Patents
Literature
150 results about "Plasma actuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
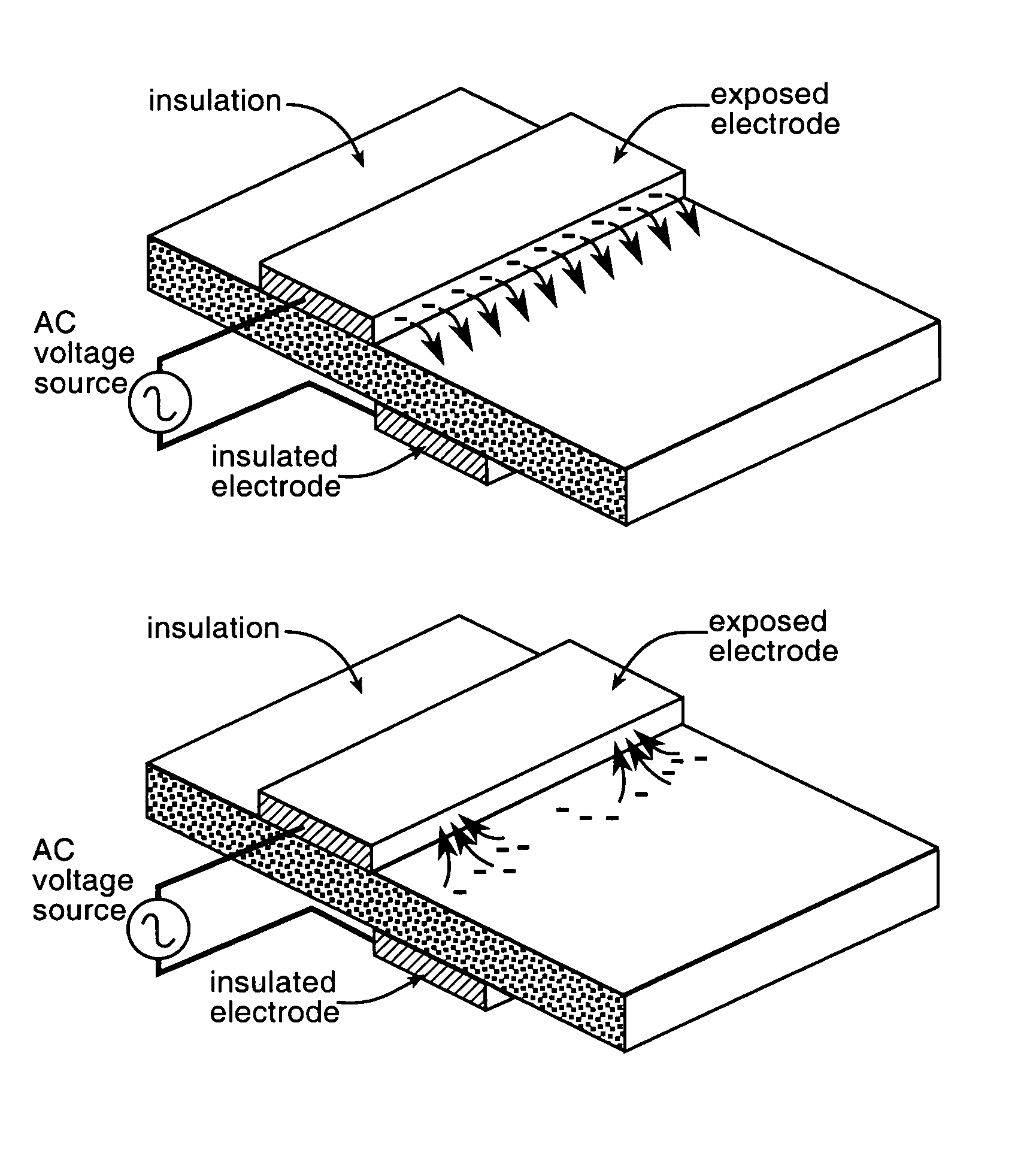
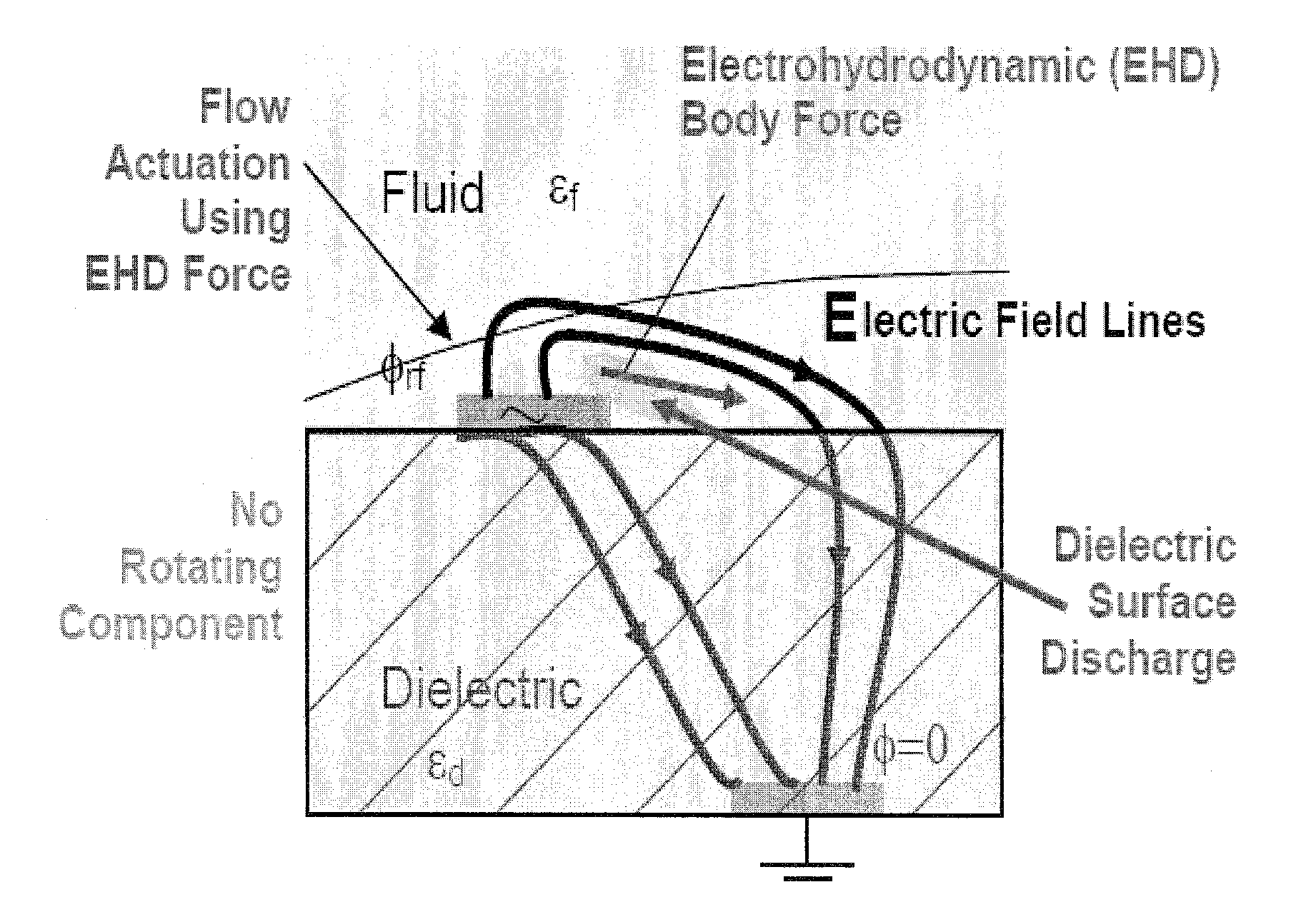
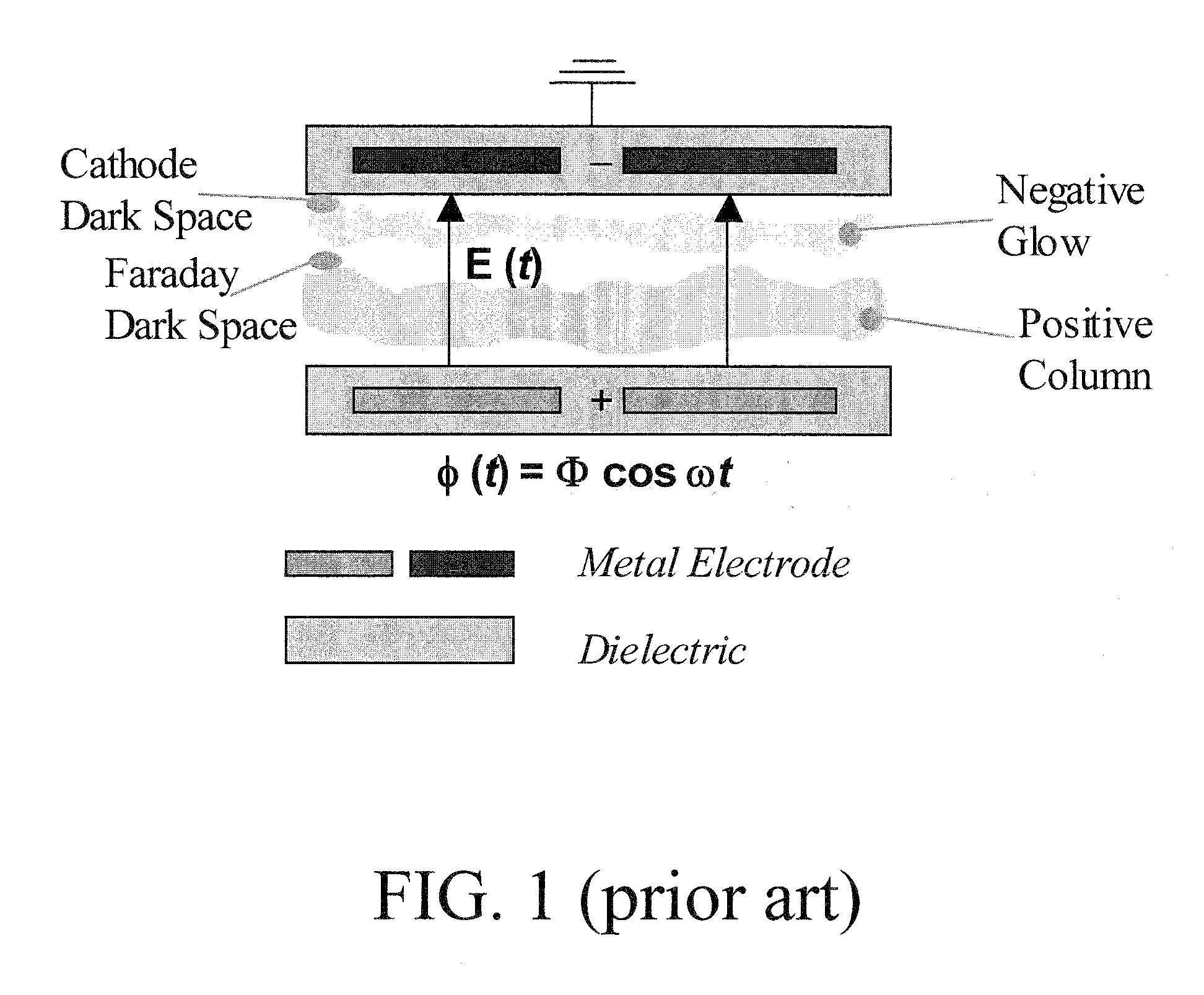
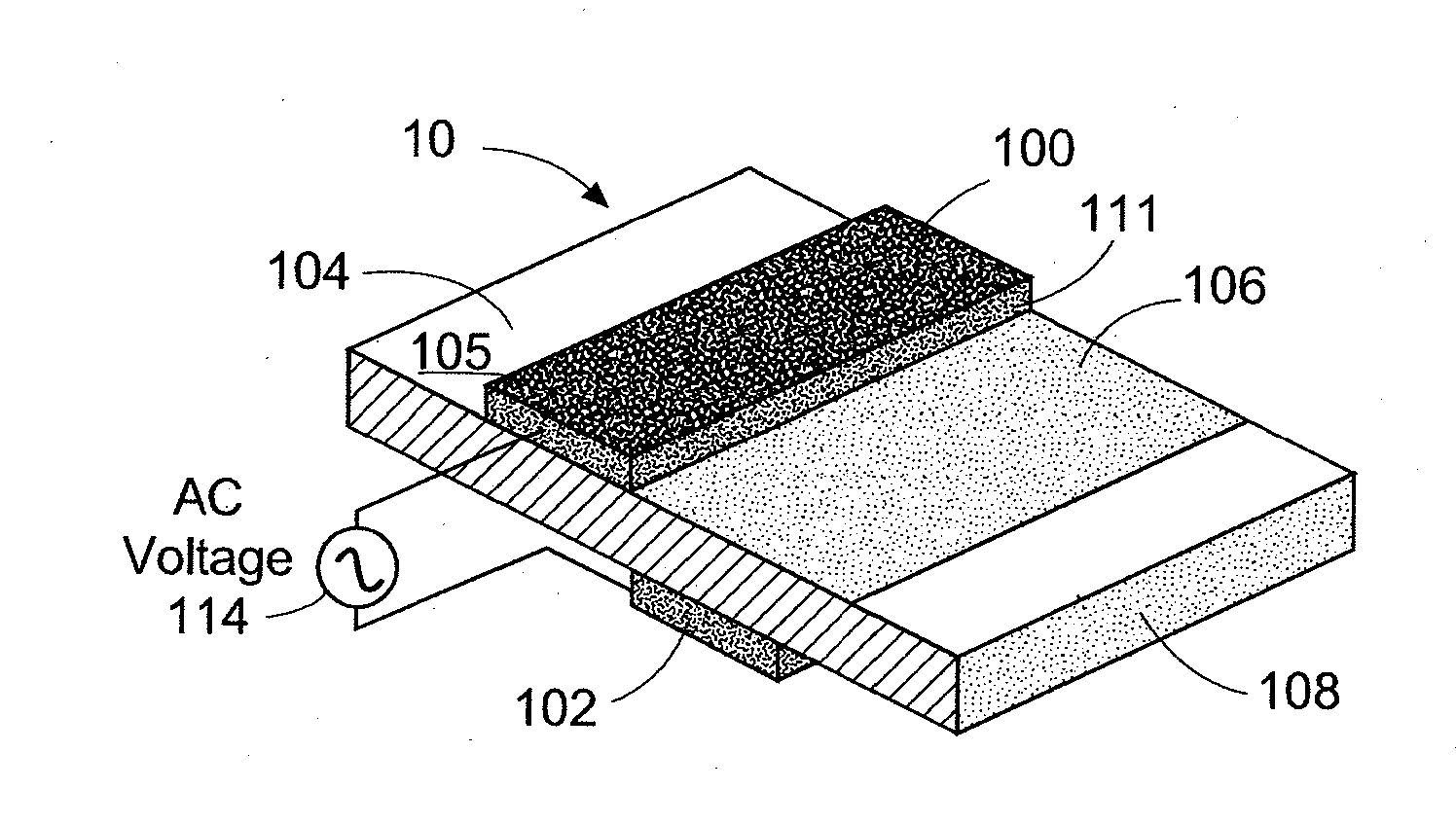
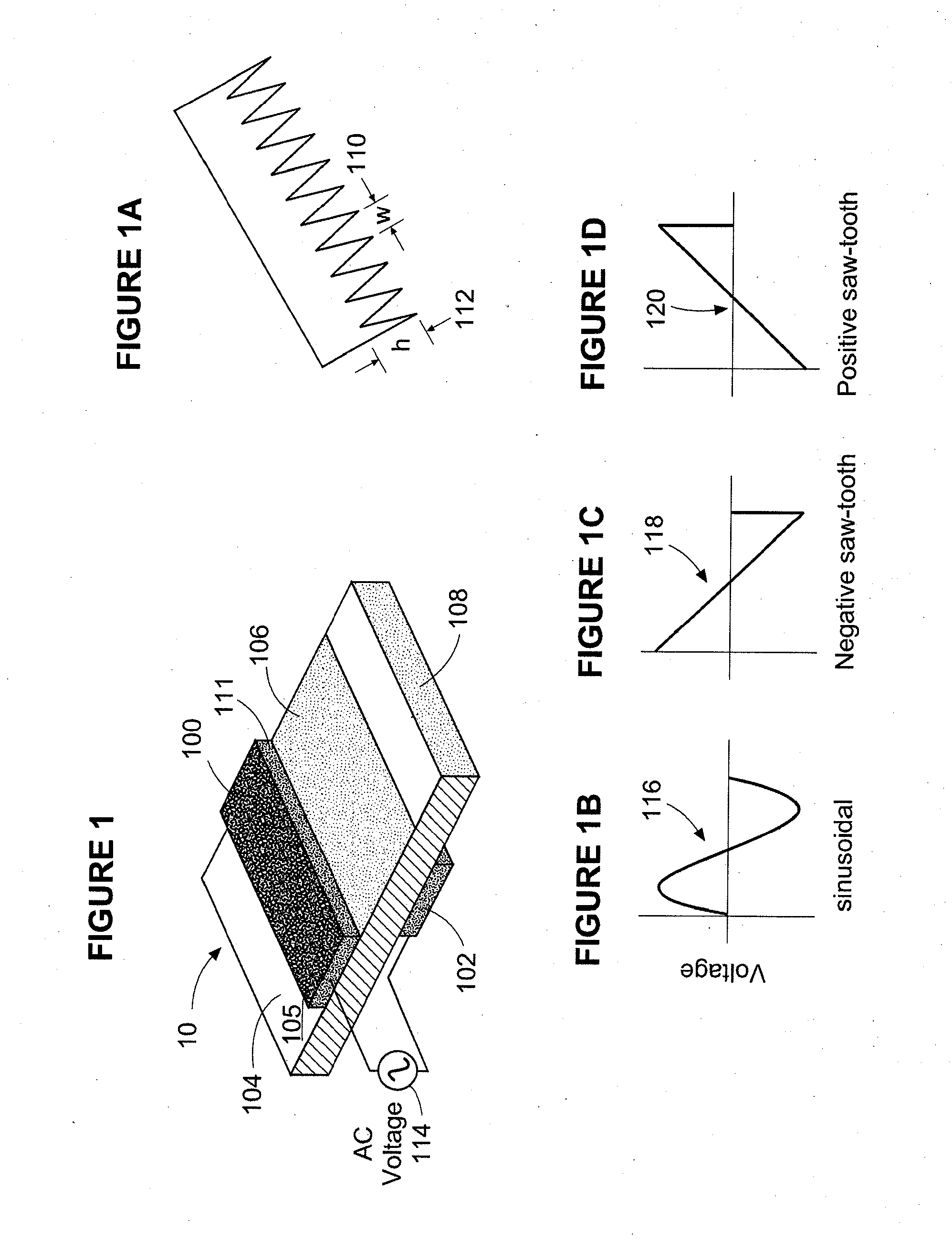
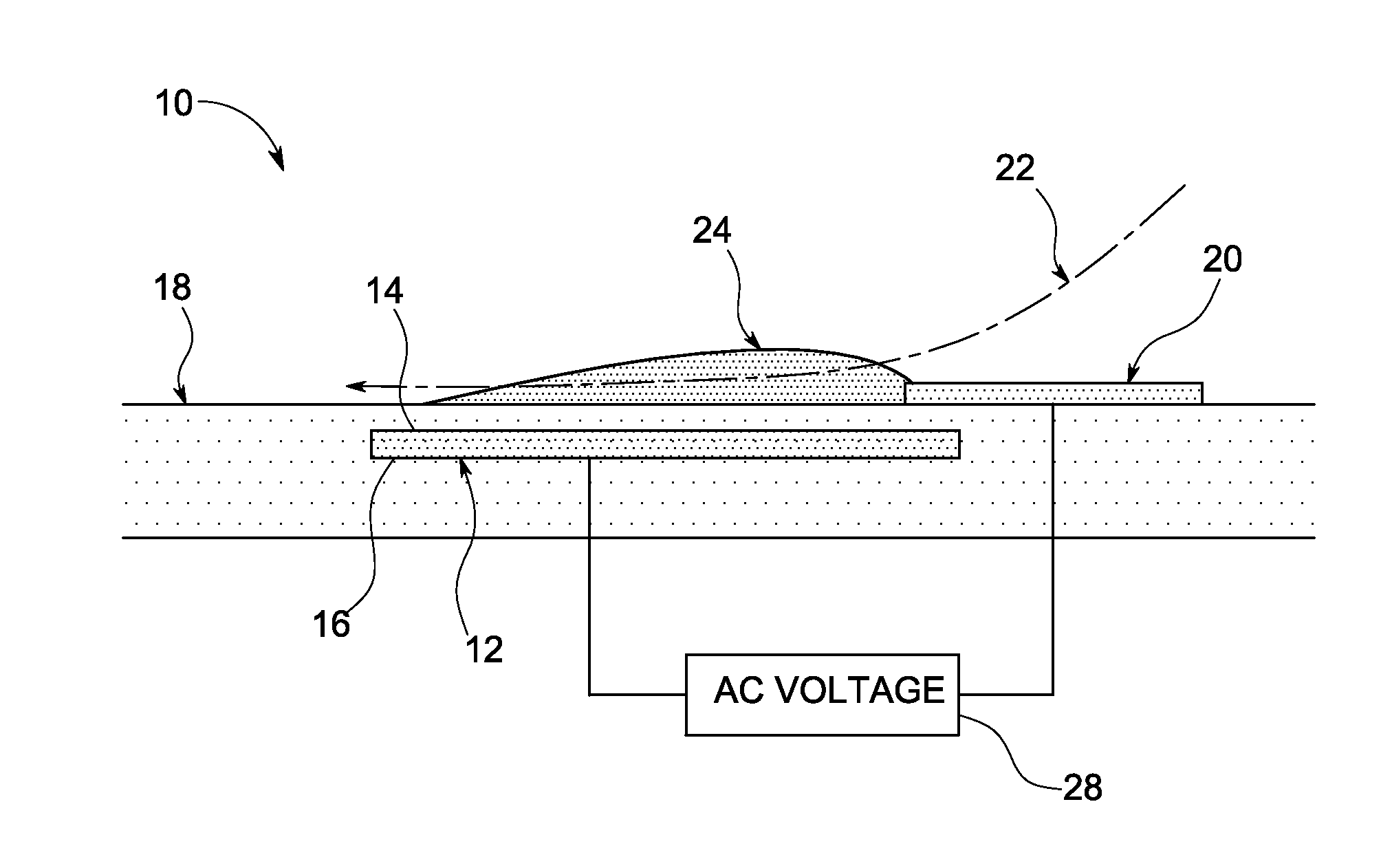
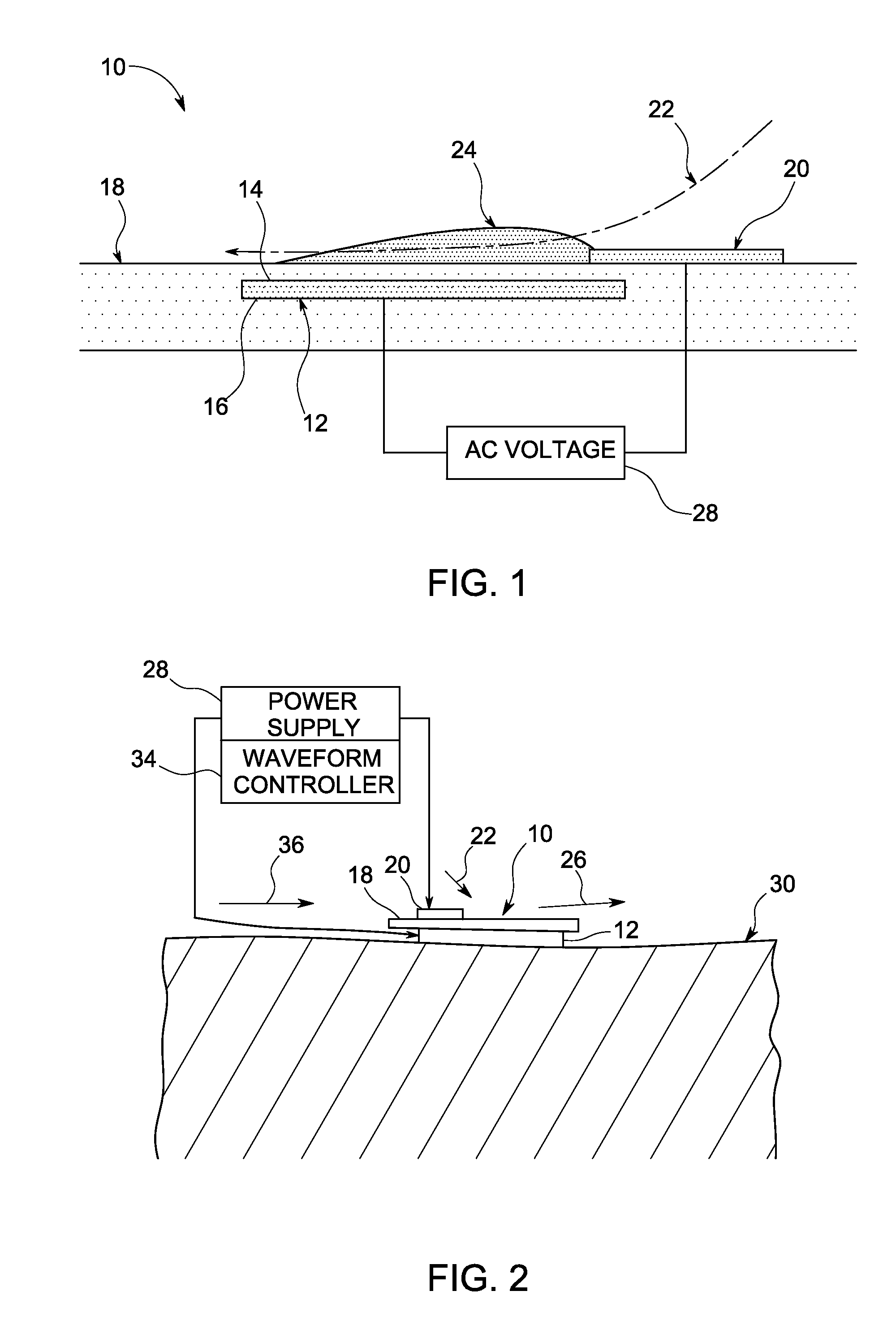
Plasma actuators are a type of actuator currently being developed for aerodynamic flow control. Plasma actuators impart force in a similar way to ionocraft. The working of these actuators is based on the formation of a low-temperature plasma between a pair of asymmetric electrodes by application of a high-voltage AC signal across the electrodes. Consequently, air molecules from the air surrounding the electrodes are ionized, and are accelerated through the electric field.
