Patents
Literature
161results about "Canard-type aircraft" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
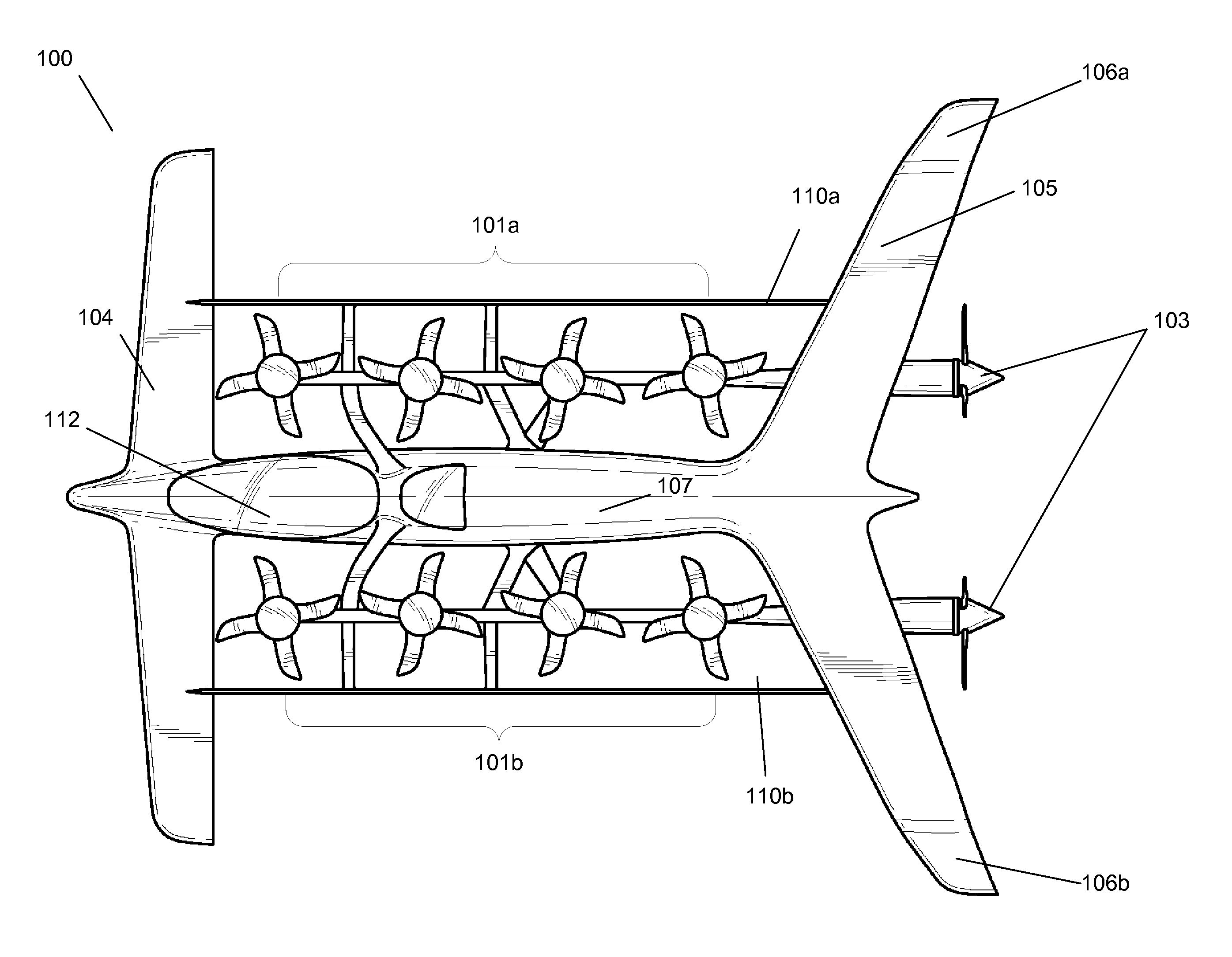
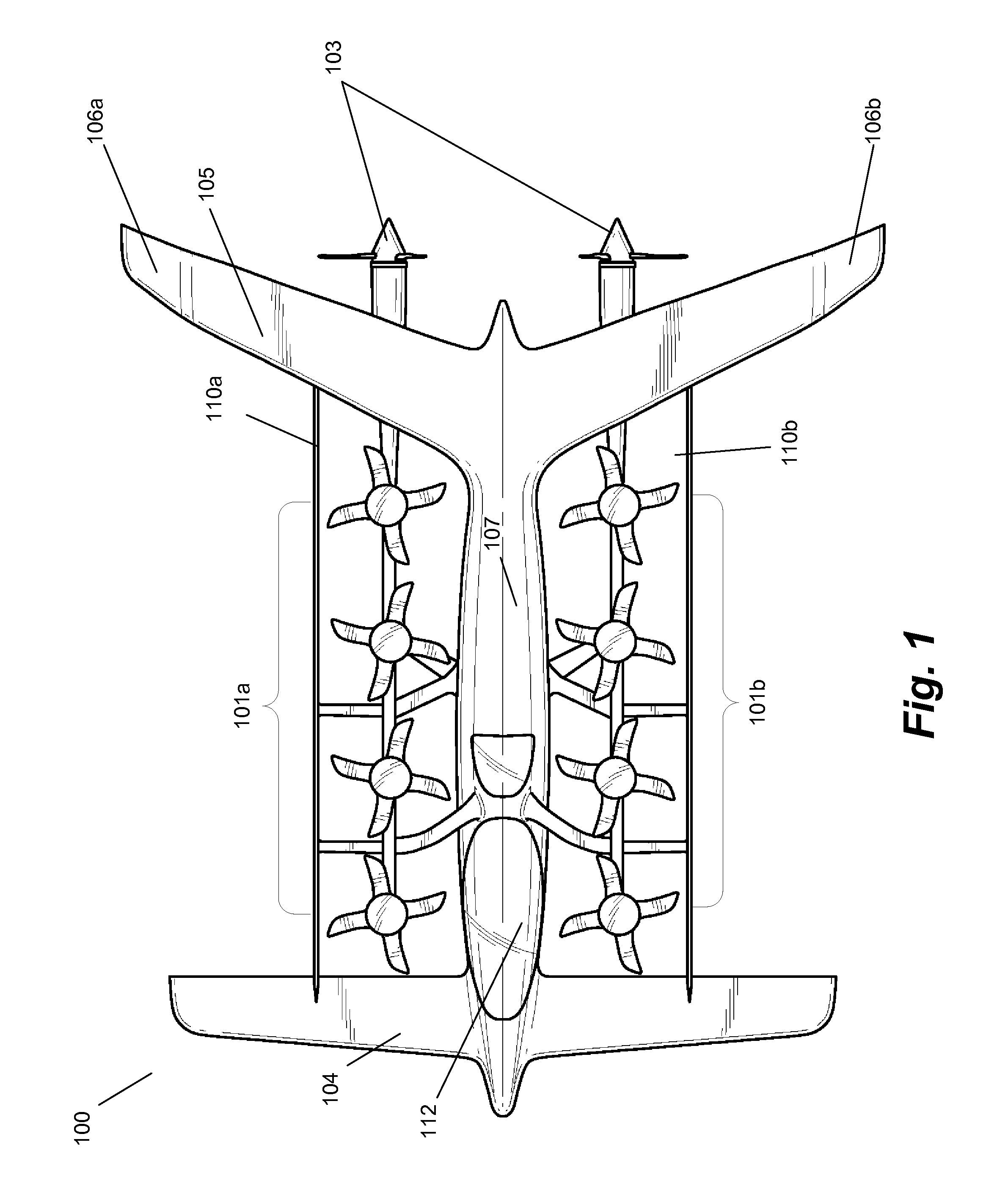
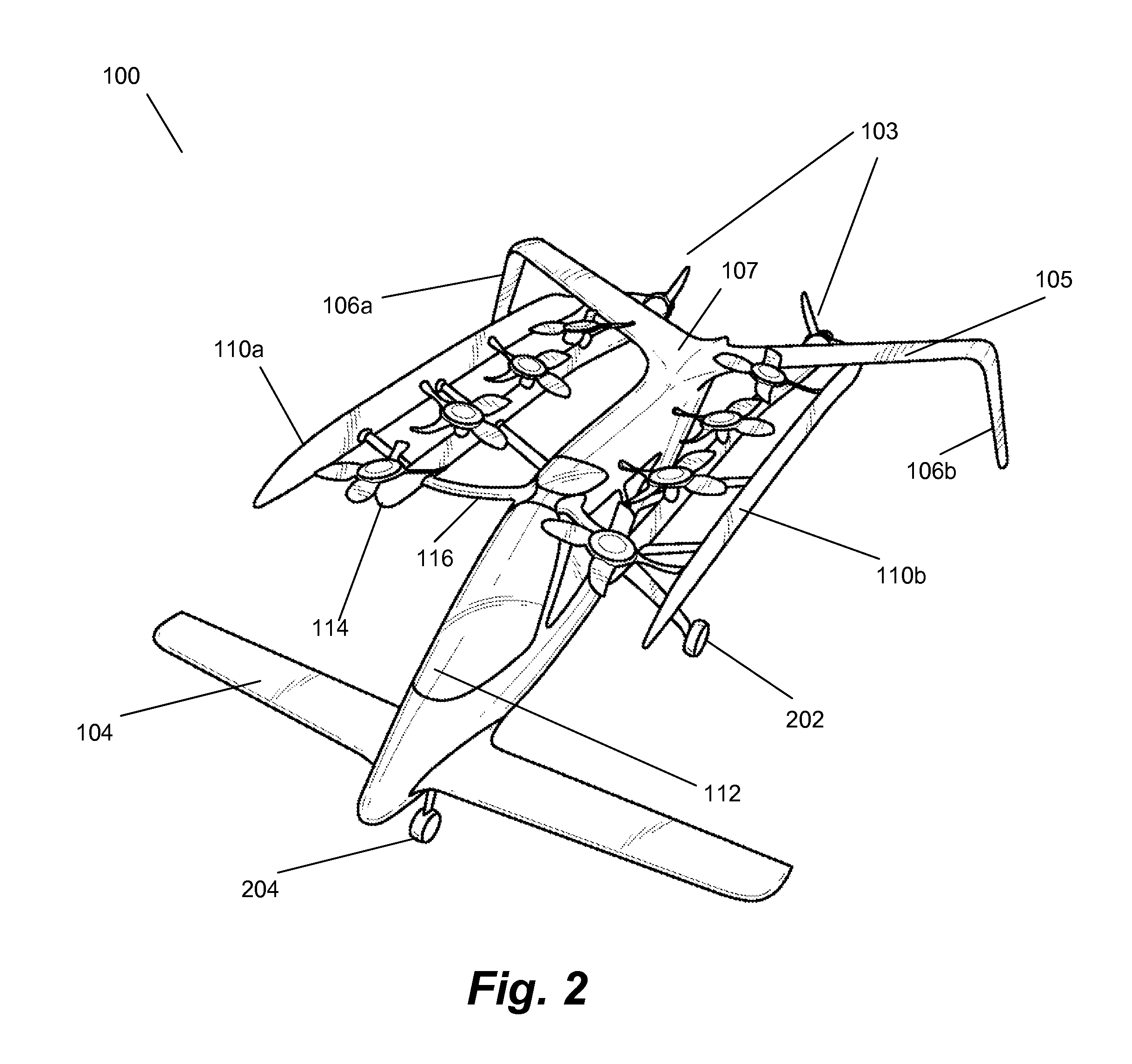
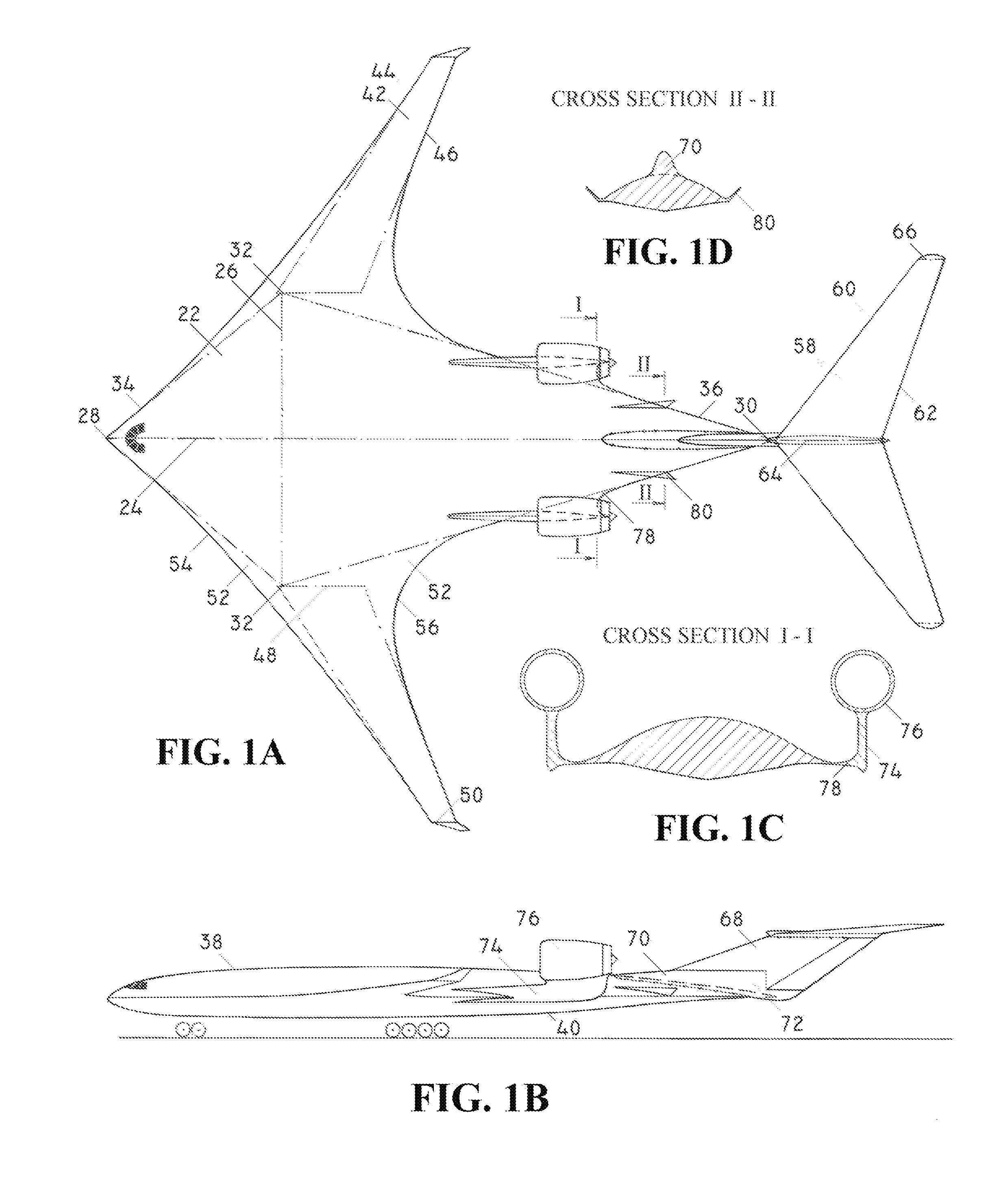
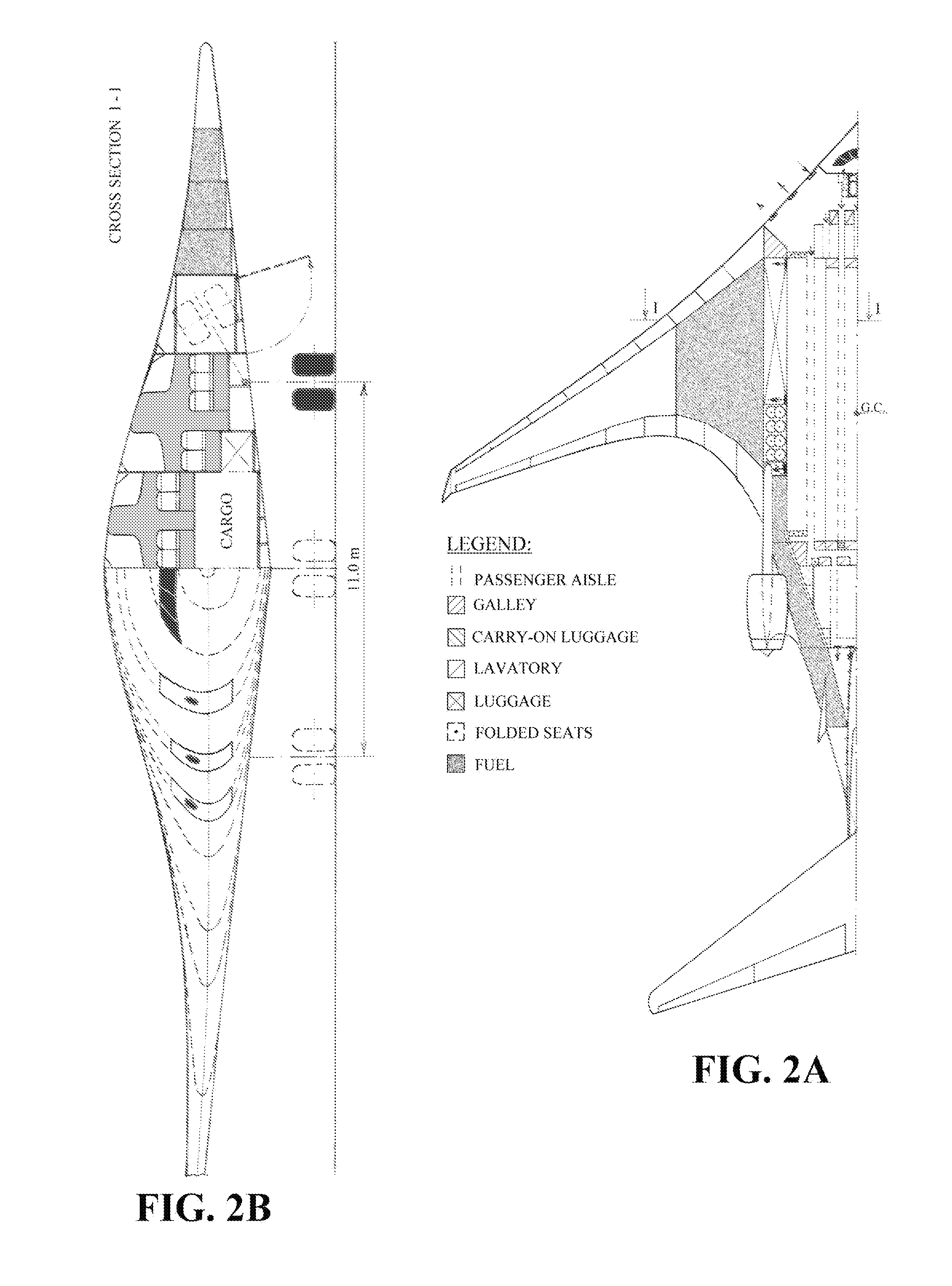
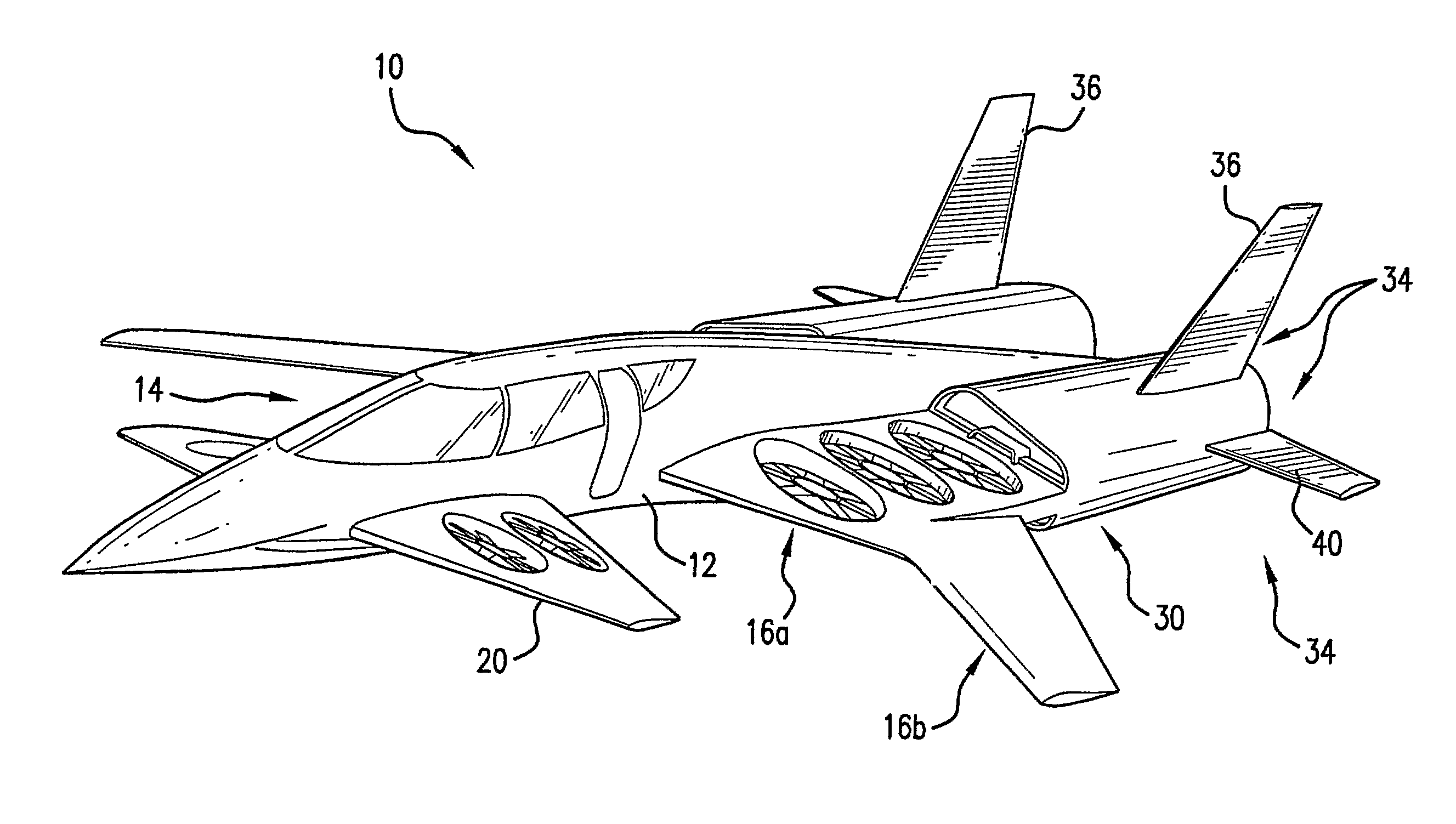
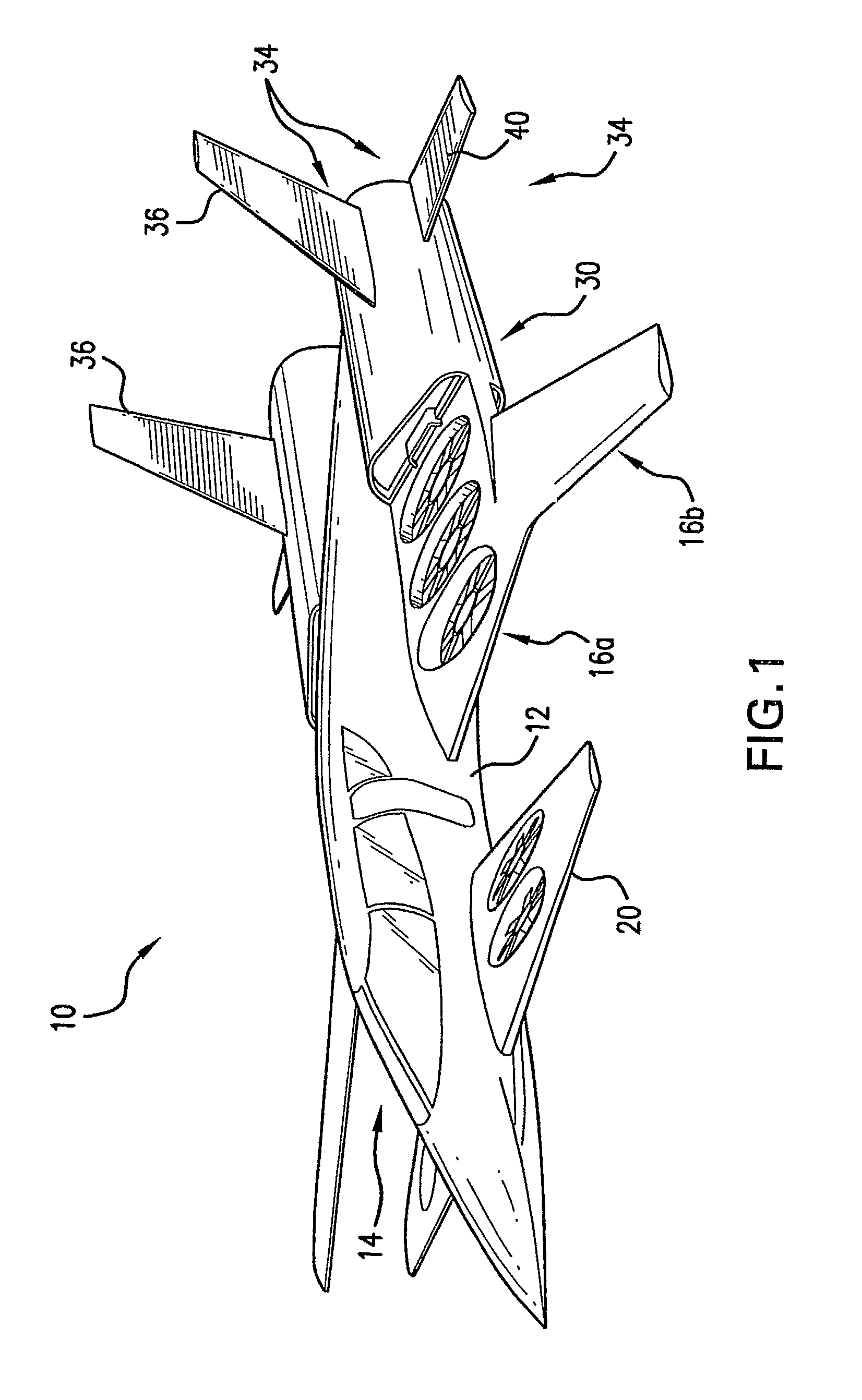
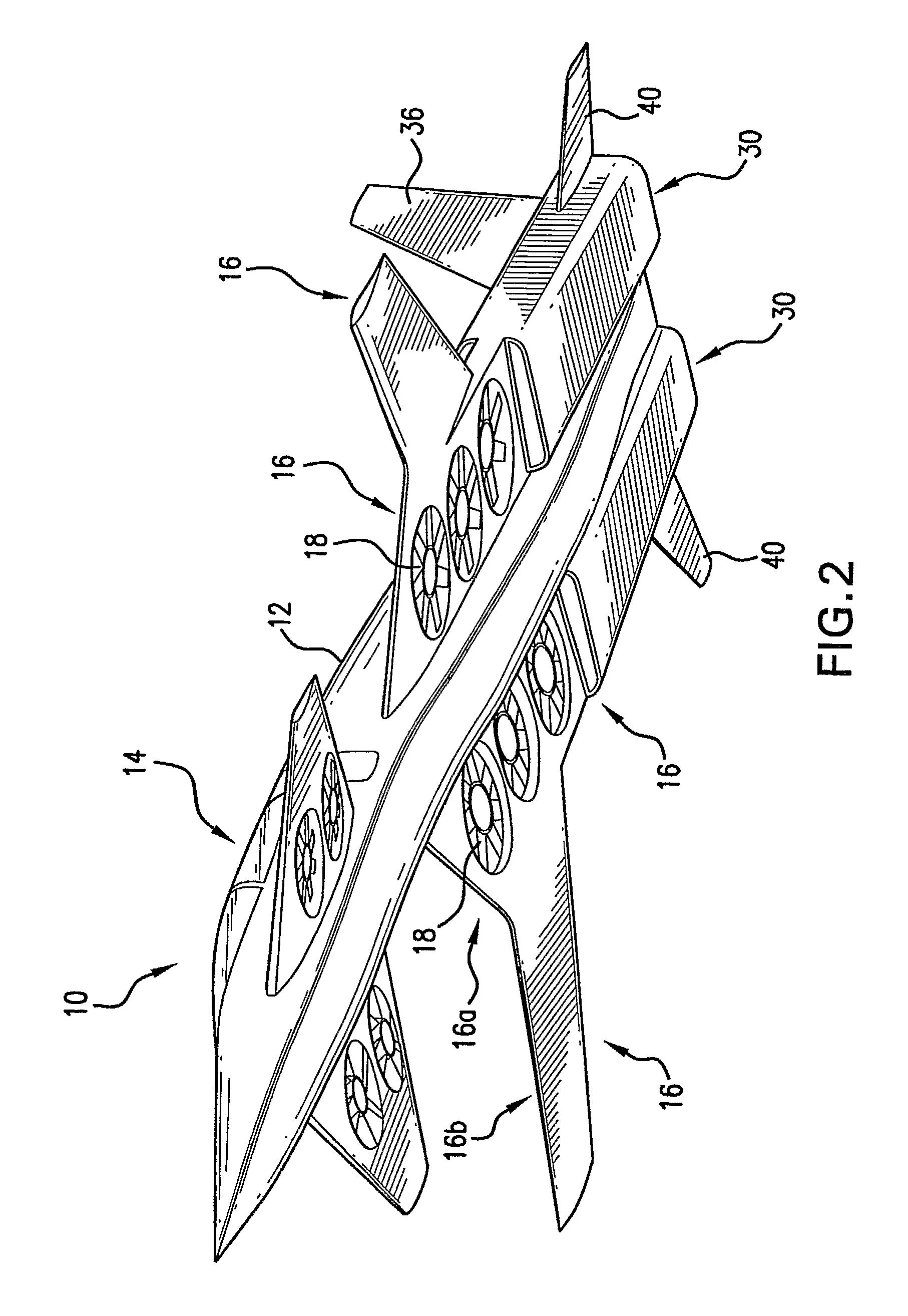
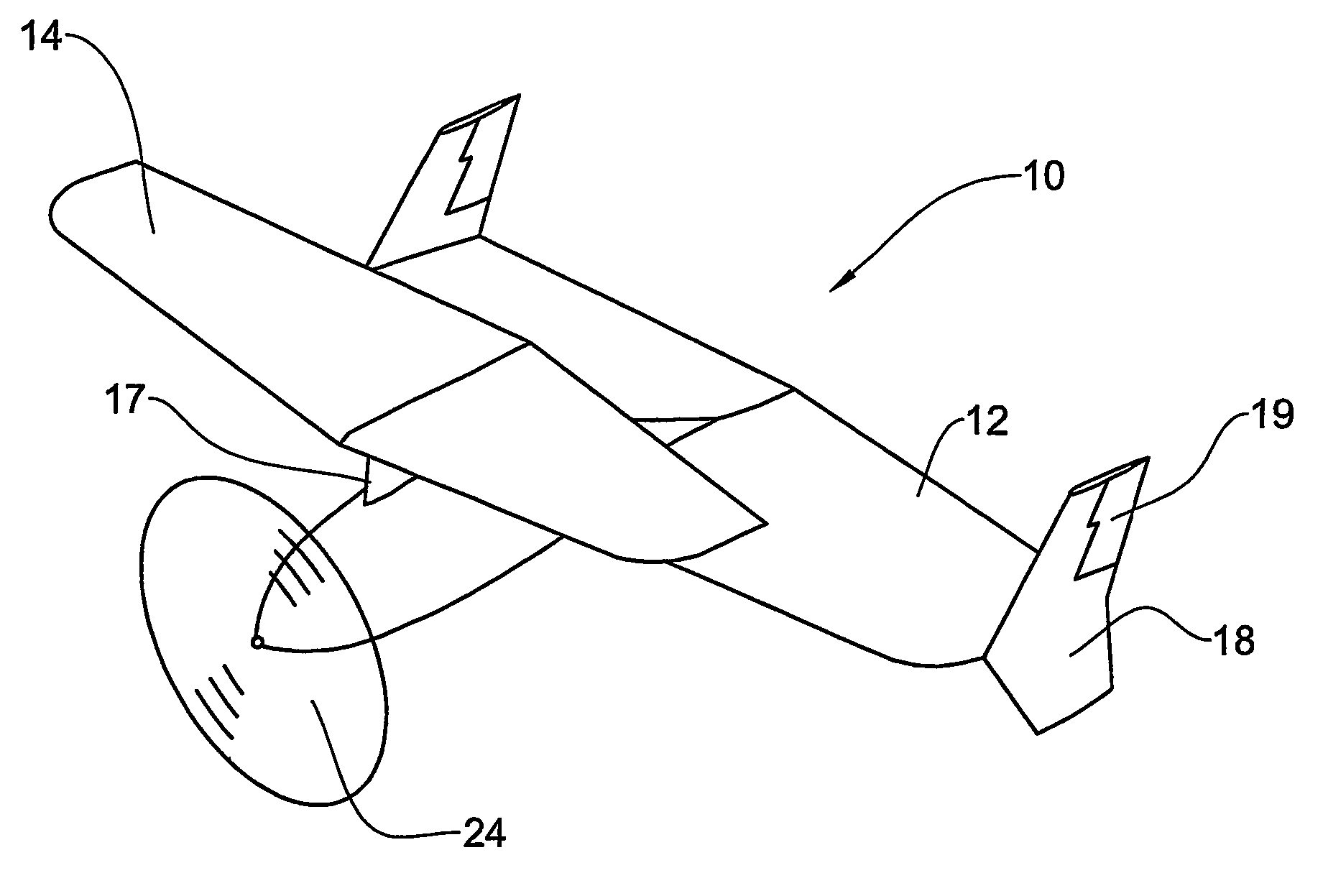
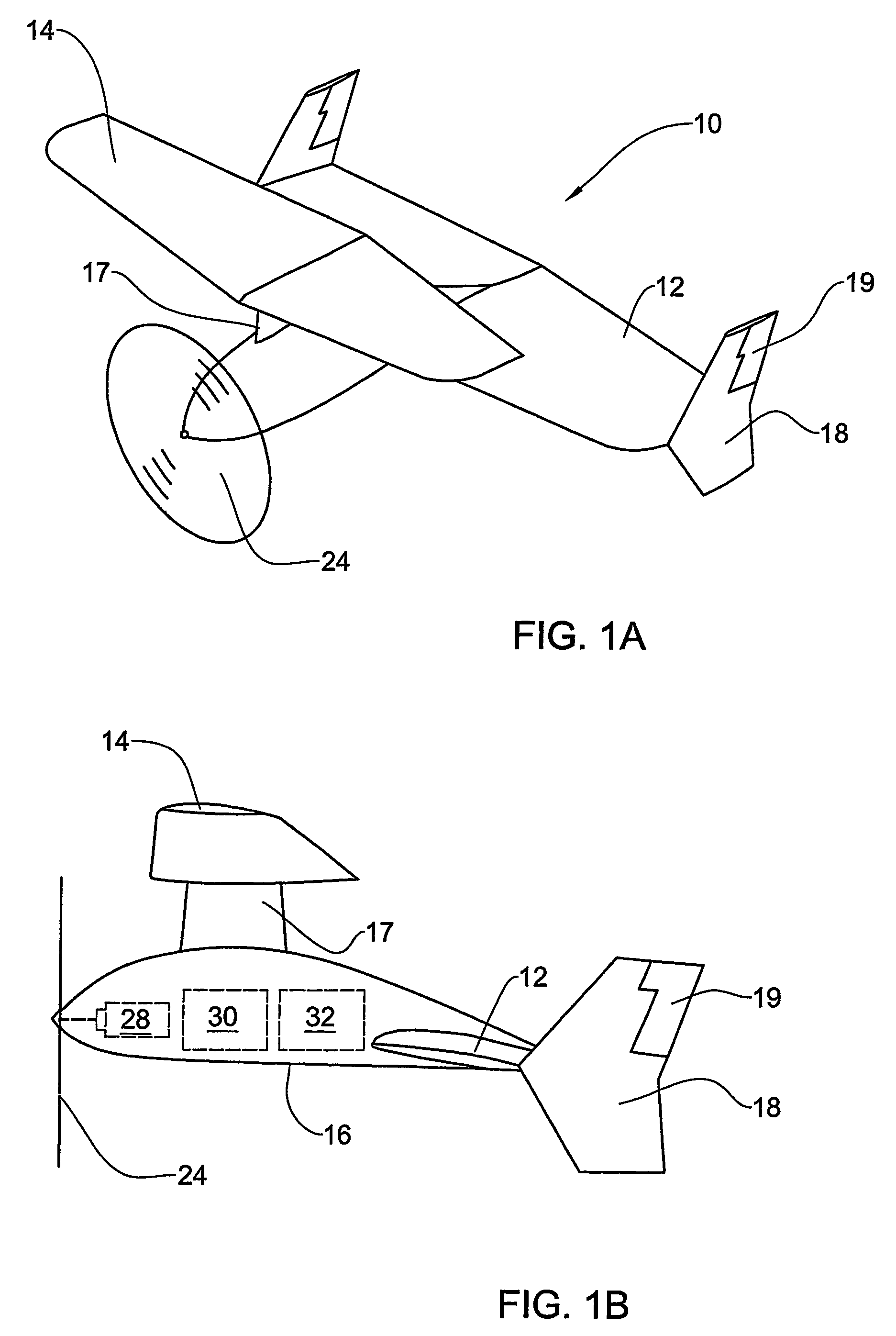
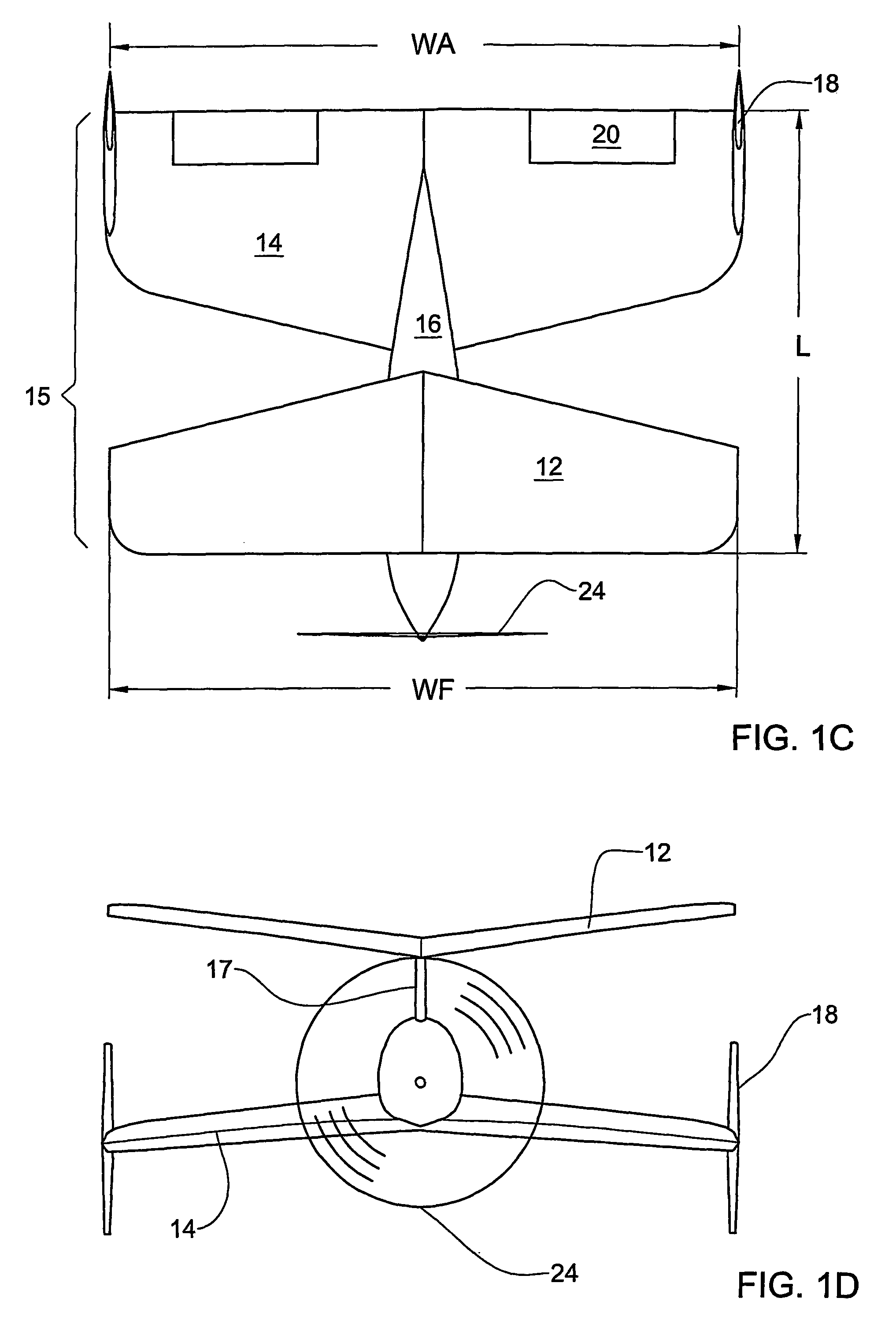
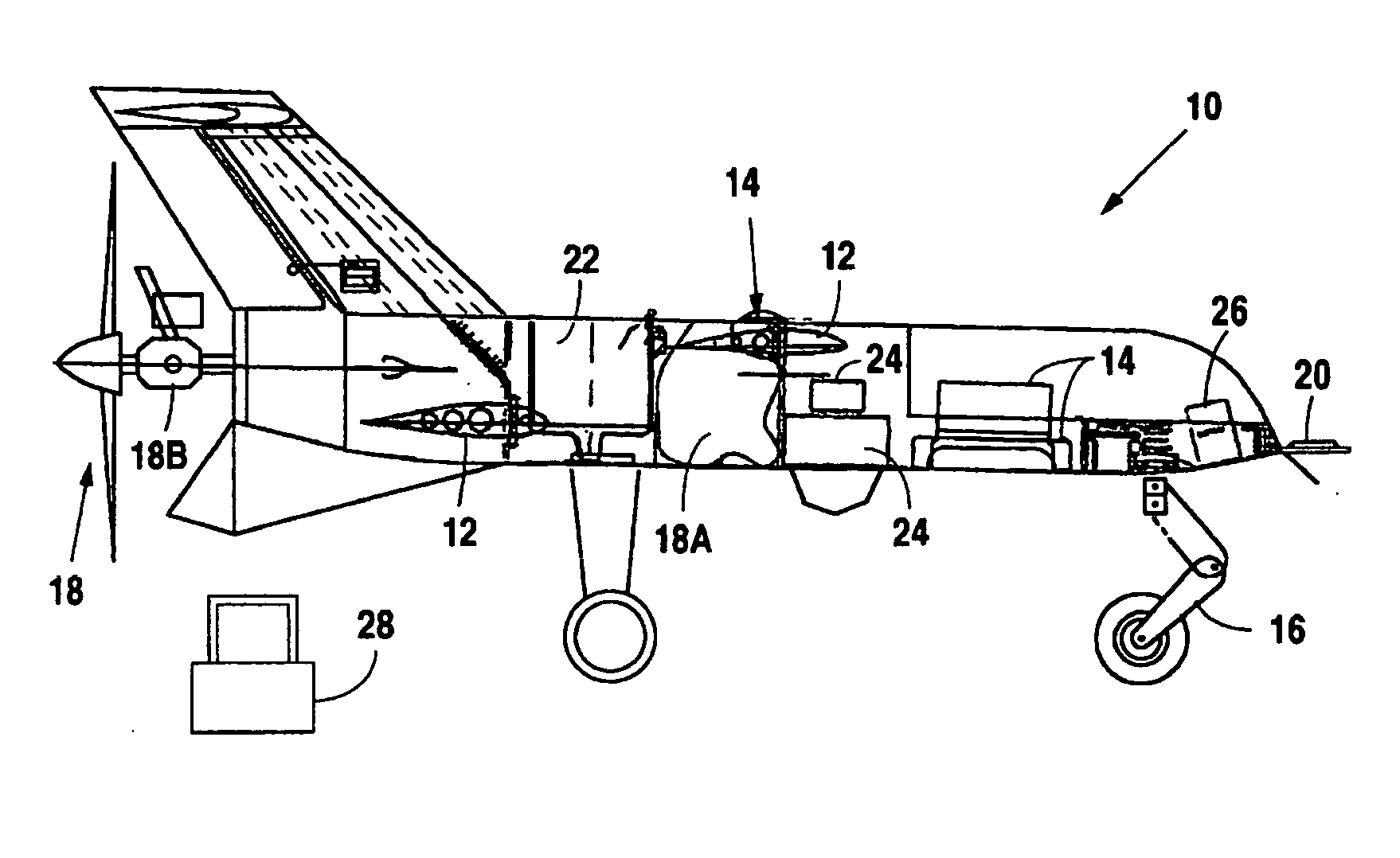
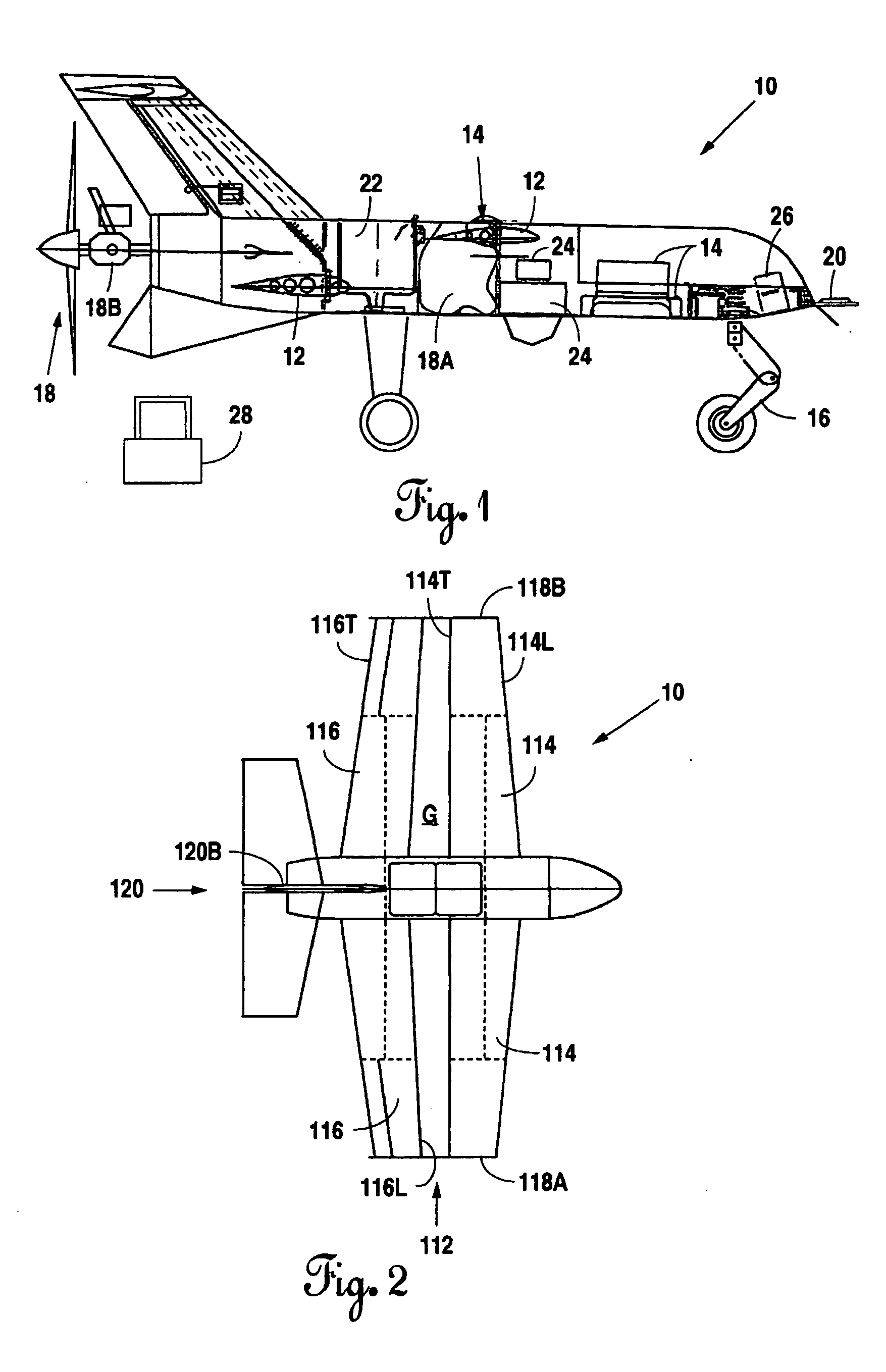
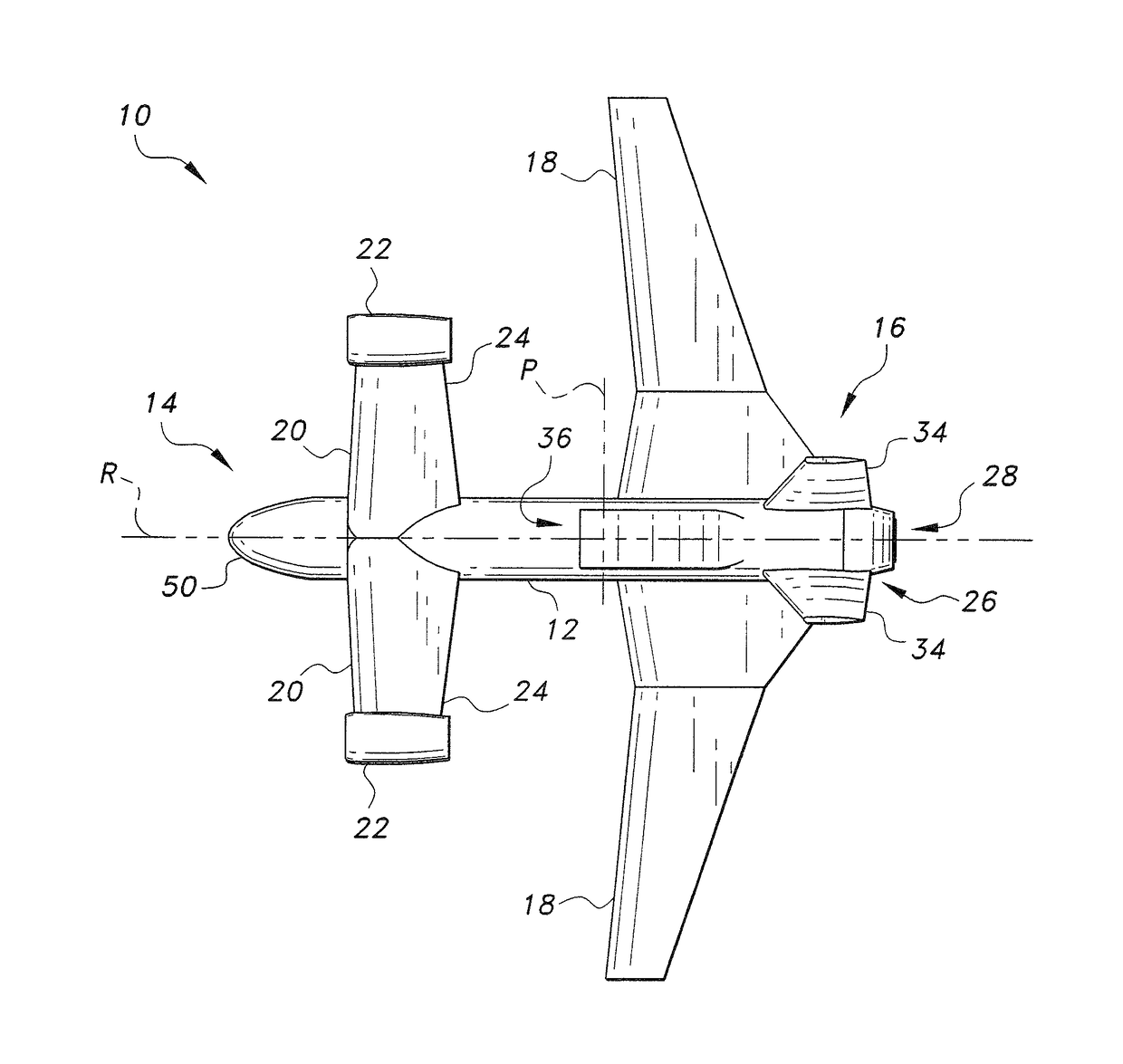
