Patents
Literature
453results about "Tunable filters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
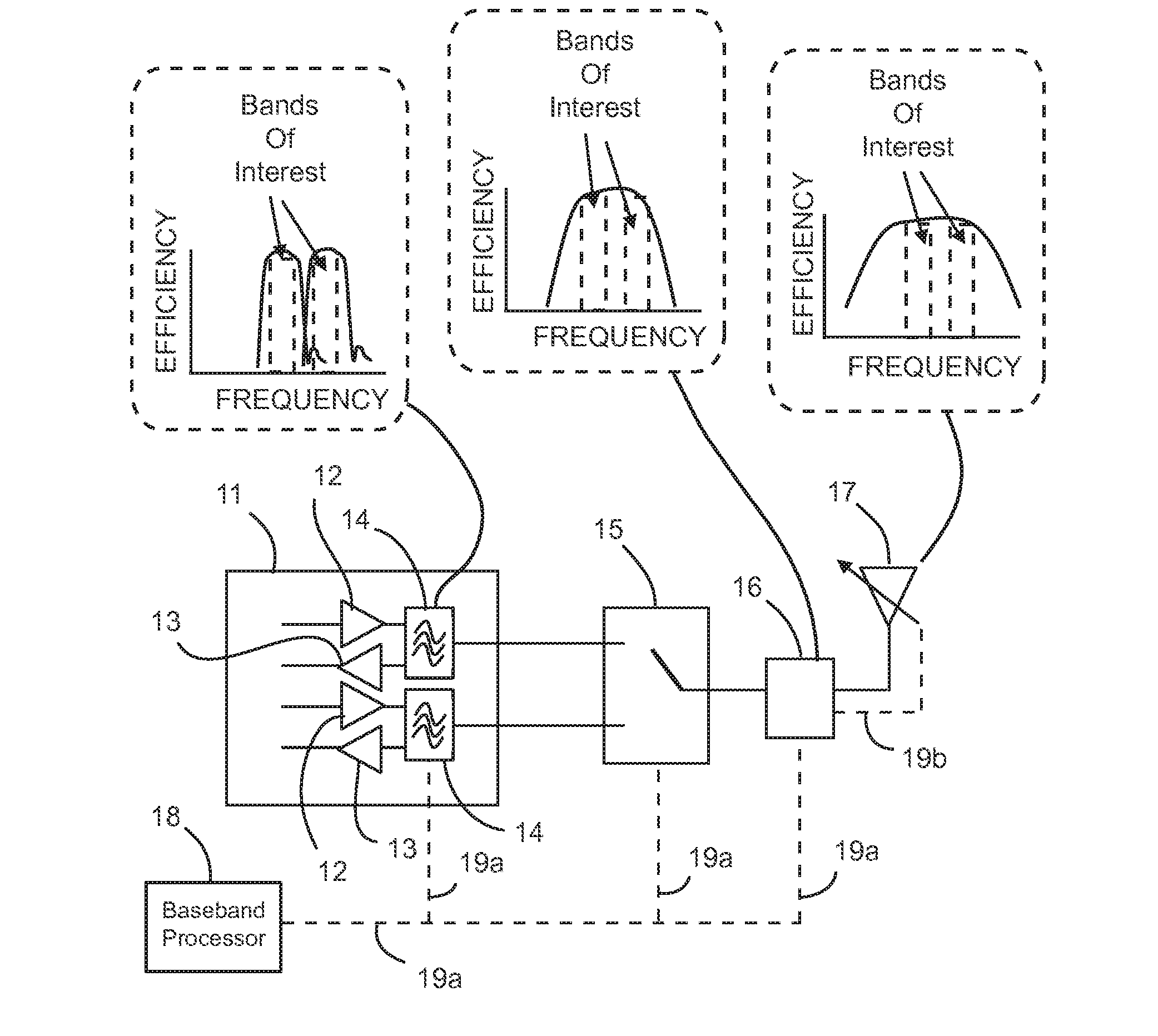
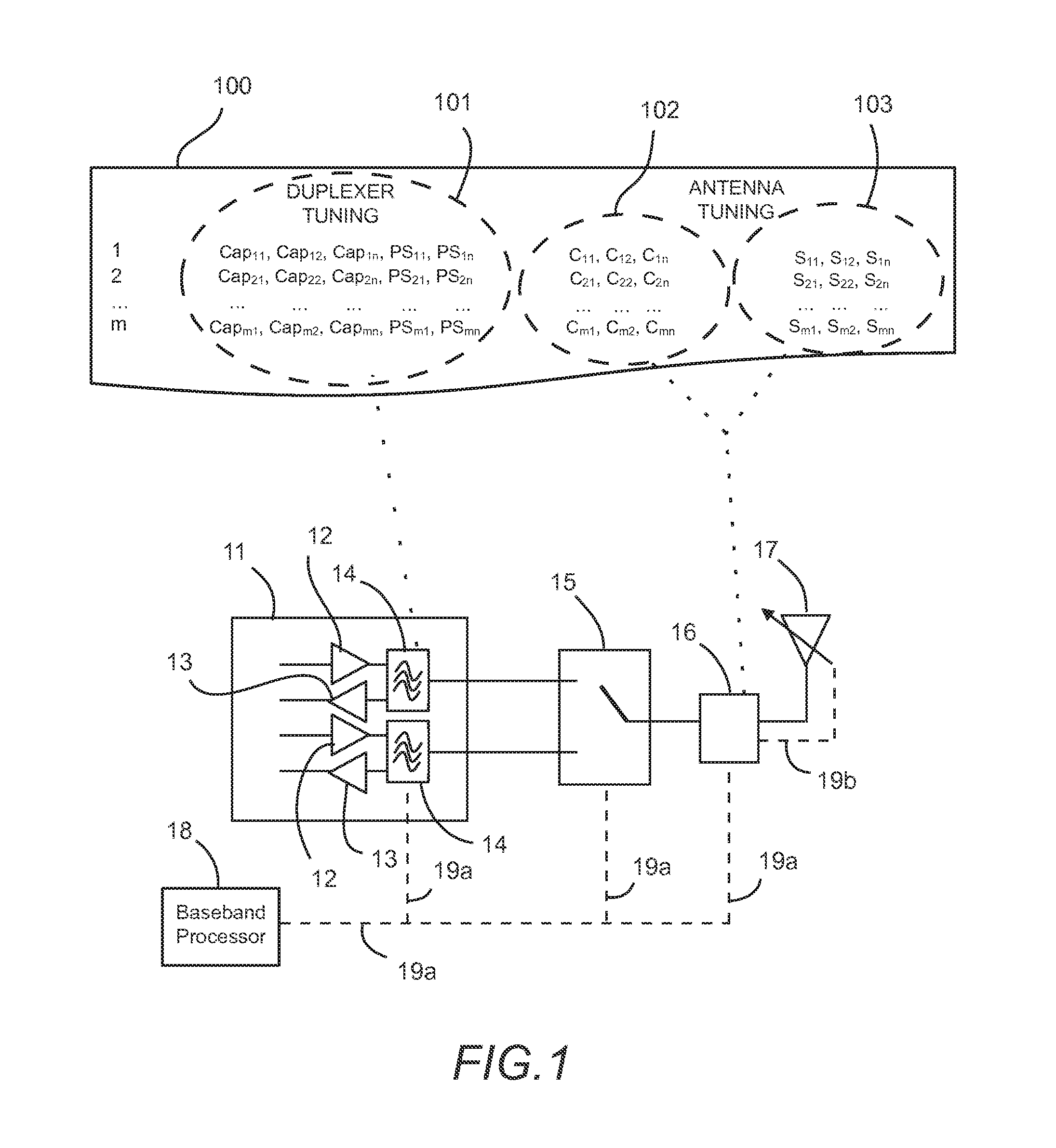
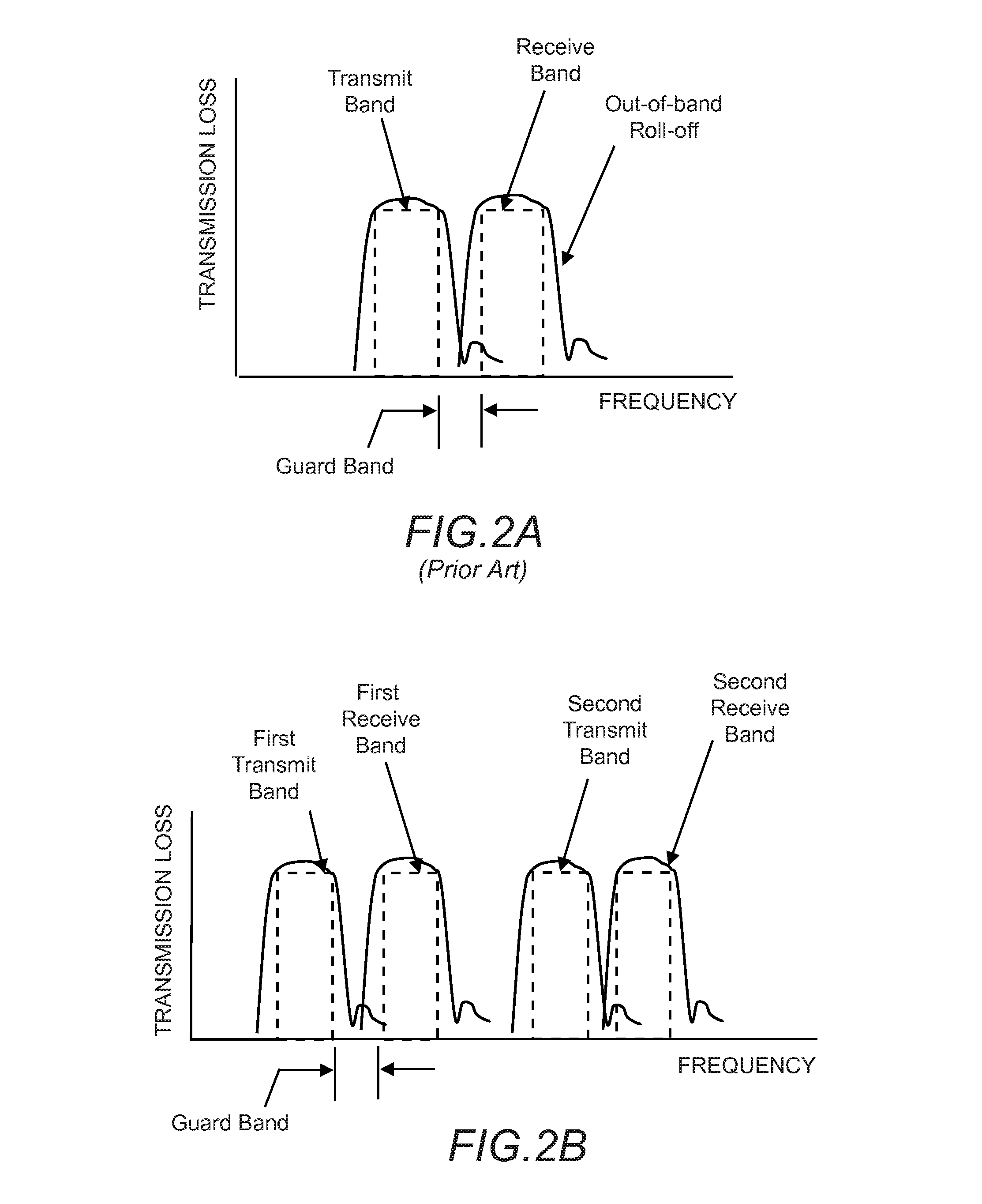
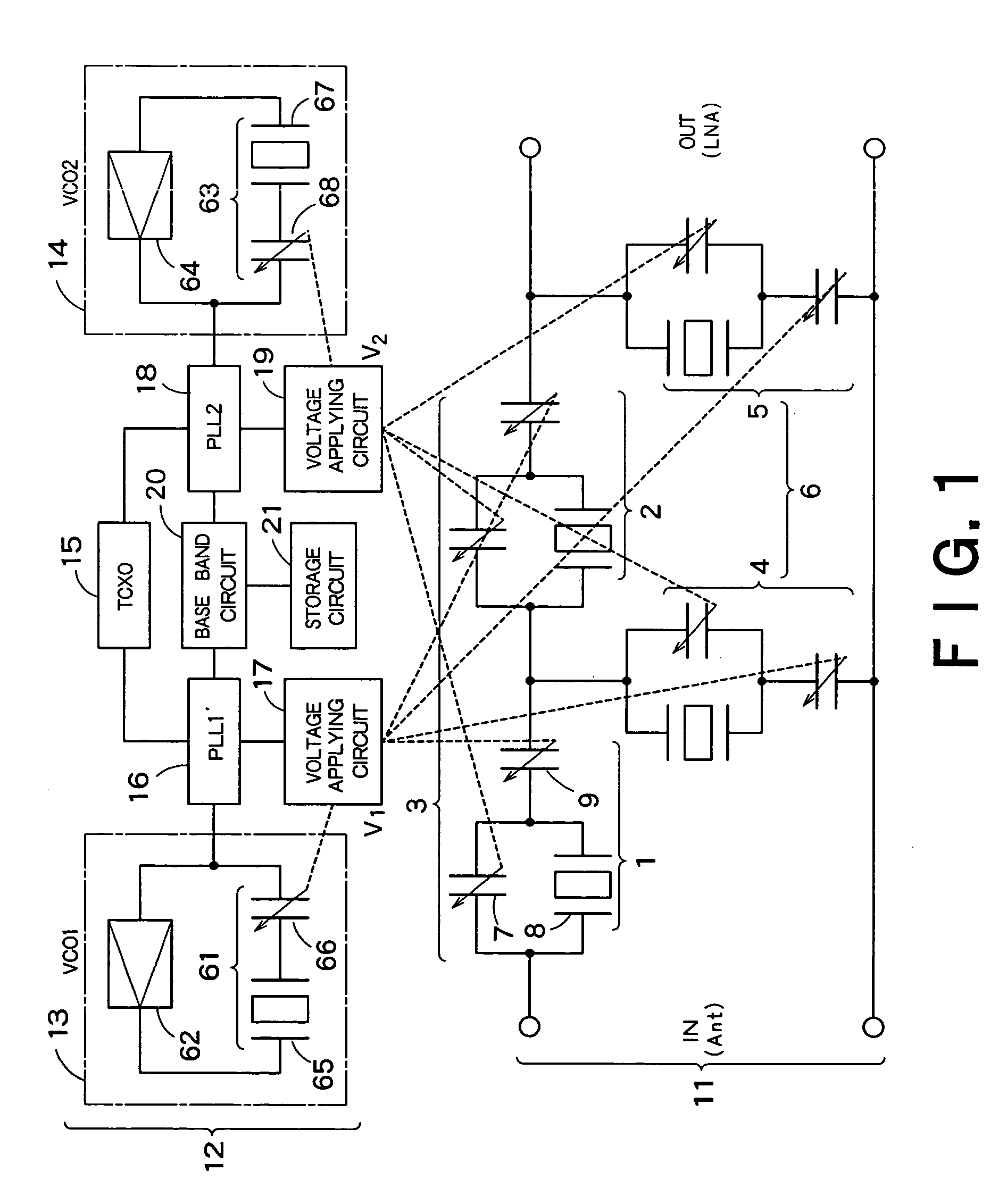
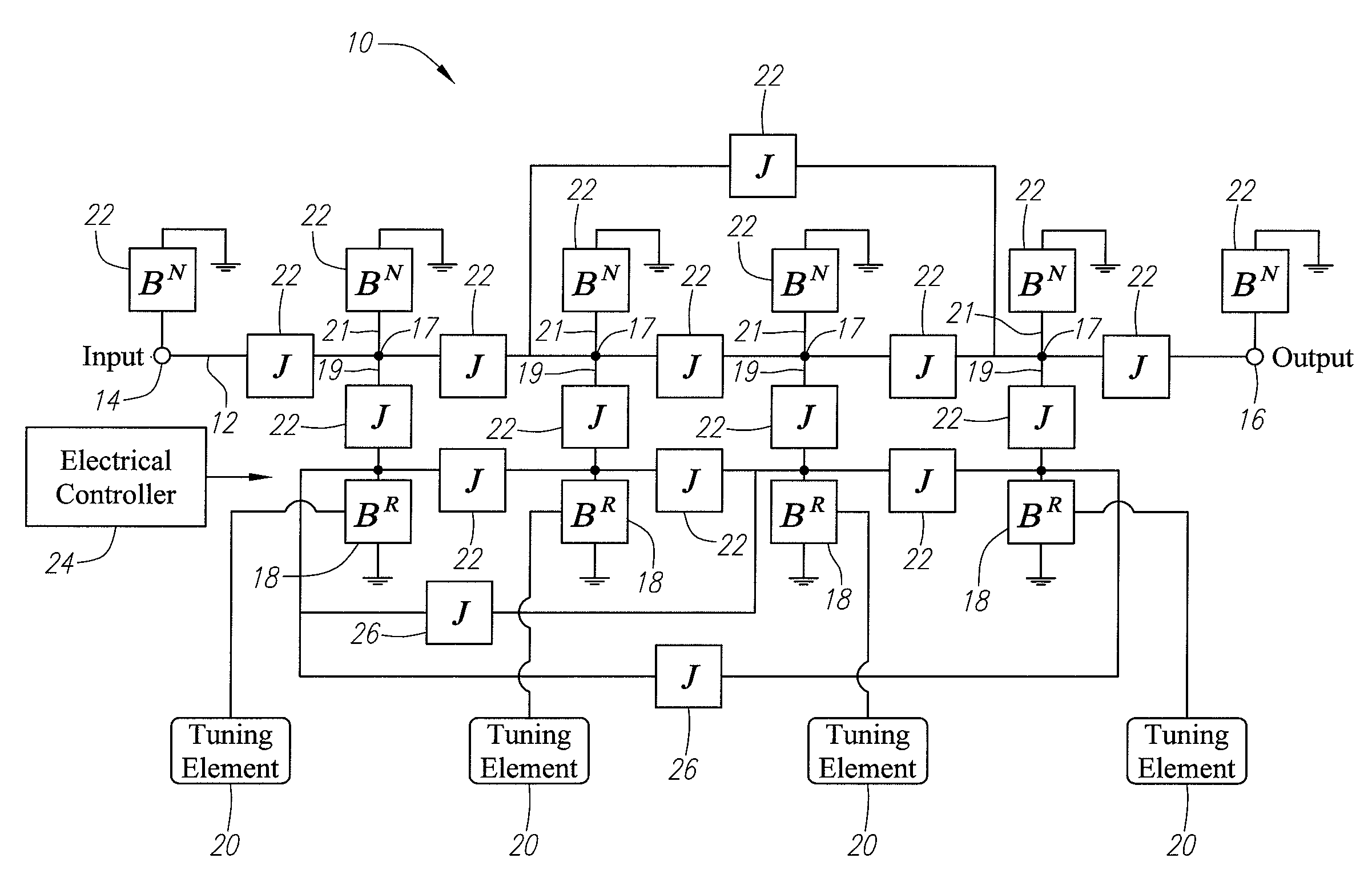
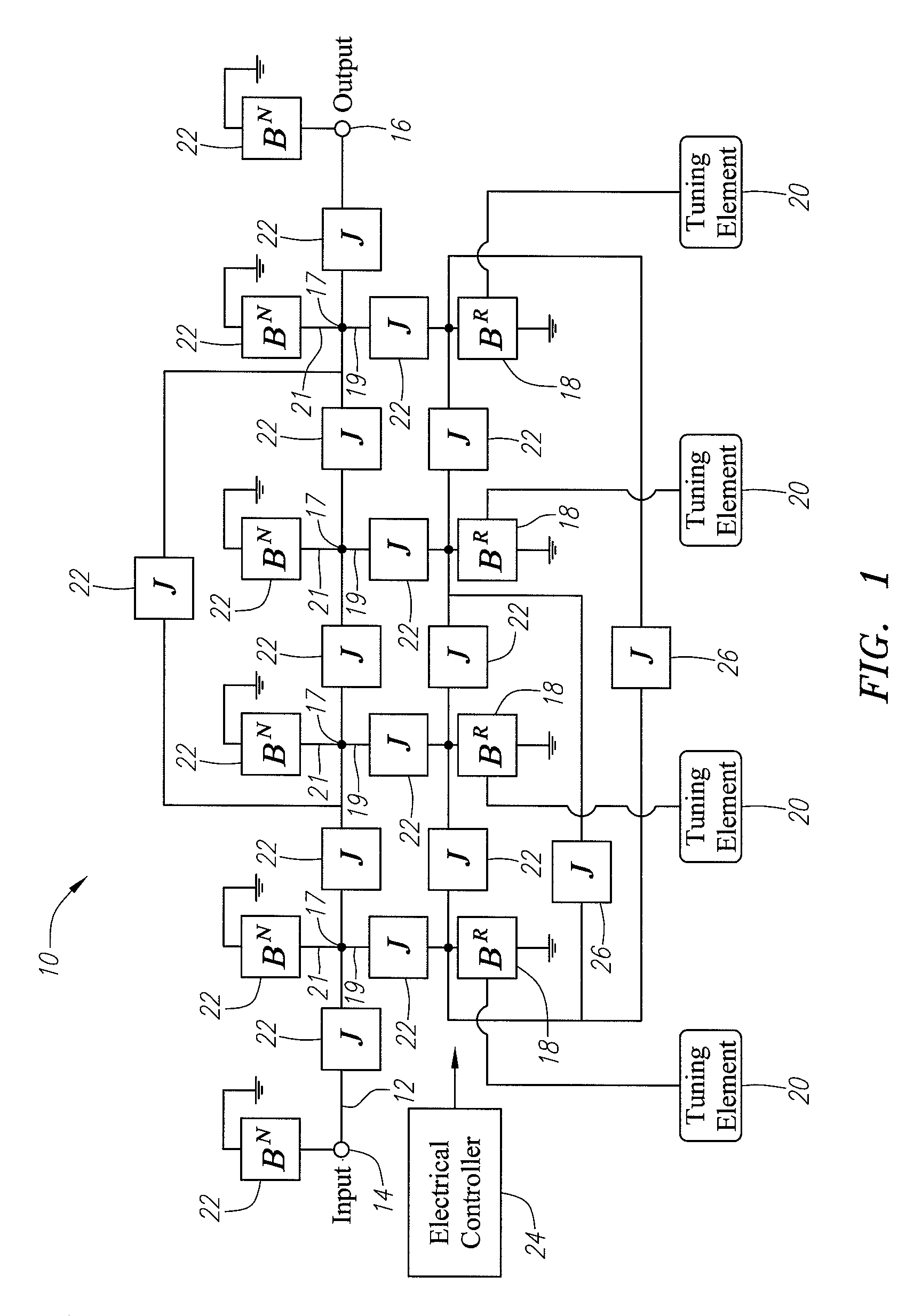
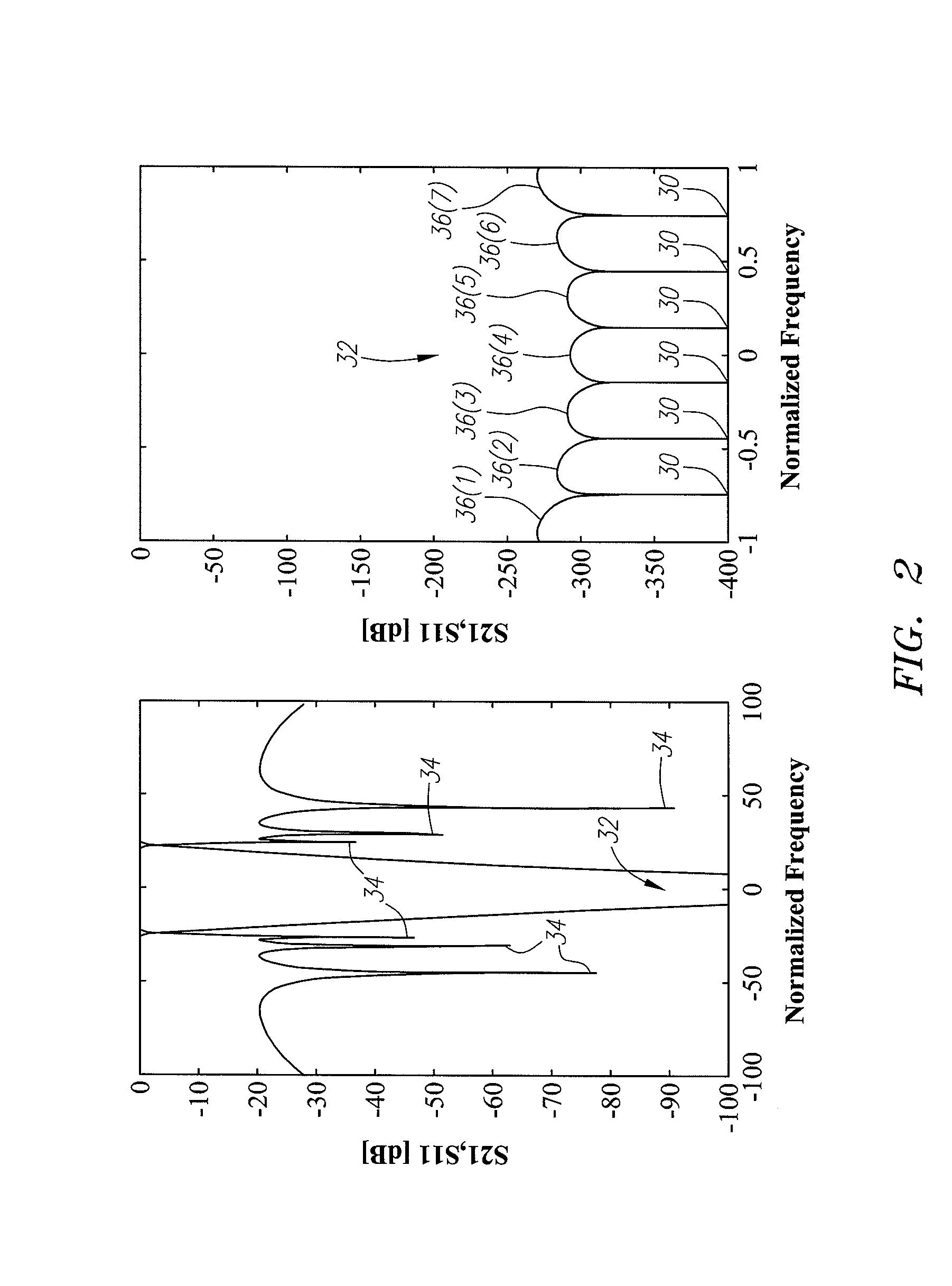
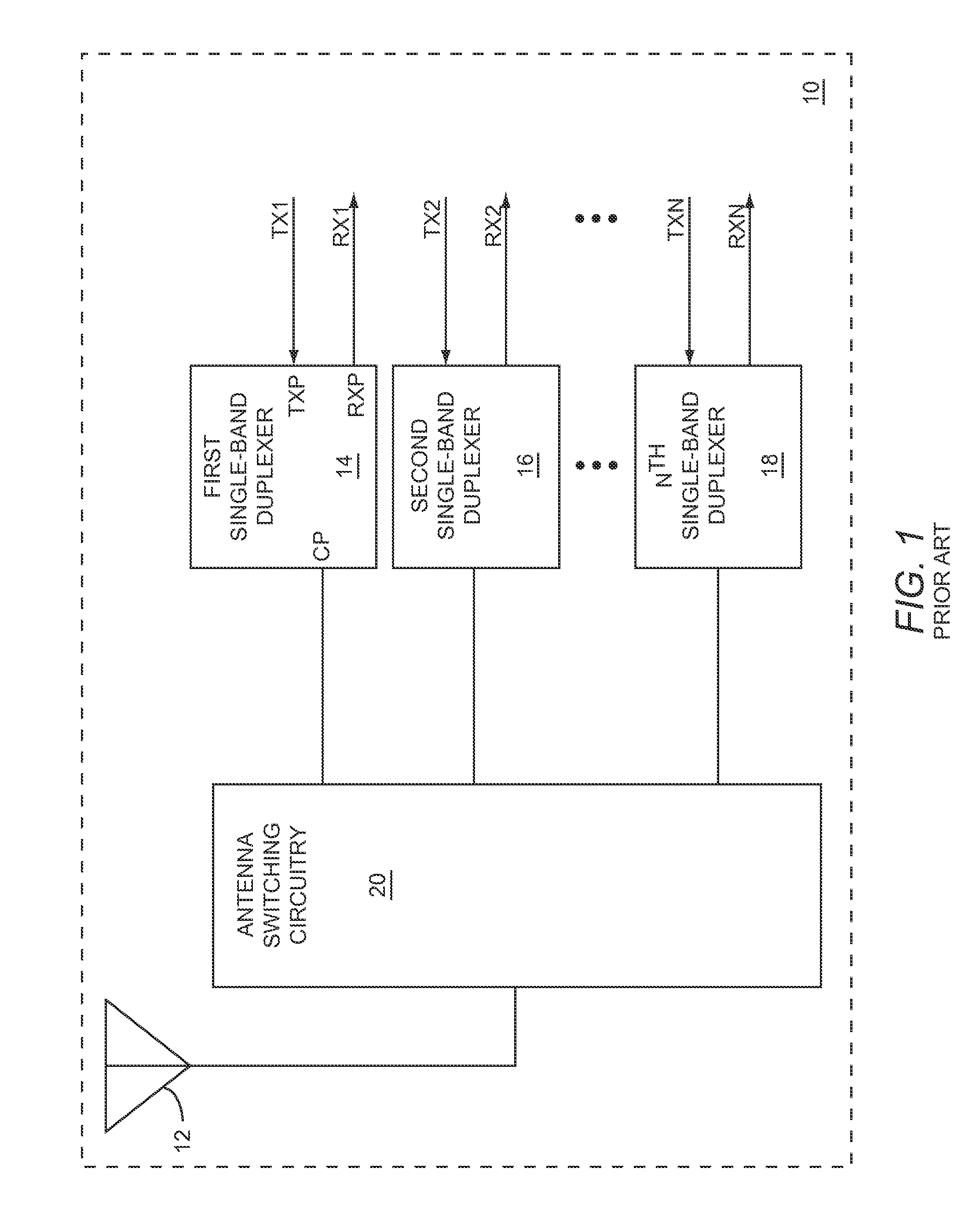
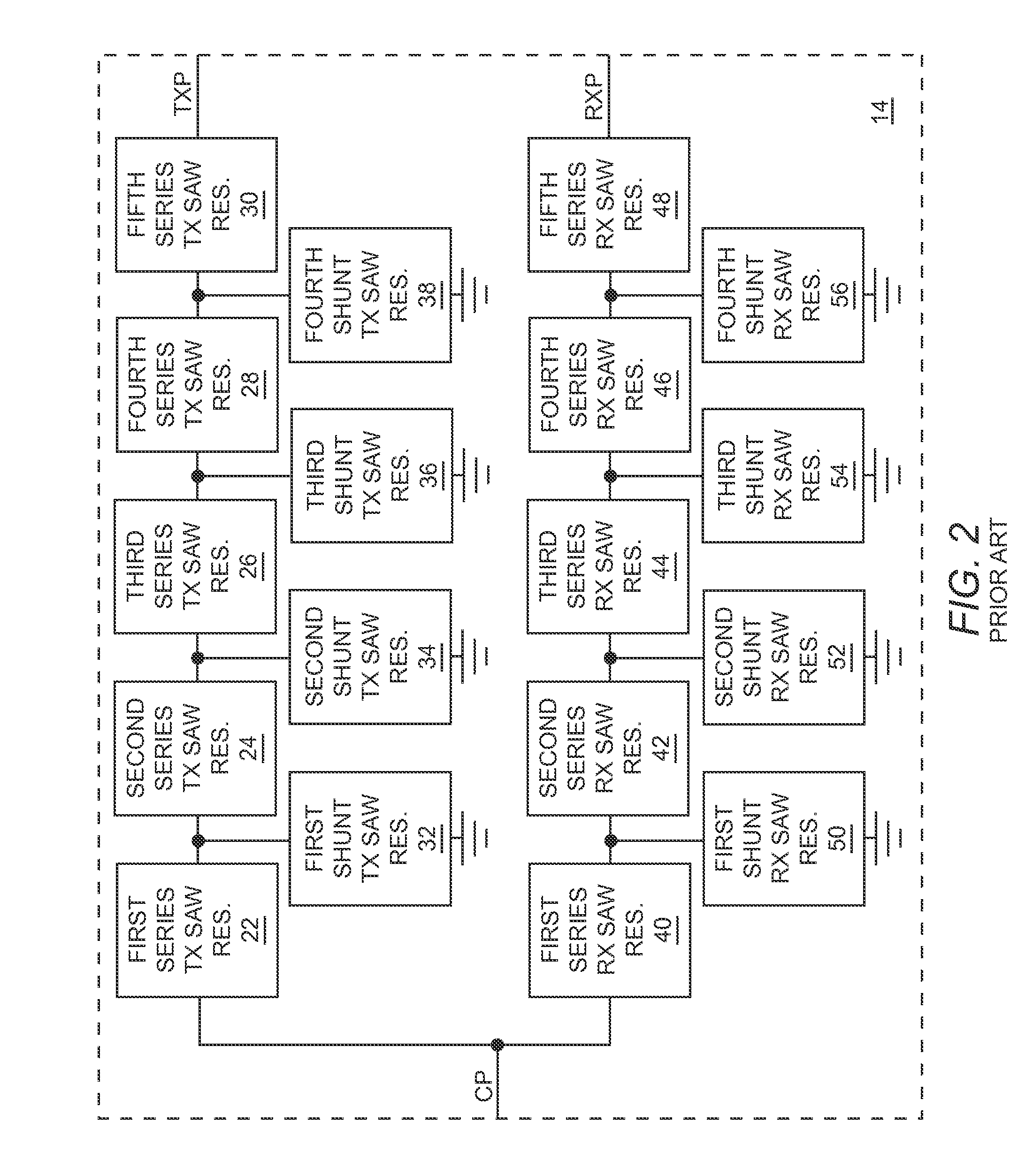
Tunable duplexing circuit
ActiveUS20150303892A1Improve performanceImprove out-of-band rejection performanceMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkRF front endTransceiver
A tunable duplexer circuit is described, wherein the frequency response as well as bandwidth and transmission loss characteristics can be dynamically altered, providing improved performance for transceiver front-end applications. The rate of roll-off of the frequency response can be adjusted to improve performance when used in duplexer applications. A method is described where the duplexer circuit characteristics are optimized in conjunction with a specific antenna frequency response to provide additional out-of-band rejection in a communication system. Dynamic optimization of both the duplexer circuit and an active antenna system is described to provide improved out-of-band rejection when implemented in RF front-end circuits of communication systems. Other features and embodiments are described in the following detailed descriptions.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Calibration of integrated circuit time constants
