Patents
Literature
540results about "Pulse train pattern monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
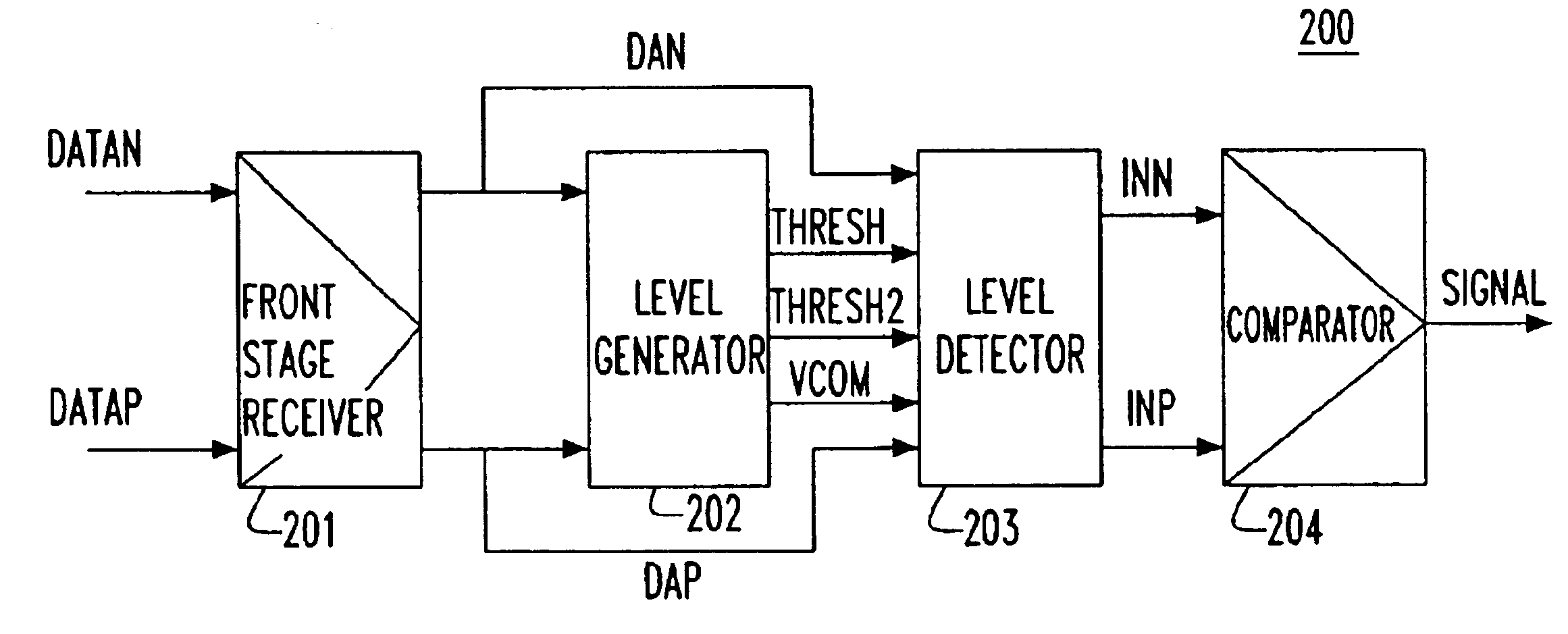
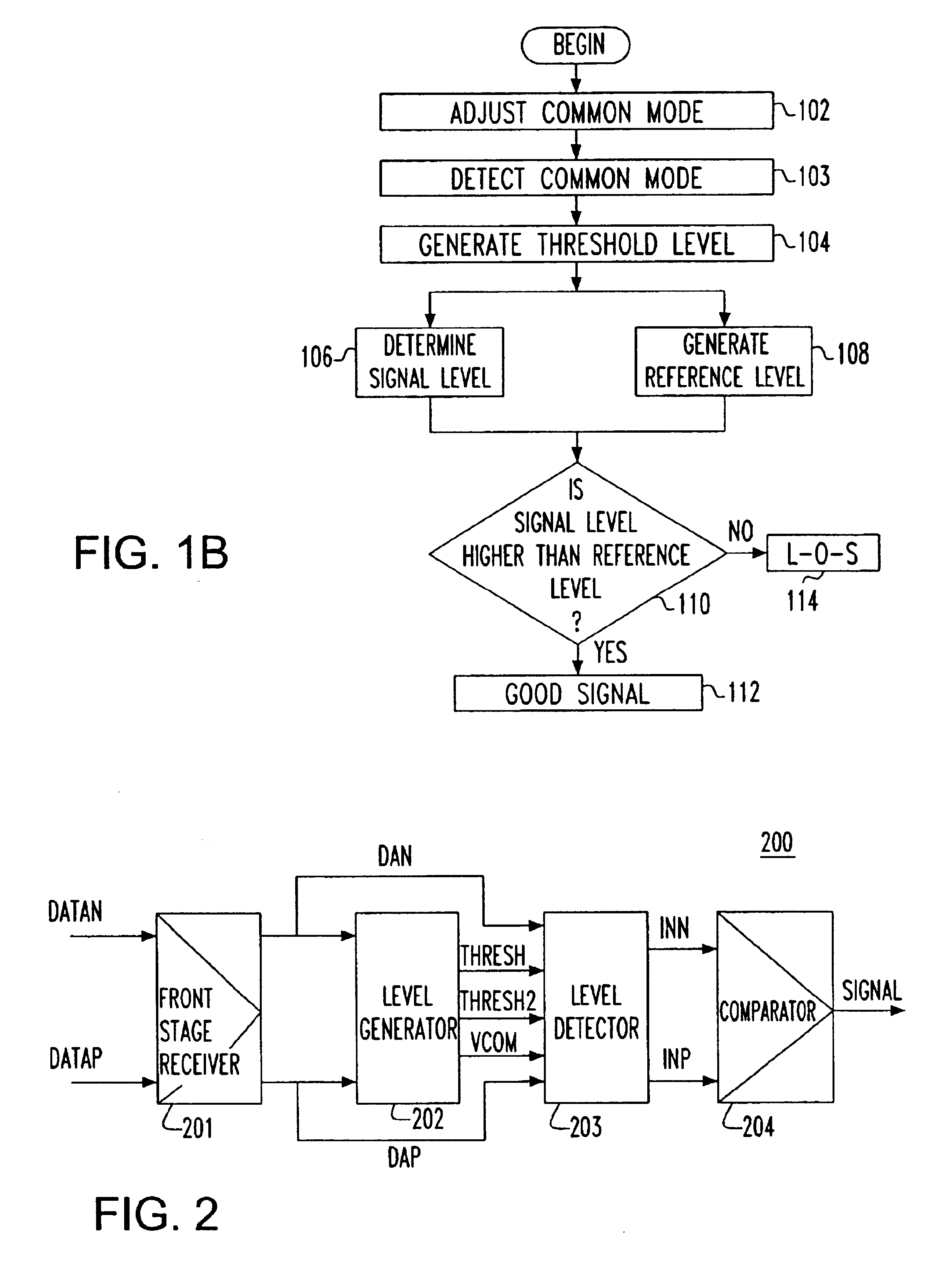
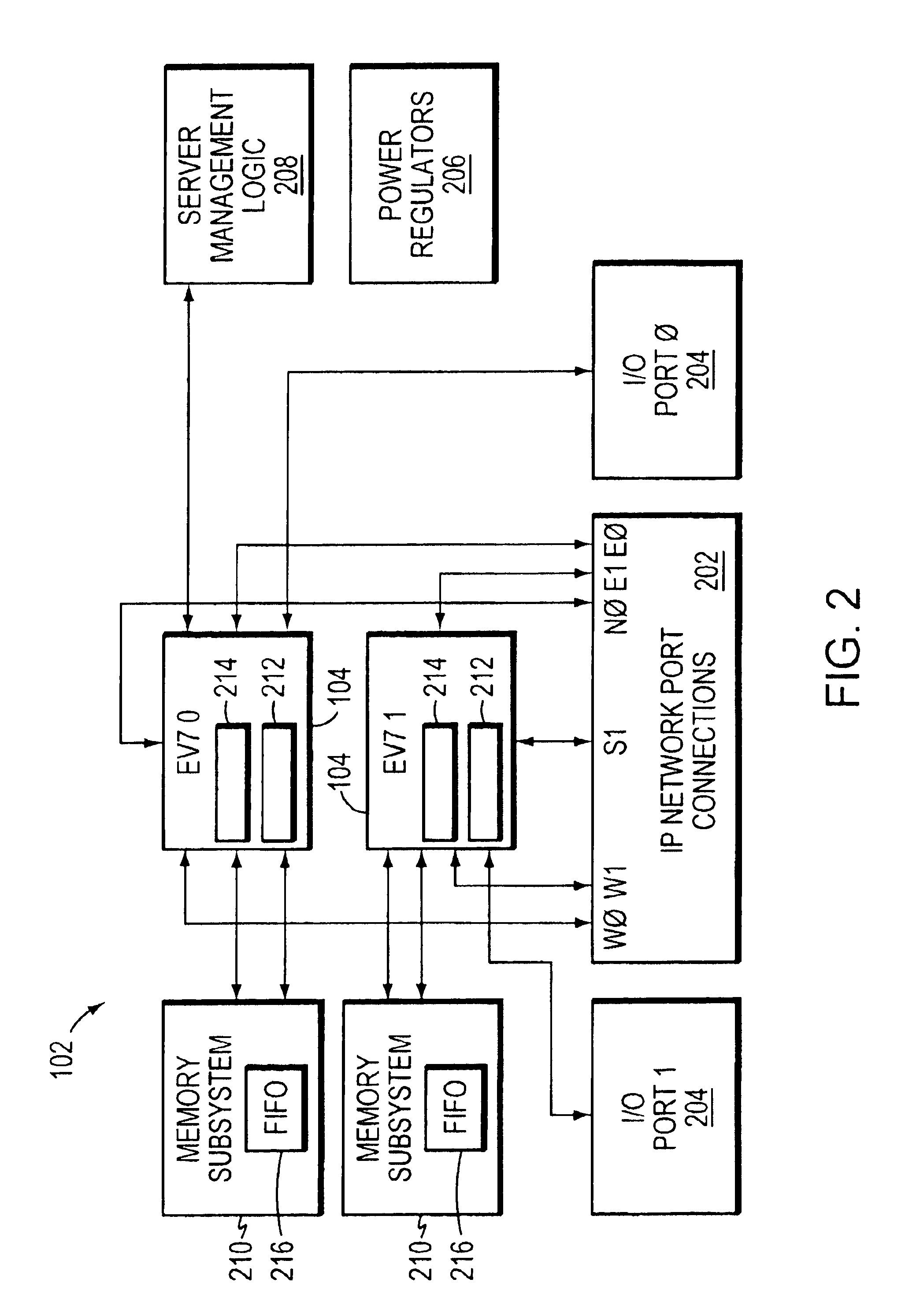
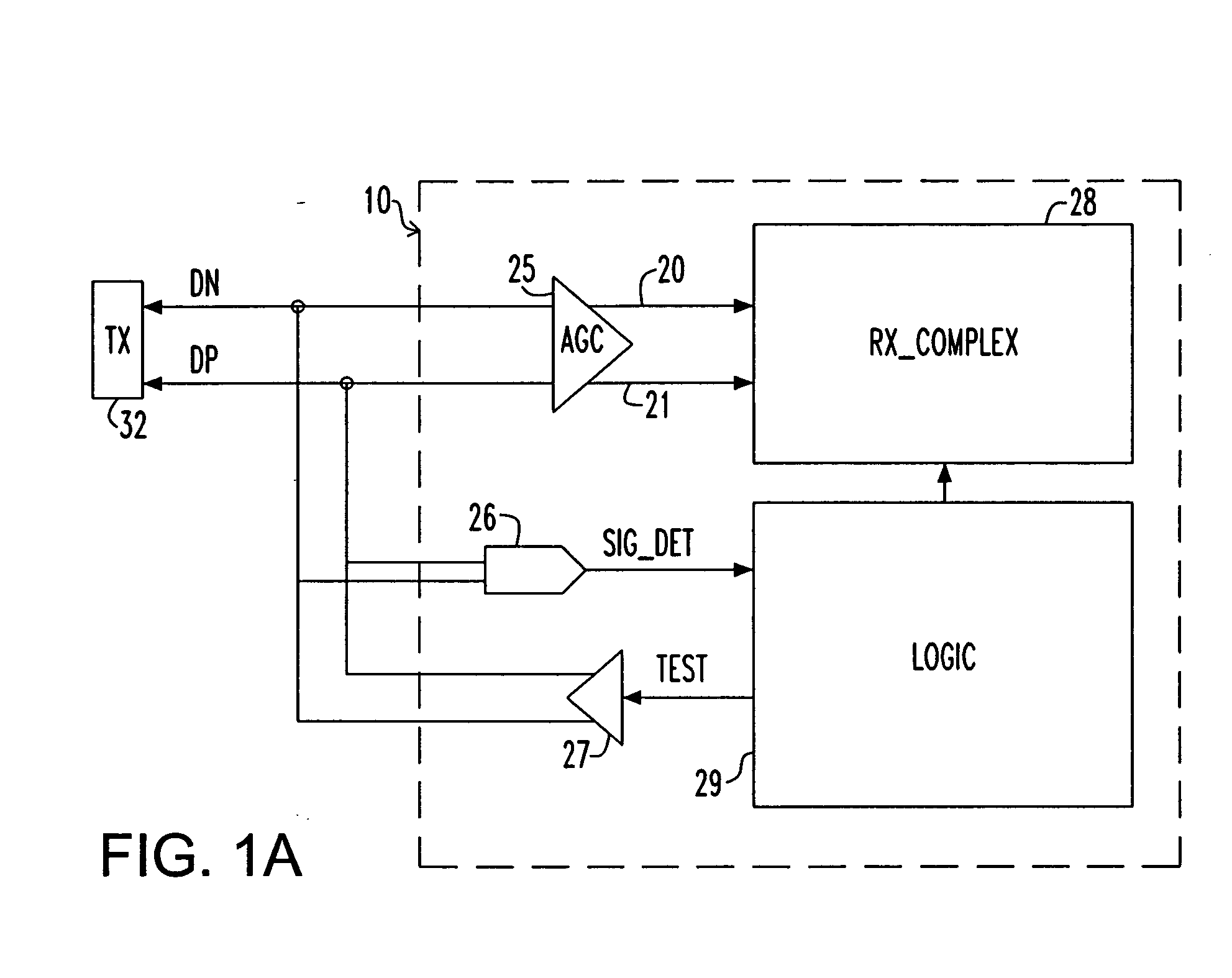
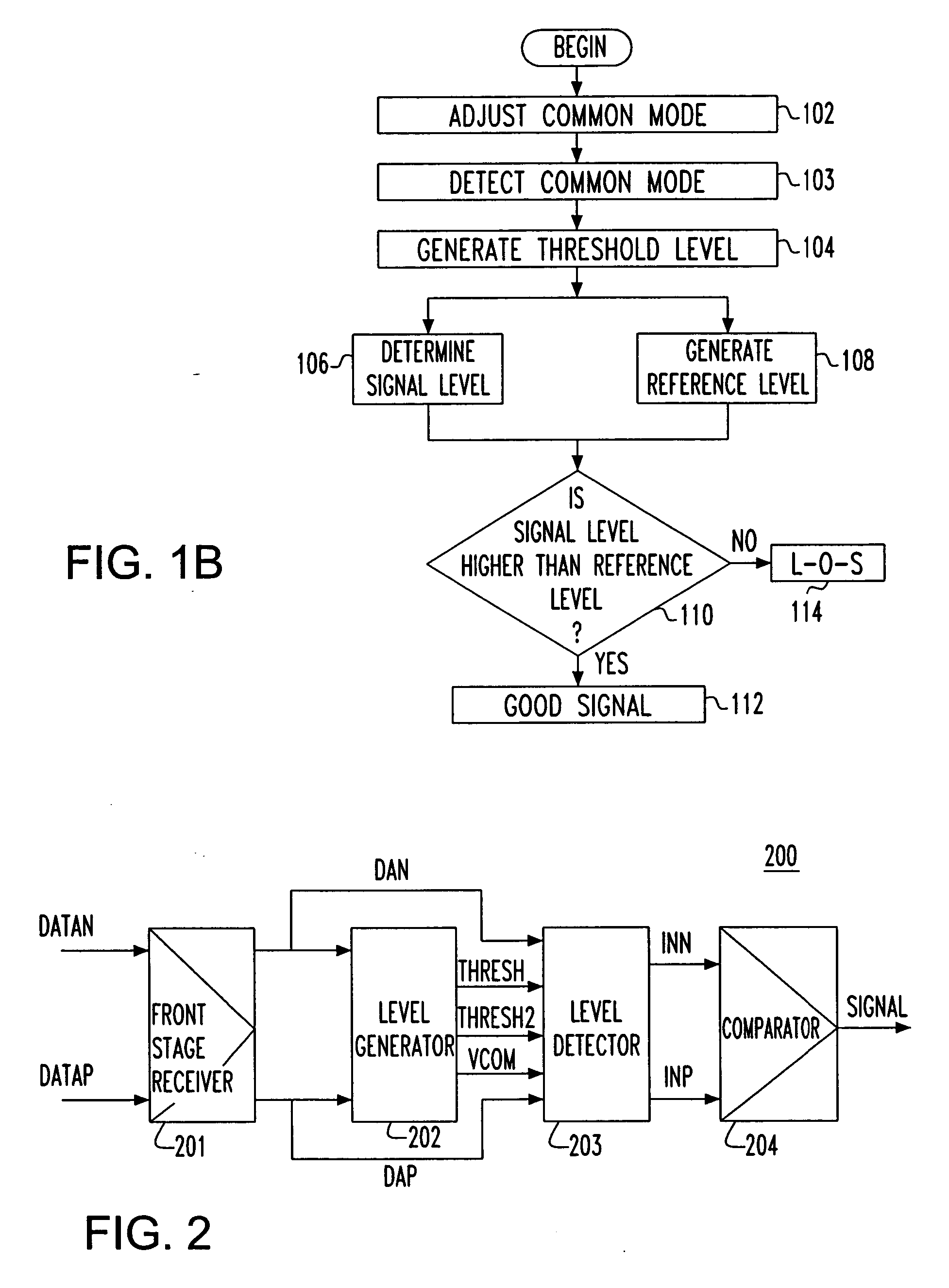
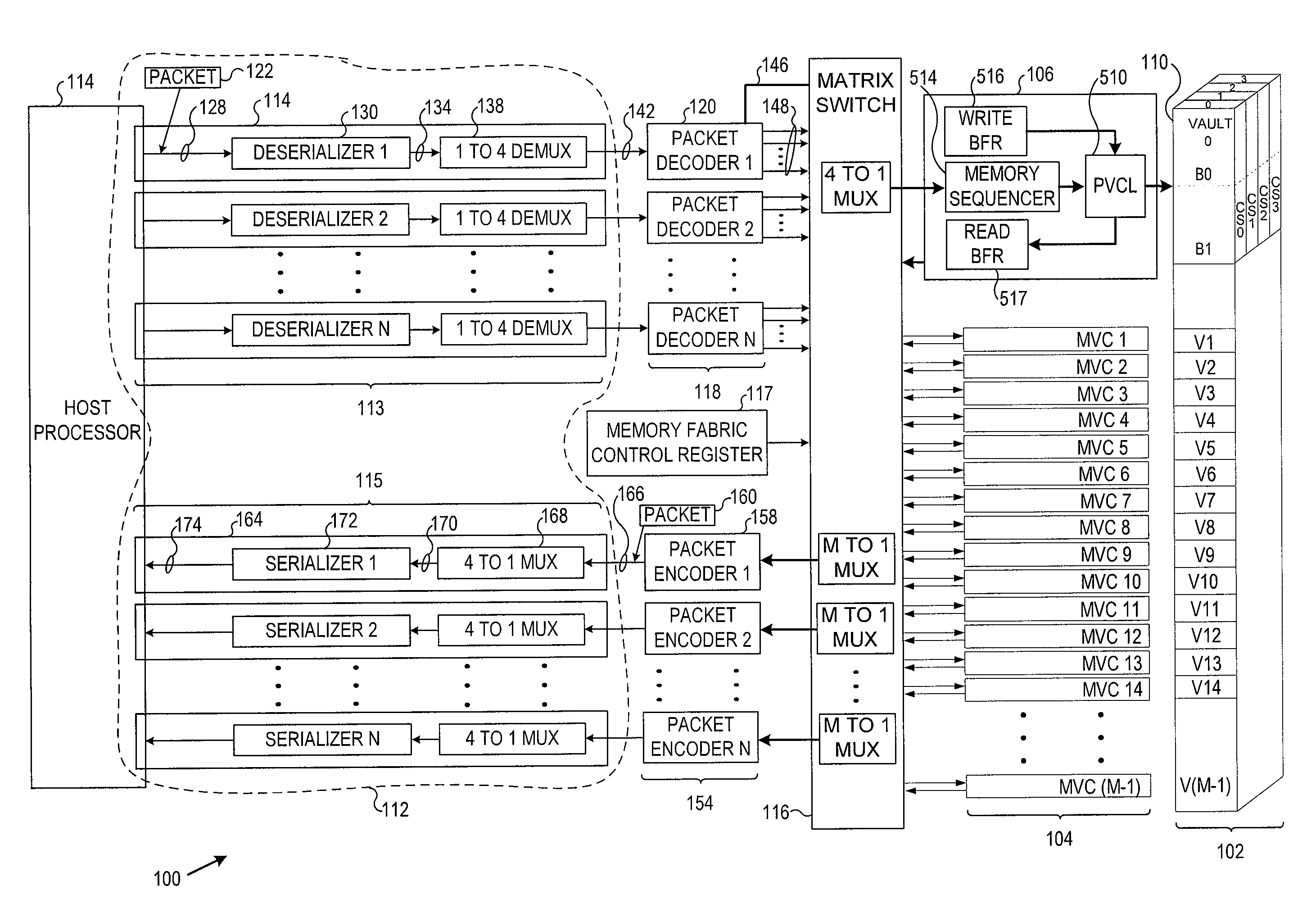
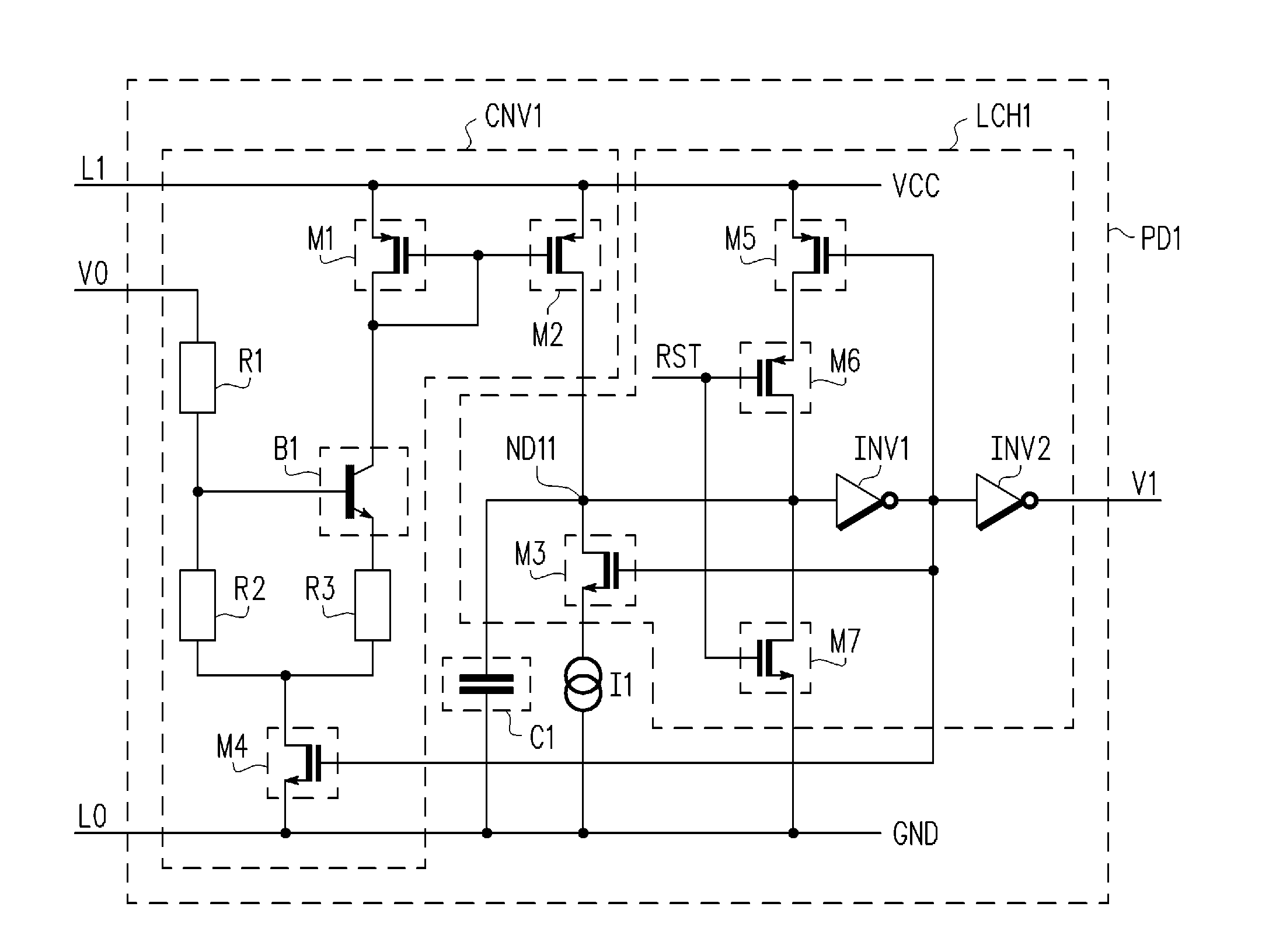
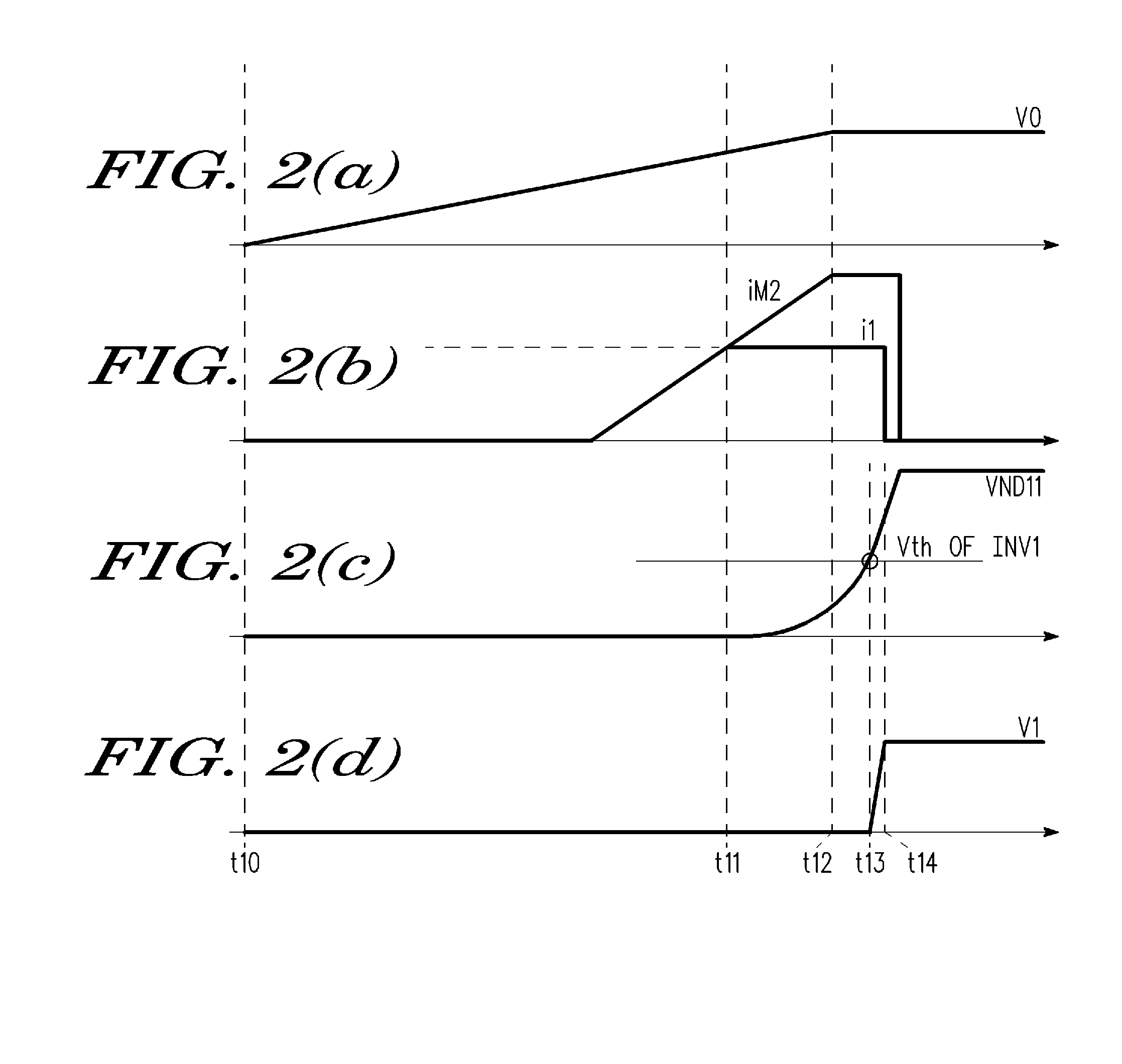
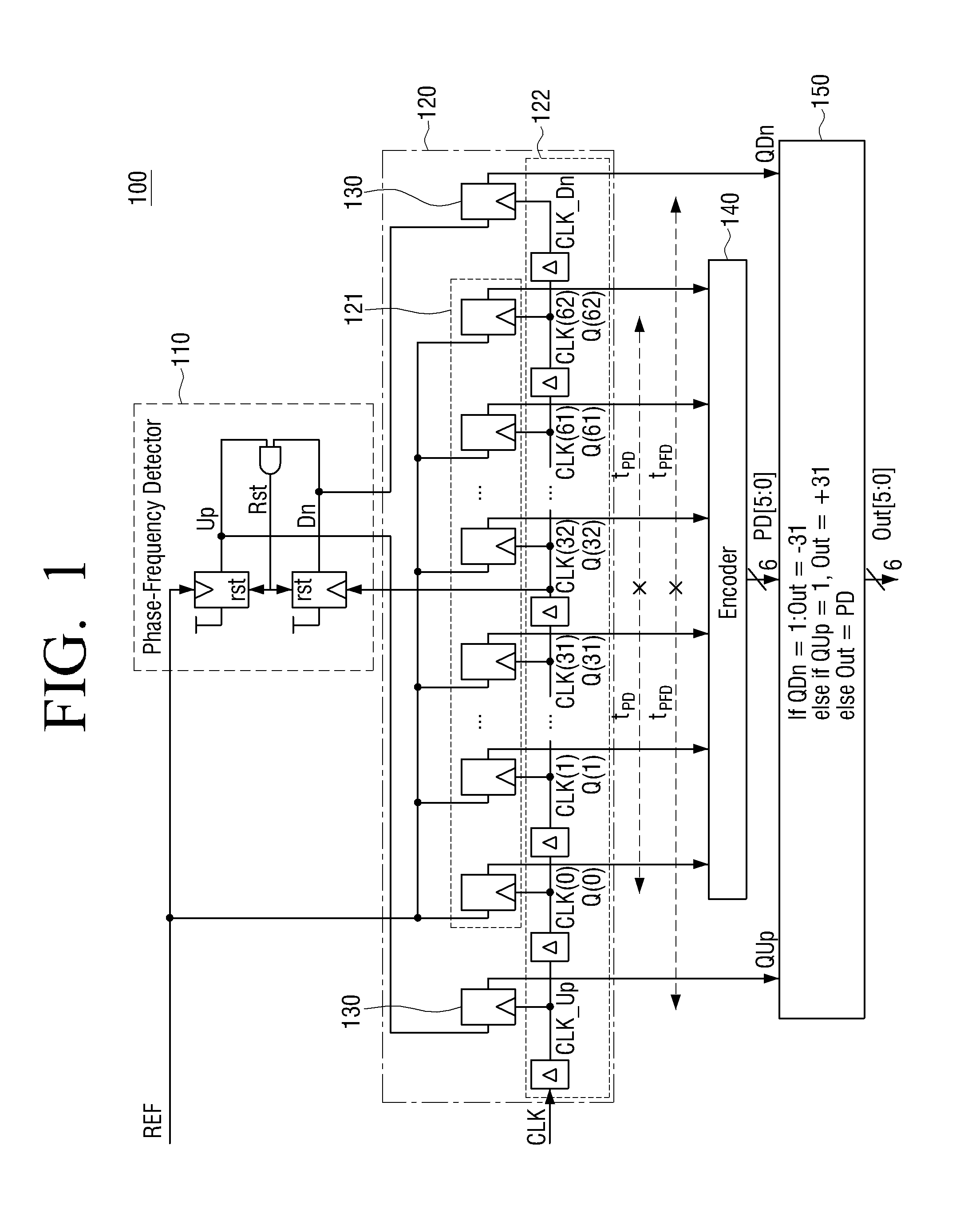
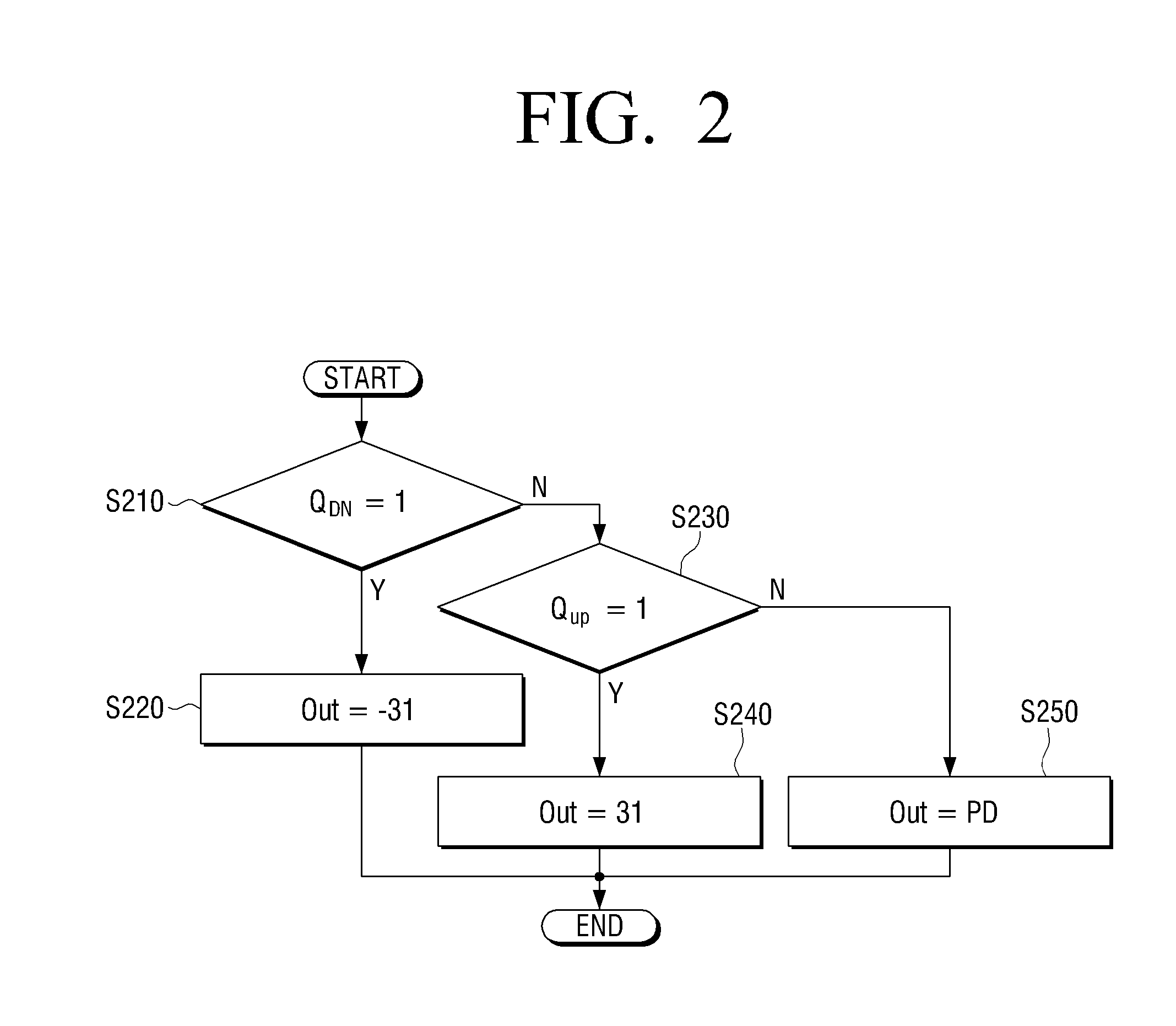
Apparatus and method for detecting loss of high-speed signal
InactiveUS6897712B2Multiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse train pattern monitoringDifferential signalingTime segment
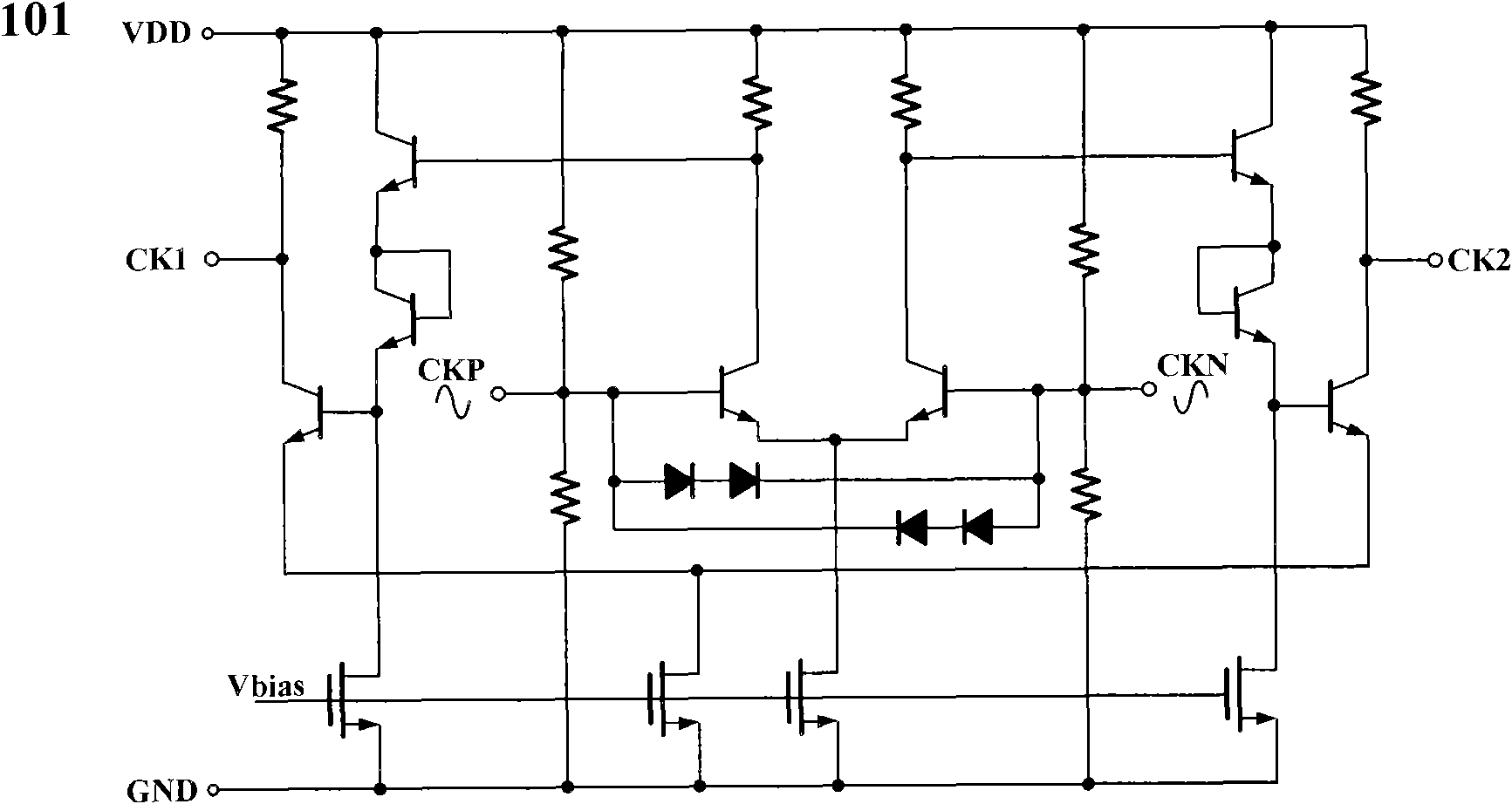
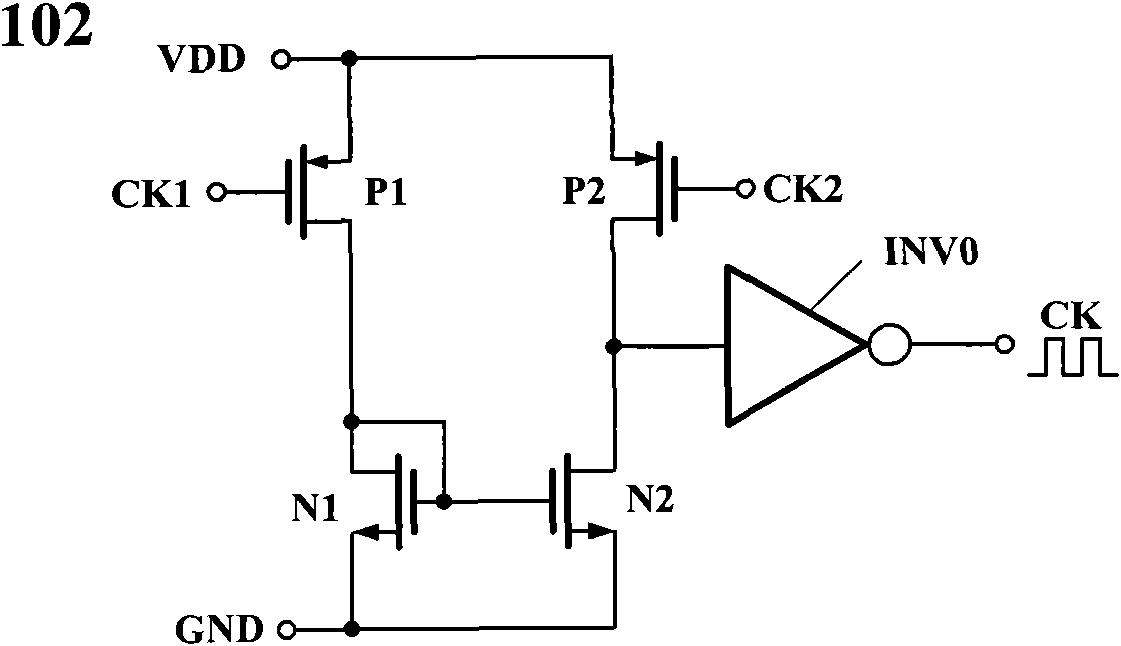
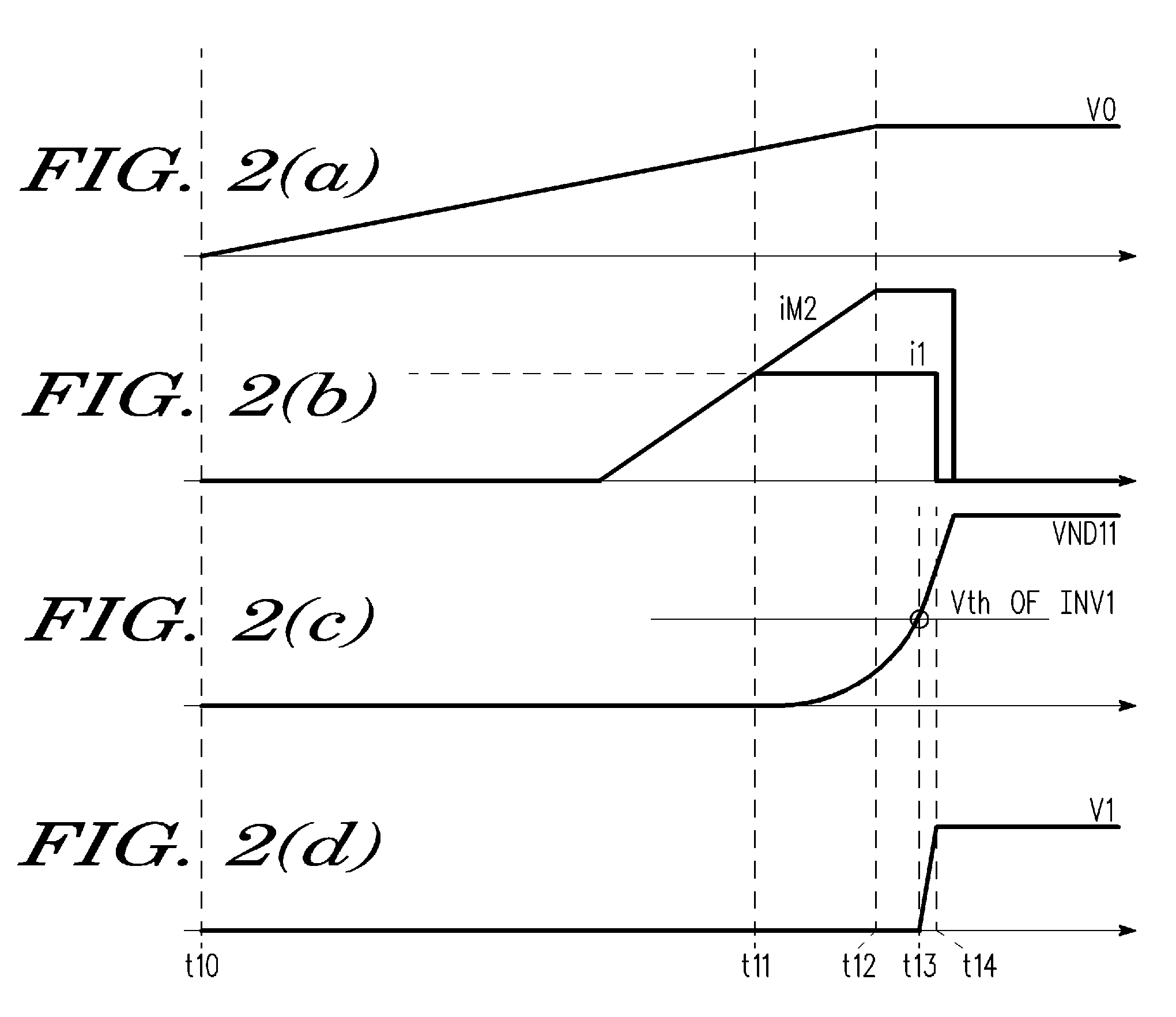
An apparatus and method is provided for detecting loss of differential signal carried by a pair of differential signal lines. According to the method, a common mode level is detected from voltages on the pair of differential signal lines. A threshold level is generated, referenced to the detected common mode level. A signal level is generated from the voltages on the pair of differential signal lines, the signal level being averaged over a first period of time. From the threshold level and the detected common mode level a reference level is generated, the reference level being averaged over a second period of time longer than then the first period of time. The signal level is compared to the reference level to determine if a signal is present on the pair of differential signal lines.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
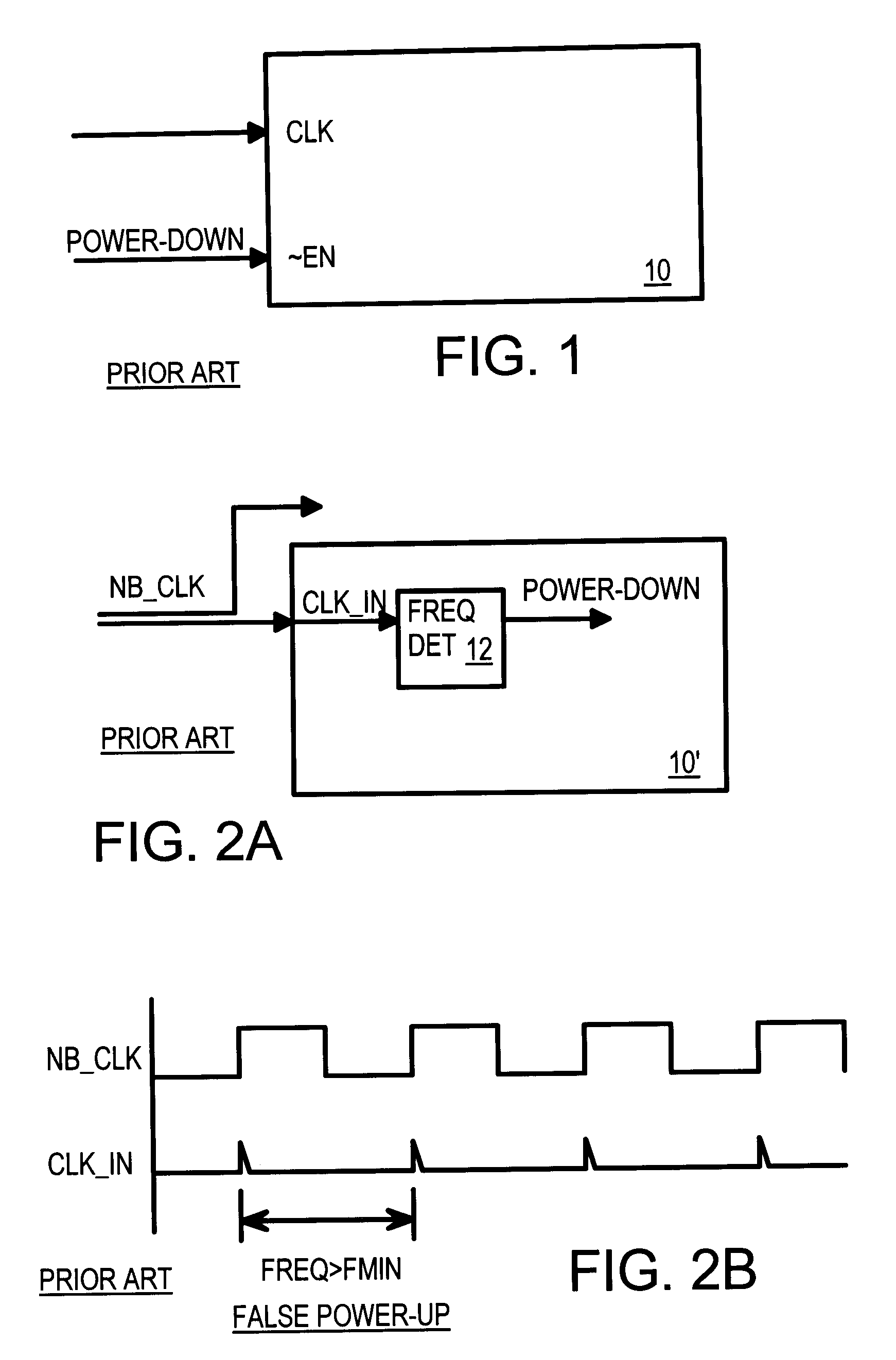
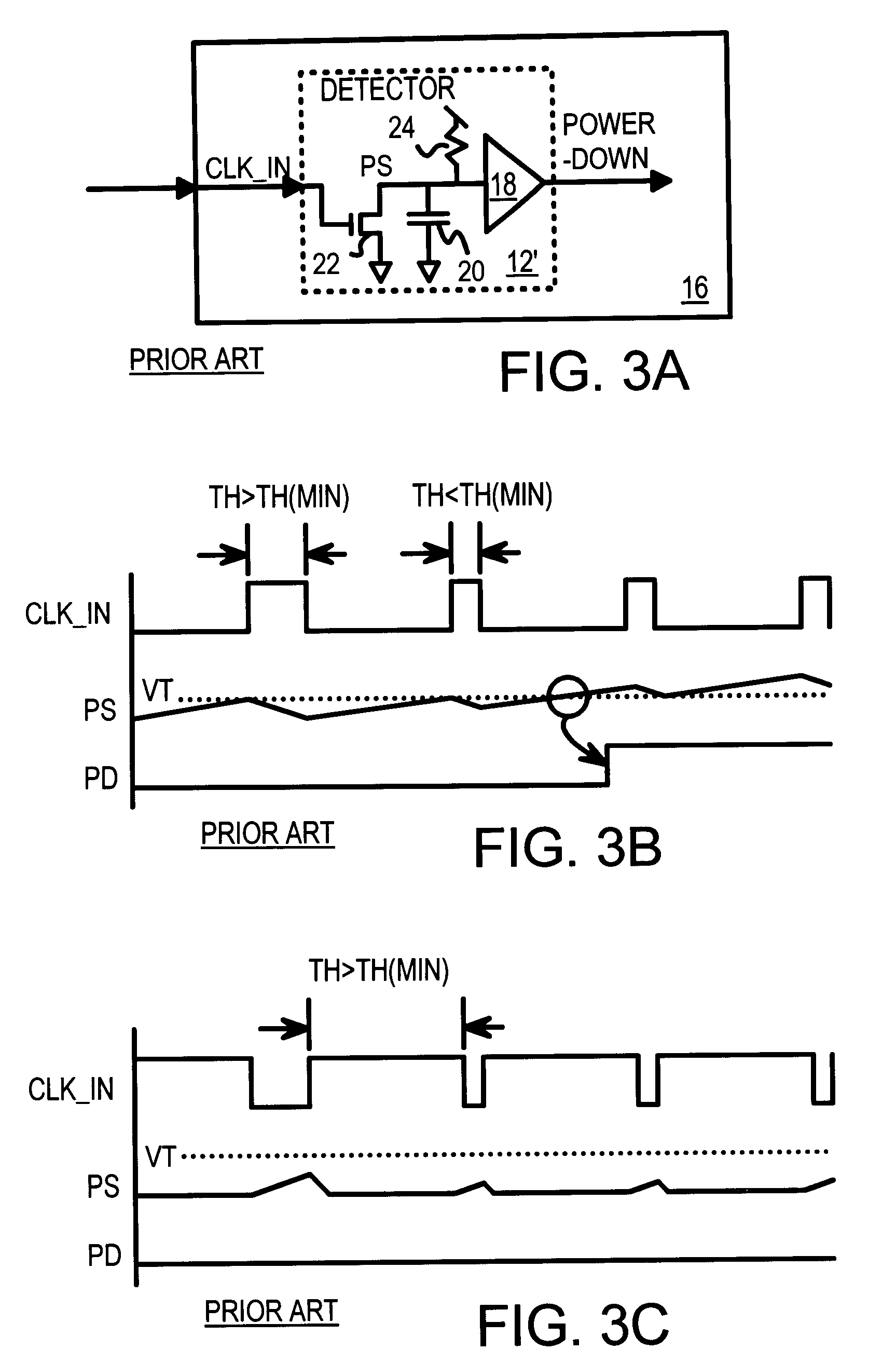
Power down circuit detecting duty cycle of input signal
InactiveUS6552578B1Energy efficient ICTMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLower limitElectricity
When the clock is stopped during a power-down mode, a clock duty-cycle detector asserts a power-down signal. The clock input is filtered to produce an average clock voltage over several clock periods. The average clock voltage is compared to an upper reference voltage to determine when the clock's duty cycle (high pulse-width percent) is above an upper limit. The average clock voltage is also compared to a lower reference voltage to determine when the clock's duty cycle is below a lower limit. When the clock's duty cycle is above the upper limit or below the lower limit the power-down signal is activated by logic. The logic disables the power-down signal when the clock's duty cycle is between the upper and lower limits. High-frequency clock glitches do not falsely trigger a power-up, since glitches are usually narrow and not sufficiently wide to reach the lower limit.
Owner:DIODES INC
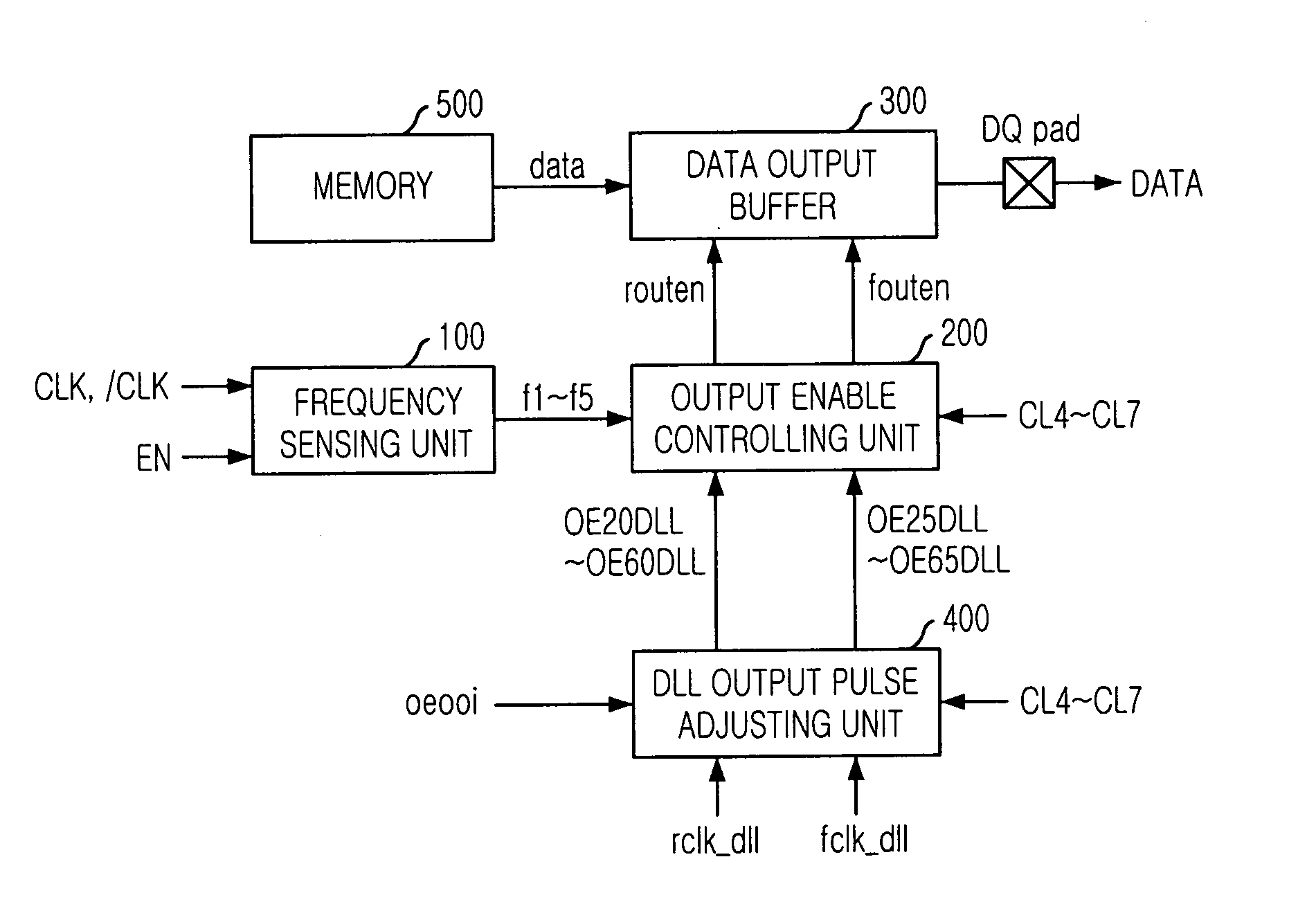
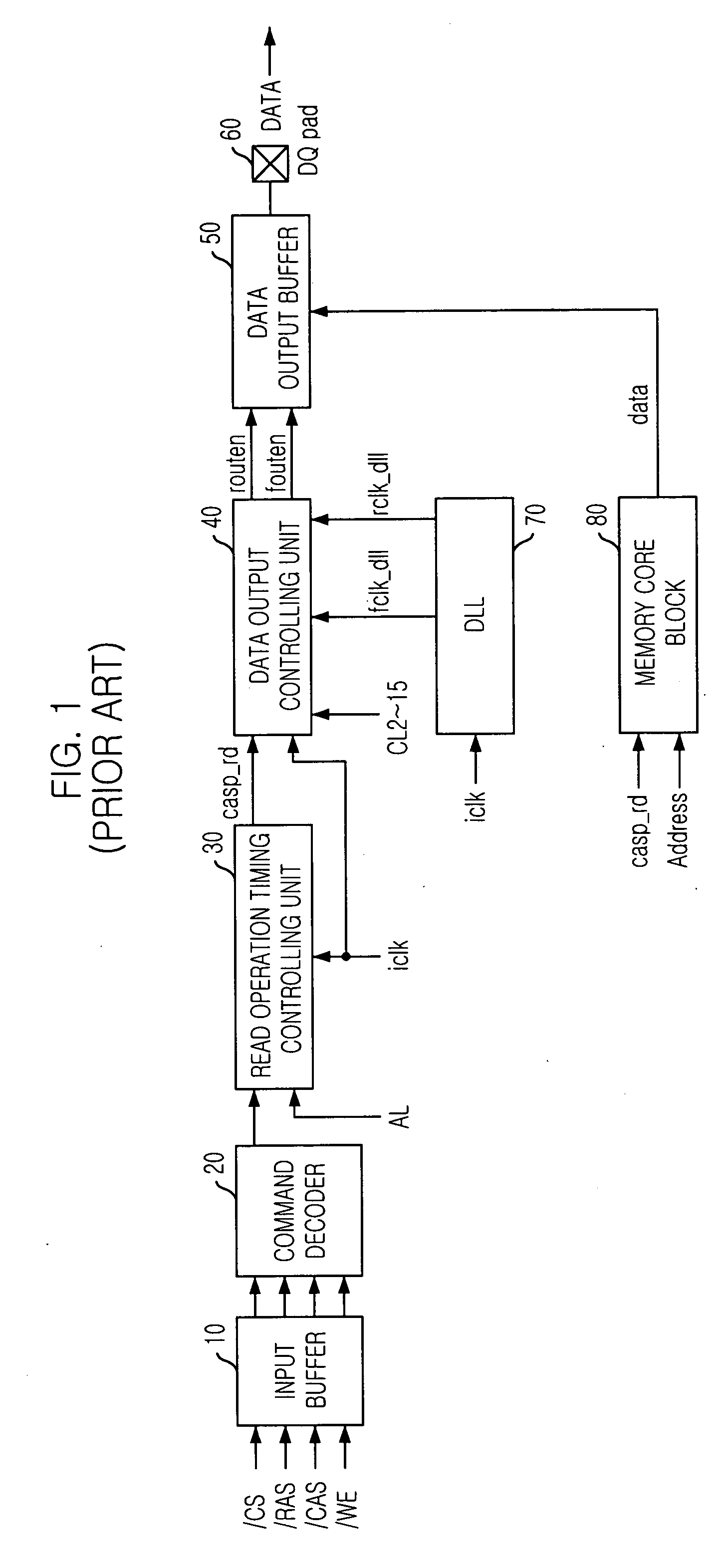
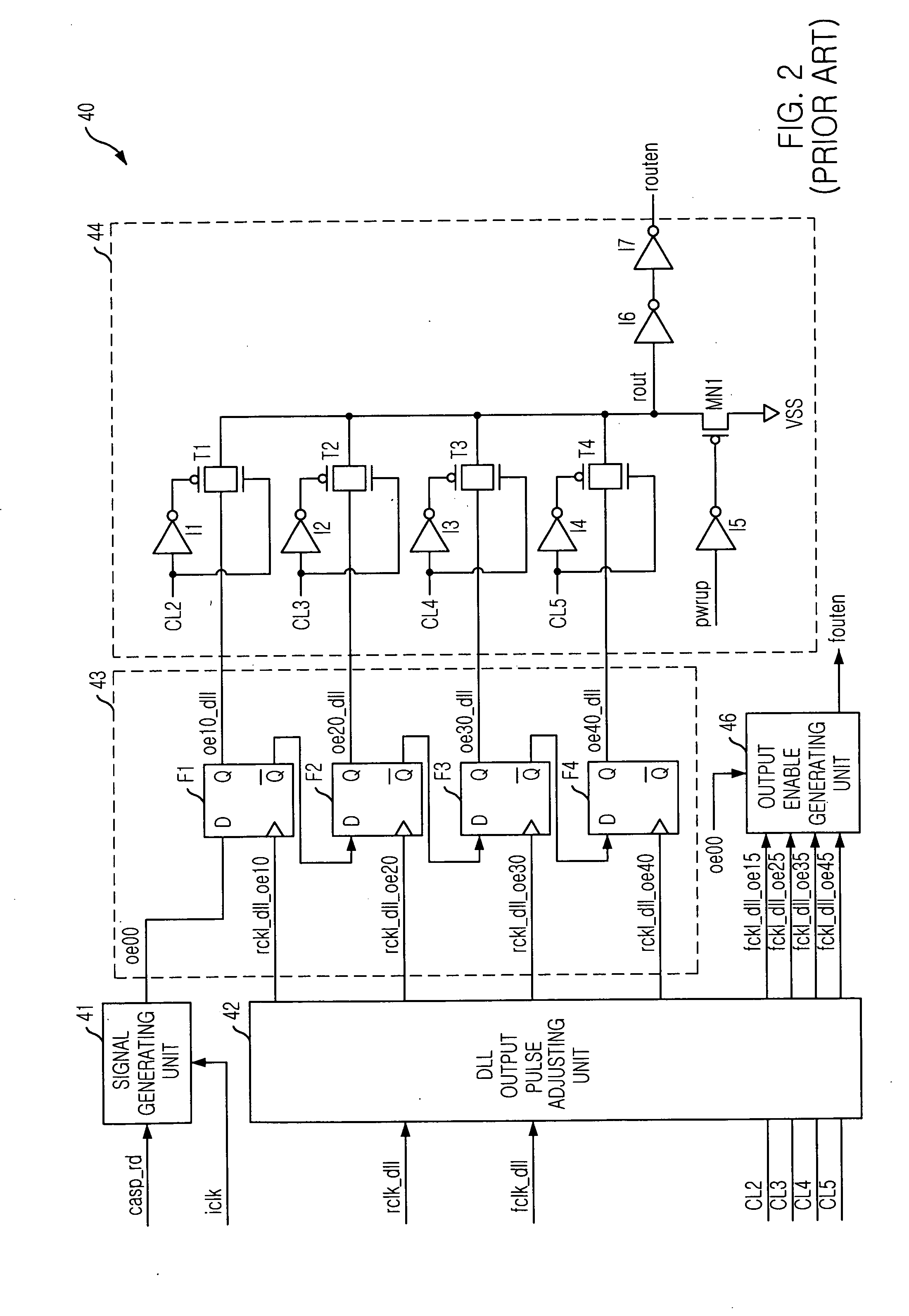
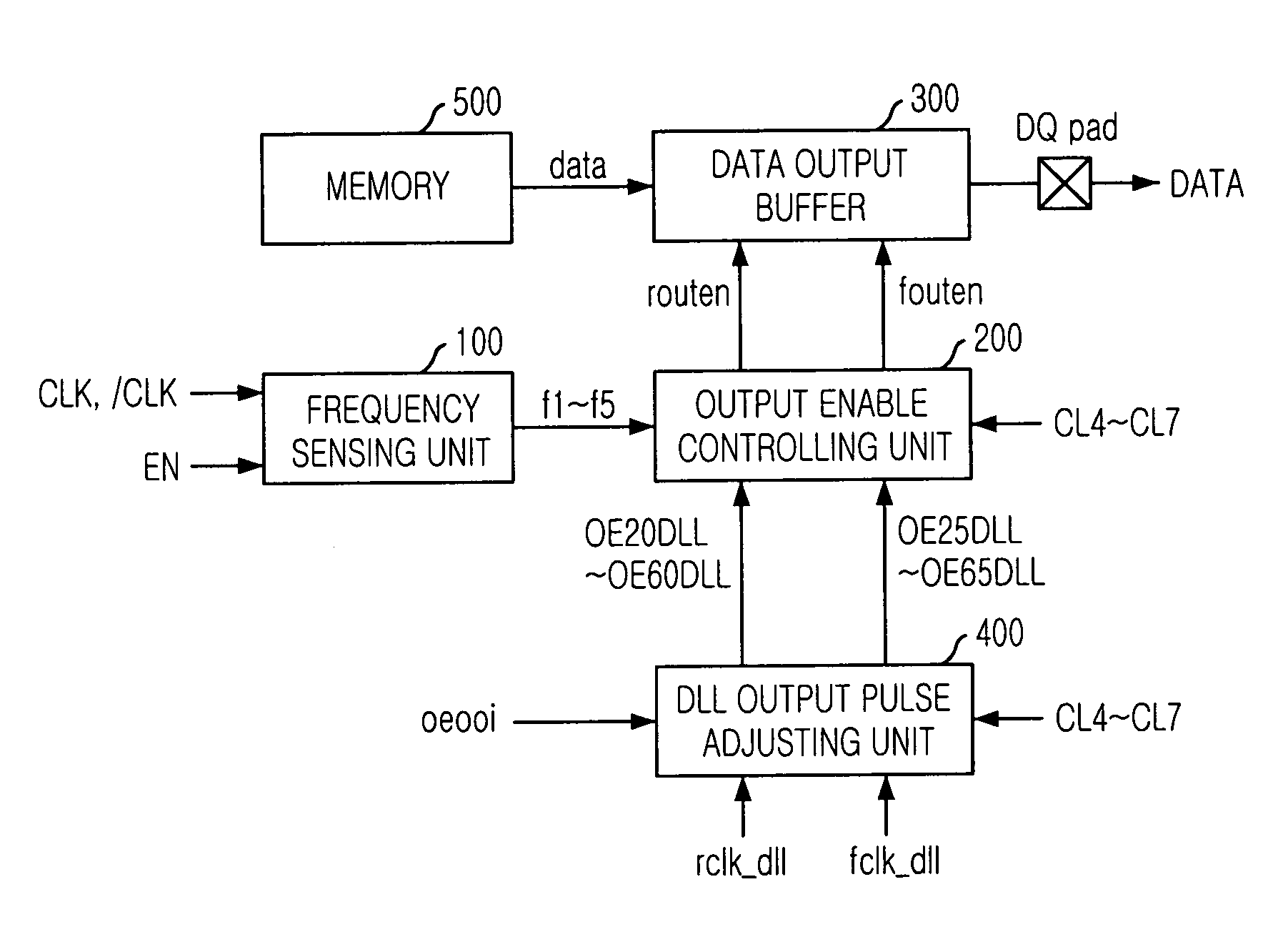
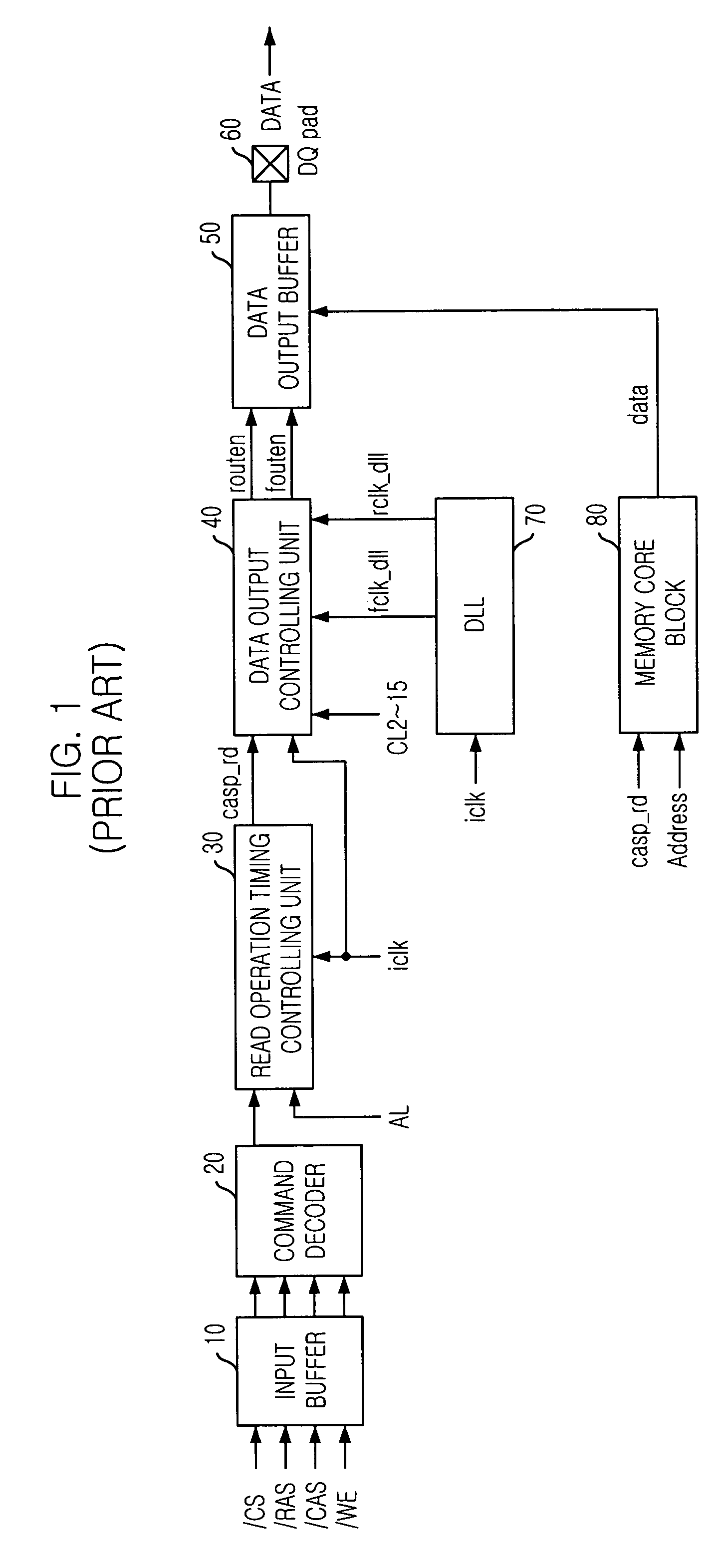
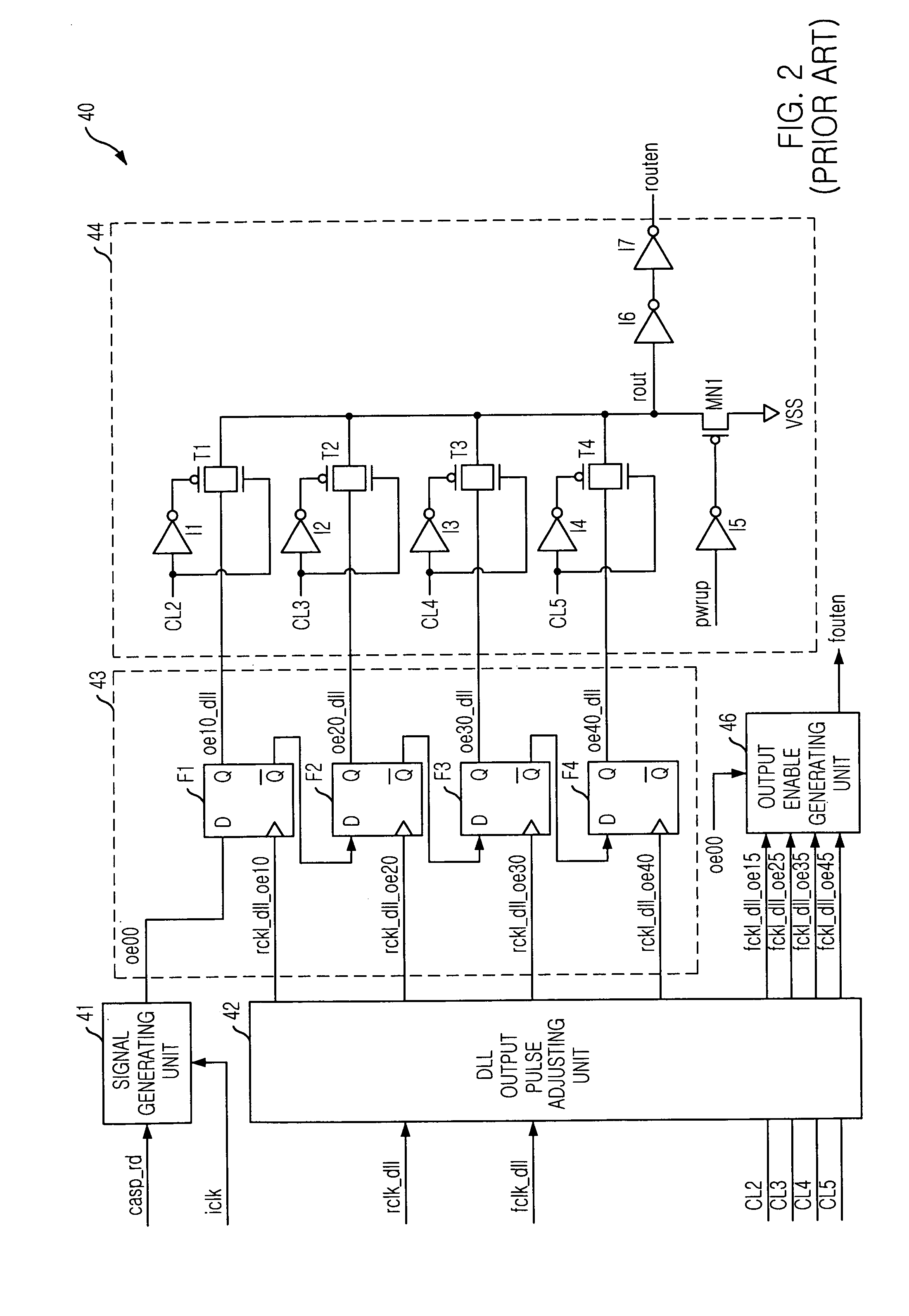
Semiconductor memory device for controlling output timing of data depending on frequency variation
