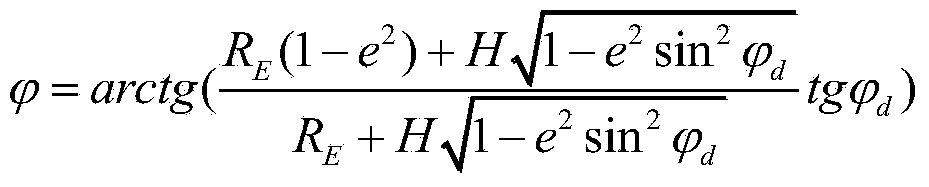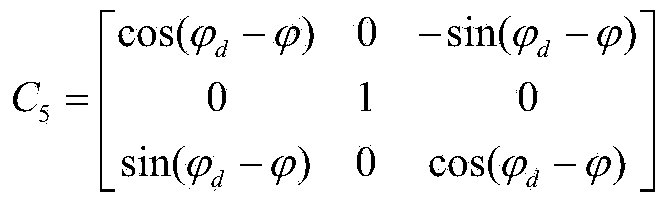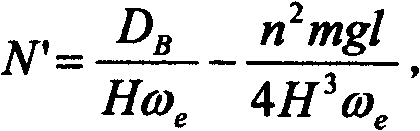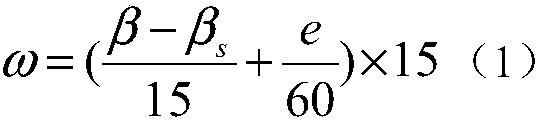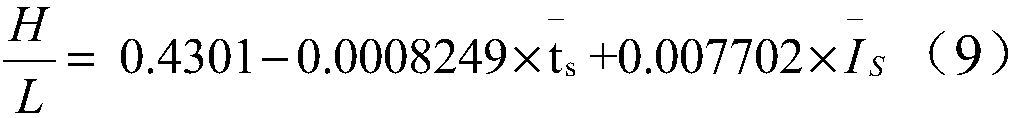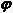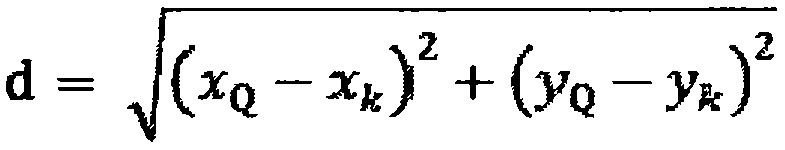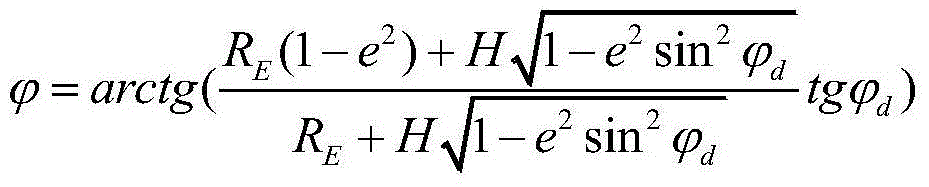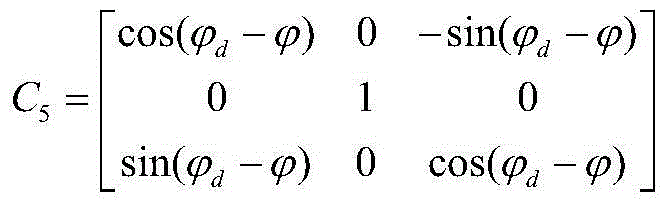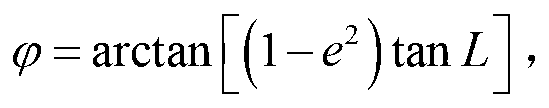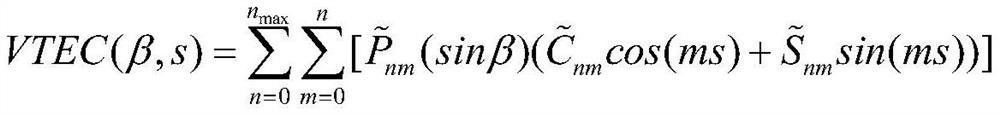Patents
Literature
39 results about "Geographical latitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-performance location management platform
InactiveUS6868410B2Quick translationEliminate mass-storage accessesData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsMass storageLongitude
An apparatus and method for rapid translation of geographic latitude and longitude into any of a number of application-specific location designations or location classifications, including street address, nearest intersection, PSAP (Public Safety Answering Point) zone, telephone rate zone, franchise zone, or other geographic, administrative, governmental or commercial division of territory. The speed of translation meets call-setup requirements for call-processing applications such as PSAP determination, and meets caller response expectations for caller queries such as the location of the nearest commercial establishment of a given type. To complete its translation process in a timely manner, a memory-stored spatial database is used to eliminate mass-storage accesses during operation, a spatial indexing scheme such as an R-tree over the spatial database is used to locate a caller within a specific rectangular area, and an optimized set of point-in-polygon algorithms is used to narrow the caller's location to a specific zone identified in the database. Additional validation processing is supplied to verify intersections or street addresses returned for a given latitude and longitude. Automatic conversion of latitude-longitude into coordinates in different map projection systems is provided.The memory-stored database is built in a compact and optimized form from a relational spatial database as required. The R-tree spatial indexing of the memory-stored database allows for substantially unlimited scalability of database size without degradation of response time. Maximum performance for database retrievals is assured by isolating the retrieval process from all updating and maintenance processes. Hot update of the in-memory database is provided without degradation of response time.
Owner:PRECISELY SOFTWARE INC +1
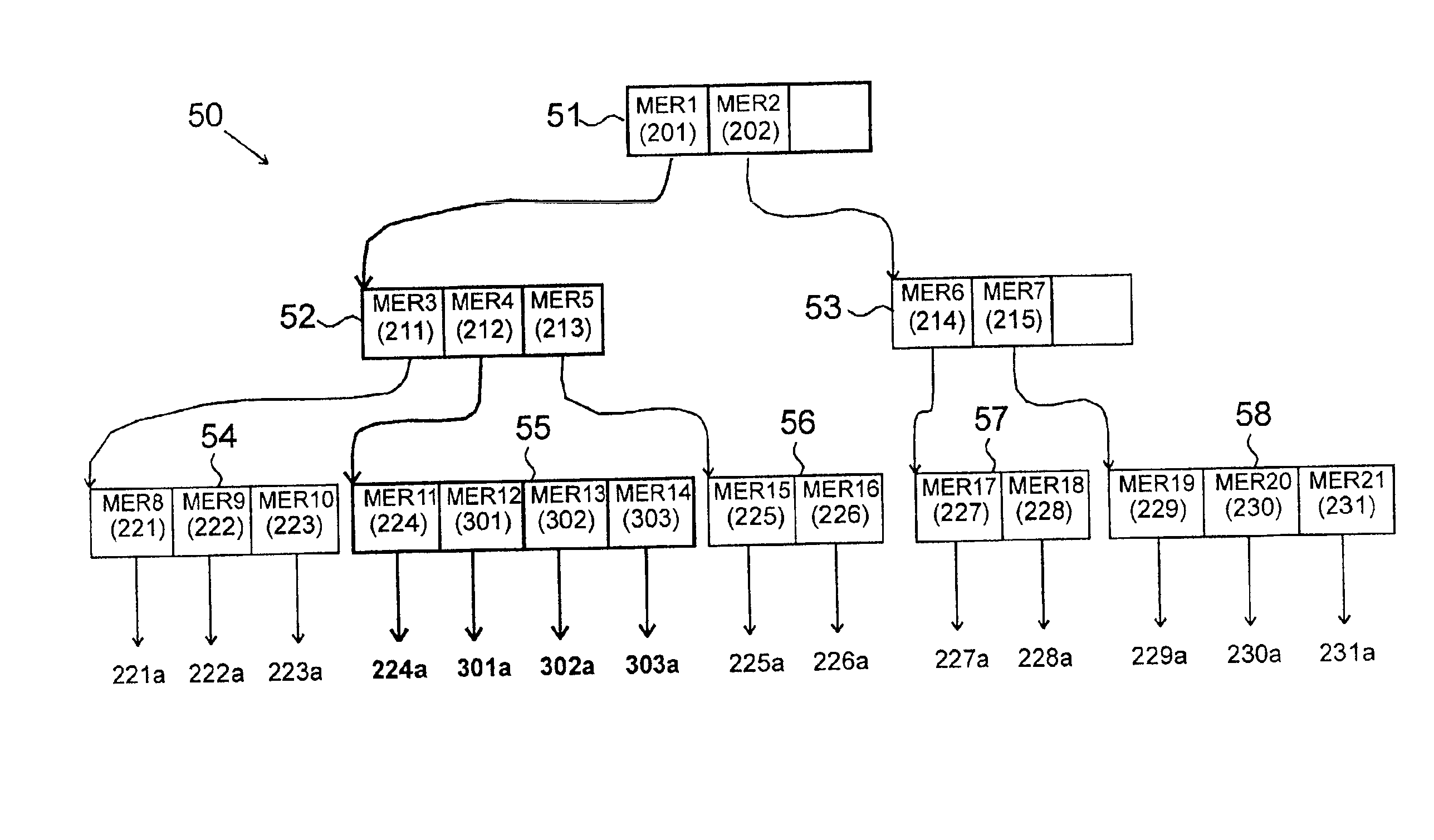
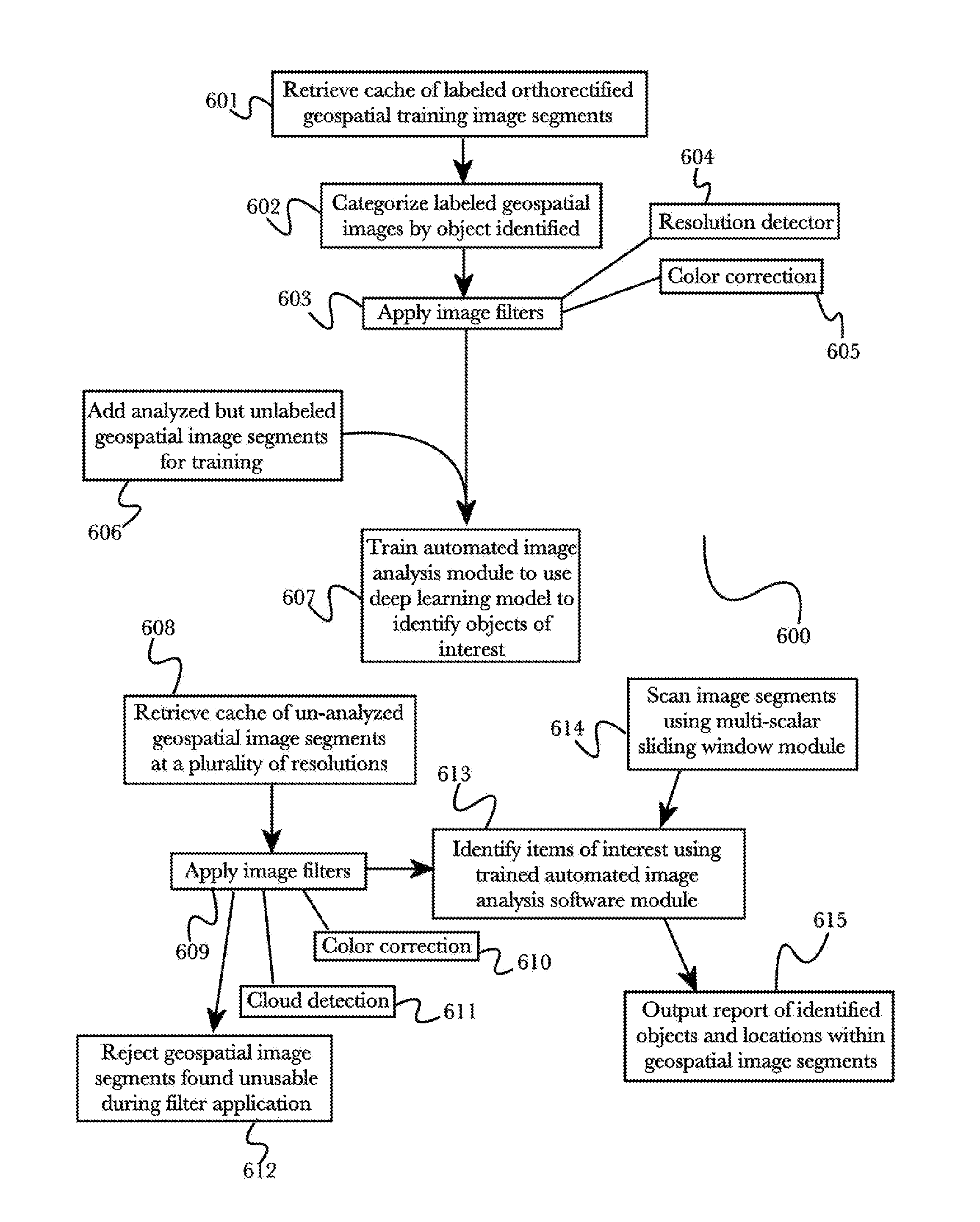
Broad area geospatial object detection using autogenerated deep learning models
A system for automated geospatial image analysis comprising a deep learning model module and a convolutional neural network serving as an automated image analysis software module. The deep learning module receives a plurality of orthorectified geospatial images, pre-labeled to demarcate objects of interest, and optimized for the purpose of training the neural network of the image analysis software module. The module presents marked geospatial images and a second set of unmarked, optimized, training geospatial images to the convolutional neural network. This process may be repeated so that an image analysis software module can detect multiple object types or categories. The image analysis software module receives a plurality of orthorectified geospatial images from one or more geospatial image caches. Using multi-scale sliding window submodule, image analysis modules scan geospatial images, detect objects present and locate them on the geographical latitude-longitude system. The system reports the results in the requestor's preferred format.