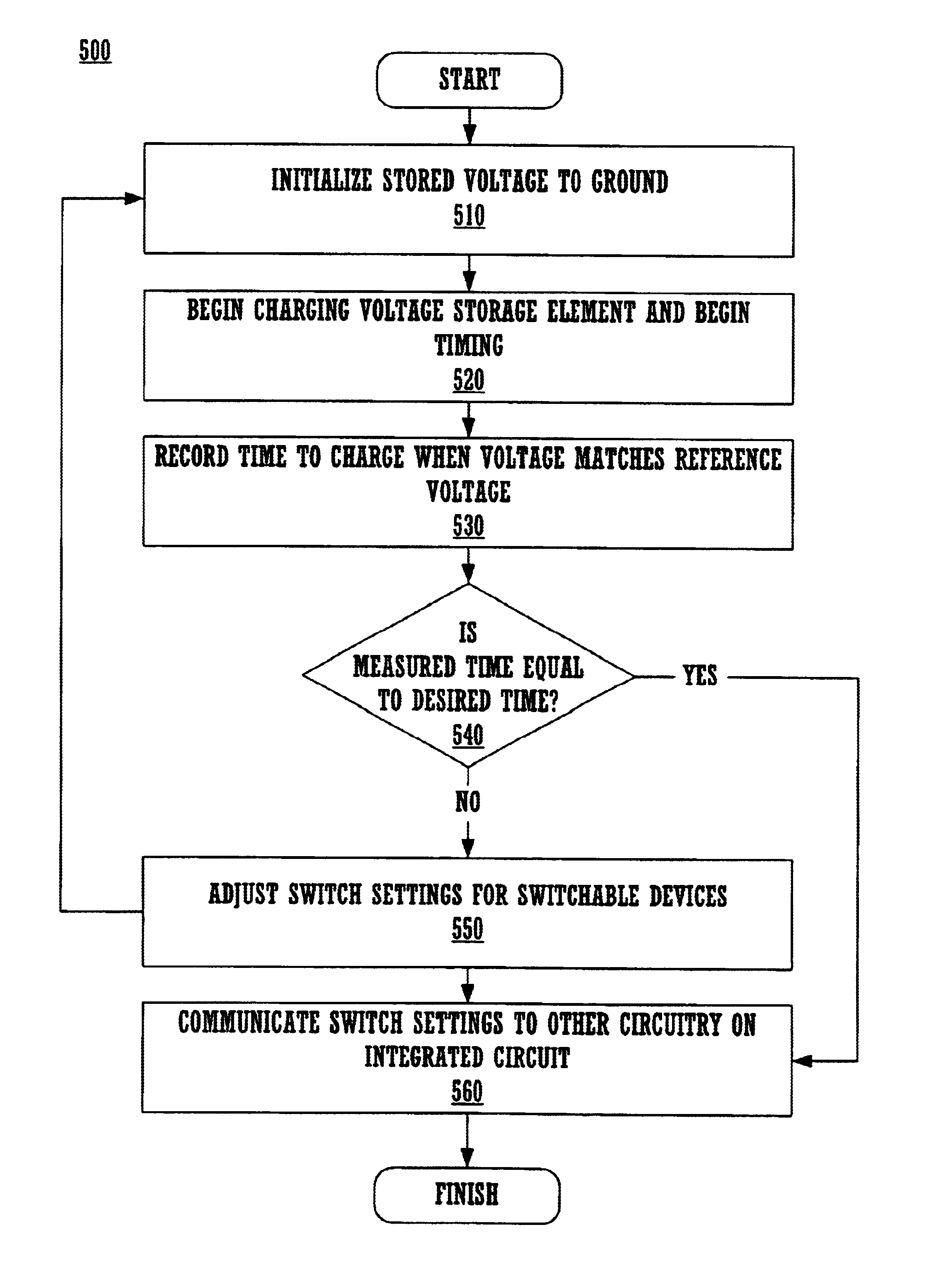
InactiveUS6842710B1Computing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationRC time constantVoltage reference
A method and system for calibrating a time constant within an integrated circuit. A voltage storage element is charged, and the time required to achieve a reference voltage on the storage element is measured. The measured time is compared to a desired time. It necessary, an adjustable impedance is modified to change the charging time, and the cycle may be repeated until the charging time matches the desired time. In this novel manner, an actual RC time constant, as rendered in a particular integrated circuit, is measured and potentially adjusted to match a desired time constant. Advantageously, configuration information of the adjustable impedance may be communicated to other circuitry within the integrated circuit to enable such circuitry to implement the same RC time constant in analog signal processing. Consequently, embodiments of the present invention overcome incidences of wide tolerance in passive components implemented in integrated circuits. Beneficially, no external test equipment is required.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Adaptive radio transceiver with floating MOSFET capacitors
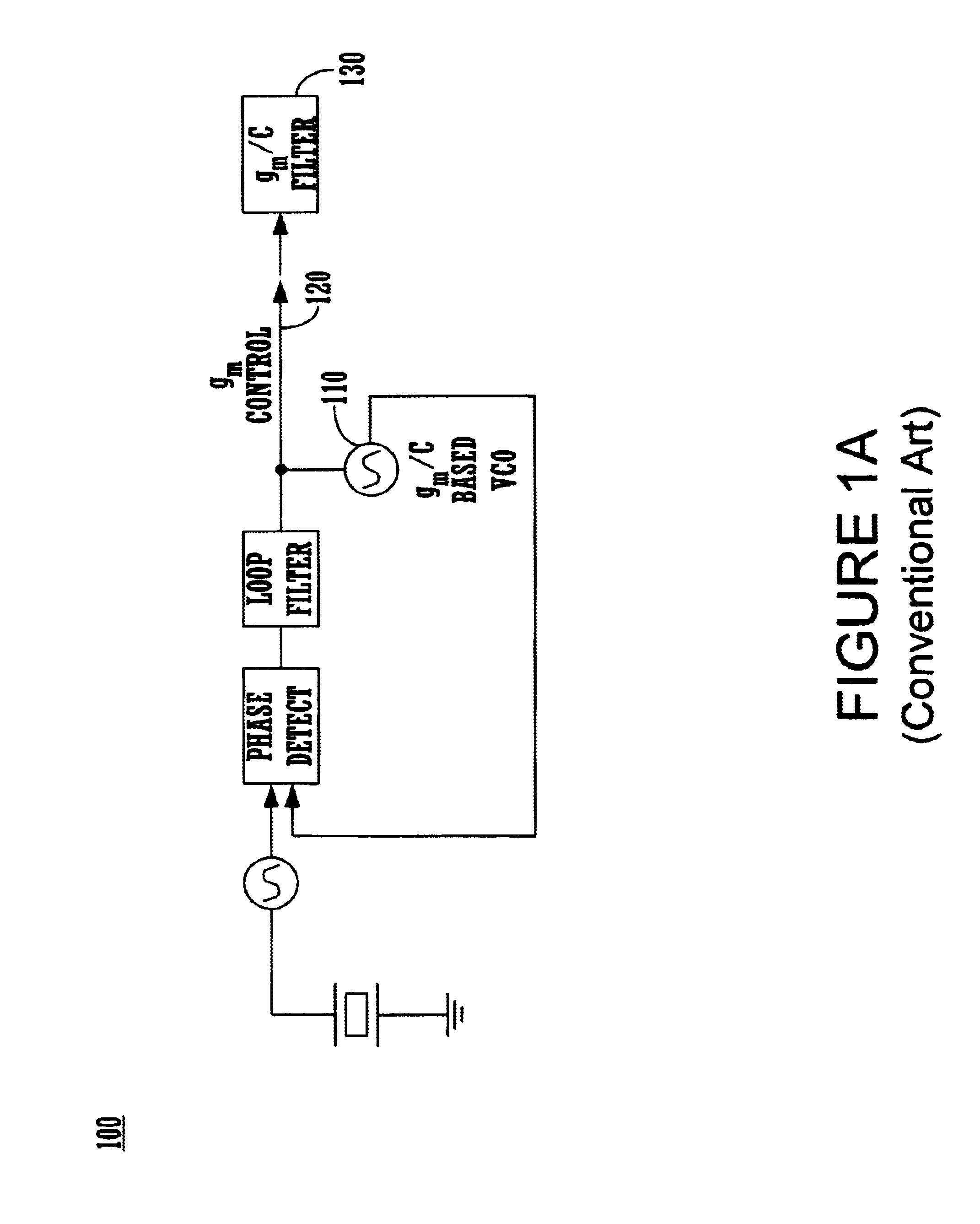
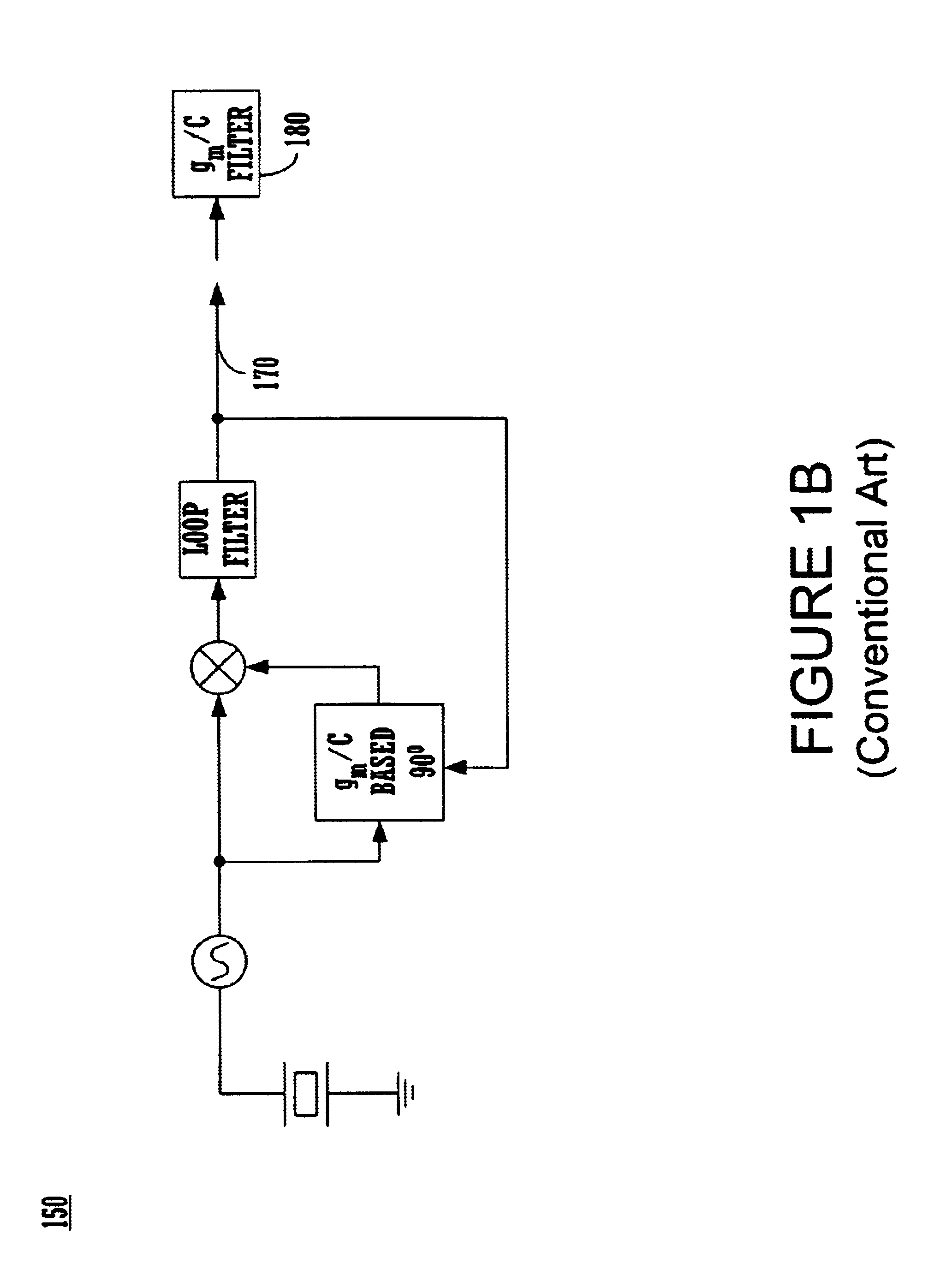
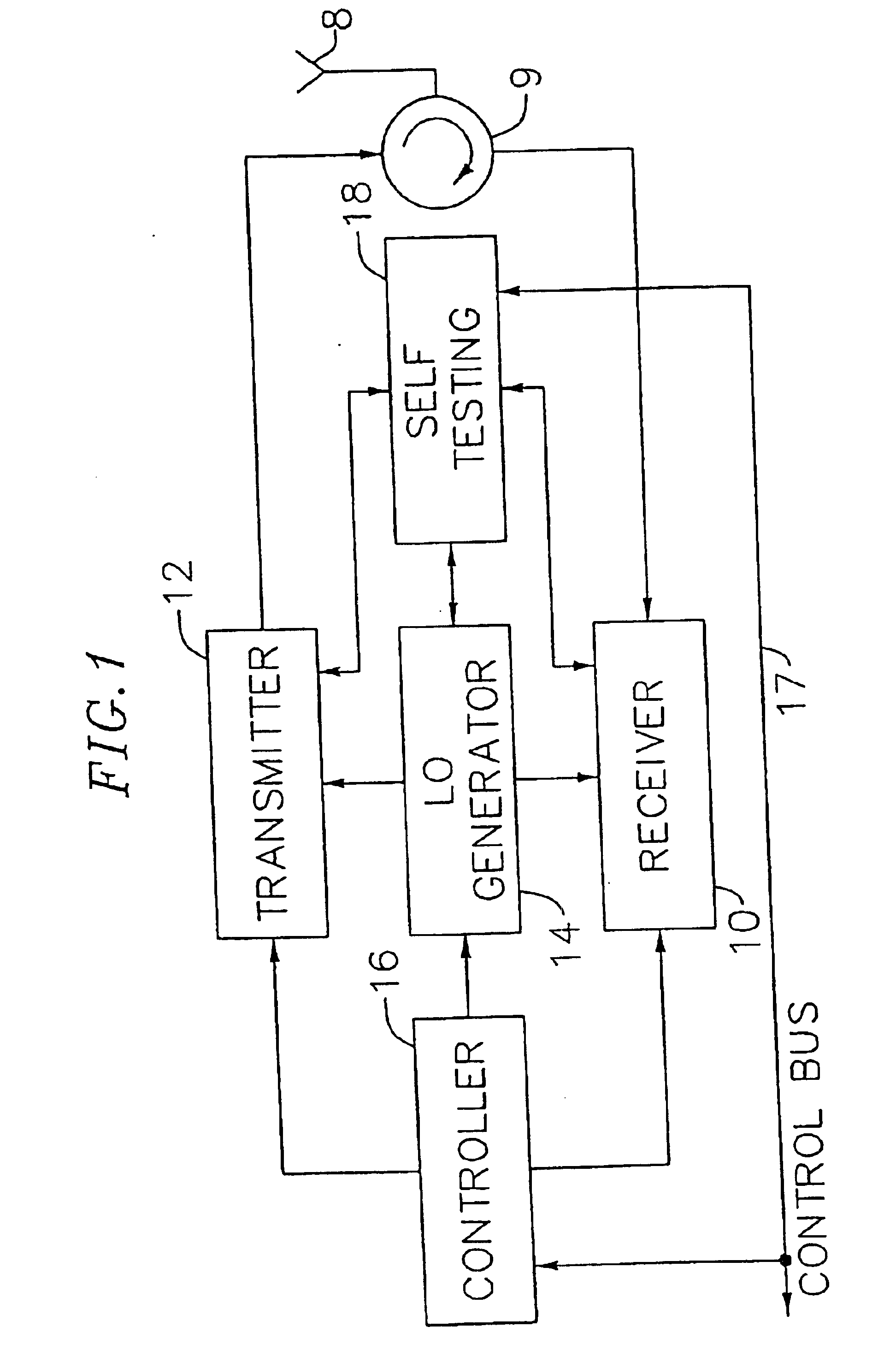
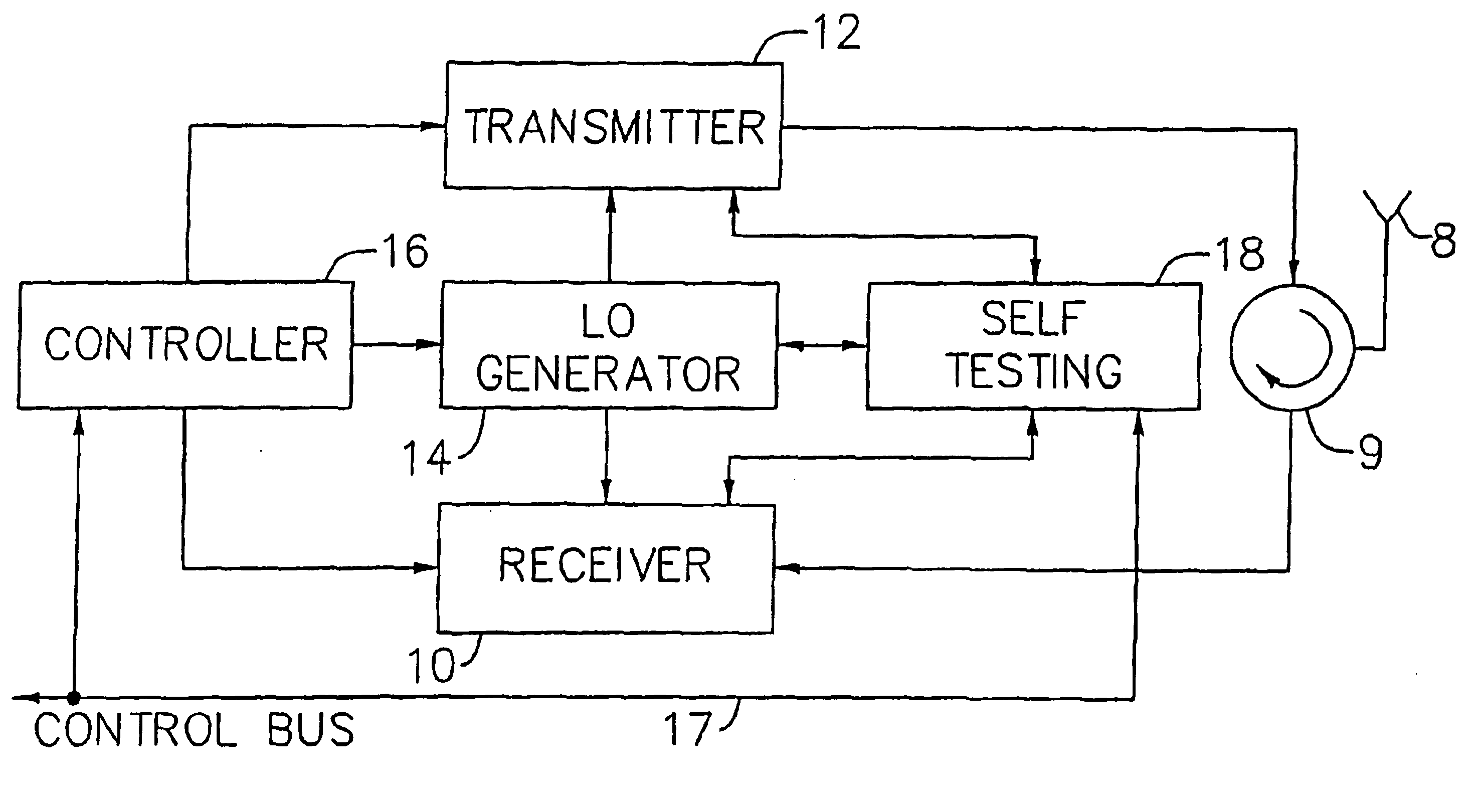
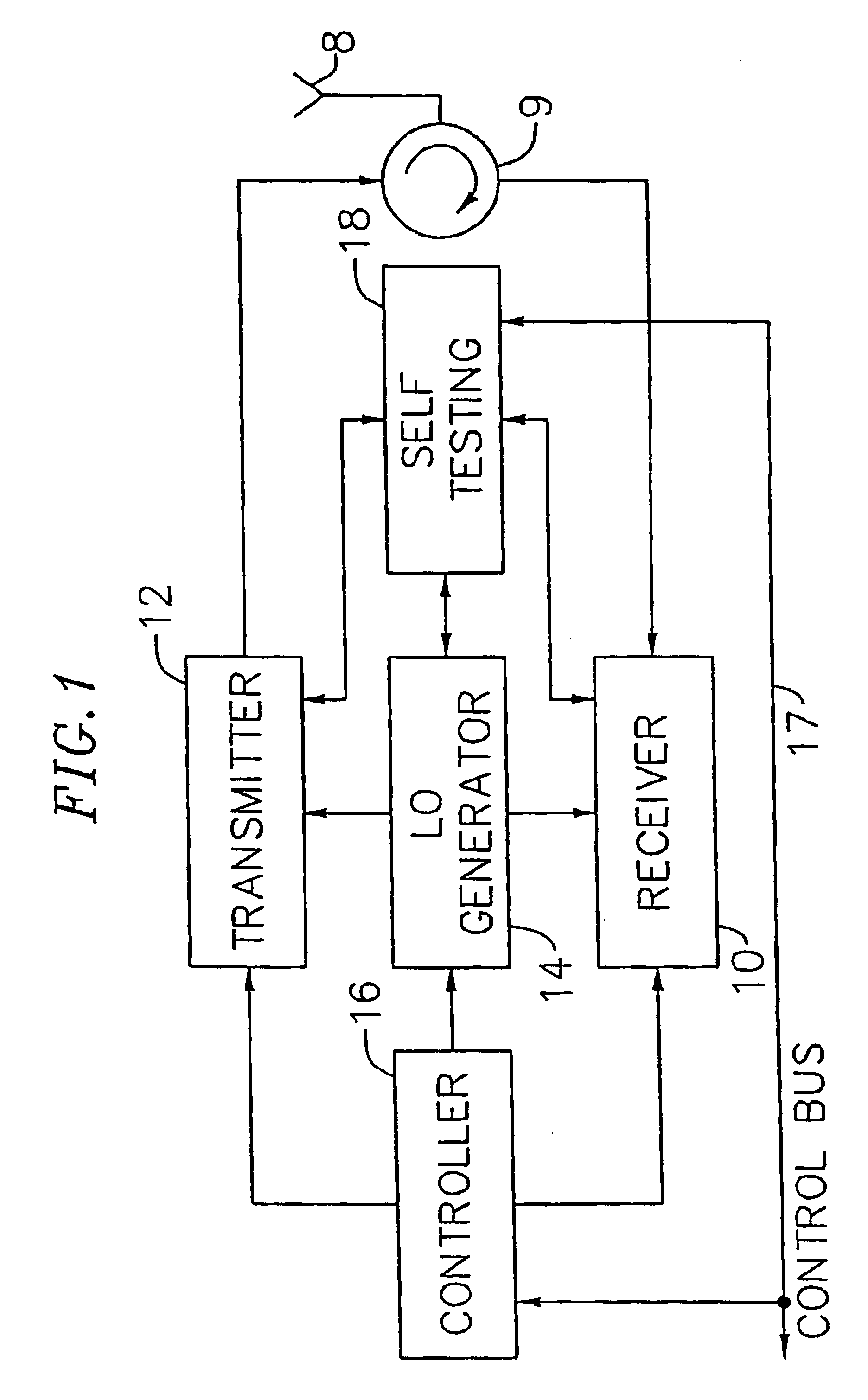
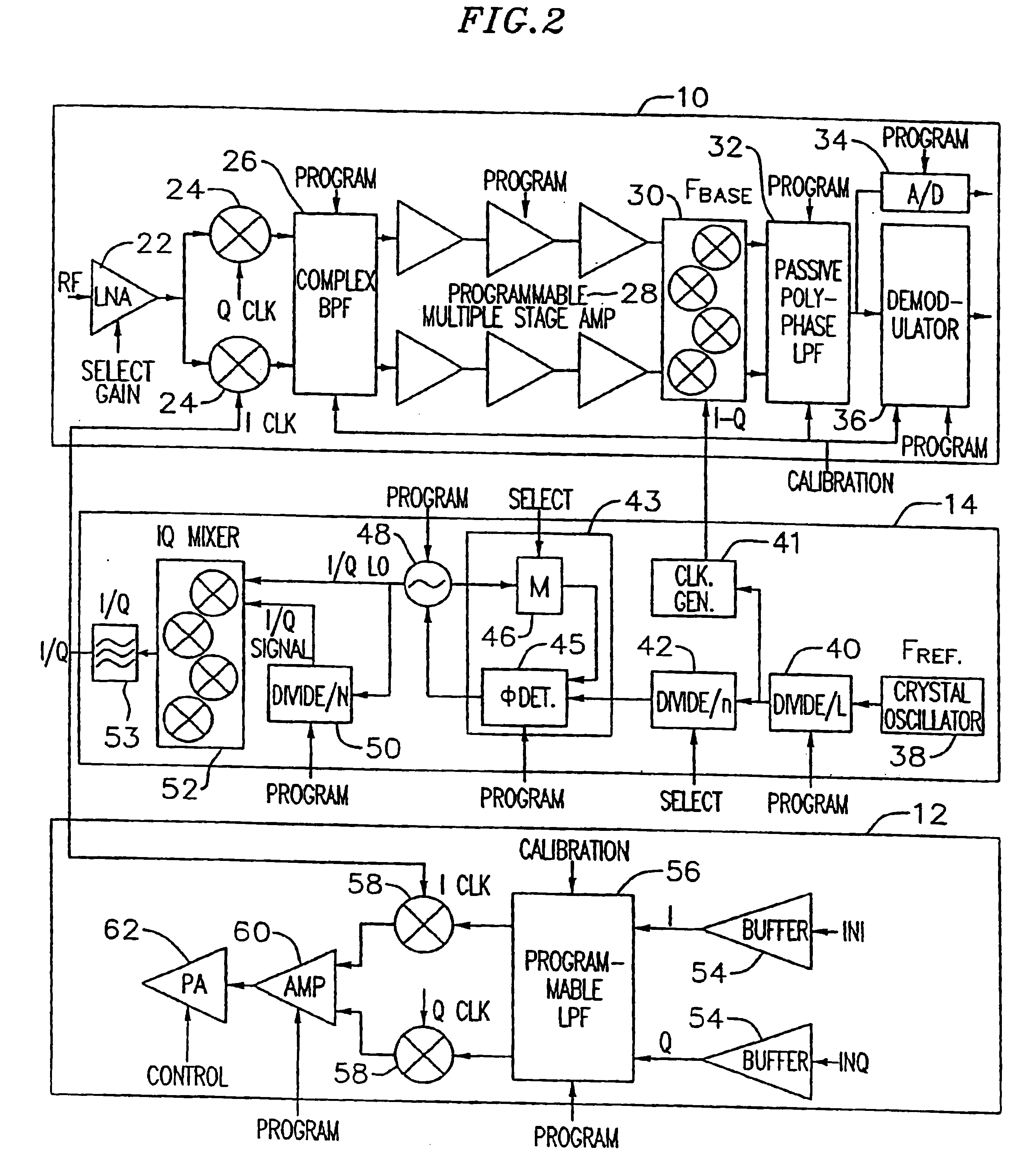
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tunable filter and portable telephone