InactiveUS20050248997A1Pulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringDelay-locked loopEngineering
A semiconductor memory device is capable of controlling the data output timing depending on the operating frequency so as to output data with optimized for the operating frequency. Further, in the high frequency operation, the memory device can output data reliably so as to facilitate development of high frequency memory device. The semiconductor memory device comprises a frequency sensing unit for sensing an operating frequency by sensing an amount of lead of a delay locked clock in a delay locked loop compared to an external clock signal, an output enable controlling unit for outputting an output enable signal in response to a CAS latency with controlling the output timing of the output enable signal based on the frequency that is sensed by the frequency sensing unit, and a data output buffer for outputting data that is transferred from a memory core region in response to the output enable signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
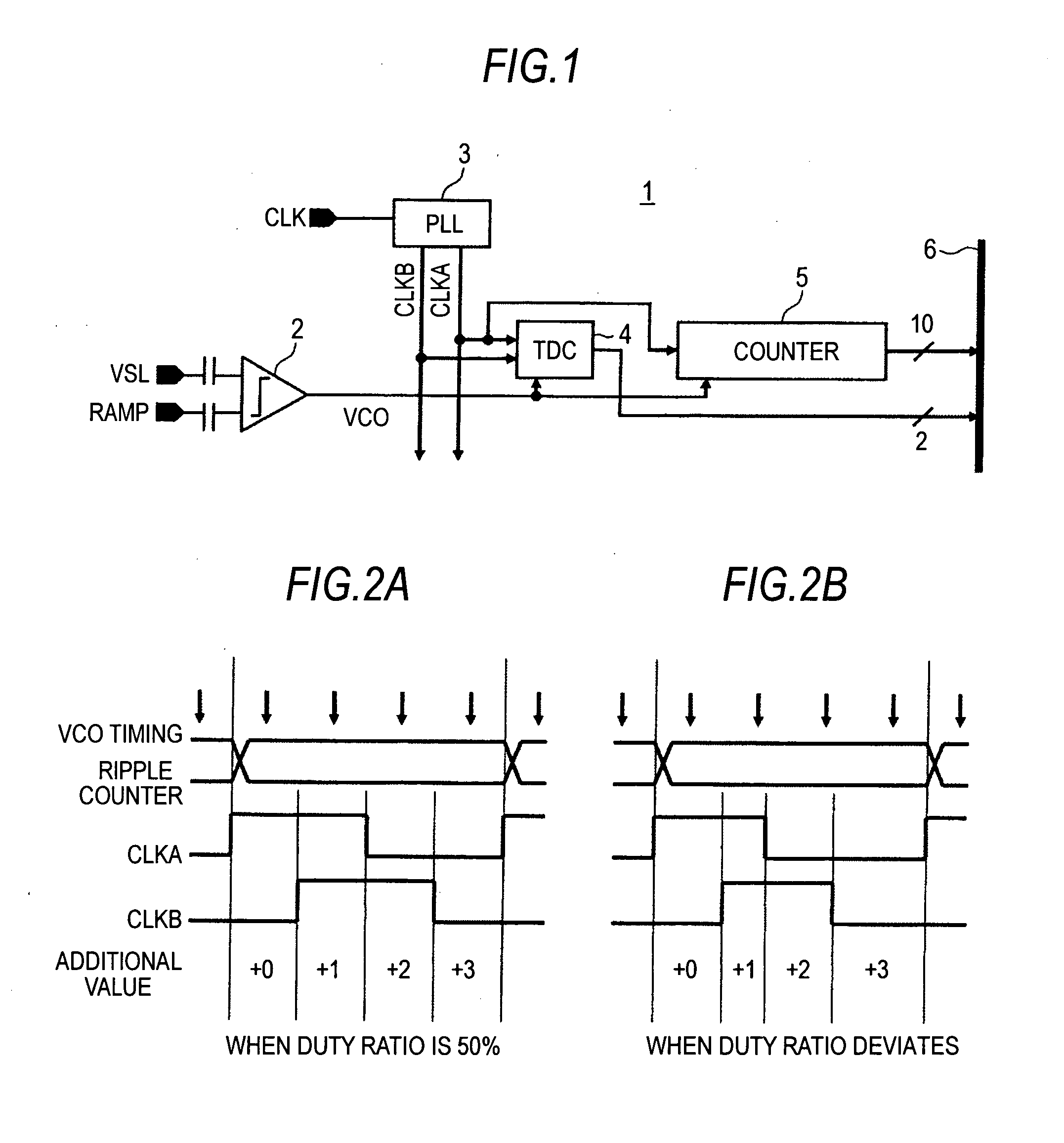
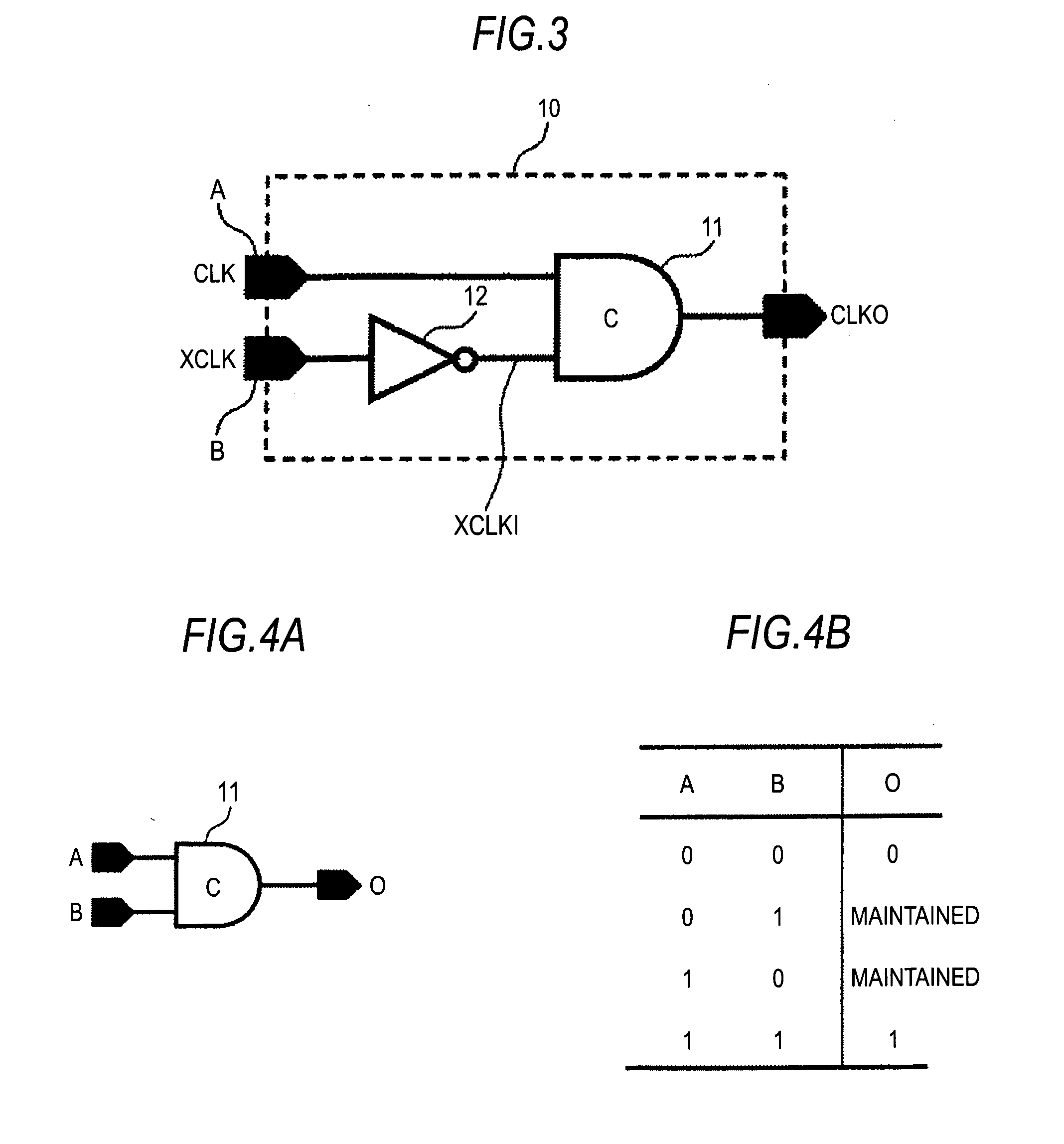
Duty correction circuit, delay locked loop circuit, column a/d converter, solid-state imaging device and camera system
ActiveUS20110187907A1Reduce in quantityReduce the number of timesAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
A duty correction circuit includes: a C-element including a first input and a second input; and an inverter connected to the second input of the C-element, wherein the C-element obtains an output of a logic “1” when both inputs are the logic “1”, obtains an output of a logic “0” when both inputs are the logic “0”, and maintains the output to a previous state in other conditions, and complementary clocks having a phase difference of an approximately half cycle are inputted to the first input of the C-element and the inverter respectively.
Owner:SONY CORP
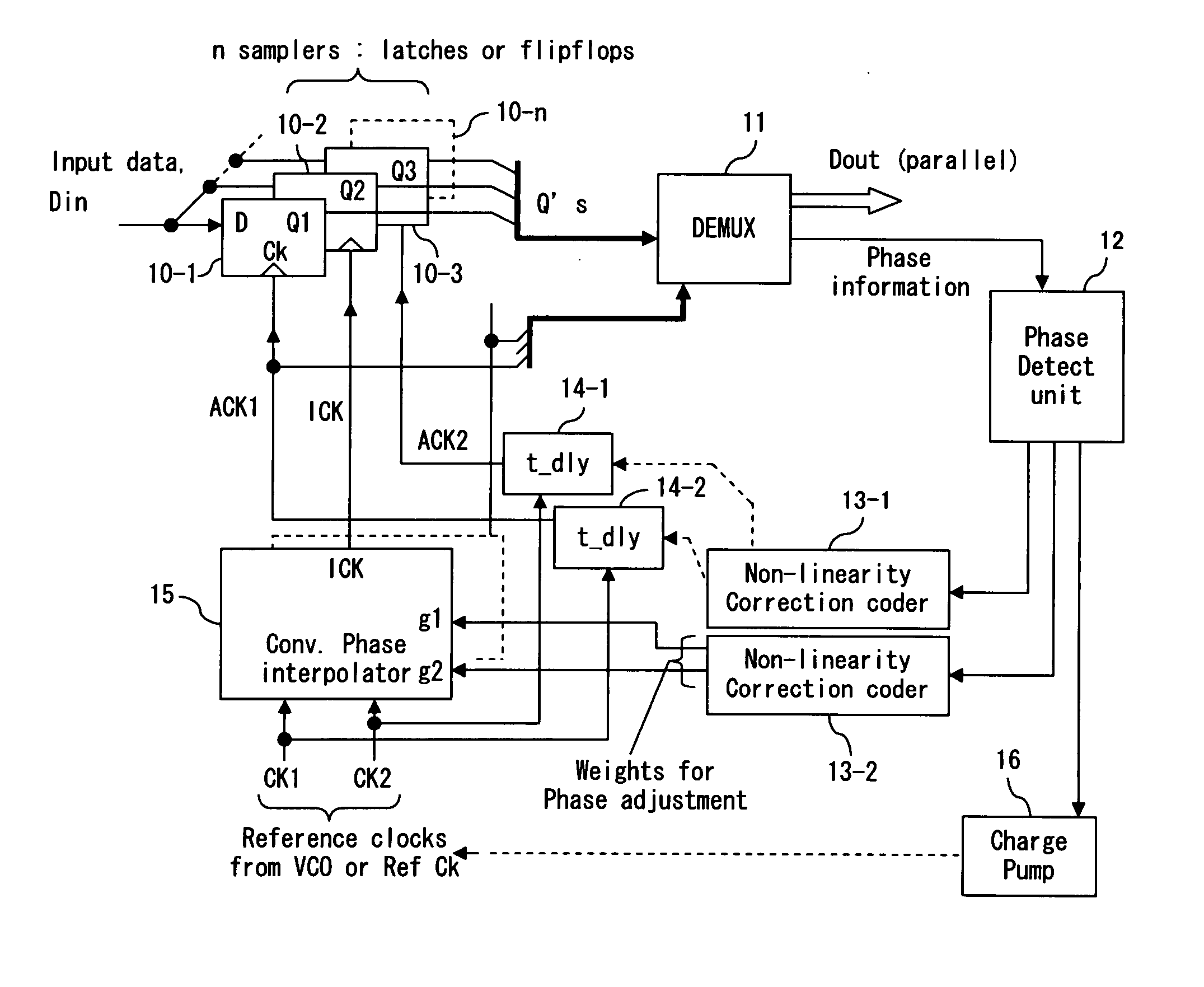
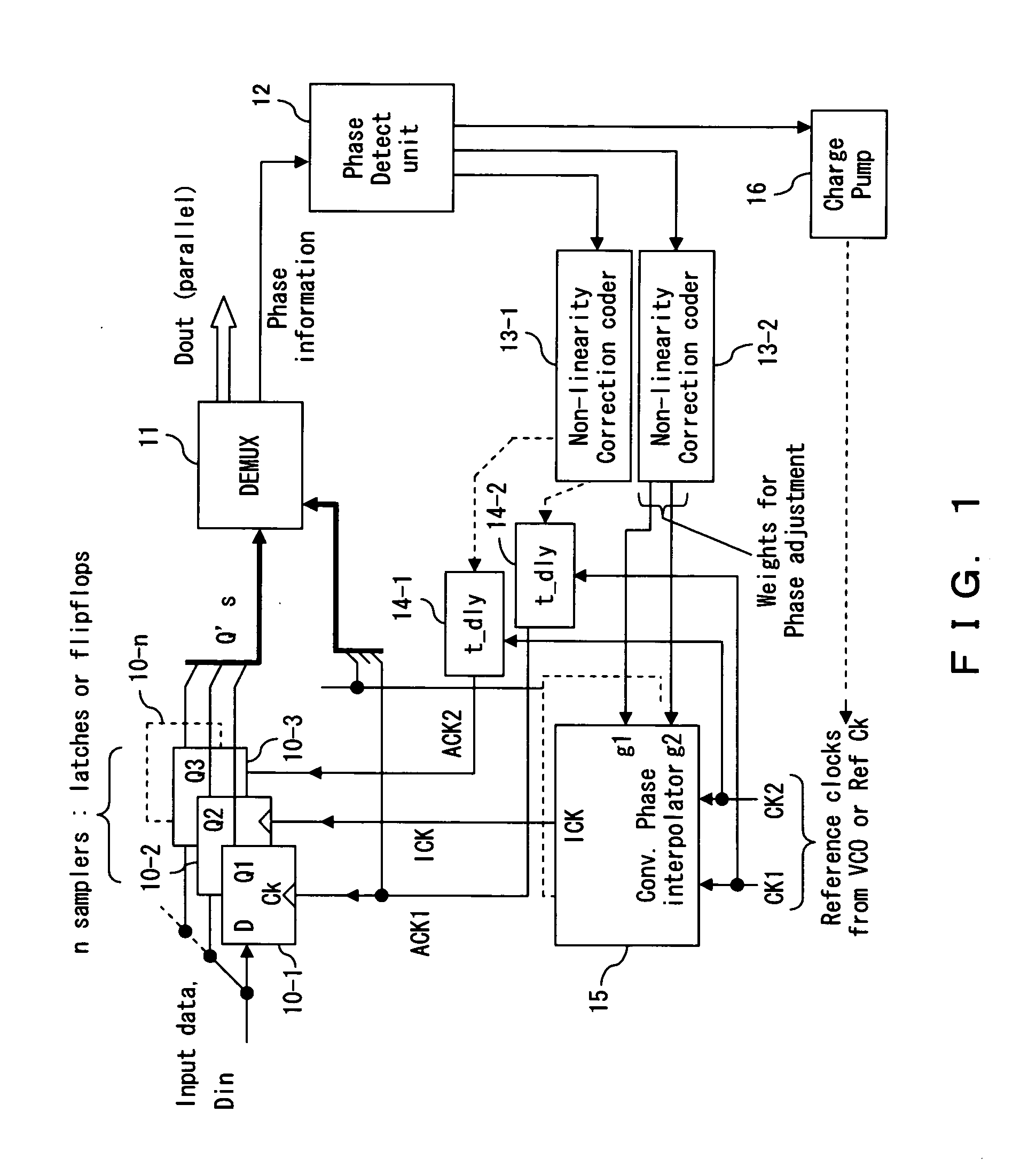
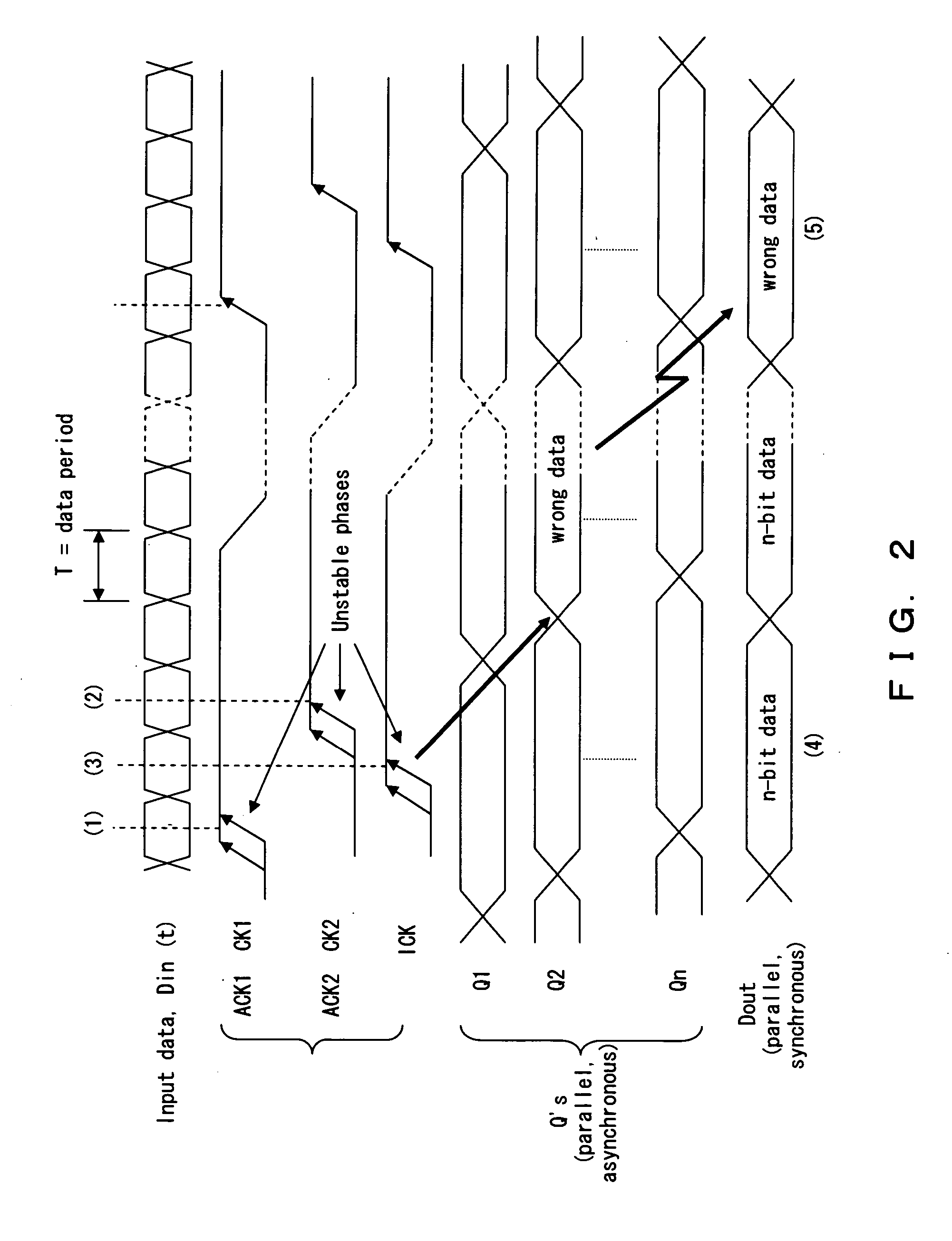
Phase interpolator with adaptive delay adjustment
InactiveUS20070146014A1Small and simple configurationReduce phase differencePulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringIntegratorPhase difference
The phase interpolator includes two adjustable delays 30 and 31, phase comparator 32 which detects a phase difference between a signal delayed by the adjustable delay 30 and a signal delayed by the adjustable delay 31, an integrator 33 which integrates the outputs of the phase comparator 32 and multipliers 34-1 and 34-2 which set a control voltage for the adjustable delays 30 and 31. The feedback loop comprising phase comparator 32 and integrator 33 controls a delay amount of the adjustable delay 30 thereby securing a phase relation between {ACK1, ACK2} and ICK to achieve a stable ICK phase.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Semiconductor memory device for controlling output timing of data depending on frequency variation
InactiveUS7027336B2Pulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringDelay-locked loopEngineering
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
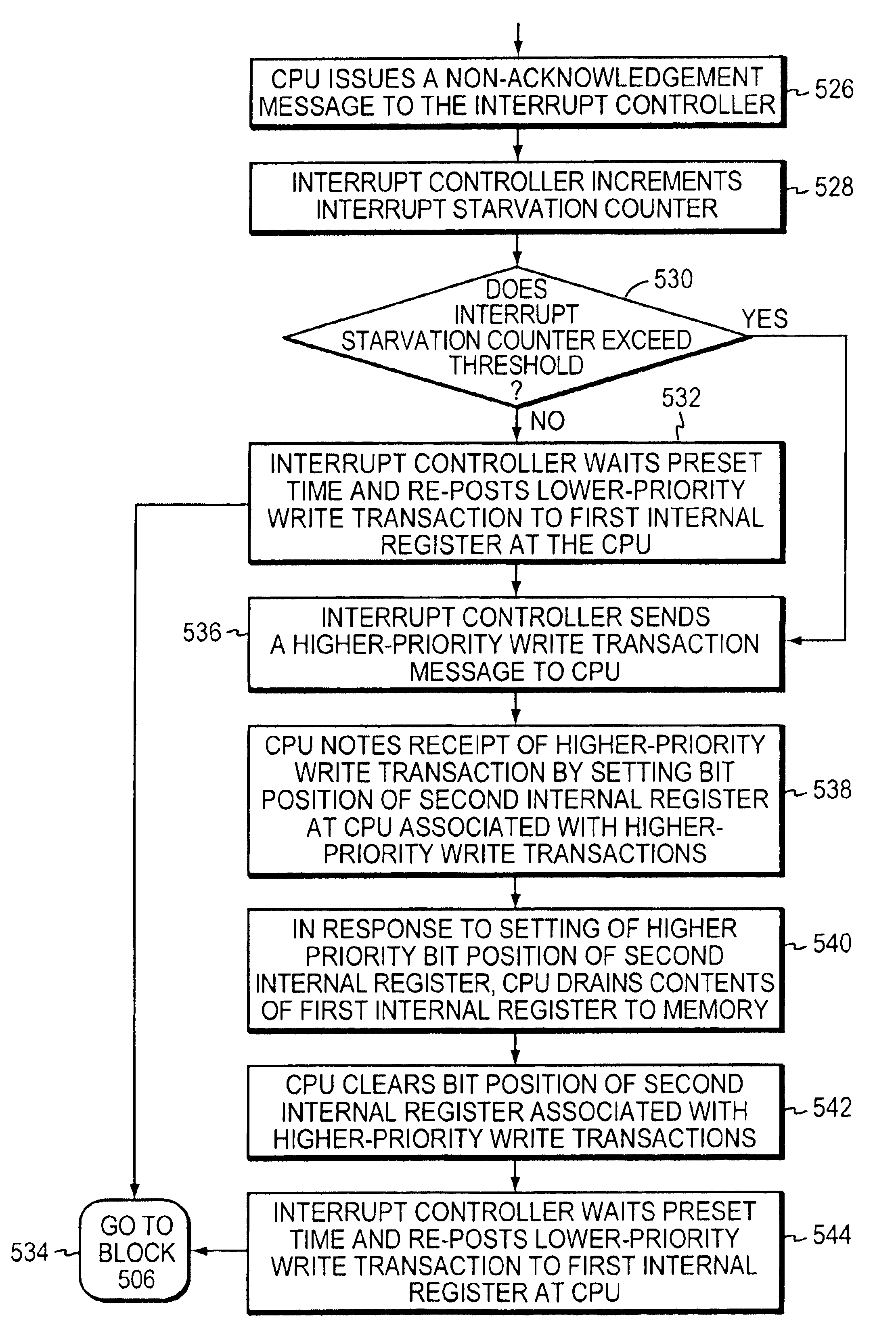
Anti-starvation interrupt protocol
