Patents
Literature
418 results about "Swashplate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
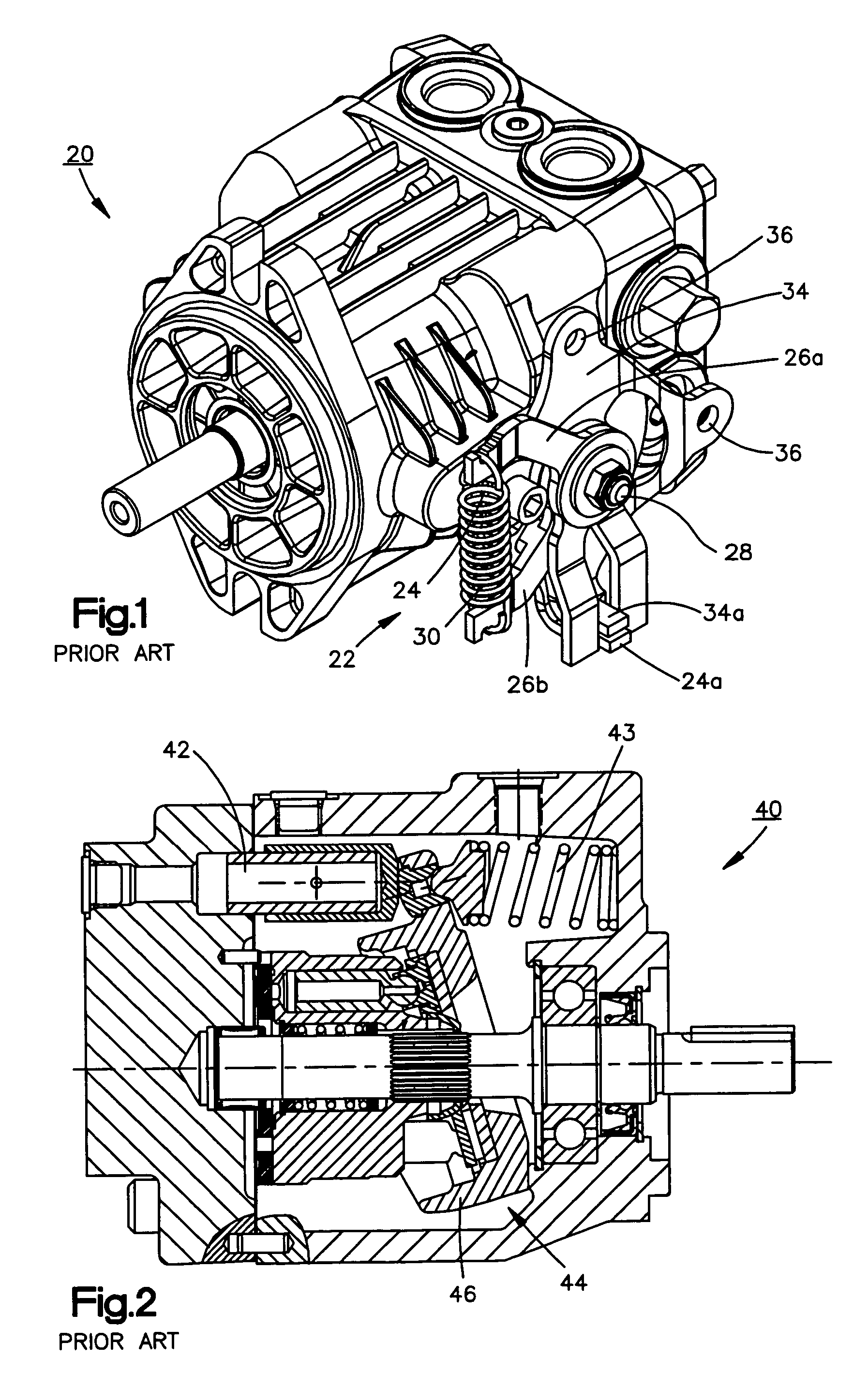
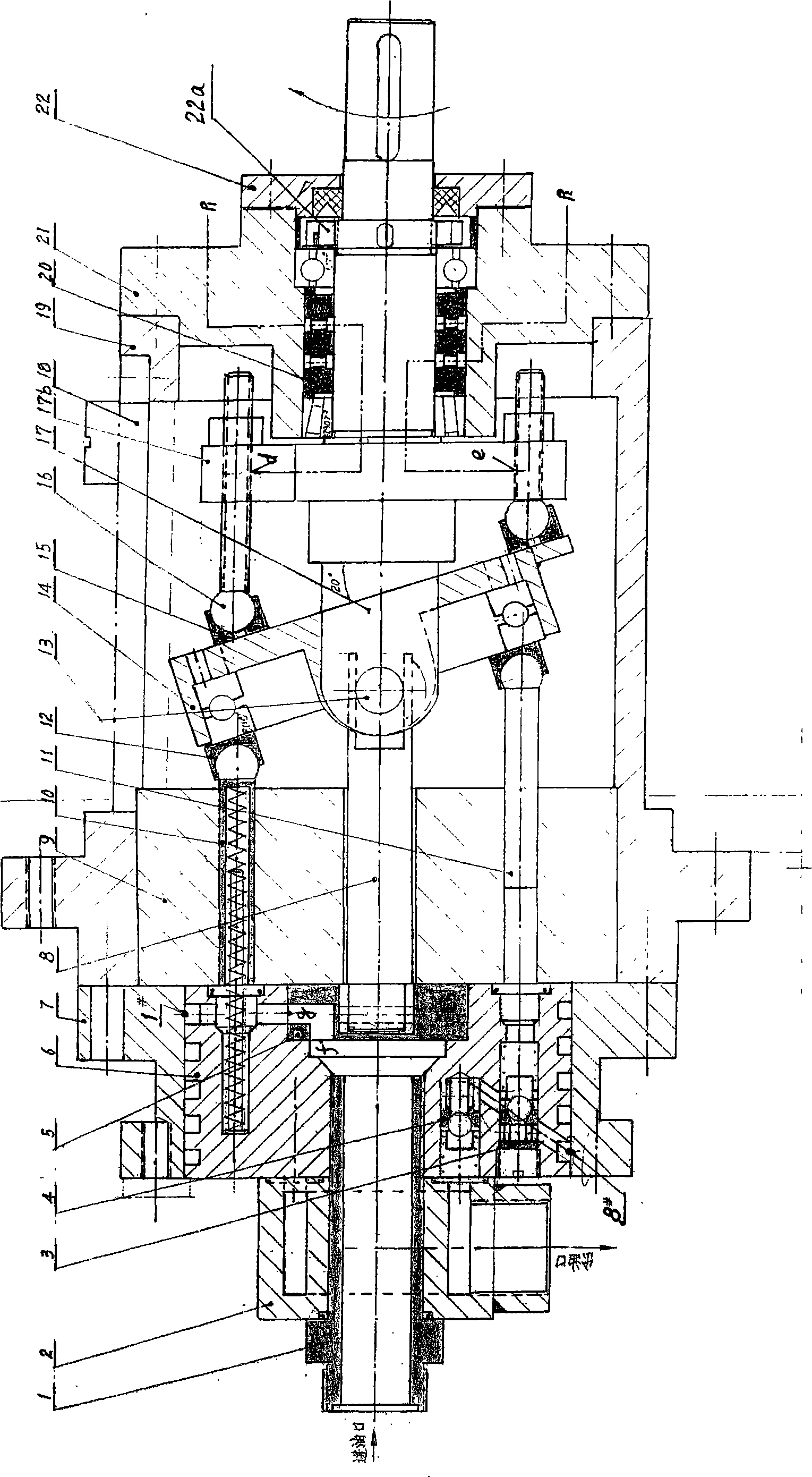
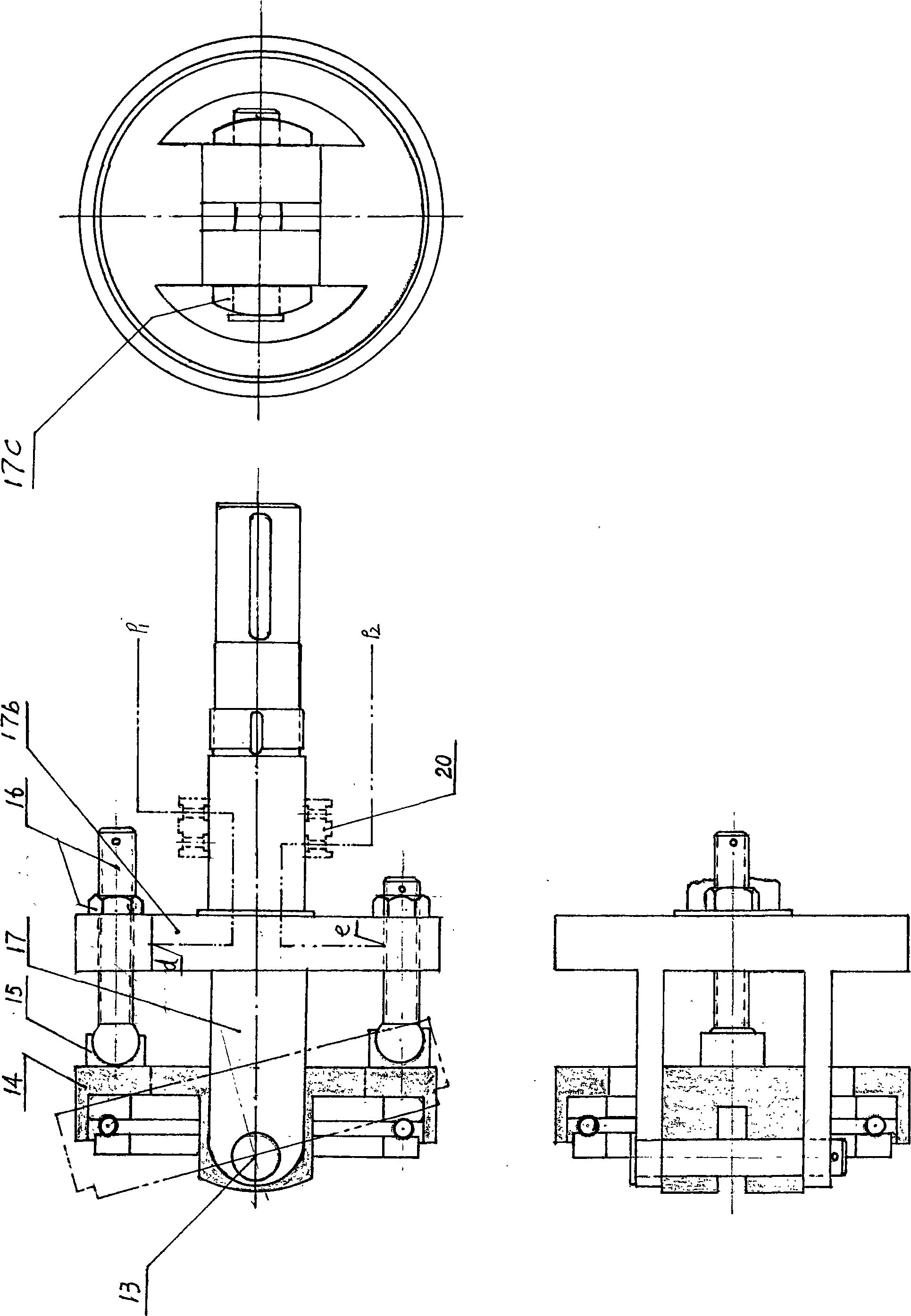
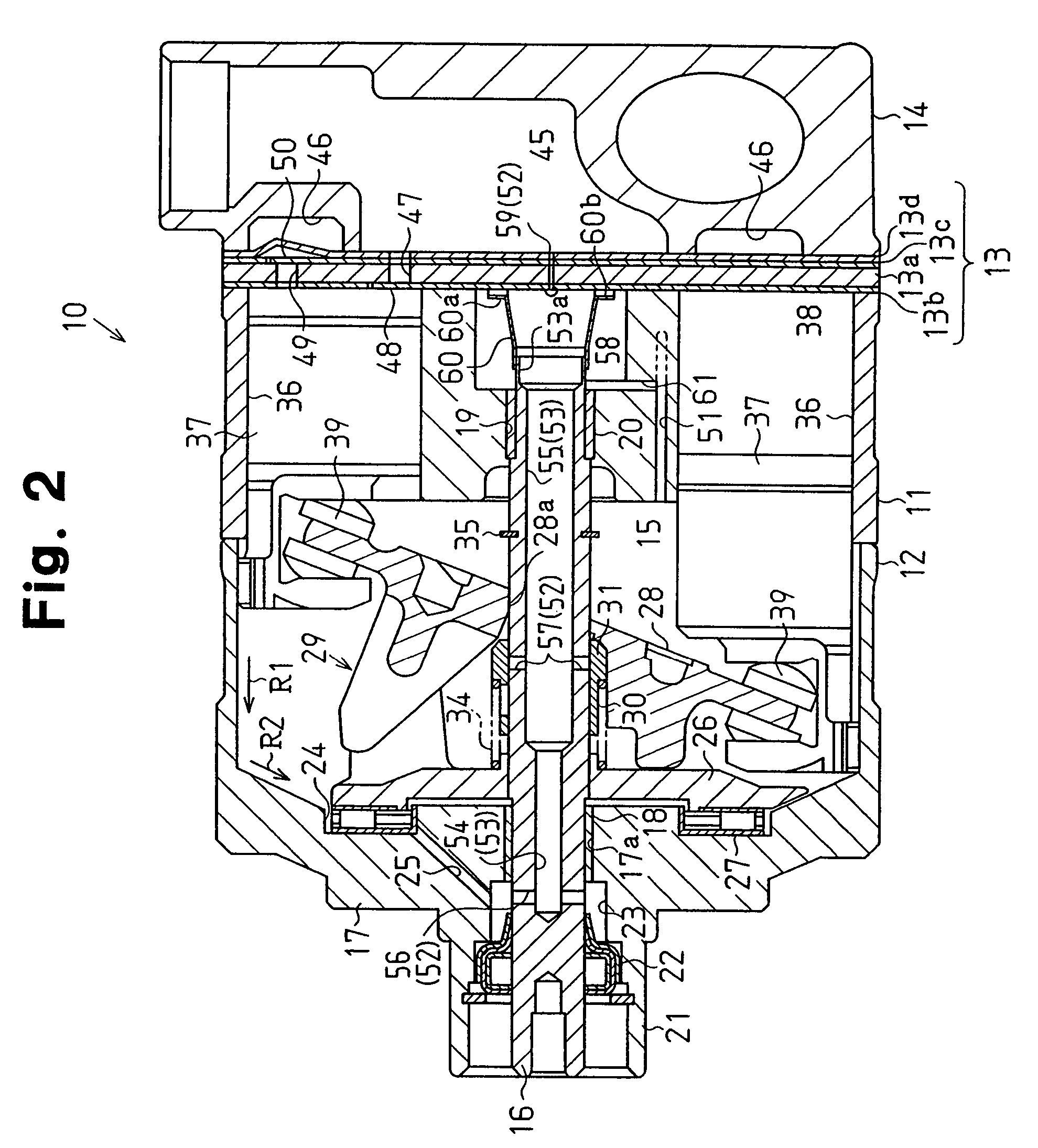
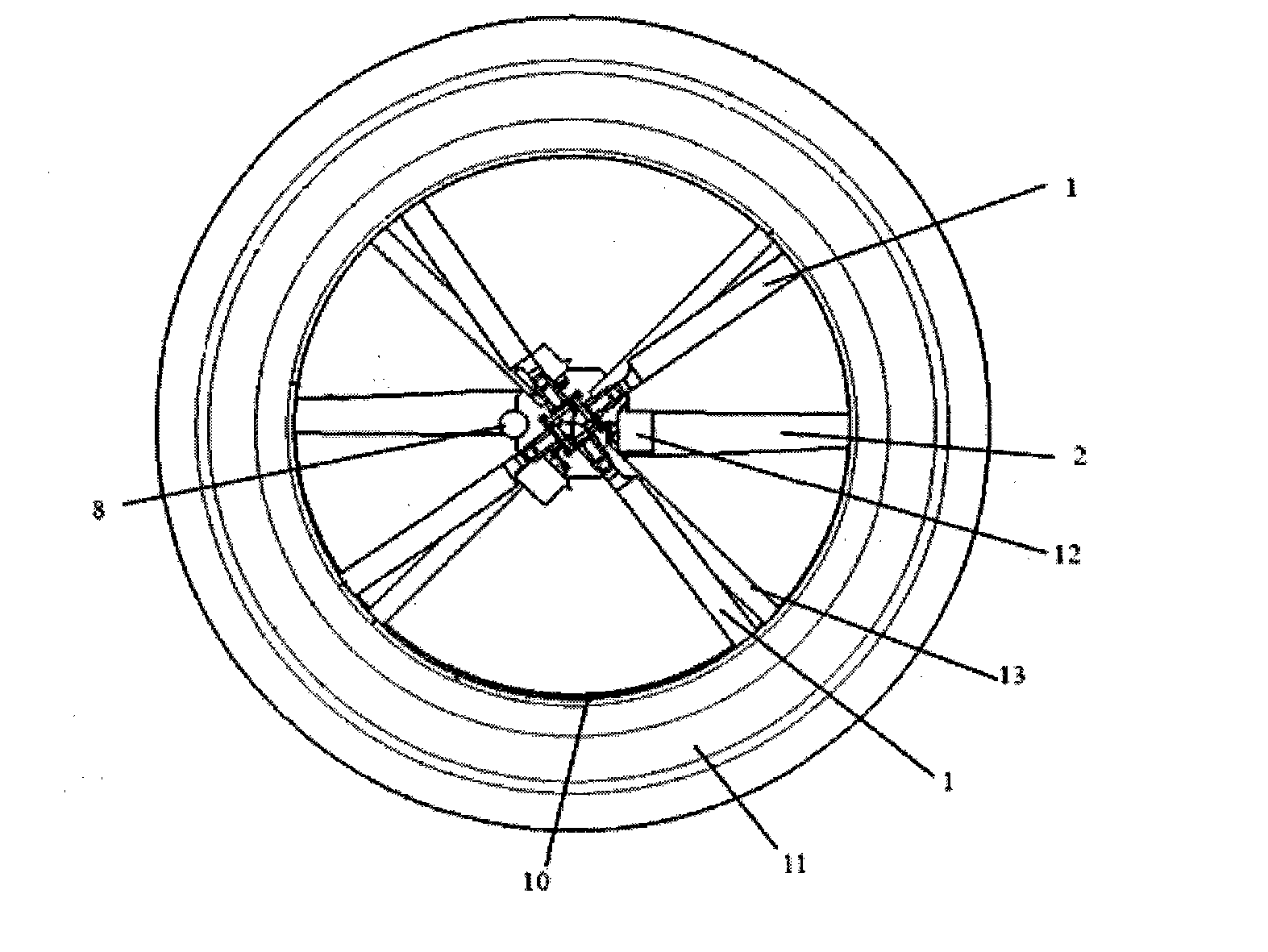
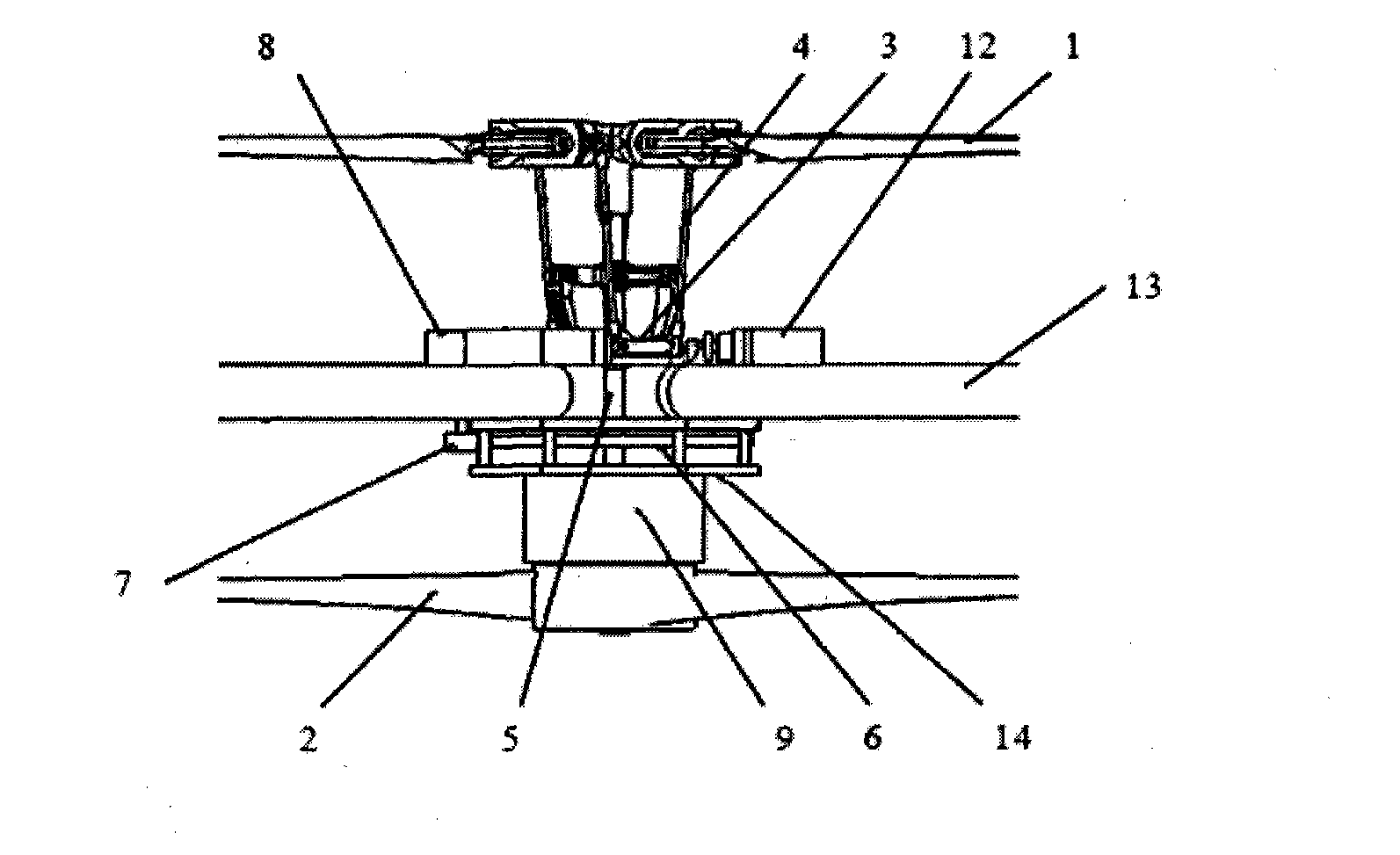
A swashplate (also known as slant disk), invented by Anthony George Maldon Michell in 1917, is a device used in mechanical engineering to translate the motion of a rotating shaft into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The working principles is similar to crankshaft, Scotch yoke, or wobble/nutator/Z-crank drives, in engine designs. It was originally invented to replace a crankshaft, and is one of the most popular concepts used in crankless engines.
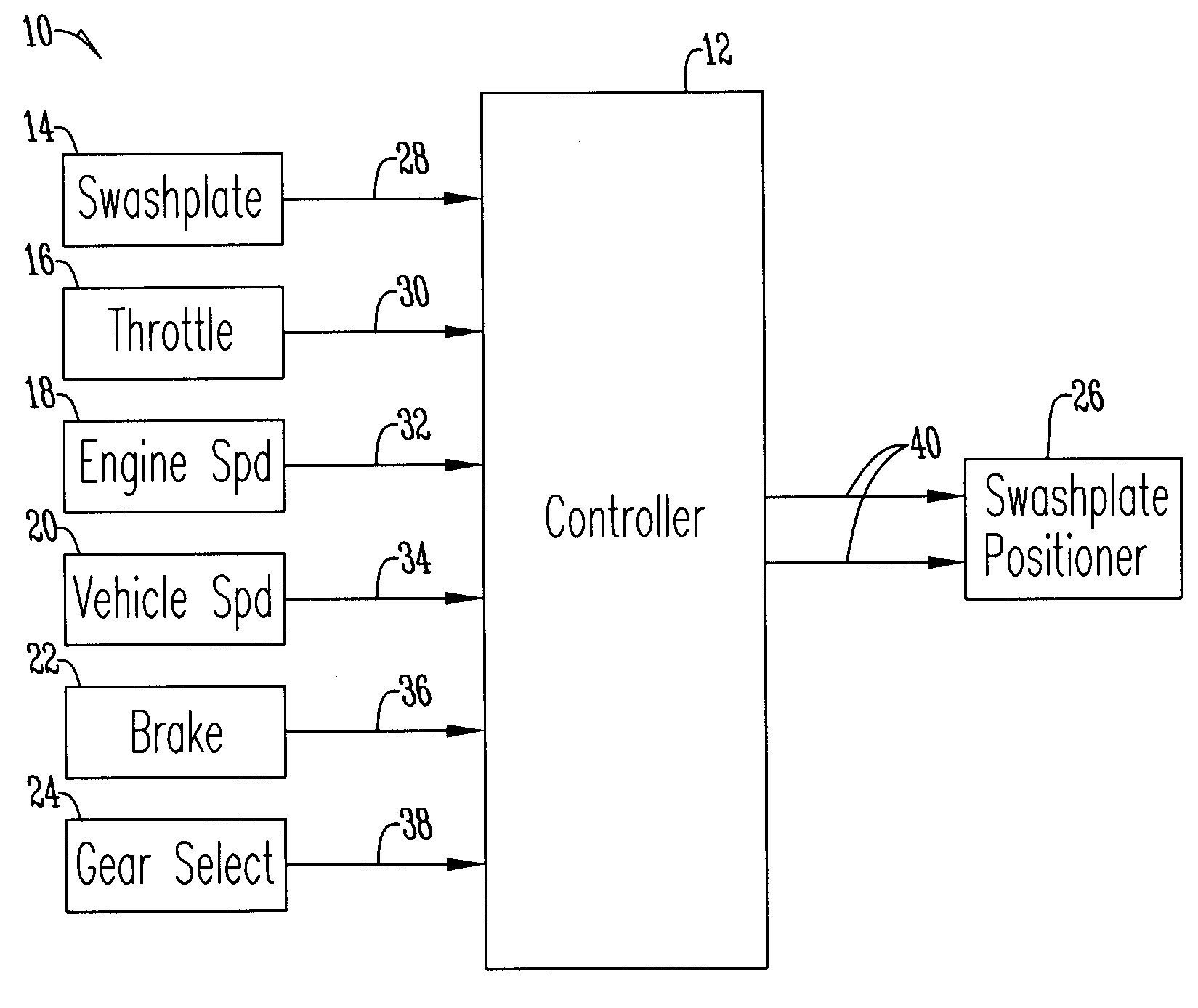
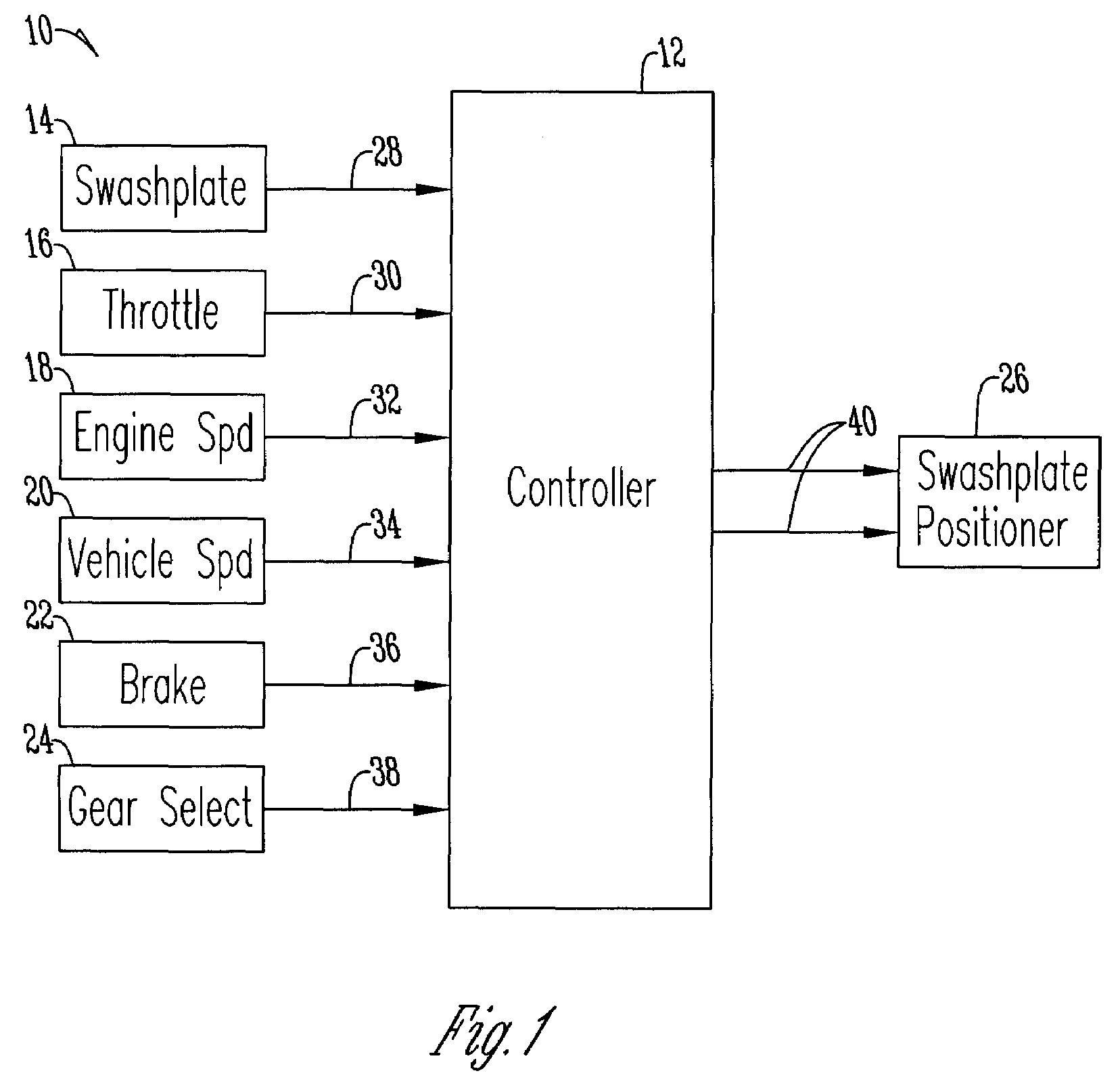
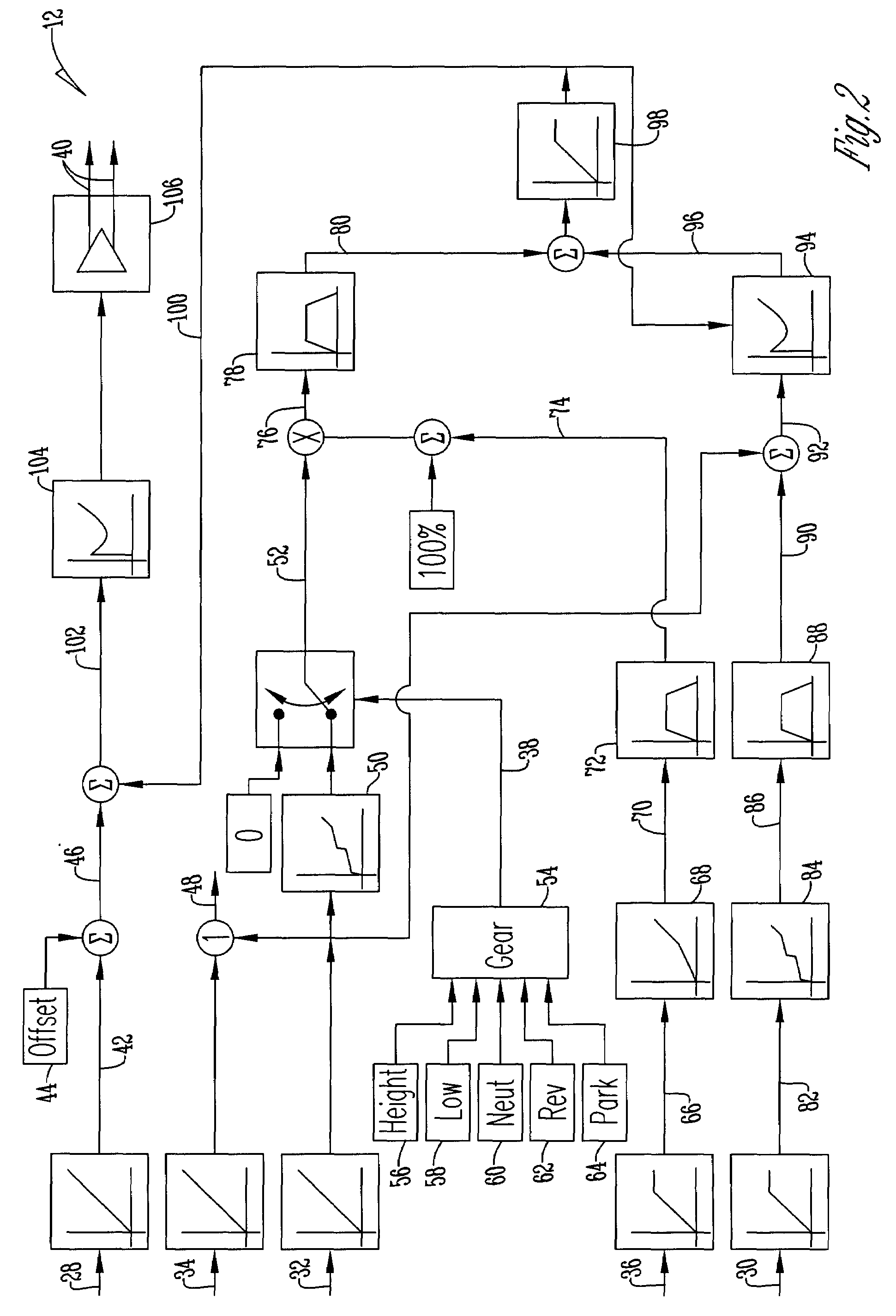
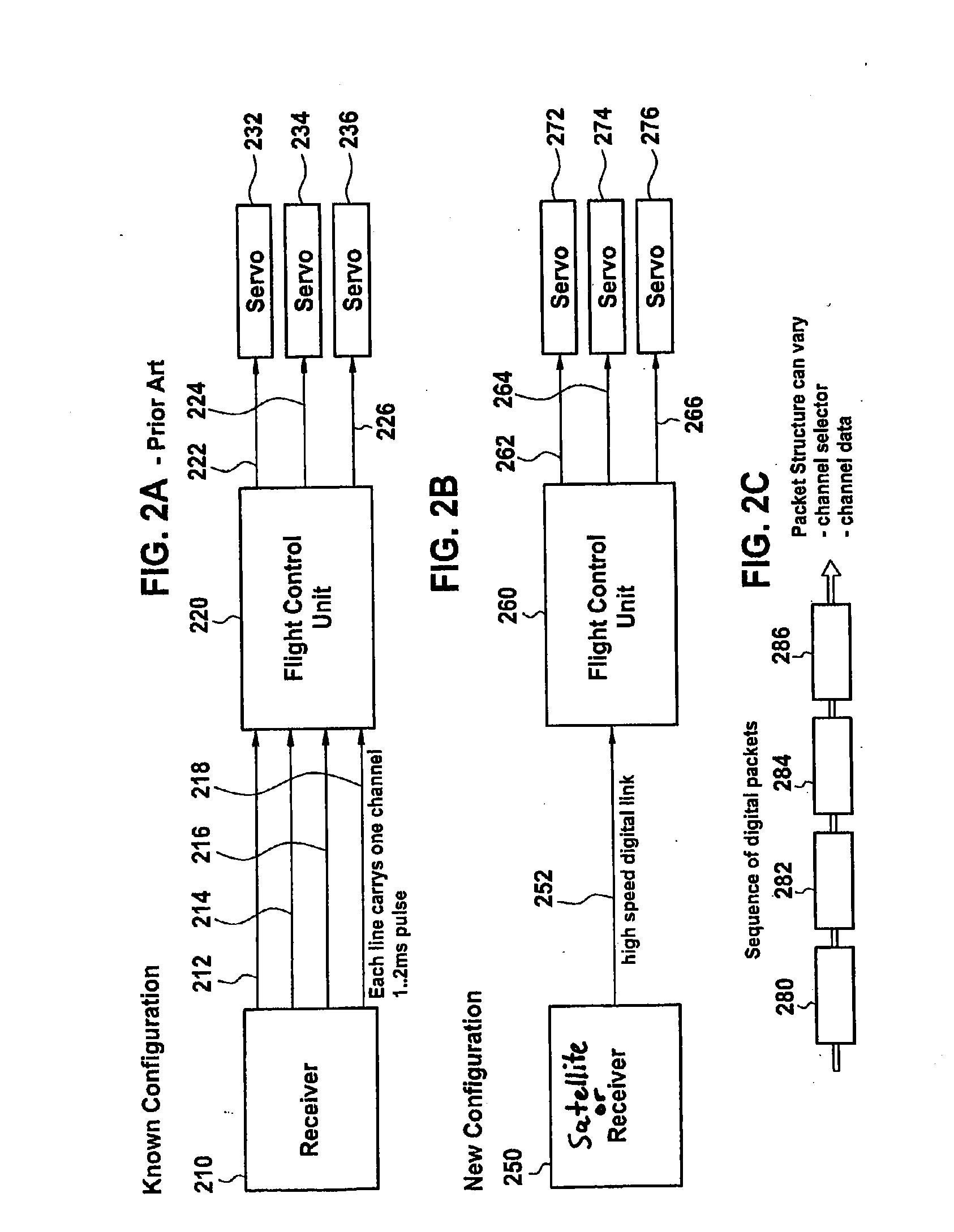
Engine speed control for a low power hydromechanical transmission
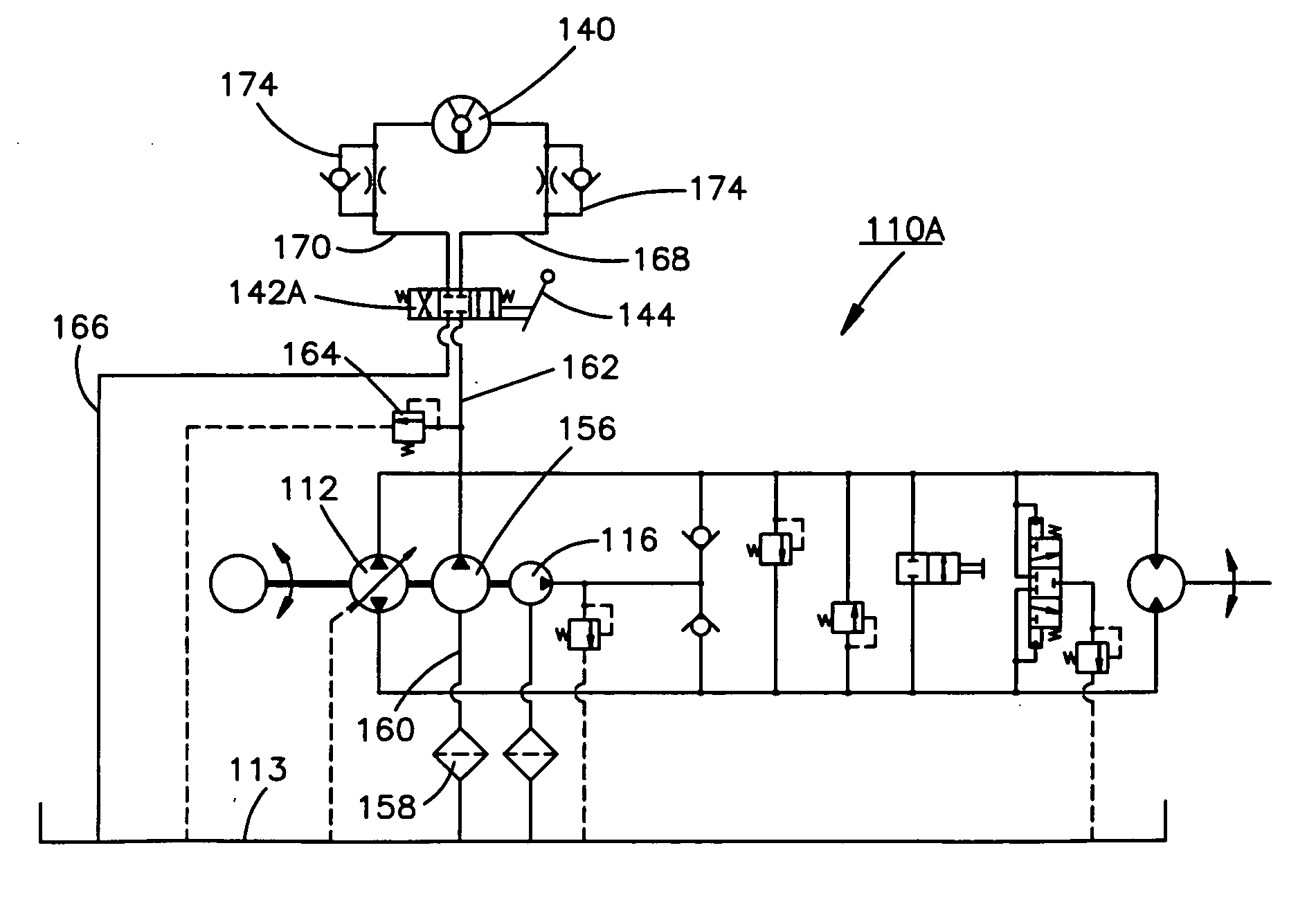
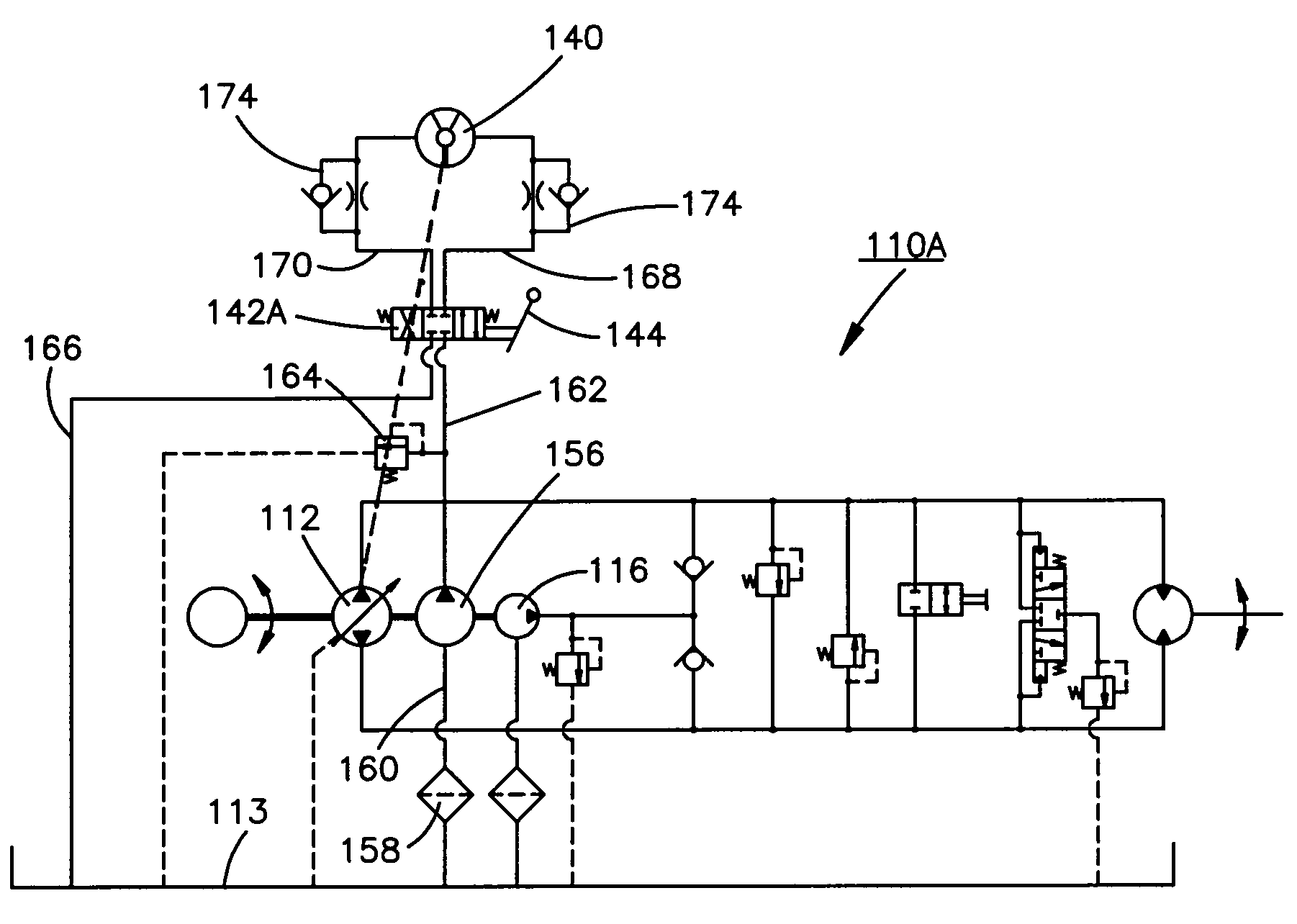
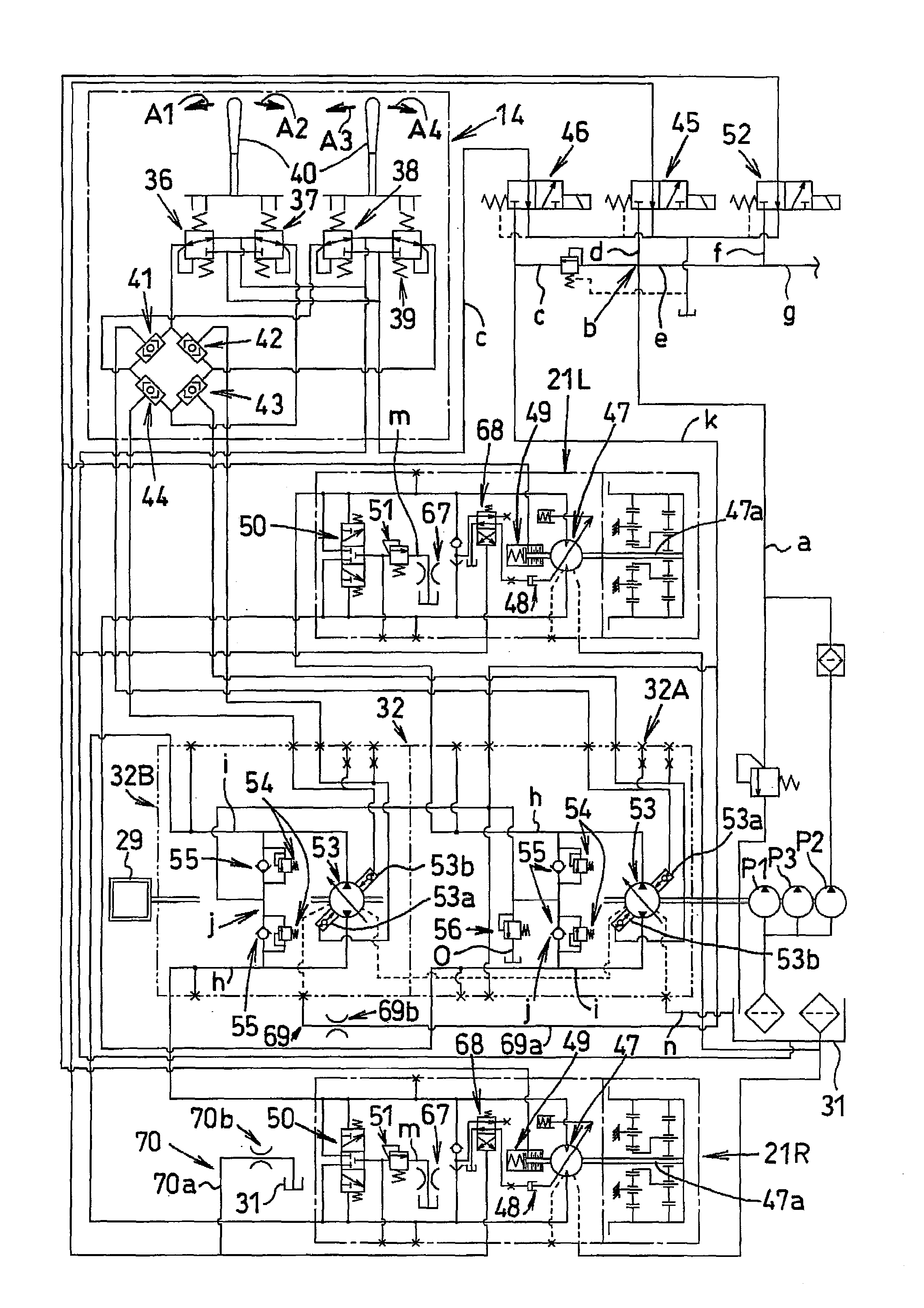
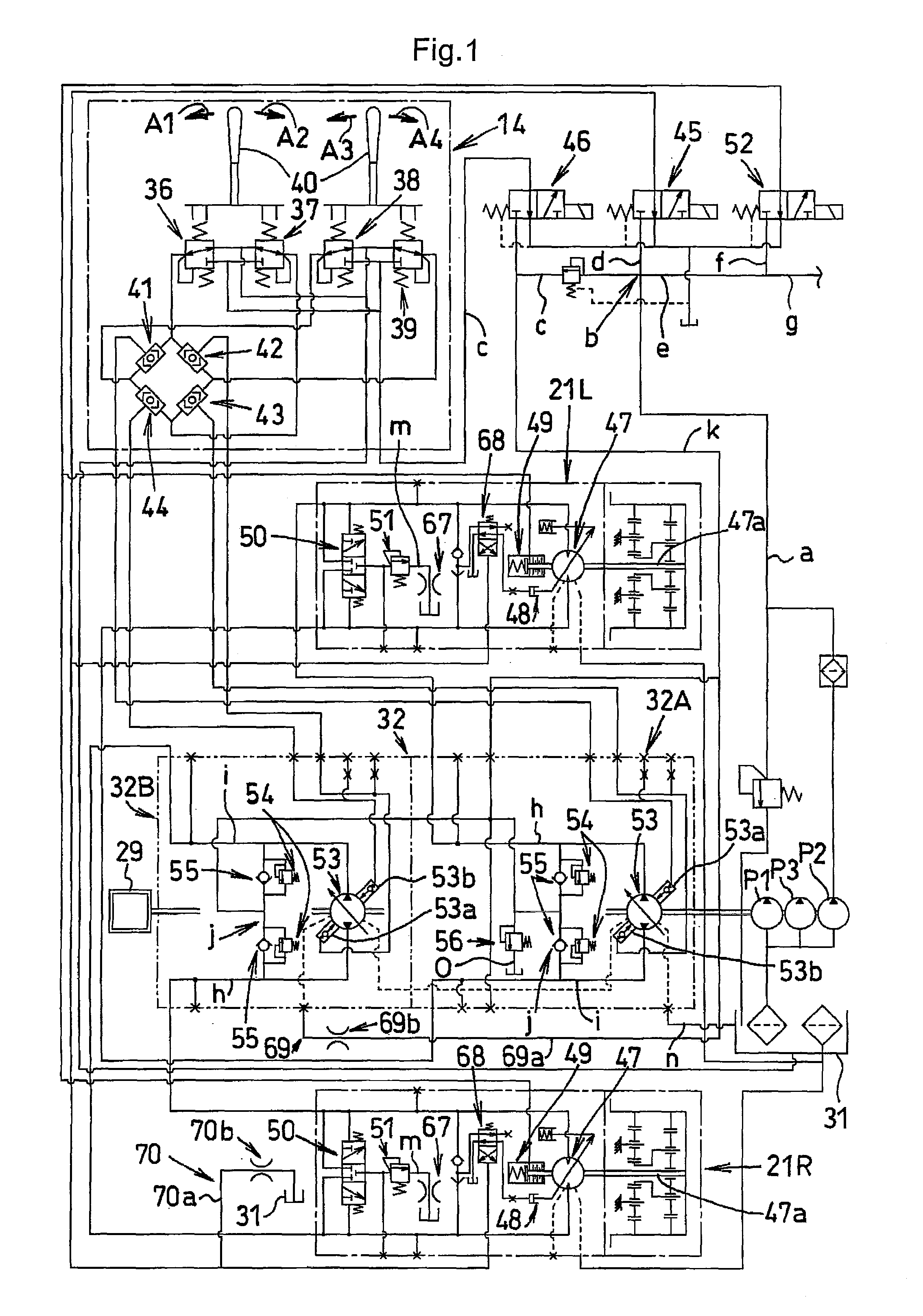
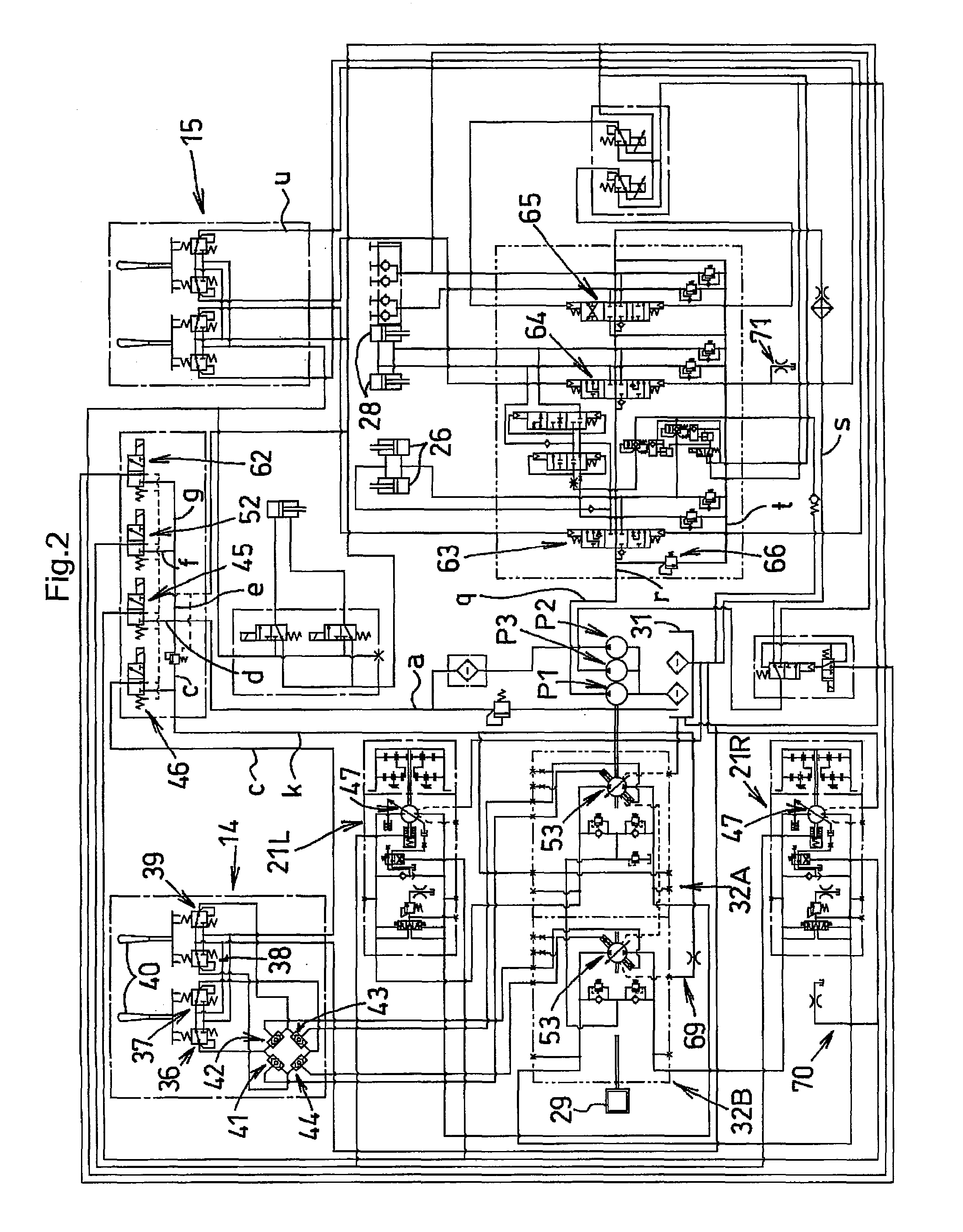
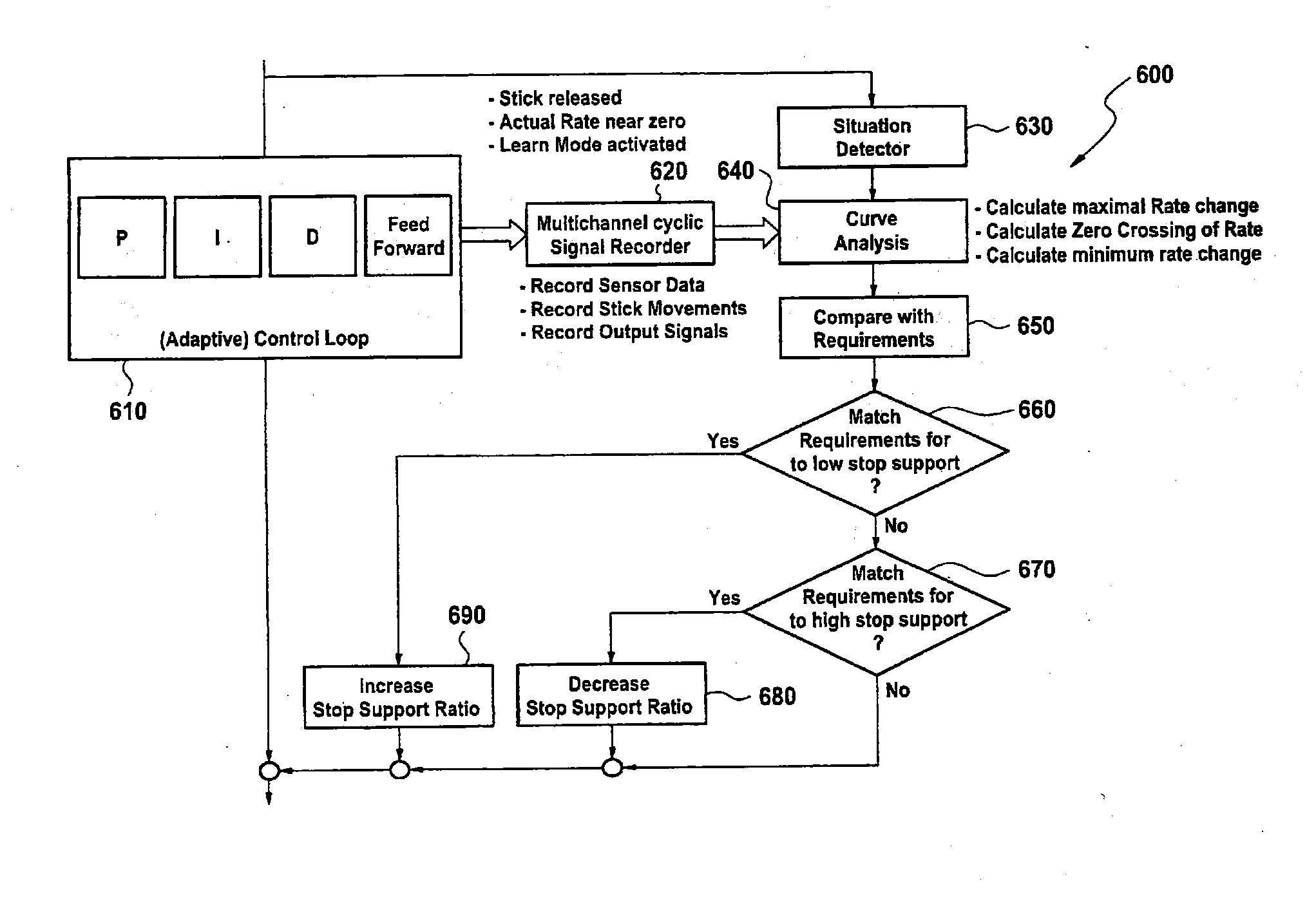
A method of operating a transmission of a vehicle. The method includes determining an open loop ratio percentage from an engine RPM input signal and a brake input signal using a first algorithm. Determining a closed loop ratio percentage from the engine RPM input signal, a vehicle RPM input signal and a throttle input signal using a second algorithm. Summing the open loop percentage and closed loop ratio percentage to calculate a ratio command percentage that is used to sum with a swashplate input to actuate a swashplate positioner and operate the transmission.
Owner:DANFOSS POWER SOLUTIONS INC
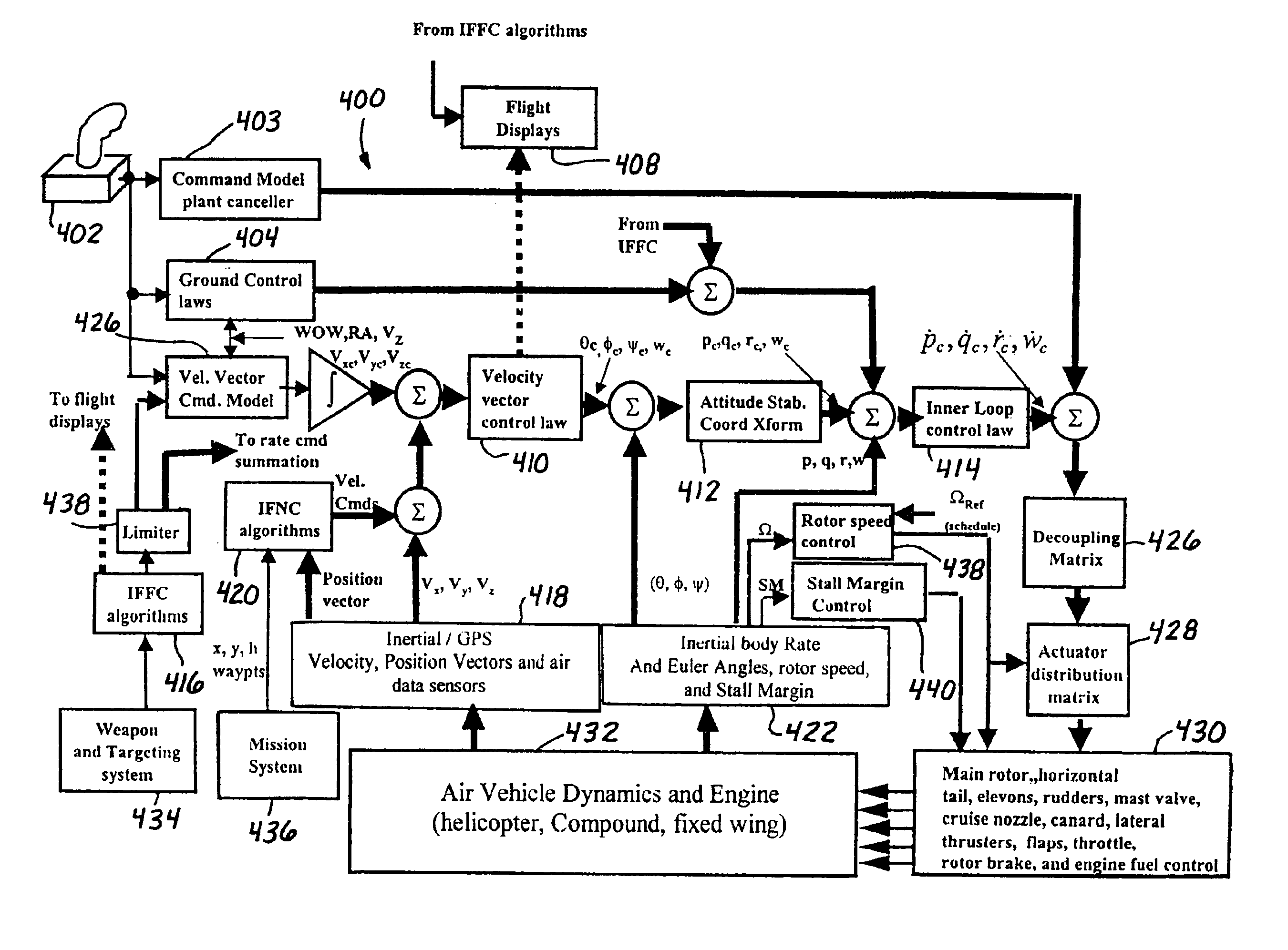
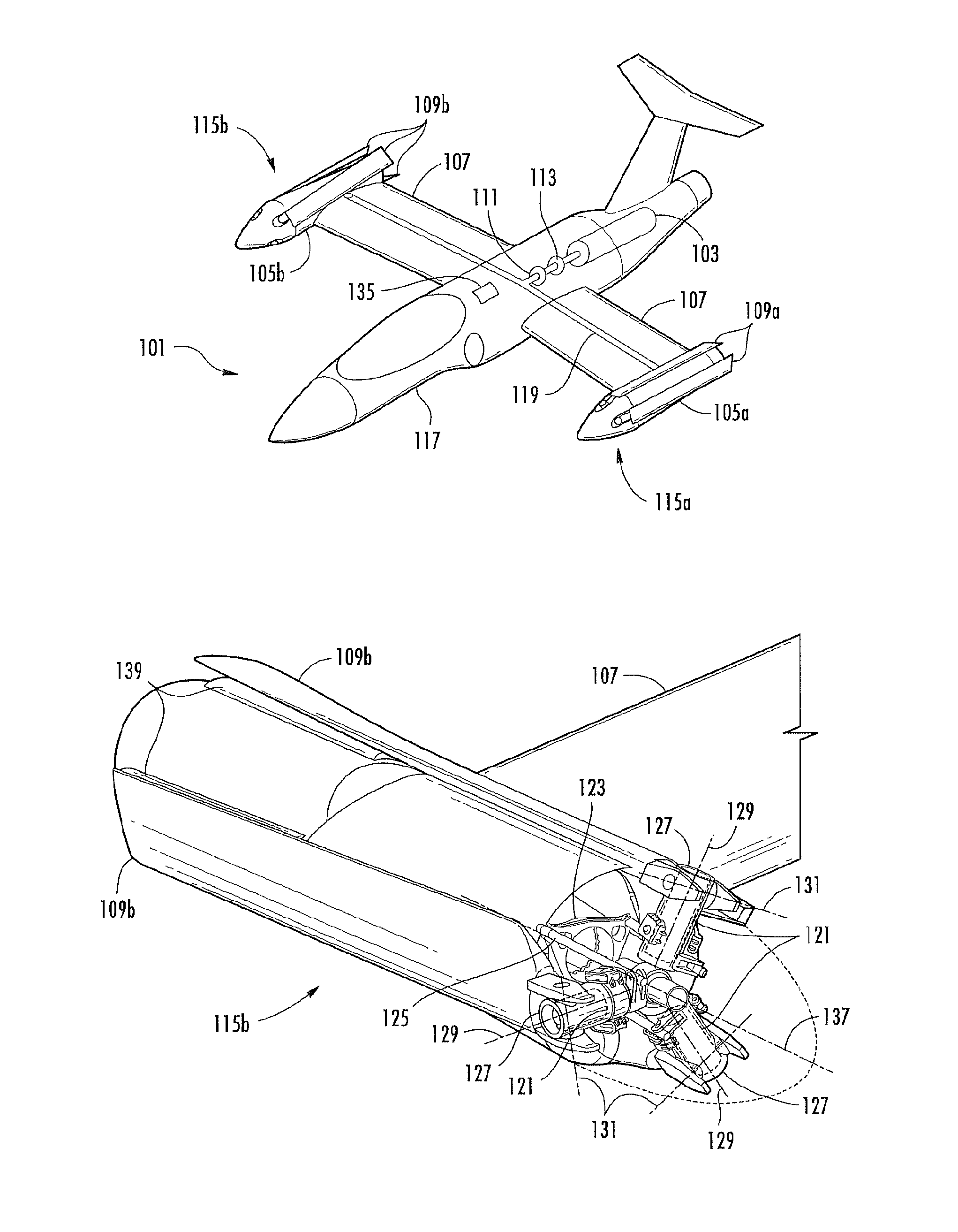
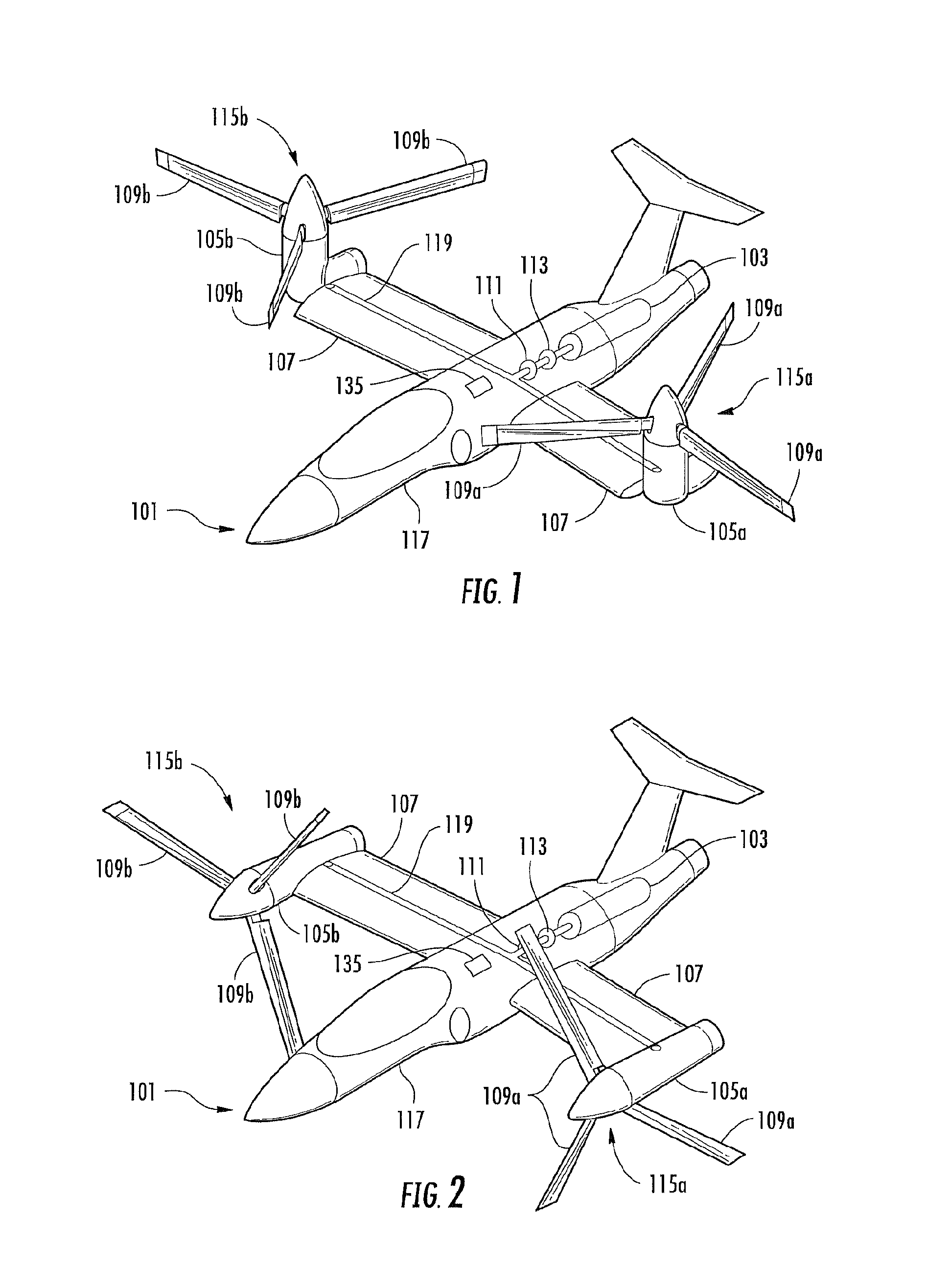