InactiveUS20050212612A1Low insertion lossImprove reliabilityMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCapacitanceEngineering
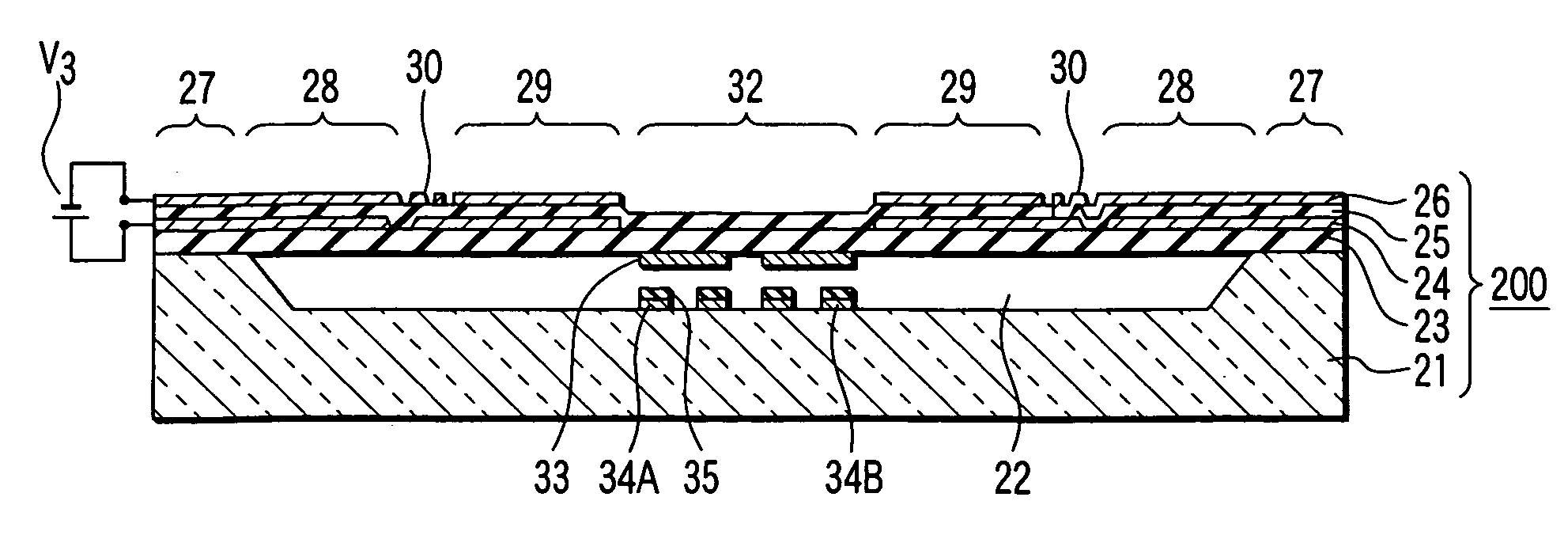
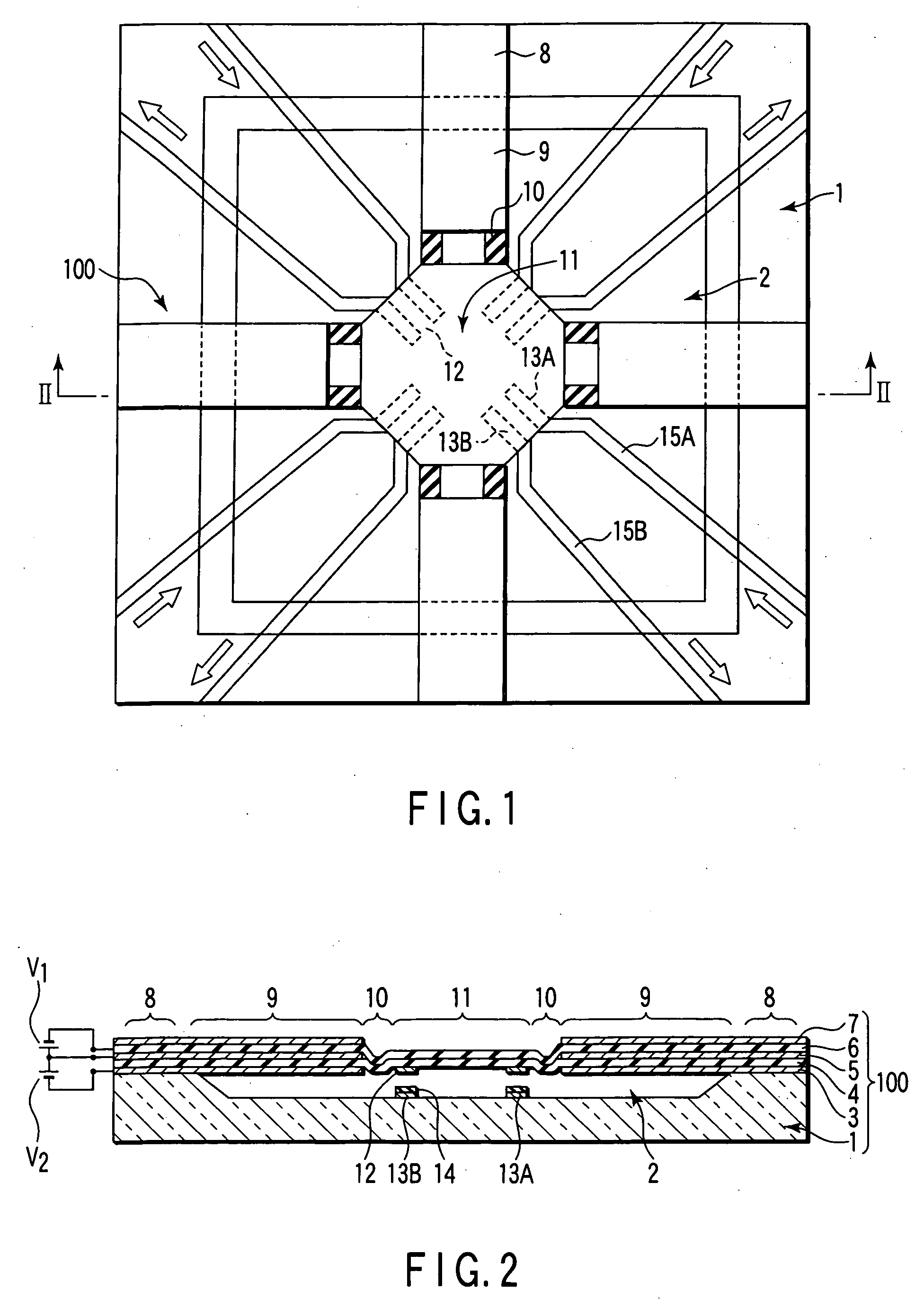
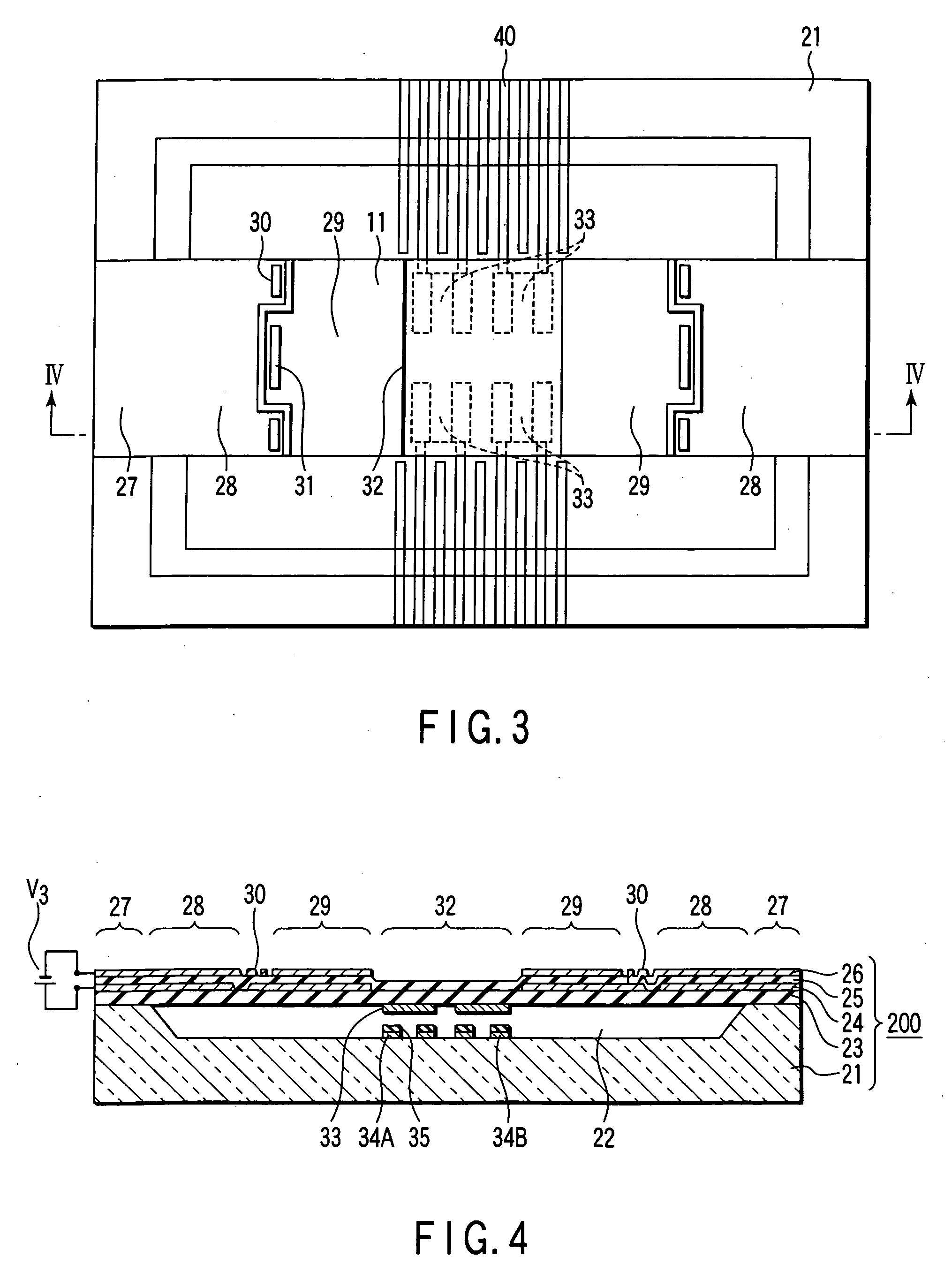
A tunable filter has a plurality of variable capacitors and a plurality of inductor elements, each being formed on a common substrate, a filter circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a monitor circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a detecting circuit which detects a prescribed circuit constant of the monitor circuit, a storage which stores information relating to a reference circuit constant of the monitor circuit, and a capacitance control circuit which controls capacitance of the variable capacitors in the monitor circuit and capacitance of the variable capacitors in the filter circuit, based on a result detected by the detecting circuit and information stored in the storage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Tuning circuit for a filter
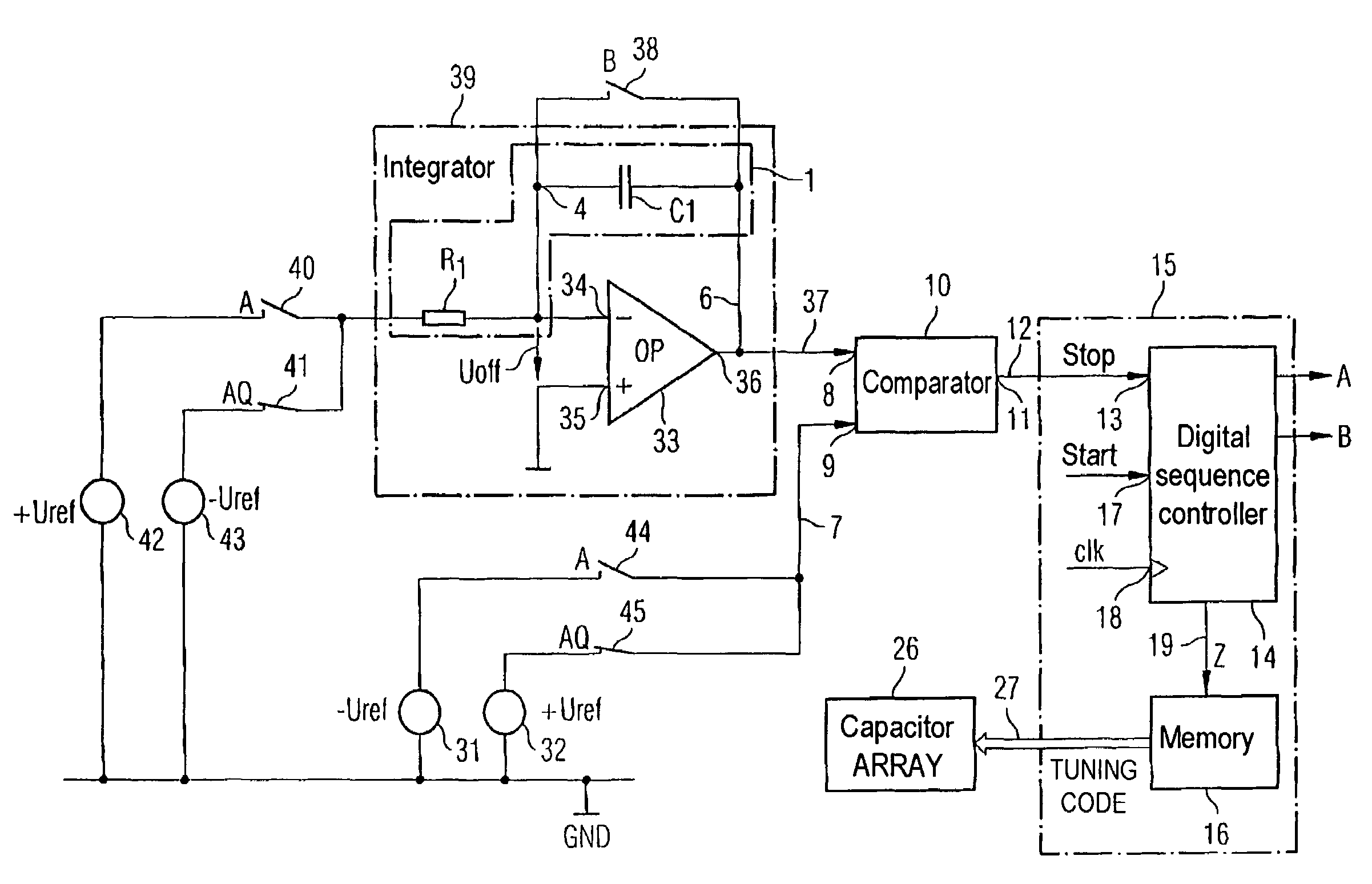
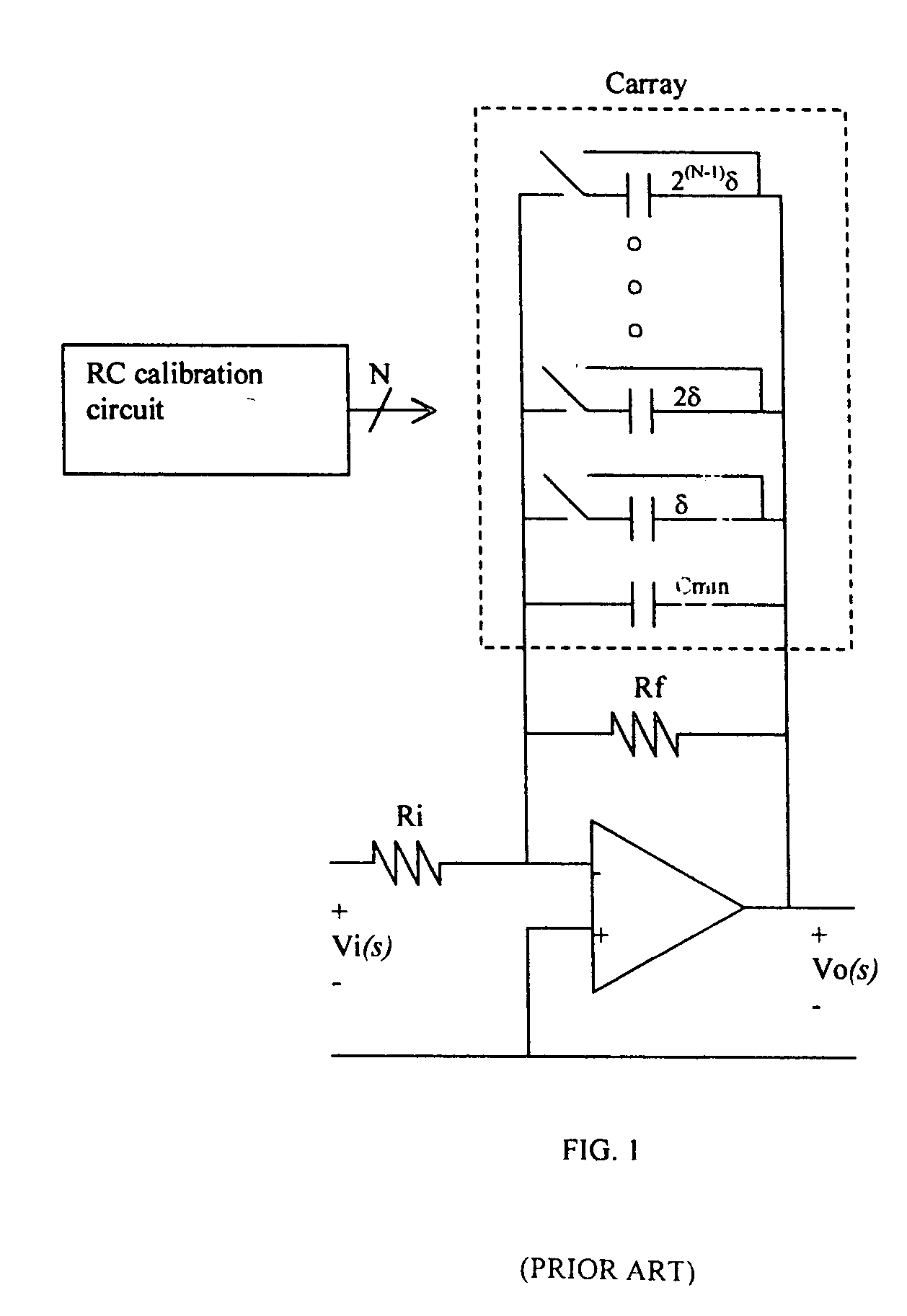
ActiveUS7002404B2Space minimizationImprove accuracyMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCapacitanceRC time constant
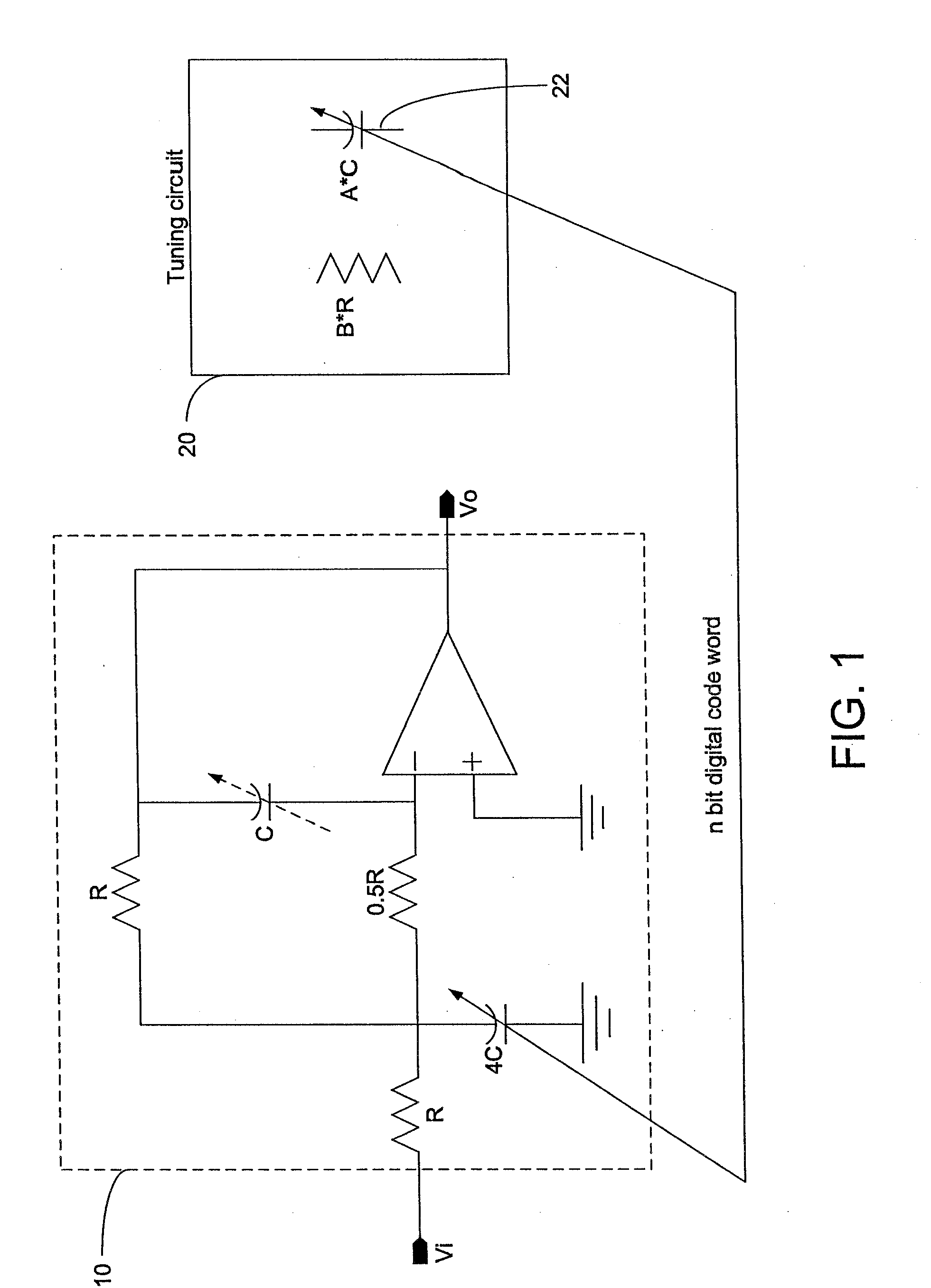
The invention relates to a tuning circuit for tuning a filter stage, which has an RC element (1) with an RC time constant (τ), with the RC time constant (τ) being the product of the resistance of a resistor (R1) in the RC element (1) and the capacitance of a