InactiveUS6920516B2Livelock can be preventedPulse train pattern monitoringGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerMulti processor
An anti-starvation interrupt protocol for use in avoiding livelock in a multiprocessor computer system is provided. At least one processor is configured to include first and second control status registers (CSRs). The first CSR buffers information, such as interrupts, received by the processor, while the second CSR keeps track of the priority level of the interrupts. When an interrupt controller receives an interrupt, it issues a write transaction to the first CSR at the processor. If the first CSR has room to accept the write transaction, the processor returns an acknowledgement, whereas if the first CSR is already full, the processor returns a no acknowledgment. In response to a no acknowledgment, the interrupt controller increments an interrupt starvation counter, and checks to see whether the counter exceeds a threshold. If not, the interrupt controller waits a preset time and reposts the write transaction. If it does, the interrupt controller issues a write transaction having a higher priority to the second CSR. In response, the processor copies all of the pending interrupts from the first CSR into the memory subsystem, thereby freeing up the first CSR to accept additional write transactions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
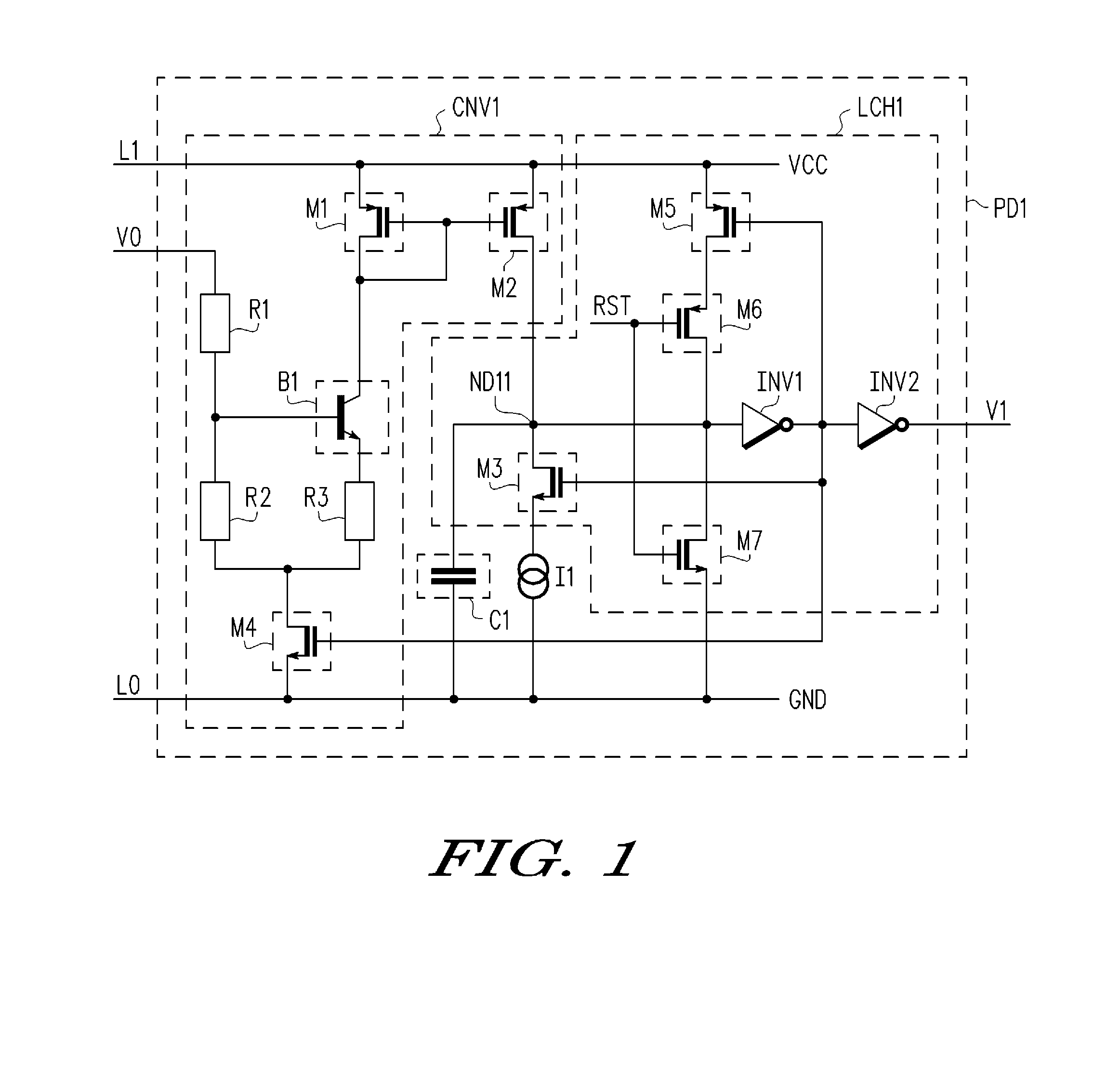
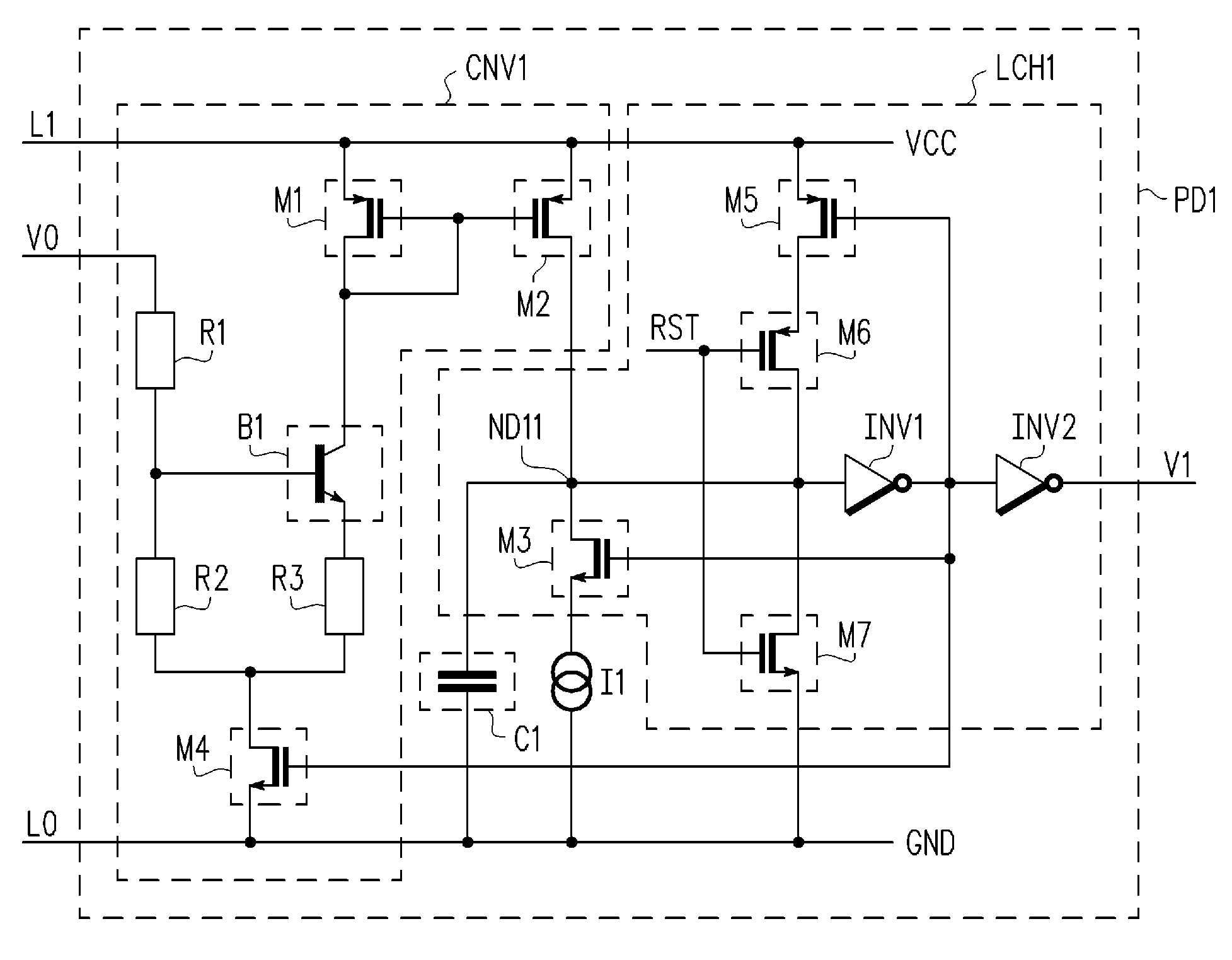
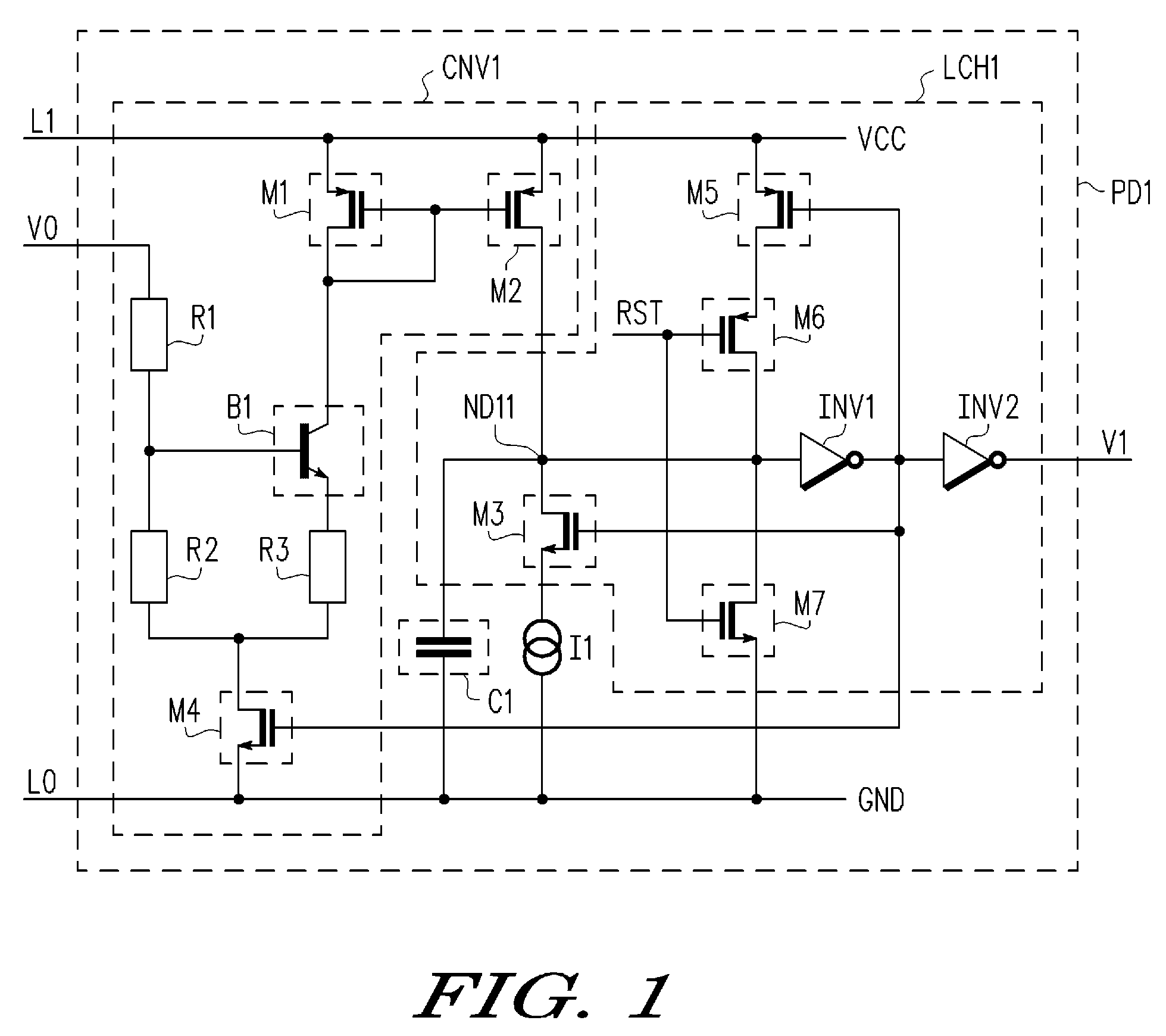
Apparatus and method for detecting loss of high-speed signal
InactiveUS20050040864A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse train pattern monitoringTime segmentEngineering
An apparatus and method is provided for detecting loss of differential signal carried by a pair of differential signal lines. According to the method, a common mode level is detected from voltages on the pair of differential signal lines. A threshold level is generated, referenced to the detected common mode level. A signal level is generated from the voltages on the pair of differential signal lines, the signal level being averaged over a first period of time. From the threshold level and the detected common mode level a reference level is generated, the reference level being averaged over a second period of time longer than then the first period of time. The signal level is compared to the reference level to determine if a signal is present on the pair of differential signal lines.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Systems and methods for monitoring a memory system
ActiveUS8032804B2Energy efficient ICTPulse train pattern monitoringMemory systemsReal-time computing
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
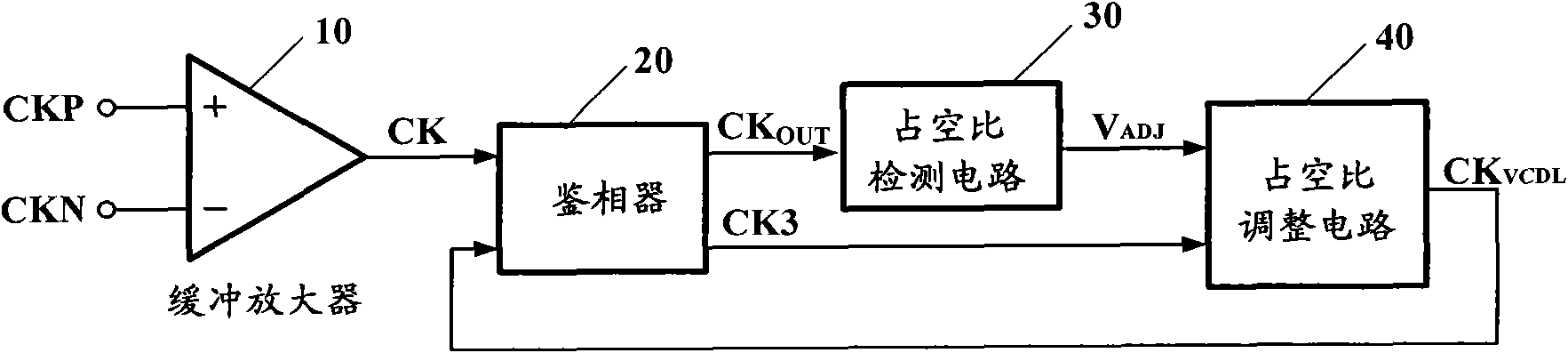
Clock adjustment circuit and adjustment method for clock circuit