Single dielectric barrier aerodynamic plasma actuation
ActiveUS7380756B1Increase patternAircraft stabilisationActuated automaticallyPresent dayIonization current
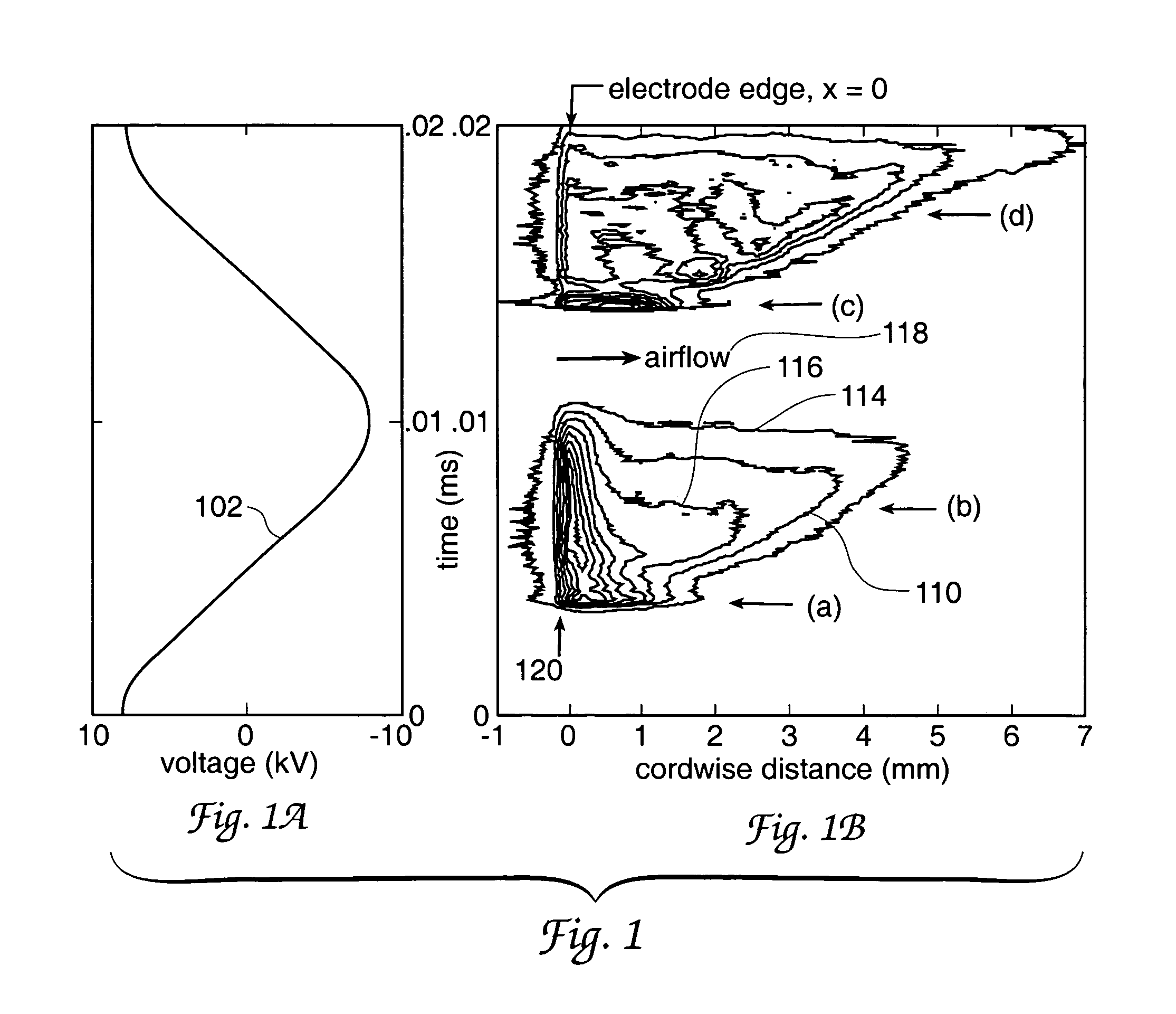
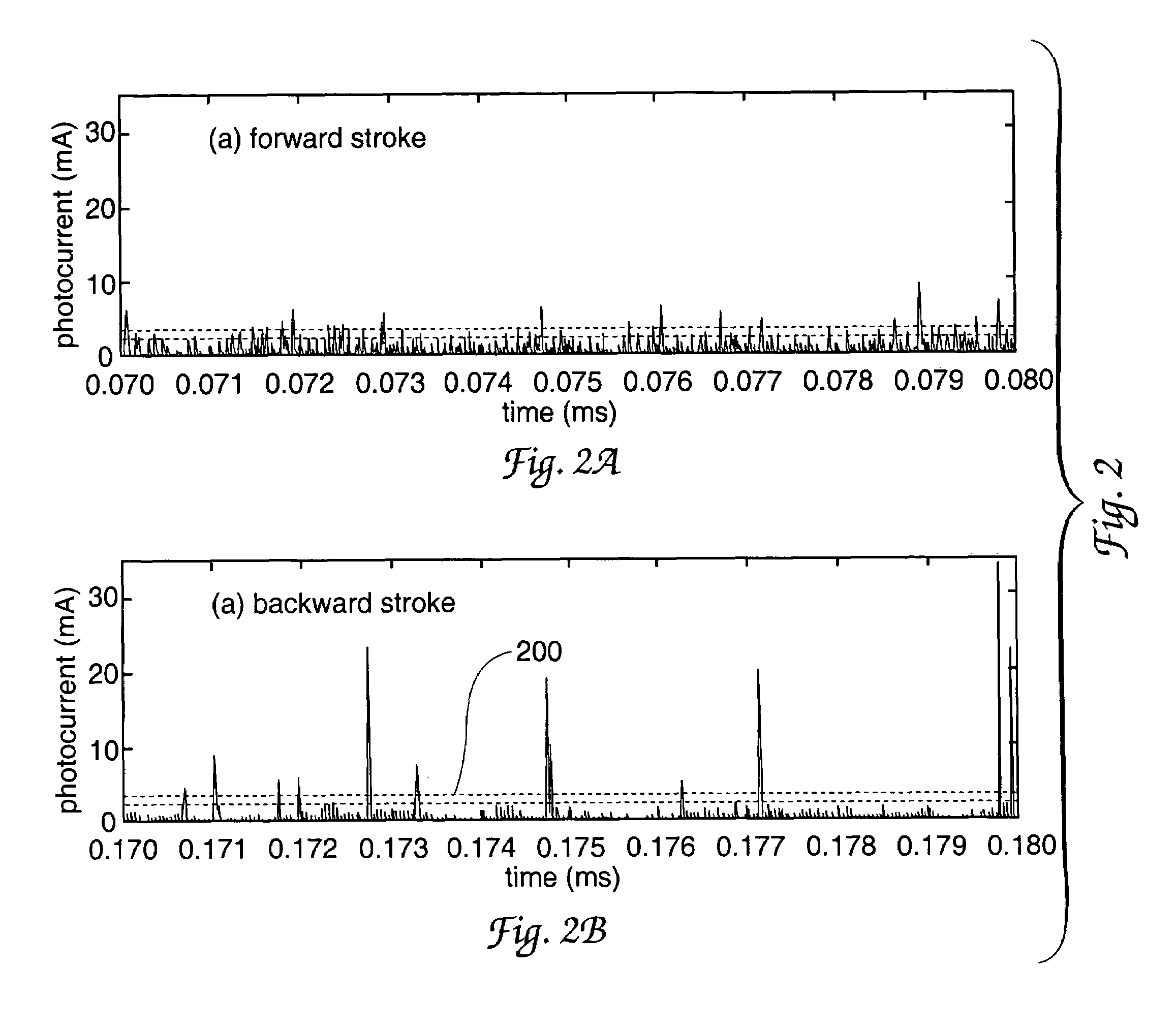
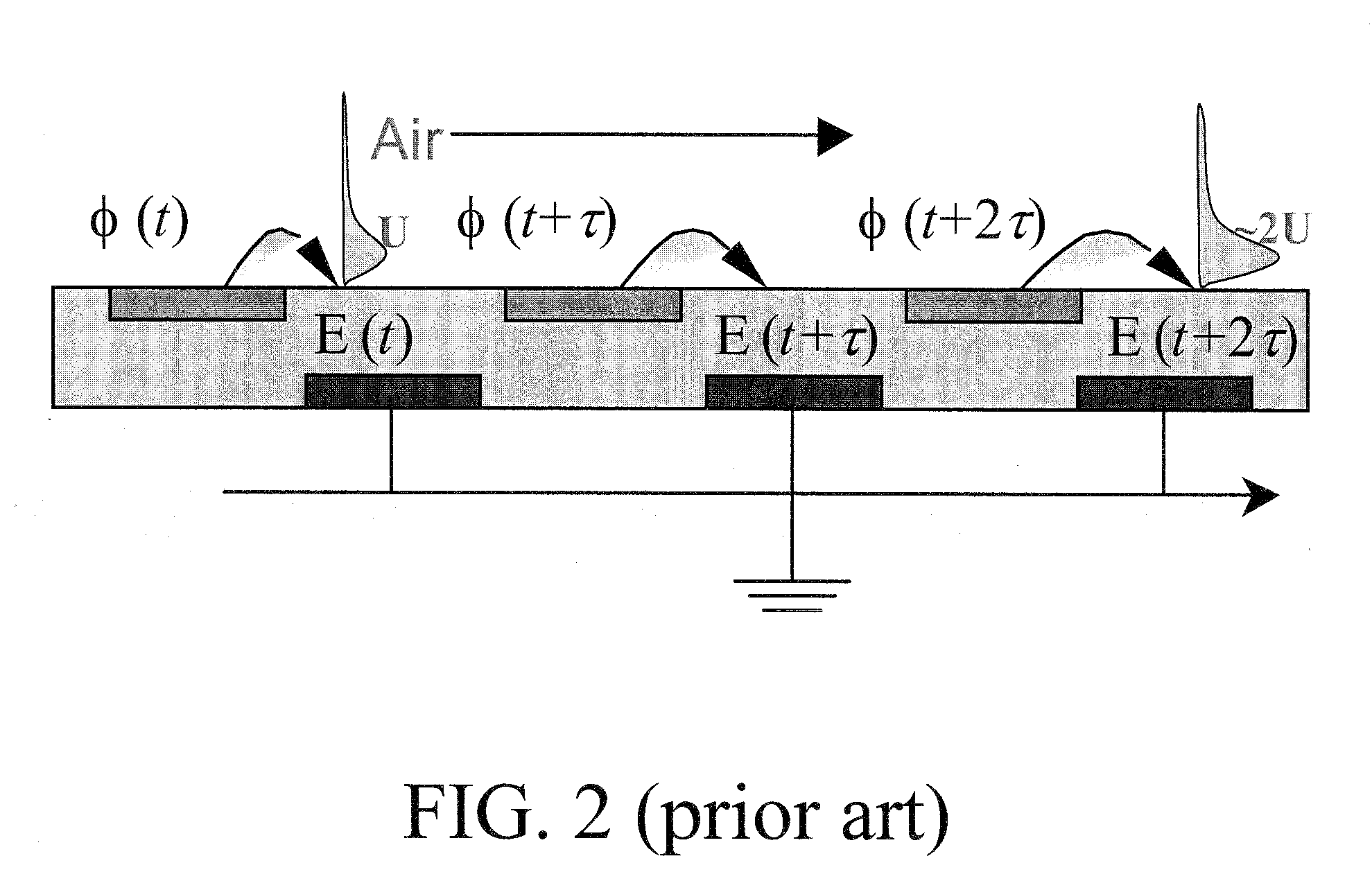
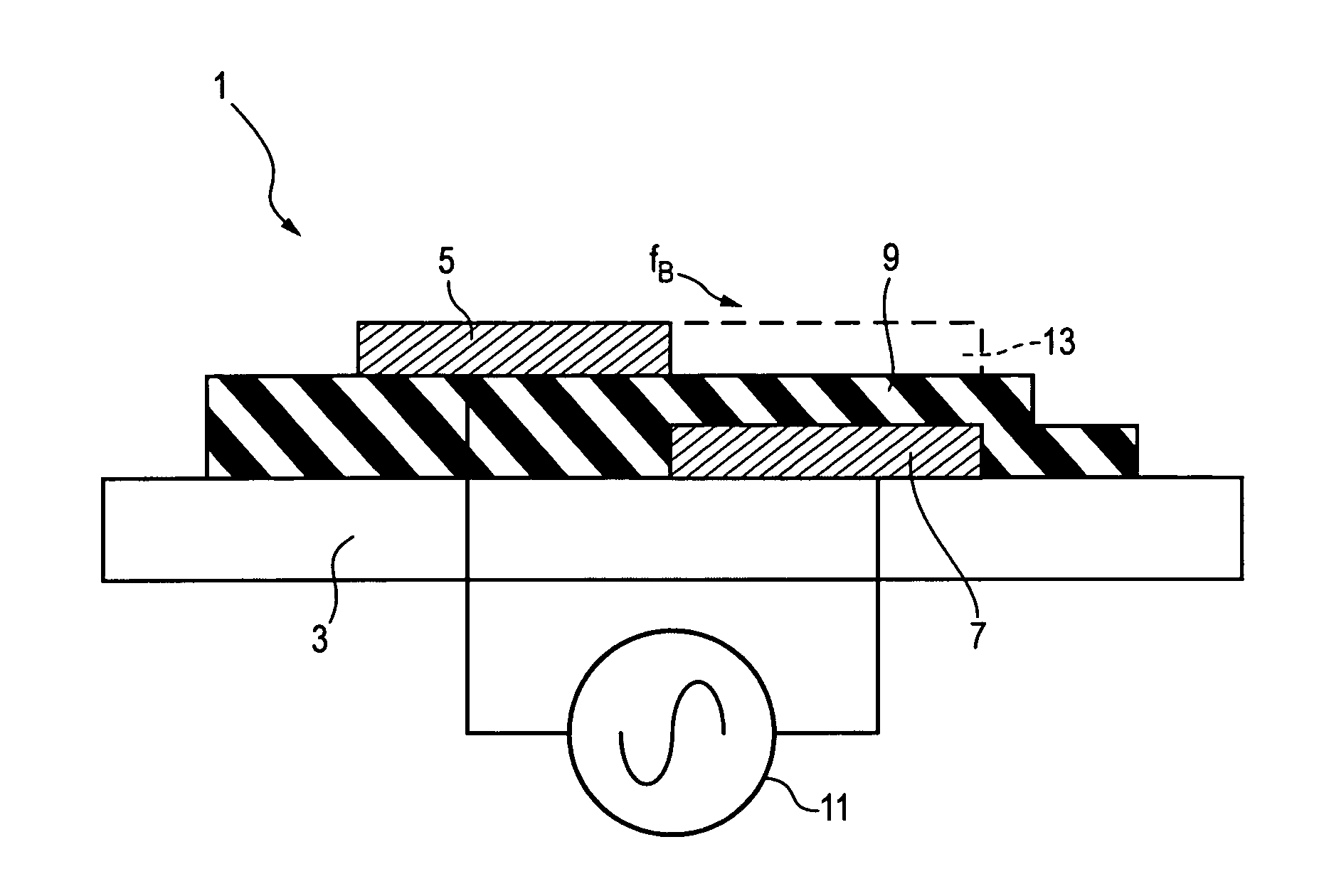
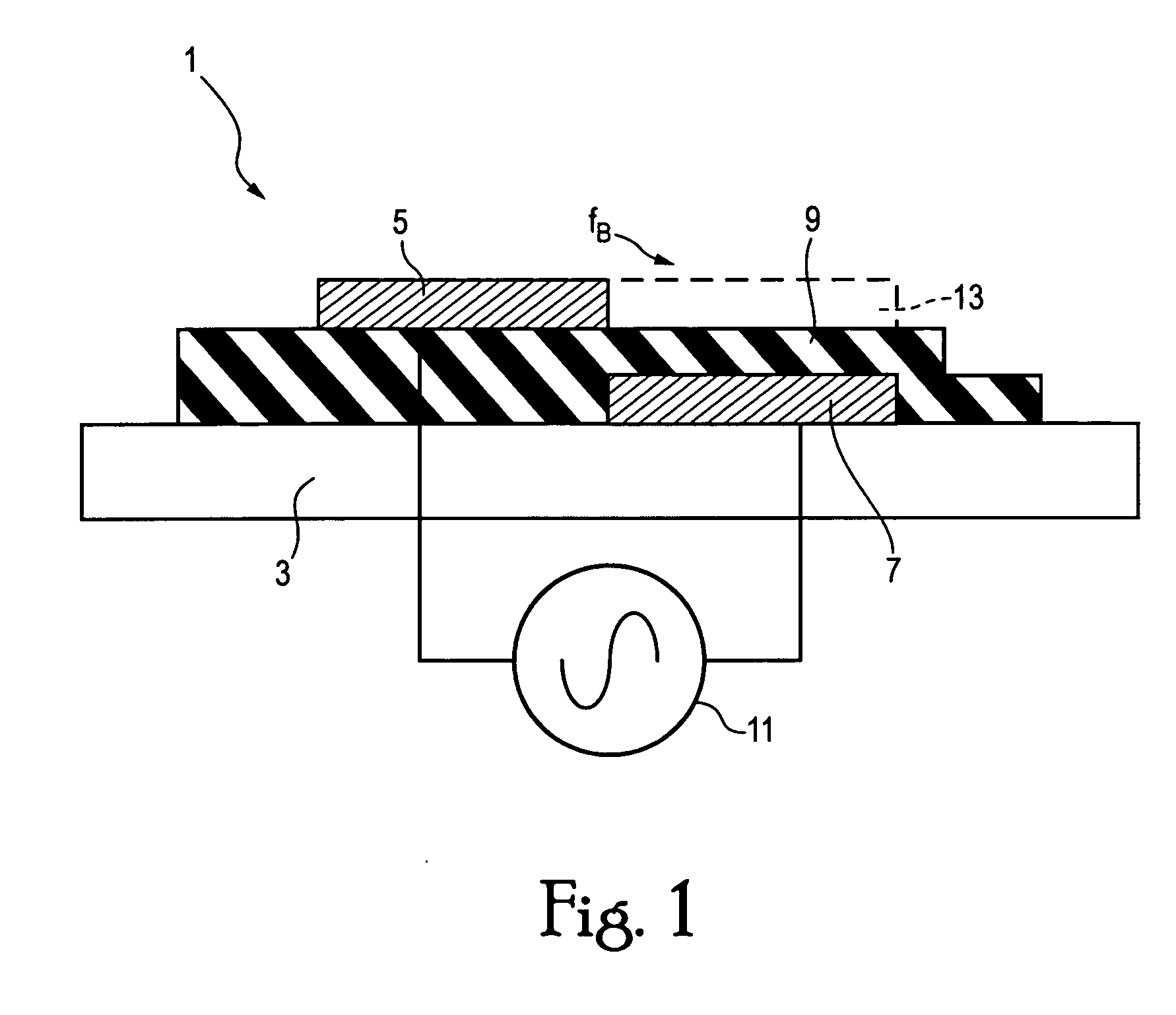
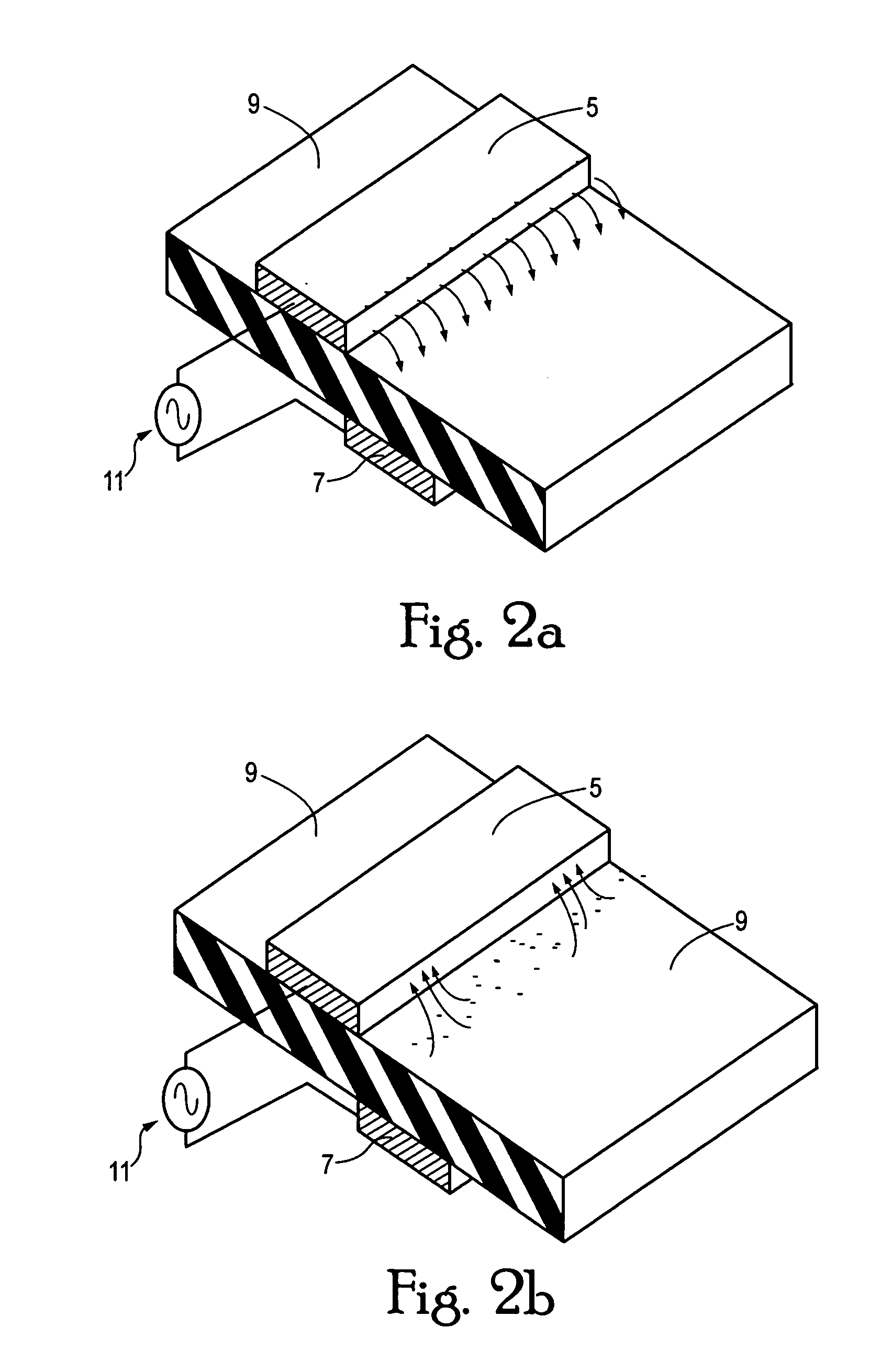
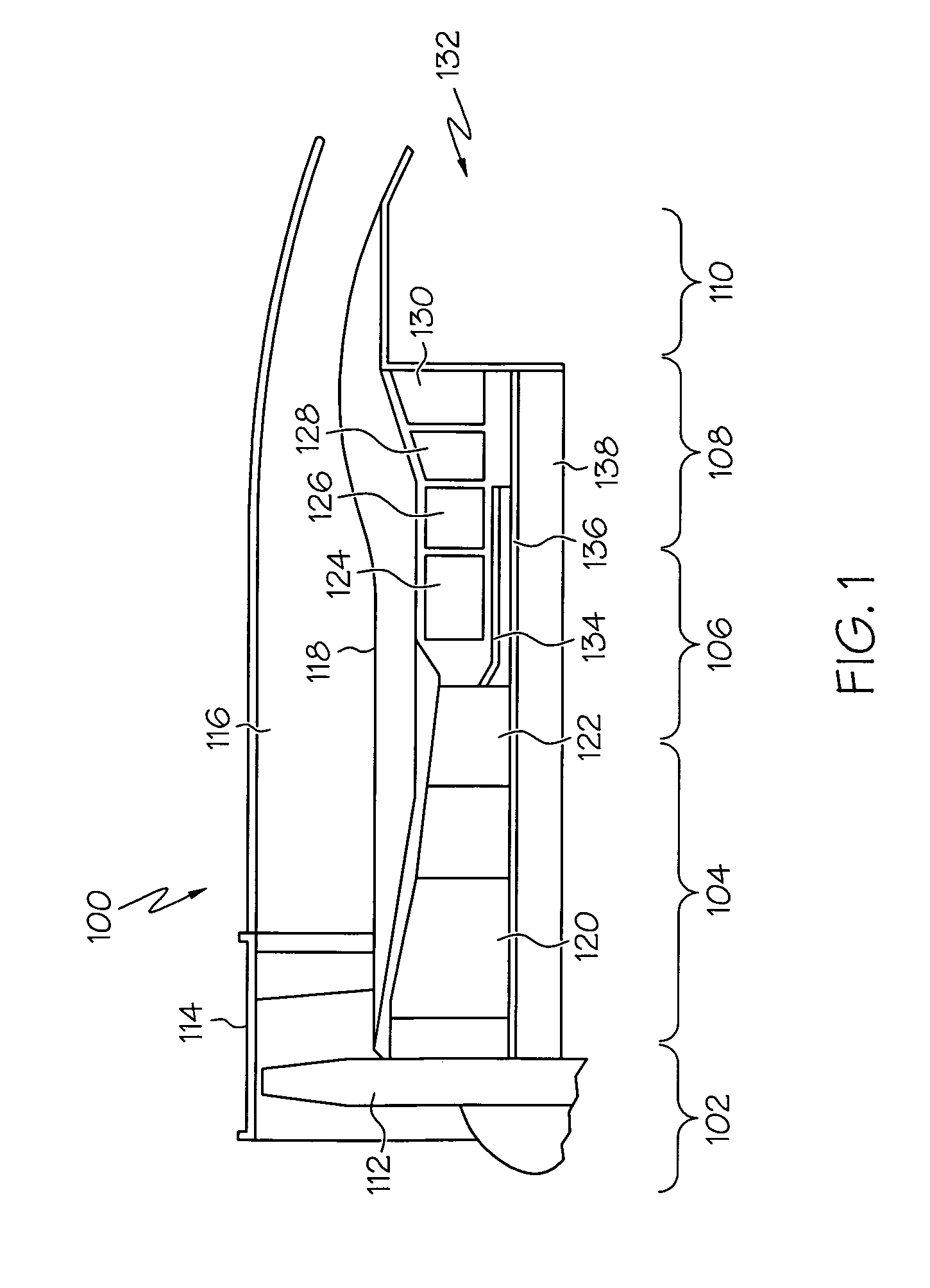
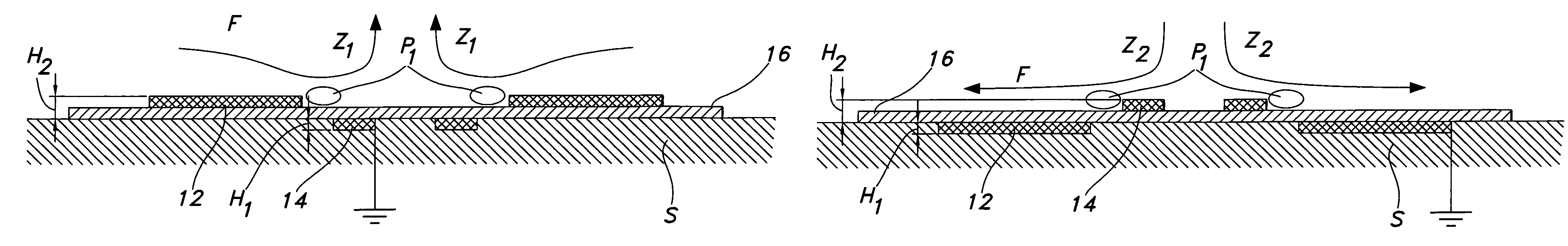
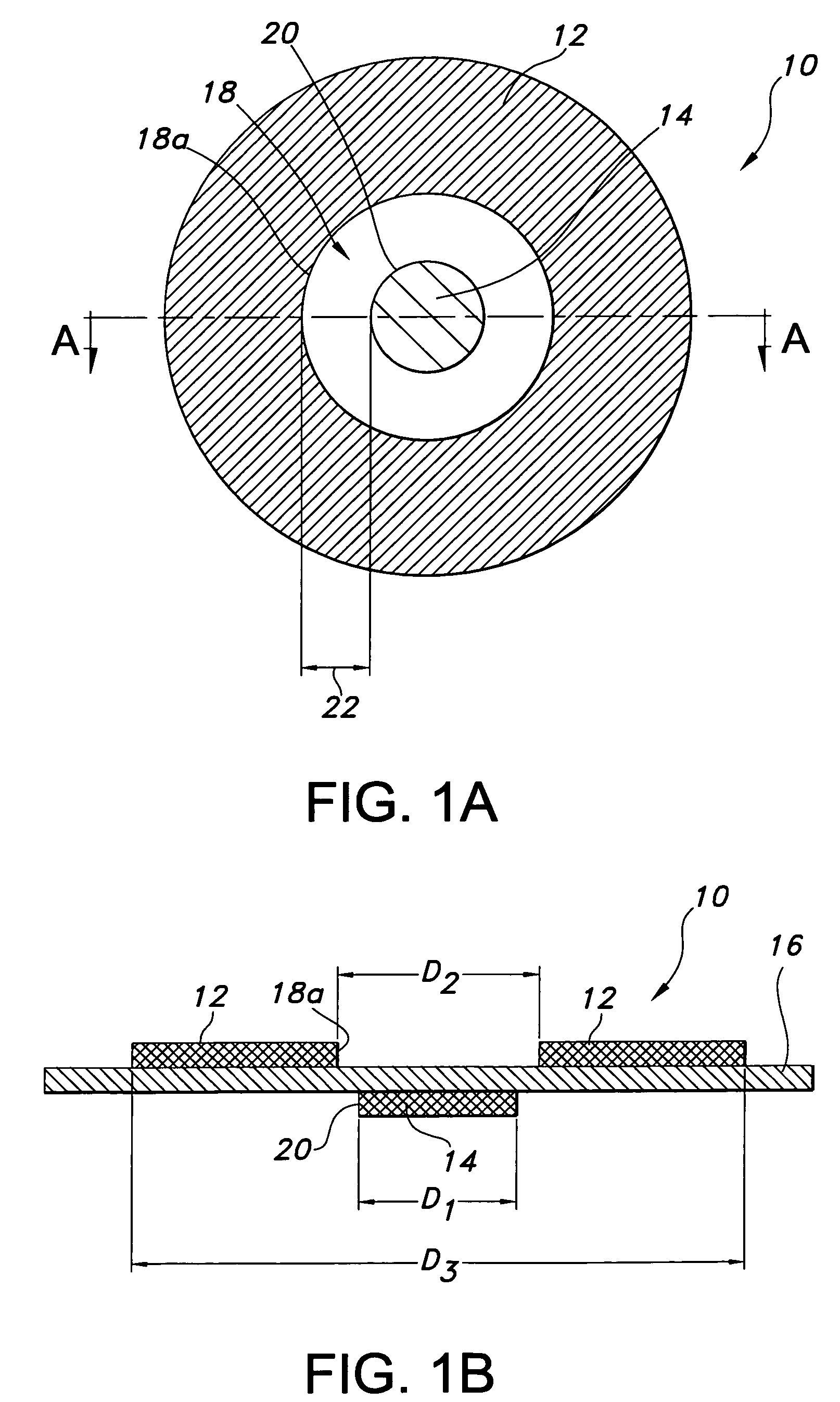
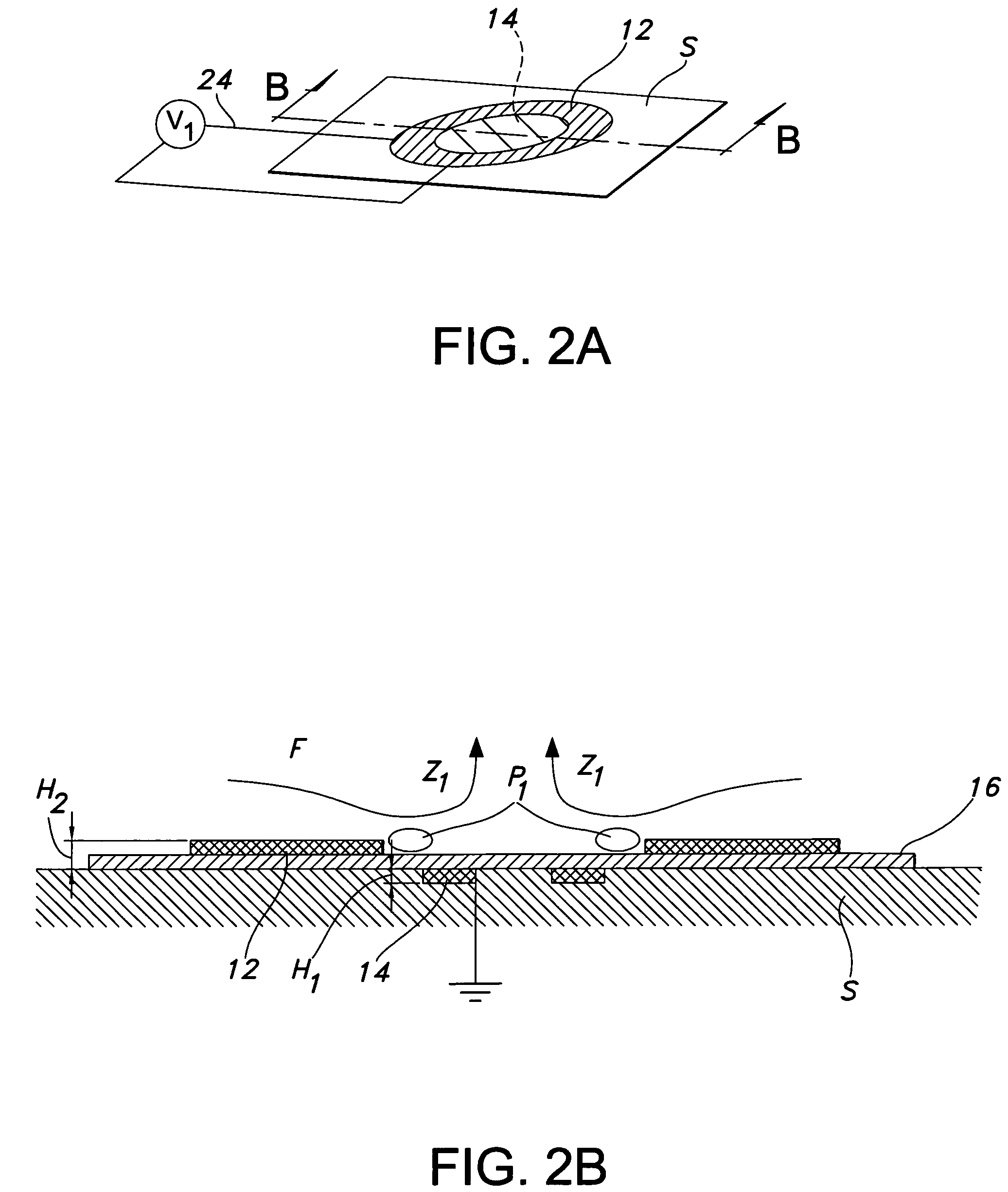
A single dielectric barrier aerodynamic plasma actuator apparatus based on the dielectric barrier discharge phenomenon is disclosed and suggested for application to aerodynamic uses for drag reduction, stall elimination and airfoil efficiency improvement. In the plasma actuator apparatus non-uniform in time and space, partially ionized gasses are generated by one or more electrode pairs each having one electrically encapsulated electrode and one air stream exposed electrode and energization by a high-voltage alternating current waveform. The influence of electrical waveform variation, electrode polarity, electrode size and electrode shape on the achieved plasma are considered along with theoretical verification of achieved results. Light output, generated thrust, ionizing current waveform and magnitude and other variables are considered. Misconceptions prevailing in the present day plasma generation art are addressed and are believed-to-be corrected. The influence of electrostatic shielding effects of the developed plasma on the applied electric field are also considered.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Method of controlling aircraft, missiles, munitions and ground vehicles with plasma actuators
ActiveUS7624941B1Improve efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsDirection controllersBoundary layer controlsJet aeroplanePlasma actuator