capacitor (C1), which is connected in series with the resistor (R1), in the RC element (1), having a comparator (10) for comparison of the voltage which is produced at the potential node (4) between the resistor (R1) and the capacitor (C1), with a reference ground voltage; and having a controller (15) which varies the charge on the capacitor (C1) in the RC element (1) until the comparator (10) indicates that the voltage which is produced at the potential node (4) is equal to the reference ground voltage, with the controller (15) switching a capacitor array (26) as a function of the charge variation time, which capacitor array (26) is connected in parallel with the capacitor (C1) in the RC element (1), in order to compensate for any discrepancy between the RC time constant (τ) of the RC element (1) and a nominal value.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Tunable filter and portable telephone
InactiveUS7135940B2Good reproducibility and reliabilityLow insertion lossMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCapacitanceInductor
A tunable filter has a plurality of variable capacitors and a plurality of inductor elements, each being formed on a common substrate, a filter circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a monitor circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a detecting circuit which detects a prescribed circuit constant of the monitor circuit, a storage which stores information relating to a reference circuit constant of the monitor circuit, and a capacitance control circuit which controls capacitance of the variable capacitors in the monitor circuit and capacitance of the variable capacitors in the filter circuit, based on a result detected by the detecting circuit and information stored in the storage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
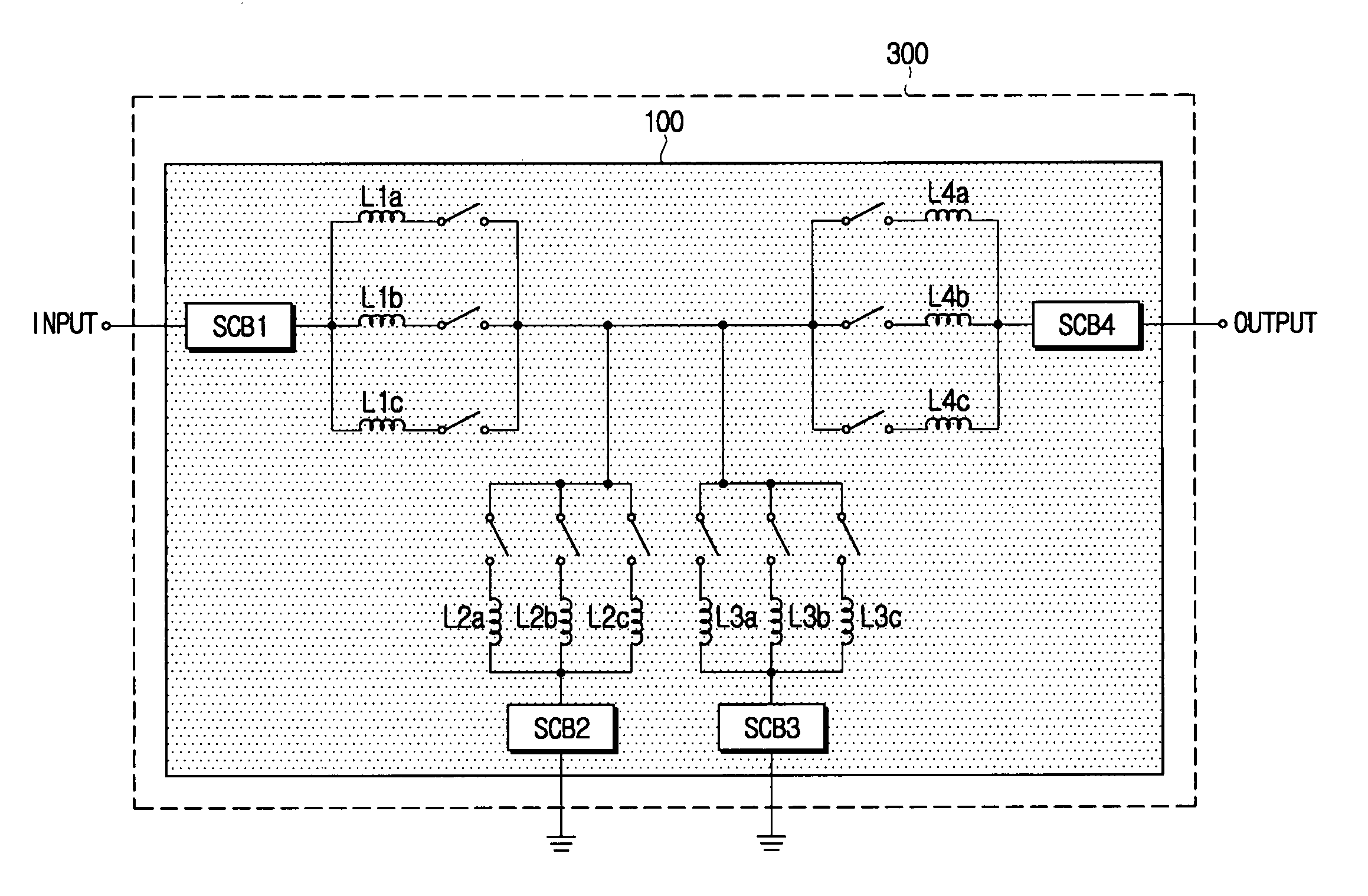
Tunable wideband bandpass filter, tunable multi-band wideband bandpass filter using the same, and methods therefore
ActiveUS20050184828A1Reduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksResonant circuit tuningCapacitanceMulti band
A tunable wideband bandpass filter that can digitally vary the center frequency and bandwidth of a signal to be filtered, and includes a plurality of switched-capacitor banks for varying capacitance and converting the center frequency and bandwidth into a digital signal, and a plurality of inductors provided for inductance to generate the center frequency, the plurality of switched-capacitor banks that may be integrated into a signal chip.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Tunable wideband bandpass filter, tunable multi-band bandpass filter using the same, and methods therefore
A tunable wideband bandpass filter that can digitally vary the center frequency and bandwidth of a signal to be filtered, and includes a plurality of switched-capacitor banks for varying capacitance and converting the center frequency and bandwidth into a digital signal, and a plurality of inductors provided for inductance to generate the center frequency, the plurality of switched-capacitor banks that may be integrated into a signal chip.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