InactiveCN102075167AReduce complexityFast adjustmentPulse train pattern monitoringDiscriminatorAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a clock adjustment circuit and an adjustment method for a clock circuit. The clock adjustment circuit comprises a clock buffer amplifier, a phase discriminator and a duty cycle adjustment circuit, wherein the clock buffer amplifier is used for receiving an external differential clock signal, shaping the differential clock signal into a single-end square wave clock signal and outputting the single-end square wave clock signal; the phase discriminator is used for receiving the single-end square wave clock signal from the clock buffer amplifier and a feedback signal from the duty cycle adjustment circuit, comparing the phase of the single-end square wave clock signal with the phase of the feedback signal to acquire a phase difference, and outputting the phase difference; and the duty cycle adjustment circuit is used for adjusting the duty cycle of the feedback signal by using the phase difference to acquire an adjusted feedback signal. The differential signal is shaped into the single-end square wave clock signal, the single-end square wave clock signal is compared with the feedback signal to acquire the phase difference, and the duty cycle is adjusted according to the phase difference, so that the complexity of duty cycle adjustment and hardware implementation can be effectively reduced, phase errors and the ripple waves of control voltage can be reduced, and adjustment accuracy is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Detection of a disturbance in the state of an electronic circuit flip-flop
ActiveUS20090315603A1Pulse train pattern monitoringInternal/peripheral component protectionEngineeringData input
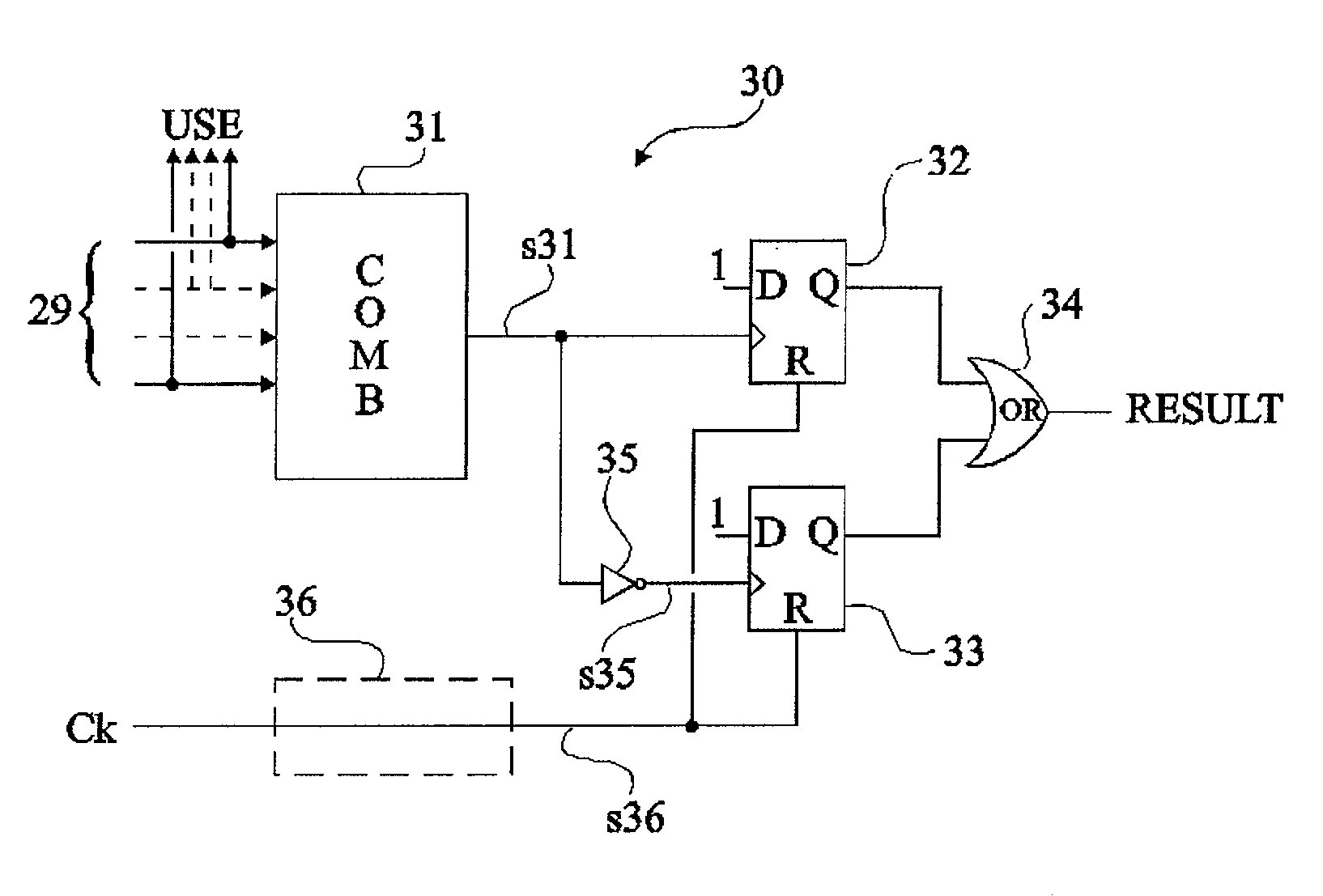
A method and a circuit for detecting a disturbance of a state of at least one first flip-flop from a group of several first flip-flops of an electronic circuit, wherein: the respective outputs of the first flip-flops in the group are, independently from their functional purpose, combined to provide a signal and its inverse, triggering two second flip-flops having data inputs forced to a same state, the respective outputs of the second flip-flops being combined to provide the result of the detection; and a pulse signal comprising a pulse at least for each triggering edge of one of the first flip-flops in the group initializes the second flip-flops.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
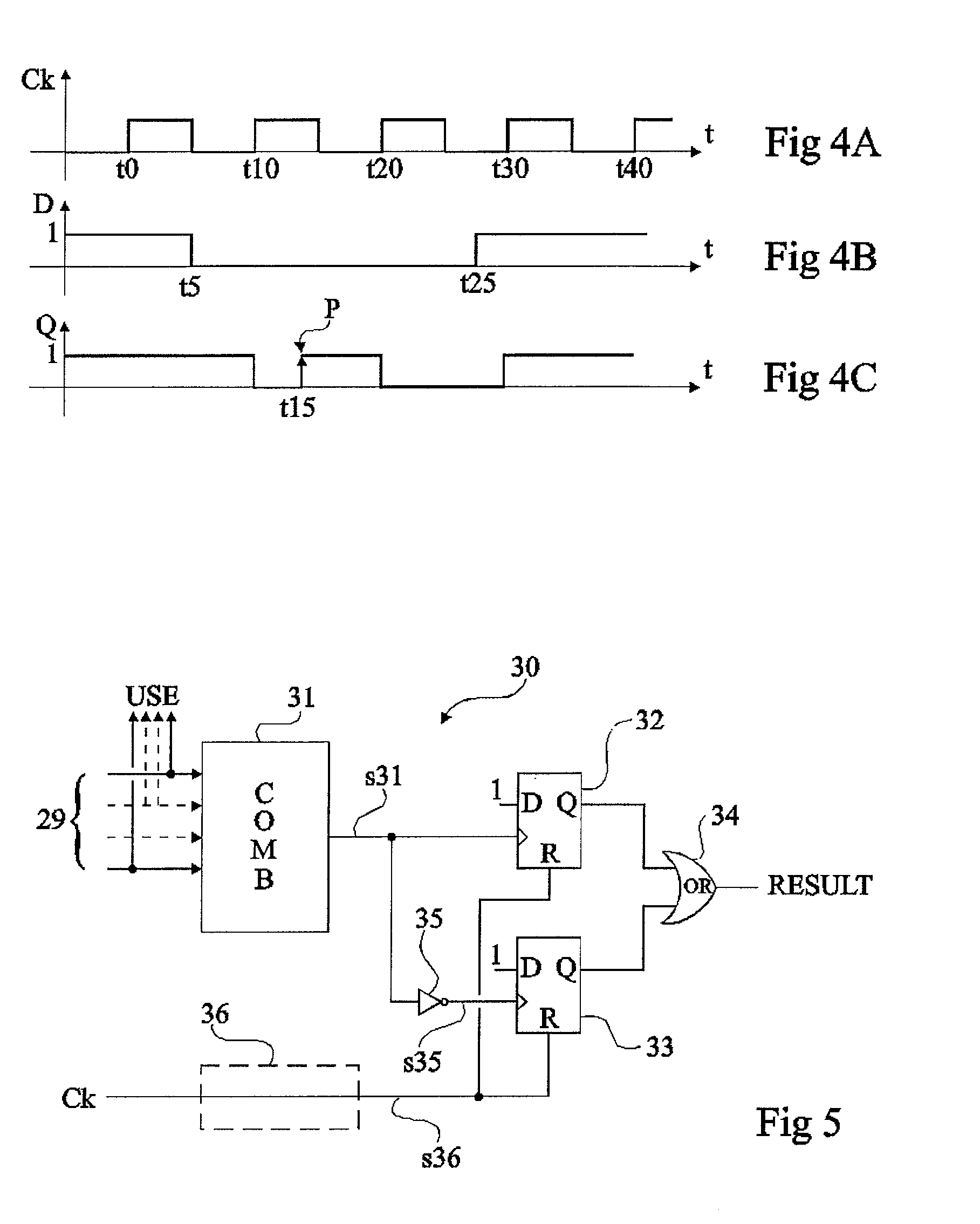
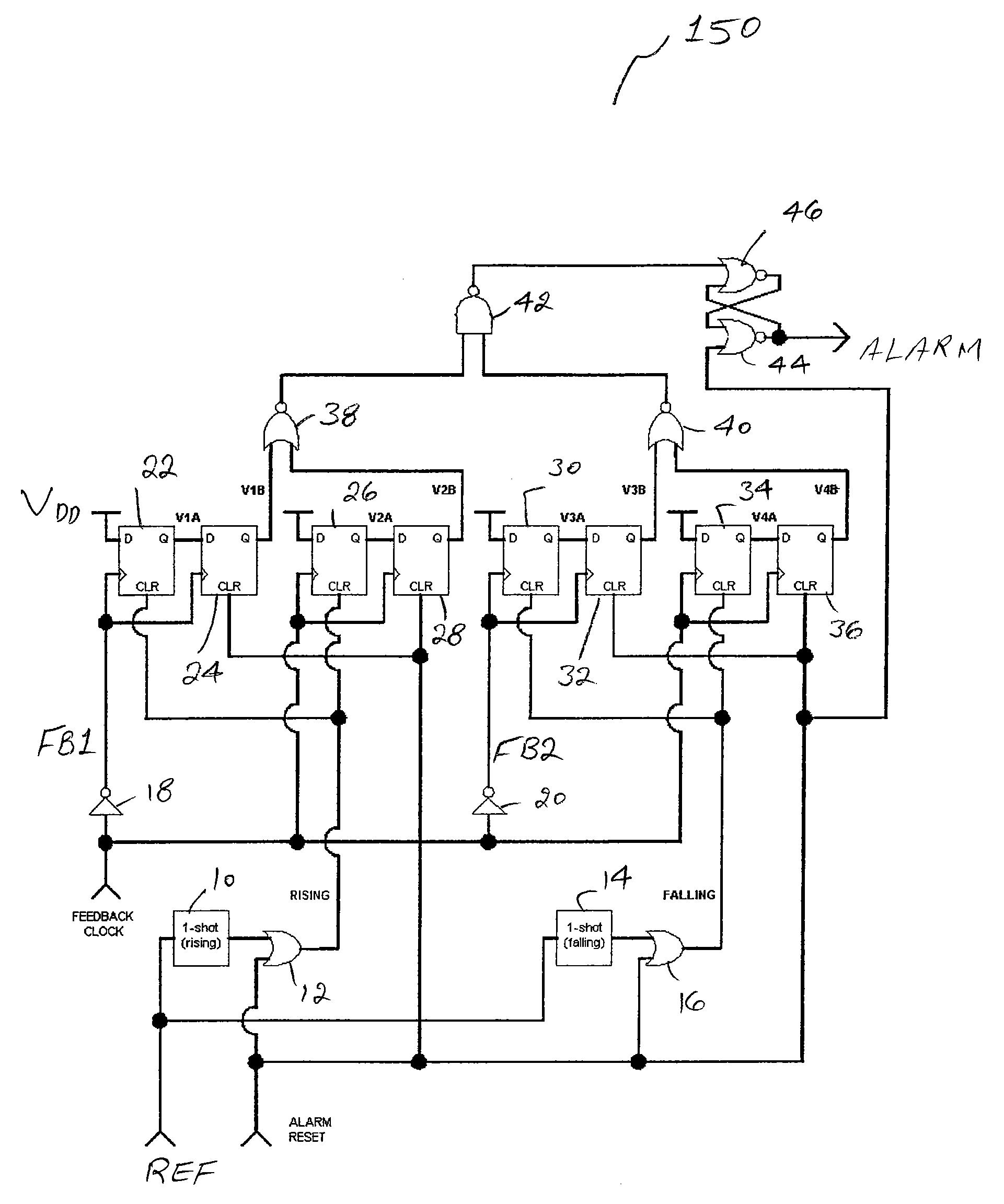
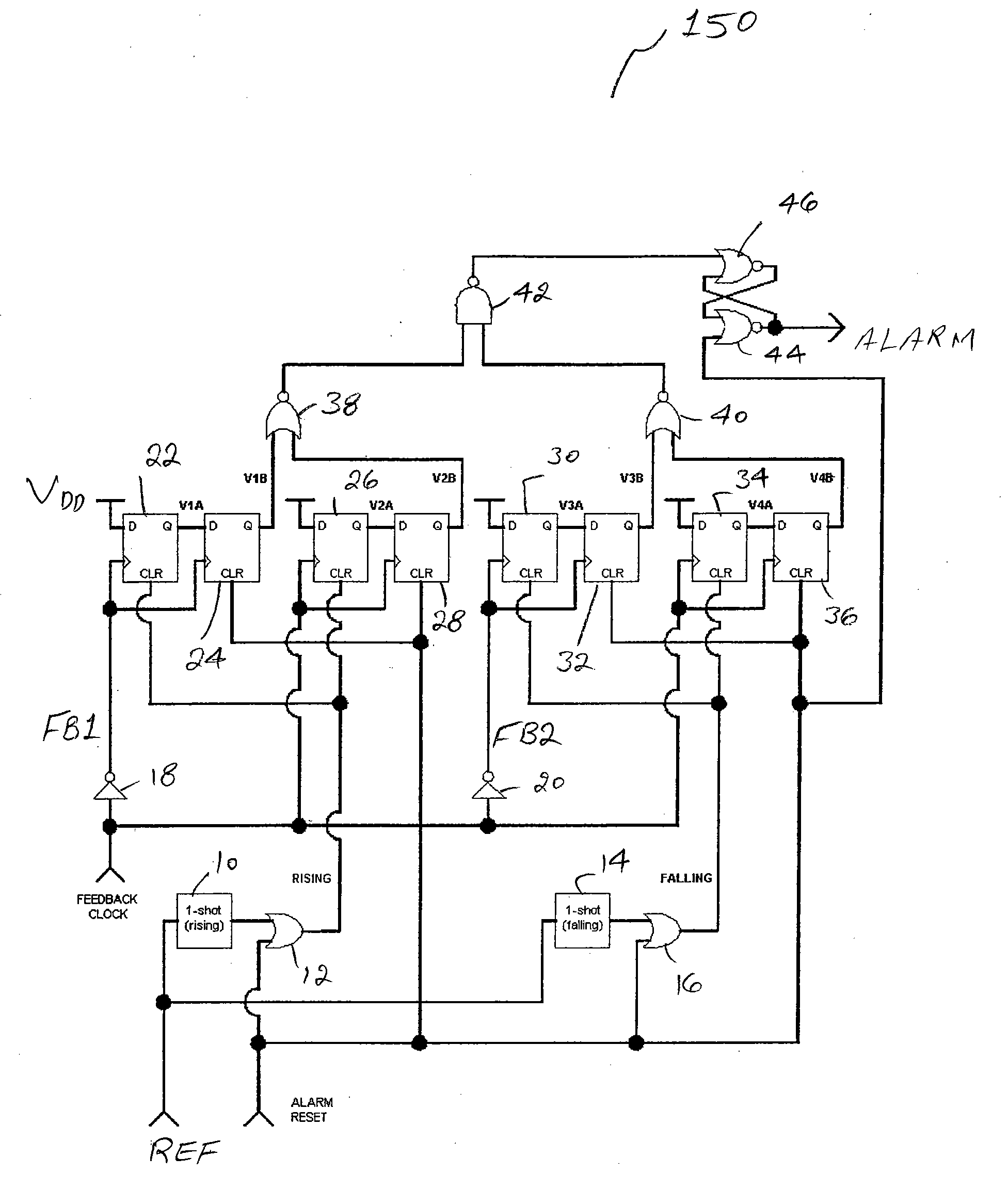
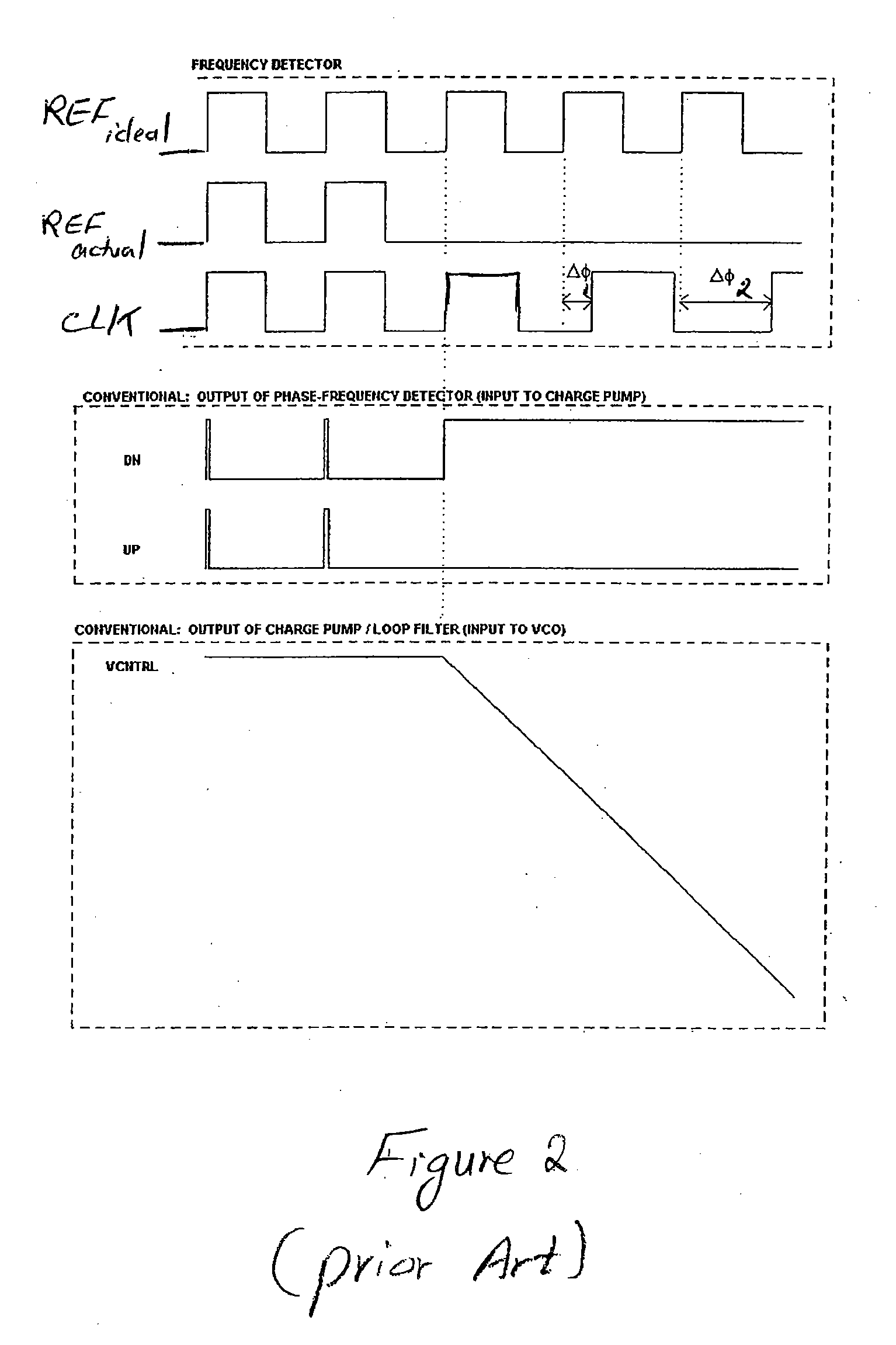
Means to detect a missing pulse and reduce the associated PLL phase bump
A phase / frequency locked loop (PLL) includes circuitry adapted to detect missing pulses of a reference clock and to control the phase bump of the PLL. The circuitry includes, in part, first and second flip-flops, as well as a one-shot block. The first flip-flop has a data input terminal responsive to a voltage supply, and a clock terminal responsive to an inverse of feedback clock. The second flip-flop has a data input terminal responsive to an output of the first flip-flop, and a clock terminal responsive to the inverse of the feedback clock. The one-shot block generates a pulse in response to a rising edge of the reference clock that is used to generate the feedback clock. The one-shot block generates an output signal applied to a reset terminal of the first flip-flop.
