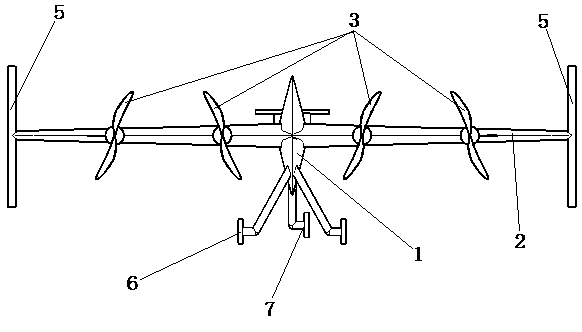
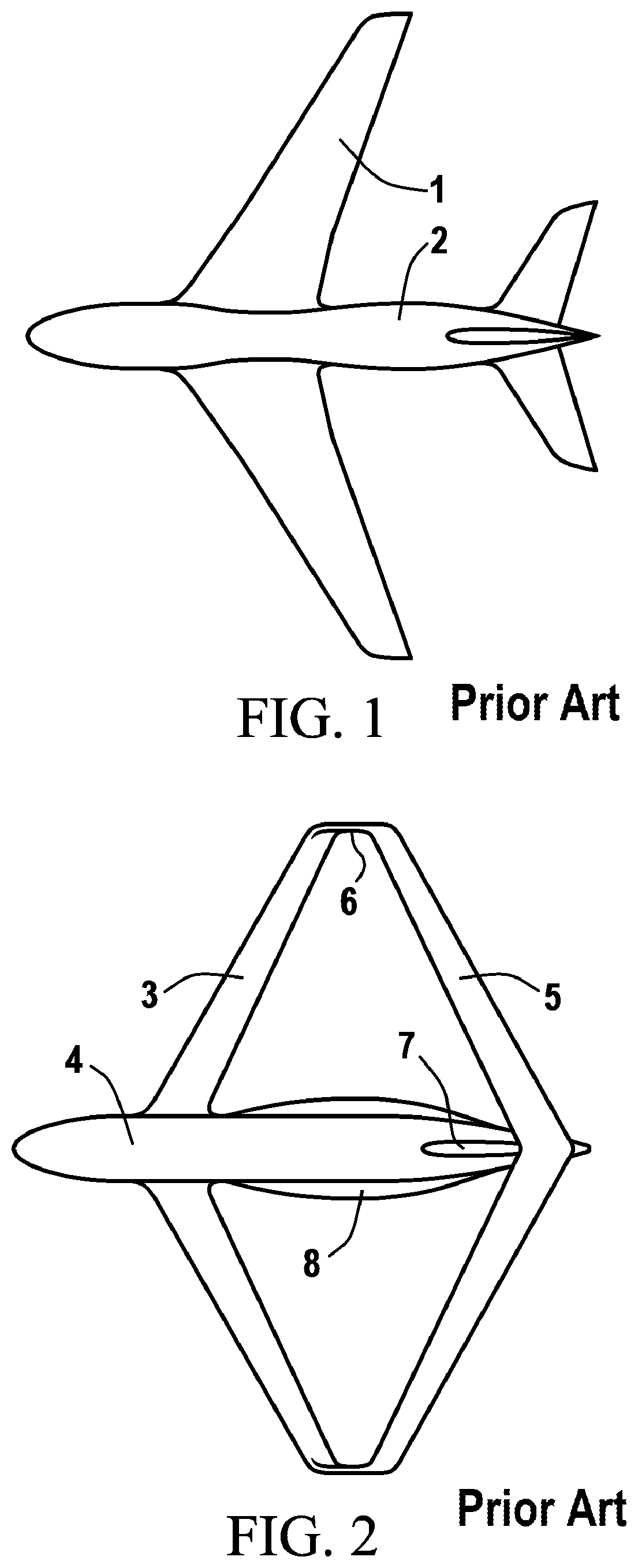
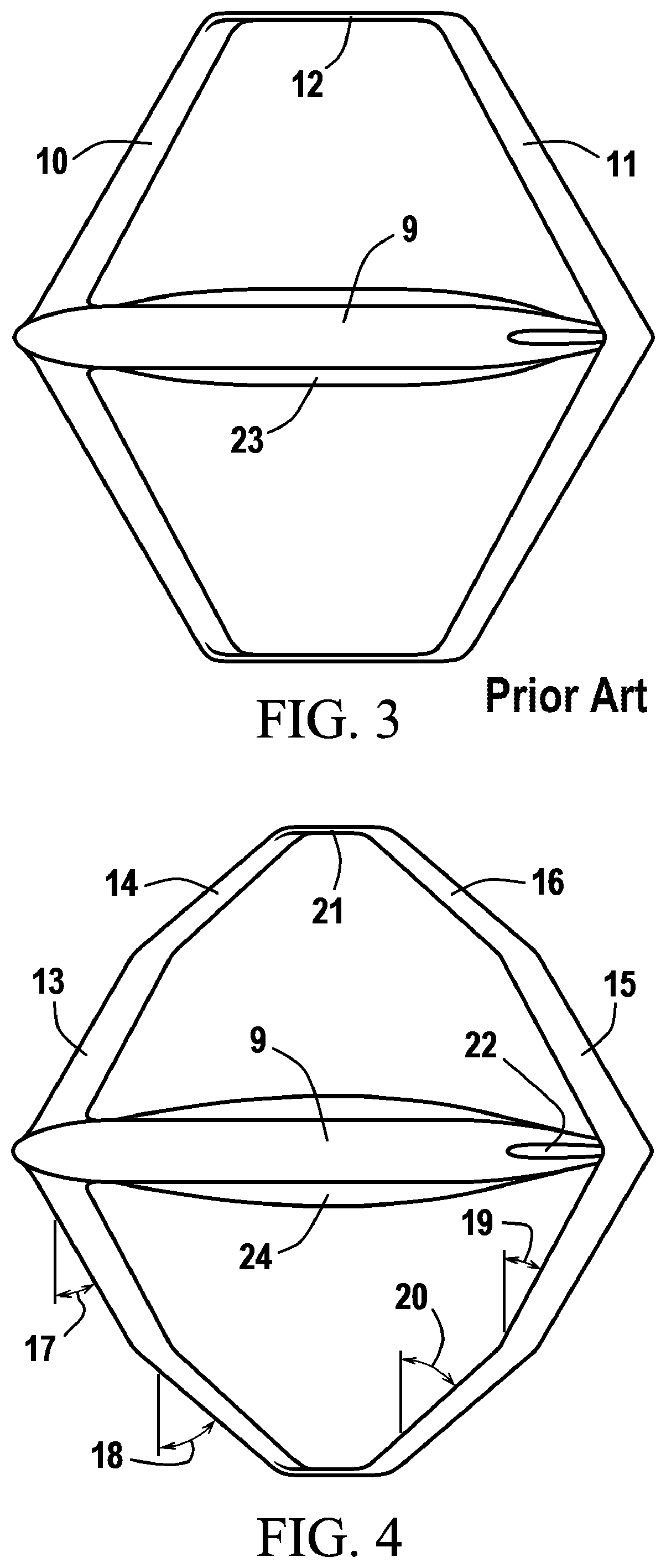
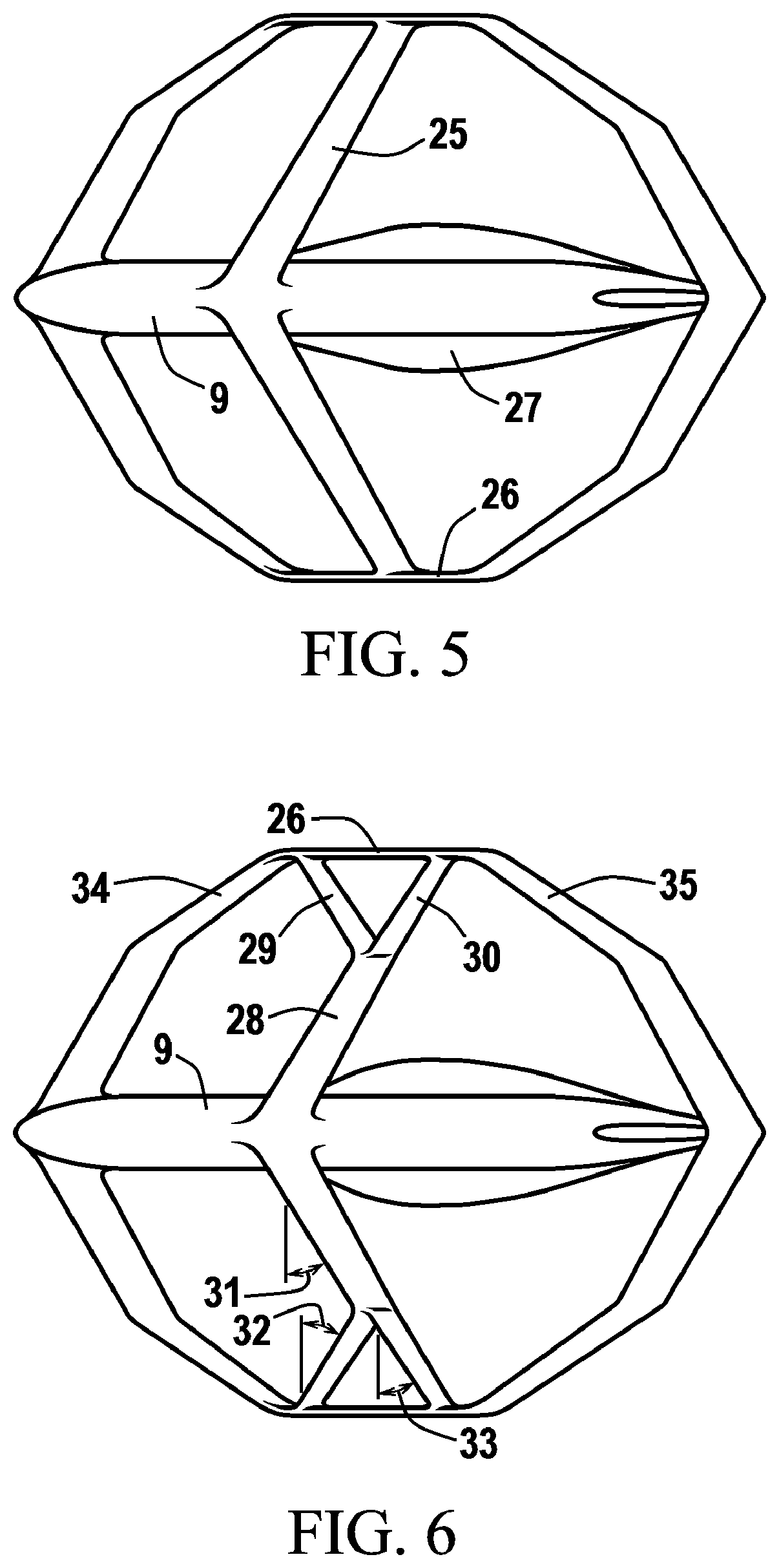
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Forward-swept wing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
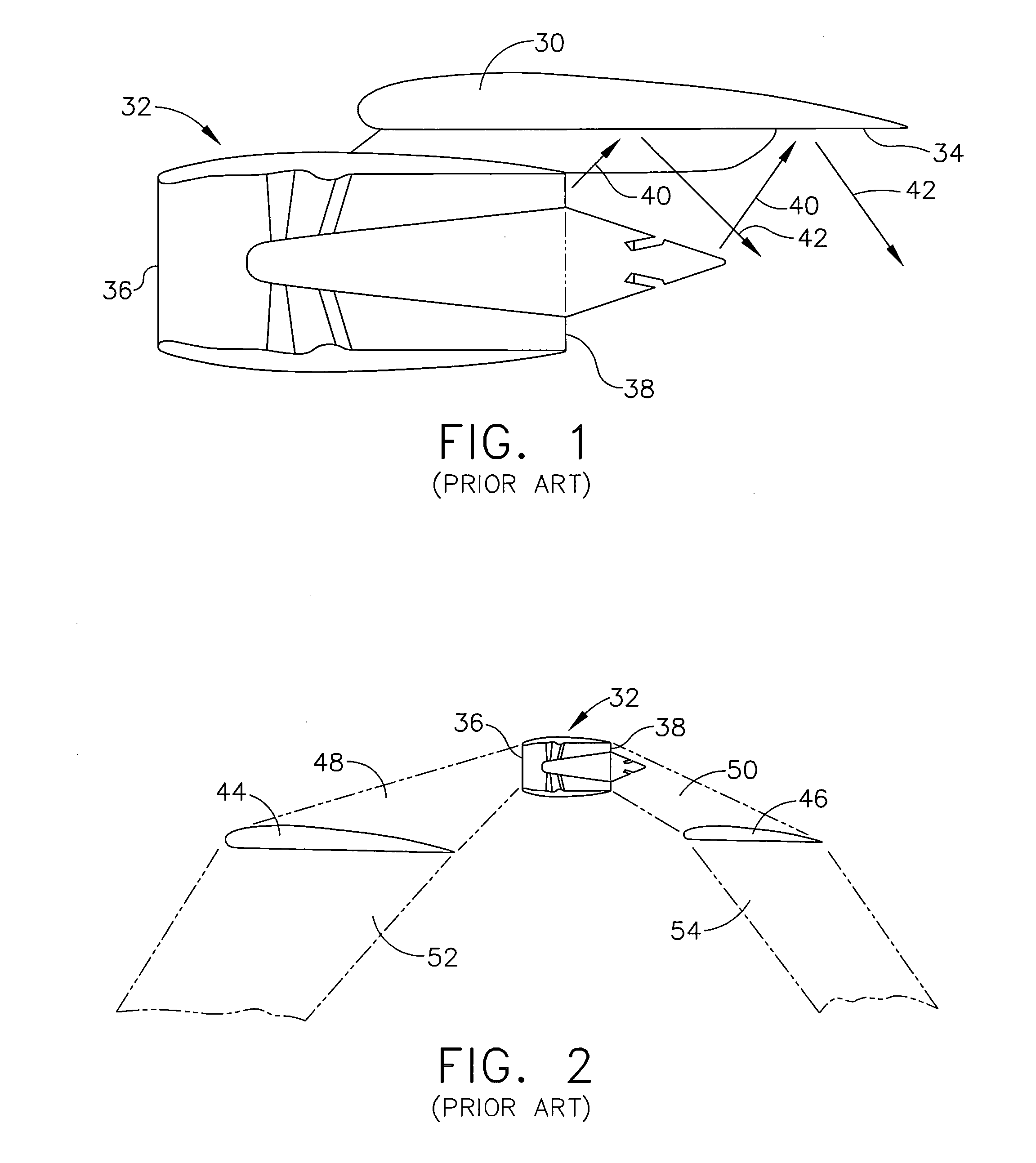
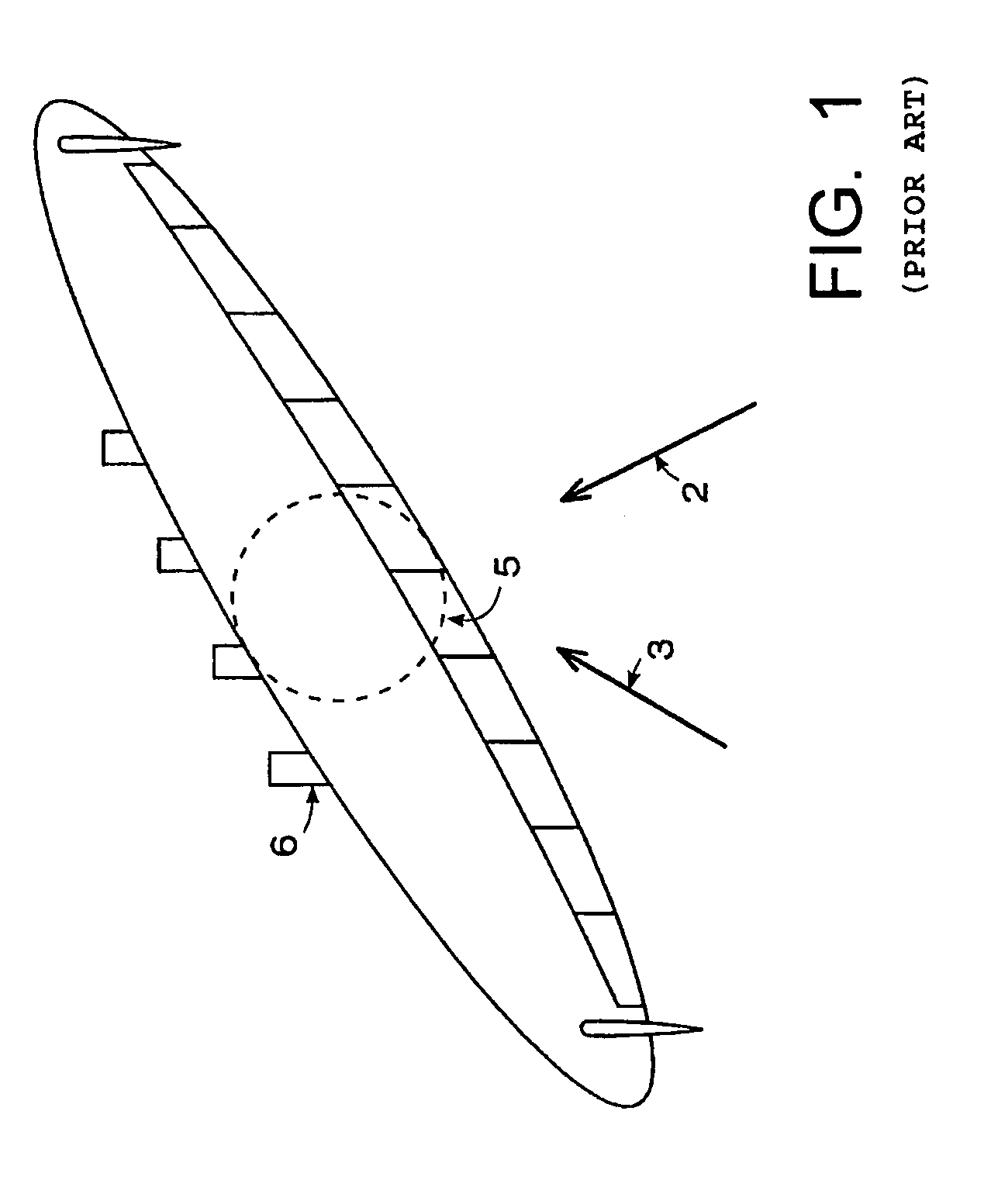
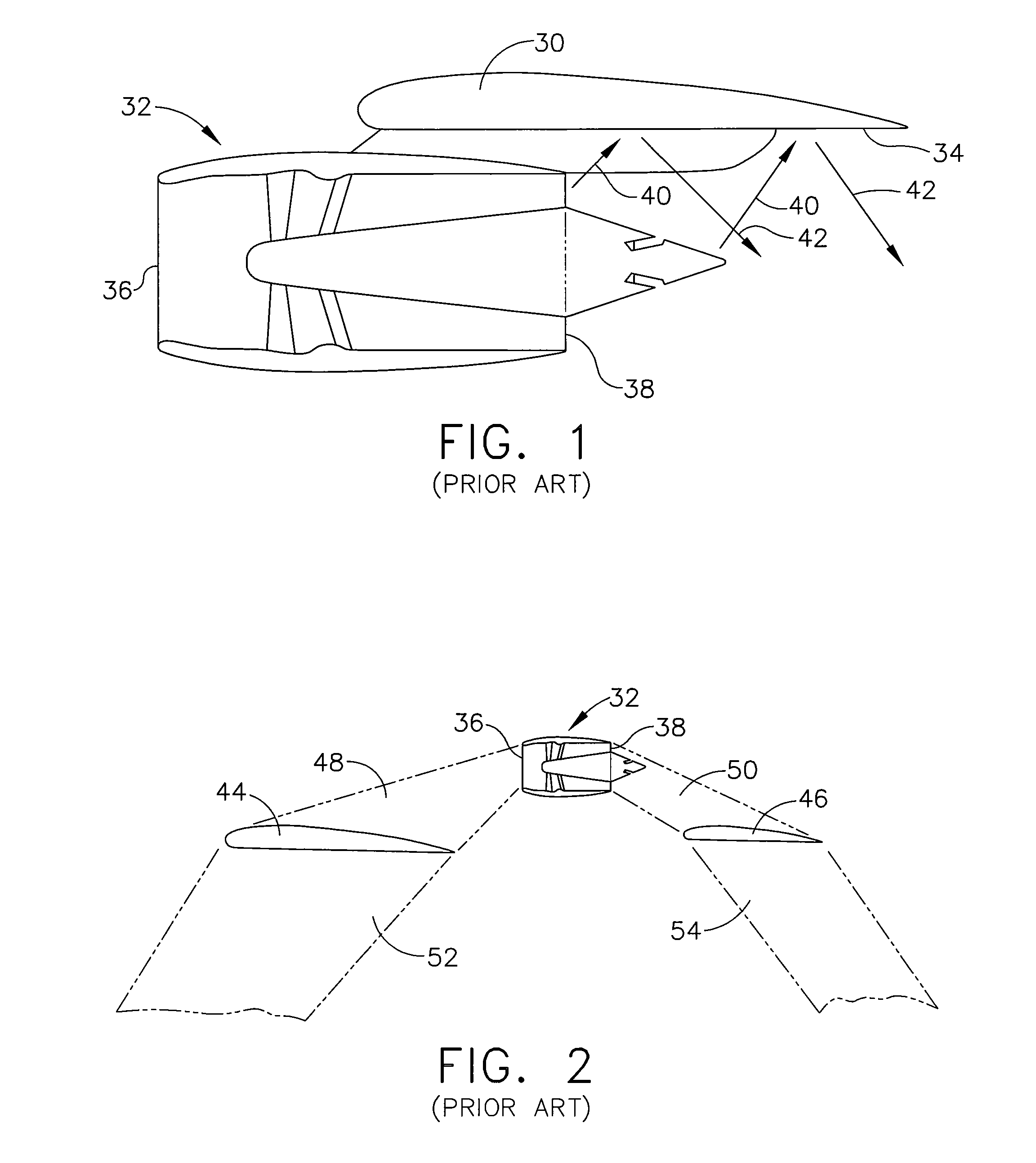
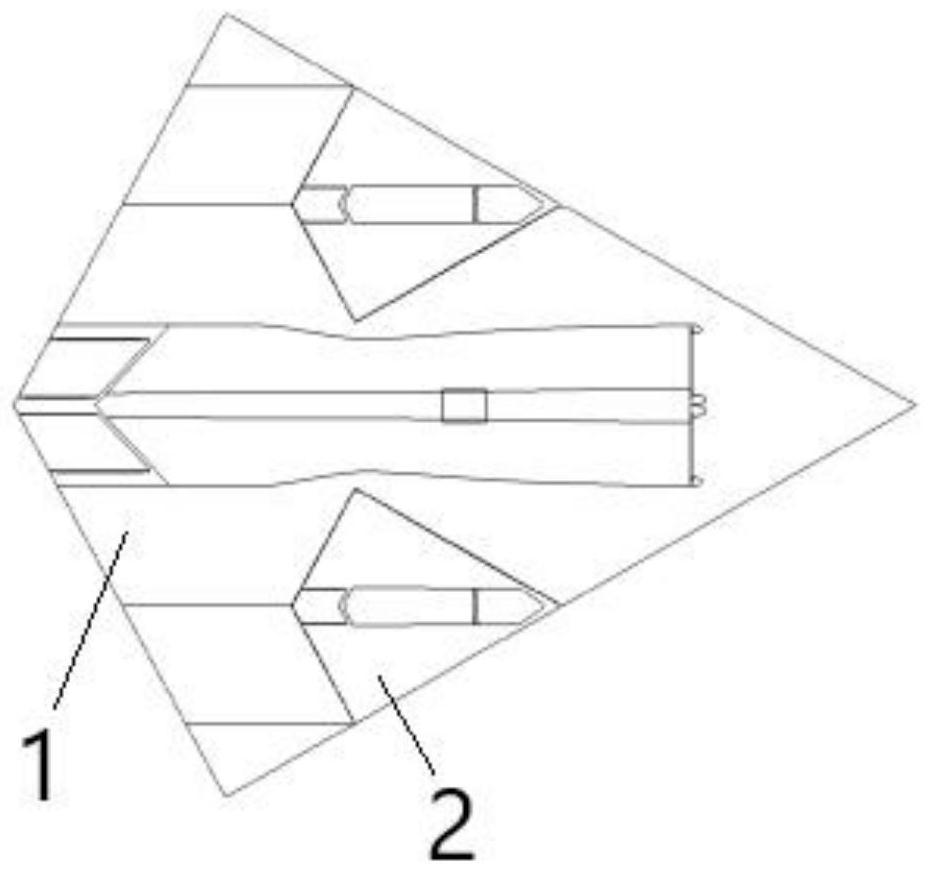
A forward-swept wing is an aircraft wing configuration in which the quarter-chord line of the wing has a forward sweep. Typically, the leading edge also sweeps forward.