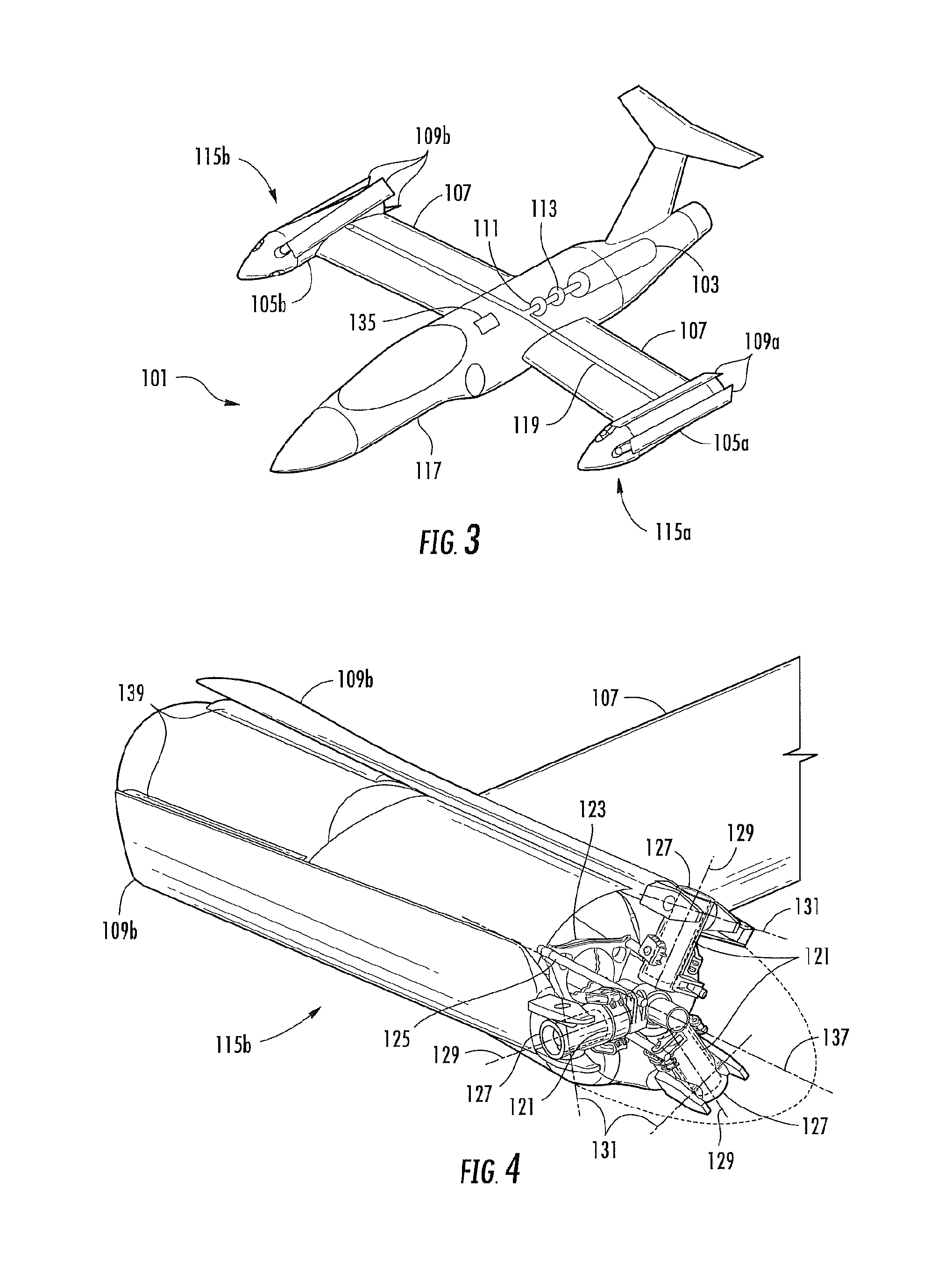
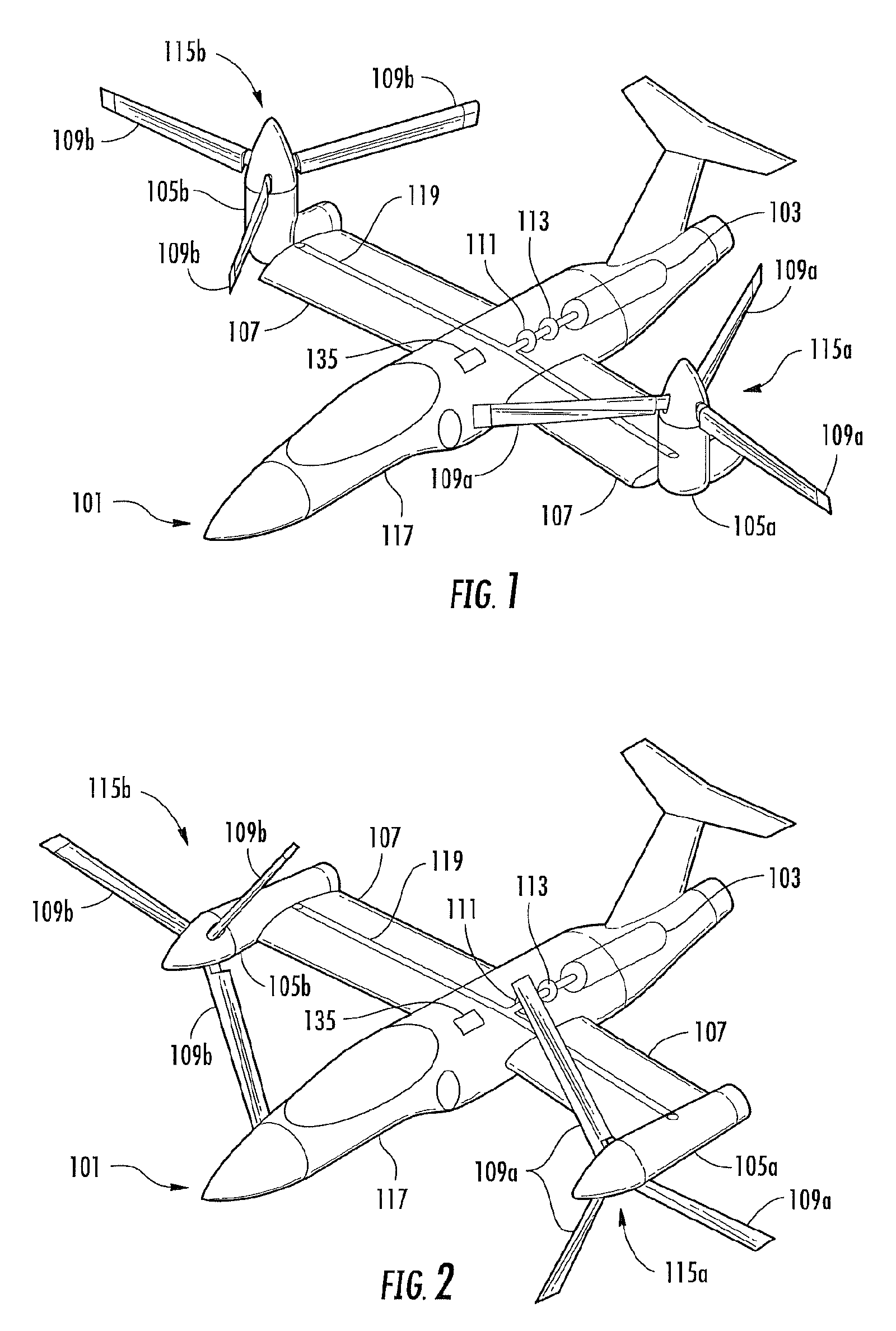
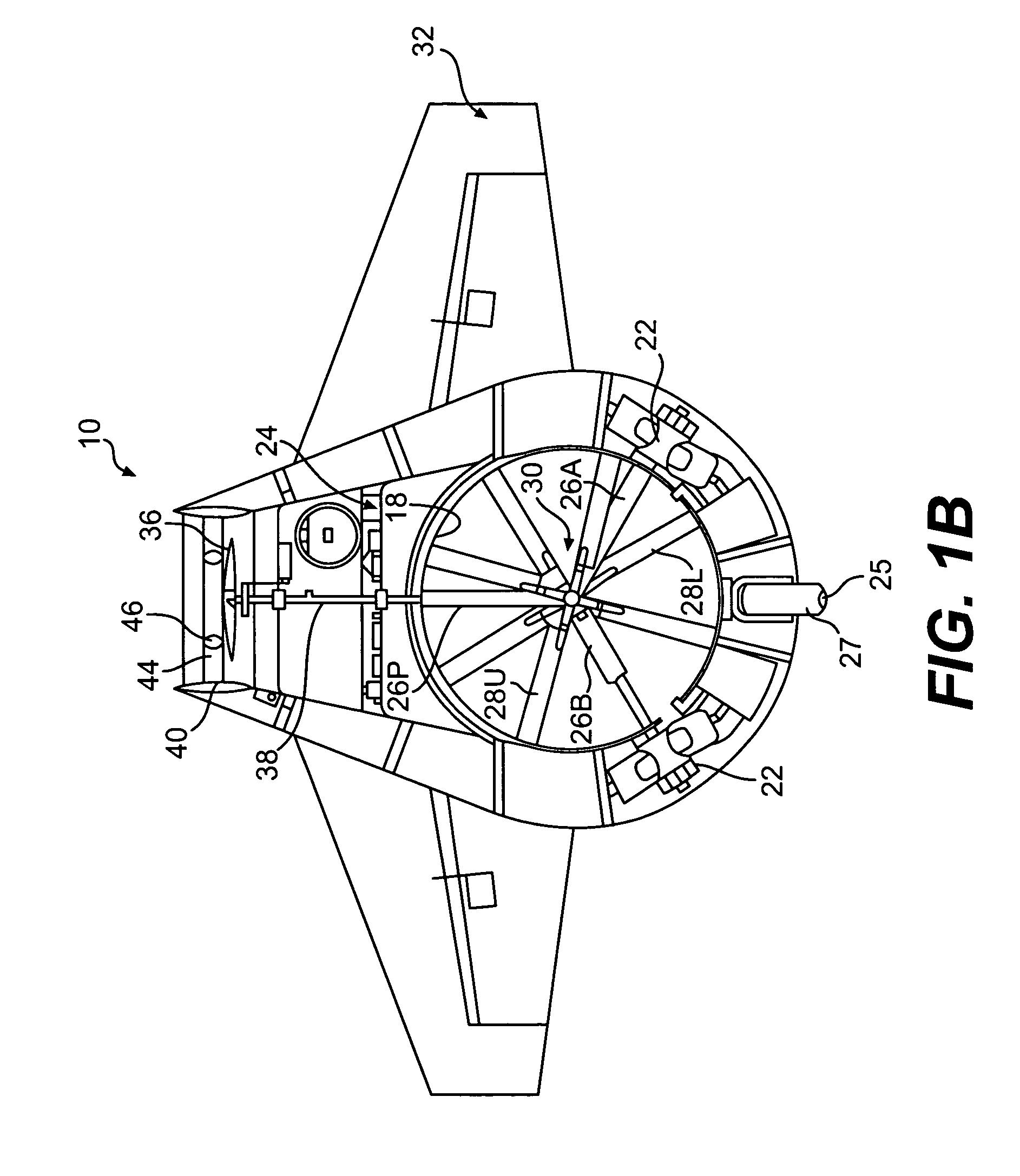
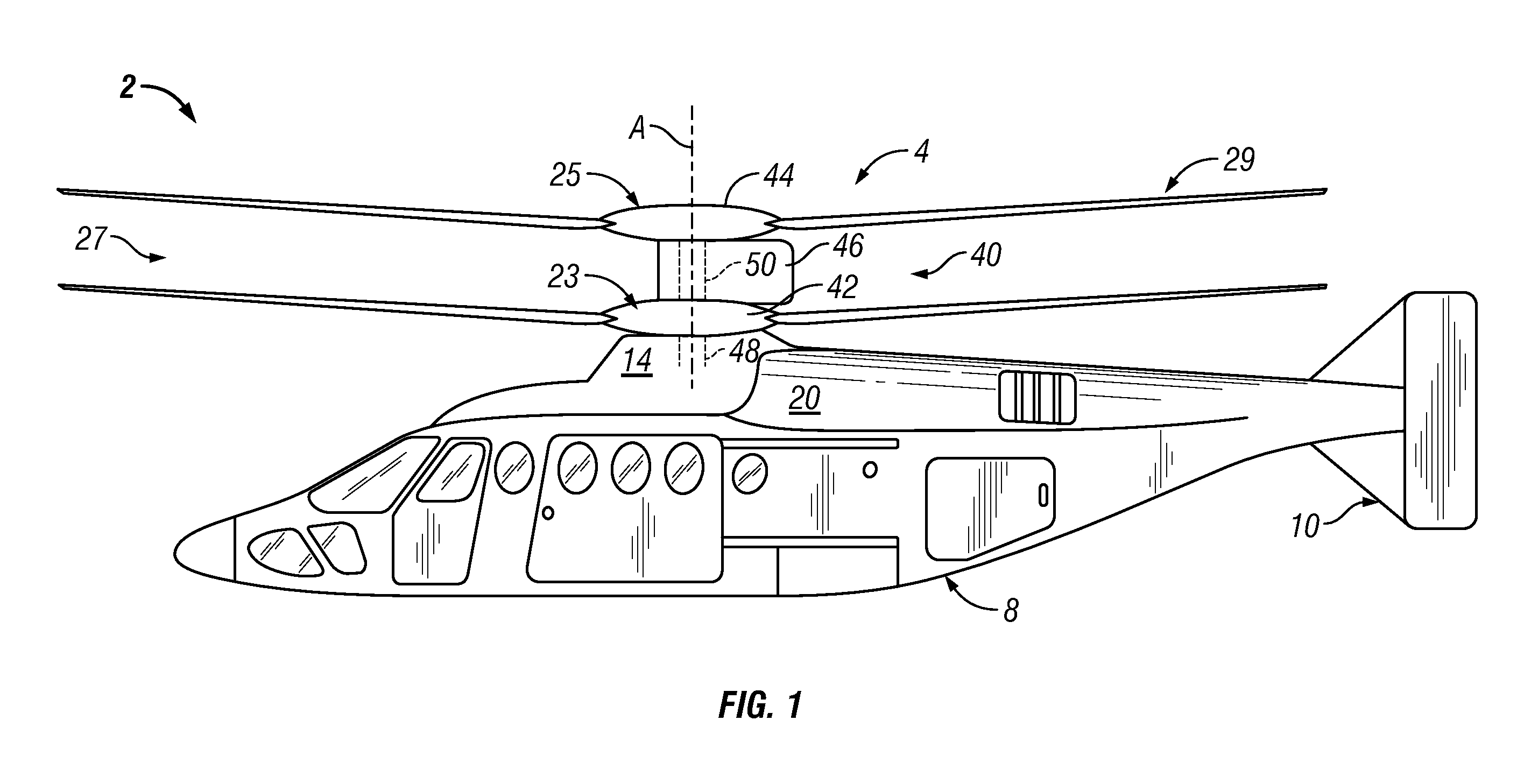
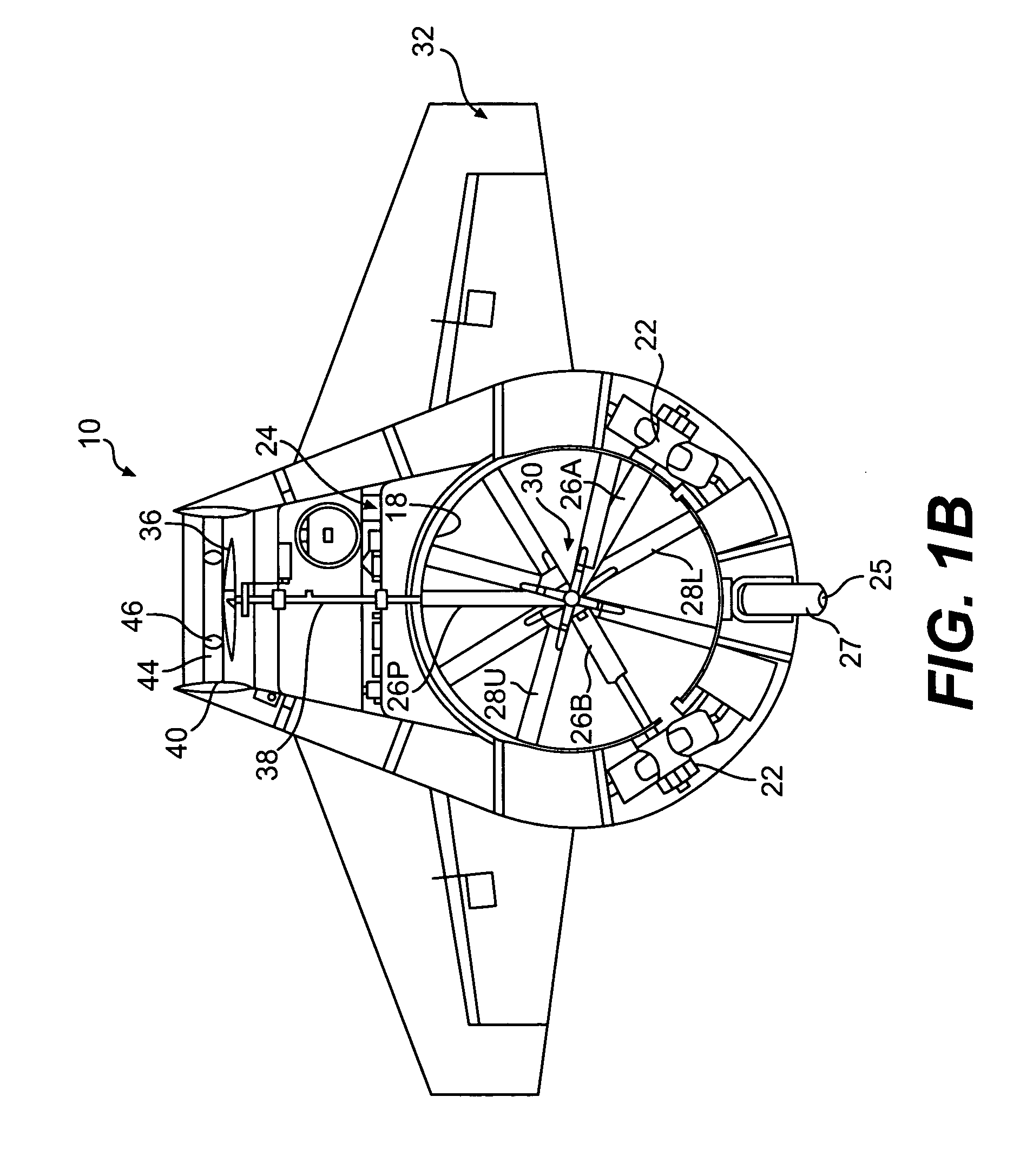
Enhanced flight control systems and methods for a jet powered tri-mode aircraft
ActiveUS6885917B2Easy to operateIncreases flight envelopeAircraft navigation controlDigital data processing detailsForward speedFixed wing
A method of stabilizing a jet-powered tri-mode aircraft as the aircraft travels in a helicopter mode, a compound mode, and a fixed-wing mode is disclosed. The method includes receiving a plurality of velocity vector component values and velocity vector commands derived from either (1) a number of pilot operated controllers or (2) a commanded array of waypoints, which are used for fully automated flights, and a rotor speed reference value, which is decreased with increasing forward speed to unload the rotor, thereby permitting conditions for stopping the rotor in flight. Stabilization of the commanded velocity vector is achieved in all modes of flight using blended combinations of rotor swashplate controls and aerodynamic controls such as elevons, canards, rudders, and a horizontal tail. Stabilization to the commanded velocity vector includes a plurality of control constraints applied to the pilot stick controllers that prevent penetration of envelope limits.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and Apparatus for Flight Control of Tiltrotor Aircraft
ActiveUS20070221780A1Short response timeImprove accuracyVehicle position/course/altitude controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsAutomatic controlNacelle
A method and apparatus provide for automatically controlling the flight of a tiltrotor aircraft while the aircraft is in flight that is at least partially rotor-borne. The method and apparatus provide for automatically tilting nacelles in response to a longitudinal-velocity control signal so as to produce a longitudinal thrust-vector component for controlling longitudinal