Owner:MAXAR INTELLIGENCE INC
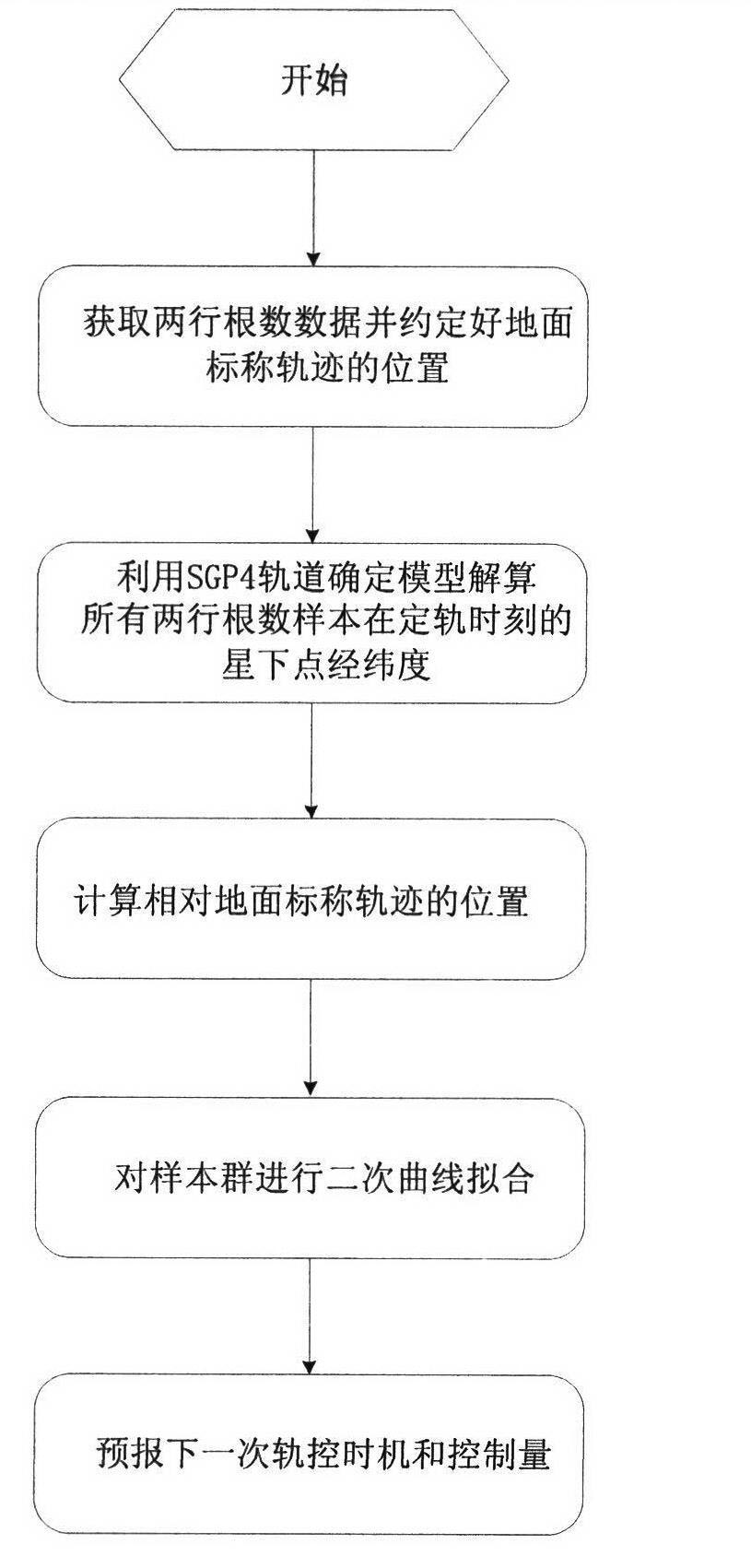
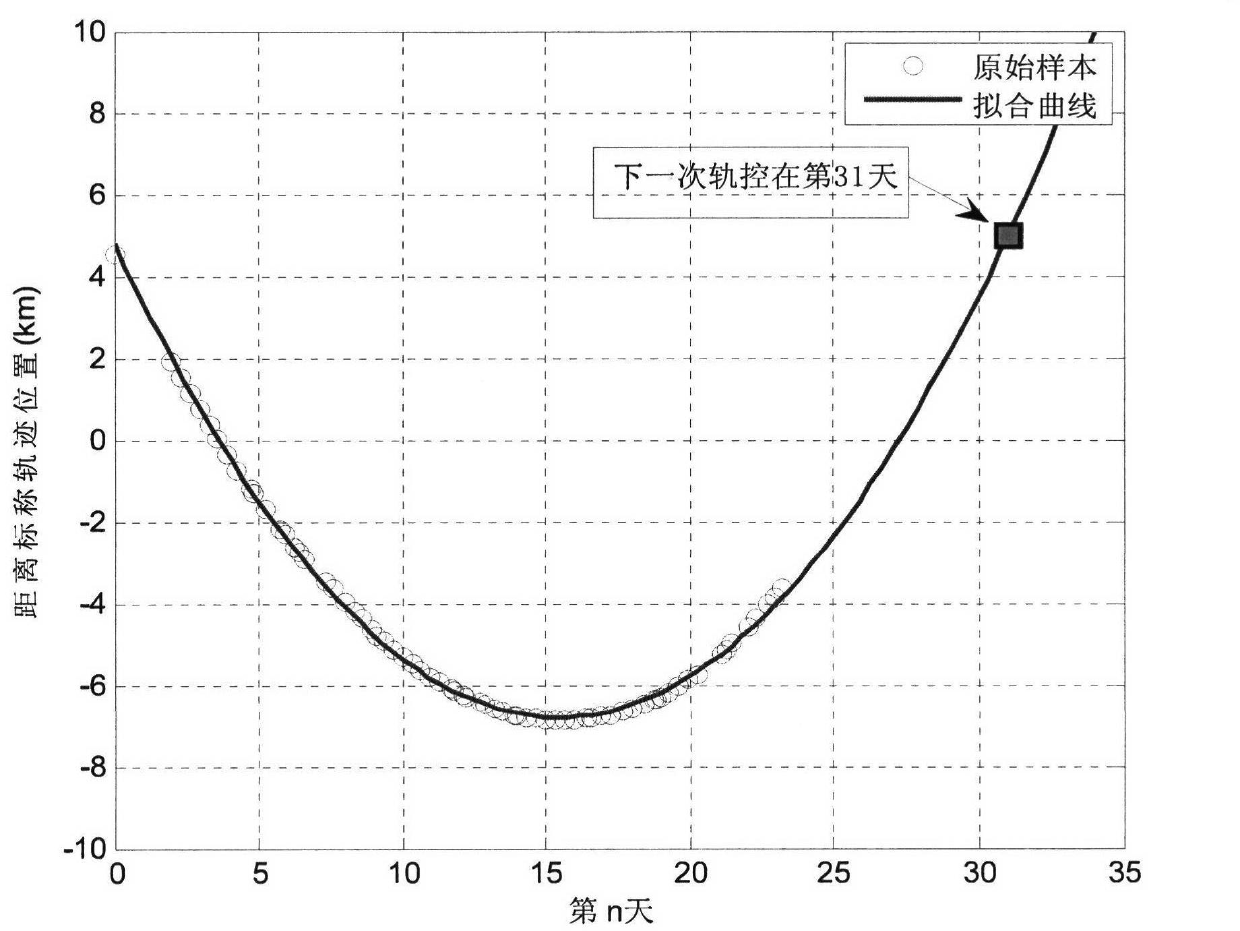
Satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals
ActiveCN102591343AGood serviceFacilitate maintenance of control forecastsPosition/course control in two dimensionsUltrasound attenuationGeographical latitude
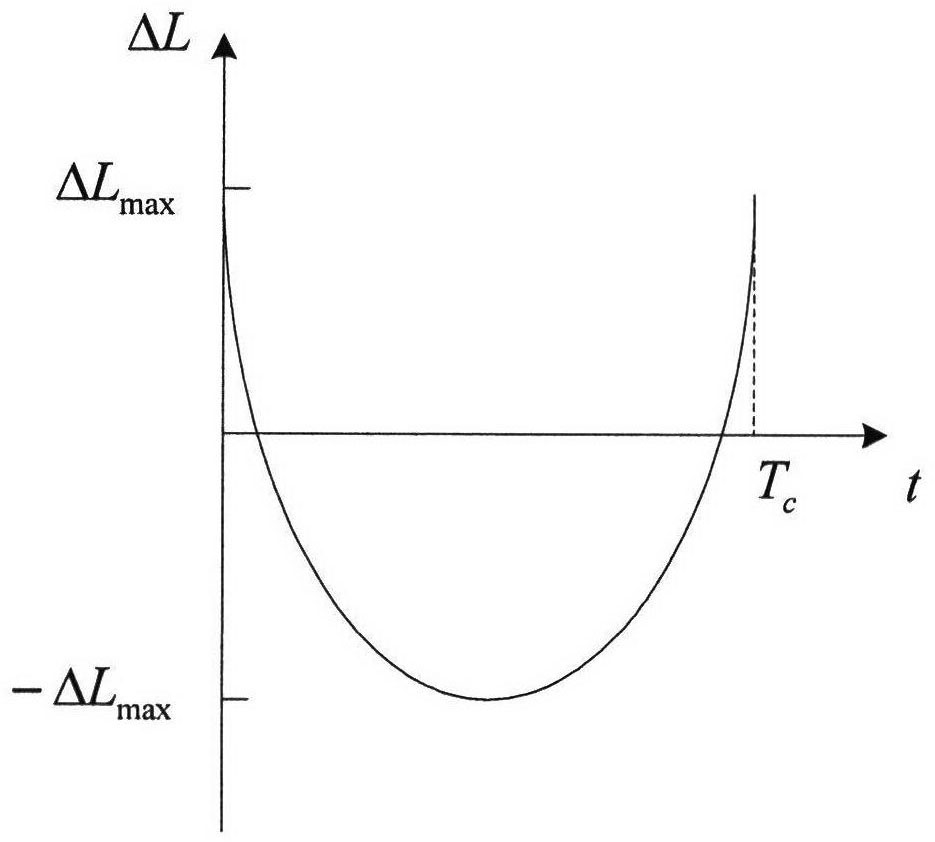
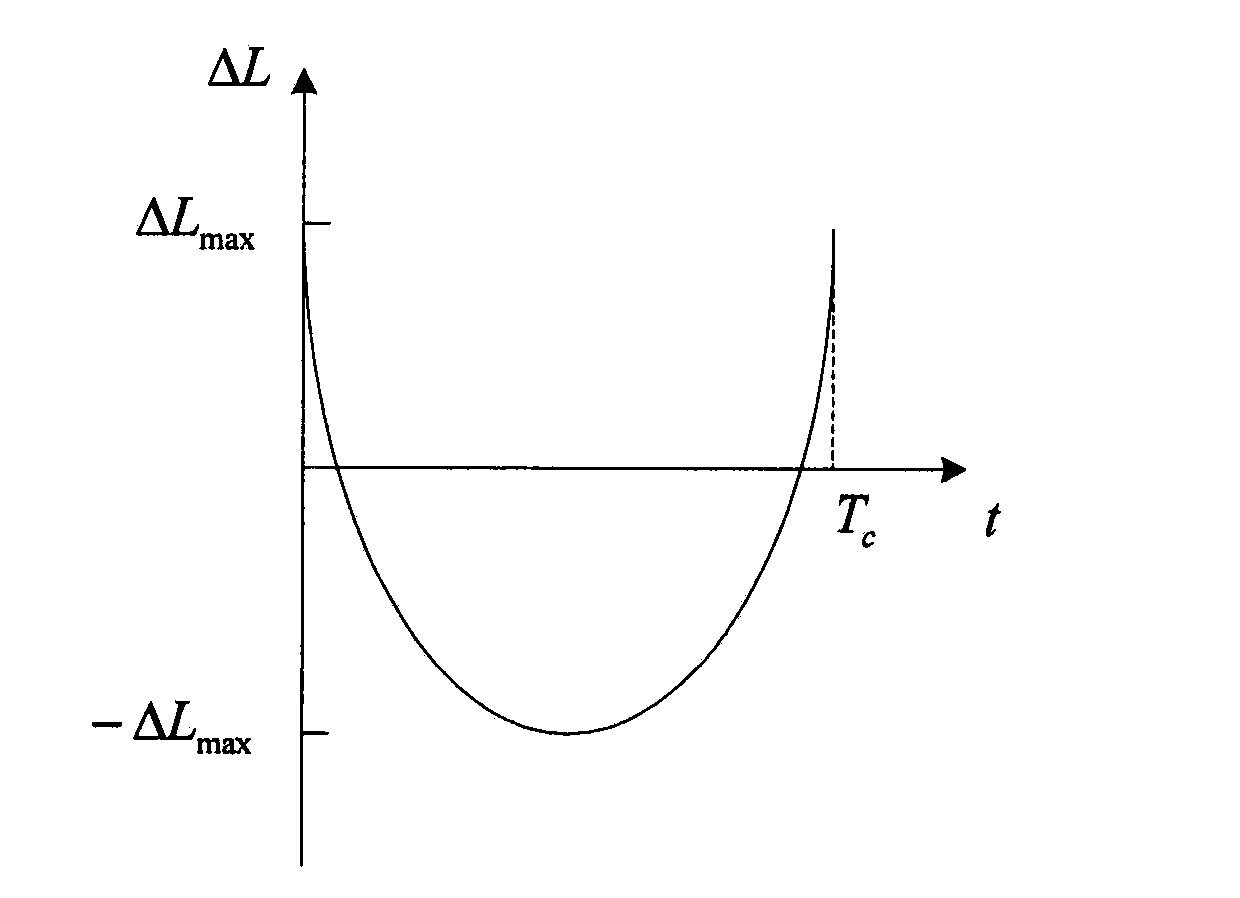
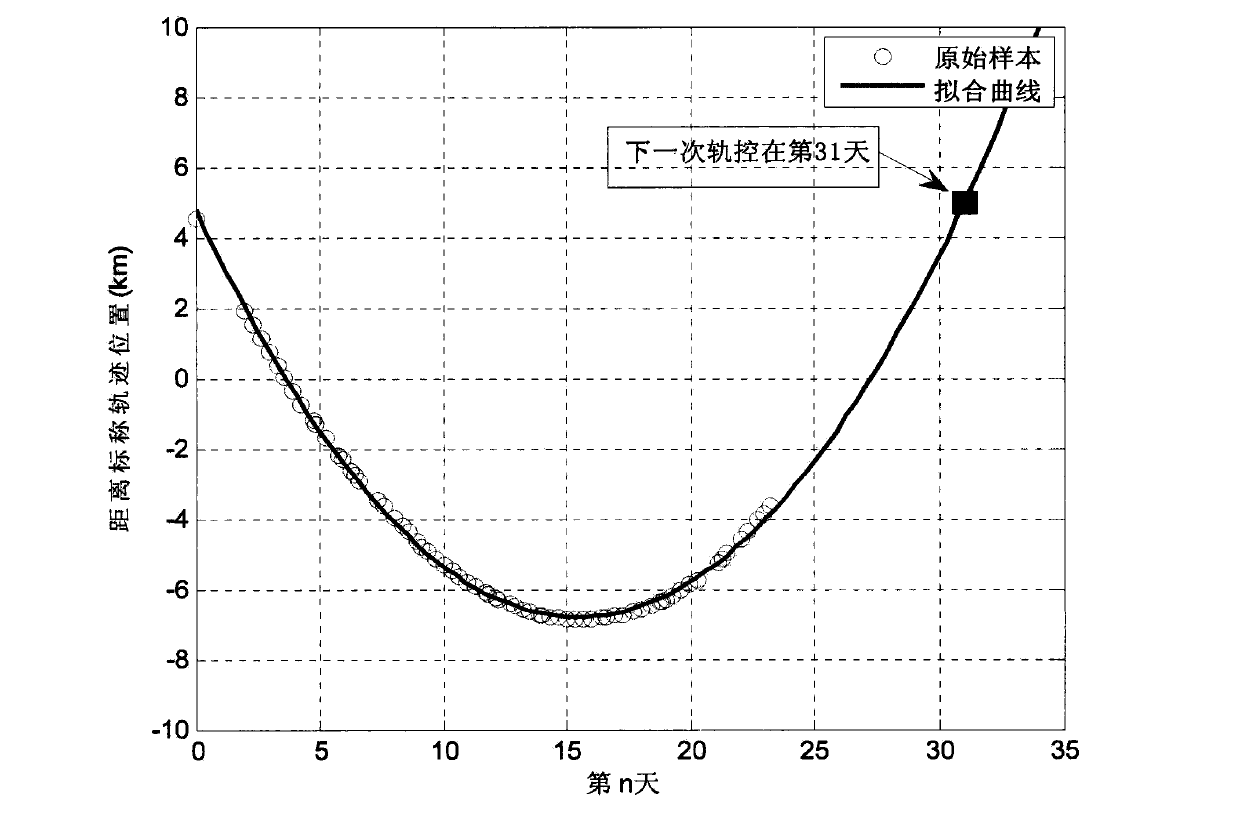
The invention relates to a satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals, which comprises the following steps of: calculating two lines of radical data disclosed by a satellite by utilizing a SGP4 orbit determination model, calculating and obtaining a geographical latitude and a geographical longitude of a sub-satellite point of the satellite and comparing with an agreed ground nominal track. Through taking the duration of a first sample opposite to an orbit epoch moment as an independent variable and taking the ground track distance difference as a variable, all samples are subjected to quadratic curve fitting by using an average method; the difference delta at between an actual value of a satellite orbit semi-major axis and a nominal value by a latest sample moment as well as the average attenuation rate of the satellite orbit semi-major axis within the time interval of the sample are calculated and obtained through a fitting polynomial coefficient; and finally, the next orbit control time Tc as well as the control quantity delta af required to be used are predicted and obtained by utilizing a fitted secondary curve and an allowable drift range [-delta Lmax and delta Lmax] to ensure that the position of an actual ground track within the satellite next drift period opposite to a ground nominal track is within the allowrable drift range.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
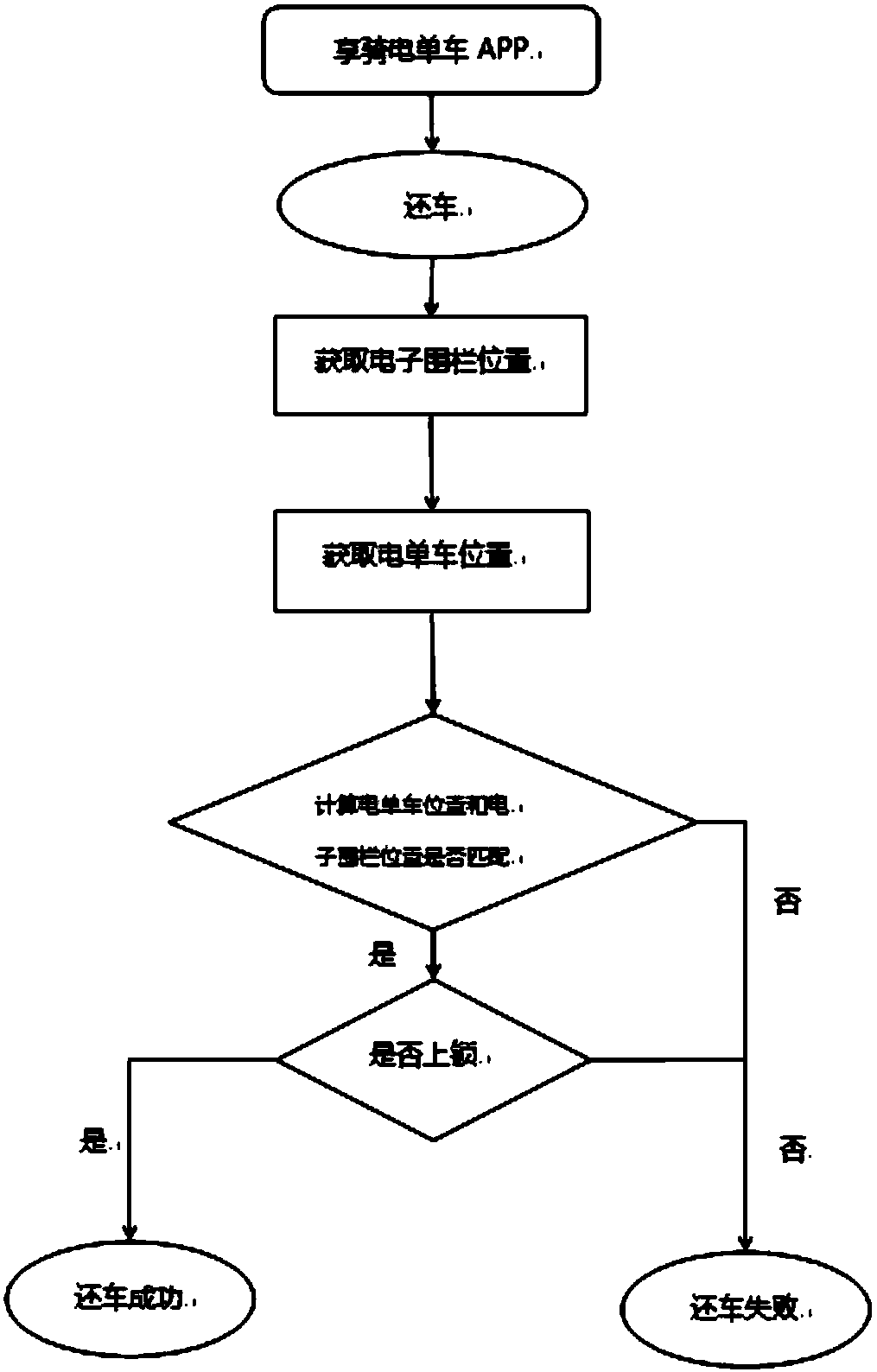
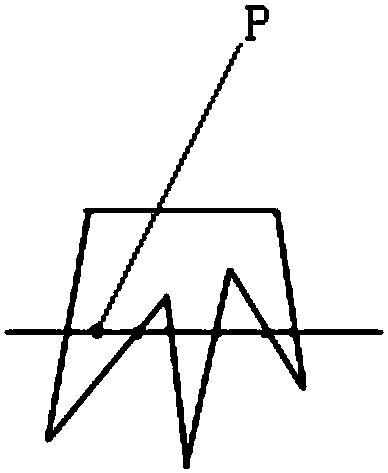
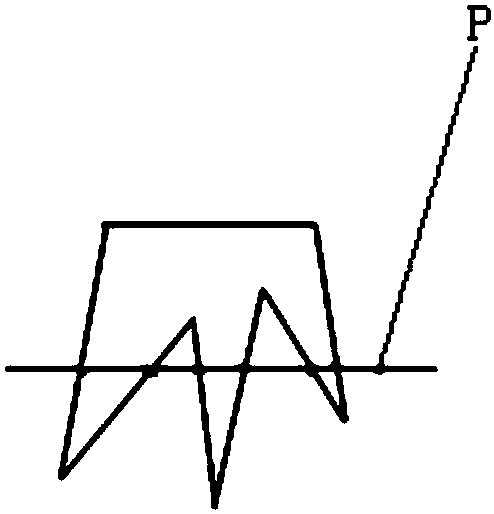
Electronic fence
InactiveCN107610455AImprove access efficiencyReduce mistakesRoad vehicles traffic controlForecastingElectricityGeographical latitude
The invention discloses an electronic fence, which comprises a dot line judgment method. According to the dot line judgment method, firstly, each edge of a polygon is taken as a directed line segmentwhich is connected in an end-to-end mode. If the direction of a certain point relative to each edge of the polygon is the same, the certain point is located in the polygon. The core step of the electronic fence is to figure out the values of two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) closest to a point (x, y), and is applied to a convex polygon. According to the electronic fence provided by the invention, the optimized algorithm of the electronic fence is achieved, so that the efficiency in searching motorcycles which drive in and out of the e electronic fence is improved. The software structure and thedatabase structure of the electronic fence are designed to realize the electronic fence. According to the design of the electronic fence, the polygon is directly drawn on a map, which has a great error with an actual geographical longitude and an actual geographical latitude. During the drawing of the electronic fence, the longitudes and the latitudes of a plurality of corners are determined as much as possible. After that, adjacent corners are connected. Meanwhile, the map is ensured at a maximum multiple, and the error can be guaranteed to be the minimum.