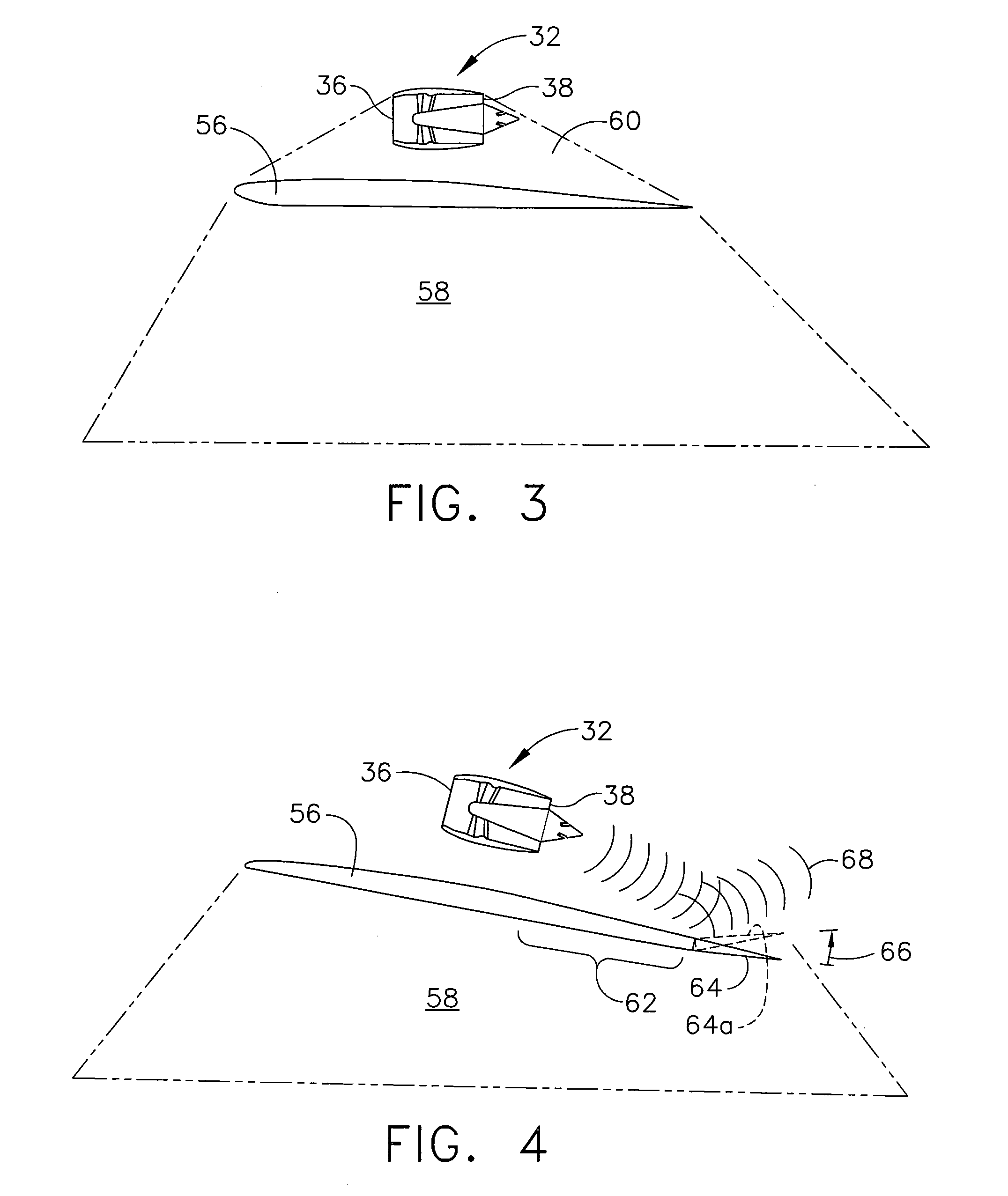
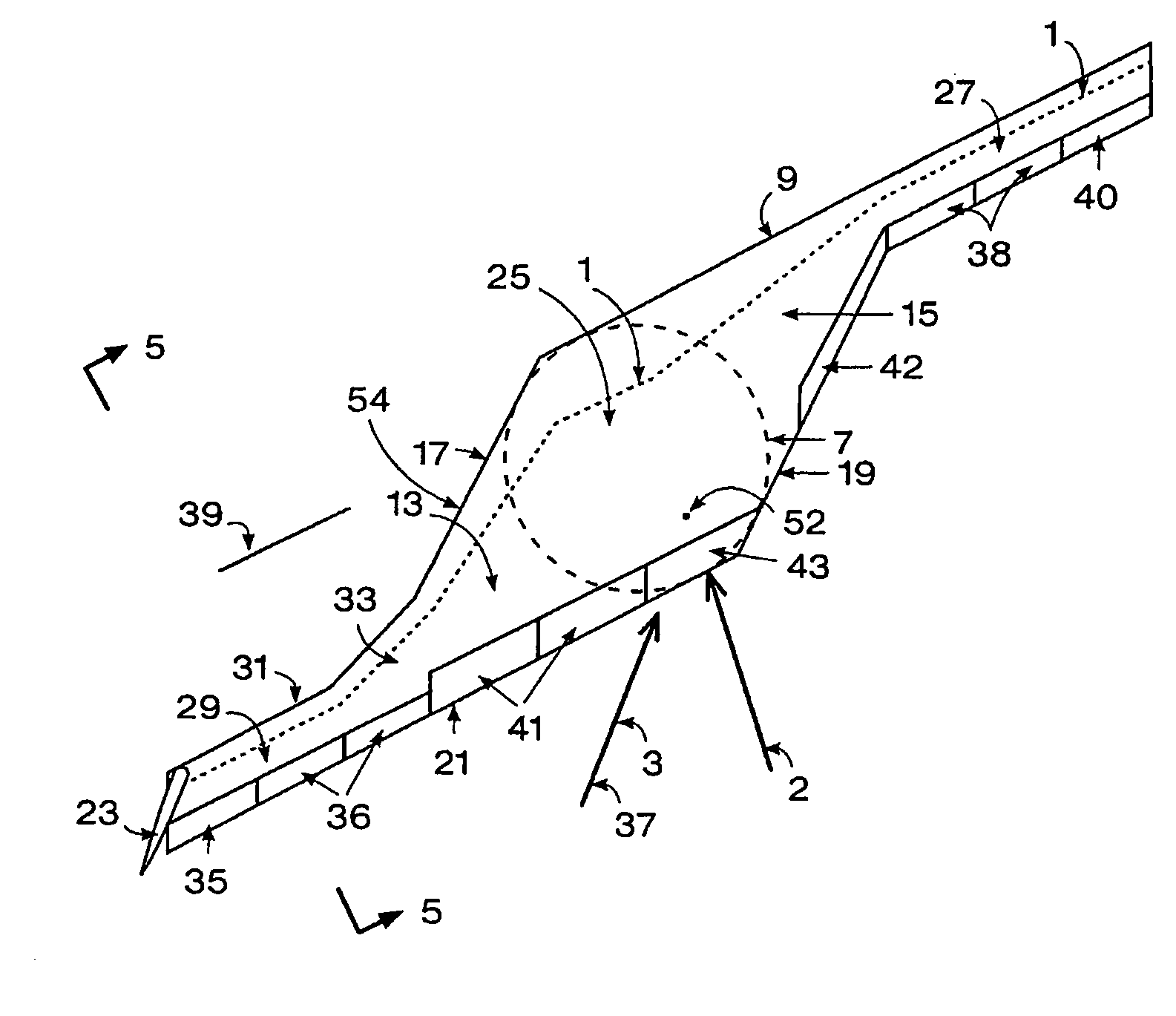
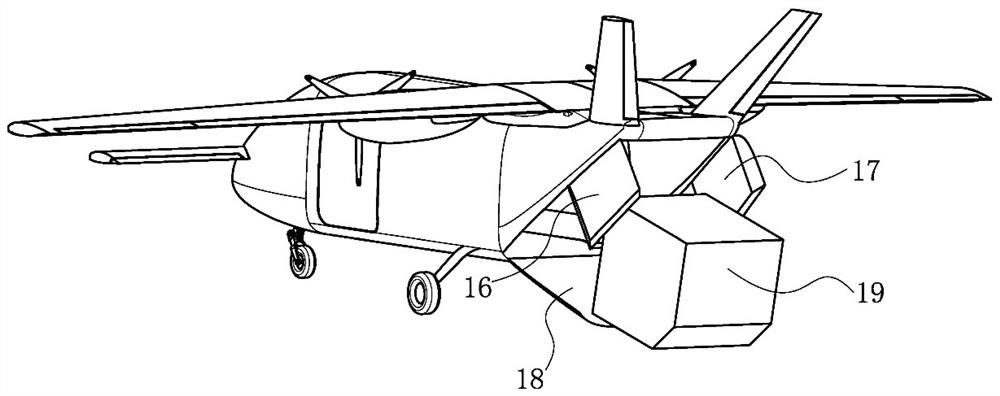
Variable forward swept wing supersonic aircraft having both low-boom characteristics and low-drag characteristics
InactiveUS20050230531A1Minimizes wave-dragReduce wave resistanceWing shapesEfficient propulsion technologiesJet aeroplaneEngineering
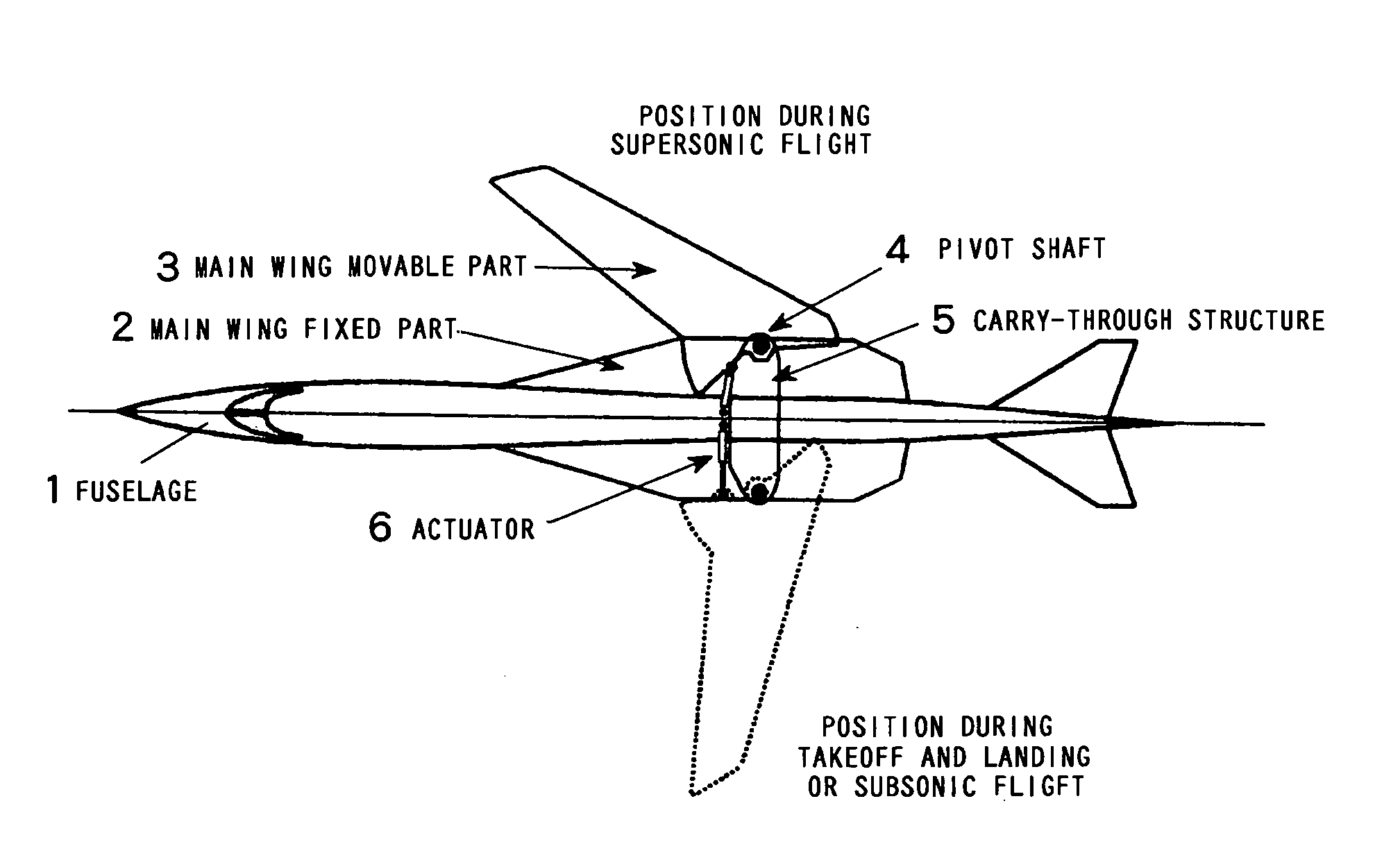
It is an object of the present invention to provide the entire airplane shape of a supersonic aircraft that can realize low sonic boom characteristics, and that can also minimize wave-drag. In order to achieve both sonic boom suppression and a reduction in wave-drag, the entire airplane shape of the supersonic aircraft of the present invention uses a variable forward swept wing configuration having a mechanism that can vary a forward sweep angle as the main wing configuration, rather than forming the fuselage shape with a blunt nose.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
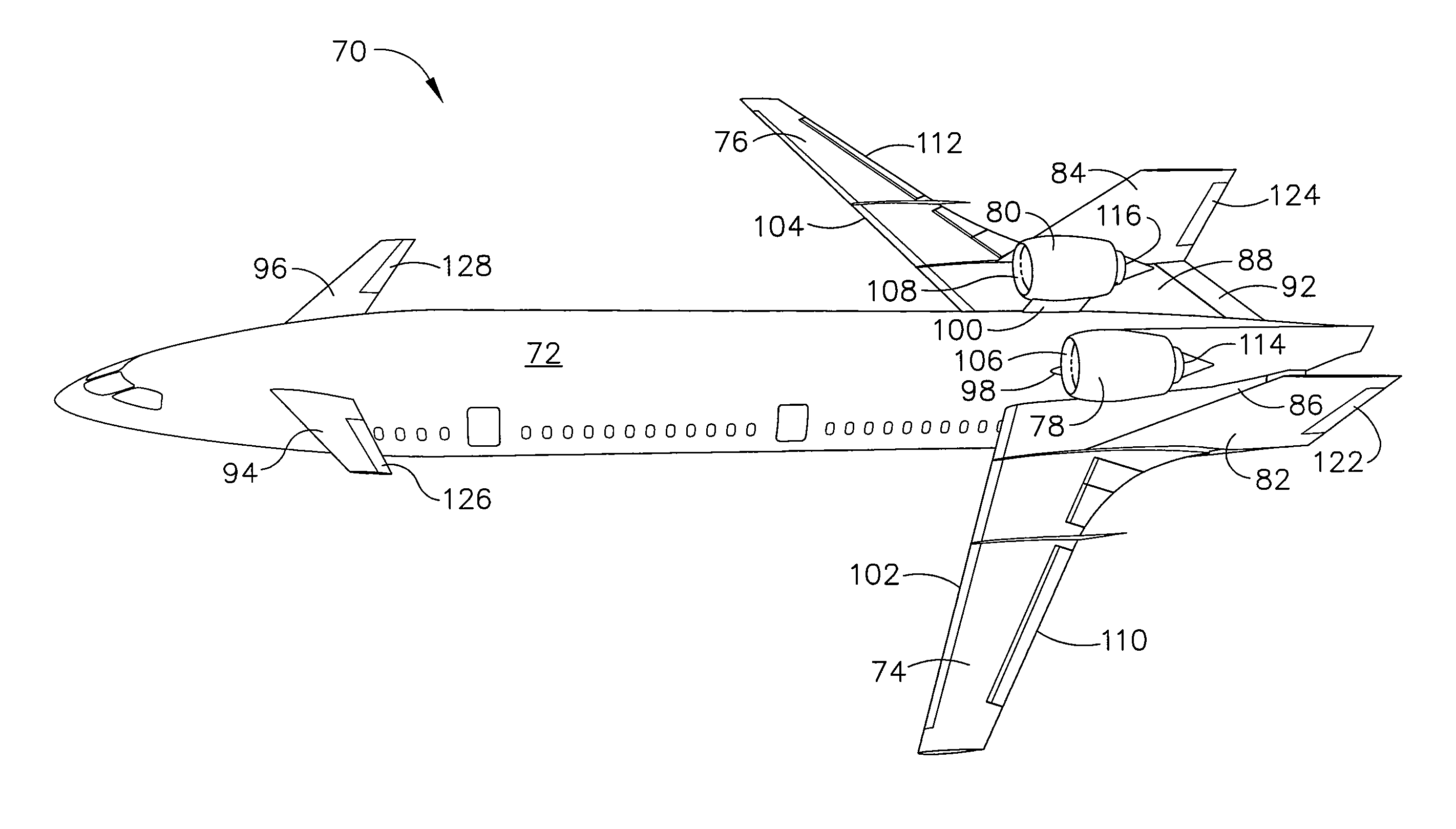
Airplane configuration
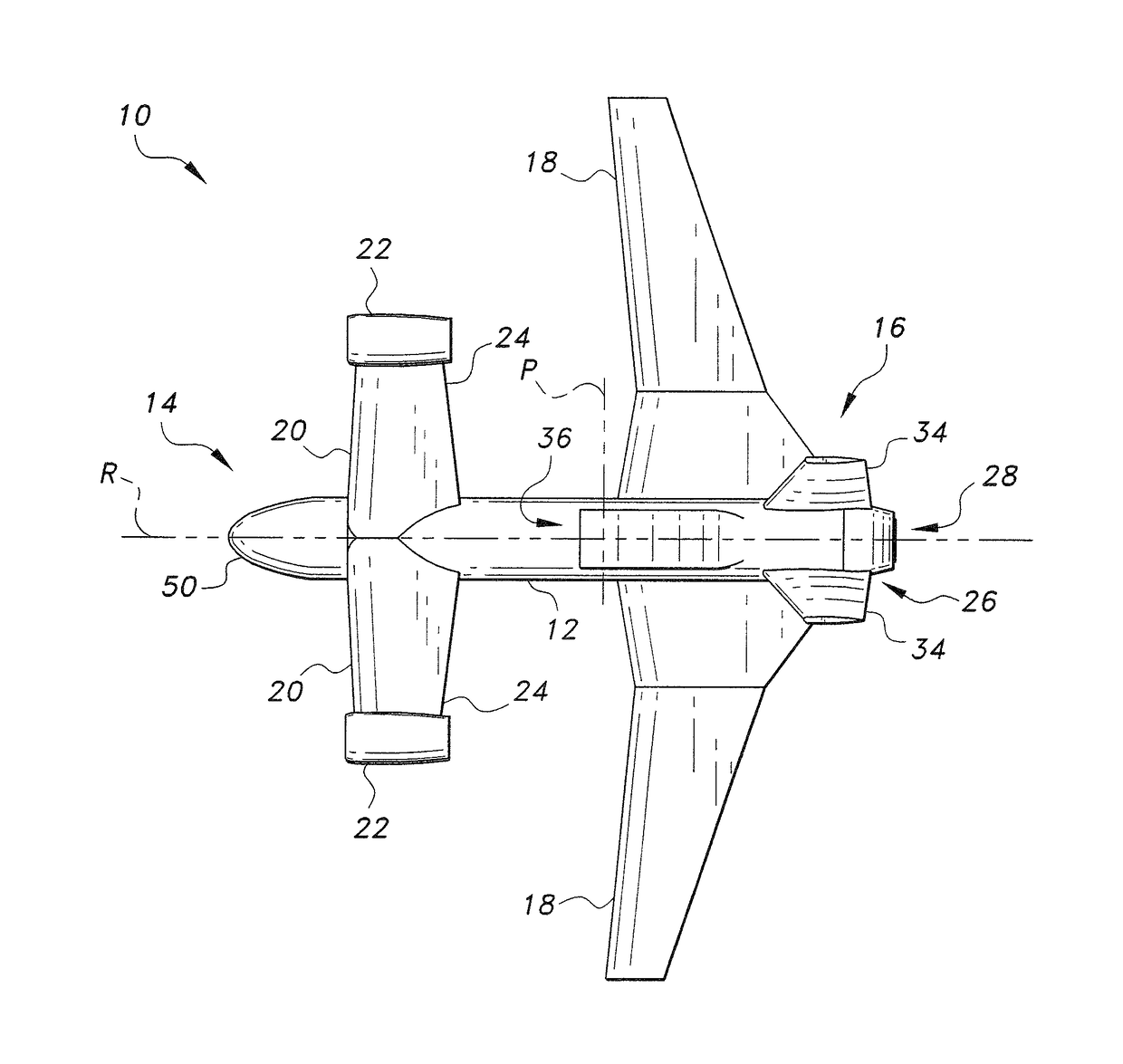
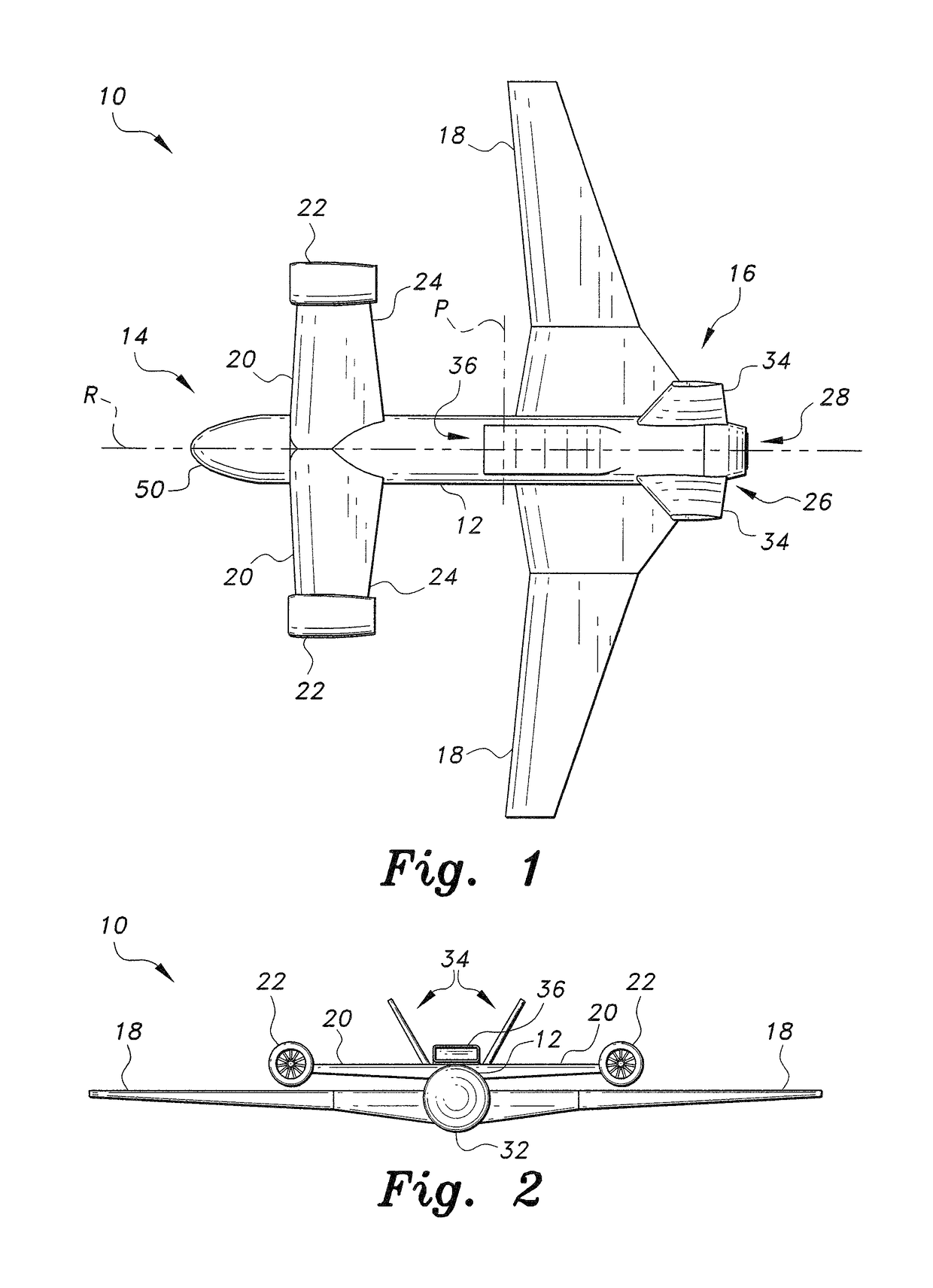
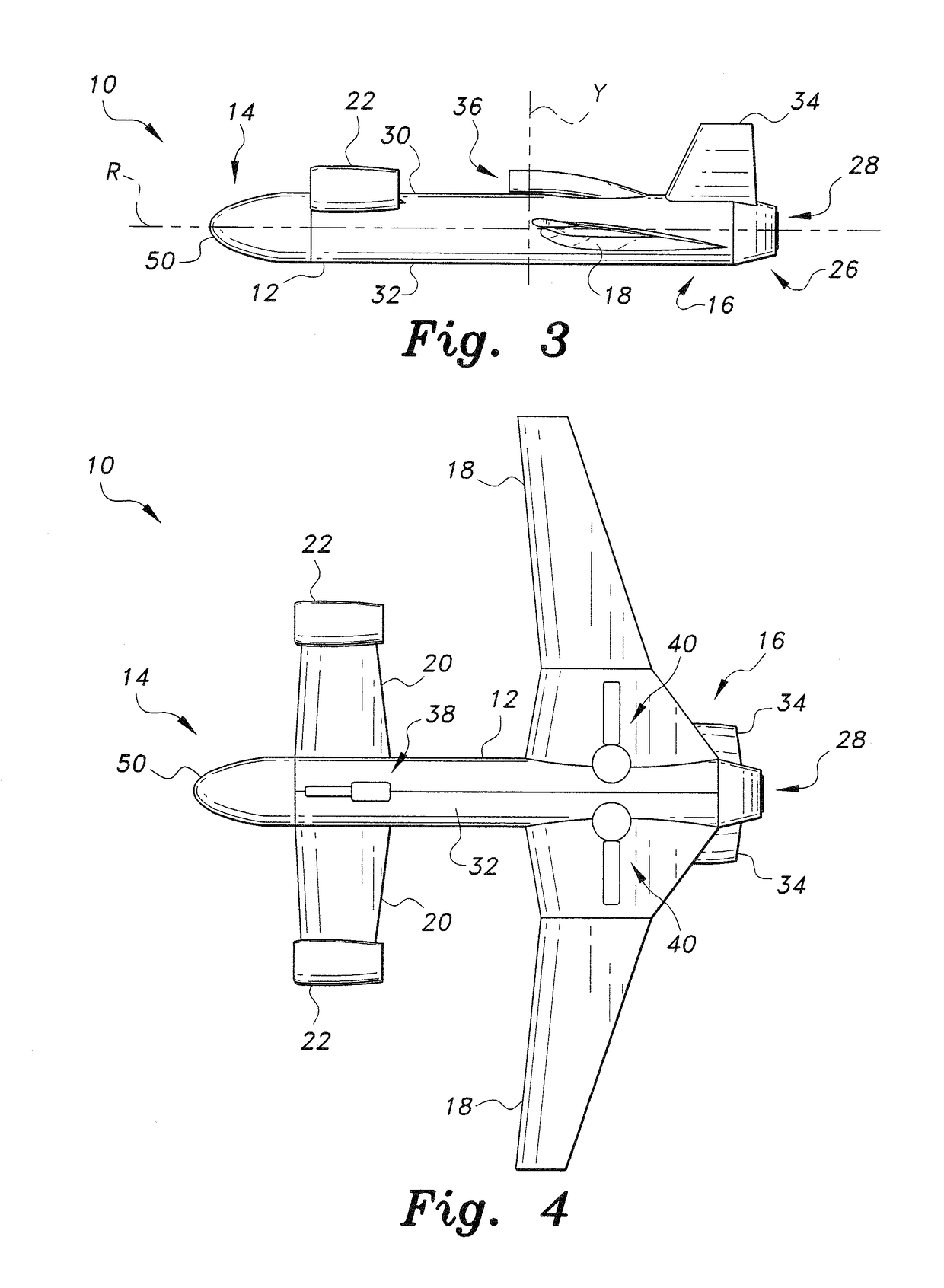
InactiveUS20080142641A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced aircraft noiseGas turbine type power plantsAircraft stabilisationJet aeroplaneLeading edge
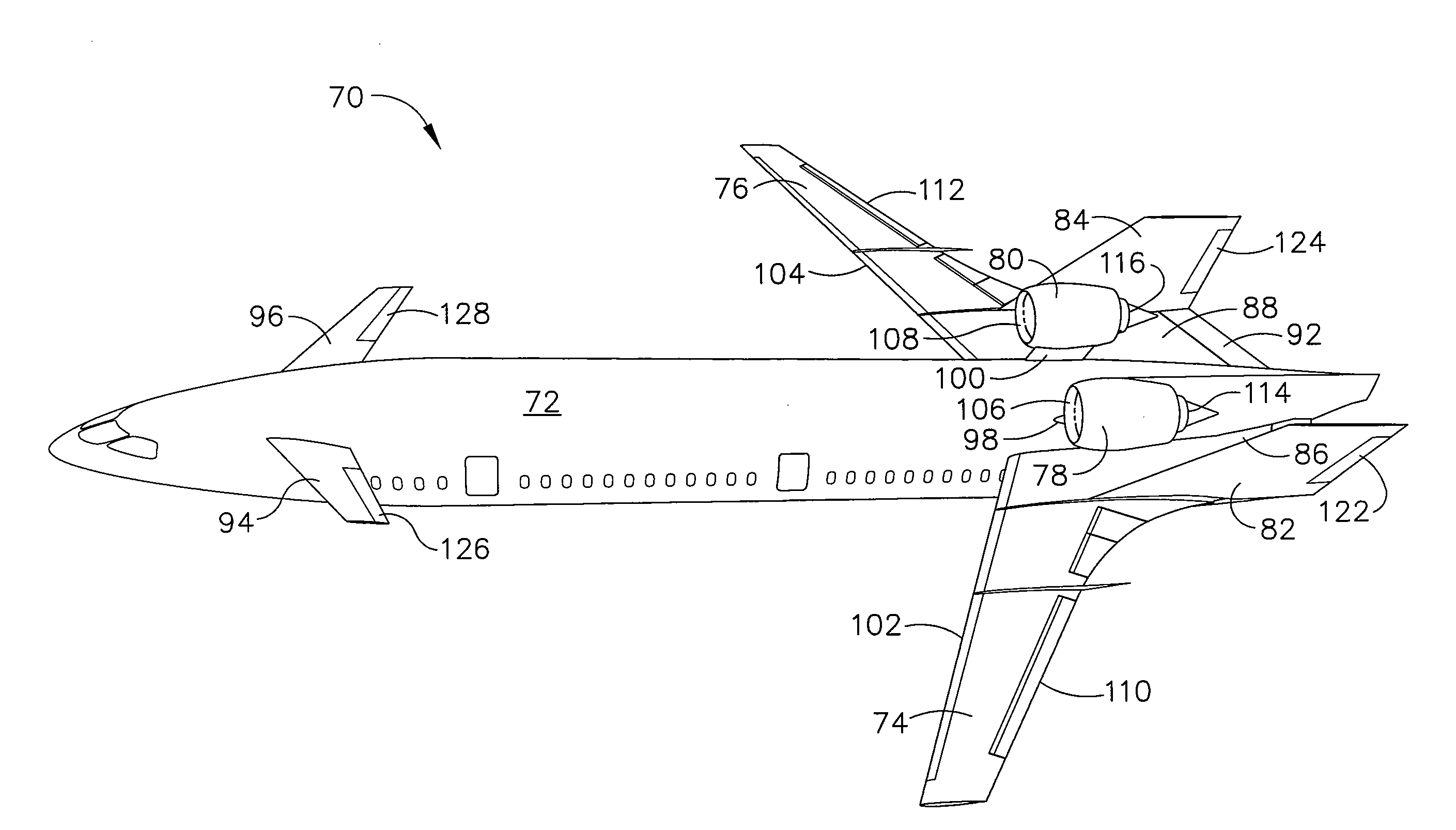
An aircraft configuration that may reduce the level of noise, infrared radiation, or combination thereof directed towards the ground from an aircraft in flight. An embodiment of an aircraft includes a fuselage, two forward swept wings, at least one engine mounted to the aircraft and higher than the wings, and vertical stabilizers mounted on each wing outboard of the outermost engine. The leading edge of the wing may extend forward of the leading end of the engine, and the trailing edge of the aft deck may extend aft of the trailing end of the engine. The aft deck