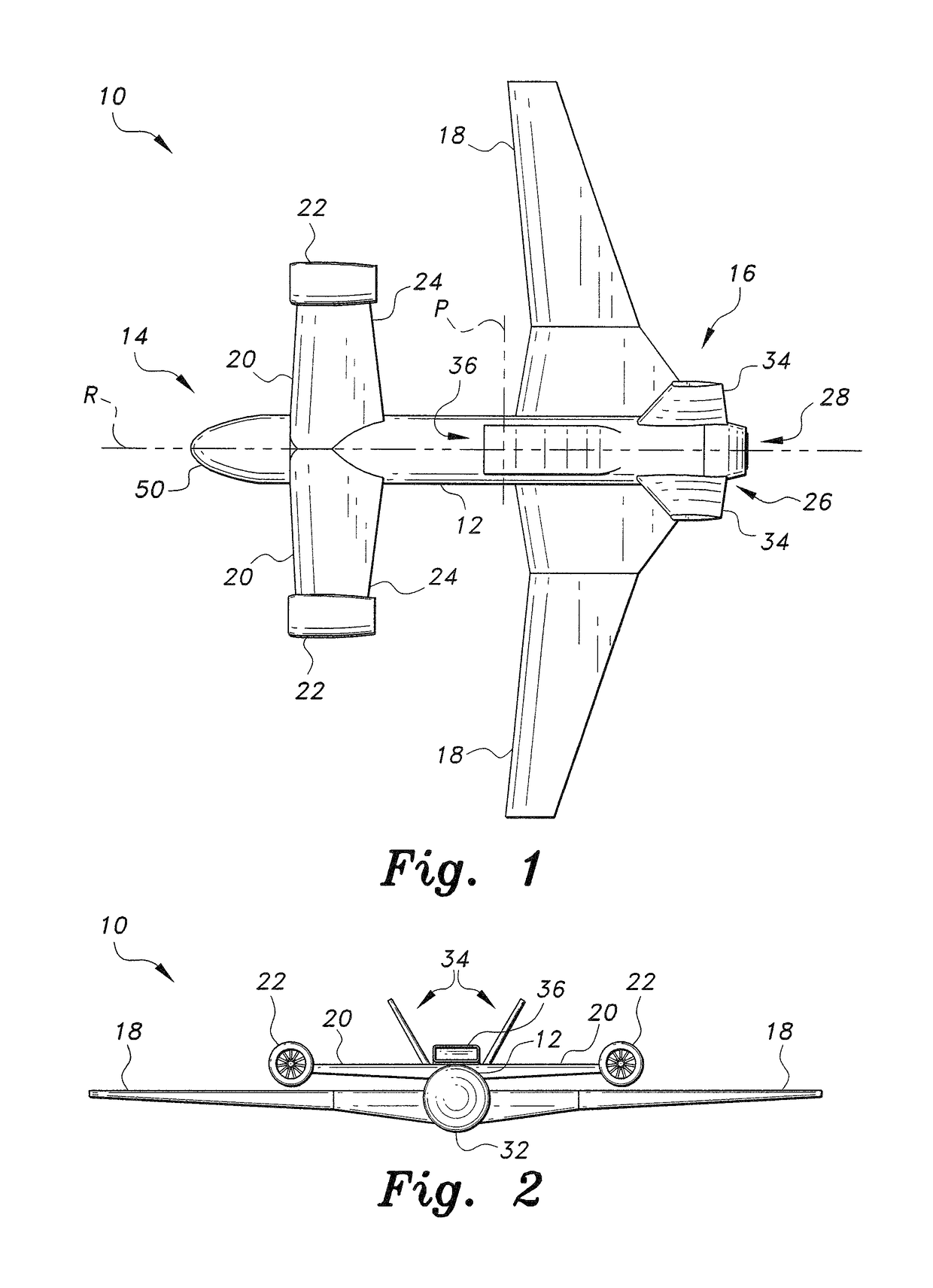
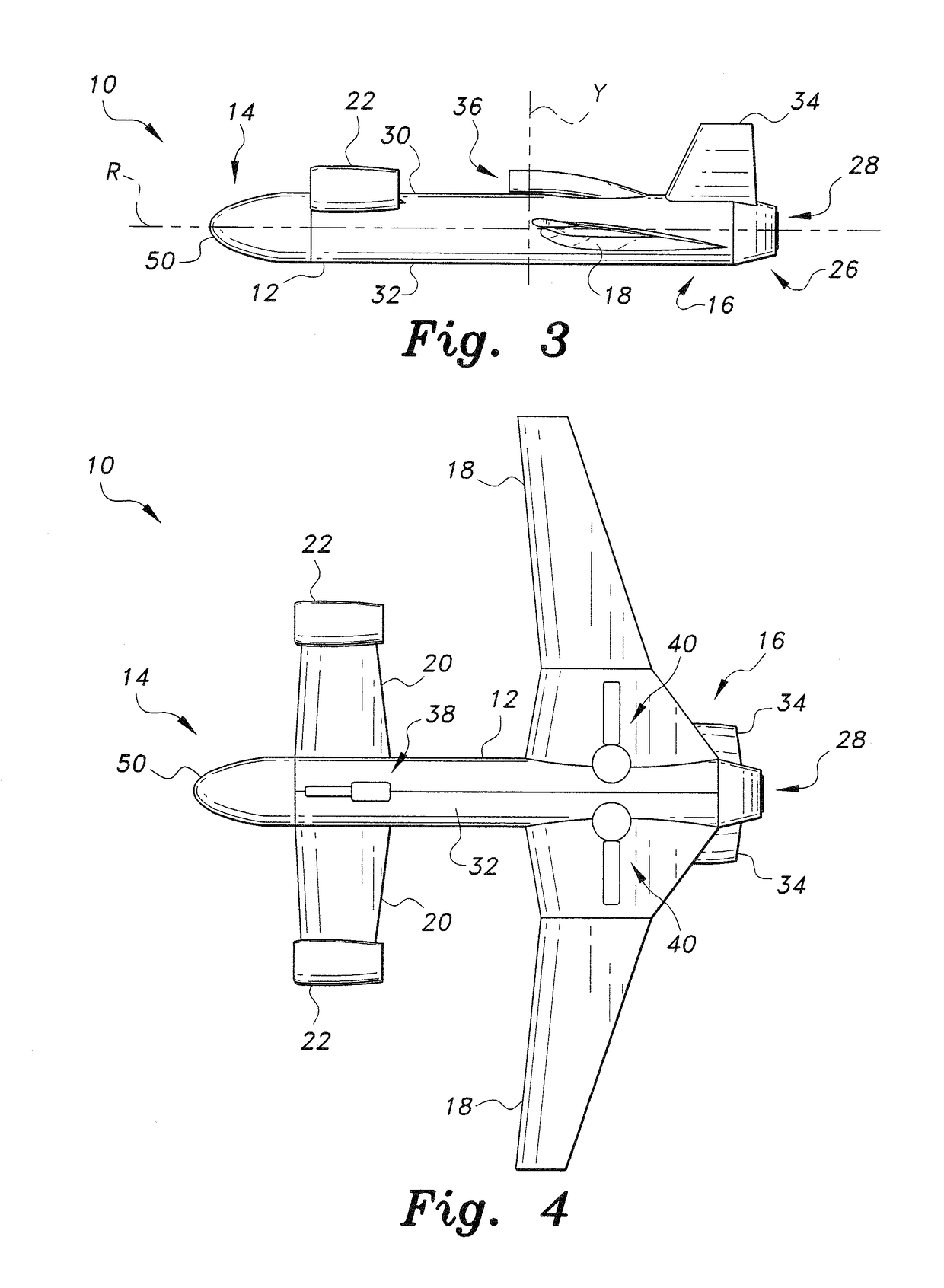
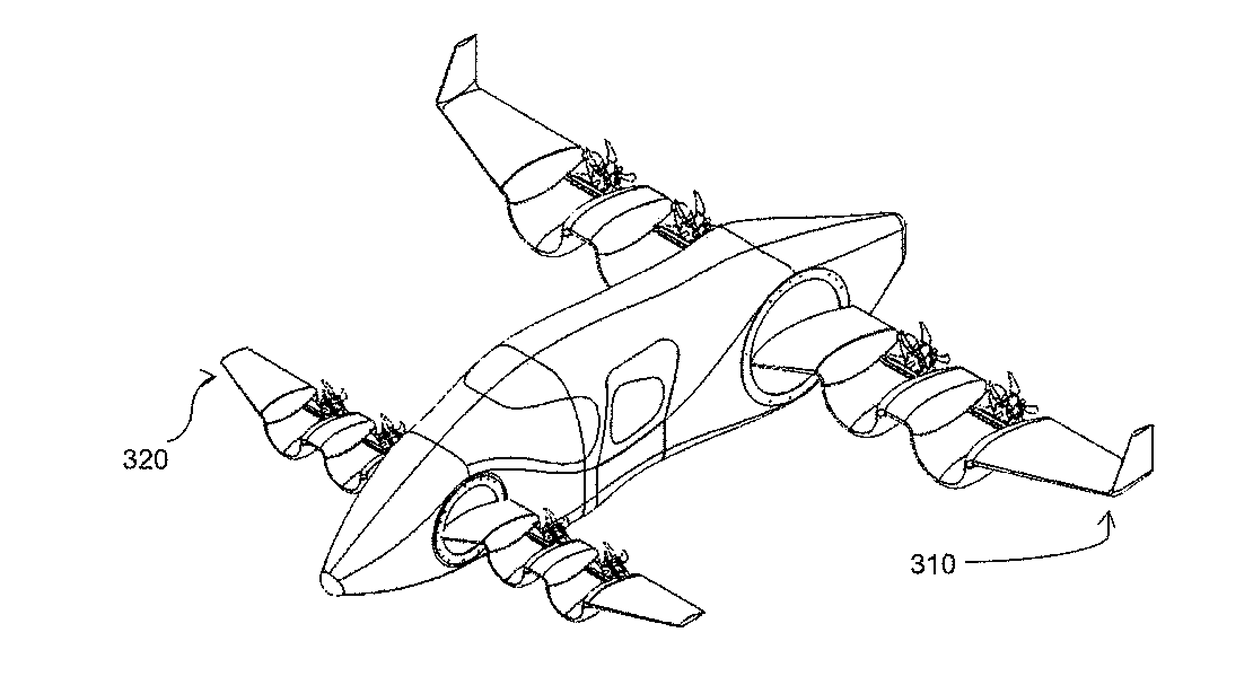
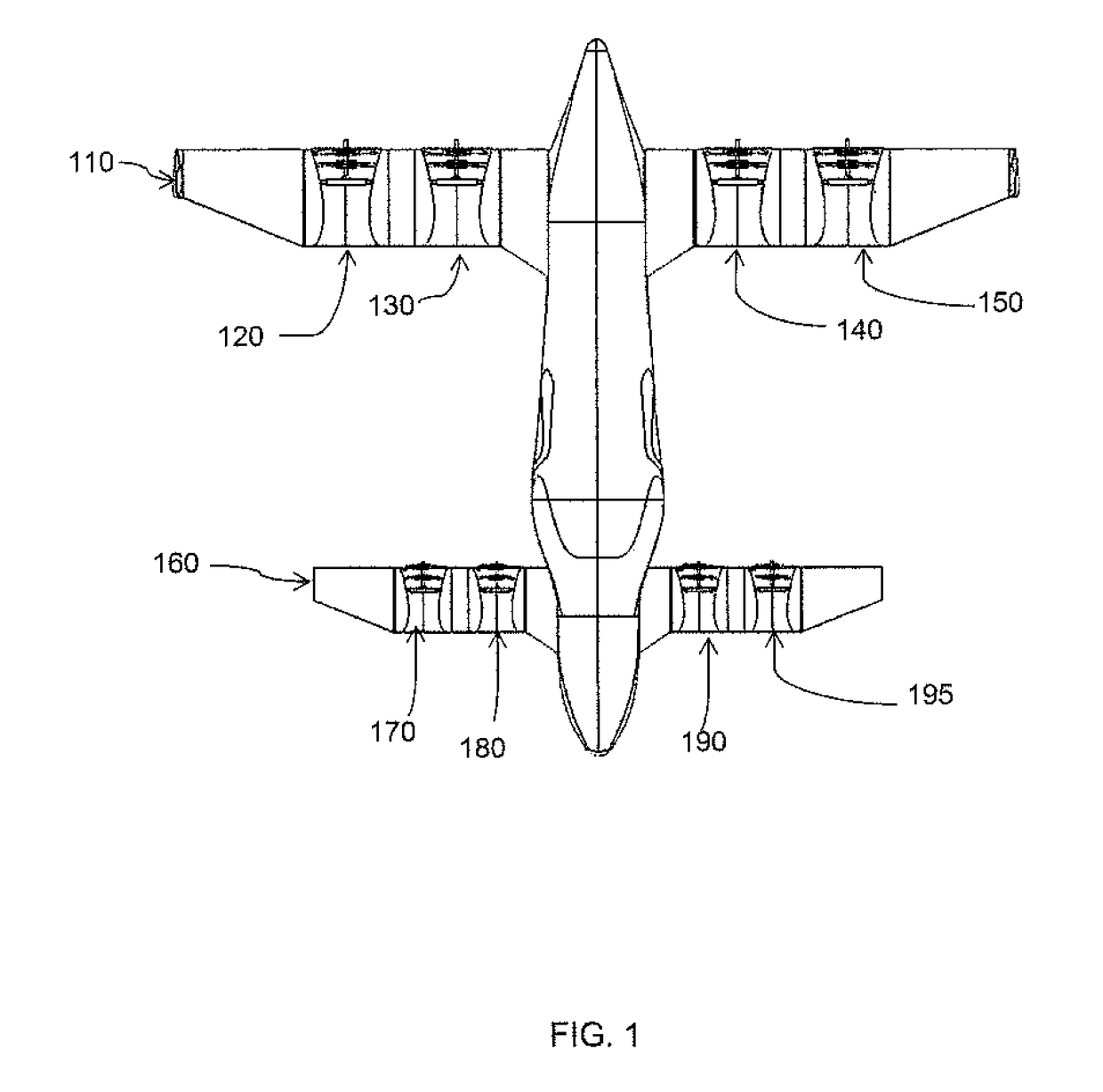
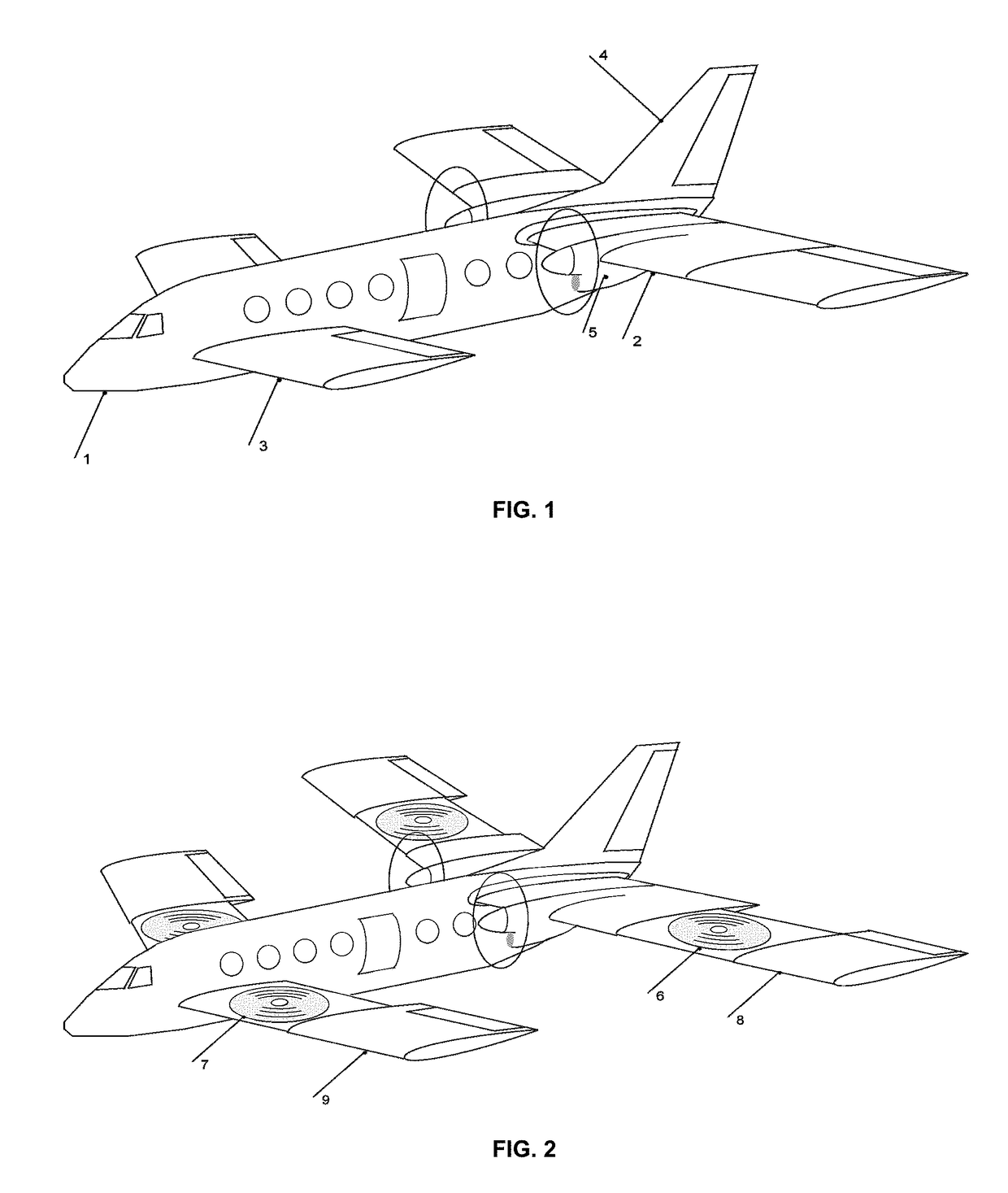
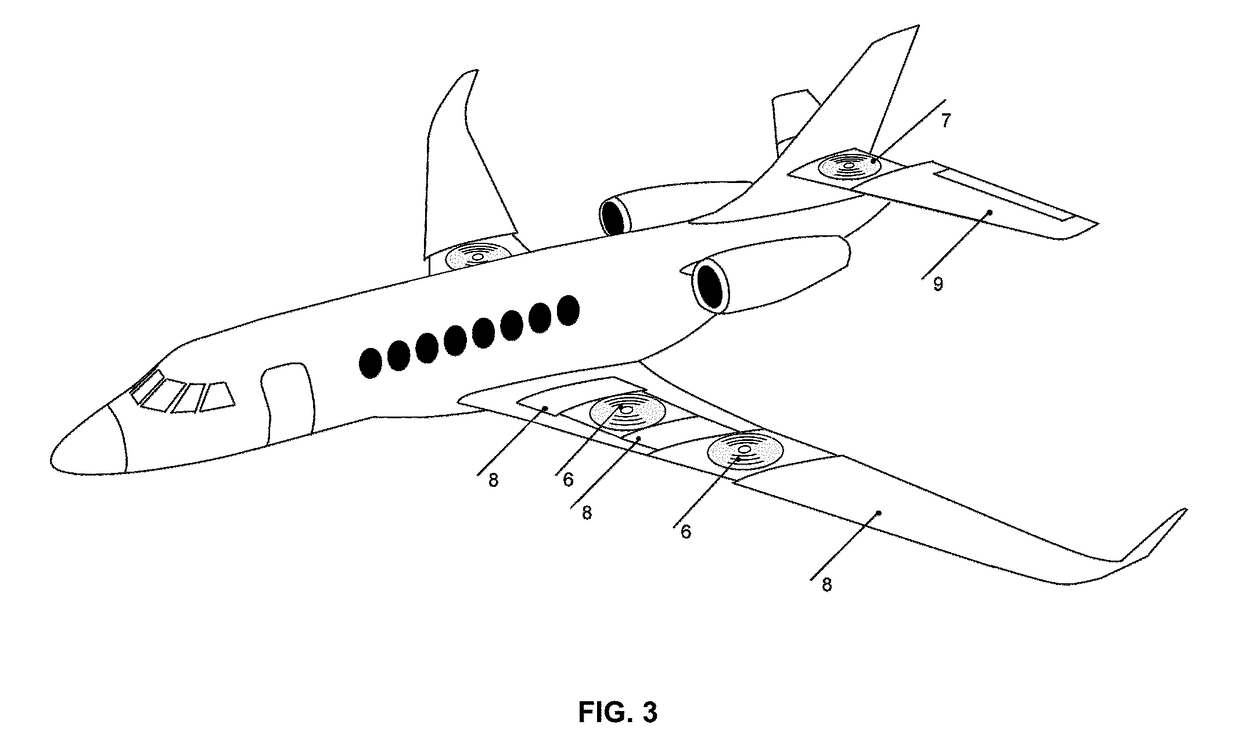
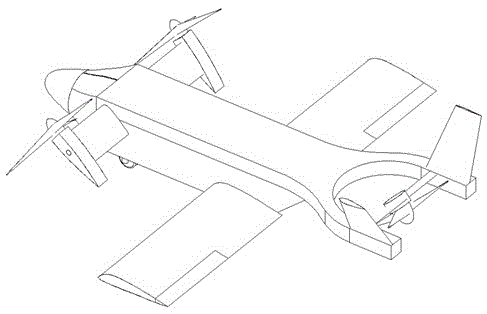
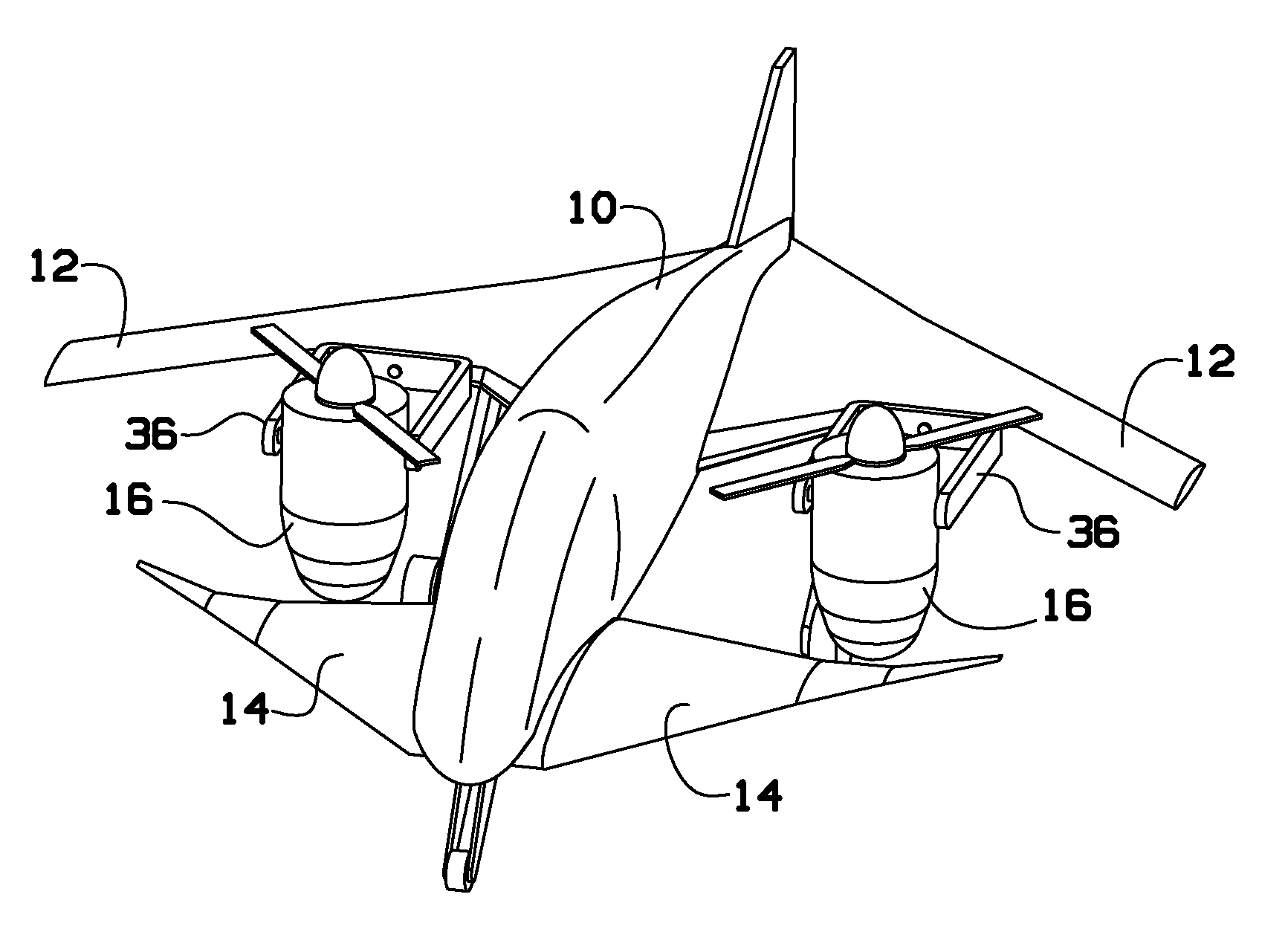
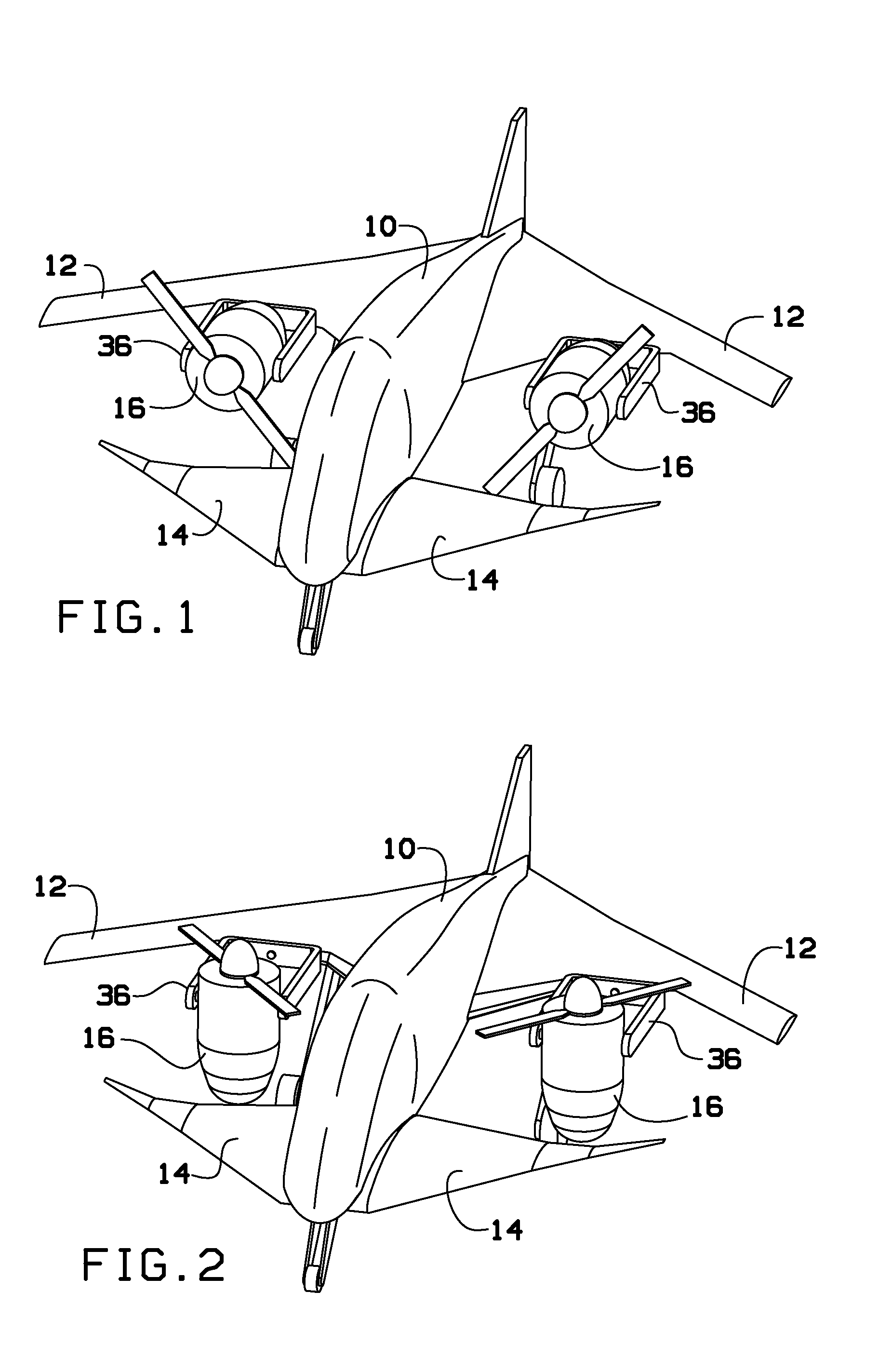
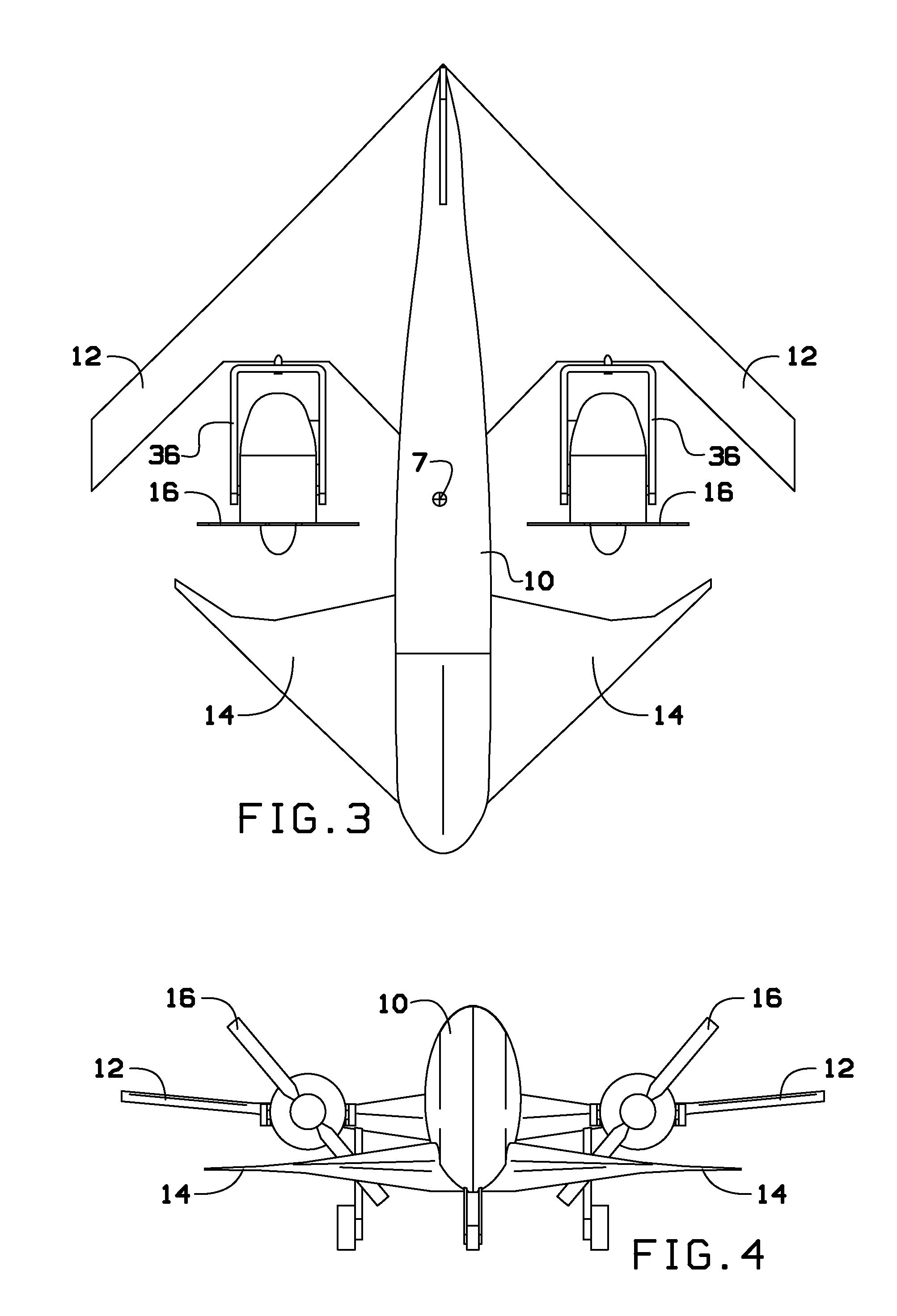
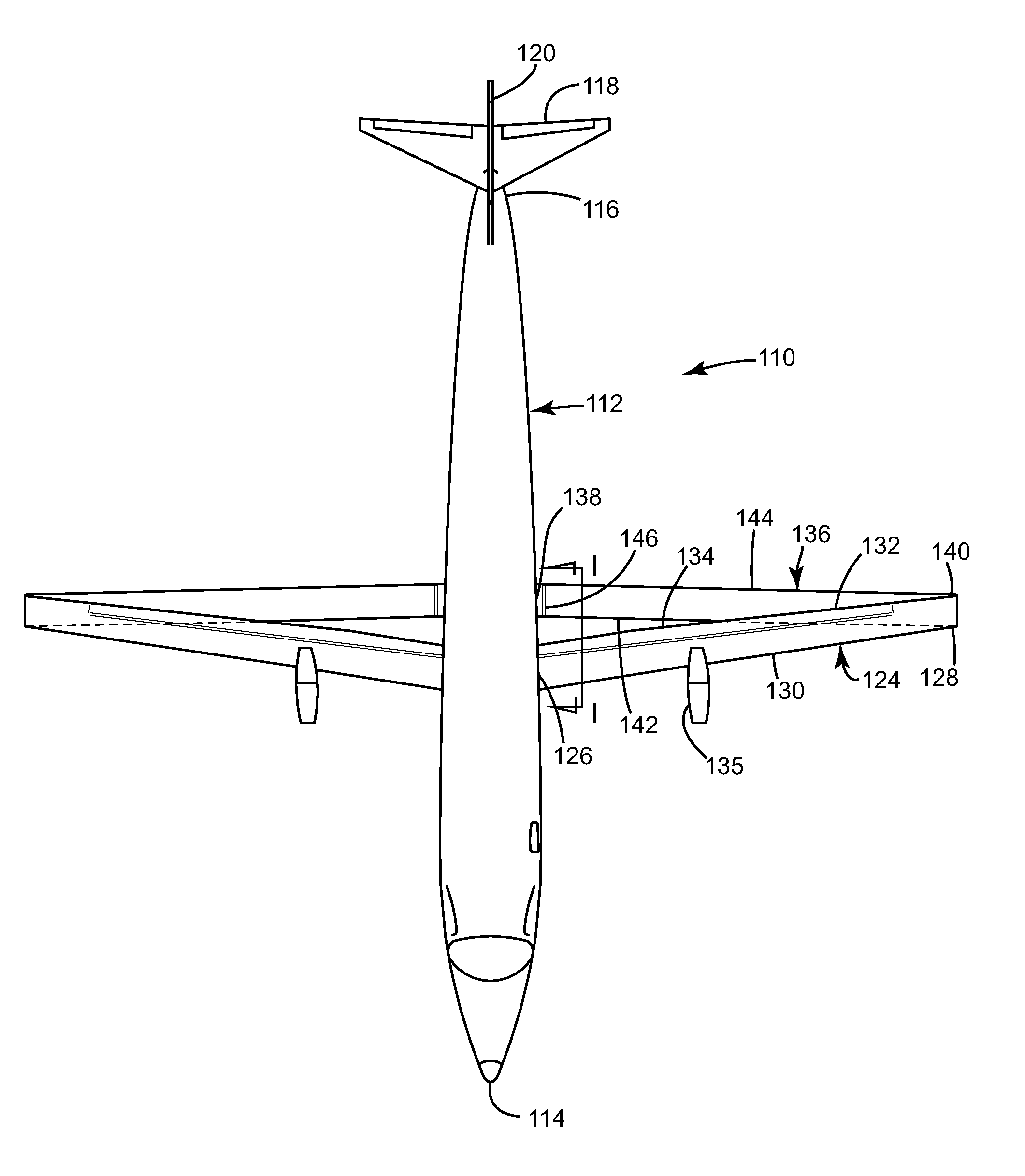
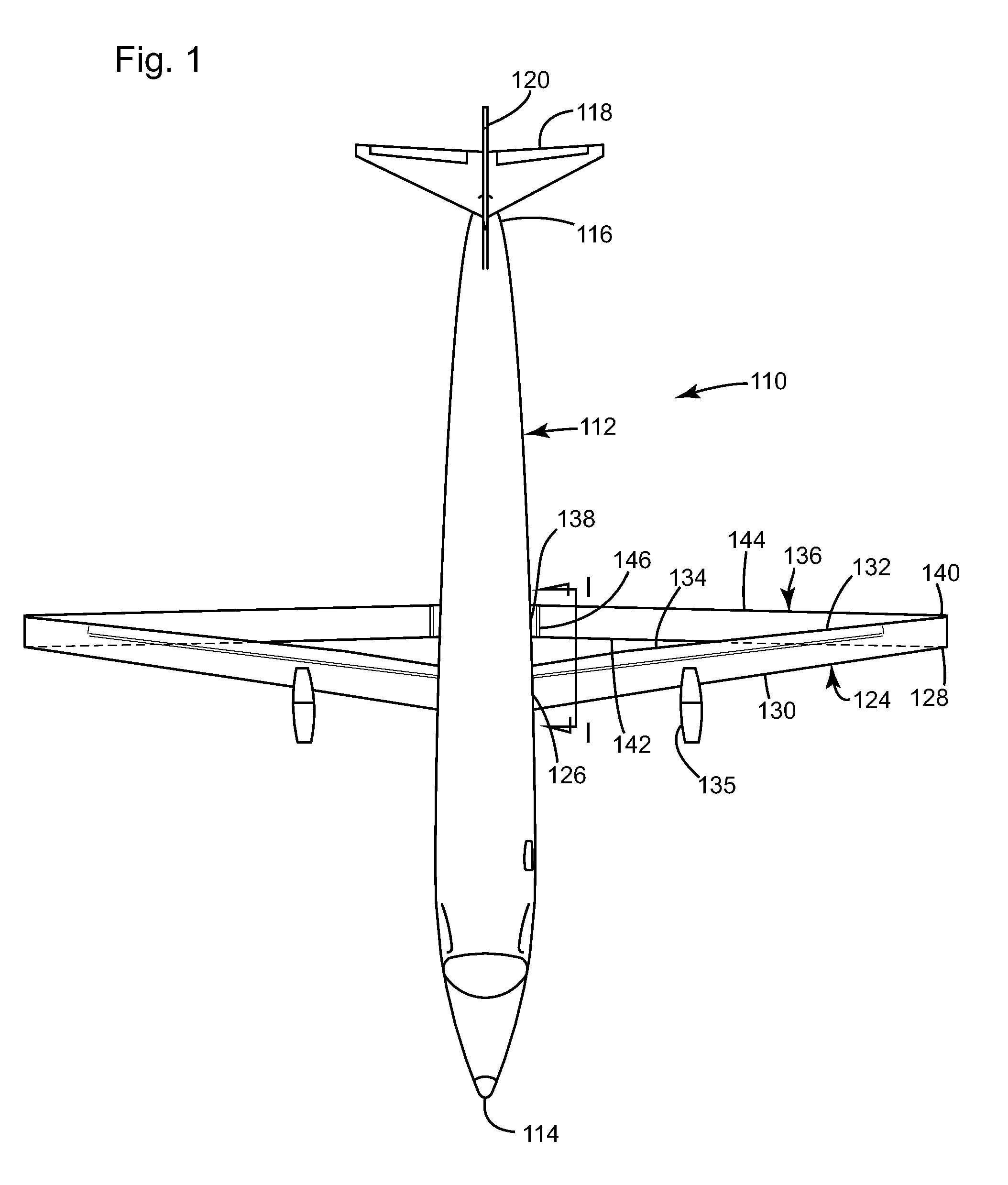
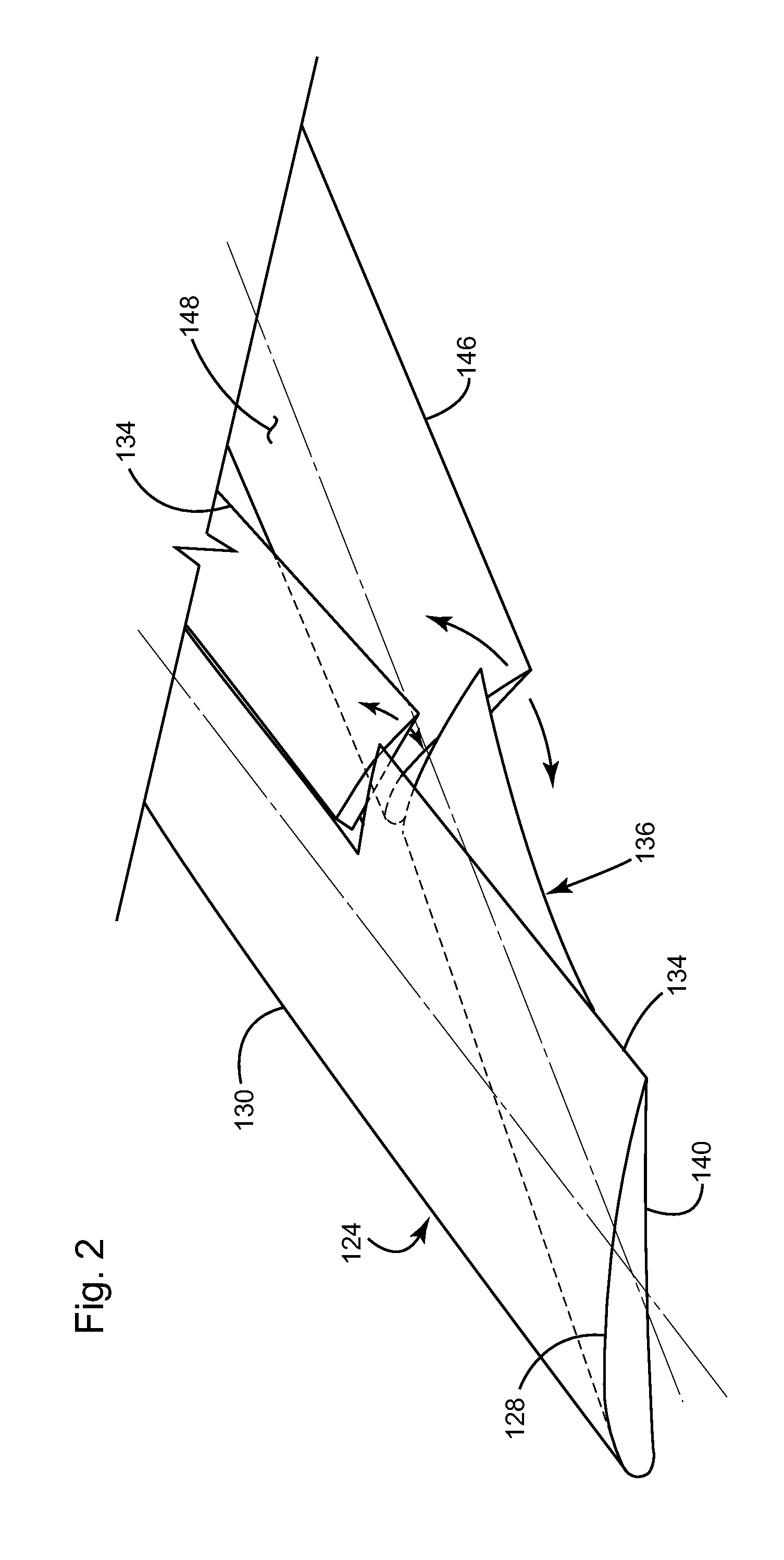
Personal Aircraft
ActiveUS20130020429A1Easy to controlMinimize disturbanceAircraft power plantsPropellersJet aeroplanePropeller
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
Hybrid jet/electric vtol aircraft
ActiveUS20130062455A1Improve efficiencyLess thrust capacityAircraft navigation controlEfficient propulsion technologiesJet aeroplaneElectricity
A fixed-wing VTOL aircraft features an array of electric lift fans distributed over the surface of the aircraft. A generator is (selectively) coupled to the gas turbine engine of the aircraft. During VTOL operation of the aircraft, the engine drives the generator to generate electricity to power the lifting fans. Power to the lifting fans is reduced as the aircraft gains forward speed and is increasingly supported by the wings.