Owner:上海享骑电动车服务有限公司
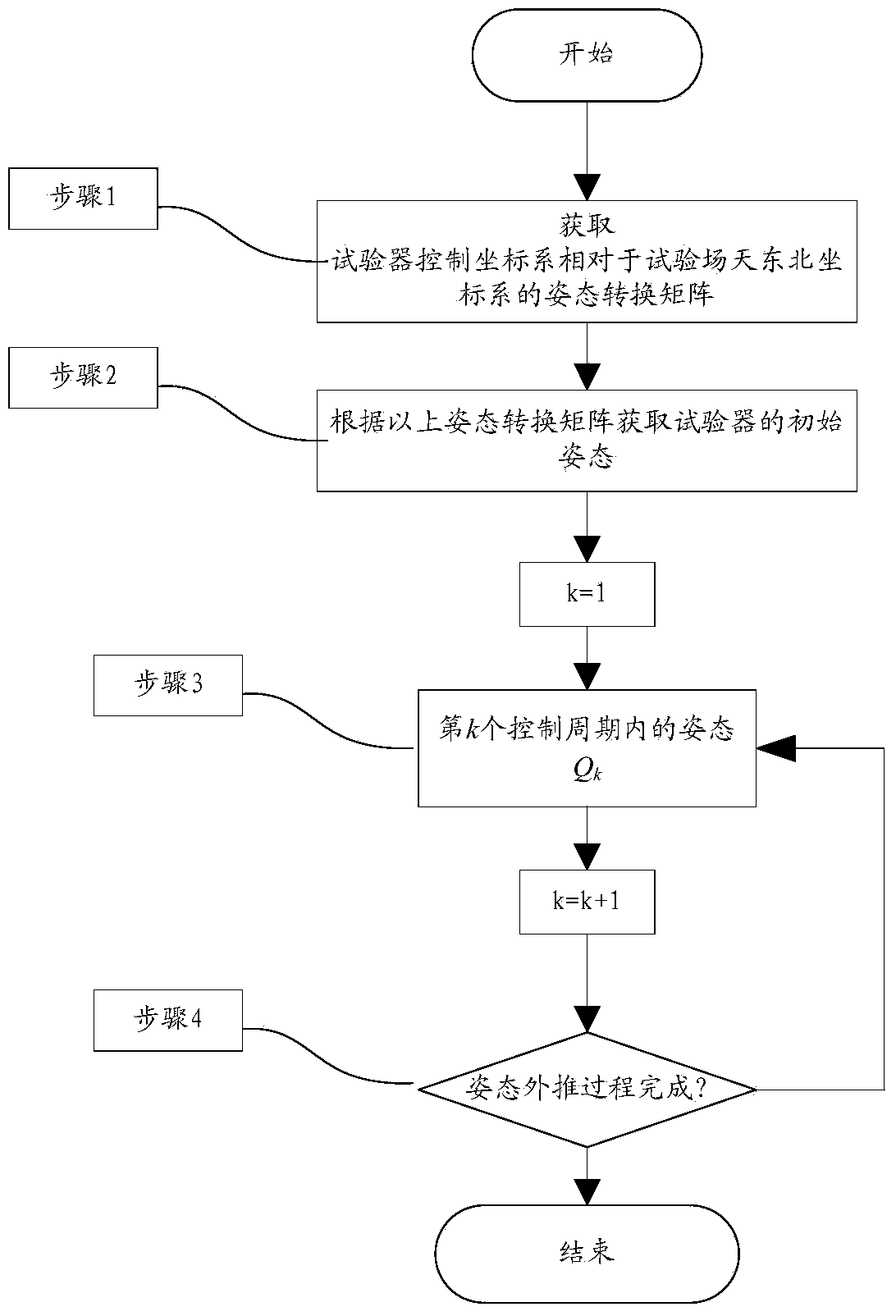
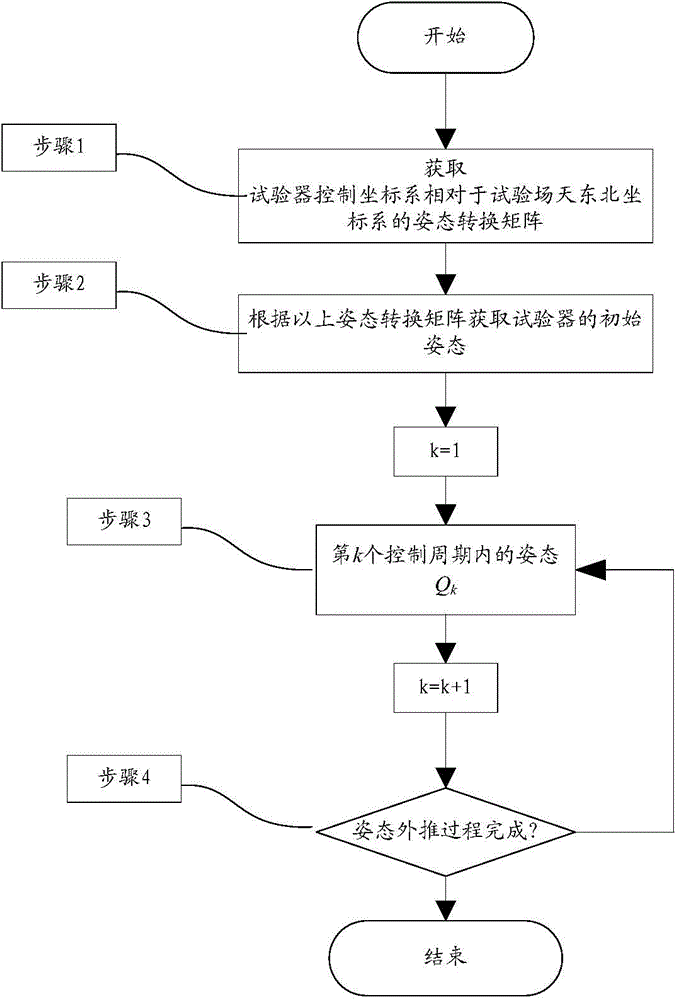
Initial attitude acquisition method for ground test for soft lunar landing by using SINS (serial inertial navigation system)
ActiveCN103759729AHigh precisionThere are many posture conversion linksNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSkyGeographical latitude
The invention discloses an initial attitude acquisition method for a ground test for soft lunar landing by using a SINS (serial inertial navigation system), and belongs to the field of lunar exploration. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly, arranging a fixed azimuth mirror near a test field, and by adopting the azimuth mirror for buffering, obtaining an attitude transformation matrix of a tester control coordinate system relative to a sky northeast coordinate system of the test field; then, through a geographical latitude of an observation point of the test field, obtaining a transformation matrix of the sky northeast coordinate system of the test field relative to a geocentric coordinate system, so that a transformation matrix C6 of the tester control coordinate system relative to the geocentric coordinate system is obtained, and then an attitude Q0 quaternion at an initial time T0 is obtained finally; starting from the initial time T0, carrying out attitude extrapolation by using gyro measurement data; and obtaining an attitude Qk during a k(th) control period, carrying out real-time output on the Qk until the tester attitude extrapolation process is completed and a landing test begins, wherein the Qk at the moment is taken as an initial attitude of a tester. The method disclosed by the invention is applicable to the ground test for lunar landing.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
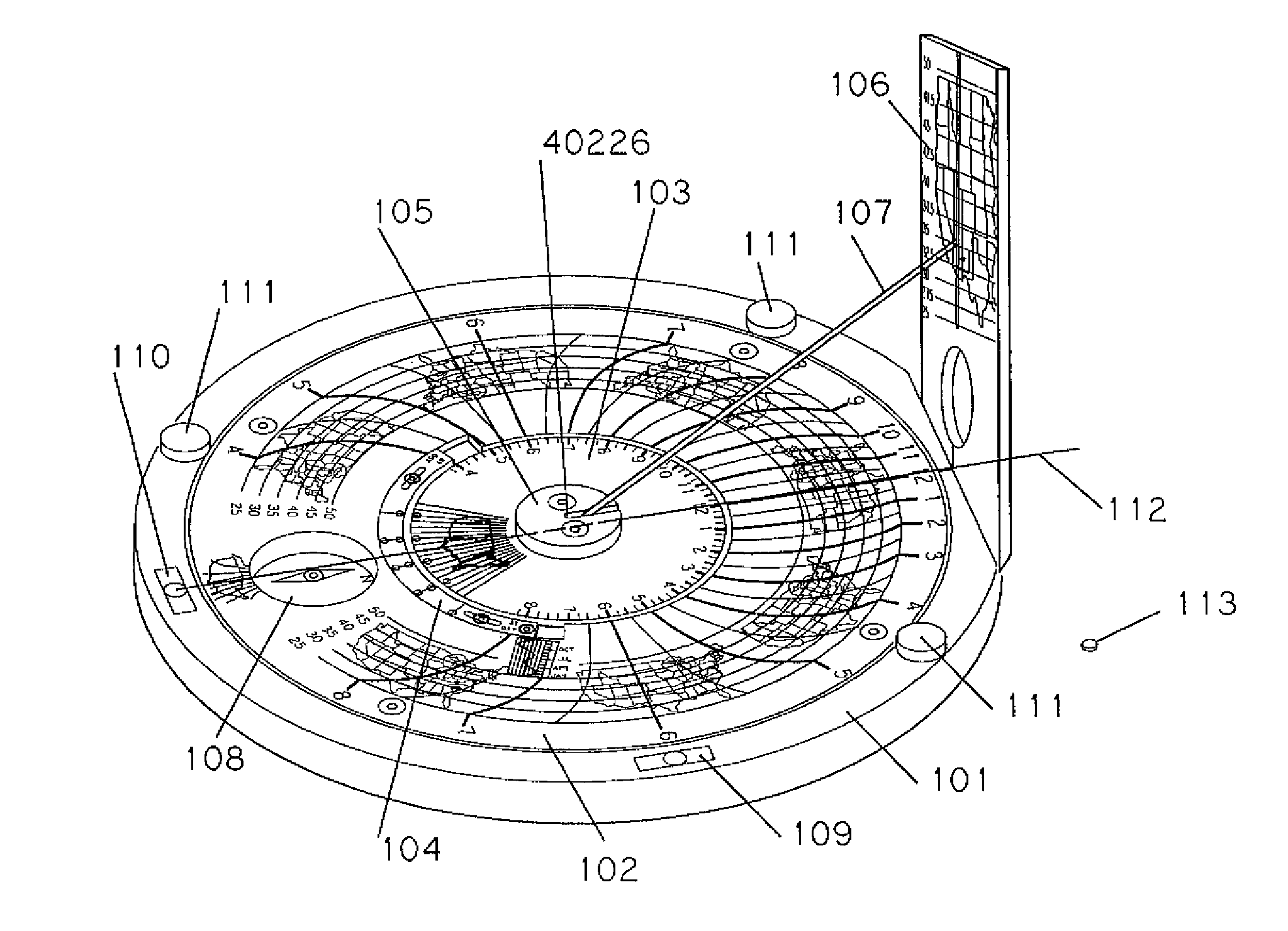
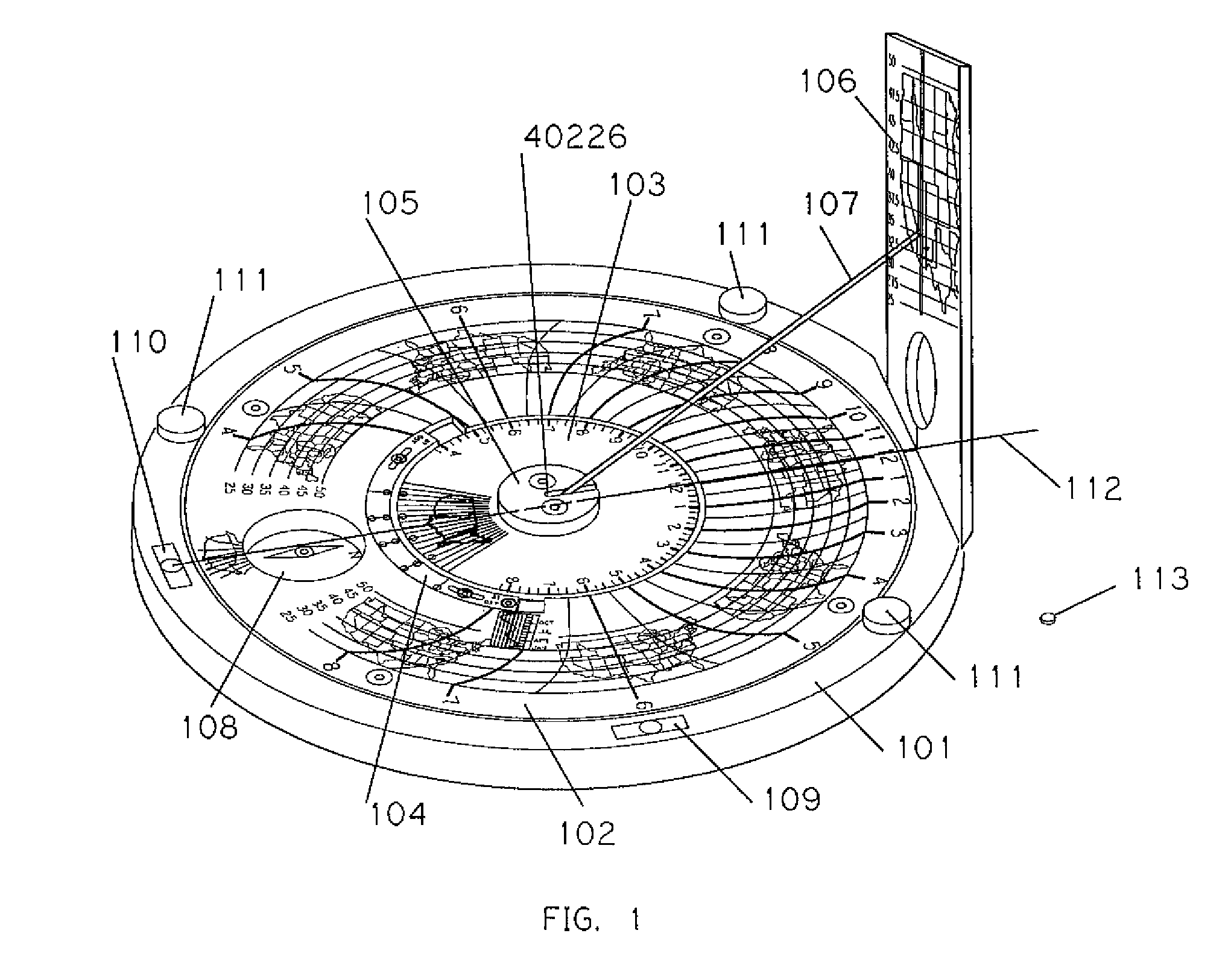
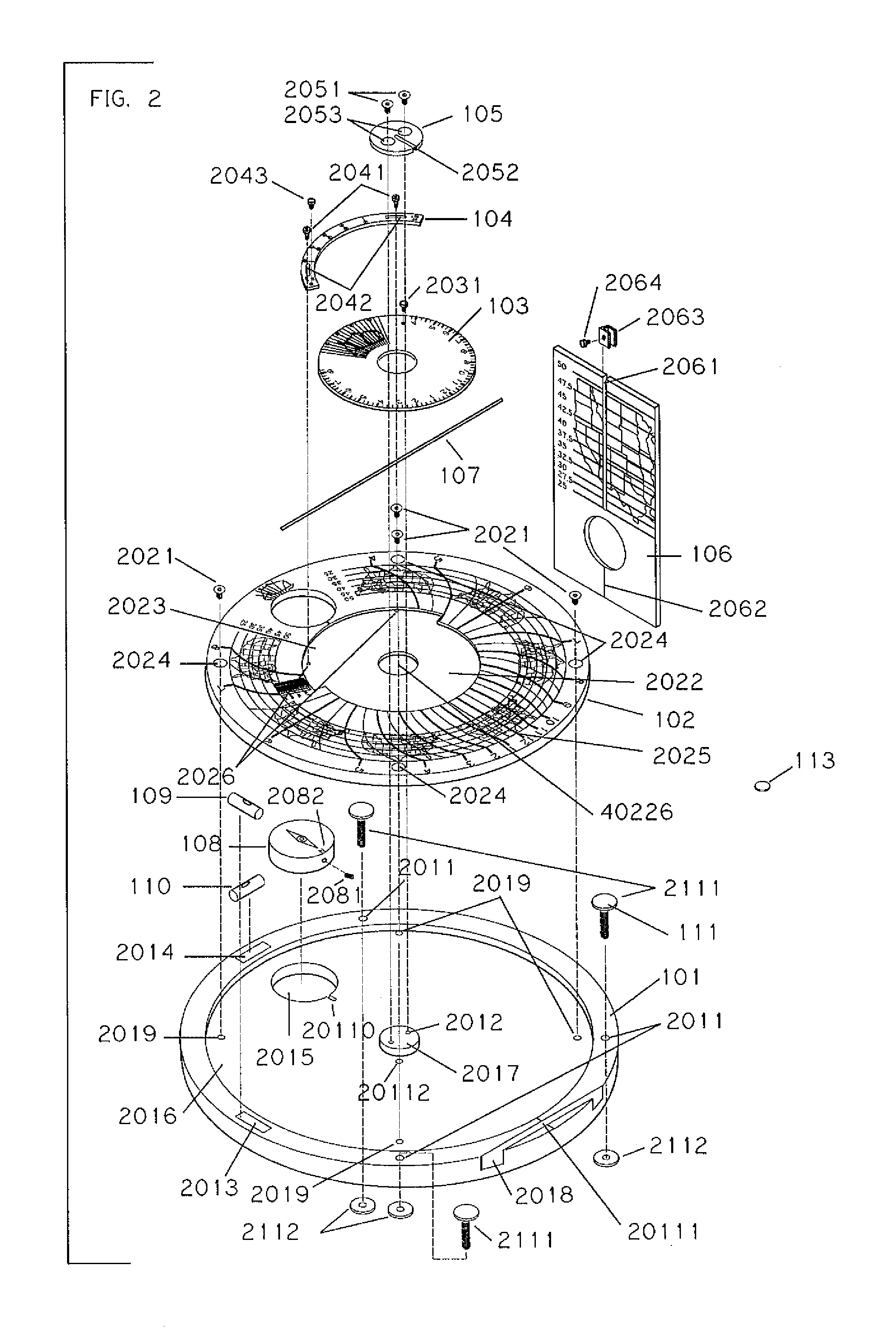
Sundial for telling solar time and clock time across a range of latitudes and longitudes
A sundial for telling apparent solar time and clock time across a range of latitudes and longitudes. A solar dial is formed with an index point and a noon hour point. A plurality of concentric latitude indicia are centered at the index point and at least one map indicium is overlaid by the concentric latitude indicia where the map indicium has geographic latitudes corresponding with the concentric latitude indicia on the solar dial. The solar dial also includes a plurality of solar time indicia radiating generally outward from the index point drawn with respect to the noon hour point according to the hour line equation at each concentric latitude indicia intercept. An elongated gnomon projects from the index point, whereby the sun's shadow cast by the gnomon intersects the solar time indicia in relation to the concentric latitude indicia to provide a reading of apparent solar time for the user's location on the map indicium.
Owner:KEELE RICHARD
Automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of pendulum gyro north seeker
The invention relates to an automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of a pendulum gyro north seeker. The method is characterized in that the geographic latitude is resolved by utilizing the pendulum period measured by an alidade of the pendulum gyro north seeker under a non-tracking state, and the directive coefficient is calculated, so that the precision compensation of deviation brought about by torsion zero deviating from true north is completed, and the method comprises the four steps of calibrating the relationship coefficient of the period and the latitude, starting a north seeking process, measuring the period under the non-tracking state, resolving the latitude by the non-tracking period, and correcting the torsion zero deviation automatically. Compared with the prior art, the automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of the pendulum gyro north seeker has the advantages that in actual applications, the latitude is not required to be input before measurement, and the directive coefficient is also not required to be calibrated and calculated; through the constant coefficient relationship of the period and the latitude, which is calculated in advance in a calibrating site, the latitude at the site can be resolved only by measuring the non-tracking pendulum period of a measured site, and further a measurement result is corrected. The method can be widely applied to the fields of aviation, aerospace, geodetic measurement, guided missile aiming and the like.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
Method for estimating the geographical latitude, longitude and elevation of a mobile electronic telecommunication device (TD)
InactiveUS20130137448A1Minimizes expected distance errorThe location information is accurateBeacon systems using radio wavesTelephonic communicationSignal qualityGeographical latitude
A method for estimating the geographical latitude, longitude and elevation of a mobile electronic telecommunication device (TD) is provided. The method draws random information over a given time period from multiple responders. A triangulation and signal quality analysis is performed to determine the possible location of the TD. Using the statistical information and its analysis the location (x, y and z coordinates) as well as the velocity and acceleration of the device is estimated. The present invention provides extremely accurate location information.
