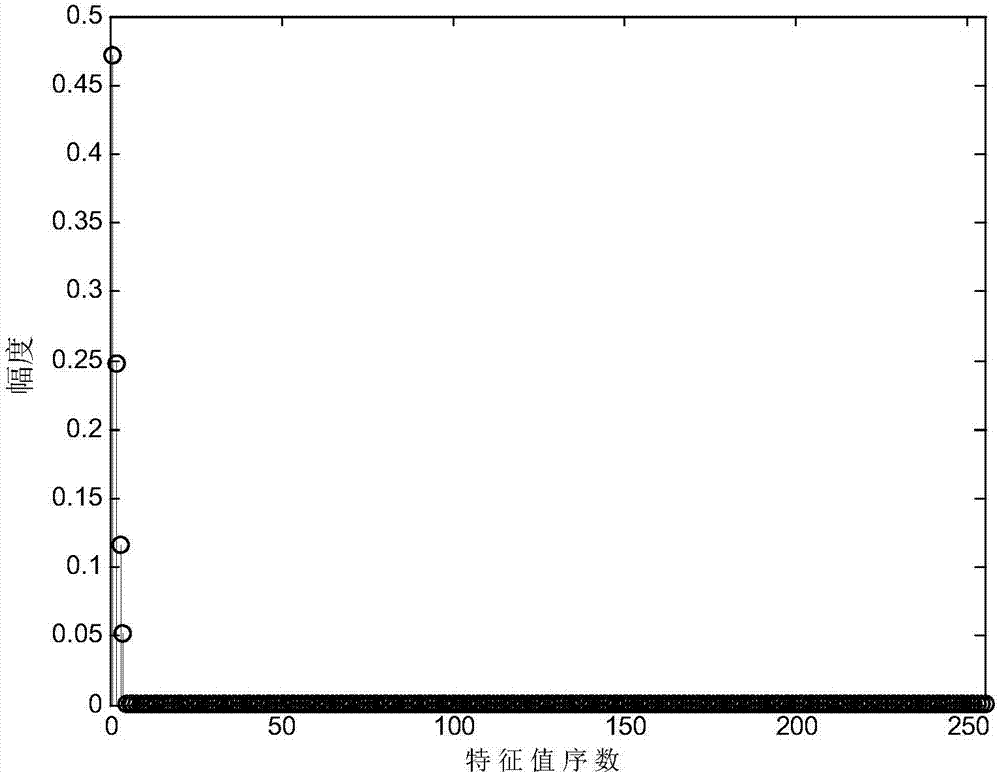
Pseudo-code sequence blind estimation of synchronous DS-CDMA (Direct Sequence-Code Division Multiple Access) signal containing residual frequency offsets
A DS-CDMA and pseudo-code sequence technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, error prevention, etc., can solve the problem of difficult estimation of the pseudo-code sequence of synchronous DS-CDMA signals, and achieve the effect of easy implementation and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The implementation of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific examples.