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
Hybrid Propulsion Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
A hybrid propulsion aircraft is described having a distributed electric propulsion system. The distributed electric propulsion system includes a turbo shaft engine that drives one or more generators through a gearbox. The generator provides AC power to a plurality of ducted fans (each being driven by an electric motor). The ducted fans may be integrated with the hybrid propulsion aircraft's wings. The wings can be pivotally attached to the fuselage, thereby allowing for vertical take-off and landing. The design of the hybrid propulsion aircraft mitigates undesirable transient behavior traditionally encountered during a transition from vertical flight to horizontal flight. Moreover, the hybrid propulsion aircraft offers a fast, constant-altitude transition, without requiring a climb or dive to transition. It also offers increased efficiency in both hover and forward flight versus other VTOL aircraft and a higher forward max speed than traditional rotorcraft.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
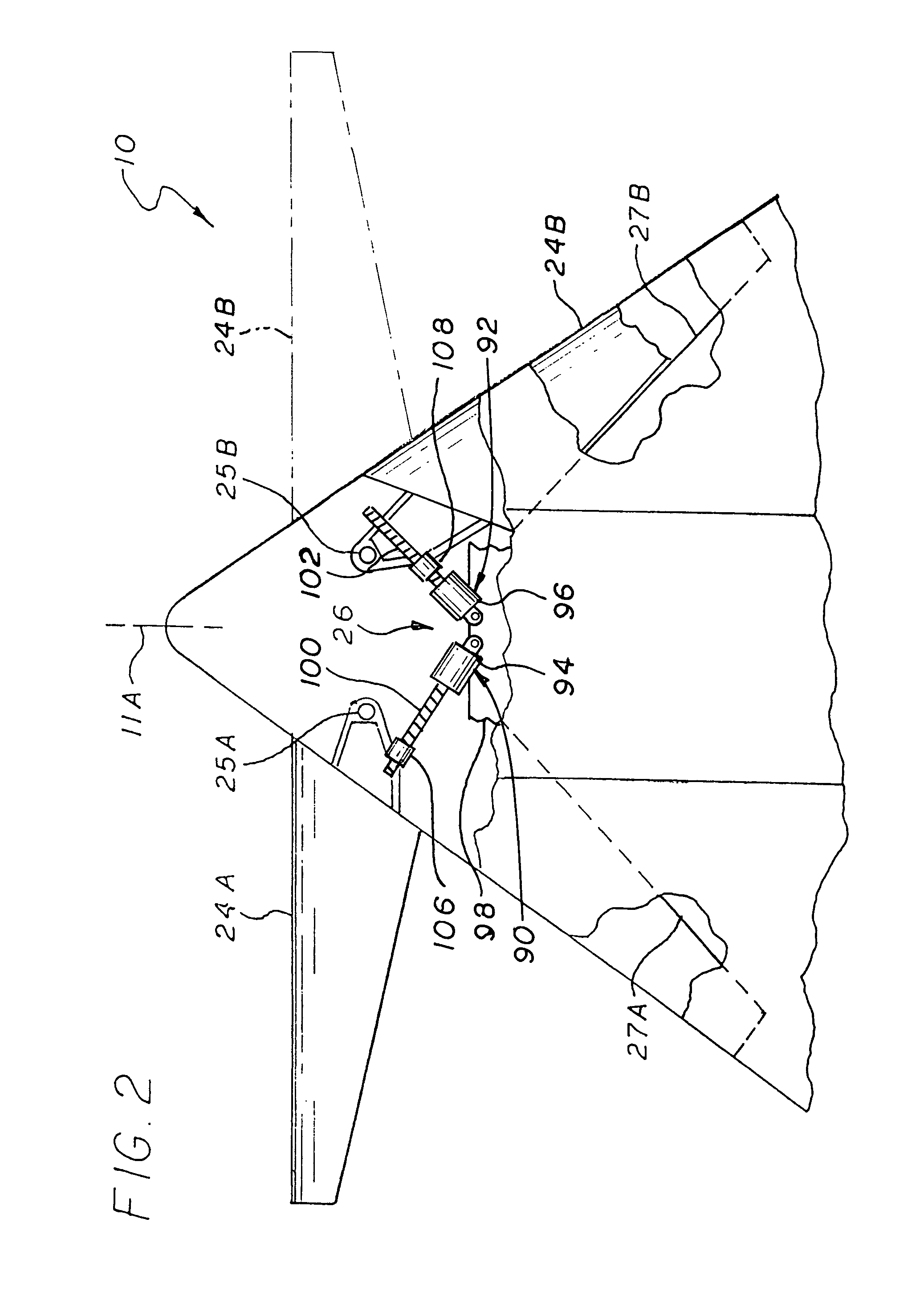
Enhanced flight control systems and methods for a jet powered tri-mode aircraft
ActiveUS6885917B2Easy to operateIncreases flight envelopeAircraft navigation controlDigital data processing detailsForward speedFixed wing
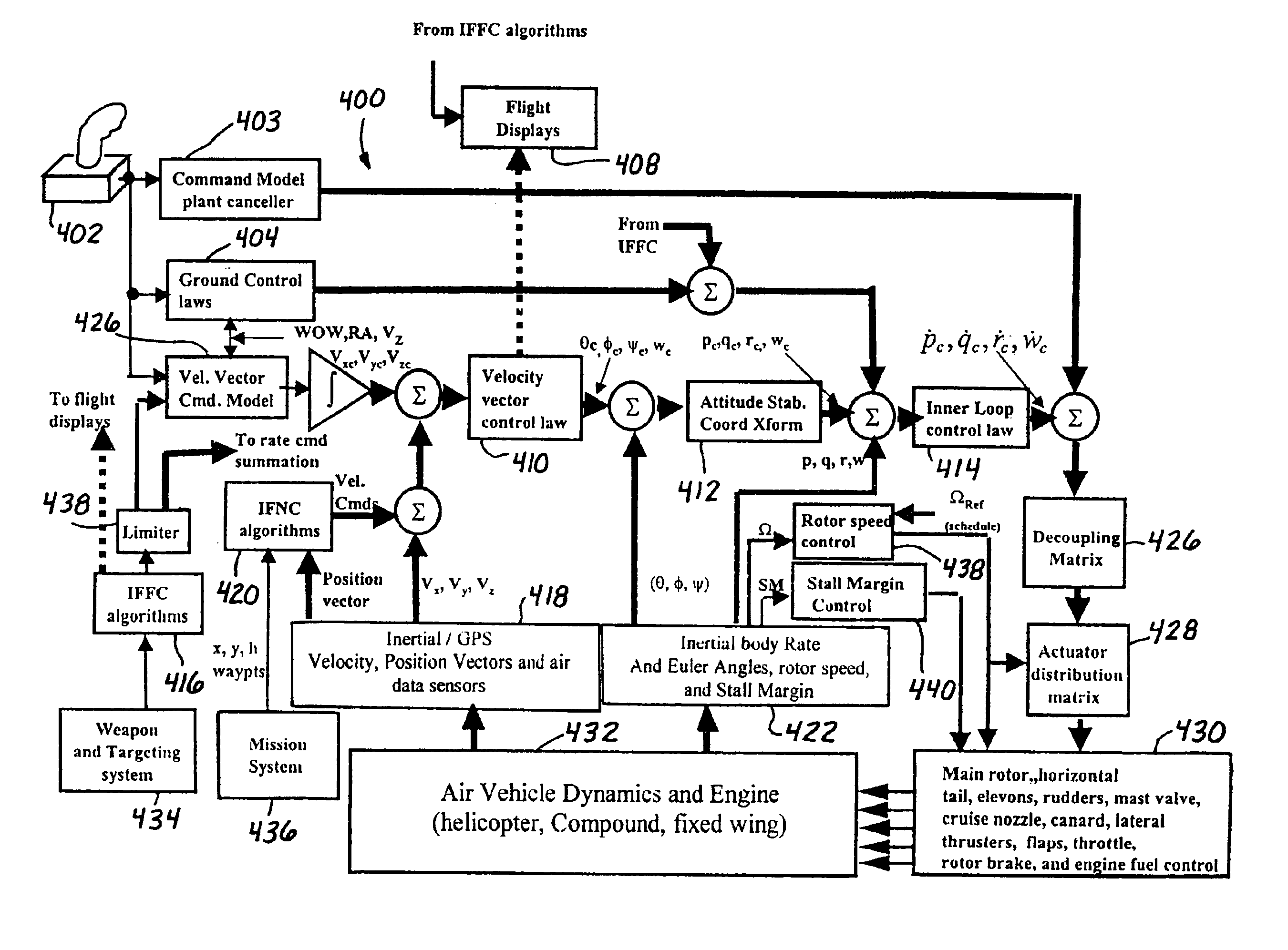
A method of stabilizing a jet-powered tri-mode aircraft as the aircraft travels in a helicopter mode, a compound mode, and a fixed-wing mode is disclosed. The method includes receiving a plurality of velocity vector component values and velocity vector commands derived from either (1) a number of pilot operated controllers or (2) a commanded array of waypoints, which are used for fully automated flights, and a rotor speed reference value, which is decreased with increasing forward speed to unload the rotor, thereby permitting conditions for stopping the rotor in flight. Stabilization of the commanded velocity vector is achieved in all modes of flight using blended combinations of rotor swashplate controls and aerodynamic controls such as elevons, canards, rudders, and a horizontal tail. Stabilization to the commanded velocity vector includes a plurality of control constraints applied to the pilot stick controllers that prevent penetration of envelope limits.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
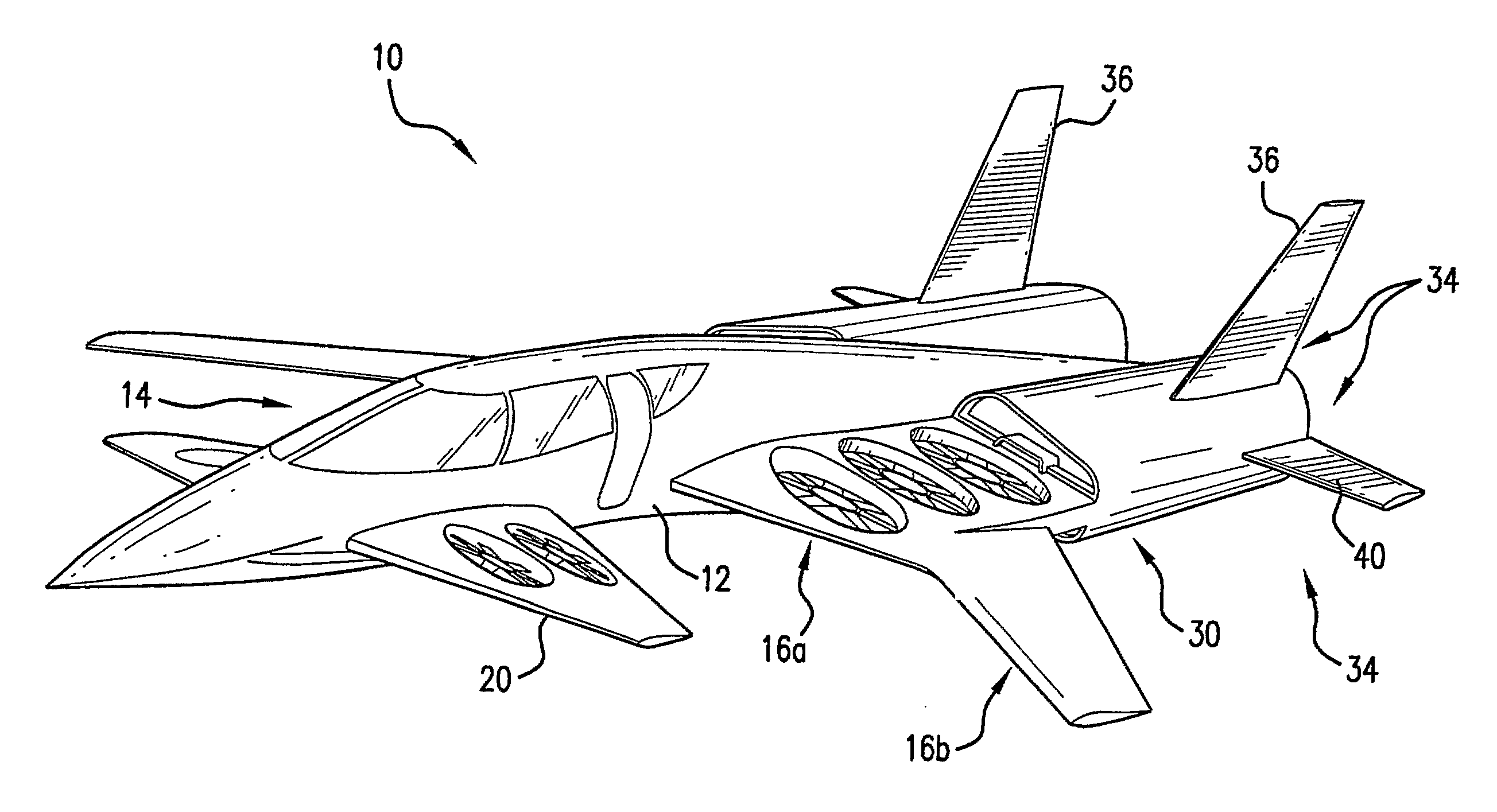
High Performance VTOL Aircraft
ActiveUS20150344134A1Maximize effective thrustMaximize useRemote controlled aircraftWing adjustmentsJet aeroplaneEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a high performance Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL) aircraft for executing hovering flight, forward flight, and transitioning between the two in a stable and efficient manner. The VTOL aircraft provides a highly stable, controllable and efficient VTOL aircraft. The preferred comprises: (1) a pusher propeller configuration with strategic placement which maximizes the effective use of thrust, (2) four propellers which allow for the highly-controllable and mechanically simple control methods used in multirotor aircraft, (3) electric motors which create mechanically simple, lightweight and reliable operation, (4) and a tandem wing configuration which is stable, controllable and efficient in both hovering and forward flight. The VTOL aircraft is capable of full runway, short runway or vertical takeoffs or landings, having unobstructed forward view for camera and sensor placement; and providing a compact, mechanically simple and low-maintenance VTOL aircraft design.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Deltoid main wing aerodynamic configurations
InactiveUS20100163670A1Improve lifting performanceReduce reflectivityAircraft stabilisationWing shapesHigh liftSupersonic speed
Deltoid Main Wing idea provides for several innovative aerodynamic configurations for large subsonic and supersonic civil and military aircraft including “T-tailed Deltoid Main Wing” configuration that allows for design of high-subsonic jumbo jet passenger aircraft with a capacity between 200 and 700 passengers whose outer dimensions fit within 80 m box on class VI airports while having more than twice lower fuel consumption per unit of payload when compared to the present classical-concept aircraft with the same passenger capacity, while further allowing for design of all-size and all-purpose, high-lift-capacity, and long-range unmanned aircraft.
Owner:DIZDAREVIC FARUK +1
Fixed-wing and electric multi-rotor composite aircraft
The present invention discloses a fixed-wing and electric multi-rotor composite aircraft, including an electric multi-rotor dynamic system and a main controller, the fixed-wing dynamic system and electric multi-rotor dynamic system are mutually independent structurally, the main controller includes the fixed-wing control system and an electric multi-rotor control system which is used for controlling the operation of the electric multi-rotor dynamic system, the main controller is also used for controlling the fixed-wing control system and the electric multi-rotor control system to operate independently or synergistically, the rotor rotating plane of the electric multi-rotor dynamic system is parallel to the airframe central shaft. The aircraft is able to shift between two flying modes freely, and takes off, lands and flies like a helicopter as well as a fixed-wing aircraft. A fixed-wing aircraft-helicopter mixed mode can also be used in the take-off, landing and flying process.
Owner:YUNEEC TECH CO LTD
Telescopic wing with articulated structural spar
A telescopic aircraft wing having an articulated structural spar. The telescopic wing includes a root portion and a tip portion that is telescopically related to the root portion. A spar assembly connects the root portion to the tip portion for providing structural support to the tip portion, and the spar assembly has a plurality of links that are pivotally connected to one another. The spar assembly moves the tip portion with respect to the root portion between an extended position and a retracted position.
Owner:DHALL SANJAY
Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
ActiveUS20180305005A1Wide rangeReduce noiseEnergy efficient board measuresEfficient propulsion technologiesCantileverFuselage
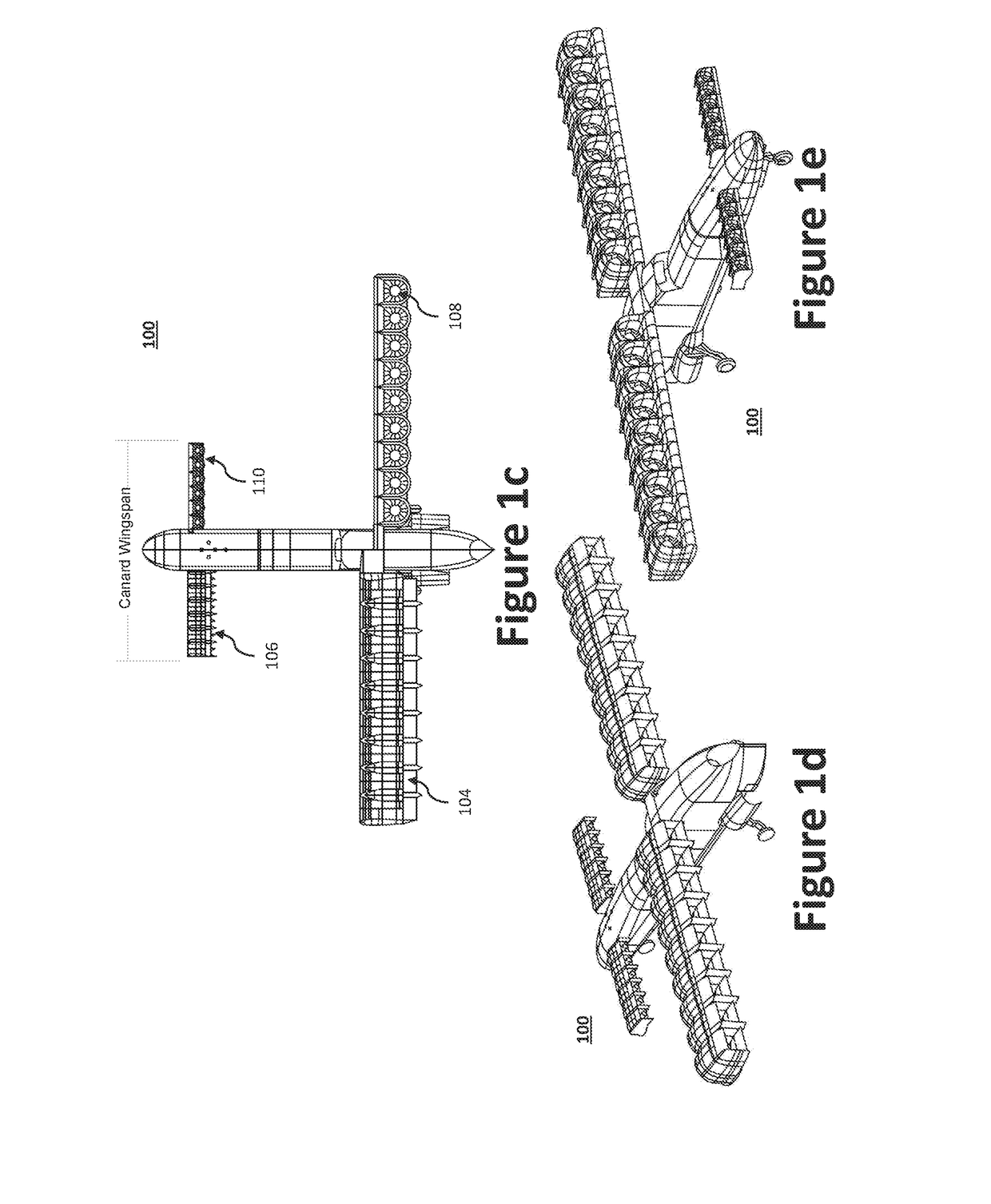
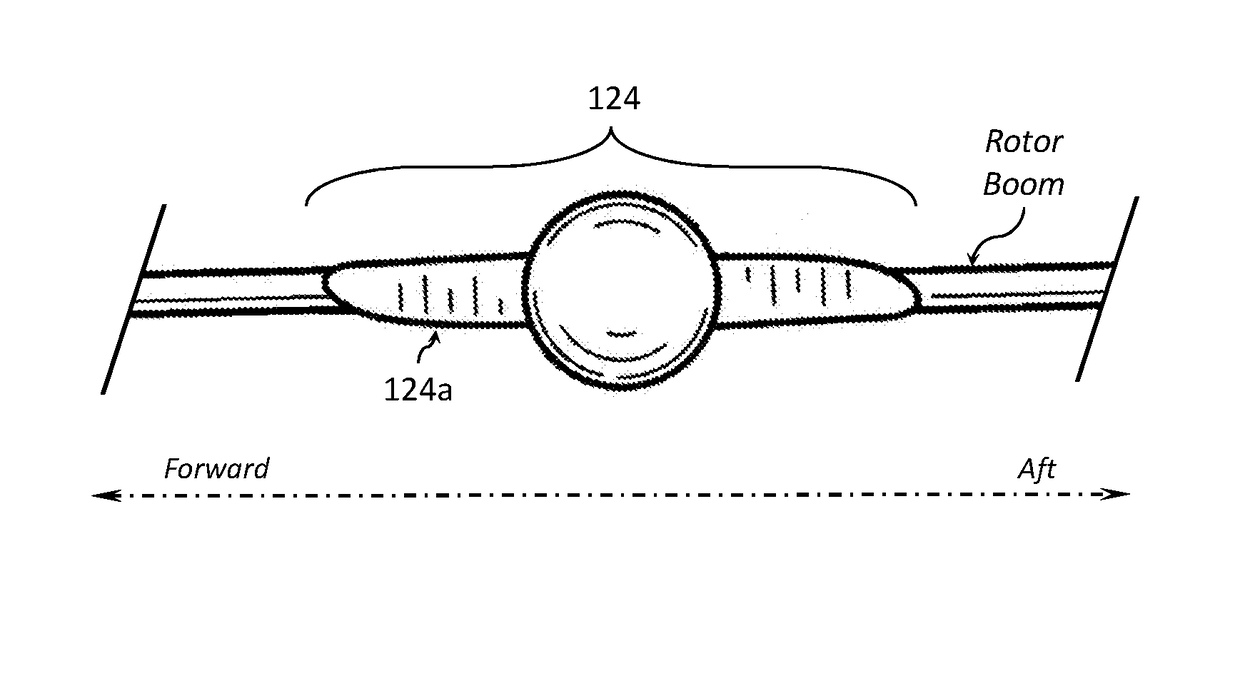
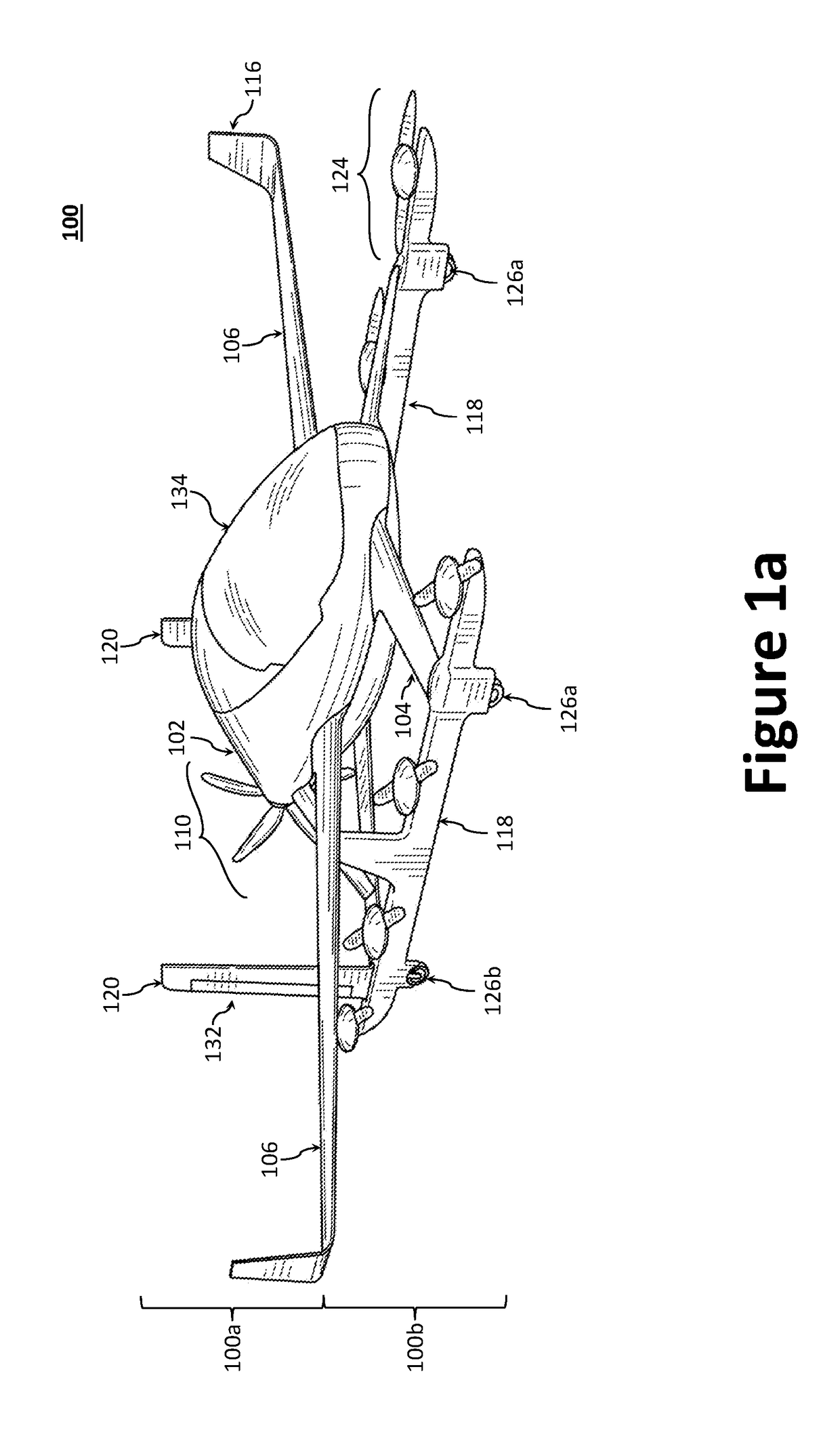
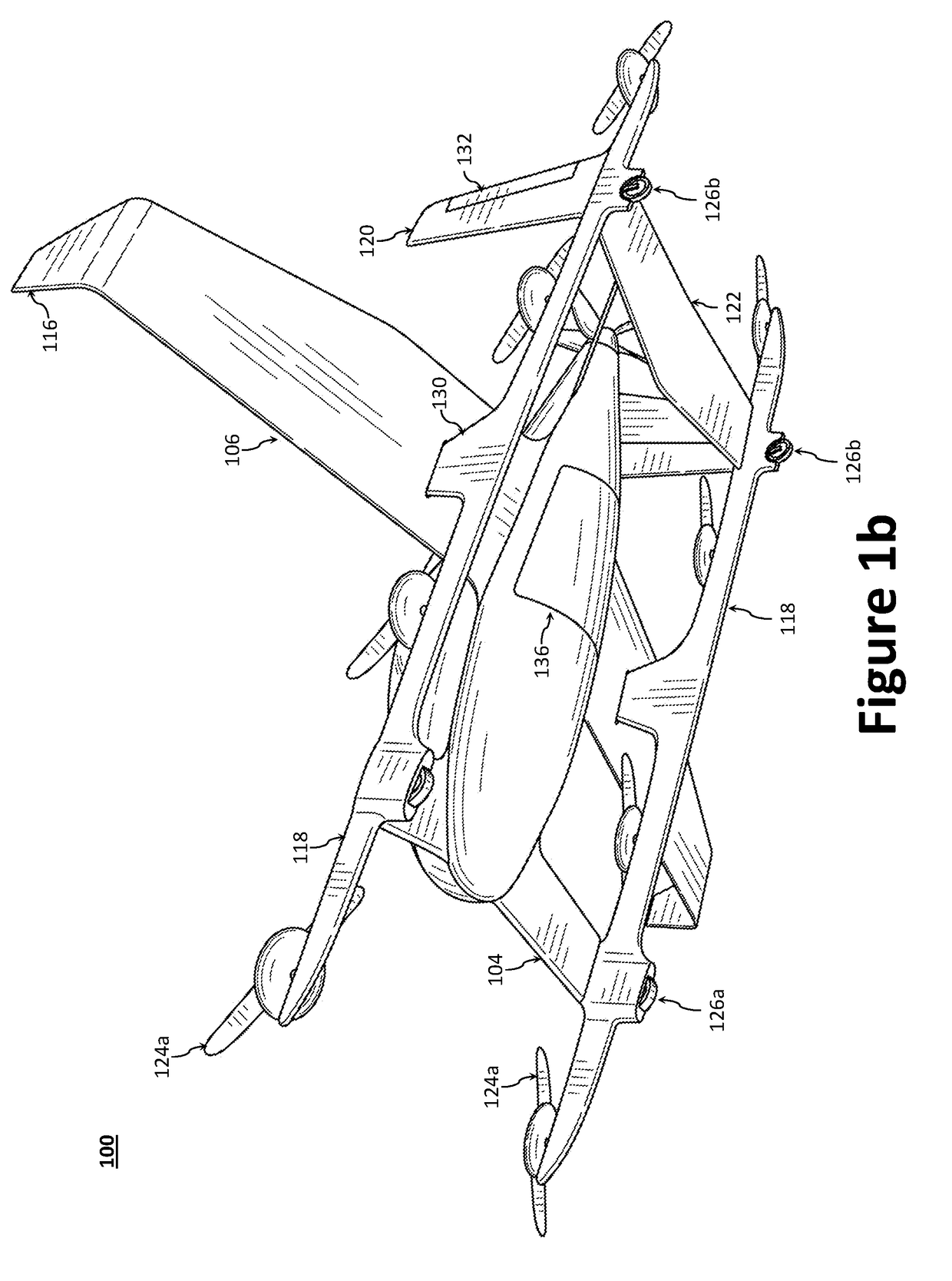
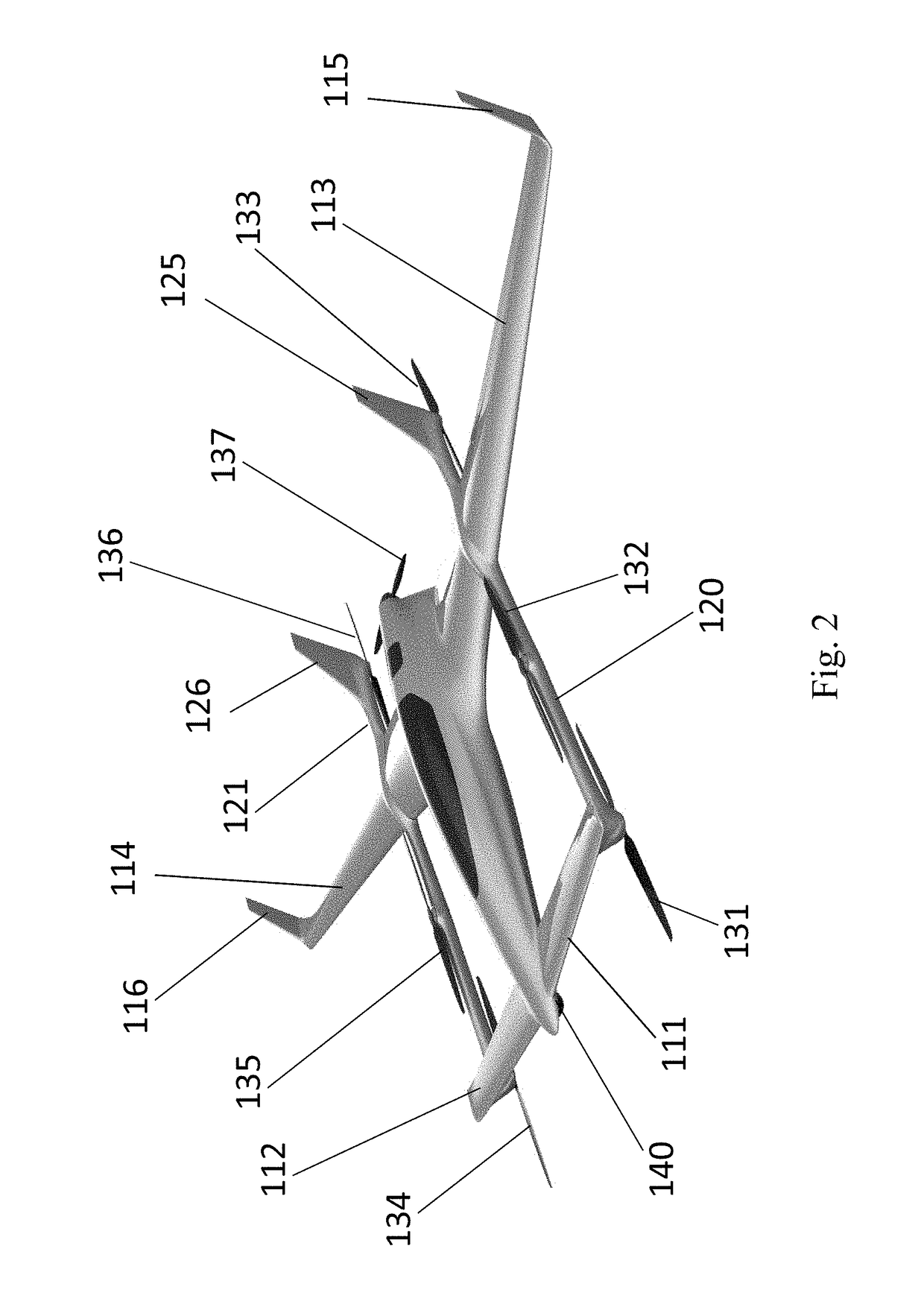
Disclosed herein is a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft having three lifting surfaces and separate lift and cruise systems. The VTOL aircraft may include a fuselage having a roll axis, a thrust rotor to produce a propulsion thrust, first and second rotor booms, first and second canard surfaces, first and second wing surfaces, first and second tail surfaces, and a plurality of lift rotors to produce a lifting thrust force. The plurality of lift rotors includes a first plurality of lift rotors positioned on the first rotor boom and a second plurality of lift rotors positioned on the second rotor boom. The first and second rotor booms may be substantially parallel to the roll axis of the fuselage, where the fuselage is positioned between the first and second rotor booms. Each of the first and second rotor booms may be secured to the aircraft at three locations.