velocity of the aircraft. Simultaneously, cyclic swashplate controls are automatically actuated so as to maintain the fuselage in a desired pitch attitude. The method and apparatus also provide for automatically actuating the cyclic swashplate controls for each rotor in response to a lateral-velocity control signal so as to produce a lateral thrust-vector component for controlling lateral velocity of the aircraft. Simultaneously, collective swashplate controls for each rotor are automatically actuated so as to maintain the fuselage in a desired roll attitude. The method and apparatus provide for yaw control through differential longitudinal thrust produced by tilting the nacelles.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
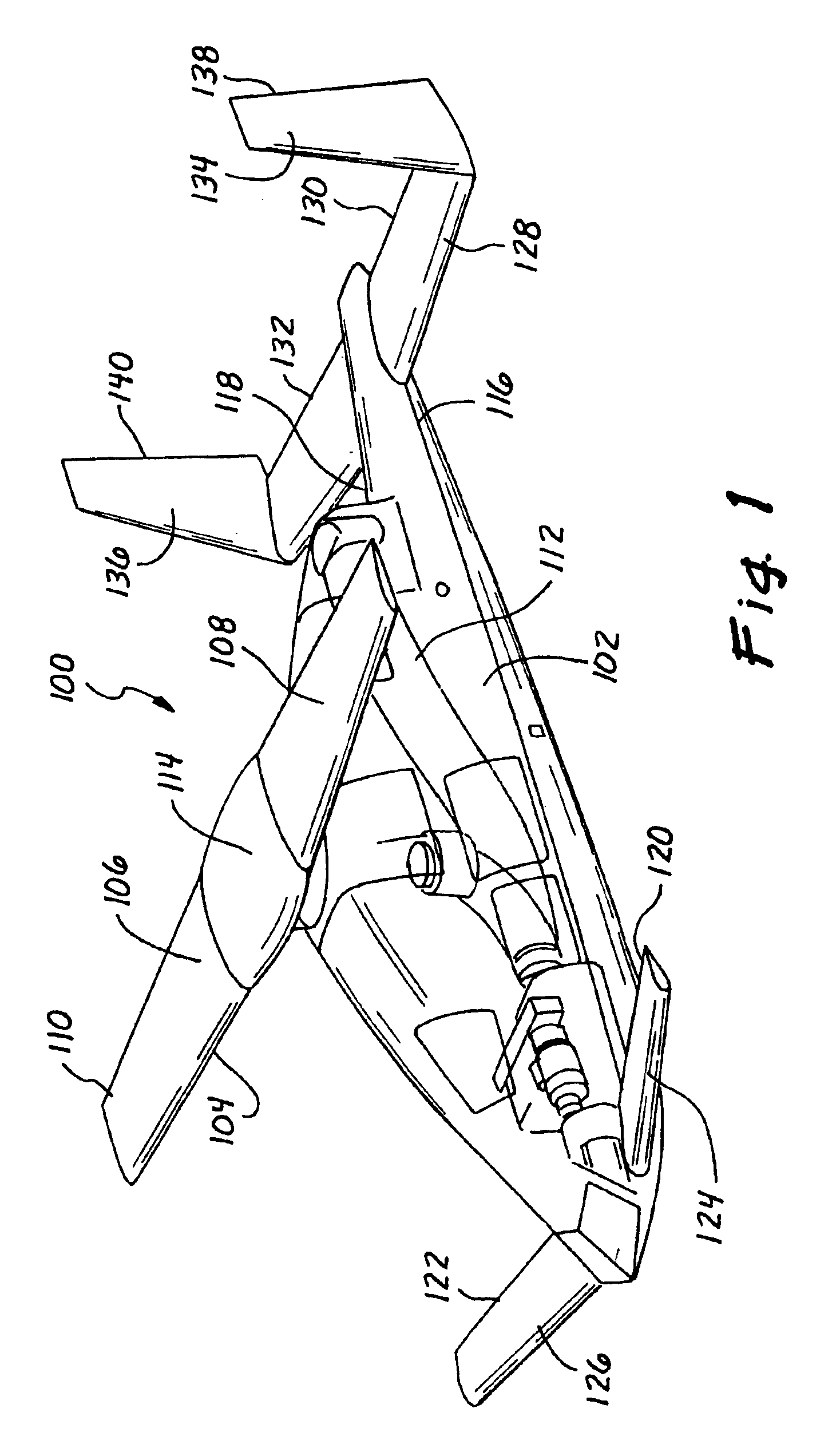
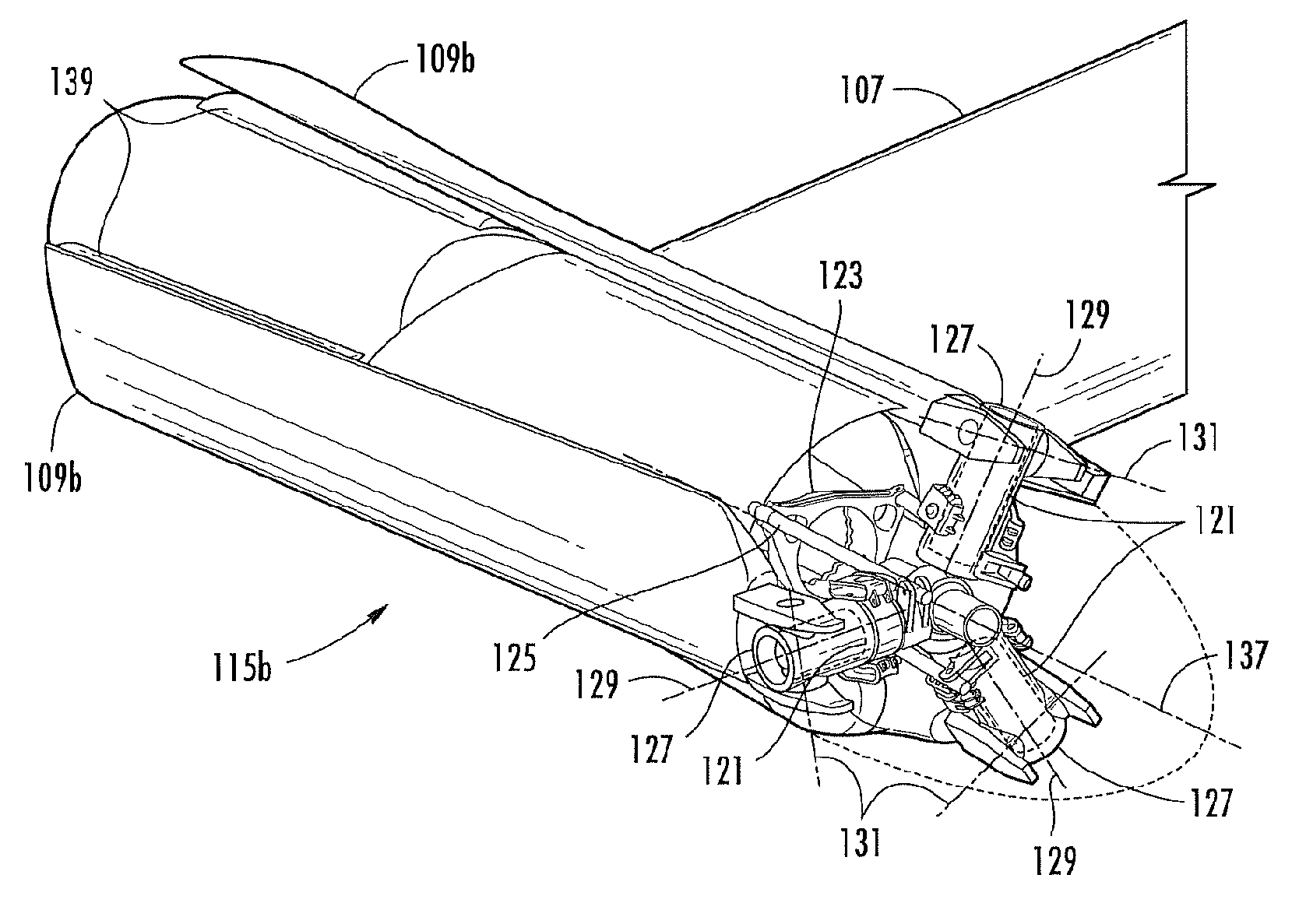
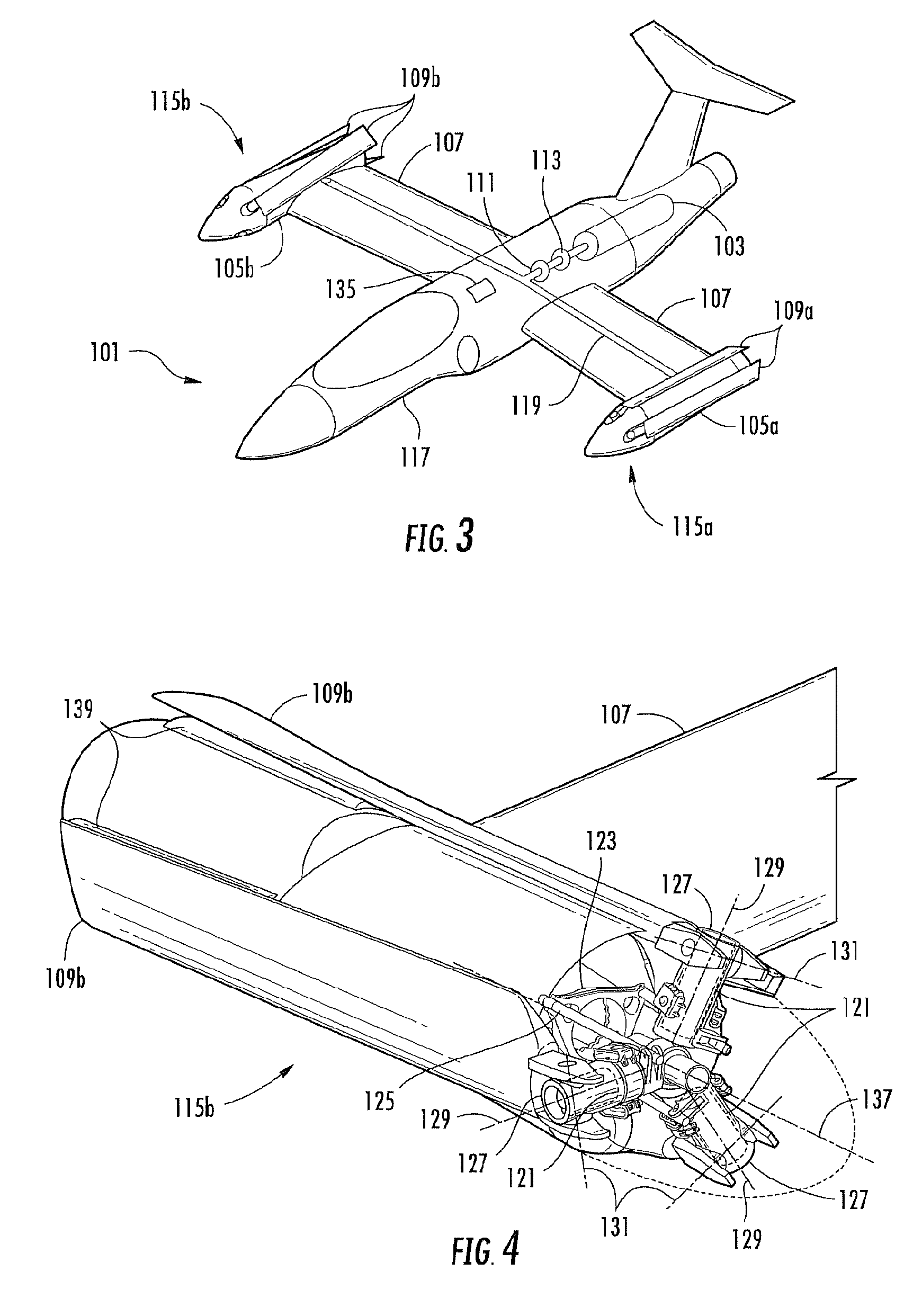
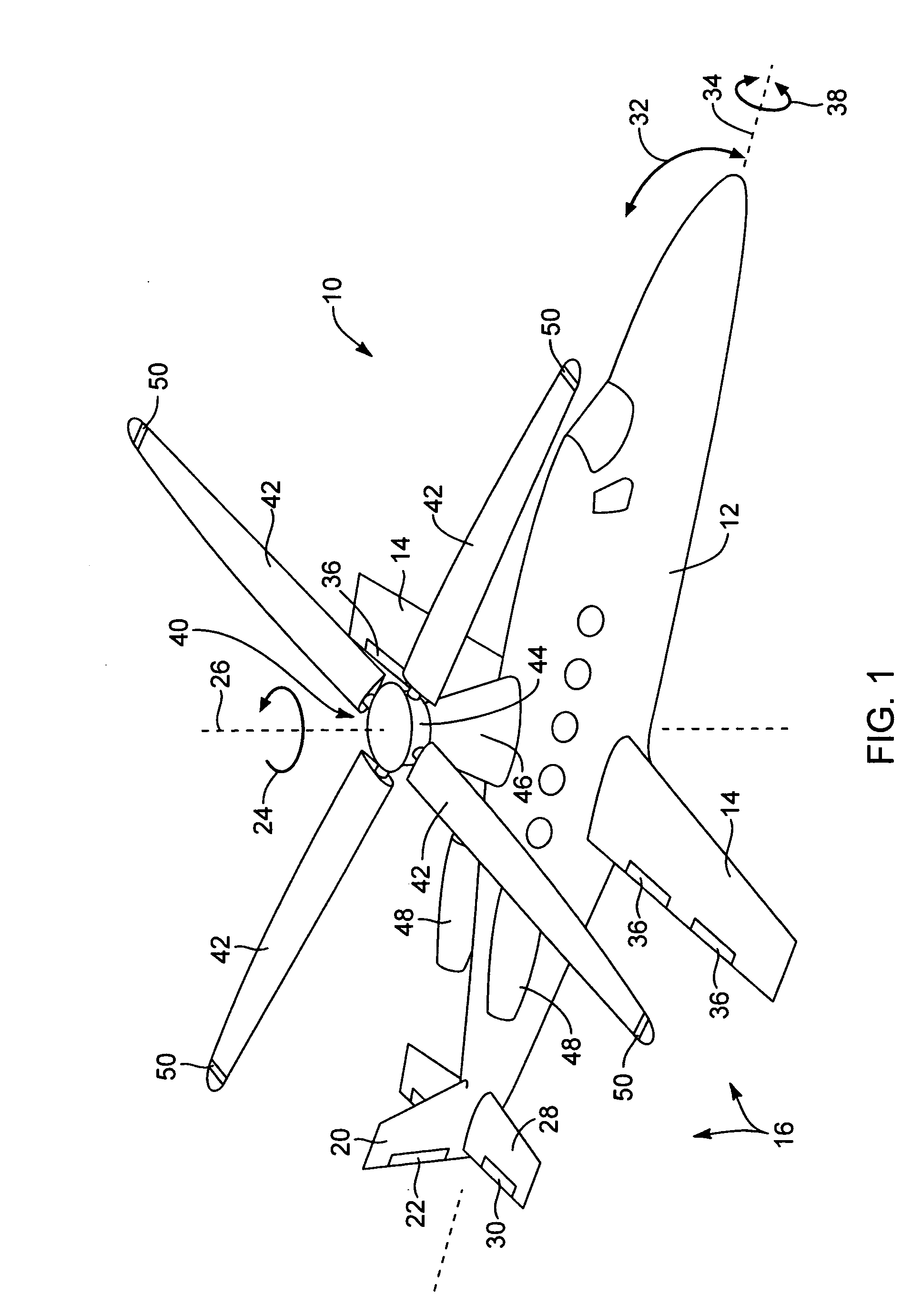
Method and apparatus for in-flight blade folding
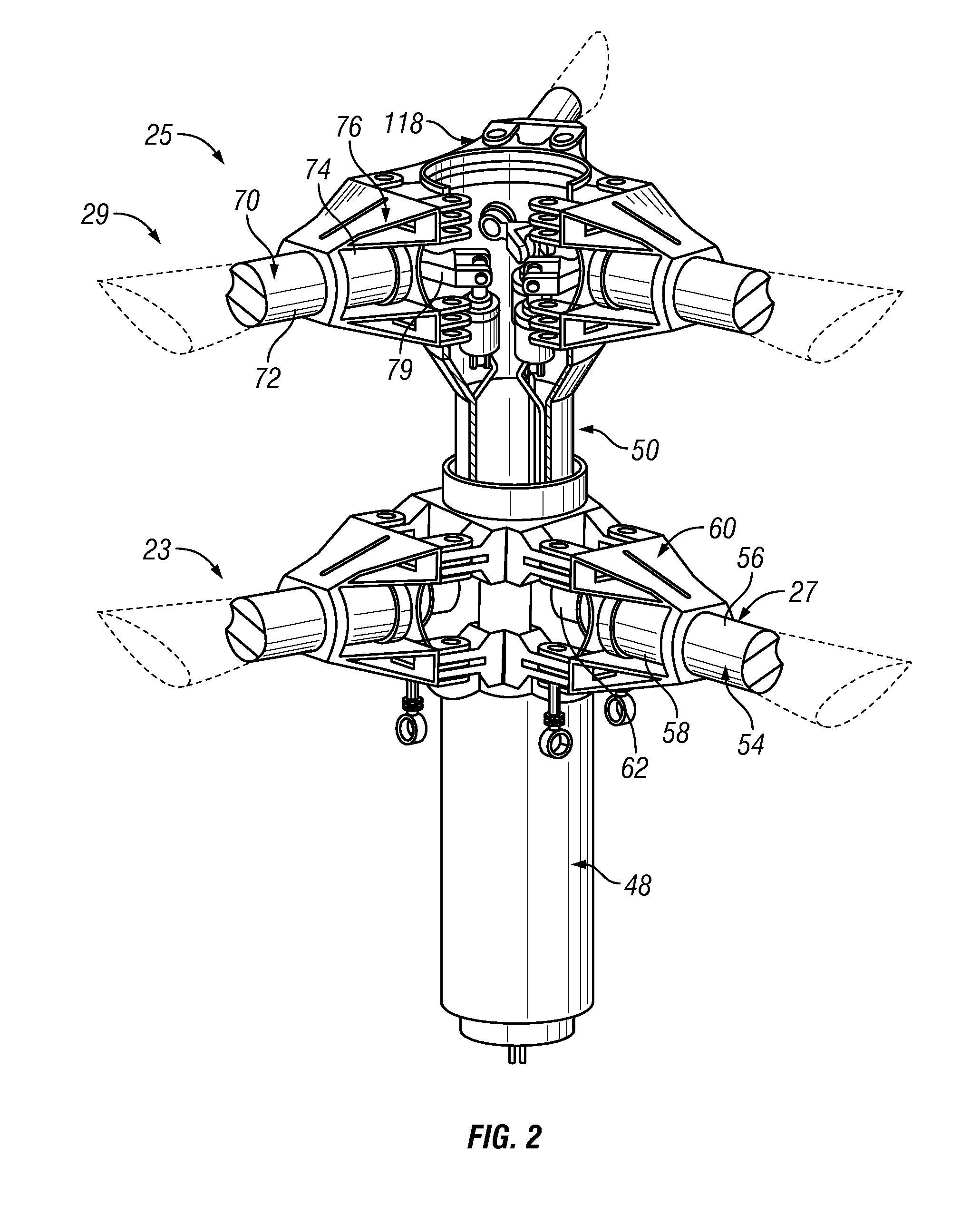
A foldable rotor system for a rotorcraft, the foldable rotor system comprising a rotor assembly operably associated with a driveshaft, the driveshaft being operable associated with an engine, the rotor assembly comprising a rotor blade connected to a grip pin. A swashplate is operable associated with the grip pin in order selectively change a pitch of the rotor blade. A blade fold actuator is operably associated with the grip pin such that the blade fold actuator is configured to fold and unfold the rotor blade about a blade fold axis. During an airplane mode, the rotorcraft can stop and fold the rotor blades so that the rotorcraft relies upon thrust from the engine for propulsion. The rotor blades are folded in a spiral fold path so that the rotor blades remain substantially edgewise, or feathered, during the folding process. The spiral fold path minimizes the aerodynamic drag experienced by the rotor blades while being folded during flight of the rotorcraft.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Method and Apparatus for In-Flight Blade Folding