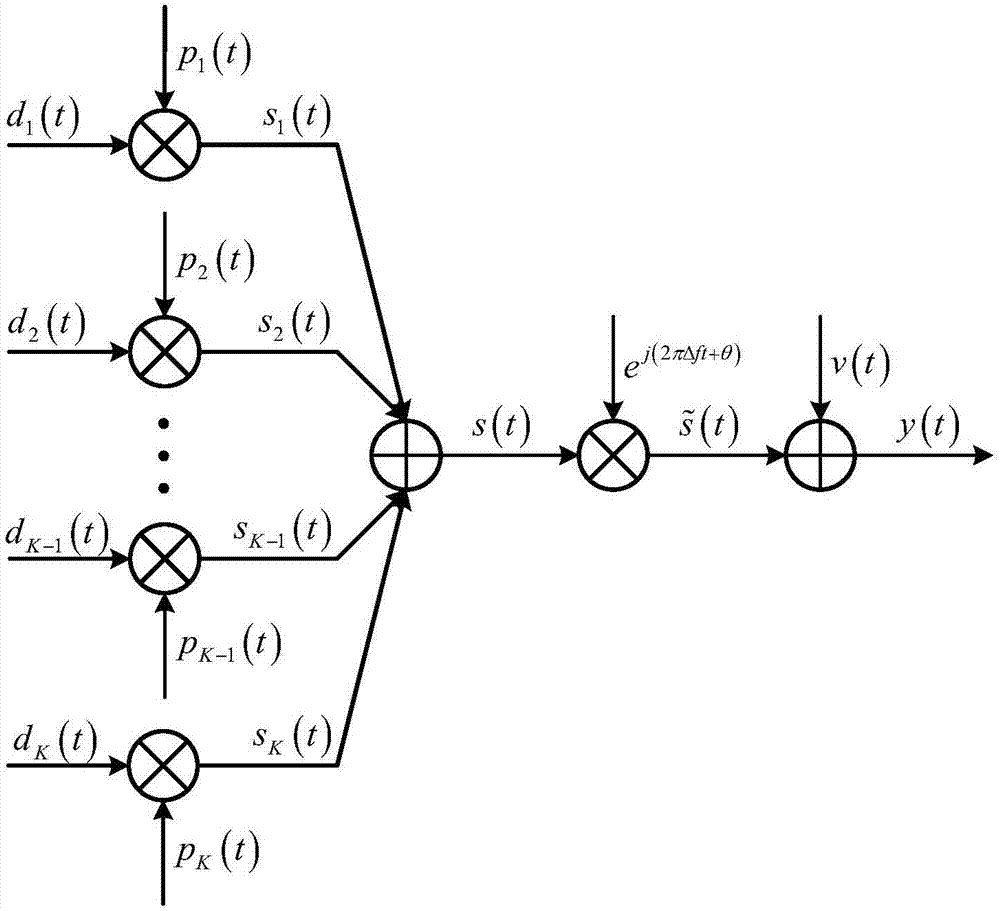
[0029] figure 1 A schematic diagram representing a synchronous DS-CDMA communication system. There are K users in this figure, and each user uses short code spread spectrum, where d k (t), p k (t), s k (t) respectively represent the information sequence, pseudo code sequence and spread spectrum signal of the kth user, Δf represents the residual frequency offset, and θ∈[0,2π] represents the random initial phase. The signals of K users are superimposed together to form the synchronous DS-CDMA signal with residual frequency offset.
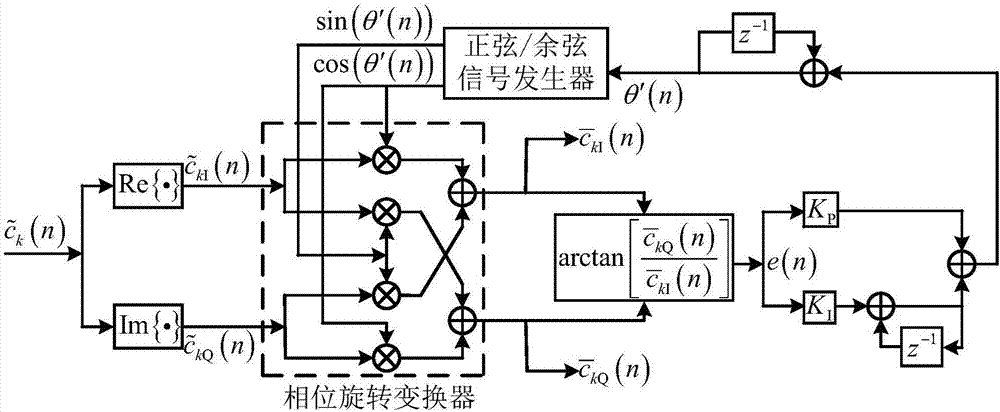
[0030] figure 2 Represents the working principle diagram of DPLL. The DPLL is composed of a sine / cosine signal generator, a phase rotation converter, a phase detector, and a loop filter. Sending the real part and imaginary part of the pseudo code sequence of the kth user's rough estimation into...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com