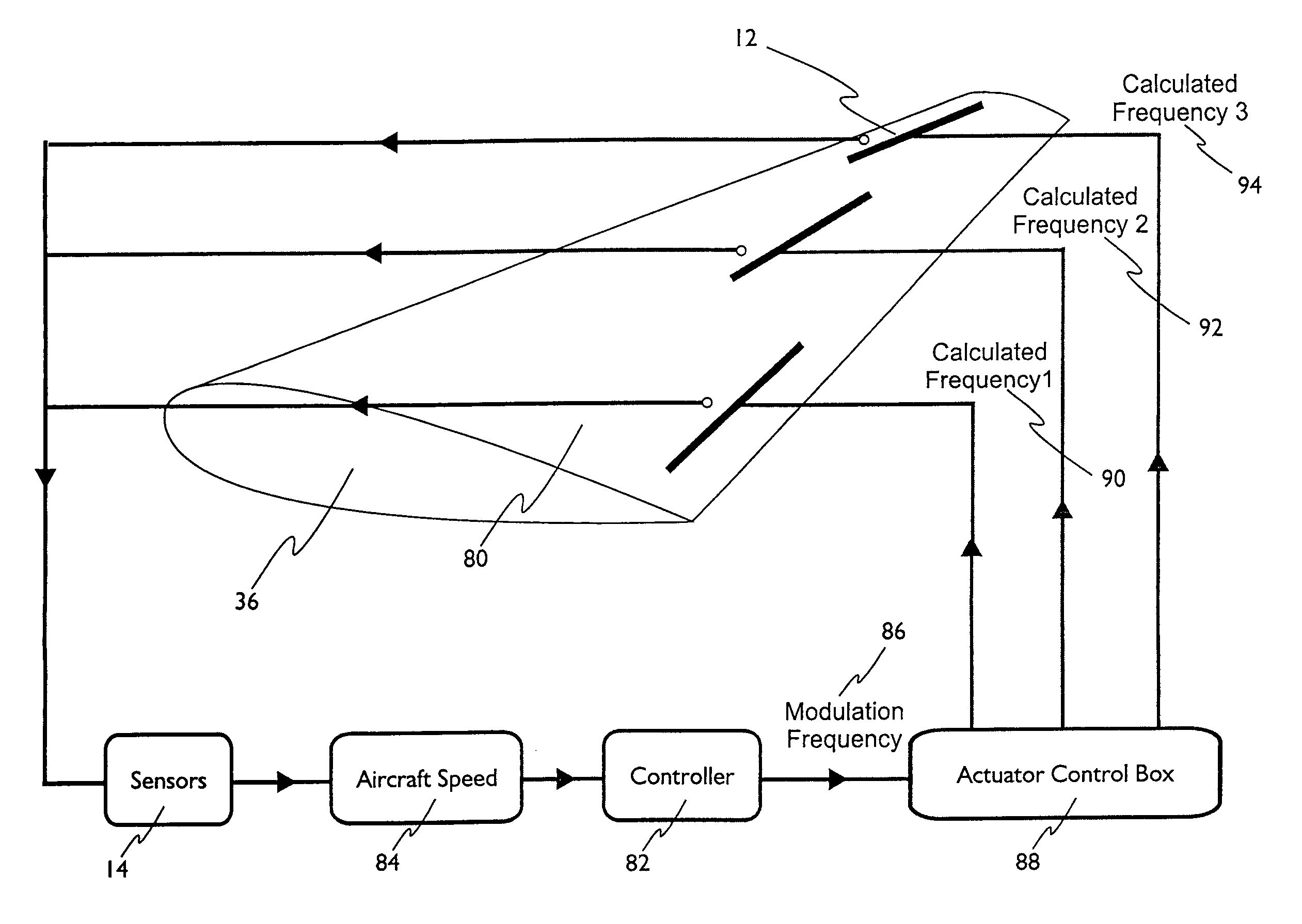
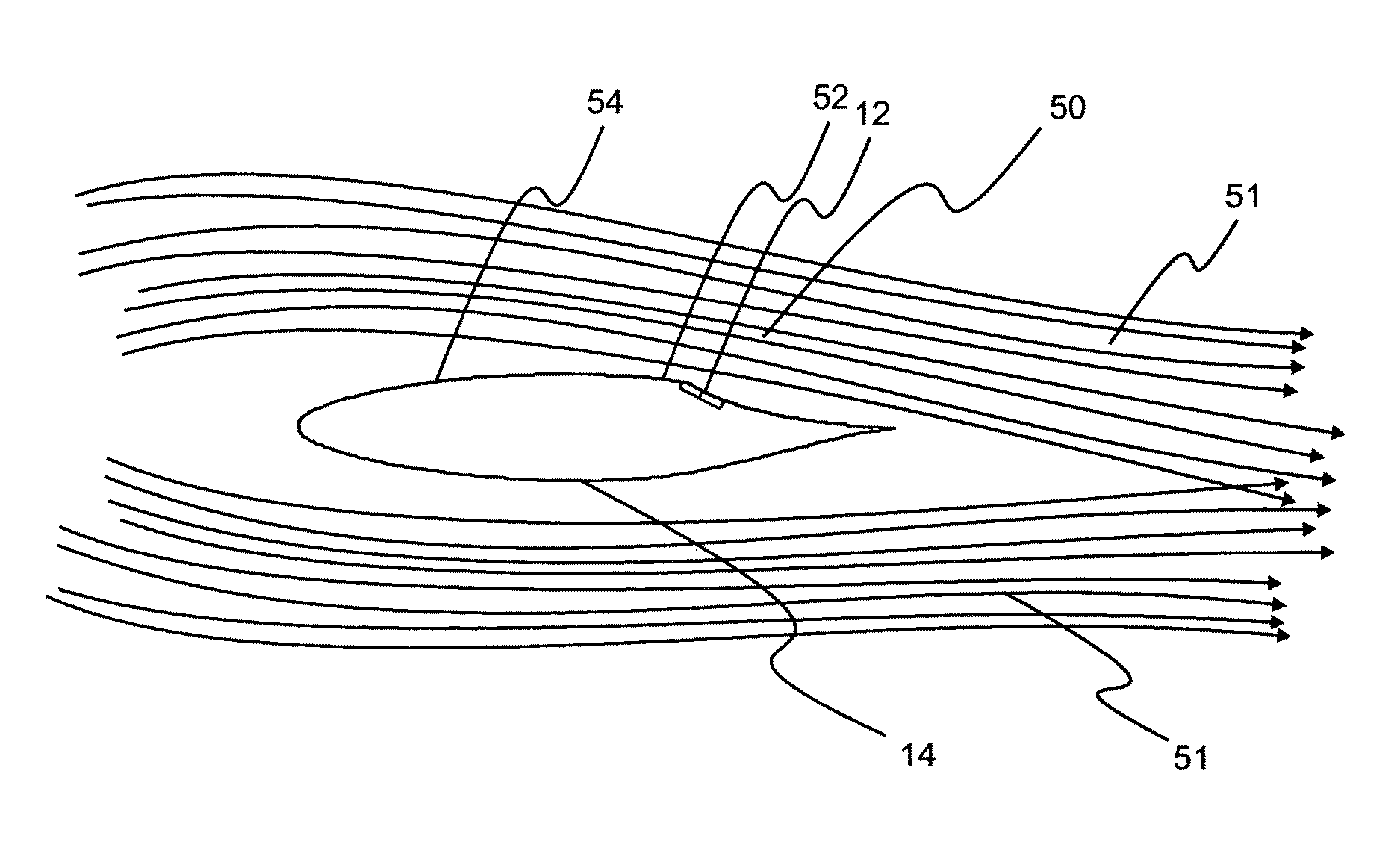
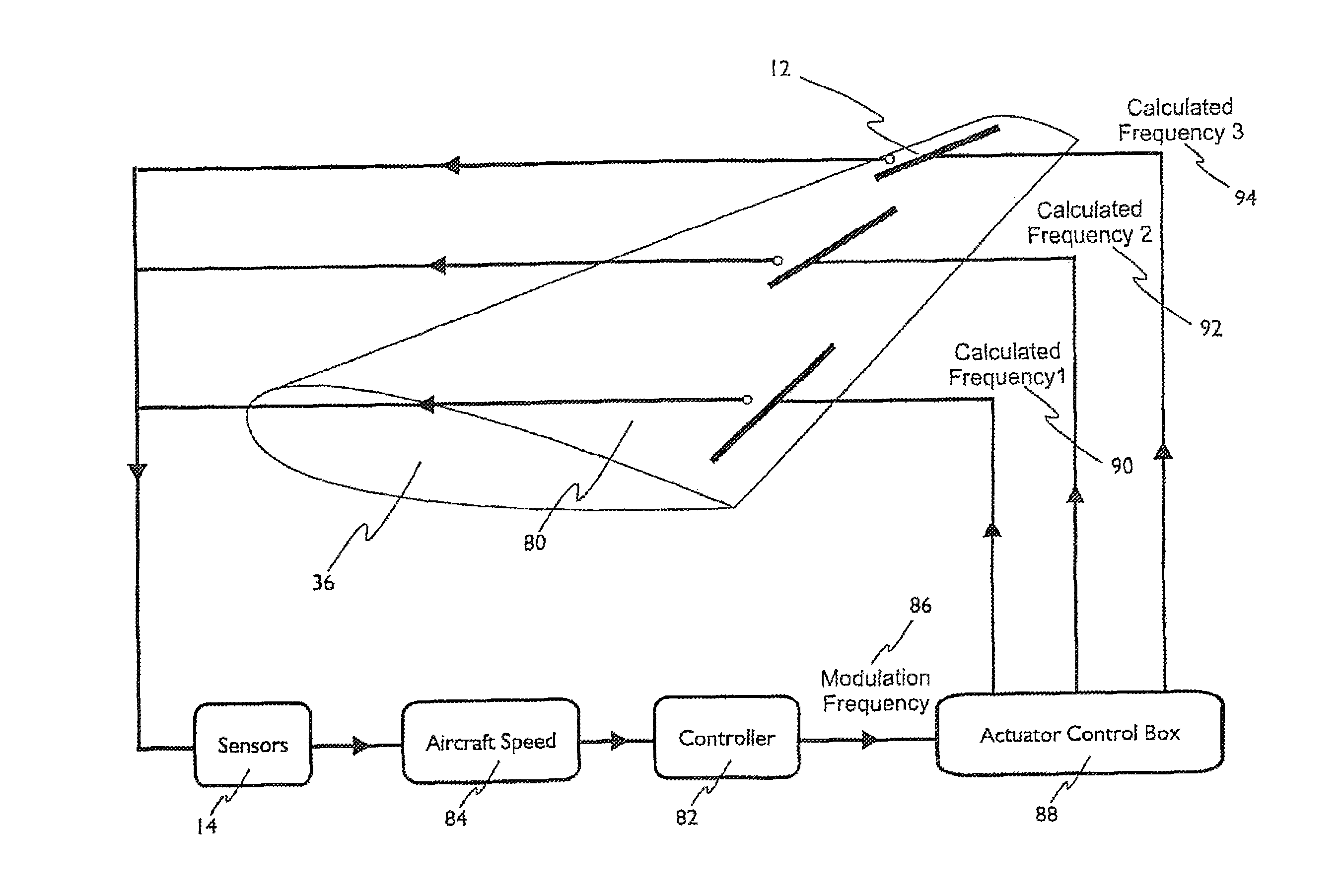
The present invention relates to a method of controlling an aircraft, missile, munition or ground vehicle with plasma actuators, and more particularly to controlling fluid flow across their surfaces or other surfaces, which would benefit from such a method. The method includes the design of an aerodynamic plasma actuator for the purpose of controlling airflow separation over a control surface of a aircraft, missile, or a ground vehicle, and more particularly to the method of determining a modulation frequency for the plasma actuator for the purpose of fluid flow control over these vehicles. The various embodiments provide the steps to increase the efficiency of aircraft, missiles, munitions and ground vehicles. The method of flow control provides a means for reducing aircraft, missile's, munition's and ground vehicle's power requirements. These methods also provide alternate means for aerodynamic control using low-power hingeless plasma actuator devices.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC +1
Methods and apparatus for reducing noise via a plasma fairing
A plasma fairing for reducing noise generated by, for example, an aircraft landing gear is disclosed. The plasma fairing includes at least one plasma generating device, such as a single dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuator, coupled to a body, such as an aircraft landing gear, and a power supply electrically coupled to the plasma generating device. When energized, the plasma generating device generates a plasma within a fluid flow and reduces body flow separation of the fluid flow over the surface of the body. In another example, the body includes a plurality of plasma generating devices mounted to the surface the body to further aid in noise reduction.