may include an upwardly rotatable pitch control surface at the trailing edge of the deck. Engine types may vary, including but not limited to turbofans, prop-fans, and turbo-props. Main wings may be mounted above the longitudinal axis of the fuselage, and canards may likewise be mounted above or below the axis.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Oblique blended wing body aircraft
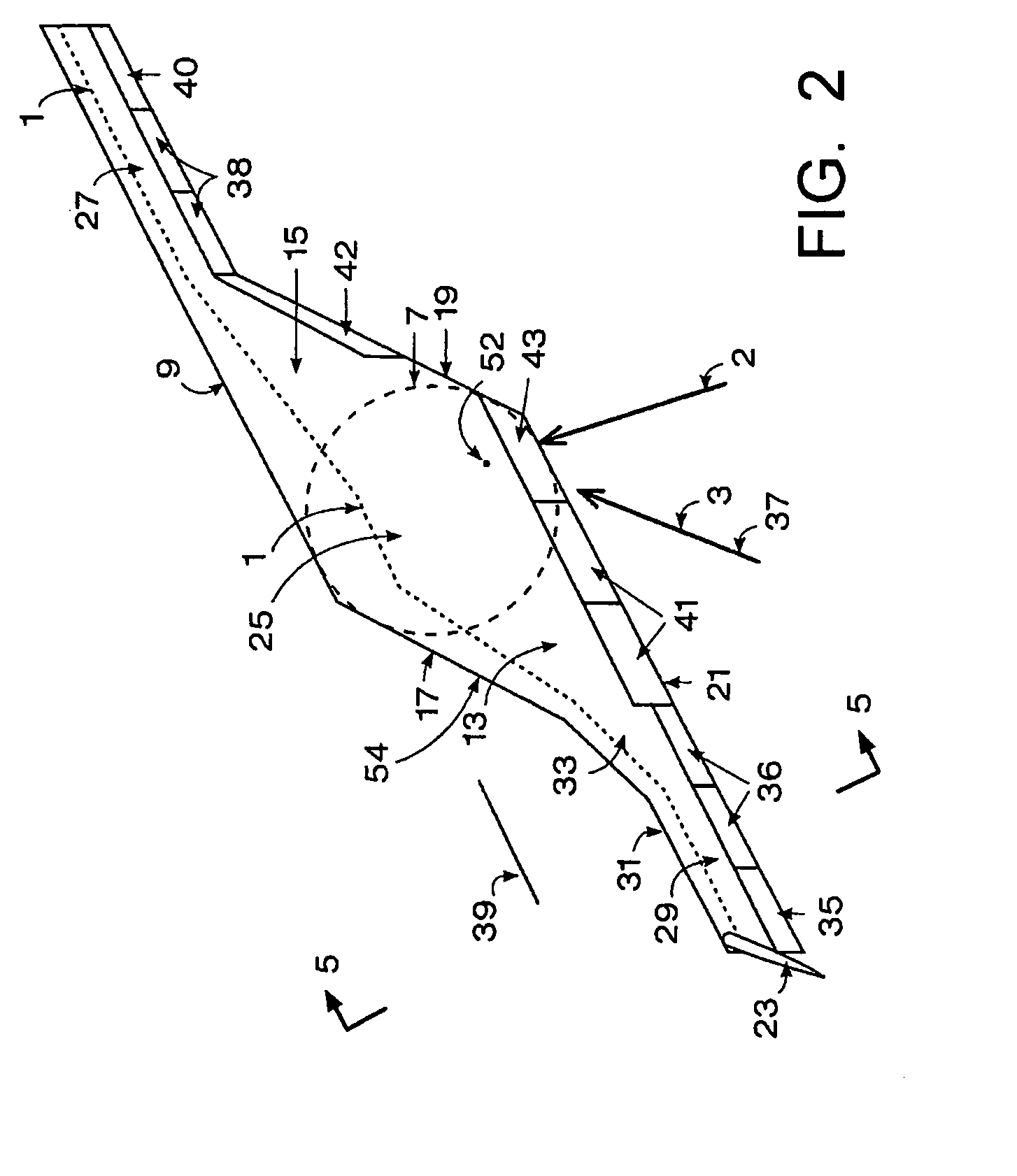
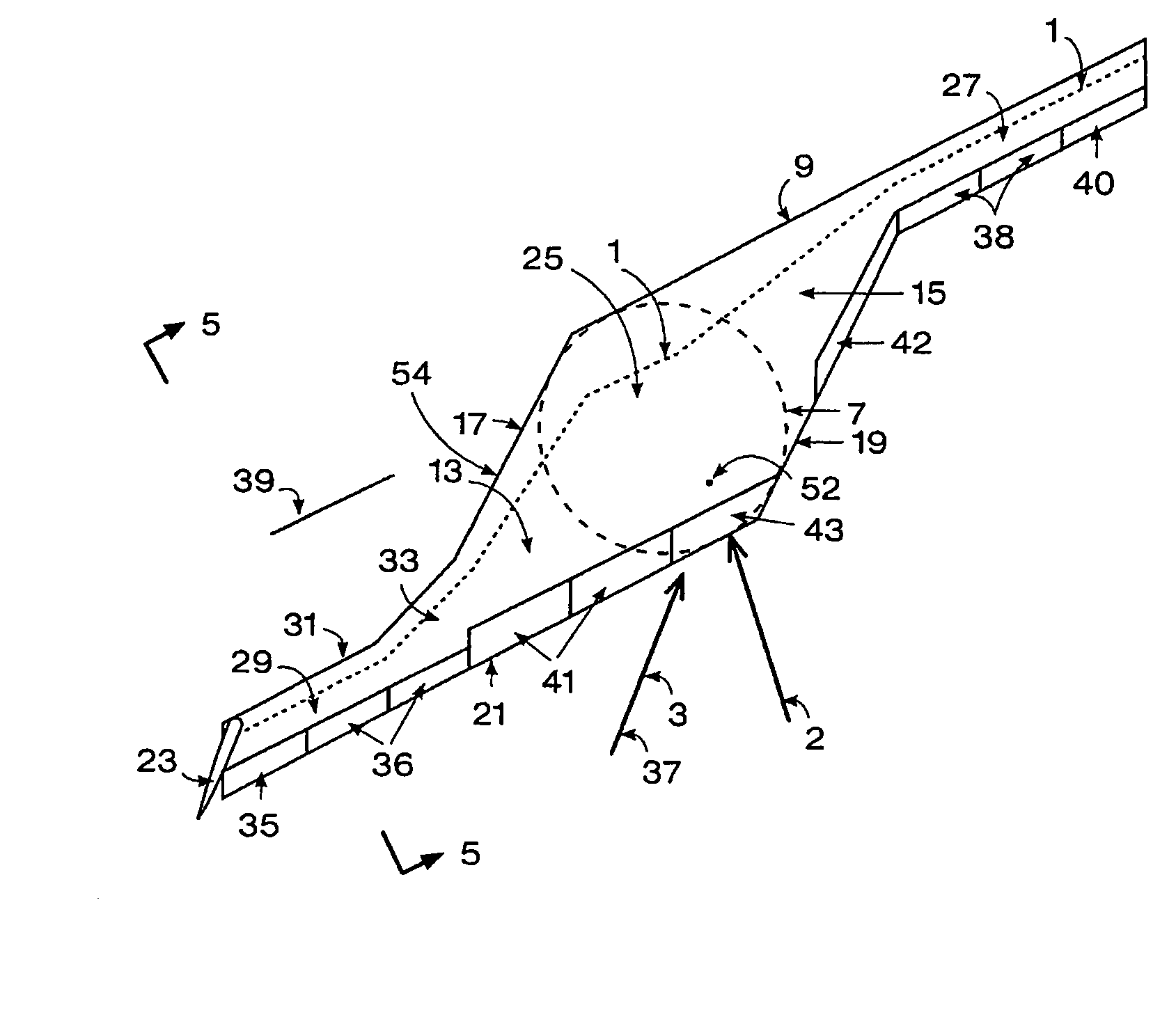
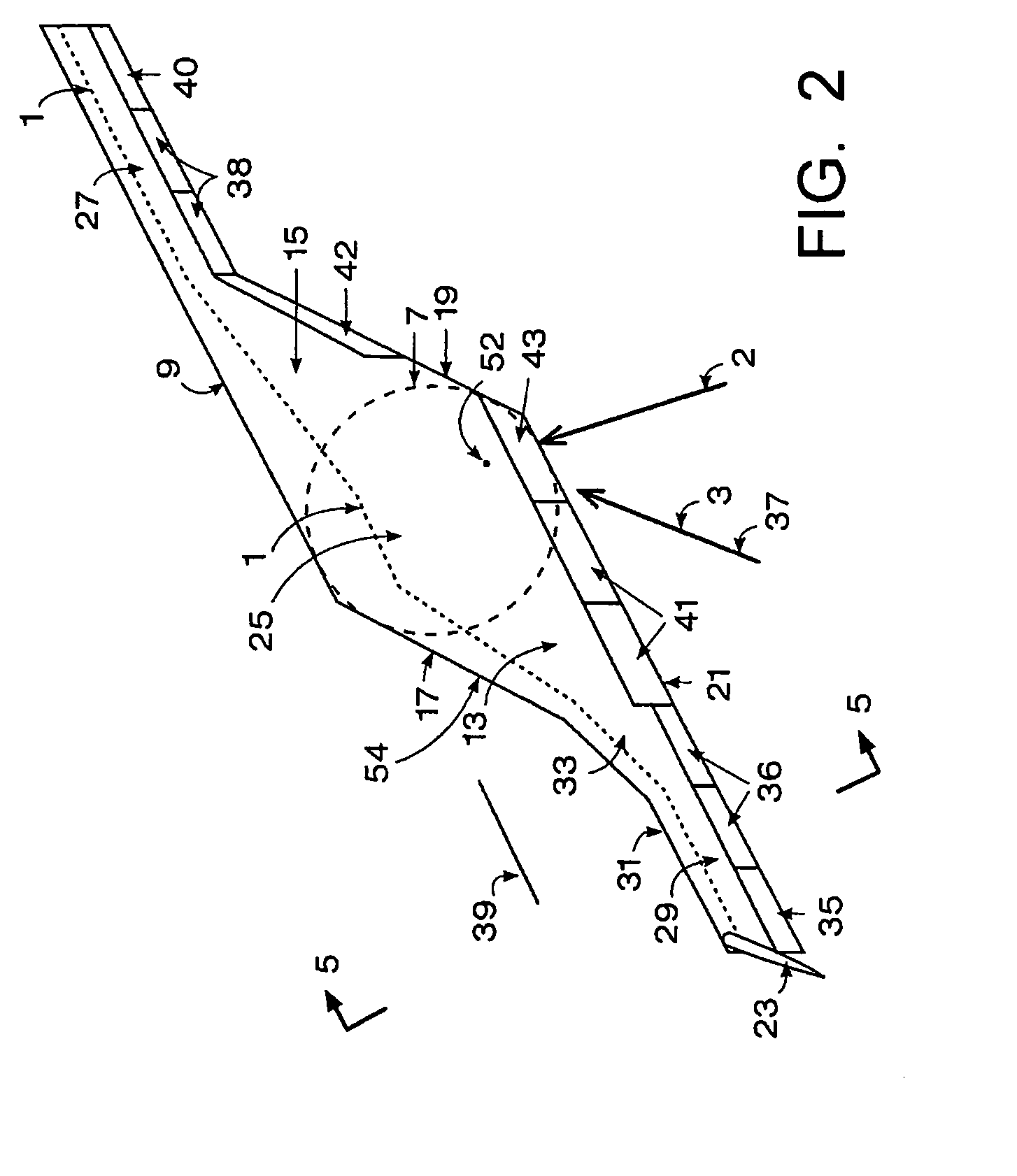
ActiveUS20100243795A1Reduce wetted areaLow compressibilityAircraft stabilisationAsymmetrical aircraftWing configurationForward-swept wing
An oblique wing aircraft (1) designed for reduced surface area to volume ratio. The aircraft has an oblique wing comprising a forward swept wing segment (27) on one side of the wing and an aft swept wing segment (29) on the opposite side of the wing. A center oblique airfoil section (25) connects the forward and aft swept wing segments. The center oblique airfoil section has a larger chord near its centerline than the chords of either of the forward or aft swept wing segments. The chord of the center oblique airfoil section tapers down more rapidly than the forward or aft wing segments as the center oblique airfoil section extends outboard toward the forward and aft swept wings. The center oblique airfoil section is not shaped solely to function as a circular fairing to fill the gap between an oblique wing and a fuselage at different oblique wing angles, nor is it a second wing in an X wing configuration. Preferably, the aircraft is an all-wing aircraft.
Owner:ADVANCED PROD DEV
Vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveUS9694906B1Readily apparentAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesFlight vehicleForward-swept wing
