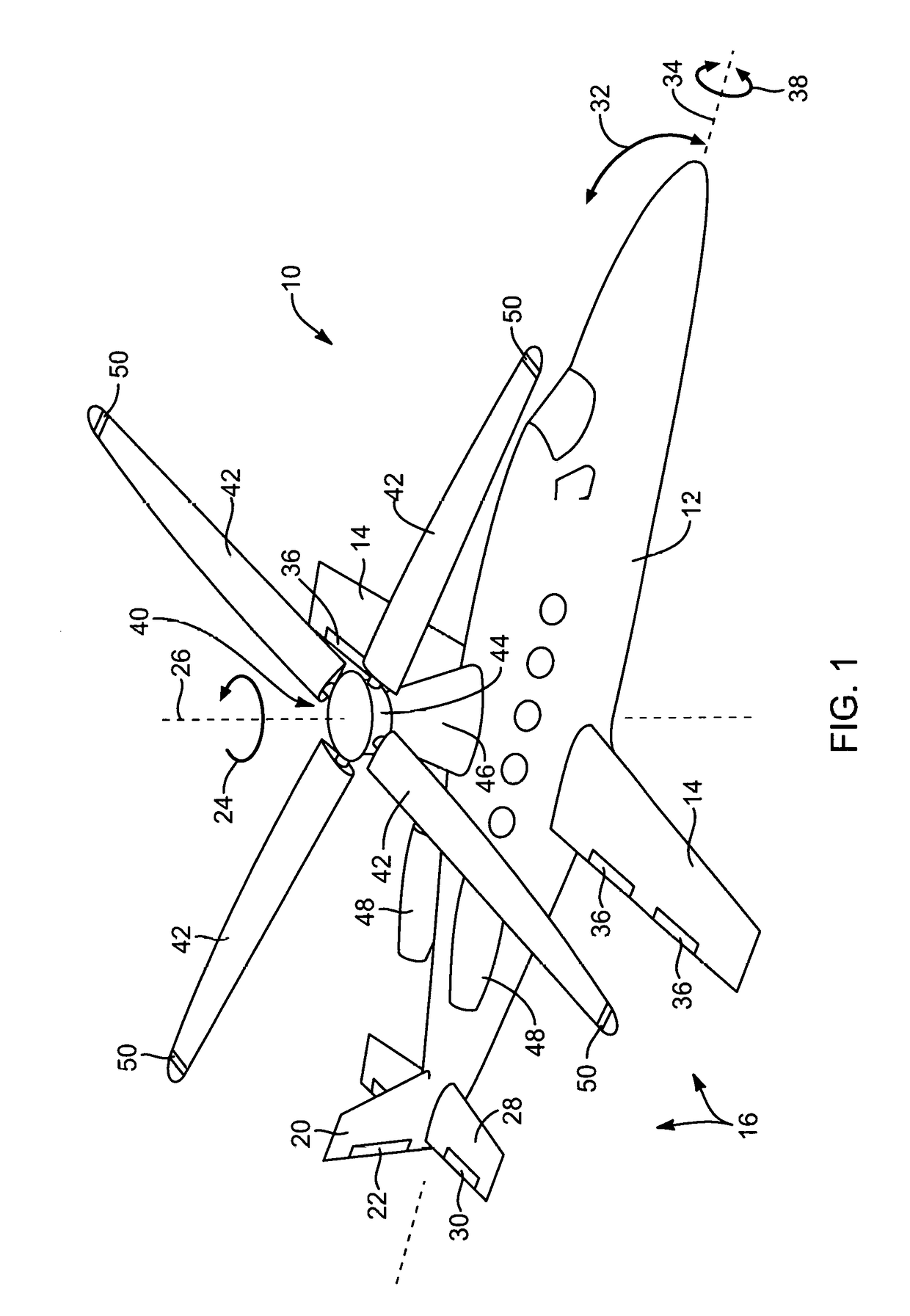
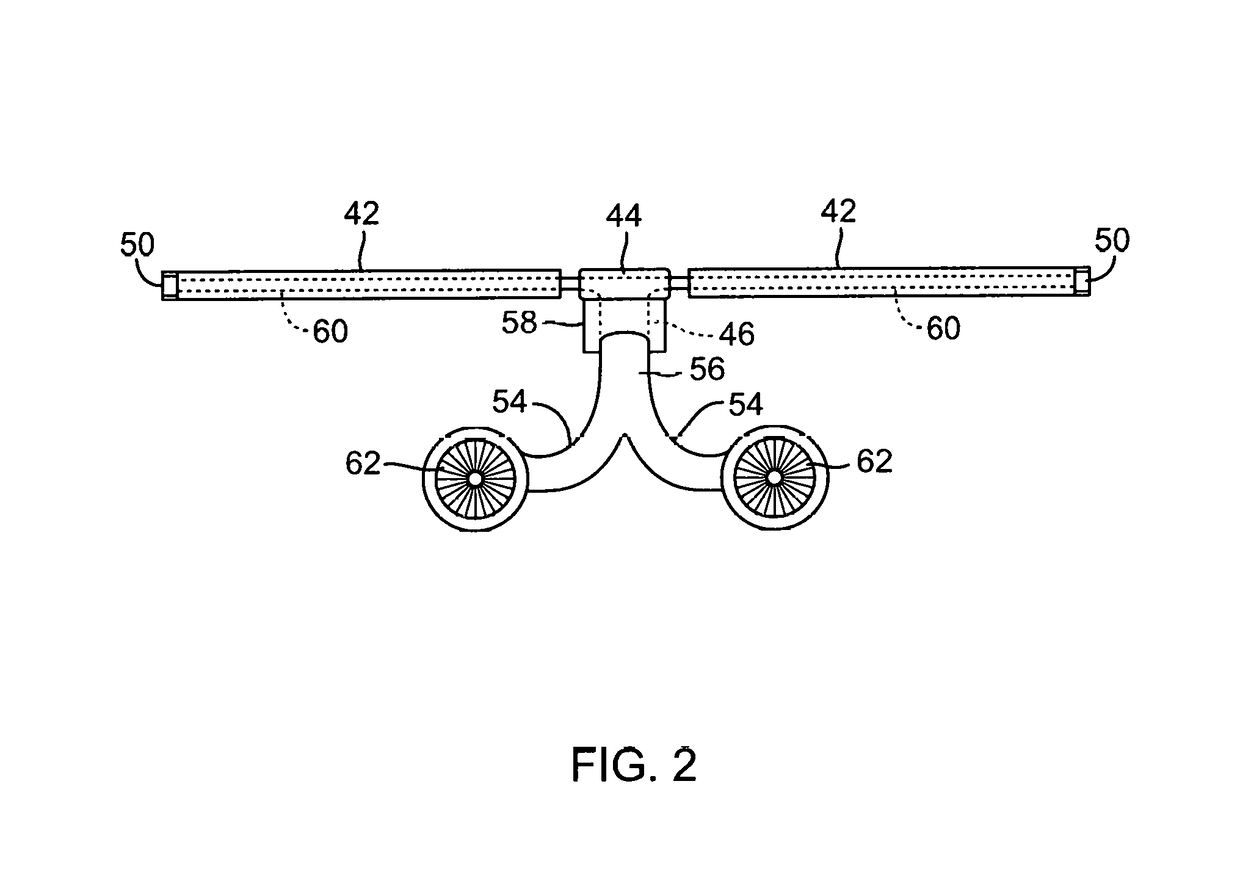
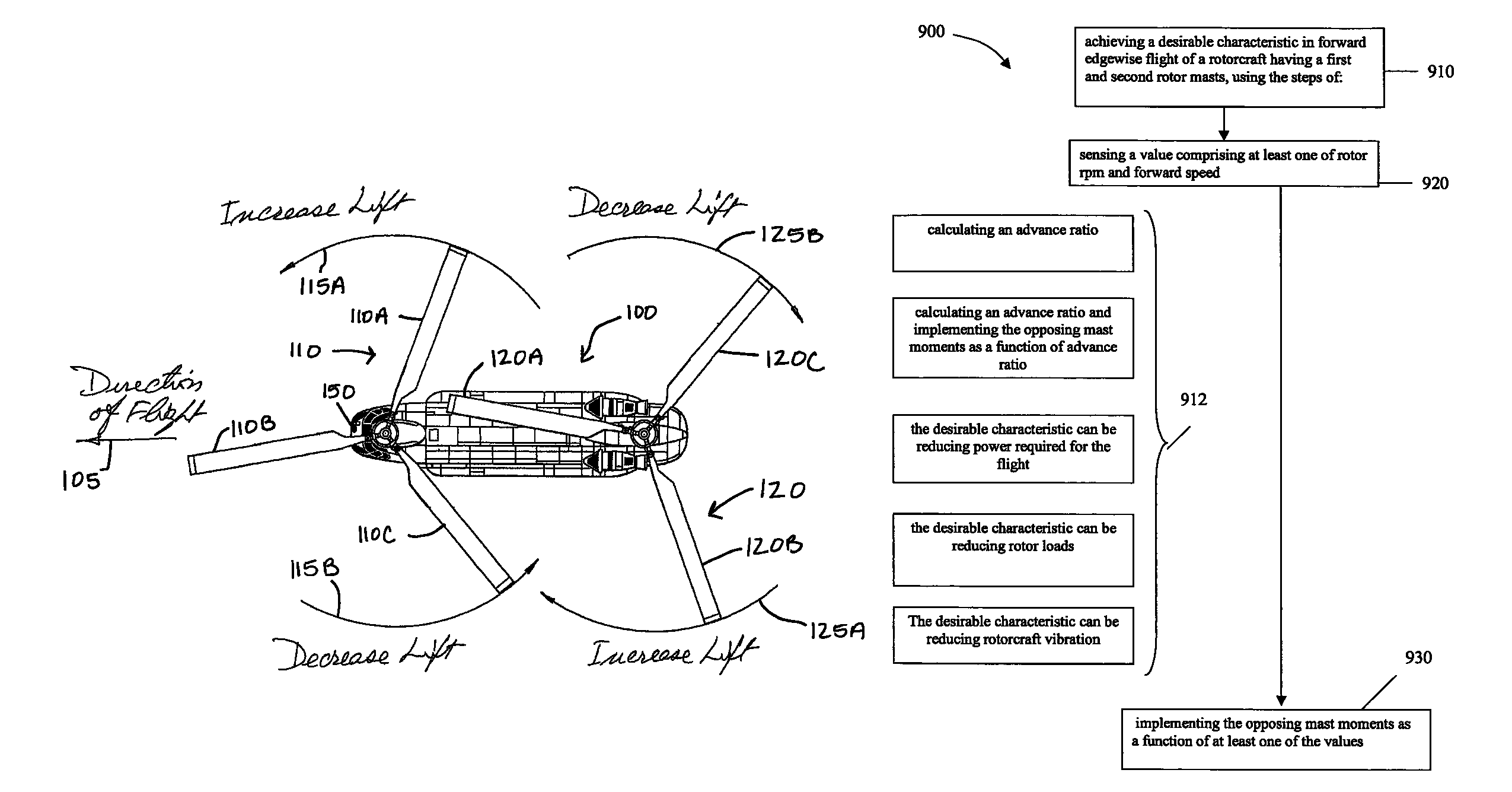
Rotorcraft with opposing roll mast moments, and related methods
ActiveUS20100270422A1High rotor gearboxHigh airframe reliabilityPropellersDigital data processing detailsRolling momentRotary wing
In rotorcraft having rotors on multiple masts, a controller causes opposing roll mast moments to be applied to the different rotors. In preferred embodiments, the opposing roll moment is the result of increasing the lift on the advancing blade and reducing the lift on the retreating blade on the second rotor. This can be accomplished in any suitable manner, such as by applying differential cyclic roll control to the two rotors by tilting the two Swashplates of the two rotors or by using Individual Blade Control (IBC).
Owner:KAREM ABE
Air-vehicle integrated kinesthetic control system