Owner:EXAR CORP
Power on detection circuit
InactiveUS20080218223A1Pulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringCurrent consumptionCapacitor
A power on detection circuit for accurately detecting an input voltage with a simple circuit structure and reduced current consumption includes a voltage conversion circuit, which converts input voltage into current, and a latch circuit, which holds the power on detection signal. The voltage conversion circuit supplies output current to a current source and a capacitor via a connection node. The current source generates a flow of current that is proportional to the absolute temperature. When the output current of the voltage conversion circuit becomes greater than the current of the current source, the capacitor is charged and the voltage at the connection node is pulled up. A latching circuit is activated in accordance with the voltage at the connection node to output a power on detection signal.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
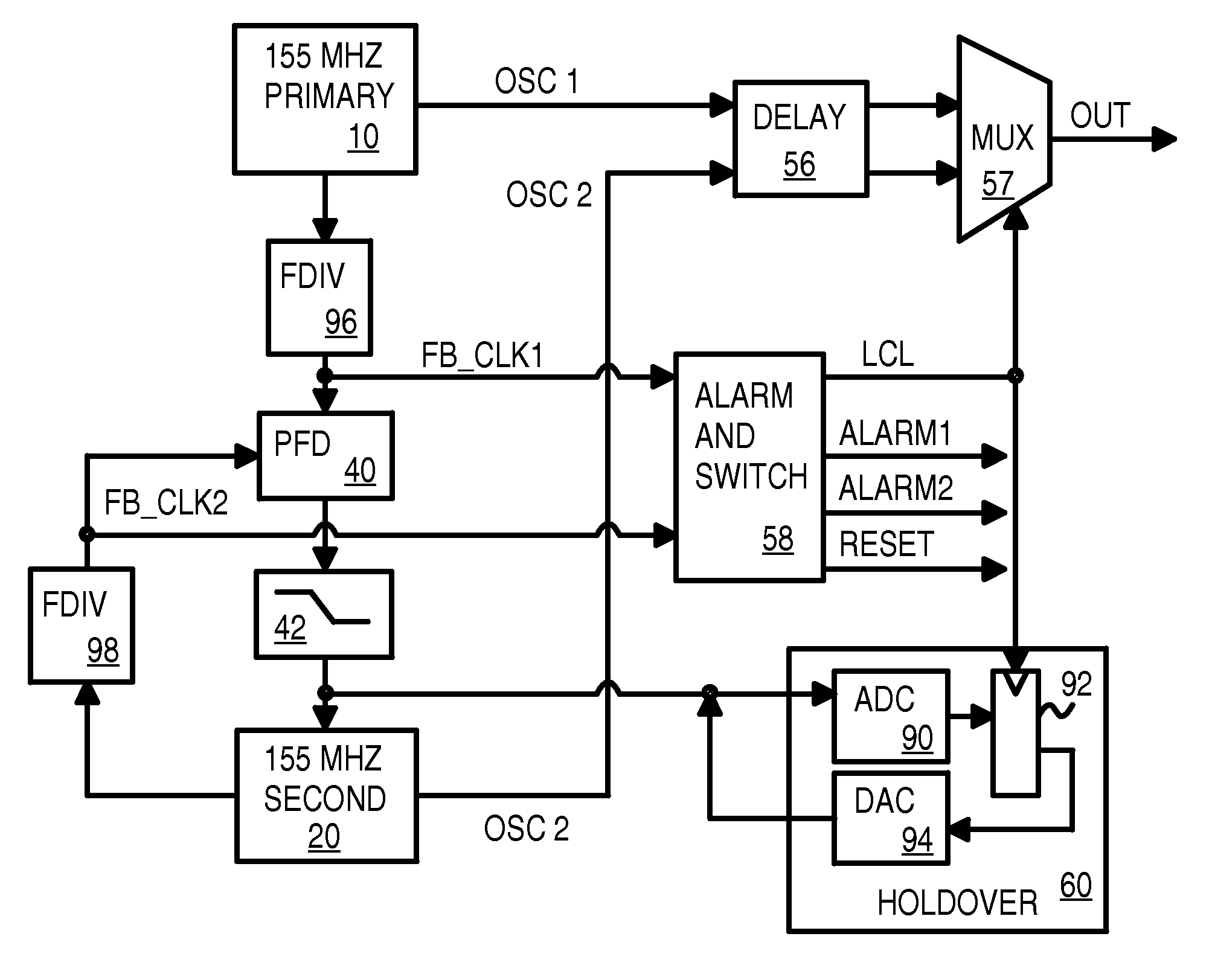
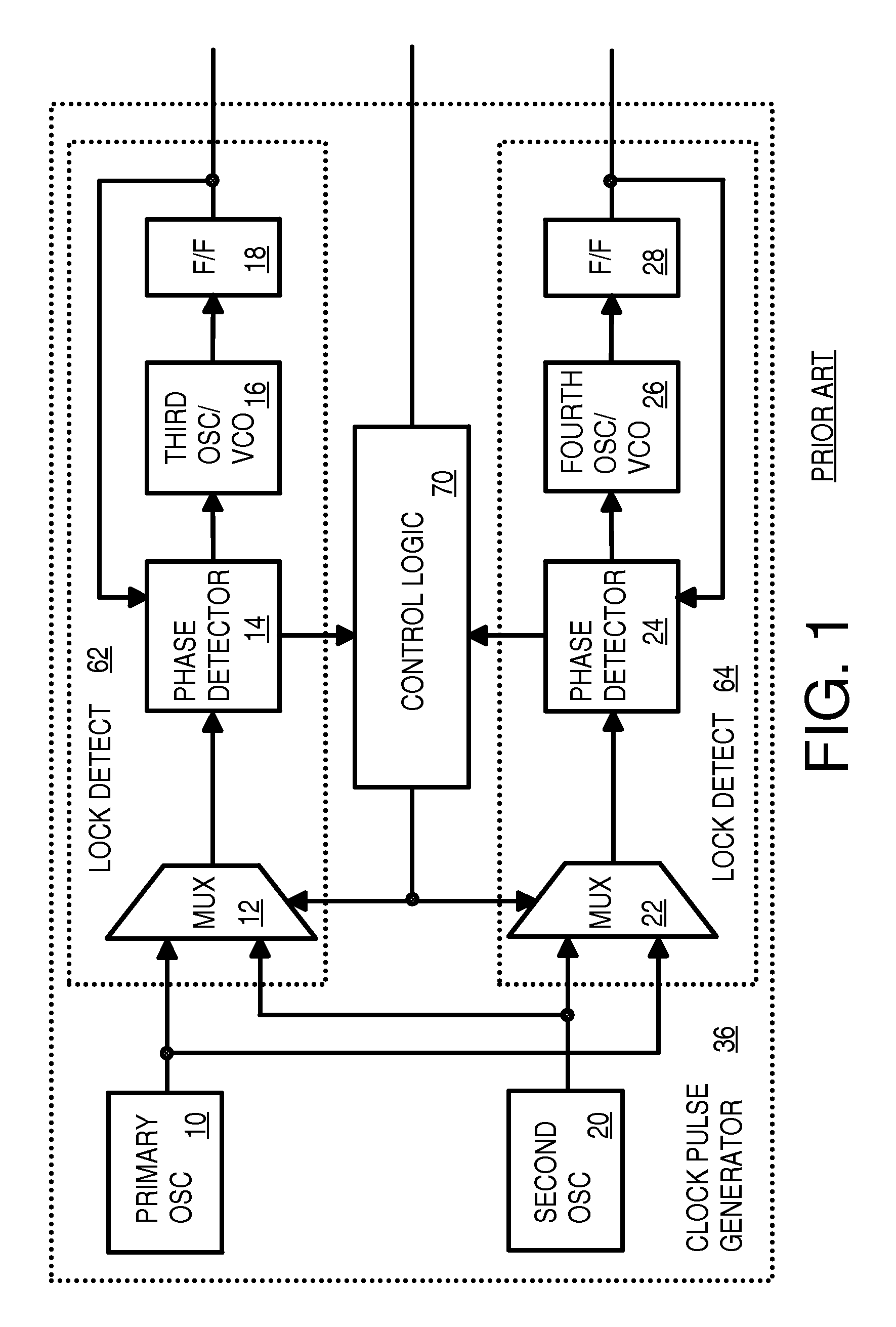
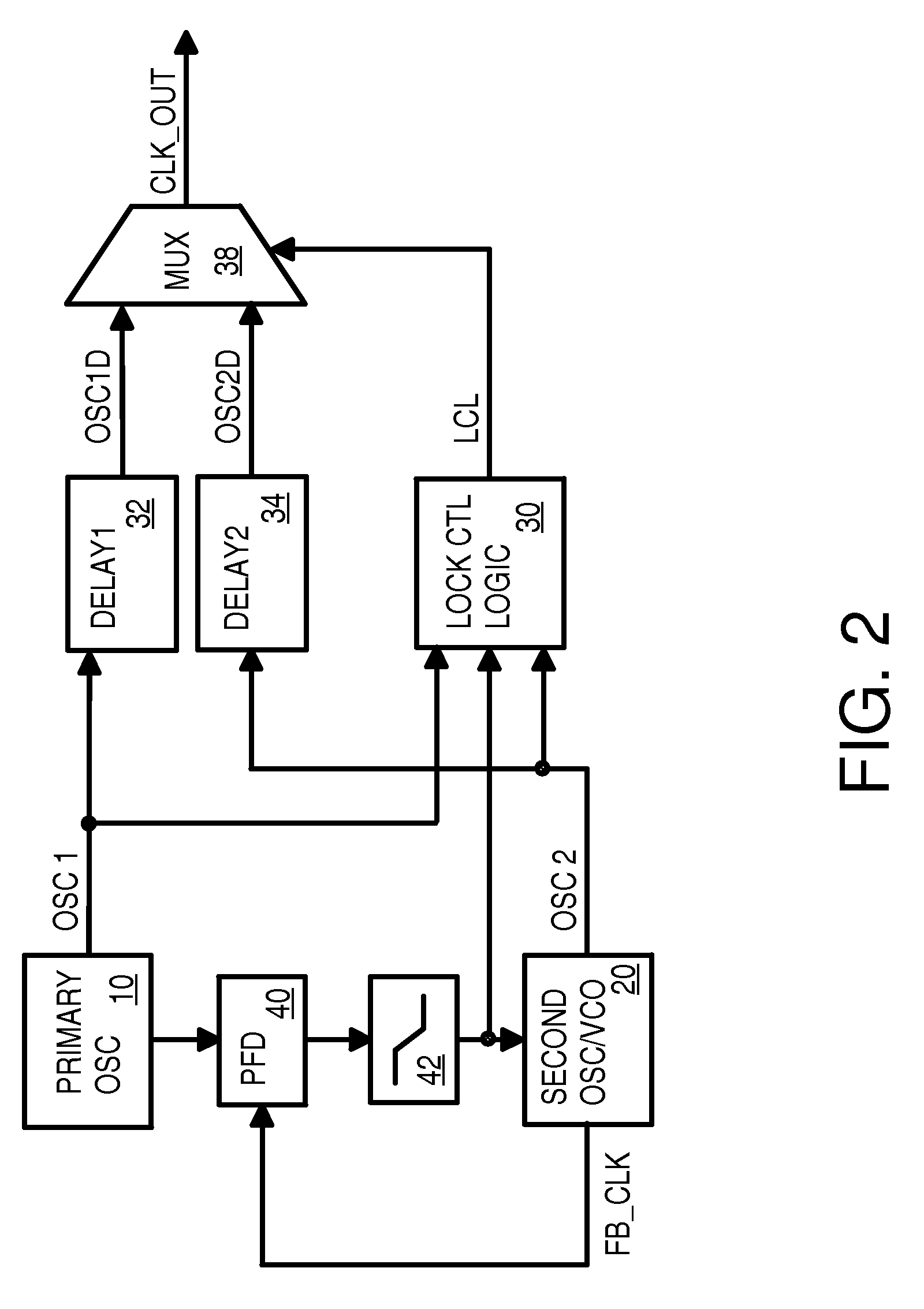
Redundant back-up PLL oscillator phase-locked to primary oscillator with fail-over to back-up oscillator without a third oscillator
A redundant-source clock generator has only two oscillators, rather than three oscillators. A secondary oscillator is phase-locked to a primary clock from a primary oscillator using a phase detector, charge pump, and filter that generate a control voltage to the secondary oscillator that determine the frequency of a secondary clock. The primary clock is compared to the secondary clock to detect primary clock failure. When clock failure is detected, a mux is switched to select a delayed secondary clock rather than a delayed primary clock to output as a system clock. Since the mux receives delayed clock signals, clock-failure detection has additional time to detect the clock failure before the clock failure is propagated through the mux. When the primary oscillator fails and the clock failure is detected, the phase detector stops comparing a feedback secondary clock to the primary clock and instead holds the control voltage steady.
Owner:DIODES INC
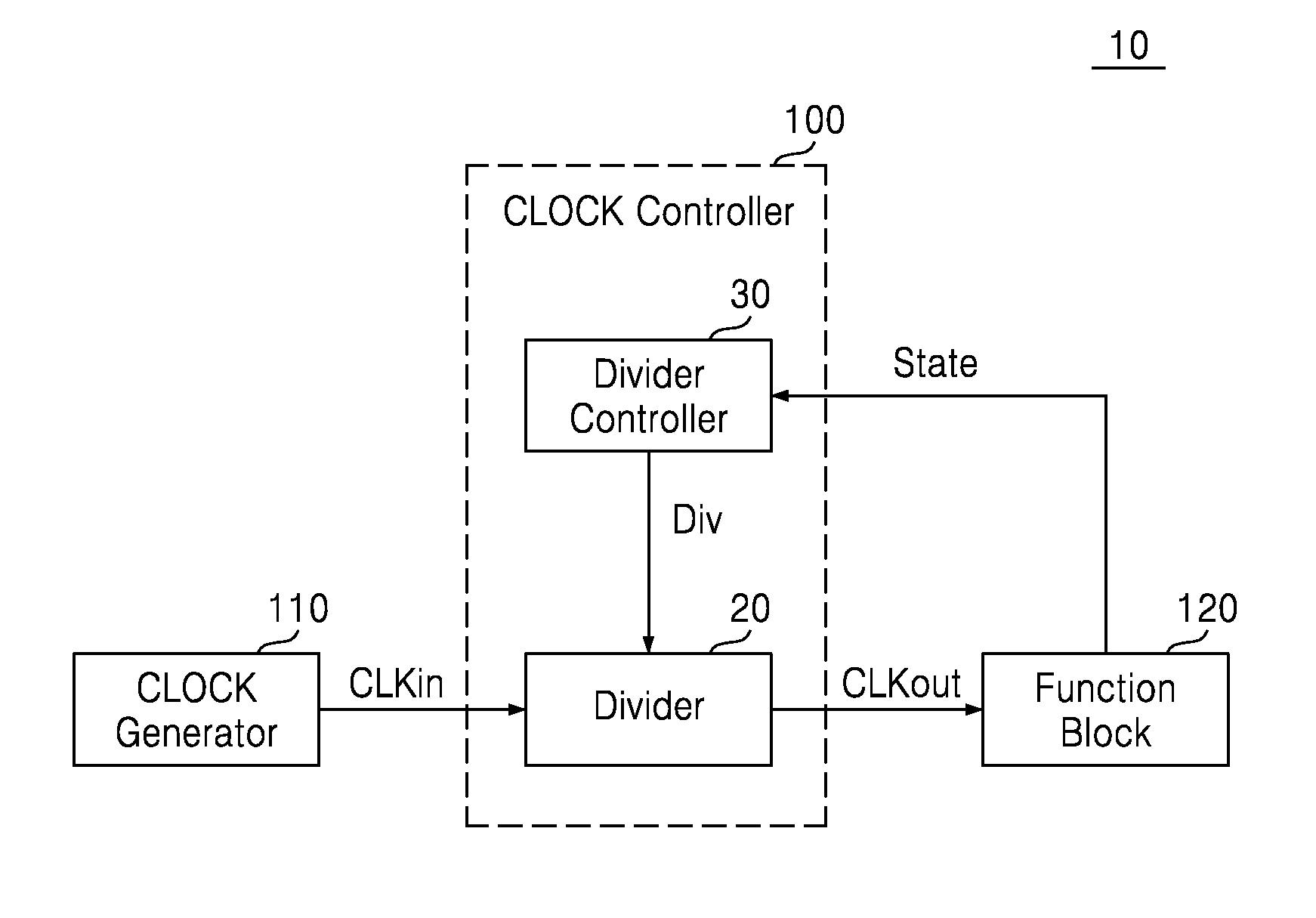
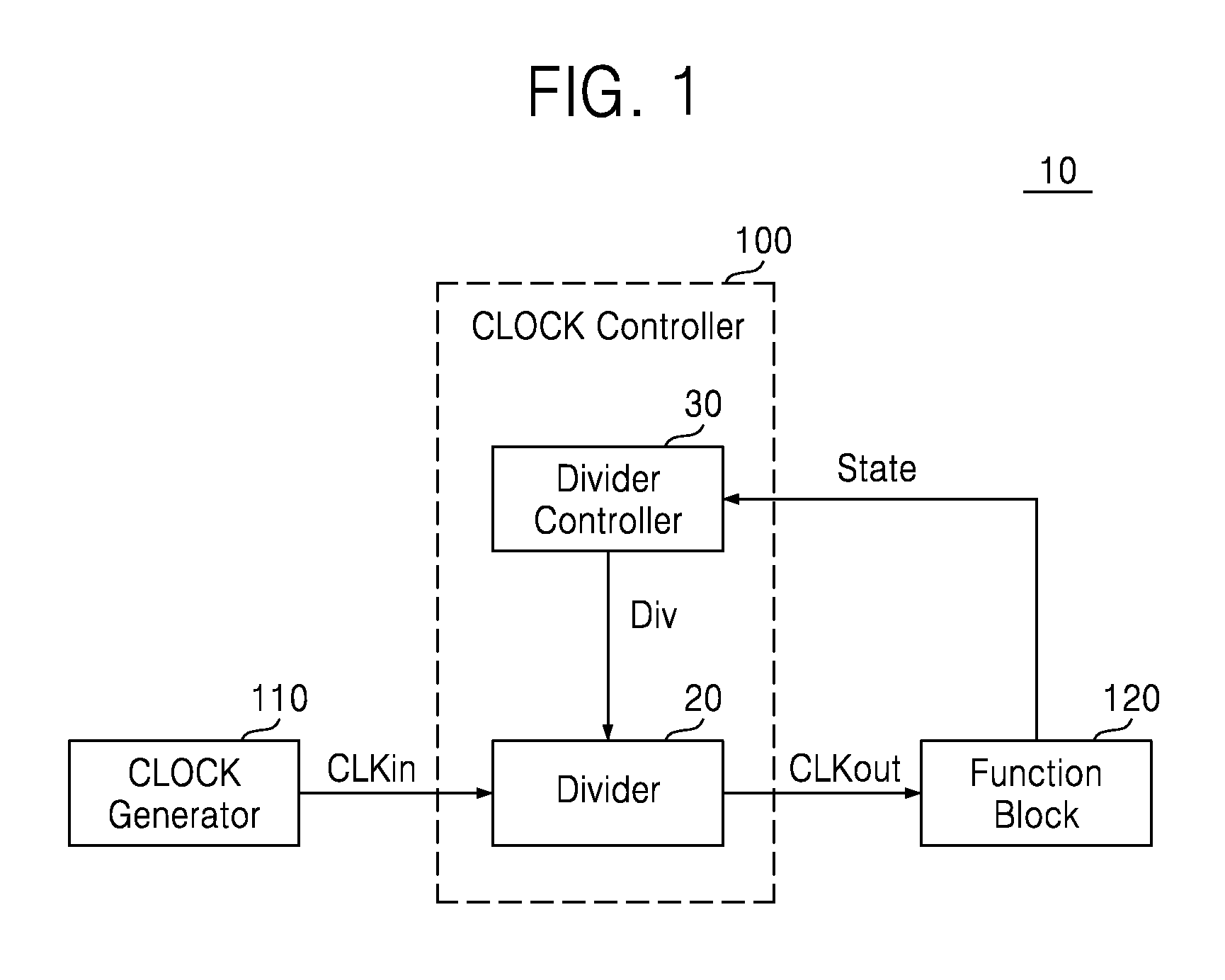
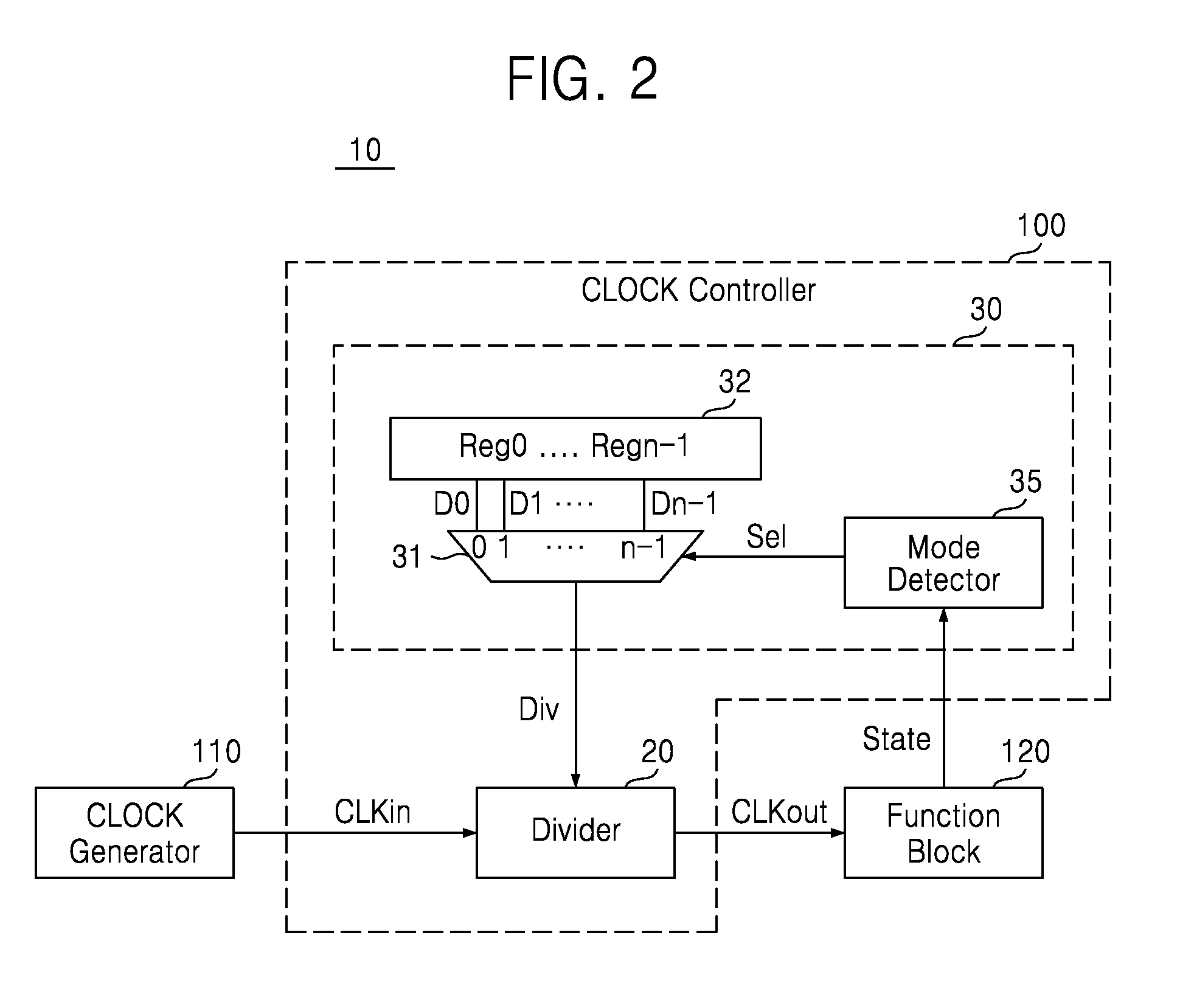
Methods of controlling clocks in system on chip including function blocks, systems on chips and semiconductor systems including the same
ActiveUS20130147526A1Reduce operating frequencyIncrease working frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringActive state
A system-on-chip includes a clock controller configured to decrease an operating frequency of at least one function block based on a change in an operating state of the at least one function block from an active state to an idle state. In a method of operating a system-on-chip including at least one function block, an operating frequency of the at least one function block is decreased based on a change in an operating state of the at least one function block from an active state to an idle state. The decreased operating frequency is greater than zero.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
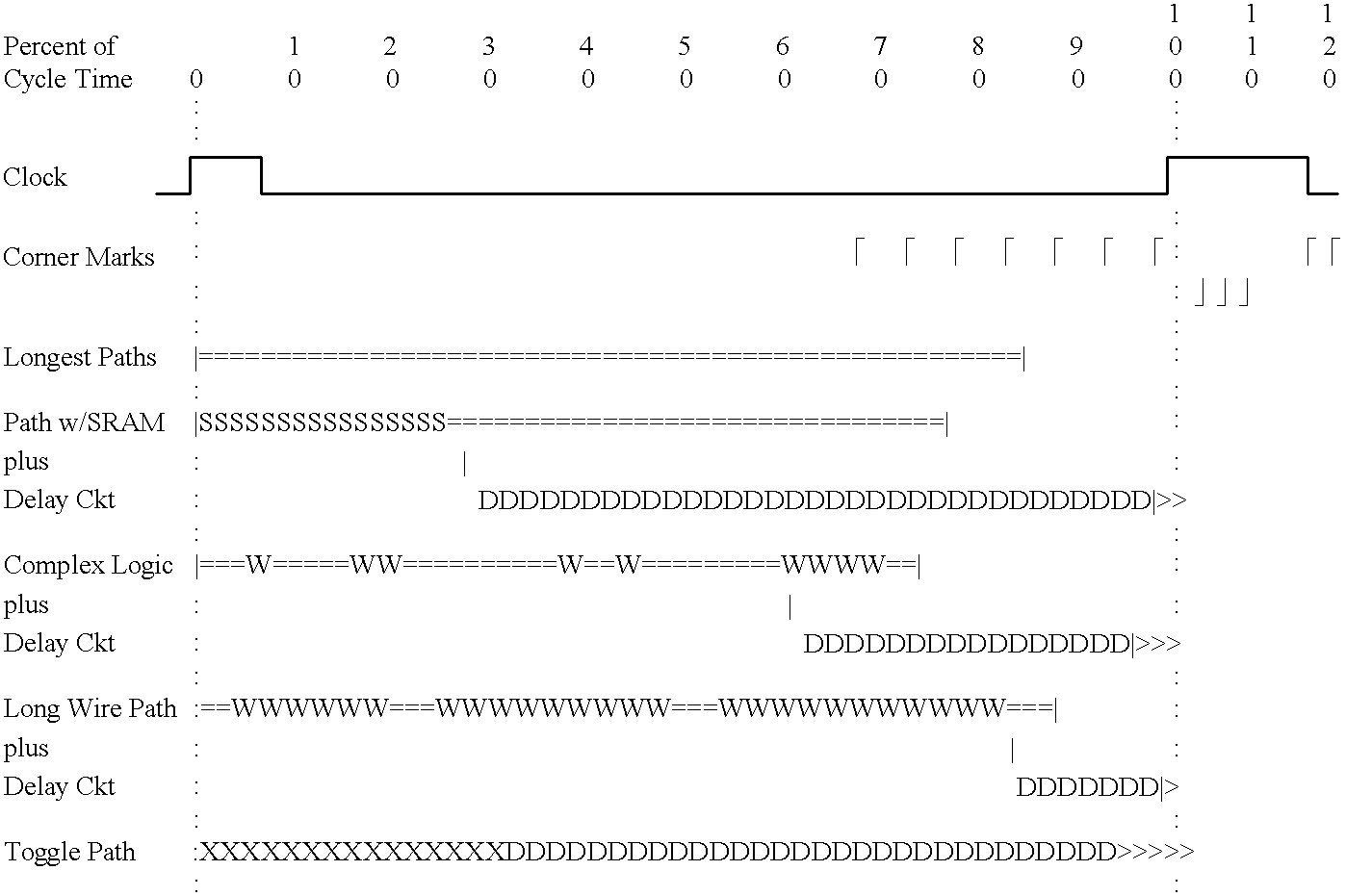
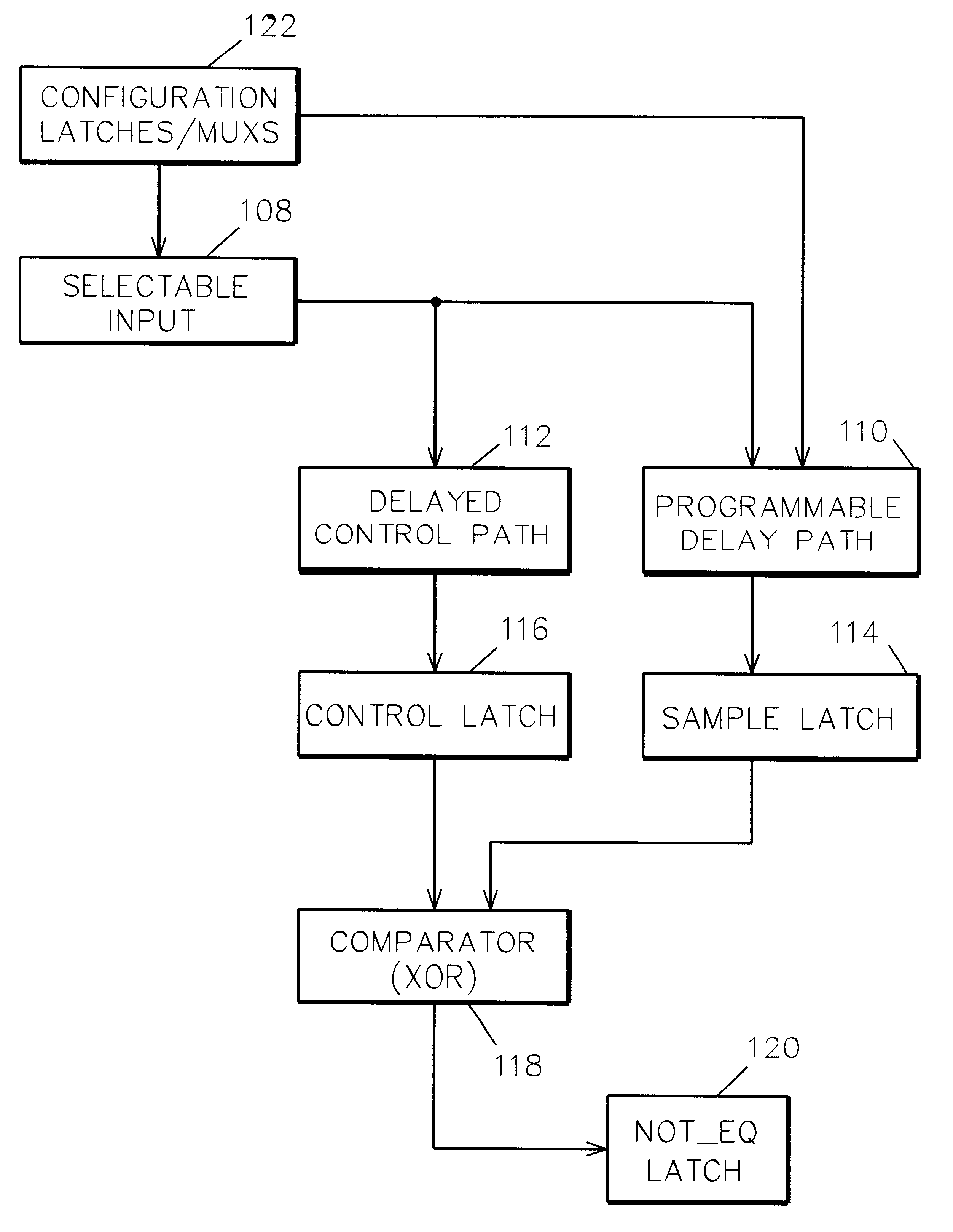
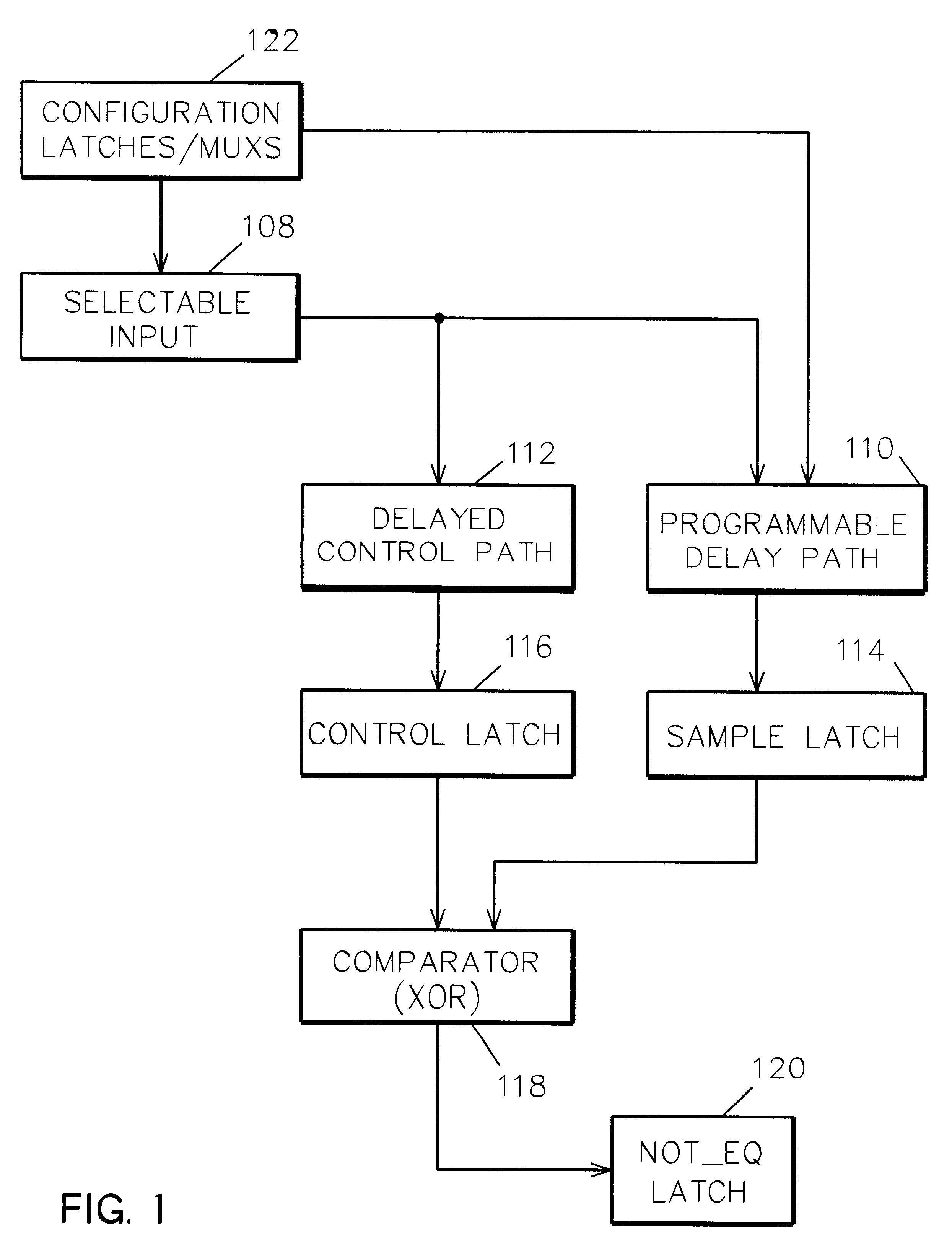
Programmable timing circuit for testing the cycle time of functional circuits on an integrated circuit chip
InactiveUS6415402B2Improve abilitiesHigh activityElectronic circuit testingCurrent/voltage measurementMultiplexerControl delay
A programmable timing circuit on an integrated circuit chip for testing the cycle time of functional circuits on the chip. The timing circuit includes a selectable input having at least two sources, one of which is a toggle circuit; a minimally delayed control path including a control latch; a programmable delay path in parallel with the control path and including a sample latch; and a comparator for comparing the state of the control latch and sample latches to provide a signal indicative of the delay path being longer than the control path. A plurality of configuration latches and multiplexers are provided for selecting the input source and routing an input signal through specific delay blocks to control the amount of delay in the delay path.