Owner:BCG DIGITAL VENTURES GMBH
Variable trailing edge geometry and spanload control
A mobile platform lift increasing system includes at least one wing-shaped structure having a leading edge, a trailing edge and a chord length perpendicularly measurable between the leading and trailing edges. A rotatable control surface is located near a trailing edge undersurface. The control surface length is approximately one to five percent of the chord length. A deployment device is positioned between the wing shaped structure and the control surface. The deployment device operably rotates the control surface through a plurality of positions ranging between an initial position and a fully deployed position. Wing lift is increased at speeds up to approximately transonic speed by continuously rotating the control surface to accommodate variables including mobile platform weight change from fuel usage.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Flying wing aircraft
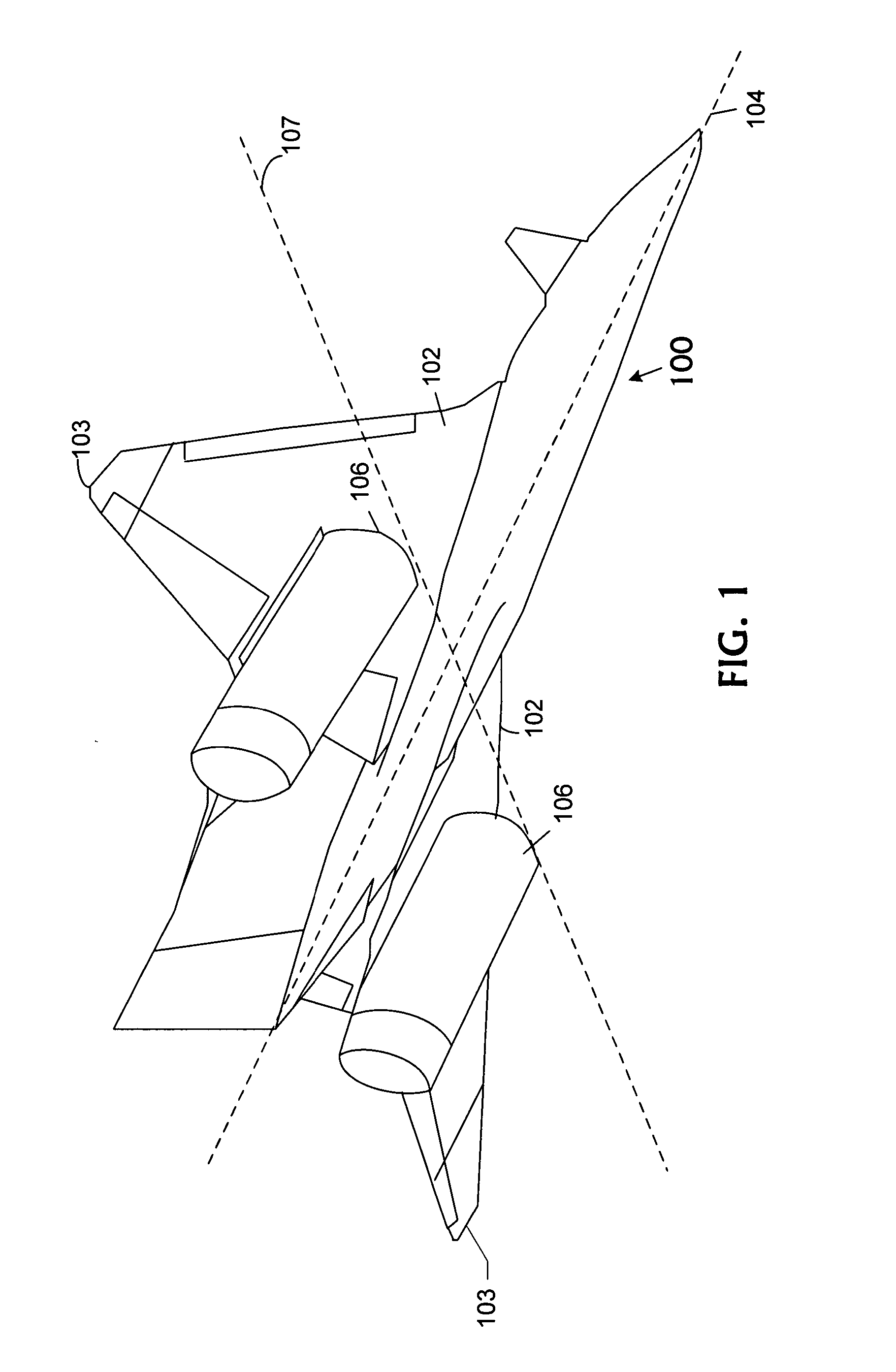
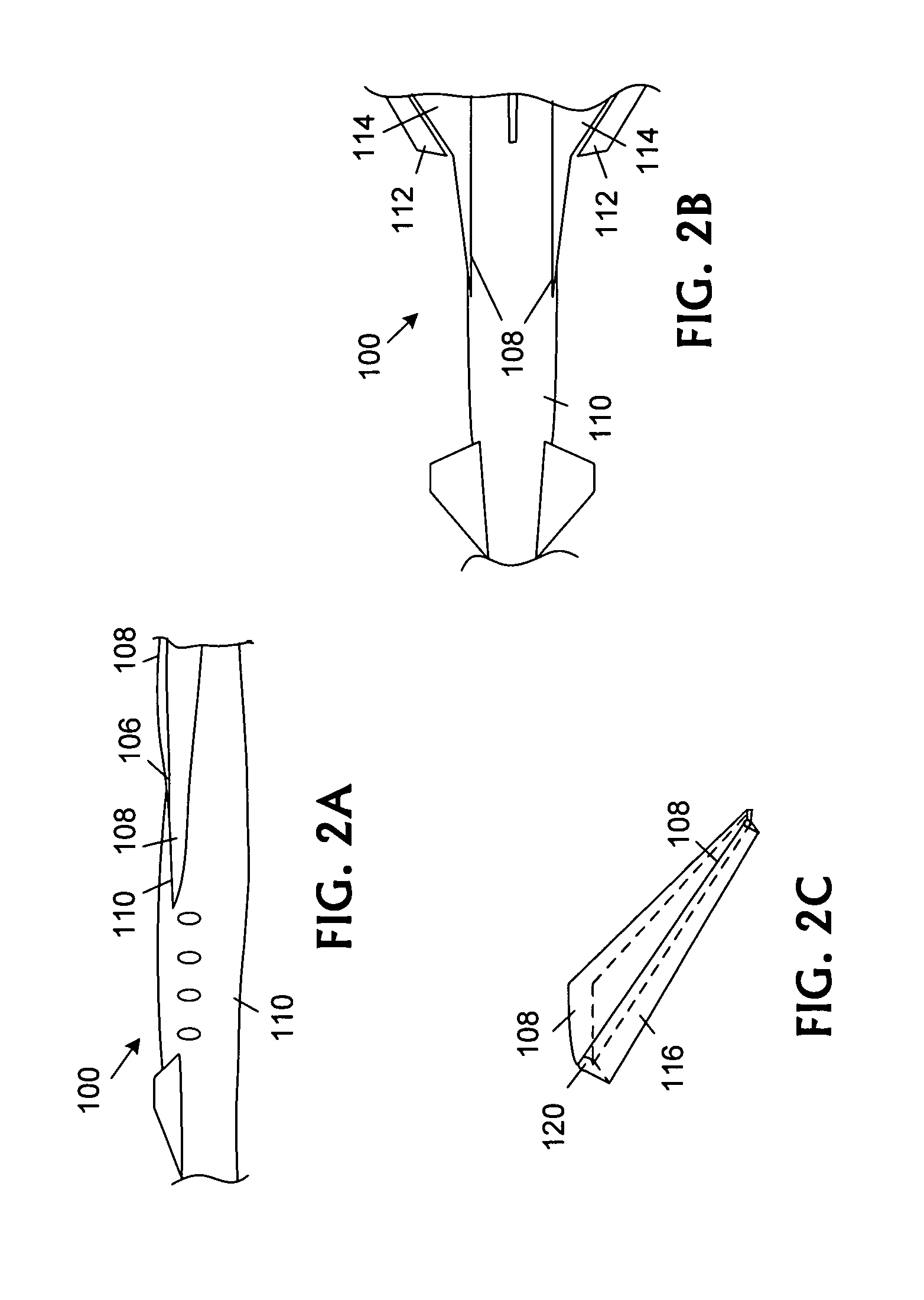
The invention is an aircraft that includes a flying wing having a plurality of extendable flaps mounted on the trailing edge of the flying wing. A canard is mounted on the nose of said flying wing. A system is mounted in the flying wing for providing high pressure air over the canard and the flaps. A second system is provided for controlling the flow of air over the canard to provide pitch control of the aircraft.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
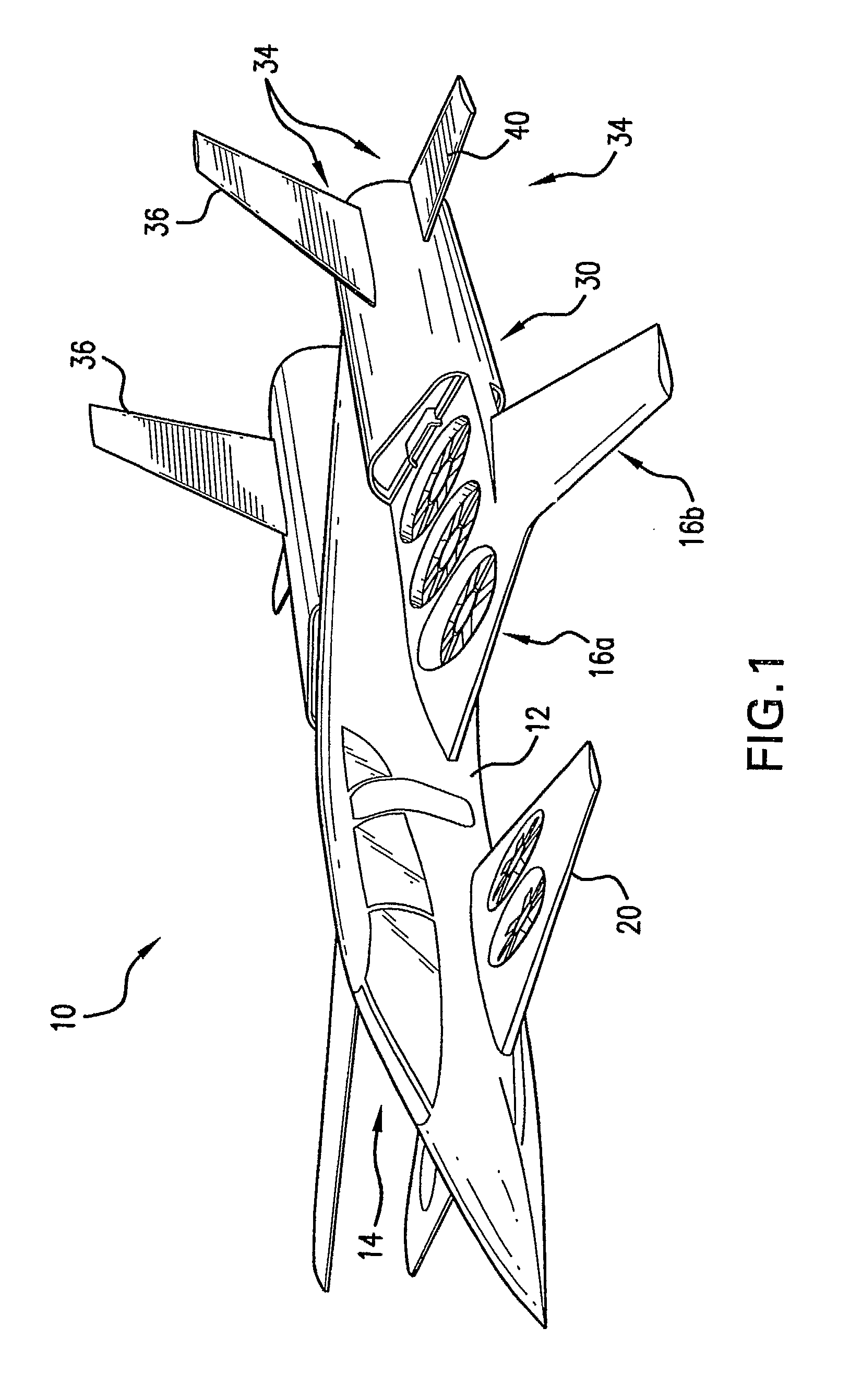
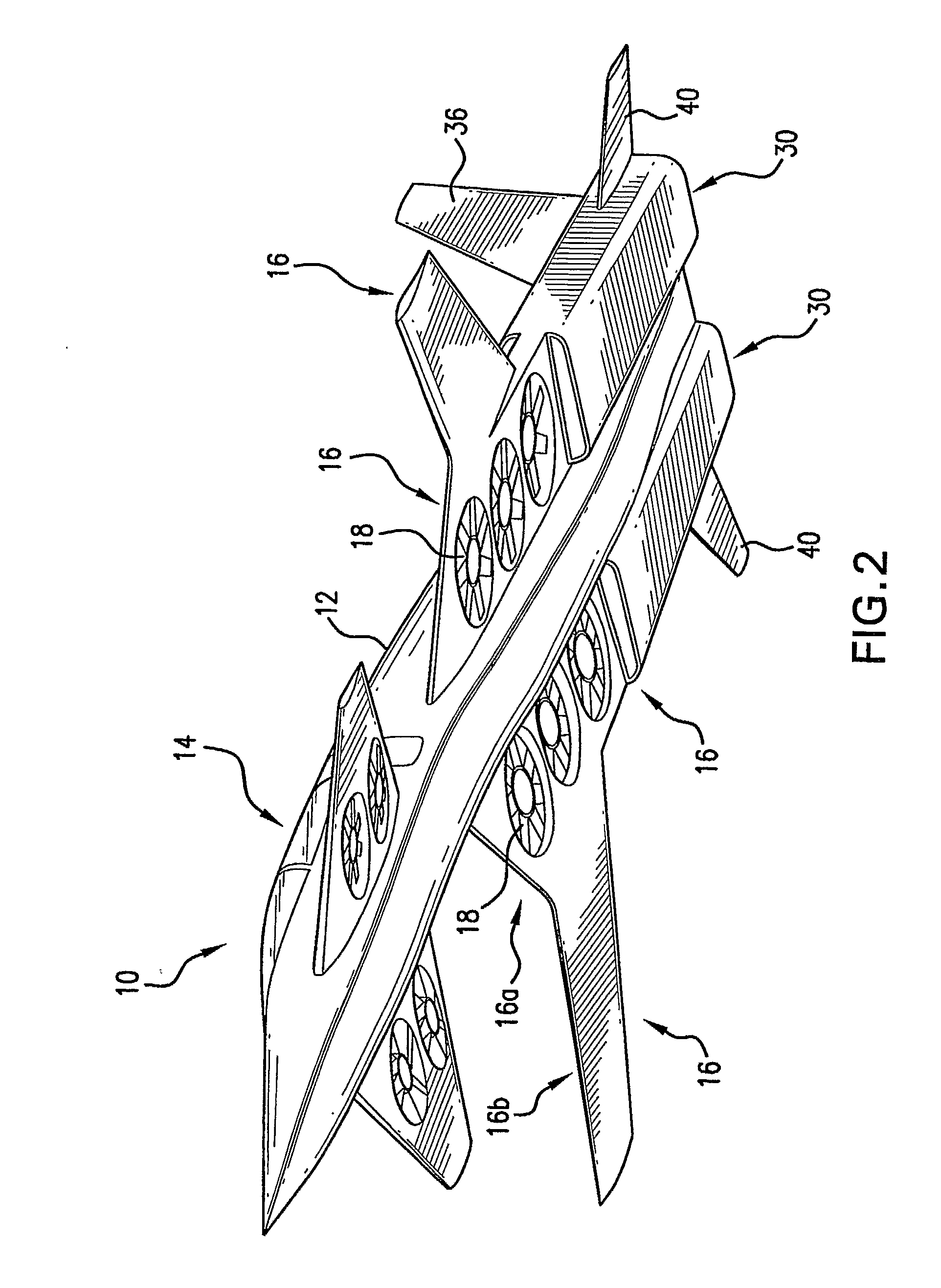