Owner:SHEN JAMES
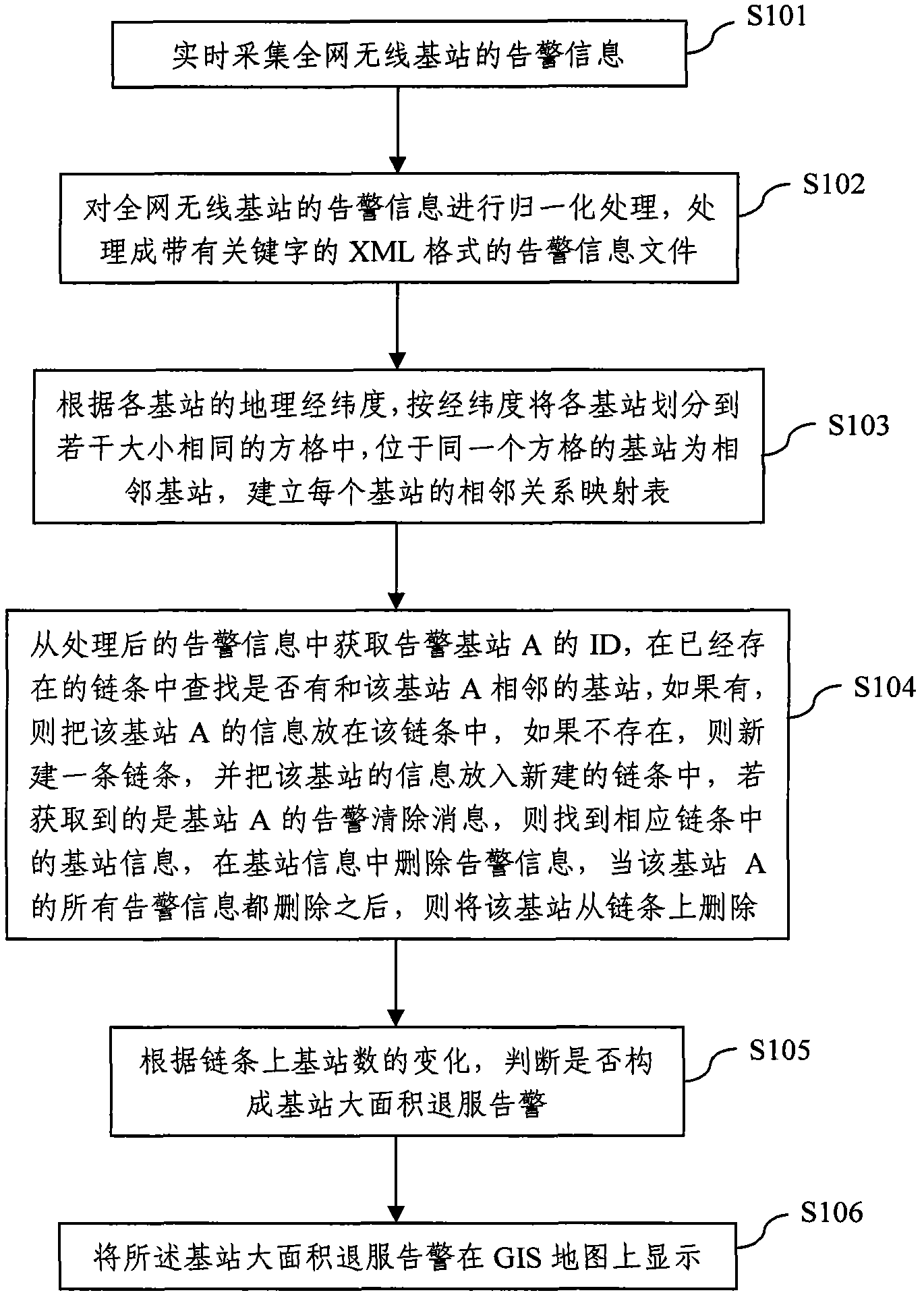
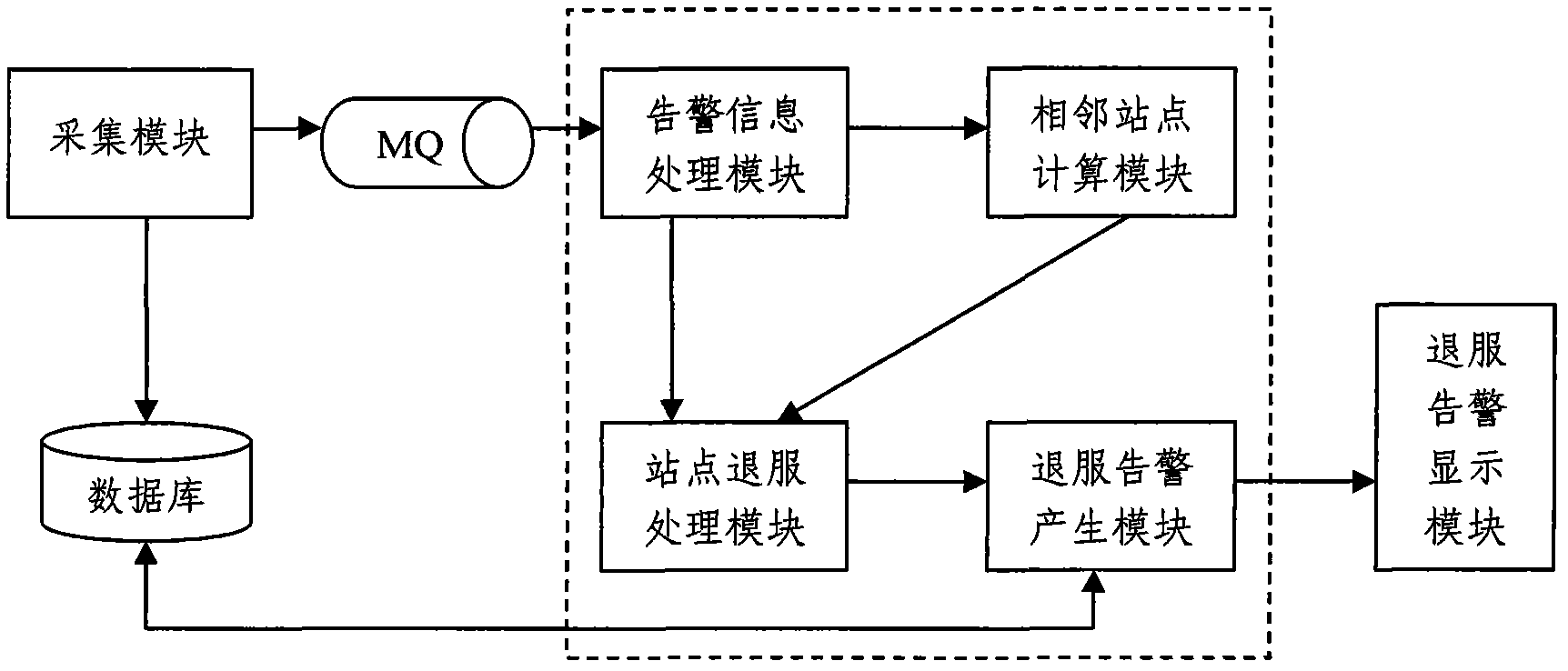
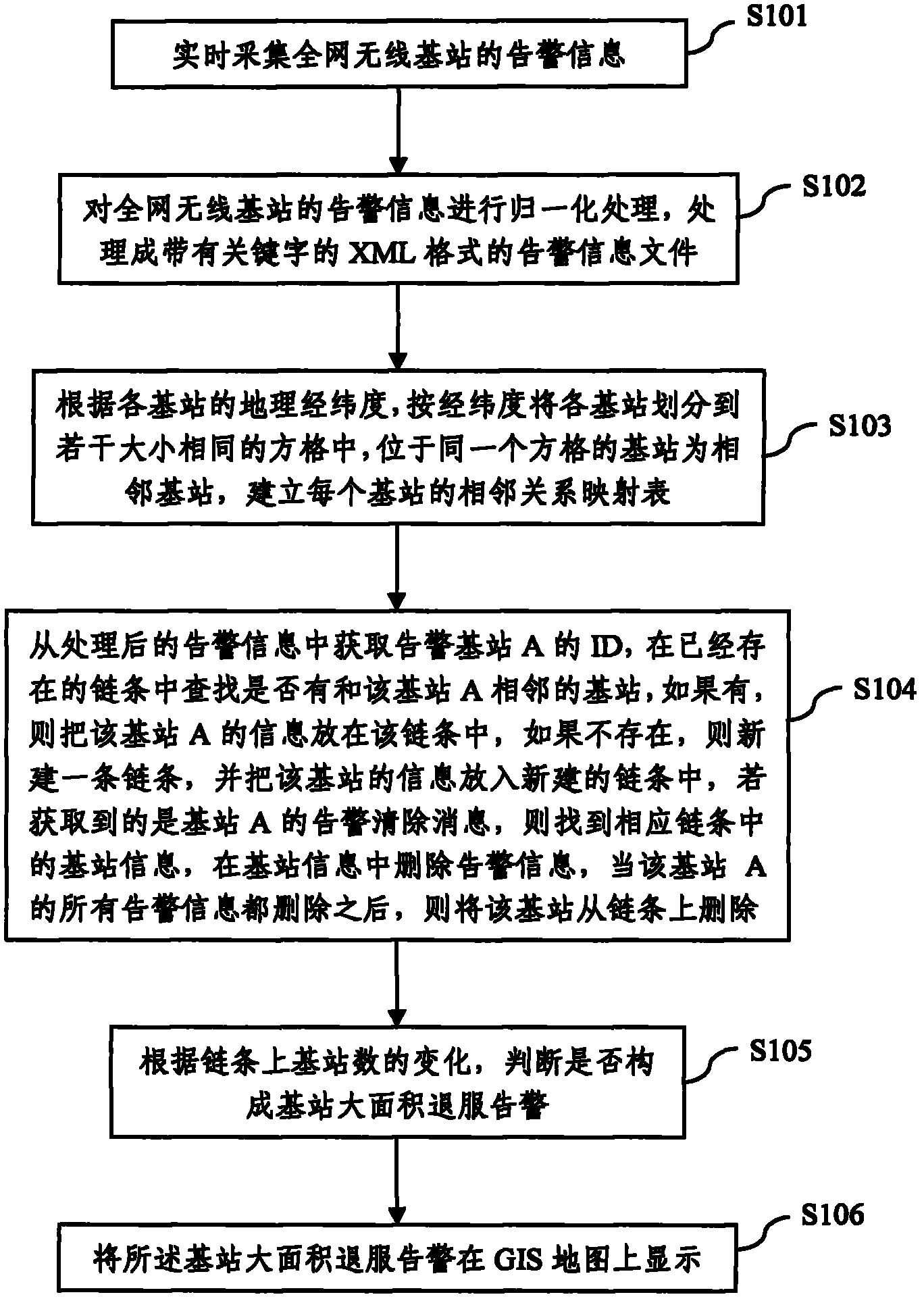
Large-area base station out-of-service alarm monitoring method and system
ActiveCN102075990AAvoid Signal IslandsAvoid blind spotsData switching networksWireless communicationNeighbor relationGeographical latitude
The invention discloses a large-area base station out-of-service alarm monitoring method and system. The method comprises the following steps: S1) acquiring alarm information of wireless base stations of the whole network in real time; S2) normalizing the alarm information of the wireless base stations of the whole network to obtain normalized alarm information; S3) classifying the base stations into a plurality of same-size squares on according to the geographical longitudes and the geographical latitudes, wherein the base stations in the same square are neighbor base stations, and creating a neighboring relation mapping table for each base station; S4) creating a relation chain for the neighbor base stations; and S5) judging whether a large-area base station out-of-service alarm is formed or not according to the change of the number of the base stations on the chain. The invention has the advantages that whether the base stations are out of service in a large area or not can be accurately judged and signal islands or dead zones caused by out-of-service base stations can be avoided.
Owner:ULTRAPOWER SOFTWARE
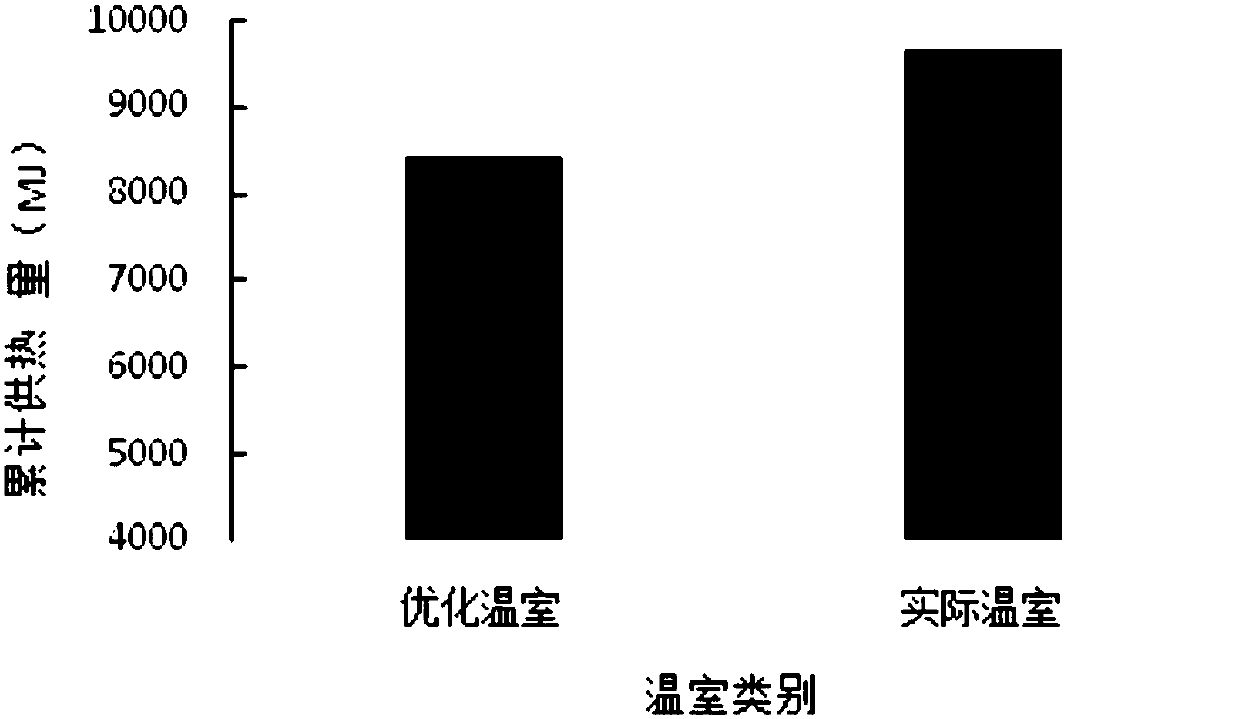
Simplified design and calculation method of morphological feature parameters of solar-greenhouse building space
ActiveCN107506539AImprove energy savingGeometric CADSystems intergating technologiesCritical periodDaylight
The invention discloses a simplified design and calculation method of morphological feature parameters of a solar-greenhouse building space, and belongs to the field of energy-saving design of facility agriculture buildings. When a geographical latitude of a construction project site, a vegetable production critical-period which a greenhouse needs to ensure and a span of the solar greenhouse which needs to be constructed are determined, optimal design values of the morphological feature parameters, such as a high-span ratio of the solar greenhouse, rear-roof projection length and north-wall height under a corresponding span condition, of the solar-greenhouse building space can be calculated and obtained according to the method of the invention by consulting local average outdoor-air temperature and daily average total solar radiation amount in the corresponding period. Calculation results show that during an overwintering production period of solar greenhouses, the amount of heat which needs to be provided to the ''optimal-design greenhouse'' is 8340 MJ under a condition of ensuring that greenhouse environment temperature is not lower than 8 DEG C, and is decreased by 14.7% as compared with 9670MJ of the ''current greenhouse'', an energy-saving effect is significant, and an advantageous condition is provided for fully utilizing solar energy or other renewable energy sources as supplemental heat sources by the greenhouse.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
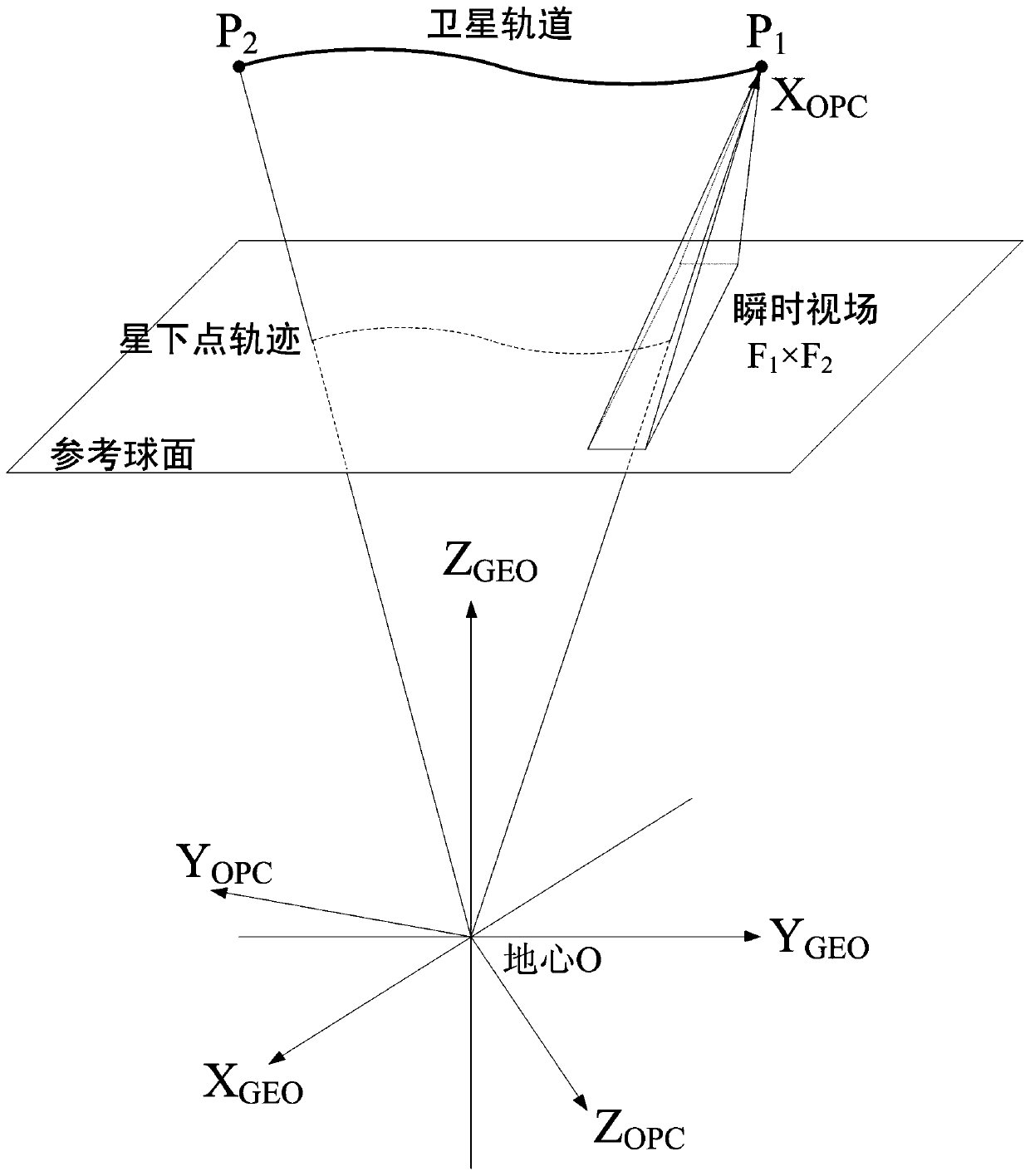
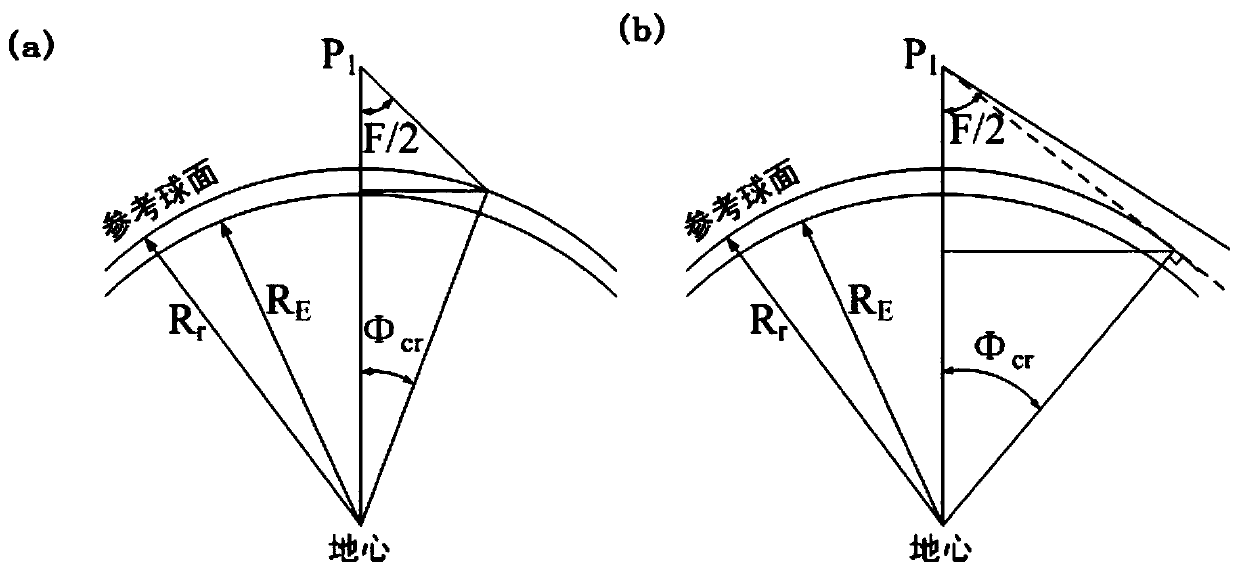
Disc projection and splicing method for large view field space to ground observation images
ActiveCN106897962AAccurate descriptionReal and accurate spatial distributionGeometric image transformationProjection imageGeographical latitude
The invention relates to a disc projection and splicing method for large view field space to ground observation images and belongs to the space remote sensing detection technology field. The method mainly comprises steps that a conversion matrix between a geocentric coordinate system GEO and a projection disc coordinate system OPC is calculated; a disc projection grid is established on a reference spherical surface in the OPC coordinate system; latitudes and longitudes of grid points and a grid center point are calculated and are then further converted to the GEO coordinate system; the actual projected image point number of two-dimensional array Np storage grid points and a main intensity value of actual projected image points of the two-dimensional array Np storage grid points are calculated; a look vector under each image point satellite coordinate system is calculated and is gradually converted to the OPC coordinate system, and a projection image data matrix, a grid point geographical latitude and longitude data matrix and a grid point center geographical latitude and longitude data matrix are lastly acquired. The method is advantaged in that time sequence observation images are projected and spliced to one grid of the reference spherical surface, so spatial distribution of observation objects can be actually and accurately described through the projection images.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
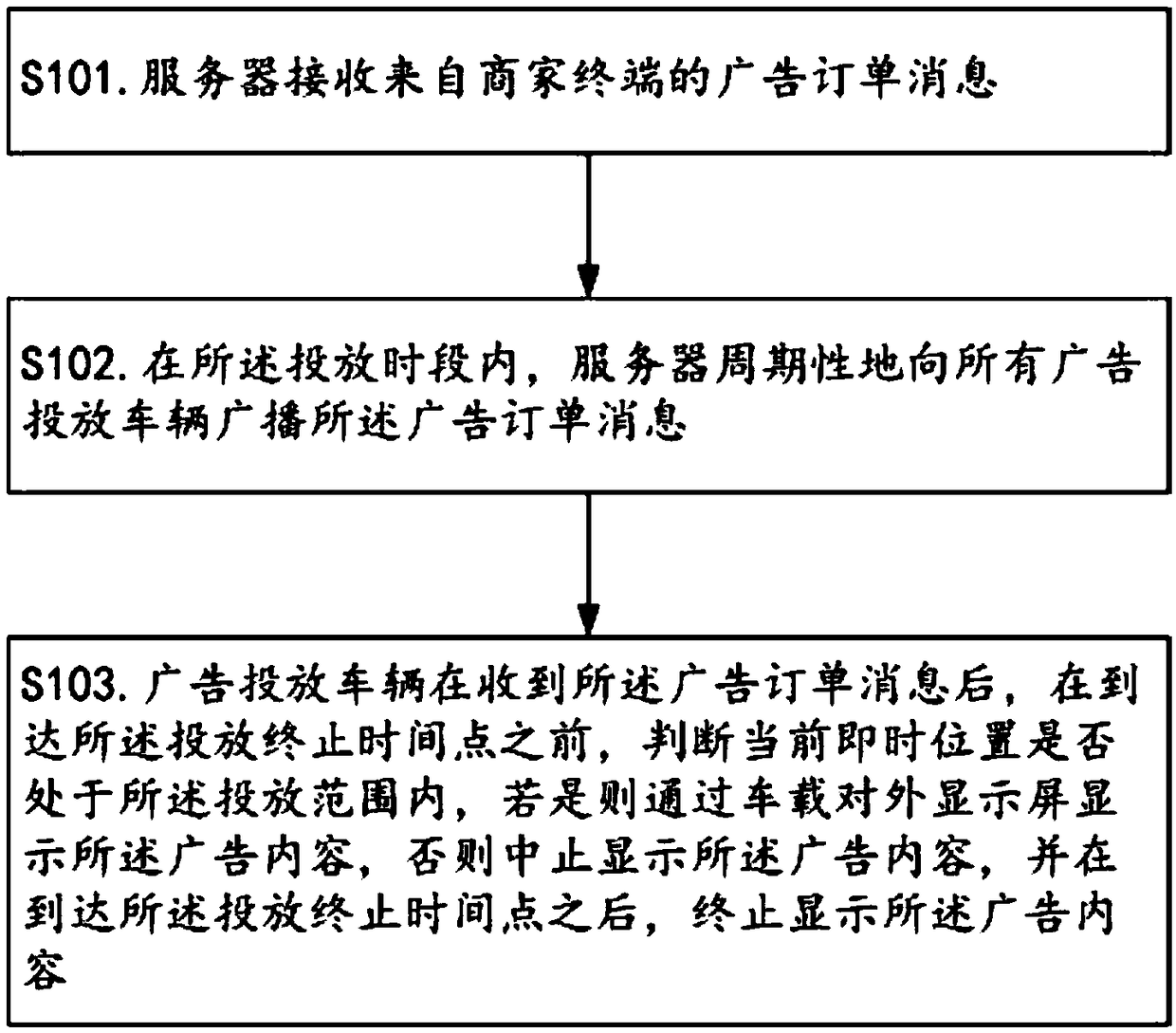
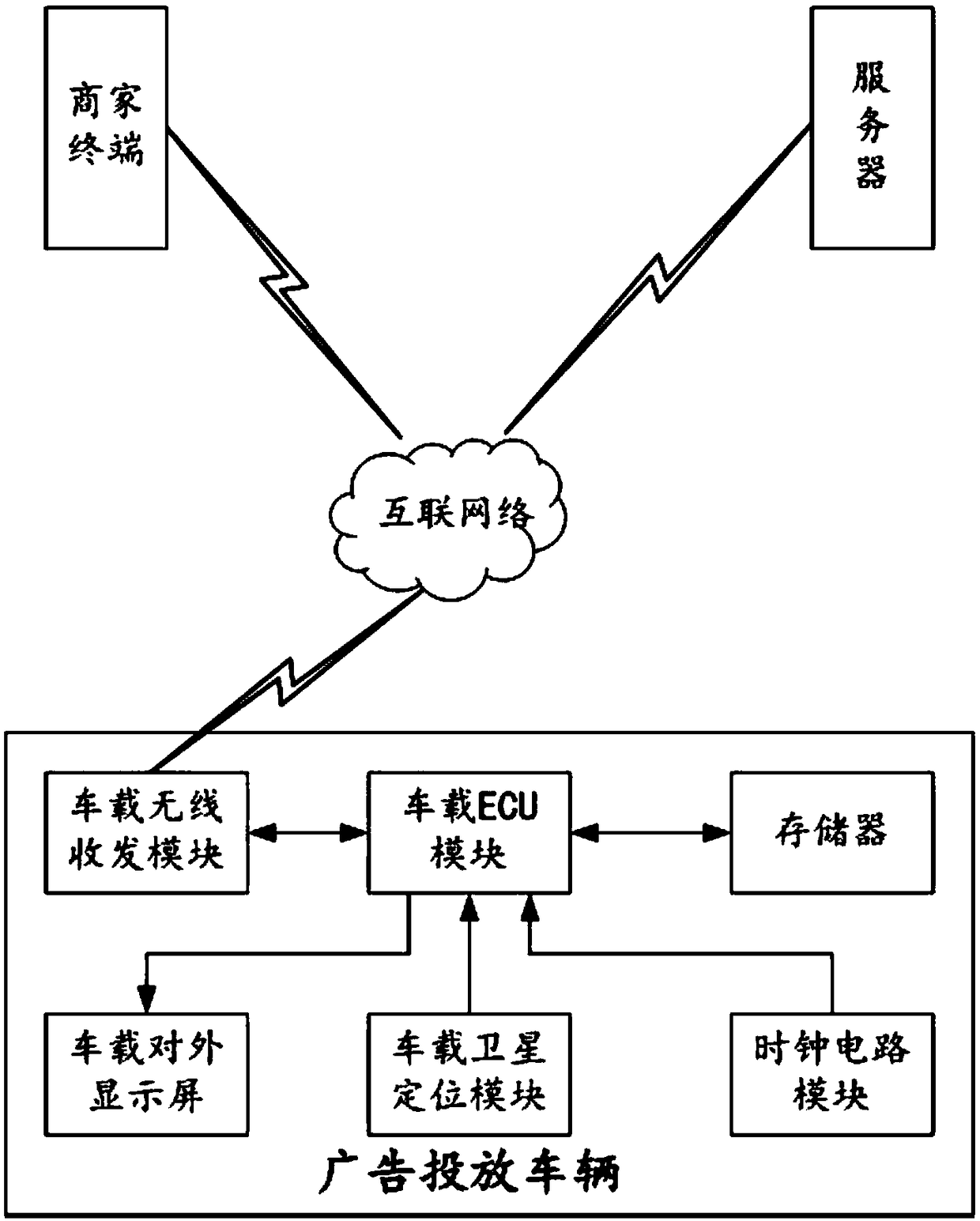
Advertisement putting method based on vehicle-mounted external display screen
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile advertisements, and discloses an advertisement putting method based on a vehicle-mounted external display screen. Through the invention, a methodfor carrying out accurate advertisement putting on the aspects of a time dimension and a geographic latitude in virtue of the vehicle-mounted external display screen can be provided, so that a merchant can determine advertisement putting contents, advertisement putting time periods and advertisement putting geographical ranges on the own, a vehicle accurately puts appointed contents in the geographical range and the time appointed by the merchant, so that the specific requirements of the merchant can be met, and the high efficiency of a putting effect is guaranteed. In addition, an advertisement toll collection mode based on time periods, sections or / and path length and the like can be provided, the flexible toll collection requirement of an advertisement provider is met, and the methodis convenient for practical application and popularization.
Owner:成都贵存科技有限公司
Method for measuring latitude by utilizing pendulum gyroscope
The invention discloses a method for measuring a latitude by utilizing a pendulum gyroscope, which particularly comprises the following steps of: 1, arranging the pendulum gyroscope at a certain station point; 2, measuring a swing period of the pendulum gyroscope; and 3, calculating the geographic latitude of the station point by using an external computer according to the obtained swing period of the gyroscope. The method of the invention has the advantages of simpleness, no need of large-scale ground-to-air connection survey, capability of independently measuring the latitude, higher late-time data processing speed and capability of monitoring variation of the latitude in real time.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Intelligent supernova alarm and observation system
