Patents
Literature
877results about "Anchors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
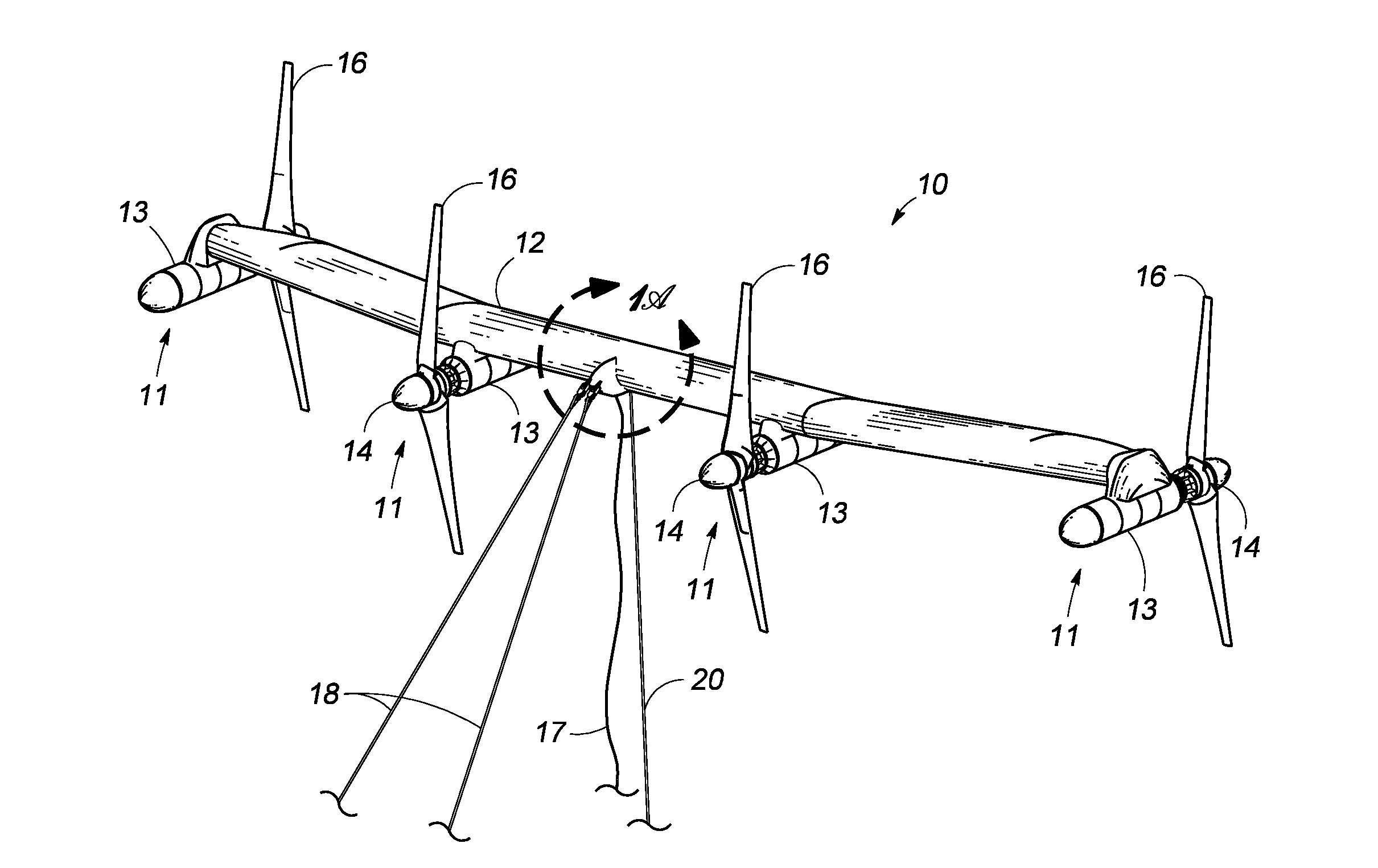
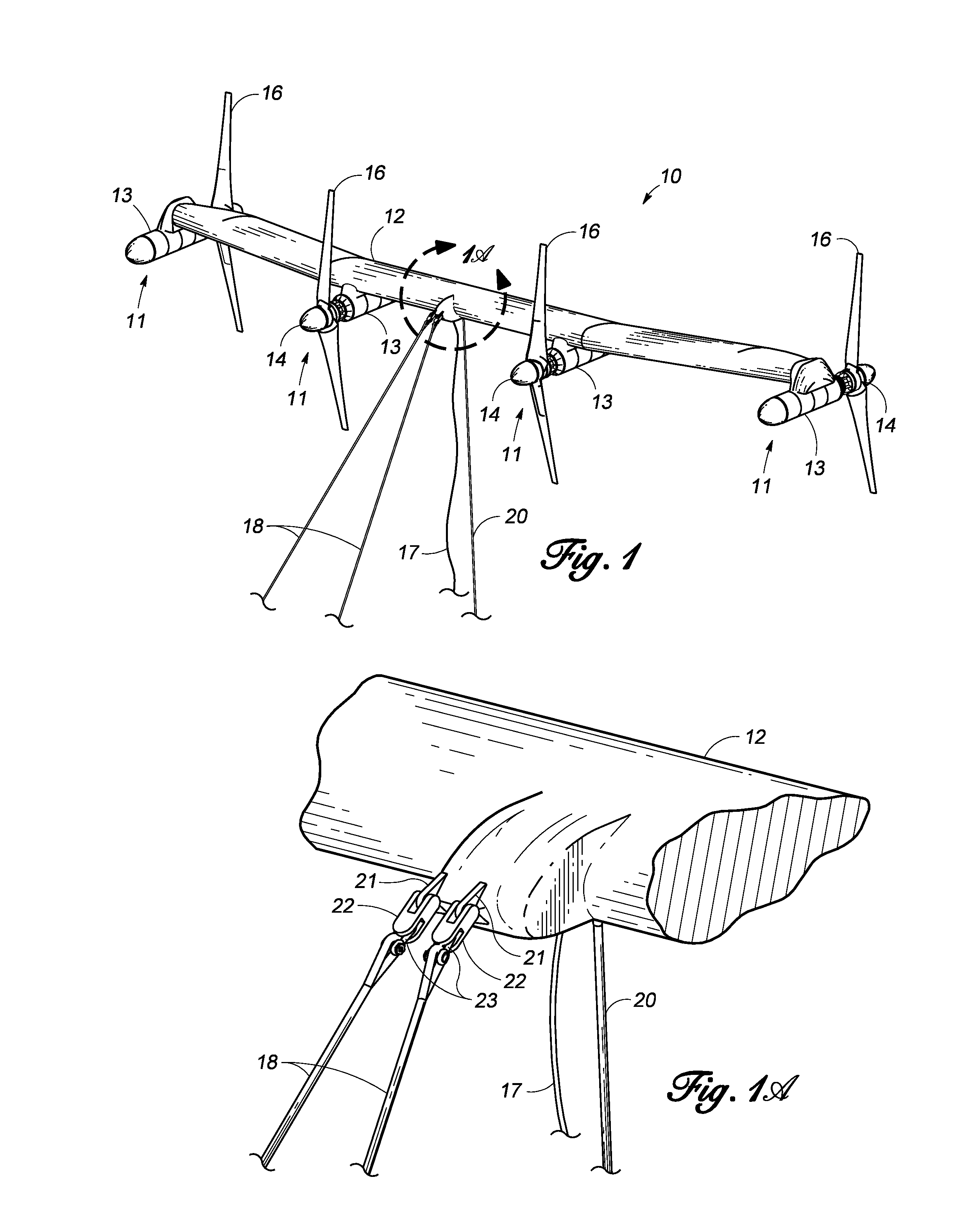
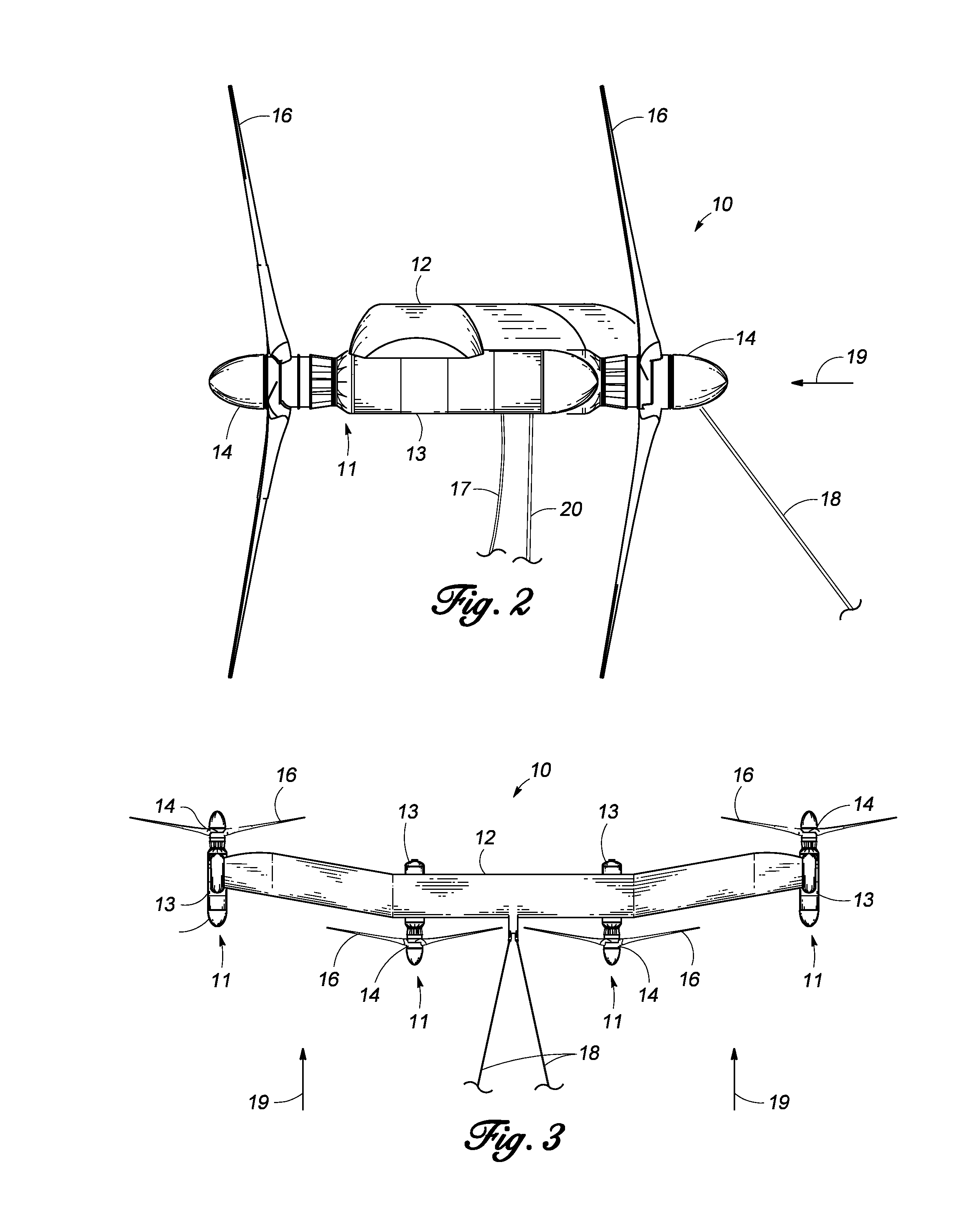
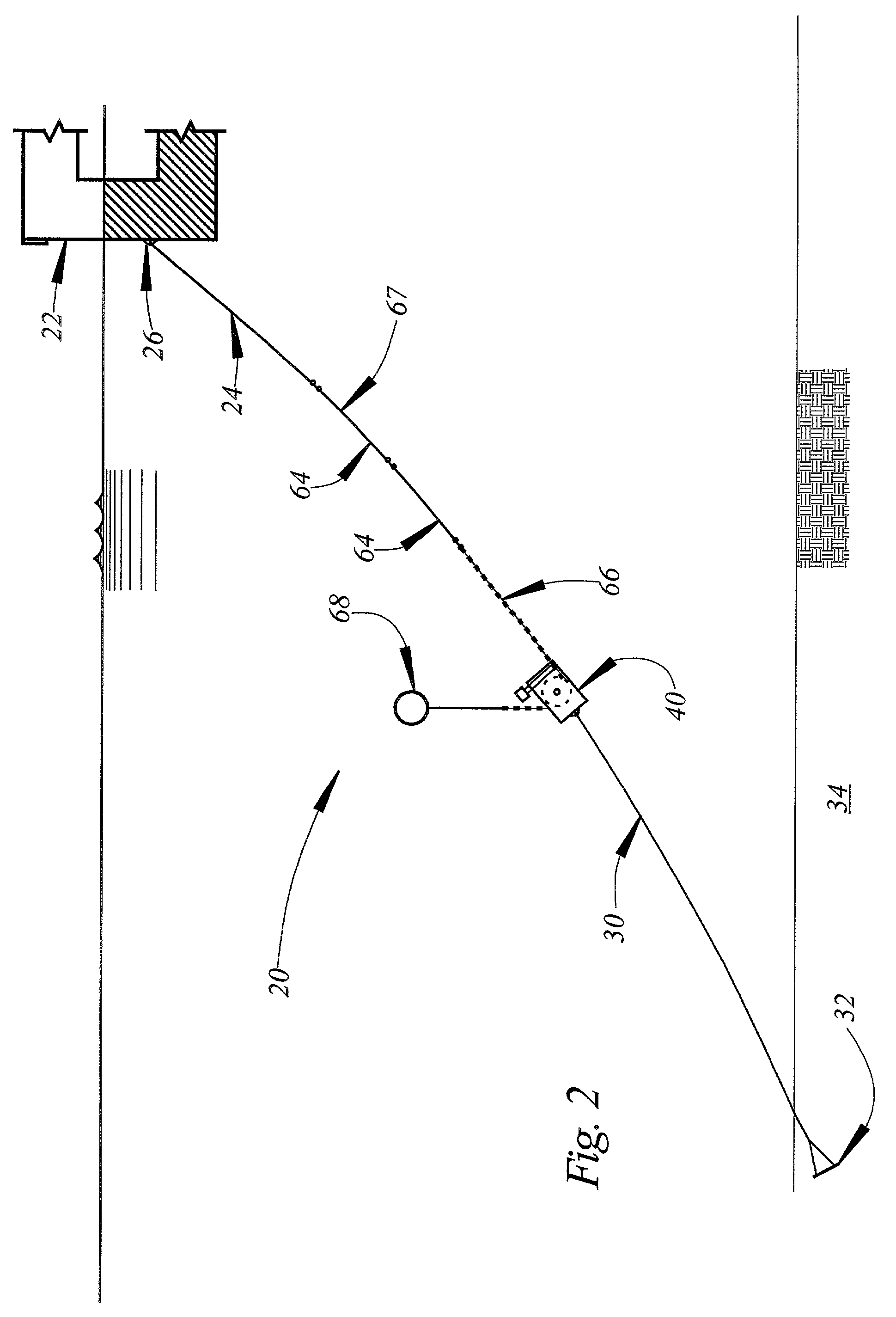
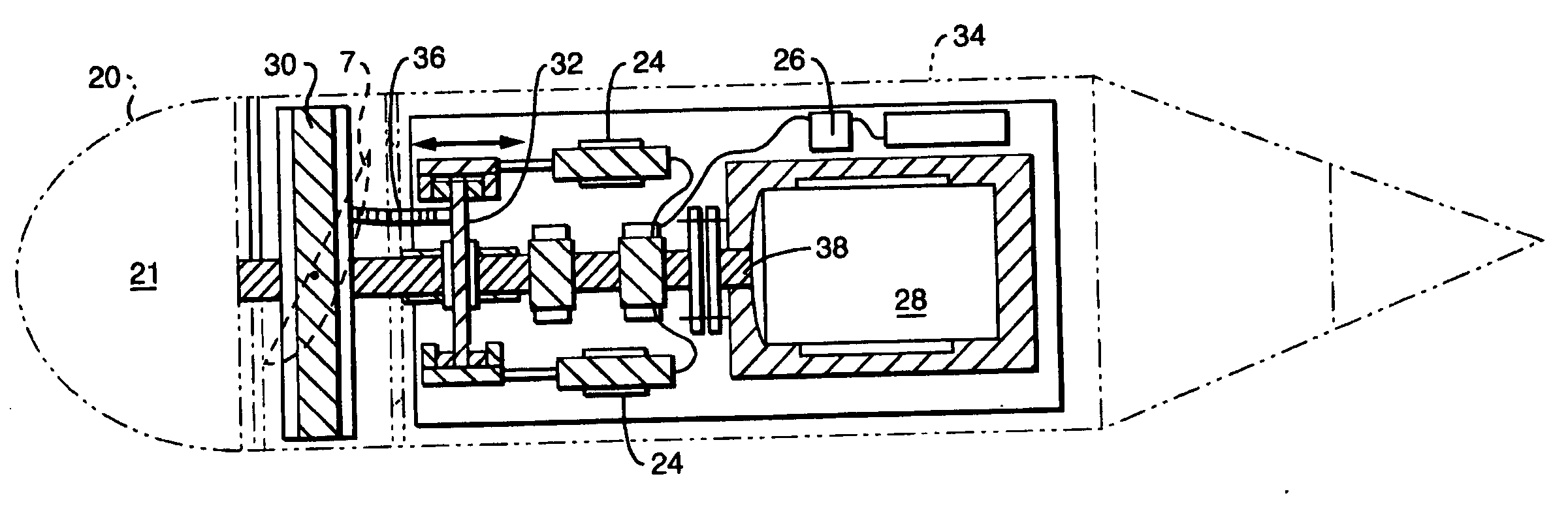
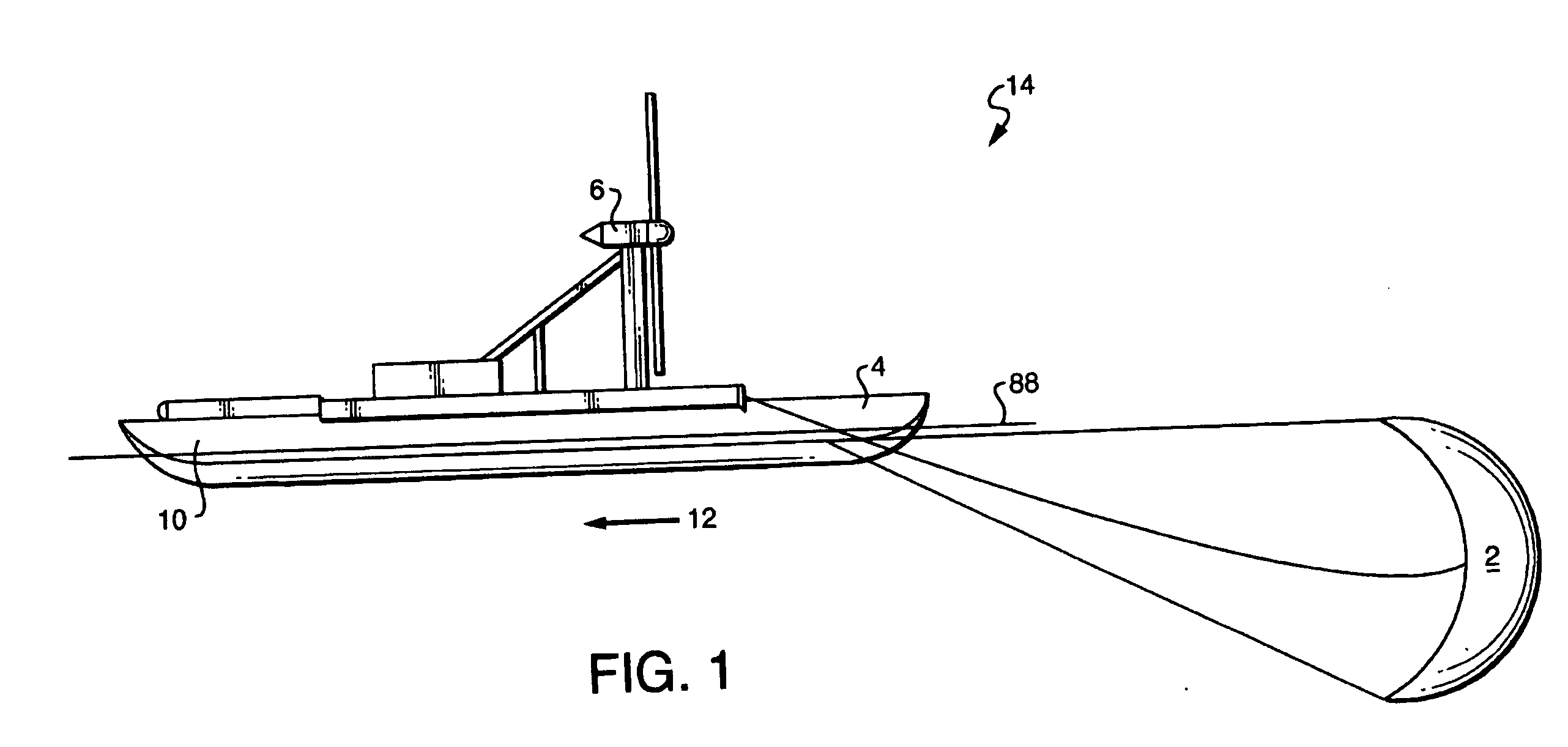
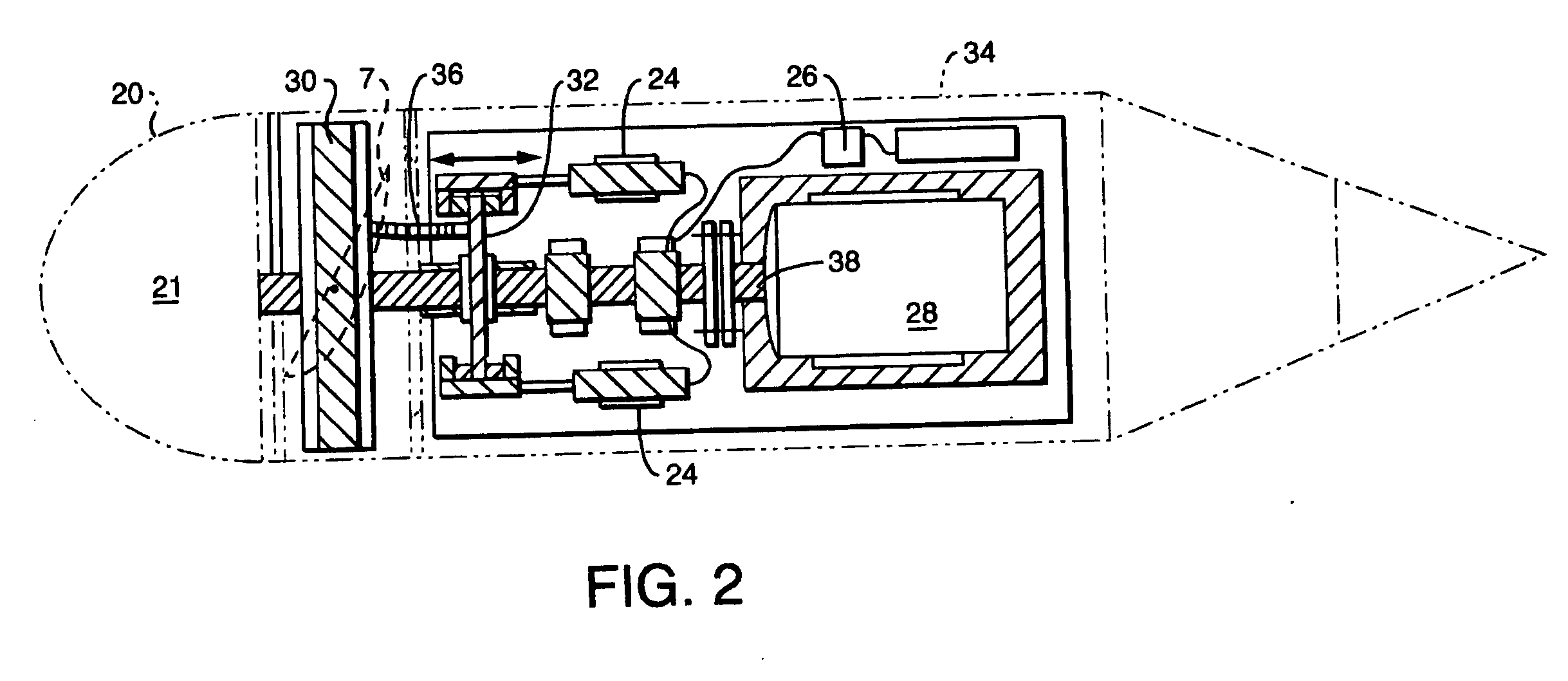
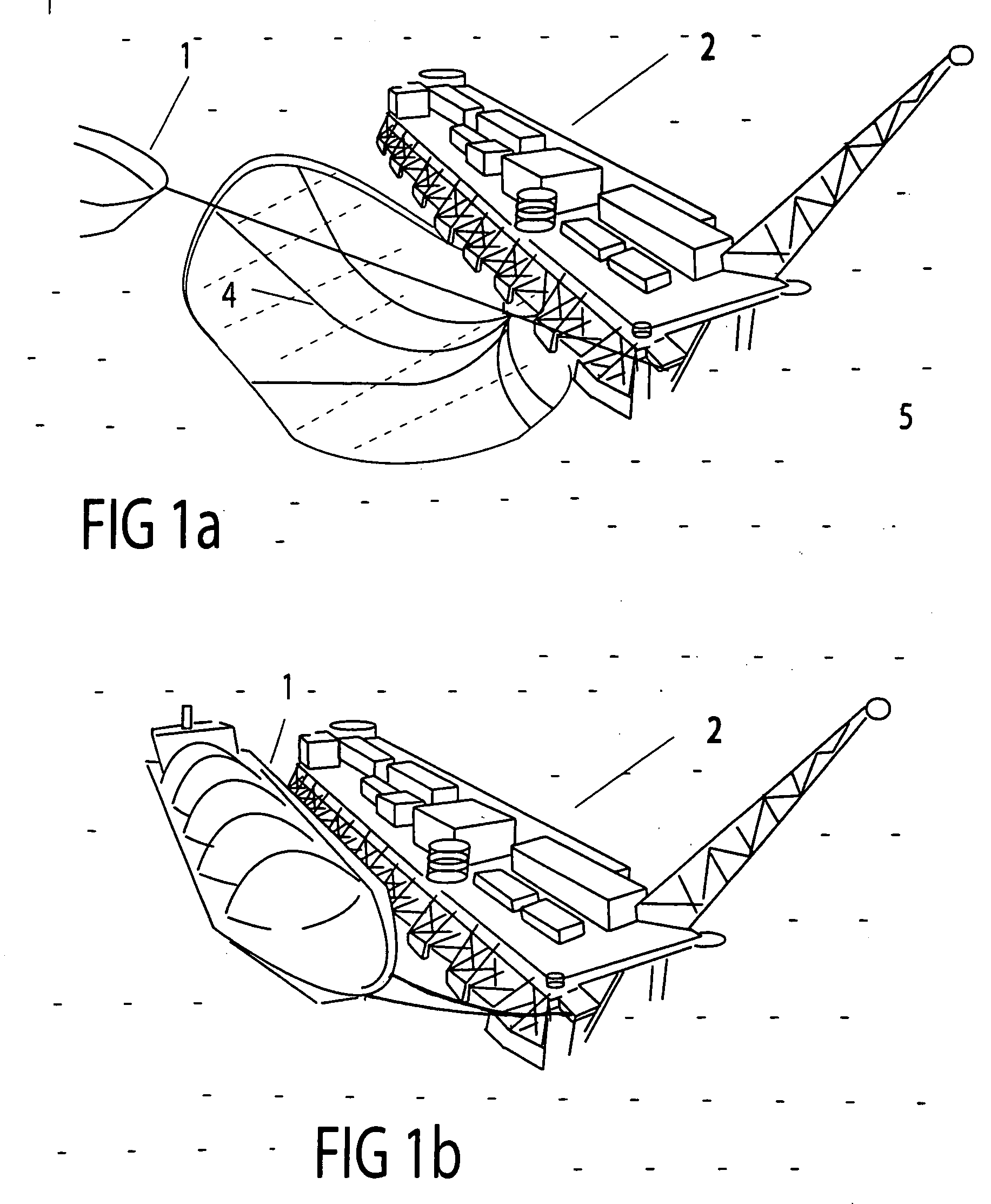
Unmanned ocean vehicle
ActiveUS20070051292A1Long range of operationDrawback can be addressedPropulsion based emission reductionPower plants using propulsion unit combinationsCommunications systemHybrid propulsion
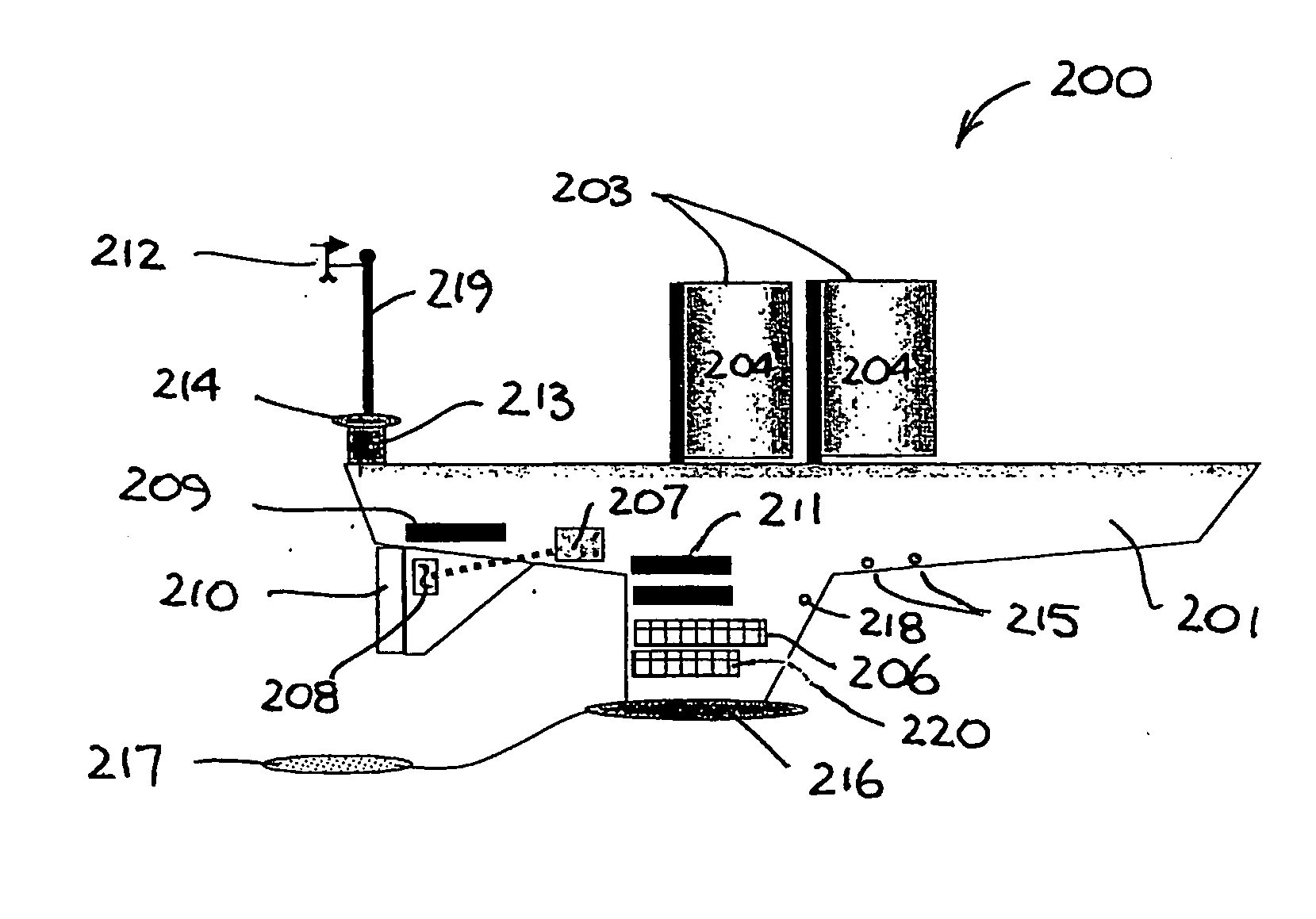
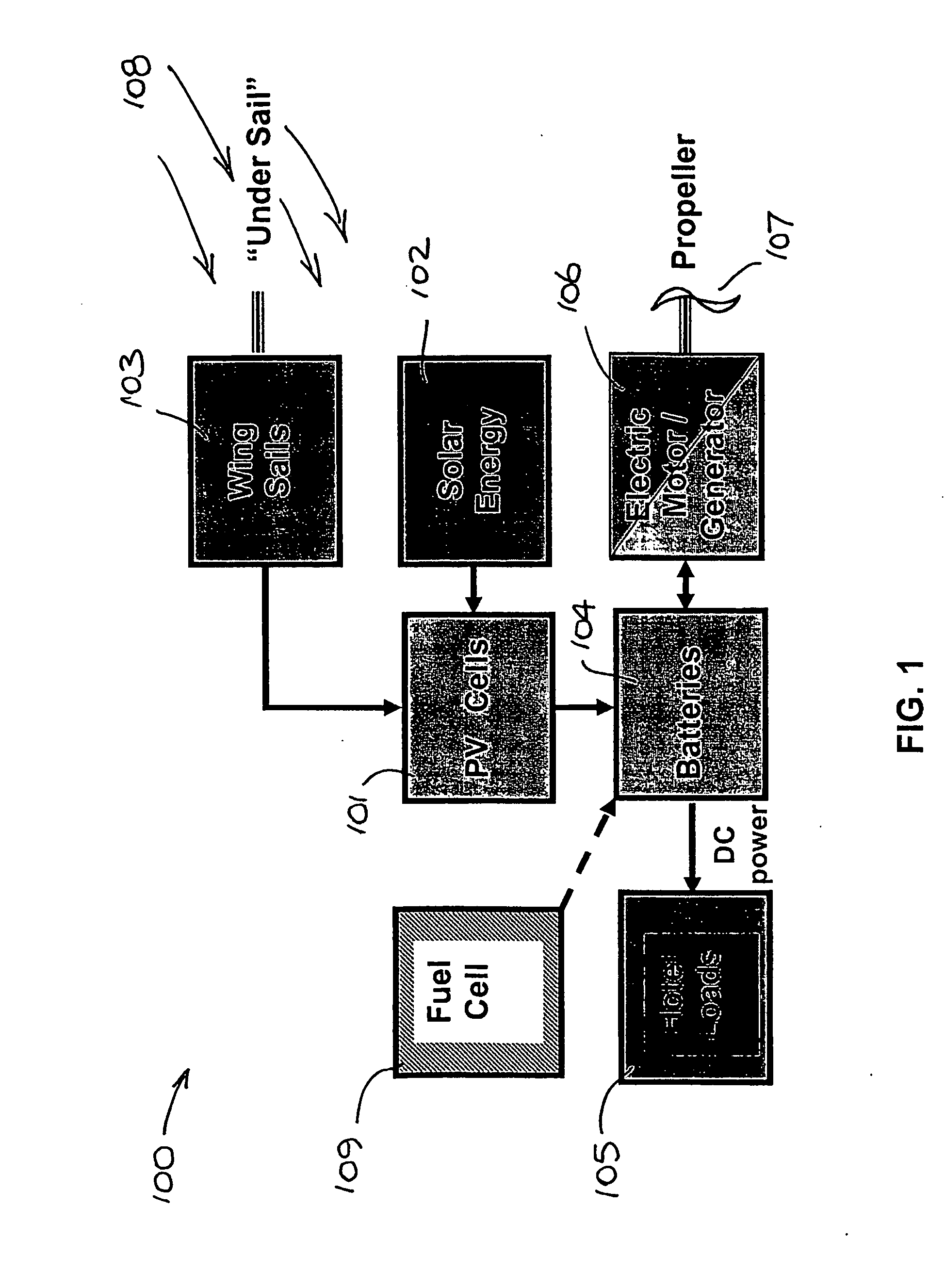
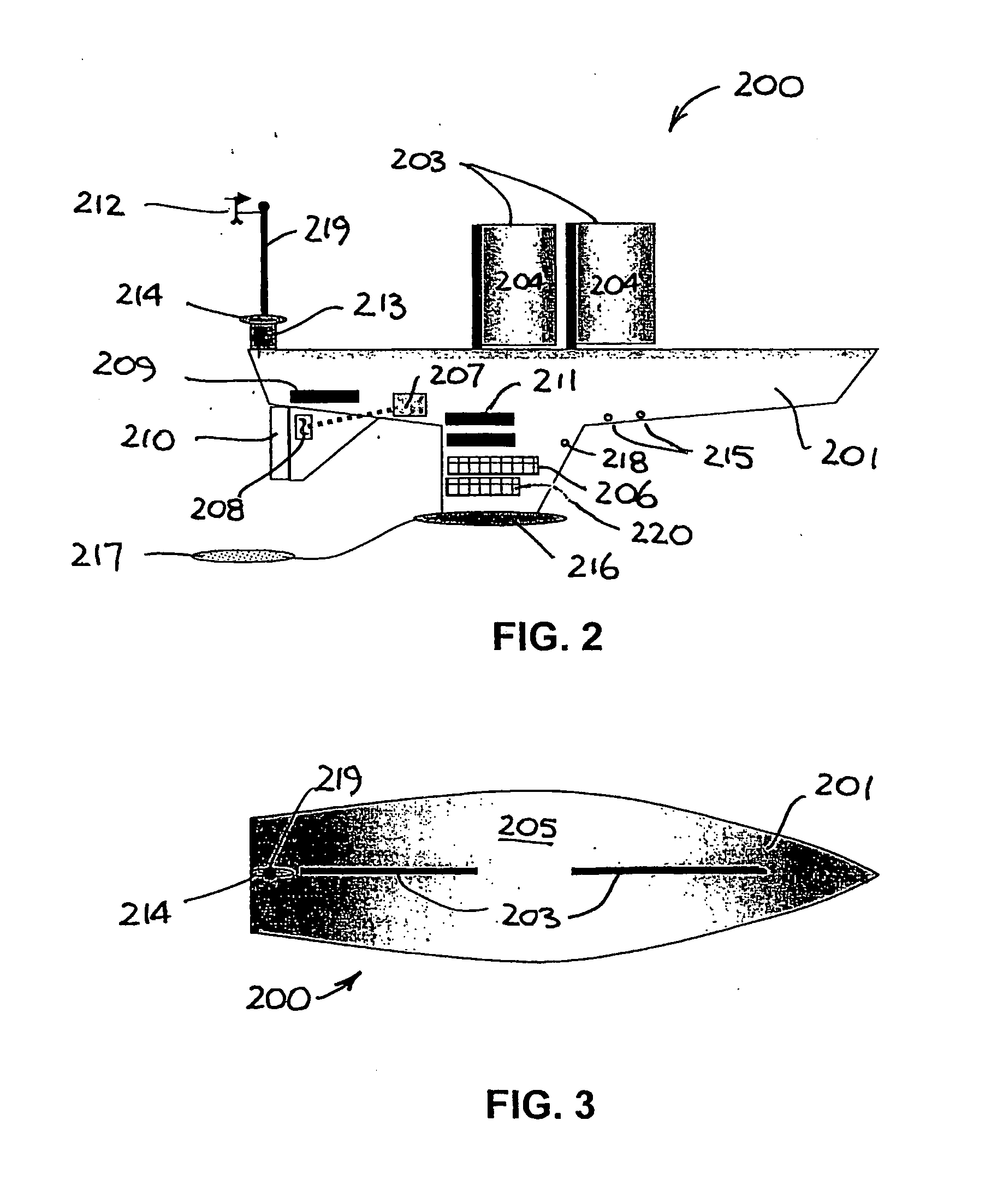
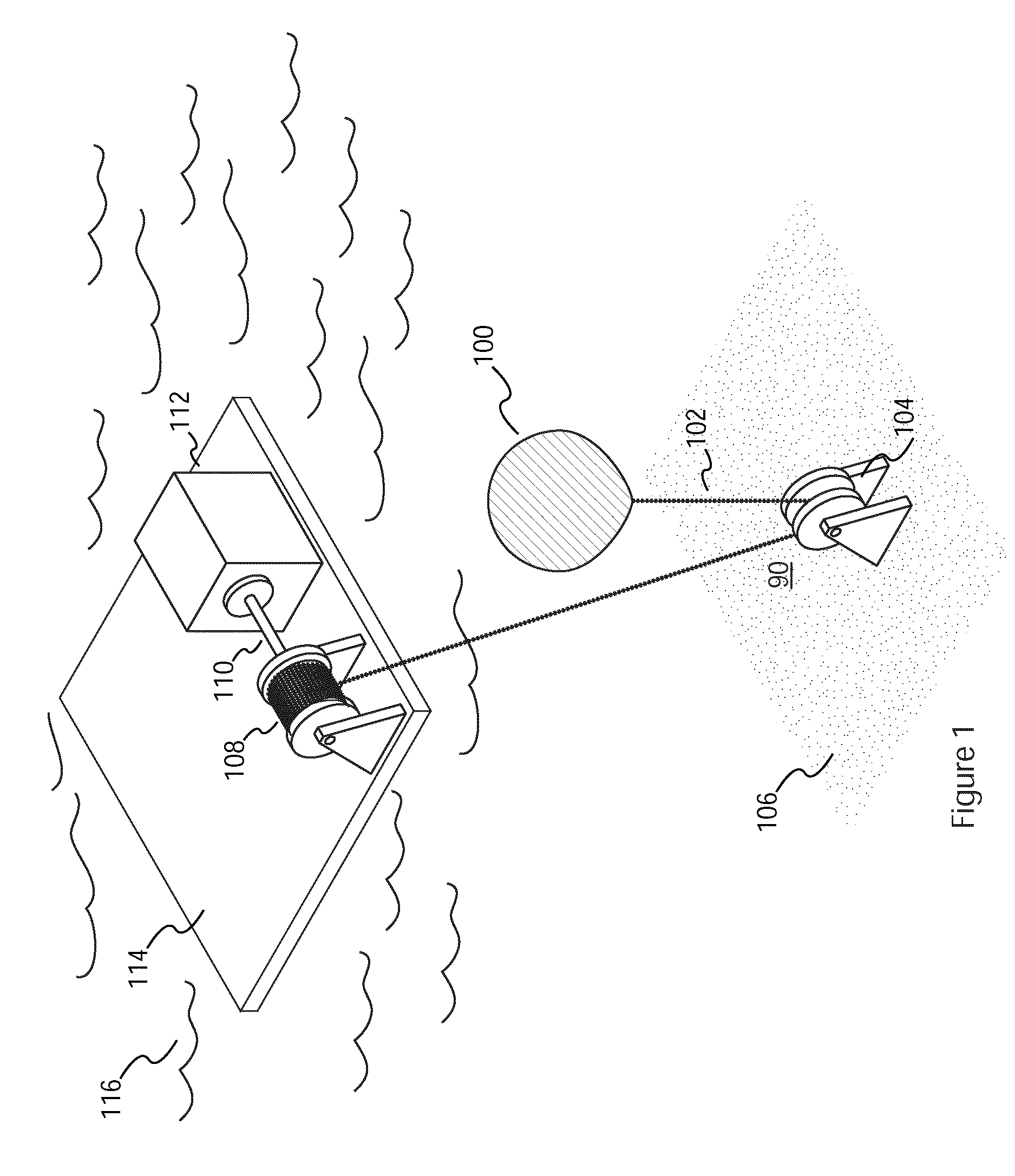
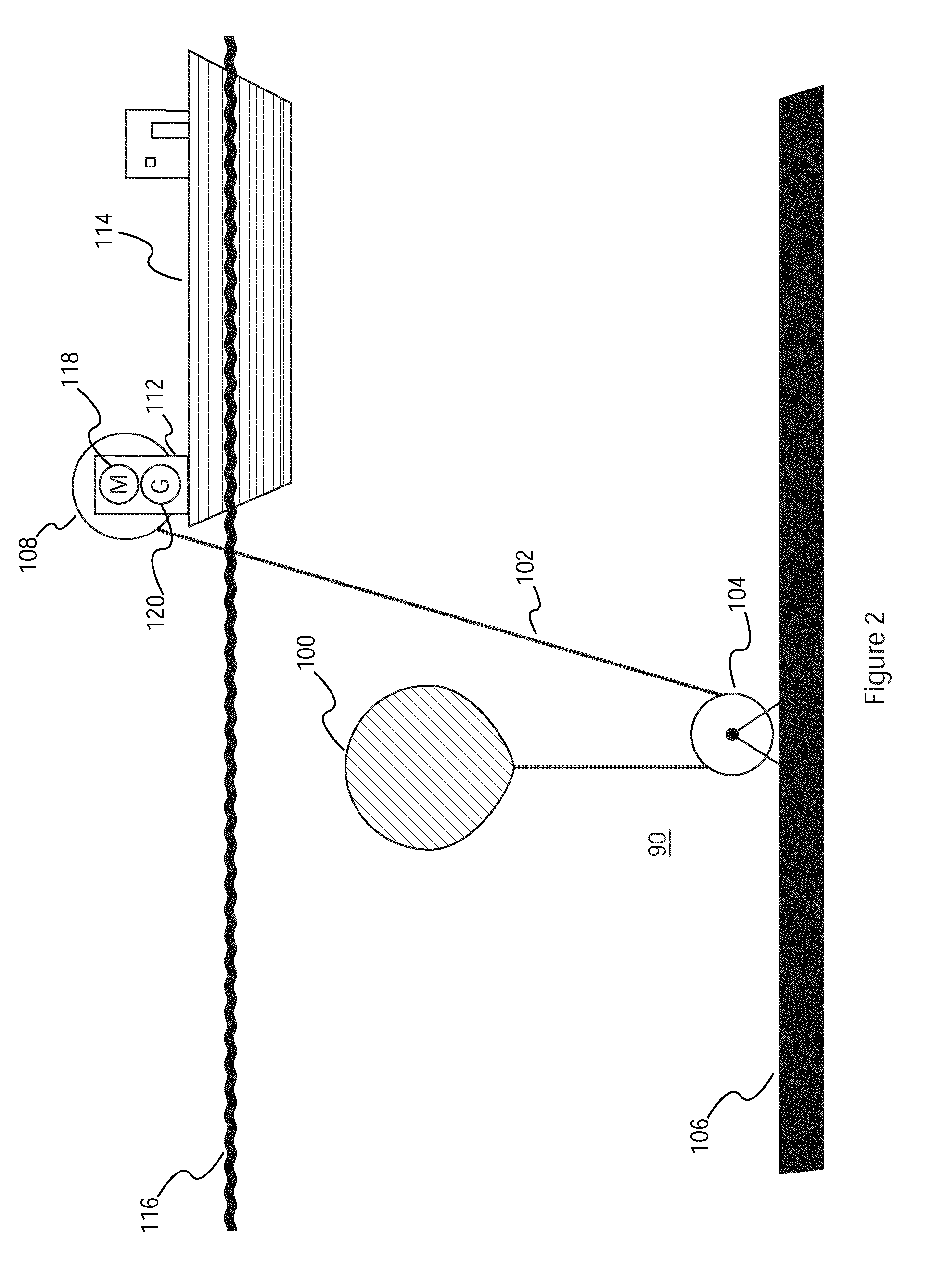
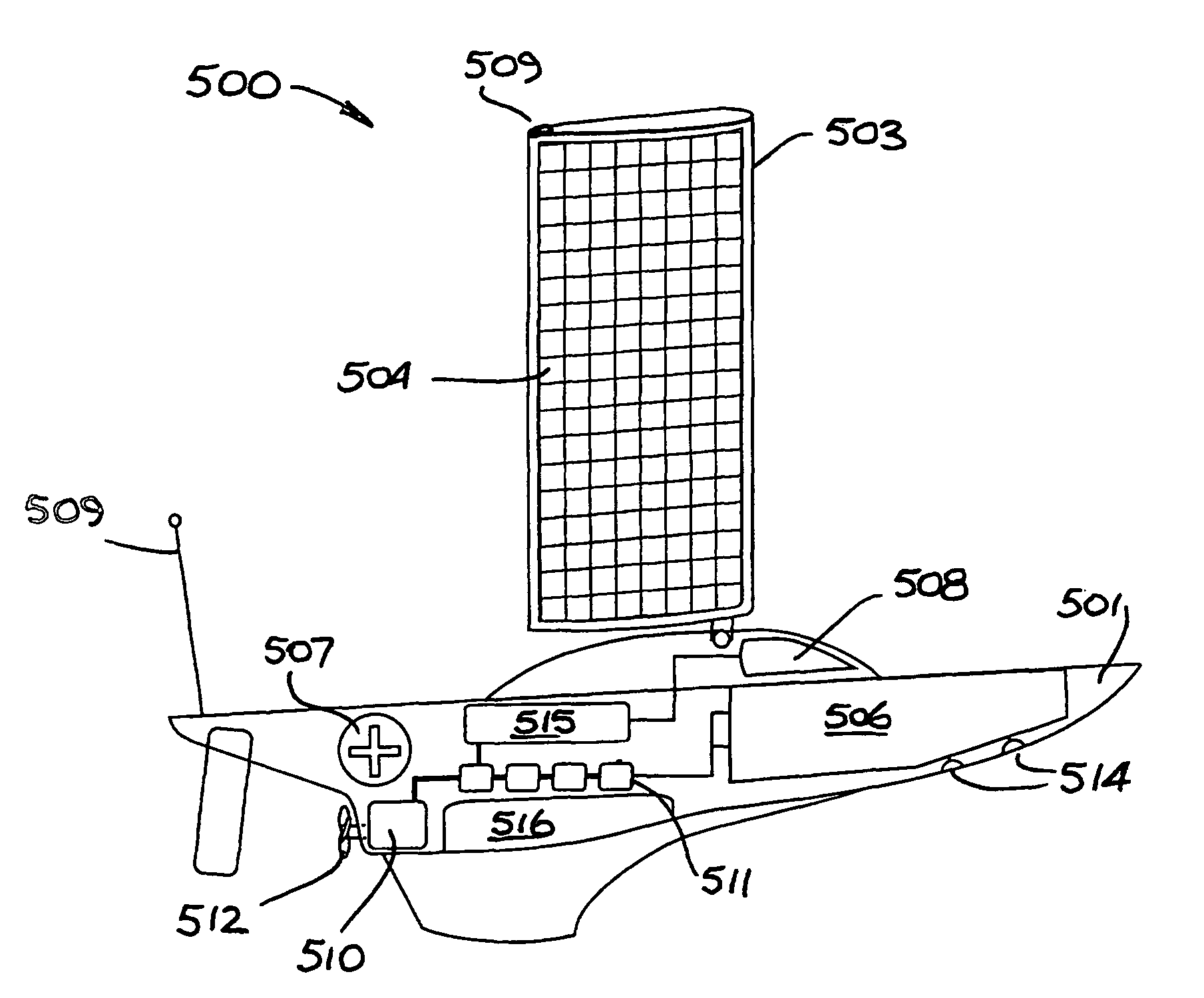
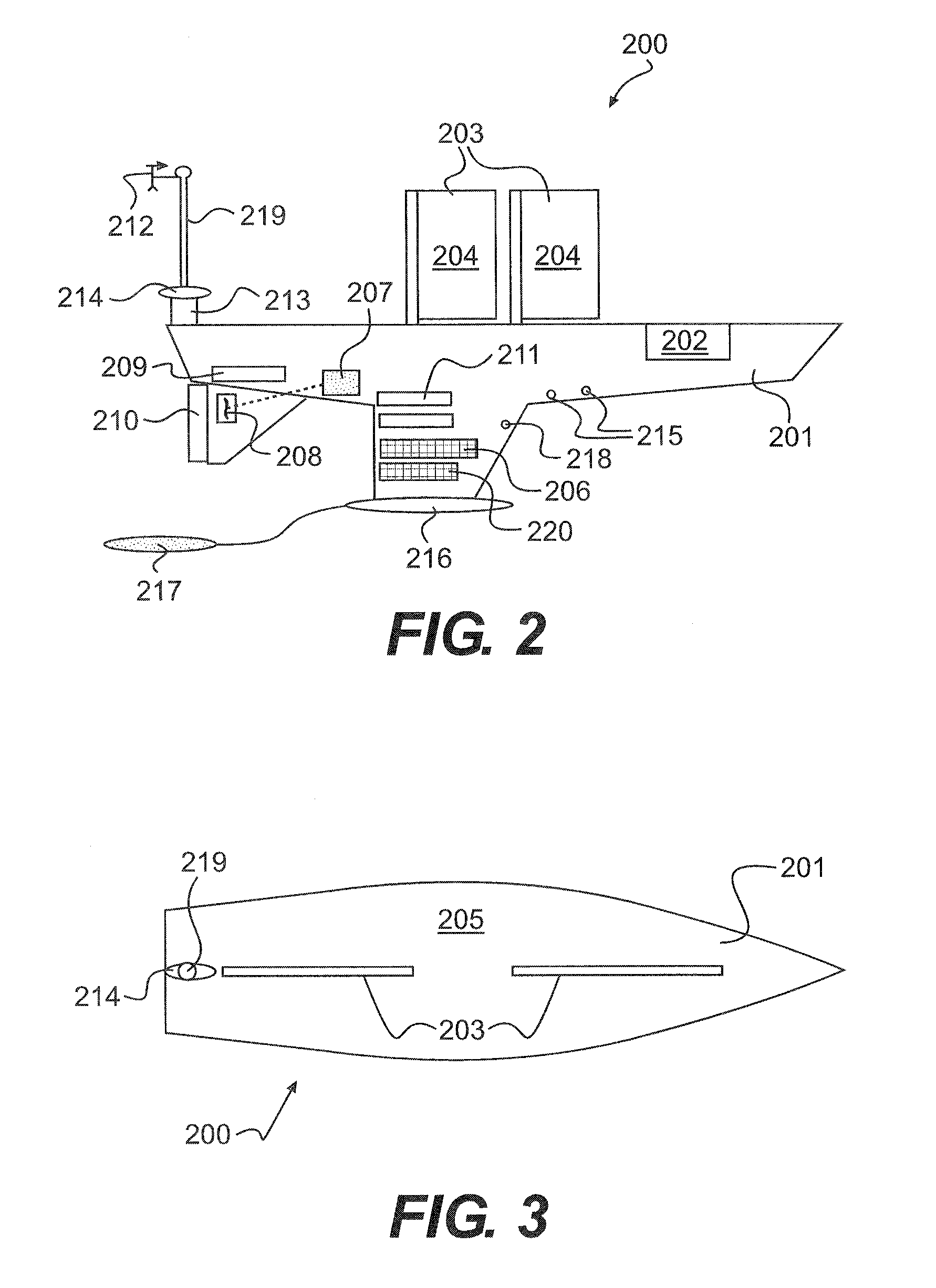
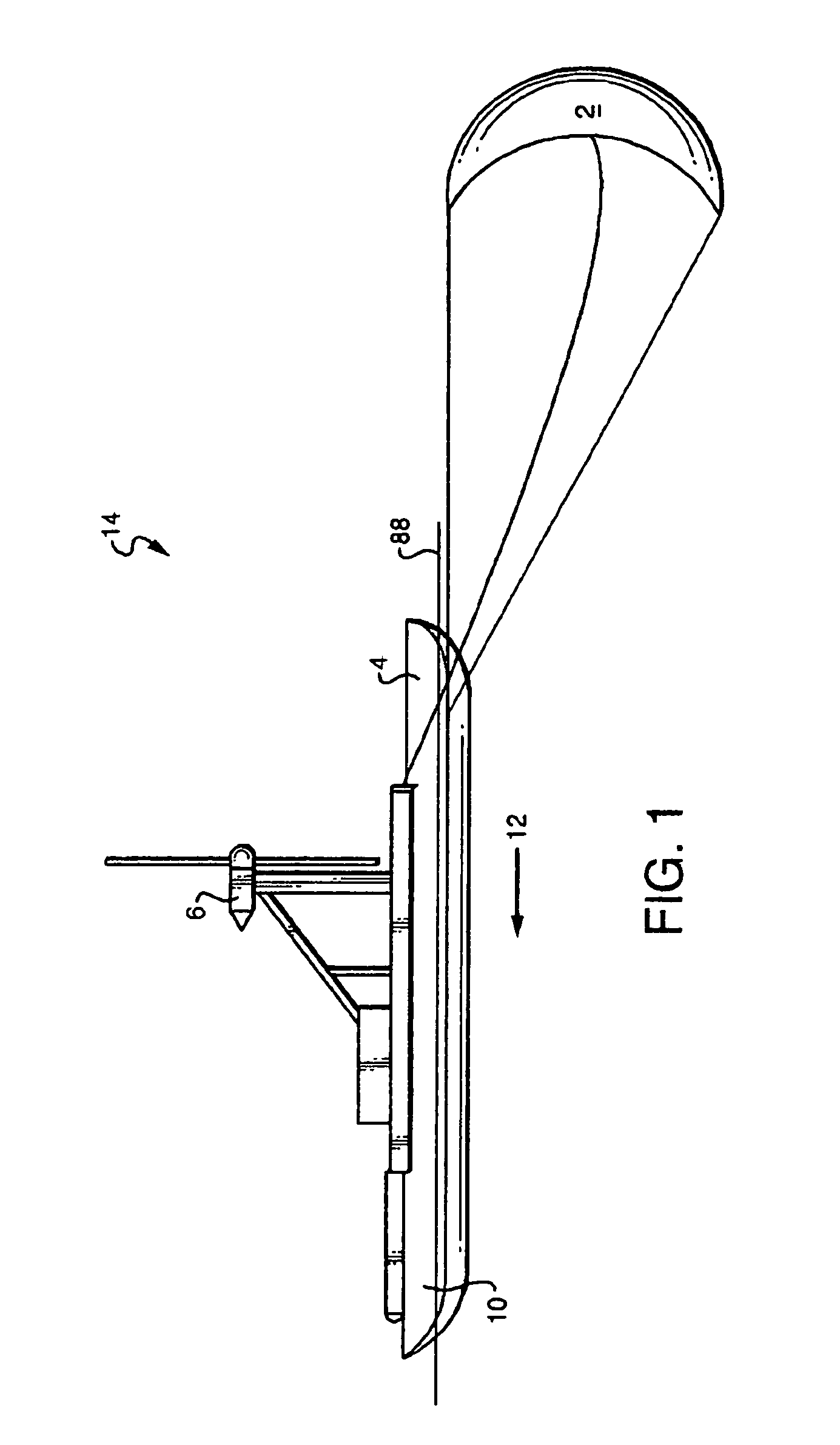
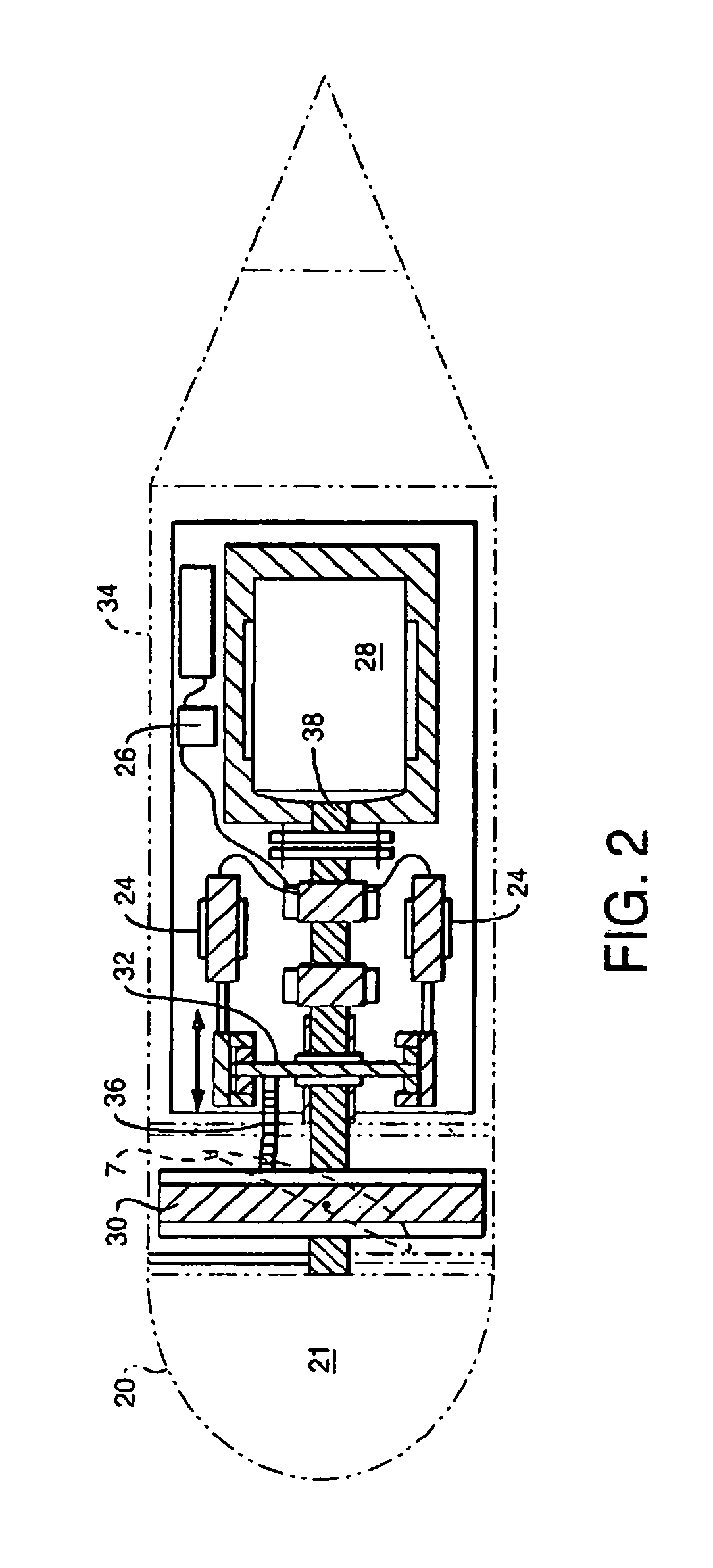
An unmanned, autonomous, waterborne vehicle (500) for marine use capable of operating on and below the surface of water, said vehicle (500) including an enclosed hull (501) having a payload bay (506), a hybrid propulsion system having energy collection means (504) in the form of a wing sail (503) covered with photovoltaic cells and energy storage means (511) for utilising at least solar energy and wind energy, a plurality of sensors (508, 514) for detecting predetermined environmental parameters and a communications system (509, 515) for transmitting data from said sensors (508, 515) to and for receiving command signals from one or more remote stations and / or cooperating vehicles.
Owner:SOLAR SAILOR PTY LTD
Buoyancy energy storage and energy generation system
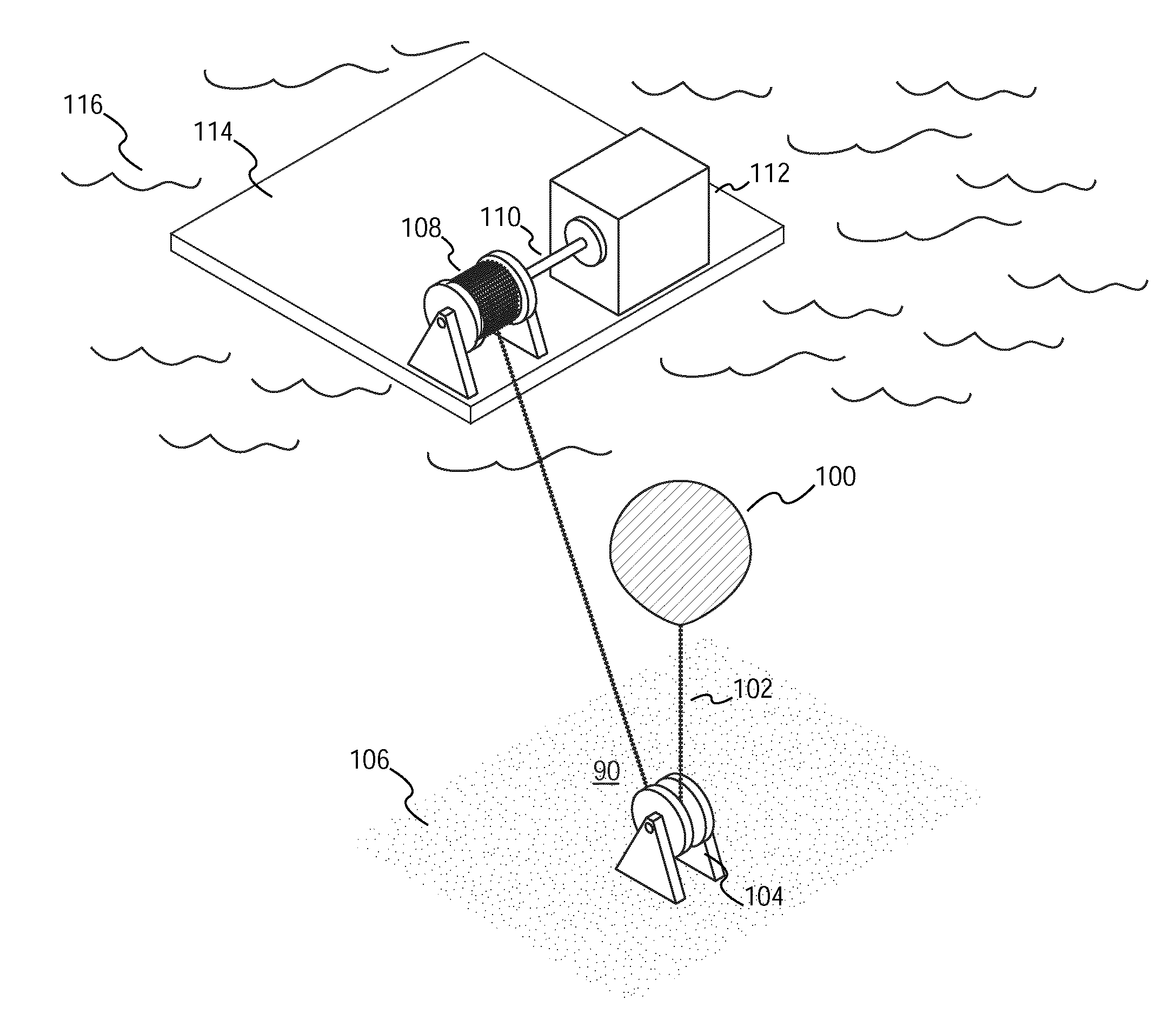
An energy generation and storage system that uses a buoyant balloon suspended in a fluid and connected by a tether to a reel. The tether is taut and keeps the balloon from rising due to the buoyant force. A motor can do work to wind the reel in such a way that the balloon is pulled down against the buoyant force. Energy can be extracted from the system by allowing the balloon to rise, pulling on the tether and turning the reel that is connected to a generator. The generator and the motor can be the same unit, or they can be independent units which both connect to the reel.
Owner:MORGAN SOLAR INC
Unmanned ocean vehicle