The vertical takeoff and landing unmanned aerial vehicle includes a pair of selectively rotatable ducted fans and a selectively rotatable thrust vectoring nozzle providing vertical takeoff and landing for an unmanned aerial vehicle or a similar type of aircraft. A pair of fixed forward-swept wings are mounted on a rear portion of a fuselage, and a pair of canards are mounted on a top end of a forward portion of the fuselage. The pair of ducted fans are respectively mounted on free ends of the pair of canards, and are selectively rotatable about an axis parallel to a pitch axis of the fuselage. An engine is mounted in the rear portion of the fuselage, and a thrust vectoring nozzle is mounted on the rear portion of the fuselage for directing thrust exhaust from the engine. The thrust vectoring nozzle is selectively rotatable about an axis parallel to the pitch axis.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Multirotor aircraft that is adapted for vertical take-off and landing
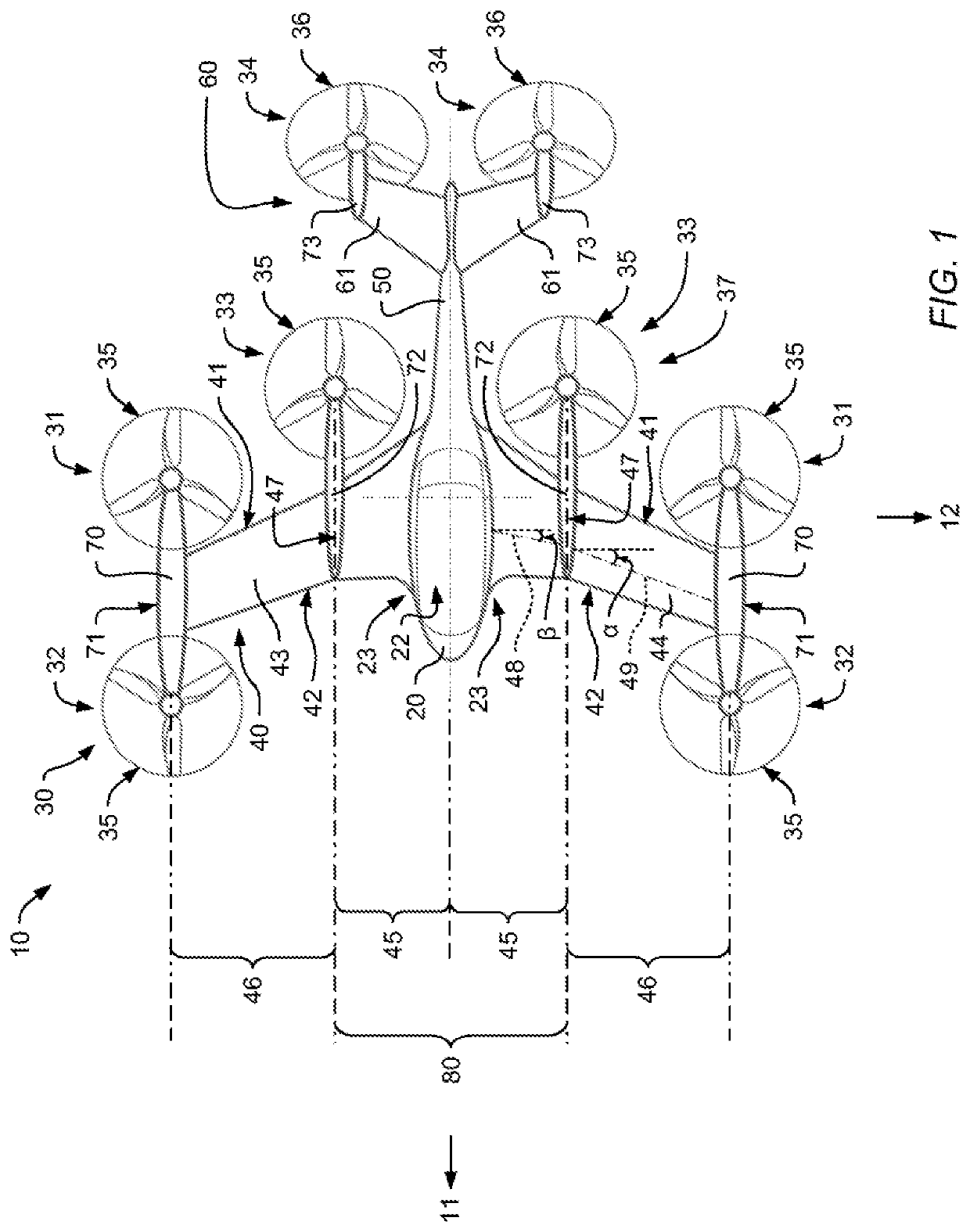
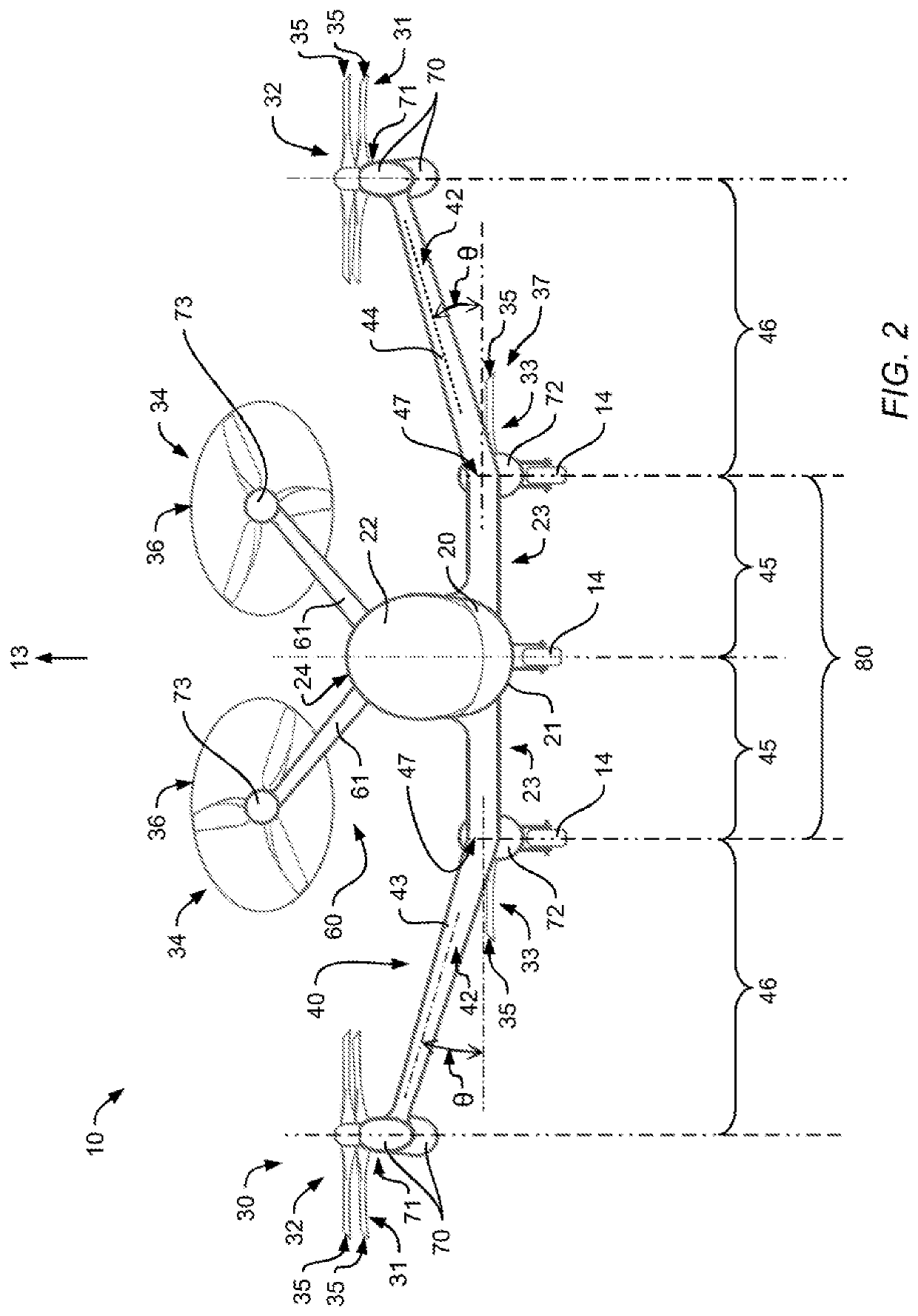
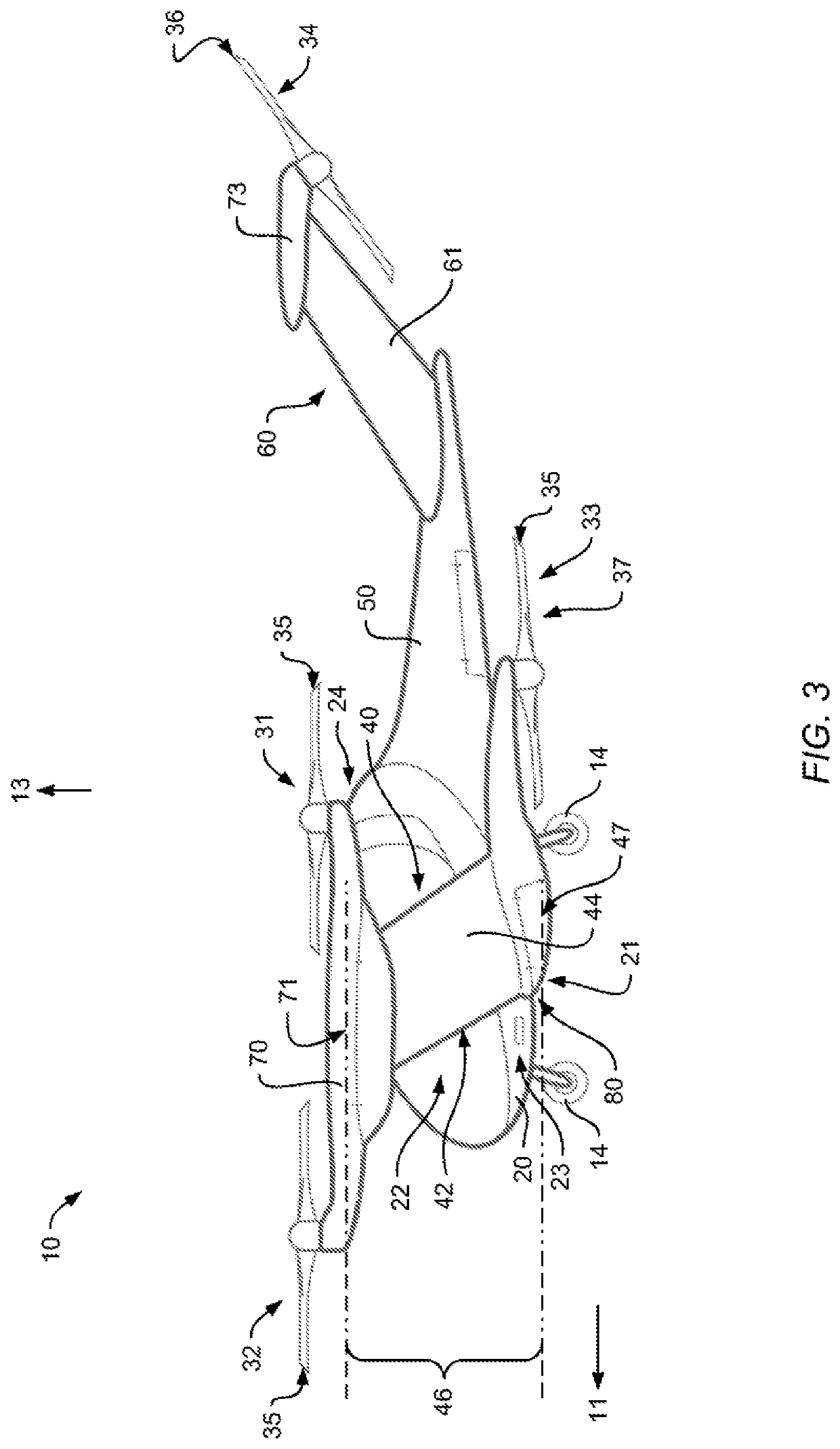
ActiveUS20200269975A1Increasing structural efficiency of structureOperational securityPower plant constructionWing shapesClassical mechanicsMechanical engineering
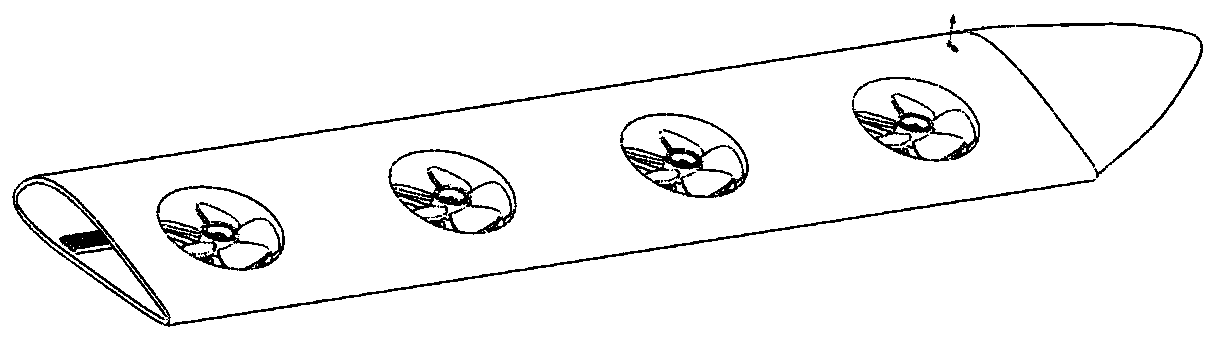
A multirotor aircraft 10 that is adapted for vertical take-off and landing, comprising a fuselage, a thrust producing units assembly that is provided for producing thrust in operation, and a forward-swept wing that comprises a portside half wing and a starboard side half wing. Each one of the portside and starboard side half wings comprises an inboard section that is connected to the fuselage and an outboard section that forms a wing tip. The inboard sections of the portside and starboard side half wings form a central wing region. The portside and starboard side half wings are respectively connected in the region of their wing tips to an associated outboard wing pod that supports at least two non-tiltably mounted thrust producing units of the thrust producing units assembly.