InactiveCN103124291AReal-time comprehensive and efficient acquisitionEfficient collectionAngle measurementTransmissionObservatoryGeographical latitude
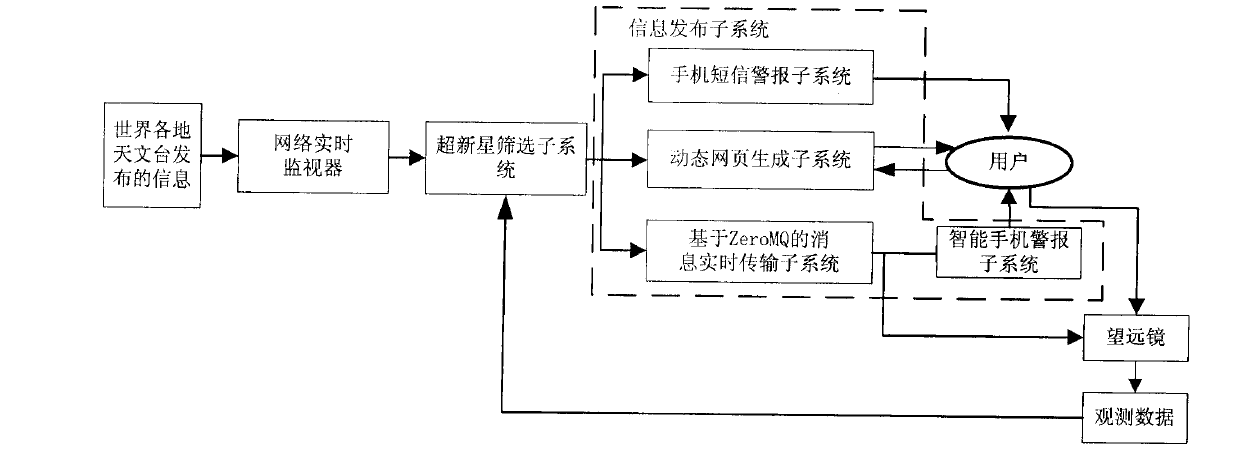
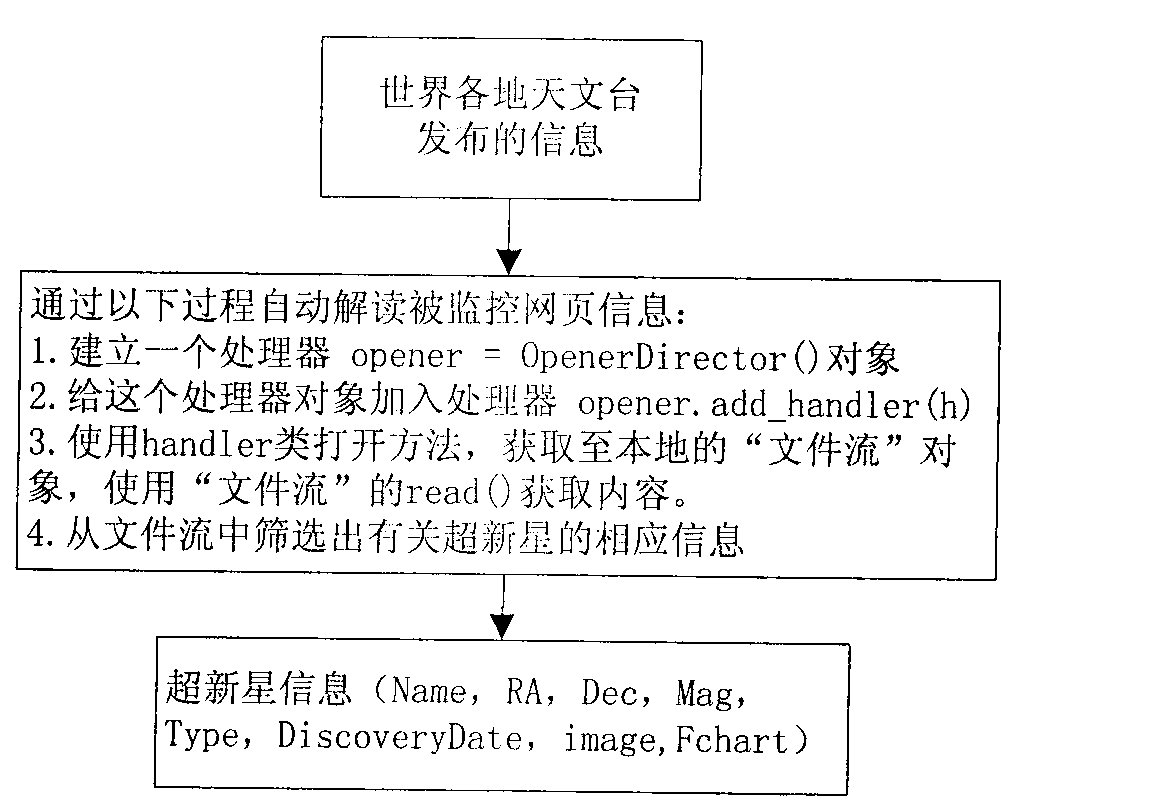
The invention discloses an intelligent supernova alarm and observation system. A network real-time monitor monitors information issued by observatories around the world in real time, automatically screens webpages reported by supernova outburst to filter supernova information of new outburst, and inputs the supernova information to a supernova screening subsystem; a supernova screening subsystem screens the supernova which is suitable for observation and calculates the optimal observation moment, an observable time interval and reference exposure time according to supernova position, supernova brightness and geographical latitude and longitude information of stations in the input supernova information and transmits the supernova suitable for observation, the optimal observation moment, the observable time interval and the reference exposure time to an information issuance subsystem; an information issuance subsystem manage the received information and issues the information transmitted by the supernova screening subsystem to a user or directly transmits the information to a telescope; the user controls the telescope for observation according to the content in the information, or uses the telescope to observes automatically and directly based on the received information; and the telescope transmits the observed data to the information issuance subsystem for management.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Celestial sphere instrument with horizontal height and azimuth angle adjusting mechanism
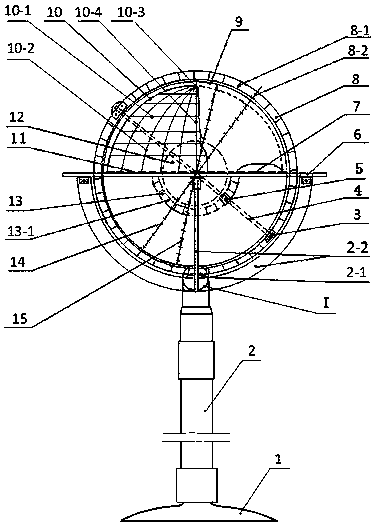
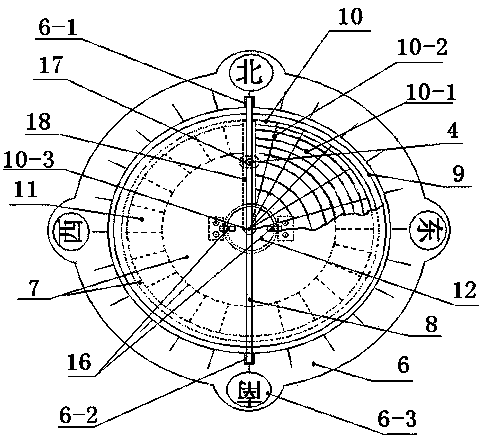
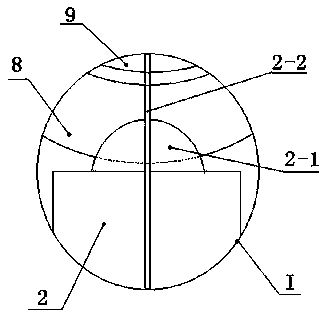
PendingCN110060565AEasy to install and adjustEasy to findPlanetaria/globesGeographical latitudeCelestial sphere
The invention belongs to science popularization and teaching instruments, and particularly relates to a celestial sphere instrument with a horizontal height and azimuth angle adjusting mechanism. Theadjusting mechanism arranged in the celestial sphere model of the celestial sphere instrument can adjust a polar axis of the celestial earth to form an arbitrary included angle with a ground plane model so as to meet the requirement of demonstrating the motion operation condition of celestial bodies in any geographical latitude; the polar axis and the ground plane model of the celestial sphere instrument can be freely, conveniently and quickly installed and adjusted to any geographical latitude to be demonstrated along with a meridian circle for global use. According to the celestial sphere instrument, a horizon height circle, an azimuth angle line, an azimuth angle disc, a zenith vertical line and the like are arranged in the celestial sphere model, so that accurate numerical values of horizon height and azimuth angles of any celestial body at any geographical latitude position at any time can be accurately demonstrated and given, great convenience is brought for astronomical observation to find a target as soon as possible, great correct and clear guidance is given to astronomical lovers searching stars, and great help is given to astronomical teaching.
Owner:张国新
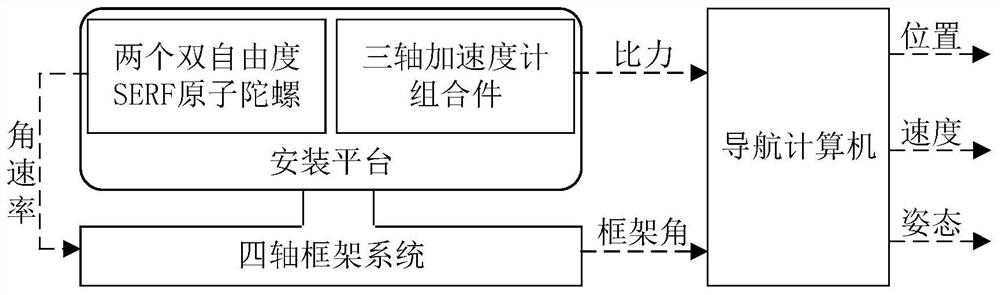
Atomic gyroscope navigation system and navigation solution method thereof
ActiveCN113203415AHigh precisionReduce the error valueNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention discloses a navigation solution method realized based on an atomic gyroscope navigation system. The method comprises the following steps of S1, constructing coordinate systems for navigation solution, S2, defining navigation parameters including geographic longitude, geographic latitude, geographic height, north speed, east speed, vertical speed and carrier attitude angle, and related physical parameters including platform attitude angle and accelerometer installation misalignment angle, S3, solving the position and the speed of the atomic gyroscope navigation system, and solving the geographic longitude, the geographic latitude, the geographic height, the north speed, the east speed and the vertical speed of the carrier, and S4, calculating the attitude angle of the carrier according to the navigation parameters. According to the atomic gyroscope navigation system and the navigation solution method thereof, a framework of an inertial navigation system for the atomic gyroscope and the navigation solution method of the atomic gyroscope are provided for the first time, the application of the atomic gyroscope in the inertial navigation system is expanded, the error value between each piece of navigation data resolved by the navigation solution steps and actually measured navigation data is small, the precision is high, and the effectiveness and the practicability are high.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
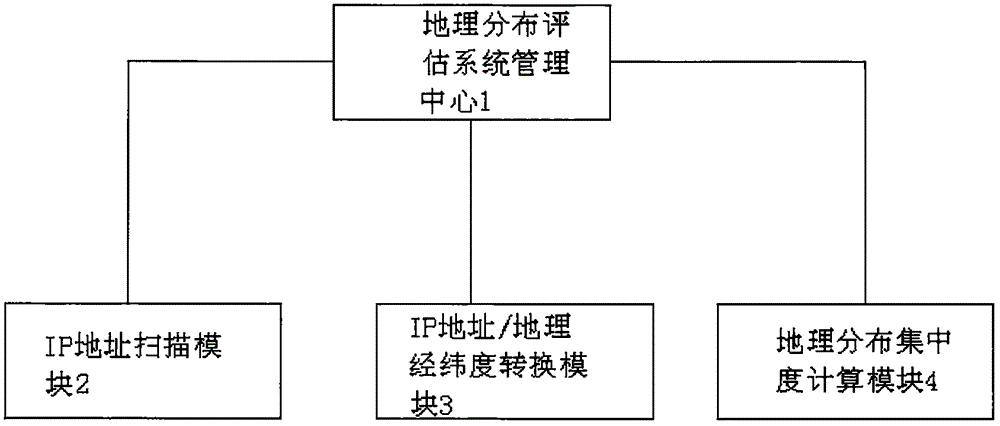
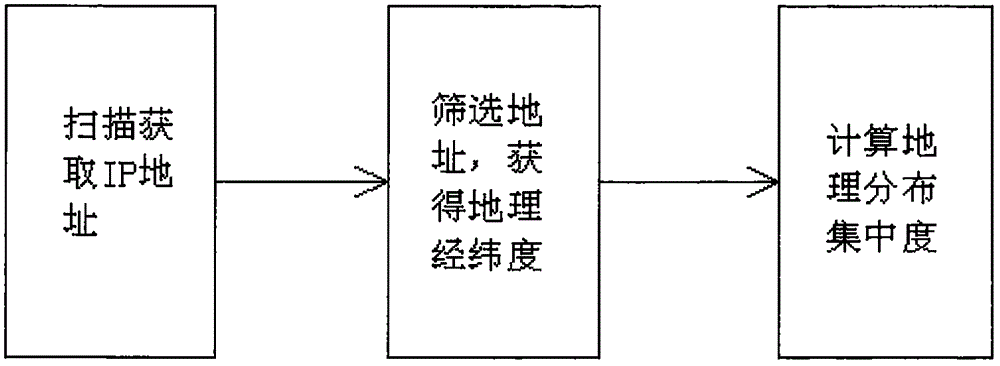
Network equipment loophole geographical distribution evaluation system and method
InactiveCN105933288AGrasp and understand the implementation of security measuresTransmissionGeographical latitudeIp address
The invention relates to a network equipment loophole geographical distribution evaluation system and a network equipment loophole geographical distribution evaluation method and belongs to the information security technical field. The system comprises a geographical distribution evaluation system management center; the geographical distribution evaluation system management center includes an IP address scanning module, an IP address / geographical latitude and longitude conversion module and a geographical distribution concentration ratio calculation module. According to the system and method of the invention, distribution in a network equipment loophole perspective is converted into distribution in a geographical perspective, and therefore, the implementation of safety measures of management institutions in different regions can be mastered and learned more clearly, and the effectiveness of safety management in a whole area can be calculated in a quantified manner.