ActiveUS7789723B2Reduce the UOV's dragExpand the scope of operationPropulsion based emission reductionPower plants using propulsion unit combinationsCommunications systemMarine engineering
An unmanned, autonomous, waterborne vehicle (500) for marine use capable of operating on and below the surface of water, said vehicle (500) including an enclosed hull (501) having a payload bay (506), a hybrid propulsion system having energy collection means (504) in the form of a wing sail (503) covered with photovoltaic cells and energy storage means (511) for utilizing at least solar energy and wind energy, a plurality of sensors (508, 514) for detecting predetermined environmental parameters and a communications system (509, 515) for transmitting data from said sensors (508, 515) to and for receiving command signals from one or more remote stations and / or cooperating vehicles.
Owner:SOLAR SAILOR PTY LTD
Water-based wind-driven power generation using a submerged platform
InactiveUS7242107B1Remarkable effectUsable energyWind motor supports/mountsMachines/enginesWater basedWind driven
Provided are systems, methods and techniques by which a wind-powered energy generating platform, secured to an anchor, can pull (or winch) itself beneath the surface of the water and thereby avoid most of the significant effects of storms and waves. In more particularized aspects, a variable-buoyancy anchor is utilized, thereby facilitating the construction and transportation of the entire assembly.
Owner:DEMPSTER HARRY EDWARD
Multi-Megawatt Ocean Current Energy Extraction Device
InactiveUS20130106105A1Counteract buoyancyReduce the average velocityEngine fuctionsBuoyancy controlOcean bottomDrivetrain
An underwater apparatus for generating electric power from ocean currents and deep water tides. A submersible platform including two or more power pods, each having a rotor with fixed-pitch blades, with drivetrains housed in pressure vessels that are connected by a transverse structure providing buoyancy, which can be a wing depressor, hydrofoil, truss, or faired tube. The platform is connected to anchors on the seafloor by forward mooring lines and a vertical mooring line that restricts the depth of the device in the water column. The platform operates using passive, rather than active, depth control. The wing depressor, along with rotor drag loads, ensures the platform seeks the desired operational current velocity. The rotors are directly coupled to a hydraulic pump that drives at least one constant-speed hydraulic-motor generator set and enables hydraulic braking. A fluidic bearing decouples non-torque rotor loads to the main shaft driving the hydraulic pumps.