Owner:NOTRE DAME DU LAC THE UNIV OF
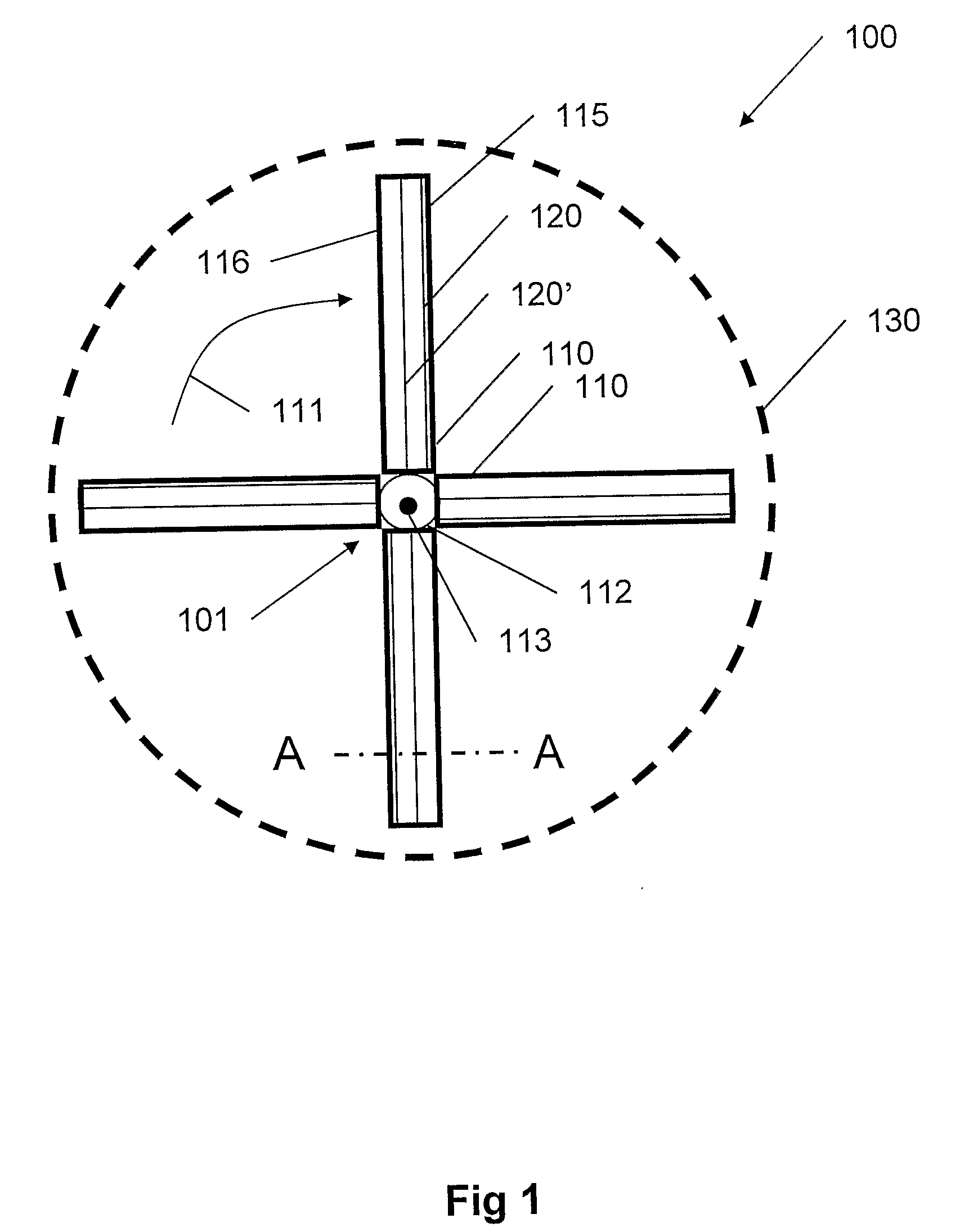
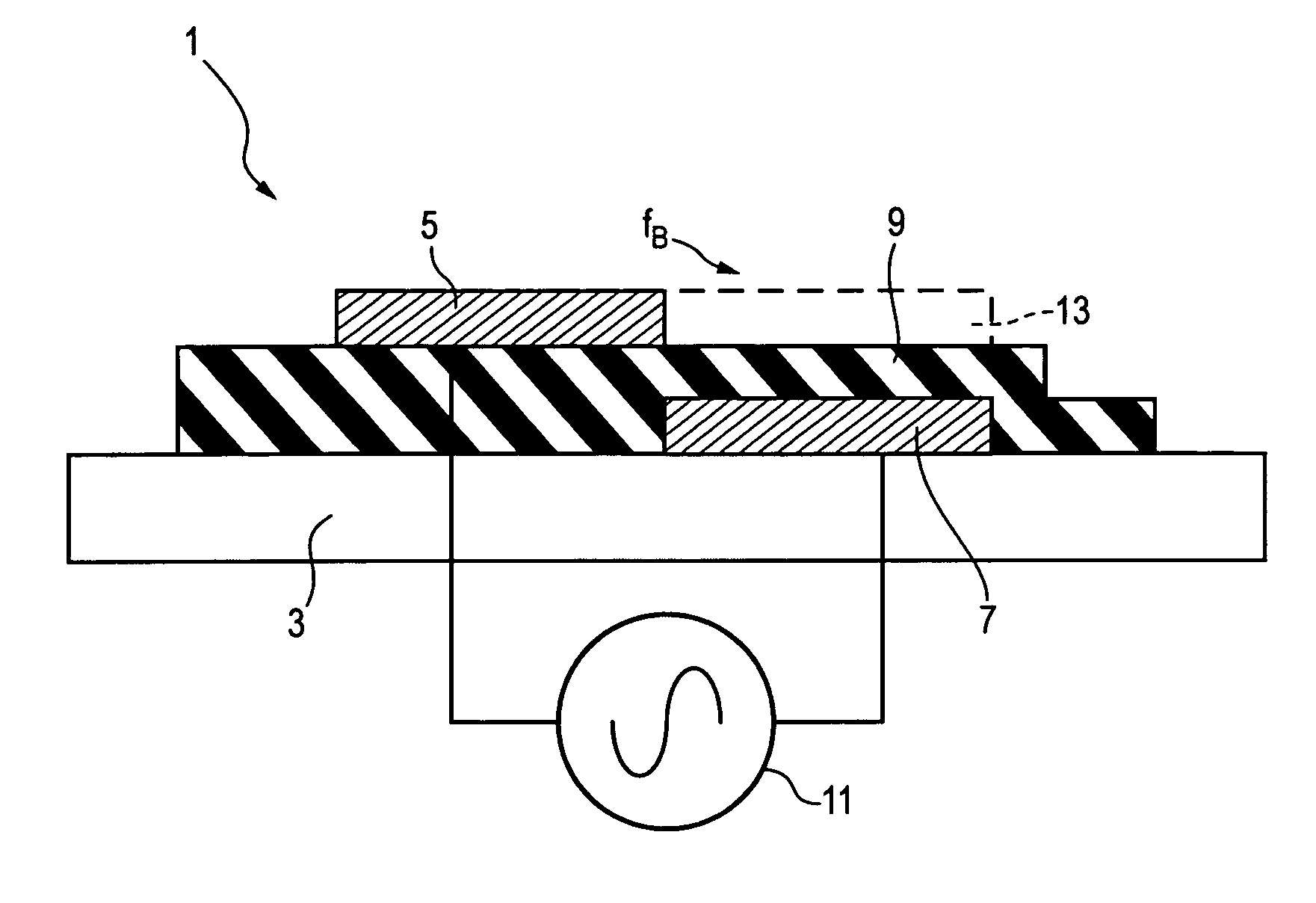
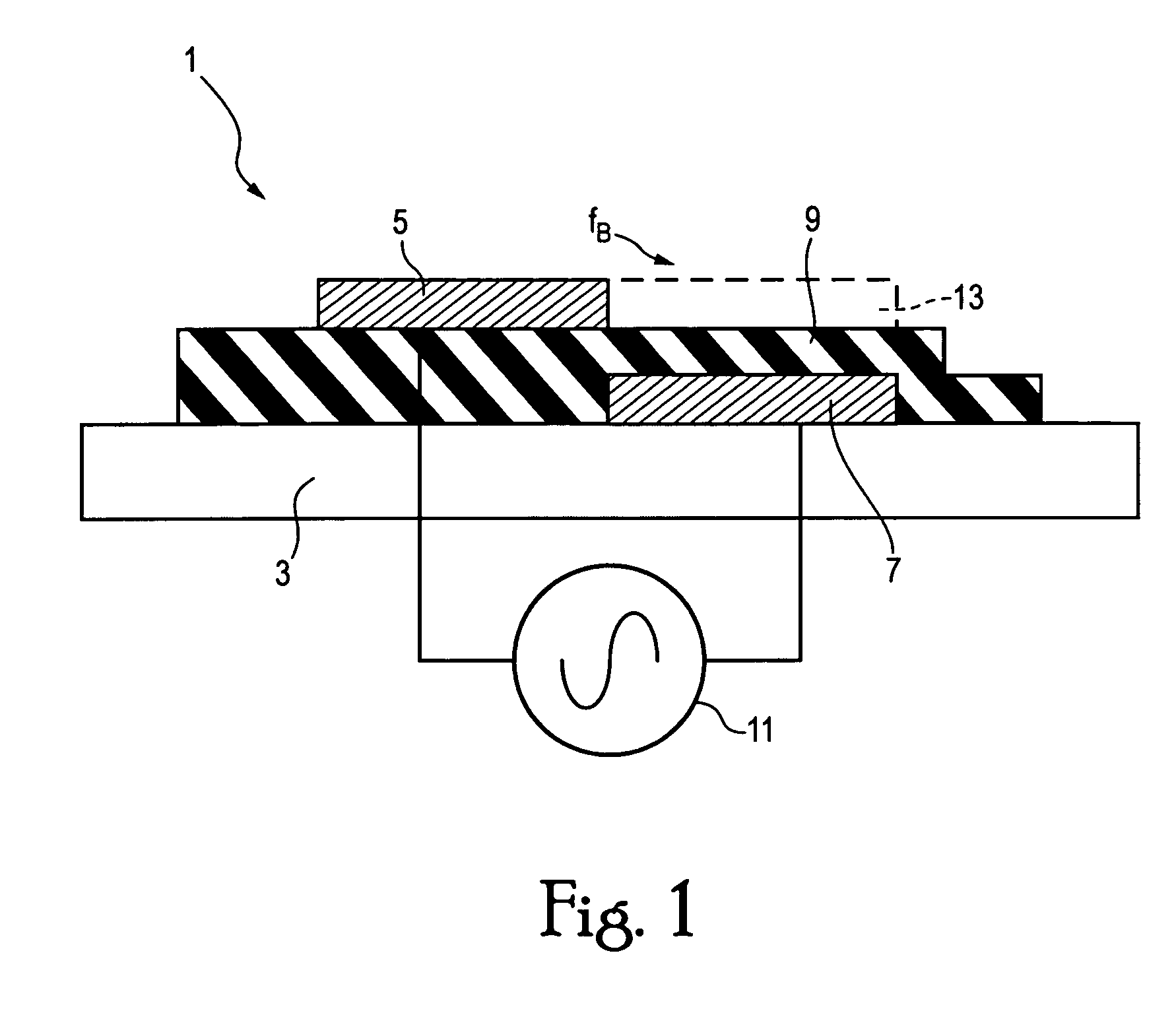
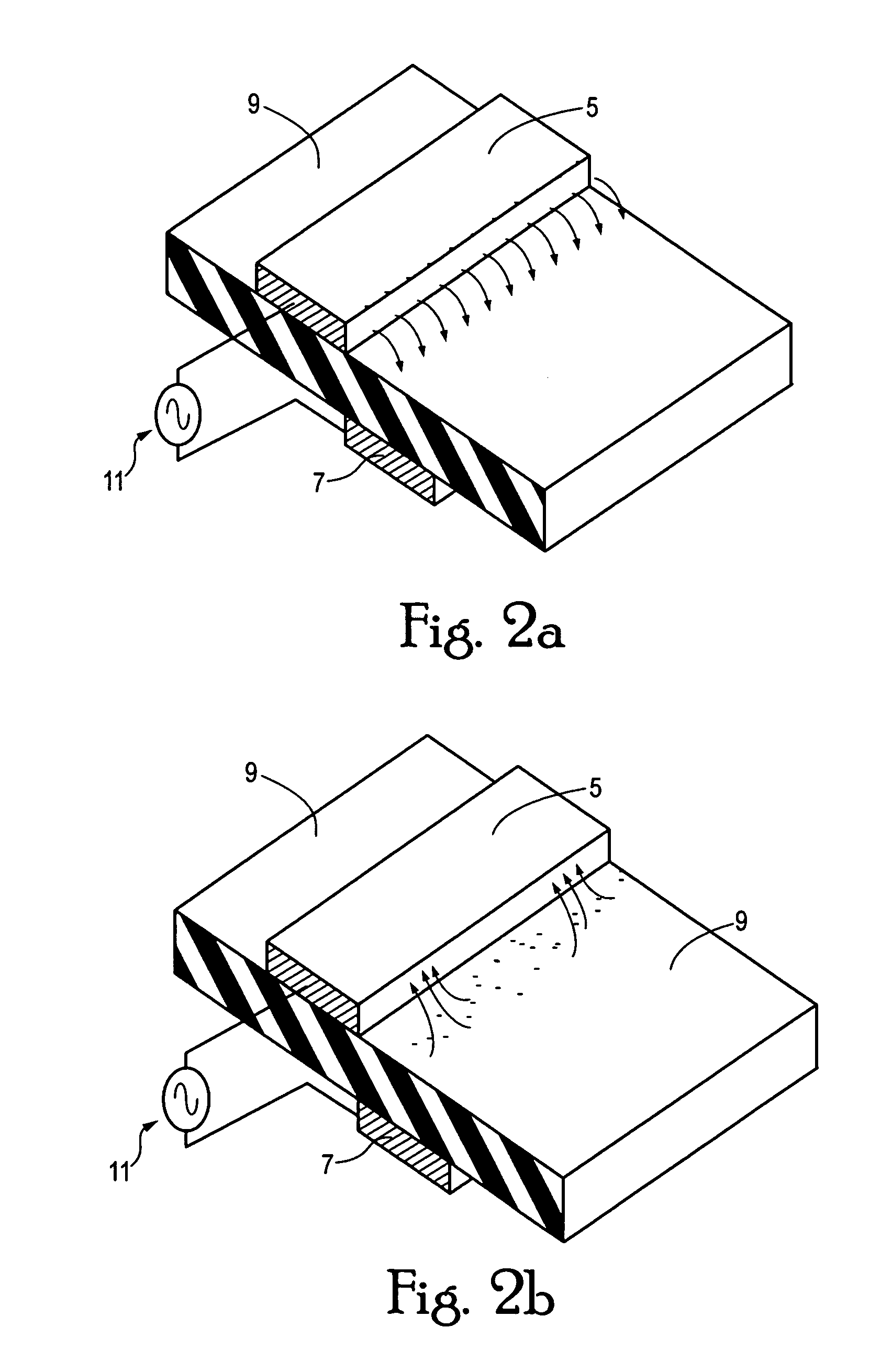
Plasma actuator
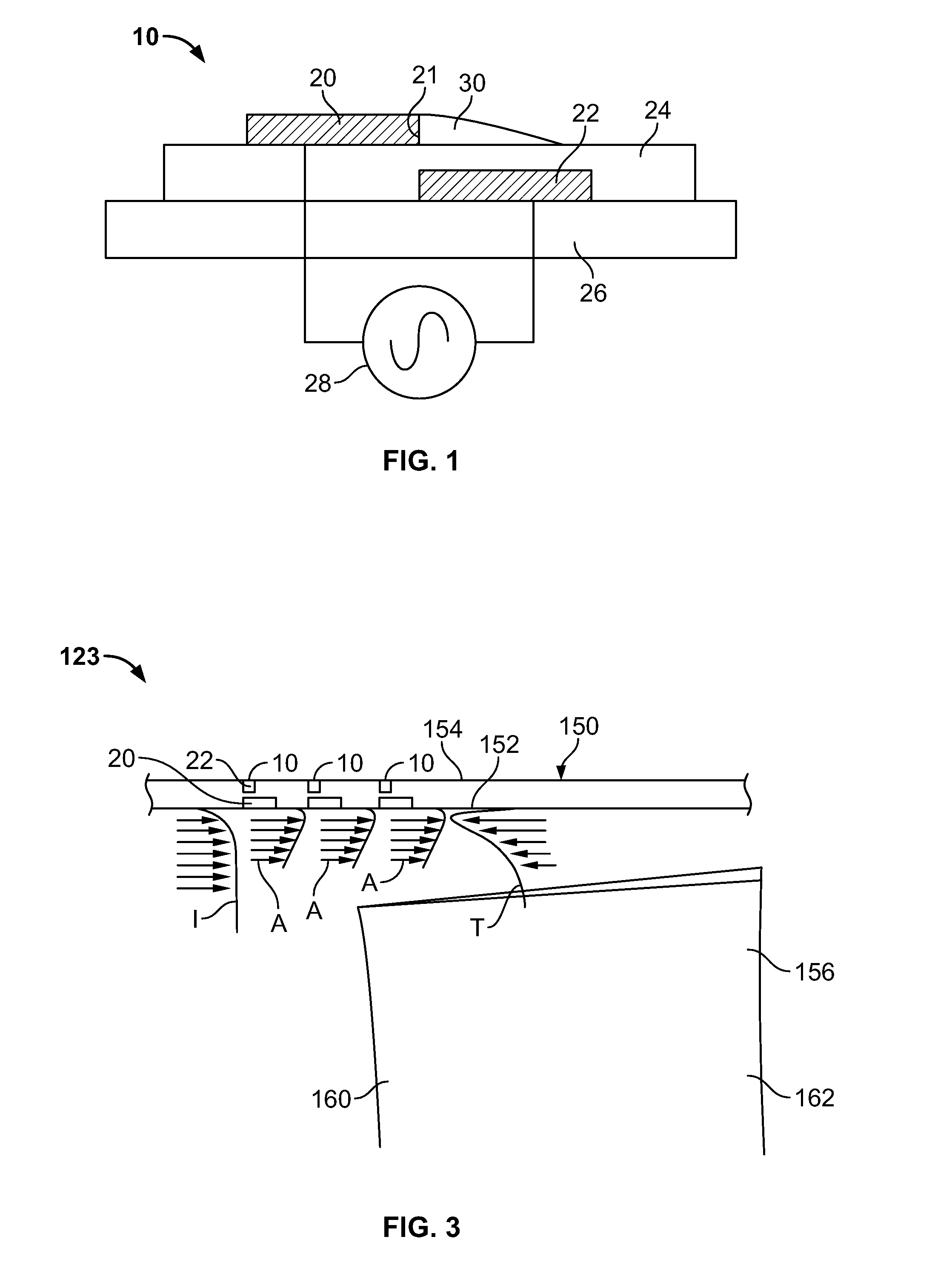
An actuator including a first and second conductor on a dielectric, wherein application of a voltage to the first conductor creates a plasma, thereby modifying a fluid flow in communication with the actuator. Related systems and methods are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Aerodynamic performance enhancements using discharge plasma actuators
ActiveUS20100329838A1Easy maintenanceImprove performanceWind motor controlPump componentsPerformance enhancementPlasma actuator
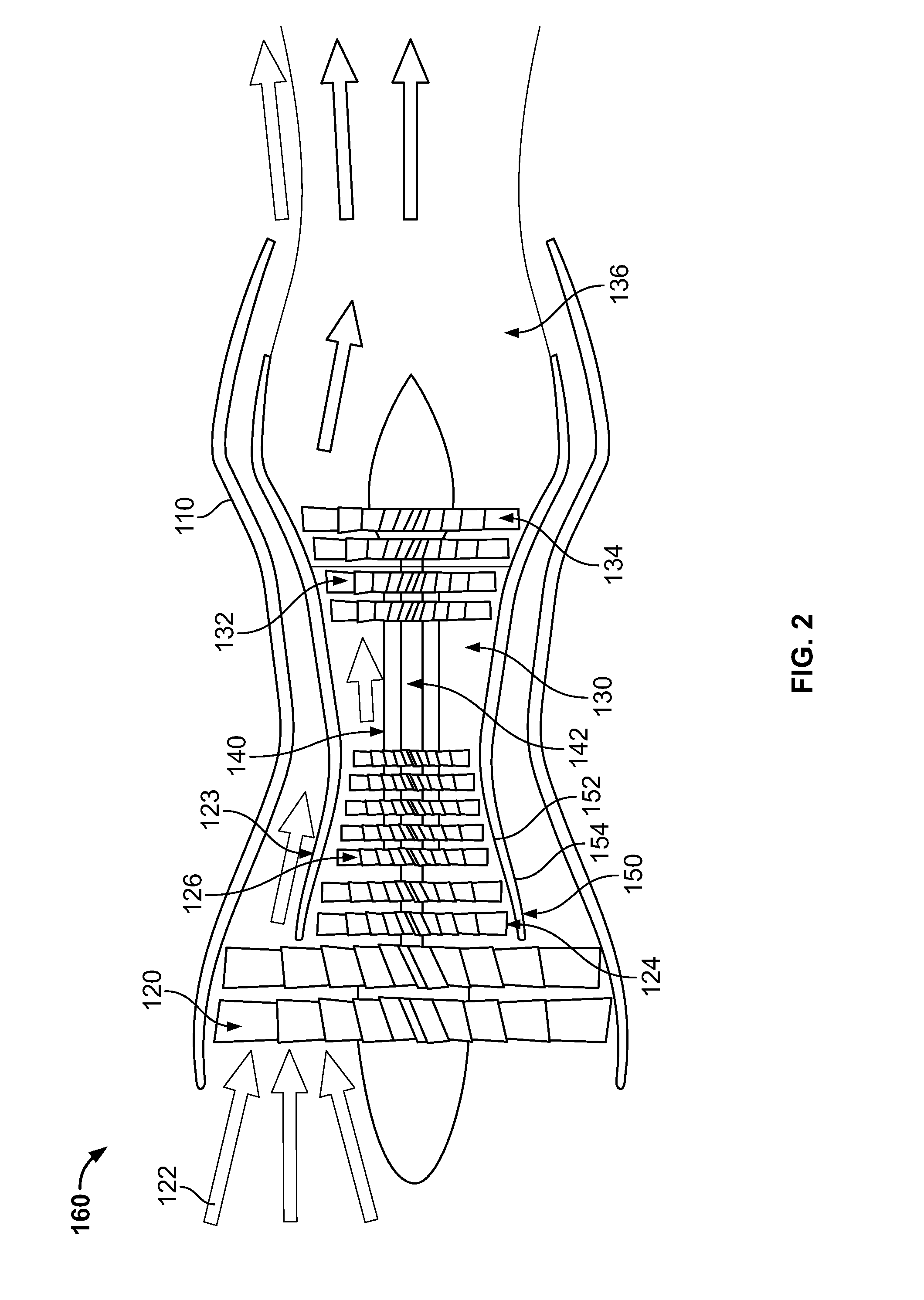
The current invention provides significant performance improvements or significant energy savings for fans used in these applications: personal, industrial and automotive cooling, ventilation, vacuuming and dust removal, inflating, computer component cooling, propulsors for unmanned and manned air vehicles, propulsors for airboats, air-cushion vehicles, airships and model aircraft. Additionally, the invention provides higher performance such as higher lift and higher lift efficiency to small air vehicles. These advantages are achieved by using plasma actuators to provide active flow control effectors into thin fan blades and wing.