Owner:CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID COMPANY
Method for estimating the geographical latitude, longitude and elevation of a mobile electronic telecommunication device (TD)
InactiveUS8521184B2Beacon systems using radio wavesTelephonic communicationSignal qualityGeographical latitude
A method for estimating the geographical latitude, longitude and elevation of a mobile electronic telecommunication device (TD) is provided. The method draws random information over a given time period from multiple responders. A triangulation and signal quality analysis is performed to determine the possible location of the TD. Using the statistical information and its analysis the location (x, y and z coordinates) as well as the velocity and acceleration of the device is estimated. The present invention provides extremely accurate location information.
Owner:SHEN JAMES
Gyro measuring instrument being capable of automatically acquiring geographic latitude and automatically seeking north
ActiveCN110108265ASolve the problem of not being able to obtain geographic latitude independentlySolve the situationRotary gyroscopesGeographical latitudeMicrocomputer system
The invention discloses a gyro measuring instrument being capable of automatically acquiring a geographic latitude and automatically seeking north. The gyro measuring instrument comprises a centeringleveling system, a microcomputer system, a collimating system, a gyro system, and a precision angle measuring and a rotary system. When the instrument is in use, the gyro system measures a geographiclatitude of a to-be-measured point; the gyro system measures a by-north corner of the instrument; and then the collimating system collimates a target point accurately and measures a horizontal rotation angle to calculate a true north angle of a to-be-measured side. According to the invention, problems that the traditional gyro directional instrument cannot obtain the geographical latitude automatically and gyro orientation cannot be performed under the condition of having unknown latitude are solved. The instrument has advantages of high automation degree, simple operation, high orientation precision, strong adaptability of the instrument environment and high anti-interference ability and the like.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
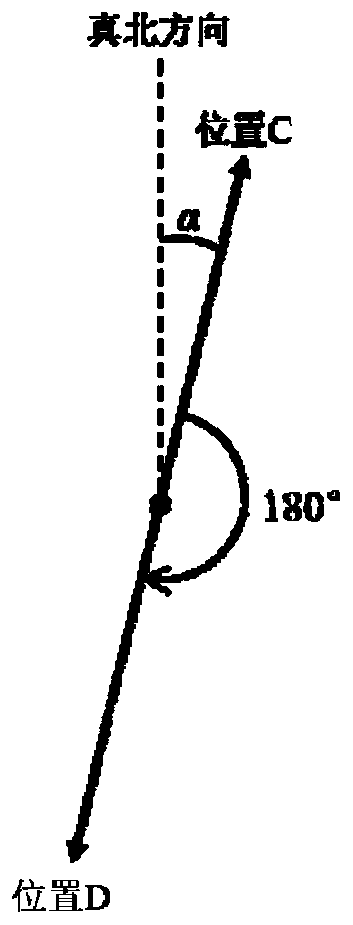
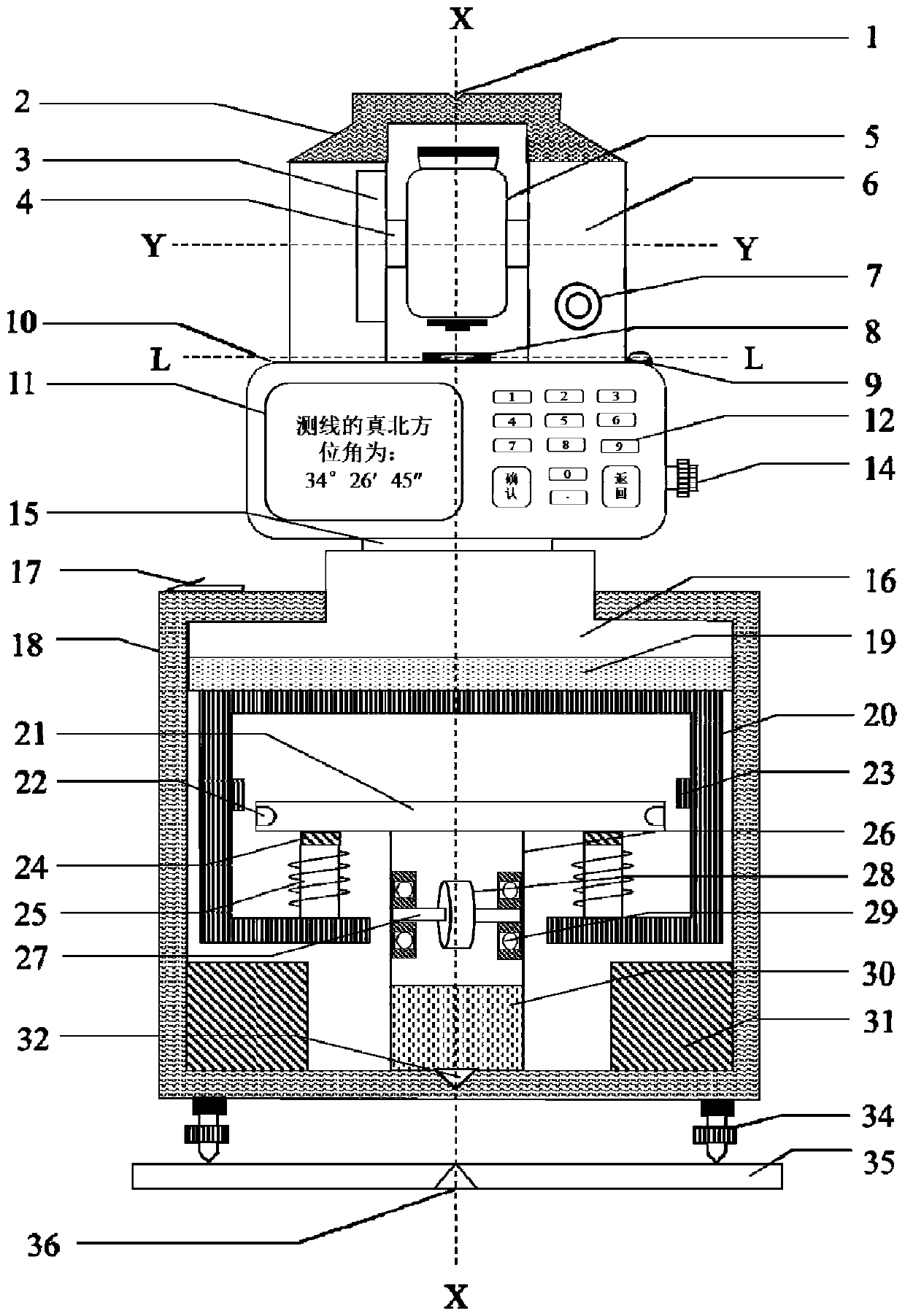
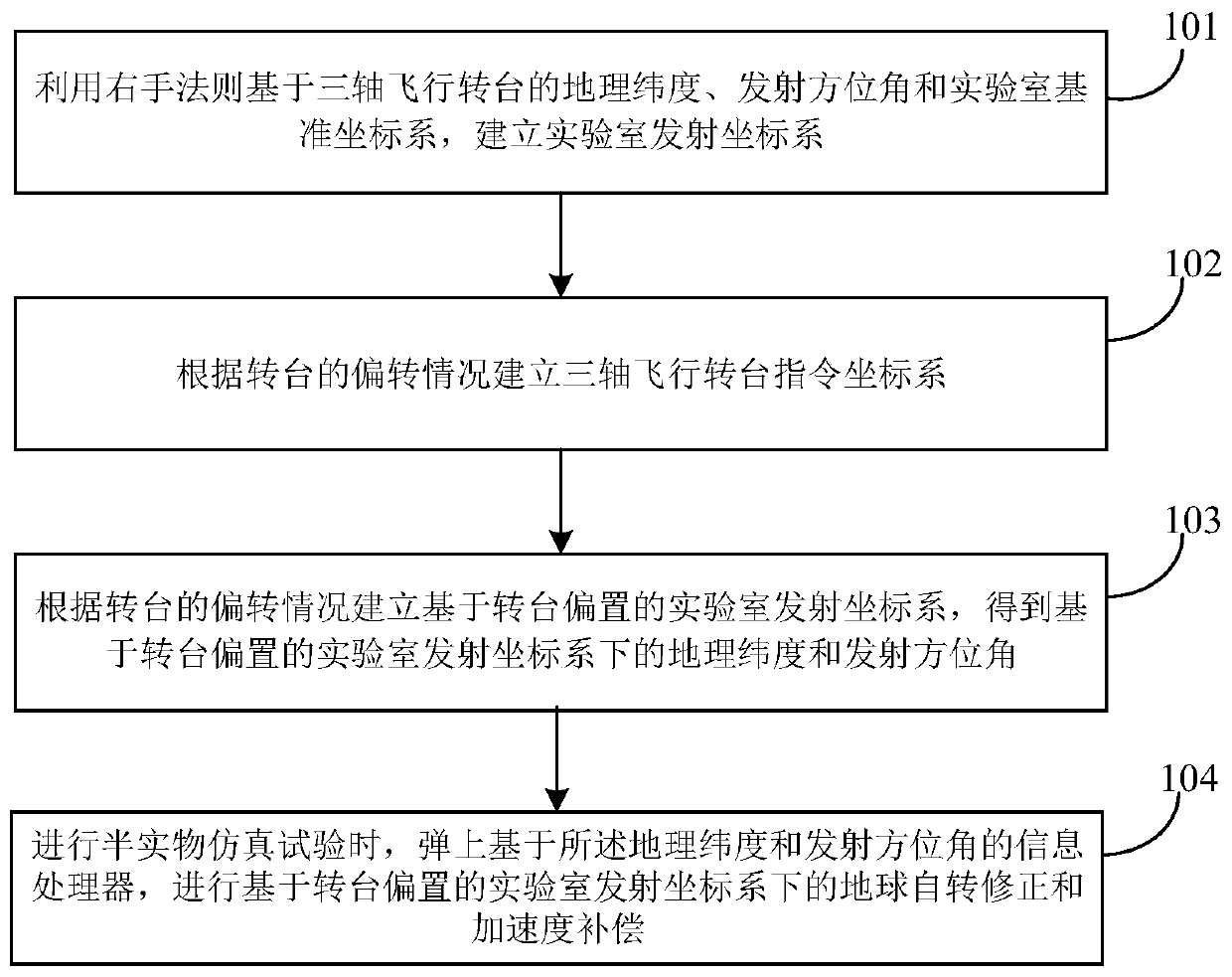
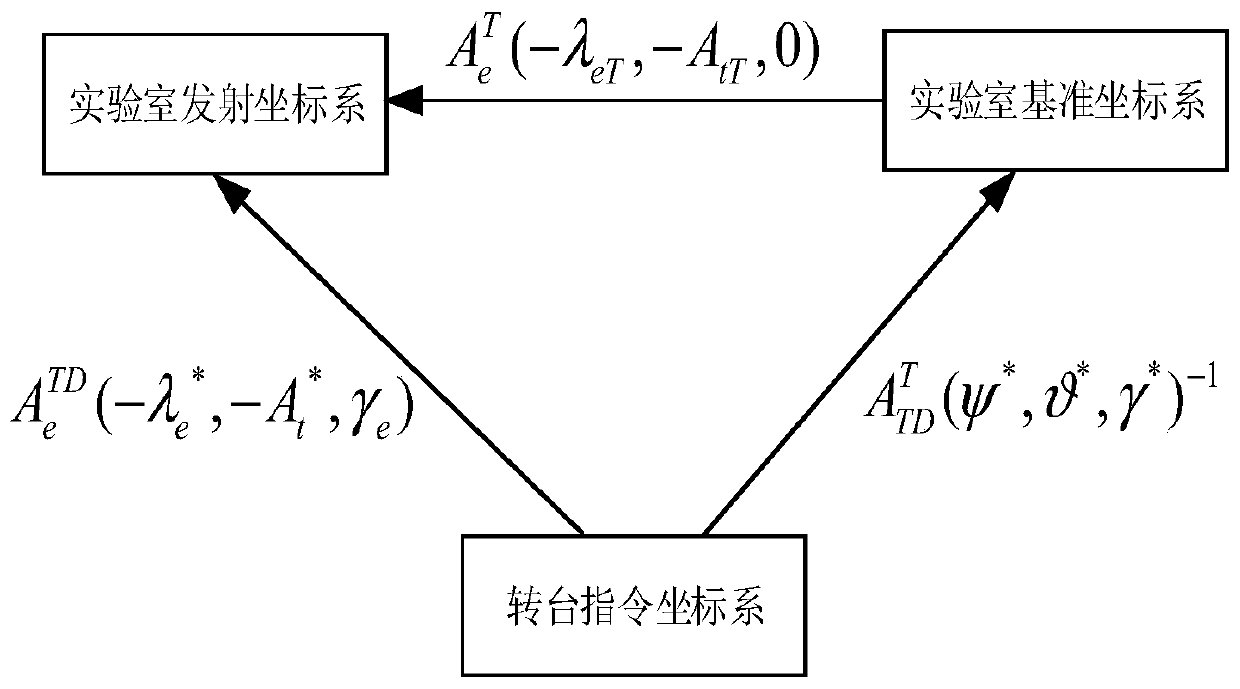
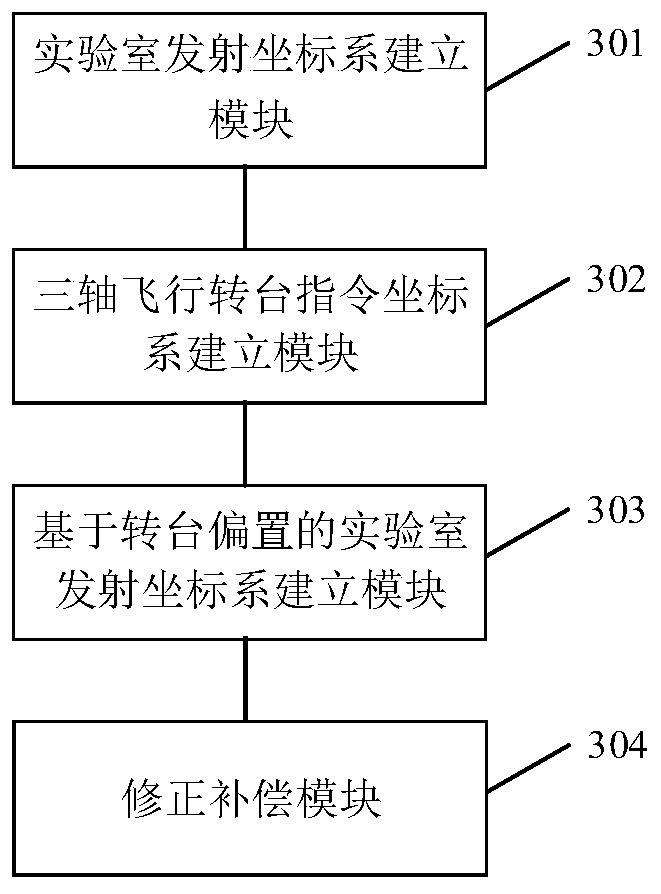
Earth rotation correction method and system under laboratory coordinate system
ActiveCN111457789ACorrection for rotation effectsSolve the problem of rotation angular velocity distortionAiming meansGeographical latitudeClassical mechanics
The embodiment of the invention discloses an earth rotation correction method and system under a laboratory coordinate system. The method comprises the steps of establishing a laboratory launch coordinate system based on geographic latitude lambda <eT> and launch azimuth A <tT> of a three-axis flight rotary table and a laboratory reference coordinate system through a right-hand rule; establishinga three-axis flight rotary table instruction coordinate system according to the bias condition of the rotary table; establishing a laboratory launch coordinate system based on rotary table bias according to the bias condition of the rotary table to obtain geographic latitude lambda < e > <*> and launch azimuth A < t > <*> under the laboratory launch coordinate system based on rotary table bias; and carrying out earth rotation correction and acceleration compensation under the laboratory launch coordinate system based on rotary table bias through a missile-borne information processor based on the geographic latitude lambda < e > <*> and the launch azimuth A < t > <*> during semi-physical simulation test. According to the method and system, the problem that the distortion occurs when the earth rotation angular velocity is measured through an inertial measurement unit in a laboratory environment is solved, and the earth rotation influence caused by mismatching between a launching site anda laboratory is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING SIMULATION CENT
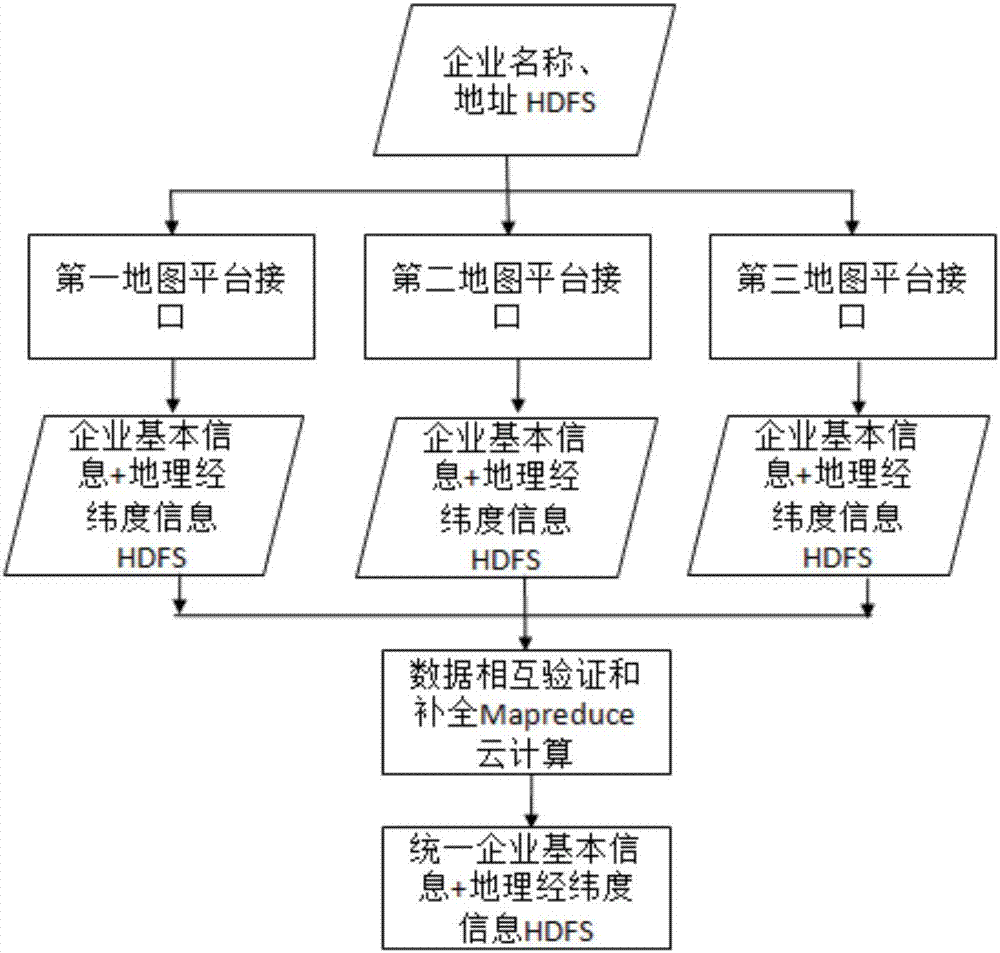
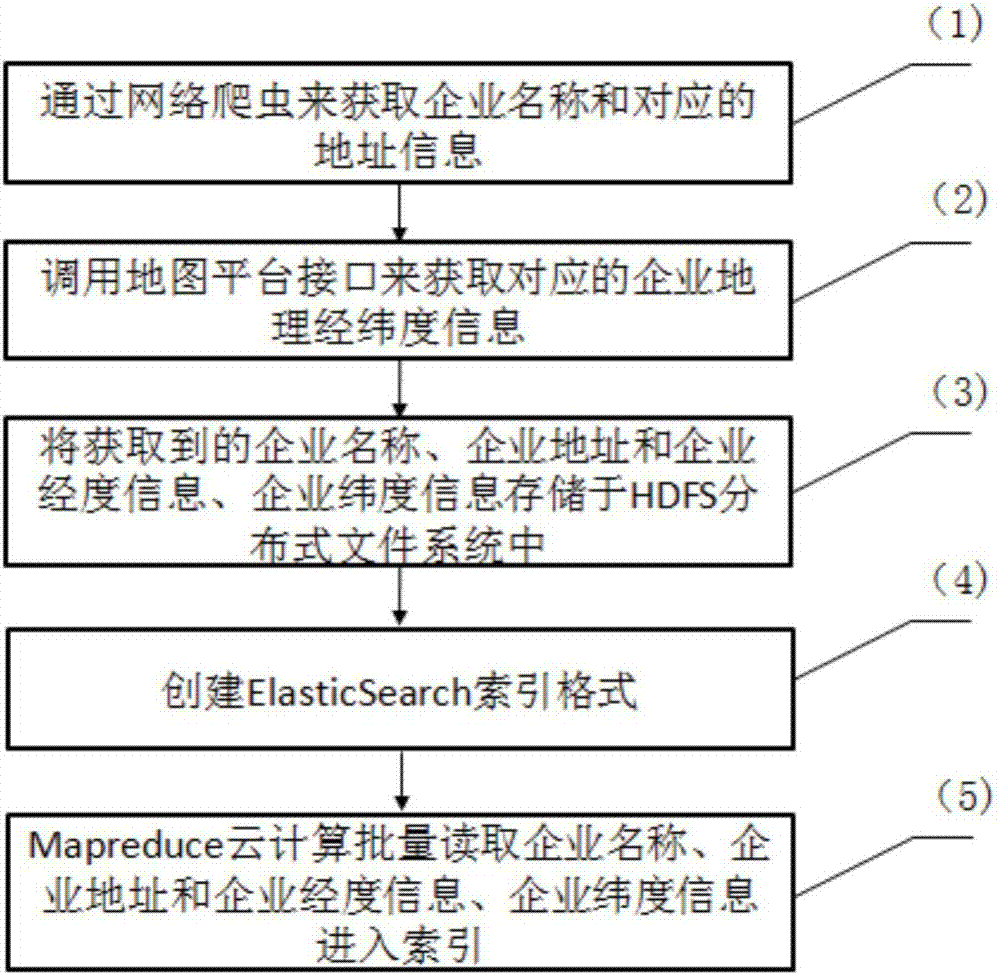
Enterprise location information acquisition and analysis method used for vertical searching
InactiveCN107463558AMeet the need for high fault toleranceIncrease credibilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingThe Internet
The invention relates to the field of internet information processing, and particularly to an enterprise location information acquisition and analysis method used for vertical searching. According to the method of the invention, geographical information of an enterprise is acquired through invoking data interfaces of public platforms, relevant verification and completion are carried out through the information acquired on at least two map platforms, latitude and longitude information with higher credibility is found out to use the same as the geographical latitude and longitude information corresponding to the enterprise, and the accuracy of a result of enterprise latitude and longitude information collection is improved; the acquired information is stored into a distributed file system; and technical support of data acquisition is provided for analysis, querying, business expansion and value mining of a geographical area and location of the enterprise and analysis and mining of hidden geographical region and geographical commerce values.