Owner:AQUANTIS
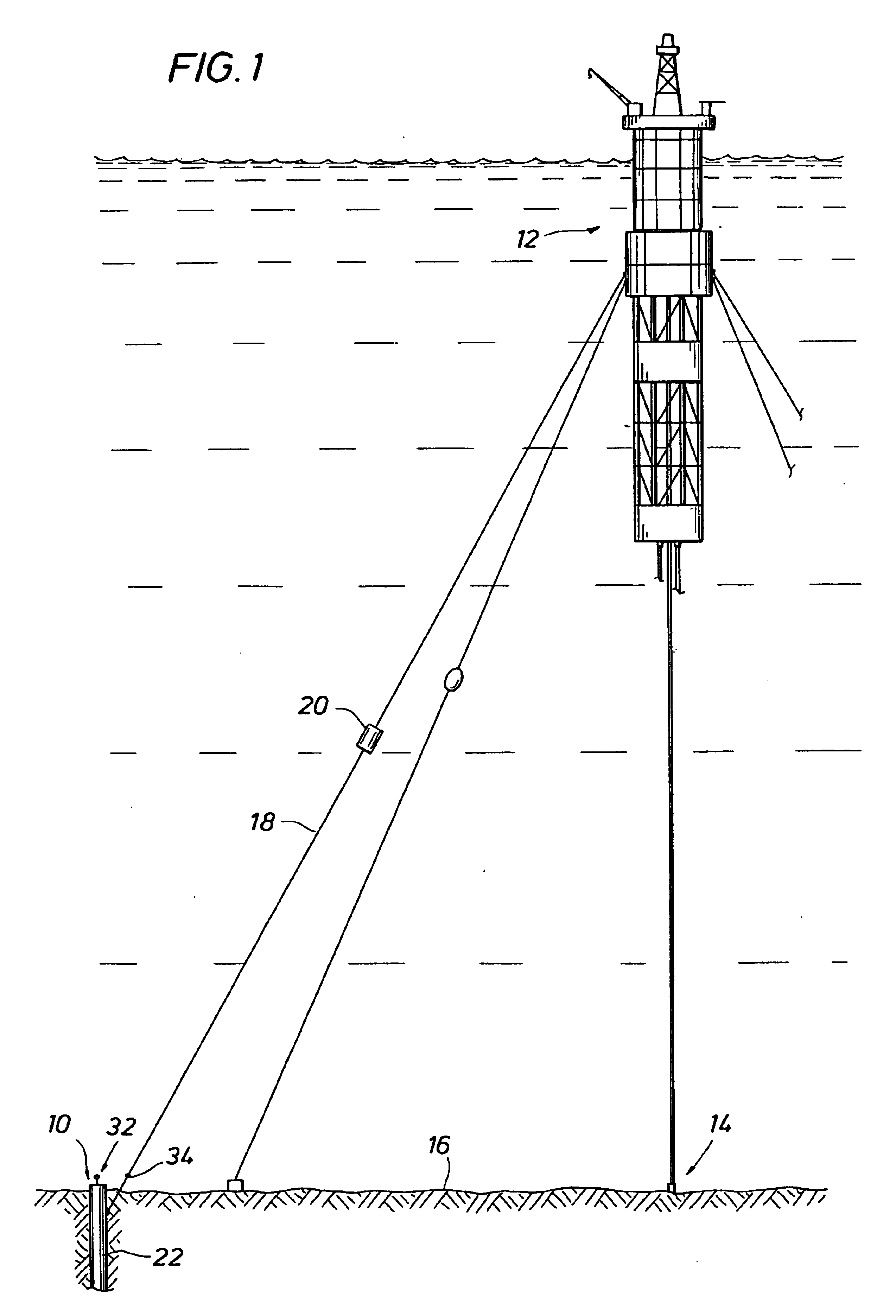
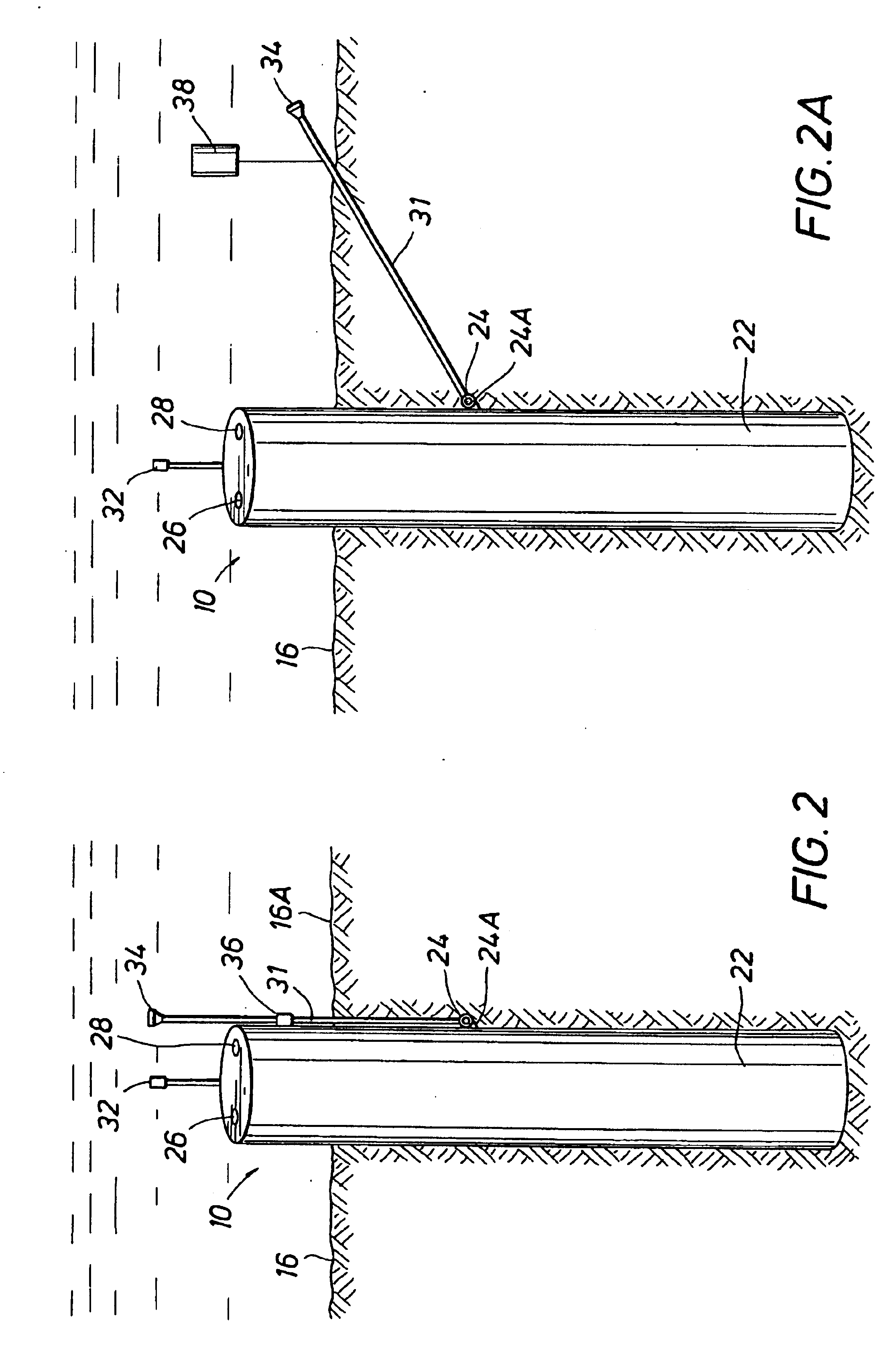
ROV installed suction piles
A method is disclosed for deploying a suction pile anchor in which flood valves are opened on the top of a suction pile and the suction pile anchor is off loaded from the anchor boat and lowered it to the sea floor. The suction pile anchor is set down and the rate of feed is adjusted to match the rate of self-penetration. An ROV with pump capability closes the flood valves on the top of the suction pile and attaches to the pumping port of the suction pile. The pump of the ROV operates to draw down the suction pile to full depth and brings the first load line connection and the attached first end of the load line well below the mudline while the second load connection at the second end of the load line is supported above the mudline. The ROV disconnects from the pump port and connects a mooring line to second the load connection. Another aspect of the present invention is a suction pile system having a suction pile with an ROV compatible pressure port and a flood valve at the top. A load support system includes a first load connection on the side of the suction pile with a load line connected to the first load connection. A second, ROV accessible load connection is provided at the distal end of the load line.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Methods and arrangements for rapid trim adjustment
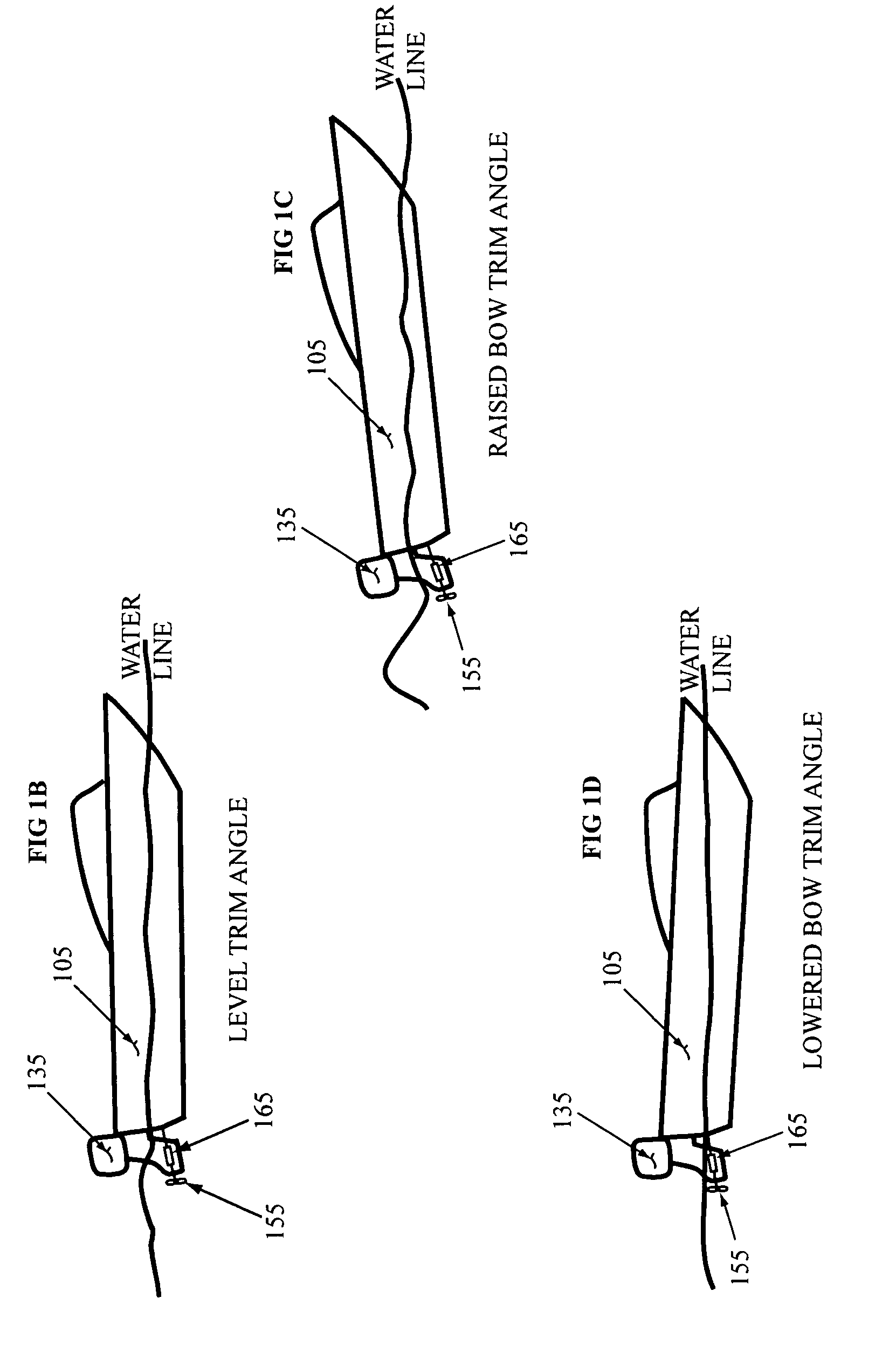
InactiveUS8216007B2Easy to adjustPropulsion power plantsOutboard propulsion unitsTrim tabHydraulic pump
Methods and arrangements to rapidly adjust the trim of a watercraft are disclosed. More specifically, embodiments comprise a sensor to quickly detect changes in the trim angle of a watercraft and a driver adapted to effect rapid changes in the trim angle. For example, many embodiments include large hydraulic pumps and hydraulic connections to adjust the angle of a trim adjuster such as the angle of trim tabs, an outboard motor, or a stern drive. Some embodiments implement high torque electric motors or high capacity pneumatic systems. The drivers may, for example, effect changes in the angle of the trim adjuster within two seconds. In one embodiment, the driver may effect a change in the trim angle within one second or less.