Owner:AIRBUS URBAN MOBILITY GMBH
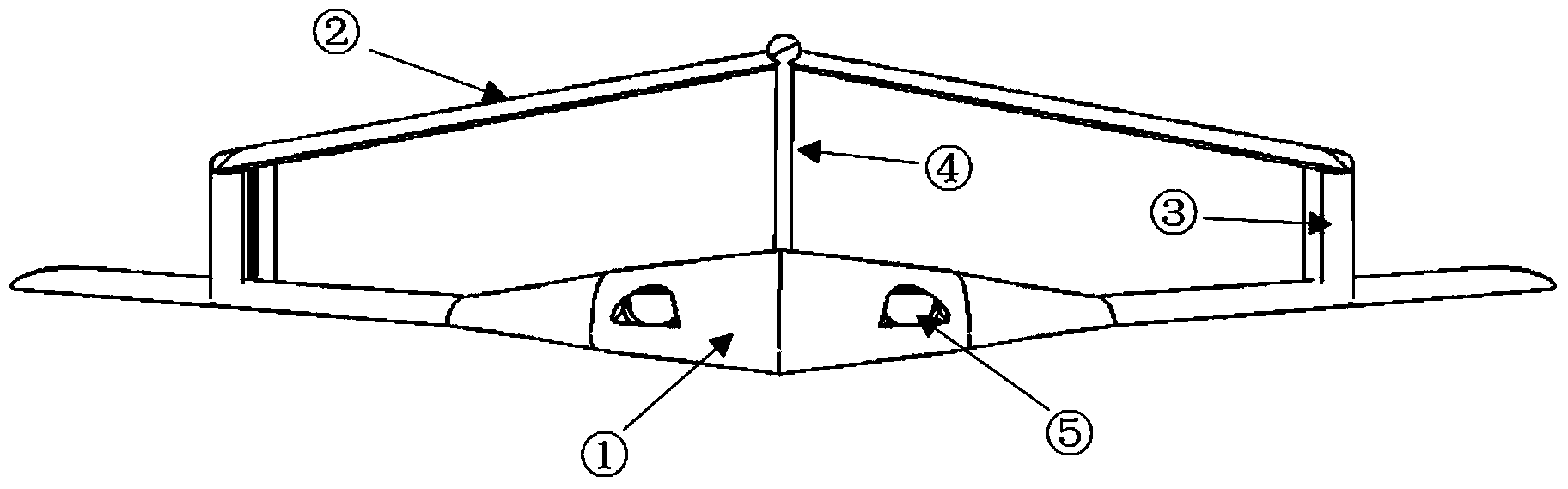
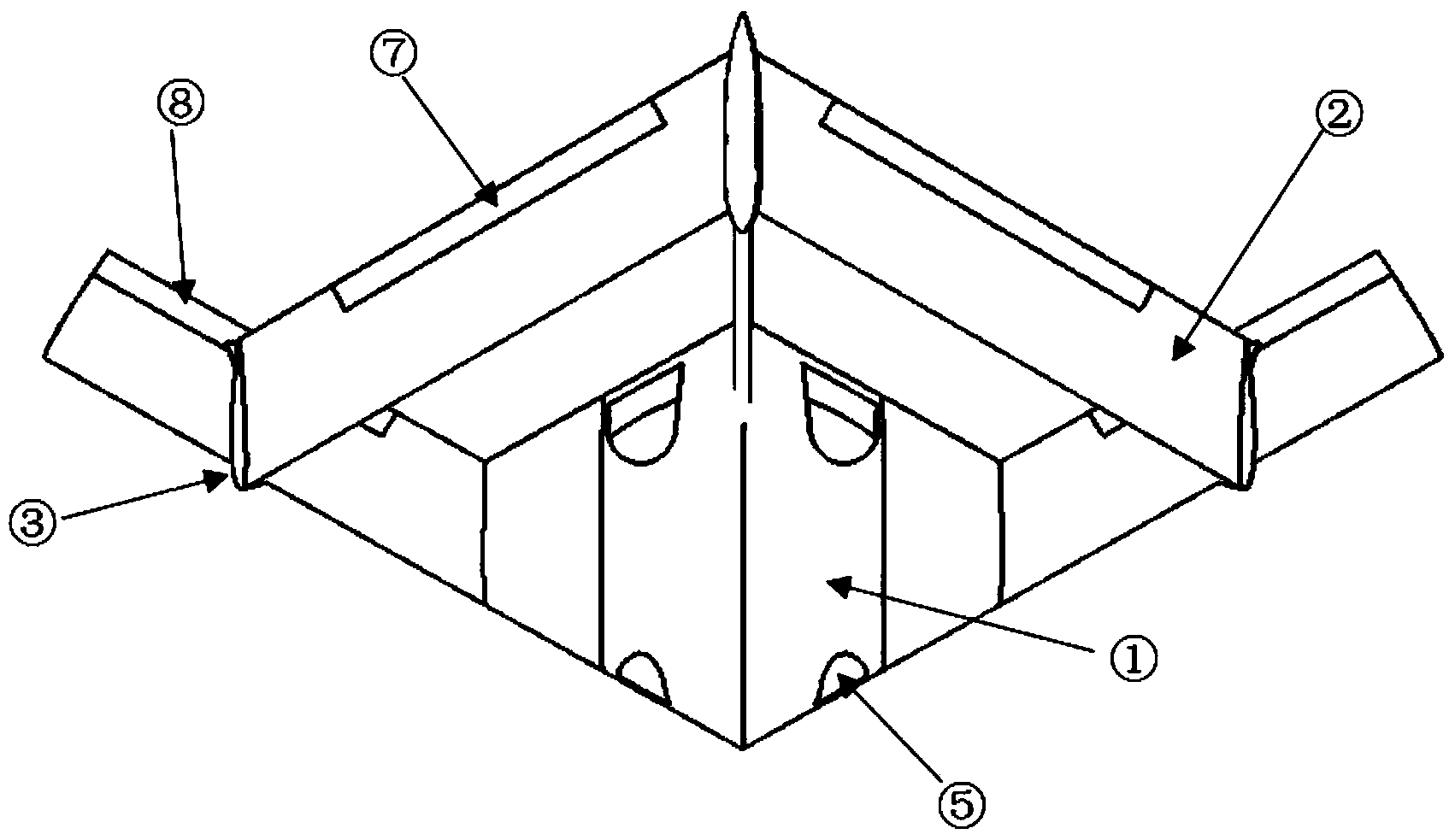
Airplane with combined-wing layout of flying wing and forward-swept wings
ActiveCN103552682AGood aerodynamic liftOptimize layoutAircraft stabilisationWingsJet aeroplaneInlet channel
The invention provides an airplane with a combined-wing layout of a flying wing and forward-swept wings. The airplane is characterized in that thin-wing type vertical columns A and B are additionally arranged at the 70% wingspan positions of the outer sides of two side wings of a flying-wing airplane with backward-swept wings, a thin-wing type vertical column C is additionally arranged at the tail part of the flying-wing airplane, and horizontal forward-swept wings are additionally arranged at the top ends of the three thin-wing type vertical columns A, B and C so as to form the combined-wing layout of the flying wing and the forward-swept wings; elevators are arranged on the horizontal forward-swept wings and a rudder is arranged on the vertical column C; a duct type air inlet channel is adopted on the upper wing surface of the flying wing, and cracking type drag rudders are distributed at the thin-wing type vertical columns A and B. The airplane provided by the invention has the advantages that under the condition that the structure strength is effectively guaranteed, the effective aspect ratio of the wings is increased, the induced drag is reduced, the lift-drag characteristics of the airplane are improved, the stealth performance of the airplane is improved, direct-force control of the airplane in the vertical direction is realized and the detecting accuracy under the maneuvering condition is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Airplane configuration
InactiveUS7900865B2Lower Level RequirementsReduced aircraft noiseGas turbine type power plantsJet type power plantsLeading edgeJet aeroplane
An aircraft configuration that may reduce the level of noise, infrared radiation, or combination thereof directed towards the ground from an aircraft in flight. An embodiment of an aircraft includes a fuselage, two forward swept wings, at least one engine mounted to the aircraft and higher than the wings, and vertical stabilizers mounted on each wing outboard of the outermost engine. The leading edge of the wing may extend forward of the leading end of the engine, and the trailing edge of the aft deck may extend aft of the trailing end of the engine. The aft deck may include an upwardly rotatable pitch control surface at the trailing edge of the deck. Engine types may vary, including but not limited to turbofans, prop-fans, and turbo-props. Main wings may be mounted above the longitudinal axis of the fuselage, and canards may likewise be mounted above or below the axis.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
VTOL aircraft with forward-swept fixed wing
InactiveUS7735774B2Increased longitudinal stabilityEliminates or significantly reduces “suckdown”Aircraft navigation controlAircraft stabilisationJet aeroplaneFixed wing
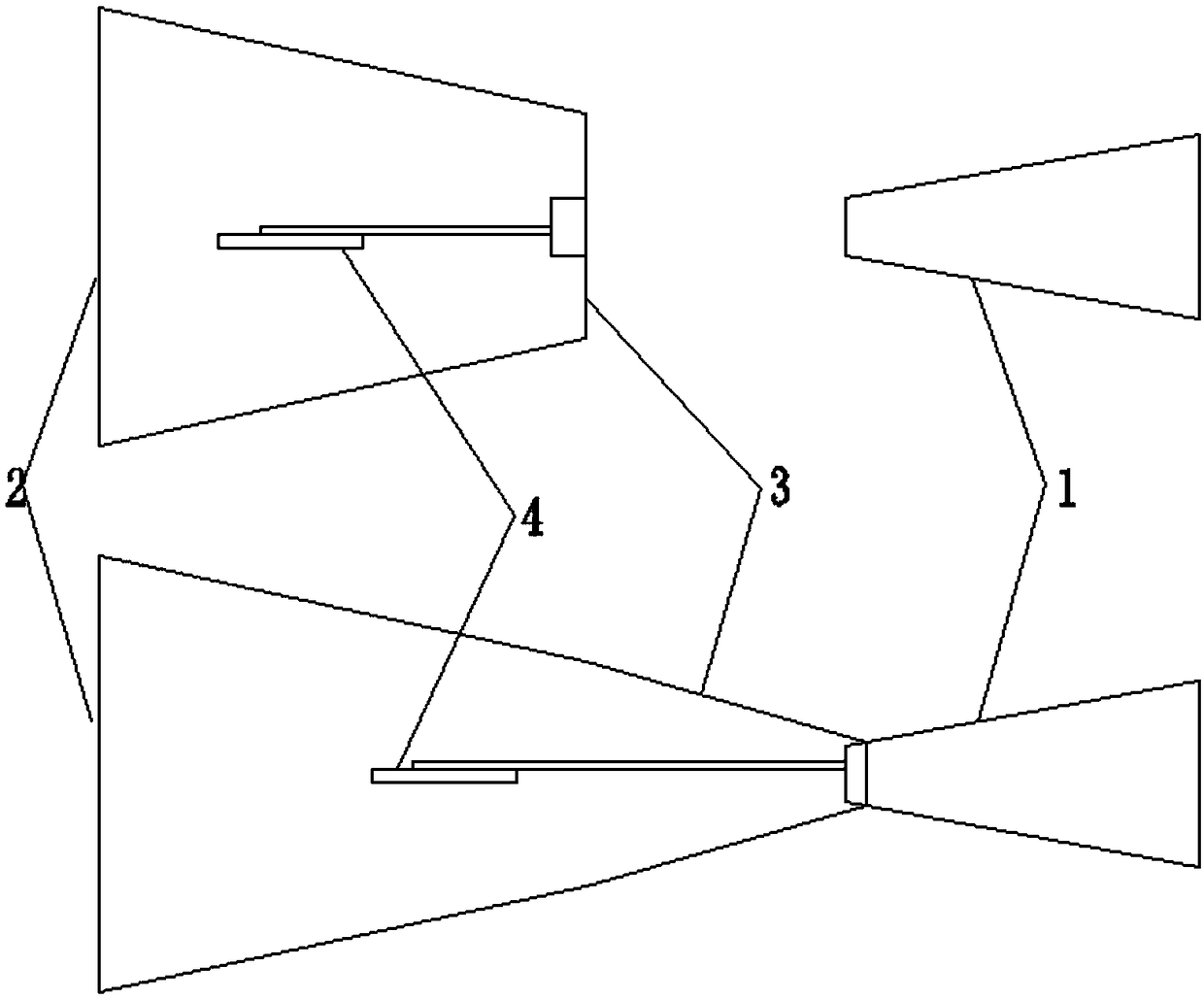
A fixed-wing VTOL aircraft features a forward-swept wing configuration coupled with a tripod arrangement of the engines (two forward, one rear), a forward-swept empennage or tail assembly, and a forward canard. The engines and wings / empennage are located relative to each other such that the engine outlet nozzles, which pivot downwardly to provide lift-off thrust, are minimally covered by the wings / empennage, if at all. The wings and empennage may include lifting fans to supplement lift and provide pitch and / or roll control.
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
Oblique blended wing body aircraft
ActiveUS8408490B2Reduce wetted areaLow compressibilityAsymmetrical aircraftWing shapesWing configurationForward-swept wing
An oblique wing aircraft (1) designed for reduced surface area to volume ratio. The aircraft has an oblique wing comprising a forward swept wing segment (27) on one side of the wing and an aft swept wing segment (29) on the opposite side of the wing. A center oblique airfoil section (25) connects the forward and aft swept wing segments. The center oblique airfoil section has a larger chord near its centerline than the chords of either of the forward or aft swept wing segments. The chord of the center oblique airfoil section tapers down more rapidly than the forward or aft wing segments as the center oblique airfoil section extends outboard toward the forward and aft swept wings. The center oblique airfoil section is not shaped solely to function as a circular fairing to fill the gap between an oblique wing and a fuselage at different oblique wing angles, nor is it a second wing in an X wing configuration. Preferably, the aircraft is an all-wing aircraft.