Owner:贵州双龙数联科技有限公司
Method of Acquiring Initial Attitude for Lunar Soft Landing Ground Test Using Strapdown Inertial Navigation
ActiveCN103759729BHigh precisionThere are many posture conversion linksNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSkyQuaternion
The invention discloses an initial attitude acquisition method for a ground test for soft lunar landing by using a SINS (serial inertial navigation system), and belongs to the field of lunar exploration. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly, arranging a fixed azimuth mirror near a test field, and by adopting the azimuth mirror for buffering, obtaining an attitude transformation matrix of a tester control coordinate system relative to a sky northeast coordinate system of the test field; then, through a geographical latitude of an observation point of the test field, obtaining a transformation matrix of the sky northeast coordinate system of the test field relative to a geocentric coordinate system, so that a transformation matrix C6 of the tester control coordinate system relative to the geocentric coordinate system is obtained, and then an attitude Q0 quaternion at an initial time T0 is obtained finally; starting from the initial time T0, carrying out attitude extrapolation by using gyro measurement data; and obtaining an attitude Qk during a k(th) control period, carrying out real-time output on the Qk until the tester attitude extrapolation process is completed and a landing test begins, wherein the Qk at the moment is taken as an initial attitude of a tester. The method disclosed by the invention is applicable to the ground test for lunar landing.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
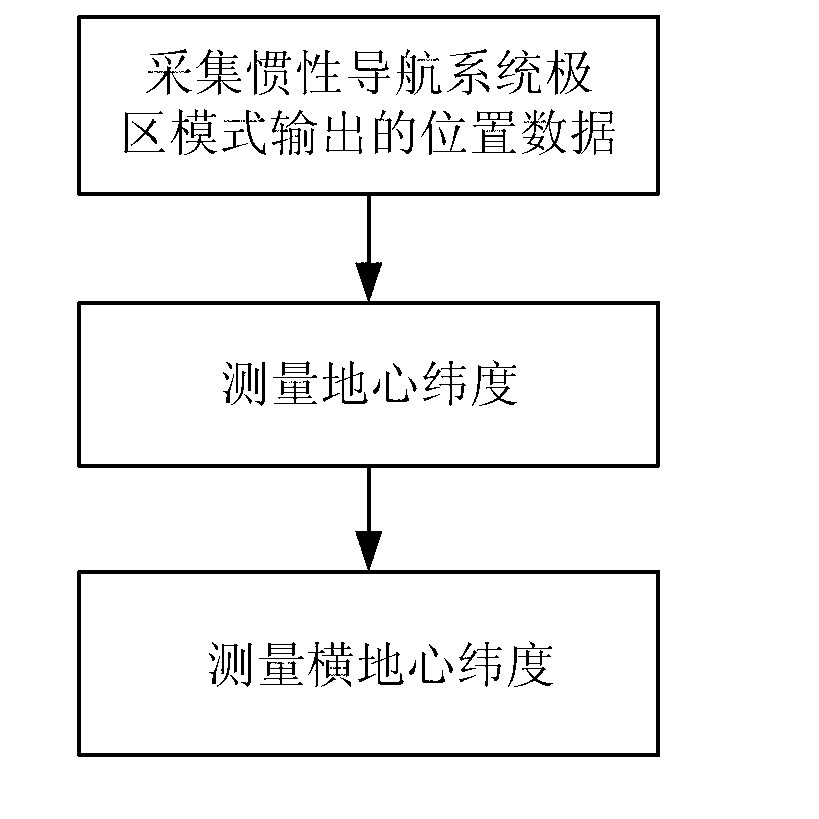
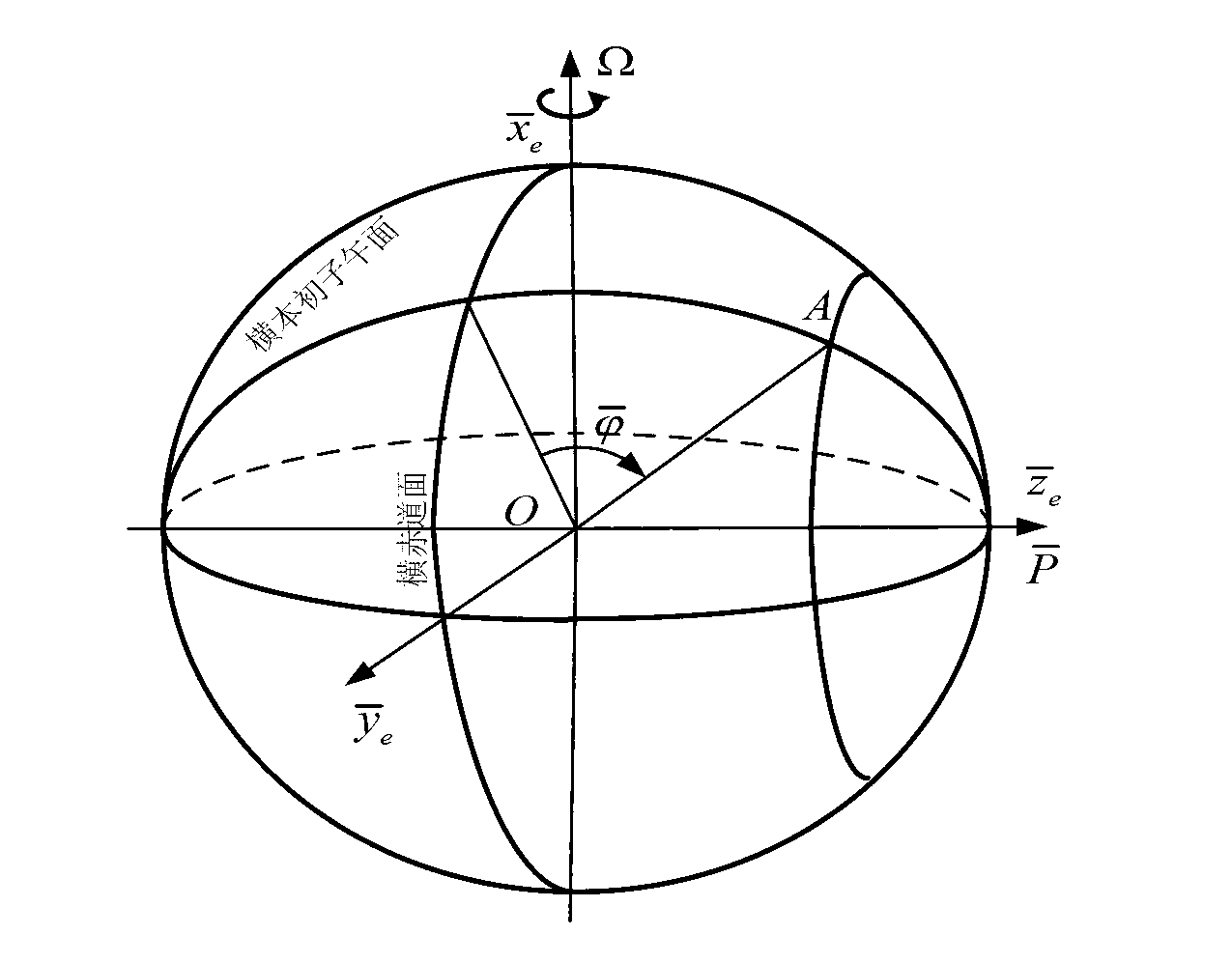
Inertial navigation system transverse geocentric latitude measurement method
InactiveCN103323004ASolve the initialization problemAvoid errorsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGeographical latitudeLongitude
The invention belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation system polar region navigation, and specifically relates to a method for an inertial navigation system to measure a transverse geocentric latitude by using latitude and longitude information outputted under a normal mode, such that a conversion of the inertial navigation system from a normal mode to a polar region mode is realized. According to the invention, longitude and geographical latitude of a position of a vessel are obtained according to position data outputted by the inertial navigation system under a normal mode; according to the geographical latitude of the position of the vessel, a geocentric latitude measurement value is determined; and according to the vessel longitude outputted by the inertial navigation system and the geocentric latitude, the transverse geocentric latitude measurement method value is obtained. With the method, a common error caused by that a latitude information outputted by the inertial navigation system is approximated as the geocentric latitude is avoided, and measurement precision of transverse geocentric latitude is improved, such that the error of inertial navigation system mode conversion is reduced. The measuring method provided by the invention is simple and convenient, and is suitable for actual application.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A Sub-satellite Point Surface Attribute Prediction Method Based on Surface Model Diagram
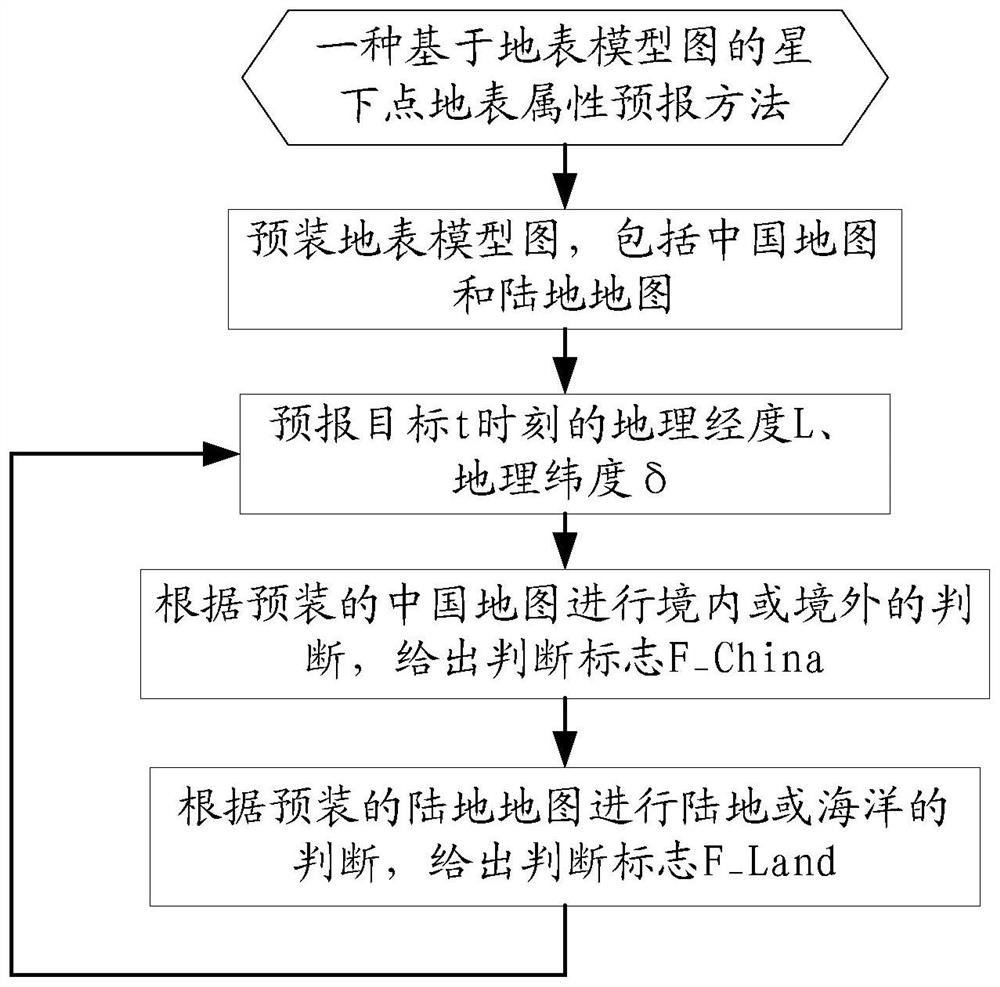
ActiveCN111637881BSolve computationally demanding problemsImproving Autonomous Mission Planning CapabilitiesNavigation by terrestrial meansSatellite radio beaconingSpacecraft attitude controlGeographical latitude
A method for predicting surface properties of sub-satellite points based on a surface model map, which belongs to the field of spacecraft attitude control. First, the surface model map is pre-installed, and the surface model map uses equidistant longitude strips, and each strip gives the strip area The upper and lower limits of the geographical latitude of "domestic or land" are used to simplify the surface positioning algorithm on the satellite. Secondly, the satellite independently predicts the geographic longitude L and geographic latitude δ of the sub-satellite point at time t of the target. Finally, the domestic or overseas forecast is performed according to the pre-installed map of China, and the land or ocean forecast is performed according to the pre-installed land map. The method of the invention solves the problems that the data storage capacity of the DEM digital elevation model is large and the search algorithm has high requirements for software calculation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Global ionosphere TEC model forecasting method and system
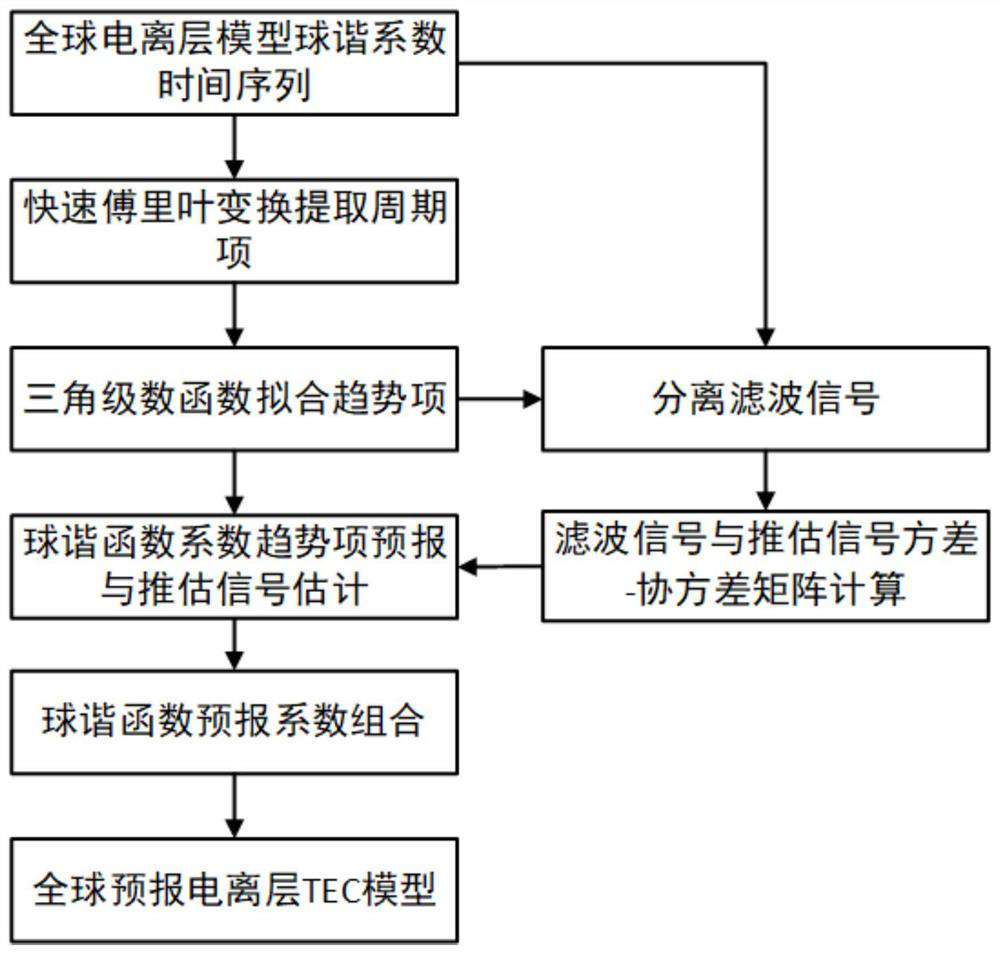
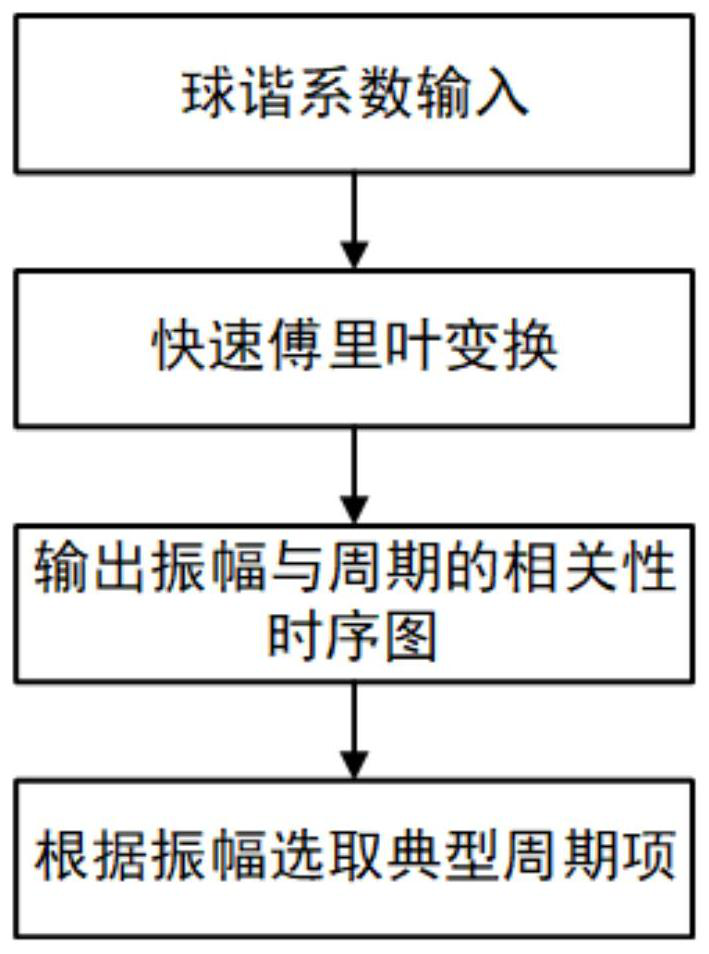
PendingCN113902184ASimple modelEasy to operateForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationFast Fourier transformGeographical latitude
The invention relates to a global ionosphere TEC model forecasting method and system, wherein the method comprises the steps: extracting a periodic term of a global ionosphere TEC model spherical harmonic function coefficient time sequence through employing fast Fourier transform, carrying out the fitting estimation of a spherical harmonic coefficient through employing a trigonometric series function, and forecasting a short-term spherical harmonic function coefficient; and generating a global forecast ionosphere TEC model according to the forecast spherical harmonic coefficient. According to the invention, the spherical harmonic function is adopted to describe the spatial-temporal change characteristics of the ionized layer TEC, the model is simple, and the operability is high; wherein the spherical harmonic function takes an orthogonal Legendre polynomial as a primary function and can represent physical meanings of the ionized layer TEC related to geographic latitude and geographic longitude; thus, not only is the trend term of the ionized layer TEC considered, but also the random change characteristic of the ionized layer TEC is considered.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Disc Projection and Stitching Method of Earth Observation Images in Space with Large Field of View
ActiveCN106897962BAccurate descriptionReal and accurate spatial distributionGeometric image transformationCircular discProjection image