Owner:IBM CORP
Test outputs using an idle bus
InactiveUS6782336B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsMultiplexingEngineering
A test circuit receives a plurality of internal test signals and delivers a group of the plurality of internal test signals onto a bus during an idle state of the bus. The bus is coupled to output pins so that the group of internal test signals can be used in debugging operations. The test circuit may include a multiplexing circuit that receives the plurality of internal test signals as inputs and that delivers a selected group of the internal test signals as outputs. The test circuit may also include a switch that couples the selected group of the internal test signals onto the bus during an idle state.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
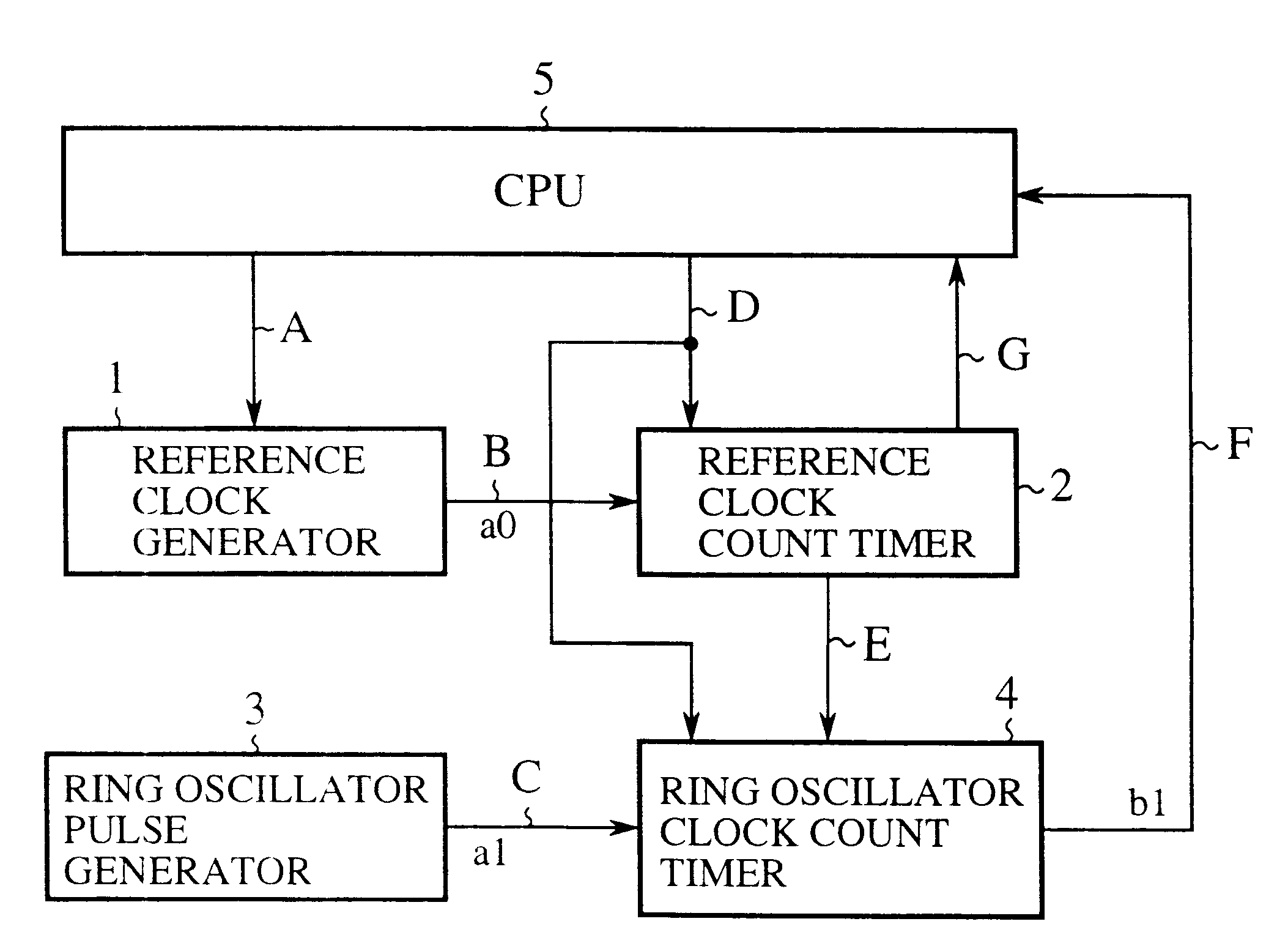
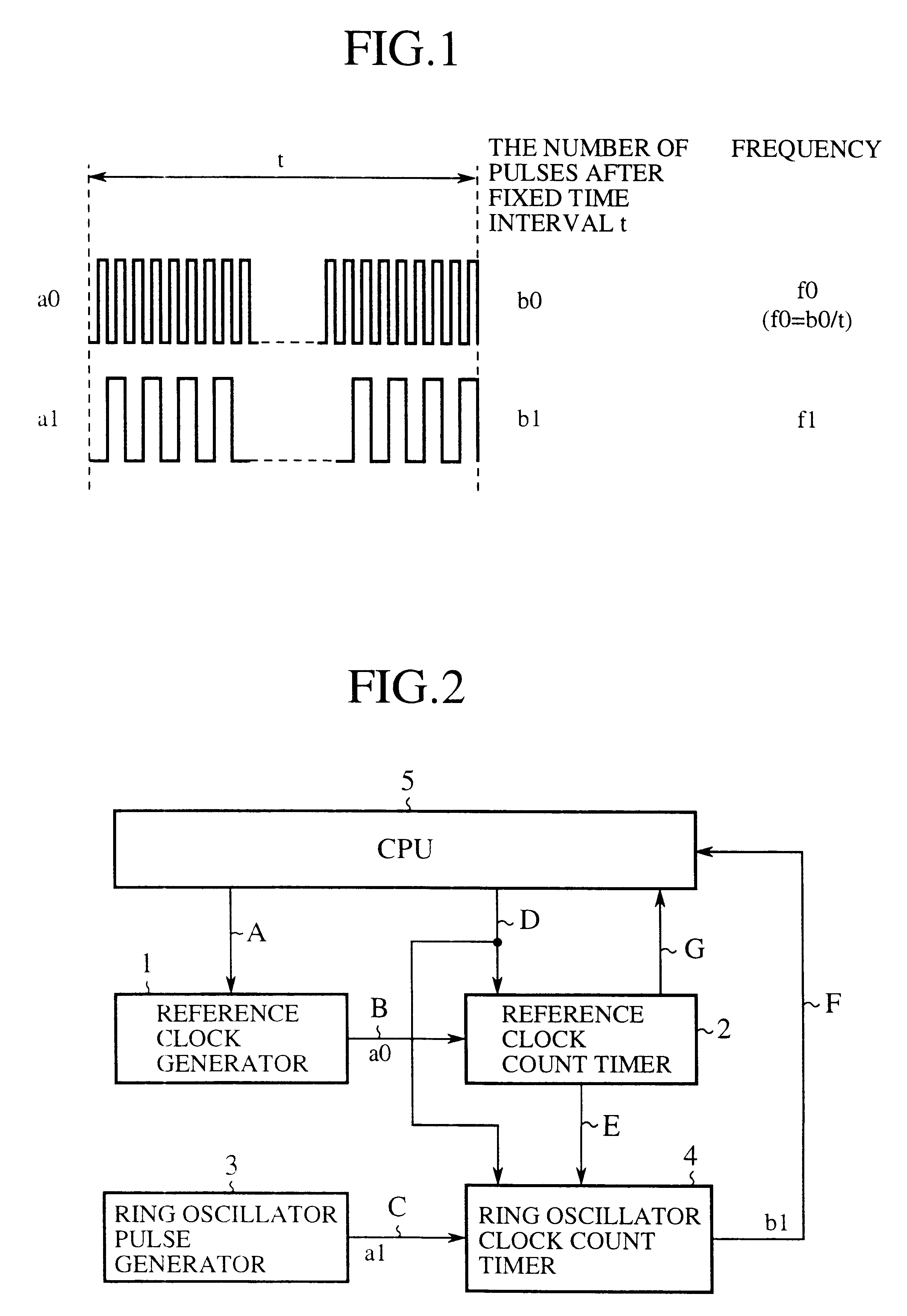
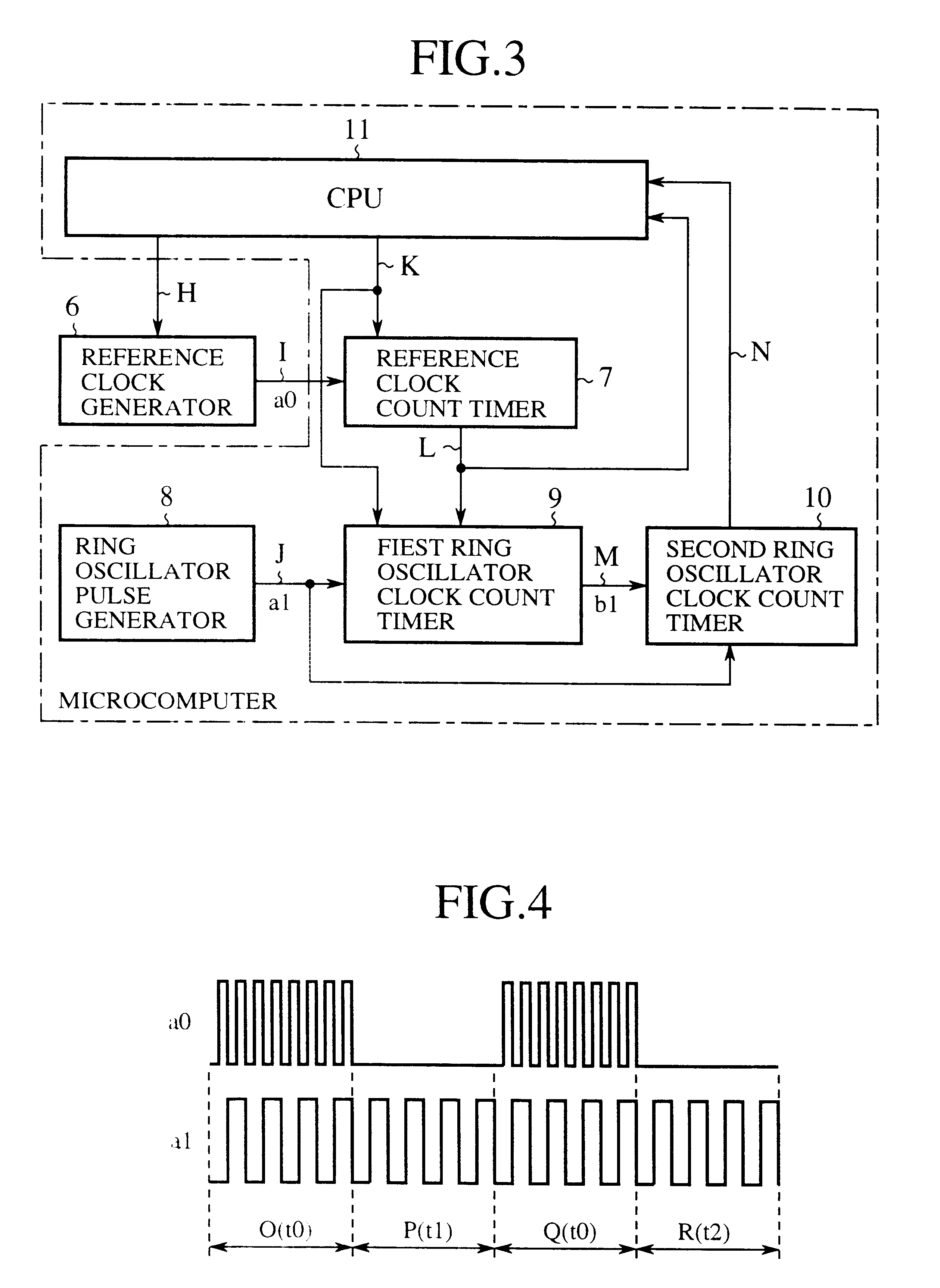
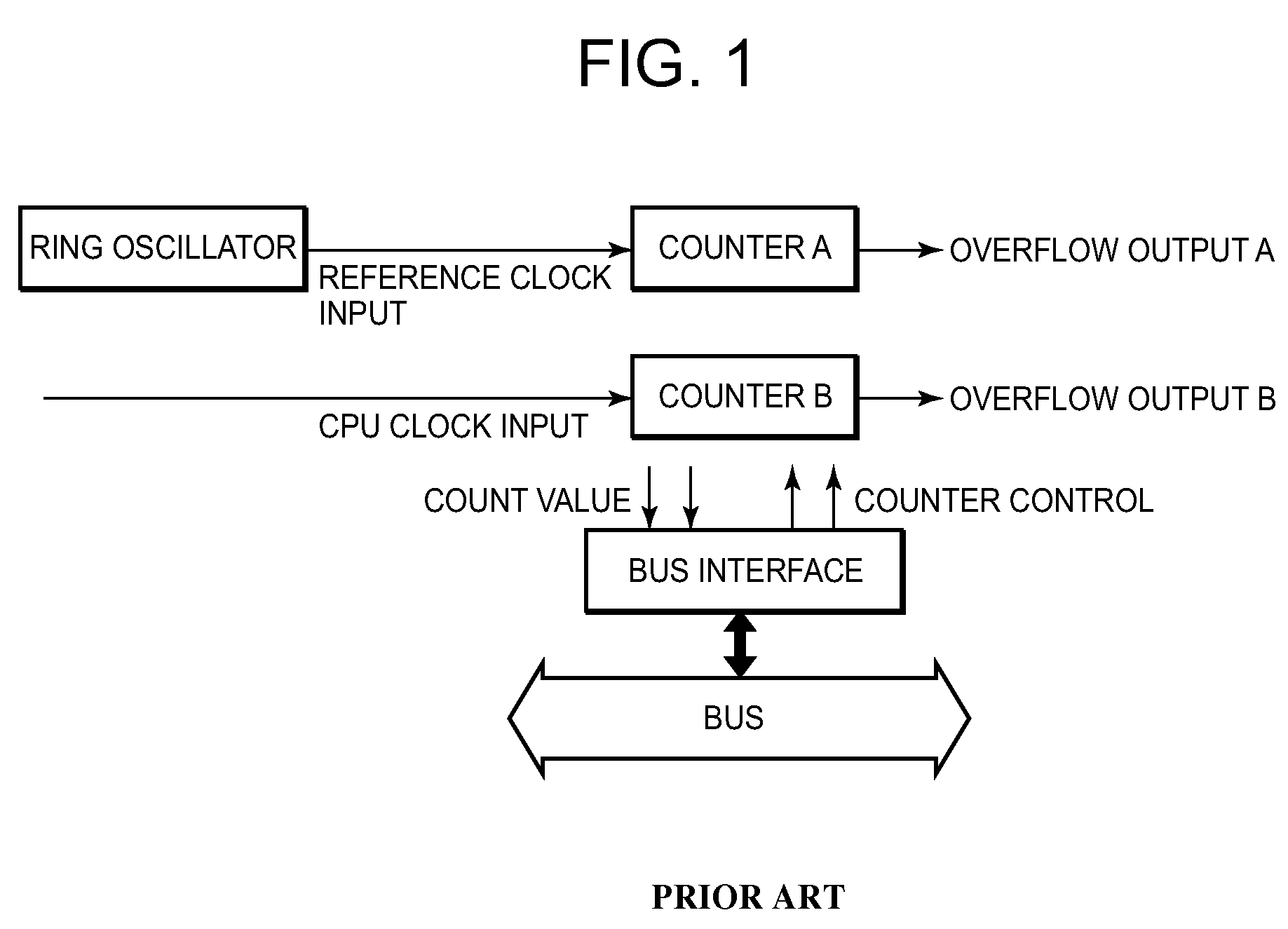
Ring oscillator clock frequency measuring method, ring oscillator clock frequency measuring circuit, and microcomputer
InactiveUS6442704B1Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementPulse train pattern monitoringPulse generation by logic circuitsMicrocomputerFrequency measurements
A ring oscillator clock frequency measuring circuit includes a reference clock count timer and a ring oscillator clock count timer. The reference clock count timer starts its counting of a reference clock signal in response to a start instruction fed from a CPU, and outputs an overflow signal when its counting reaches a preset value. The ring oscillator clock count timer starts its counting of pulses of a ring oscillator clock signal in response to the start instruction fed from the CPU, and continues its counting until the reference clock count timer generates the overflow signal. The frequency of the ring oscillator clock signal is obtained from the count value of the ring oscillator clock count timer. This makes it possible to measure the frequency of the ring oscillator clock signal at high accuracy, and to reduce the current consumption by operating the CPU based on the ring oscillator clock signal after the measurement.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC SYST LSI DESIGN +1
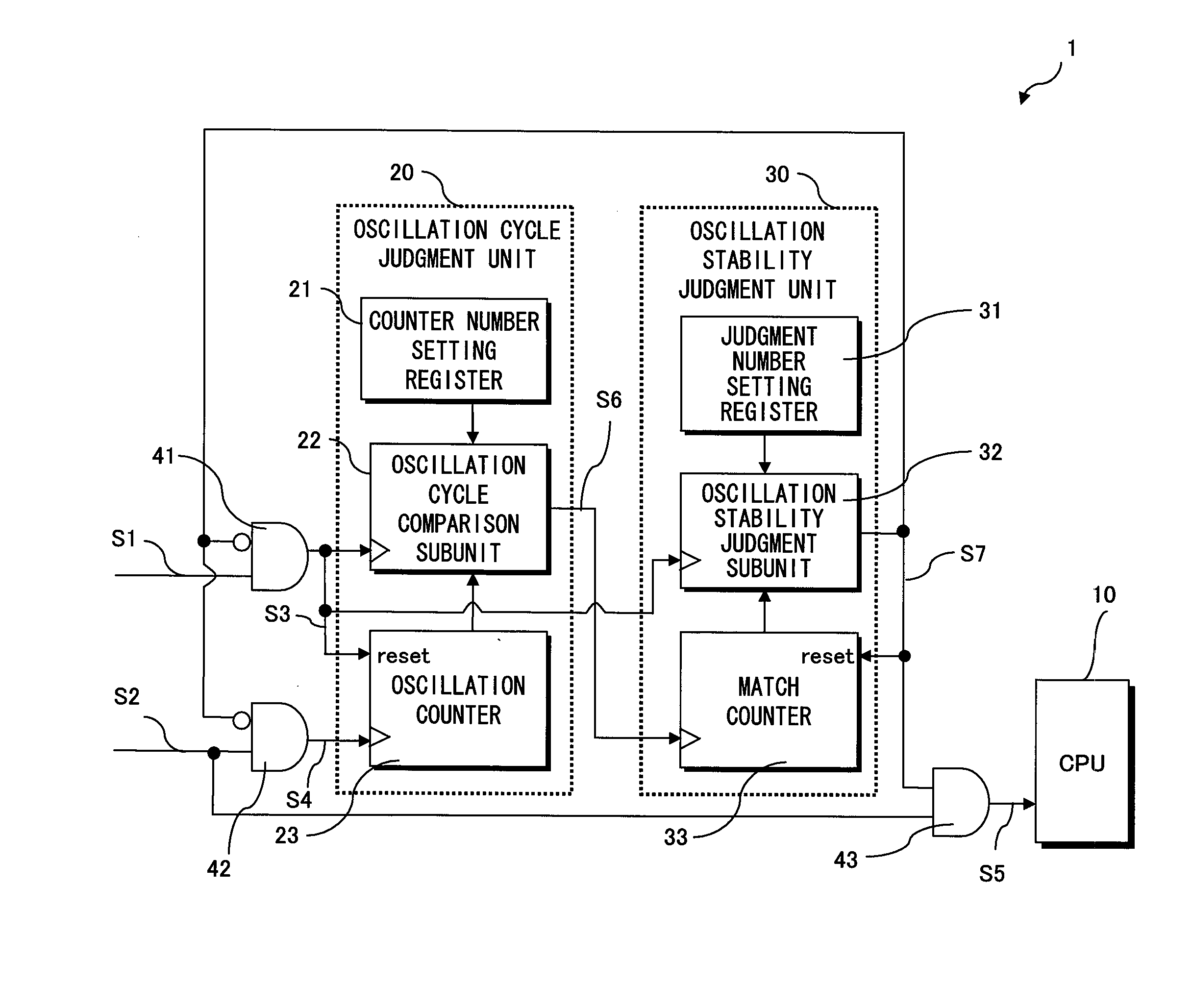
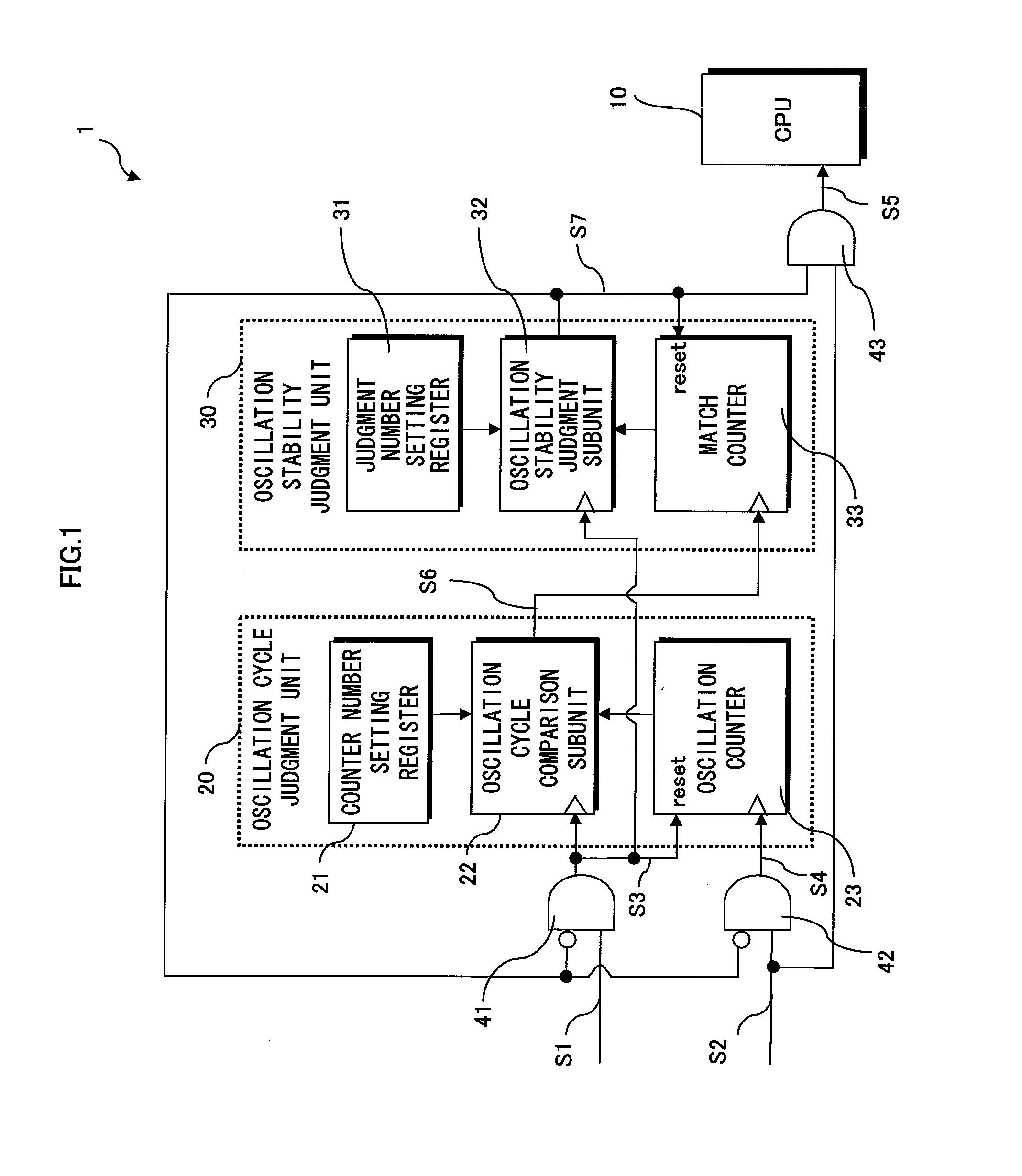
Semiconductor integrated circuit and information processing system
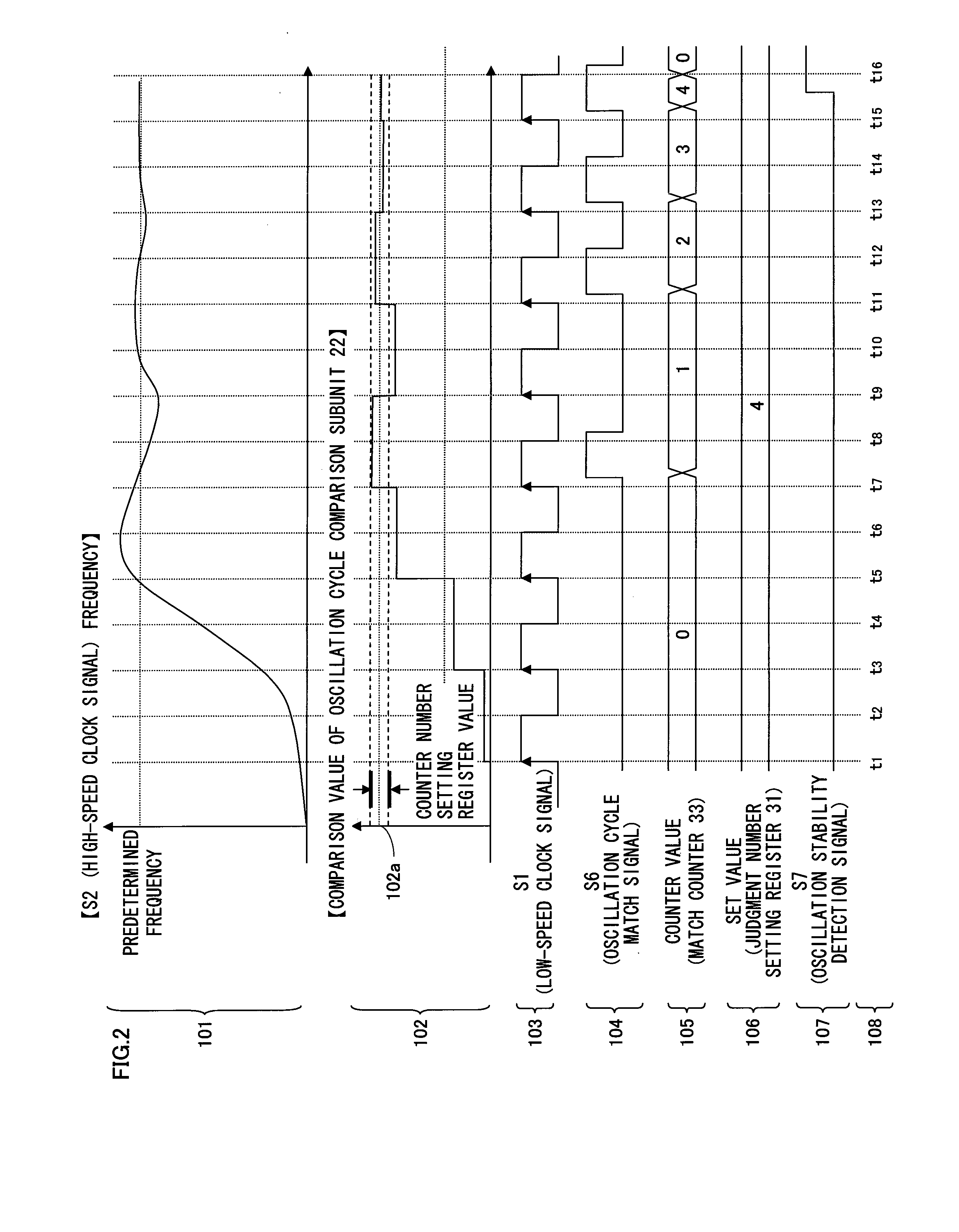
InactiveUS20080297202A1Improve reliabilityHighly reliable detectionPulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringInformation processingLow speed
In a semiconductor integrated circuit, a counter counts the number of high-speed clock signals that have been generated in a predetermined number of clock cycles of a low-speed clock signal. In synchronization with the low-speed clock signal, the semiconductor integrated circuit compares the counter value and a predetermined value, and judges whether the frequency of the high-speed clock signal has reaches a predetermined frequency. Since variations in the frequency become smaller as the oscillation of a high-speed oscillator stabilizes, the semiconductor integrated circuit detects that the oscillation is stable when the semiconductor integrated circuit has judged affirmatively a plurality of times.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Means To Detect A Missing Pulse And Reduce The Associated PLL Phase Bump
A phase / frequency locked loop (PLL) includes circuitry adapted to detect missing pulses of a reference clock and to control the phase bump of the PLL. The circuitry includes, in part, first and second flip-flops, as well as a one-shot block. The first flip-flop has a data input terminal responsive to a voltage supply, and a clock terminal responsive to an inverse of feedback clock. The second flip-flop has a data input terminal responsive to an output of the first flip-flop, and a clock terminal responsive to the inverse of the feedback clock. The one-shot block generates a pulse in response to a rising edge of the reference clock that is used to generate the feedback clock. The one-shot block generates an output signal applied to a reset terminal of the first flip-flop.
Owner:EXAR CORP
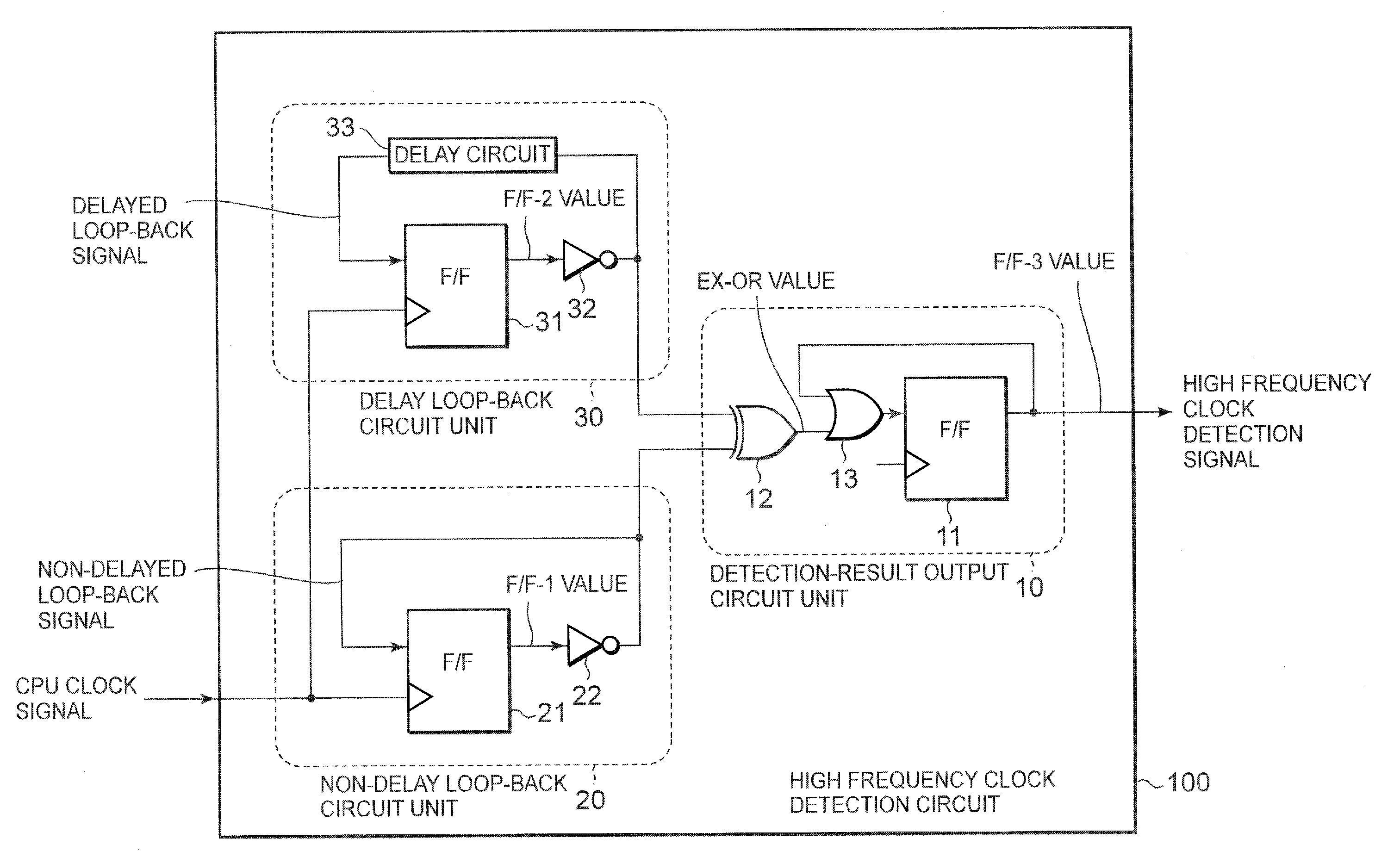
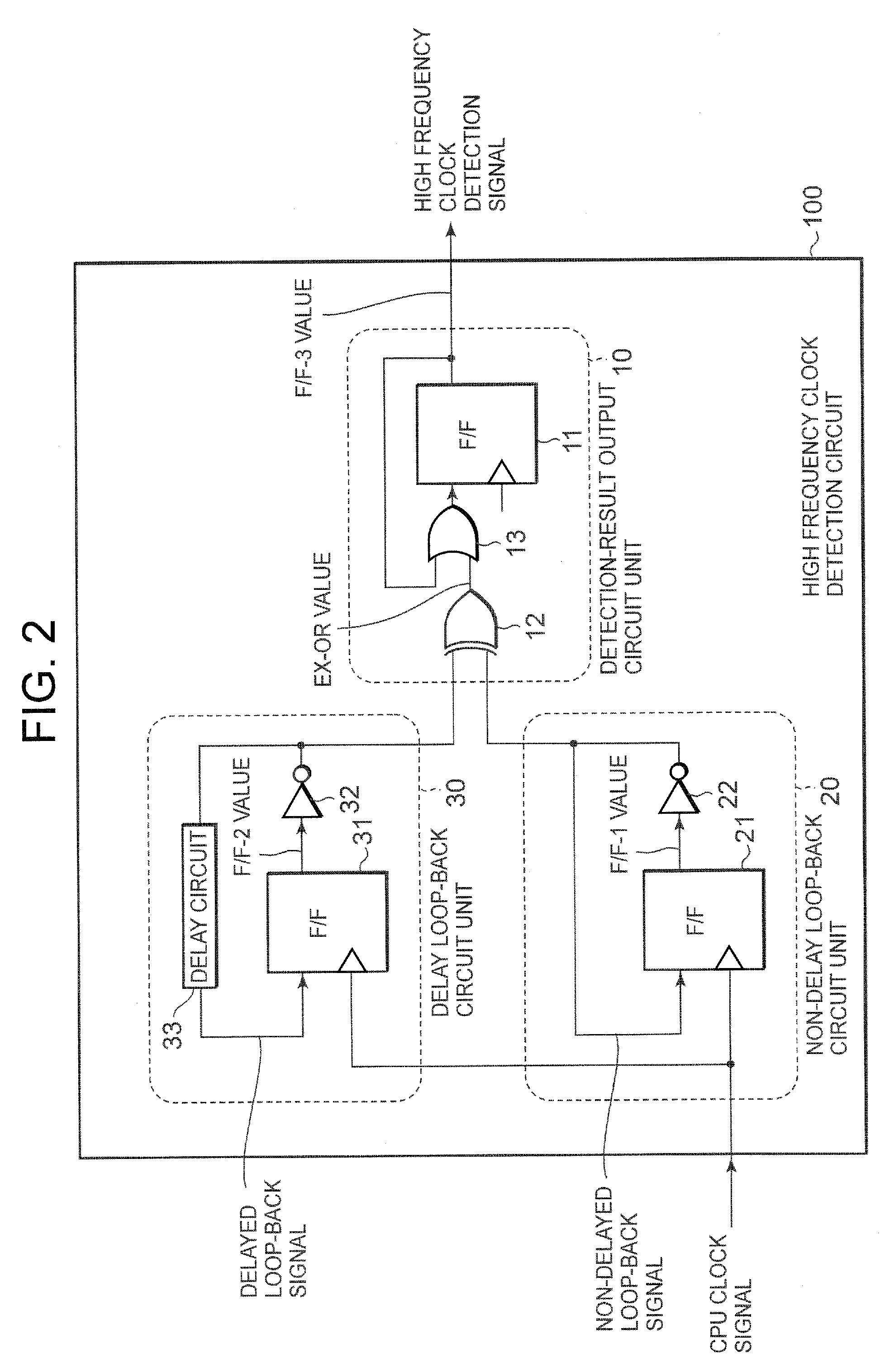
High-frequency clock detection circuit
InactiveUS7714619B2Current/voltage measurementPulse train pattern monitoringEngineeringHigh frequency
In order to provide a high frequency clock detection circuit capable to detect a high frequency clock using any period as a threshold, the high frequency clock detection circuit of the present invention includes a delay circuit having a delay time set to be longer than a clock period corresponding to the irregular high frequency state, a first flip-flop circuit for delay flip-flopping according to the clock signal and for being provided with the inverted and feedback inputted output from the first flip-flop circuit, a second flip-flop circuit for delay flip-flopping according to the clock signal and for being provided with the inverted and feedback inputted output from the second flip-flop circuit through the delay circuit, and a detection-result output circuit for detecting a difference between the output signal from the first flip-flop circuit and the output signal from the second flip-flop circuit and for providing the function circuit with the high frequency clock detection signal indicating the irregular high frequency state corresponding to an occurrence of the difference.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