A lift platform with a kinesthetic control system that is coupled to means for altering air flow through the first and second longitudinally-spaced ducts comprising the lift platform is provided. The control system includes a control handle bar with left and right hand grips, and first and second control roll bars located on either side of the lift platform's central cowling. Forward / rearward movement of the control handle bar from a neutral position generates nose-down / nose-up pitching moments, respectively; counterclockwise / clockwise movement of the control handle bar from the neutral position generates counterclockwise rotation / clockwise rotation of the lift platform about a lift platform vertical centerline; and left movement / right movement of the control roll bars generates left roll / right roll moments about the lift platform roll axis.
Owner:AEROFEX
Mass transfer system for stabilizing an airship and other vehicles subject to pitch and roll moments
The invention relates to a mechanism to control the pitch and / or roll and / or center of gravity of a vehicle. The first embodiment is a track-based mass transfer system in which pathways are positioned along or radially terminate at a central horizontal plane of the vehicle to move one or more mass transfer devices to a desired location to control the pitch and / or roll and / or center of gravity of the vehicle. A second embodiment is a fluid mass distribution system in which one or more conduits selectively distribute a fluid to one or more tanks positioned near a central horizontal plane of the vehicle to control the pitch and / or roll and / or center of gravity of the vehicle.
Owner:LTAS HLDG
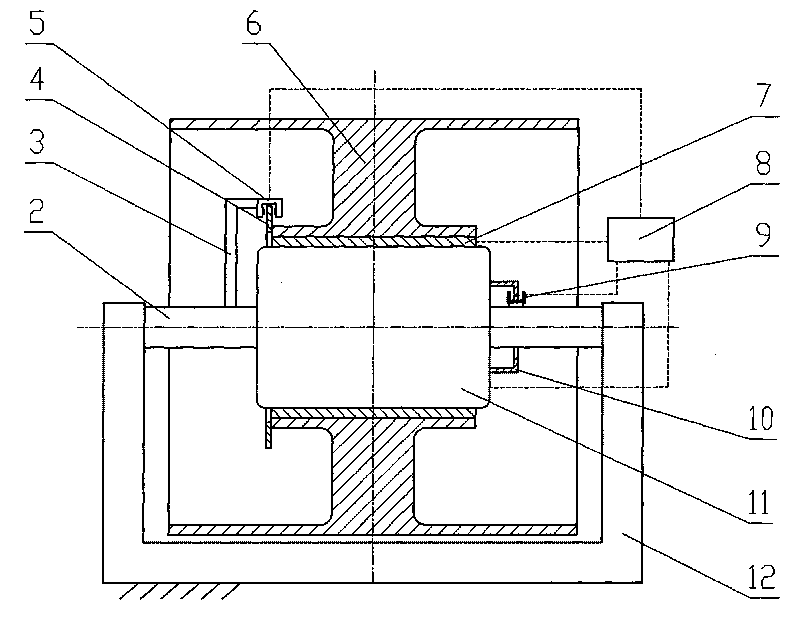
Disc brake apparatus
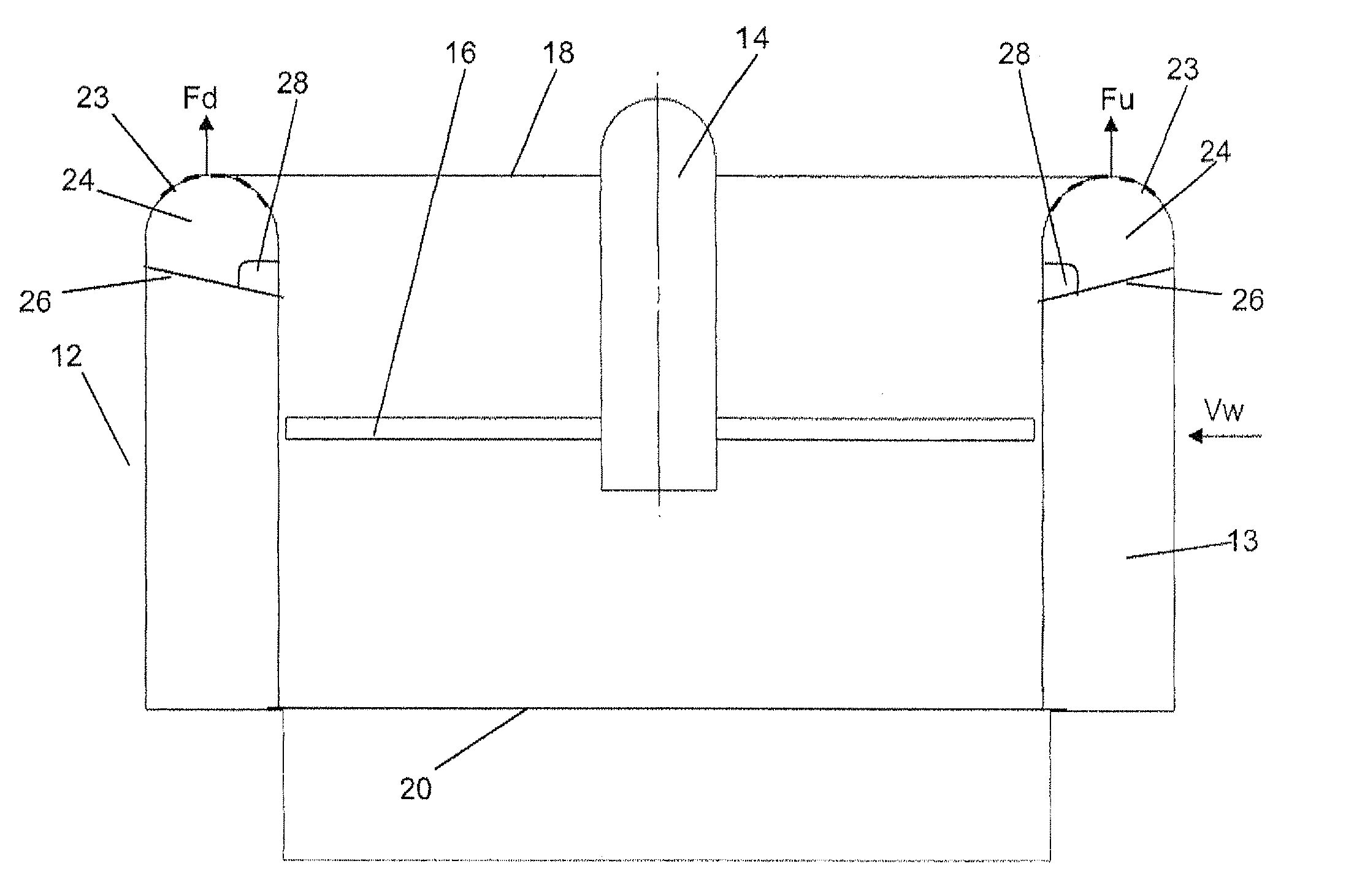
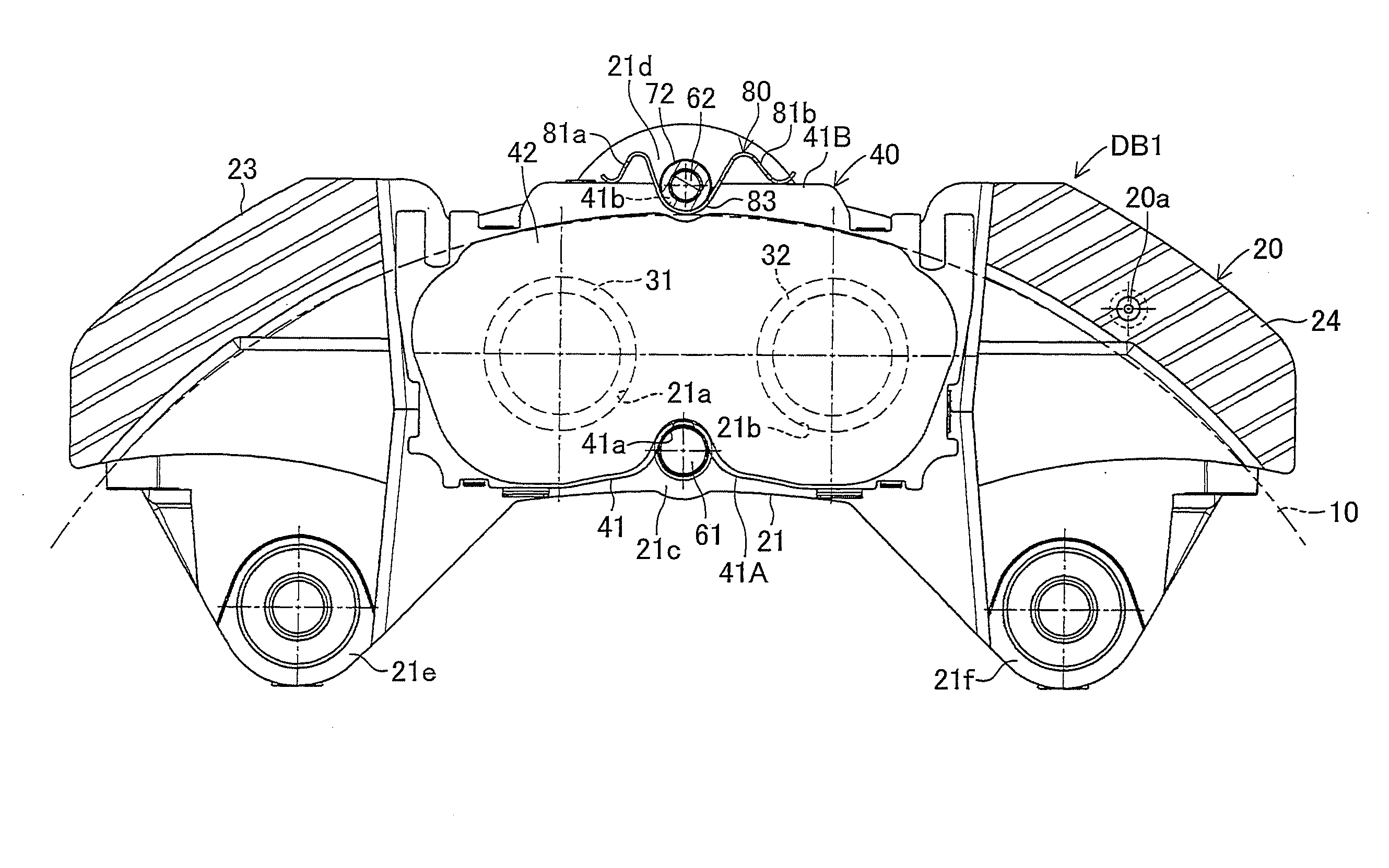
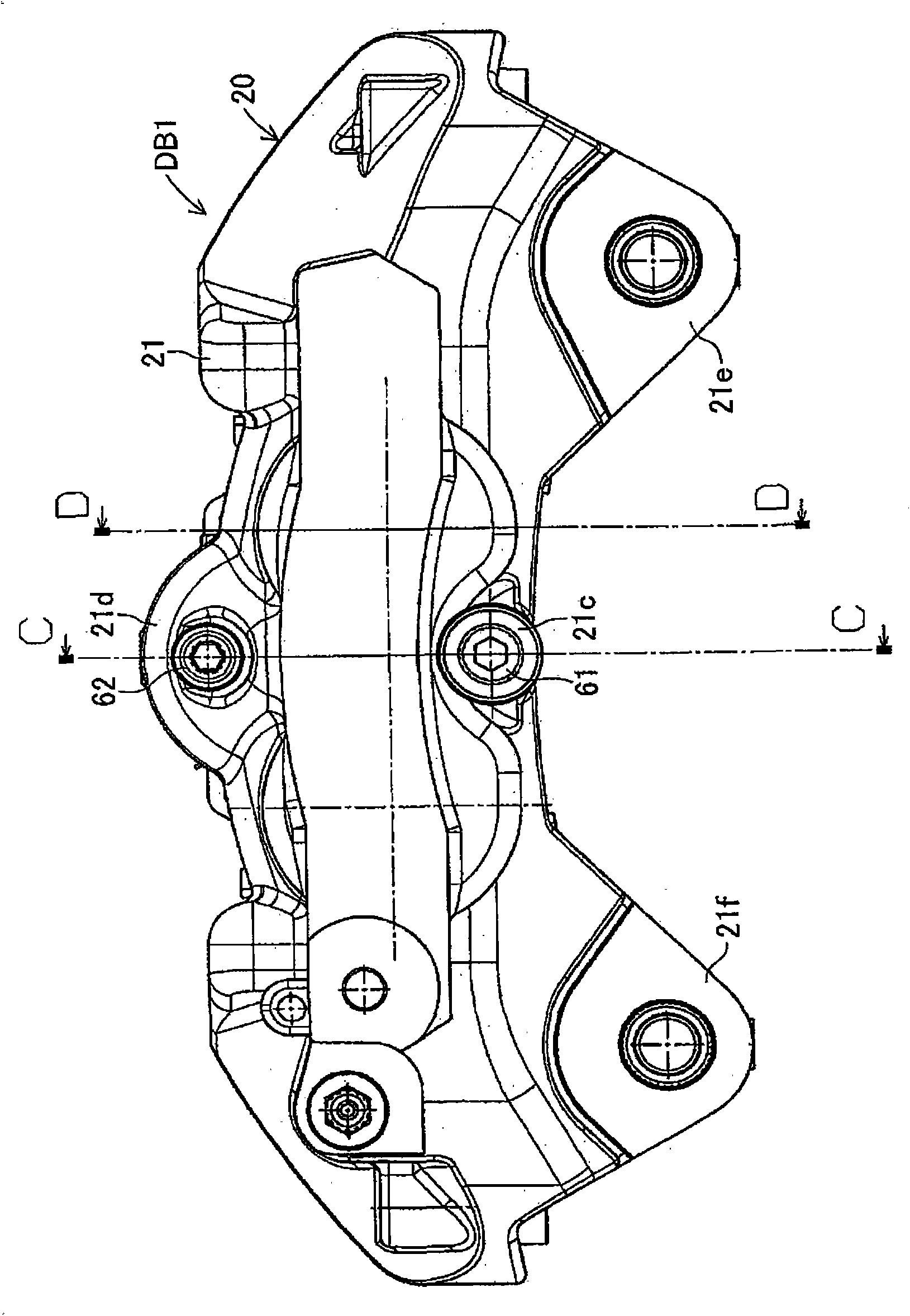
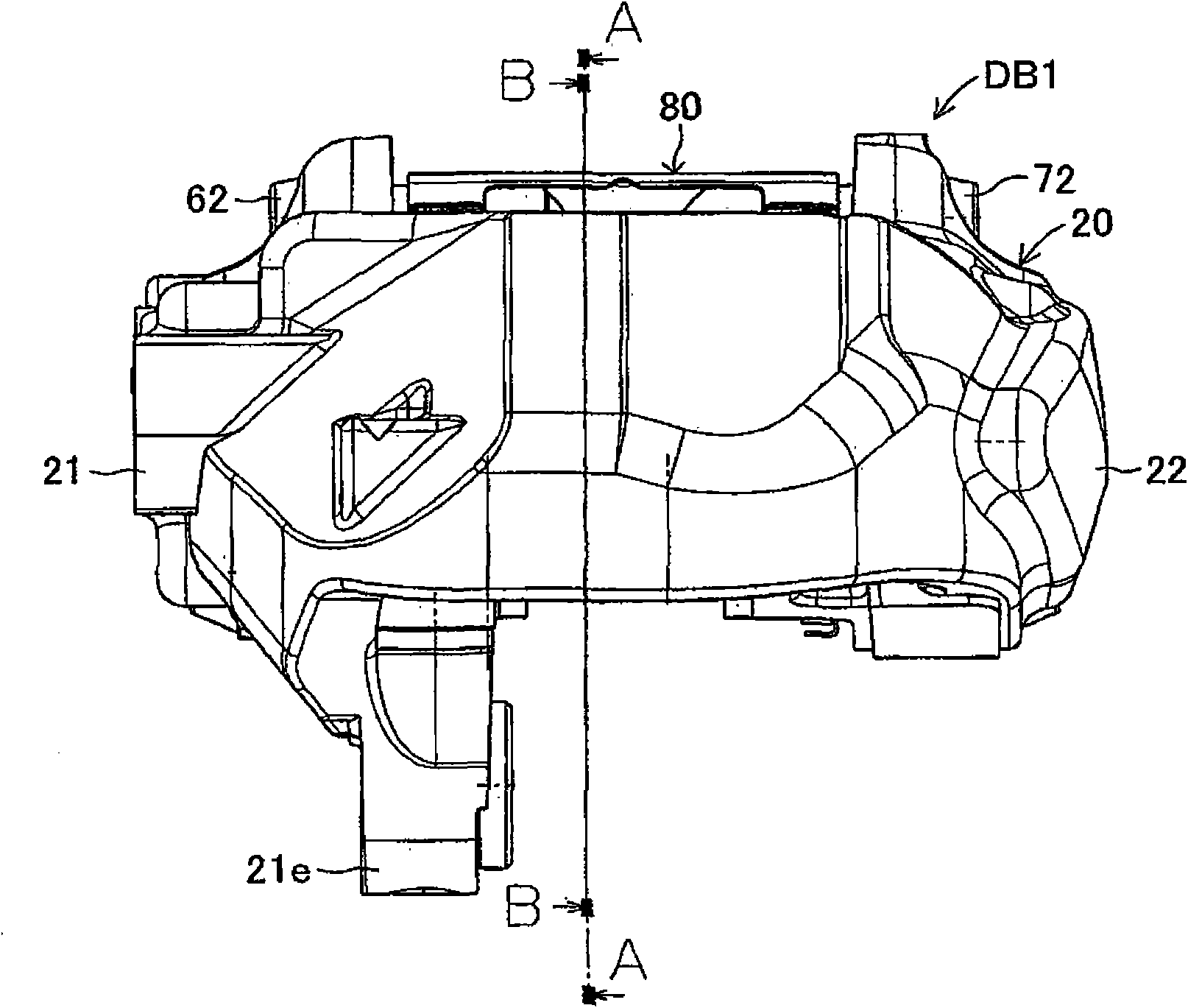
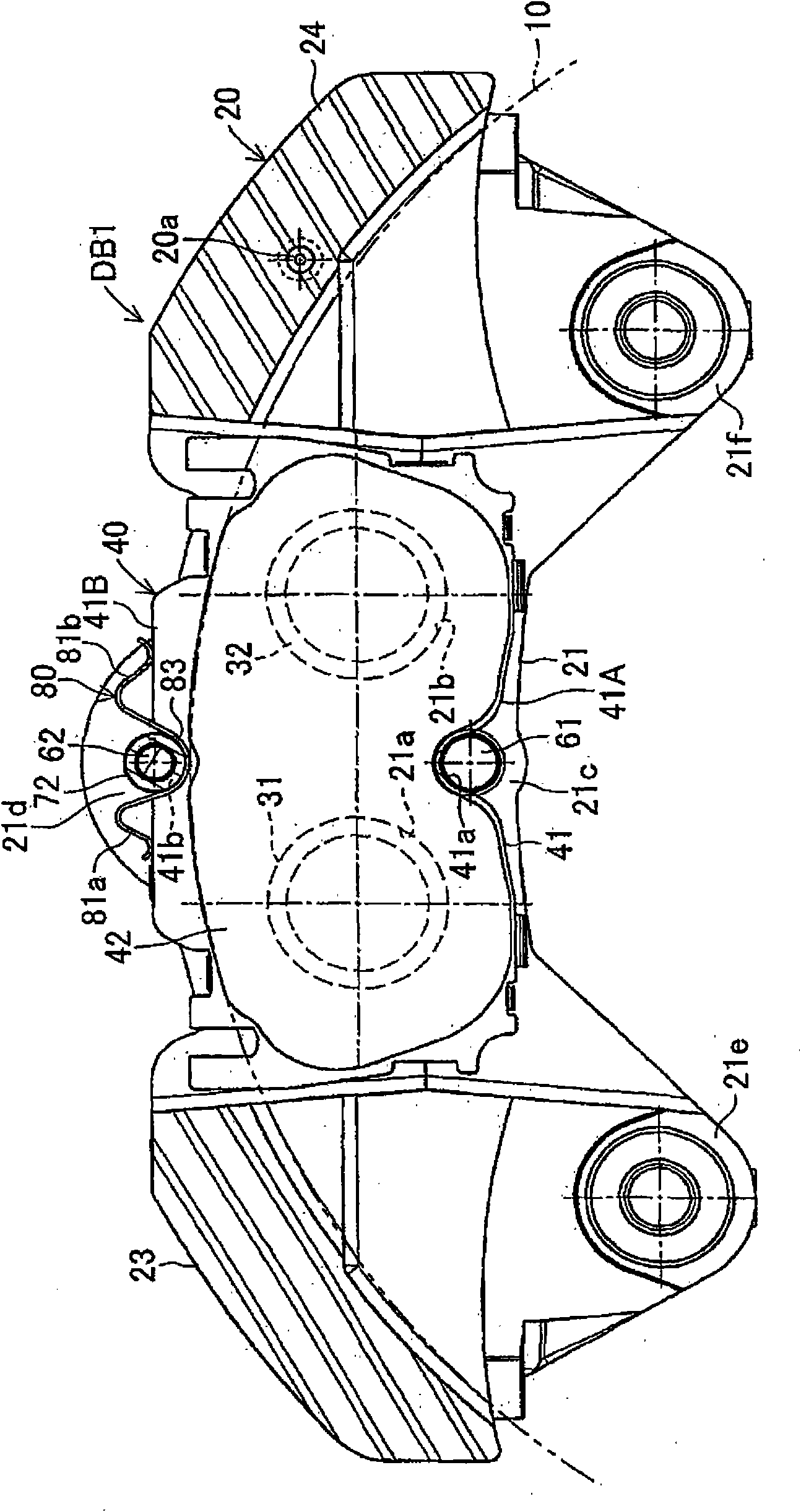
InactiveUS20100243384A1Suppress generation of brake noiseReduce processing costsAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsRolling momentAbutment
The present invention is to stabilize behavior of brake pads at the time of braking of a disc brake so as to suppress generation of brake noise, and also to reduce the roll moment of the brake pads generated at the time of braking so as to suppress uneven abrasion of linings. A back plate (41) of a brake pad (40) is biased inward in the rotor radial direction by a plate spring (80). The back plate (41) is engaged at two points with an inner periphery support shaft (61) provided integrally with a caliper (20) on a V-shape inner peripheral abutment (41a) (provided in the back plate (41) on the inner side of a lining (42) in the rotor radial direction and on the center in the rotor circumferential direction), and engaged at one point with an outer periphery support shaft (62) provided integrally with the caliper (20) on an outer peripheral abutment (41b) (provided in the back plate (41) on the outer side of the lining (42) in the rotor radial direction and on the center in the rotor circumferential direction).