The invention relates to a disc projection and splicing method for large field of view space earth observation images, belonging to the technical field of space remote sensing. The method mainly includes: calculating the conversion matrix between the geocentric coordinate system GEO and the projected disc coordinate system OPC; establishing a disc projection grid on the reference sphere in the OPC coordinate system; Latitude and longitude, and convert to GEO coordinate system at the same time; create a two-dimensional array N p Store the actual number of projected image points and the two-dimensional array R of the storage grid p Store the total intensity value of the actual projected image point of the grid point; calculate the view vector of each image point in the satellite coordinate system, and gradually transform it into the OPC coordinate system, and finally obtain the projection image data matrix, the grid point geographic latitude and longitude data matrix and Grid point center geographic longitude and latitude data matrix. In this method, the time series of observation images are projected into the same grid of the reference sphere, and the obtained projection images truly and accurately describe the spatial distribution of the observation objects.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Calculation method of solar illumination compensation value
ActiveCN111413278BReduce computational complexityRun fastMethod using image detector and image signal processingDesign optimisation/simulationGeostationary orbitGeographical latitude
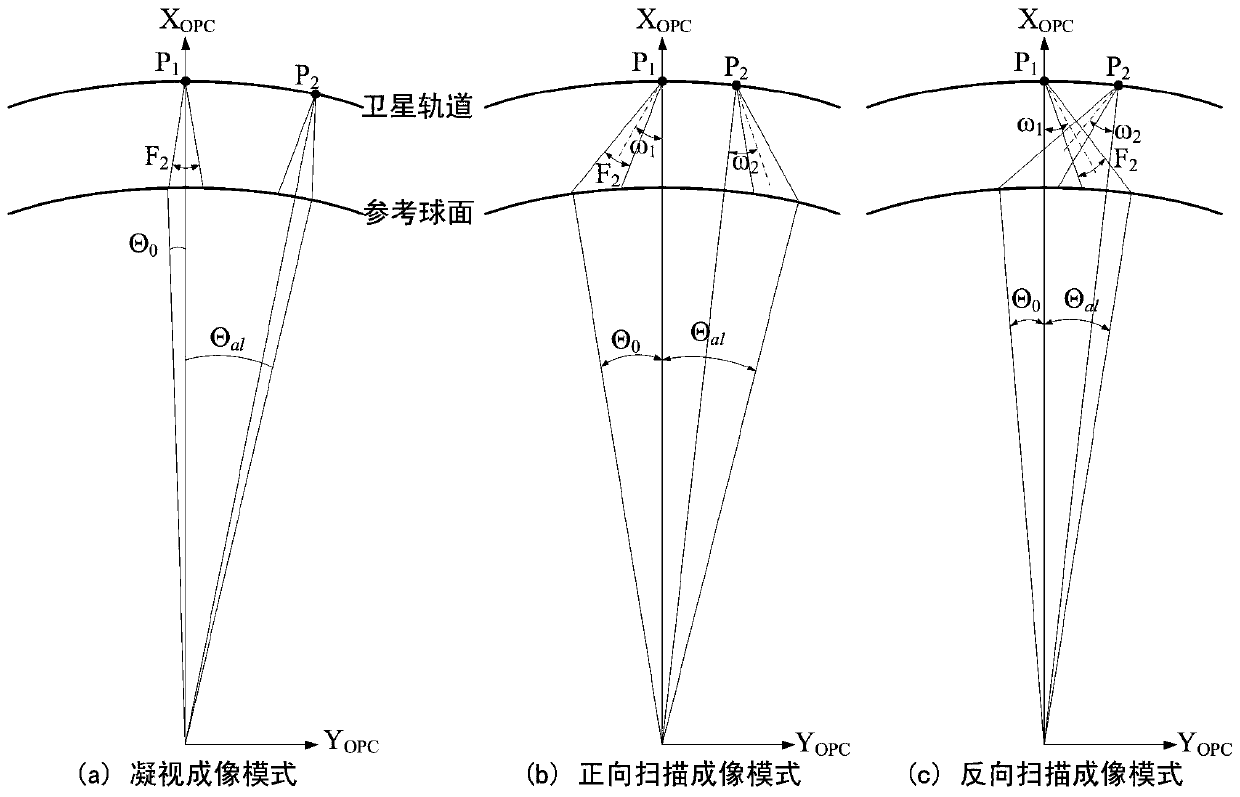
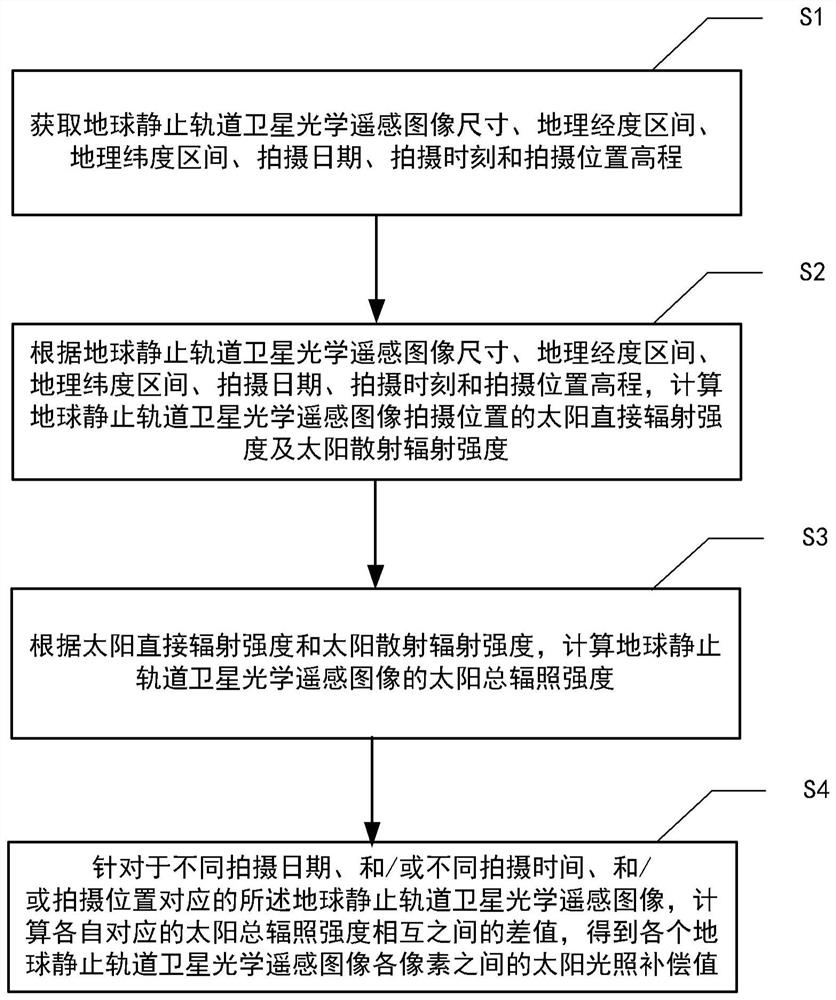
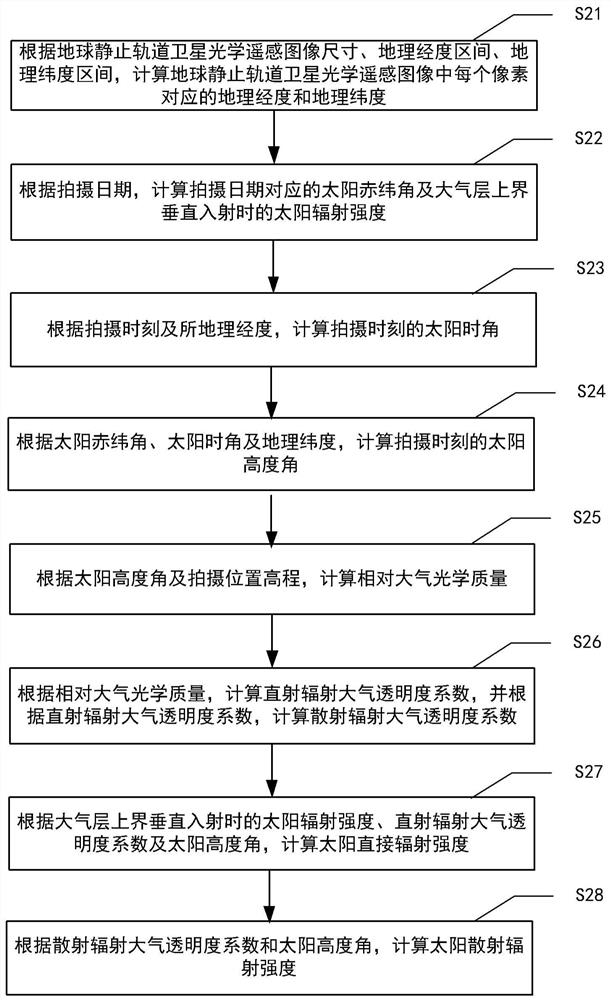
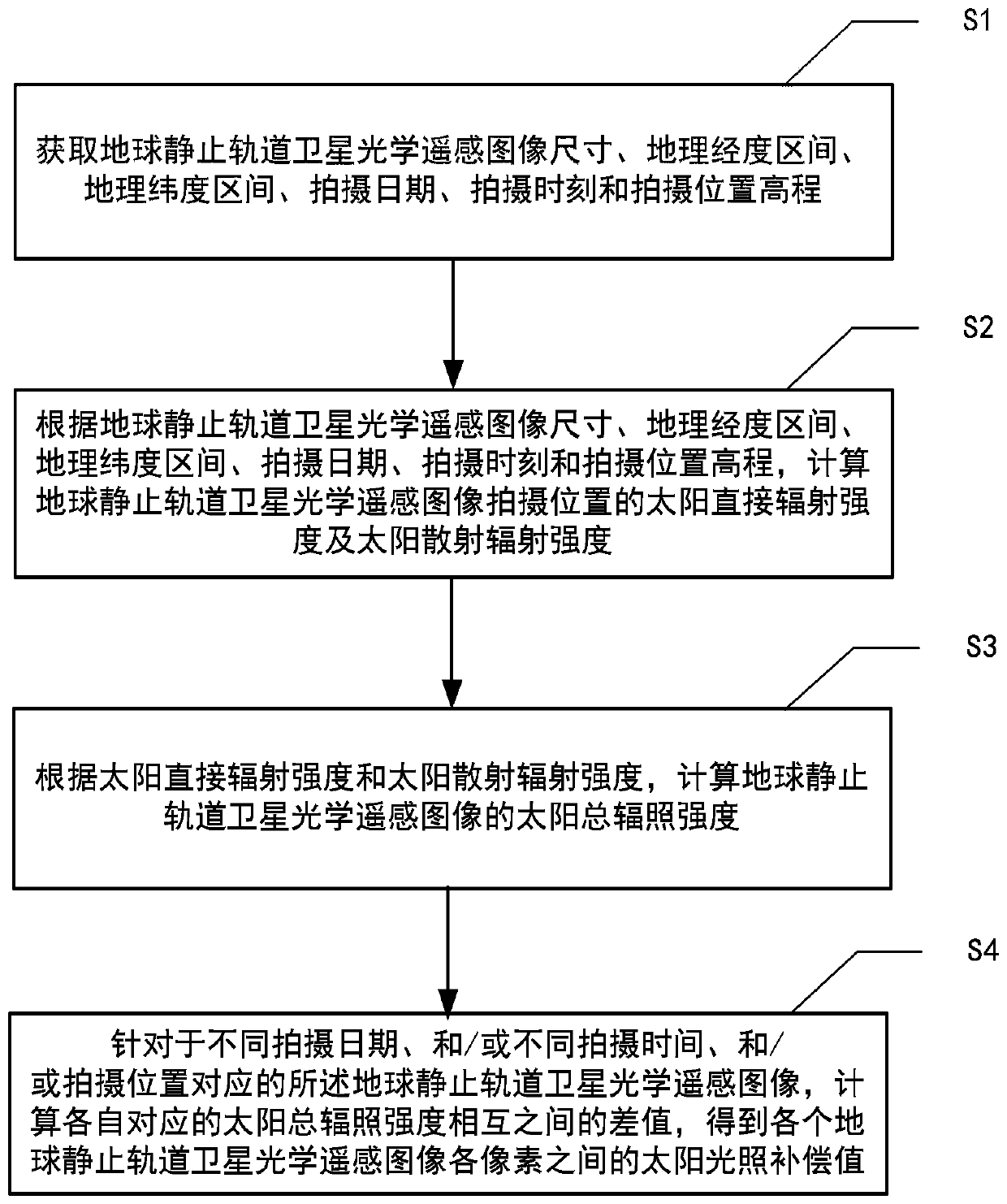
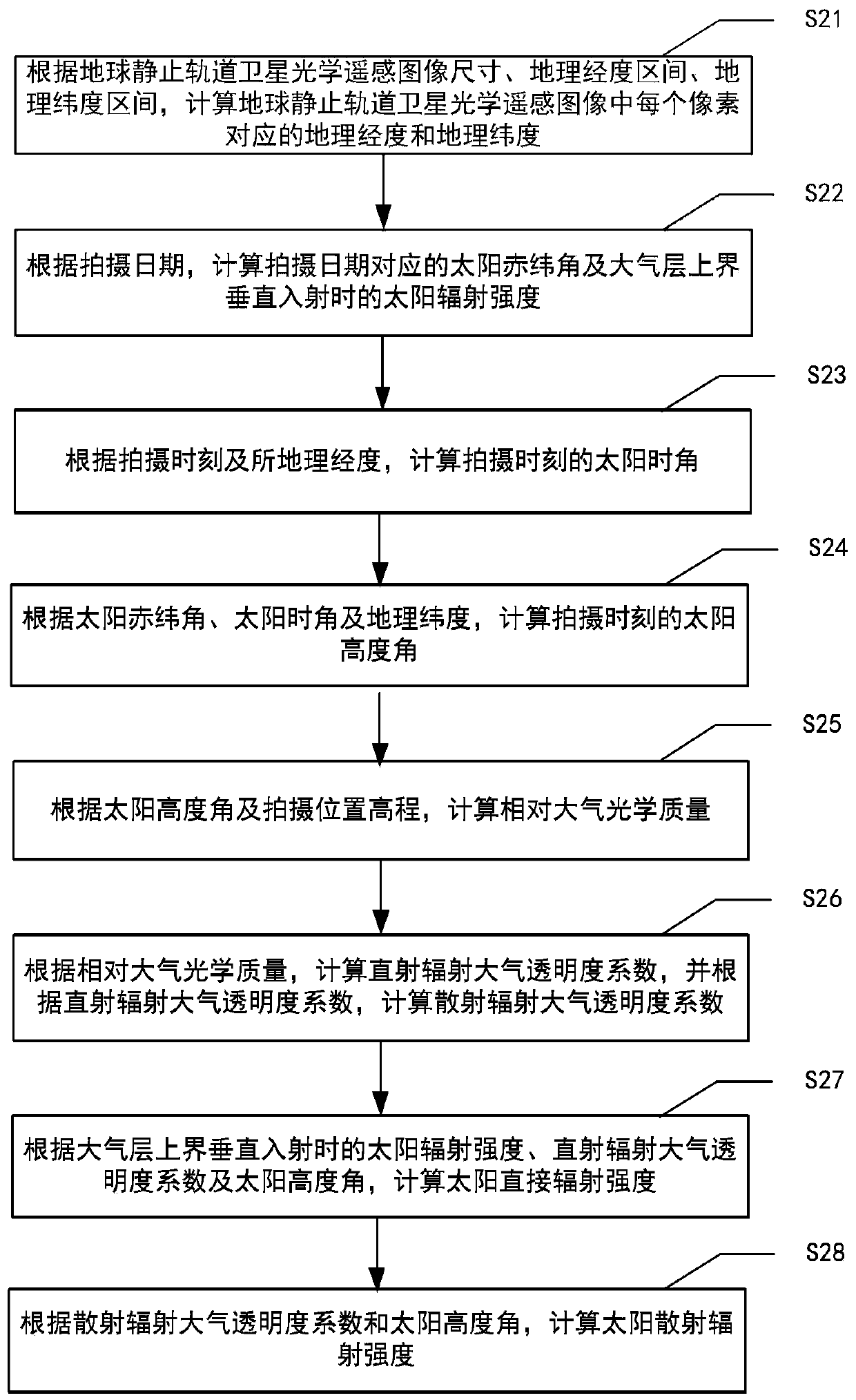
A calculation method for solar illumination compensation value, comprising: obtaining the size, geographic longitude interval, geographic latitude interval, shooting date, shooting time, and shooting location elevation of an optical remote sensing image of a geostationary satellite; according to the remote sensing image size, geographic longitude interval, geographic Latitude interval, shooting date, shooting time and shooting position elevation, calculate the direct radiation intensity and scattered radiation intensity of the shooting position of the optical remote sensing image of the geostationary satellite; according to the direct radiation intensity and scattered radiation intensity, calculate the Total solar irradiance; for the optical remote sensing images of geostationary satellites corresponding to different shooting dates, different shooting times, and shooting positions, calculate the difference between the corresponding total solar irradiance and obtain the optical data of each geostationary satellite. The solar illumination compensation value between each pixel of the remote sensing image. The method has low computational complexity, fast running speed and easy engineering implementation.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals
ActiveCN102591343BGood serviceFacilitate maintenance of control forecastsPosition/course control in two dimensionsNatural satelliteUltrasound attenuation
The invention relates to a satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals, which comprises the following steps of: calculating two lines of radical data disclosed by a satellite by utilizing a SGP4 orbit determination model, calculating and obtaining a geographical latitude and a geographical longitude of a sub-satellite point of the satellite and comparing with an agreed ground nominal track. Through taking the duration of a first sample opposite to an orbit epoch moment as an independent variable and taking the ground track distance difference as a variable, all samples are subjected to quadratic curve fitting by using an average method; the difference delta at between an actual value of a satellite orbit semi-major axis and a nominal value by a latest sample moment as well as the average attenuation rate of the satellite orbit semi-major axis within the time interval of the sample are calculated and obtained through a fitting polynomial coefficient; and finally, the next orbit control time Tc as well as the control quantity delta af required to be used are predicted and obtained by utilizing a fitted secondary curve and an allowable drift range [-delta Lmax and delta Lmax] to ensure that the position of an actual ground track within the satellite next drift period opposite to a ground nominal track is within the allowrable drift range.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
A Modeling Method of Ionospheric Vertical Total Electron Content Based on Ellipsoid Harmonic Theory
ActiveCN108491616BDescribe nonlinear vibration characteristicsHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSatellite radio beaconingGeographical latitudeIonosphere
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Sun illumination compensation value calculation method
ActiveCN111413278AReduce computational complexityRun fastMethod using image detector and image signal processingDesign optimisation/simulationGeostationary orbitGeographical latitude
The invention discloses a sun illumination compensation value calculation method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the size, geographic longitude interval, geographic latitude interval, shooting date, shooting moment and shooting position elevation of an optical remote sensing image of a geostationary orbit satellite; calculating the direct radiation intensity and the scatteredradiation intensity of the shooting position of the geostationary orbit satellite optical remote sensing image according to the remote sensing image size, the geographic longitude interval, the geographic latitude interval, the shooting date, the shooting moment and the shooting position elevation; calculating the total solar radiation intensity of the optical remote sensing image of the geostationary orbit satellite according to the direct radiation intensity and the scattered radiation intensity; aiming at the geostationary orbit satellite optical remote sensing images corresponding to different shooting dates, different shooting time and different shooting positions, calculating the difference value between the corresponding solar total irradiation intensities to obtain the solar illumination compensation value between the pixels of each geostationary orbit satellite optical remote sensing image. The method is low in calculation complexity, high in operation speed and easy for engineering realization.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com