Owner:GREENBLATT DAVID
Method and Apparatus for Multibarrier Plasma Actuated High Performance Flow Control
ActiveUS20100127624A1Easy flow controlEasy to moveElectric discharge tubesCircuit elementsPhase differencePlasma actuator
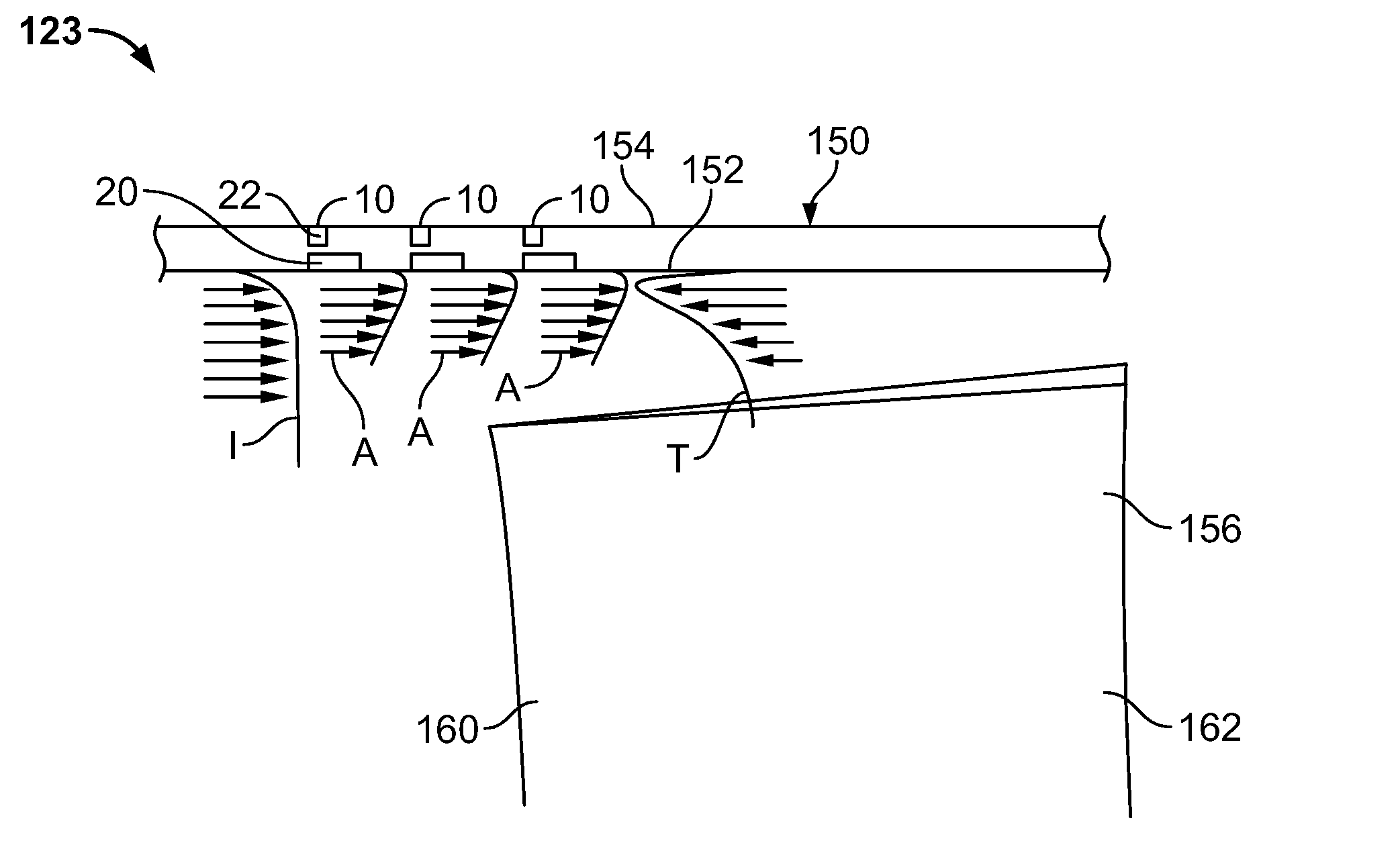
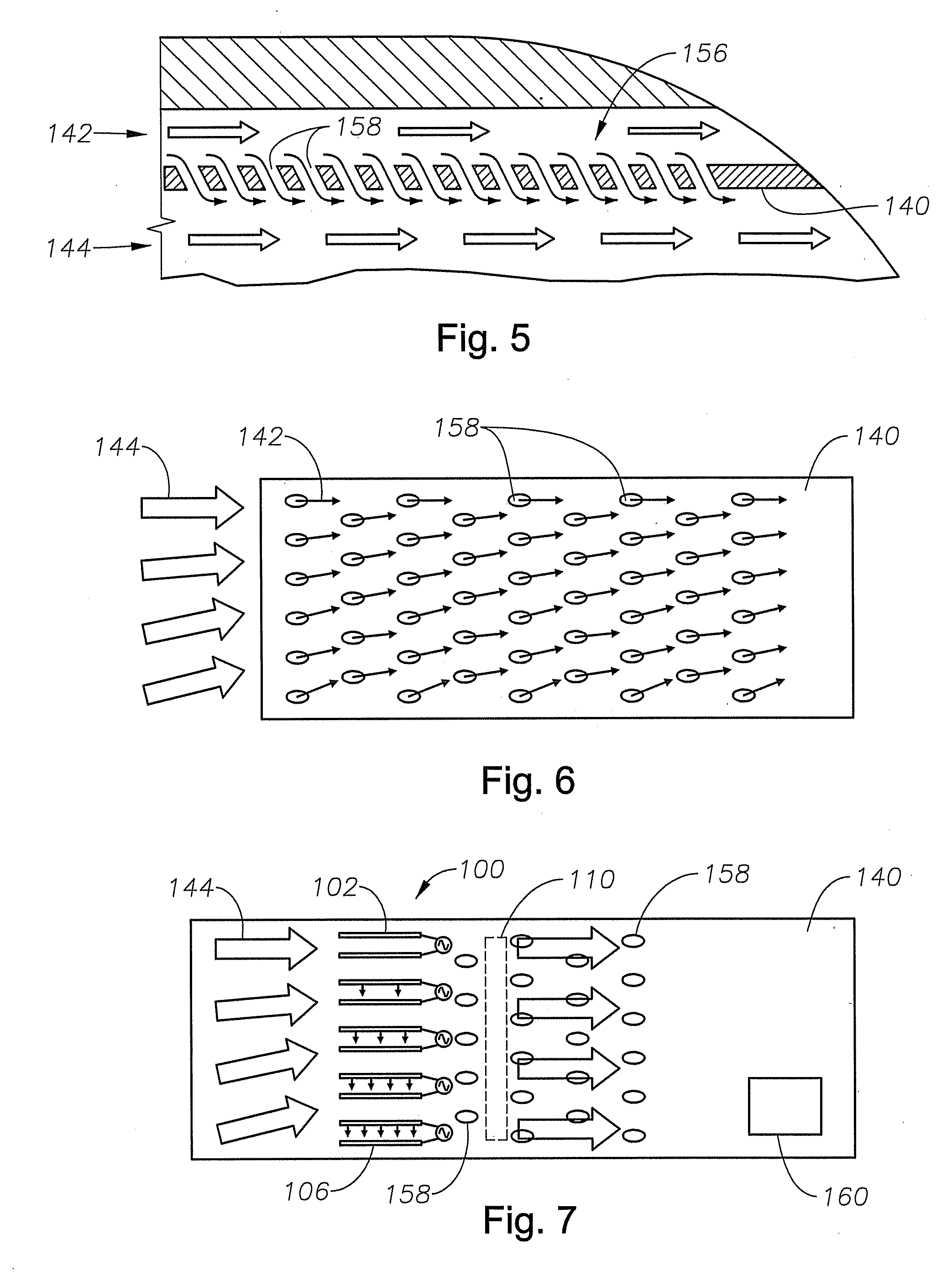
Embodiments of the invention relate to a method and apparatus for plasma actuated high performance flow control. A specific embodiment of a plasma actuator can incorporate a power source; a first electrode in contact with a first dielectric layer and connected to the power source; a second electrode in contact with a second dielectric layer and connected to the power source; and a ground electrode. The power source drives the first electrode with a first ac voltage pattern with respect to the ground electrode and drives the second electrode with a second ac voltage pattern with respect to the ground electrode such that application of the first voltage pattern produces a first plasma discharge in a flow region, and a first electric field pattern in the flow region, and application of the second voltage pattern produces a second plasma discharge in the flow region and a second electric field pattern in the flow region. The first and second electrodes are offset along the direction of flow in the flow region and the first voltage pattern and the second voltage pattern have a phase difference such that the first and second electric fields drive flow in the flow region in different portions of the flow region at different times.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Localized arc filament plasma actuators for noise mitigation and mixing enhancement
InactiveUS20060005545A1Increase amplitudeEnhance and weaken vorticityAircraft navigation controlEngine fuctionsPlasma actuatorStreaming instability
A device for controlling fluid flow. The device includes an arc generator coupled to electrodes. The electrodes are placed adjacent a fluid flowpath such that upon being energized by the arc generator, an arc filament plasma adjacent the electrodes is formed. In turn, this plasma forms a localized high temperature, high pressure perturbation in the adjacent fluid flowpath. The