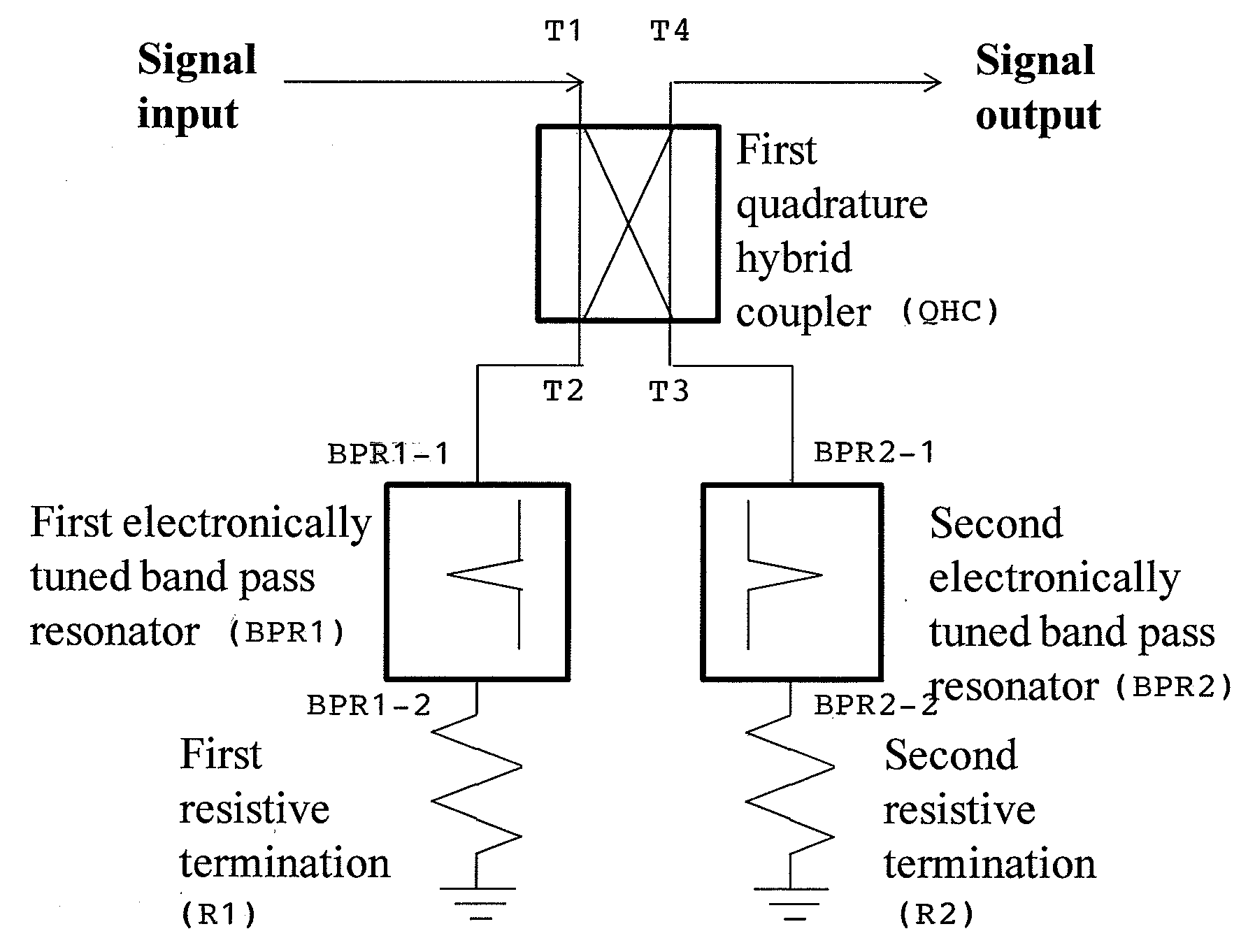
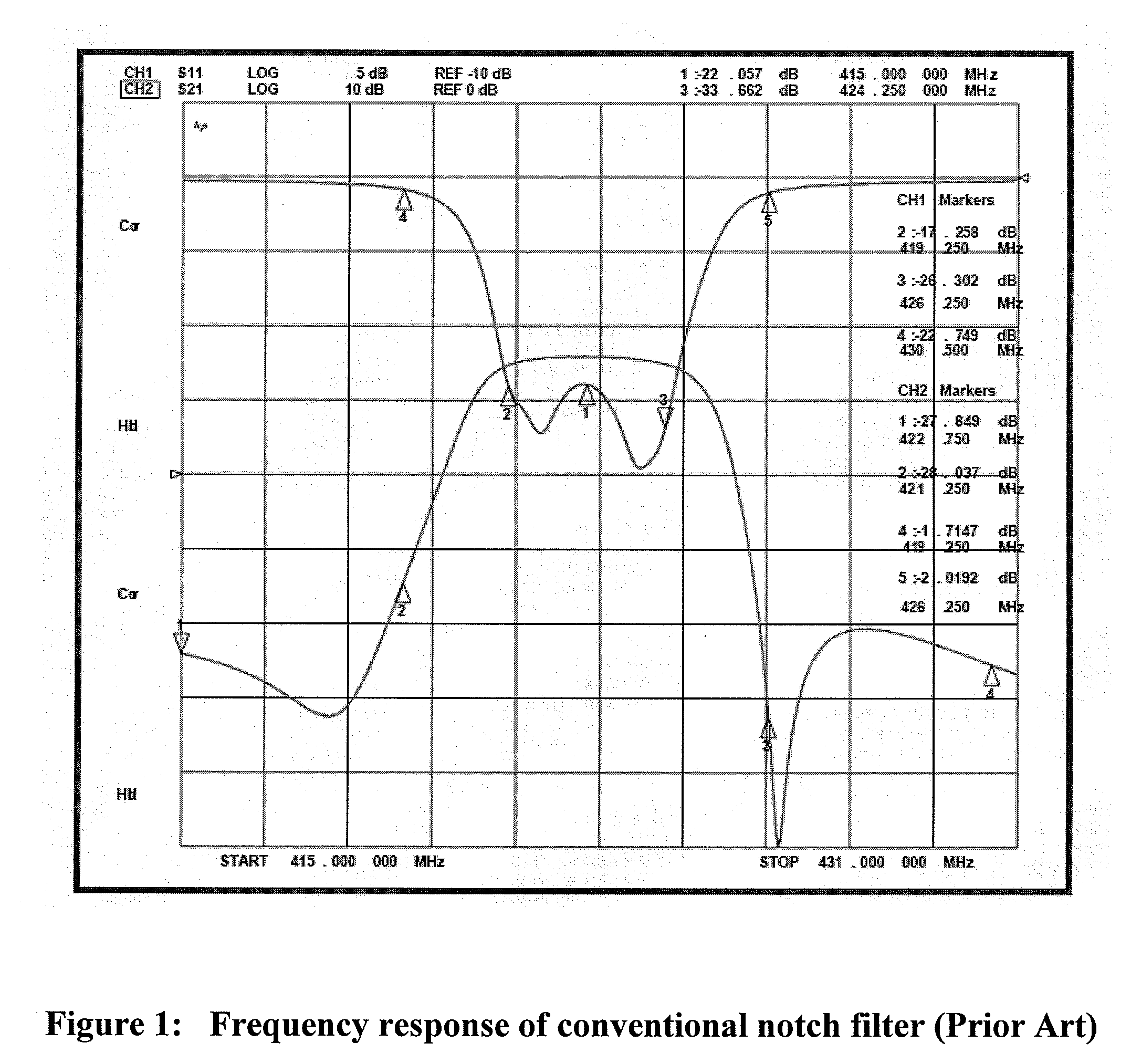
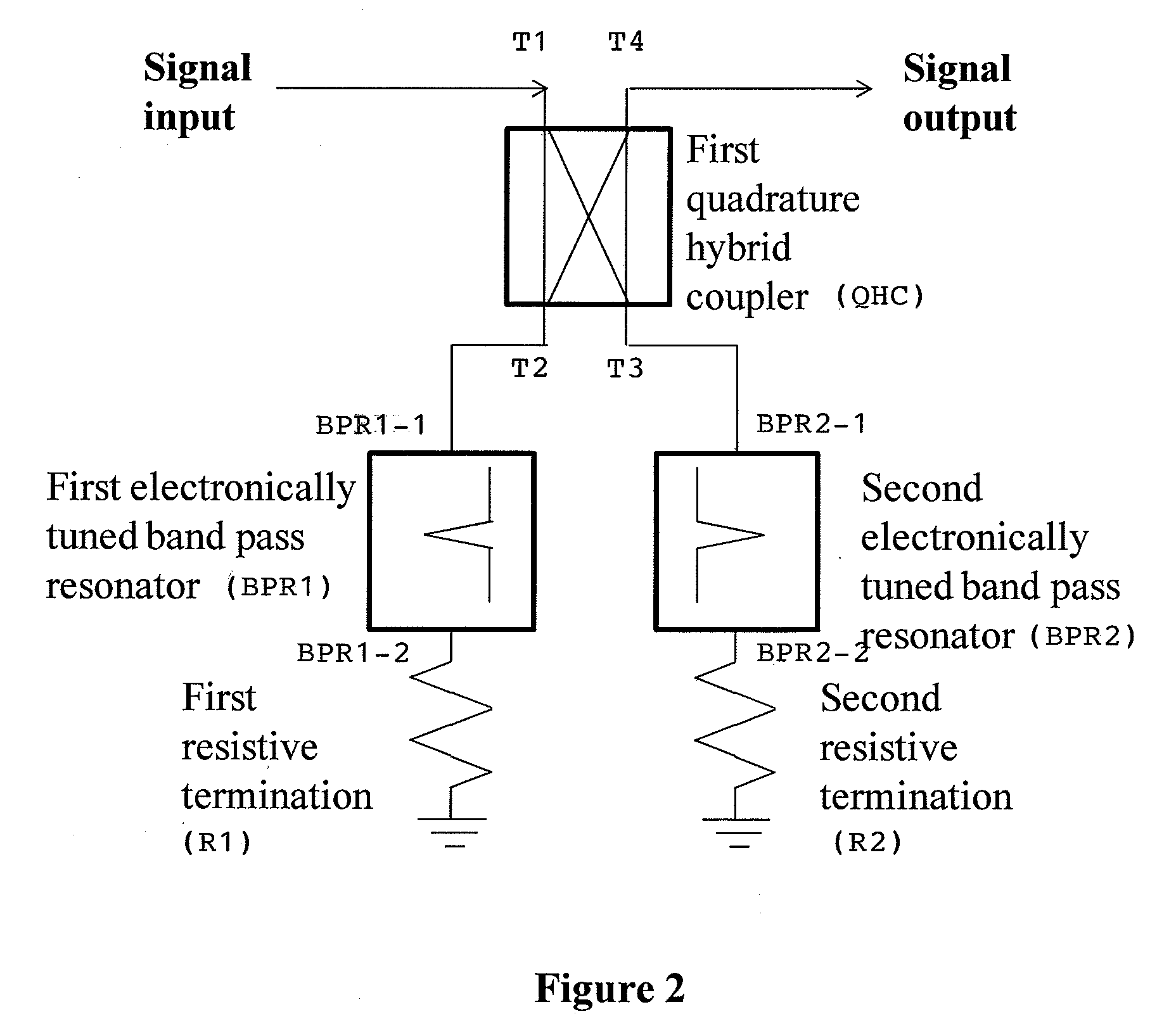
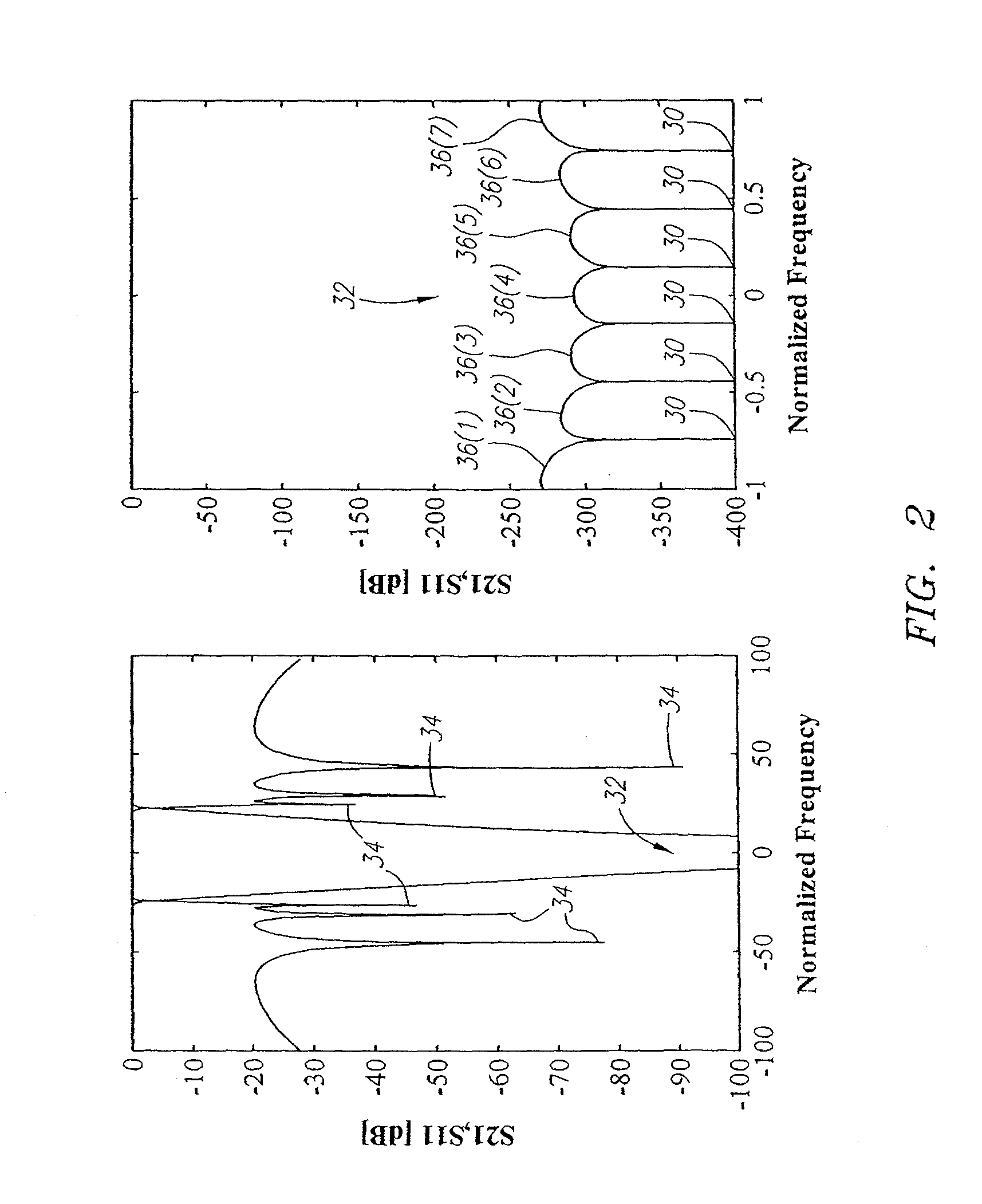
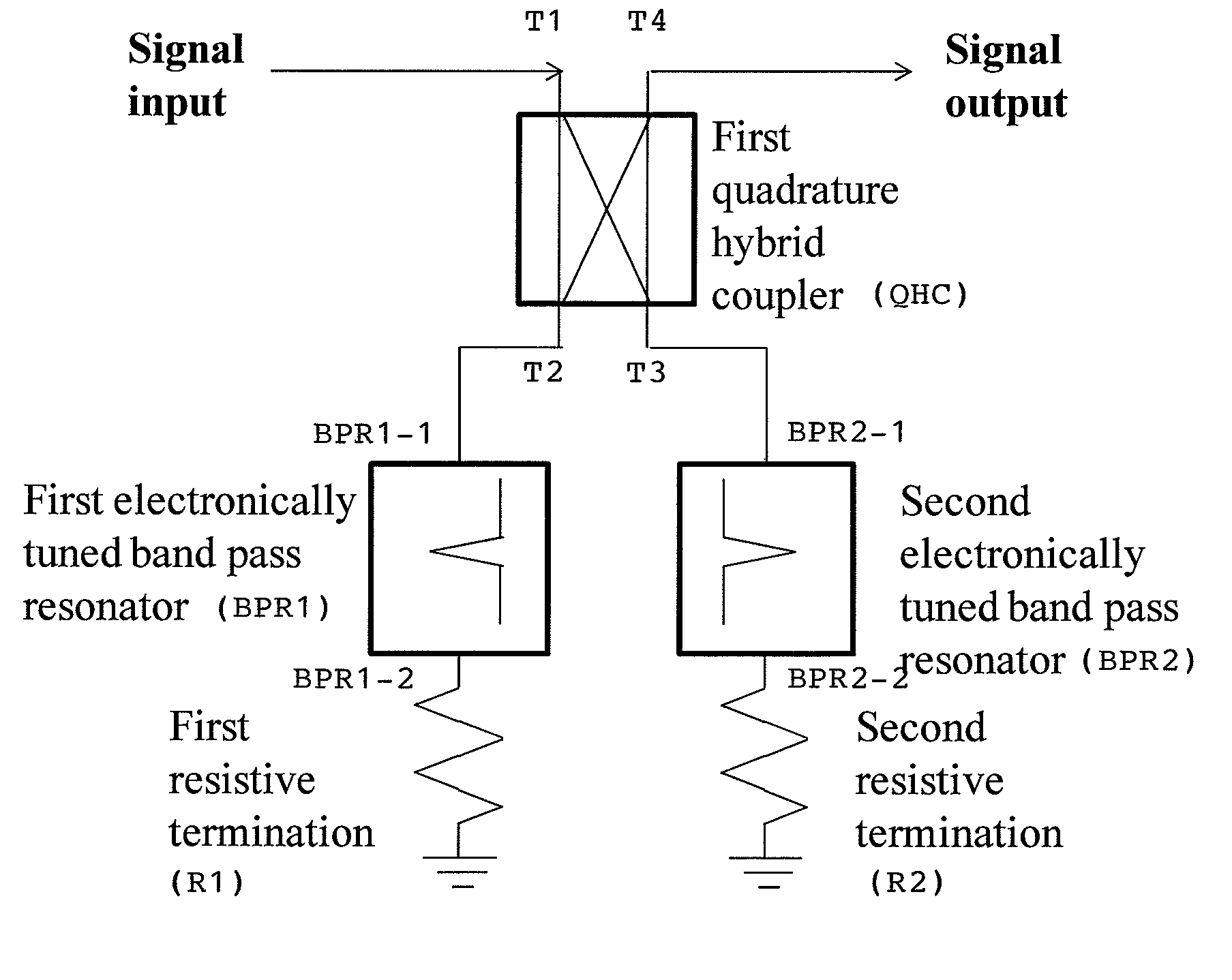
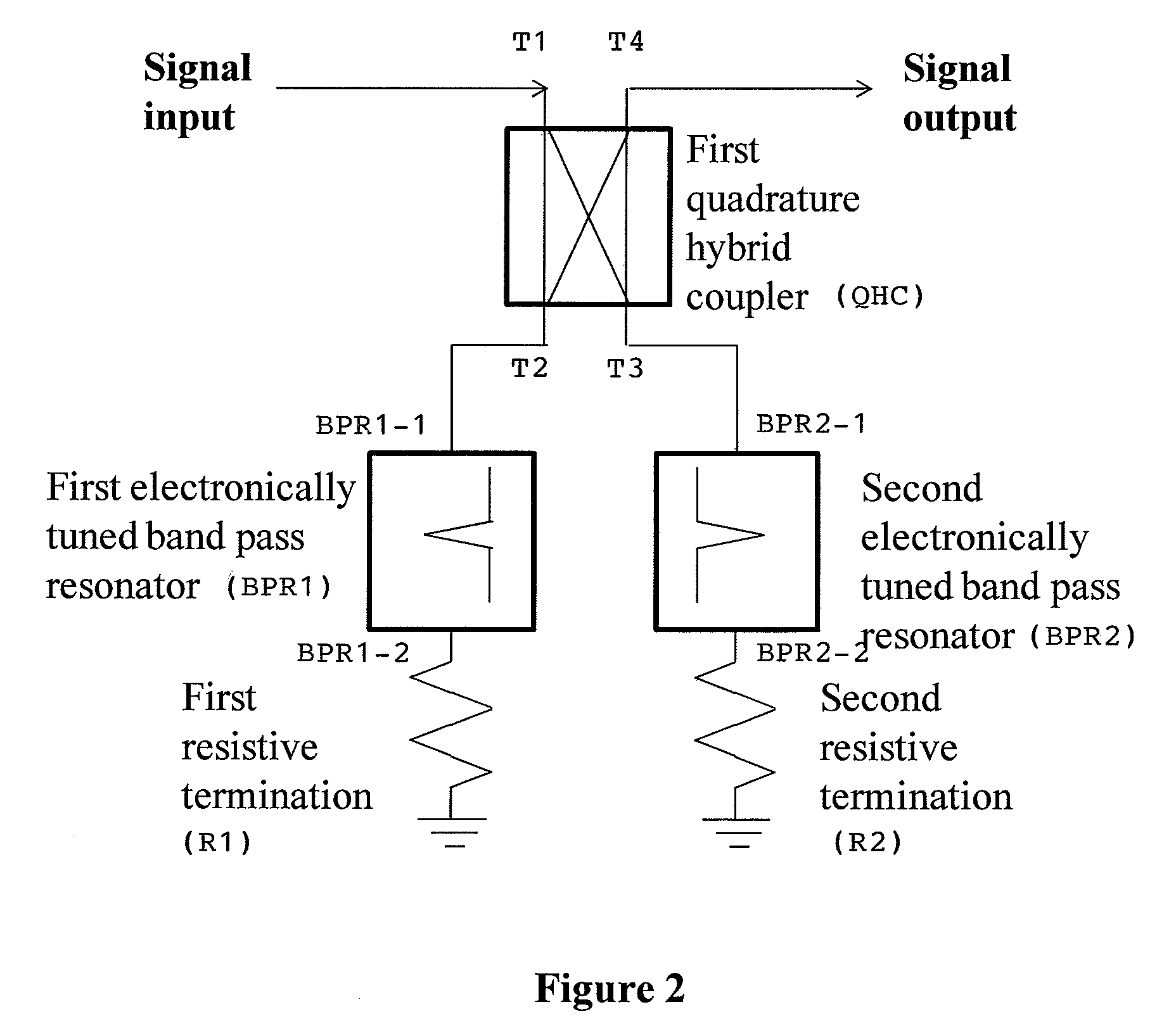
Electronically tunable, absorptive, low-loss notch filter
InactiveUS20090289744A1Little and no lossImproved power handlingMultiple-port networksTunable filtersWireless routerMatched pair
An electronically tuned, absorptive, low-loss notch filter with high RF power handling capability is obtained using a four-port quadrature hybrid coupler connected to a matched pair of band pass resonator devices and resistive terminations. The notch filter design uses series-only tuning elements for the band pass resonator devices to raise the RF power handling of the band pass resonators far above conventional techniques while also being tunable at high speeds. The notch filter architecture and method can be used for interference cancellation in a wide range of wireless technologies, such as cellular phone, wireless routers, hand-held radios, satellite communications, and any other environments where there are a number of wireless technologies in close signal proximity.
Owner:TERASYS TECH
Reconfigurable baseband filter
ActiveUS20040209591A1Reduce switching noiseSimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationActive element networkCommunications systemEngineering