Owner:MOORE STEVEN CLAY
Ocean wave energy system
ActiveUS20130099496A1Improve efficiencyHigh output powerWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesAir movementSea waves
An ocean wave energy system for generating power from ocean waves includes a platform supporting an array of hollow columns whose respective lower ends are in fluidic communication with ocean waves and whose respective upper ends are in air communication with a turbine arrangement such that wave motion occurring at the lower ends is operable to cause air movement within the columns for propelling the turbine arrangement to generate power output. The system further includes one or more position-adjustable and / or angle-adjustable submerged structures near the lower ends of the columns for forming ocean waves propagating in operation towards the lower ends of the columns to couple the waves in a controllable manner into the hollow columns.
Owner:HAVKRAFT
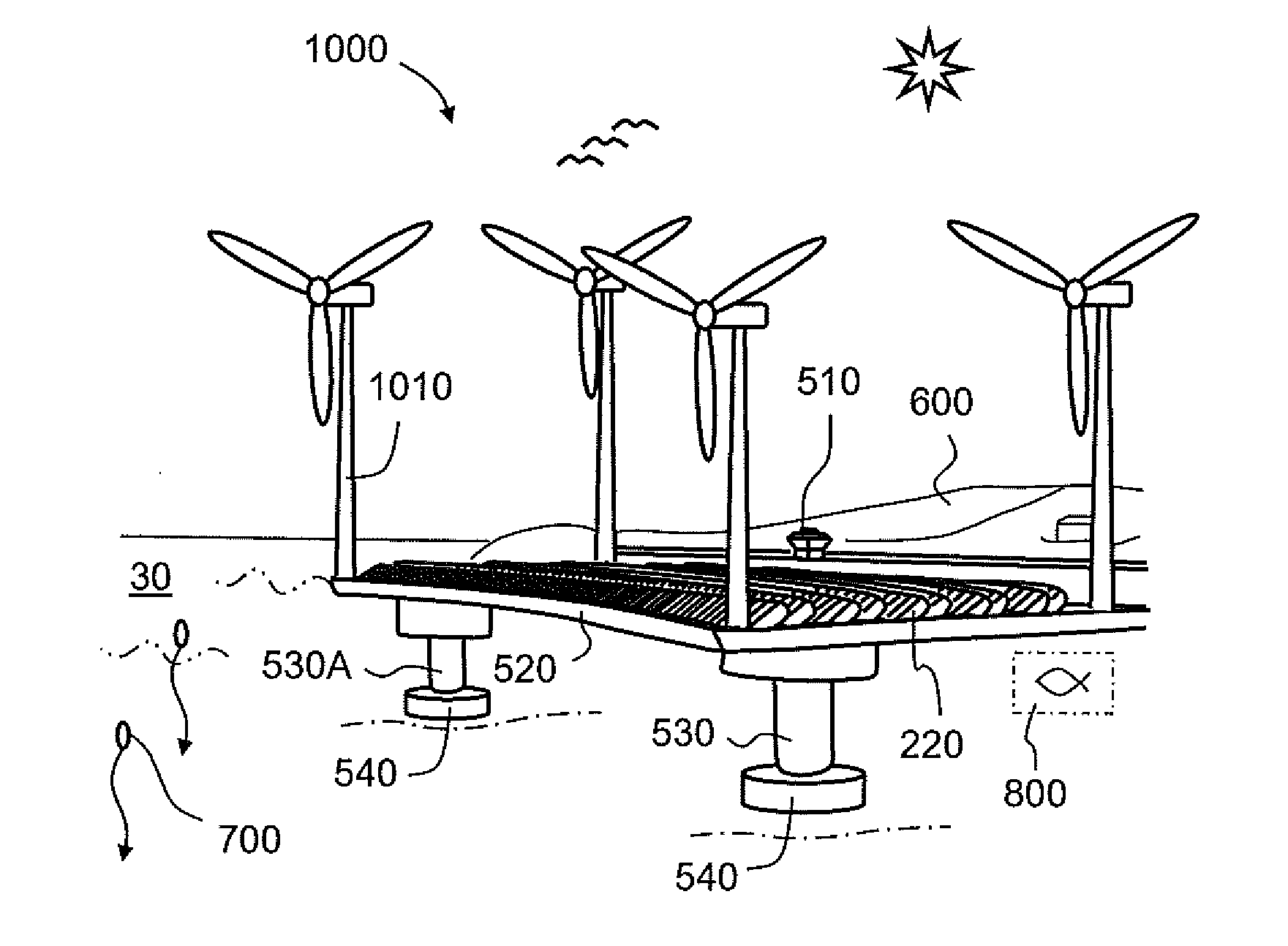
Offshore energy harvesting, storage, and power generation system
ActiveUS20110215650A1Improve efficiencyEmission reductionLarge containersWind motor supports/mountsOcean bottomExcess energy
A system for harvesting, storing, and generating energy, that includes floating structure supporting machinery to extract energy from wind, waves, surface generators, or currents. At least one energy storage and power generating unit is anchored to the seafloor and adapted to tether the floating structure to the unit. The unit includes an internal chamber into which water flows through a hydroelectric turbine to generate electrical energy. A pump is provided, powered by energy from the floating structure machinery, to evacuate water from the unit and a control system directs power from the machinery to pump water out of the unit during periods of excess energy extraction by the machinery and to allow water to flow into the chamber through the hydroelectric turbine to generate electrical energy during periods of lower energy extraction by the machinery. The same internal chamber design can be utilized to store hydrocarbons in the vicinity of undersea wellheads during “shut-in” procedures when the wellhead would otherwise be secured.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for suction anchor and mooring deployment and connection
A method and apparatus for deployment of mooring systems for buoyant marine structure such as mobile offshore drilling units (MODU's) and for connecting the same to the mooring lines thereof. An anchor handling vessel carries one or more anchors each having a deployment connection and a mooring connection and individually moves each anchor over its stern roller and deploys it to the sea bottom for installation. A handling line is disconnected by ROV from the deployment connection and is moved from the deployment connection to the mooring connection so as to become the main mooring line. Syntactic buoys are then mounted on the main mooring line for elevating it above the sea bottom for recovery. When MODU stationing is desired the anchor handling vessel then recovers the surface buoy and connects to the rig mooring line using a short section of mooring chain. A J-chaser stopper device is then installed in the mooring string and is connected to the mooring line of the MODU by a short section of chain. The J-chaser lowers the mooring string, completing the mooring connection between the anchor and the MODU. A plurality of mooring strings, typically eight, are deployed in this manner to properly station the MODU. Disconnection of the MODU is accomplished essentially by the reverse of the above deployment procedure.
Owner:DELMAR SYST
Method of and apparatus for offshore mooring
ActiveUS6983714B2Expensive to operateClamp firmlyAnchorsAnchoring arrangementsMarine engineeringPulley
In a method of and apparatus for offshore mooring, a clamping apparatus includes a clamping mechanism and a pulley. A mooring line connected to an anchor or a pendant line connected to a vessel to be moored extends through the clamping mechanism and around the pulley of the clamping apparatus. The distal end of the line extending through the clamping apparatus is connected to an anchor handling vessel. The anchor handling vessel is employed to apply a predetermined tension to the pendant line and the preset mooring line. A remote operated vehicle is then employed to actuate the clamping apparatus and to disengage the anchor handling vessel.
Owner:TECH FRANCE SA
Sea-based hydrogen-oxygen generation system
A method for generation of gasses contained in a salt solution in accomplished by disposing automated, floating wave power collection vessels in waters distant from shore, the vessels navigating within one or more predetermined geographic zones, having suitable wave conditions for such operation. The wave power devices generating electricity and the gasses are extracted from the salt solution by electrolysis. Automated storage vessels are used as shuttles to deliver the gasses to shore facilities.
Owner:MORSE ARTHUR +1
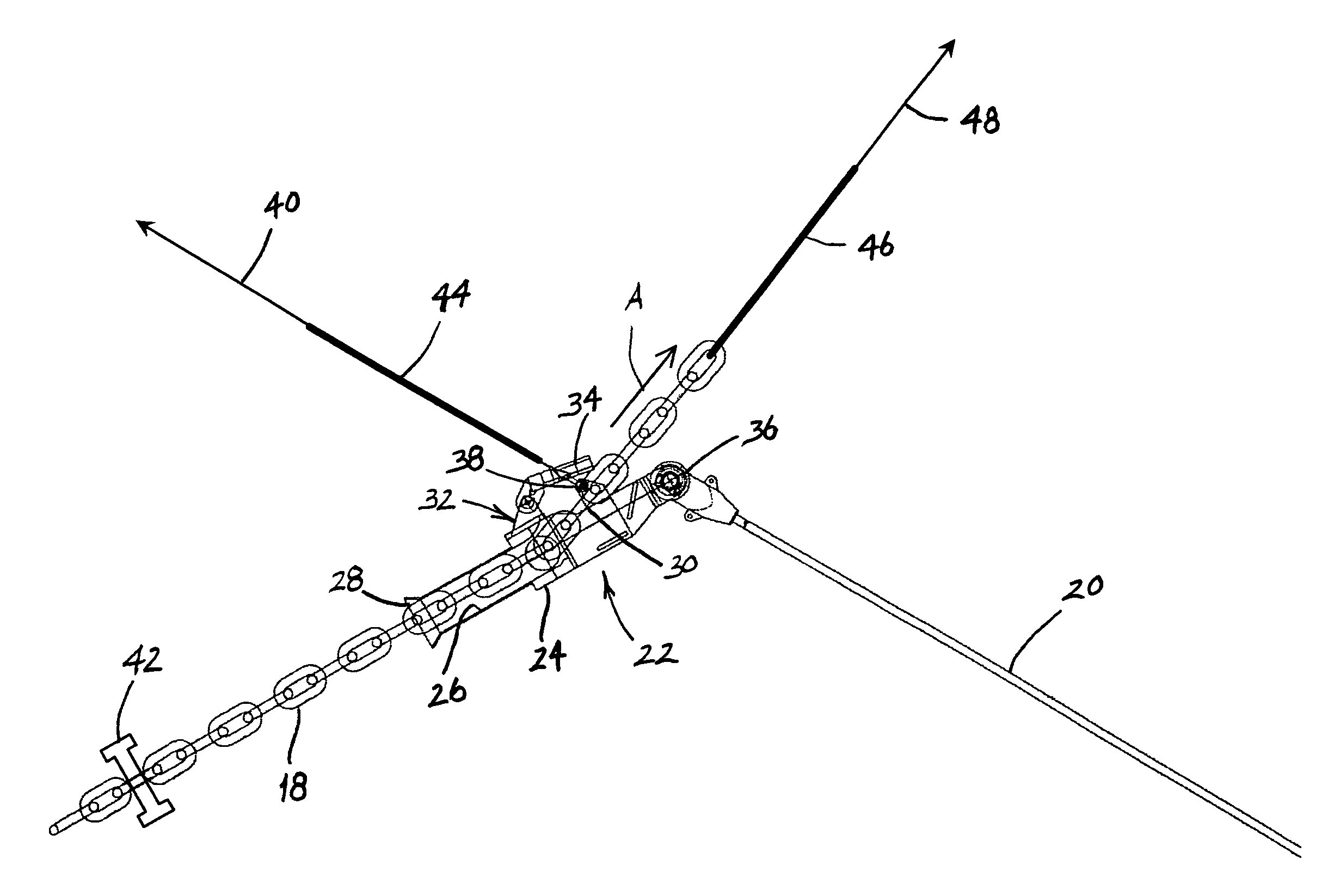
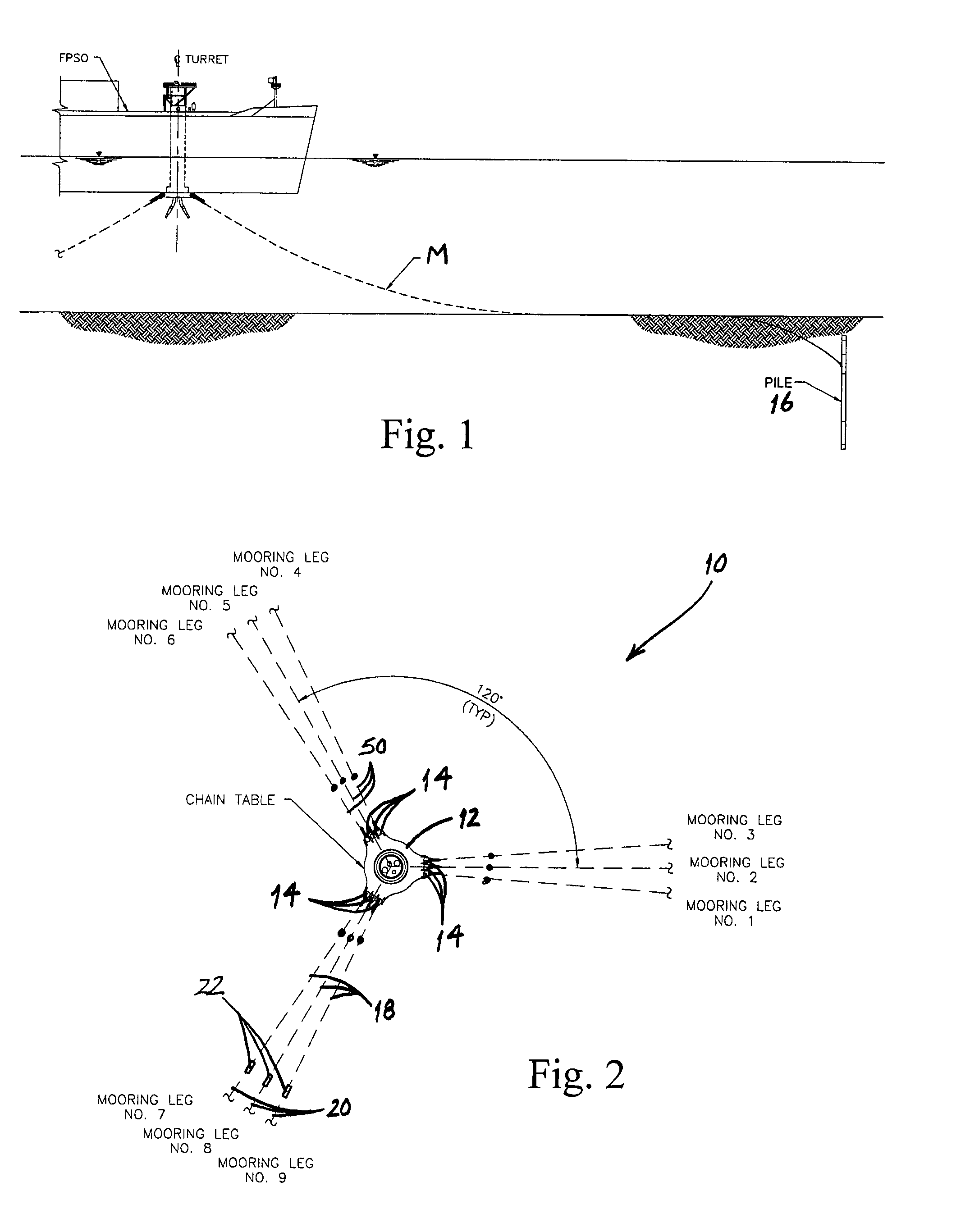
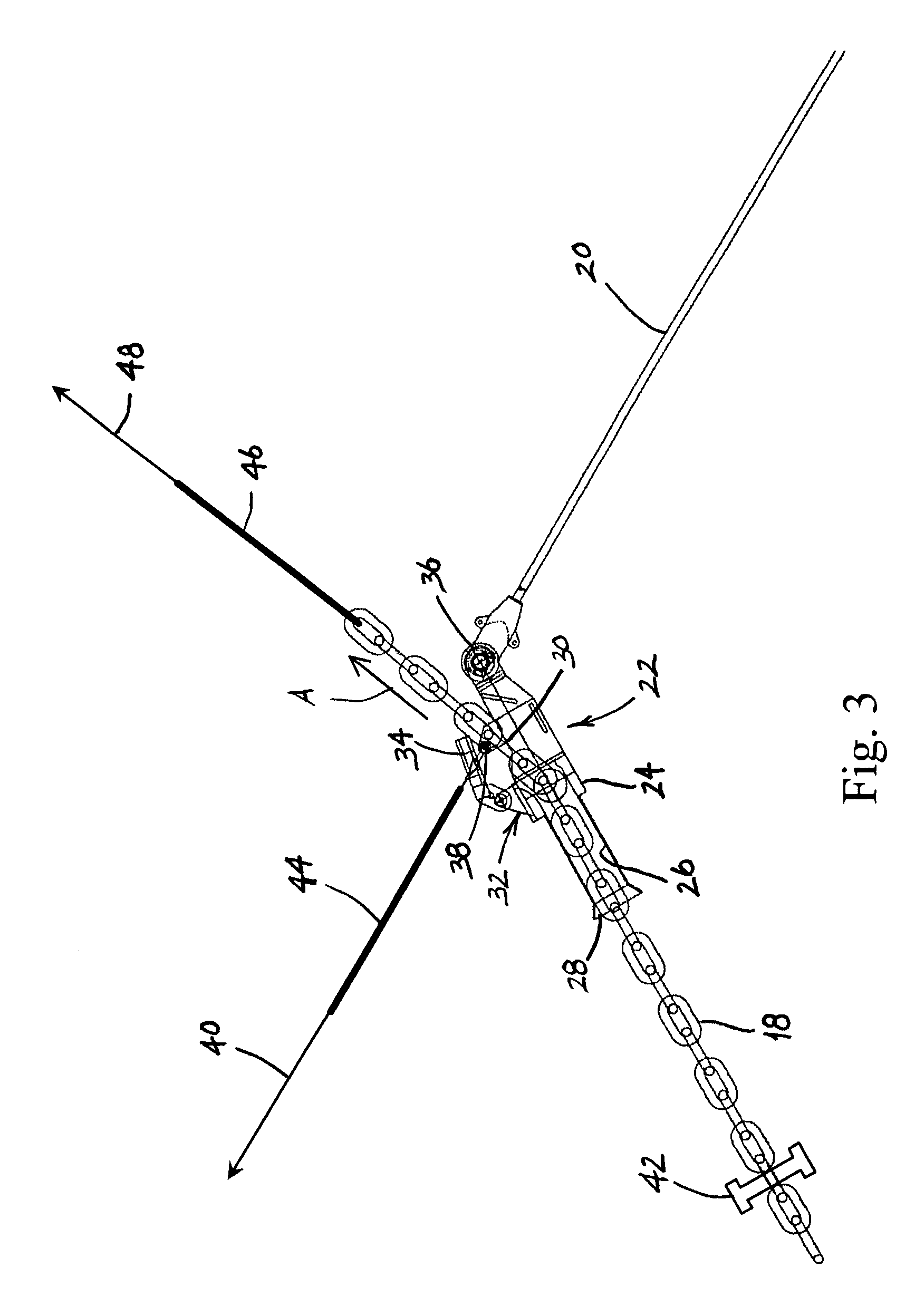
Mooring apparatus and method
ActiveUS7421967B1The process is convenient and fastReduce forceAnchorsMooring equipmentOcean bottomMooring system
A mooring system for securing a floating vessel to the sea floor comprises a plurality of mooring legs, at least one of which includes separate first and second mooring lines. The first mooring line comprises a first end which is connected to the vessel and the second mooring line comprises a first end which is secured to the sea floor. The mooring system also comprises a connection and tensioning device which includes a body, a bore which extends through the body, a chain stopper for adjustably securing the first mooring line to the body, and a connector for connecting a second end of the second mooring line to the body. In use, a second end of the first mooring line is inserted into the bore and the first mooring line is pulled through the bore while the body is subject to an opposing pulling force. Once the first mooring line is pulled through the bore a desired distance, the chain stopper maintains the first mooring line in position relative to the body to thereby secure the vessel to the sea floor.