perturbations can be arranged to produce vortices, such as streamwise vortices, in the flowing fluid to control mixing and noise in such flows. The electrodes can further be arranged within a conduit configured to contain the flowing fluid such that when energized in a particular frequency and sequence, can excite flow instabilities in the flowing fluid. The placement of the electrodes is such that they are unobtrusive relative to the fluid flowpath being controlled.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
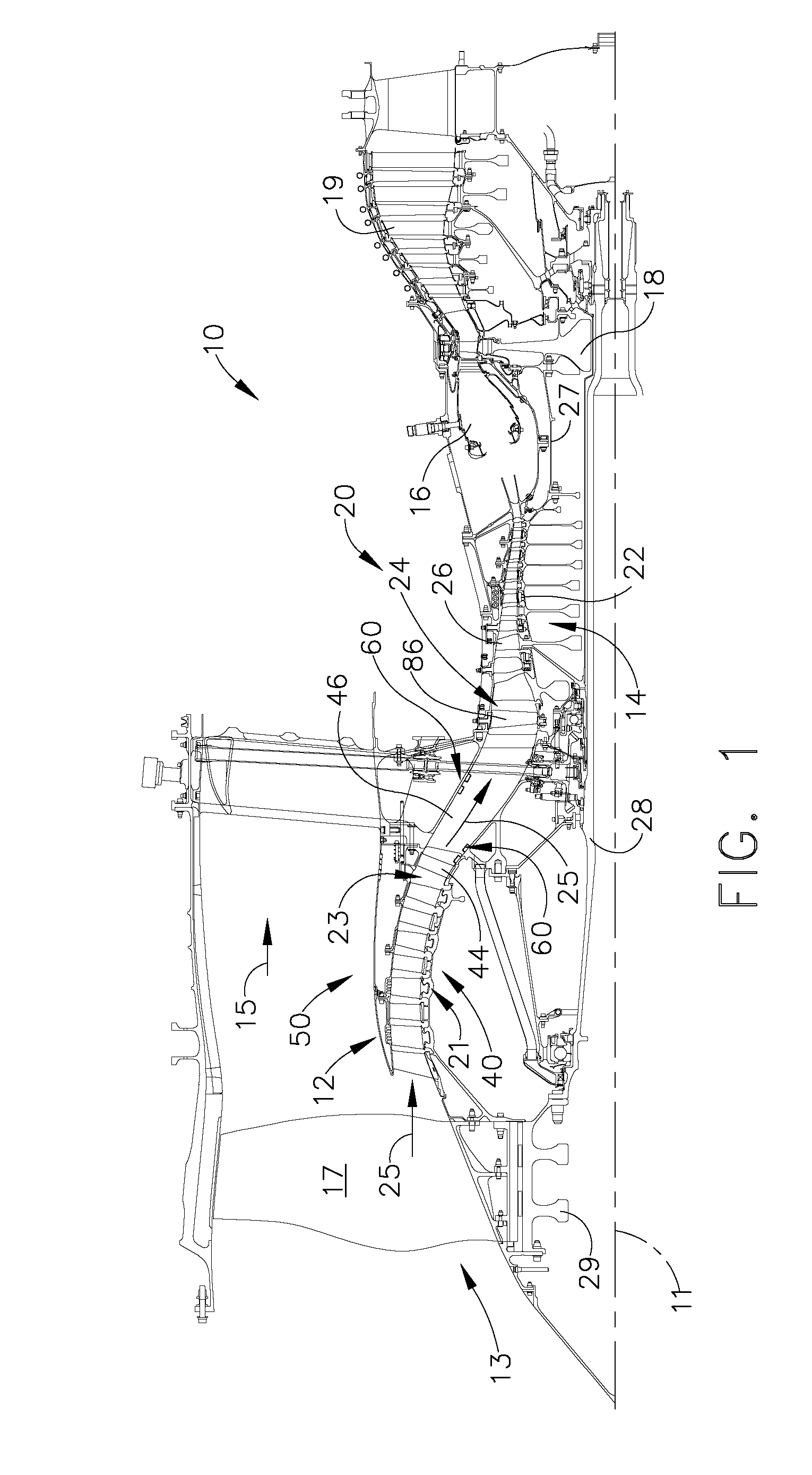
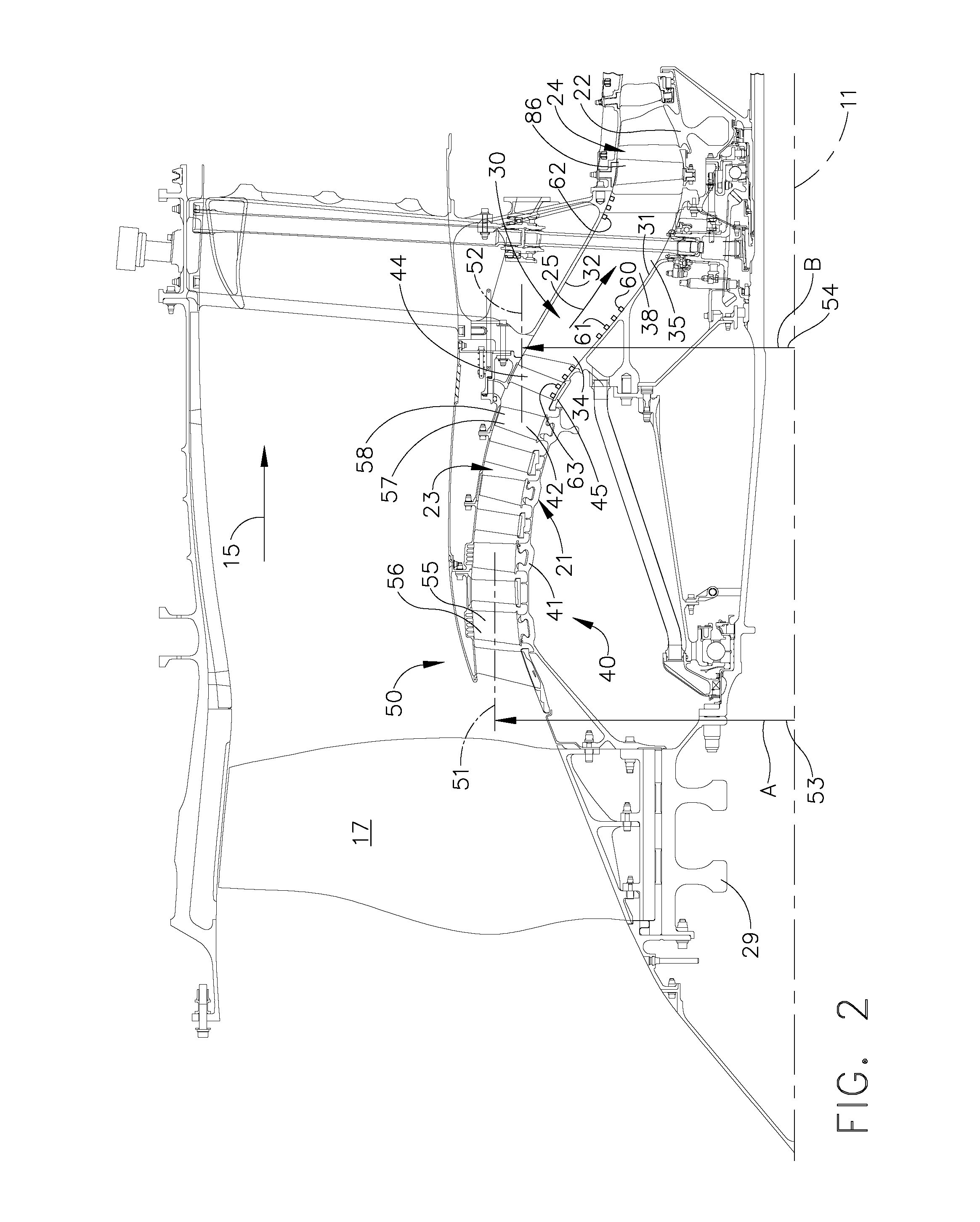
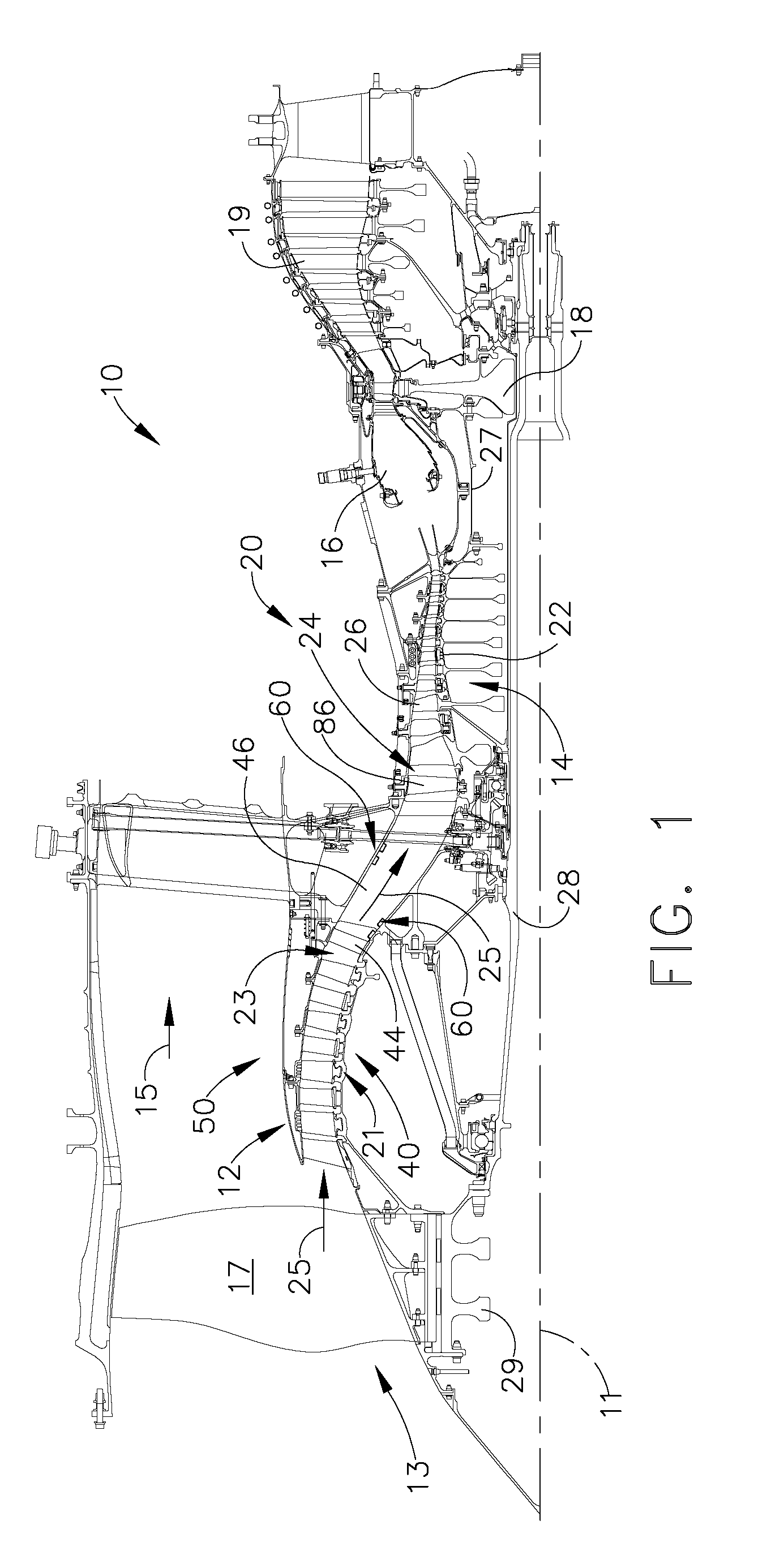
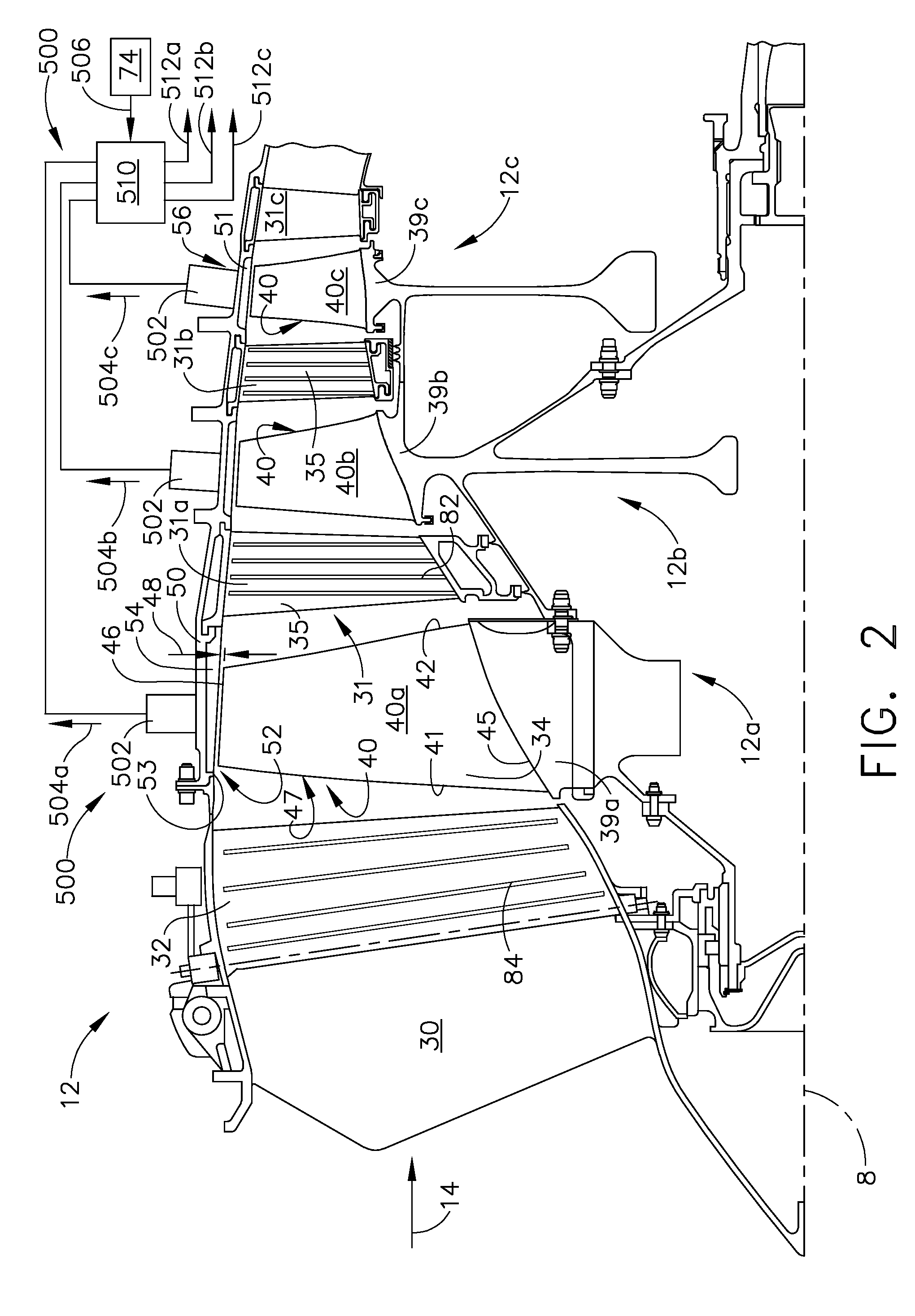
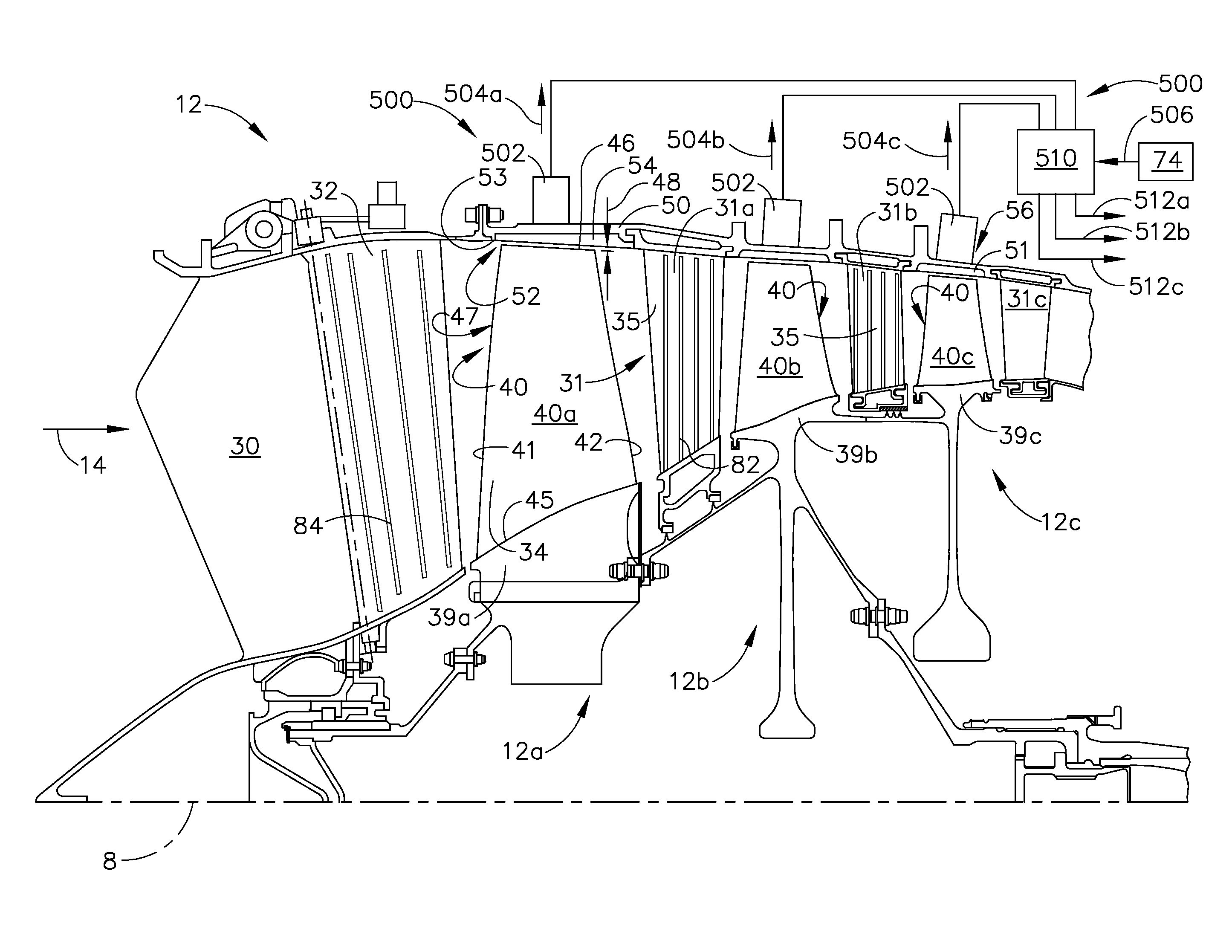
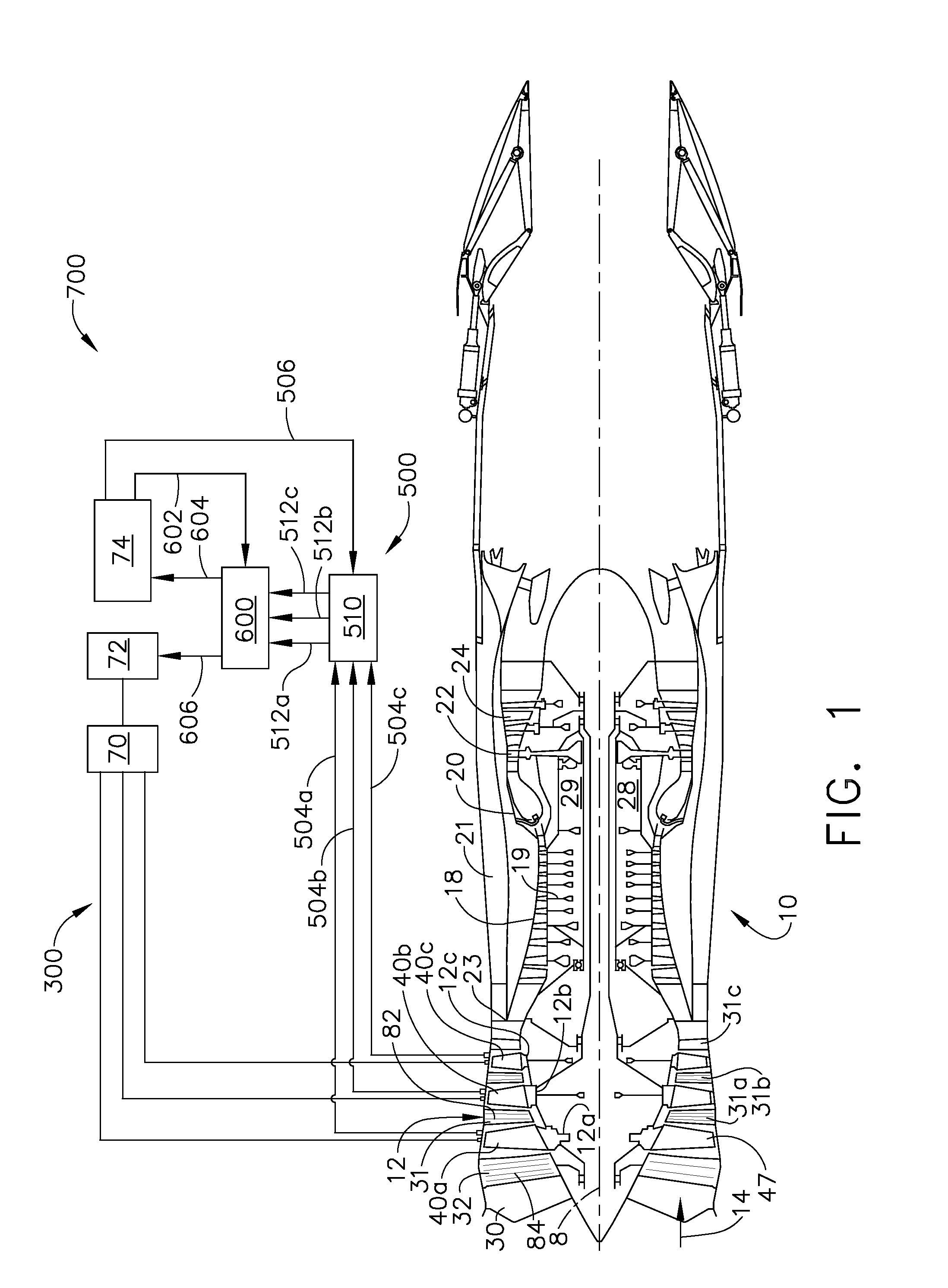
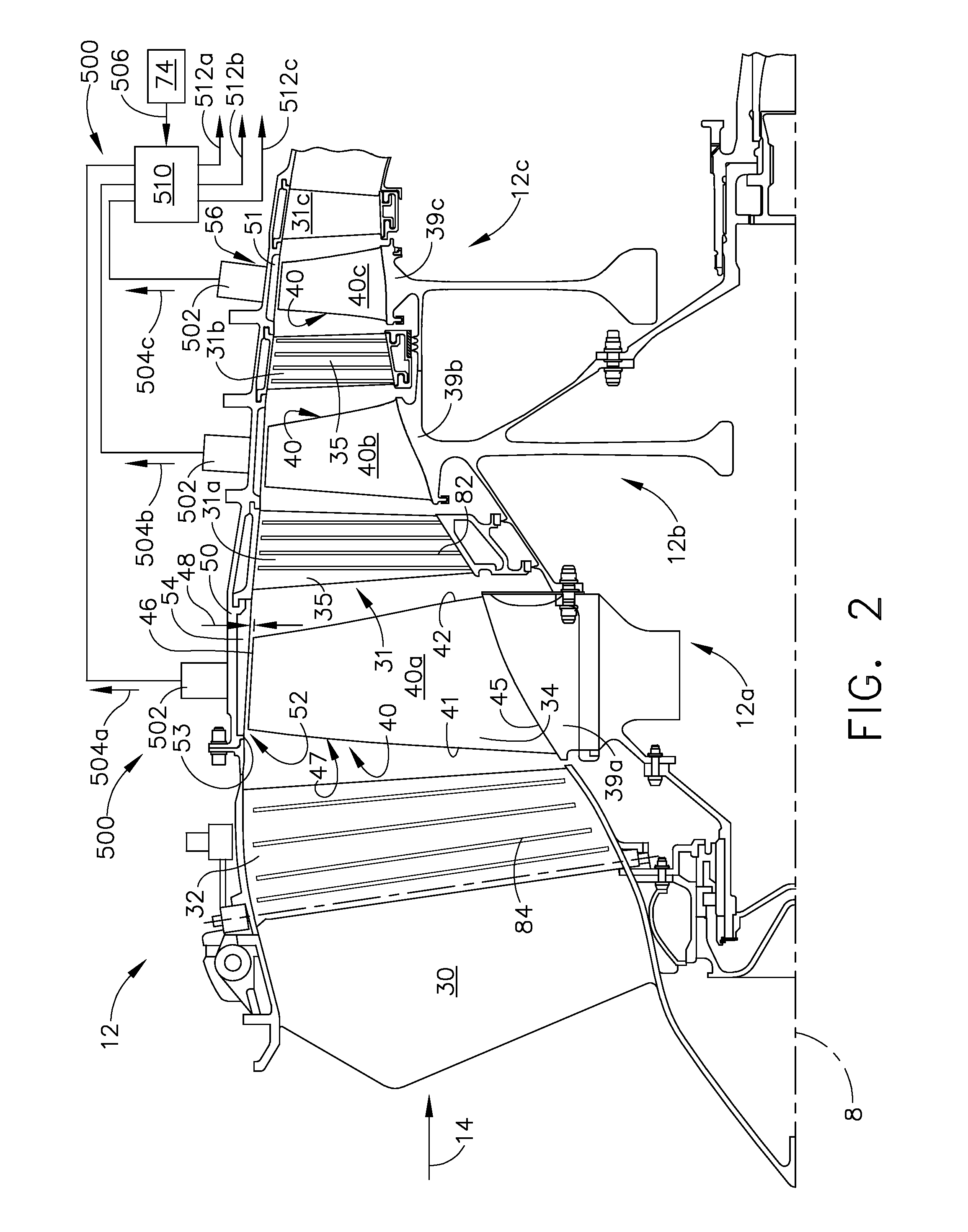
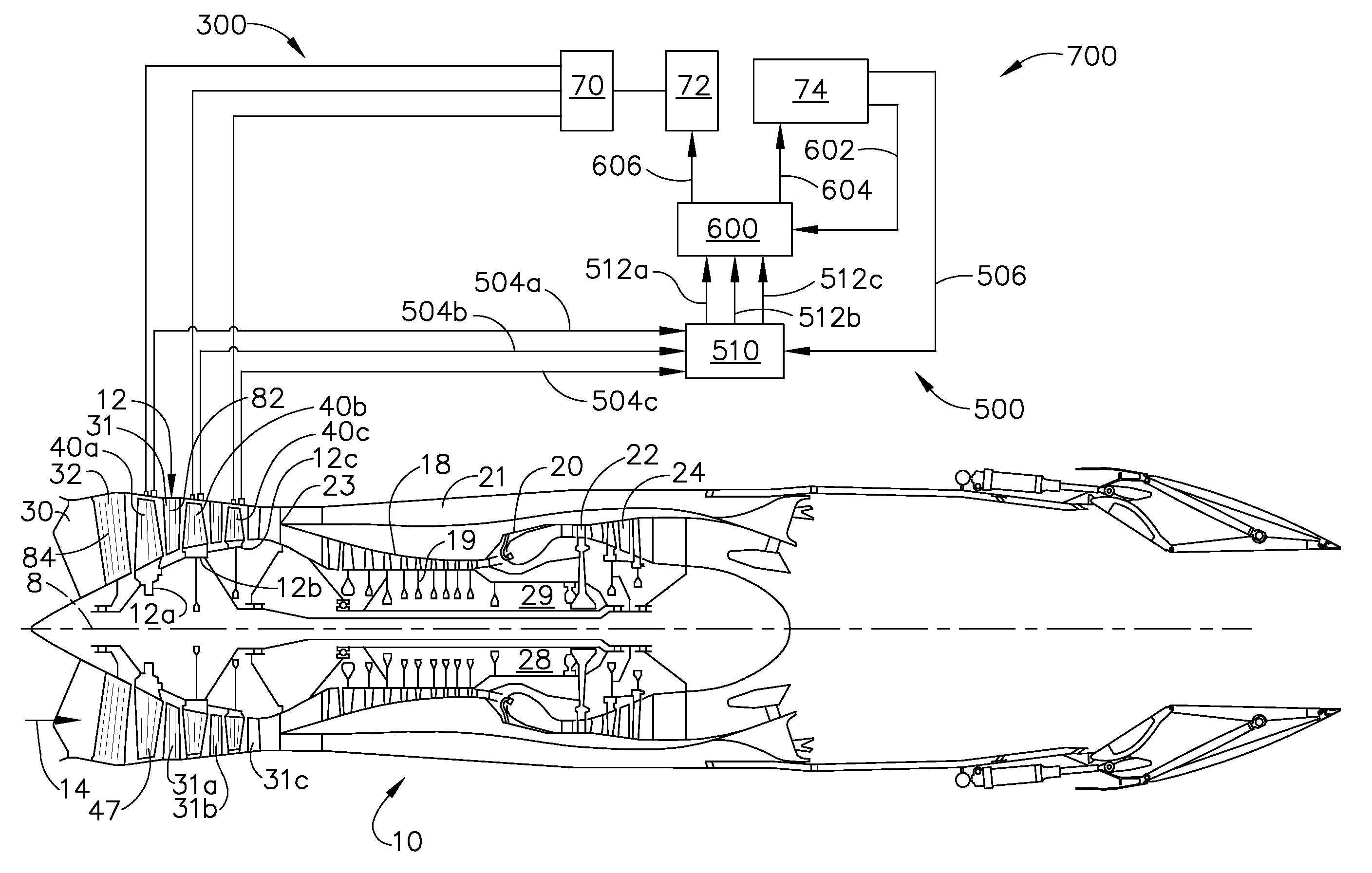
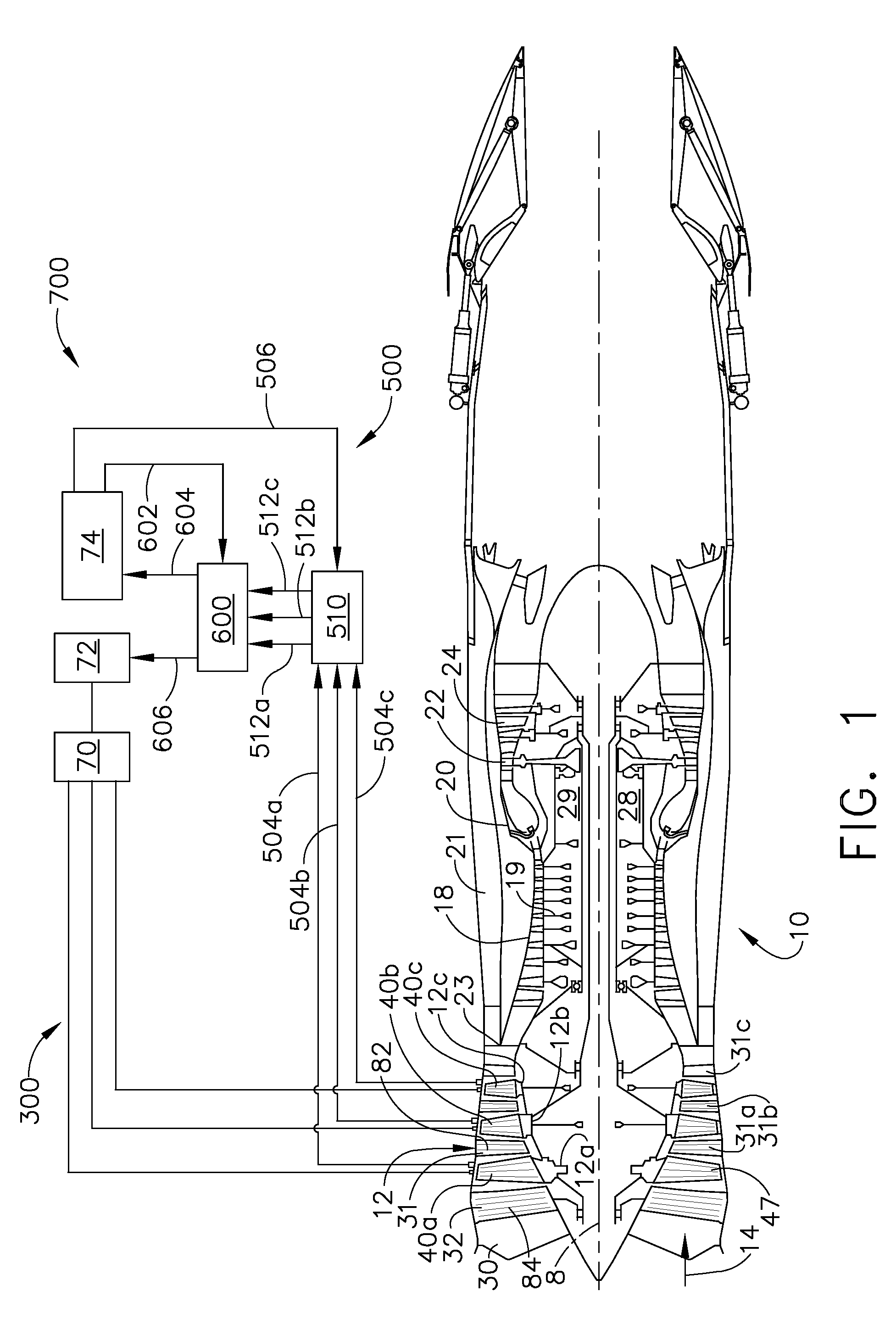
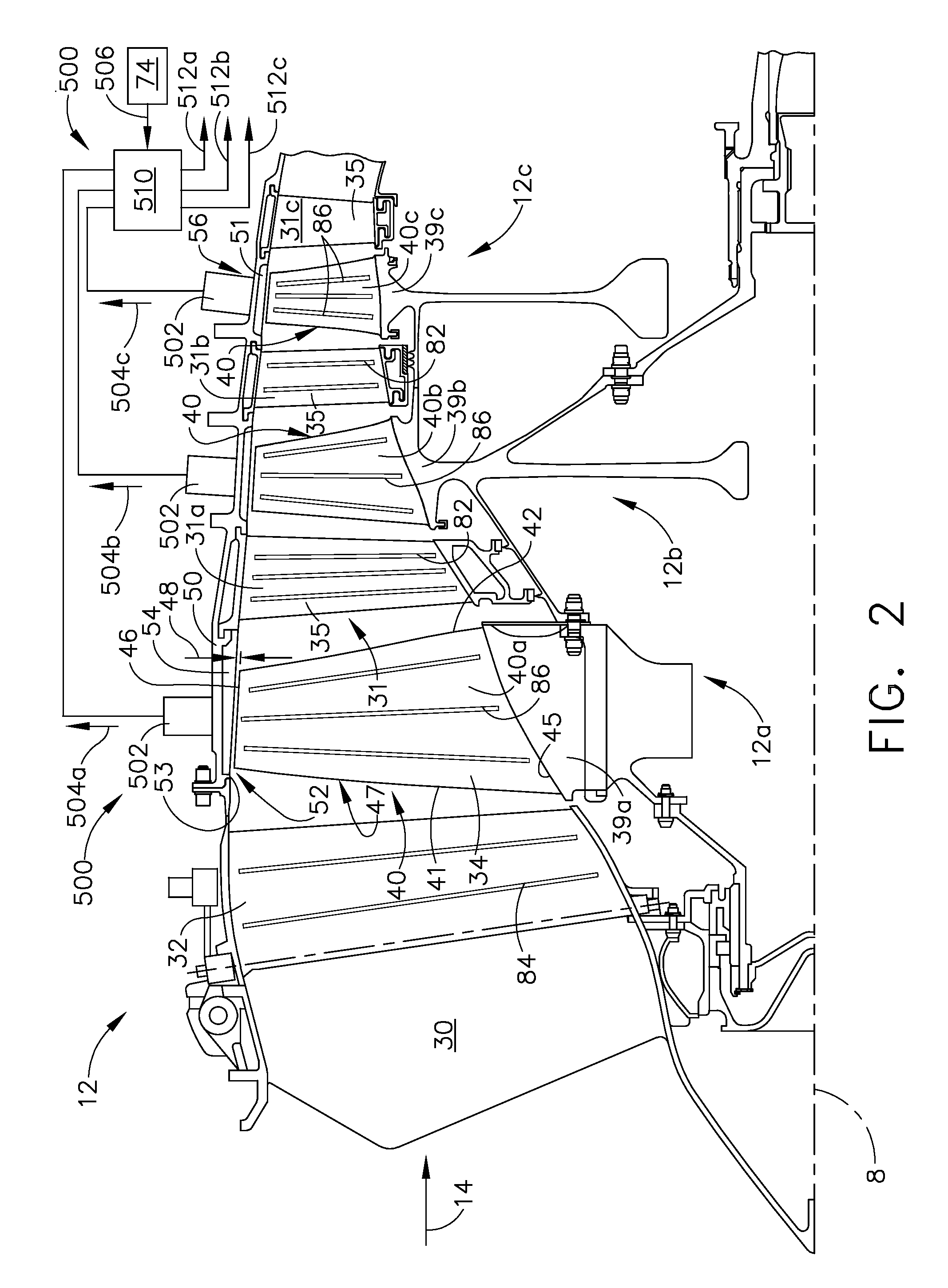
Plasma enhanced compressor duct
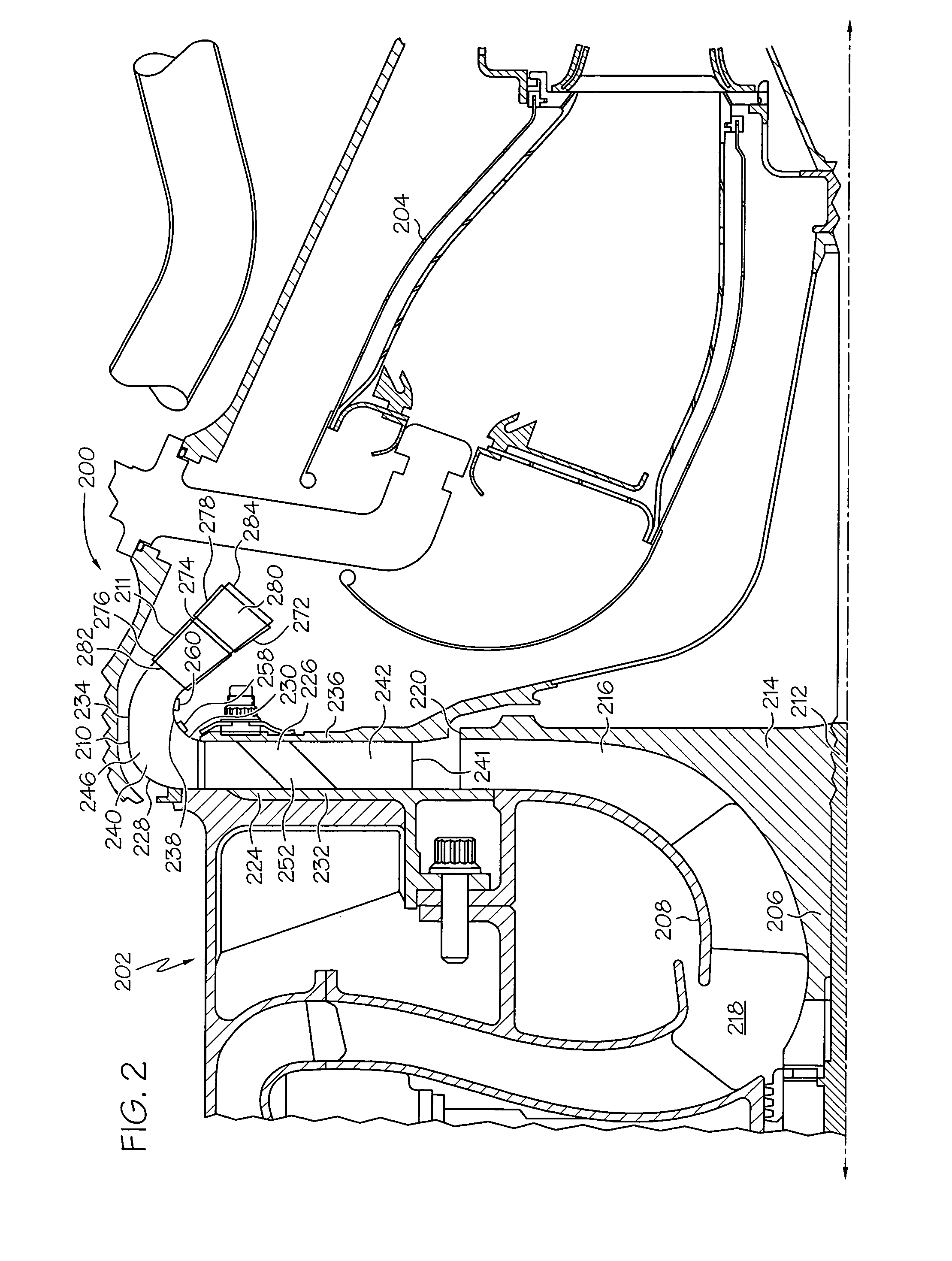
A compression system is disclosed, comprising a first compressor having a first flowpath, a second compressor having a second flowpath located axially aft from the first compressor, and a transition duct capable of flowing an airfow from the first compressor to the second compressor, the transition duct having at least one plasma actuator mounted in the transition duct.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
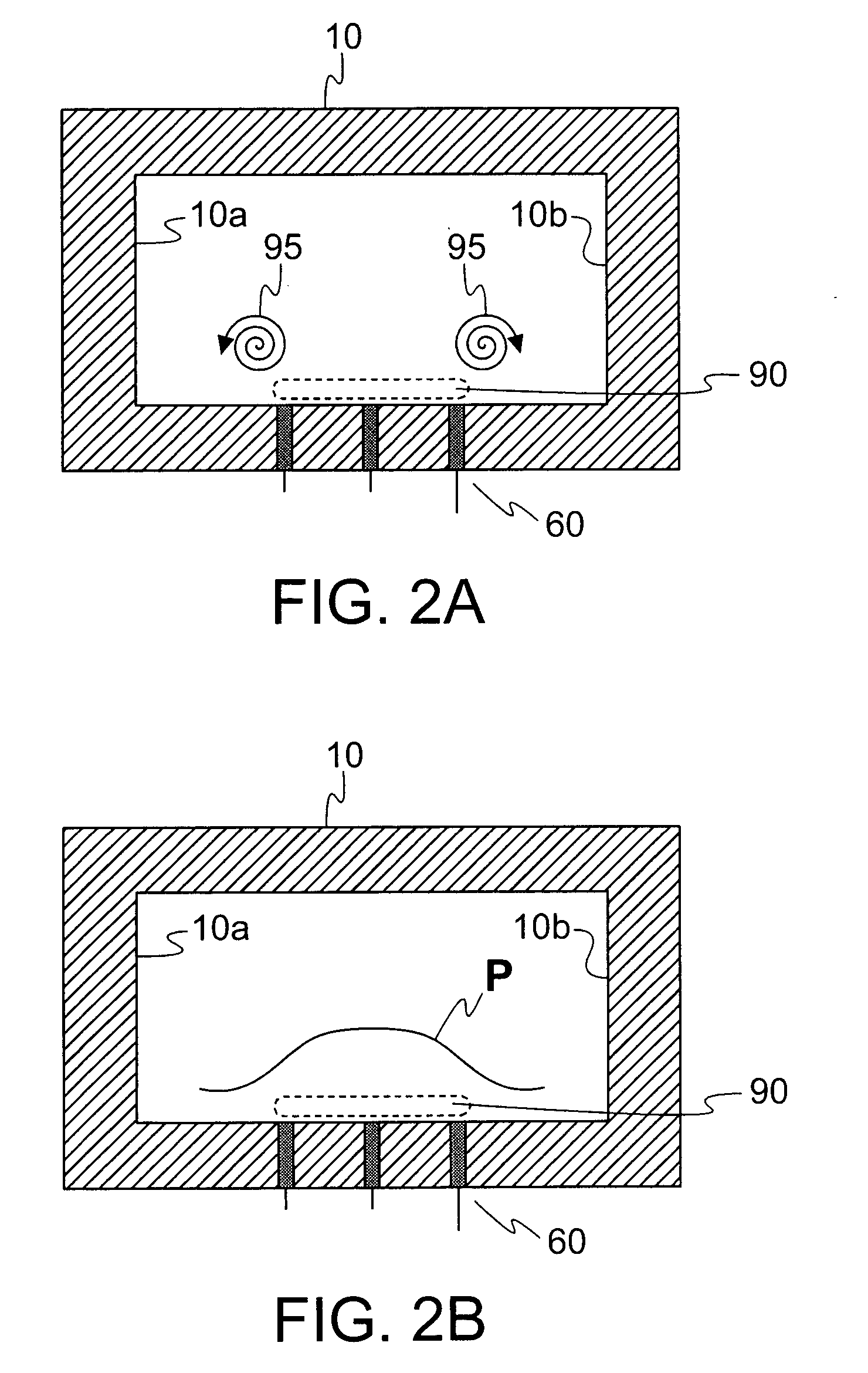
Compressor tip gap flow control using plasma actuators
A plasma generator for delaying the onset of rotation stall by tip gap flow control in, for example, an axial flow compressor is disclosed. The tip gap flow control system includes a housing surrounding a rotor of blades and having an inner wall. At least one plasma generating device is coupled to the inner wall of the housing and circumscribes at least a portion of the rotor of blades. A power supply is electrically coupled to the plasma generating device such that when the power supply energizes the plasma generating device, the axial momentum of a fluid flow between the inner wall of the housing and the tips of the rotor of blades in increased in the direction of the fluid flow.