A foldable rotor system for a rotorcraft, the foldable rotor system comprising a rotor assembly operably associated with a driveshaft, the driveshaft being operable associated with an engine, the rotor assembly comprising a rotor blade connected to a grip pin. A swashplate is operable associated with the grip pin in order selectively change a pitch of the rotor blade. A blade fold actuator is operably associated with the grip pin such that the blade fold actuator is configured to fold and unfold the rotor blade about a blade fold axis. During an airplane mode, the rotorcraft can stop and fold the rotor blades so that the rotorcraft relies upon thrust from the engine for propulsion. The rotor blades are folded in a spiral fold path so that the rotor blades remain substantially edgewise, or feathered, during the folding process. The spiral fold path minimizes the aerodynamic drag experienced by the rotor blades while being folded during flight of the rotorcraft.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
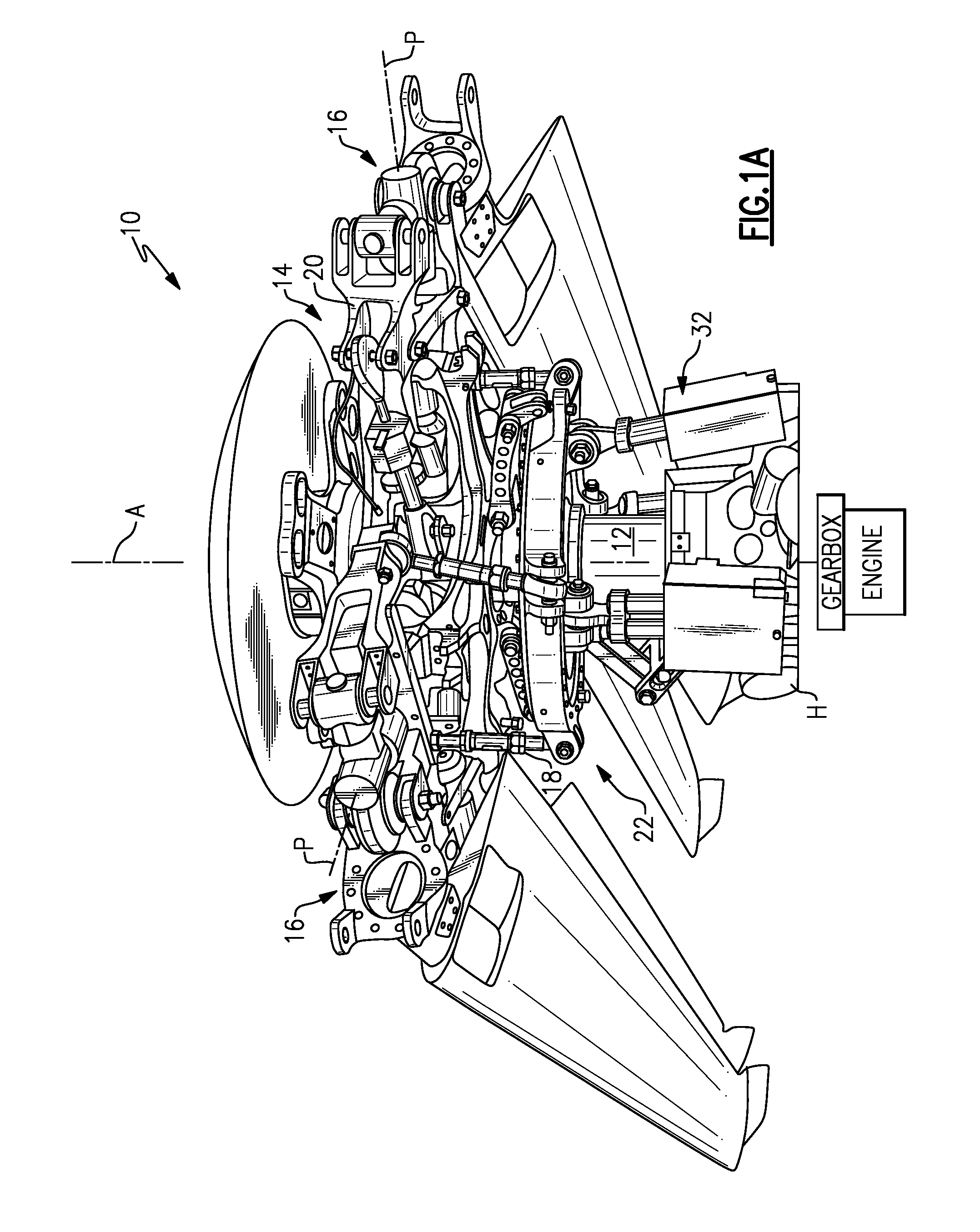
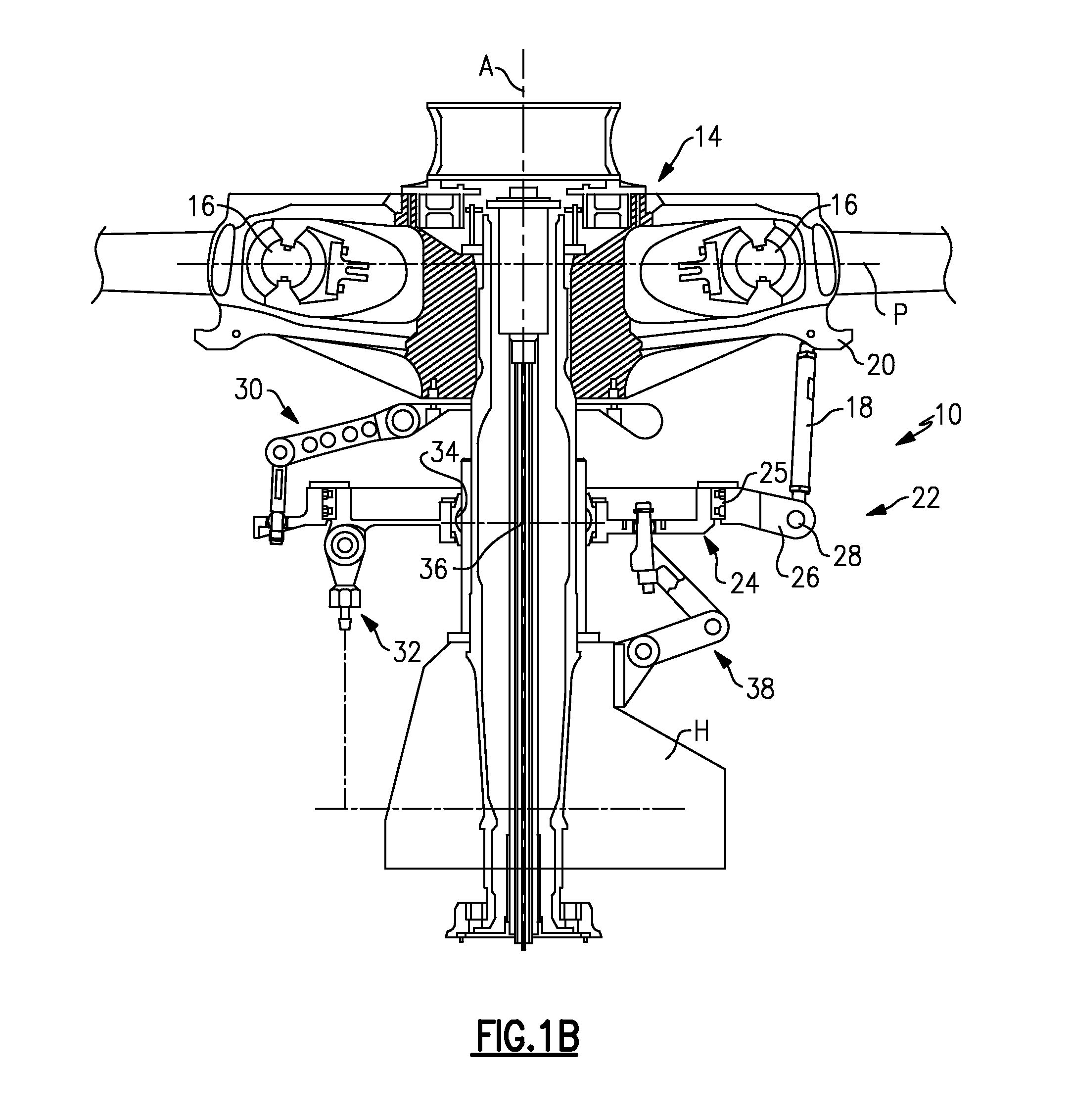
Swash Plate Anti-Torque Mechanism
InactiveUS20080253891A1Facilitates optimal placementReduce tangential loadPropellersPump componentsDegrees of freedomSwashplate
An anti-torque mechanism which permits a full range of swashplate assembly motion. The anti-torque mechanism generally includes an anti-torque shaft and a compound bearing mounted thereto to provide five-degrees-of-freedom (spherical-linear-elastomeric) so as to permit a swashplate attachment point to move axially in response to pitch input; pivot in response to swashplate tilt; and move in / out in the radial direction.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
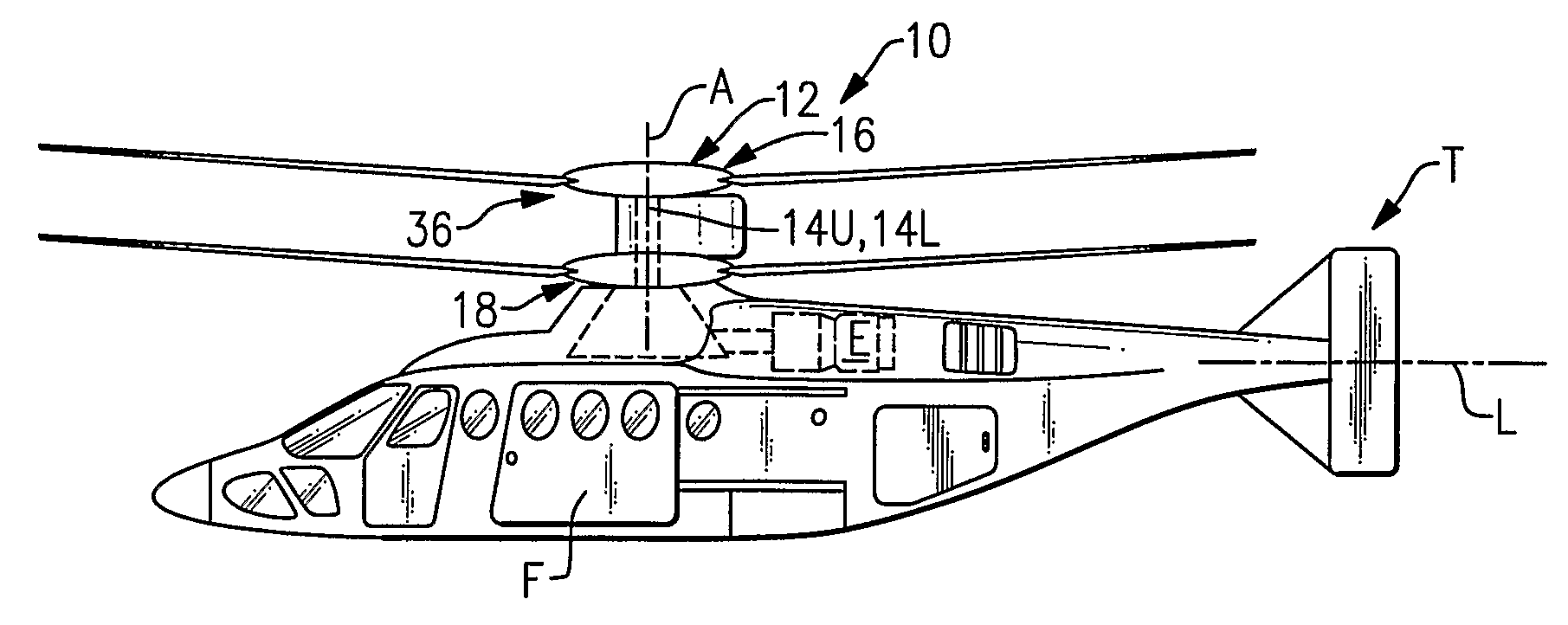
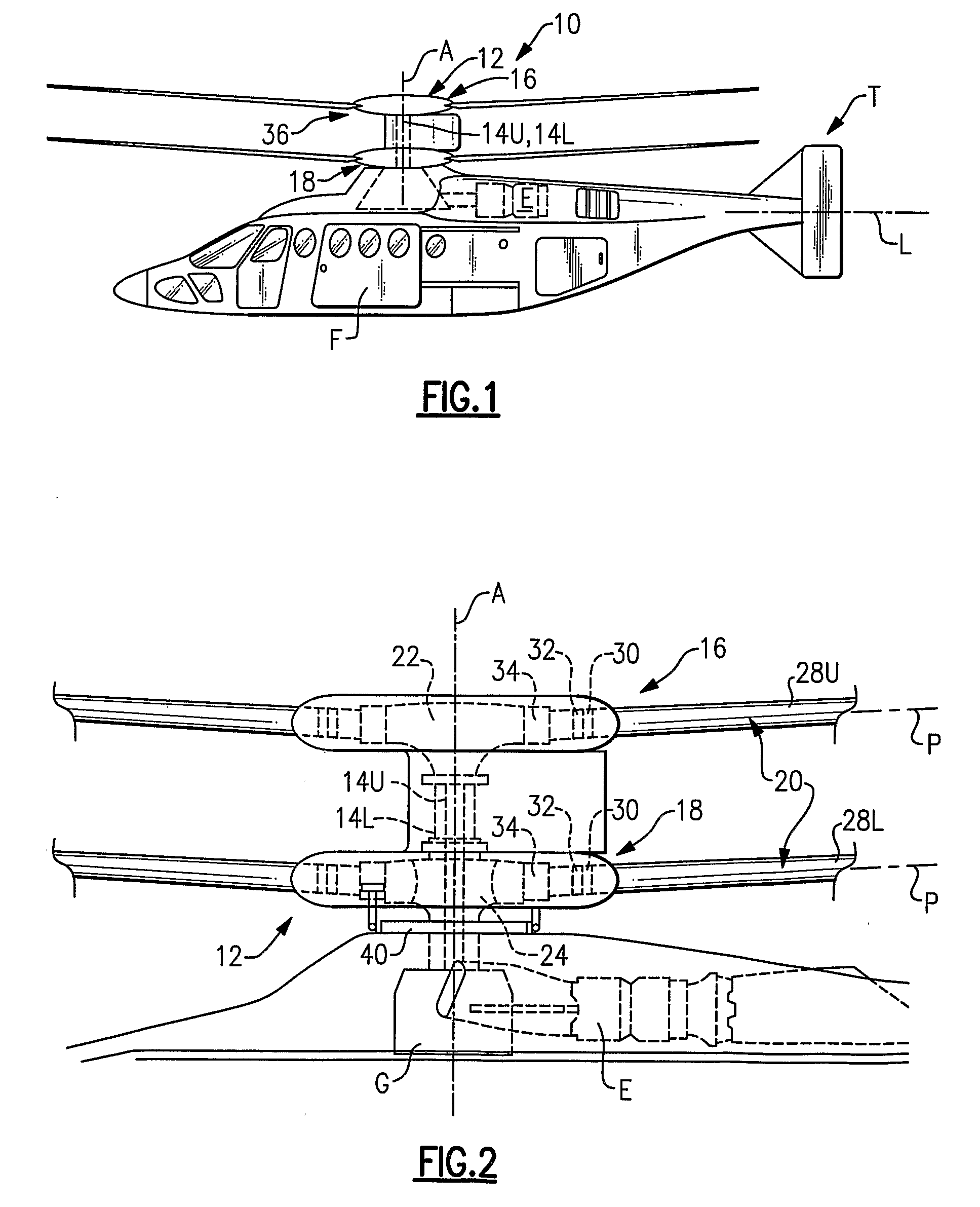
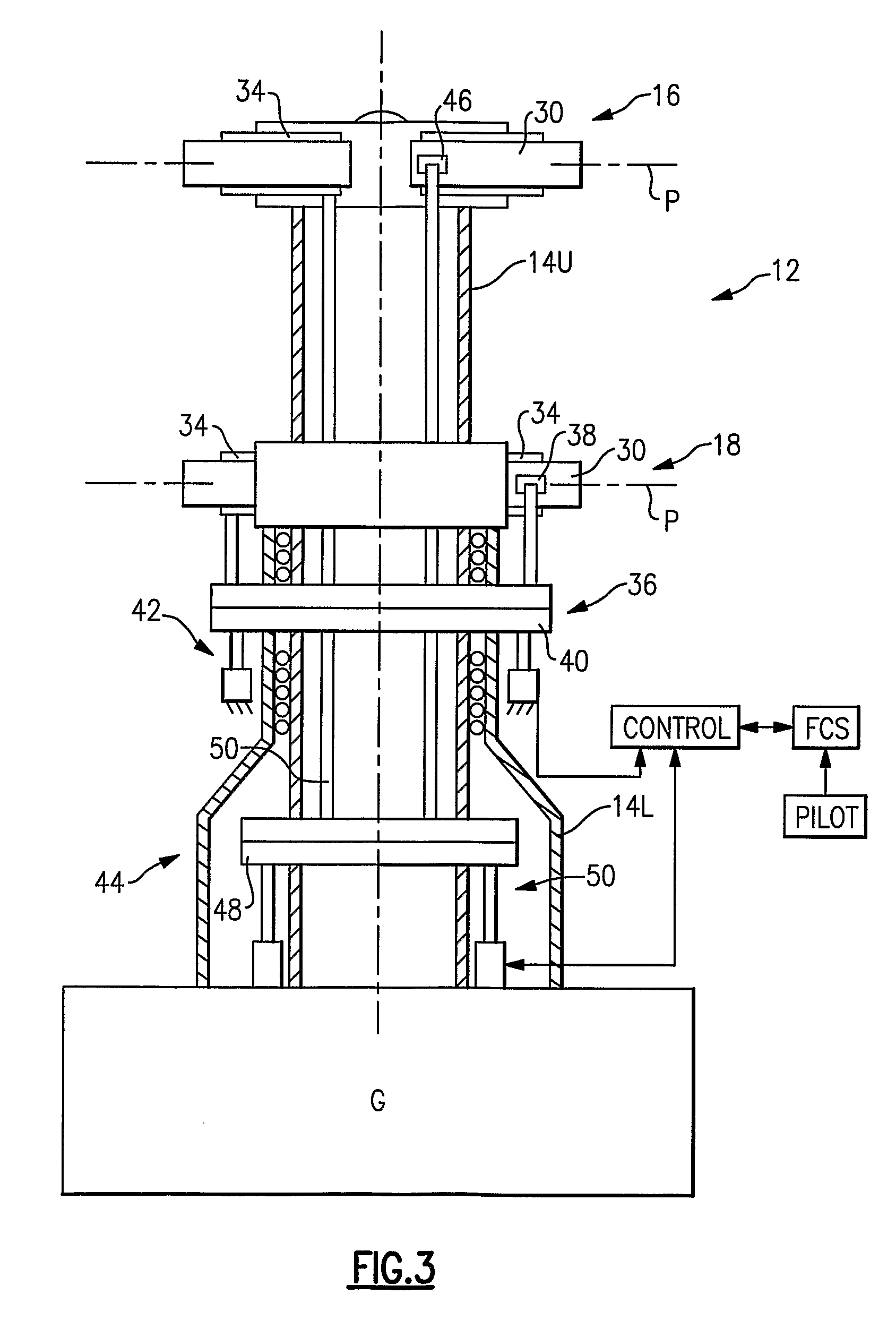
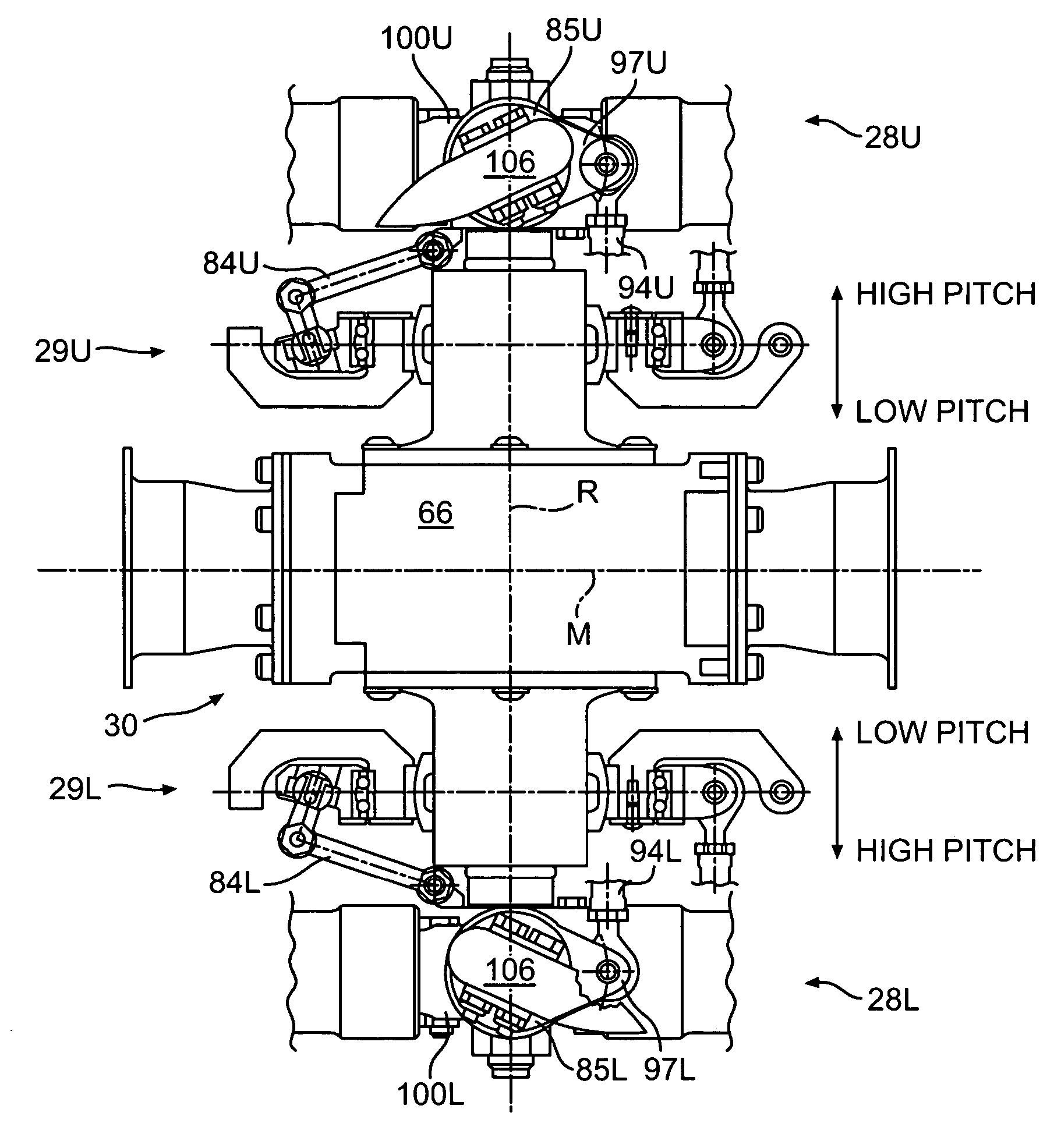
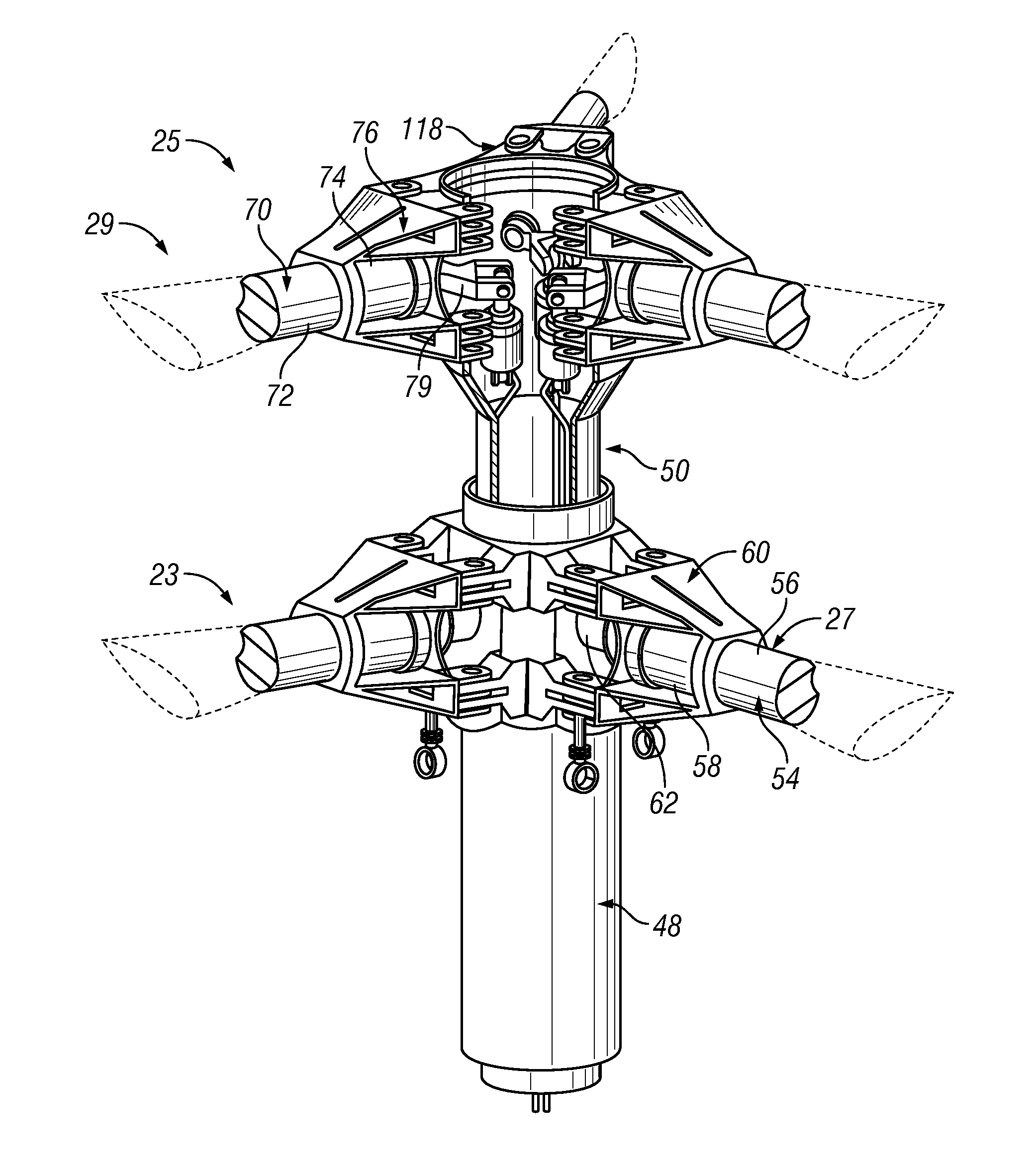
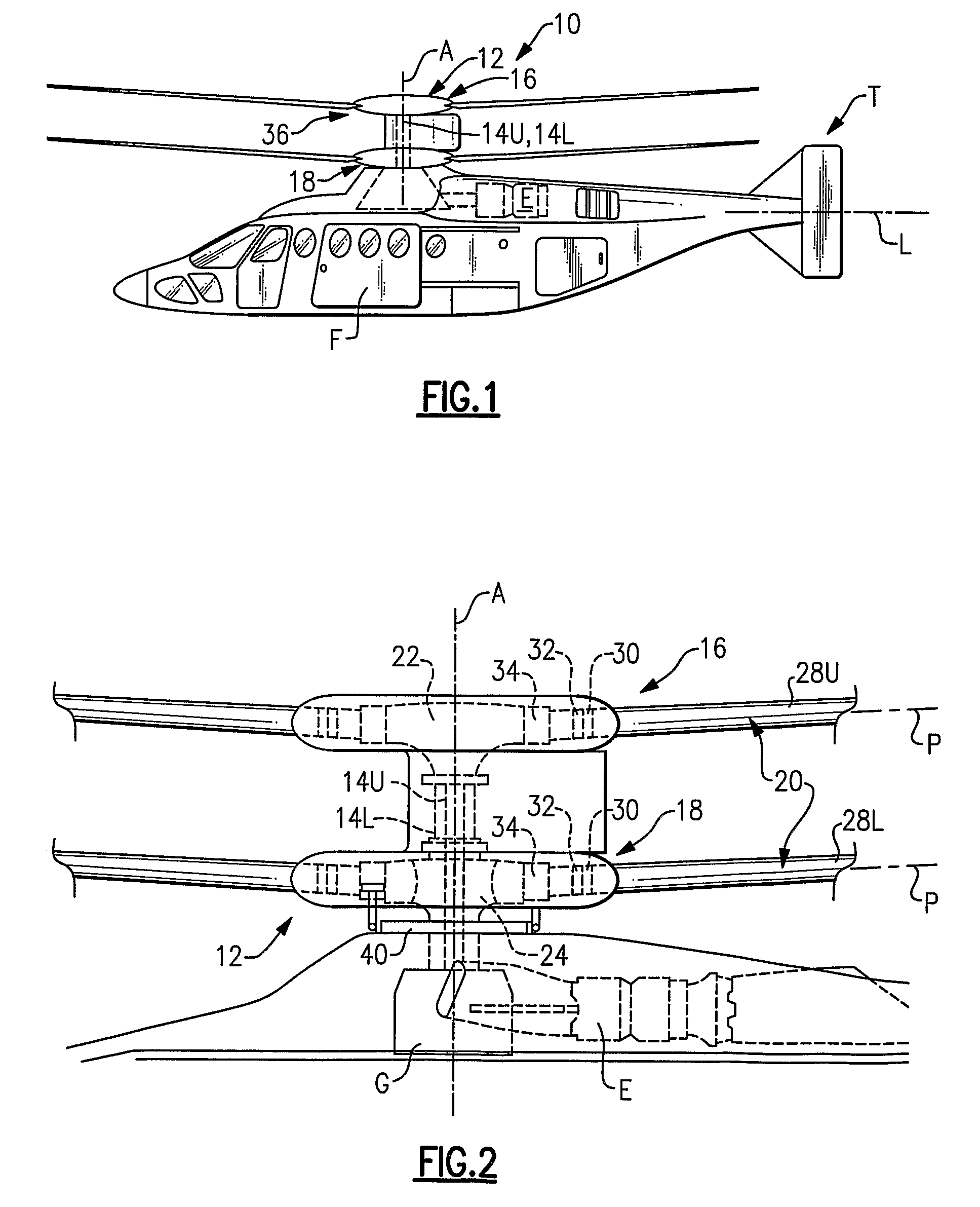