Owner:SOFEC
Undersea suction anchor
InactiveCN103132521AImprove stabilityImprove pullout resistanceArtificial islandsAnchorsCorrosionSeabed
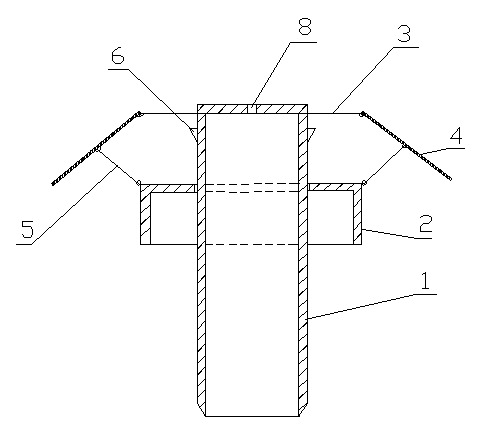
The invention discloses an undersea suction anchor which comprises a main drum, a top face of the main barrel is sealed, a lower end of the main barrel is opened, and a main barrel drainage hole is arranged on the top face of the main drum. The undersea suction anchor is characterized in that a barrel skirt is movably sleeved on the main drum, the barrel skirt comprises a horizontal top face and a barrel-shaped lateral wall, a barrel skirt drainage hole is formed in the horizontal top face of the barrel skirt, a telescopic hook locating the barrel skirt at the upper portion of the main barrel is arranged on the barrel-shaped lateral wall at the upper portion of the main barrel, an anchor ring concentric with the main barrel is arranged at the upper end of the main barrel, anchor branches are evenly arranged on the anchor ring, one ends of the anchor branches are hinged to the anchor ring, and the other ends of the anchor branches are hinged to the barrel skirt through inclined support rods. The whole vertical section of the suction anchor is in an umbrella shape, in the sinking process of the anchor body, along with landing-on-seabed of the barrel skirt, the anchor branches are driven by the inclined support rods to be gradually opened, and after the main barrel sinking is finished, the anchor branches cling to the surface of the seabed in a horizontal extending mode. The undersea suction anchor can improve the integral stability of the suction anchor, increases pulling resistance and horizontal bearing force, and reinforces wave-corrosion-resistance performance.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
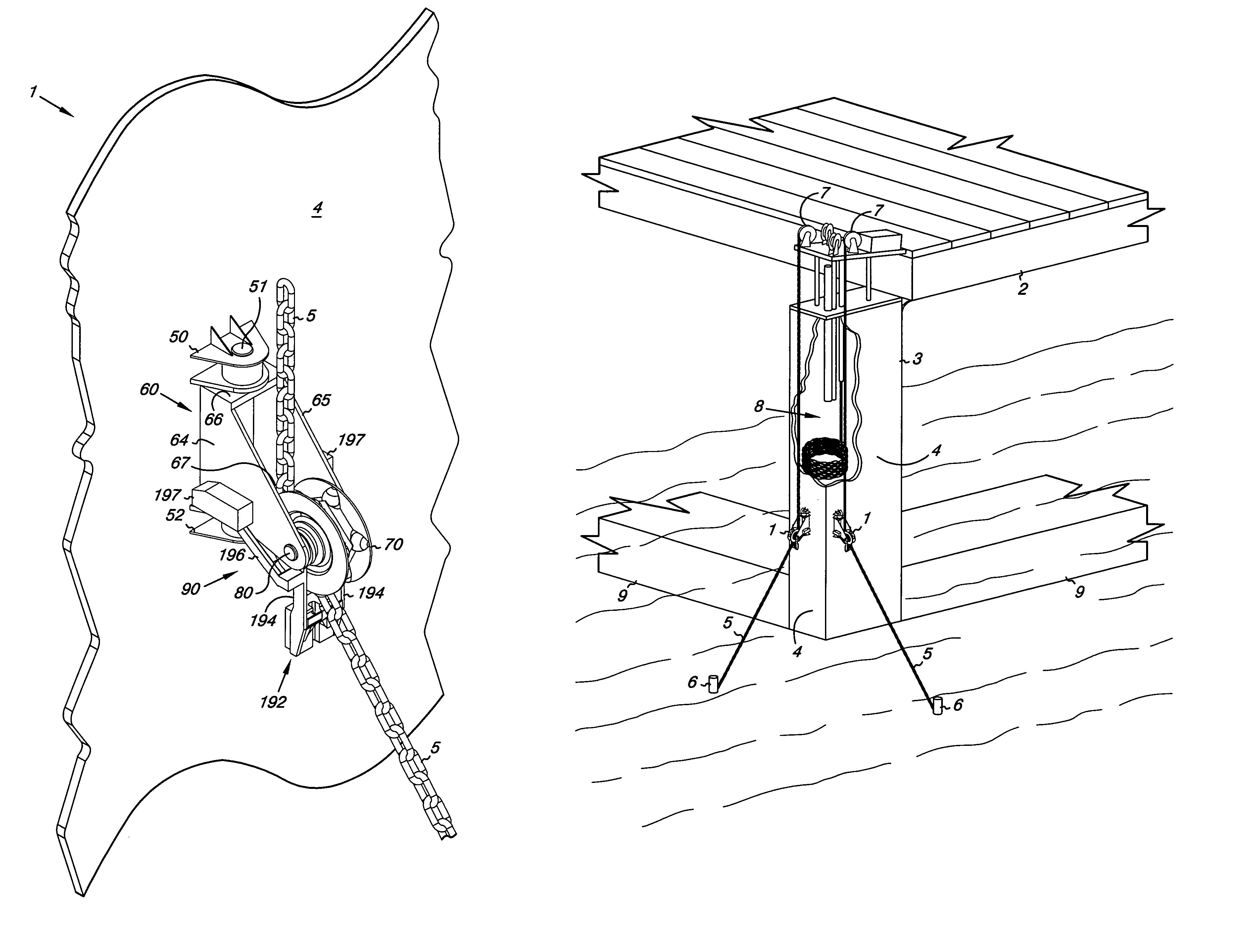
Air cannon and associated launch canister for a line-fouling system
ActiveUS20160161225A1Rapidly deployableDirect forceDefence devicesPeptide/protein ingredientsCouplingEqualization
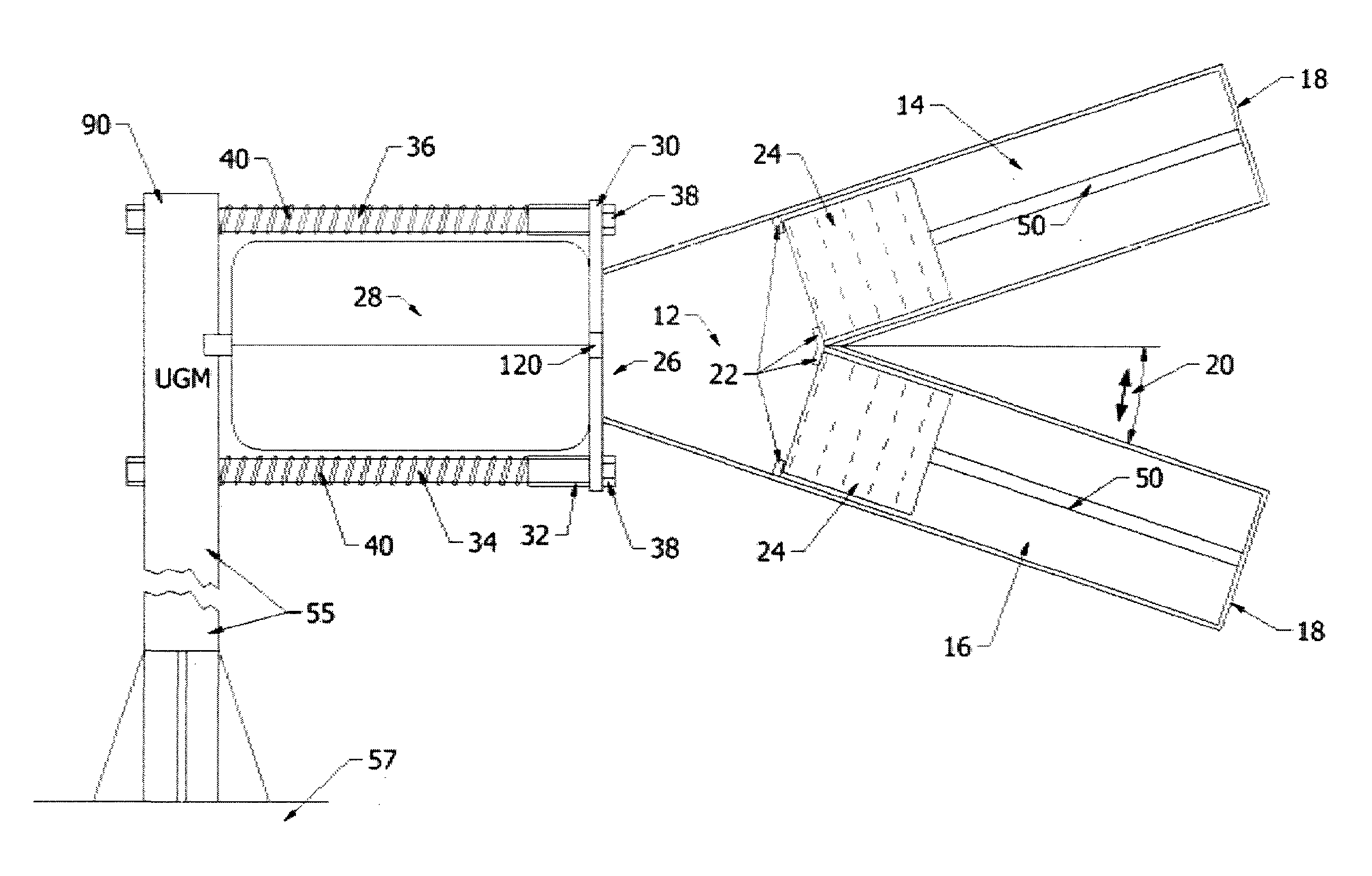
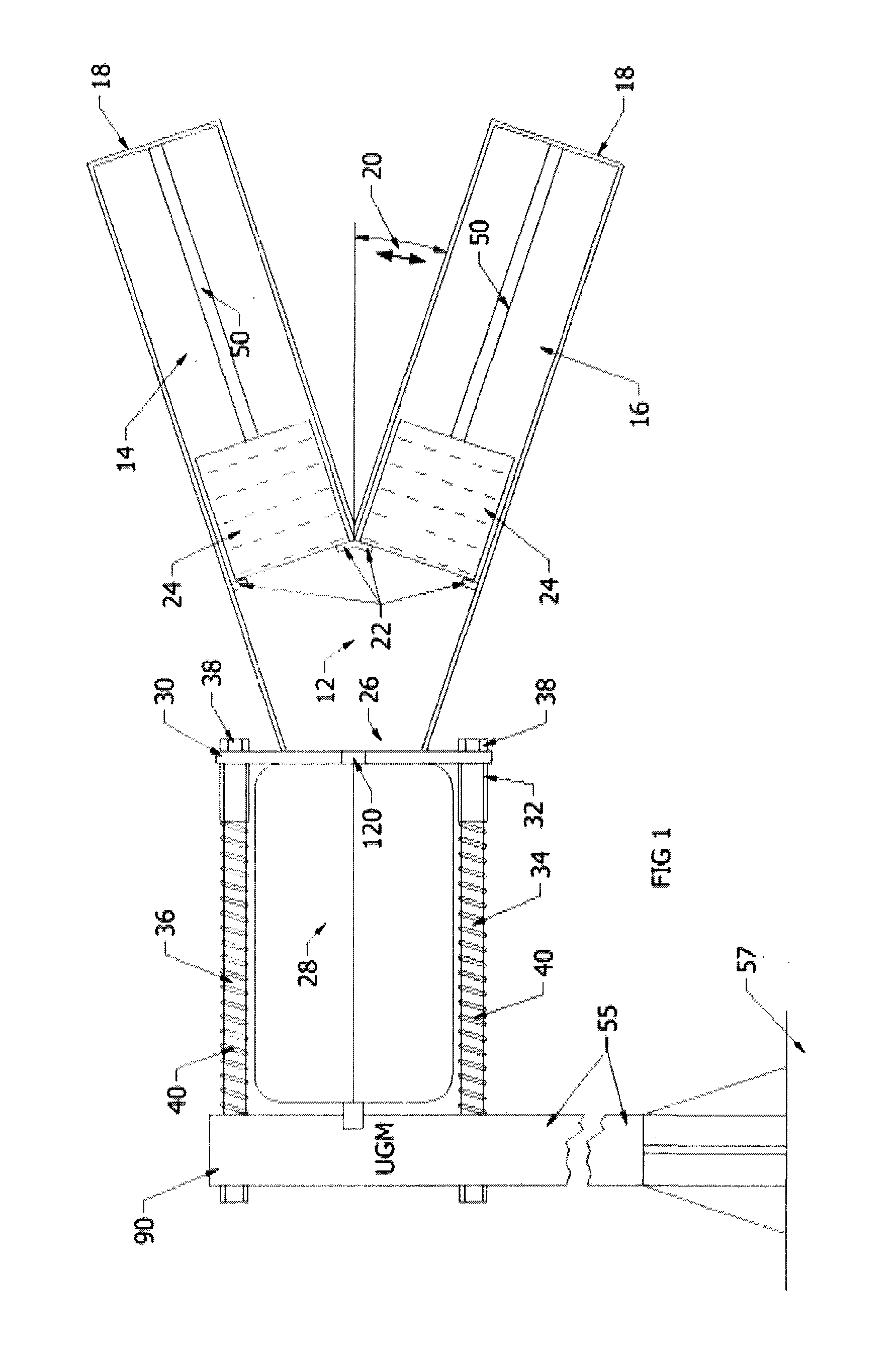
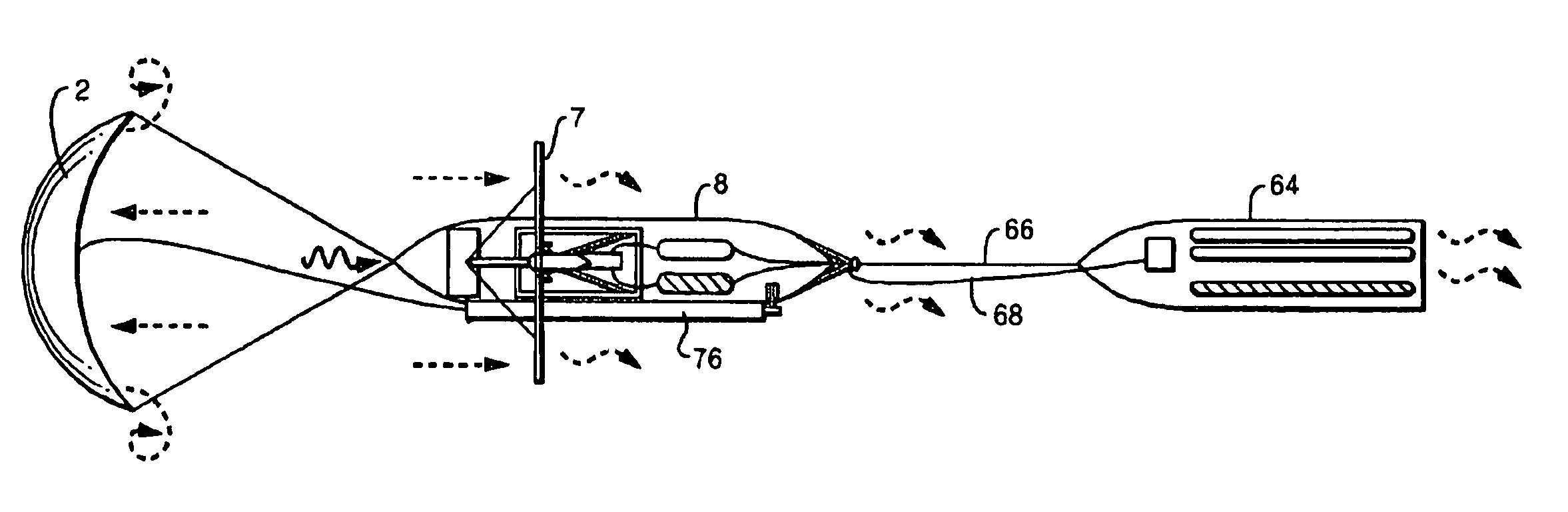
FIG. 7 shows an air cannon system loaded with a launch canister containing a prop-fouler. A pressure vessel (28) contains an inlet including a poppet valve (100) that, upon command, can be selectively placed in either a one-way flow position to permit charging of the pressure vessel or otherwise opened to trigger rapid discharge through pressure equalization with the ambient environment. The air cannon may include multiple splayed barrels or a single barrel (158). A launch canister (202), realized in the form of a tube, has a driving plate (350) that closes an end of the launch tube. The driving plate is the first point loaded into the barrel. Within the launch canister (202) a first portion of a floating prop-fouling line is stored. The prop-fouling line, such as made from Dyneema®, has at its ends two drogues that, upon entry into the water, fill with water to produce drag resistance to movement of the prop-fouling line. To avoid undue stress on canopy panels of each drogue and to avoid twisting of shroud lines (312) to the canopy, a rotating shackle (310a, 310b) acts as a coupling point between the shroud lines (312) and the prop-fouling line. Only one drogue (306), its associated coupling and a selected length prop-fouling line are loaded into the launch canister, with the other drogue and its rotating shackle (310b) loaded into a cradle (166). Upon firing, gas expansion causes the rapid acceleration and ejection of the launch tube (202) and generally straight line deployment of the prop-fouling line (302).
Owner:BCB INT
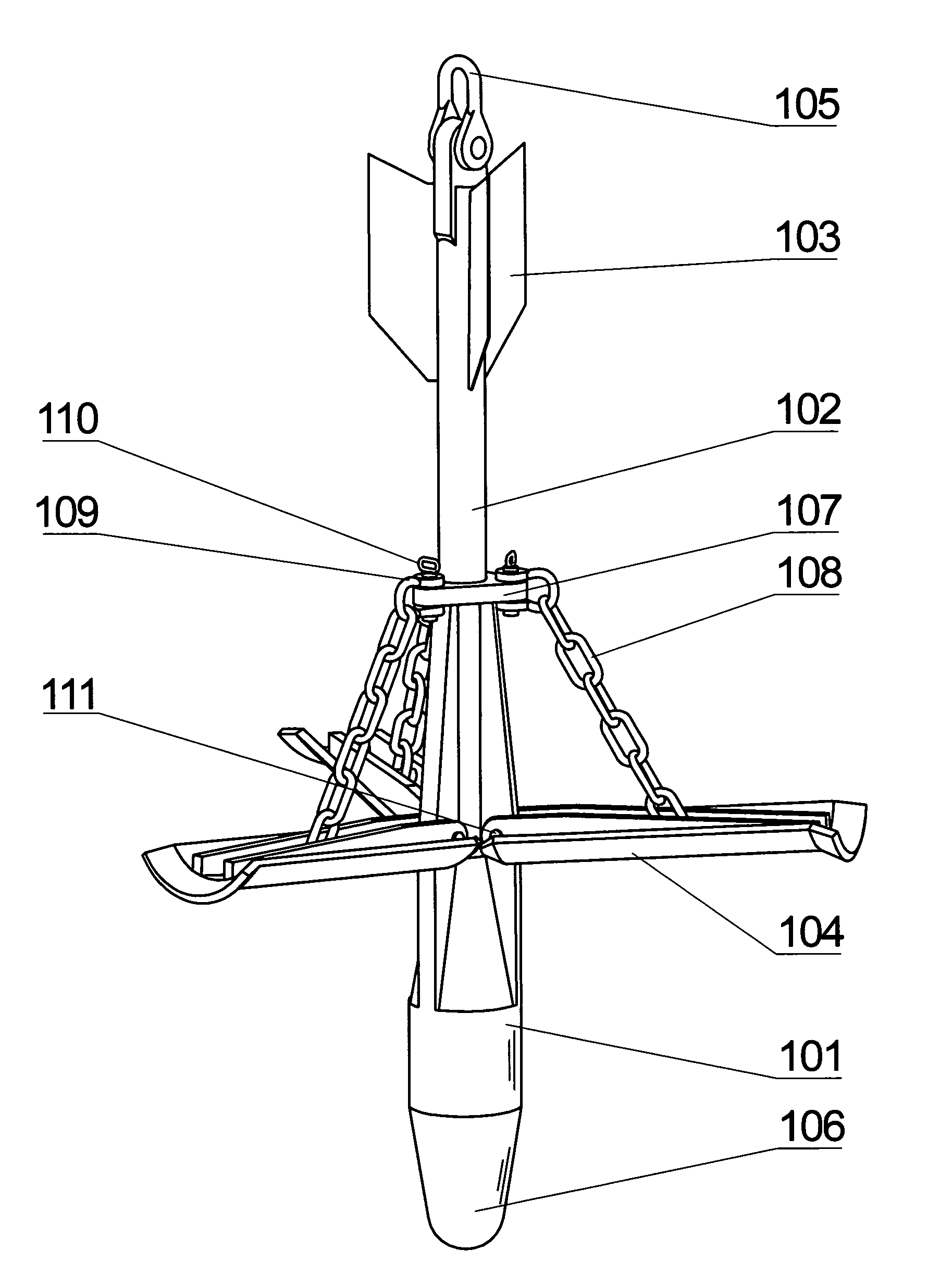
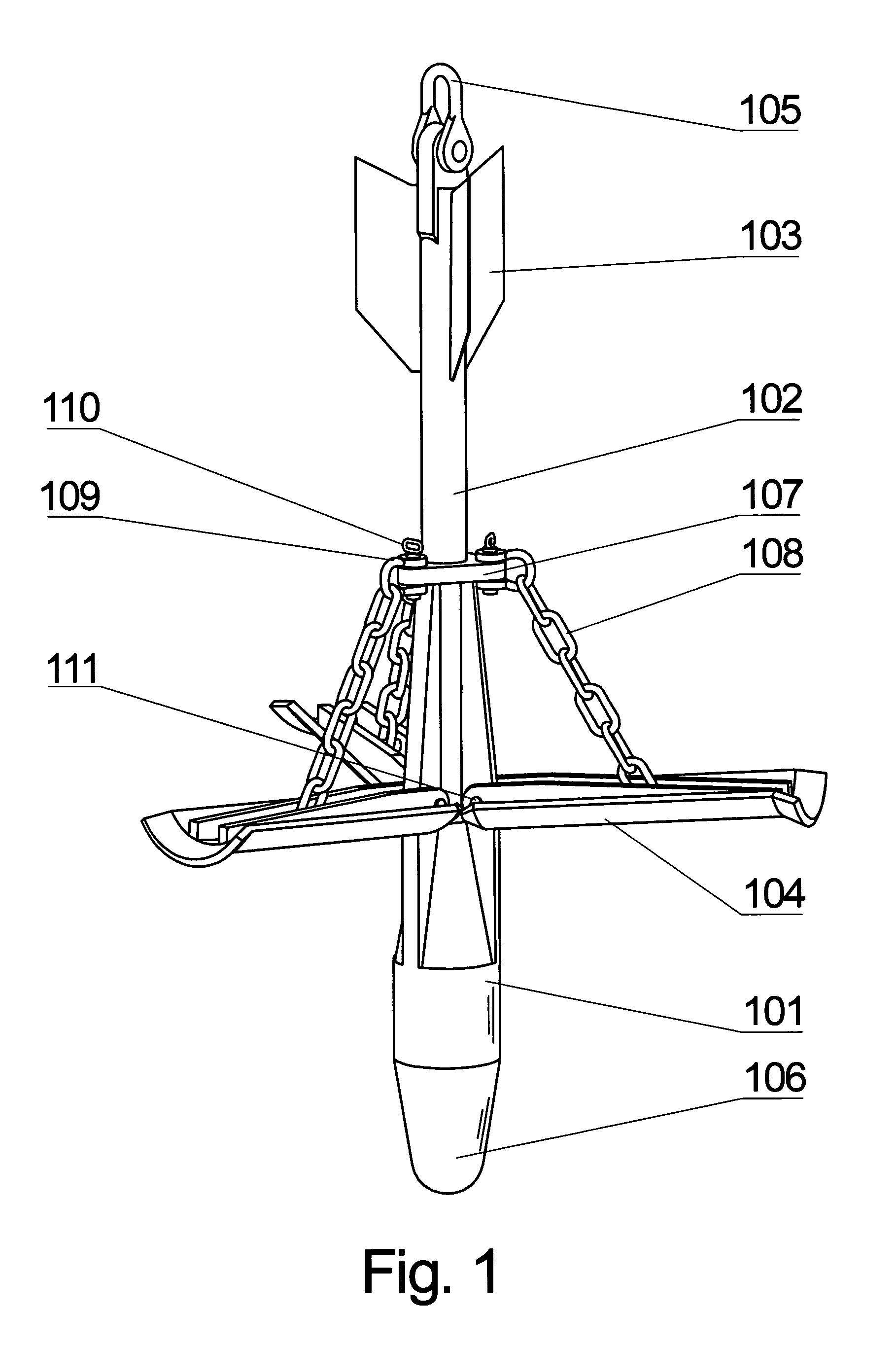
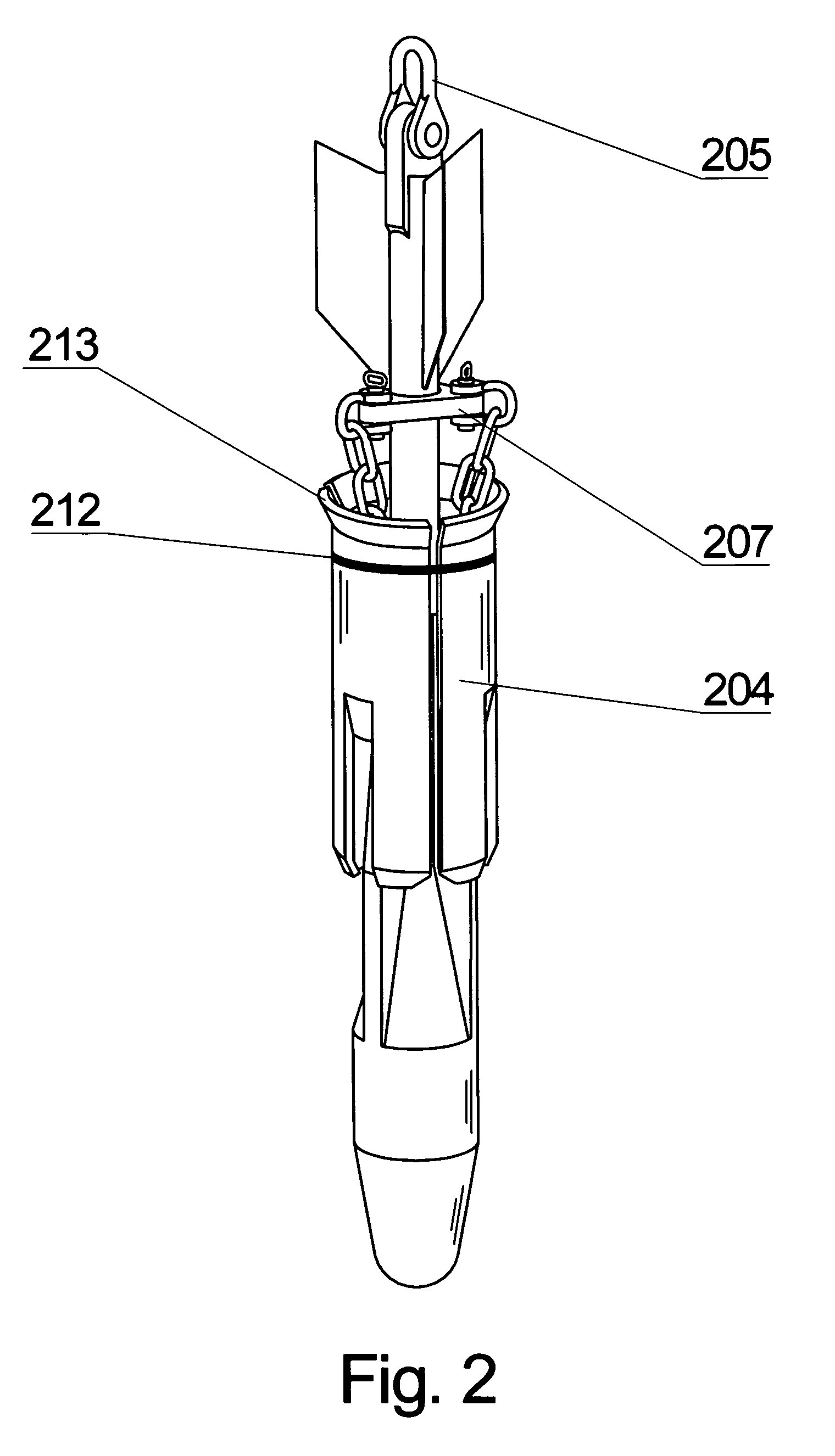
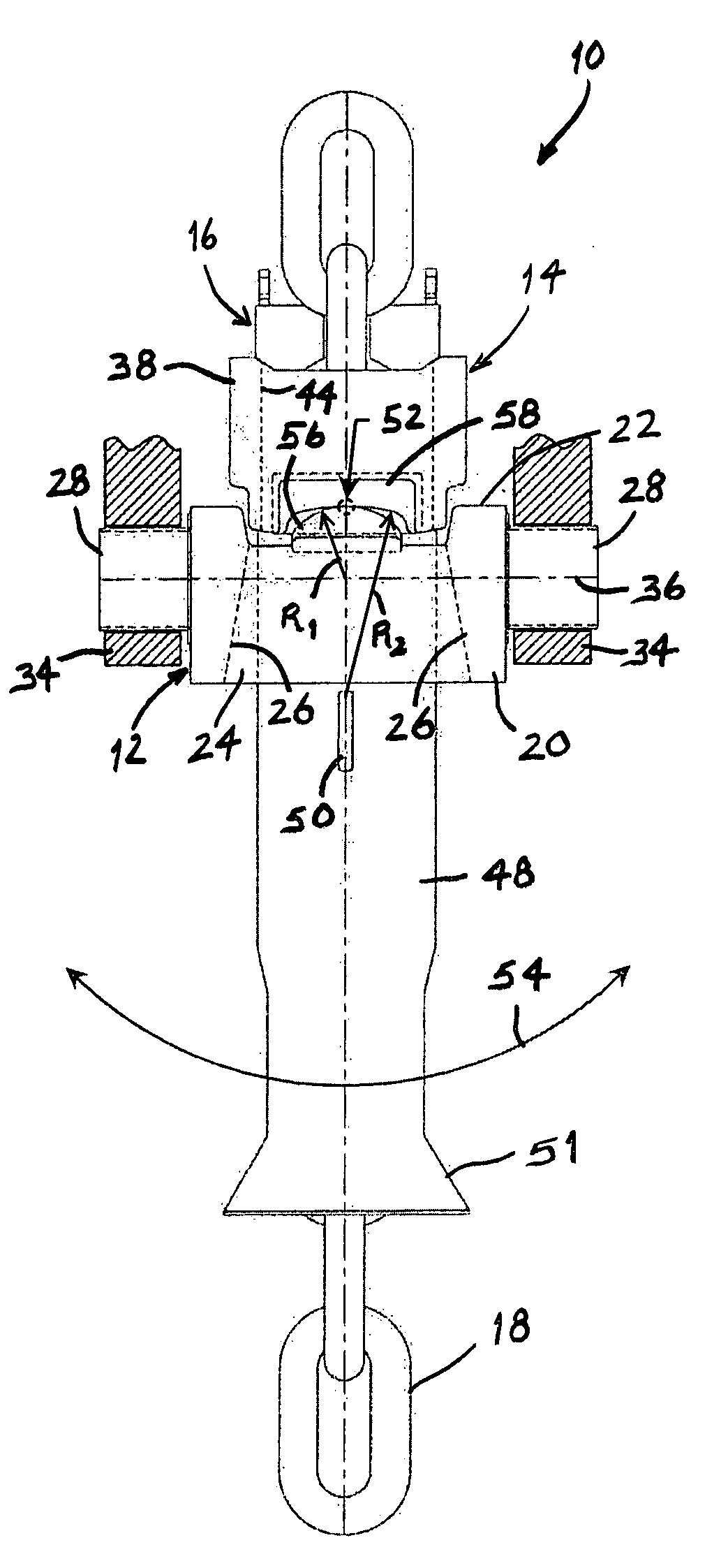
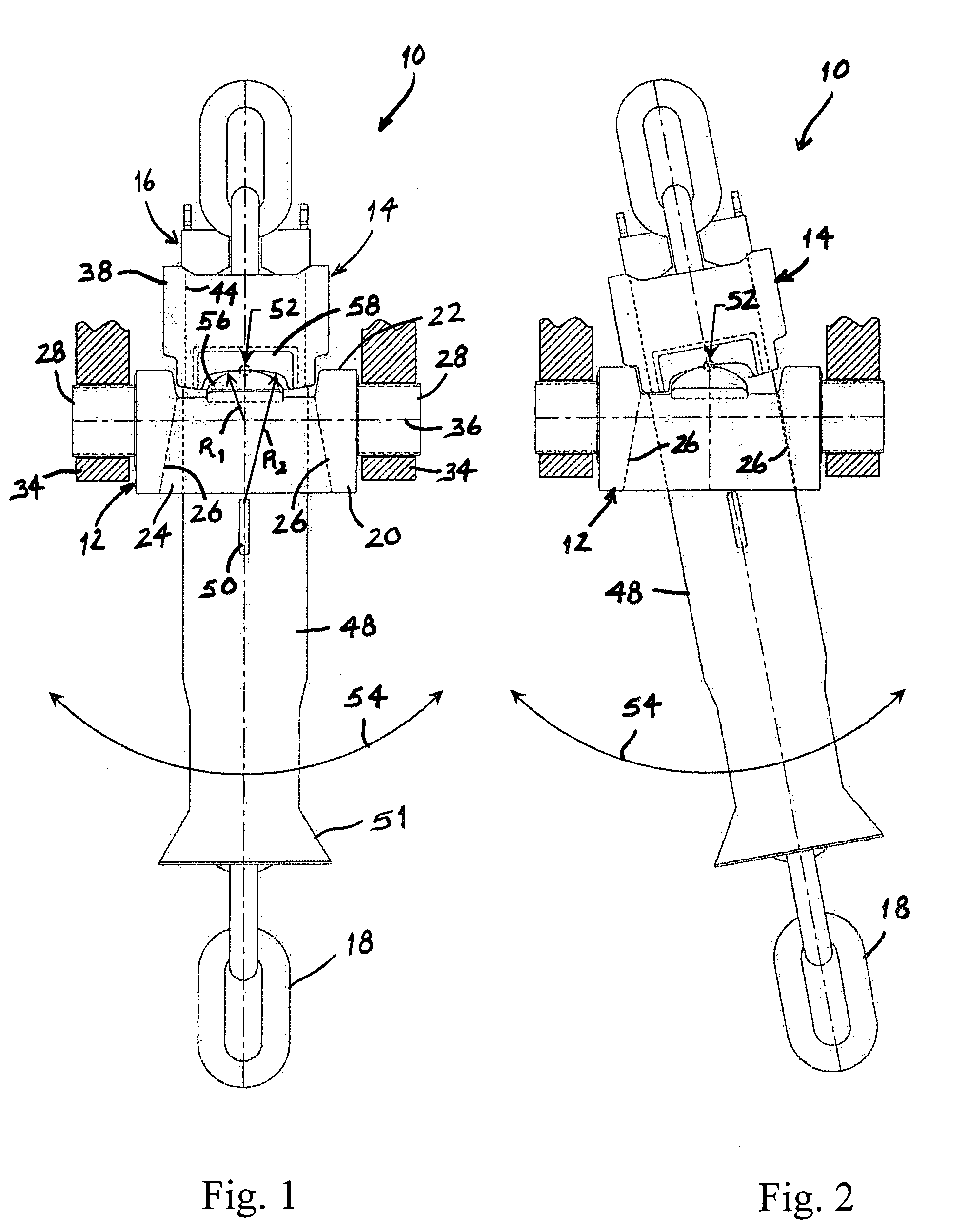
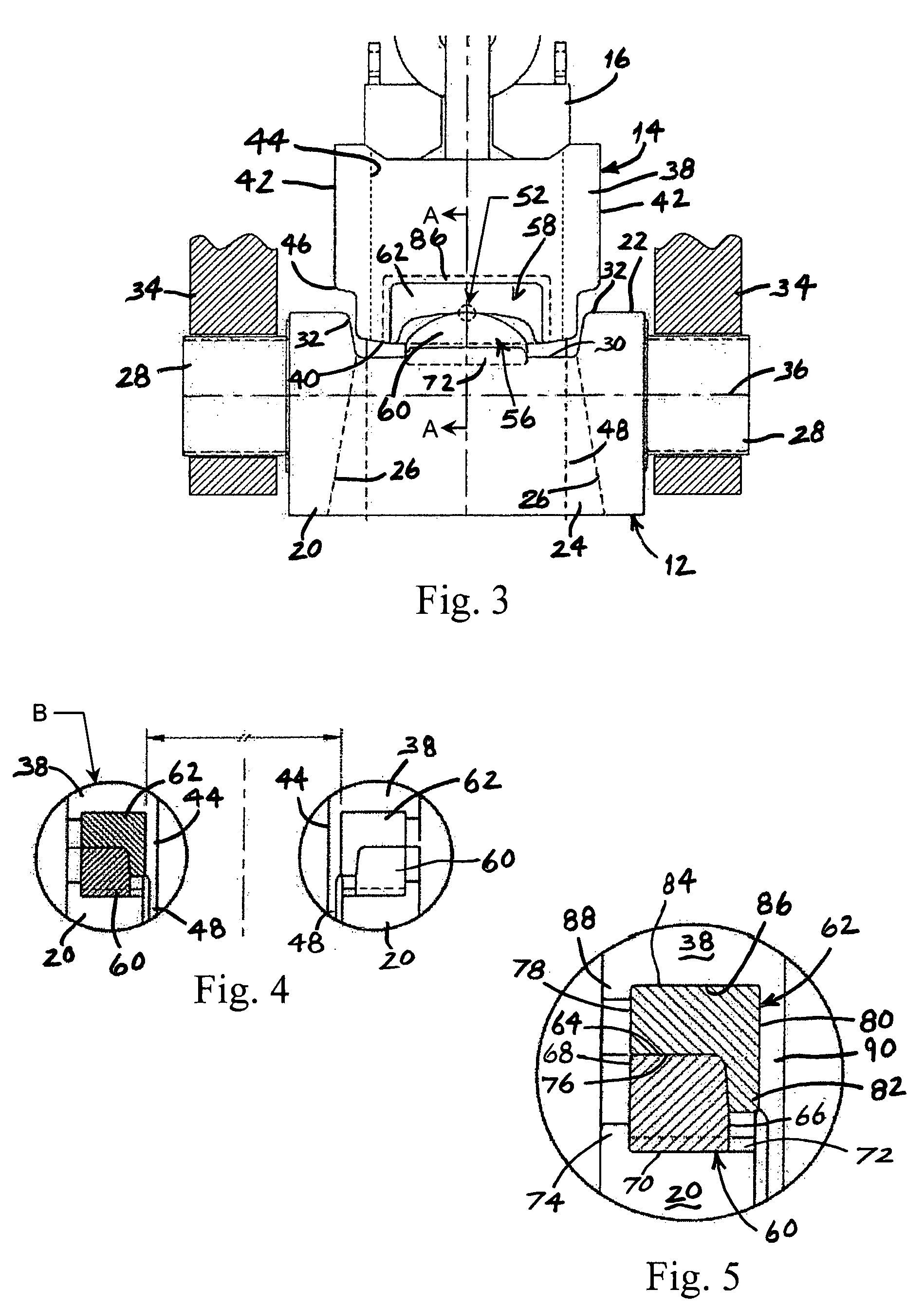
Folding torpedo anchor for marine moorings
The present invention comprises a deepwater anchor that combines the high holding capacity of a plate anchor with the simple installation procedures associated with torpedo anchors. The complex embedding procedure typical for plate anchors is avoided. Instead, the anchor is installed by allowing it to free-fall through the water and then impact into the seabed. After penetrating the seabed, a pull on the anchor line causes the deployment of initially folded flukes. In their deployed positions, one or more flukes or plate-like structures extend perpendicularly toward the anchor shank, and function similar to conventional plate anchors. As a result of the fluke deployment, the holding capacity of the anchor against uplift loads is significantly greater than with a conventional torpedo anchor. Another aspect of the invention relates to the modular construction of a torpedo anchor, wherein the properties of an anchor can be adapted to the specific conditions determined at the deployment site. Still another aspect of the invention relates to fast, inexpensive procedures for installing a torpedo anchor in a desired operational environment.
Owner:MUEHLNER EDMUND
Dual-axis chain support assembly
ActiveUS20060213418A1Reduce and eliminate bending momentAnchorsAnchoring arrangementsConvex sideEngineering
A support assembly for a mooring line of a floating vessel comprises a trunnion block which is pivotally supported on the vessel and a stopper block to which the mooring line is releasably secured. One of the trunnion block and the stopper block comprises a convex surface and the other of the trunnion block and the stopper block comprises a concave surface. In operation, the convex surface engages the concave surface to thereby pivotally support the stopper block on the trunnion block.
Owner:SOFEC
Fairlead with integrated chain stopper