Owner:NOTRE DAME DU LAC UNIV OF
Plasma enhanced booster and method of operation
A booster system is disclosed, comprising a first rotor stage having a plurality of first rotor blades spaced circumferentially around a rotor hub with a longitudinal axis and having a first pitch-line radius extending from the longitudinal axis, a last rotor stage located axially aft from the first rotor stage, the last rotor stage comprising a plurality of last rotor blades spaced circumferentially around the longitudinal axis and having a second pitch-line radius extending from the longitudinal axis, and a gooseneck duct located axially aft from the last rotor stage and capable of receiving an airflow, the gooseneck duct comprising an inlet end and an exit end located at a distance axially aft from the inlet end and having at least one plasma actuator mounted in the gooseneck duct.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
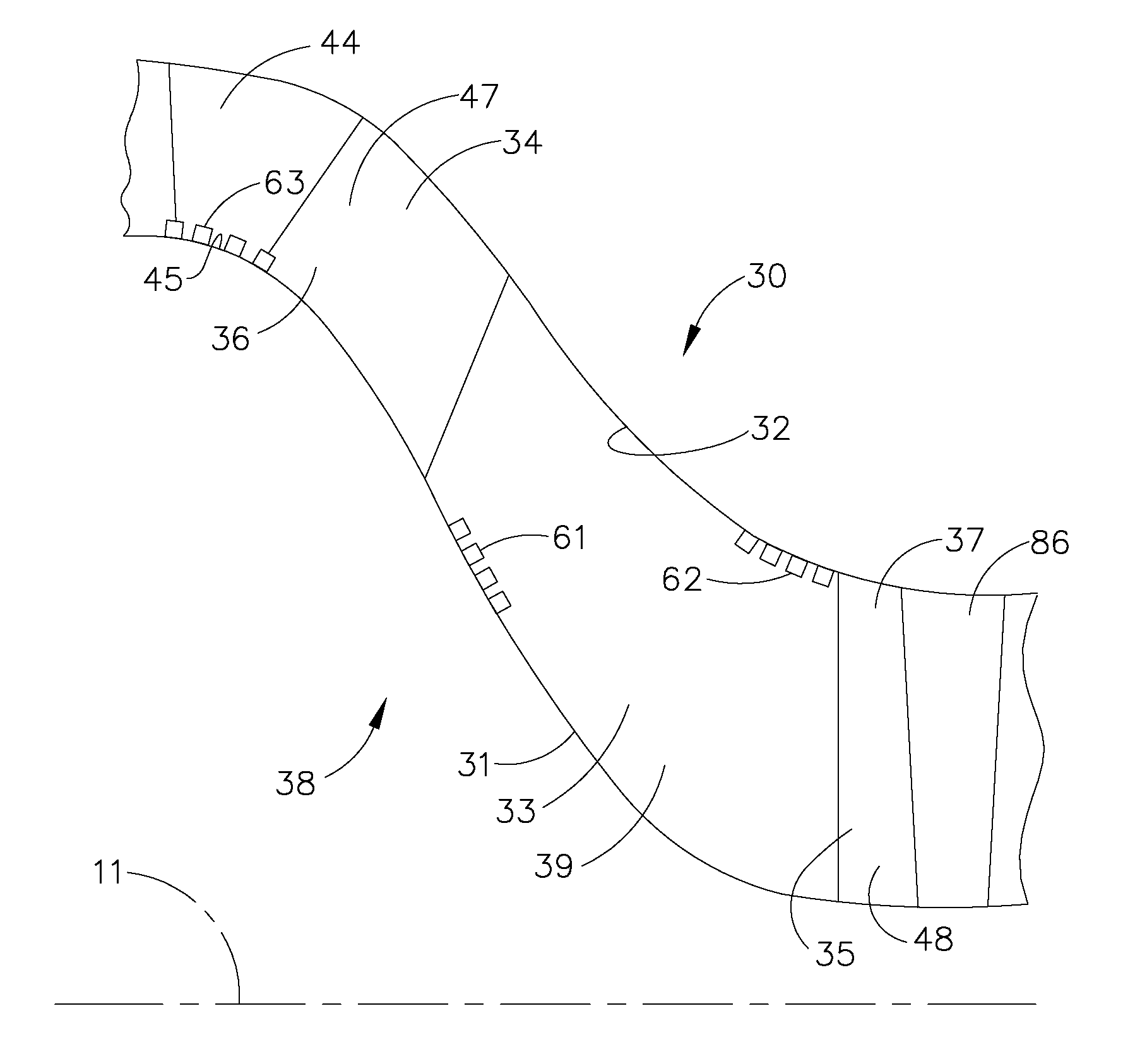
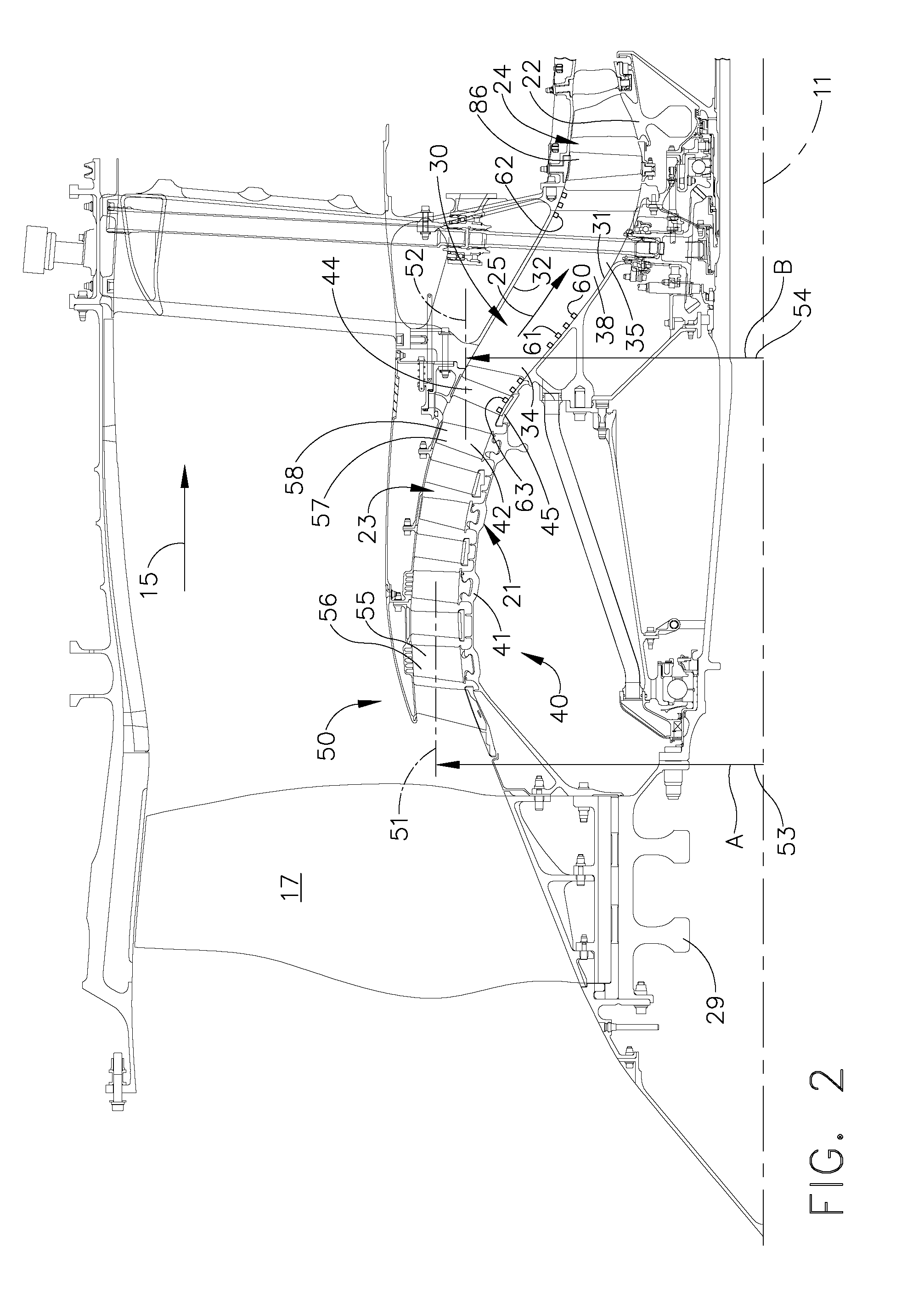
Instability Mitigation System Using Stator Plasma Actuators
ActiveUS20090169367A1Mitigate compression system instabilityBroaden the stable operating rangeAnalogue computers for vehiclesPump componentsControl systemPlasma actuator
An instability mitigation system is disclosed, comprising a stator stage located axially proximate to a rotor, the stator stage having a row of a plurality of stator vanes arranged around a centerline axis, and a mitigation system comprising at least one plasma actuator mounted on the stator vane that facilitates the improvement of the stability of the rotor, and a control system for controlling the operation of the mitigation system. An instability mitigation system further comprising a detection system for detecting an onset of an instability in a rotor and a control system for controlling the detection system and the mitigation system are disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Plasma actuators for drag reduction on wings, nacelles and/or fuselage of vertical take-off and landing aircraft
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Plasma Enhanced Stator
InactiveUS20090169363A1Mitigate compression system instabilityBroaden the stable operating rangePump componentsBlade accessoriesPlasma actuatorInstability
A compression system is disclosed, the compression system comprising a stator stage having a row of a plurality of stator vanes arranged around a centerline axis, each stator vane having a vane airfoil and at least one plasma actuator located on the stator stage. Exemplary embodiments of a detection system for detecting an instability in a compression system rotor and a mitigation system that facilitates the improvement of the stability of the rotor are disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
SINGLE DIELECTRIC BARRIER DISCHARGE PLASMA ACTUATORS WITH IN-PLASMA catalysts AND METHOD OF FABRICATING THE SAME
InactiveUS20110180149A1High strengthRaise transfer toFluid dynamicsPipeline systemsPlasma actuatorEngineering
A single dielectric barrier plasma actuator is disclosed which includes a pair of offset electrodes and a dielectric barrier therebetween which includes a catalyst at least in the area adjacent one of the electrodes for enhancing the force created in the background gas by the actuator.
Owner:FINE NEAL E +1
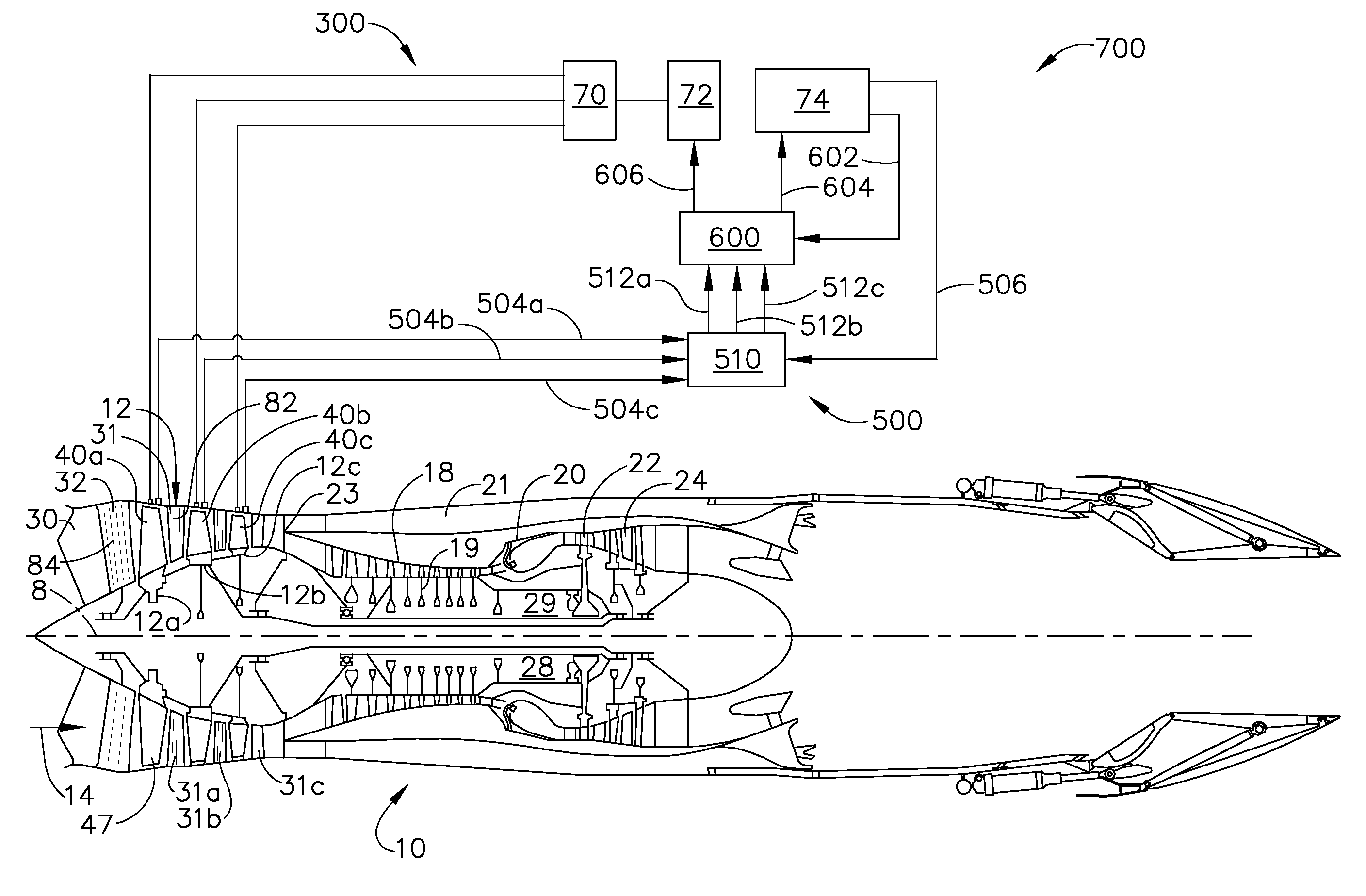
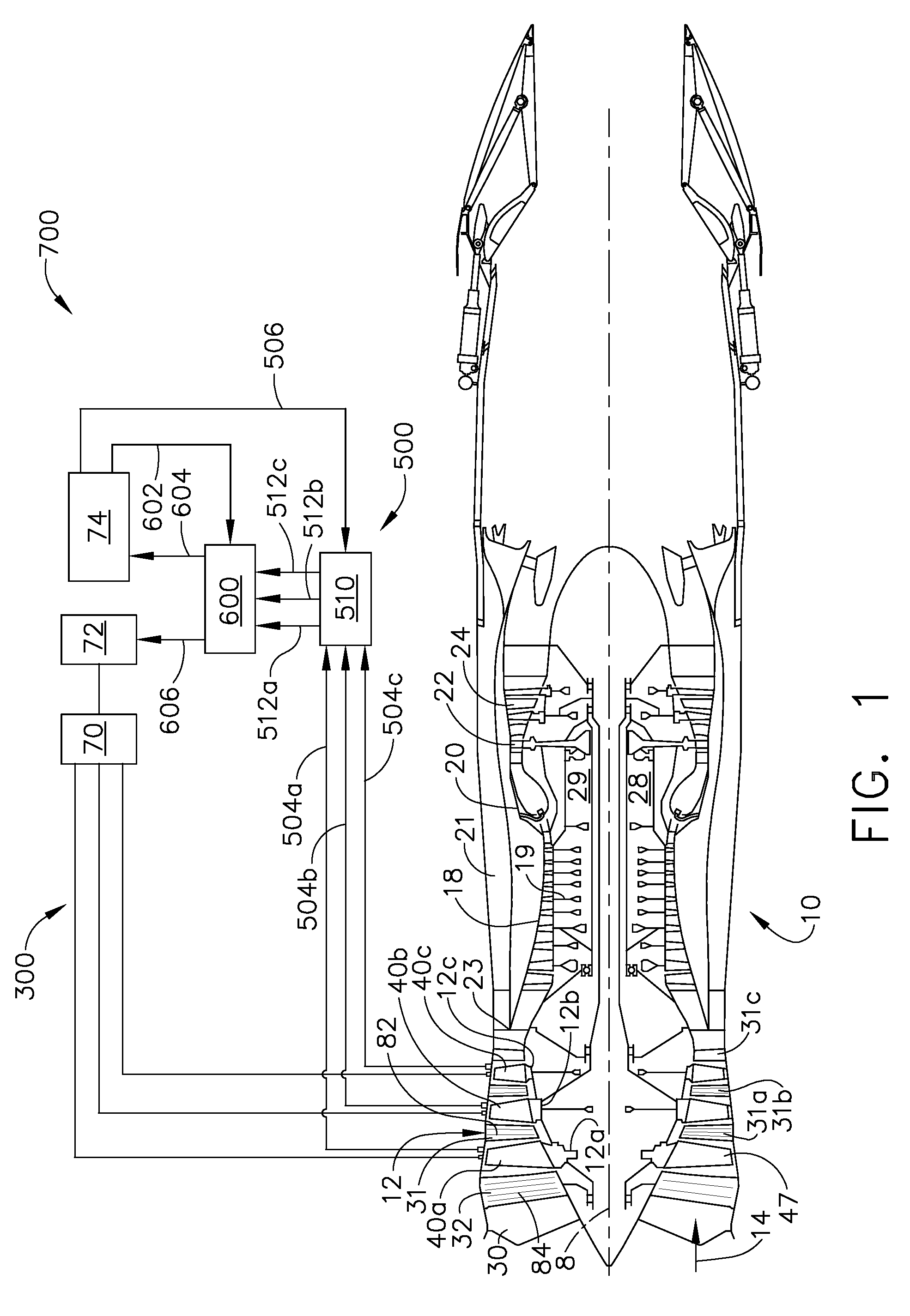
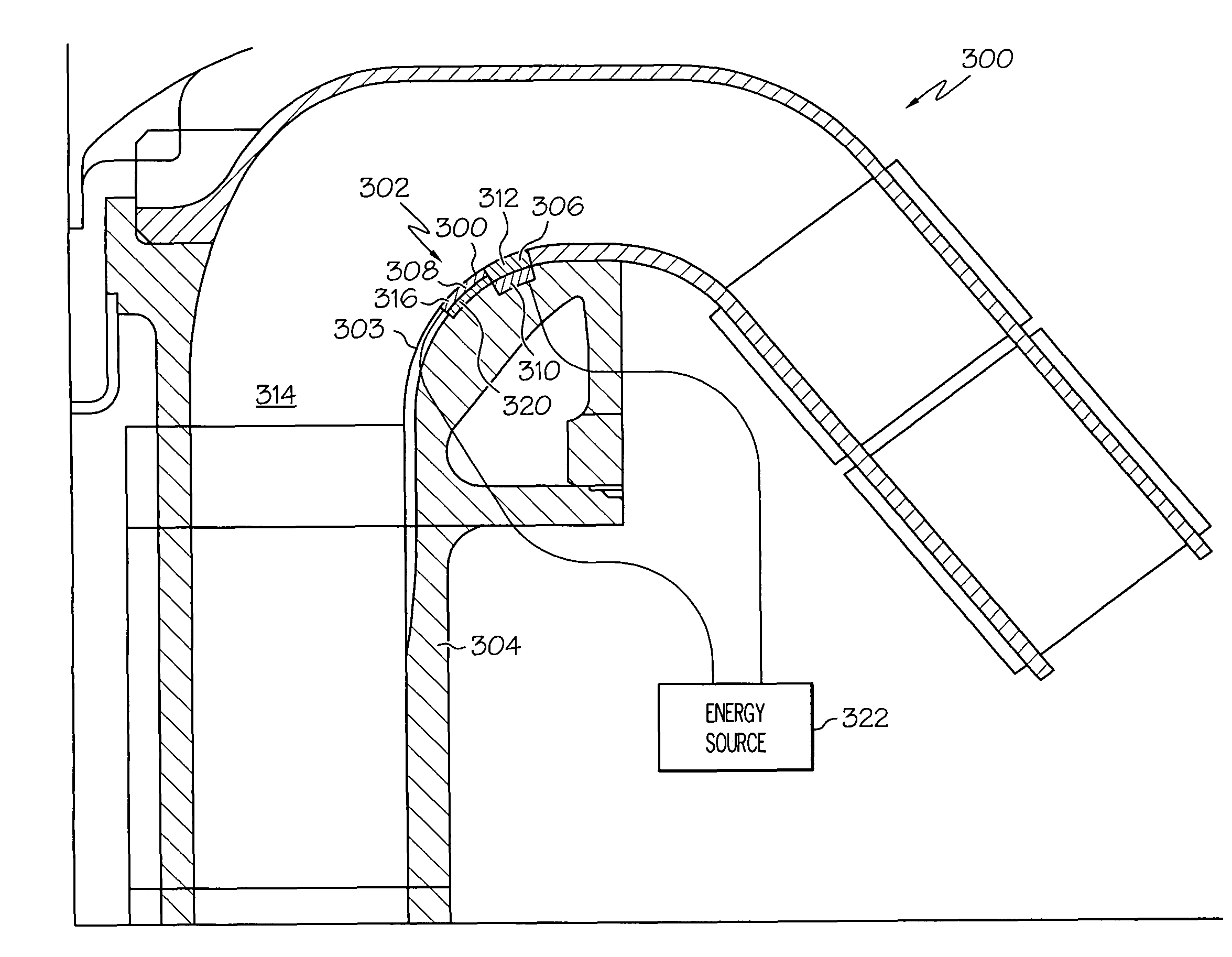
Plasma flow controlled diffuser system
A diffuser system for a compressor for a gas turbine engine includes a diffuser and a plasma actuator. The diffuser comprises a first wall and a second wall. The first and second walls form a diffuser flow passage therebetween. The plasma actuator is disposed at least partially proximate the second wall. The plasma actuator is adapted to generate an electric field to ionize a portion of air flowing through the flow passage.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Localized arc filament plasma actuators for noise mitigation and mixing enhancement
InactiveUS7334394B2Increase amplitudeHigh bandwidthAircraft navigation controlEngine fuctionsPlasma actuatorStreaming instability
A device for controlling fluid flow. The device includes an arc generator coupled to electrodes. The electrodes are placed adjacent a fluid flowpath such that upon being energized by the arc generator, an arc filament plasma adjacent the electrodes is formed. In turn, this plasma forms a localized high temperature, high pressure perturbation in the adjacent fluid flowpath. The perturbations can be arranged to produce vortices, such as streamwise vortices, in the flowing fluid to control mixing and noise in such flows. The electrodes can further be arranged within a conduit configured to contain the flowing fluid such that when energized in a particular frequency and sequence, can excite flow instabilities in the flowing fluid. The placement of the electrodes is such that they are unobtrusive relative to the fluid flowpath being controlled.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Plasma actuators for drag reduction on wings, nacelles and/or fuselage of vertical take-off and landing aircraft
An aircraft includes a surface over which an airflow passes. A plasma actuator is configured to generate a plasma above the surface, the plasma coupling a directed momentum into the air surrounding the surface to reduce separation of the airflow from the surface. A method of reducing separation of an airflow from a surface of an aircraft includes generating a plasma in air surrounding the surface at a position where the airflow would separate from the surface in the absence of the plasma.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Diffusers, diffusion systems, and methods for controlling airflow through diffusion systems
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Nozzle plasma flow control utilizing dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators
InactiveUS20110048025A1Reduce gradientReduce wall temperatureAircraft navigation controlGas-filled discharge tubesJet enginePlasma actuator
Dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators are used to manipulate exhaust flow within and behind a jet engine nozzle. The dielectric barrier discharge plasma actuators may be used to direct cooling airflow near the surface of the nozzle to reduce heating of the nozzle, create thrust vectoring, and reduce noise associated with the exhaust flow exiting the nozzle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Plasma actuator
An actuator including a first and second conductor on a dielectric, wherein application of a voltage to the first conductor creates a plasma, thereby modifying a fluid flow in communication with the actuator. Related systems and methods are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for controlling a compressor
A compressor comprises a casing having an inner surface surrounding a rotor assembly, the rotor assembly having a plurality of circumferentially spaced radially outwardly extending rotor blades, each blade having leading and trailing edges and a tip, the compressor further comprising at least one plasma actuator for suppressing rotating stall inception of the compressor, the at least one plasma actuator being mounted adjacent to the blade tips.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP +1