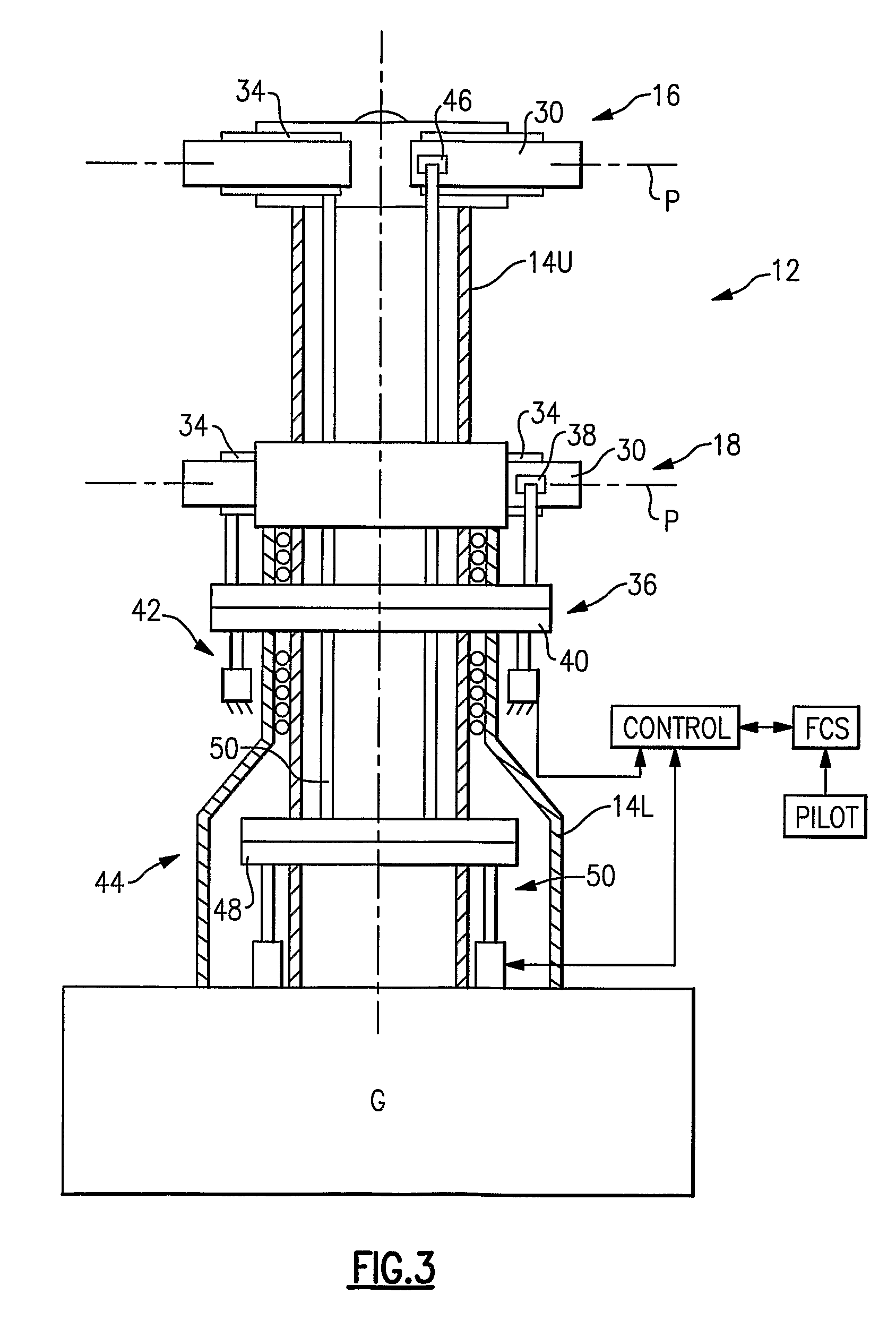
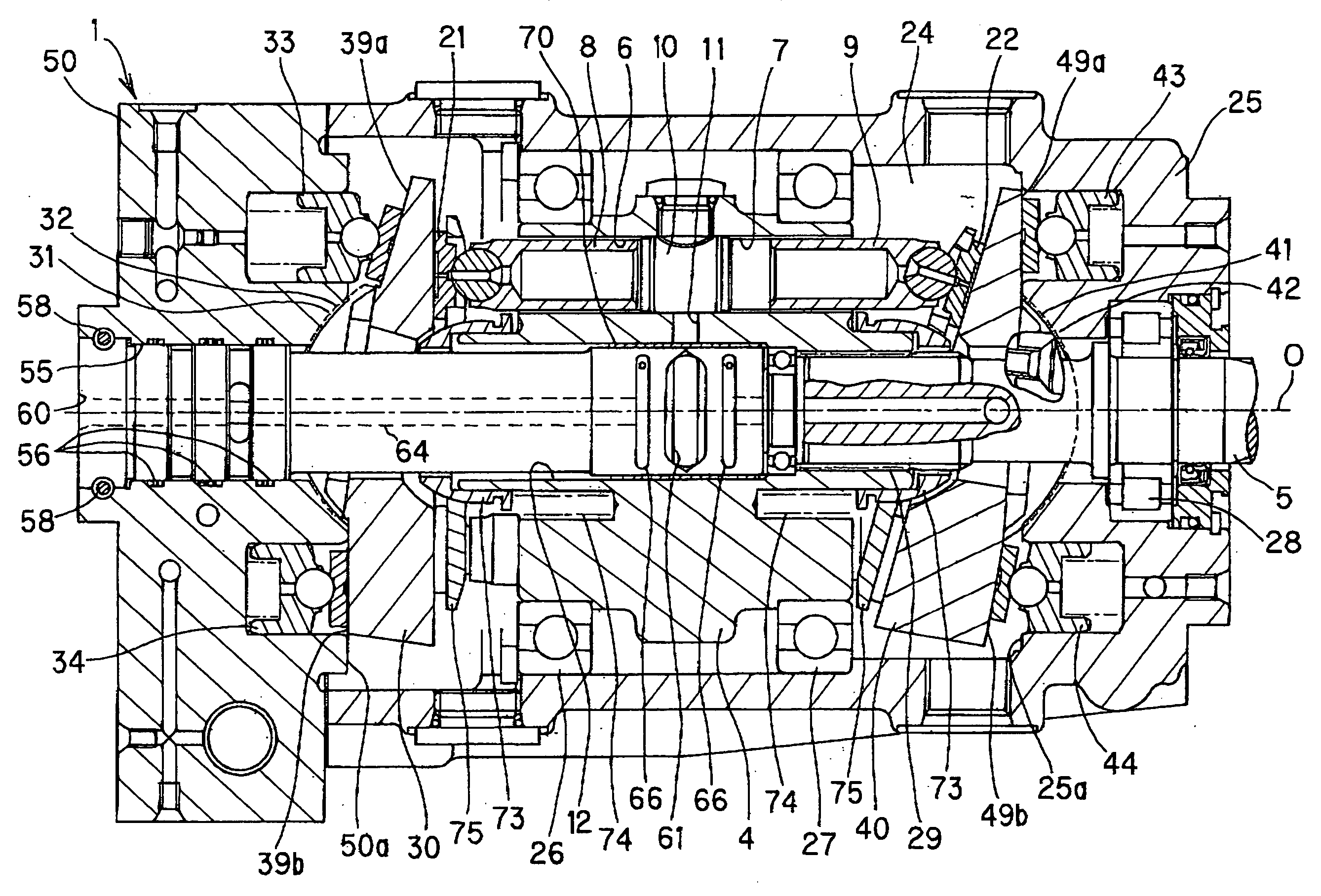
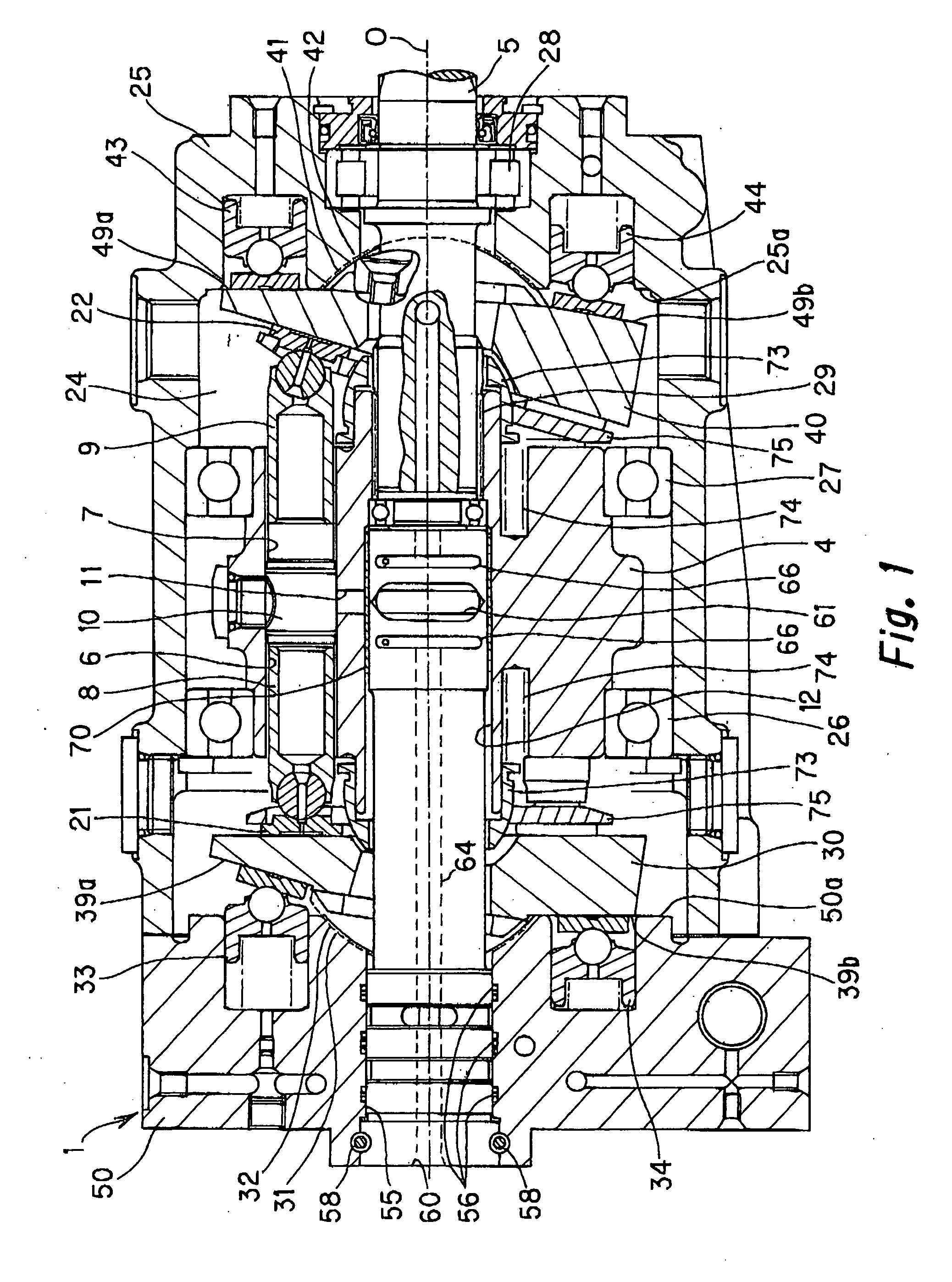
Swashplate and pitch link arrangement for a coaxial counter rotating rotor system
A coaxial counter-rotating rotor system for a hybrid aircraft includes an upper swashplate assembly and a lower swashplate assembly with a coaxial transmission system therebetween. Movement of the upper and lower swashplate assembly is reflected about a midplane of the coaxial transmission housing to generate sufficient cyclic and / or collective pitch inputs within a compact structural in which the rotor systems are closely spaced along an axis of rotation.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Device for varying blade pitch of a lift rotor
ActiveUS20130119187A1Little strengthImprove performancePropellersPump componentsTrailing edgeActuator
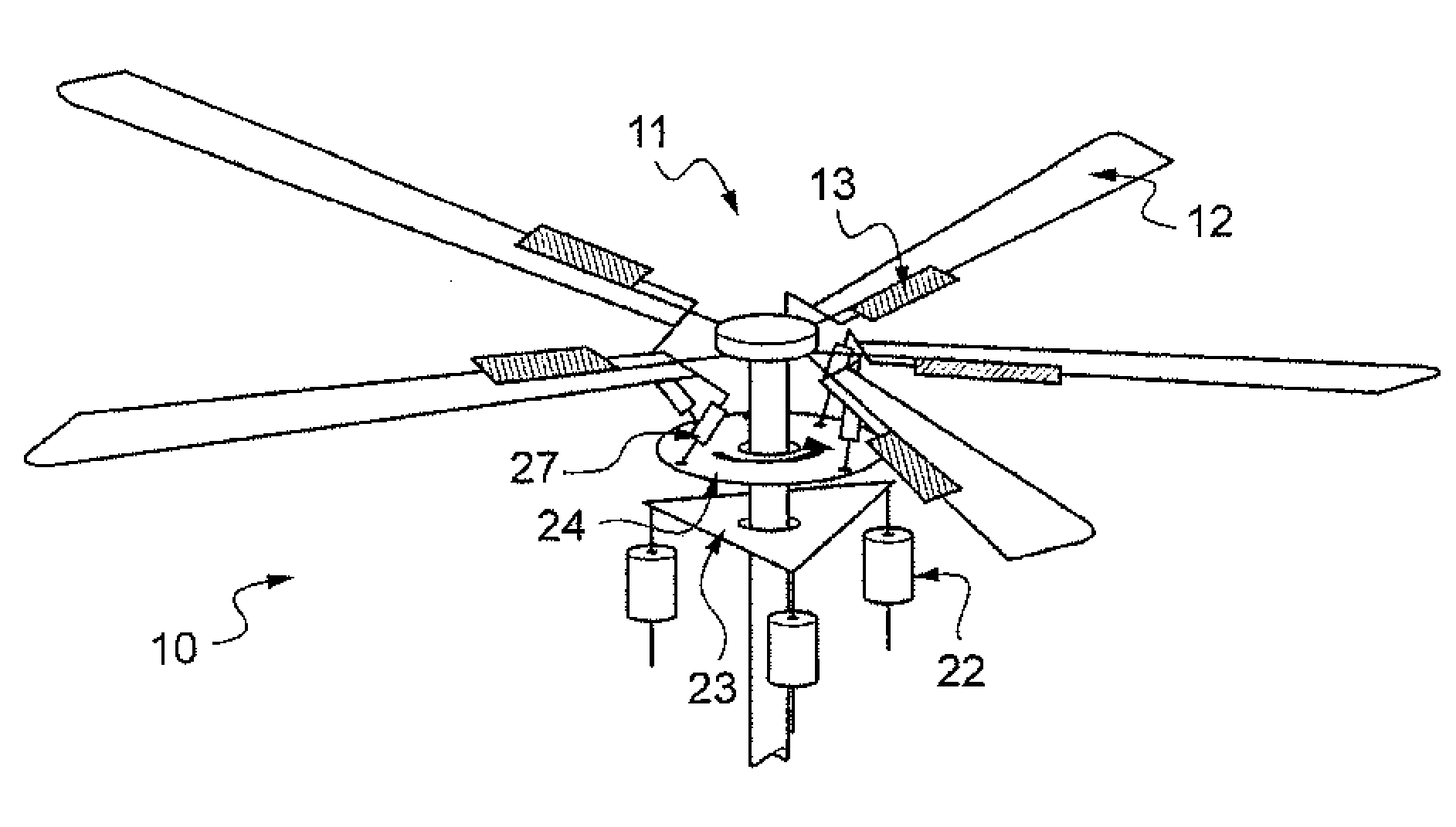
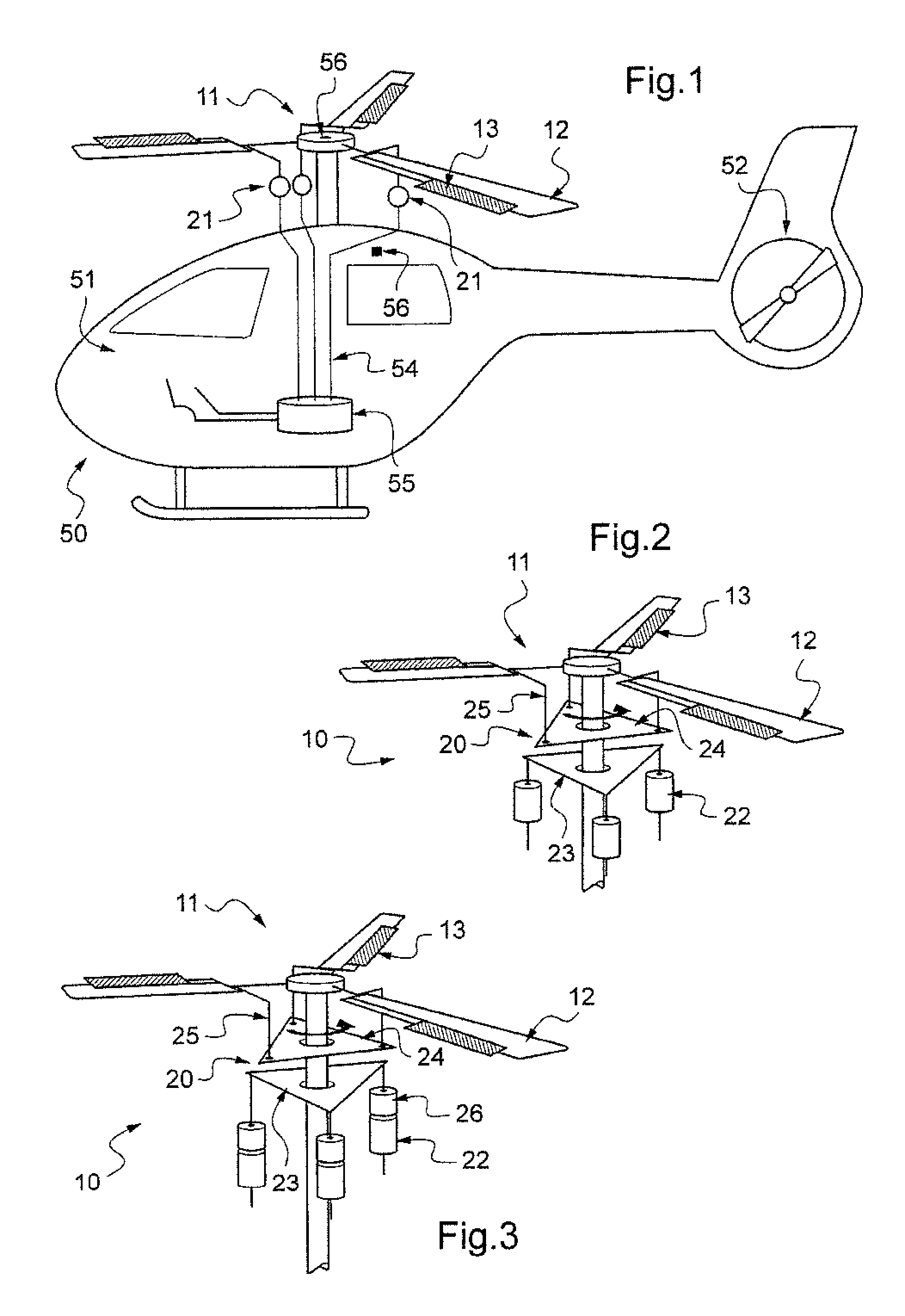
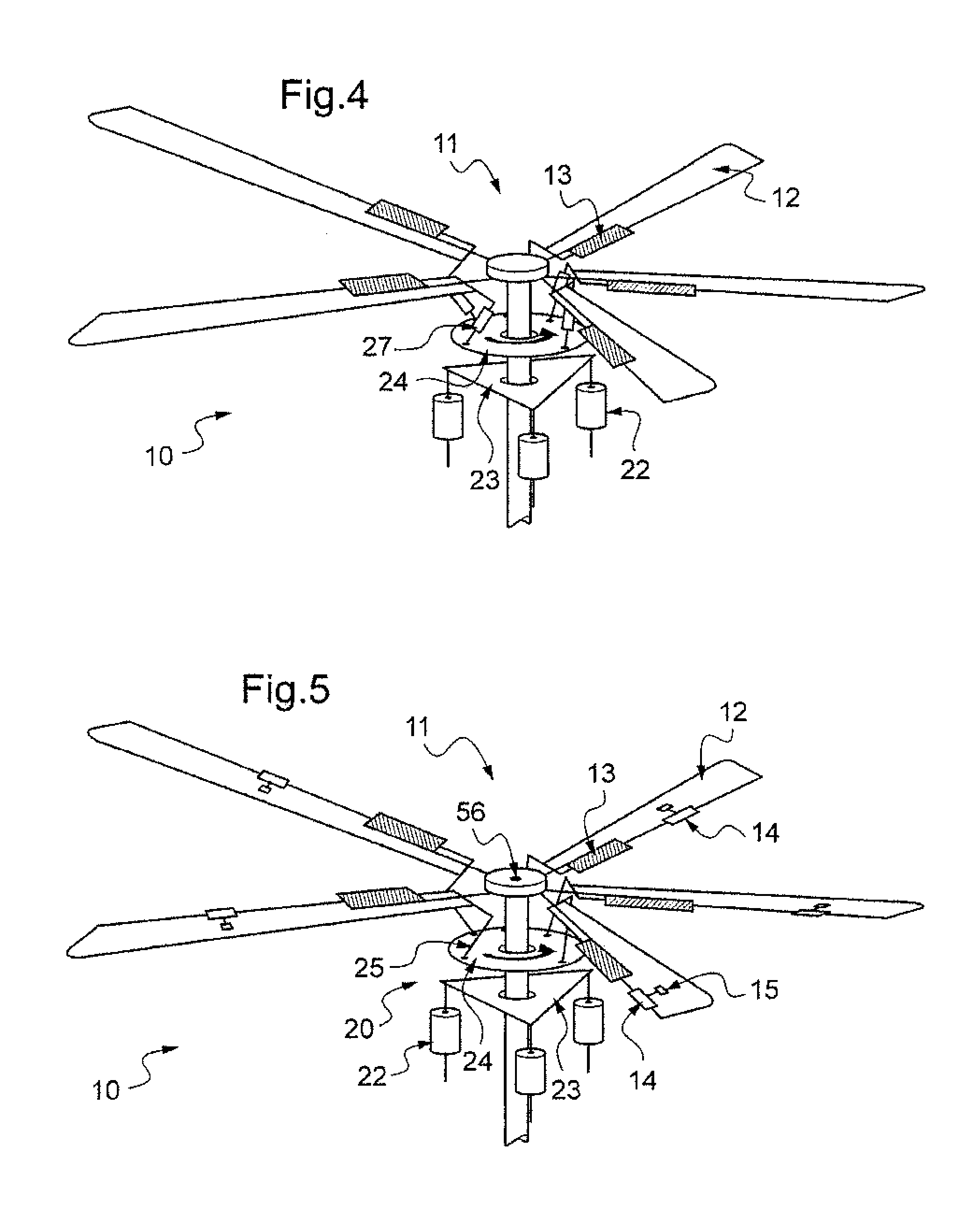
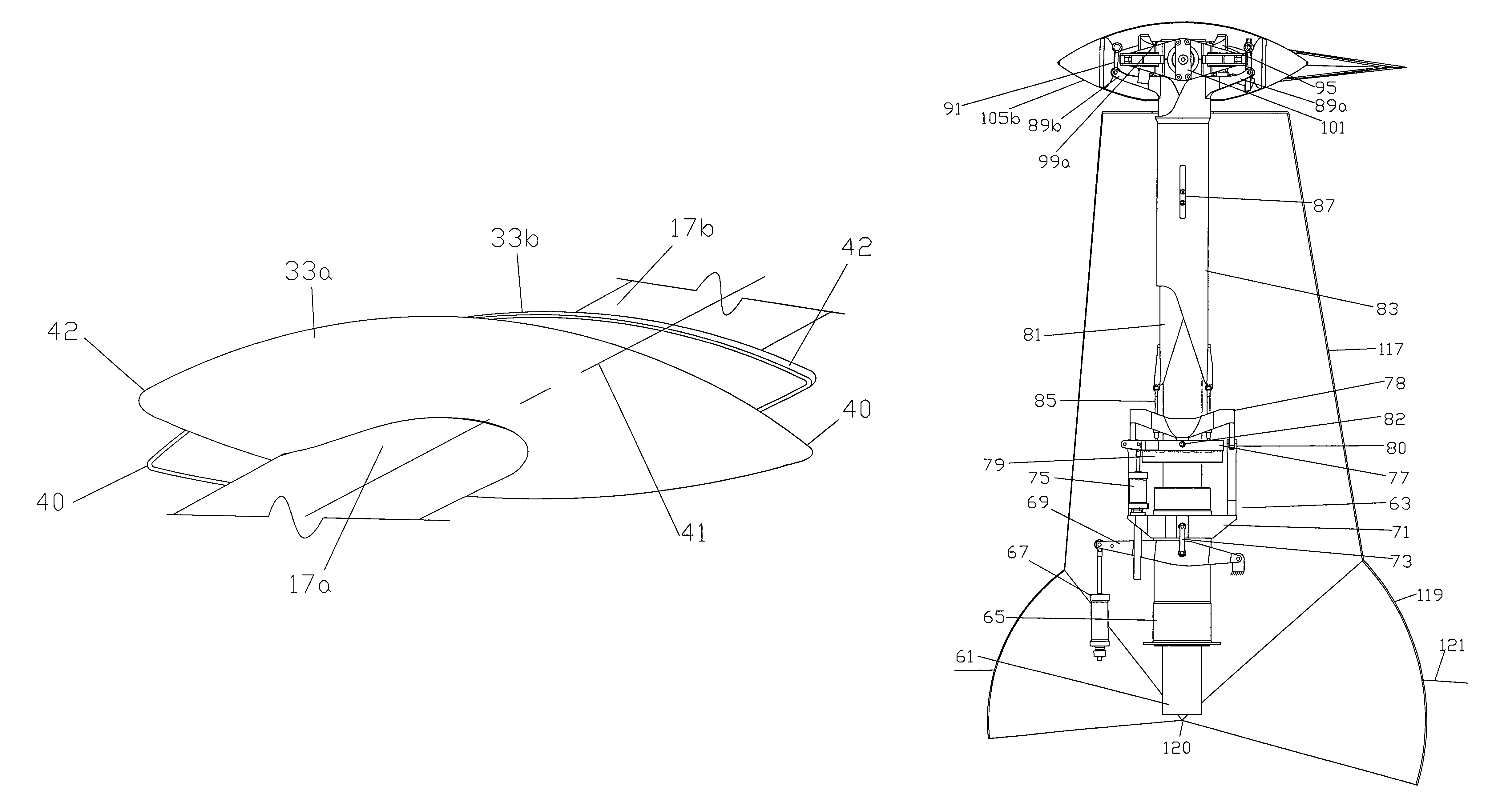
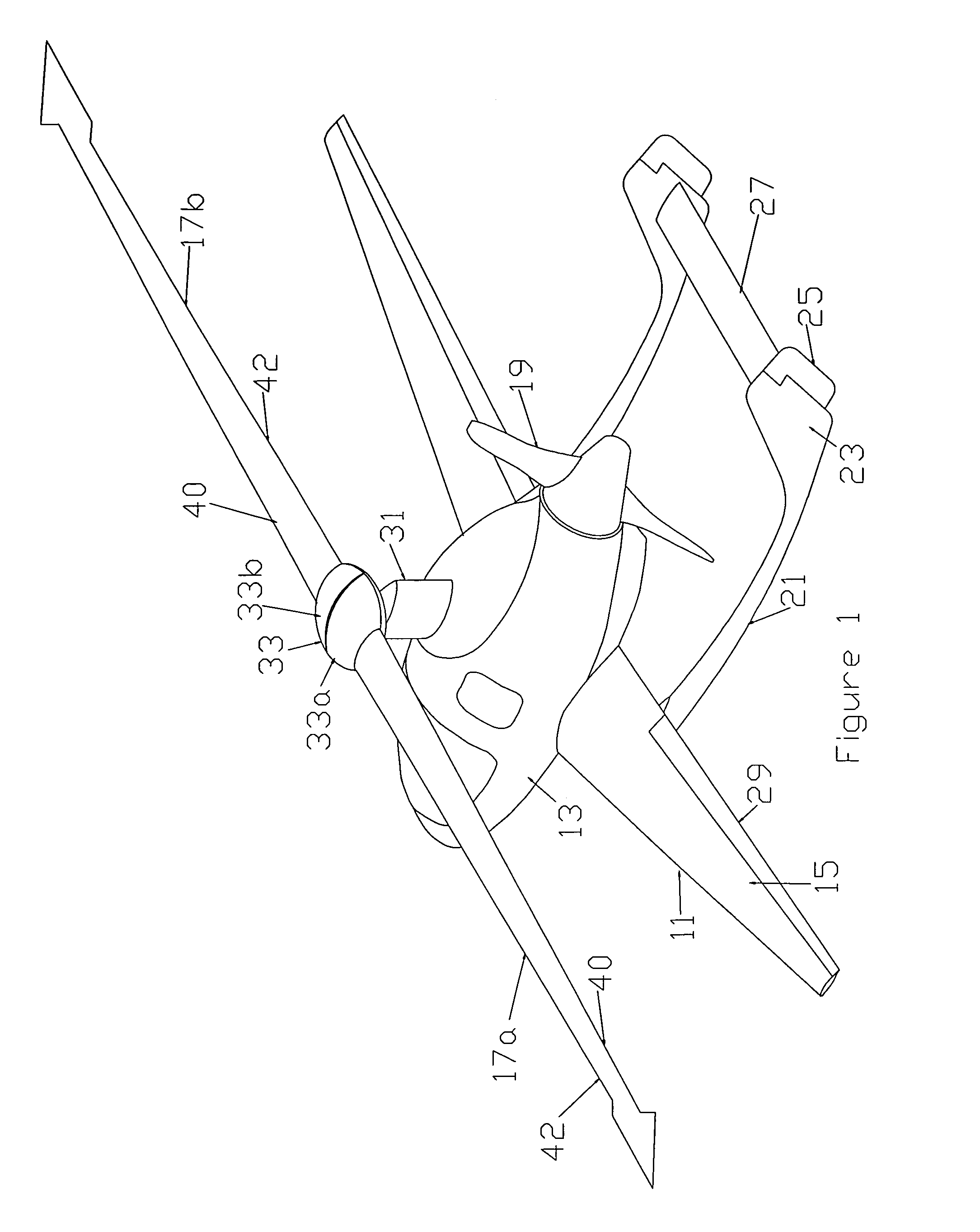
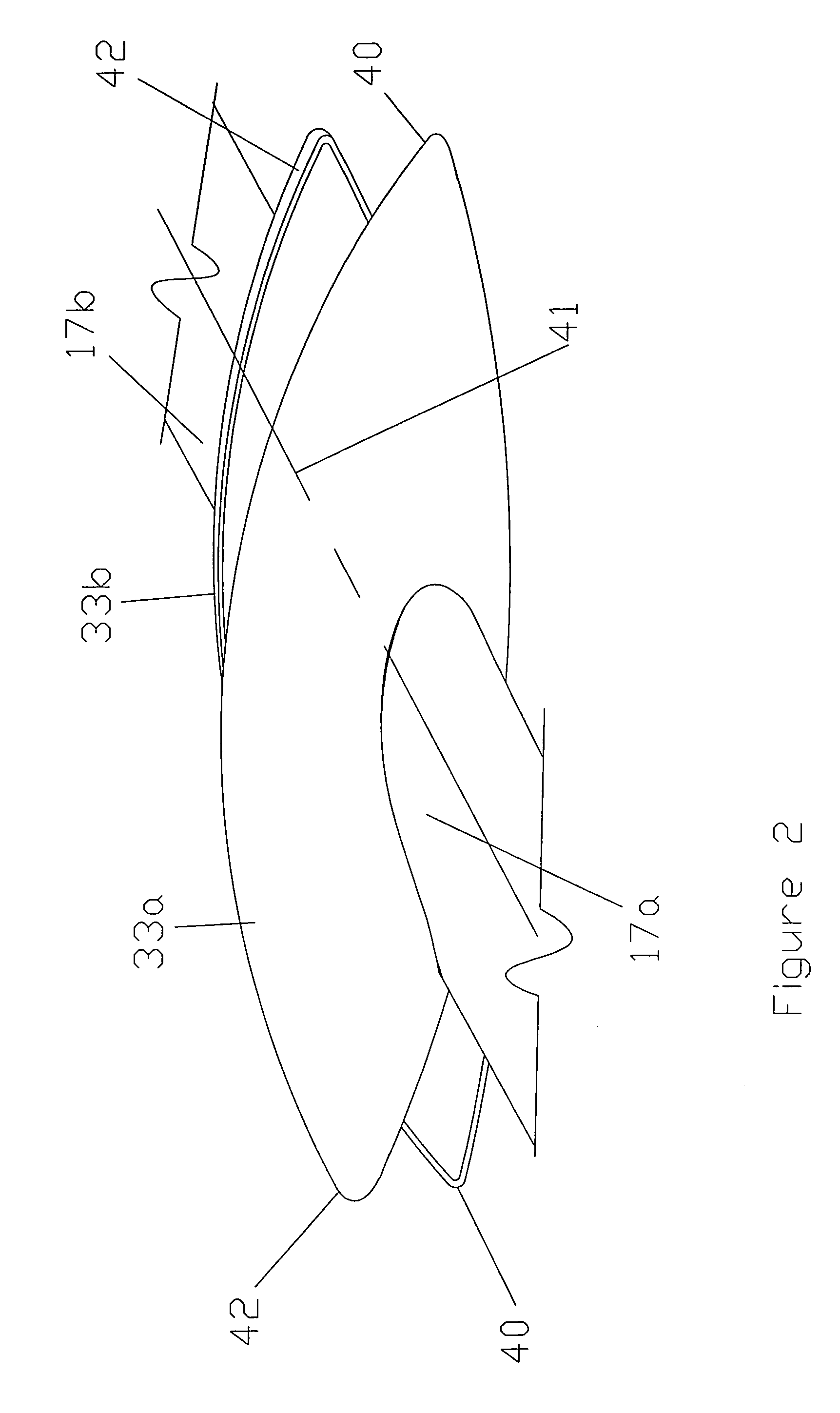
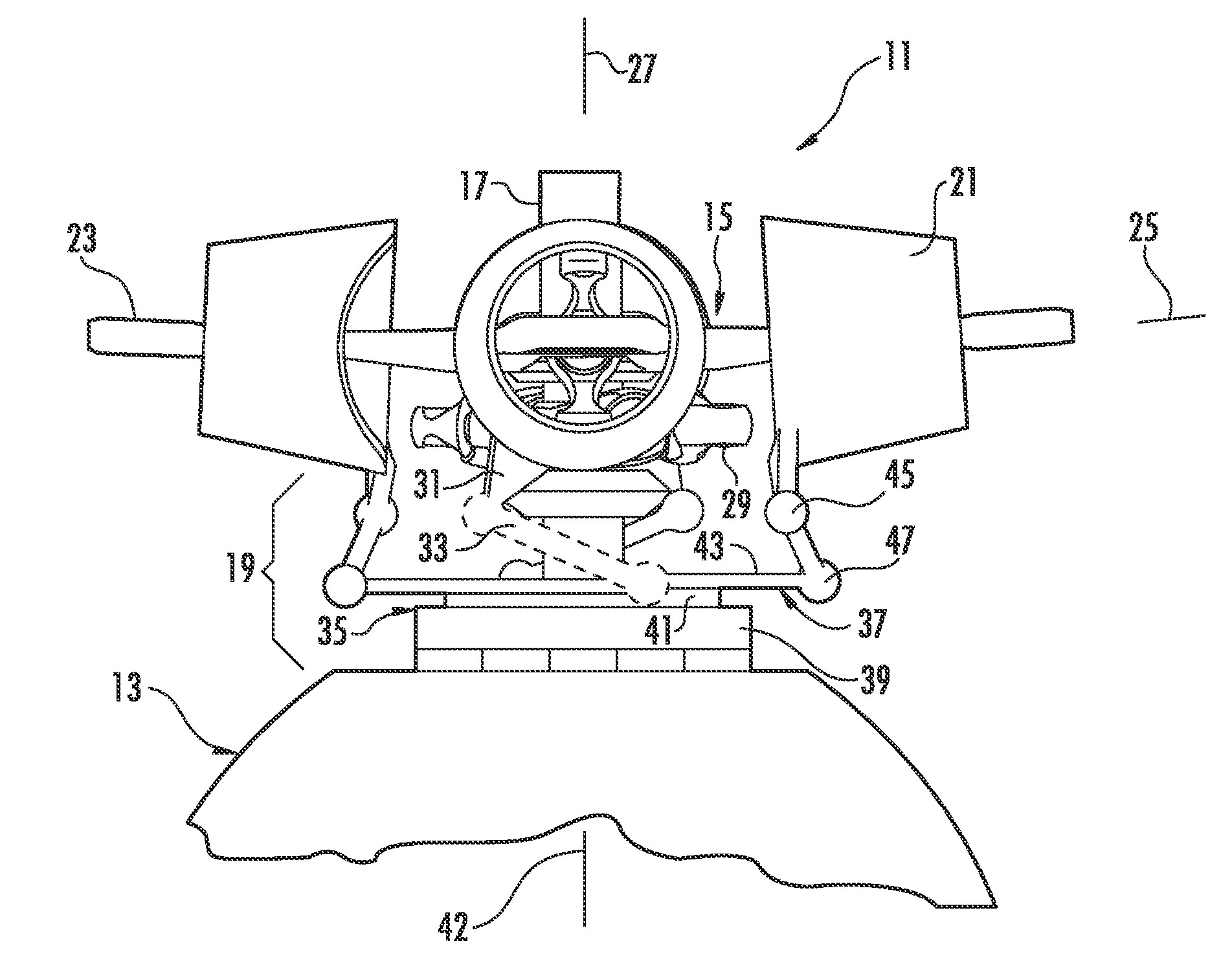
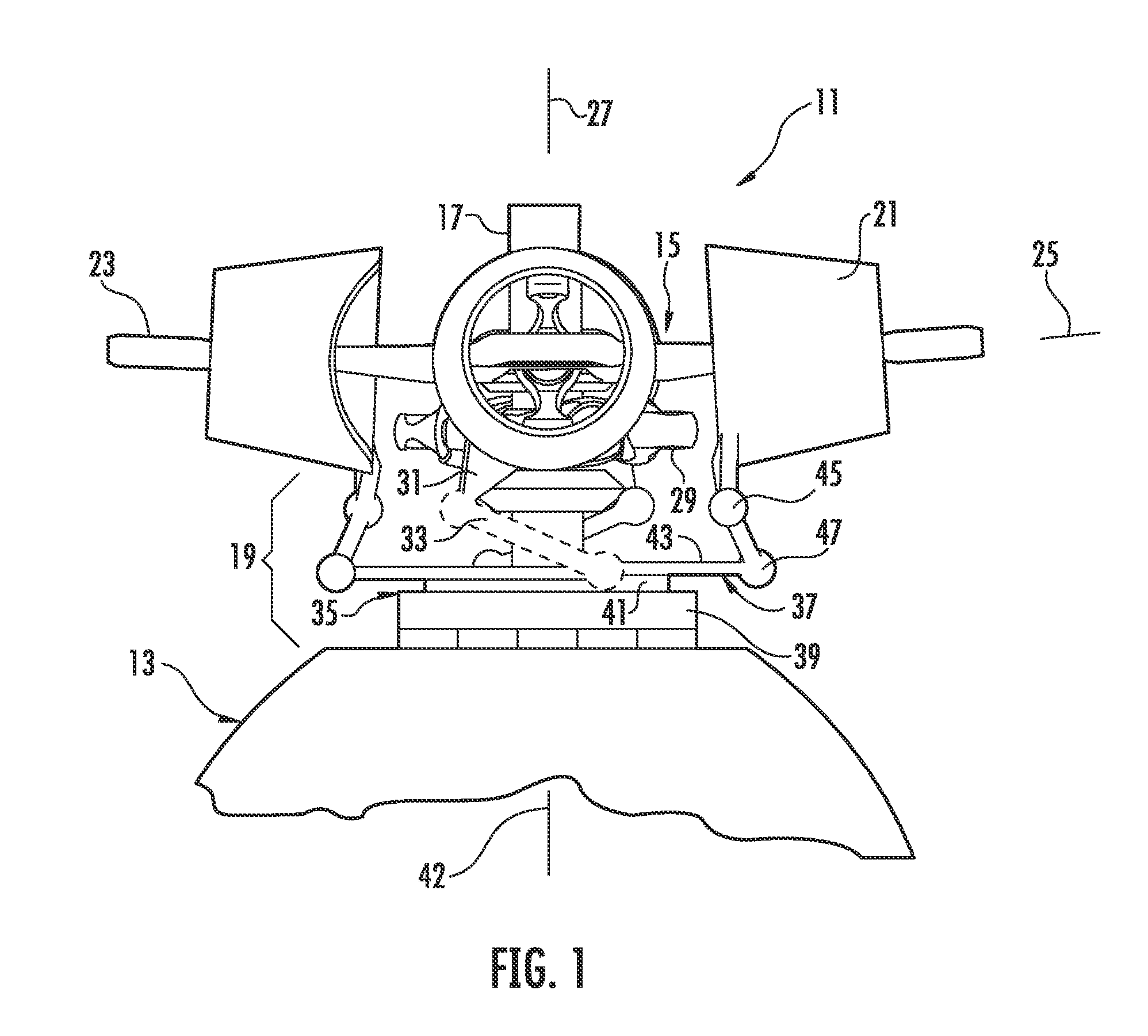
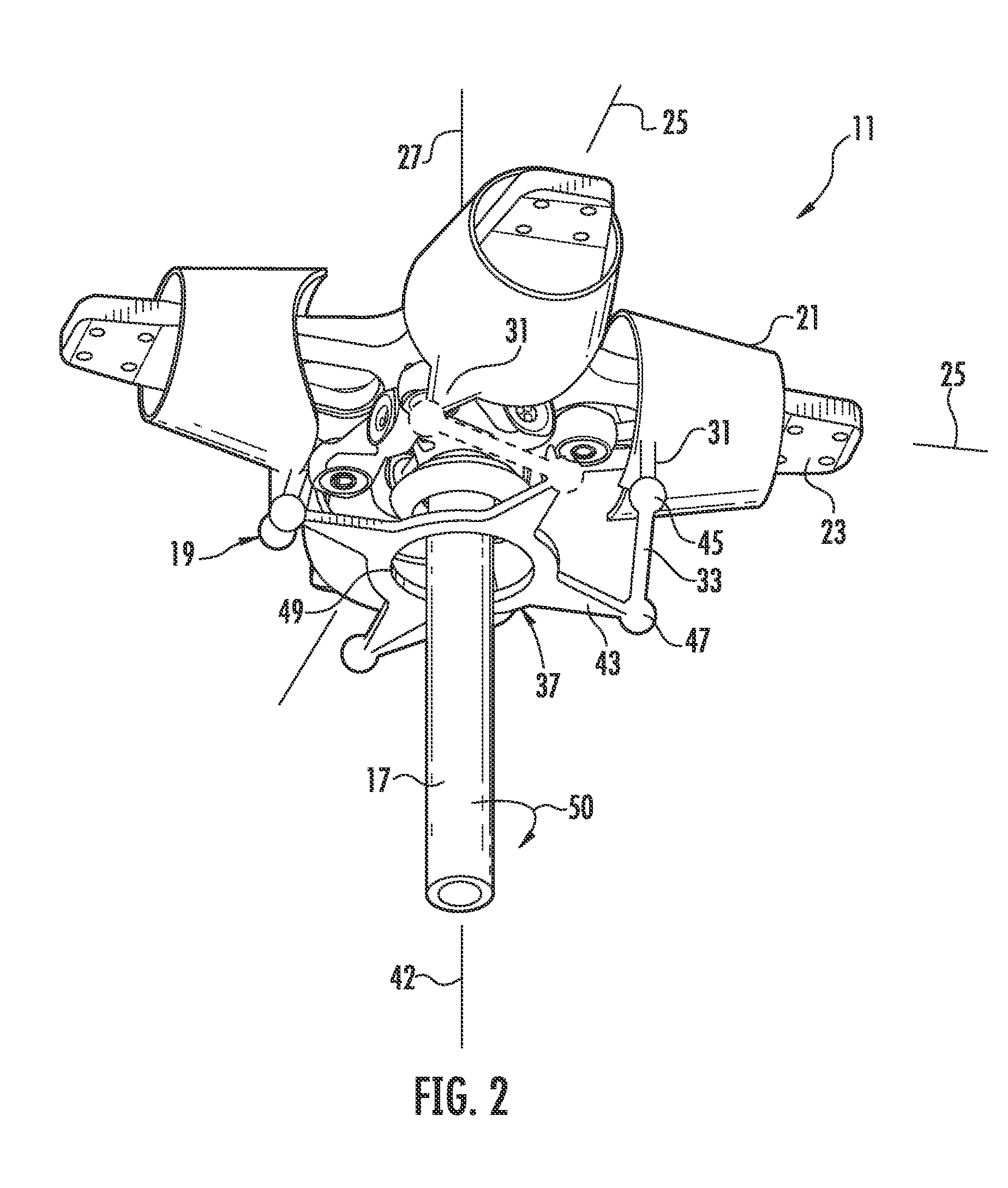
The present invention relates to a device (10) for varying blade pitch of a rotary wing aircraft (50) having a main rotor (11) with a plurality of blades (12), each blade (12) including at least one main flap (13) fastened to the trailing edge of the blade (12). The angle of inclination of each flap (13) is controlled via a swashplate (20). The device (10) makes provision for electric actuators controlled by a flight control system (54) to be mounted in a stationary frame of reference for the purpose of moving and varying the angle of inclination of the non-rotary plate of the swashplate (20). The electric actuators provide primary flight control and also multi-cyclic control for the purpose of attenuating noise and vibration as generated in particular by the blades (12) and the rotor (11).