The present invention is a fairlead for guiding and securing an anchor chain between an offshore structure and an anchor. The fairlead comprises a fairlead frame, a pivoting latch, and an actuator. The fairlead frame is pivotally mounted to the offshore structure and supports an axle for a chain sheave. The pivoting latch is mounted to pivot on the axle and comprises a tension link with a chain latch and a counterweight for urging the chain latch into engagement with the chain. The pivoting latch is configured to engage the chain only when the chain is traveling in the payout direction. The actuator controls the action of the counterweight.
Owner:HYDRALIFT AMCLYDE INC
Power embedment anchor with high-frequency small amplitude vibration
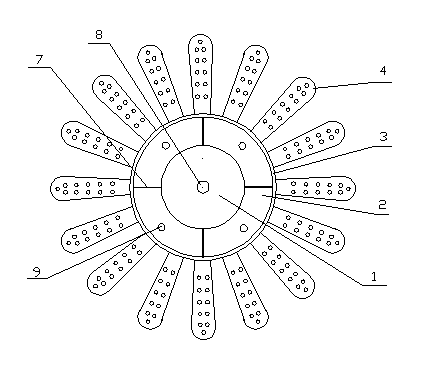
The invention relates to a power embedment anchor with high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration in the ship and ocean engineering technical field. The embedment anchor comprises an anchor cover, an anchor shank, an anchor hammer, a lifting lug, a high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device, a main fin, an anchor chain, a power source and a cable, wherein the anchor cover is arranged on the upper part of the anchor shank; the anchor hammer is arranged on the lower part of the anchor shank; the lifting lug is arranged on the surface of the outer wall of the anchor shank; the anchor chain is connected with the lifting lug; the high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device is arranged inside the anchor shank; the main fin consists of two to four sheets which are uniformly and symmetrically arranged on the surface of the outer wall of the anchor shank; the power source supplies power to the high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device through the cable; and the cable is connected with the power source and the high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device through an outer cover. The embedment anchor has good holding power and underwater anchor weight ratio under different submarine sediment, can rapidly hold seabed, and is little in windlass tension needed in the process of raising anchors.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for suction anchor and mooring deployment and connection
A method and apparatus for deployment of mooring systems for buoyant marine structures such as mobile offshore drilling units (MODU's) and for connecting the same to the mooring lines thereof. An anchor handling vessel carries one or more anchors each having a deployment connection and a mooring connection and individually moves each anchor over its stem roller and deploys it to the sea bottom for installation. A handling line is disconnected by ROV from the deployment connection and is moved from the deployment connection to the mooring connection so as to become the main mooring line. Syntactic buoys are then mounted on the main mooring line for elevating it above the sea bottom for recovery. When MODU stationing is desired the anchor handling vessel then recovers the surface buoy and connects to the rig mooring line using a short section of mooring chain. A J-chaser stopper device is then installed in the mooring string and is connected to the mooring line of the MODU by a short section of chain. The J-chaser lowers the mooring string, completing the mooring connection between the anchor and the MODU. A plurality of mooring strings, typically eight, are deployed in this manner to properly station the MODU. Disconnection of the MODU is accomplished essentially by the reverse of the above deployment procedure.
Owner:BERGERON BILLY J
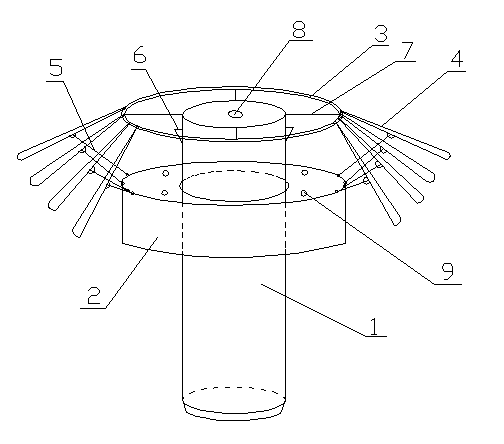
Anchoring systems and methods for anchoring an object
The present invention is a novel anchoring system comprising: a housing; a connector that connects the housing to an object; at least one motor which is contained within and fixed to said housing; and at least three movable elongated members, each having a proximal tip, a distal tip, a retracted storage position and an extended operative position relative to the housing. Each elongated member is operably linked to at least one motor, and an elongated member is essentially contained within the housing when said elongated member is in a storage position and the elongated member extends away from the distal surface of said housing into a penetrable environment when the elongated member is in an extended operative position.
Owner:VELAZQUEZ VICTOR ELI
Ground anchors with compression plates
InactiveUS7302904B2Restrict movementTrend downTents/canopiesAnchorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
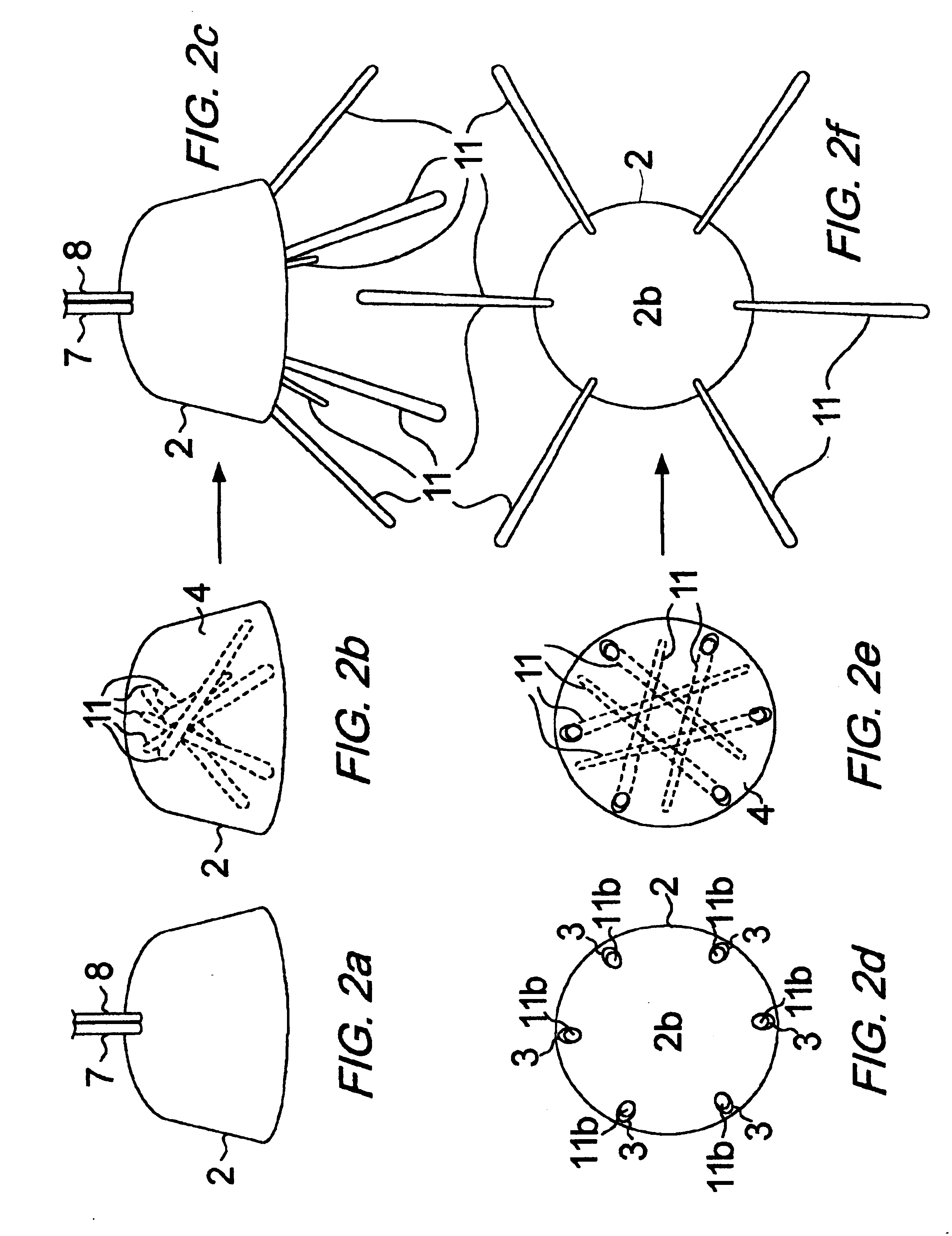
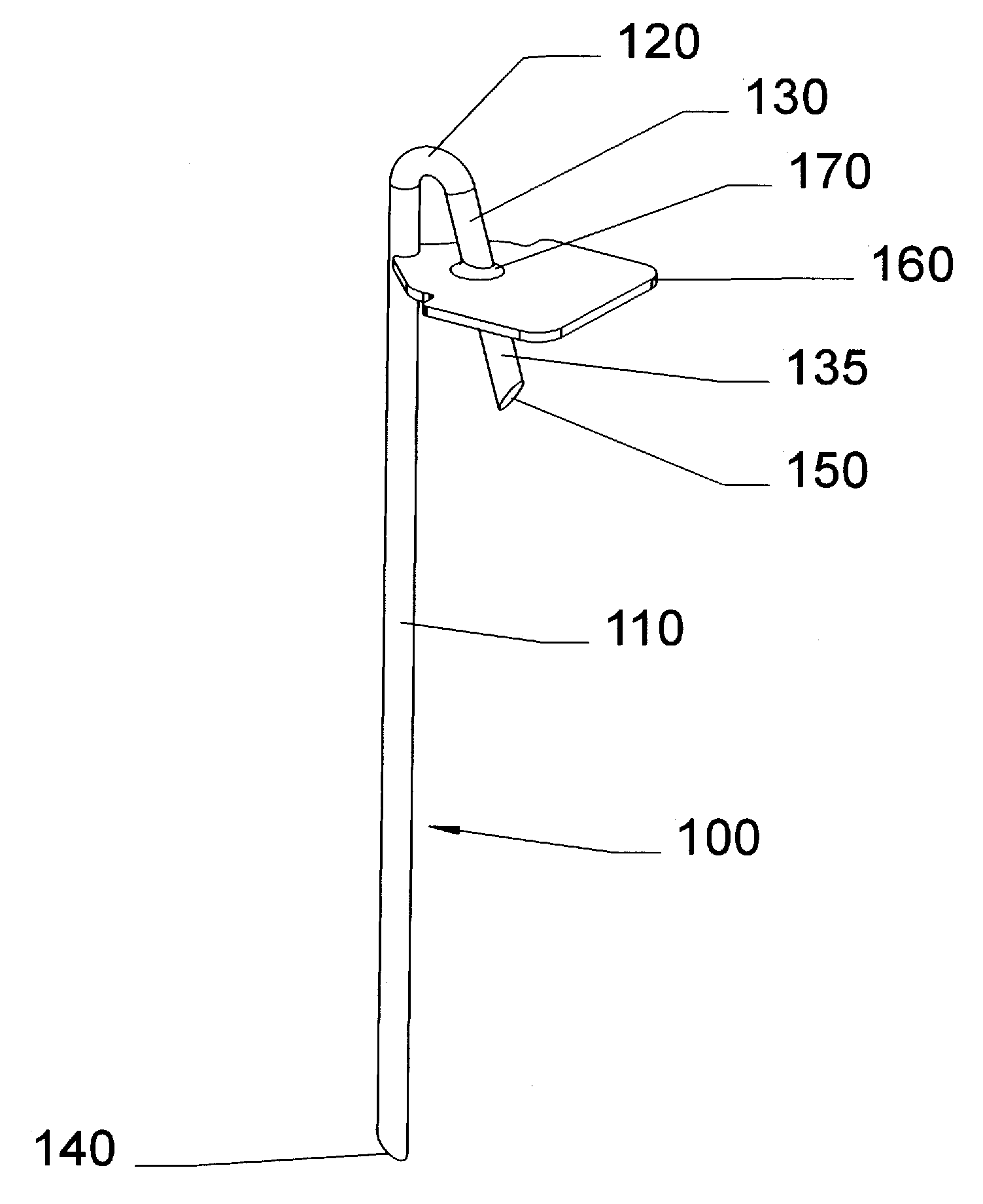
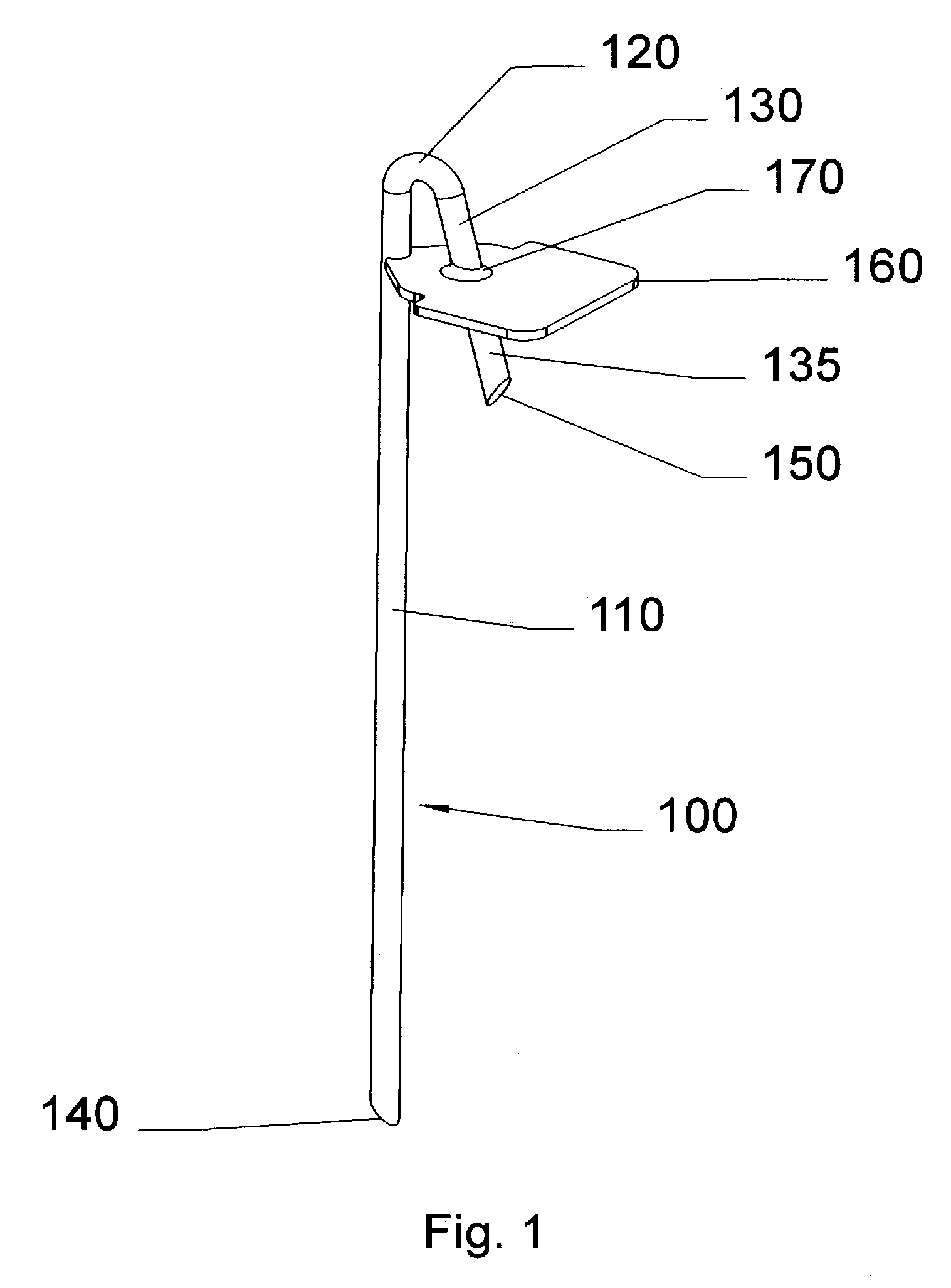
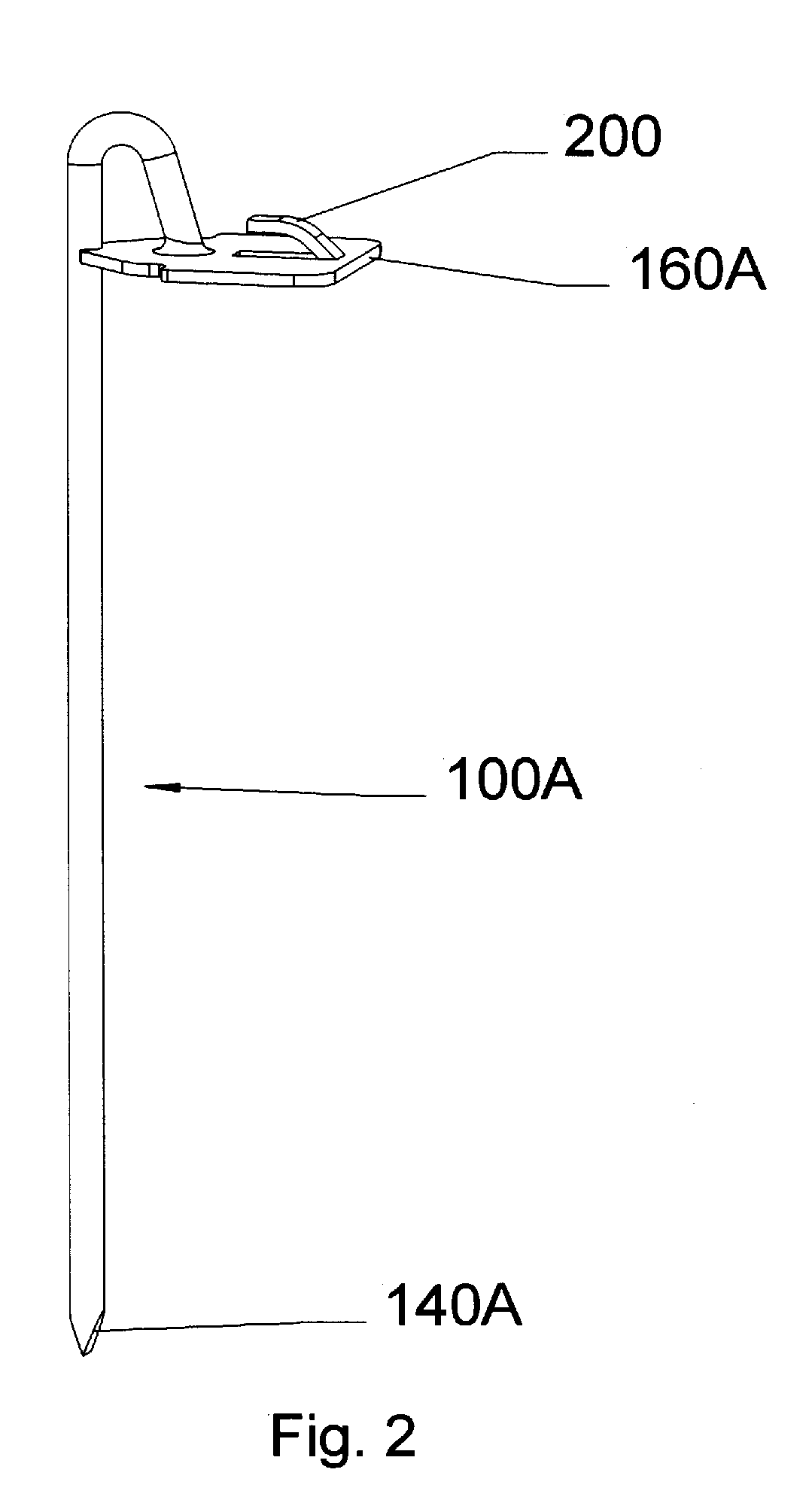
Ground anchors, in particular tent stakes (100), comprise one or more inherently flexible tines (110), a ground compression plate (160), and various tie points (420, etc.) for attaching a guy rope or the like to the top of anchor. The compression plate extends perpendicularly or at a large angle to the tine so that when the guy rope pulls on the anchor, the tine will tend to rotate about an underground fulcrum so that the compression plate will press against the ground and help the anchor resist pullout. The anchors are driven into the ground with a hammer or mallet. The tie points include hooks (420), closed holes (520), and swivel types comprising vertical members (810) with restraining, bulbous tops (820). An additional spring tie point (1600) can be inserted into optional lugs (1094, 1096) in the compression plate. The stakes can be driven into the ground vertically, or at an angle for additional holding force in some situations. They can also incorporate angled compression plates (160H, 160I). A curved stake (100I) provides additional holding force in sand or friable soils. The stakes can be manufactured by a variety of means in various materials, such as glass-reinforced or other plastics and forged or stamped metals.