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
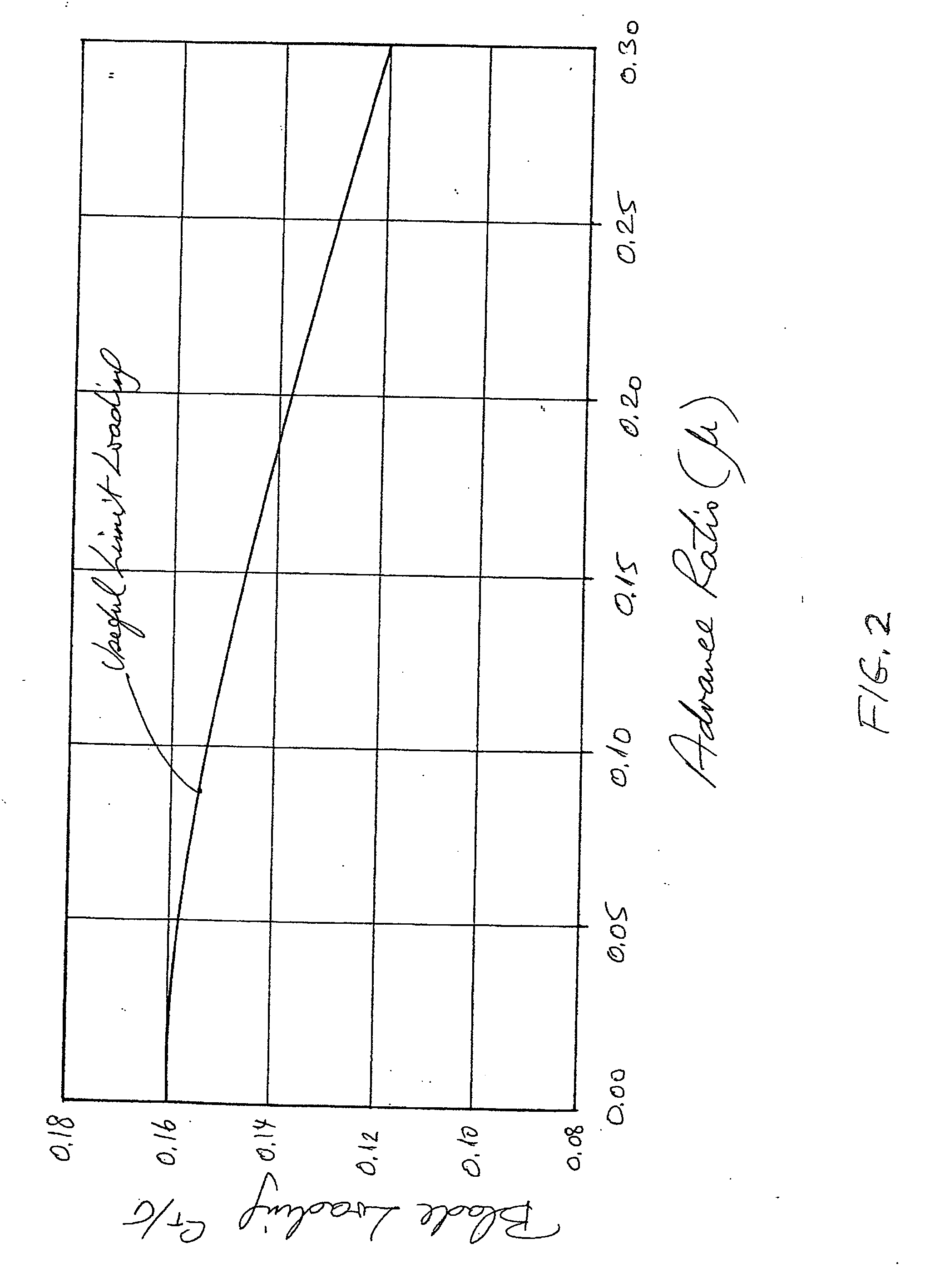
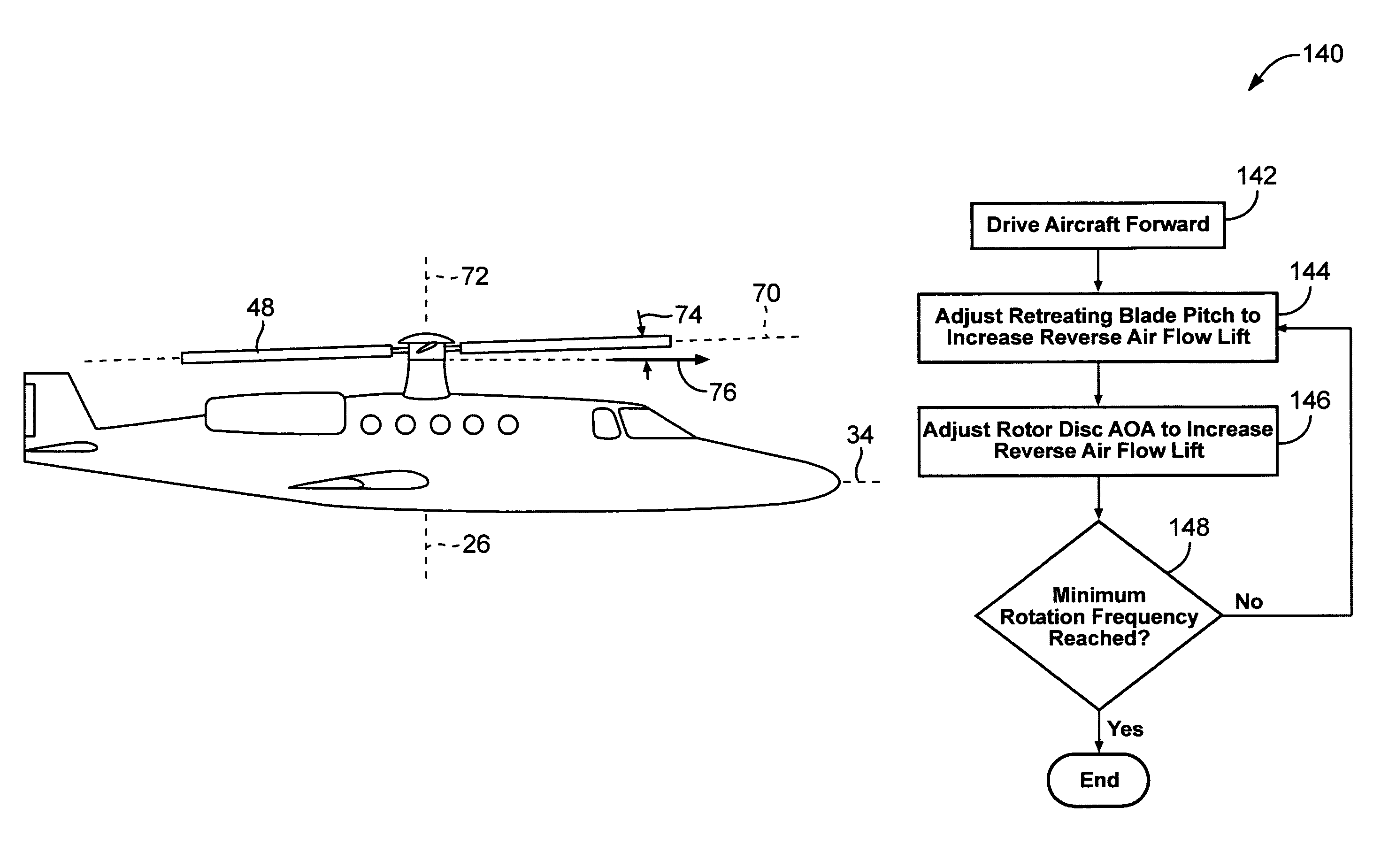
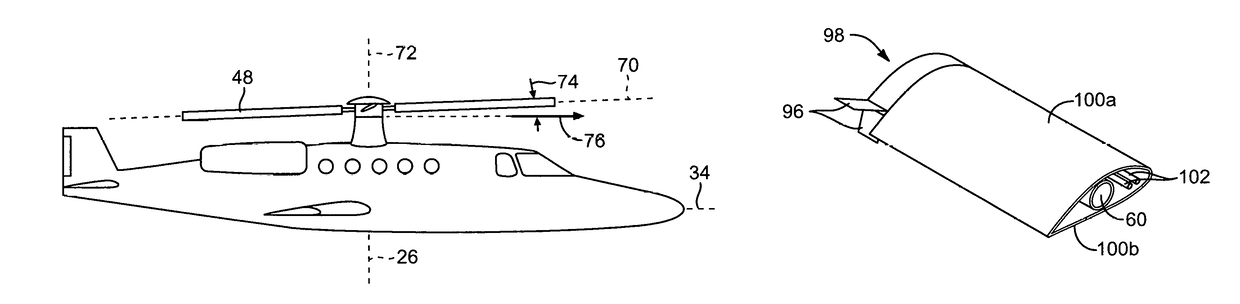
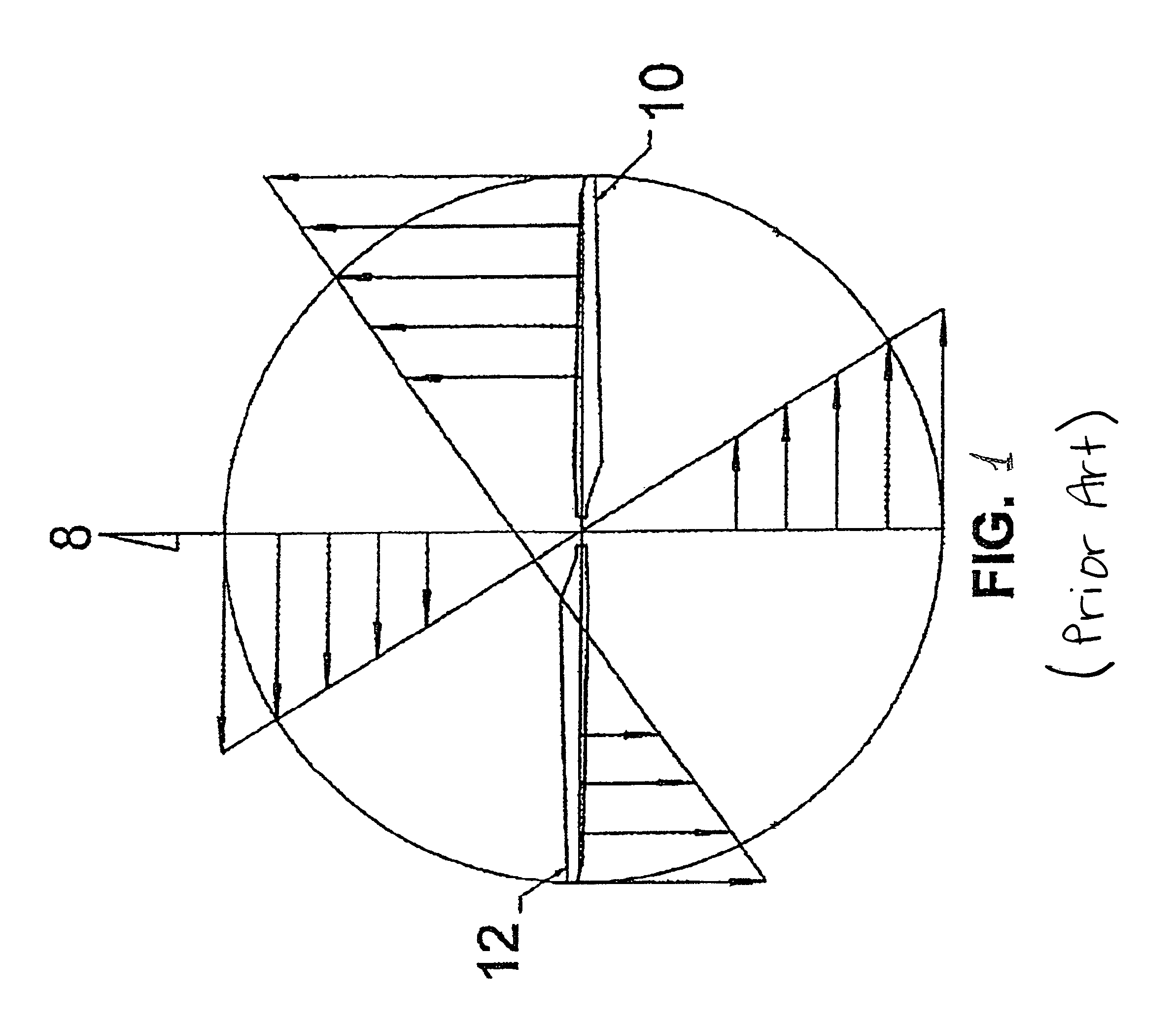
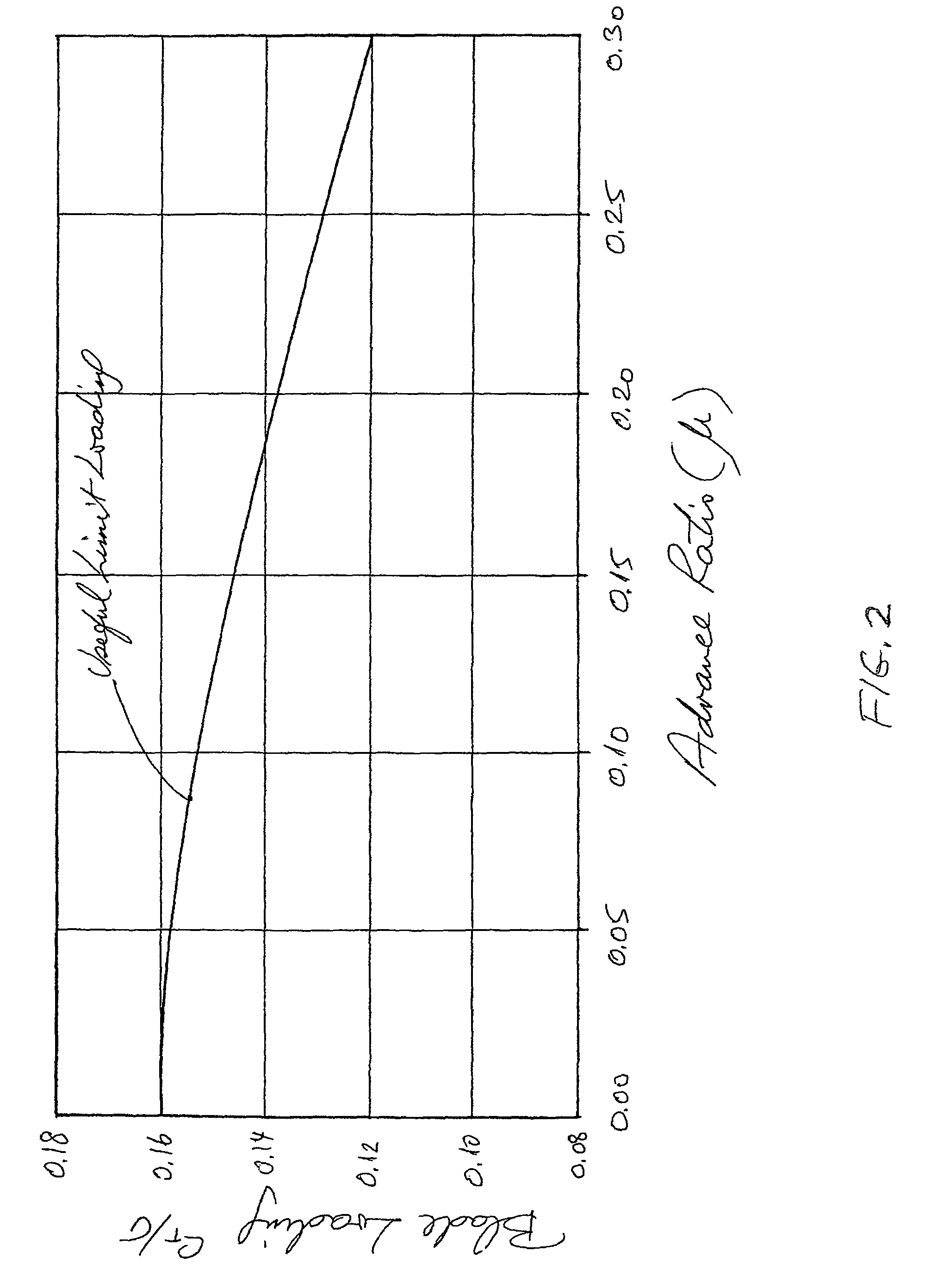
Apparatus and method for roll moment equalization at high advance ratios for rotary wing aircraft
Owner:SKYWORKS GLOBAL INC
Apparatus and method for roll moment equalization at high advance ratios for rotary wing aircraft
A method for equalizing rolling moments at high advance ratios is disclosed including impelling an aircraft in a forward direction at an airspeed by means of a thrust source and rotating a rotor of the aircraft at an angular velocity with respect to the airspeed effective to cause a positive total lift on each blade due to air flow over the blades in the retreating direction when the blade is moving in the retreating direction. The rotor includes an even number of blades placed at equal angular intervals around the rotor hub. One or both of cyclic pitch and rotor angle of attack are adjusted such that a rolling moment of the retreating blade due to reverse air flow is between 0.3 and 0.7 times a rolling moment on the advancing blade due to lift.