Owner:ADVANCED PROD DEV
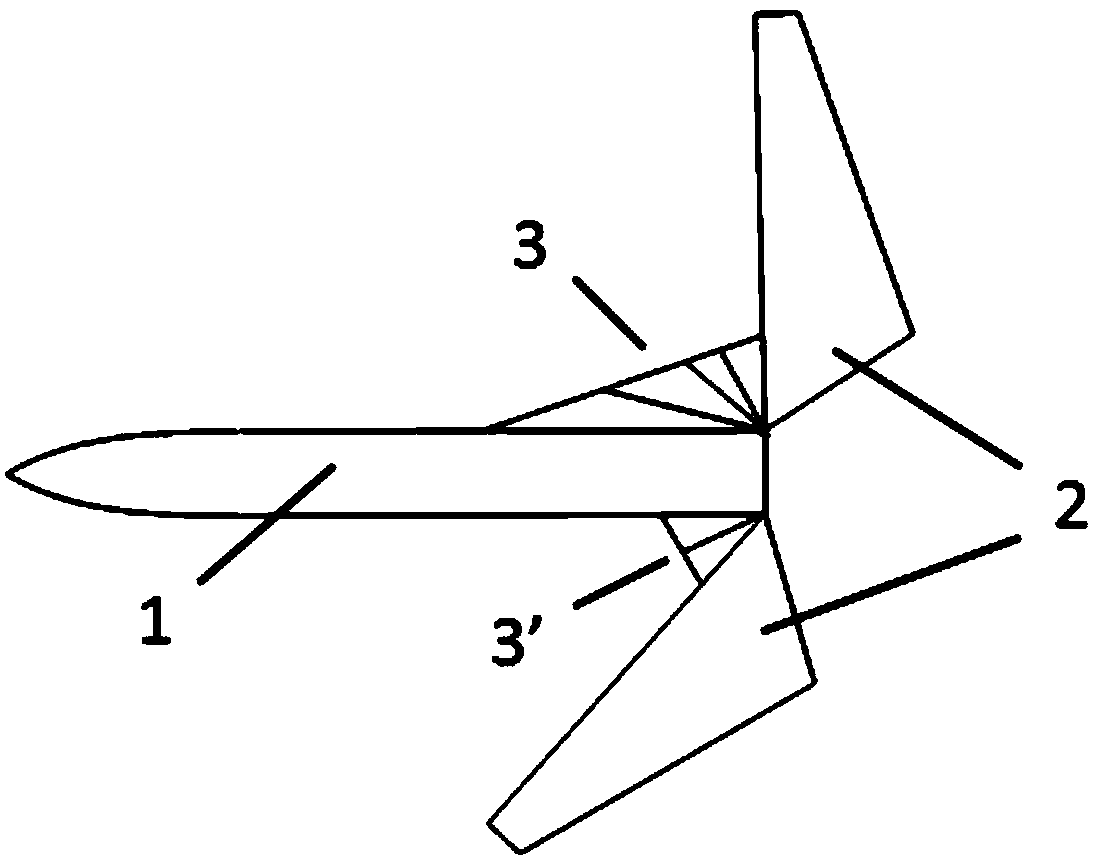
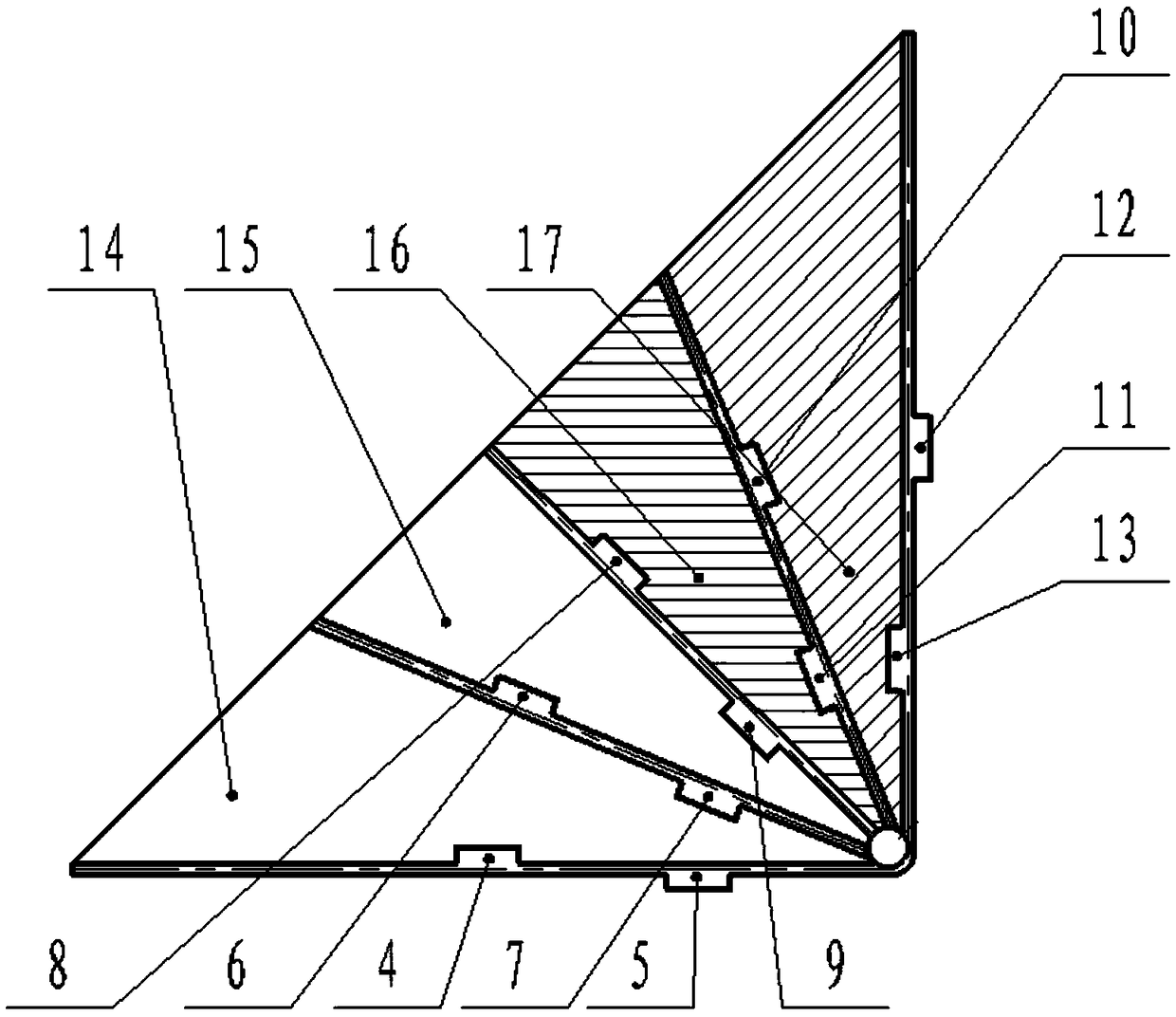
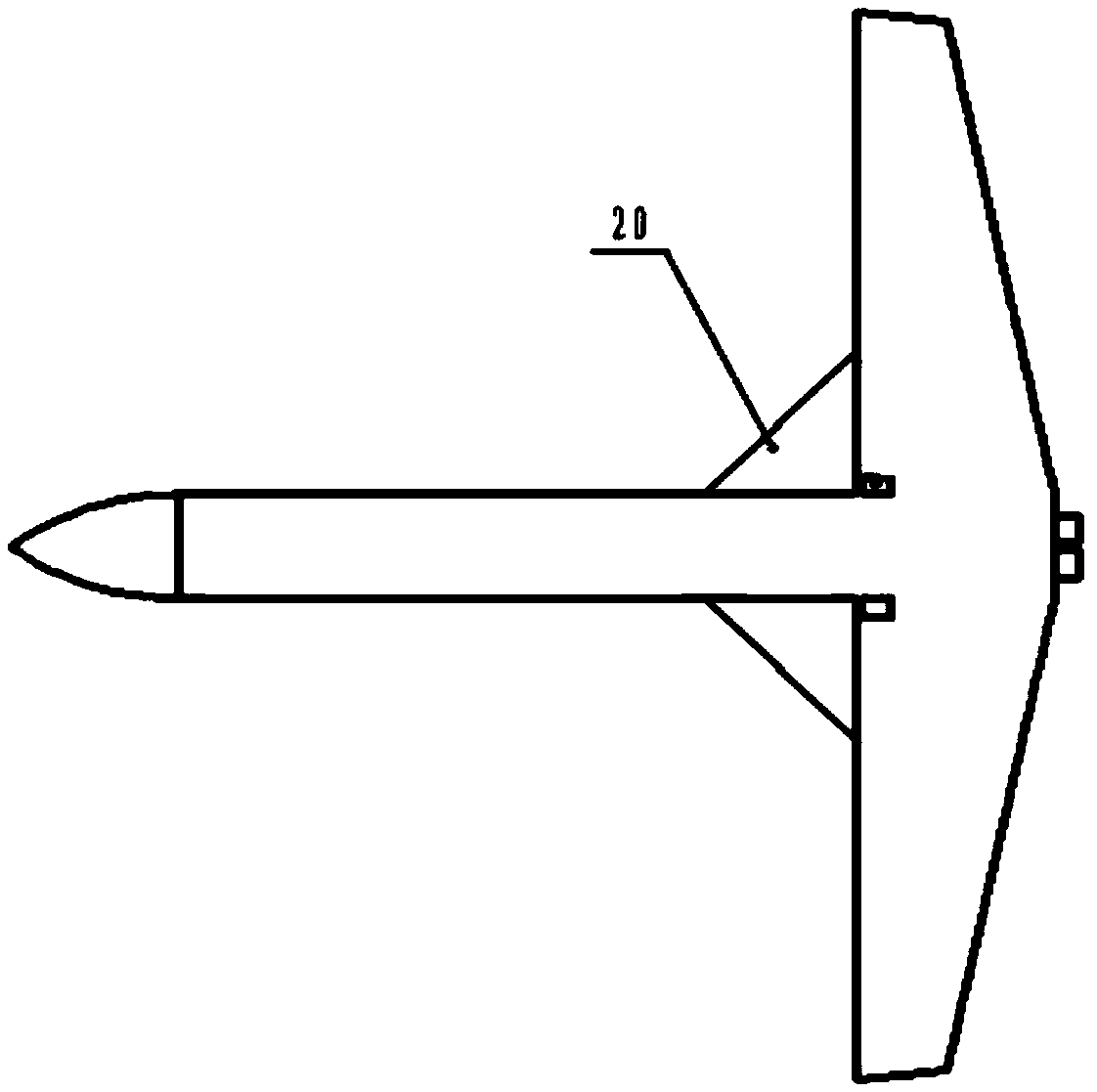
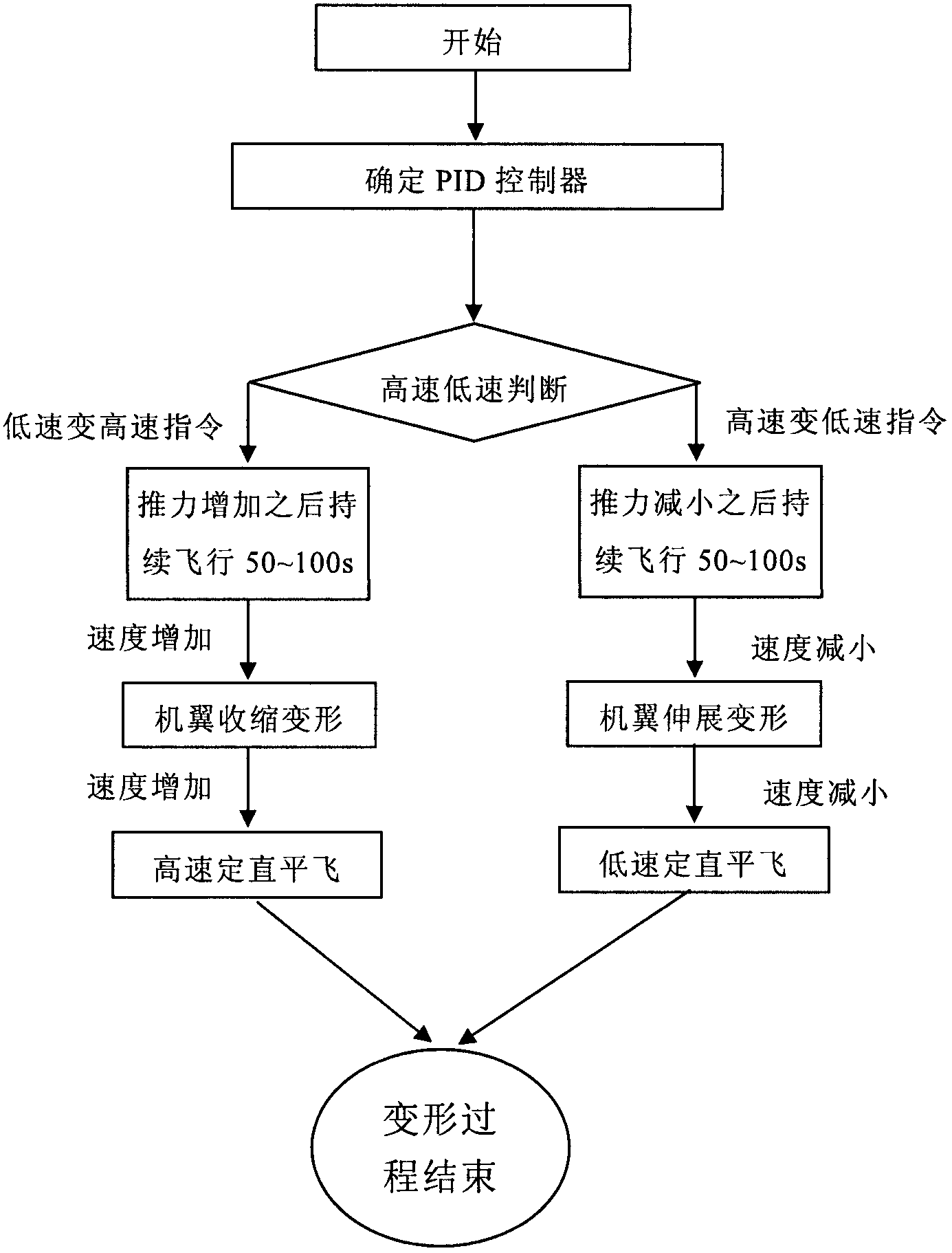
Flight control method of deformable unmanned aerial vehicle
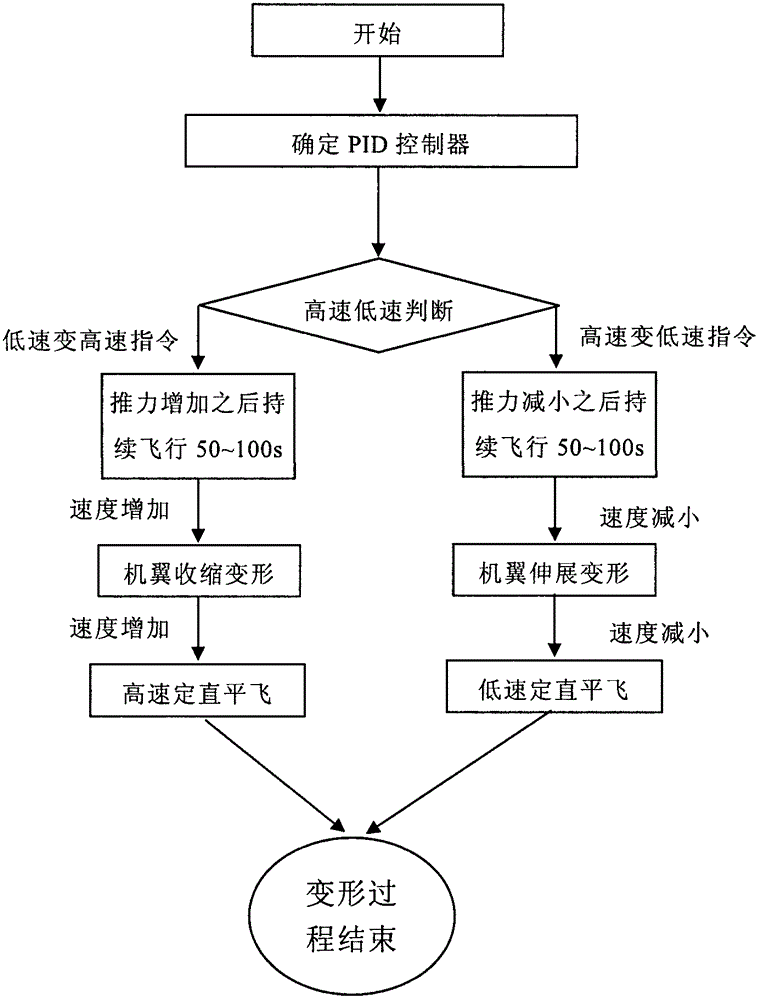
ActiveCN102722176AStable flightPosition/course control in three dimensionsLow speedFlight control modes
The invention provides a flight control method of a deformable unmanned aerial vehicle. The deformable unmanned aerial vehicle has a canard type telescopic forward-swept wing and single vertical fin aerodynamic arrangement; according to the adjustment and analysis of a root-locus method, a high-low speed deformable unmanned aerial vehicle can perform the adjustment on parameters of a controller through a design method of a low-speed controller, and therefore the design requirement on the controllers under two flight speeds can be met. Matching the deformation time and the control time of an engine is part of a control strategy of the deformable unmanned aerial vehicle; and as shown in the analysis of the flight mechanics design, the thrust of the engine is changed prior to implementing the process and the strategy under the deformation time.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Vtol aircraft with forward-swept fixed wing
InactiveUS20090127379A1Eliminates and significantly reduces “ suckdown ”Strong roll controlAircraft navigation controlWing shapesJet aeroplaneFixed wing
A fixed-wing VTOL aircraft features a forward-swept wing configuration coupled with a tripod arrangement of the engines (two forward, one rear), a forward-swept empennage or tail assembly, and a forward canard. The engines and wings / empennage are located relative to each other such that the engine outlet nozzles, which pivot downwardly to provide lift-off thrust, are minimally covered by the wings / empennage, if at all. The wings and empennage may include lifting fans to supplement lift and provide pitch and / or roll control.
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
Airplane configuration
InactiveUS20110089290A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced aircraft noiseGas turbine type power plantsAircraft stabilisationJet aeroplaneLeading edge
An aircraft configuration that may reduce the level of noise, infrared radiation, or combination thereof directed towards the ground from an aircraft in flight. An embodiment of an aircraft includes a fuselage, two forward swept wings, at least one engine mounted to the aircraft and higher than the wings, and vertical stabilizers mounted on each wing outboard of the outermost engine. The leading edge of the wing may extend forward of the leading end of the engine, and the trailing edge of the aft deck may extend aft of the trailing end of the engine. The aft deck may include an upwardly rotatable pitch control surface at the trailing edge of the deck. Engine types may vary, including but not limited to turbofans, prop-fans, and turbo-props. Main wings may be mounted above the longitudinal axis of the fuselage, and canards may likewise be mounted above or below the axis.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Aerodynamic configuration of aircraft
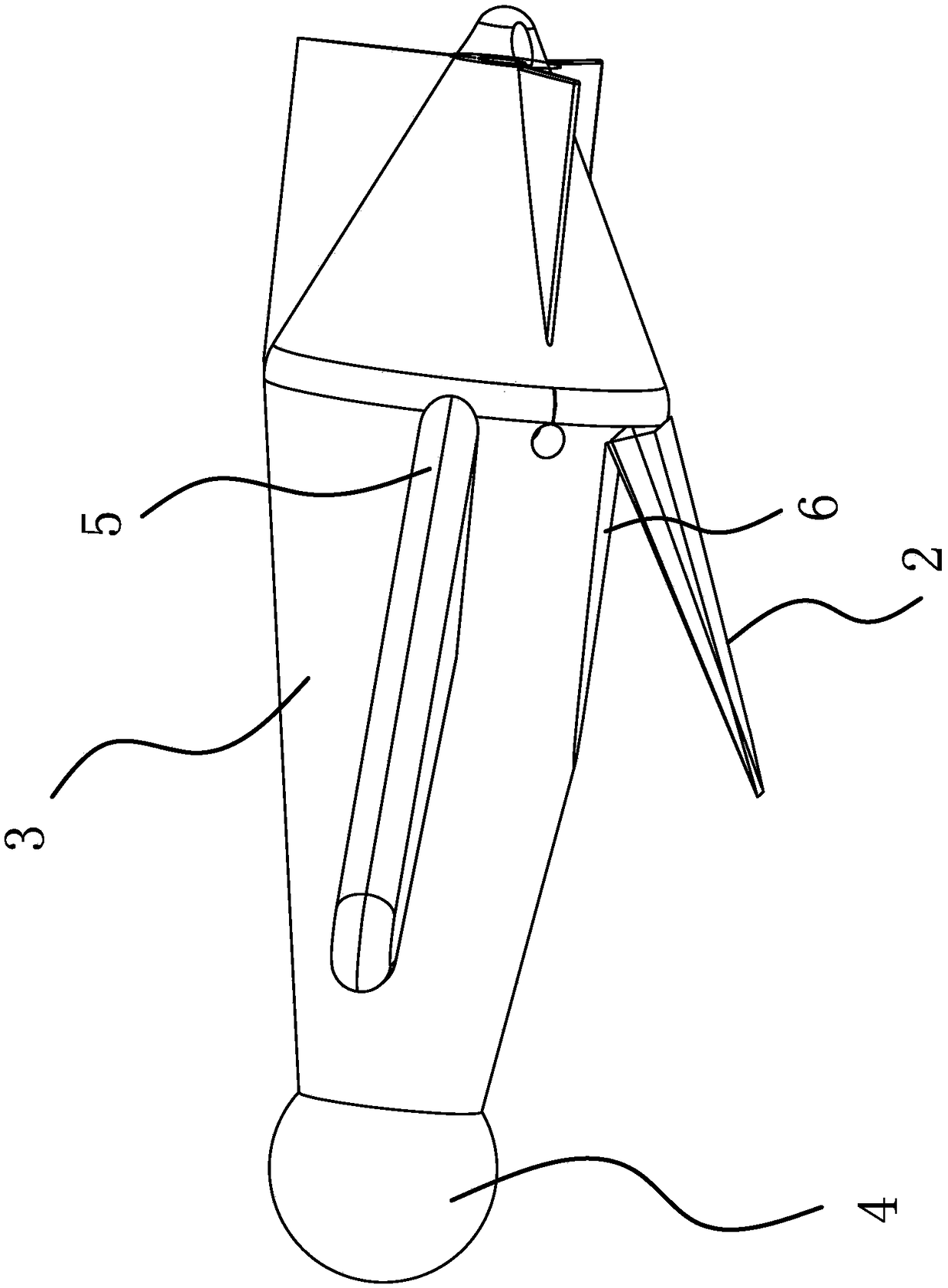
InactiveCN102826216AMeet the requirements of high subsonic cruiseFlying fastWing shapesJet aeroplaneConfiguration design
The invention relates to the technical field of aerodynamic configuration design of aircrafts, in particular to an aerodynamic configuration of an aircraft. The aerodynamic configuration of the aircraft comprises an aircraft body (3), outer wing sections (1) and inner wing sections, and is characterized in that the surfaces of the outer wing sections (1) and the inner wing sections (2) are laminar flow airfoils; the inner wing sections (2) are wing-body transition sections, adopt back-swept wings with a moderate sweep back angle and a small span-chord ratio and are connected with the aircraft body; the wings and the aircraft body are fused together; and the outer wing sections (1) adopt forward-swept wings with a moderate sweep forward angle and a moderate span-chord ratio. Due to the aerodynamic configuration of the aircraft, not only can the requirement on high-altitude long-endurance high-subsonic-speed cruise of the aircraft be satisfied, but also the flight speed is improved and the problem of trimming difficulty is solved.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
Folding mechanism for aircraft, and control method thereof
InactiveCN108202861AReduce horizontal footprintSimple structureWing adjustmentsAviationFlight vehicle
The embodiments of the present invention disclose a folding mechanism for an aircraft, and a control method thereof, and relate to the folding mechanism design technology in aerospace aircrafts. A purpose of the present invention is to solve the problem of complicated folding mechanism. According to the folding mechanism, a fixed guide rail is fixed at the bottom portion of an aircraft body, a sliding block can slide back and forth at both ends of the fixed guide rail, one ends of a swept-back wing and a forward-swept wing at the same side of the aircraft body are fixed through a rotation shaft, the swept-back wing and the forward-swept wing at the same side of the aircraft body form a connection rod mechanism through the rotation shaft, the other end of the swept-back wing is fixed at oneend of the fixed guide rail through a vertical shaft, the swept-back wing can rotate around the vertical shaft, the other end of the forward-swept wing is fixed on the sliding block, and an actuatingcylinder is fixed on the fixed guide rail.