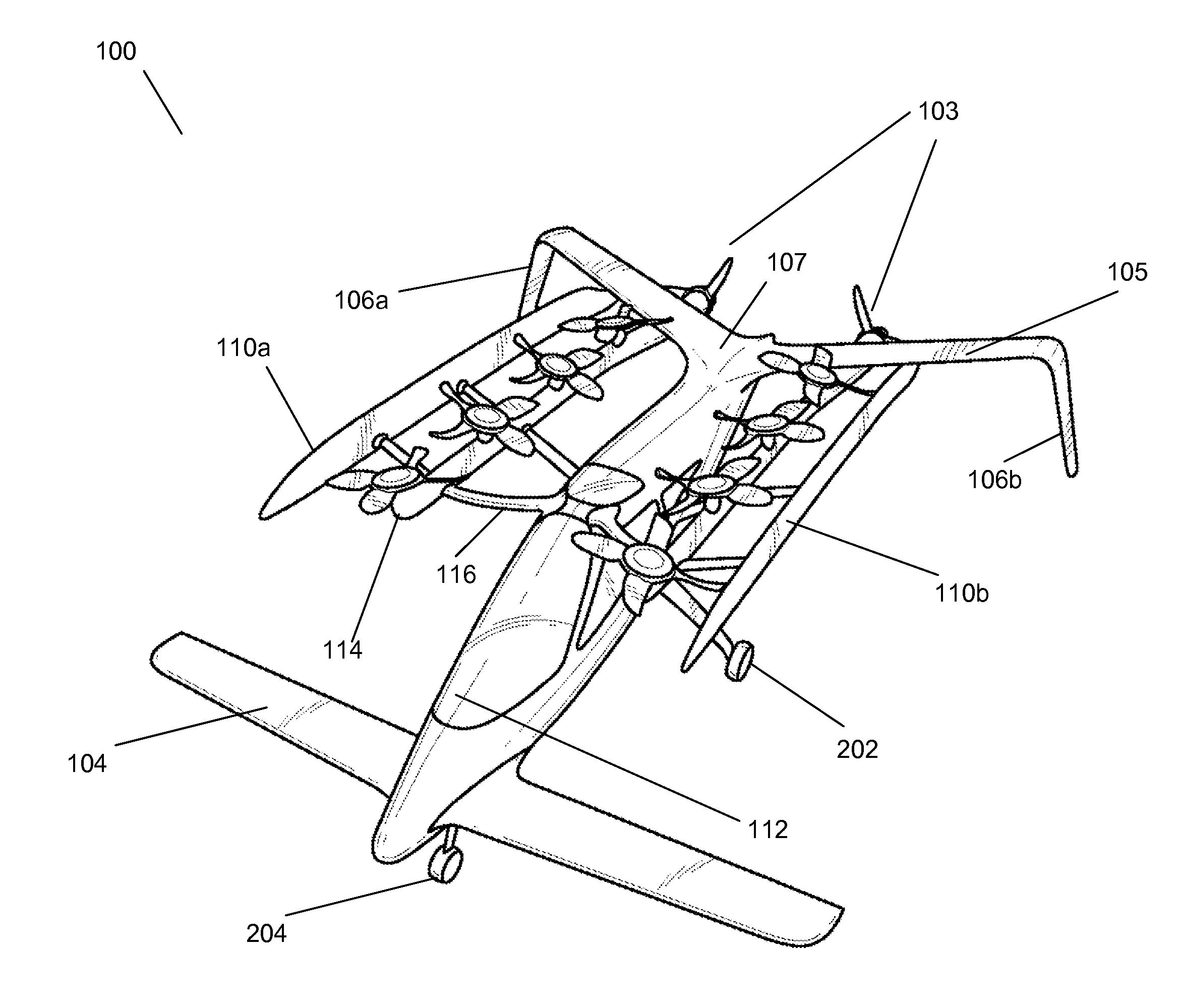
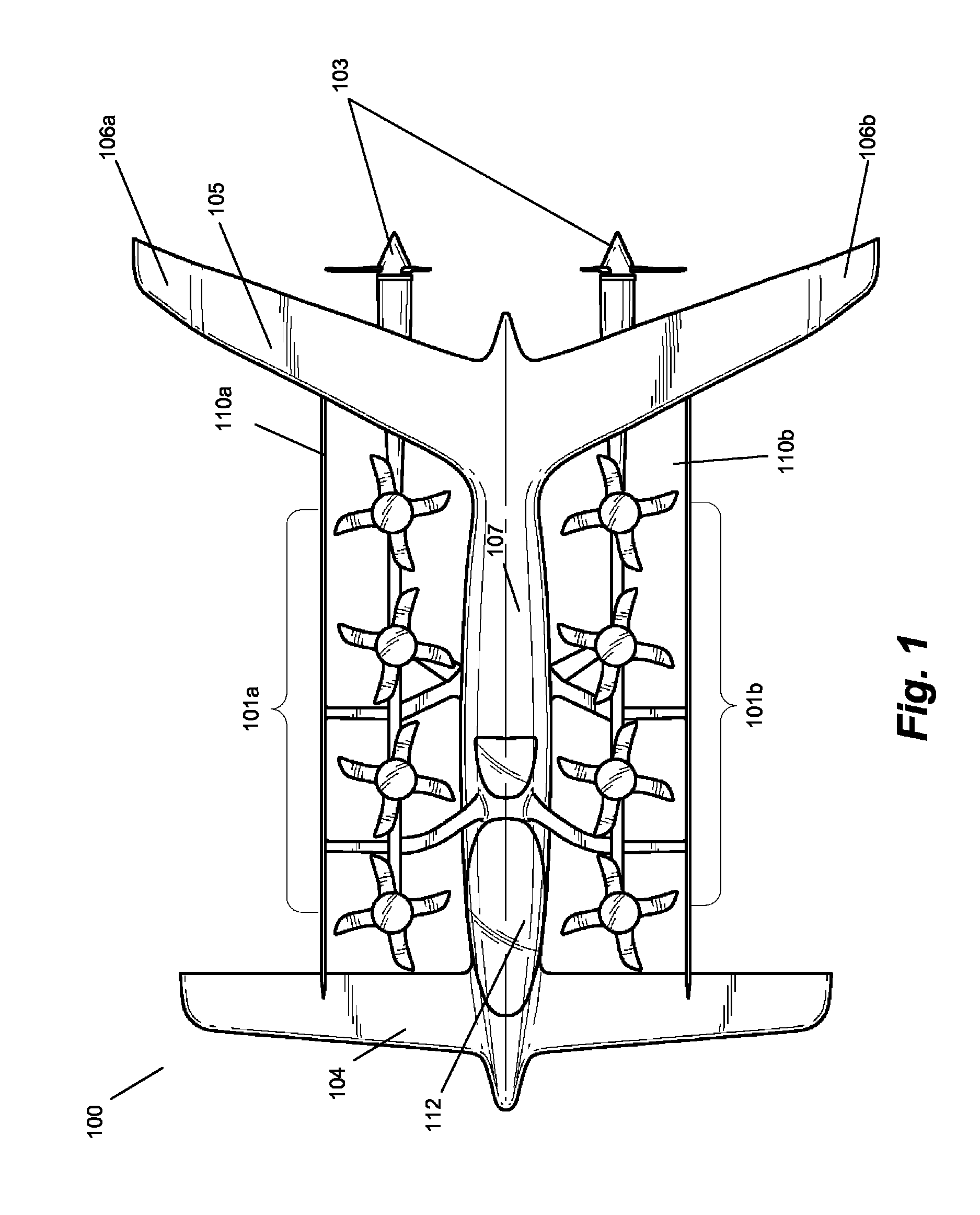
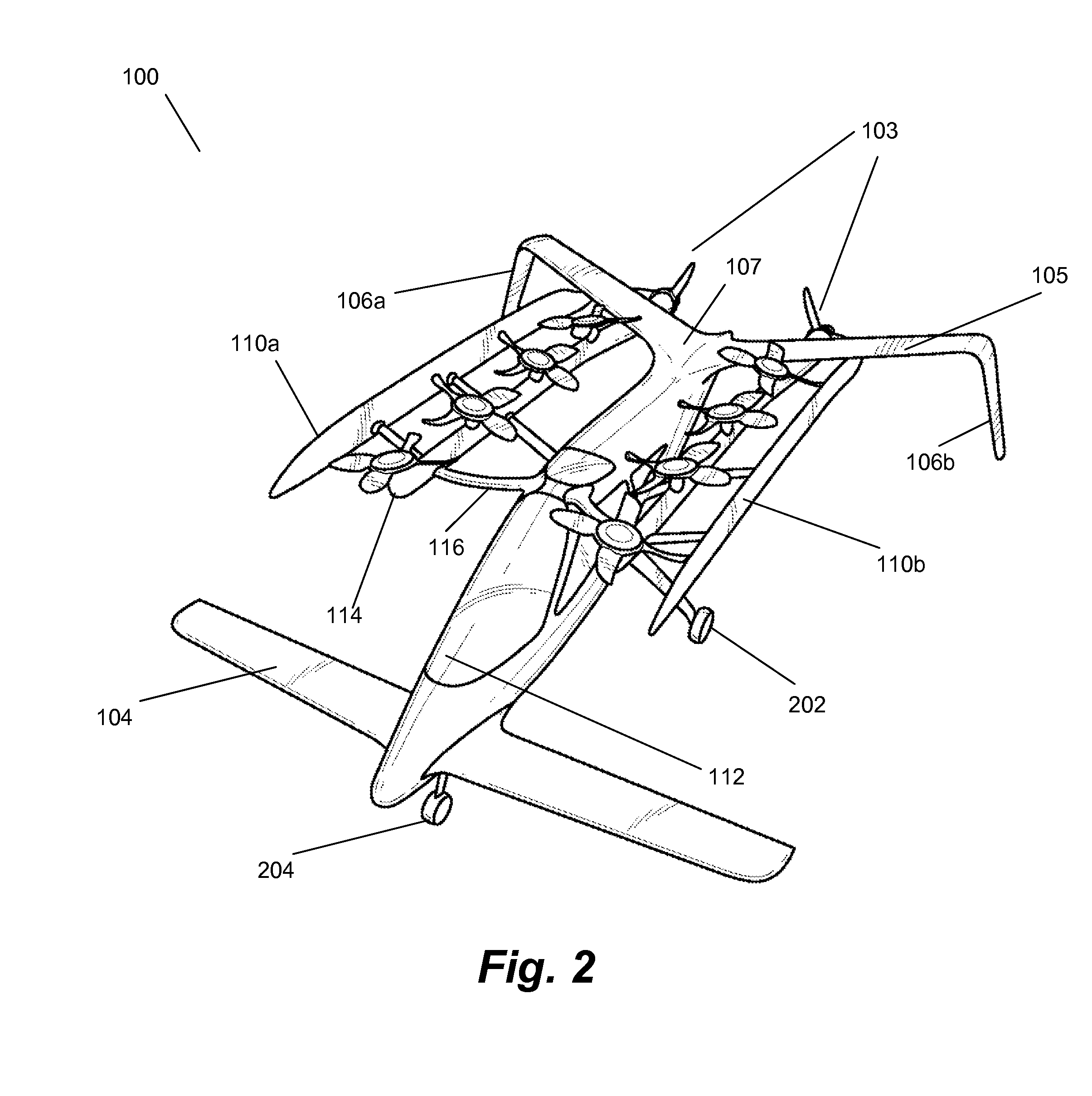
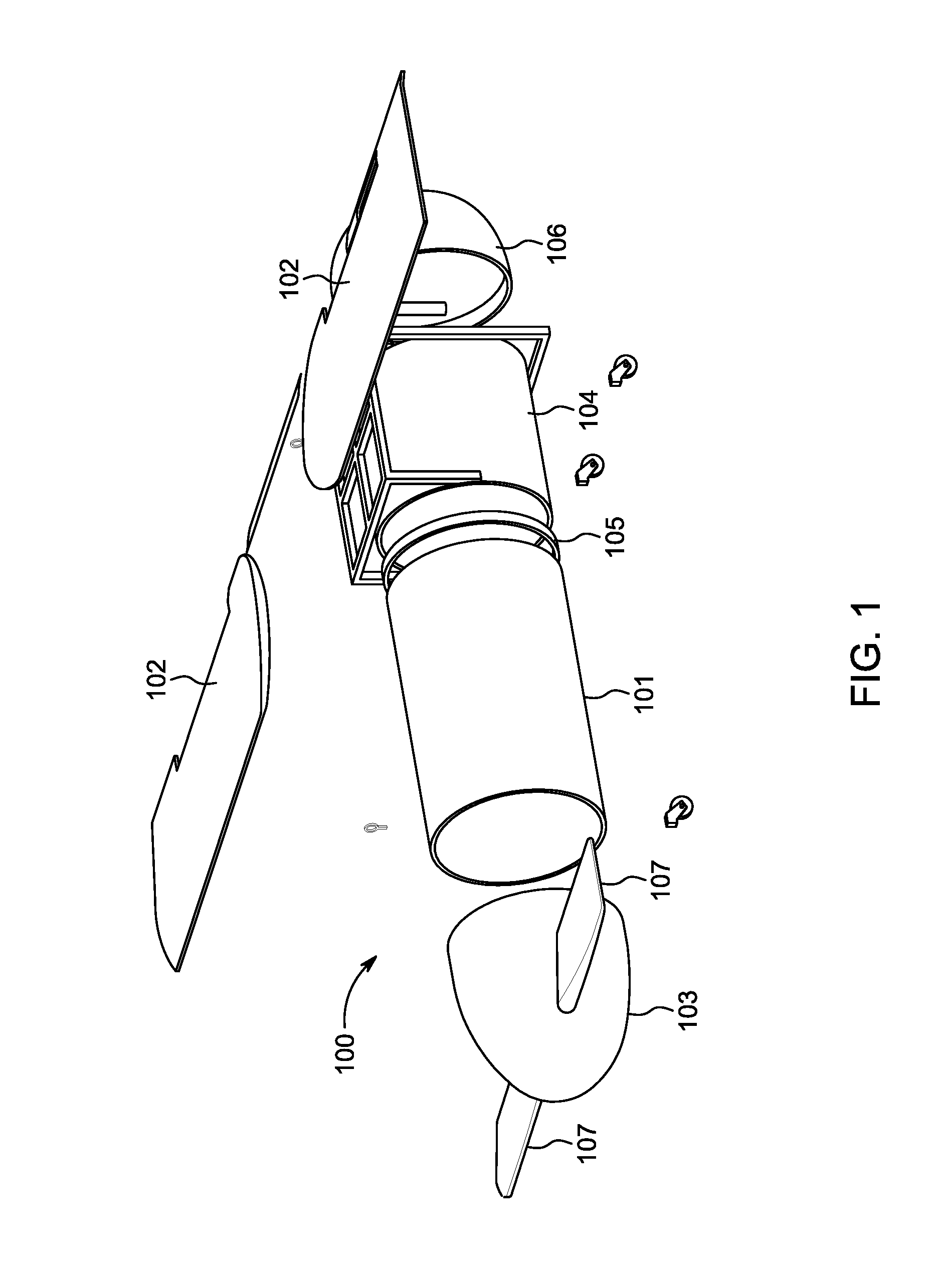
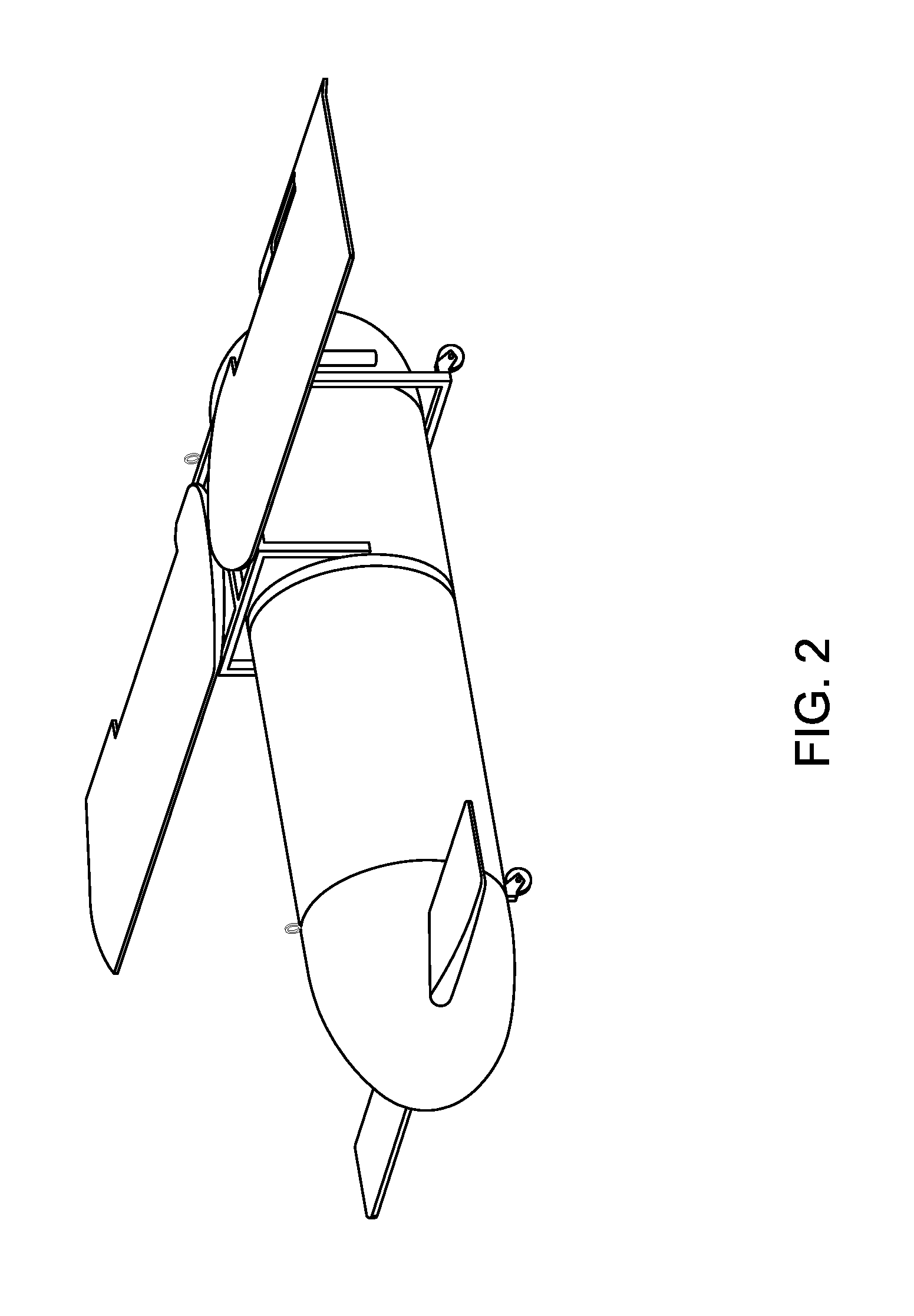
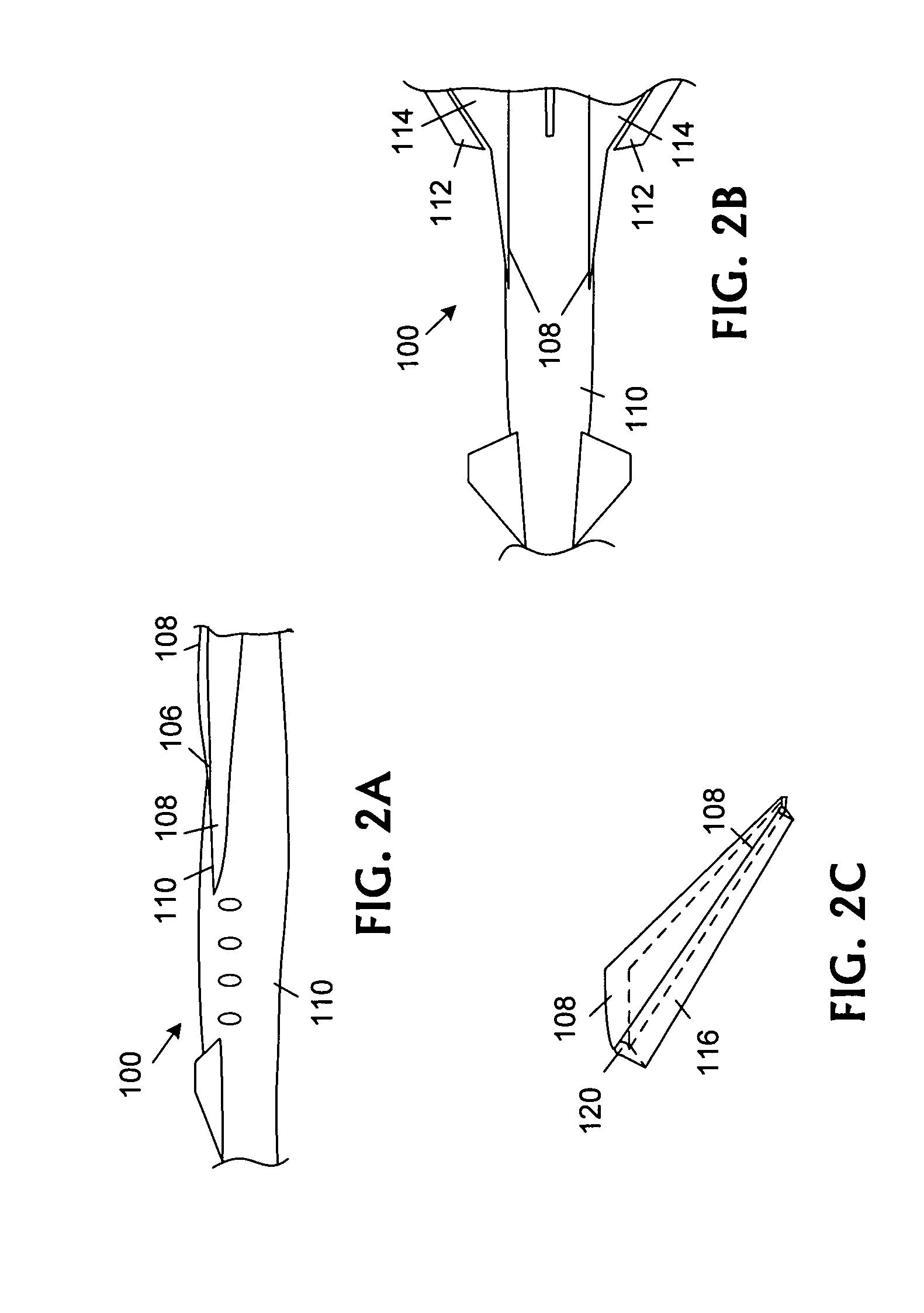
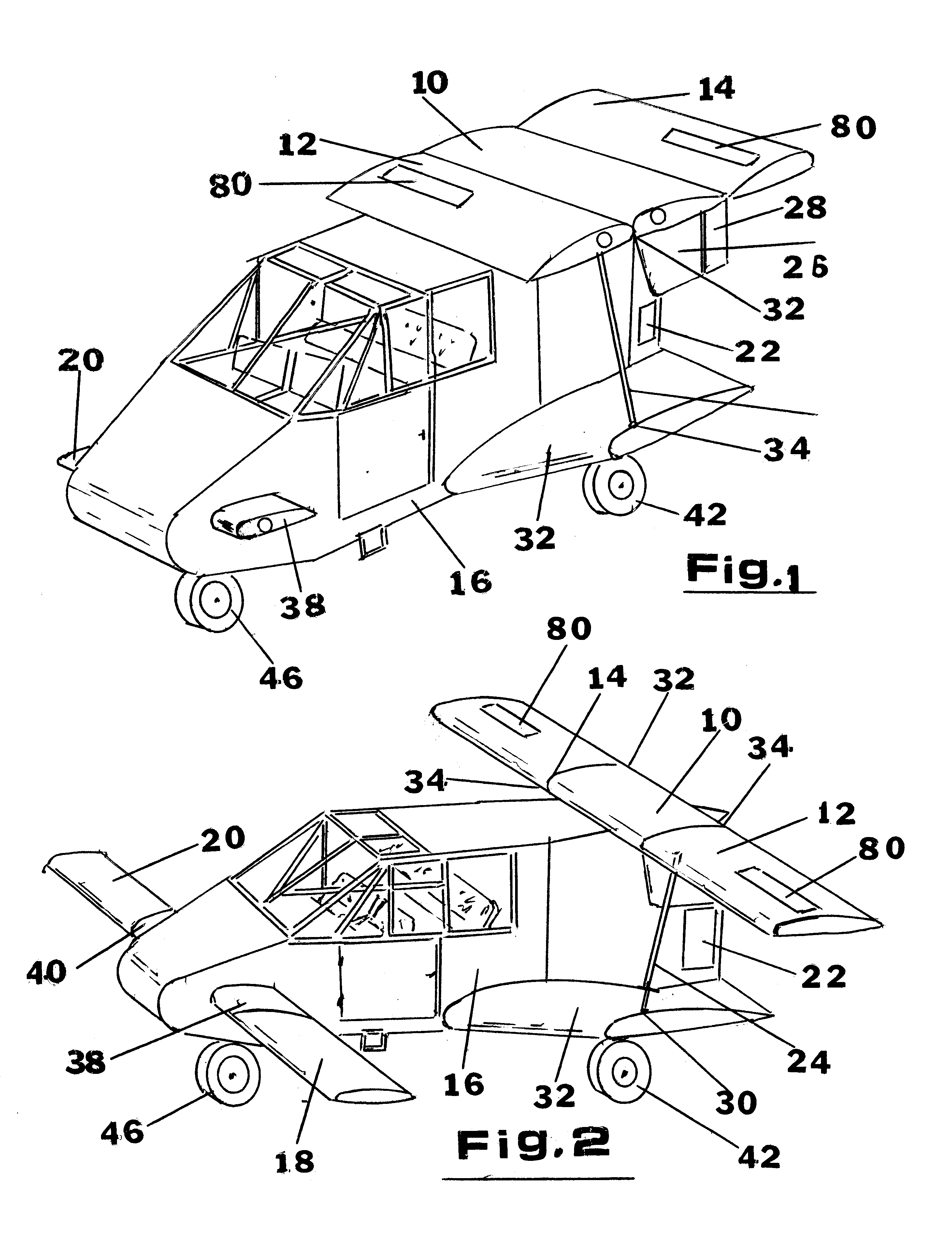
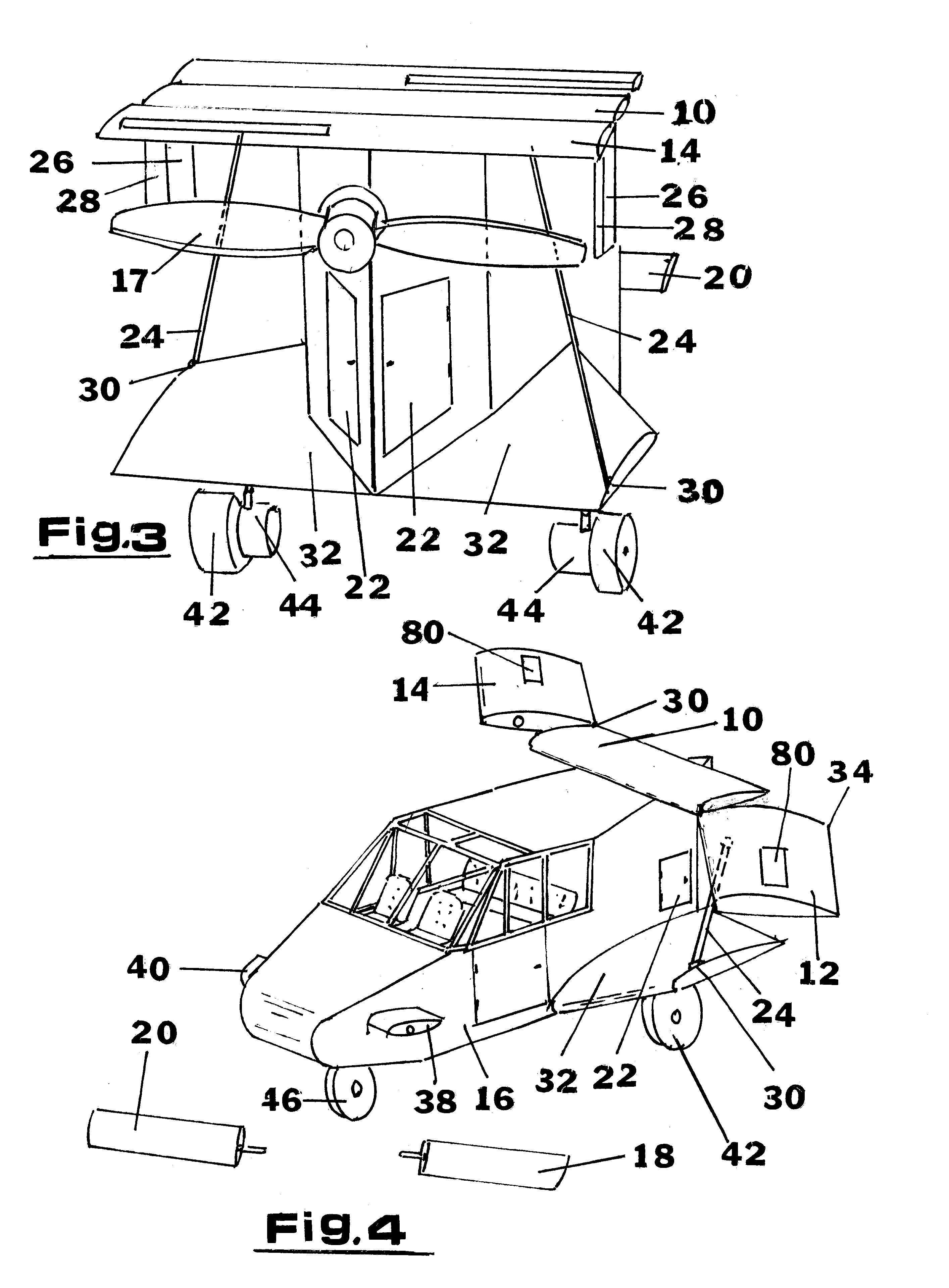
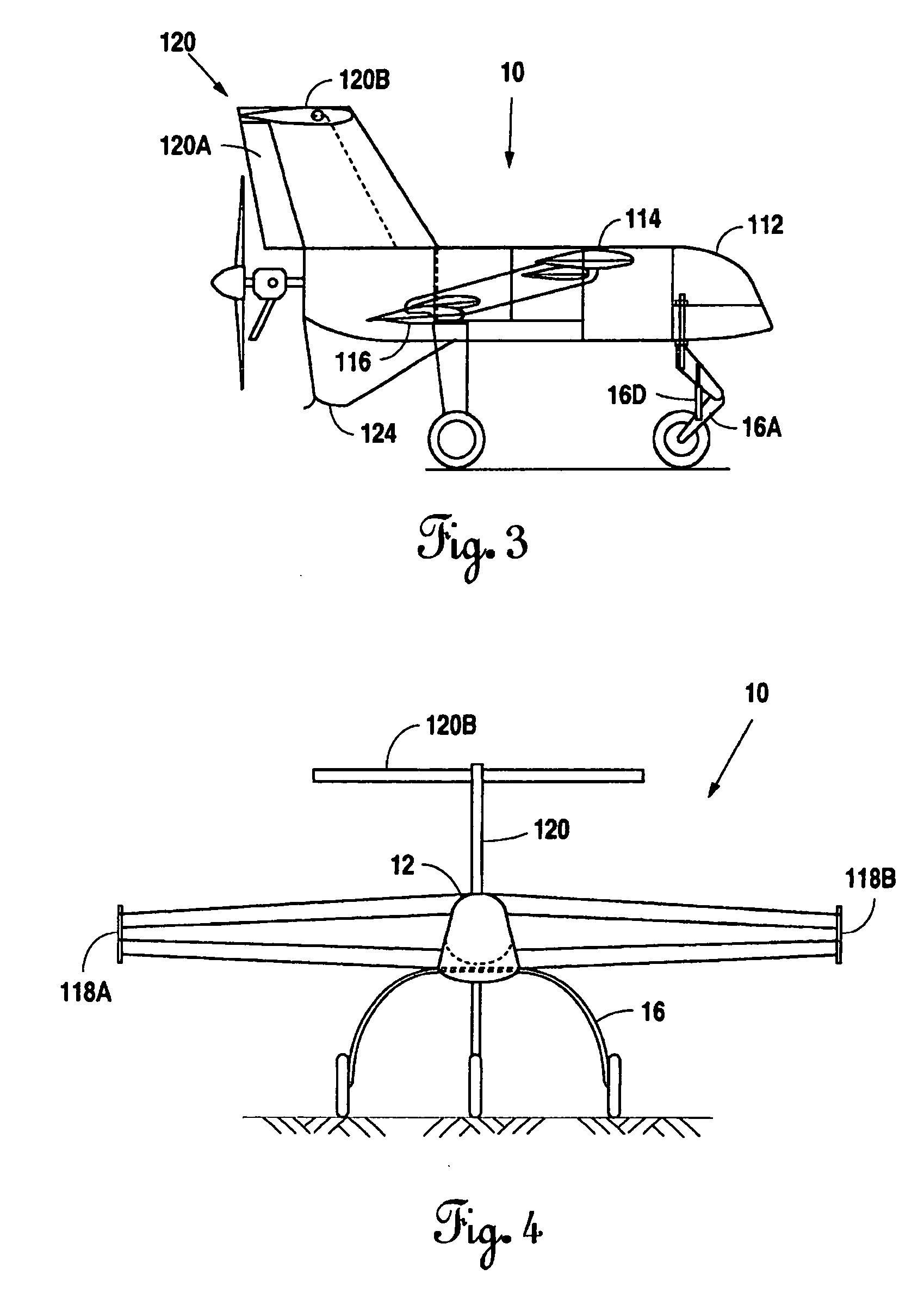
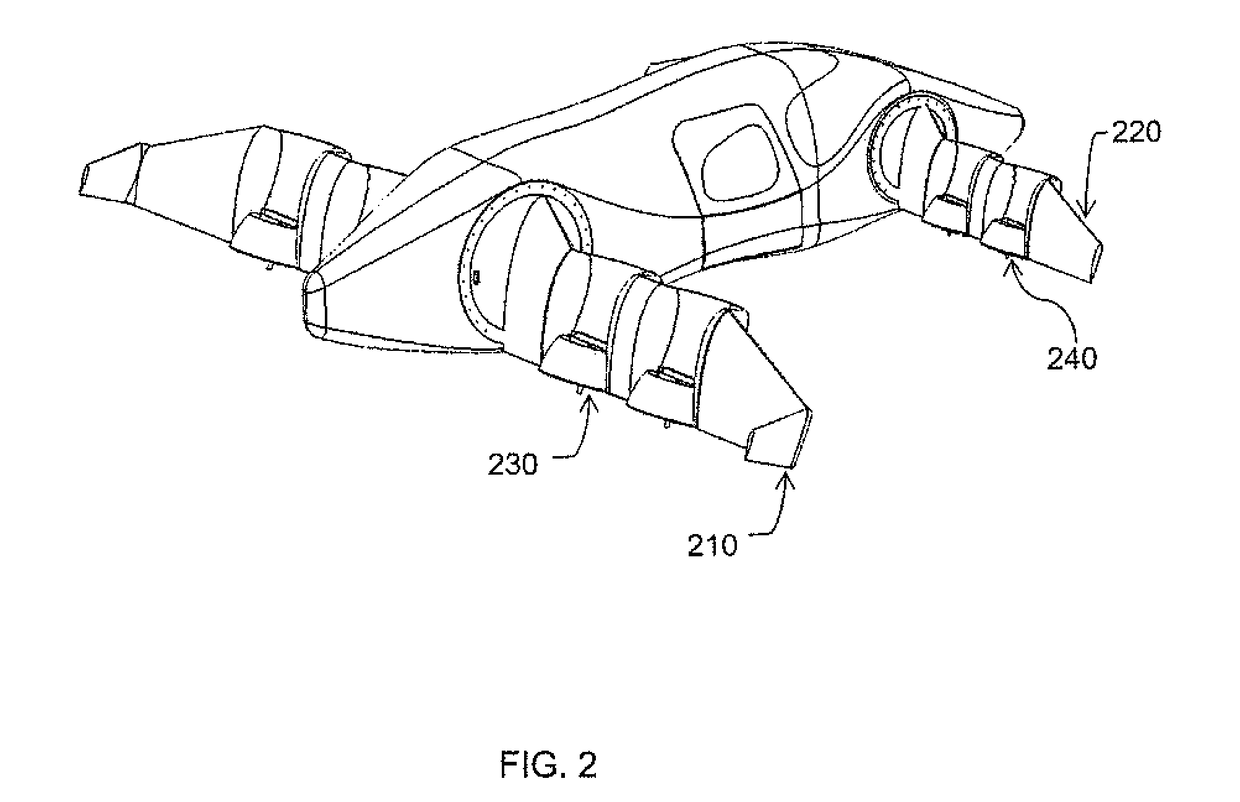
Personal aircraft
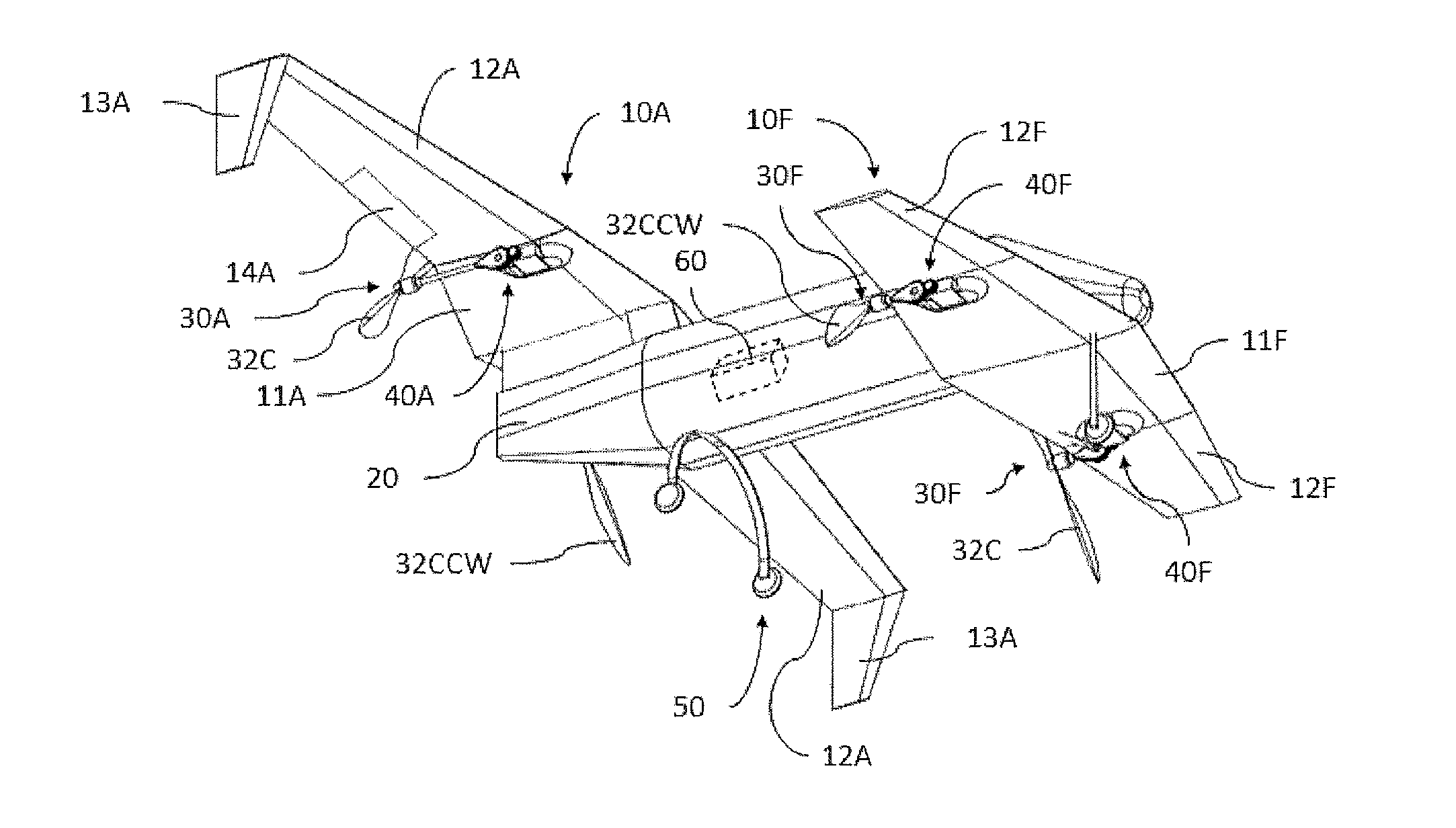
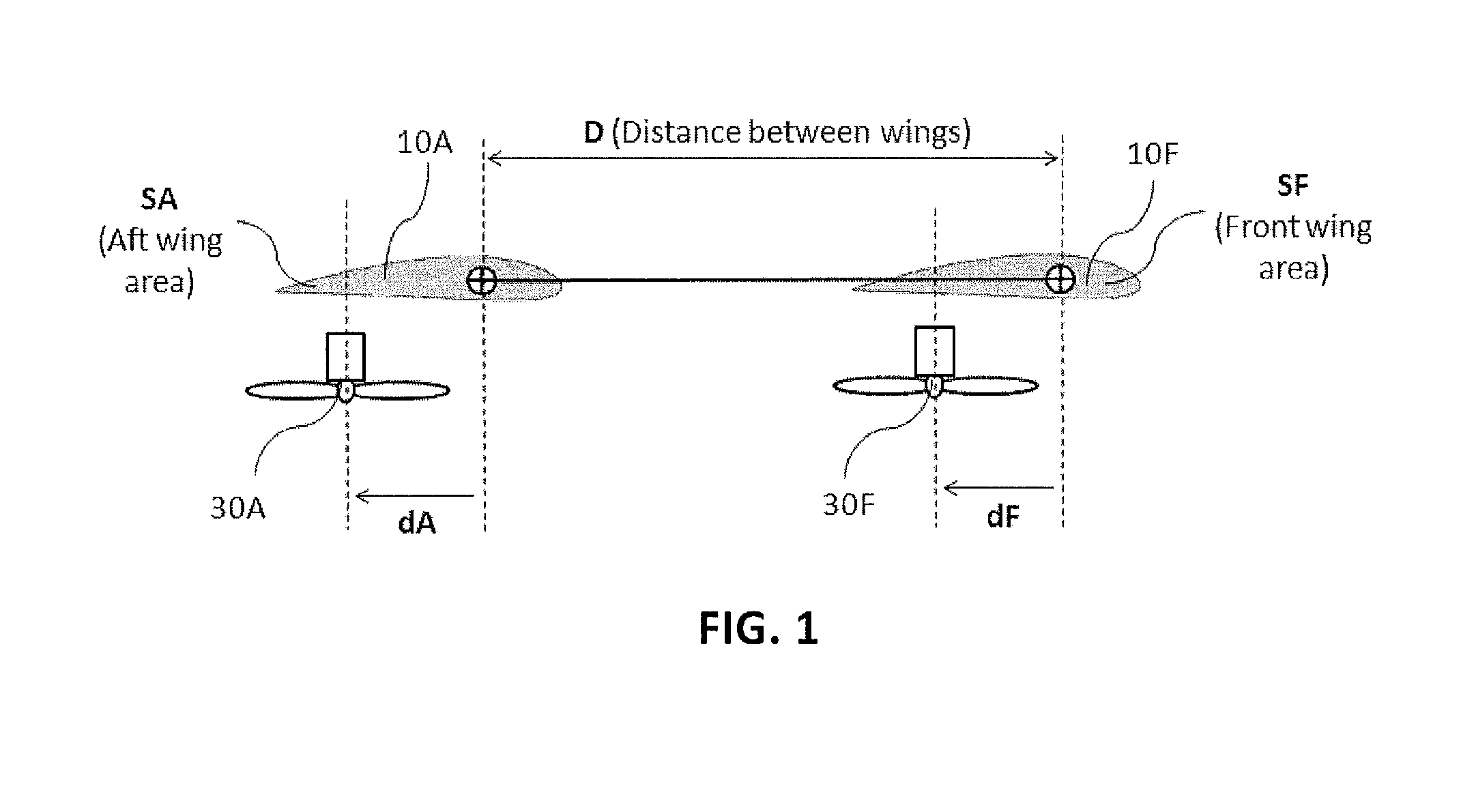
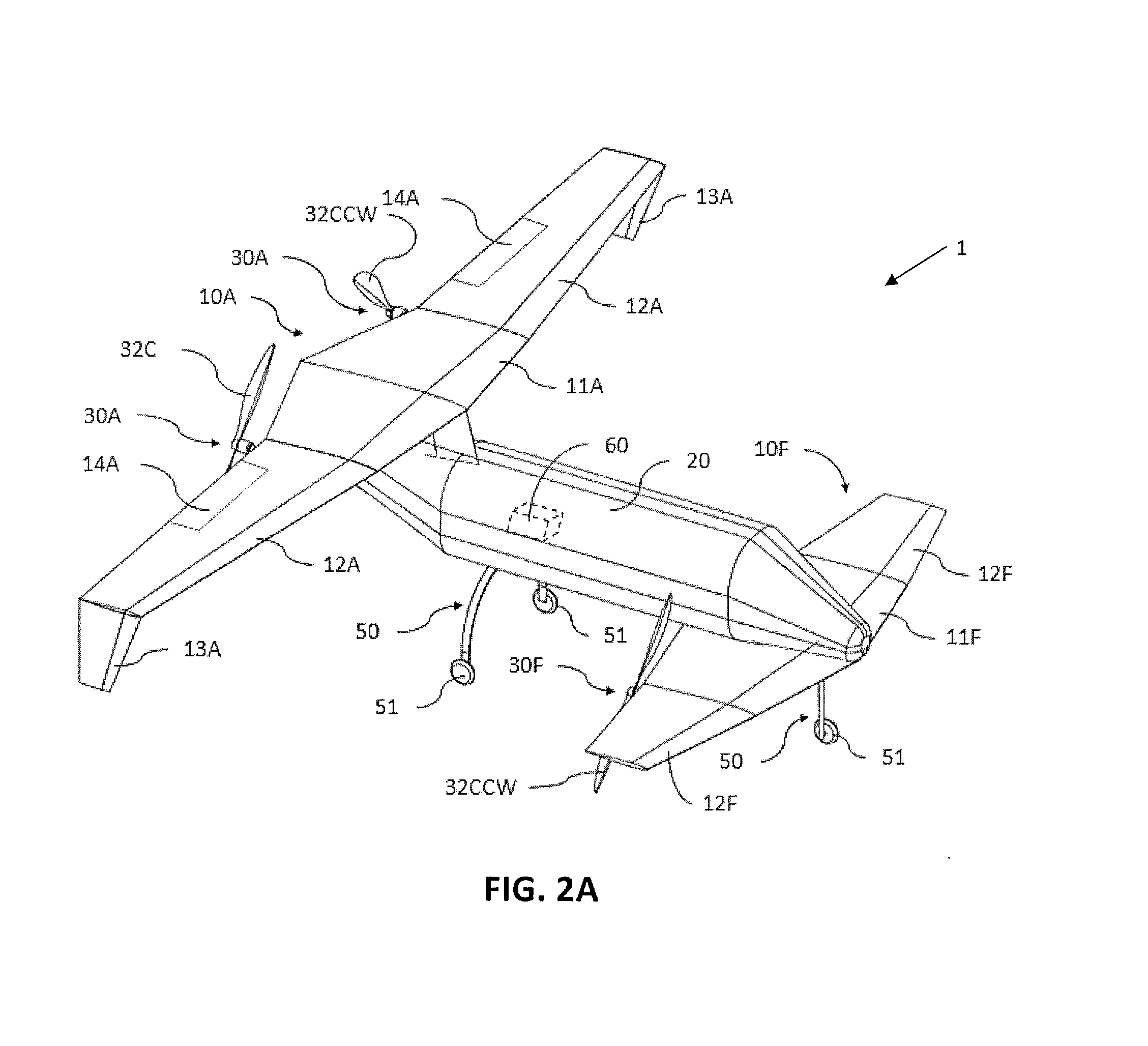
ActiveUS8485464B2Easy to controlMinimize disturbanceAircraft power plantsPropellersLevel flightPropeller
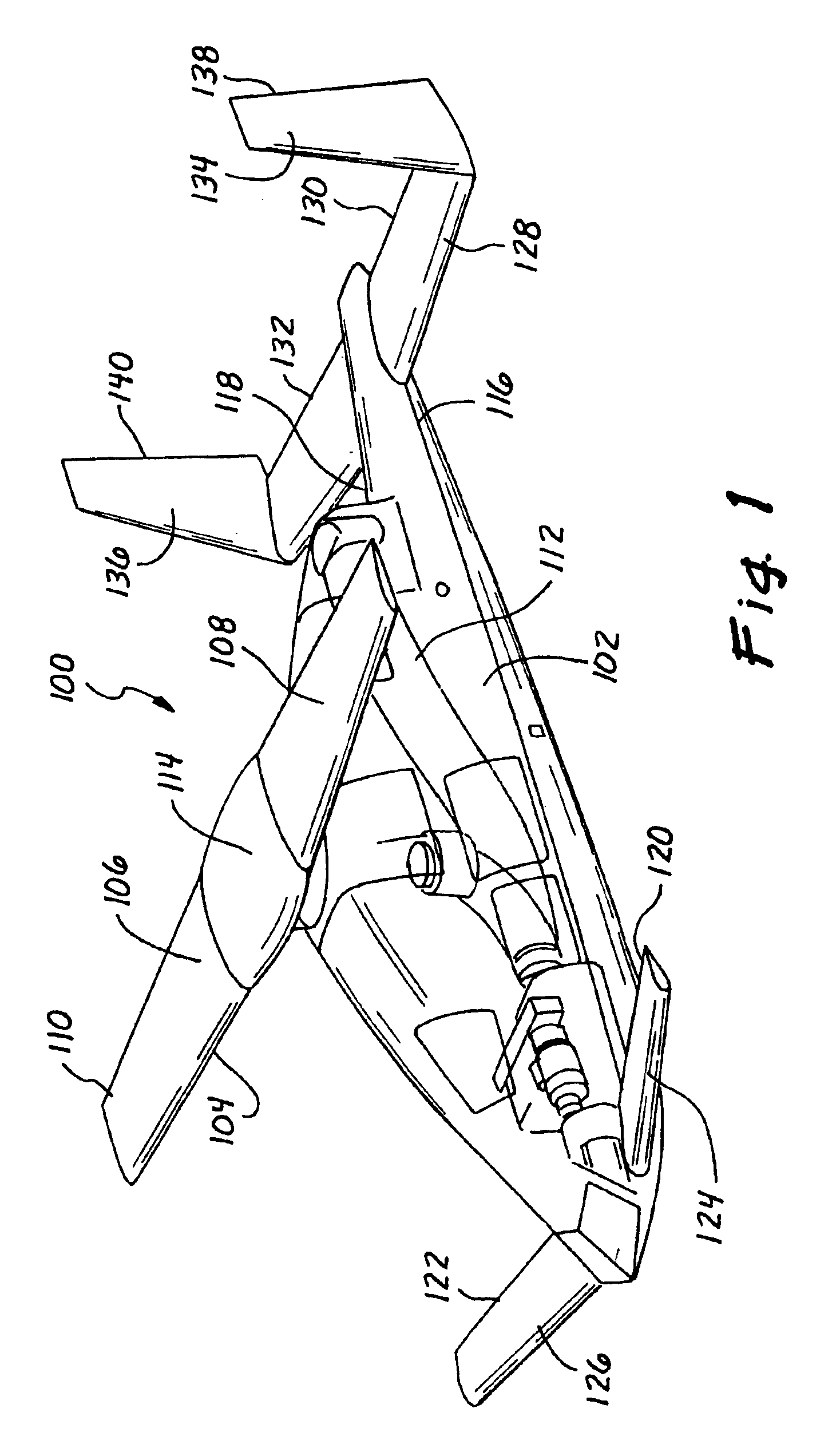
A safe, quiet, easy to control, efficient, and compact aircraft configuration is enabled through the combination of multiple vertical lift rotors, tandem wings, and forward thrust propellers. The vertical lift rotors, in combination with a front and rear wing, permits a balancing of the center of lift with the center of gravity for both vertical and horizontal flight. This wing and multiple rotor system has the ability to tolerate a relatively large variation of the payload weight for hover, transition, or cruise flight while also providing vertical thrust redundancy. The propulsion system uses multiple lift rotors and forward thrust propellers of a small enough size to be shielded from potential blade strike and provide increased perceived and real safety to the passengers. Using multiple independent rotors provides redundancy and the elimination of single point failure modes that can make the vehicle non-operable in flight.