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Control devices for swashplate type variable displacement piston pump
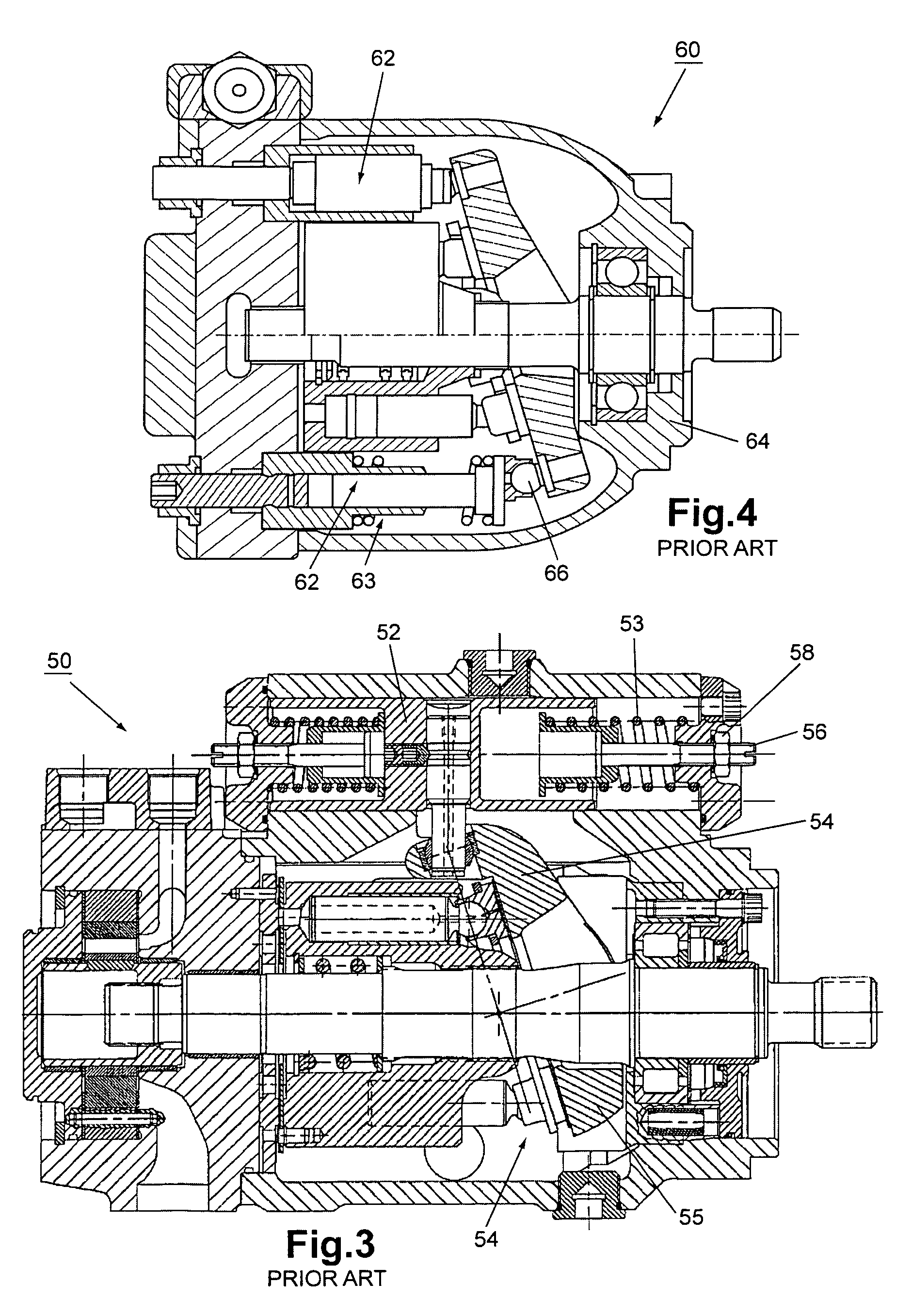
Improvements in trunnion shaft-controlled swashplate axial hydraulic piston pumps as well as hydraulic systems used in hydrostatic transmissions utilized. e.g., in zero-turn-radius (ZTR) wheeled vehicles, such as grass mowers, with one embodiment thereof pertaining to, in combination, the noted pump, devoid of any internal servo control, and a reversible power actuator, for controlling the angle of the swashplate, externally affixed to the housing containing the pump and operatively interconnected with an end of the trunnion shaft extending from the pump housing, with the power actuator being one of a rotary actuator, a fluid power axial cylinder and a rotary electronic actuator. Usage in a ZTR wheeled vehicle requires the prime mover to independently drive two hydraulic transmissions that are controlled by a human operator via a mechanical lever, either two single-axis or one dual-axis joystick control, or a steer-by-wire unit, connected with right and left power actuators
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Control devices for swashplate type variable displacement piston pump
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Helicopter rotor control system
A rotor control system operatively linked to a plurality of rotor blades includes a swashplate assembly having a stationary member and a rotating member. A blade attachment member is operatively connected to the plurality of rotor blades and a control horn is operatively connected to the blade attachment member and one of the plurality of rotor blades. At least one hydraulic actuator member is operatively coupled to the control horn and at least one hydraulic actuator element is operatively coupled to the swashplate assembly and the at least one hydraulic actuator member. The at least one hydraulic actuator member transmits control signals from the swashplate assembly to the one of the plurality of rotor blades through the at least one hydraulic actuator member.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Methods and apparatus for swash plate guidance and control
InactiveUS6360987B1Direction controllersSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringRotary actuator
Apparatuses and methods for controlling an object spinning at a first rate in a first direction. The apparatus includes a swash plate, a rotor, a spin actuator, a roll actuator, and a pitch actuator. The rotor is coupled to the swash plate. The spin actuator is coupled to the rotor and is configured to spin the rotor in a second direction opposite the first direction at a second rate. The roll actuator is coupled to the rotor and is configured to displace the swash plate along a longitudinal axis. The pitch actuator is coupled to the rotor and is configured to tilt the swash plate in a tilt direction about the longitudinal axis, the tilt direction being adjustable by adjusting the second rate relative to the first rate. The roll actuator may be coupled to the pitch actuator so that the pitch actuator keeps a substantially identical orientation with the swash plate as the swash plate is displaced along the longitudinal axis by the roll actuator.
Owner:BAE SYST INTEGRATED DEFENSE SOLUTIONS
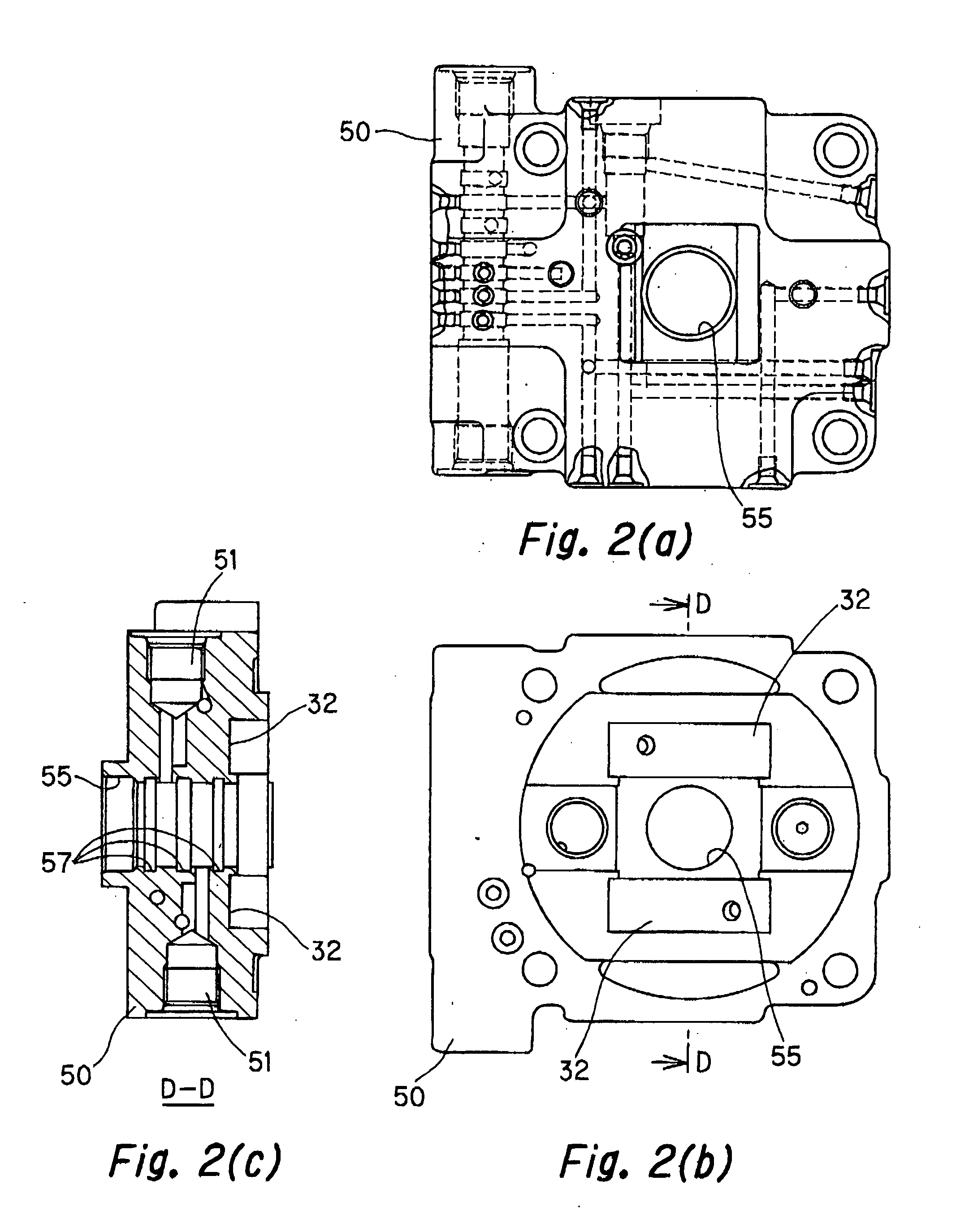
Axial variable displacement plunger pump of swash plate
InactiveCN101487458APositive-displacement liquid enginesMulti-cylinder pumpsEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention provides a power element used in a hydraulic transmission system. A swash plate variable axial plunger pump consists of a swash plate, a plunger cylinder body and a port plate. The angle-variable swash plate rotates with a drive rotating shaft which is connected by a hinge, and the swash plate drives the plunger to only have reciprocating motion in a fixed cylinder barrel, thus avoiding the disadvantages of large rotating inertia, large friction surface of port surface and easy leakage of a common swash plate axial plunger pump. The swash plate can be divided into a manual swash plate, a hydraulic-control swash plate and a hydraulic-control and spring combined variable swash plate. The swash plate can be conveniently adjusted by a window above a variable shell. The plunger pump has various uses and advantages of small rotating inertia, little friction surface, and high mechanical efficiency and volumetric efficiency, and being insensitive to pollution, generating little heat, being capable of taking as an economical combination pump with 'low pressure and large flow or high pressure and small flow' and the like. Besides as a common pump, the axial plunger pump can also be used in the superhigh pressure and synchronous cylinder field. The axial plunger pump has the advantages of general working accuracy and low production cost.
Owner:张全根
Swash plate anti-torque mechanism
InactiveUS8303248B2Facilitates optimal placementReduce tangential loadPropellersPump componentsDegrees of freedomSwashplate
An anti-torque mechanism which permits a full range of swashplate assembly motion. The anti-torque mechanism generally includes an anti-torque shaft and a compound bearing mounted thereto to provide five-degrees-of-freedom (spherical-linear-elastomeric) so as to permit a swashplate attachment point to move axially in response to pitch input; pivot in response to swashplate tilt; and move in / out in the radial direction.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Variable displacement compressor
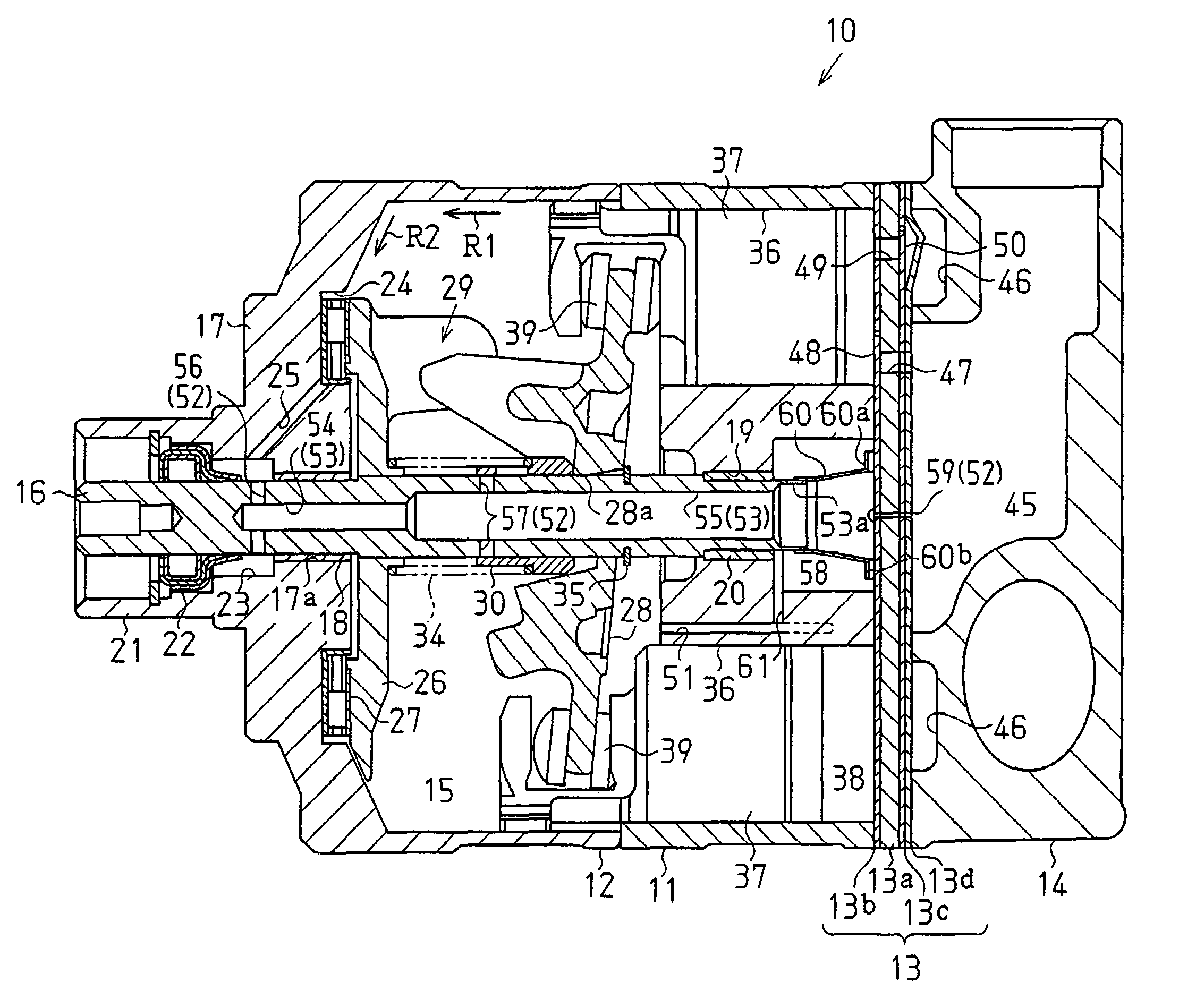
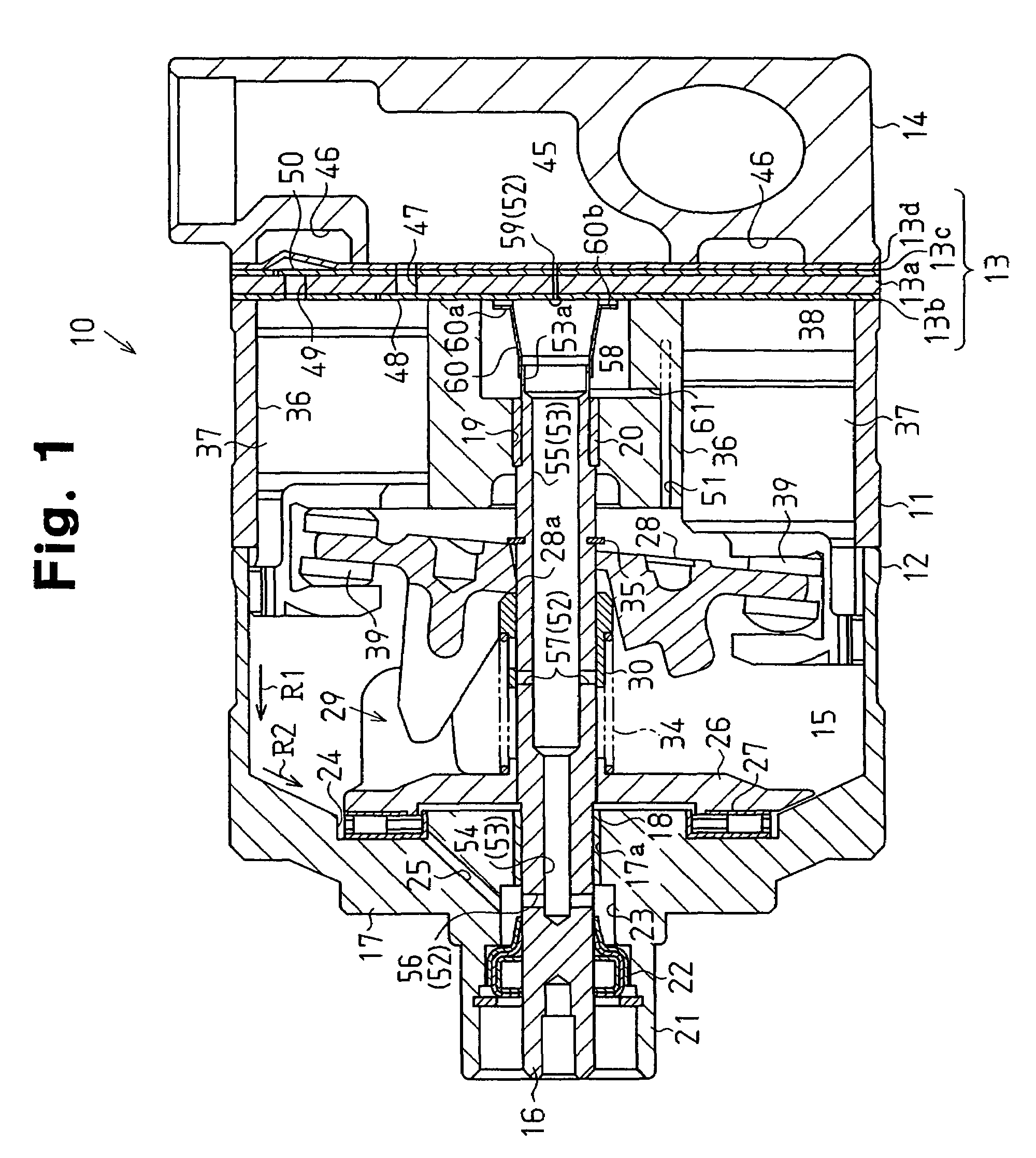
A variable displacement compressor including a drive shaft through which a gas passage extends between front and rear ends of the drive shaft. The gas passage is connected to a suction chamber at the rear end of the drive shaft. The drive shaft includes a first gas inlet passage, which connects the gas passage to a crank chamber through a lip seal, an oil chamber, and a thrust bearing, and a second gas inlet passage, which connects the gas passage to a central portion of the crank chamber. The drive shaft further includes a sleeve movable along the drive shaft as a swash plate inclines to adjust an open amount of the second gas inlet passage in accordance with the inclination angle of the swash plate, that is, the displacement of the compressor.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP
Swash plate type hydraulic pump or motor
InactiveUS20050095144A1Efficient dischargeEfficient supplyMulti-stage pumpsReciprocating piston enginesFree rotationReciprocating motion
A swash plate type hydraulic pump or motor has a first swash plate (30) and a second swash plate (40) which cause a first piston (8) and a second piston (9), respectively, to move reciprocally, opposing each other, so as to expand and contract a volume chamber (10) according to rotation of a cylinder block (4). A rod shape valve body (60) is disposed pushed into a through hole (12) of a shaft axis of the cylinder block (4) so as to be free to rotate relative to the cylinder block (4). A pair of supply and discharge ports (61) that open and supply high pressure and low pressure, respectively, are formed in an outer circumferential surface of the valve body (60). A cylinder port (11) is formed connecting the volume chamber (10) and an inner circumferential surface of the through hole of the cylinder block. The cylinder port (11) is arranged in a position opposite to the supply and discharge port (61).
Owner:KYB CORP
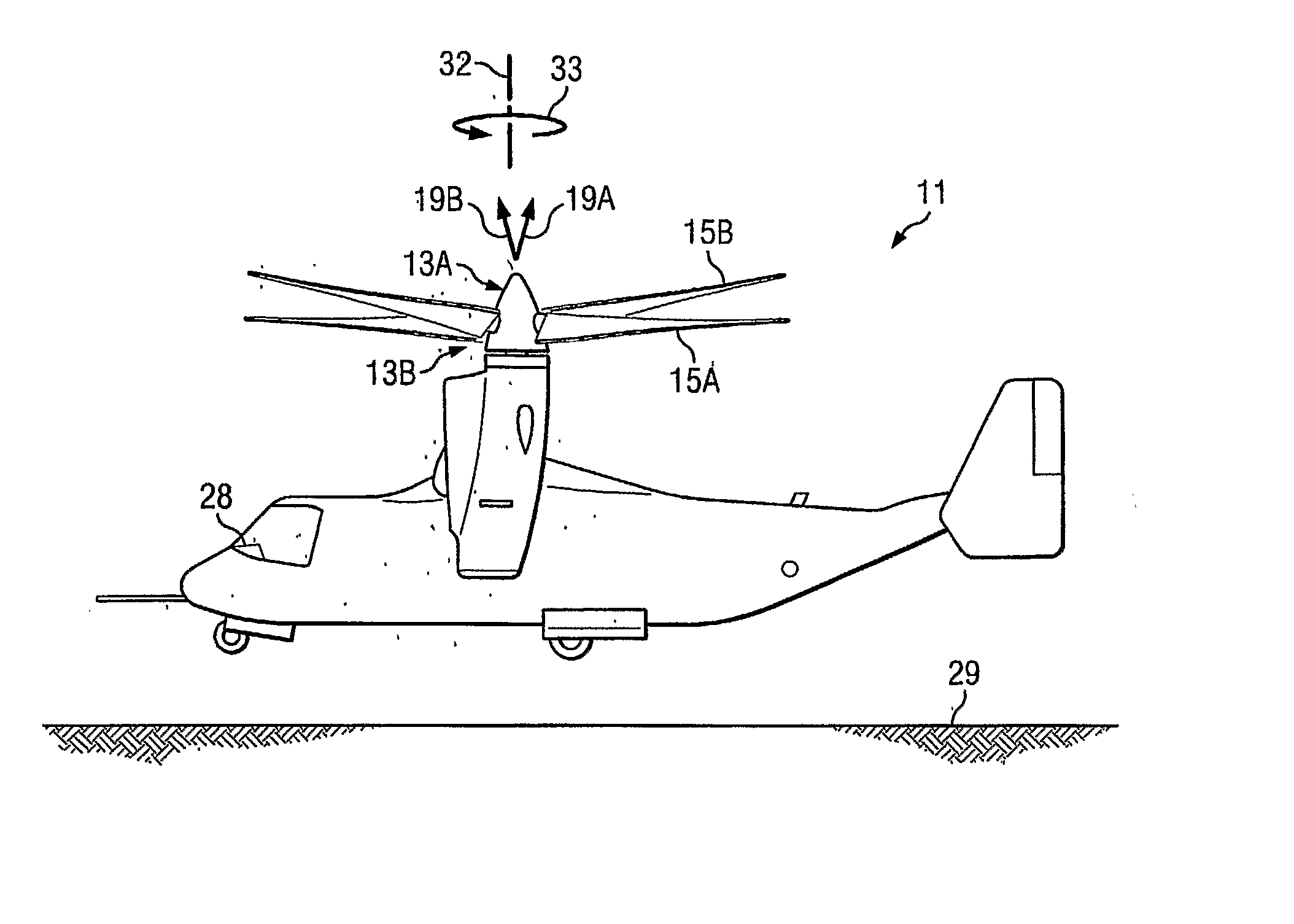
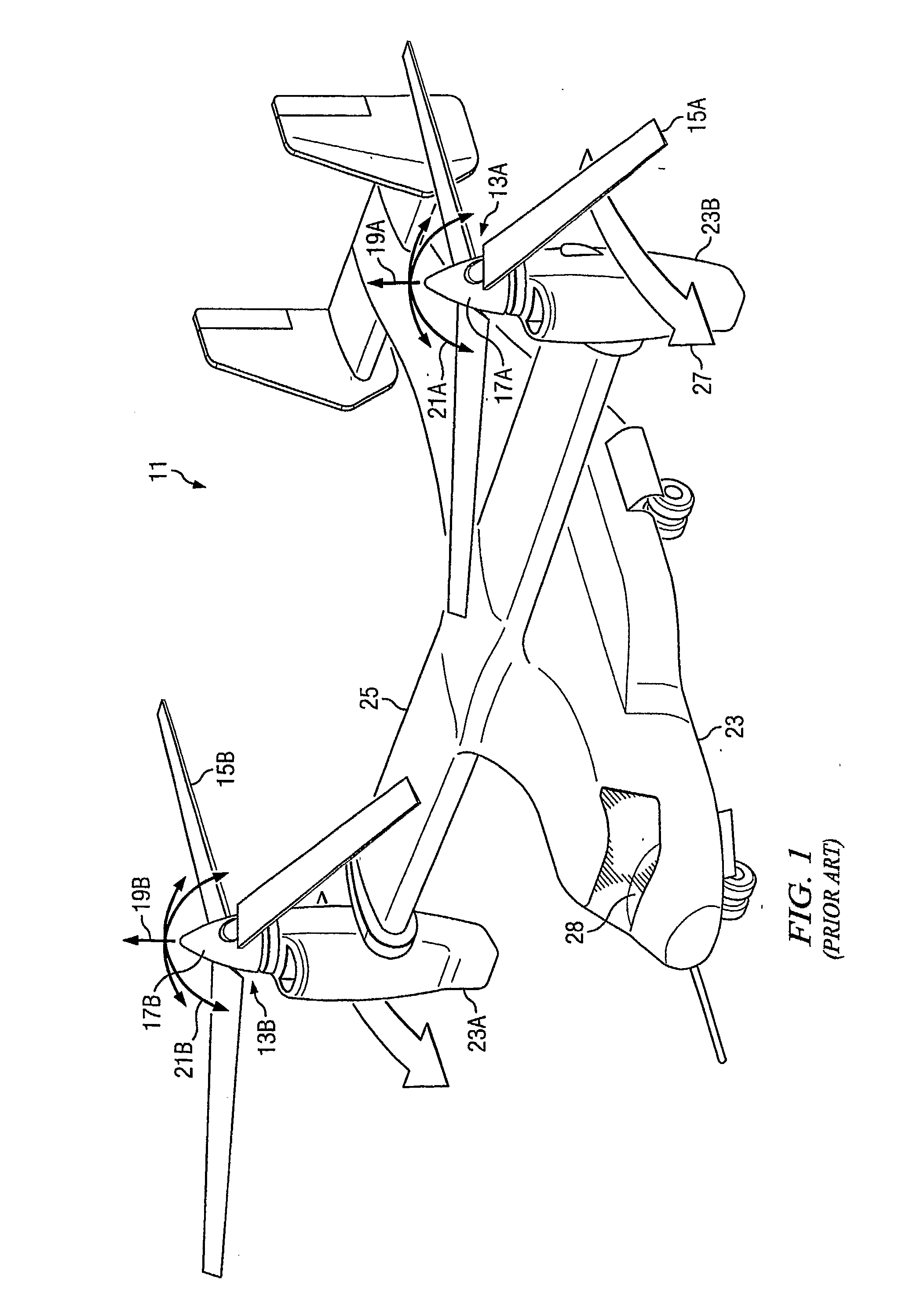
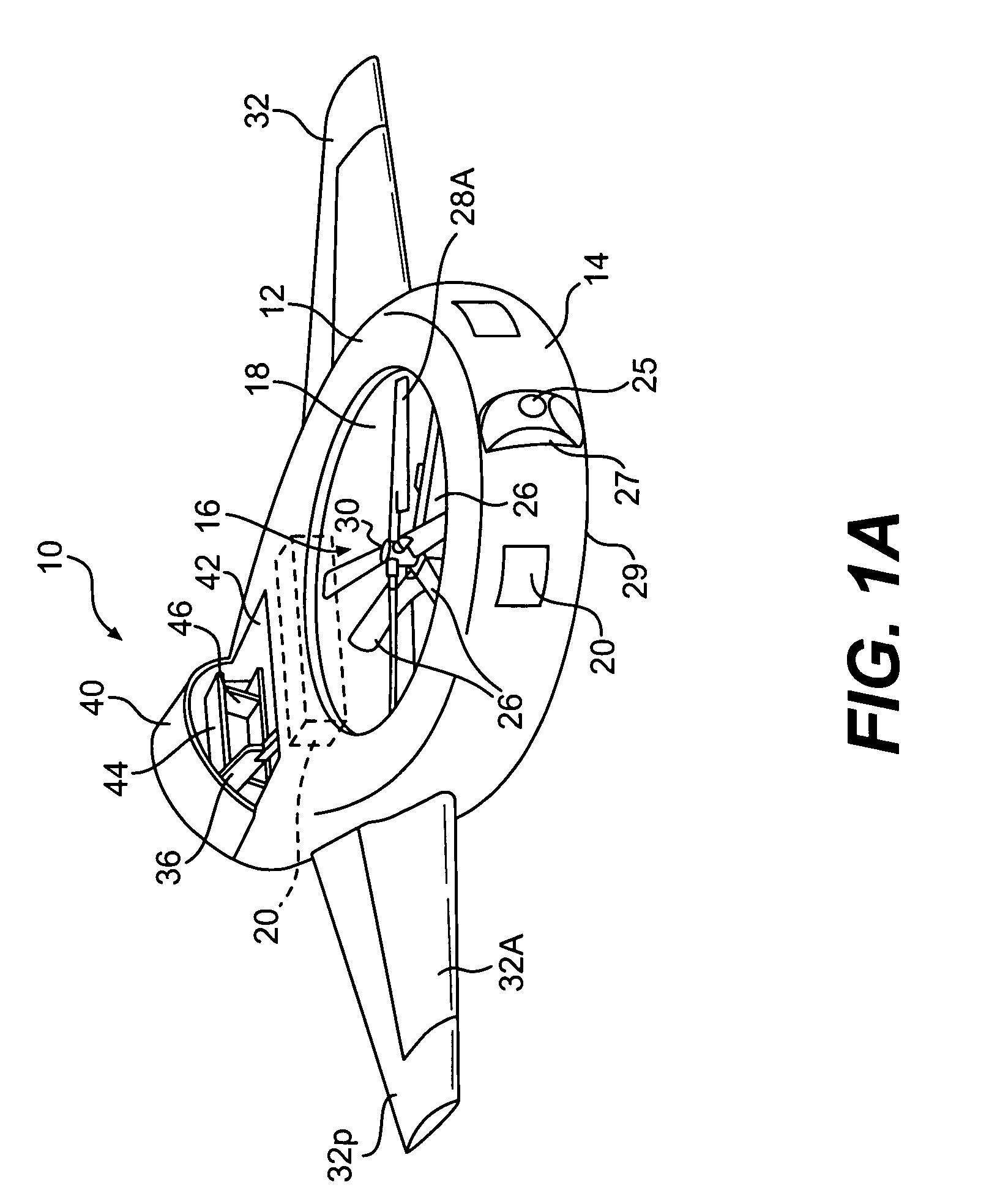
Rotor aircraft tilting hub with reduced drag rotor head and mast
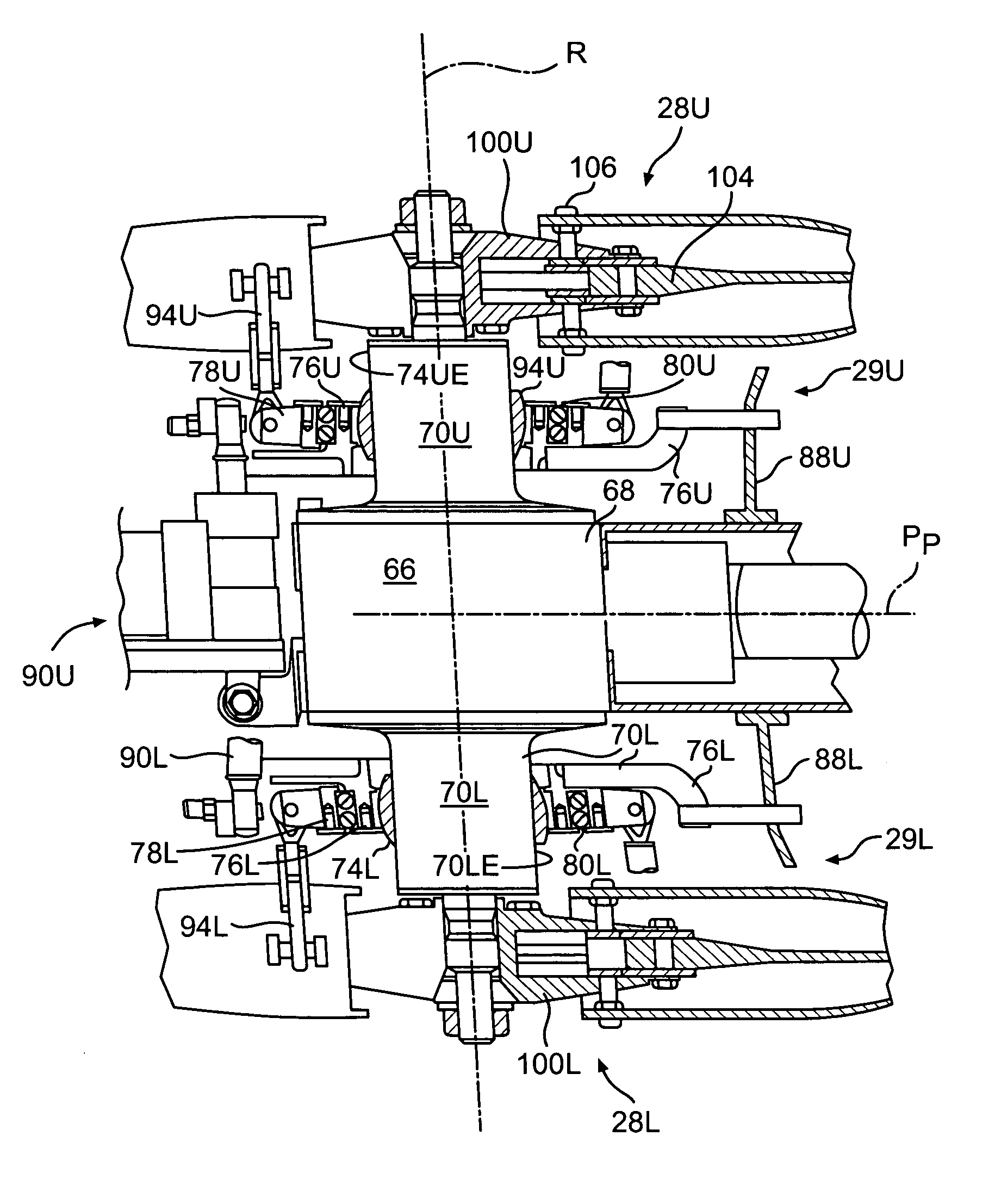
ActiveUS7510377B1Eliminating oscillatory featheringSimple tilting spindlePropulsive elementsReaction enginesDrive shaftEngineering
A rotor aircraft has a tilting hub for cyclic control operated by either a tilting spindle or swash plate mounted to the upper end of the drive shaft. A spinner housing with two separate half portions encloses the hub. The blades of the rotor have root portions that are integrally joined to the separate half portions. During a collective pitch change, the half portions rotate relative to each other, but at advance ratios greater than about 0.7, when the collective can be held constant, the spinner half portions can be in perfect alignment. Concentric control sleeves surround the drive shaft for changing collective pitch as well as cyclic pitch.
