Wireless Communication Apparatus and Wireless Communication Method
a wireless communication and wireless communication technology, applied in the direction of signal characterisation, transmission path division, transmission path sub-channel allocation, etc., can solve the problems of low throughput, degrade reception performance, and increase the overhead of feedback information, so as to reduce the amount of data in feedback information and achieve high throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
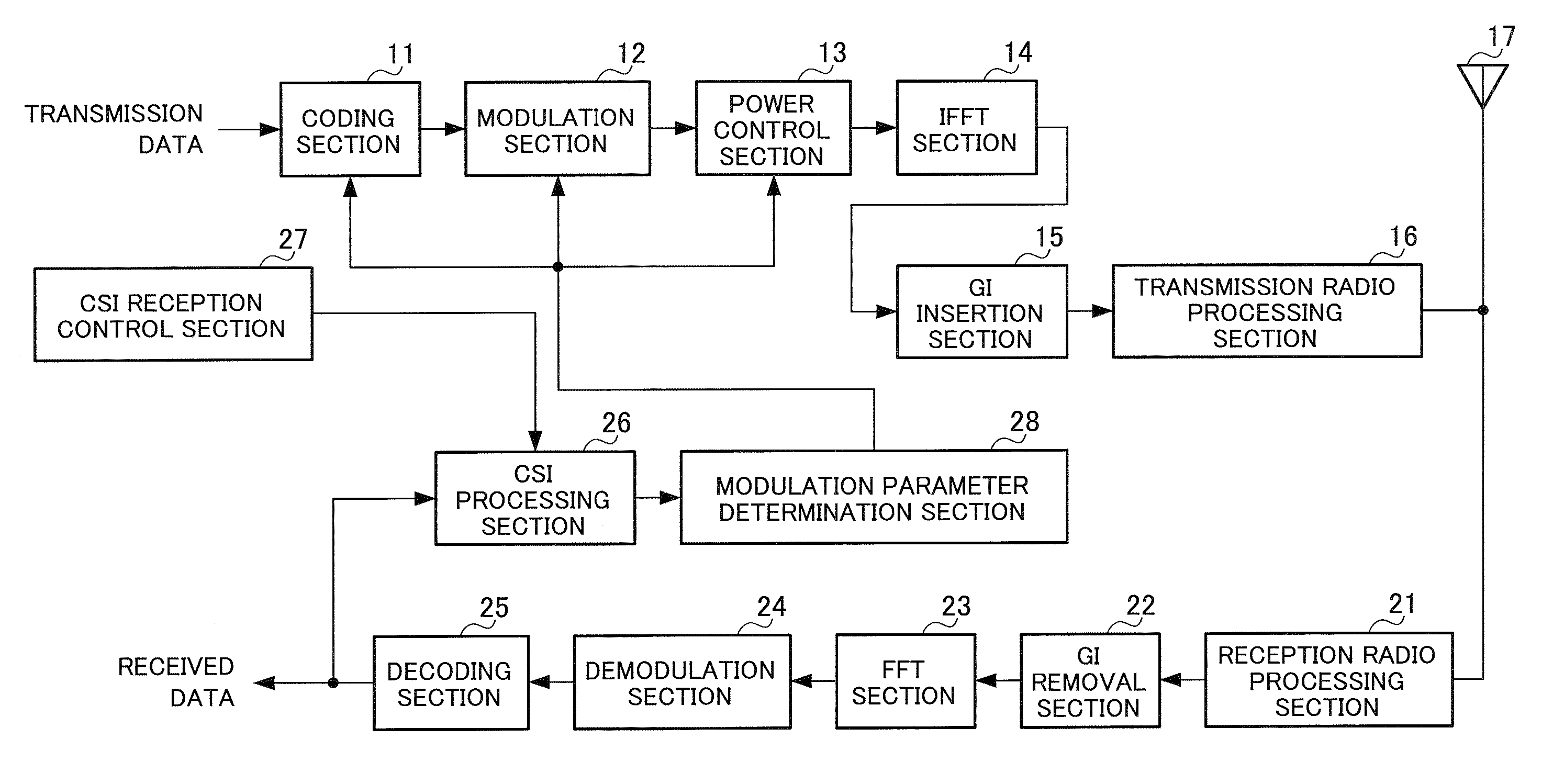
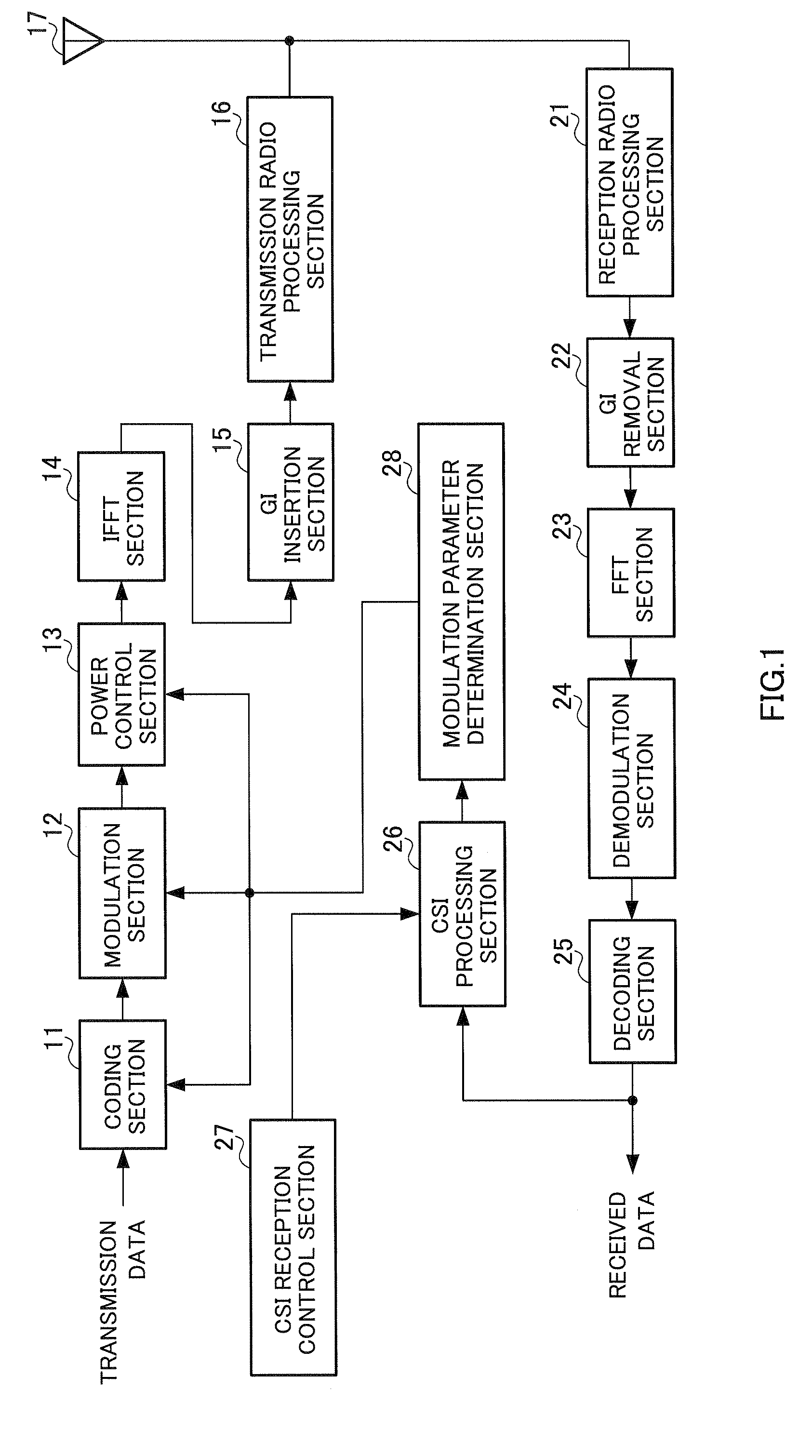
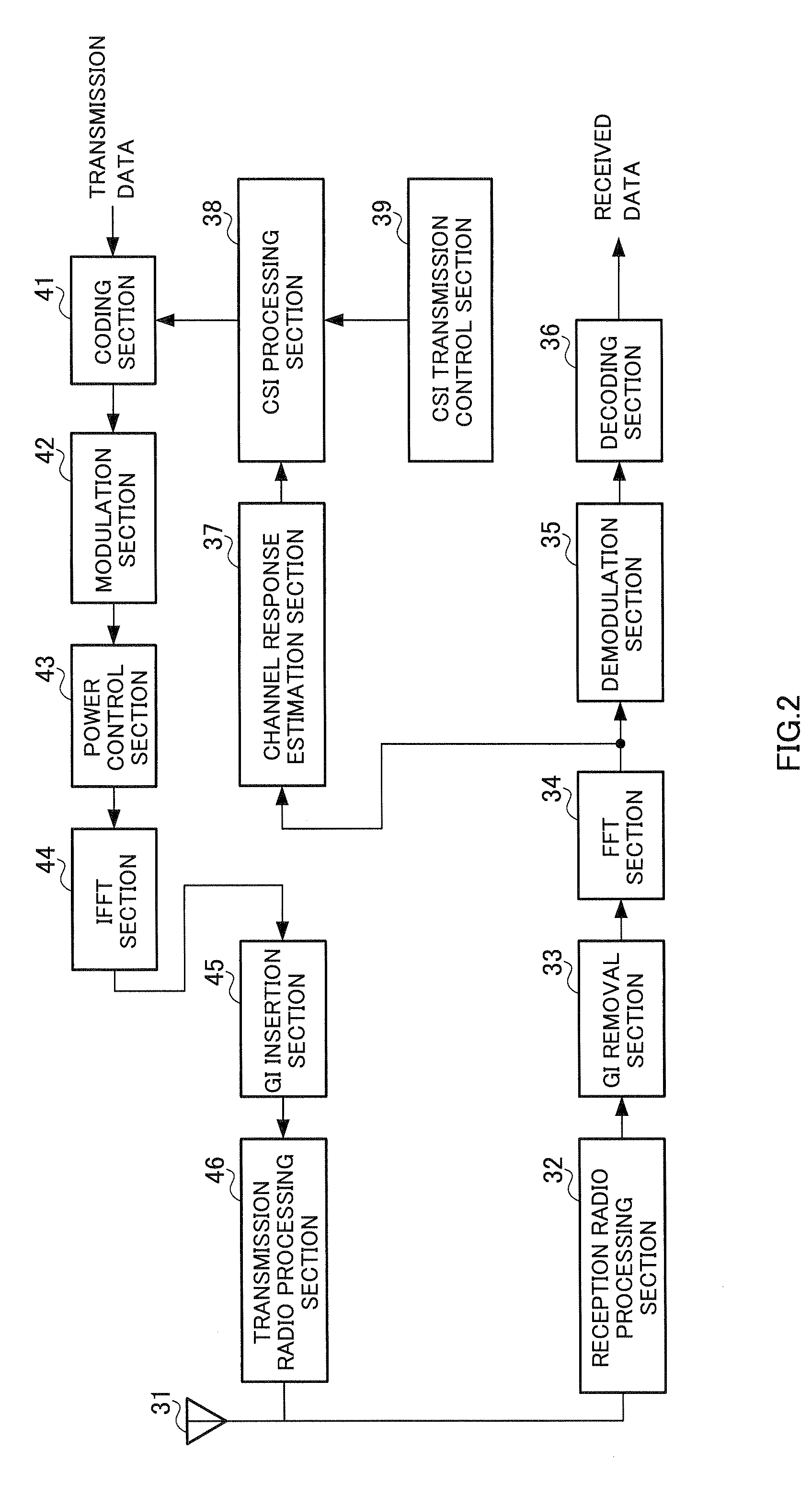
[0072] The radio communication apparatus shown in FIG. 1 is a CSI receiving-side radio communication apparatus, and the radio communication apparatus shown in FIG. 2 is a CSI transmitting-side radio communication apparatus. In the following description, a CSI receiving-side radio communication apparatus is referred to as a CSI receiving apparatus, and a CSI transmitting-side radio communication apparatus is referred to as a CSI transmitting apparatus. A CSI receiving apparatus transmits a multicarrier signal composed of a plurality of subcarriers to a CSI transmitting apparatus using modulation