Owner:WISK AERO LLC
Hybrid jet/electric VTOL aircraft
ActiveUS8636241B2Improve efficiencyLess thrust capacityAircraft navigation controlEfficient propulsion technologiesElectricityForward speed
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
Unmanned supply delivery aircraft
ActiveUS20170001724A1Safe and accurate deliveryQuick and easy retrievalAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesDrogue parachuteAirplane
A heavy payload, autonomous UAV able to deliver supply by way of airdrop with more precision and at a lower cost. The UAV can be equipped with a movable wing system. The UAV can include a removable storage box. The UAV can be equipped with a drogue parachute for deploying the wings upon jettison of the UAV from a mothership. The UAV can be controlled remotely or it can operate autonomously. The UAV can include canard wings. The canard wings and the movable wings can include ailerons to effectuate flight control of the UAV. The UAV can be reusable or can be an expandable UAV. The UAV's wings can be configured to automatically separate from the UAV during the landing sequence.
Owner:W MORRISON CONSULTING GRP
Wing employing leading edge flaps and winglets to achieve improved aerodynamic performance
ActiveUS7475848B2Facilitate sonic boom reductionEasy to controlInfluencers by generating vorticesWith power amplificationLeading edgeControl system
Owner:SUPERSONIC AEROSPACE INT
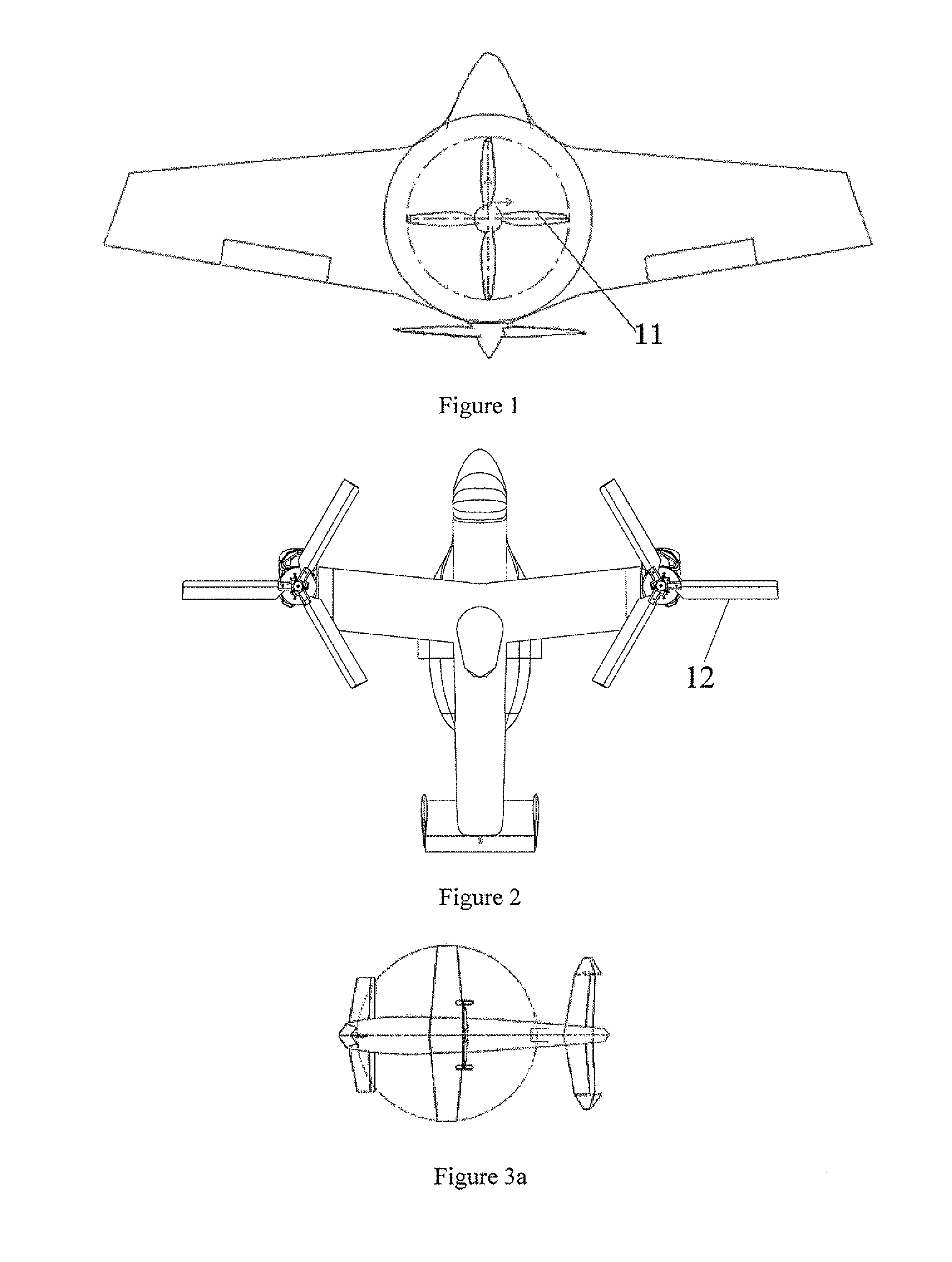
Aircraft configuration for micro and mini UAV
An aircraft arrangement for Mini or Micro UAV comprising a fore wing (14) and an aft wing (12) in tandem closed-coupled arrangement. The aft wing (12) has side panels (18) and control surfaces (19), and tapered planform with positive sweep, while the fore wing (14) has non-positive trailing edge sweep. The fore wing (14) and the aft wing (12) are disposed at different height, and the aircraft arrangement has no other wings or tail arrangements.
Owner:ISRAEL AEROSPACE IND
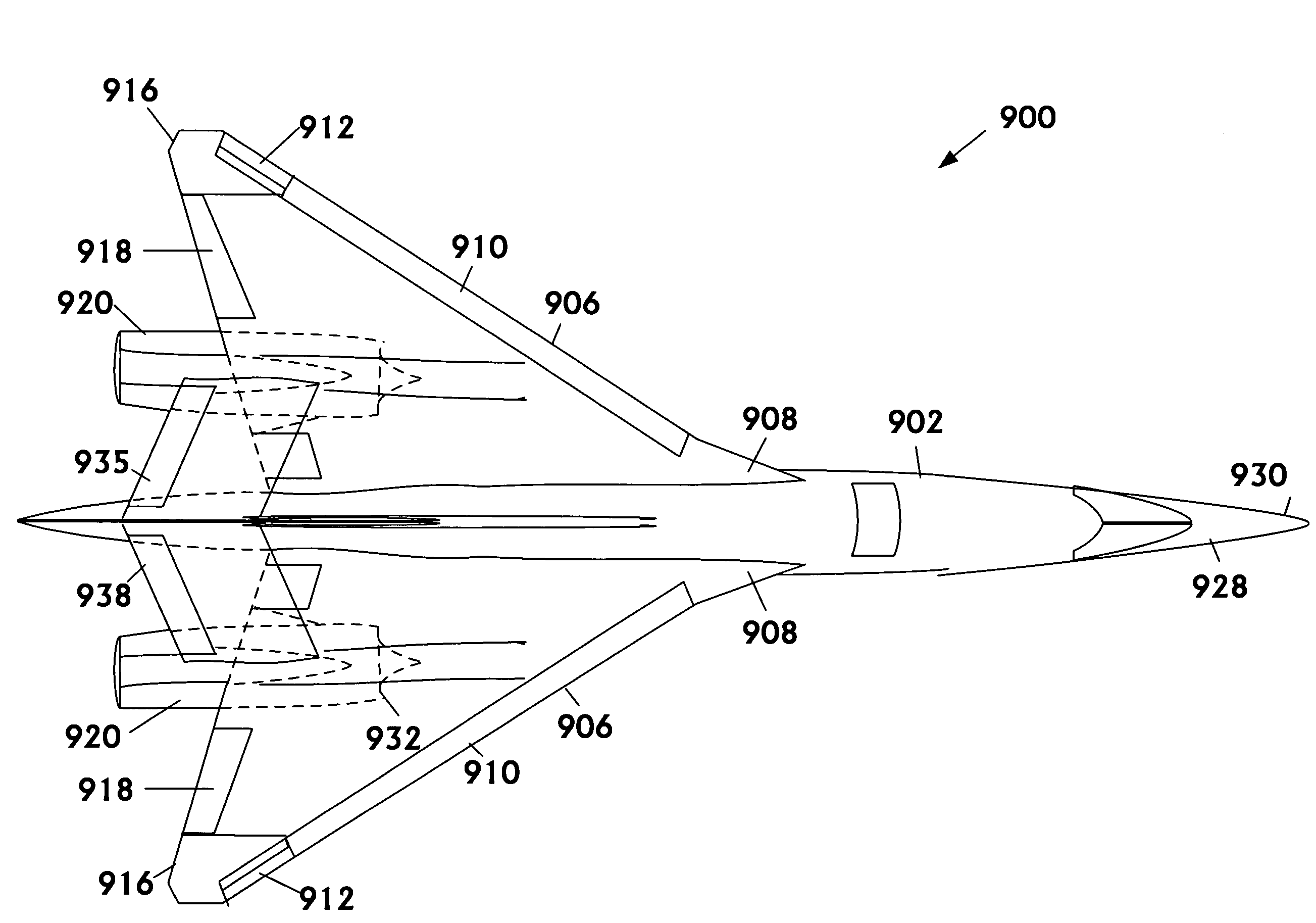
Airplane configuration
InactiveUS20080142641A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced aircraft noiseGas turbine type power plantsAircraft stabilisationJet aeroplaneLeading edge
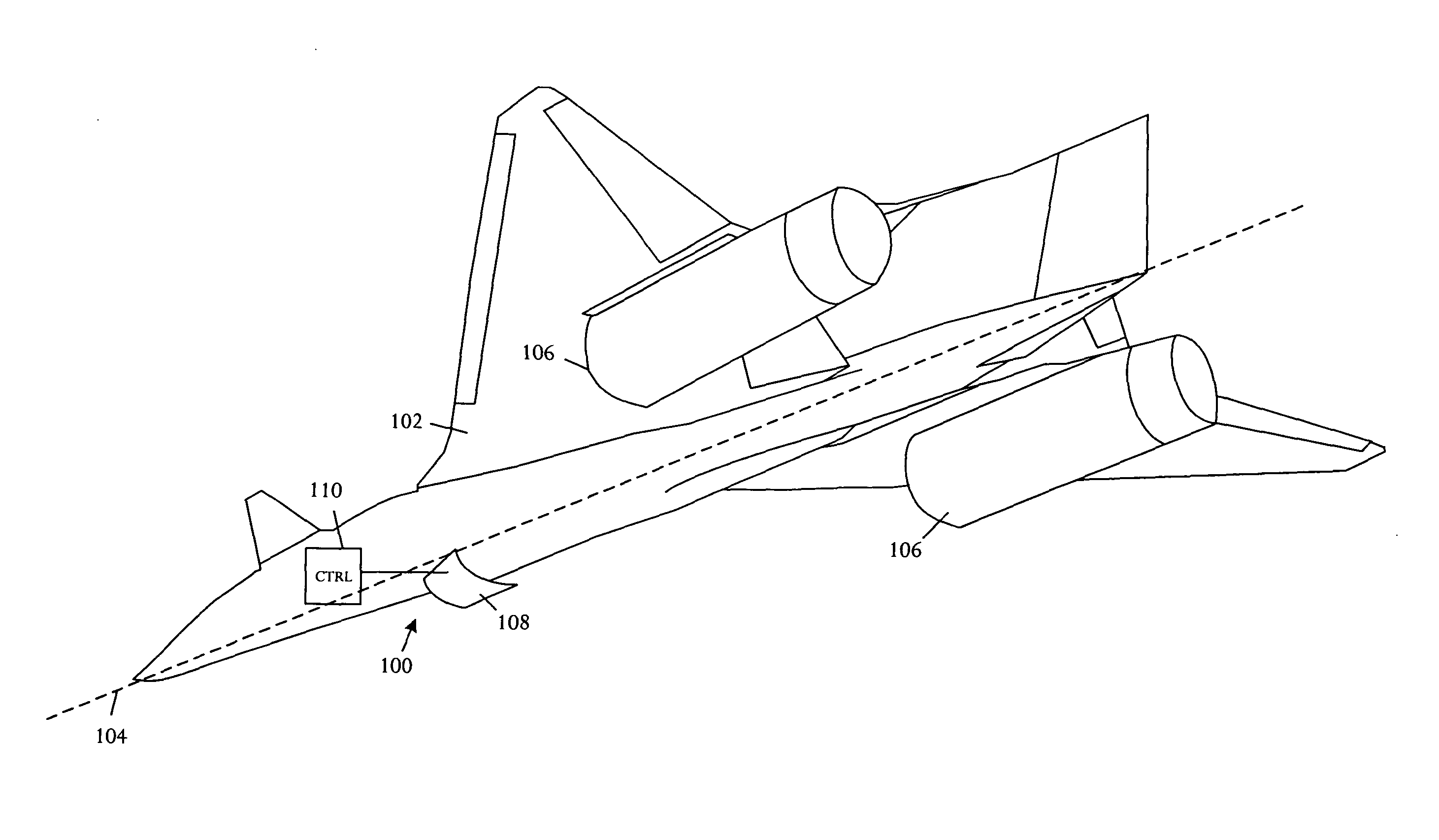
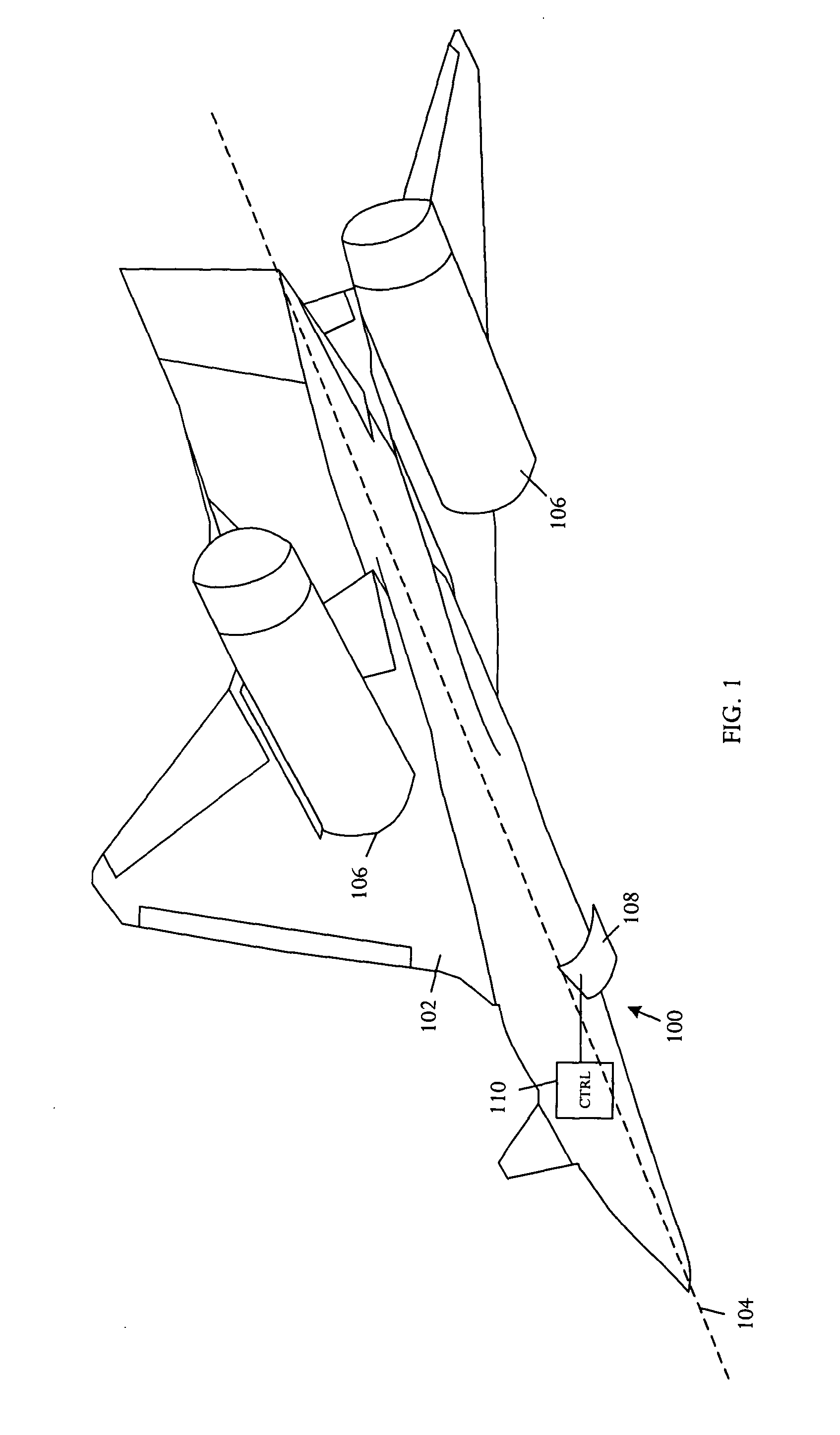
An aircraft configuration that may reduce the level of noise, infrared radiation, or combination thereof directed towards the ground from an aircraft in flight. An embodiment of an aircraft includes a fuselage, two forward swept wings, at least one engine mounted to the aircraft and higher than the wings, and vertical stabilizers mounted on each wing outboard of the outermost engine. The leading edge of the wing may extend forward of the leading end of the engine, and the trailing edge of the aft deck may extend aft of the trailing end of the engine. The aft deck may include an upwardly rotatable pitch control surface at the trailing edge of the deck. Engine types may vary, including but not limited to turbofans, prop-fans, and turbo-props. Main wings may be mounted above the longitudinal axis of the fuselage, and canards may likewise be mounted above or below the axis.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
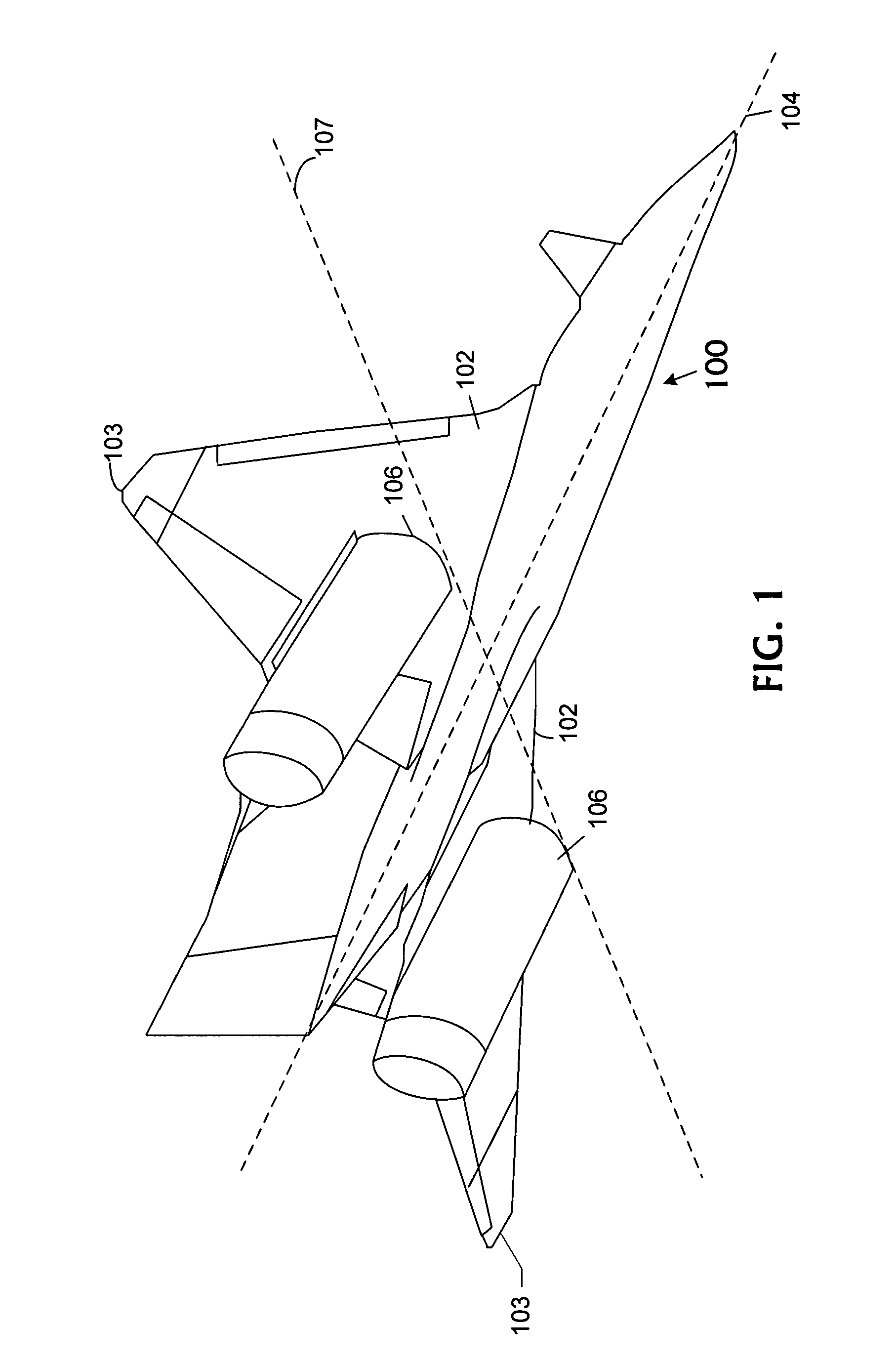
Rapidly-convertible roadable aircraft
InactiveUS6786450B1Small hangar spaceReduce resistanceConvertible aircraftsAircraft stabilisationJet aeroplaneHydraulic motor
A pusher canard aircraft convertible for road use. Canard outer sections are removable and are stored within the aircraft fuselage and the outer main wing sections rotate horizontally for storage on the fuselage top. The fuselage is designed as a lifting body which gives the aircraft three lifting surfaces. The lifting body takes advantage of ground effect, resulting in a lower landing speed. In road mode the vehicle as a 2 or 4 passenger model is smaller than a full size automobile. Hydraulic motor wheels propel the aircraft / vehicle for road use. An internal combustion engine within the fuselage drives the propeller for air operation. The propeller is disengaged, not removed, for land operation and the engine is used to drive an hydraulic pump to power the motor wheels for road use. A single nose wheel or two front wheels are used for both steering in landing / taxiing and for road use. In road mode, the appearance is as much like a van than as an aircraft. In flying mode, the appearance is not to unconventional.
Owner:EINSTEIN HARRY
Hybrid VTOL fixed-wing drone
ActiveUS10081436B1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityAircraft power plantsUnmanned aerial vehiclesPropellerEngineering
A long-distance drone is disclosed having a canard body style with a main body, a left main wing, a right main wing, a left forewing, and a right forewing. The left forewing is attached to the main body forward of the left main wing, and the right forewing is attached to the main body forward of the right main wing. There is a left linear support connecting the left forewing to the left main wing, and a right linear support connecting the right forewing to the right main wing. A plurality of propellers are disposed on the left and the right linear supports.
Owner:SHANGHAI AUTOFLIGHT CO LTD
Aircraft thickness/camber control device for low sonic boom
ActiveUS20050067525A1Cancellation effectReducing sonic boomAircraft stabilisationWith power amplificationOff designFuselage
An aircraft thickness / camber control device mounts to the lower surface of a airfoil configuration, for example on a fuselage, and extends along a longitudinal axis. The device, when deployed, generates expansions ahead of compressions generated by off-design conditions, inlet spillage for example, and enables maintenance of a low boom signature. The device, when positioned at appropriate locations, may also be used as a drag reduction device. The thickness / camber control device comprises a structural member capable of coupling to the airfoil at a position forward of the concentrated source of added compression and a control element. The control element is coupled to the structural member and controls the structural member to adjust thickness / camber of the configuration to cancel the far-field effect of the extra compression or concentrated pressure source.
Owner:SUPERSONIC AEROSPACE INT
Roadable aircraft with collapsible wings and ductless fan
InactiveUS20110036938A1Maintain tensionRemove complexityPropellersConvertible aircraftsEngineeringFuselage
A roadable aircraft may be registered and driven as a motorcycle on the roadways, does not require that any parts be “left behind” at the airport when configuring to roadable use and does not require removing portions of the aircraft and towing them behind. A foldable and collapsible wing comprises a number of wing ribs, which are hinged to a main forward spar. To fold for road usage, the wing ribs fold about a hinge fitting to collapse against the wing spar. To maintain tension on the wing skin (to prevent flutter) tensioning bladder(s) may be used to keep the fabric taut. Once retracted and folded, the wings align with tail booms to form a compact and aerodynamic package. The ductless fan may be provided with a center-mounted extraction fan ducted to inlets along the fuselage to draw low energy air in toward the fuselage and thus prevent boundary layer separation.
Owner:BLOMELEY LEWIS E
Aircraft and methods for operating an aircraft
An aircraft (10) comprising a fuselage (12) having a longitudinal axis (16), at least one helicopter main rotor (40) operably mounted to the fuselage (12), the at least one helicopter main rotor (40) comprising rotor blades (41) rotatable about a rotation axis (44), wherein the rotor blades (41) can be stopped in flight and adapted to provide symmetrical wing surfaces relative to the longitudinal axis (16); and the aircraft (10) having at least one control surface (62, 82) operable to provide a relative airflow (306) in flight substantially aligned with the rotation axis (44) of the at least one helicopter main rotor (40).