Owner:HIWING TECH ACAD OF CASIC
Variable-area canard forward-swept wing morphing aircraft
InactiveCN110979682AIncreased wingspanEasy to liftWing adjustmentsCanard-type aircraftInlet channelFuselage
The invention discloses a variable-area canard forward-swept wing morphing aircraft which adopts a canard layout. The plane shape of an airfoil is quadrilateral, and when wings are completely retracted, the wings and a canard wing are connected to form a delta wing. The canard wing is arranged at the head of a fuselage. The wings on the two sides of the tail of the fuselage can be synchronously folded forwards towards the inner fuselage side around a wing body connecting rotating shaft or unfolded backwards towards the outer side. When the wings are folded forwards, the wings are gradually folded forwards to reduce the sweepforward angle, the wings are completely attached to the fuselage, and the whole aircraft is of a curved streamline aerodynamic configuration. When the wings are completely unfolded into forward-swept wings, the wing span of the aircraft is greatly increased, so that the aircraft can ensure large lift force. Double vertical tails are symmetrically arranged on the rear portion of the fuselage, lifting ailerons are installed at the rear end of the fuselage and located on the rear portions of the two vertical tails, and an air inlet channel is located below the fuselage. Through reasonable cooperation of the variable-area canard forward-swept wing variants, the aircraft has small flight resistance when the wings are in the unfolded state and the folded state, and the flight flexibility of the aircraft is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Aircraft with folding fan-shaped wings
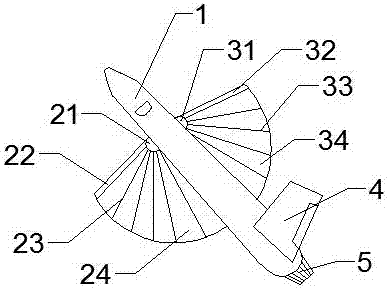
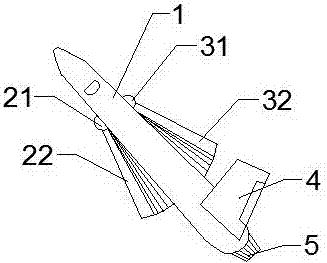
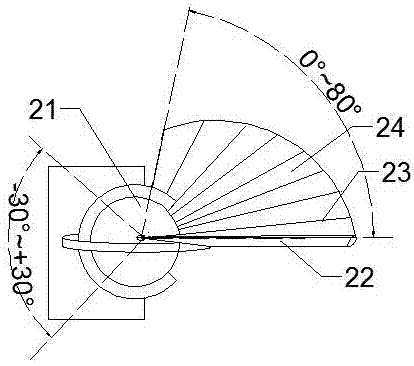
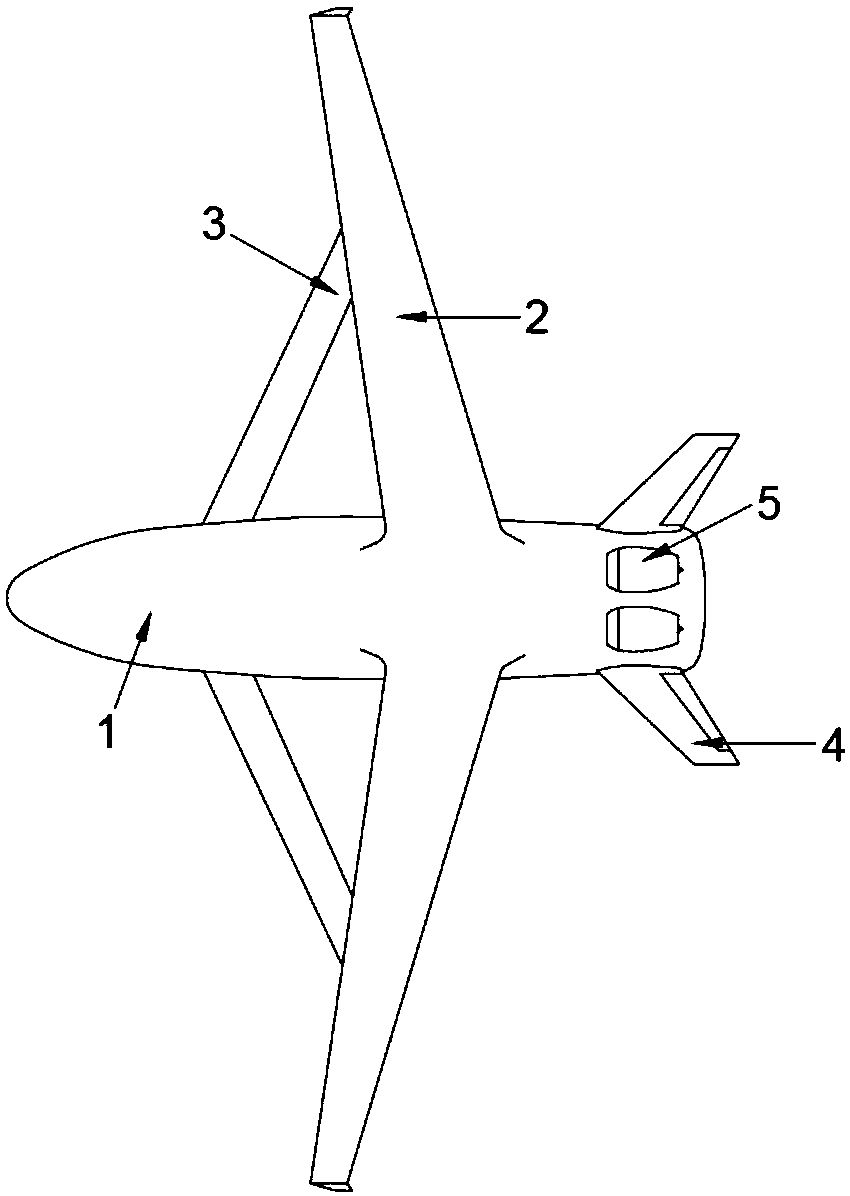
InactiveCN107499498ARealize the foldable function of the wingsFree to adjust the angleWing adjustmentsJet engineForward-swept wing
The invention discloses an aircraft with folding fan-shaped wings, which relates to the field of aircrafts. The aircraft mainly comprises a fuselage, a left wing-connecting mechanism, a left forward-swept wing, a left wing skeleton, a left wing skin, a right wing-connecting mechanism, a right forward-swept wing, a right wing skeleton, a right wing skin, an empennage and a jet engine. The aircraft adopts a fan-shaped wing design method in cooperation with the special connecting structures to achieve the folding function of the wings of the aircraft, and moreover, an opening and closing angle and an inclination angle can be freely adjusted as well; by means of the specially designed wing-connecting structures and the fan-shaped folding wing design, the space occupied by the wings of the folded aircraft can be small, and furthermore, the wingspans of the left wing and the right wing can be freely unfolded and folded; moreover, the wings can also be turned up and down to freely adjust windward angles, so that the maneuverability and flexibility of the aircraft flying in the air can be increased; and furthermore, the size of the fuselage is small after the wings are folded. The aircraft is suitable for being applied in the aspect of ship-borne fighter plane designs or small passenger planes, and has high application value.
Owner:FOSHAN SHENFENG AVIATION SCI & TECH
Pneumatic layout of forward swept wing wide-body high subsonic aircraft adopting leading edge support wings
InactiveCN108502138AImprove aerodynamic efficiencyIncrease volumeHeat reducing structuresFuselagesShock waveLeading edge
The invention relates to a pneumatic layout of a wide-body high subsonic aircraft adopting leading edge support wings. The support wings are arranged at a certain distance below the fronts of main wings so as to form leading edge support, and a design of the front swept main wings and a wide-body fuselage is adopted; the relative position of the leading edge support wings and the main wings and the forward swept arrangement form of the main wings are rationally designed; the main wing adopts a way of arranging upper single wings upsidedown at the lower part, and have forward sweep angles. Thesupport wings adopt a way of arranging lower single wings upsidedown at the upper part, and have backward sweep angles; the tips of the support wings are connected with the lower surfaces of the tip parts of the main wings, and less overlap only exists at the joint positions of the tip parts of the support wings and the main wings. By adopting the pneumatic layout of the wide-body high subsonic aircraft adopting the leading edge support wings, waste resistance and induced drag are reduced, and the aerodynamic efficiency and volume of the aircraft are increased; the traditional arrangement formof placing the support wings under the main wings is changed into arranging the supporting wings in front, so that the overlooked overlapping area of the support wings and the main wings is minimized, and the defect that shock waves are formed due to too early layout of the traditional support wings can be avoided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A three-purpose vertical take-off and landing aircraft
InactiveCN109263967ALong sailing timeStable flightSteering ruddersAircraft controlLeading edgePost disaster
The invention relates to a three-purpose vertical take-off and landing aircraft, belonging to the technical field of aircraft, comprising a fuselage, a wing, a reversing lifting device, a vertical lifting device and a rudder. The fuselage has a flat rhombus structure, and a main controller is arranged in the fuselage, and the main controller is connected with a reversing lifting device, a verticallifting device and a rudder. The wing adopts forward swept wing. The reversing lifting device is located at the leading edge of the wing and can be steered 90 degrees under the control of the mastercontroller to provide vertical lift or forward pull for the aircraft. The vertical lifting device is arranged at the rear end of the fuselage, and the vertical lifting device provides the upward lifting force for the aircraft in the form of rotating the paddle blades driven by an electric motor. The rudders are arranged at the tips of both sides of the wing. The invention can carry out vertical take-off and landing, has long sailing time, stable flight process, has two lifting modes, has high safety coefficient, and is suitable for logistics transportation, air fire extinguishing, post-disaster rescue and the like.
Owner:FOSHAN SHENFENG AVIATION SCI & TECH
Methods for improvements of the box wing aircraft concept and corresponding aircraft configuration
ActiveUS10899447B2Reduced concerns as regards stallingEasy to operateAircraft stabilisationWing shapesClassical mechanicsWingspan
Aircraft configuration by applying the following method steps for improving the conventional box wing aircraft concept: dividing both the backward swept front and the forward swept rear wings into root and tip sections, wherein the tip sections (34) of the front wings are more backward swept than the root sections (37), and the tip sections (35) of the rear wings are more forward swept than the root sections (38). Preferred embodiments comprise moving the front wing to the nose and the rear wing towards the rear end of a long fuselage; adding a middle wing and thereby decreasing the wingspan by one third; dividing the middle wing into a backward swept root section (28) and two tip sections (29,30), one forward and another backward swept. The four wingtips on each side are interconnected by a wingtip fence (26), obtaining seven closed frame structures, as well as seven aerodynamic channels for the stream flow.
Owner:HERNADI ANDRAS
Air vehicle airfoil folding mechanism
ActiveCN109436290AAchieving large-scale changeHas variantsWing adjustmentsFuselagesFlight vehicleFront edge
The invention relates to the technical field of air vehicles and in particular relates to an air vehicle airfoil folding mechanism. The air vehicle airfoil folding mechanism comprises a transformationsystem, wherein the transformation system is arranged between a fuselage and a wing of the air vehicle; the transformation system comprises a plurality of groups of folding hinges and a plurality offolding planes; the transformation system is movably connected with the fuselage and the wing of the air vehicle respectively through the folding hinges; in a transformation process of the transformation system, a front edge of the wing can keep moving along a tail edge of the transformation system all the time; advanced aerodynamic properties of a forward-swept wing and a folding wing are integrated to realize a novel forward-swept wing and folding wing combinatory transformation manner; the flight stability and the wide-speed-region flight performance are improved.
Owner:AVIC SHENYANG AERODYNAMICS RES INST
Flight control method of deformable unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN102722176BStable flightPosition/course control in three dimensionsLow speedFlight control modes
The invention provides a flight control method of a deformable unmanned aerial vehicle. The deformable unmanned aerial vehicle has a canard type telescopic forward-swept wing and single vertical fin aerodynamic arrangement; according to the adjustment and analysis of a root-locus method, a high-low speed deformable unmanned aerial vehicle can perform the adjustment on parameters of a controller through a design method of a low-speed controller, and therefore the design requirement on the controllers under two flight speeds can be met. Matching the deformation time and the control time of an engine is part of a control strategy of the deformable unmanned aerial vehicle; and as shown in the analysis of the flight mechanics design, the thrust of the engine is changed prior to implementing the process and the strategy under the deformation time.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Canard forward-swept wing unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN112644684AShorten the lengthHigh strengthAircraft stabilisationWing shapesFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a canard forward-swept wing unmanned transport plane, relates to the field of aircraft design, and particularly relates to a canard forward-swept wing unmanned transport plane which comprises a plane body unit, a wing unit, an undercarriage unit and a power unit. The transport plane adopts a canard layout, and the length of the plane body is shorter under the condition of having the same longitudinal balancing capacity as a conventional layout, so that the plane body is higher in strength and lighter in weight. The wings adopt sweepforward wings, so that the average pneumatic chord positions of the wings move forwards, the balancing of the gravity center of the unmanned aerial vehicle is facilitated, and the problems of unreasonable aircraft weight distribution and small available gravity center range of the aircraft due to the fact that an engine of a common canard aircraft can only be arranged backwards and the gravity center of the aircraft is balanced through the weight of the engine are solved.
Owner:河北利翔航空科技有限公司
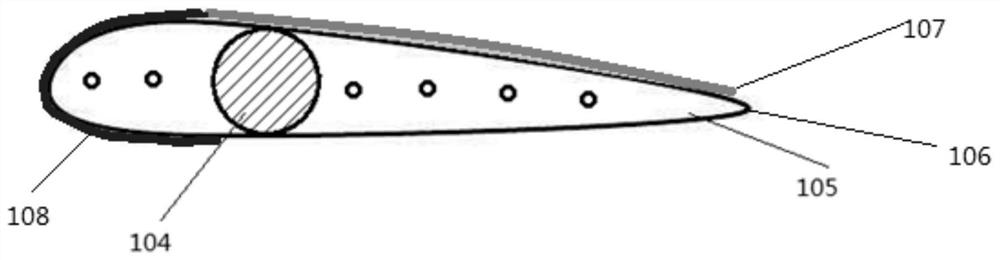
High-capacity forced-oil circulation air cooler
InactiveCN105810401AImprove heat transfer effectComposite tightTransformers/inductances coolingCompression moldingLow noise
The invention discloses a large-capacity strong oil circulation air cooler. The heat transfer core element adopts an elliptical bimetal composite integral finned tube structure, and corrugated notches are opened on the fins of the cooling tubes, and internal ribs are juxtaposed in the tubes. There is a vortex generator, the fan blade of the cooler is molded with high-strength aluminum alloy plate, and the fan motor adopts an optimized combination of three types of motors. The centrifugal force of the fan is loaded into the mainstream, which ensures the laminar flow state, reduces the speed, and forms a cooler with low noise and large capacity. Under the same wind speed and oil flow conditions, the overall heat transfer coefficient K value is higher than that of circular finned tubes of the same specification. Products increased by 30%.
Owner:SHENYANG TIANTONG ELECTRICITY
Combined aircraft aerodynamic layout structure for cooperative tasks
PendingCN113928537AStable controlLittle changeConvertible aircraftsWing shapesFlight vehicleControl engineering
The invention discloses a combined aircraft aerodynamic layout structure for cooperative tasks, and particularly relates to the field of overall design of aircrafts. The combined aircraft aerodynamic layout structure for the cooperative tasks comprises a main machine and two sub-machines, the main machine adopts the layout of a front rhombic wing and a rear sweep-forward wing, the two sub-machines are symmetrically distributed on the two sides of the main machine, each sub-machine is embedded between the rhombic wing and the sweep-forward wing of the main machine, and the main machine and the two sub-machines have a complete flying wing layout in a combined state. By the adoption of the technical scheme, the problem that gravity center change and pneumatic center change are caused by neutron machine separation of an existing combined aircraft is solved, and different flight task requirements can be met.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心空天技术研究所
Active load reduction large wind electric generator blade
InactiveCN111472927AAdjust the loadAvoid breakingWind motor controlMachines/enginesElectric machineTurbine blade
The invention relates to an active load reduction large wind electric generator blade, and belongs to the technical field of wind power generation equipment. The technical problem that according to anexisting method, wind loads borne by blades are not effectively reduced, and under the strong wind, the wind electric generator blades are prone to breaking can be solved. The active load reduction large wind electric generator blade comprises a wind turbine blade and a control circuit, and further comprises multiple structure fans, the structure fans are mounted in the wind turbine blade, the control circuit is mounted in the wind turbine blade and is attached to the inner wall of the wind turbine blade, one end of the control circuit is connected with the structure fans, the other end of the control circuit is connected with a controller, and each structure fan comprises a fan blade, a fan blade fixing nut, a fan blade frame, a clamping screw, a motor, a support and a structure frame. The active load reduction large wind electric generator blade has the advantages that the pressure difference between a front swept wing area and a rear swept wing area of the wind turbine blade can beadjusted, and the load borne by a blade structure can be changed.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Variable forward swept wing and canard overlapping mechanism and working method thereof
ActiveCN109278983AImproved supersonic aerodynamic performanceGive full play to the advanced natureWingsDrag reductionEngineeringControl theory
The invention relates to a variable forward swept wing and canard overlapping mechanism and a working method thereof, relates to the technical field of wing mechanisms of aircraft, and solves the technical problem that the slot flow between a canard and a fully forward swept wing interferes with the flow around the wings and a fuselage. The variable forward swept wing and canard overlapping mechanism concretely includes a canard and a forward swept wing. The canard and the forward swept wing are respectively arranged on the two sides of a fuselage, the forward swept wing is arranged at the front end of the canard, the wing tip side wall surface of the forward swept wing is provided with a spar in the chordwise direction, and the wing tip side wall surface of the forward swept wing is covered with a flexible skin structure; and a drive system is also arranged inside the flexible skin structure, and the drive system drives the spar to drive the flexible skin structure to smoothly and continuously deform. As the flexible skin structure is arranged at the outer end of the forward swept wing, the drive system drives the spar to drive the flexible skin structure to smoothly and continuously deform; the shape of the forward swept wing is driven by the spar to change, and then the distance between the forward swept wing and the canard is changed, and finally the seamless overlapping ofthe two is achieved.