Owner:SKYWORKS GLOBAL INC
Automobile kinetics dynamical property test system based on integrated rollers
InactiveCN101762394ASimple structureCompact layoutVehicle testingMeasurement of force componentsControl systemTangential force
The invention discloses an automobile kinetics dynamical property test system based on integrated rollers. The system is composed of a measurement and control system and a plurality of integrated rollers; the number and arrangement of the integrated rollers are determined by automobile type and test requirement, each integrated roller consists of a central shaft, a brake fixing bracket, a brake disc, a floating-caliper brake, a roller, a six-component sensor, a rotation speed sensor, a code disc, an external rotor electric machine and a bracket. The invention has the beneficial effects that the six-component sensor is used for measuring tangential force, axial force, vertical force, turning moment, moment resulting from sideway and yawing moment to realize measurement on tyre longitudinal force, yawing force, vertical load, turning moment, moment resulting from sideway and aligning torque, and that the test system has the advantages of simple and compact structure, reduced installation space and the like. The attached drawings are diagrammatic drawings for structure of the integrated rollers and connection between the integrated rollers and the measurement and control system.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Vehicle suspension system with roll stiffness distribution control
ActiveUS7725226B2Prevent and suppress undesirable changePrevents and suppresses undesirable changeDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesDistribution controlEngineering
In a target rotational angle determining routine, based on a roll moment and longitudinal acceleration that are calculated, target rotational angles of actuators on a subject side (one of front-wheel and rear-wheel sides) and a counterpart side are obtained using a common map. An actual rotational angle on the counterpart side is read. It is determined whether the absolute value of a difference obtained by subtracting the actual rotational angle supplied from the counterpart side from the target rotational angle on the counterpart side that is obtained by the subject side is equal to or greater than a set angle difference Δθ0. If YES, it is determined that roll stiffness on the counterpart side is insufficient, and the target rotational angle on the subject side is changed so that a roll stiffness distribution ratio between the front-wheel side and the rear-wheel side comes close to a set distribution ratio.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Roll rigidity controller of vehicle
Roll rigidity of a vehicle is controlled optimally regardless of the situation of turning motion of the vehicle by estimating the transverse acceleration of the vehicle at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position, and controlling a roll rigidity varying means at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position by a controlled variable based on the transverse acceleration thus estimated. Target roll angle of the vehicle is operated based on the actual transverse acceleration of the vehicle at the center of gravity, and transverse acceleration of the vehicle at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position is operated by correcting the transverse acceleration of the vehicle at the center of gravity by a correction amount of transverse acceleration based on the yaw rate of the vehicle. Thereafter, target anti-roll moments at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position are operated based on the target roll angle and the acceleration of the vehicle at the front wheel position and the rear wheel position, and the active stabilizers of the front wheel and the rear wheel are controlled based on these target anti-roll moments.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
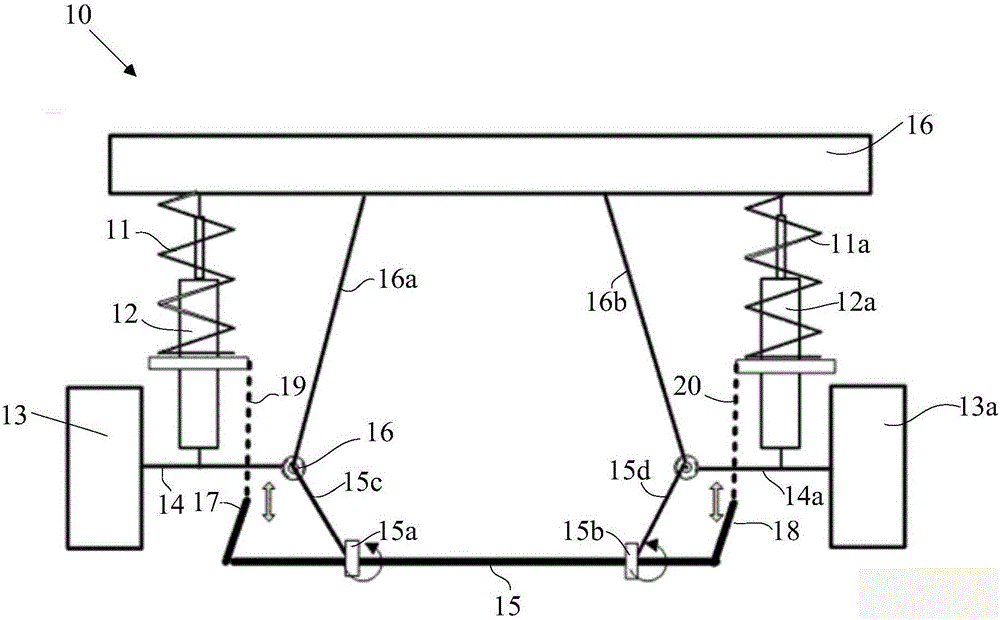
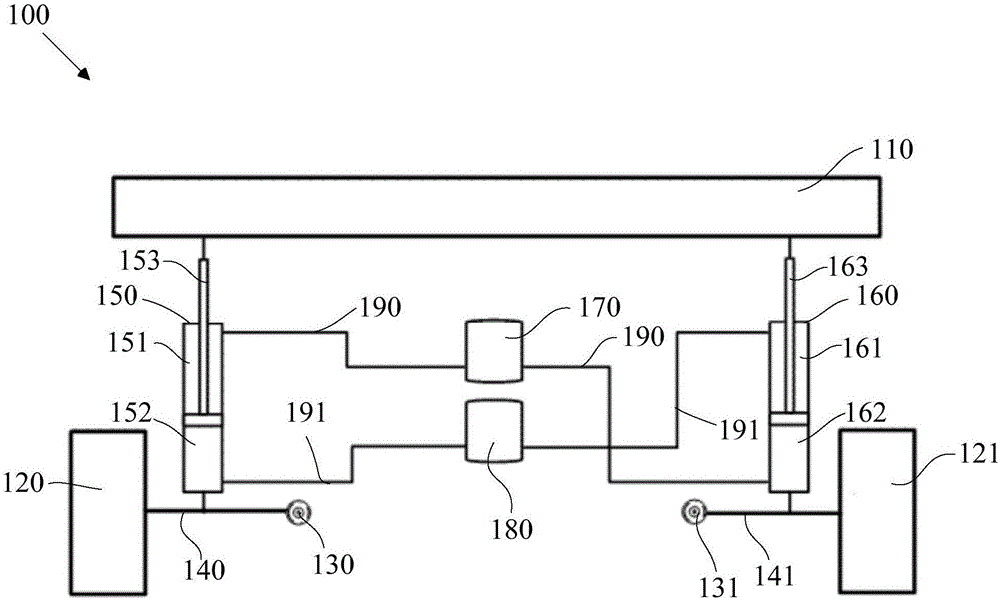
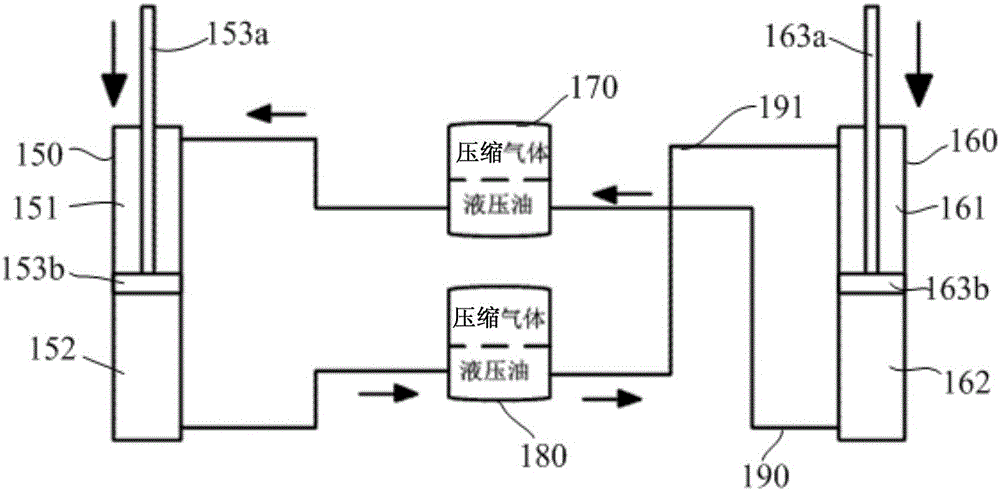
Automobile against side-roll stabilizing device and suspension system and automobile