Owner:STOPROTOR TECH
Unmanned biplane for airborne reconnaissance and surveillance having staggered and gapped wings
InactiveUS20060102798A1Easy to assembleLight weightUnmanned aerial vehiclesActuated automaticallyFlight vehicleVertical stabilizer
The present invention provides an unmanned airborne reconnaissance vehicle having a fuselage, a forward wing pair and a rearward wing pair vertically separated by a gap and staggered fore and aft therebetween such that a general biplane configuration is formed. The present invention provides a pair of wing tip plates for joining the wing tips of the forward and rearward wings. The unmanned airborne reconnaissance vehicle of the present invention includes a power plant to propel the vehicle through the air and a generally T-shaped tail having a vertical stabilizer including a rudder and a full span elevator.
Owner:MISSION TECH
Vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveUS9694906B1Readily apparentAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesFlight vehicleForward-swept wing
The vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle includes a pair of selectively rotatable ducted fans and a selectively rotatable thrust vectoring nozzle providing vertical takeoff and landing for an unmanned aerial vehicle or a similar type of aircraft. A pair of fixed forward-swept wings are mounted on a rear portion of a fuselage, and a pair of canards are mounted on a top end of a forward portion of the fuselage. The pair of ducted fans are respectively mounted on free ends of the pair of canards, and are selectively rotatable about an axis parallel to a pitch axis of the fuselage. An engine is mounted in the rear portion of the fuselage, and a thrust vectoring nozzle is mounted on the rear portion of the fuselage for directing thrust exhaust from the engine. The thrust vectoring nozzle is selectively rotatable about an axis parallel to the pitch axis.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Aircraft having independently variable incidence channel wings with independently variable incidence channel canards
ActiveUS20180086447A1Improve mobilityStay in controlGas turbine type power plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesJet aeroplaneHybrid system
An aircraft includes a fuselage and a pair of channel wings which may vary incidence with respect to the fuselage and a pair of channel canards which can also vary incidence with respect to the fuselage and that can move independently of each other for the purpose of vertical takeoff and landing as well as forward and reverse flight. The wings may have multiple channels and may be powered by single propeller or contra-rotating propellers. The thrust to the propellers may be provided with an internal combustion engine or electric motors or a turbo prop or hybrid system. The channel wing allows the fuselage to maintain a level pitch with respect to the horizon. The aircraft will also have increased maneuverability in hover because it can independently vary the incidence of the wings and canards and be able to tightly turn about a point.
Owner:HOP FLYT INC
Convertible airplane with exposable rotors
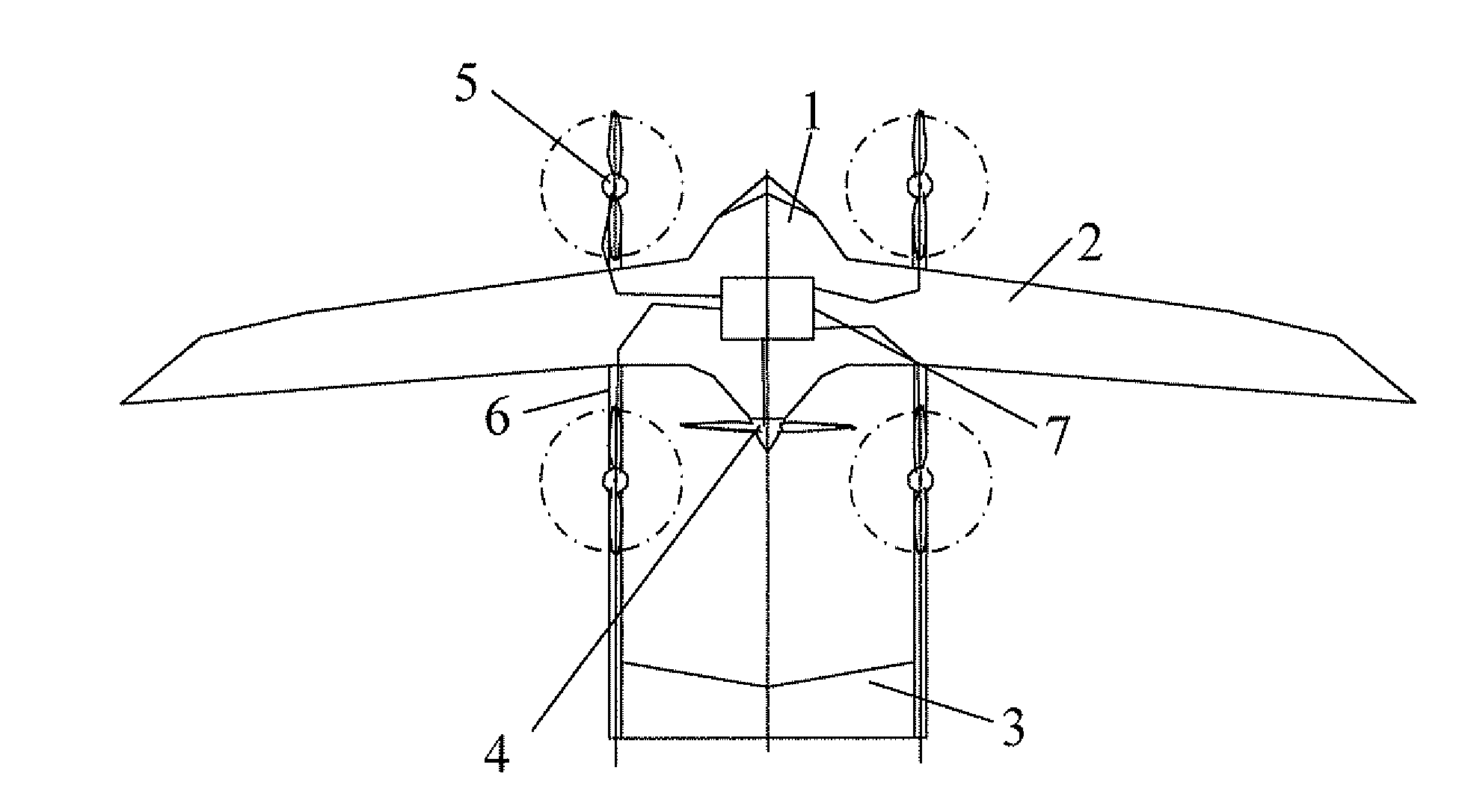
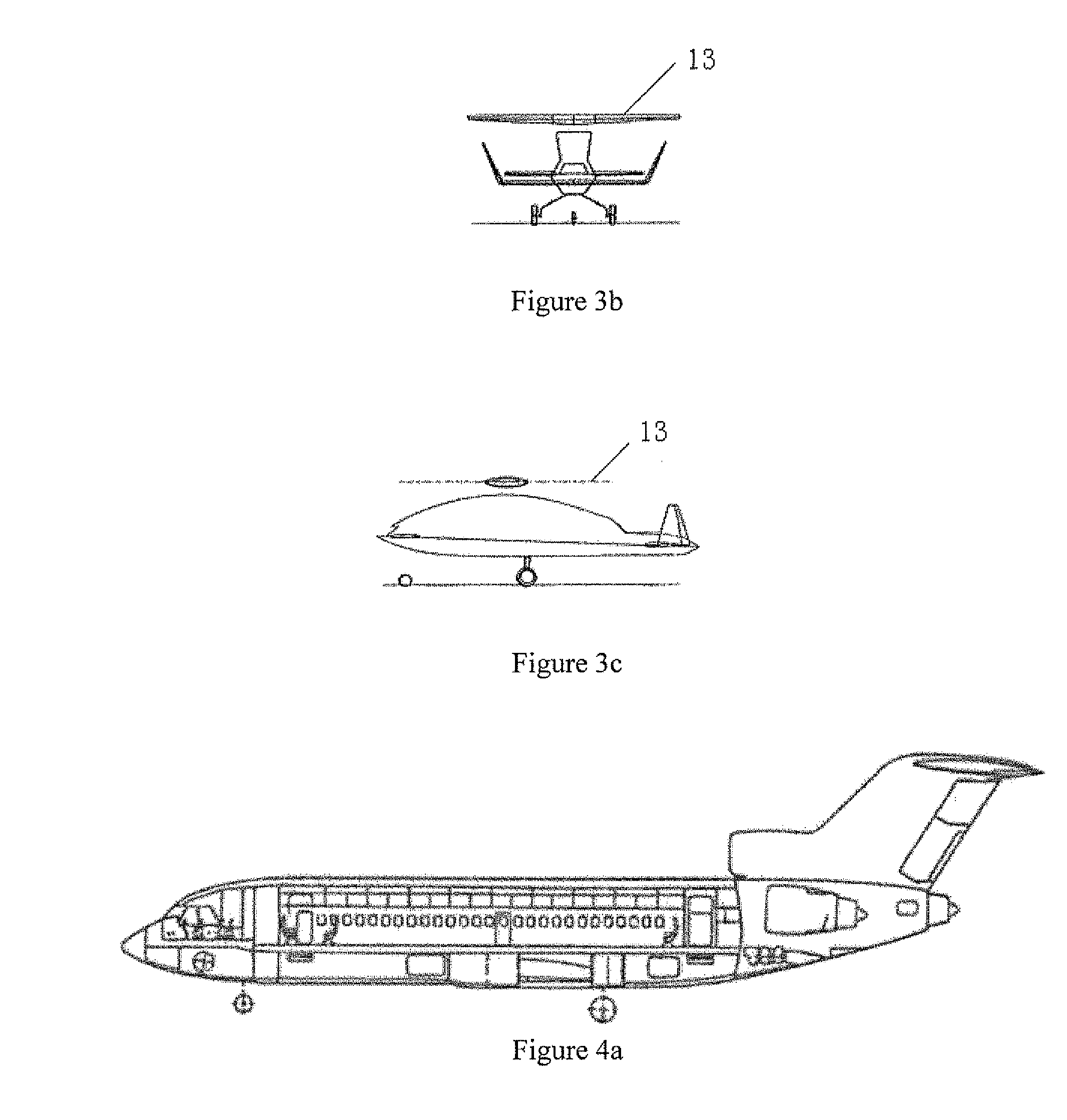
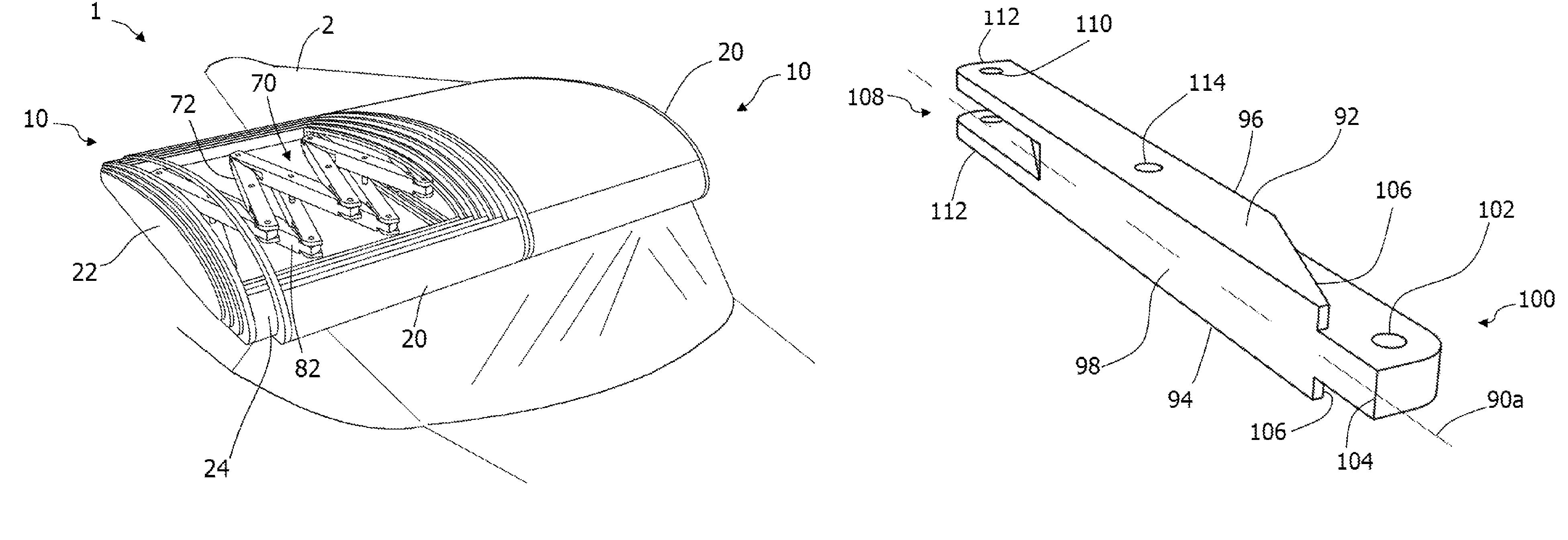
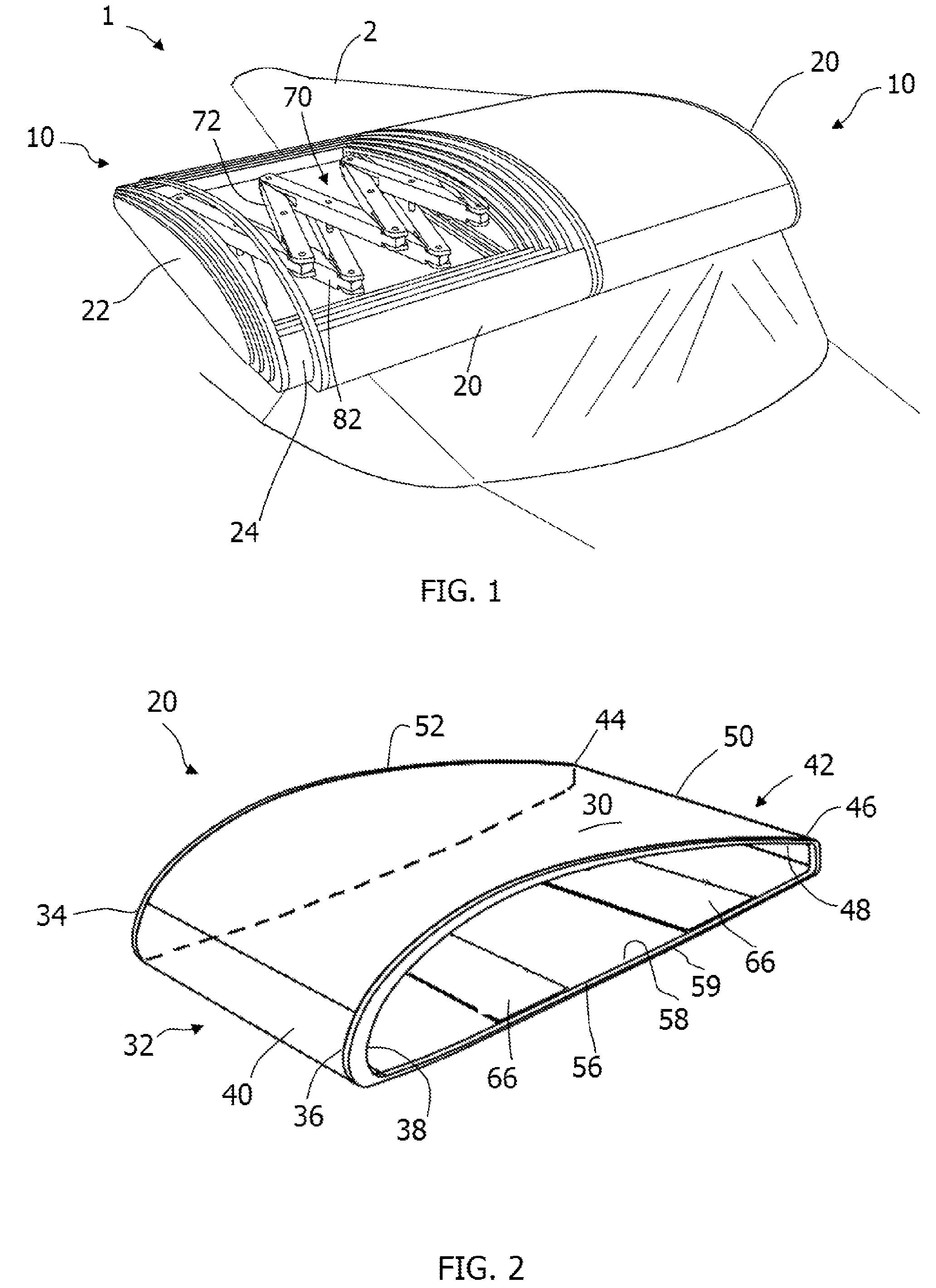
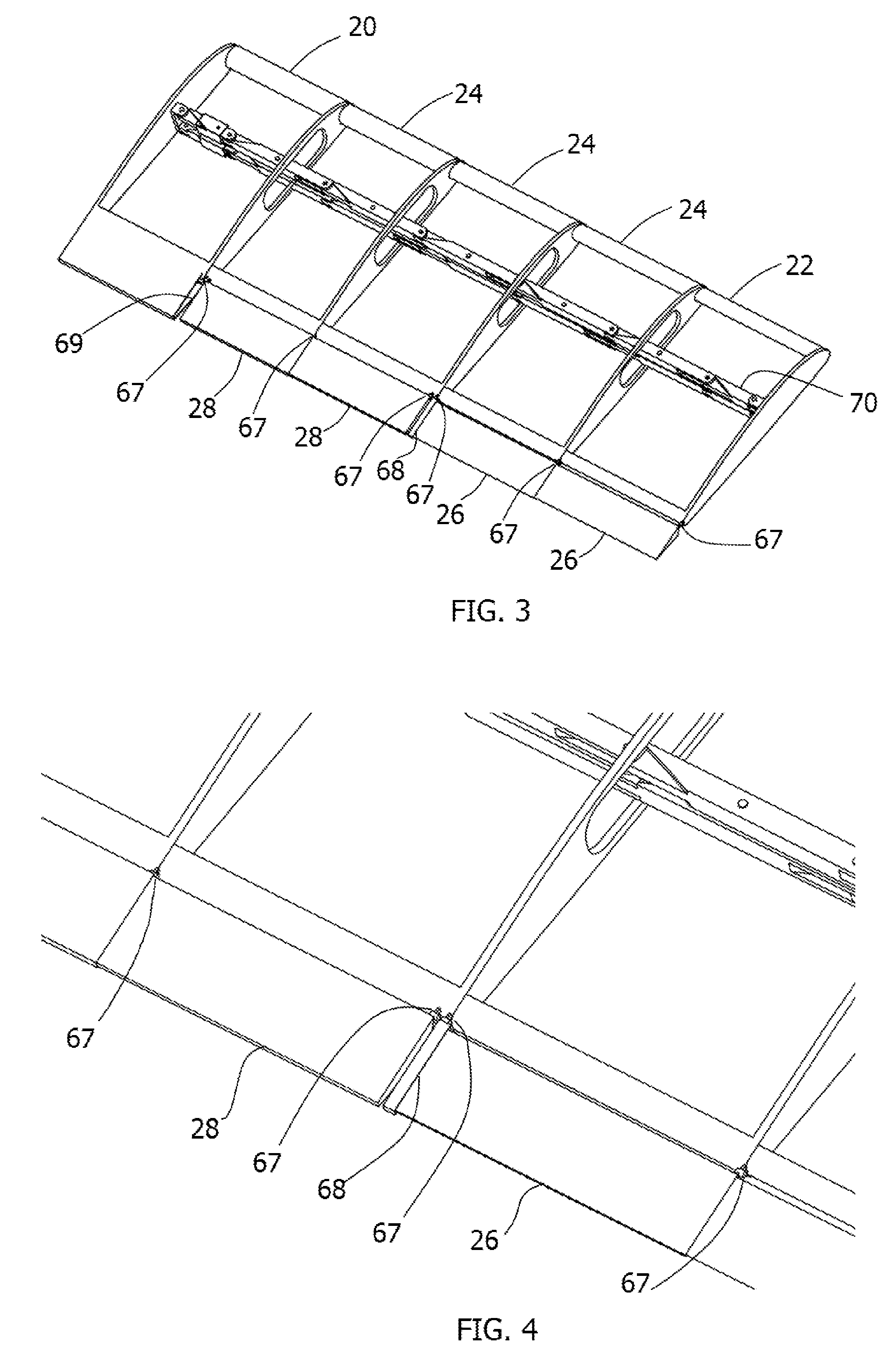
ActiveUS20180141652A1Reduce noiseSolve excessive vibrationWing adjustmentsCanard-type aircraftJet aeroplaneJet engine
Convertible-type aircraft, able to fly with the speed and the reduced operating costs of a fixed-wing aircraft and also to take-off / land vertically and hover / manoeuvre like an helicopter.The aircraft object of the invention comes in the form of a classical plane, with a fuselage (1), a fixed wing (2), an horizontal stabilizer (3) and a vertical fin (4), as well as one or several jet engines or turboprops (5) for propulsion and it comprises exposable rotors (6 and 7) installed inside the wing and possibly inside the horizontal stabilizer or the fuselage for lifting the aircraft for vertical take-off / landing and stationary flight.For the flight and the horizontal take-off / landing, the rotors are completely enclosed inside the wing and possibly inside the horizontal stabilizer or the fuselage.
Owner:DESLYPPER CHRISTIAN ROGER RENE
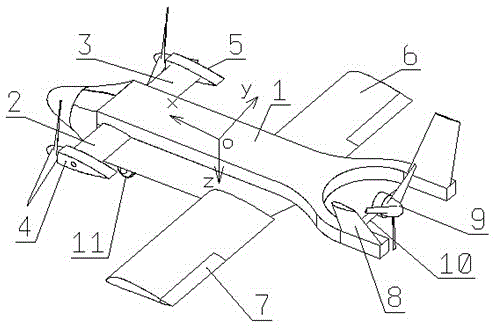
Power-driven tilt three-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN106800089AImprove flight efficiencyImprove applicabilityCanard-type aircraftVertical landing/take-off aircraftsRotational axisShortest distance
The invention provides a power-driven tilt three-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle. The power-driven tilt three-rotator unmanned aerial vehicle has flight characteristics of both a helicopter and a fixed-wing aircraft and can take off and land in a vertical and short-distance way. The integral structure of the power-driven tilt three-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is composed of all-moving canard wings, straight low wings and a fixed V tail. Two motors and rotors of the unmanned aerial vehicle are fixed at the wing tips of the canard wings and can independently tilt by certain angles along with the canard wings, and another motor and rotor of the unmanned aerial vehicle are installed in the V tail and can tilt by certain angles around a rotating shaft. When the rotating shafts of the thee rotors of the unmanned aerial vehicle tilt to a position near a Z axis, the unmanned aerial vehicle can fly like the helicopter; and when the thee rotors tilt to a position near an X axis, the unmanned aerial vehicle can fly like the fixed-wing aircraft. Through simultaneous control of the thrust and directions of the thee rotors, the reaction torque of the rotors is overcome and the posture of the unmanned aerial vehicle is controlled. The unmanned aerial vehicle provided by the invention can take off and land in a limited place or runway to execute special tasks and is improved in flight speed, duration of flight and payload.
Owner:AVIC GUIZHOU AIRPLANE
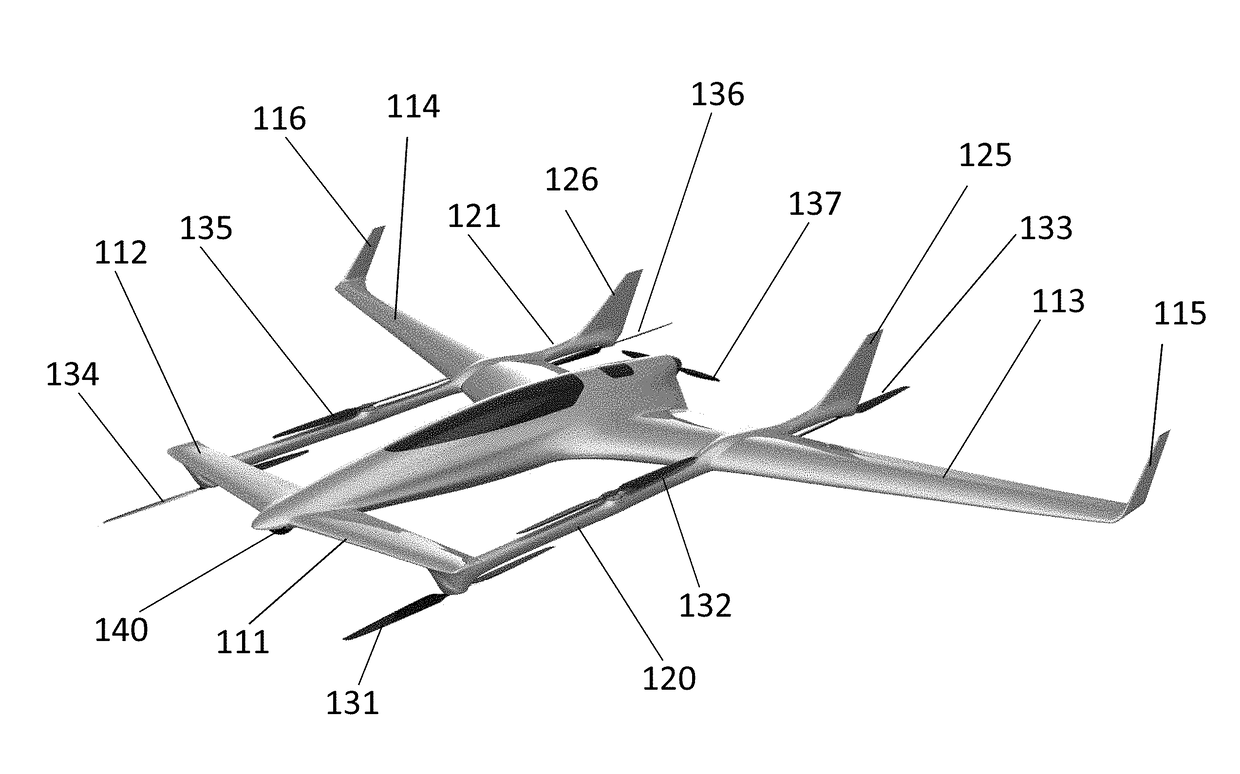
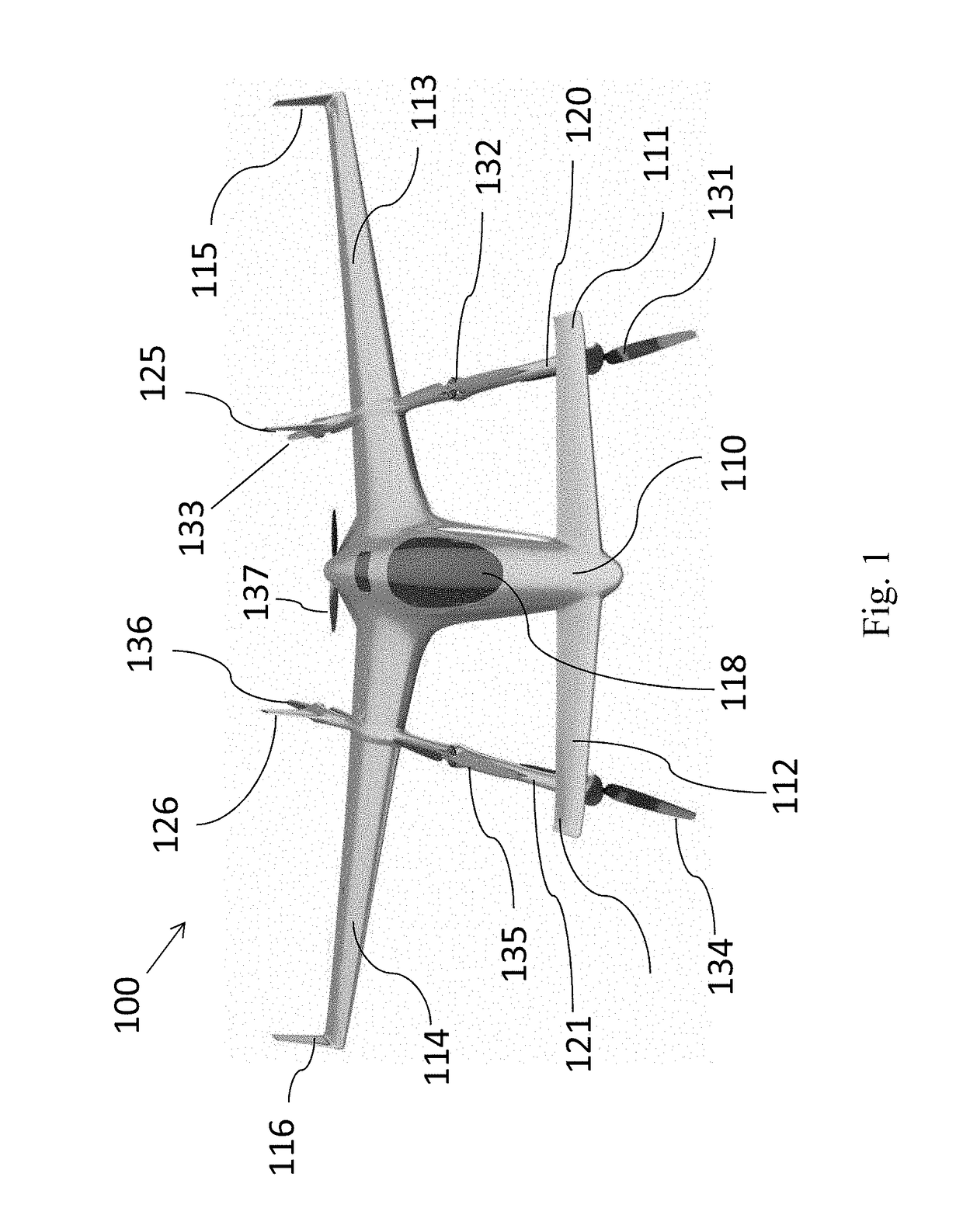
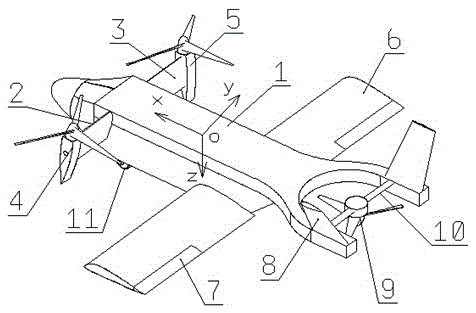
Vertical take off and landing aircraft
A vertical takeoff and landing aircraft is provided. The aircraft includes a fuselage having a first end, a second end, and a center of gravity in between the first end and the second end. Wings may extend from the side of the fuselage. The wings may include a canard at the first end, and a wing at the second end. The present invention may further include a pair of engines pivotally attached on either side of the fuselage and substantially aligning with the center of gravity.
Owner:TOPPENBERG DAVID WAYNE
Airplane wing
InactiveUS20120074264A1Improved airplane wing configurationSlow down the landing speedAircraft controlPiston type power plantsJet aeroplaneWing configuration
An airplane wing configuration includes a first wing positioned above and forward of a second wing on an airplane fuselage. The first wing is operable to direct airflow over an upper surface of the second wing, whereby the first and second wings are capable of generating greater lift than a sum of their individual lifts. The first wing may include an adjustable wing flap that redirects airflow over the upper surface of the second wing, and the second wing may include a rotatable portion that pivots to vary the angle of attack of the second wing independent of the first wing.
Owner:HEATON CLIFFORD D
Wing employing leading edge flaps and winglets to achieve improved aerodynamic performance
ActiveUS20070262207A1Increase aft liftImprove aerodynamic flow fieldInfluencers by generating vorticesWith power amplificationLeading edgeControl system
A wing for use on a supersonic aircraft that includes an inboard section a central section of the wing outboard of the inboard portion, and an outboard section. The outboard section can be a winglet oriented anhedrally relative to a lateral axis of the supersonic aircraft. Leading edge segments on the inboard section, central section and outboard winglet may have mounted thereon leading-edge flaps. These flaps are adjusted by a control system operable to reposition the leading-edge flaps in order to improve the aerodynamic performance of the supersonic aircraft. This winglet promotes sonic boom minimization. Further, the wing tip anhedral allows greater inboard dihedral. This effectively pushes lift aft for sonic boom and control purposes while minimizing the movement of control surfaces.
Owner:SUPERSONIC AEROSPACE INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com