Owner:AVIC SHENYANG AERODYNAMICS RES INST
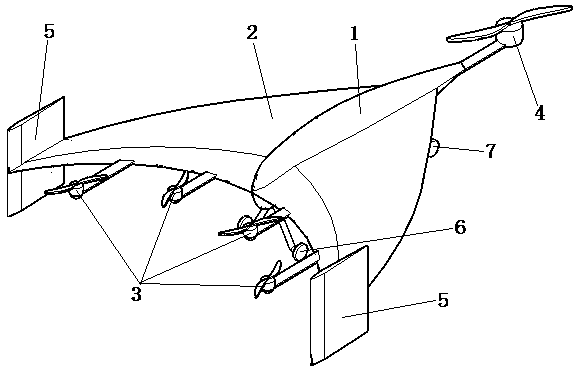
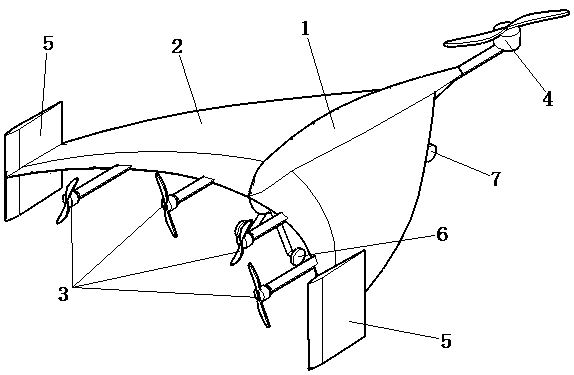
Small unmanned aerial vehicle adopting linked wing type pneumatic layout
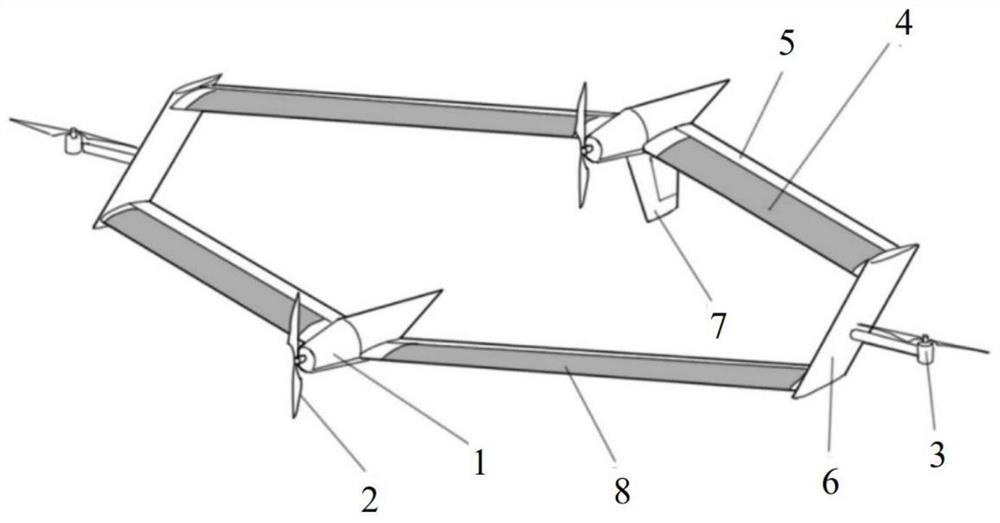
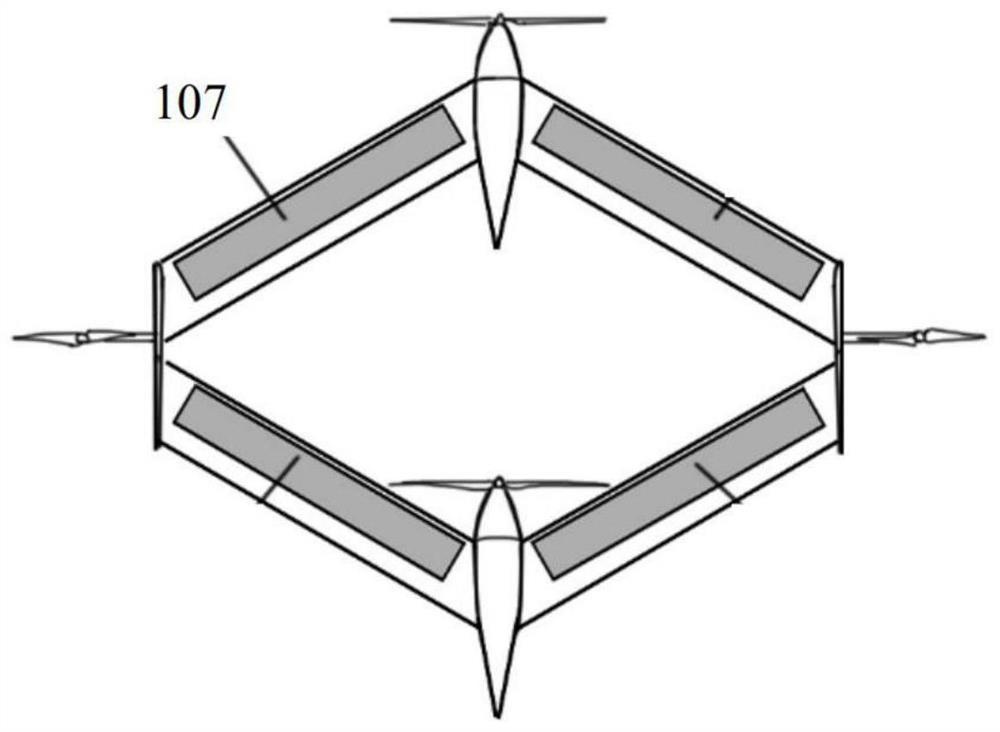
ActiveCN112937834AReduce speedHeat reducing structuresVertical landing/take-off aircraftsSolar batteryFuselage
The invention discloses a linked-wing small solar unmanned aerial vehicle. The unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a front fuselage and a rear fuselage, front-end sweepback wings and rear-end sweepforward wings, a double-engine motor and propellers which are arranged at the front ends of the two fuselages, bridge arms which are connected with the front and rear wing sections, two motors and propellers which are arranged on the outer sides of the left bridge arm and the right bridge arm, and an inverted vertical fin which is connected with the rear fuselage. The upper surfaces of the left sweepback wing, the right sweepback wing, the left sweepforward wing and the right sweepforward wing of the wings are each provided with a solar cell panel set, and energy is provided for continuous flight of the unmanned aerial vehicle. During takeoff, the left and right propellers can be used for vertical takeoff and landing, so that the usability and takeoff stability of the aircraft are improved; the maneuvering characteristics and higher reliability of the aircraft are improved through control of multiple groups of propellers; the inverted vertical fin can replace an undercarriage as a support, so that the structure is simplified and the weight is saved; the unmanned aerial vehicle is not provided with an undercarriage, can realize short-distance throwing flight without a runway requirement during take-off, realizes gliding landing during landing, and also can realize vertical take-off and landing and hovering.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Sweepforward canard flying wing aerodynamic layout unmanned aerial vehicle
PendingCN112319813ASolve aerodynamic divergenceSolve quality problemsFuselage framesAircraft stabilisationFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a sweepforward canard flying wing aerodynamic layout unmanned aerial vehicle, and the unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a vehicle body, main wings, edge strip wings, full-motion canard wings and full-motion vertical tail wings, wherein the main wings, the edge strip wings, the full-motion canard wings and the full-motion vertical tail wings are connected with the vehicle body, and the full-motion canard wings and the full-motion vertical tail wings are arranged at the front end of the vehicle body; the main wings and the edging wings are arranged at the rear end of thefuselage and are of an integrated structure; the flying wing aerodynamic layout, the canard aerodynamic layout and the sweepforward wing aerodynamic layout are fused, so the flying performance of thefixed-wing aircraft is well improved, the contradiction between sweepforward wing aerodynamic divergence and structural quality is solved, the problems that the maximum lift coefficient Clmax of the flying wing layout is too small and the pitching maneuverability is poor are solved, and the problem that a canard layout structure is complex is solved; the maneuvering performance, the loading capacity, the low-speed performance and the like of the canard layout structure are greatly improved, and compared with a conventional aerodynamic layout fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle, the effective load of the canard layout structure is increased by 20%, the take-off and landing distance is shortened by 35%, the maximum flight speed is increased by 5%, and the minimum flight speed is reduced by 30%.
Owner:珠海中科华创科技有限公司
A small unmanned aerial vehicle with winged aerodynamic layout
ActiveCN112937834BReduce speedHeat reducing structuresVertical landing/take-off aircraftsUncrewed vehicleElectric machinery
A small solar unmanned aerial vehicle with wing layout of the present invention: front and rear two-part fuselage; front-end swept wing and rear-end forward-swept wing; twin motors and propellers arranged at the front end of the two-part fuselage; connecting the front and rear wings The bridge arm of the section; two motors and propellers arranged on the outside of the left and right bridge arms; an inverted vertical tail connected to the rear part of the fuselage. A solar panel group is respectively arranged on the upper surfaces of the left swept wing, right swept wing, left forward swept wing, and right forward swept wing to provide energy for the continuous flight of the drone. When taking off, the left and right propellers can be used for vertical take-off and landing, which improves the ease of use and take-off stability of the aircraft; multi-set propeller control improves the maneuverability and reliability of the aircraft; the inverted tail can replace the landing gear As a support, the structure is simplified to save weight; the invention does not have landing gear, and can realize short-distance throwing without runway requirements when taking off, and can realize gliding and landing when landing, and can also realize vertical take-off and landing and hovering in the air.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Deep-sea mineral deposit collection system
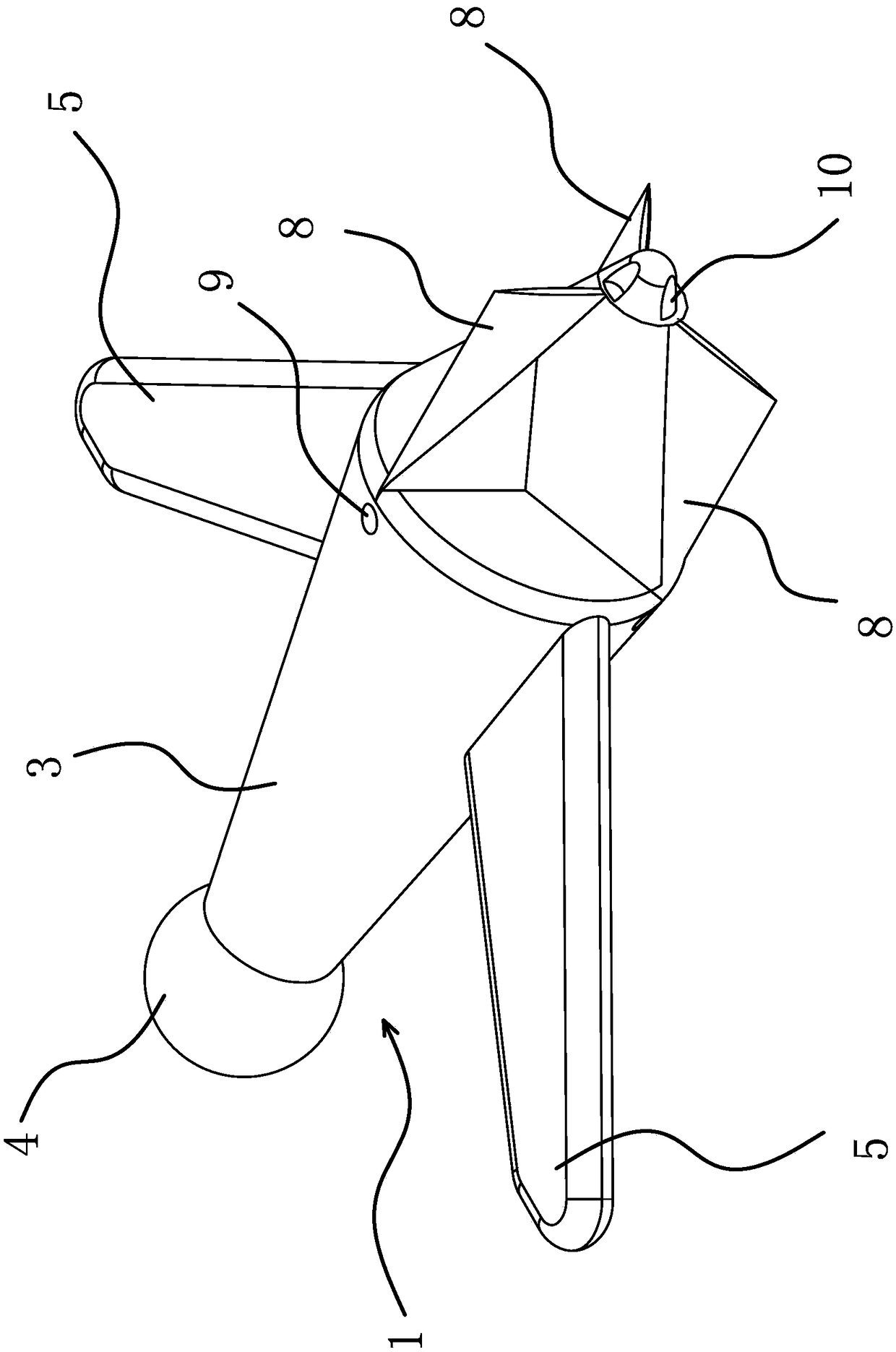
ActiveCN109162718AReduce consumptionReduce collection costsMineral miningCollection systemManganese nodule
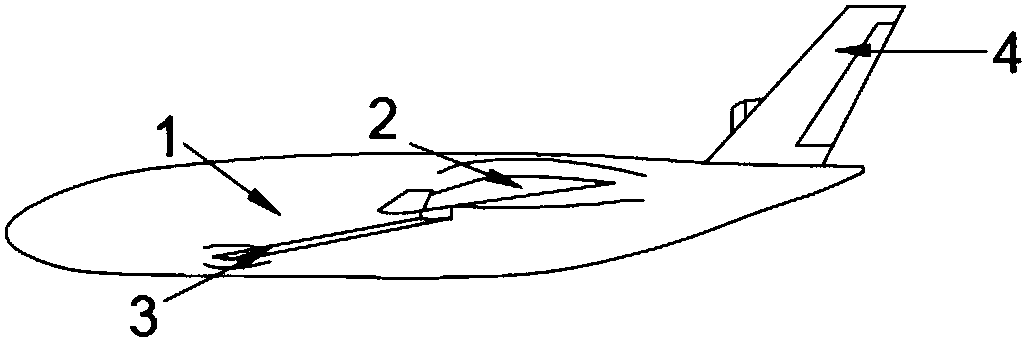
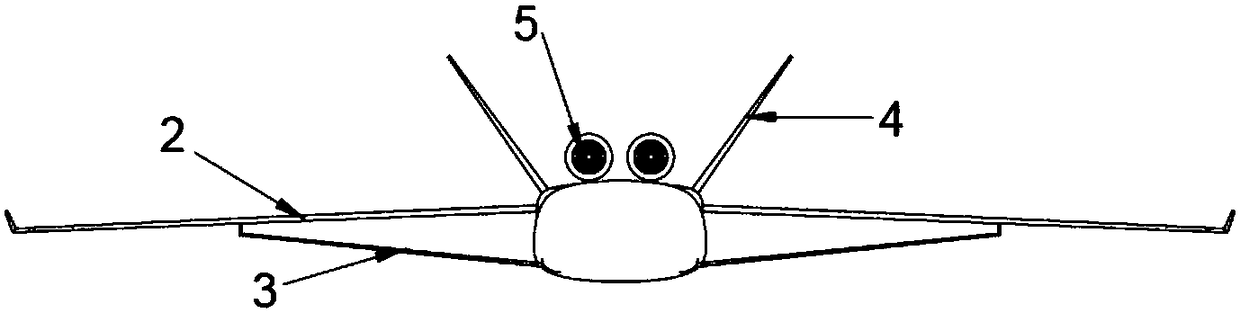
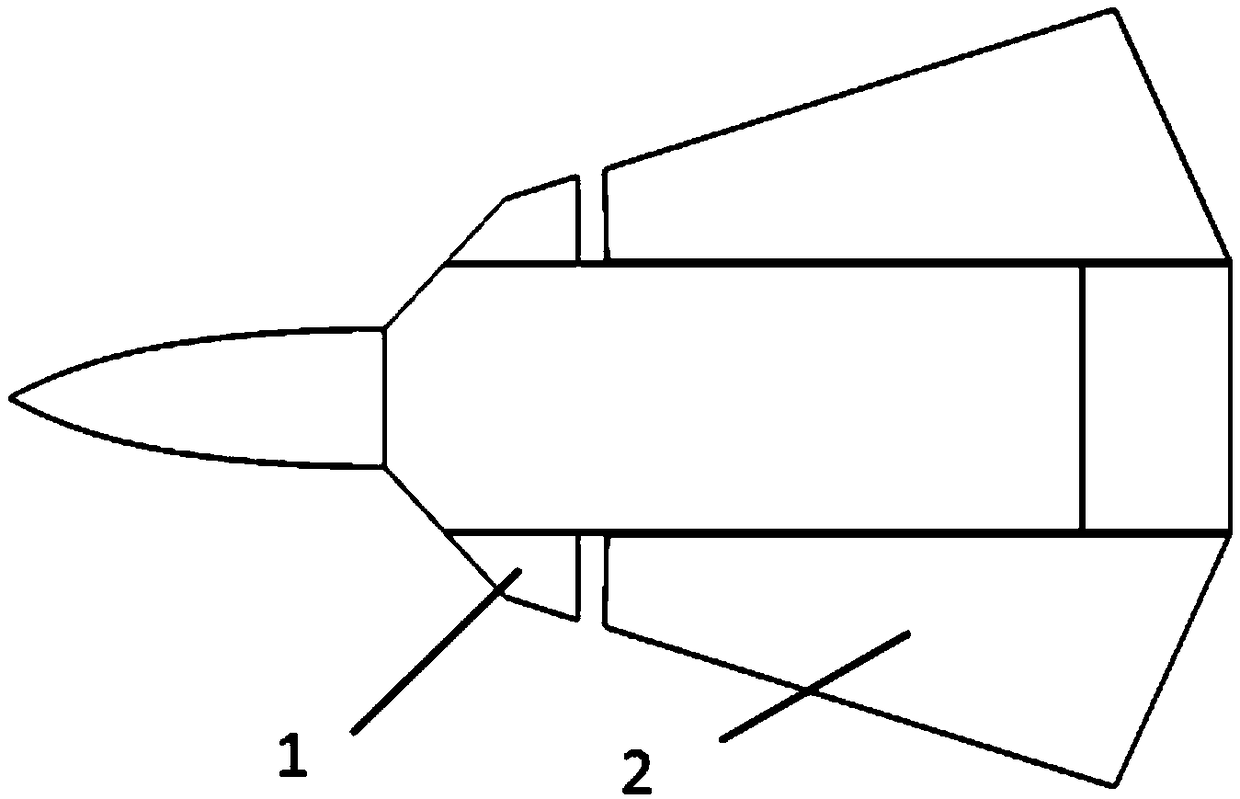
The invention belongs to the technical field of machinery and relates to a deep-sea mineral deposit collection system. The problem that the existing manganese nodule collector has high collection costand low efficiency is solved. The collection system comprises an underwater glider and a collecting shovel; the underwater glider comprises a machine body; the head of the machine body is provided with a spherical vortex generator; forward-swept wings are arranged on the two sides of the middle part of the machine body; a storage cavity for storing manganese nodule is formed in the machine body;the collecting shovel is movably arranged at the bottom of the machine body; and a driving source capable of driving the collecting shovel to open and close the storage cavity is arranged on the machine body. The deep-sea mineral deposit collection system can effectively reduce the collection cost and can improve the collection efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com