A reconfigurable baseband filter for use in a multimode communication system is disclosed. One or more filter elements can each be configured as a plurality of sub-elements. The value of each of the filter elements can be varied by switching between at least two of the plurality of sub-elements. Switching noise within a desired passband can be reduced by switching at a rate that is greater than the desired passband. The switching noise in the passband can be further reduced by pseudo-randomly switching between the sub-elements. The filter can use a delta-sigma modulator to generate a pseudo-random switching signal.
Owner:SPREADTRUM
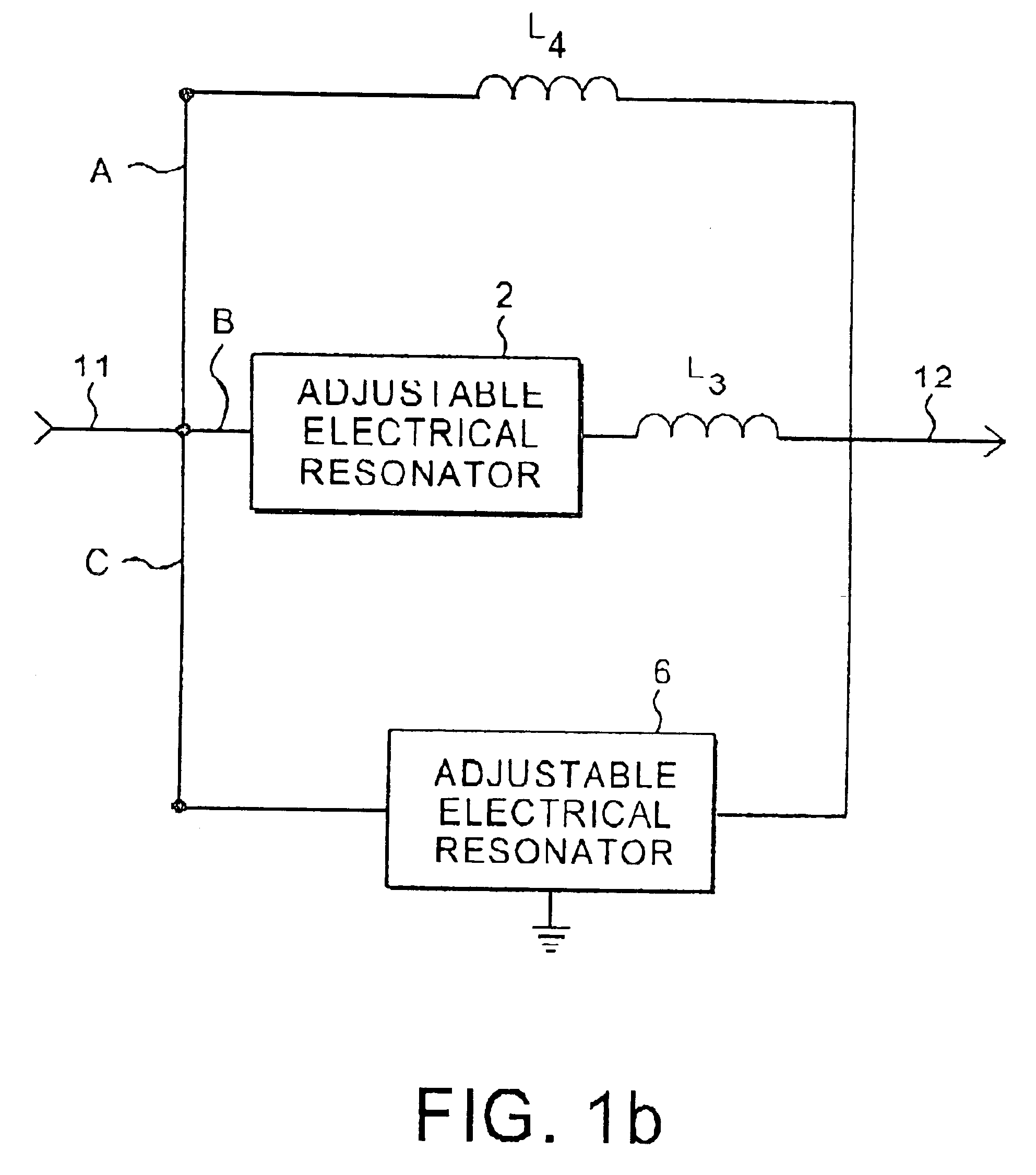
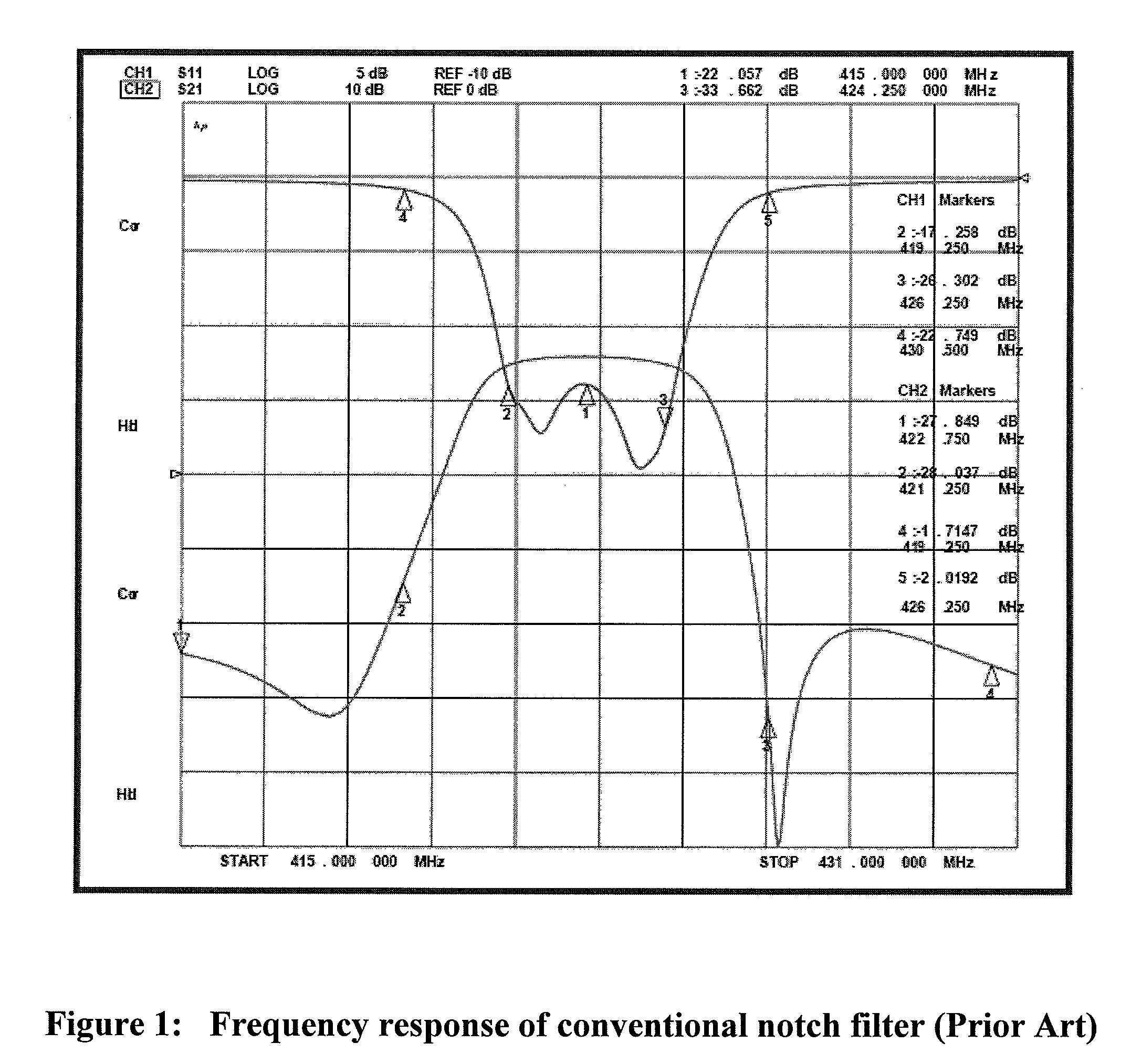
Two-pole notch filter
InactiveUS6842086B1Improve long-term stabilityWider inband bandwidth characteristicMultiple-port networksTunable filtersInductorFrequency response
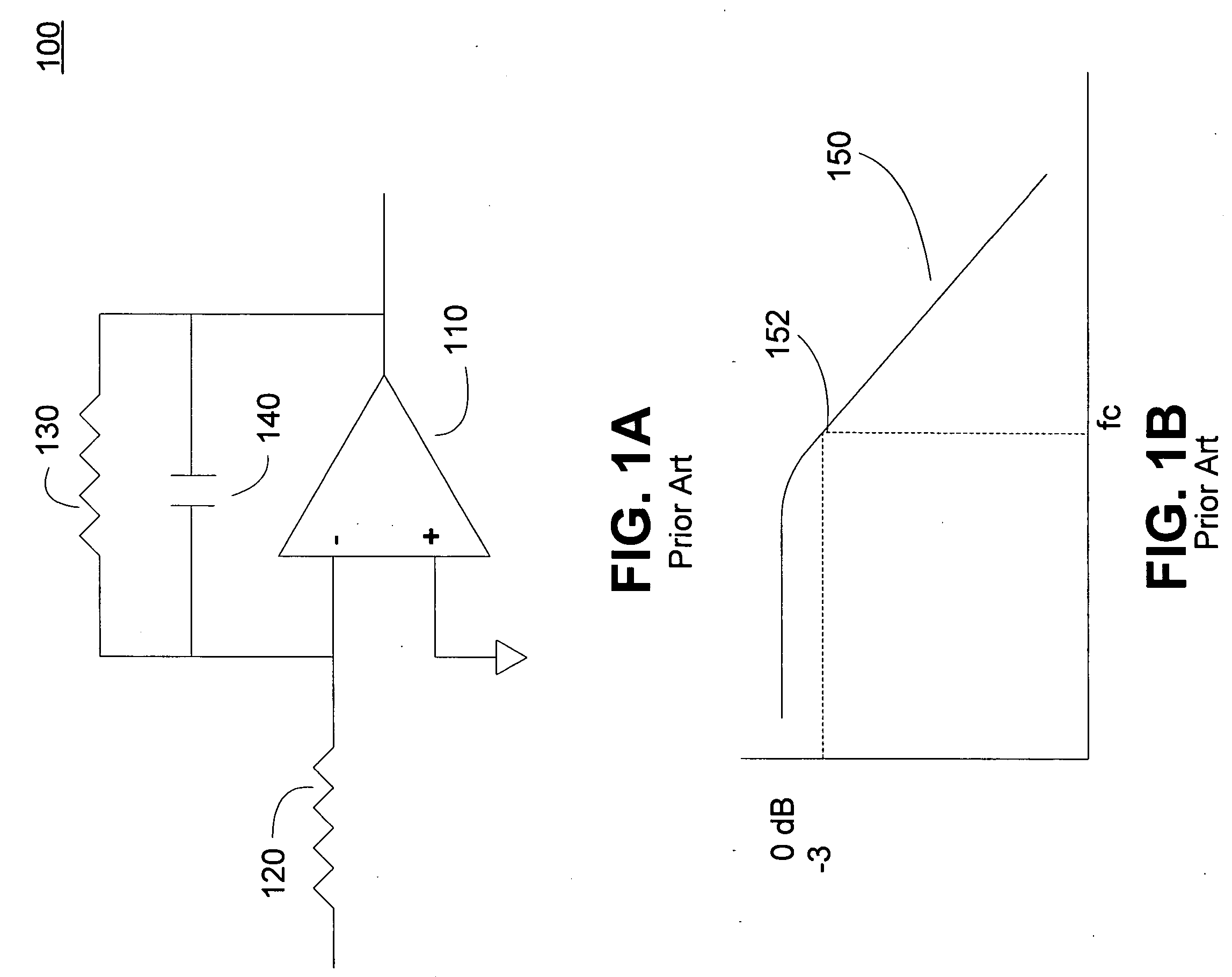
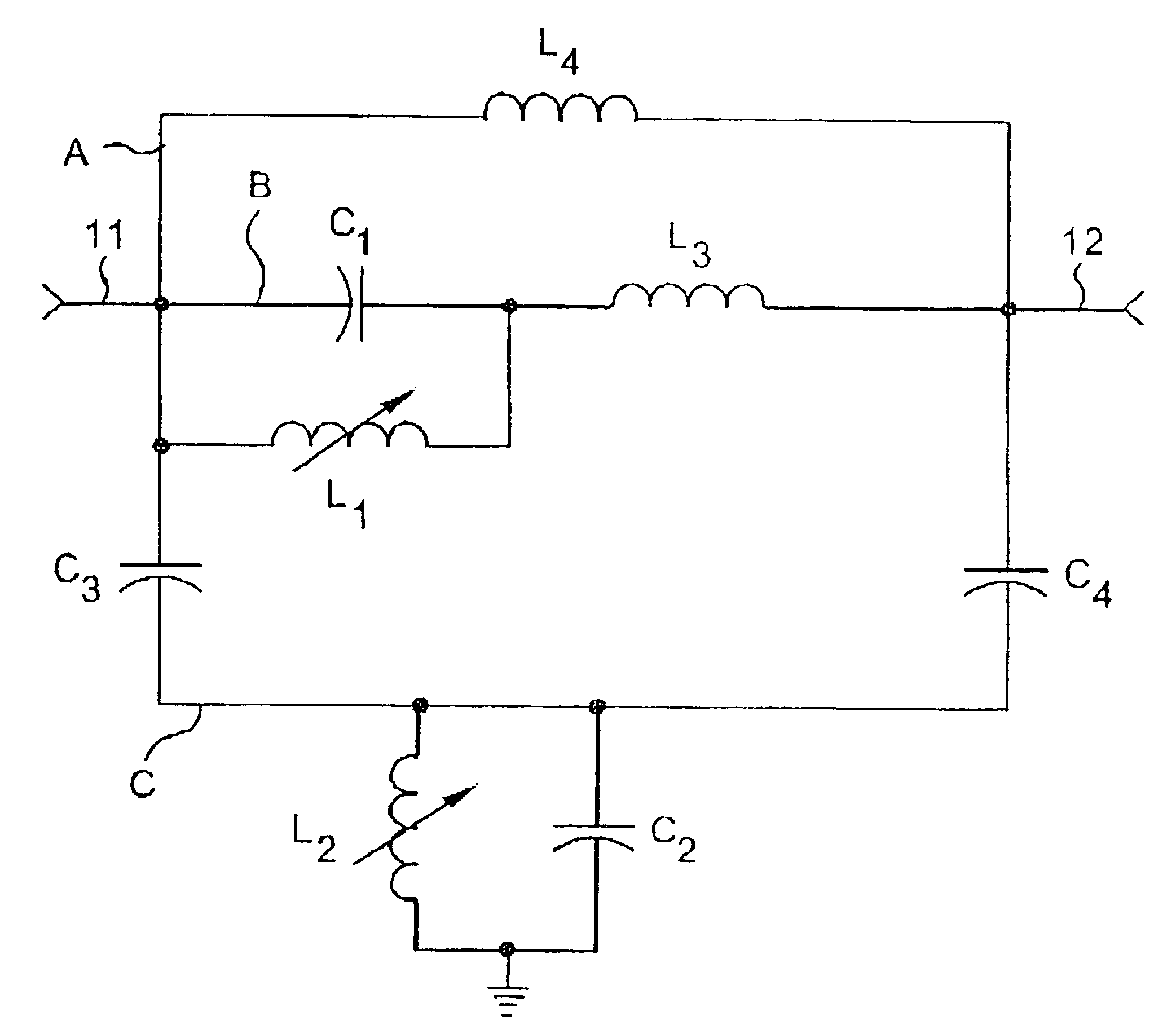
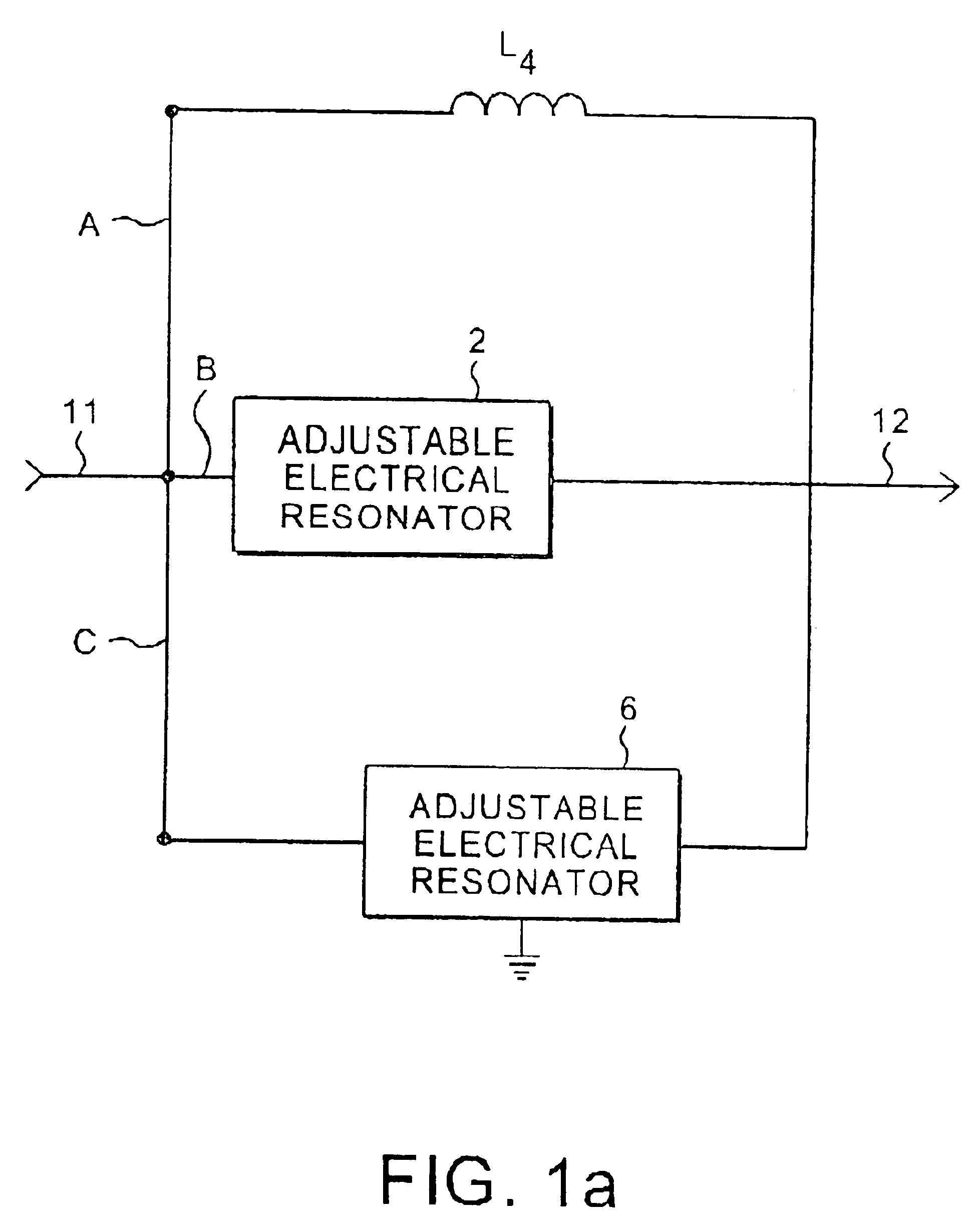
A tunable top-pole passive notch circuit for attenuating select frequencies of a multi-frequency CATV signal. The circuit includes an input for receiving a multi-frequency CATV signal, and an output for transmitting a portion of the multi-frequency CATV signal, A filter network for attenuating a band of frequencies from the multi-frequency signal is distributed been the input and the output. The filter network includes three parallel branches A, B, and C, each being arranged in series connection between the input and the output. Branch A includes an inductor. Branch B includes an adjustable parallel tank circuit Branch C includes a second adjustable electrical resonator. The filter has frequency response characteristics that are more stable than prior art two-pole notch filters, and similar to the response characteristics of more complex three pole or four pole notch filters. The two-pole tunable notch filter circuit provides a passband response to 1 GHz.