An automobile against side-roll stabilizing device and suspension system and automobile, wherein the automobile against side-roll stabilizing device includes a first hydraulic pressure cylinder and a second hydraulic pressure cylinder, respectively used for being installed inside a left automobile wheel and inside a right automobile wheel; the push rods of the first hydraulic pressure cylinder, one of the bottom ends of the push rods is connected with a sprung mass, the other is connected with an unsprung mass; the push rods of the second hydraulic pressure cylinder, one of the bottom ends of the push rods is connected with the sprung mass, the other is connected with the unsprung mass; the device also includes a first oil gas chamber and a second oil gas chamber, the lower parts of the first oil gas chamber and the second oil gas chamber are hydraulic pressure oil, the upper parts are compressed gases. When the beat amplitudes of the left wheel and the right wheel are inconsistent, the push rods inside the first hydraulic pressure cylinder and the second hydraulic pressure cylinder apply forces to the automobile body in varying directions, the forces from varying directions produce an anti side roll moment, obstructing the automobile to further side roll.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
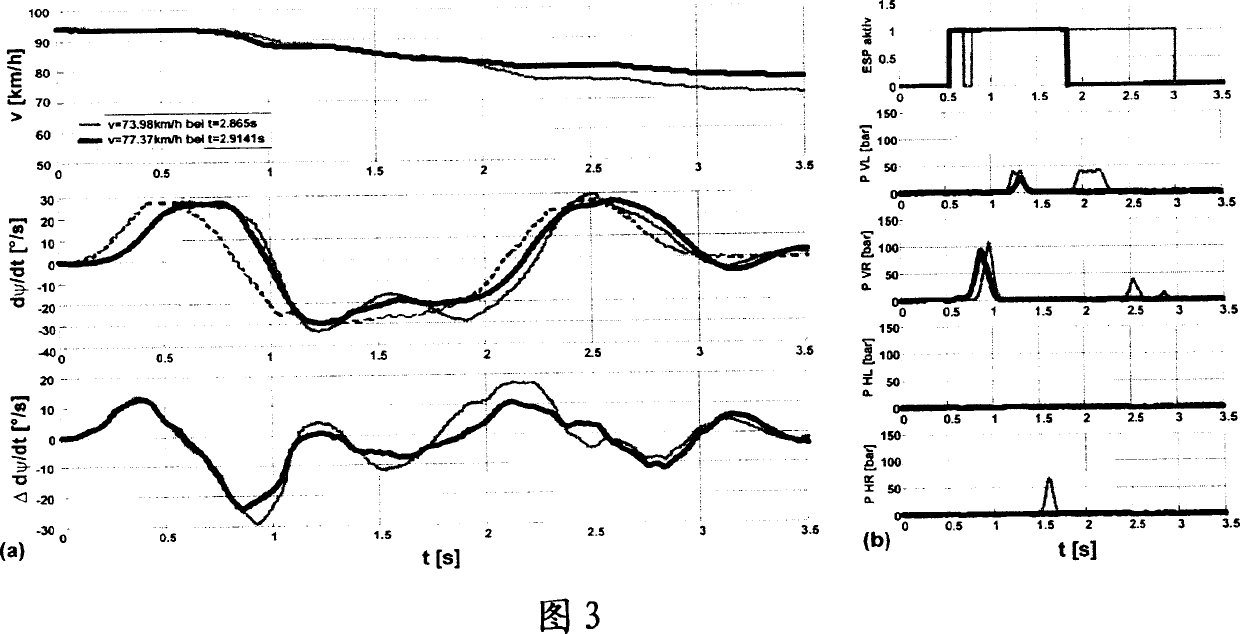
Method for regulating the driving dynamics of a vehicle, device for carrying out the method and use thereof
The invention relates to a method for regulating the driving dynamics of a vehicle, wherein a setpoint ( ) of a driving state variable corresponding to a value specified by the driver is compared with a detected actual value ( ) of the driving state variable Compare, and detect and change roll moment distribution. The method is carried out in this way, a. by comparing the given value ( ) of the driving state parameter with the actual value ( ) of the driving state parameter to determine the driving performance of the vehicle; b. A new roll moment distribution for a given driving performance; c. Adjust the new roll moment distribution. The invention also relates to a device for regulating the driving dynamics of a vehicle having means for the roll moment support on the front and rear axles of the vehicle and for detecting at least one driving state variable ( ) of the vehicle A sensor, the device is suitable for carrying out the method. The device can advantageously be used in systems for yaw moment compensation (ESP).
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE TECH GMBH
Method and apparatus for detecting rollover of an automotive vehicle based on a lateral kinetic energy rate threshold
InactiveUS7702440B2Reduce the numberLess timeDigital data processing detailsStatic/dynamic balance measurementRolloverControl signal
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Disc brake apparatus
ActiveCN101852256ASuppress tremorShock suppressionAxially engaging brakesBraking elementsRolling momentAbutment
The present invention is to stabilize behavior of brake pads at the time of braking of a disc brake so as to suppress generation of brake noise, and also to reduce the roll moment of the brake pads generated at the time of braking so as to suppress uneven abrasion of linings. A back plate (41) of a brake pad (40) is biased inward in the rotor radial direction by a plate spring (80). The back plate (41) is engaged at two points with an inner periphery support shaft (61) provided integrally with a caliper (20) on a V-shape inner peripheral abutment (41a) (provided in the back plate (41) on the inner side of a lining (42) in the rotor radial direction and on the center in the rotor circumferential direction), and engaged at one point with an outer periphery support shaft (62) provided integrally with the caliper (20) on an outer peripheral abutment (41b) (provided in the back plate (41) on the outer side of the lining (42) in the rotor radial direction and on the center in the rotor circumferential direction).
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Rotorcraft with opposing roll mast moments, and related methods
ActiveUS8128034B2High acceptanceReduce areaActuated automaticallyVehicle position/course/altitude controlRolling momentRotary wing
In rotorcraft having rotors on multiple masts, a controller causes opposing roll mast moments to be applied to the different rotors. In preferred embodiments, the opposing roll moment is the result of increasing the lift on the advancing blade and reducing the lift on the retreating blade on the second rotor. This can be accomplished in any suitable manner, such as by applying differential cyclic roll control to the two rotors by tilting the two Swashplates of the two rotors or by using Individual Blade Control (IBC).
Owner:KAREM ABE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com