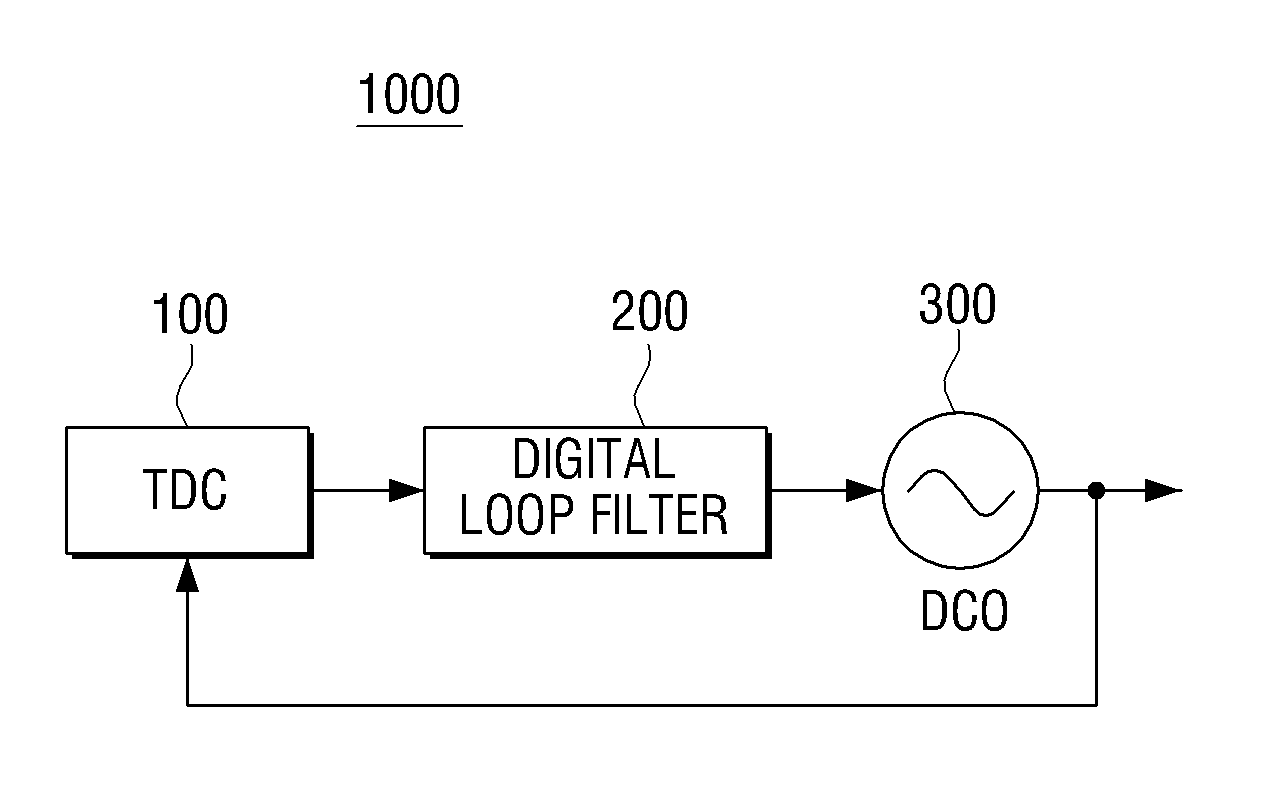
Time-to-digital converter and all-digital phase-locked loop
ActiveUS20100134165A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlPhase differencePhase frequency detector
A time-to-digital converter (TDC) includes a converter which receives a first signal and a second signal, delays the second signal in phases using a plurality of delay elements which are coupled in series, compares the delayed second signal with the first signal, and outputs a phase error of the second signal with respect to the first signal, a phase frequency detector which receives the first signal, and a third signal from one of the nodes in the plurality of delay elements, and outputs a phase difference between the first signal and the third signal, and a frequency detector which outputs a frequency error of the second signal with respect to the first signal as a digital code using an output signal of the phase frequency detector and the second signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Power on detection circuit
InactiveUS7612588B2Pulse automatic controlPulse train pattern monitoringEngineeringCurrent consumption
A power on detection circuit for accurately detecting an input voltage with a simple circuit structure and reduced current consumption includes a voltage conversion circuit, which converts input voltage into current, and a latch circuit, which holds the power on detection signal. The voltage conversion circuit supplies output current to a current source and a capacitor via a connection node. The current source generates a flow of current that is proportional to the absolute temperature. When the output current of the voltage conversion circuit becomes greater than the current of the current source, the capacitor is charged and the voltage at the connection node is pulled up. A latching circuit is activated in accordance with the voltage at the connection node to output a power on detection signal.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
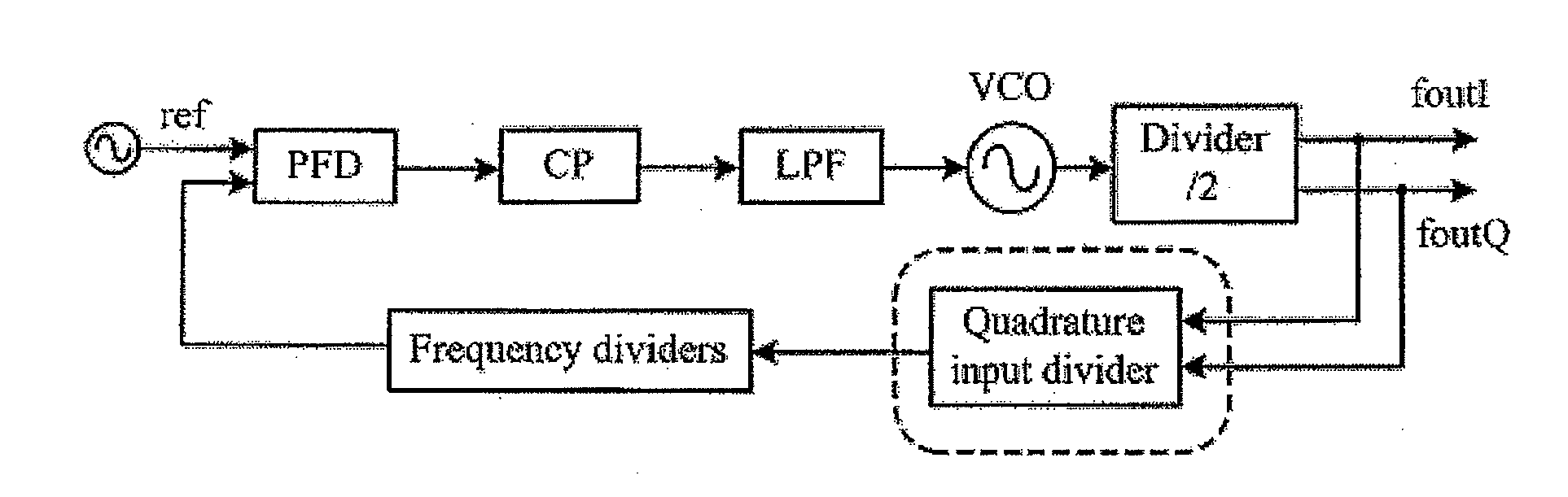
Quadrature-input, quadrature-output, divider and phase locked loop, frequency synthesiser or single side band mixer
ActiveUS20090068975A1Accurate operationMultiple-port active networksModulated-carrier systemsHarmonicFrequency mixer
The present invention relates to a quadrature divider which may be used in a phase locked loop or frequency synthesiser or with a single side band mixer. According to a preferred embodiment the divider takes a quadrature input and has a quadrature output. The divider has four analog mixers 1, 2, 3 and 4. The first two mixers 1, 2 take the in-phase quadrature input, while the second mixers 3, 4 take the quadrature-phase quadrature input. The outputs and feedback loops of the mixers are properly arranged such that the in-phase and quadrature-phase outputs of the divider have a determinisitic phase sequence relationship based on the phase sequence relationship of the corresponding quadrature inputs. Third order harmonics may be minimised or reduced by addition or subtraction of the mixer outputs. As the divider is able to take a quadrature input, there is no need for a dummy divider in the phase locked loop, thus saving space and power.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
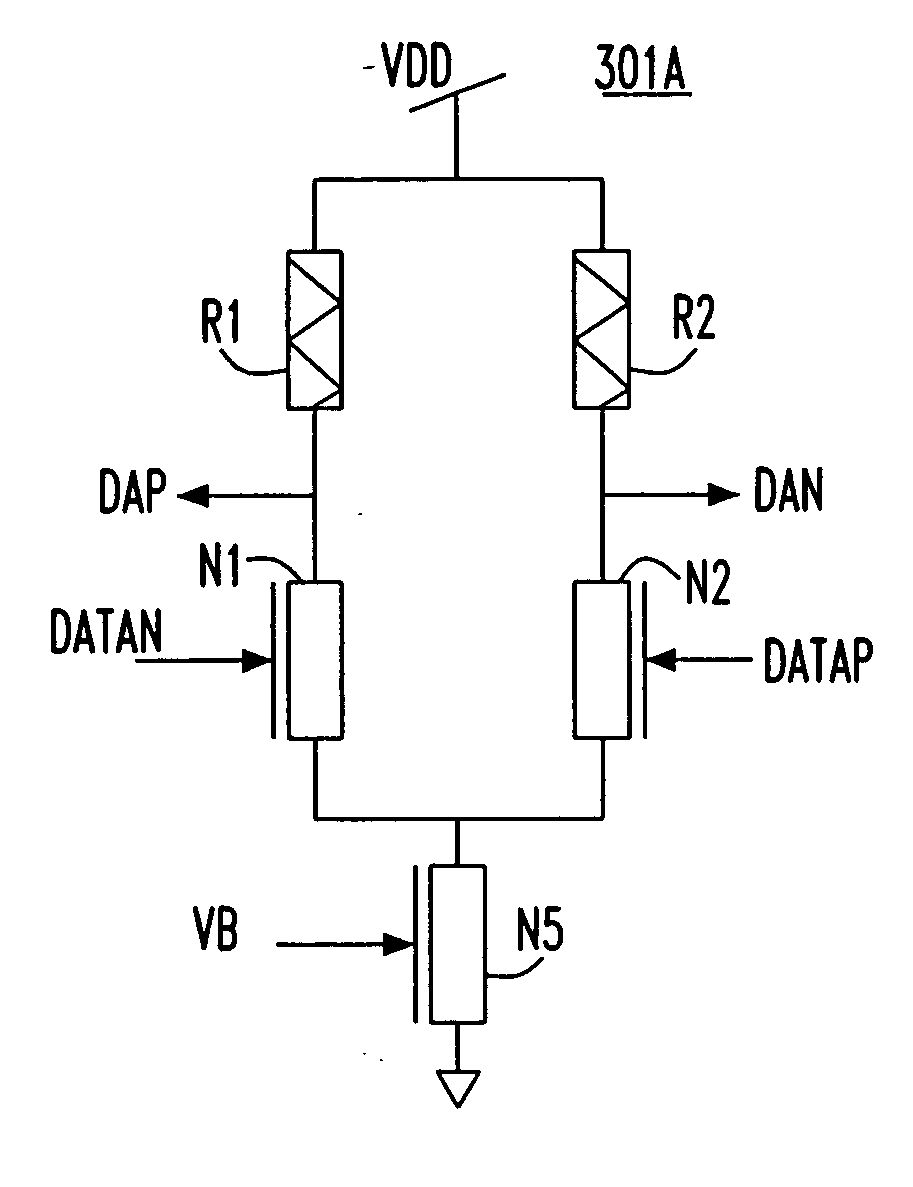
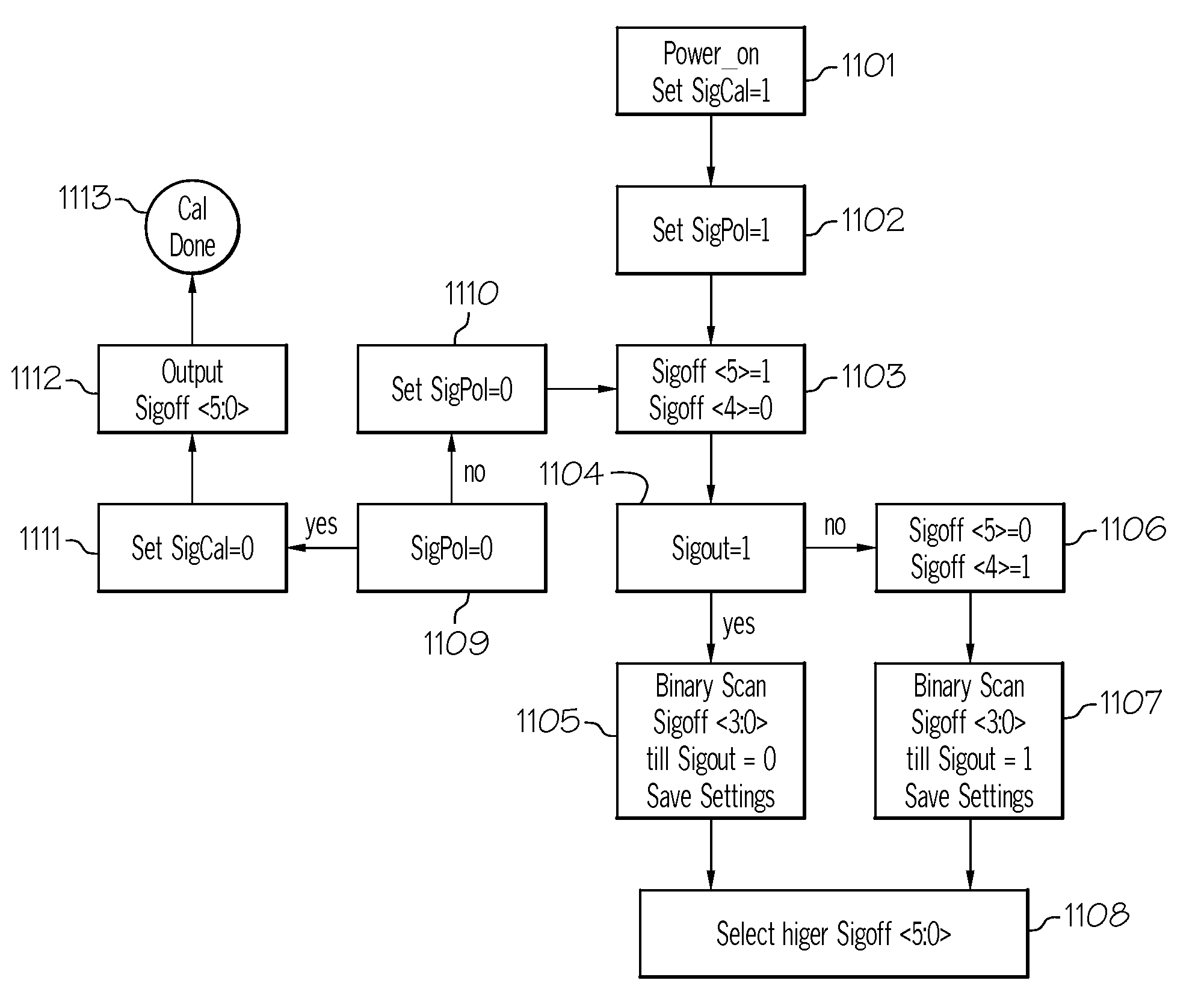
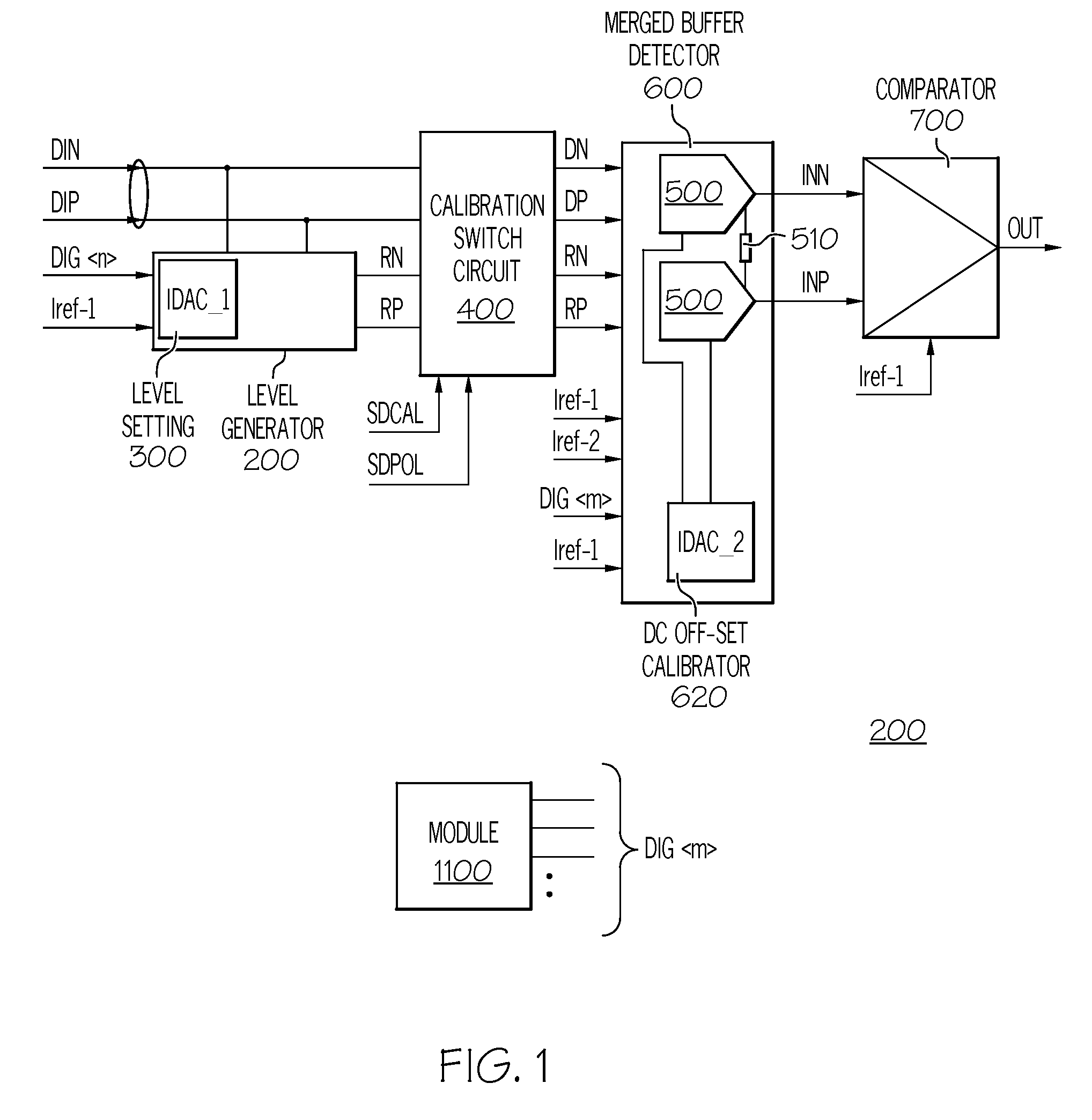
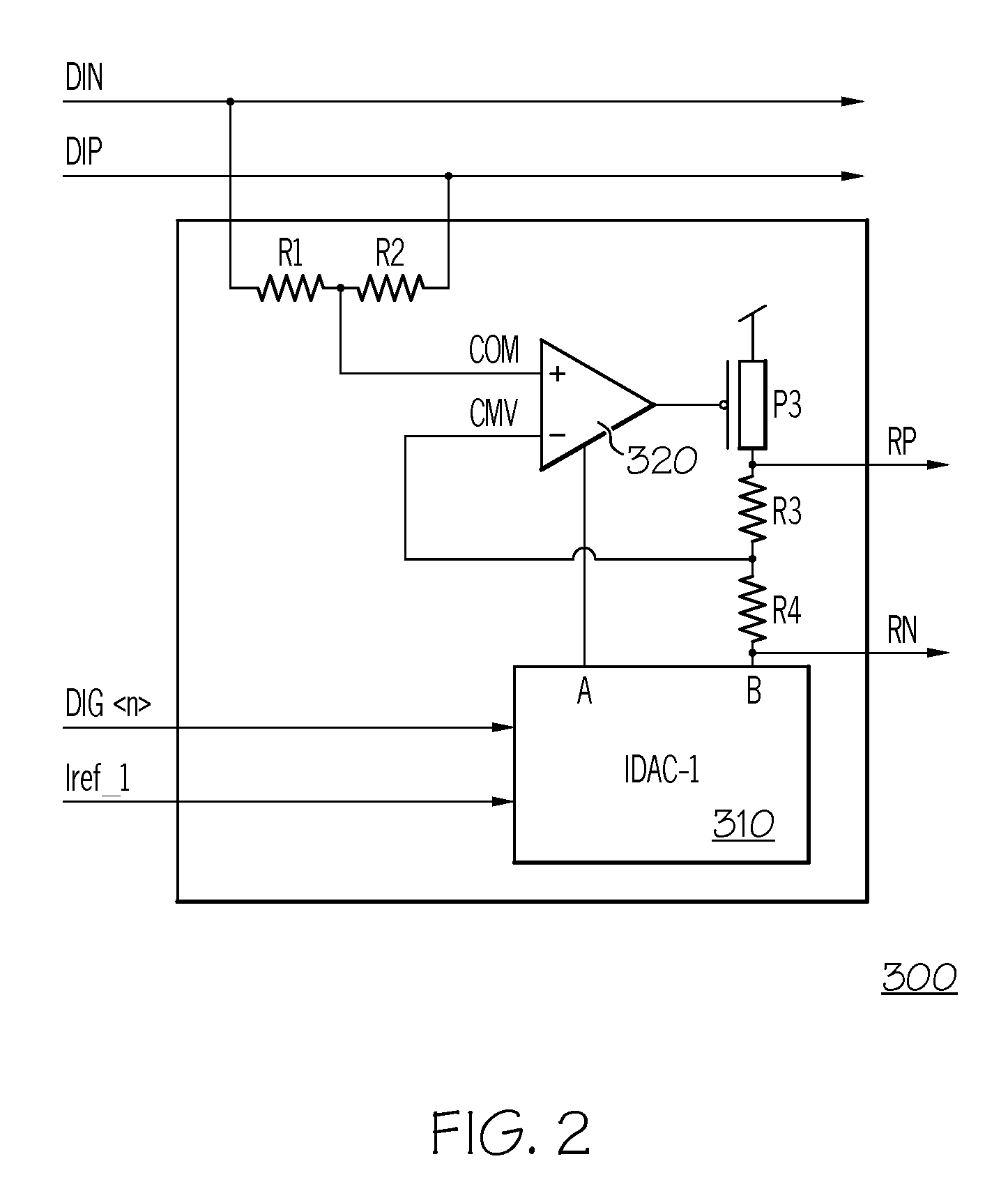
Signal Detector with Calibration Circuit Arrangement
ActiveUS20070271054A1Eliminate inherent differential signal imbalanceEliminate the inherent differential signal imbalanceMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCurrent/voltage measurementDifferential signalingImage resolution
A signal detector and method detect the presence or absence of an incoming differential signal. The method nullifies the DC off-set of the signal detector so that it can detect a signal within a very narrow window. The common mode levels of the signal and reference paths are used for calibration which is done automatically by use of an embedded algorithm residing in a digital block. The calibration range and resolution are predetermined to cope with the technology, modeling, design methodology and human error.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
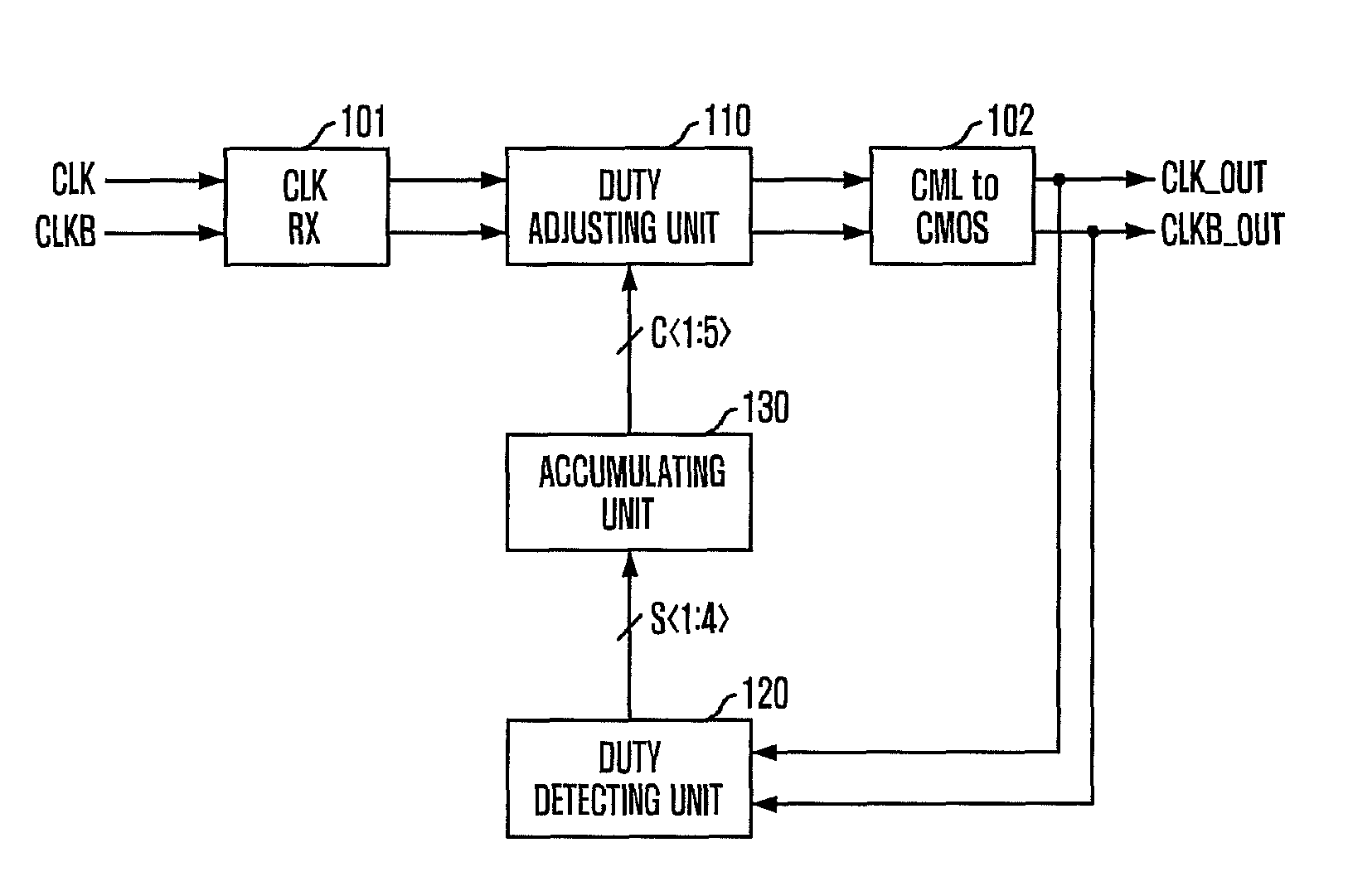
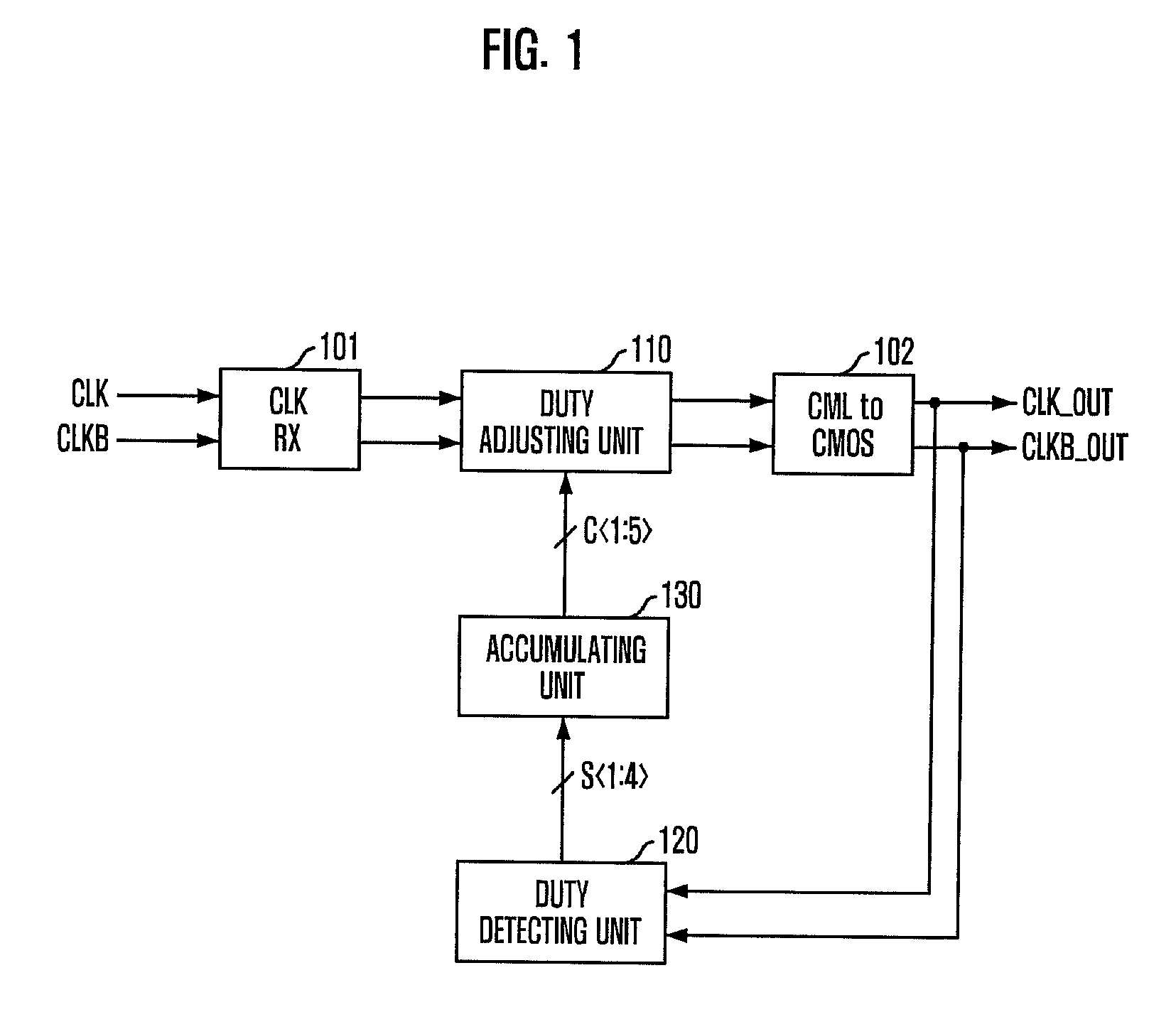
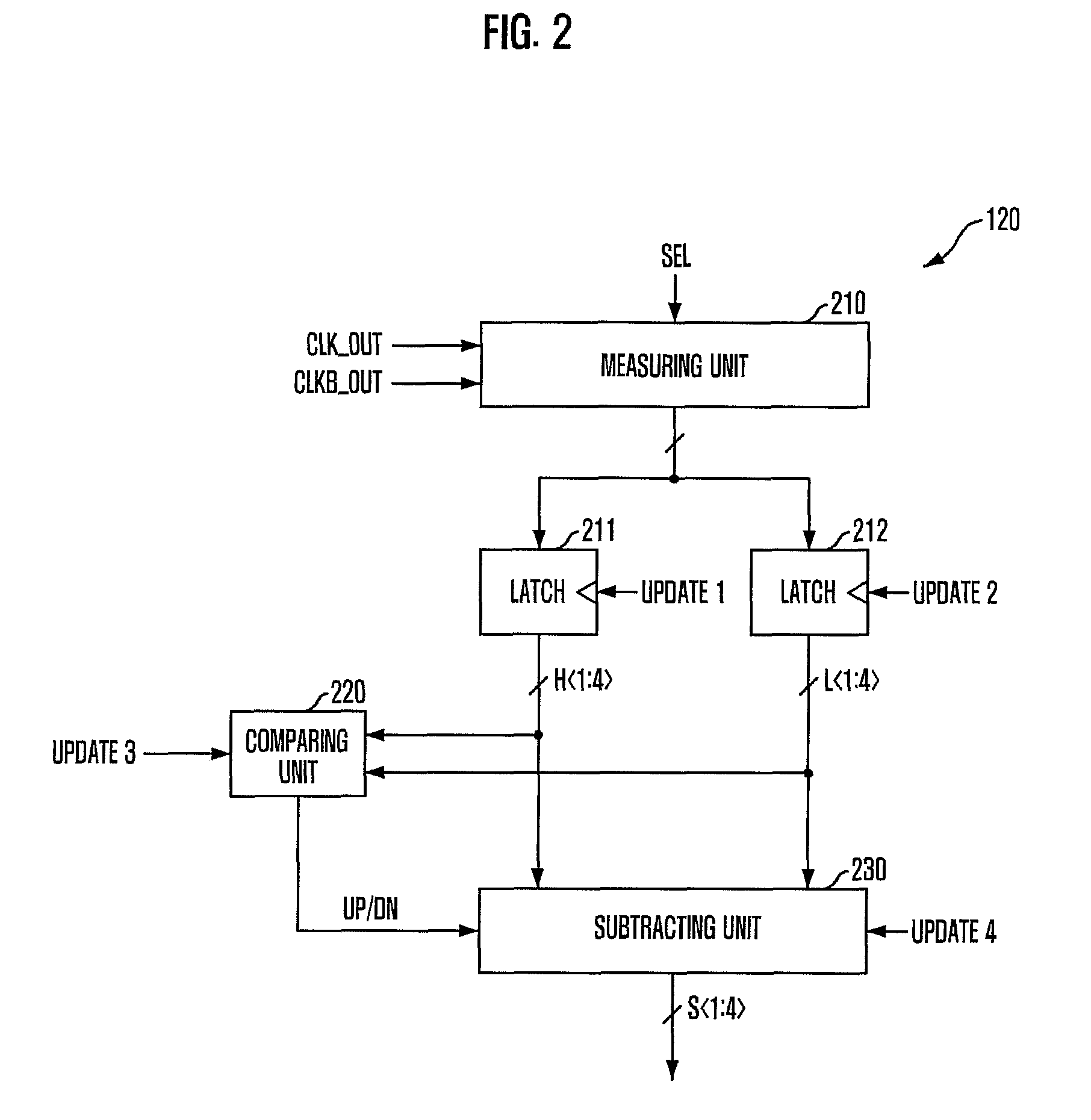
Duty detecting circuit and duty cycle corrector including the same
ActiveUS7847609B2Shorten lock timeAccurate correctionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDelay line applicationsDuty cycle correctorCorrection code
A duty cycle corrector includes a duty adjusting unit configured to adjust a duty cycle of an input clock in response to a duty correction code and generate an output clock, a duty detecting unit configured to measure a difference between a high pulse width and a low pulse width of the output clock and output a difference value, and an accumulating unit configured to accumulate the difference value to generate the duty correction code.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