Owner:BURNS PETER ROBERT
Wave Energy Harvesting and Hydrogen-Oxygen Generation Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20080038061A1Total revenue maximizationMaximize productionWater-power plantsMachines/enginesHydrogenReciprocating motion
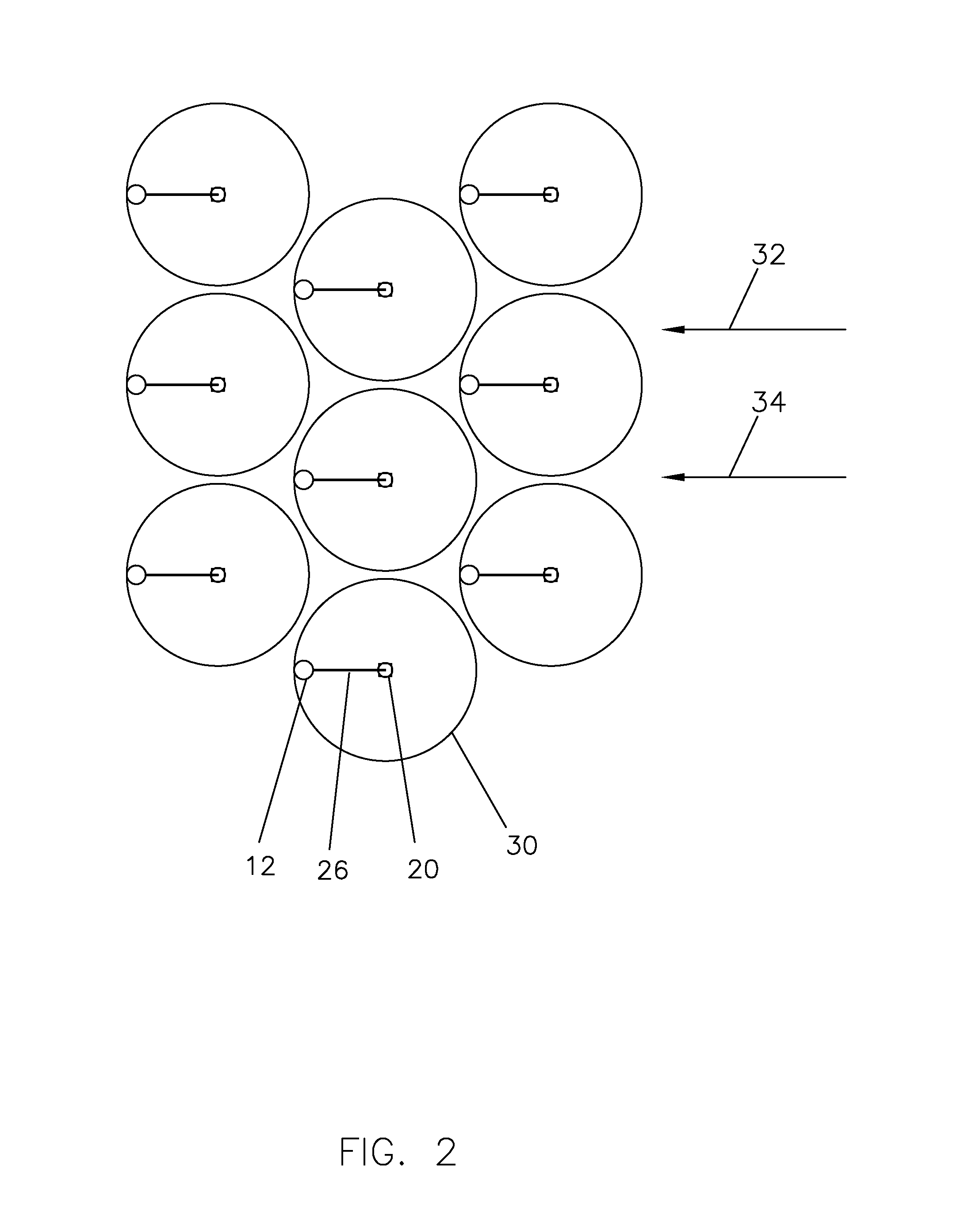
A system for harvesting energy from wave oscillation includes an energy harvesting vessel and, possibly, a transport vessel. The energy harvesting vessel can have multiple hulls disposed in parallel with wave channels therebetween for receiving incoming waves. Multiple bobber devices can be disposed in series within each wave channel to absorb energy from incoming waves. Reciprocating movement of buoyant float heads of the bobber devices can be converted to electrical energy by a hydraulic engine and a generator. The electrical energy can power an electrolyzer to separate supplied water into hydrogen and oxygen. Once harvested, the hydrogen and oxygen can be transferred between storage tanks on the energy harvesting vessel and the transport vessel for transport and usage. A horizontal movement sea anchor can resist undesired horizontal movement, and a vertical movement sea anchor can resist undesired vertical movement.
Owner:RUSSO MICHAEL L
Elevated dock
InactiveUS20110146554A1Safely elevate the boat out of the waterDry-dockingAnchorsSalt waterPontoon bridge
An elevated dock designed to lift boats out of the water when not in use is provided because storing a boat in the water exposes the boat to contaminants in both fresh and salt water. These contaminants attach to the bottom of the boat severely impeding the performance of the boat. Cleaning these contaminants off of the boat is time consuming and costly. Repeated cleaning of the boat will eventually result in damage to the hull. The elevated dock uses polymer to form adjustable pontoons that can easily be fitted to a variety of sizes and styles of boats. An embodiment of the elevated dock uses an articulated set of pontoons for lifting sailboats. The elevated dock can be deployed completely independent of the dock, eliminating unwanted stress to the dock. The unique gusset design, free-floating feature, articulated pontoon option coupled with the unique manner in which the pontoon length, width and volume can be adjusted for various boat types and sizes.
Owner:WRIGHT JEFF +2
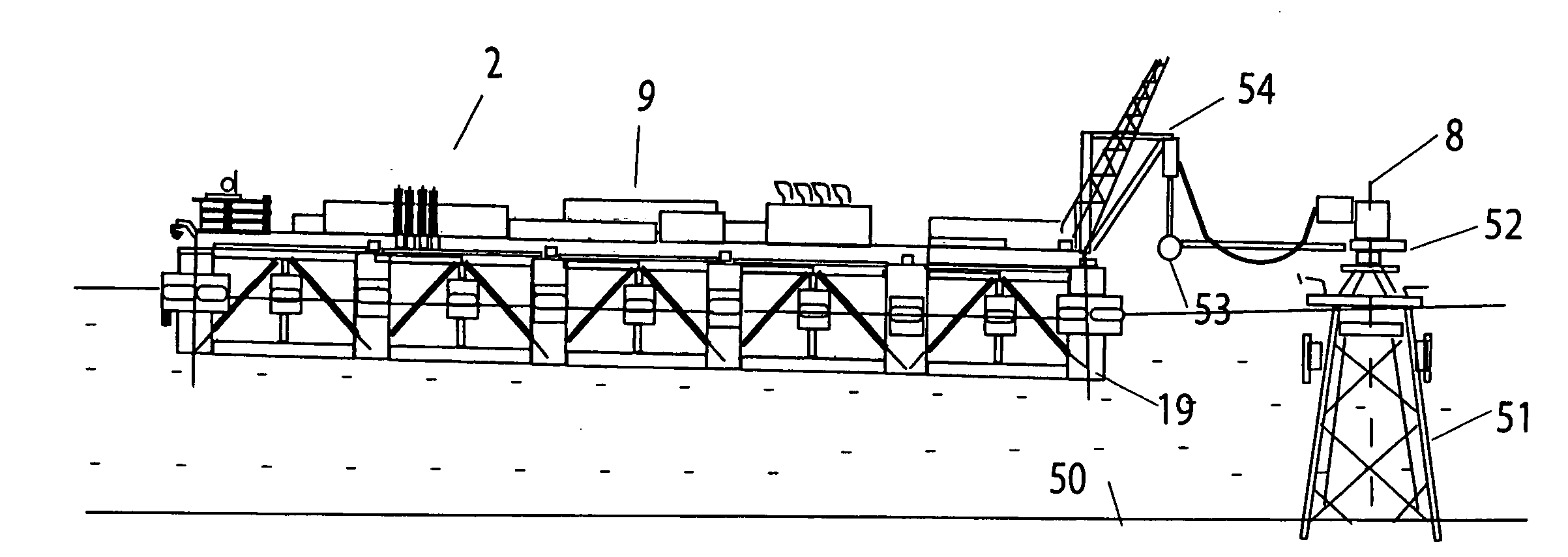
Offloading arrangements and method for spread moored FPSOs
InactiveUS6983712B2Avoid contactRapid disconnectionCargo handling apparatusPassenger handling apparatusMooring systemDynamic positioning
A mooring arrangement between a floating storage body spread moored in deep water and a shuttle tanker, the arrangement including a single point buoyant member that is adapted for mooring a shuttle tanker in offloading position relative to a floating production, storage and offloading vessel (FPSO) with a link between the floating storage body and the single point buoyant member. One embodiment (100) of the invention employs a submerged yoke (30), having one end (31) rotatably coupled to a FPSO (10) and a second end (32), supported by a buoy. A mooring hawser (28) extends from the buoy to the shuttle tanker and product hoses connect the shuttle tanker with the FPSO and extend along the submerged yoke. In another embodiment, the mooring buoy is stationed by a hold-back mooring system (303–304) and the FPSO or the tanker or both is provide with traction device (308) to move the tanker into loading position with respect to the FPSO. Other embodiments of the invention establish mooring of a shuttle tanker so that it can weathervane 360 degrees during offloading activity. In another embodiment, the mooring buoy (600) is provided with a dynamic positioning system (614) for controlling shuttle tanker positioning with respect to conditions of the environment or for moving the tanker to a desired position during loading.
Owner:SOFEC
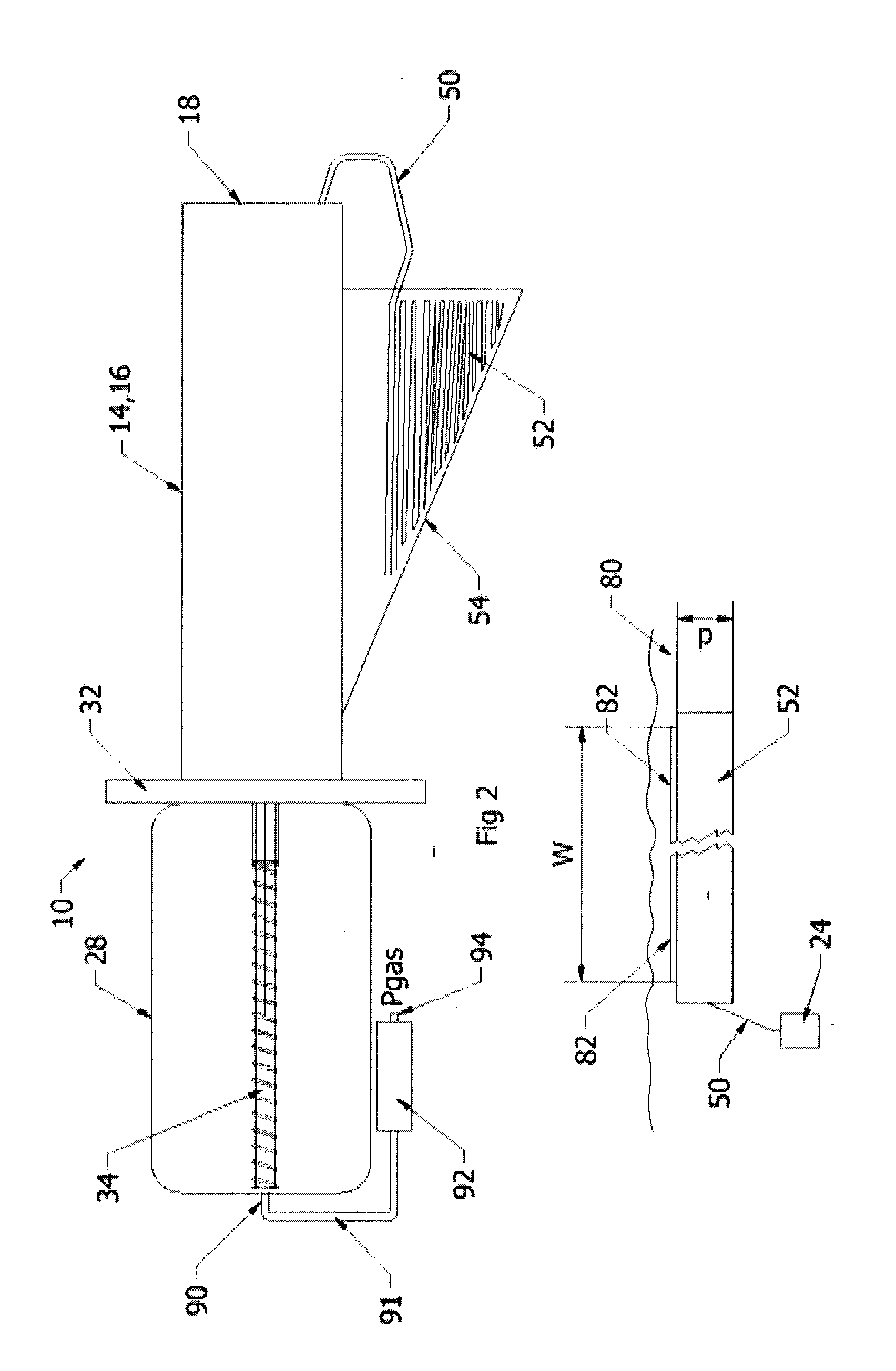