Owner:JAUNT AIR MOBILITY LLC
Work machine
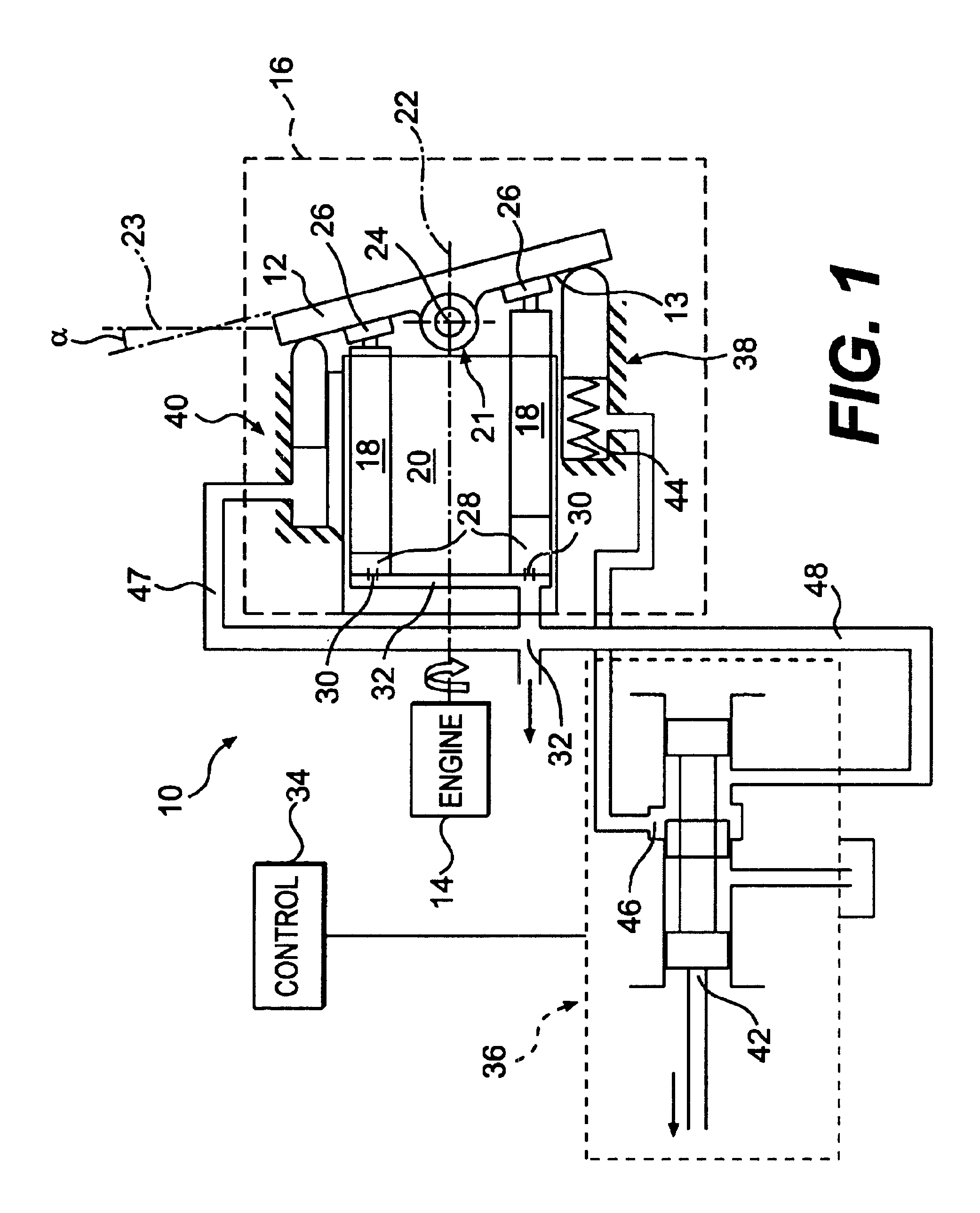
Disclosed is a work machine having a traveling apparatus and a work implement driven by an engine. A hydraulic system mounted on the work machine includes an HST pump comprising a swash plate, variable displacement pump driven by the engine, an HST motor connected in a closed circuit to the HST pump and a pair of speed-changing oil passageways, the HST motor being driven by an amount of oil supplied by the HST pump, thereby to drive the traveling apparatus, a main pump driven by the engine, the main pump supplying pressure oil to the work implement, a pilot pump driven by the engine, a swash plate positioning circuit configured to effect positioning of a swash plate of the HST pump with pilot oil supplied from the pilot pump, and a bleed circuit configured to drain, via a throttle, a portion of the pilot oil supplied to the swash plate positioning circuit.
Owner:KUBOTA LTD
Sensor for a variable displacement pump
InactiveUS6848888B2Positive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsPower flowSemiconductor chip
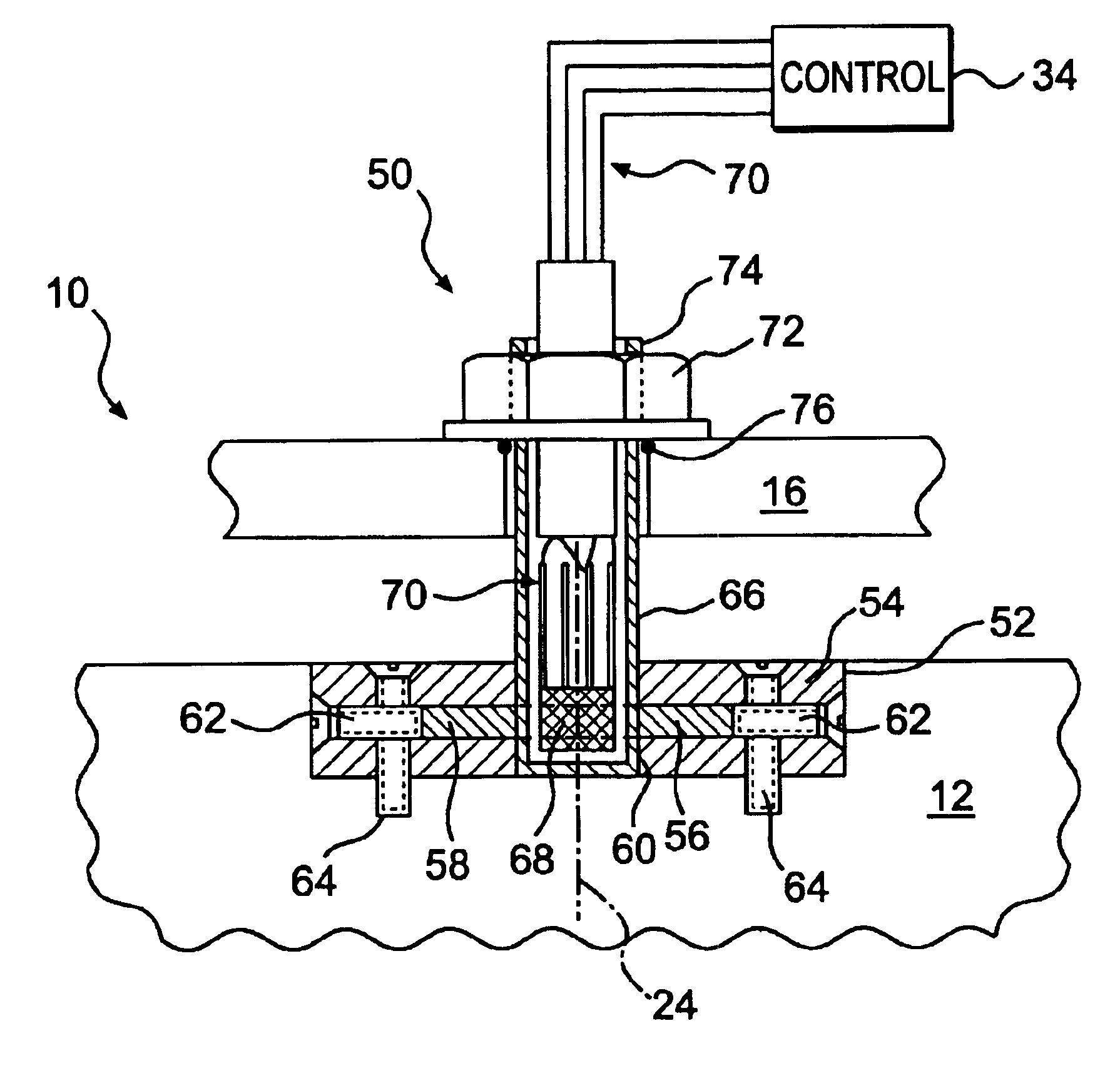
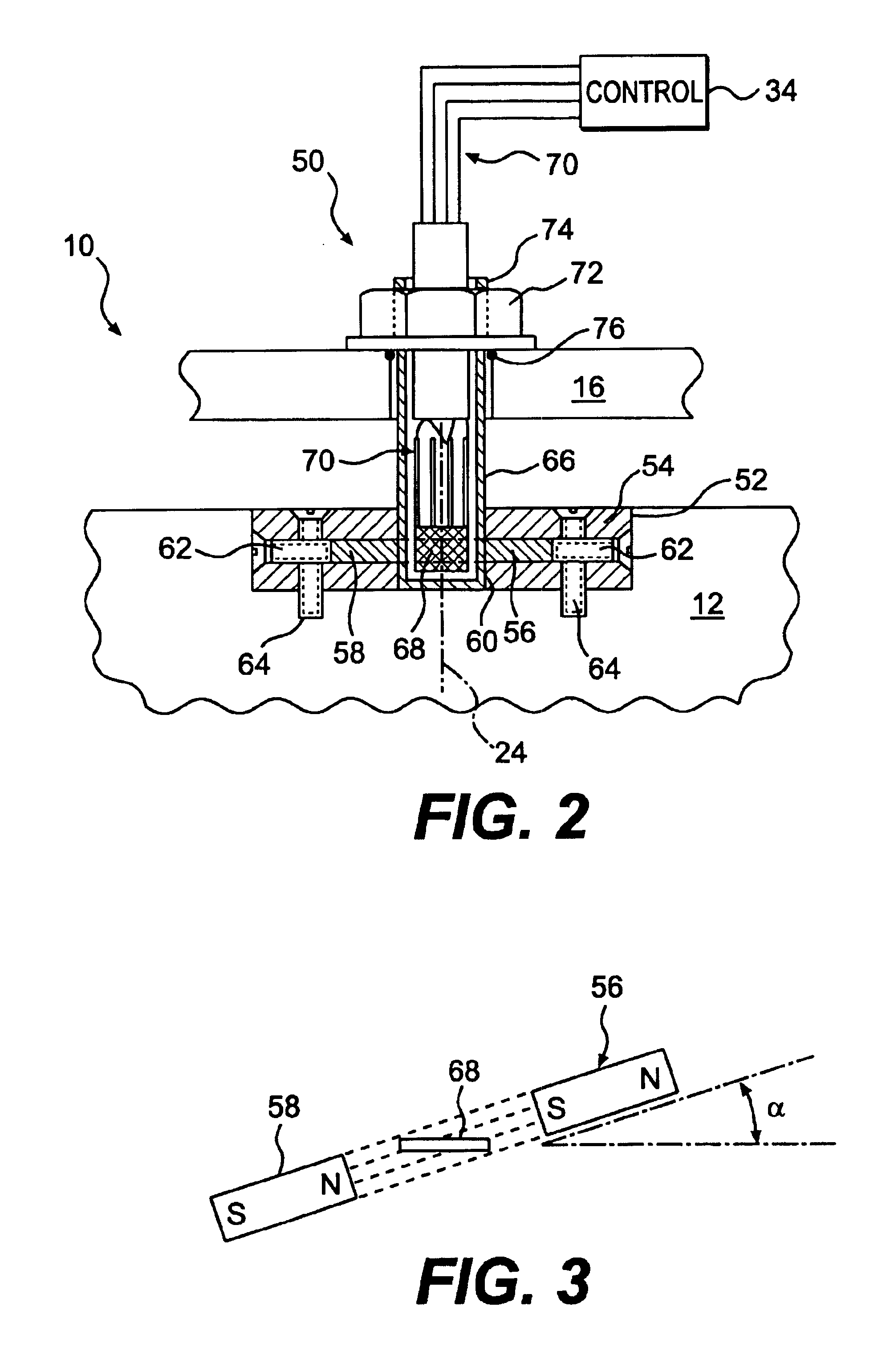
A sensor for a variable displacement pump is provided. The pump has a housing containing a swashplate that is adapted to rotate about an axis. The sensor includes a magnet connected to the swashplate to rotate with the swashplate. A semiconductor chip is disposed proximate the magnet and within the housing. A control is adapted to direct a current through the semiconductor chip and to determine the voltage across the semiconductor chip. The control is further adapted to determine the angle of the swashplate relative to the housing based on the determined voltage.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
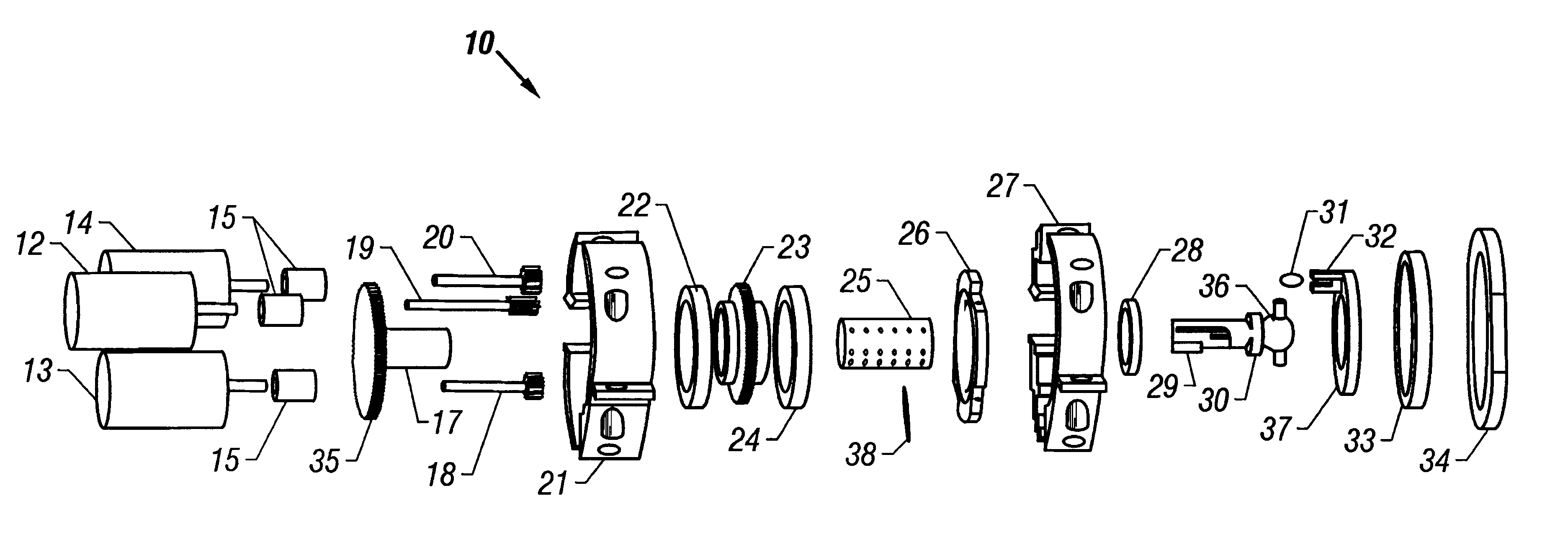
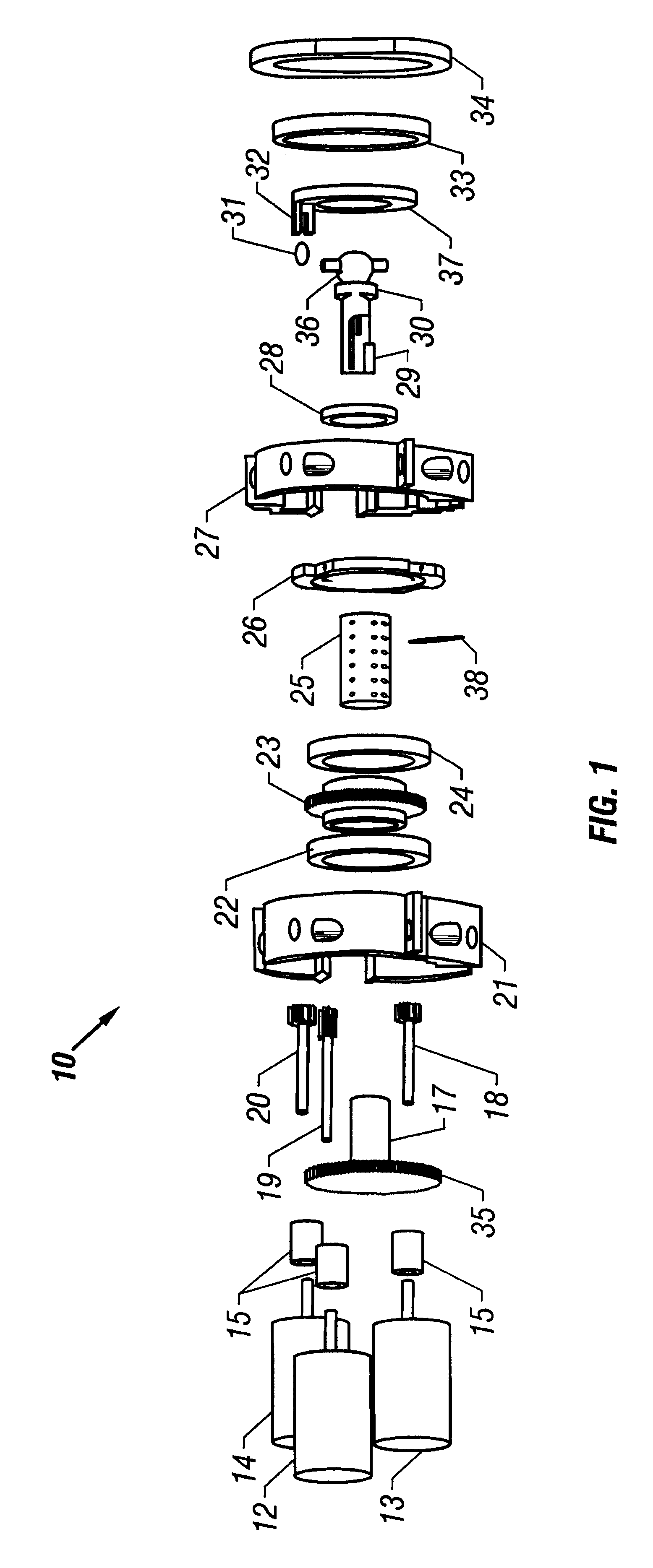
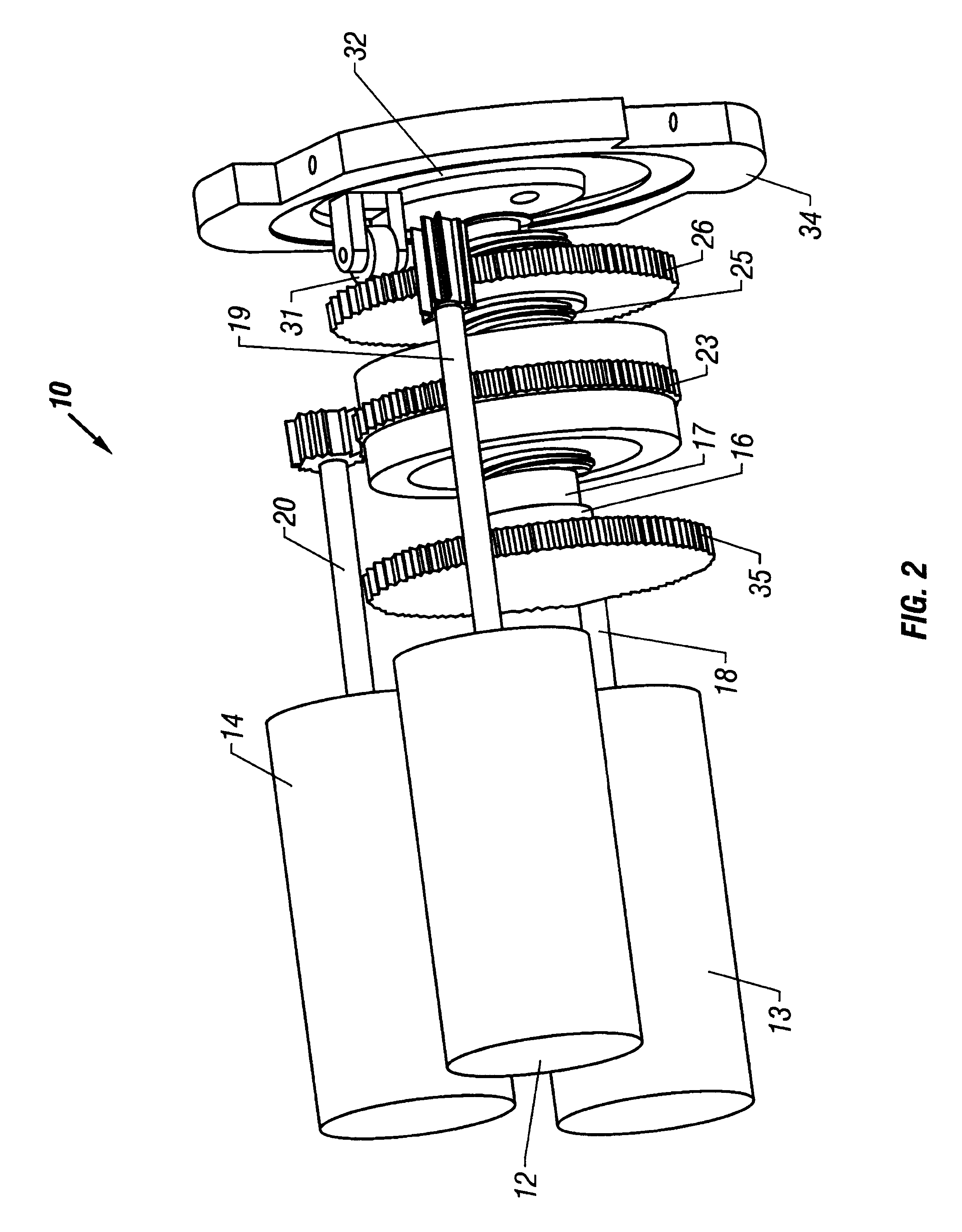
Swashplate pump
A piston pump assembly with a rotatingly driven swashplate in driving relationship with a rocker arm and piston engaged with one end of the rocker arm. A spring urges the rocker arm and piston into contact with an annular ring carried by a bearing in the swashplate. The spring may be a separate leaf spring or may be formed integrally with the rocker arm. The rocker arm engagement with the piston uses a spherical ball-joint-like surface. The contact between each of the rocker arm and piston and the annular ring utilize spherical surfaces on the rocker arm and piston, with an elongated footprint on the rocker arm and a circular footprint on the piston. The piston is allowed a slight radial play in operation.