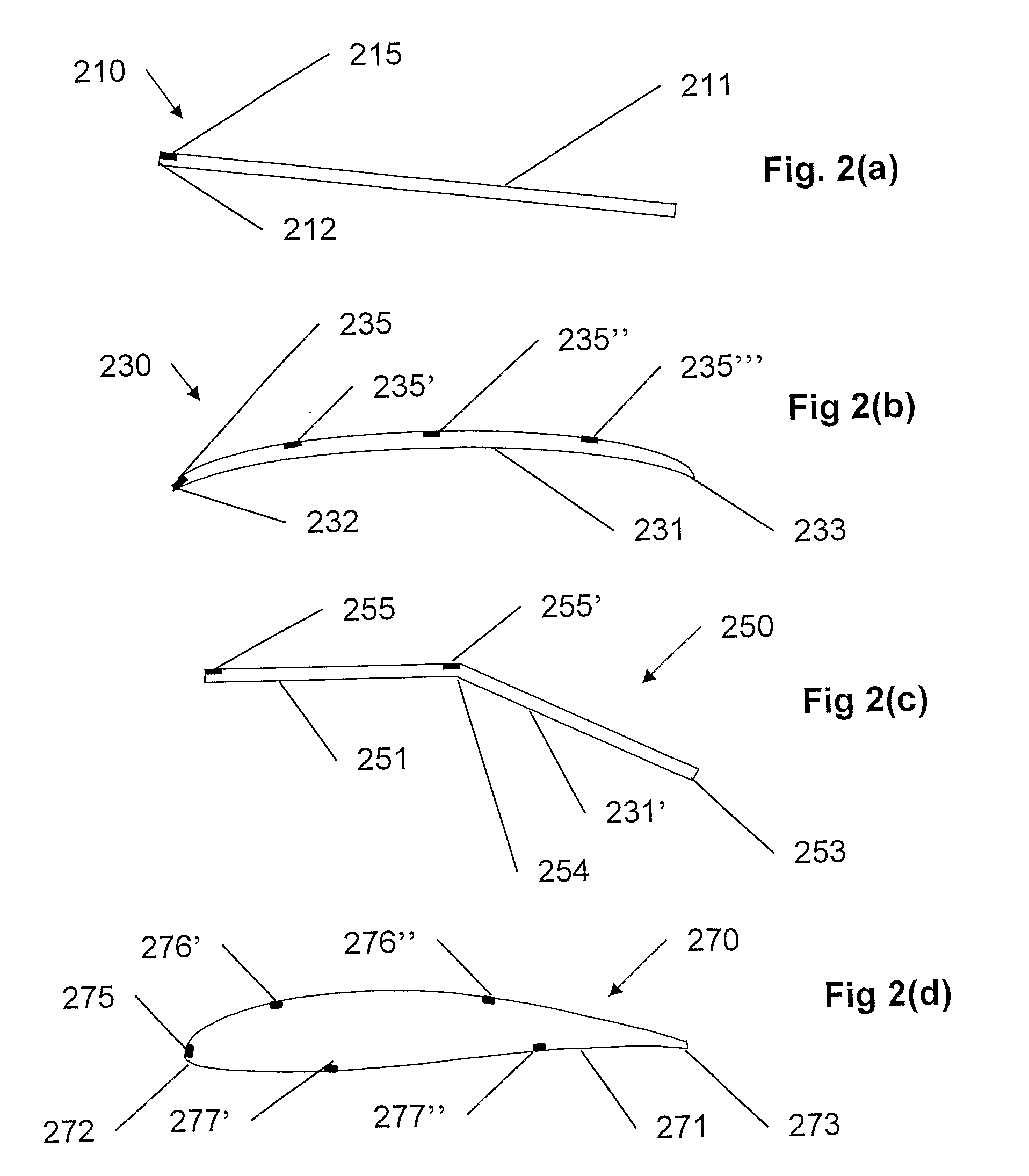
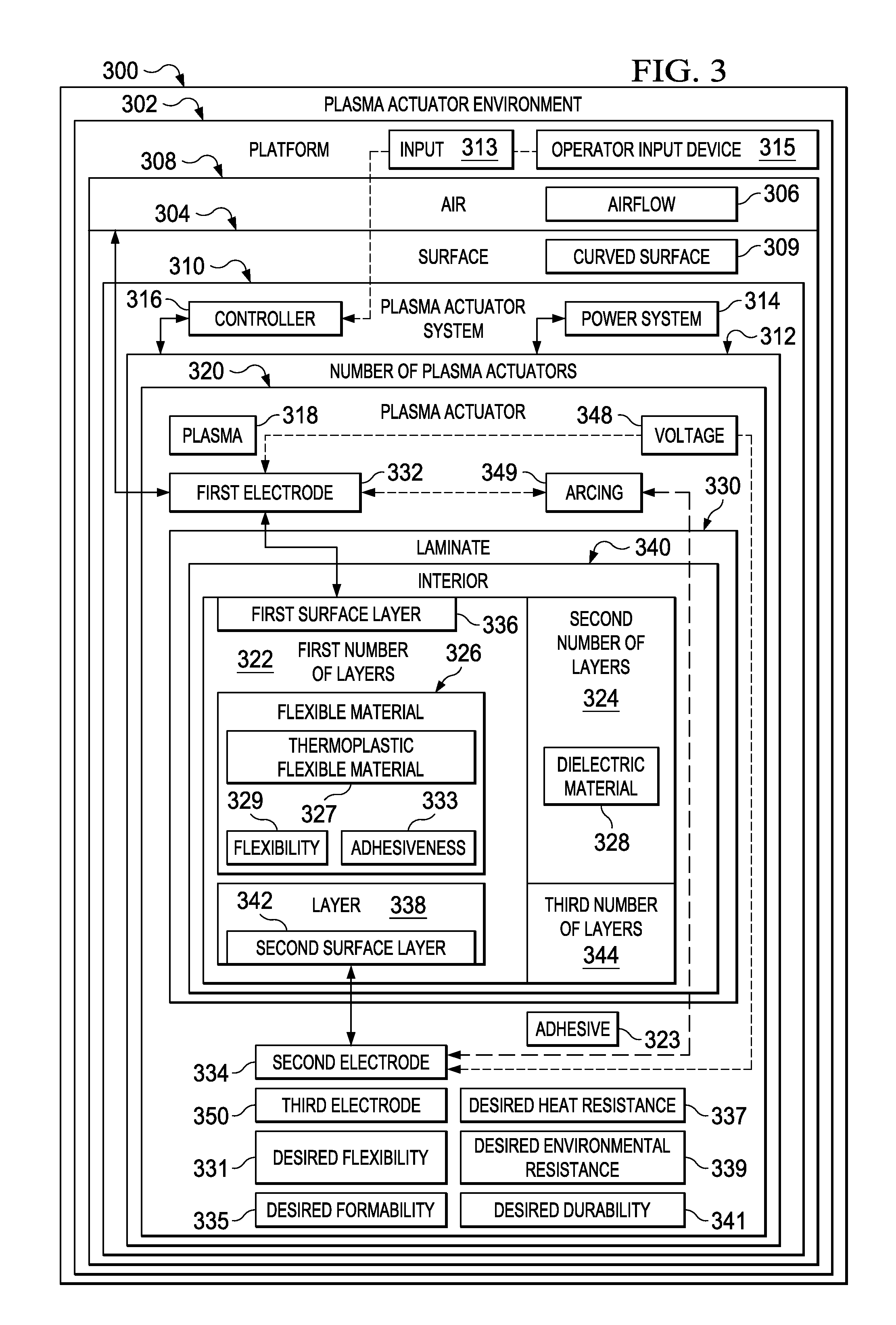
Laminated Plasma Actuator
ActiveUS20110253842A1Good flexibilityReduce arcingLamination ancillary operationsWave amplification devicesSurface layerPlasma actuator
A method and apparatus may comprise a first number of layers of a flexible material, a second number of layers of a dielectric material, a first electrode attached to a surface layer in the first number of layers, and a second electrode attached to a second layer in one of the first number of layers and the second number of layers. The first number of layers may be interspersed with the second number of layers. The first electrode may be configured to be exposed to air. The first electrode and the second electrode may be configured to form a plasma in response to a voltage.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method of deicing and prevention or delay of flow separation over wind turbine blades
ActiveUS20110135467A1Reduce and eliminate collectionIncrease surface temperaturePropellersReaction enginesPlasma actuatorTurbine blade
A system for deicing a wind turbine blade includes an electrically powered active plasma actuator applied to a desired portion of a wind turbine blade. The activated plasma actuator energizes the air in the vicinity of the plasma actuator to increase the surface temperature of the wind turbine blade in the vicinity of the plasma actuator sufficiently to reduce or eliminate the collection of ice on a desired portion of the wind turbine blade.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Plasma Enhanced Rotor
InactiveUS20100047055A1Broaden the stable operating rangeReduce instabilityWind motor controlPump componentsPlasma actuatorInstability
A compression system is disclosed, the compression system comprising a rotor having a plurality of blades arranged around a centerline axis, each blade having a blade airfoil and a blade tip, and at least one plasma actuator located on a blade. Exemplary embodiments of a detection system for detecting an instability in a compression system rotor and a mitigation system comprising at least one plasma actuator mounted on a blade to facilitate the improvement of the stability of the rotor are disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Plasma optimized aerostructures for efficient flow control
InactiveUS9541106B1Improve surface propertiesEnabling useAircraft navigation controlBoundary layer controlsPlasma actuatorAirplane
The present invention relates to a method of designing or optimizing a control surface for use with plasma actuators for controlling an aircraft, missile, munition or automobile, and more particularly to controlling fluid flow across their surfaces or other surfaces using plasma actuators, which would benefit from such a method. The various embodiments provide the steps to increase the efficiency of aircraft, missiles, munitions and automobiles. The method of flow control also provides a means for reducing aircraft, missile's, munition's and automobile's power requirements. These methods also provide alternate means for aerodynamic control using low-power hingeless plasma actuator devices.
Owner:ORBITAL RES +1
Method of controlling aircraft, missiles, munitions and ground vehicles with plasma actuators
ActiveUS8267355B1Improve efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsDirection controllersBoundary layer controlsControl flowJet aeroplane
A method of controlling an aircraft, missile, munition or ground vehicle with plasma actuators, and more particularly of controlling fluid flow across their surfaces or other surfaces which would benefit from such a method, includes the design of an aerodynamic plasma actuator for the purpose of controlling airflow separation over a control surface of a aircraft, missile, or a ground vehicle, and a method of determining a modulation frequency for the plasma actuator for the purpose of fluid flow control over these vehicles. Various embodiments provide steps to increase the efficiency of aircraft, missiles, munitions and ground vehicles. The method of flow control reduces the power requirements of the aircraft, missile, munition and or ground vehicle. These methods also provide alternative aerodynamic control using low-power hingeless plasma actuator devices.
Owner:ORBITAL RES +1
Methods and apparatus for reducing drag via a plasma actuator
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Plasma cooling heat sink
InactiveUS20080302514A1Remove heatImprove cooling effectIndirect heat exchangersHeat transfer modificationPlasma actuatorEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention uses plasma-driven gas flow to cool down electronic devices. The cooling device comprises heat sink fin assembly, plasma actuator assembly, and magnetic circuit assembly. The plasma actuator assembly comprises electrodes and dielectric pieces. Voltages are applied to electrodes to drive the plasma gas flow. The magnetic circuit assembly provides magnetic field to interact with electrical field and plasma flow, and therefore an induced gas flow is pumped into, or pumped out from, heat sink fin assembly, to cool down heat sink fins.
Owner:OUYANG CHIEN
Instability Mitigation System Using Rotor Plasma Actuators
ActiveUS20100284786A1Broaden the stable operating rangeReduce instabilityPump componentsBlade accessoriesControl systemPlasma actuator
An instability mitigation system is disclosed, comprising a rotor having a row of blades arranged around a centerline axis, and a mitigation system comprising at least one plasma actuator mounted on a blade that facilitates the improvement of the stability of the rotor, and a control system for controlling the operation of the mitigation system. An instability mitigation system further comprising a detection system for detecting an onset of an instability in a rotor and a control system for controlling the detection system and the mitigation system are disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
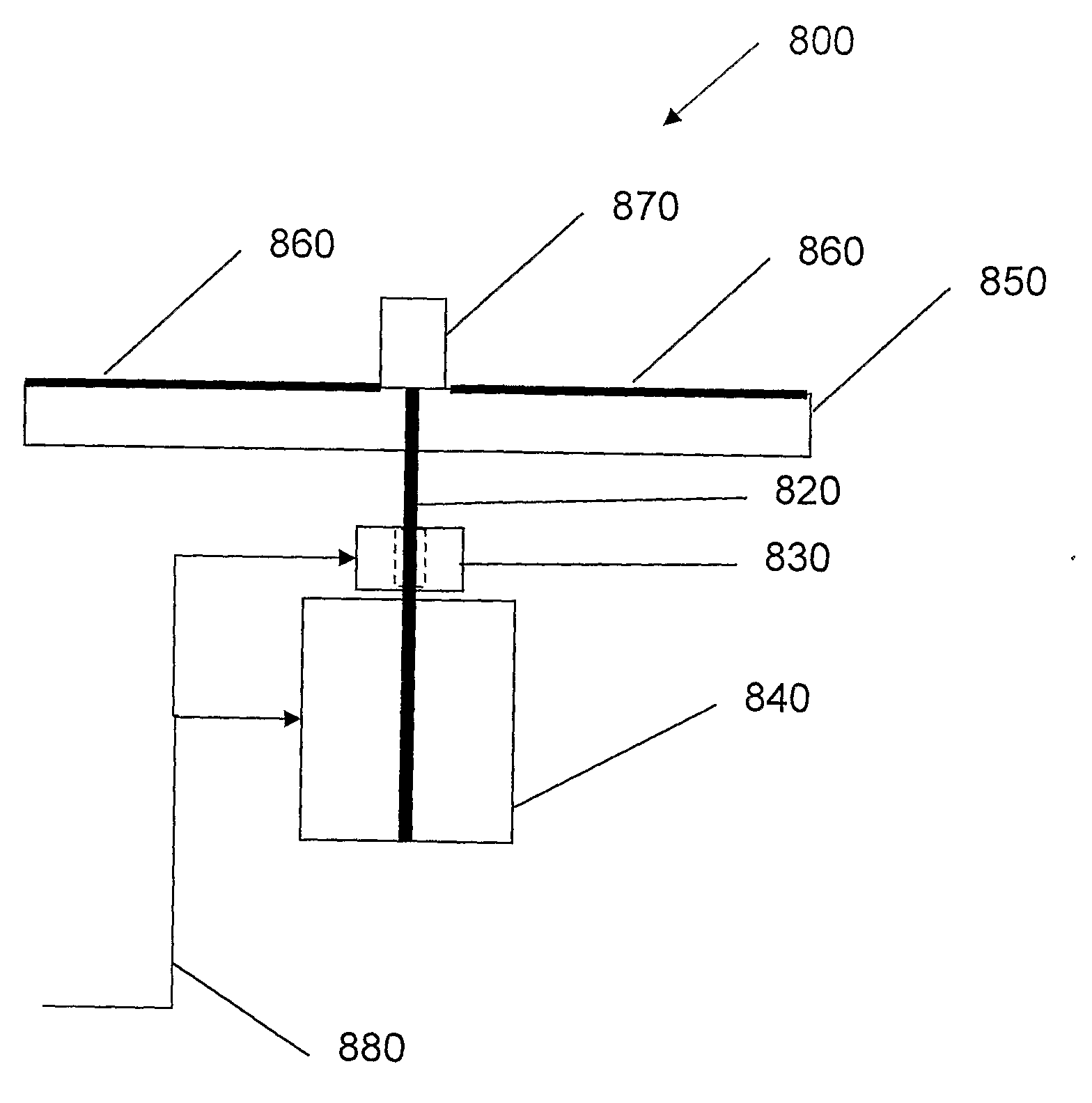
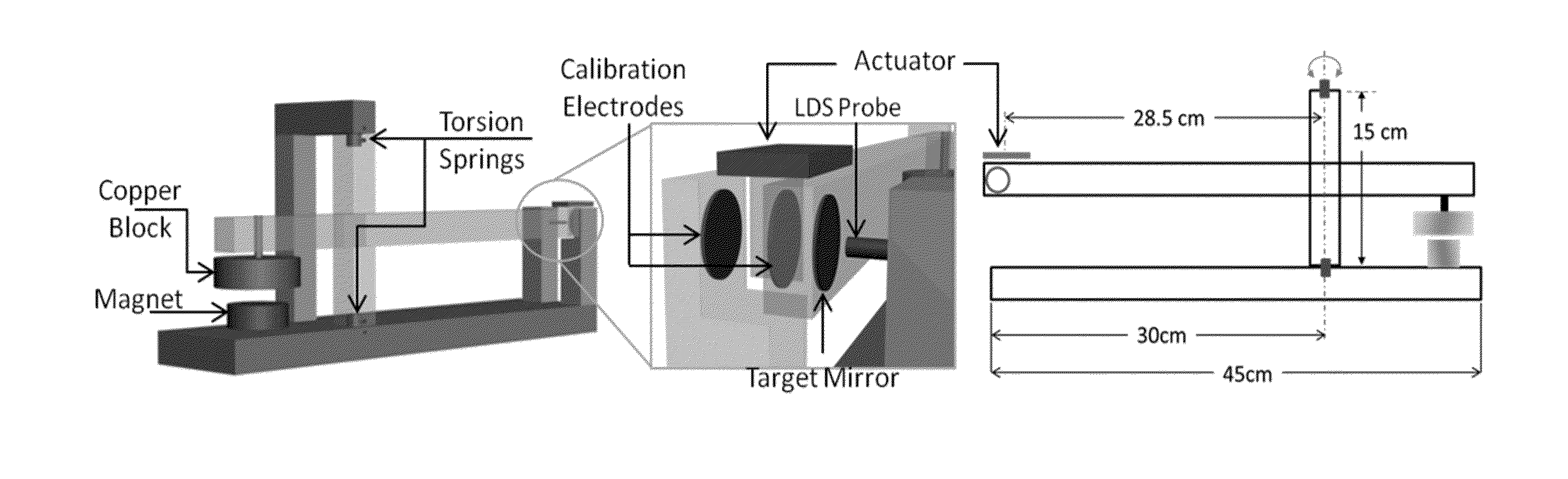
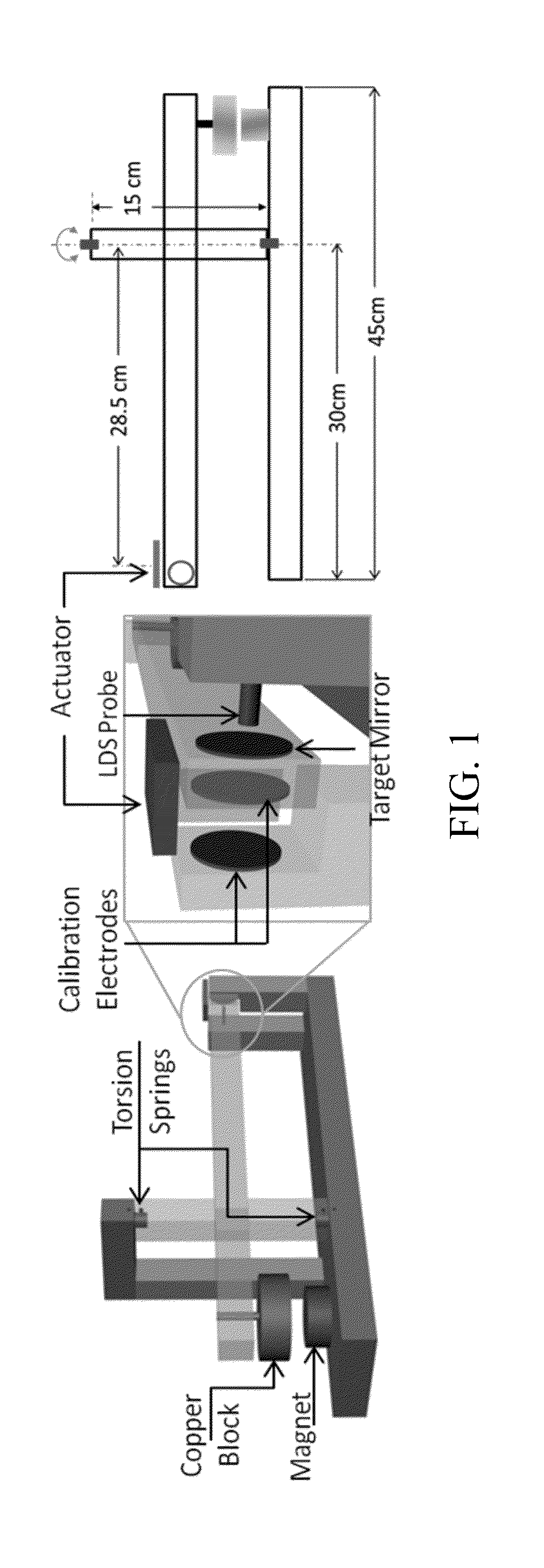
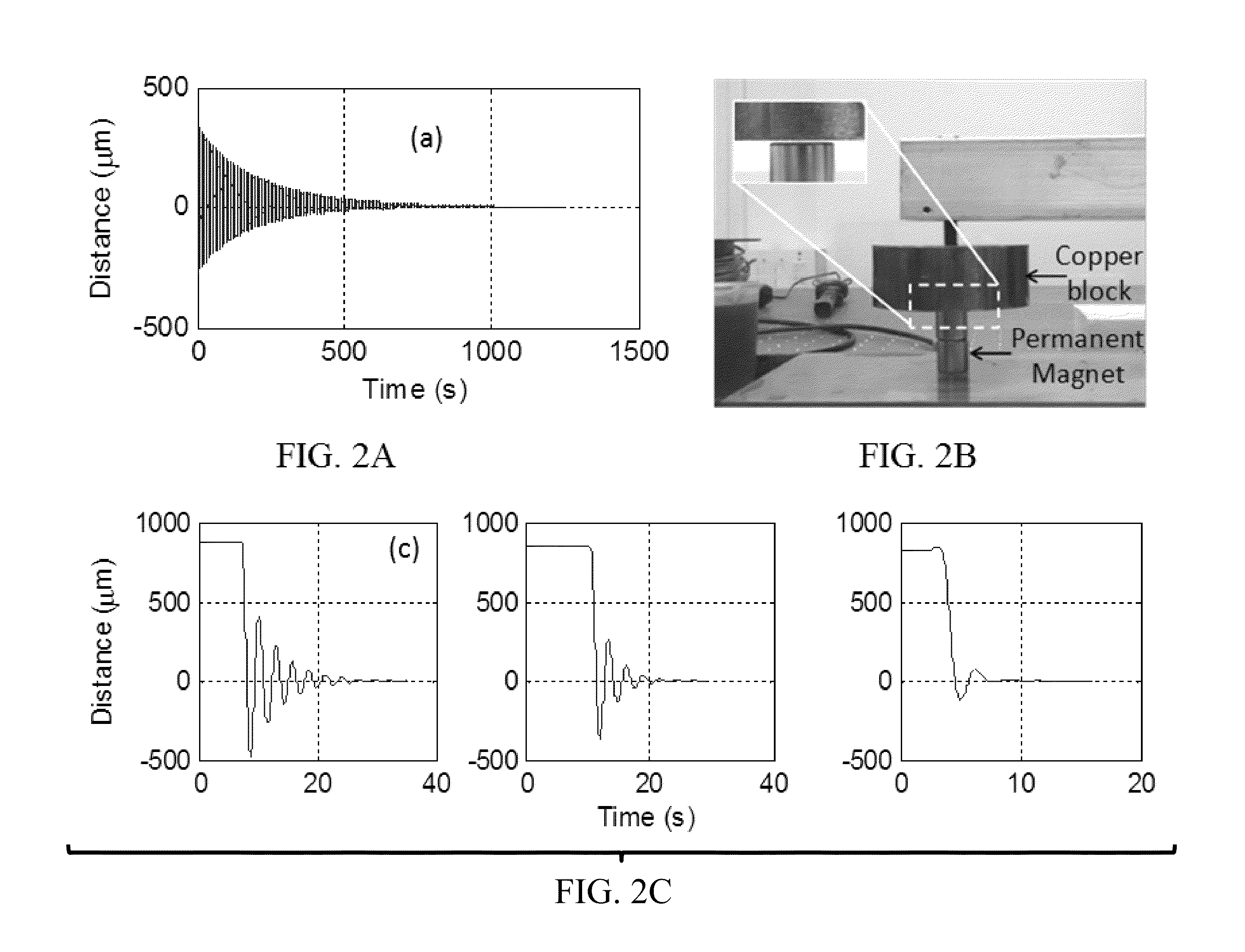
Method and Apparatus for Measuring Thrust
ActiveUS20160202131A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPlasma actuatorEddy current
Embodiments of the invention relate to a thrust stand and a method of measuring thrust. Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method of calibrating a thrust stand. Embodiments of the subject thrust stand can incorporate a passive eddy current based damper. Specific embodiments of the passive eddy current based damper can function without contact with the balance arm. Further specific embodiments of the passive eddy current based damper can be used in a vacuum. Embodiments can utilize signal analysis techniques to identify and reduce noise. A logarithmic decrement method can be used to calibrate the thrust stand. Force measurements can be made with embodiments of the subject thrust stand for a standard macroscale dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma actuator and / or other thrust producing devices.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com