parameters (one or more of: channel coding method, channel coding rate, modulation method, transmission power) determined based on CSI. On the other hand, a CSI transmitting apparatus receives a multicarrier signal transmitted from a CSI receiving apparatus, and generates CSI based on a channel response value per subcarrier or per segment of the multicarrier signal. The above CSI receiving ap...
embodiment 2
[0136] A CSI transmitting apparatus according to this embodiment has a similar configuration to that of Embodiment 1, differing from Embodiment 1 in that an update timing signal is input to comparison result memory 385 only at the timing at which CSI of all of subcarriers 1 through 24 is fed back, and comparison results are not updated at other timings.
[0137] The operation of CSI frame generation section 386 according to this embodiment is described below. In this embodiment, CSI frame generation section 386 operates as shown in FIG. 15.
[0138] In FIG. 15, first, a generation timing signal is input to CSI frame generation section 386 from CSI transmission control section 39 at timing t3n. At the same time, an update timing signal is input to comparison result memory 385, and therefore the contents of comparison result memory 385 are updated with the comparison results newly obtained by comparison section 384. After updating, the contents of comparison result memory 385 are now assu...
embodiment 3
[0155] Most multipath channel environments are NLOS (Non line of sight) environments in which there is an obstruction between a transmitting station and a receiving station, and delayed waves are known to be subject to Rayleigh variation. When the delay time of a delayed wave is large relative to the symbol time, its characteristics have frequency selectivity. In this kind of frequency selective Rayleigh fading channel, cumulative probability distribution with respect to per-subcarrier SNR is as shown below.
[0156]FIG. 21 is a graph showing per-subcarrier SNR normalized cumulative probability distribution when average SNR=30 dB in a frequency selective Rayleigh fading channel. Reference number 601 indicates the cumulative probability distribution of SNR for all subcarriers, reference number 602 indicates the cumulative probability distribution of SNR of subcarriers for which the amount of variation per unit time is less than 1 dB, and reference number 603 indicates the cumulative pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com