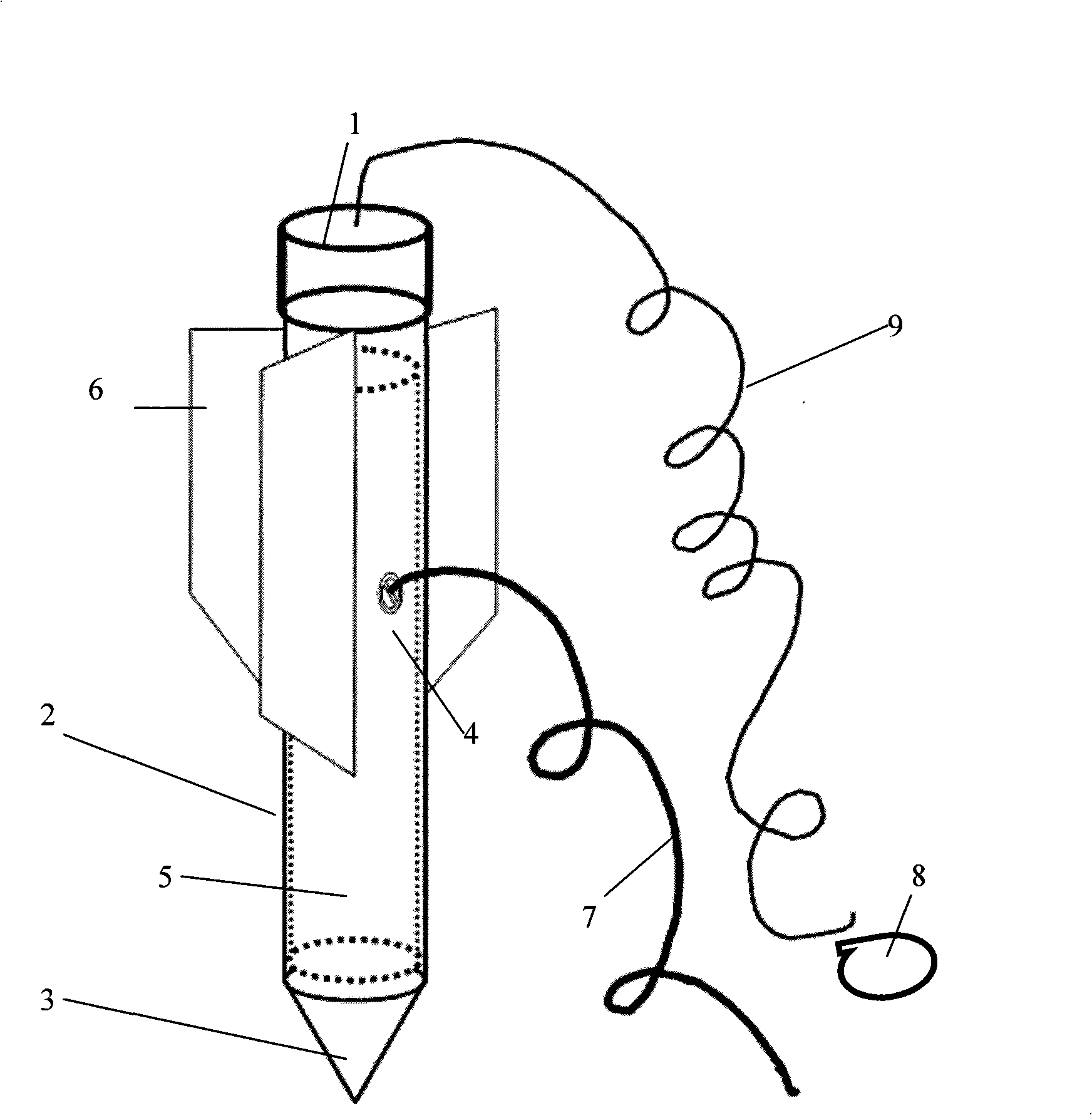
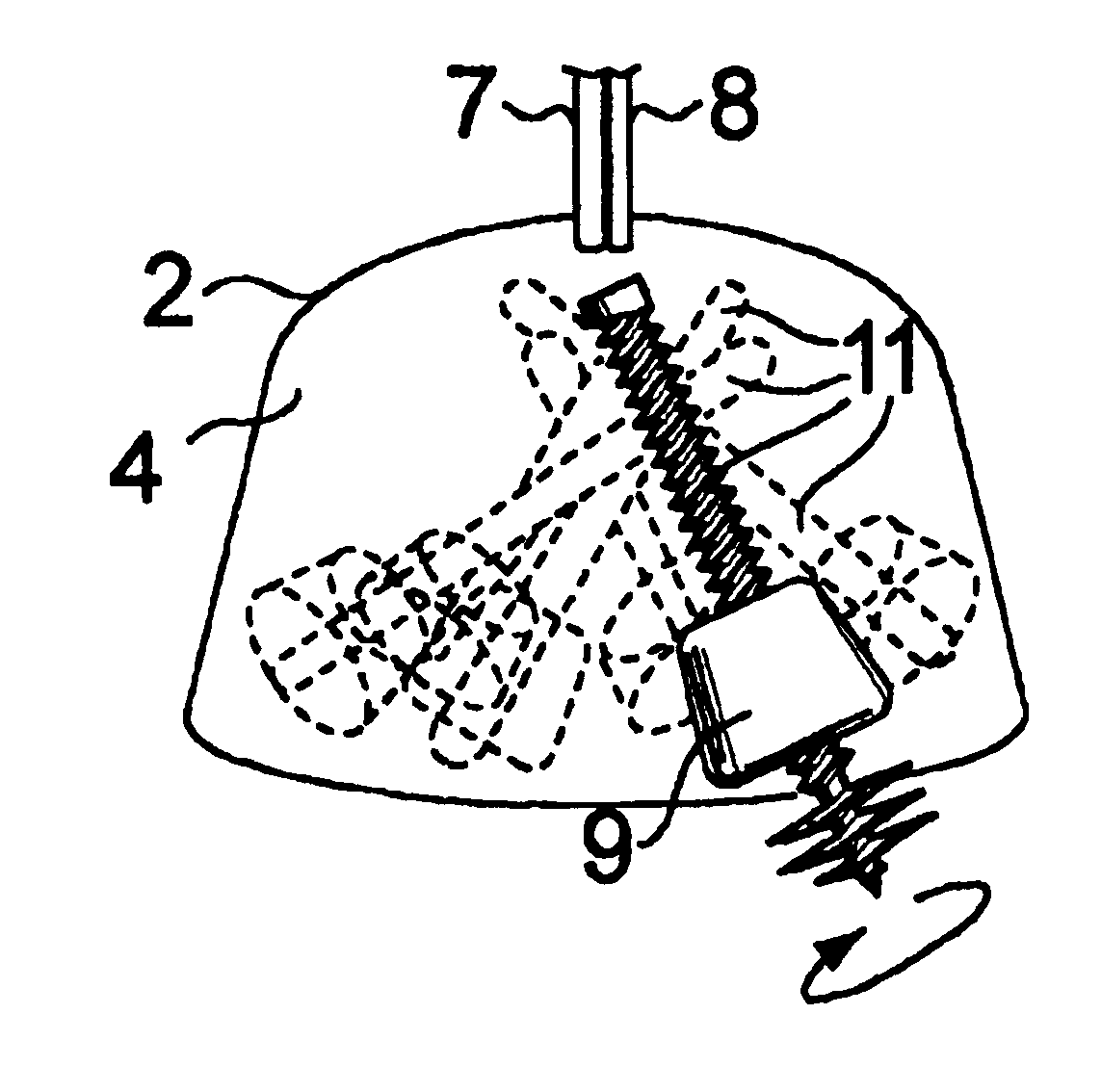
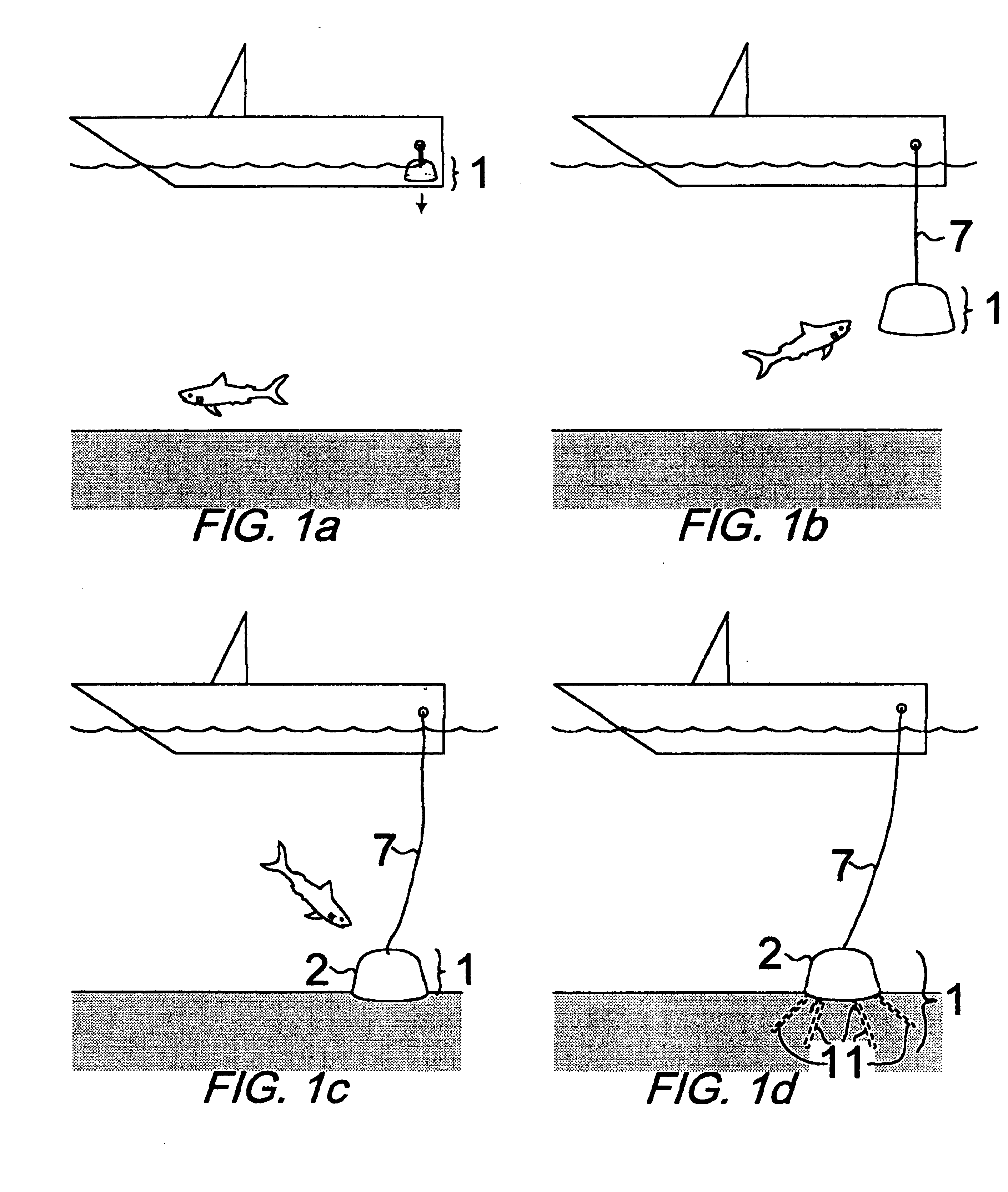
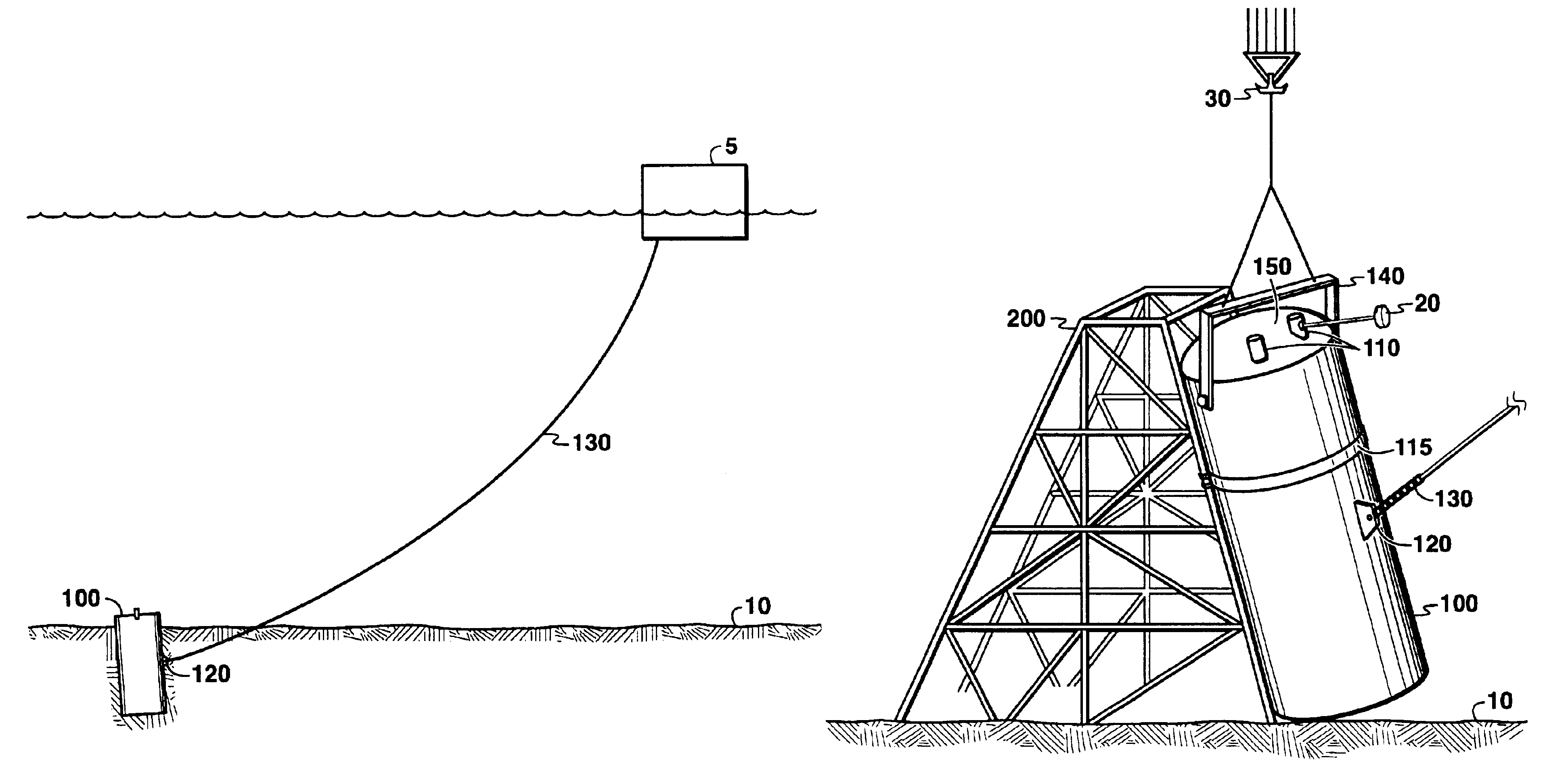
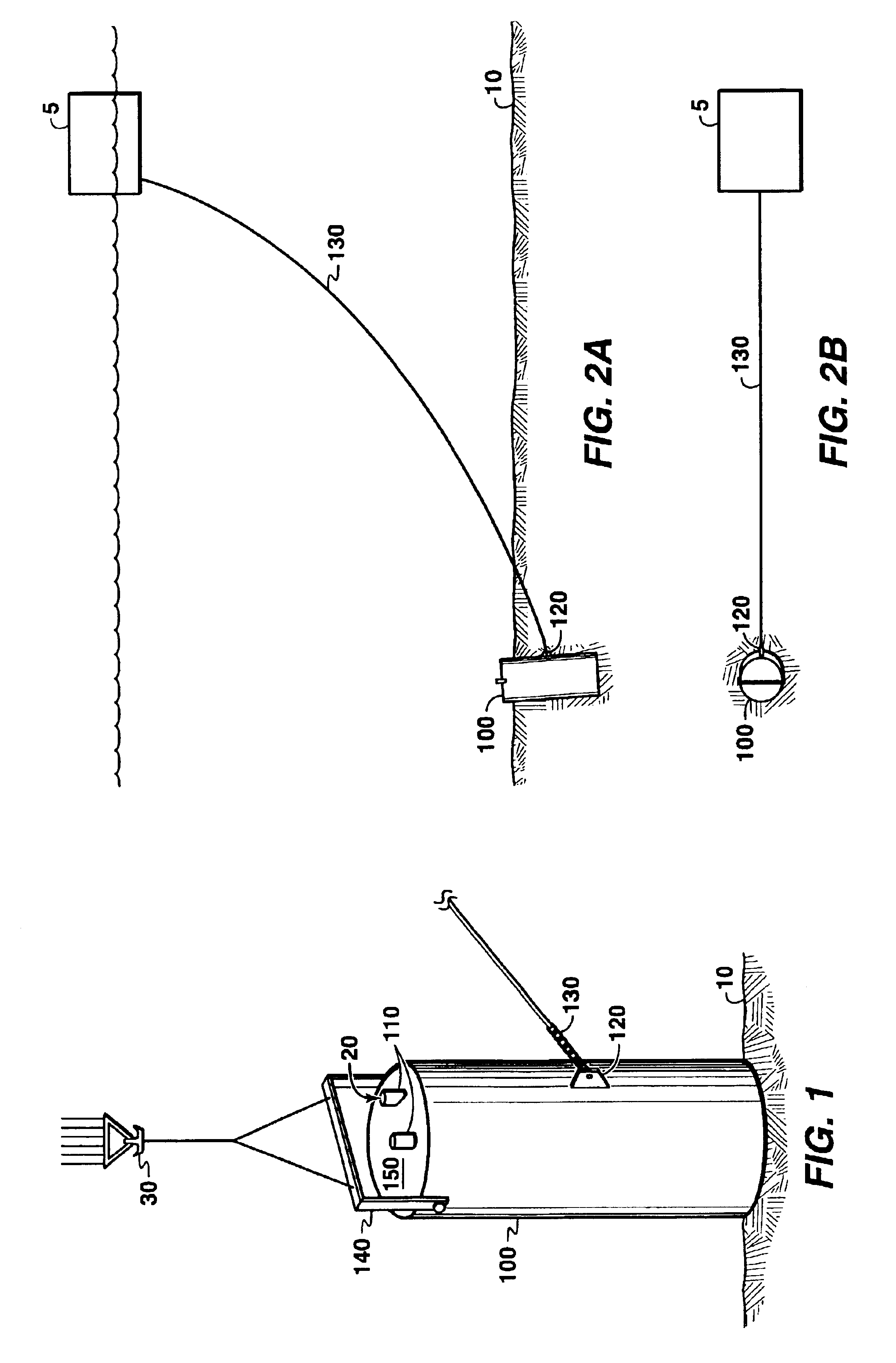
Subsea anchor
Subsea anchor (1) having a hollow cylindrical body (3) extending down from a top part (13). The anchor has a top aperture (15) and a top hatch (17) which is adapted to close and open the top aperture (15). The cylindrical body (3) is adapted to penetrate into a seabed. The area of said aperture (15) is at least 30% of the corresponding cross section area encircled by the cylindrical body (3).
Owner:AKER SOLUTIONS AS
Floating LNG import terminal and method for docking
ActiveUS20050193938A1Improve floating stabilityReduce relative motionArtificial islandsLarge containersMarine engineeringEnvironmental force
A floating terminal for offloading an LNG carrier vessel in the sea. The floating terminal of open frame construction is moored toward its front end with a rotatable mooring arrangement so that the terminal may weathervane in response to environmental forces. Marine thrusters are provided at the aft end of the terminal for swinging the terminal away from and back toward a line defined by the path toward the terminal of an approaching LNG carrier. Offloading equipment and heat exchangers are provided on a deck of the floating structure. When an LNG carrier vessel approaches the terminal, the thrusters swing the floating terminal away from the carrier vessel approach line while a hawser at the front end of the terminal pulls the vessel close to the terminal. The floating terminal swings back toward the carrier vessel in response to operating the marine thrusters in an opposite direction until the carrier vessel and floating terminal are side-by-side. The hawser continues to pull the carrier vessel forward with respect to the terminal until loading arms at the side of the terminal are aligned side-by-side with a manifold of the carrier vessel.
Owner:SOFEC
Method for installing a pile anchor
InactiveUS6910831B2Soil-shifting machines/dredgersPropulsive elementsOcean bottomStructural engineering
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method of Single Line Mooring
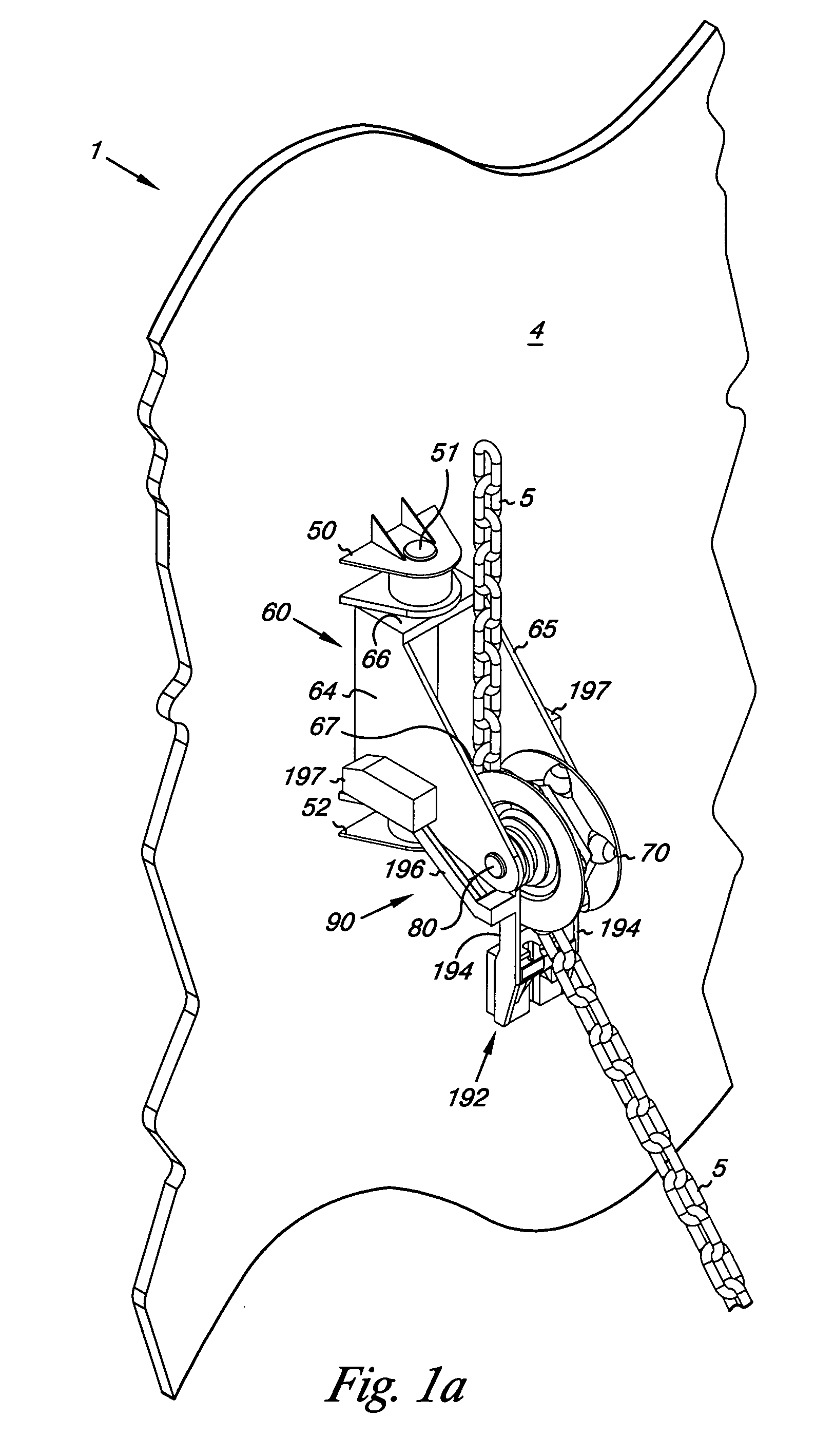
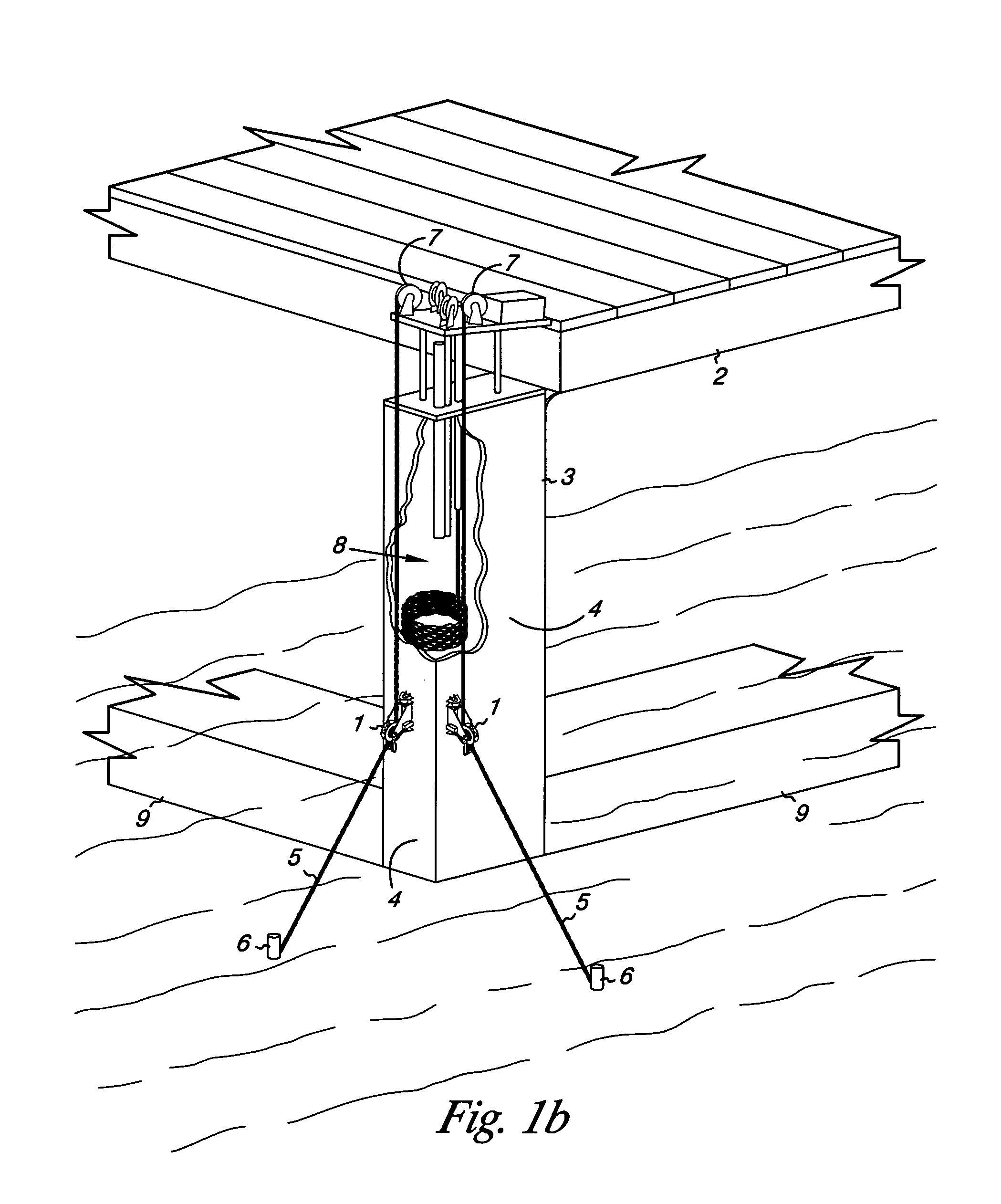
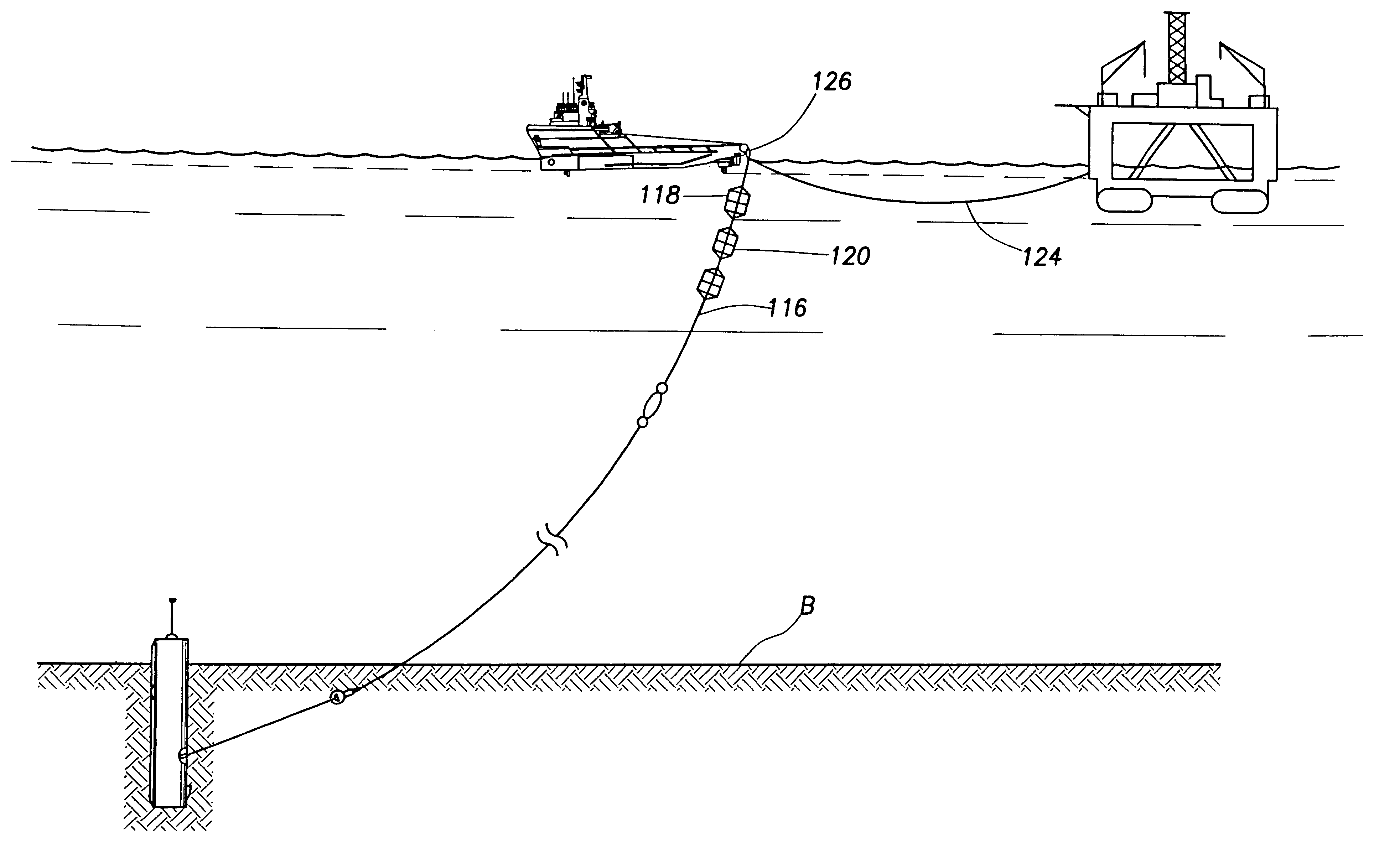
The method of mooring buoyant equipment at the surface of a body of water in a controlled position using a single line by connecting a first line from the buoyant equipment to a first diameter drum on a subsea mooring tower, connecting the first diameter drum to a second diameter drum, connecting a second line from the second diameter drum to a weight, such that when the depth of the body of water changes the tension on the first line remains the same and the vertical distance travelled by the weight is less than the change in the depth of the body of water.
Owner:REEL POWER LICENSING
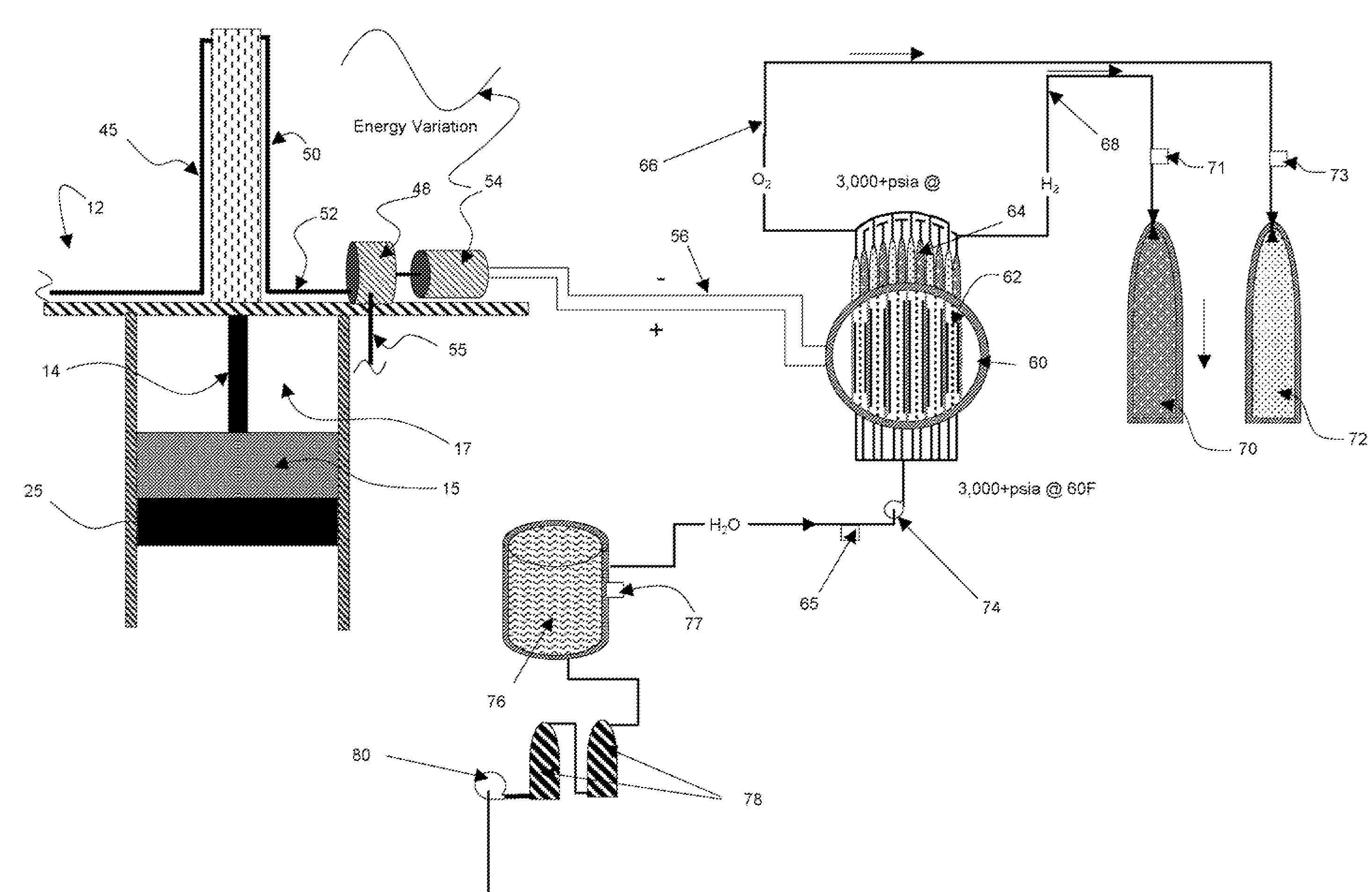
Sea-based hydrogen-oxygen generation system
InactiveUS6918350B1Maximize torqueWorking fluid for enginesWind energy with garvitational potential energyElectrolysisGas cylinder
A method for generation of hydrogen and oxygen contained in a salt solution provides for the disposing a number of wind turbines on navigable collection vessels in waters distant from shore. The wind turbines have a large number of blades, typically 30, to provide high torque for generating electricity used for extracting said gasses from the atmosphere by means of electrolysis. The collection vessels are disposed in predetermined zones, which are changed when weather conditions provide better collection conditions elsewhere. The gasses are stored in cylinders located both on the collection vessels, and on storage vessels attached to the collection vessels. After collection the cylinders are transported to shore facilities for further purification and / or distribution.
Owner:MORSE MR ARTHUR P +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com