Owner:WAGNER SPRAY TECH CORP
Method of folding the blades of a main rotor of a rotary-wing aircraft, and apparatus for implementing the method
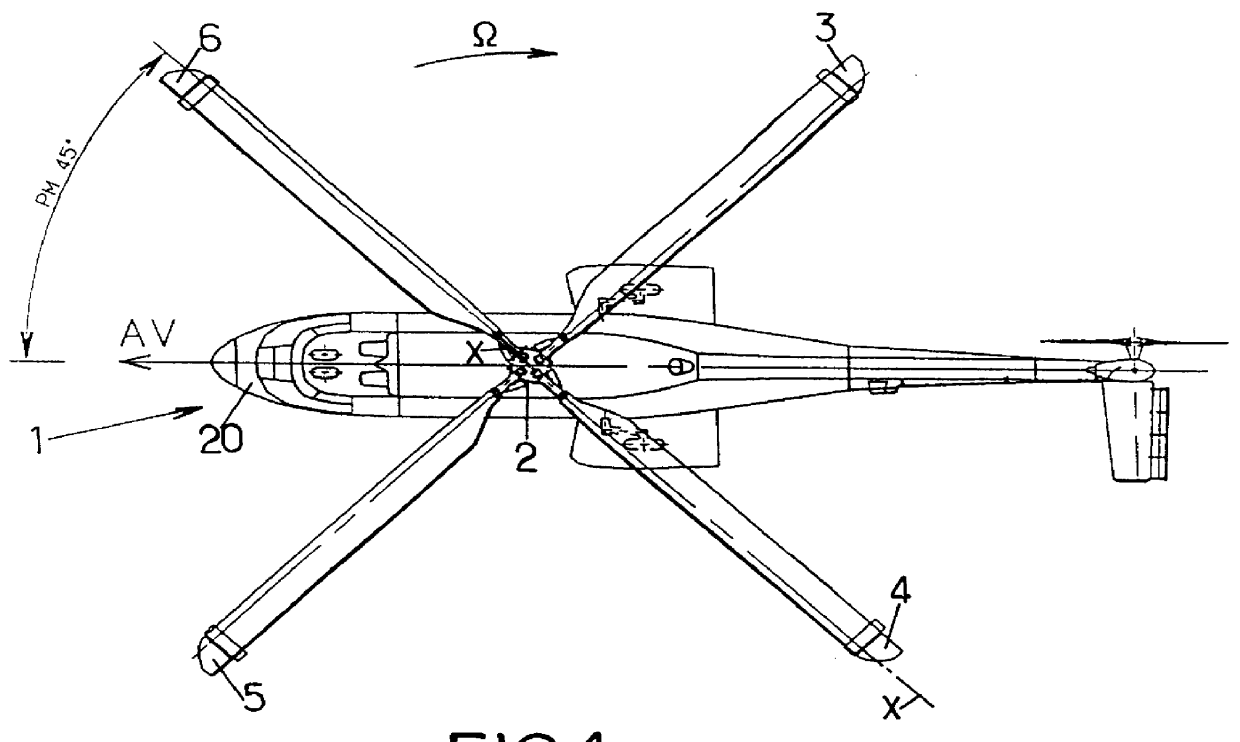
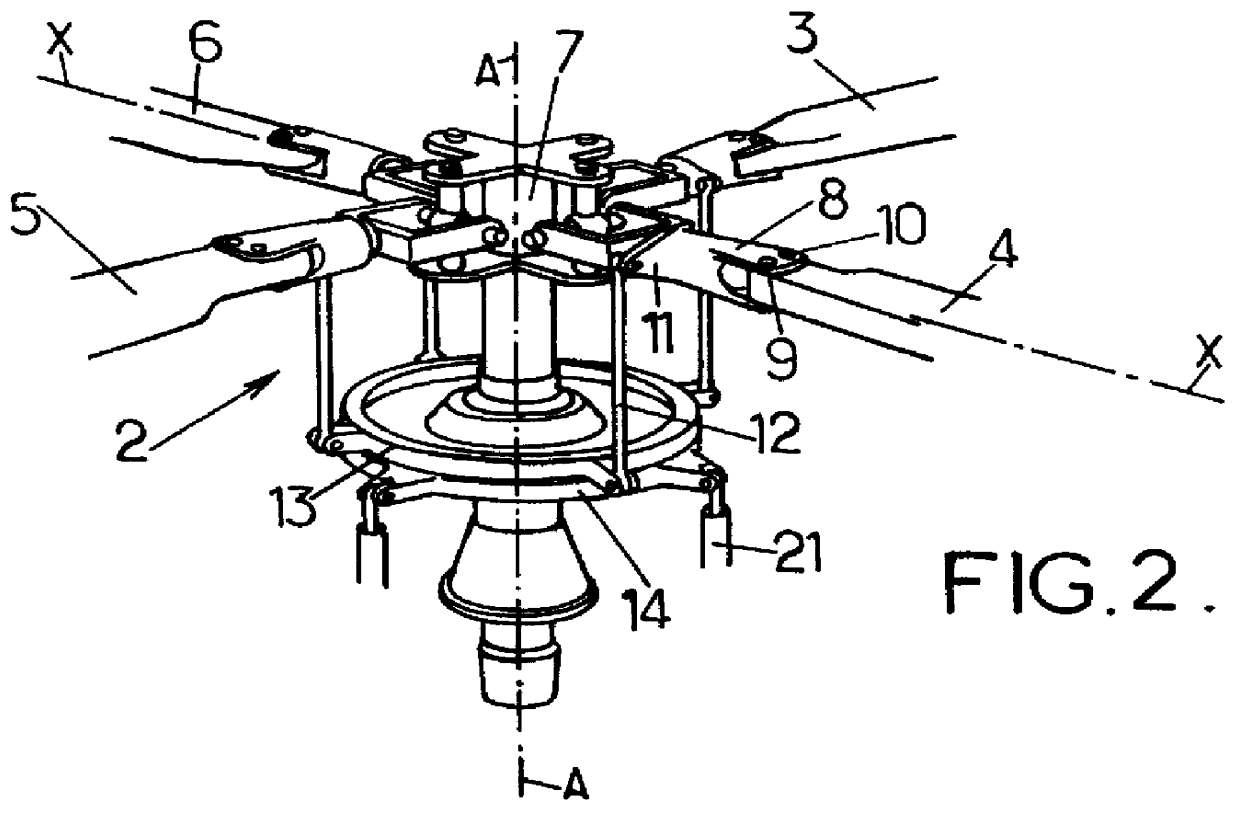
Once the rotor of a rotary-wing aircraft is held stationary in an indicated position, the method comprises steps consisting in placing the collective pitch control stick in a first predefined position corresponding to a first inclination of the blades about their longitudinal axes, in placing the cyclic pitch control stick in a second predefined position corresponding to a nose-up position of the rotary-wing aircraft, in modifying the length of the control system to cause the inclination of the blades about their longitudinal axes to go to a second value that is different from said first inclination value, in holding a rotary swashplate stationary by placing at least three locking connection rods between the rotary swashplate and a member integral in terms of rotation with a rotor mast, and in folding the blades by rotating each of them about a corresponding coupling pin for coupling it to a coupling member for coupling the blade to a rotor hub.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
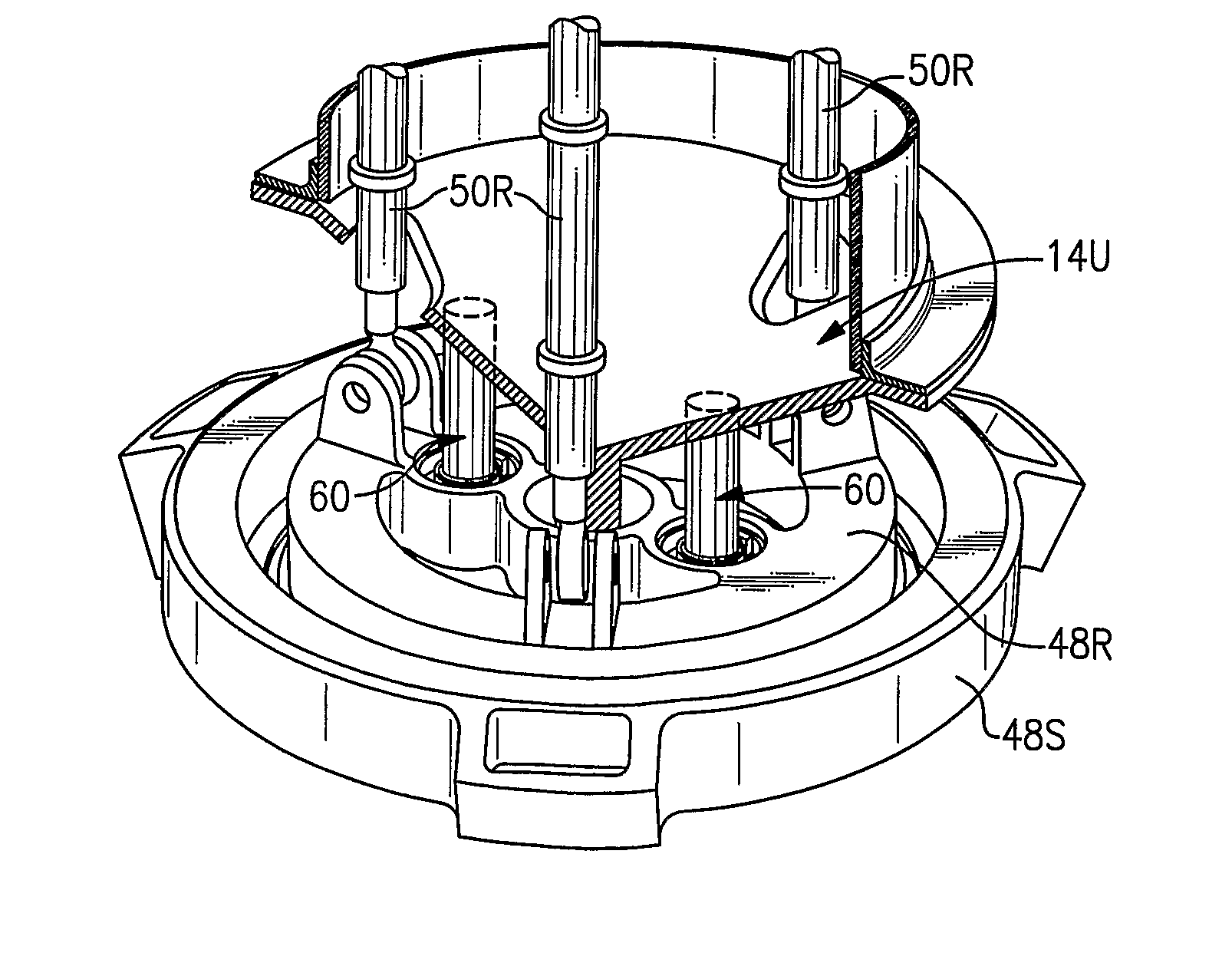
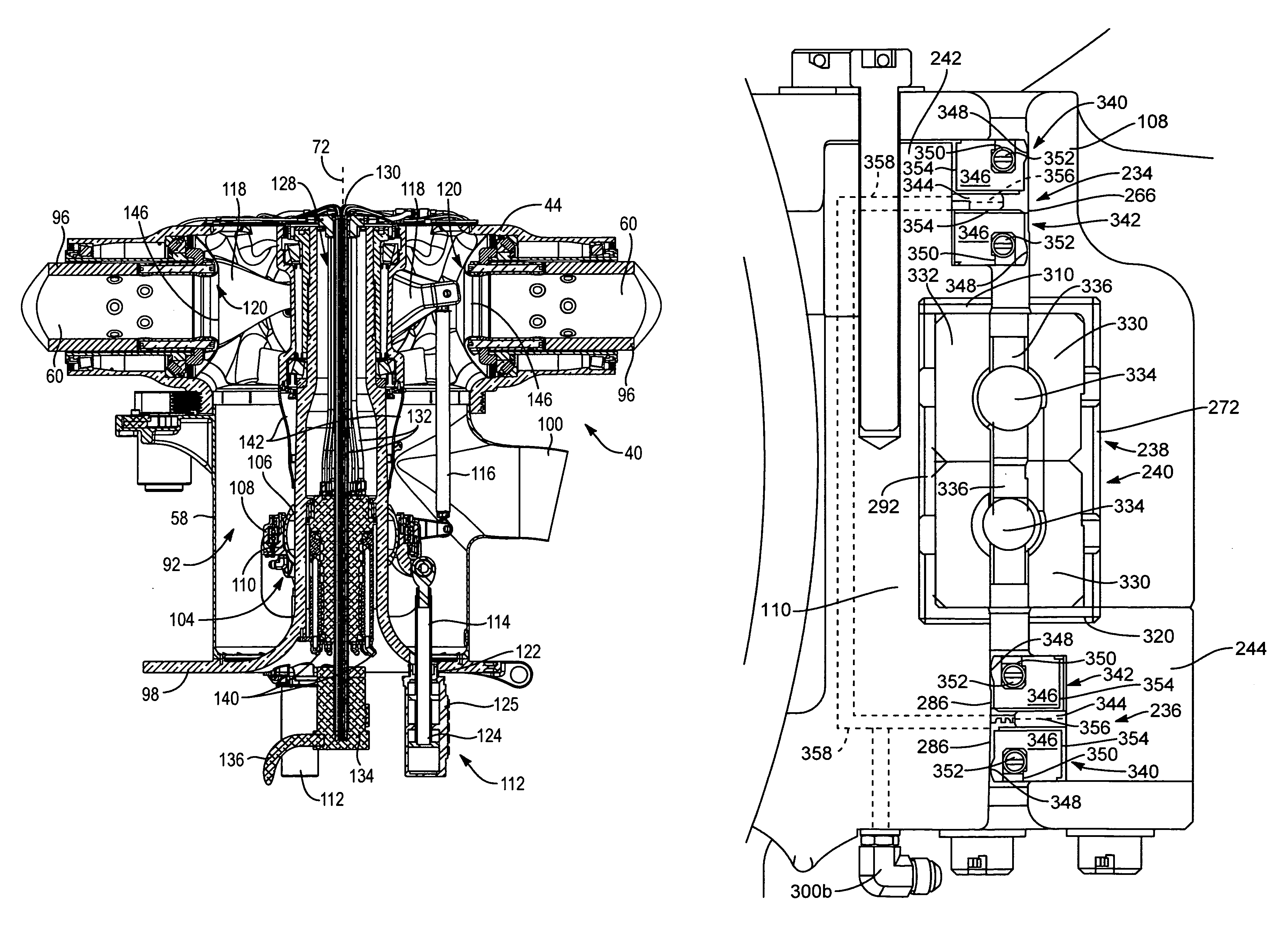
Compact load path swashplate assembly
ActiveUS8142158B2Uncomplicated attachment arrangement is facilitatedGood locking functionPropellersPump componentsEngineeringControl theory
A swash plate assembly includes a rotationally stationary swash plate and rotational swash plate which rotates relative to the rotationally stationary swash plate through a bearing system. Each servo control rod is attached to the swash plate assembly to communicate control inputs thereto through a respective servo lug. Each servo lug defines a servo pivot point off an in-line plane inboard of the bearing system. As the servo lugs extend below the rotationally stationary swash plate, a relatively uncomplicated attachment arrangement is facilitated which provides for redundant locking features at a highly inspectable location which simplifies maintenance and increased safety. By locating the servo pivot point just inboard of the bearing system, an exceeding compact load path is defined thereby. The load path is defined from the servo control, to the servo lug, through the rotationally stationary swash plate, bearing system, the rotational swash plate, the rotor pitch control point and into the pitch control rod.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Control system for hydrostatic pump
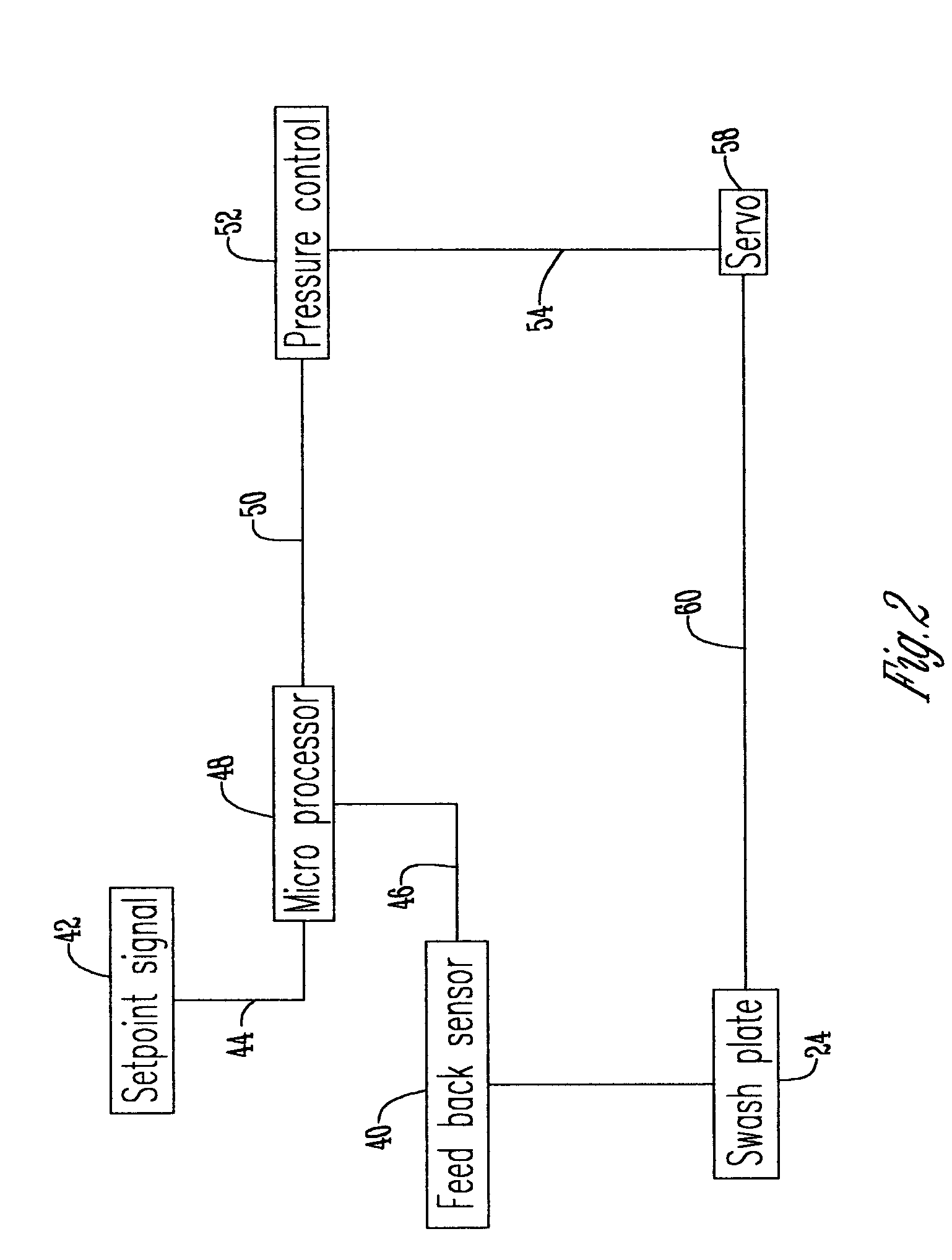
A control system that can be used on a hydrostatic pump has a feedback sensor to detect the angle of a swashplate. From the information gathered by the feedback sensor about the swashplate and another set command, this information is sent to a microprocessor. The microprocessor then uses an algorithm to create an output signal and also sends out a superimposed dither signal. This dithered output signal is then received by a pressure control that causes a dither servo pressure in a servo system. Because of the dither pressure the servo system adjusts the position of the swashplate.
Owner:SAUER DANFOSS NORDBERG
Improved Rotor-Blade Control System and Method
A blade-pitch control system has a swashplate configured for continuous rotation with an associated rotor and mast, and at least one link connects the swashplate to each blade of the rotor. The swashplate provides for collective control of the pitch angle of the blades through selective rotation of the swashplate about a swashplate axis while the swashplate is rotating with the rotor and mast. The system can be configured to provide for cyclic control of the pitch angle of the blades through planar translation of the swashplate or through tilting of the swashplate about axes generally perpendicular to the swashplate axis.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Model Aircraft Contol and Receiving Device
ActiveUS20120169484A1Low amount of consumedReduce effortElectric signal transmission systemsToy aircraftsGyroscopeCoupling
Owner:MIKADO MODEL HELICOPTERS
Control lever for controlling a rotary wing, a mechanical control system including said control lever, and an aircraft
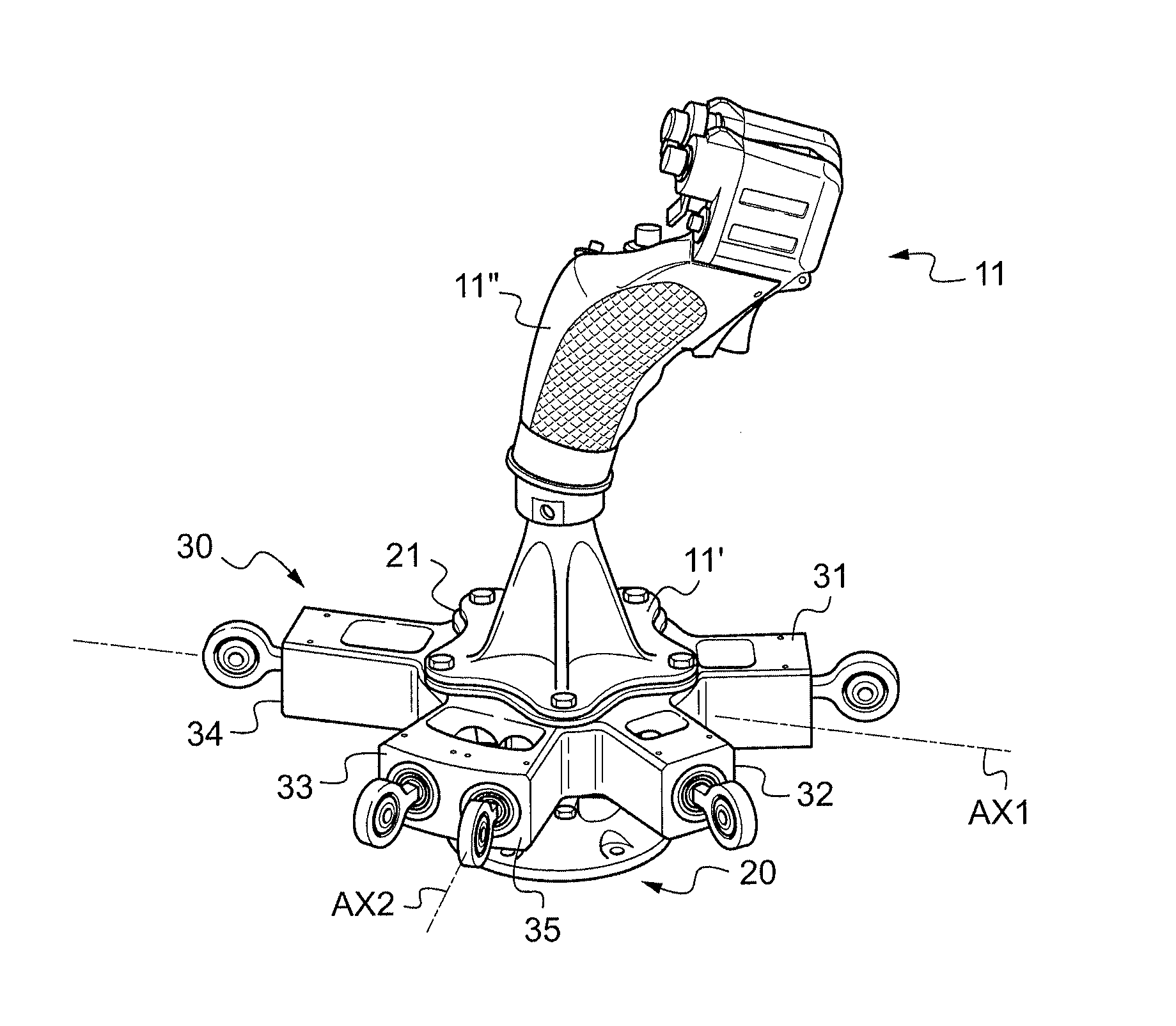
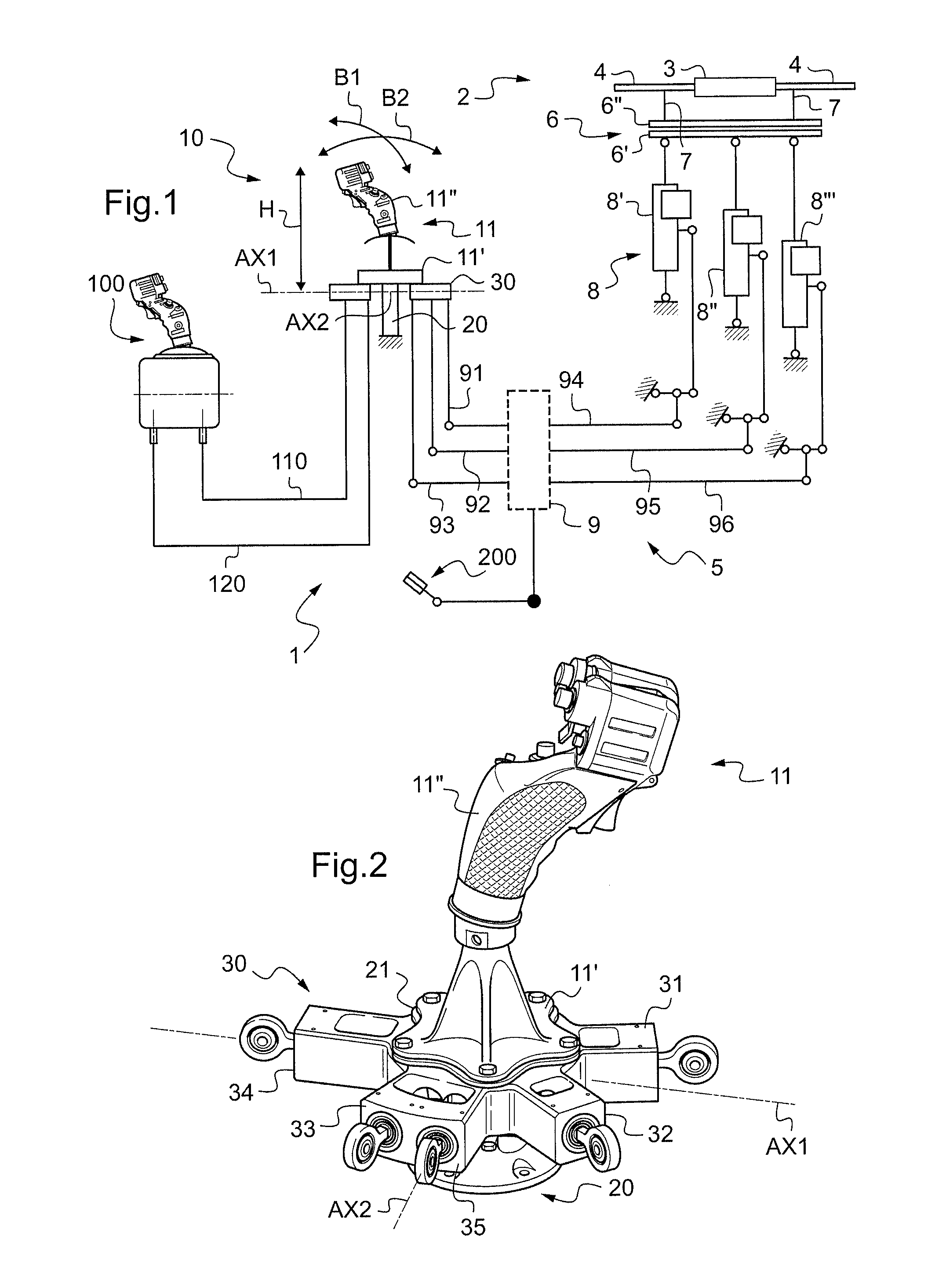
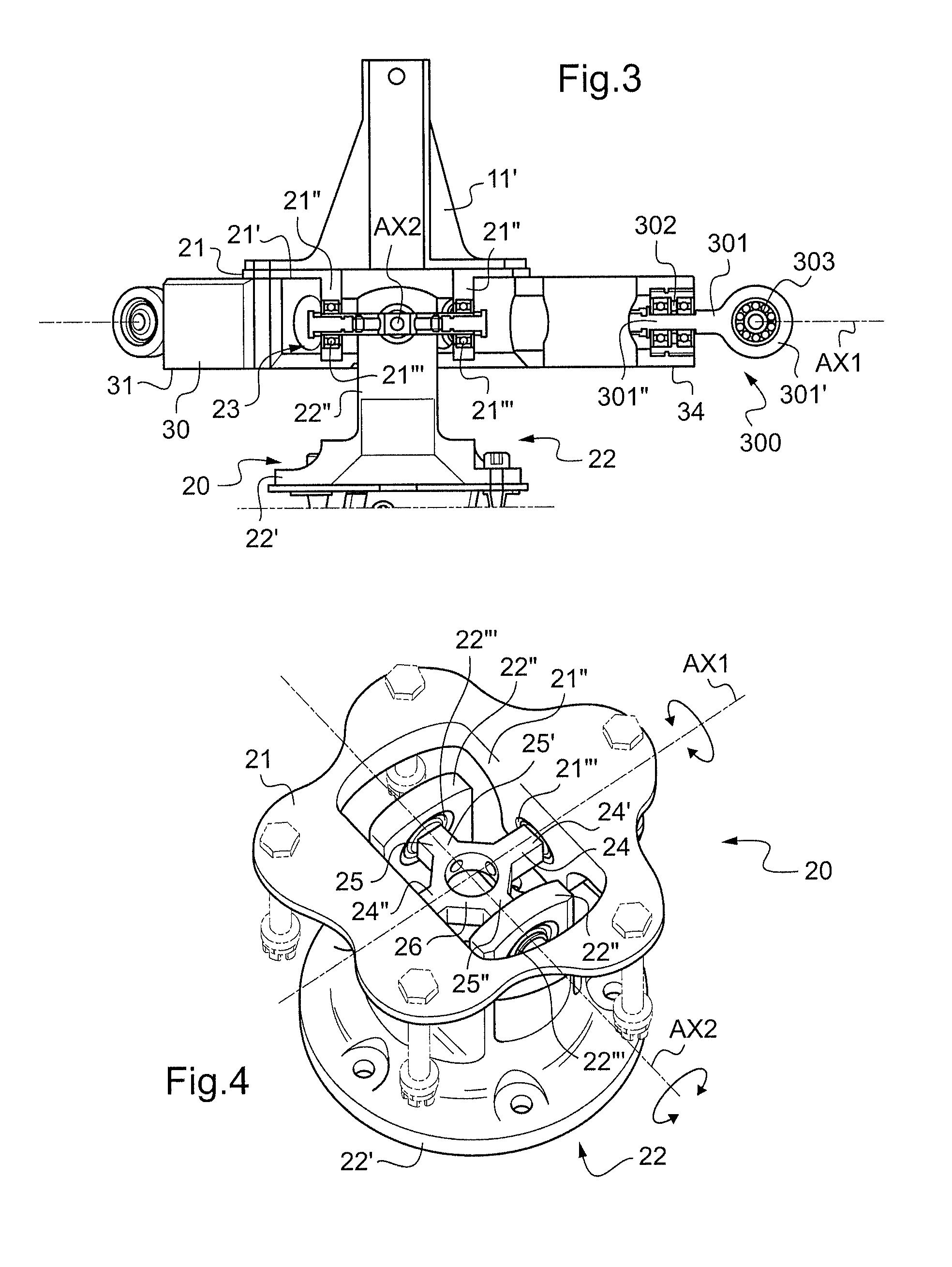
ActiveUS20120255386A1Controlled friction forceFriction minimizationManual control with multiple controlled membersMechanical apparatusFlight vehicleControl system
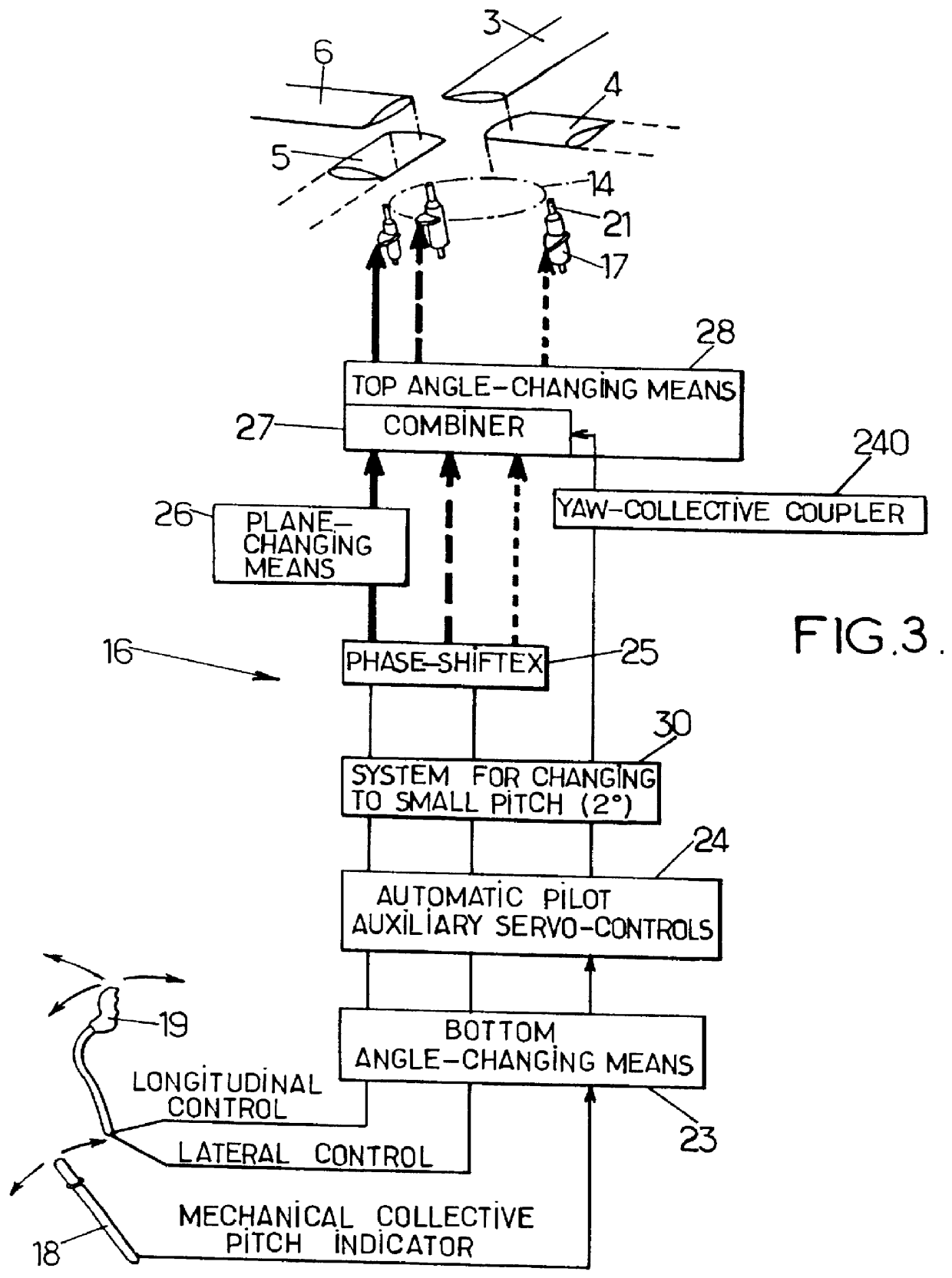
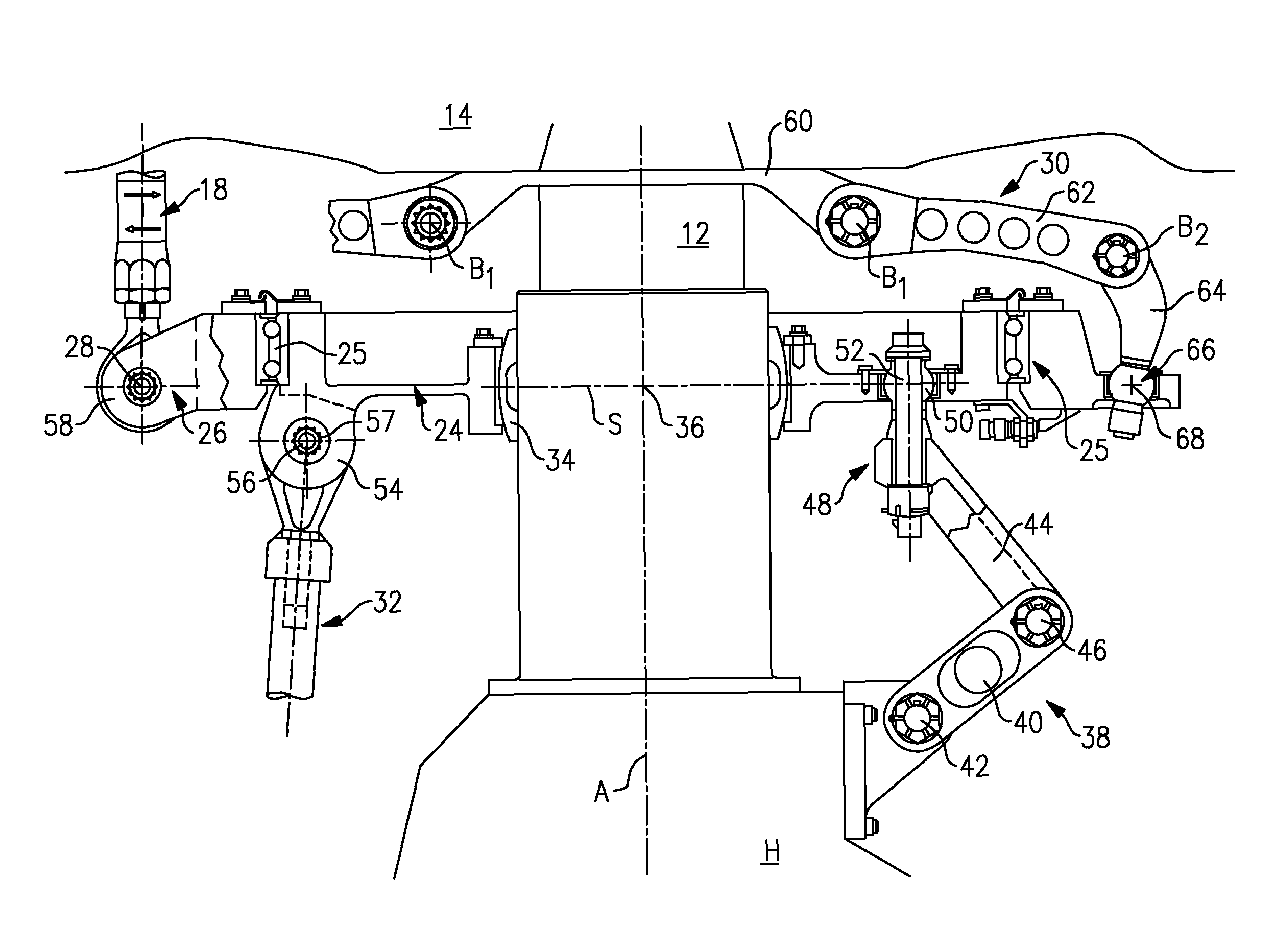
A control lever (10) provided with a stick (11) extending axially from a stand (11′) towards grip means (11″) and with a carrier structure (20) for said stick (11) that is hinged about a first hinge axis (AX1) and about a second hinge axis (AX2). The control lever (10) includes phasing means (30) constrained to move in rotation with said stick (11) about said first hinge axis (AX1) and about said second hinge axis (AX2), said phasing means (30) comprising at least three main arms (31, 32, 33), each for controlling a respective power member (8′, 8″, 8″′) that is connected to a set (6) of swashplates for controlling a rotary wing (2).
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Swashplate and pitch link arrangement for a coaxial counter rotating rotor system
A coaxial counter-rotating rotor system for a hybrid aircraft includes an upper swashplate assembly and a lower swashplate assembly with a coaxial transmission system therebetween. Movement of the upper and lower swashplate assembly is reflected about a midplane of the coaxial transmission housing to generate sufficient cyclic and / or collective pitch inputs within a compact structural in which the rotor systems are closely spaced along an axis of rotation.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Oil lubricated swashplate
A rotor system for a reactive drive rotary wing maintains the rigidity of the rotor and eliminates play between flight controls and the rotor by mounting swashplate actuators to a flange rigidly secured to the mast. Apparatus and methods perform thermal management of the rotor in order to avoid bearing failure or loss of bearing preload. Methods include modulating the temperature of oil pumped over one or more of the mast bearing, swashplate bearing, and spindle bearing. The temperature of air passively or actively drawn through rotor may also be modulated to maintain bearing temperature within a predetermined range. The rotor includes structures for reducing pressure losses and drag on components due to air flow through the rotor. A rotor facilitates thermal management by oil and air flow.
Owner:SKYWORKS GLOBAL INC
Self-cooling structure for cylinder of swashplate type plunger pump
InactiveCN105201816ADoesn't break smoothnessLow rotational resistancePositive displacement pump componentsPositive-displacement liquid enginesDifferential pressureCentrifugal force
The invention relates to a self-cooling structure for a cylinder of a swashplate type plunger pump. The self-cooling structure comprises the cylinder and a flow-distribution plate, wherein plunger cavities are formed in the front end surface of the cylinder, kidney-shaped holes communicated with the plunger cavities are formed in the back end surface of the cylinder, the back end surface of the cylinder is closely attached to the flow-distribution plate, axial cooling oil channels are formed in the cylinder, radial cooling oil channels for communicating the axial cooling oil channels with the outer circumferential surface of the cylinder are formed in the circumferential side of the cylinder, flow-distribution cooling oil channels for communicating the axial cooling oil channels with the back end surface of the cylinder are formed in the back end surface of the cylinder, an arc through hole-shaped low-pressure oil sucking area and high-pressure oil discharge areas are formed in two sides of a same end surface of the flow-distribution plate, oil grooves are formed between the low-pressure oil sucking area and the high-pressure oil discharge areas, and the plunger cavities are communicated with the low-pressure oil sucking area and the high-pressure oil discharge areas through the kidney-shaped holes. Under the action of the rotating centrifugal force of the cylinder and the pressure difference of the outer circumferential surface of the cylinder, the cooling efficiency is effectively improved; the specific oil grooves of the flow-distribution plate and the cooling oil channels of the cylinder are formed, and the cooling efficiency and reliability are further improved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Single-ducted coaxial rotor/propeller saucer-shaped aircraft
The invention provides a single-ducted coaxial rotor / propeller saucer-shaped aircraft, which comprises an upper rotor, a lower propeller, a swashplate, a connecting rod, a spindle, a large gear, a bracket, an upper rotor wing motor, a lower propeller motor, a ducted wall, a shell, a steering engine, a support rod and a support seat, wherein the upper rotor is fixedly connected with the spindle; the spindle is supported by the bracket; the bracket is formed by connecting four support rods with one support seat; the large gear is arranged in the support seat; the support seat is connected with the spindle; the spindle is connected with the propeller motor; the ducted wall is arranged inside the shell; both ends of the support rods are respectively connected with the ducted wall and the support seat; the steering engine and the upper rotor wing motor are mounted on the upper side edge of the support seat; and the upper rotor wing motor is meshed with the large gear through a gear in the upper propeller motor. Compared with a single-thrust propeller ducted aircraft, the single-ducted coaxial rotor / propeller saucer-shaped aircraft is less in thrust loss due to no air control surface, and the rotor is combined with the propeller to provide a greater elevating force; and compared with other multi-ducted aircrafts, the single-ducted coaxial rotor / propeller saucer-shaped aircraft is simple in structure.
Owner:中国航空工业空气动力研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com