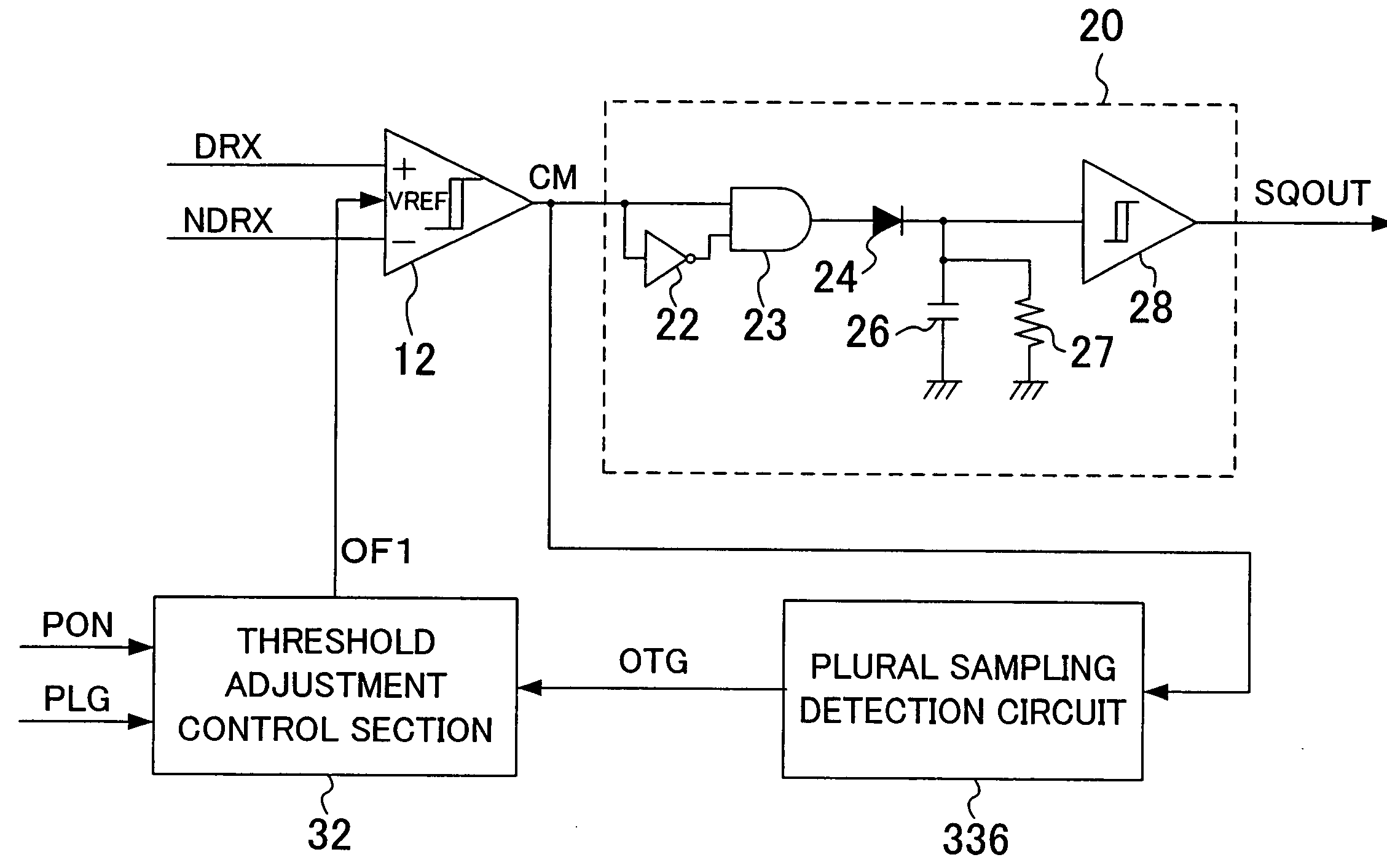
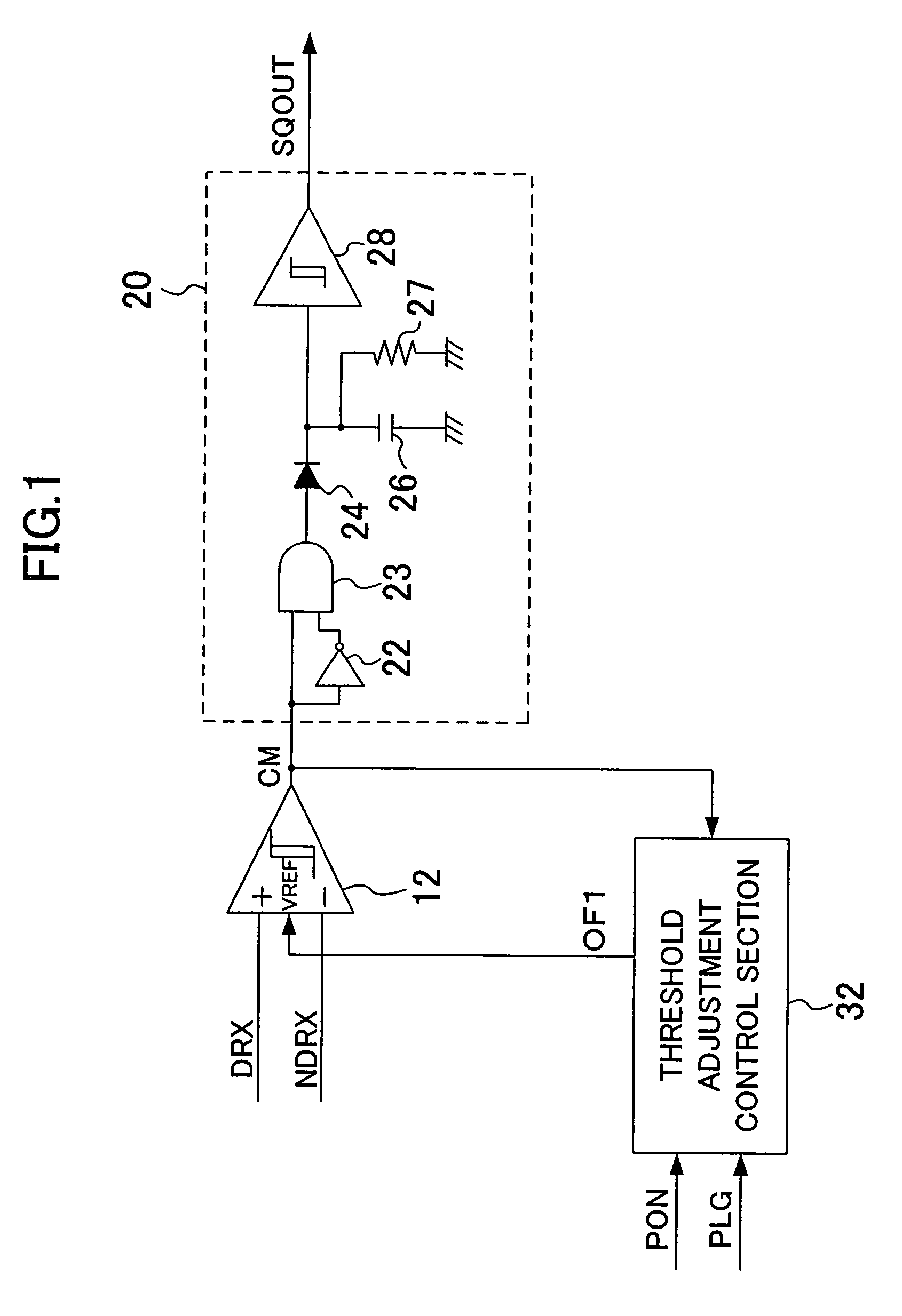
Signal detection circuit capable of automatically adjusting threshold value
InactiveUS7282965B2Suppress mutationMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse train pattern monitoringAuto regulationEngineering
The signal detection circuit of the present invention includes: a comparison section for comparing the absolute value of a voltage of an input differential signal with a threshold voltage corresponding to a first detection level adjustment signal to detect presence / absence of an input signal and outputting a detection signal indicating the detection result; a threshold adjustment control section for generating the first detection level adjustment signal in response to the detection signal and outputting the generated signal; and a detection section for detecting whether or not the level of the detection signal changes repeatedly. During the time of no input of the differential signal, the threshold adjustment control section changes the first detection level adjustment signal so that the threshold voltage monotonically increases or decreases until the detection signal is inverted, to determine the first detection level adjustment signal that makes the threshold voltage appropriate, and outputs the determined signal.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Semiconductor device, and method of diagnosing abnormality of boosting circuit of semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120081167A1High measurement accuracyConvenient and accurateCircuit monitoring/indicationPulse automatic controlPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
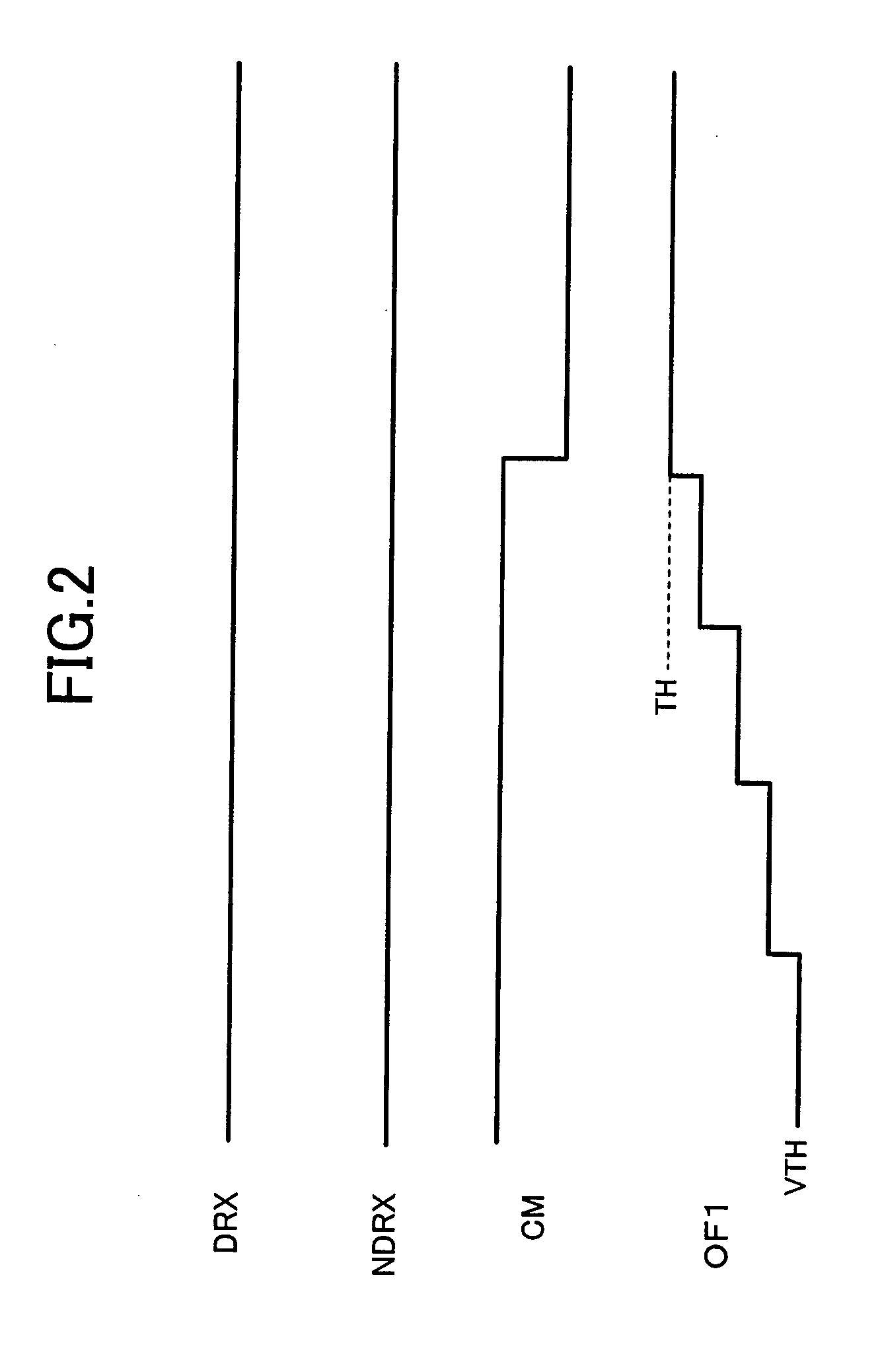
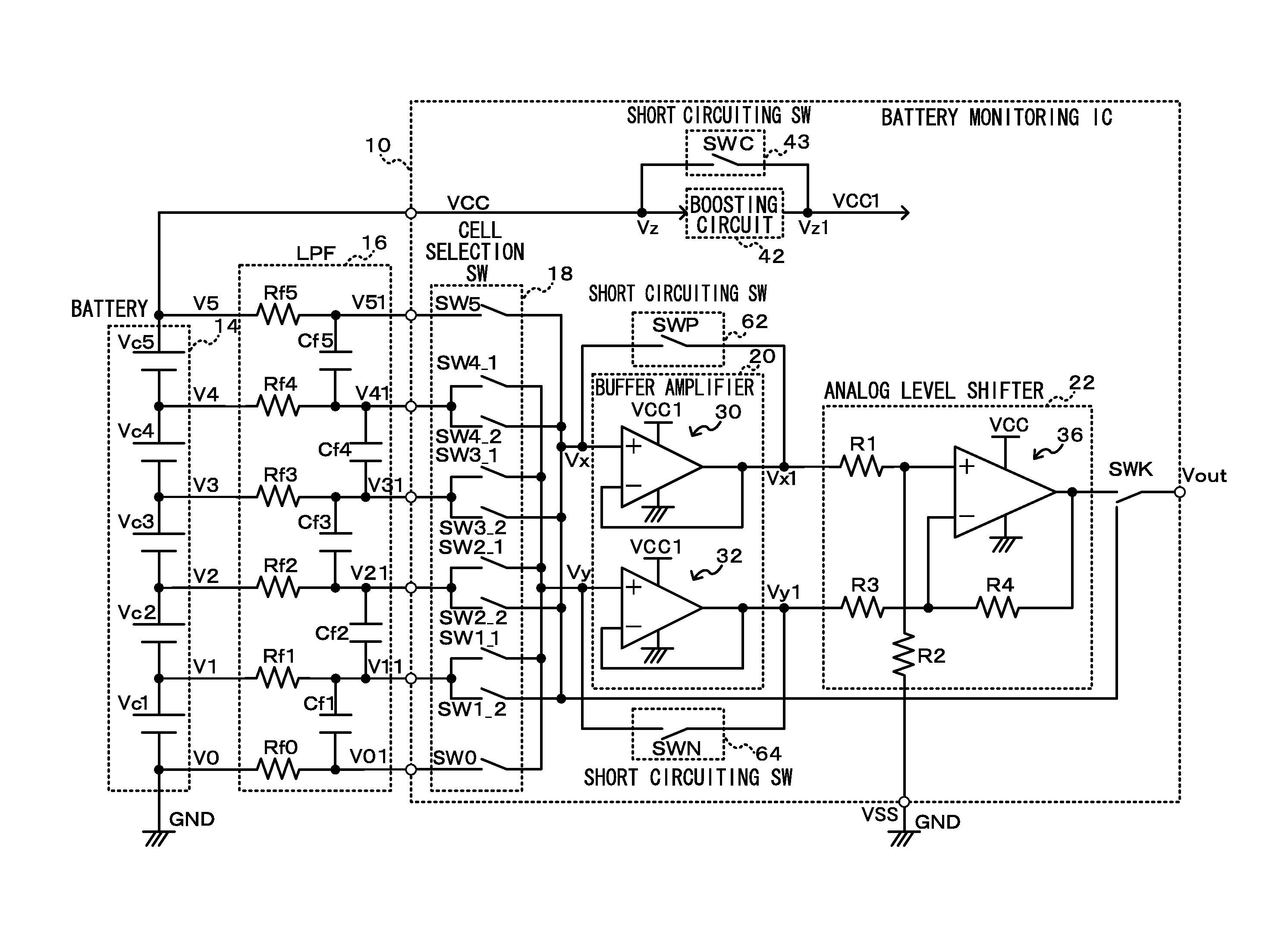
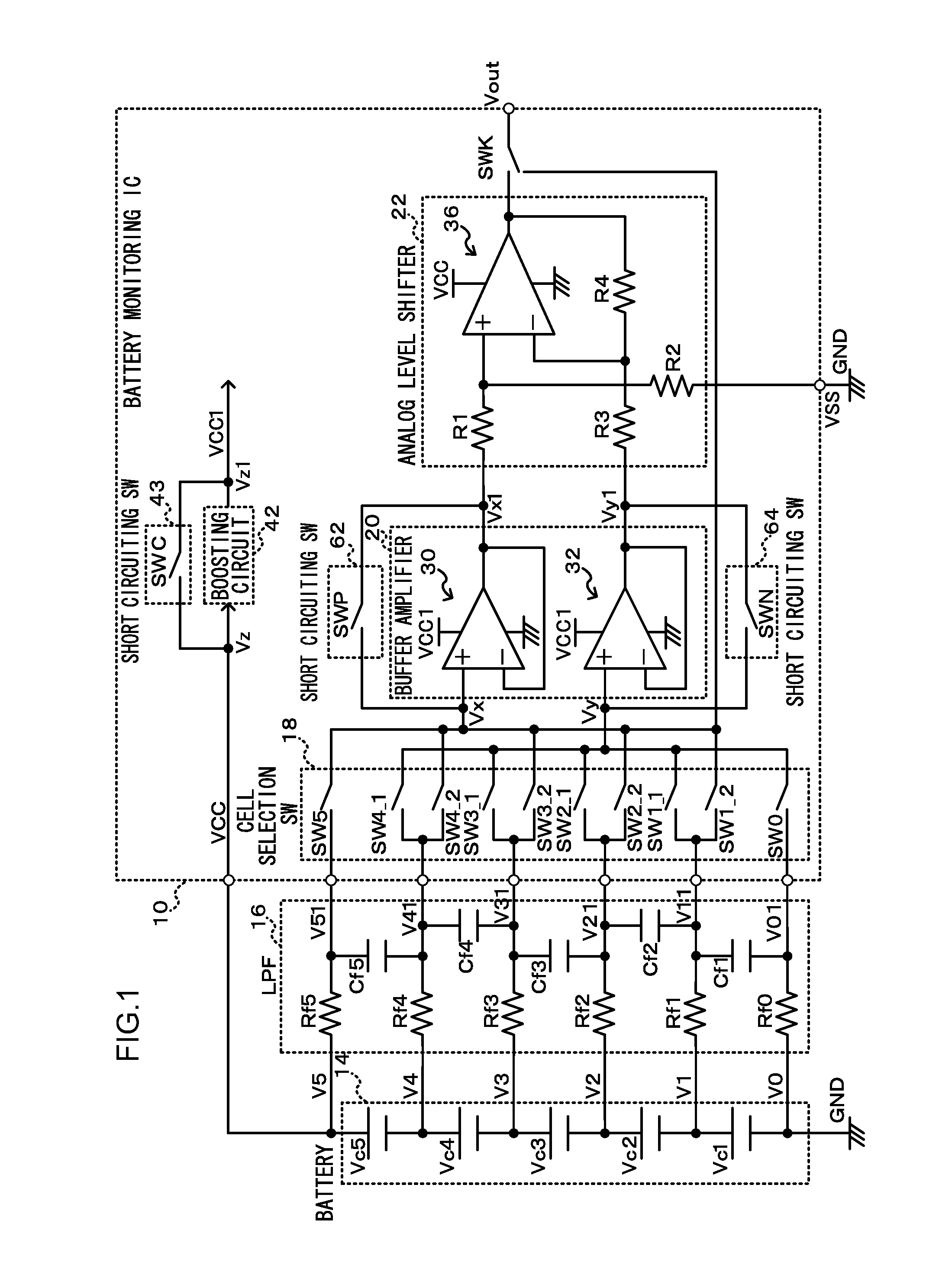
The battery monitoring IC is provided with the short circuiting switch that includes the switching element that shorts the input side and the output side of the boosting circuit that boosts the power supply voltage to the driving voltage, that can drive the MOS transistor within the buffer amplifier in the saturated region, and supplies the driving voltage as the driving voltage of the buffer amplifier. An abnormality of the boosting circuit can be diagnosed by comparing the output voltage, that is measured when the short circuiting switch is turned off and the driving voltage boosted by the boosting circuit is supplied to the buffer amplifier, and the output voltage, that is measured when the short circuiting switch is turned on and the power supply voltage is, without going through the boosting circuit, supplied as is to the buffer amplifier.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
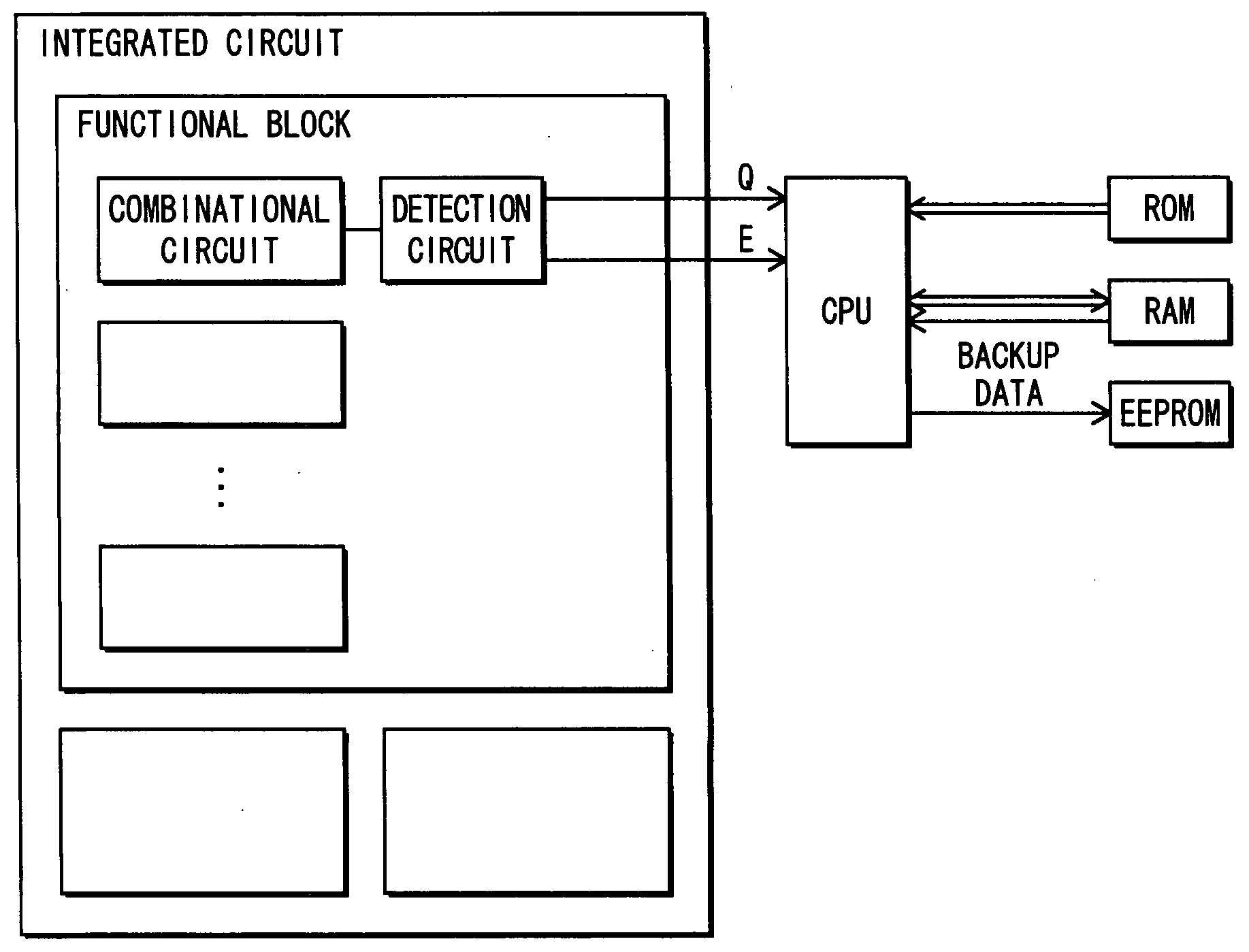
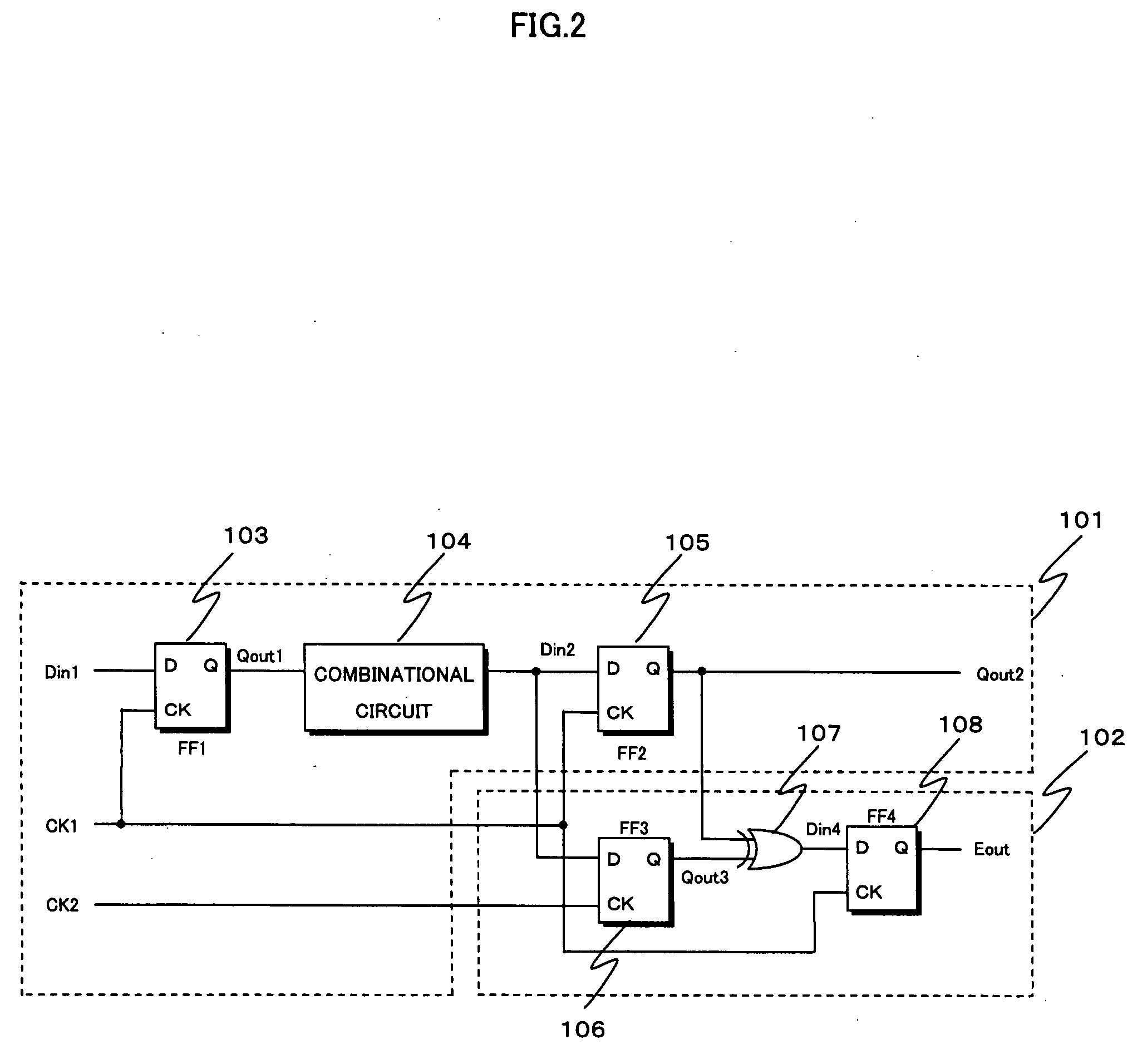
Semiconductor integrated circuit including a malfunction detection circuit, and a design method for the same
InactiveUS20080024173A1Efficient designAvoid failurePulse train pattern monitoringFail-safe circuitsCountermeasureDesign methods
A malfunction detection circuit realized by a simple circuit structure is incorporated into a semiconductor integrated circuit without increasing the scale thereof, in order to prevent loss etc. of data due to a malfunction of the semiconductor integrated circuit. Malfunctions can be prevented without relying on measuring temperature or power supply voltage which are analog values, thereby improving the reliability of the semiconductor integrated circuit. A detection-target flip-flop in a function block is synchronized to a clock, and another flip-flop is synchronized to a clock whose phase has been delayed behind or advanced ahead of the former clock. A logic operation is performed using output from both flip-flops to determine whether a latch operation has been performed at an appropriate clock pulse edge in a clock pulse train. The malfunction countermeasure is performed if the latch operation is determined to have been performed at an inappropriate clock pulse edge.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
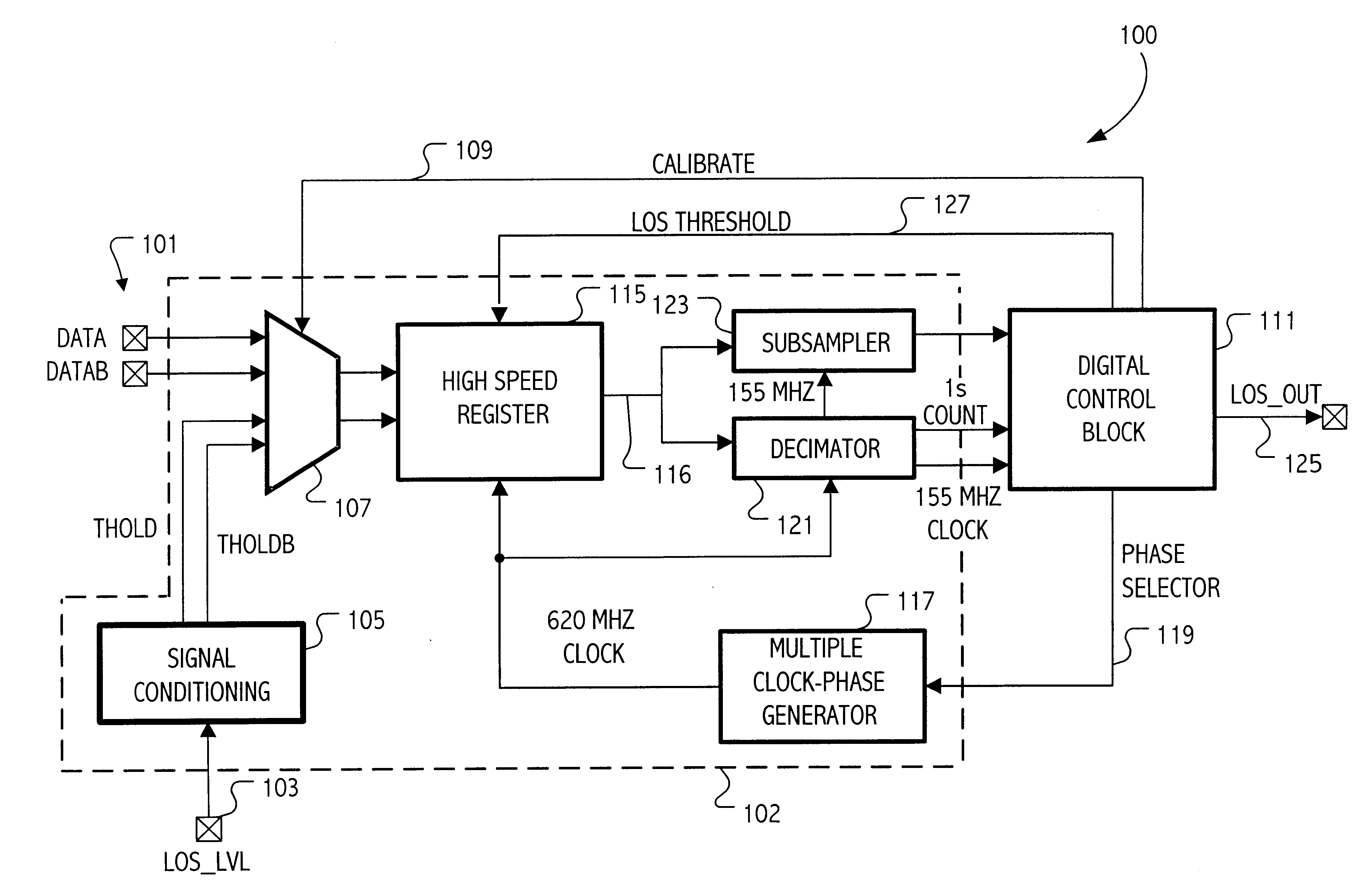
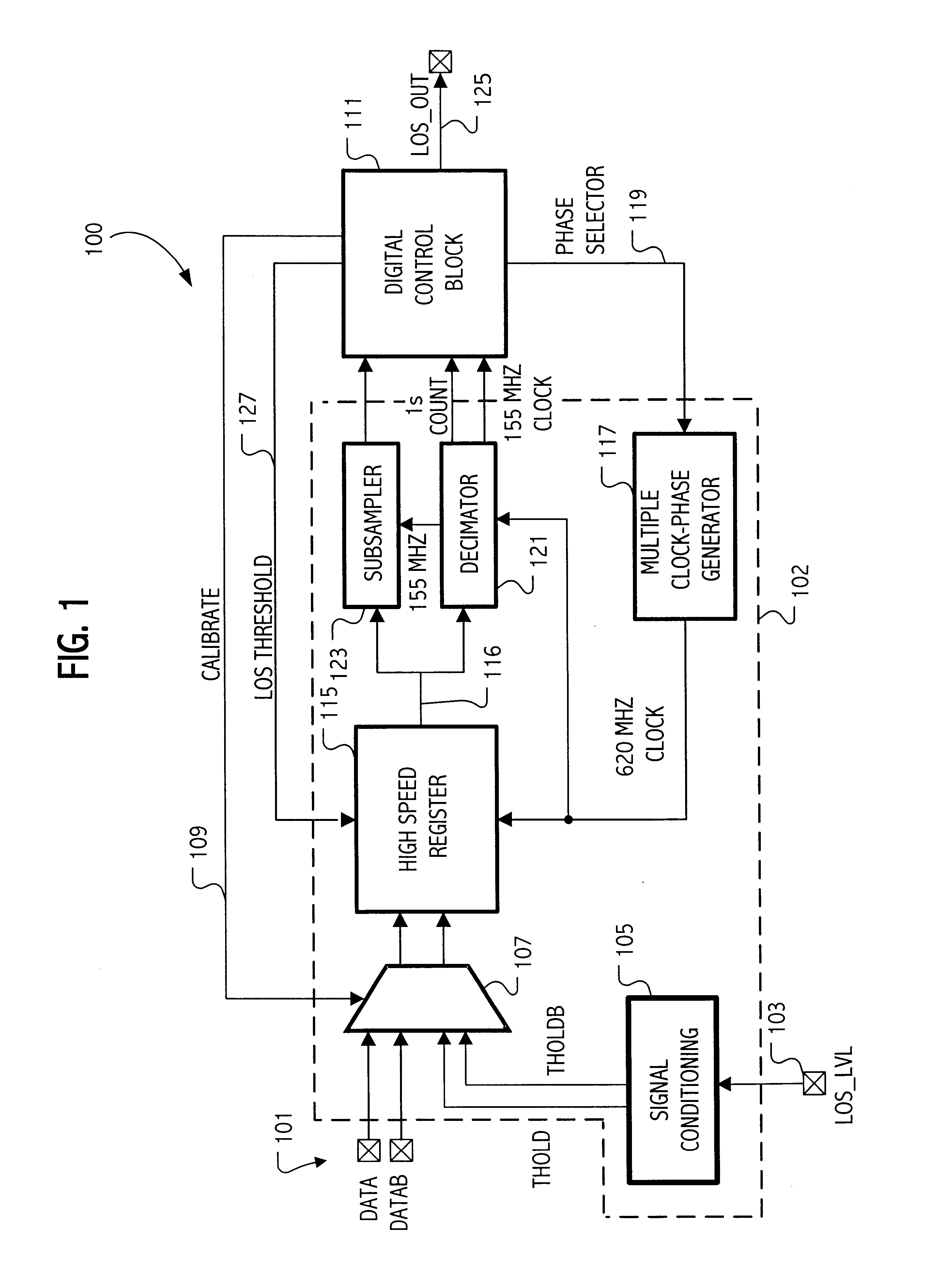
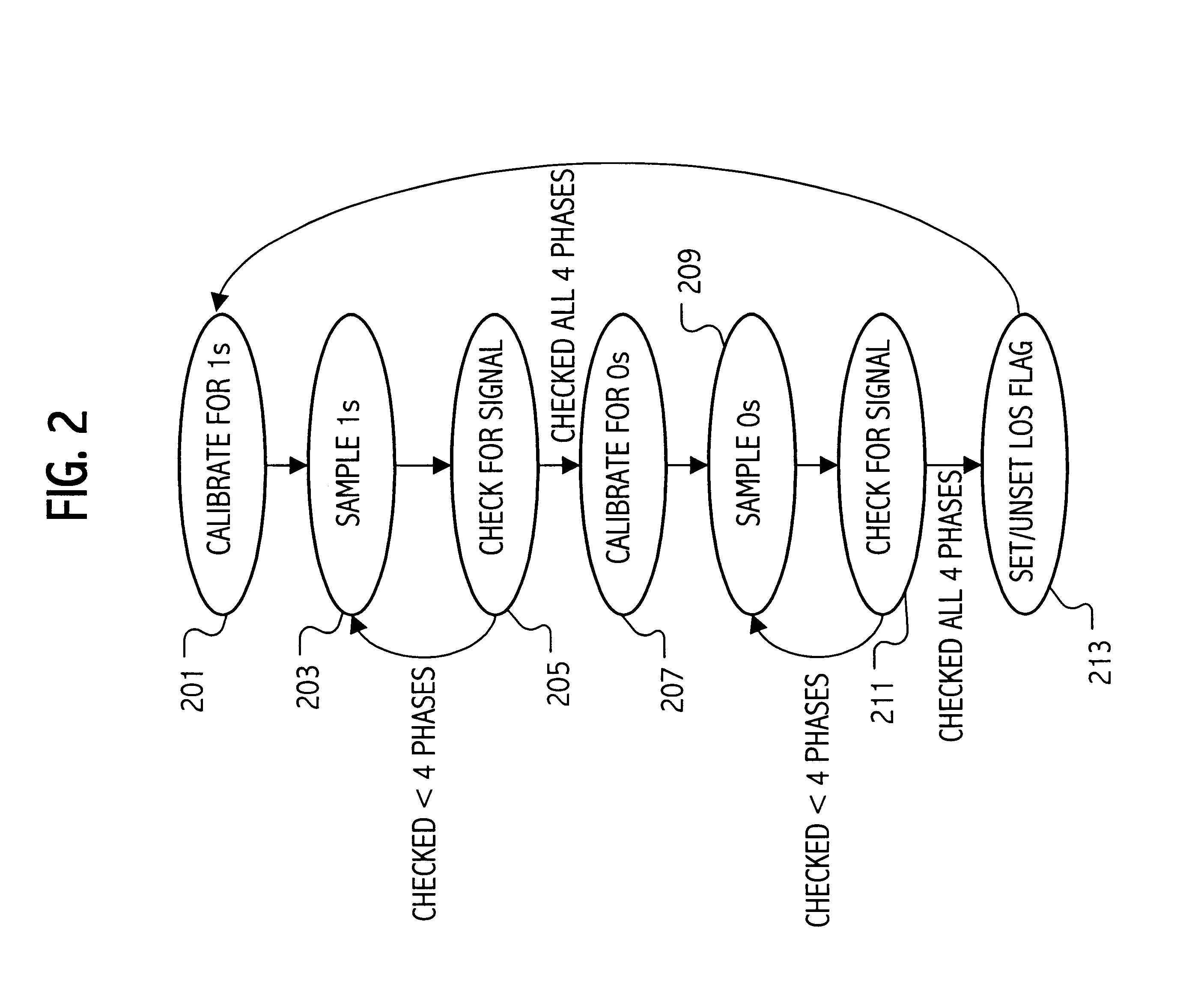
Calibration of a loss of signal detection system
InactiveUS6799131B1Avoid controlSimple designMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectric signal transmission systemsData streamDigital control
An integrated circuit has a loss of signal (LOS) system for detecting a loss of signal condition for an input data stream according to a LOS threshold. The LOS threshold specifies a minimum signal magnitude indicating the loss of signal condition. The integrated circuit includes a sampling circuit to sample a LOS signal, which receives a sampling threshold specifying a signal magnitude for a sampled signal above which the sampling circuit samples the sampled signal as a first digital value and below which the sampling circuit samples the sampled signal as a second digital value. A digital control circuit coupled to an output of the sampling circuit generates a calibrated digital representation of the sampling threshold according to a plurality of samples of the LOS signal. The calibrated sampling threshold is then used during loss of signal evaluation.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com