Owner:EAGLE COMTRONICS
Adaptive radio transceiver with an antenna matching circuit
InactiveUS6917789B1High data rateHigh power consumption , cost and sizeMultiple-port networksTransmitters monitoringDistortionInductor
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
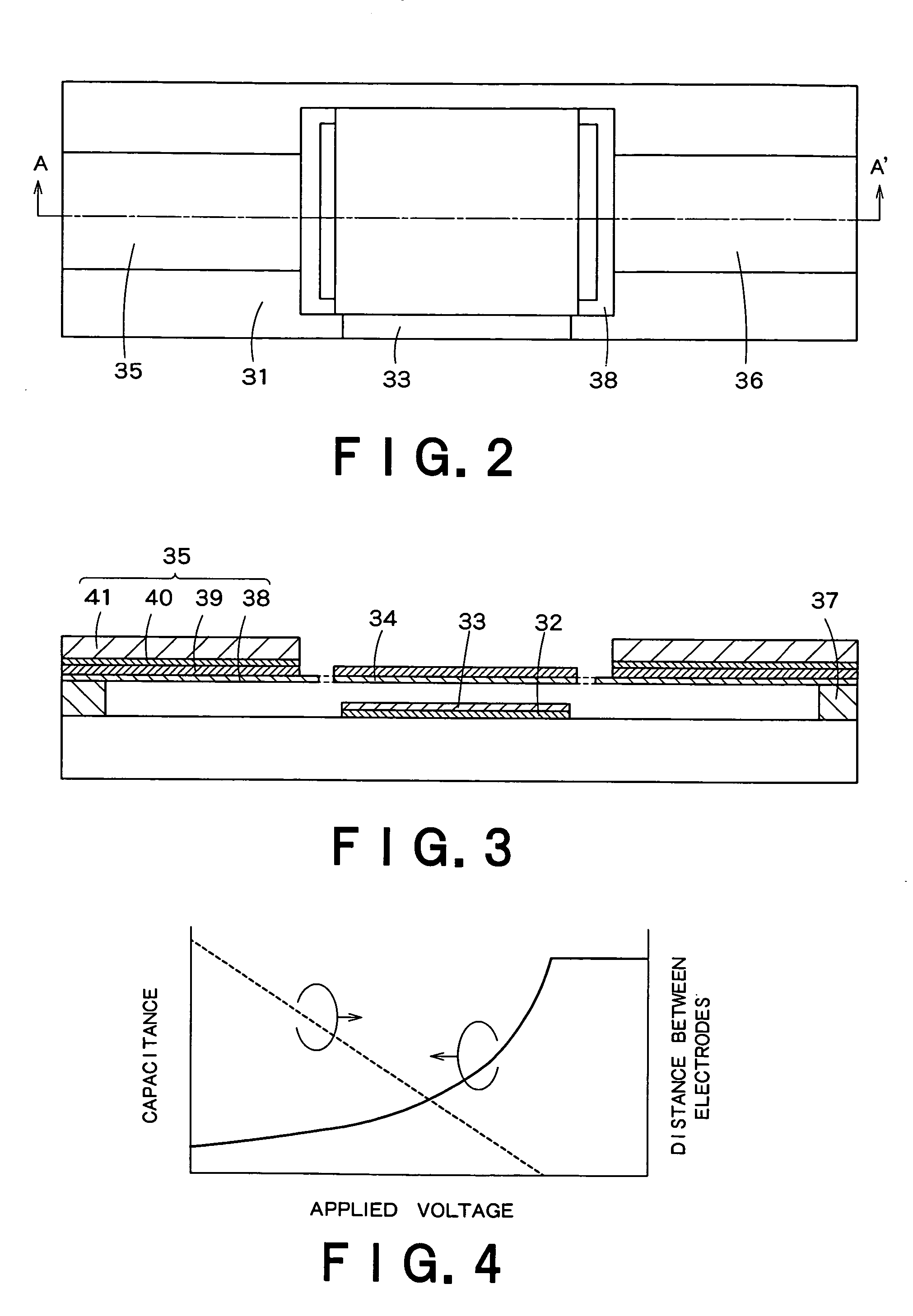
Piezoelectric MEMS element and tunable filter equipped with the piezoelectric MEMS element
InactiveUS20060067840A1Multiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityCapacitance
In a MEMS type variable capacity having a piezoelectric driving mechanism, a movable head having movable electrodes are arranged thereon, stationary electrodes is positioned to face the movable electrodes, and a piezoelectric driving beam structure is joined to the movable head and have one end fixed to the substrate. The movable electrode and the stationary electrode form a variable capacity. In the variable capacity, the distance and capacitance between the movable electrode and the stationary electrode of the variable capacity can be maintained constant so as to realize a reproducibility and a reliable controllability.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nth Order Tunable Low-Pass Continuous Time Filter for Fiber Optic Receivers
ActiveUS20100052778A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsActive element networkNegative feedbackSoftware engineering
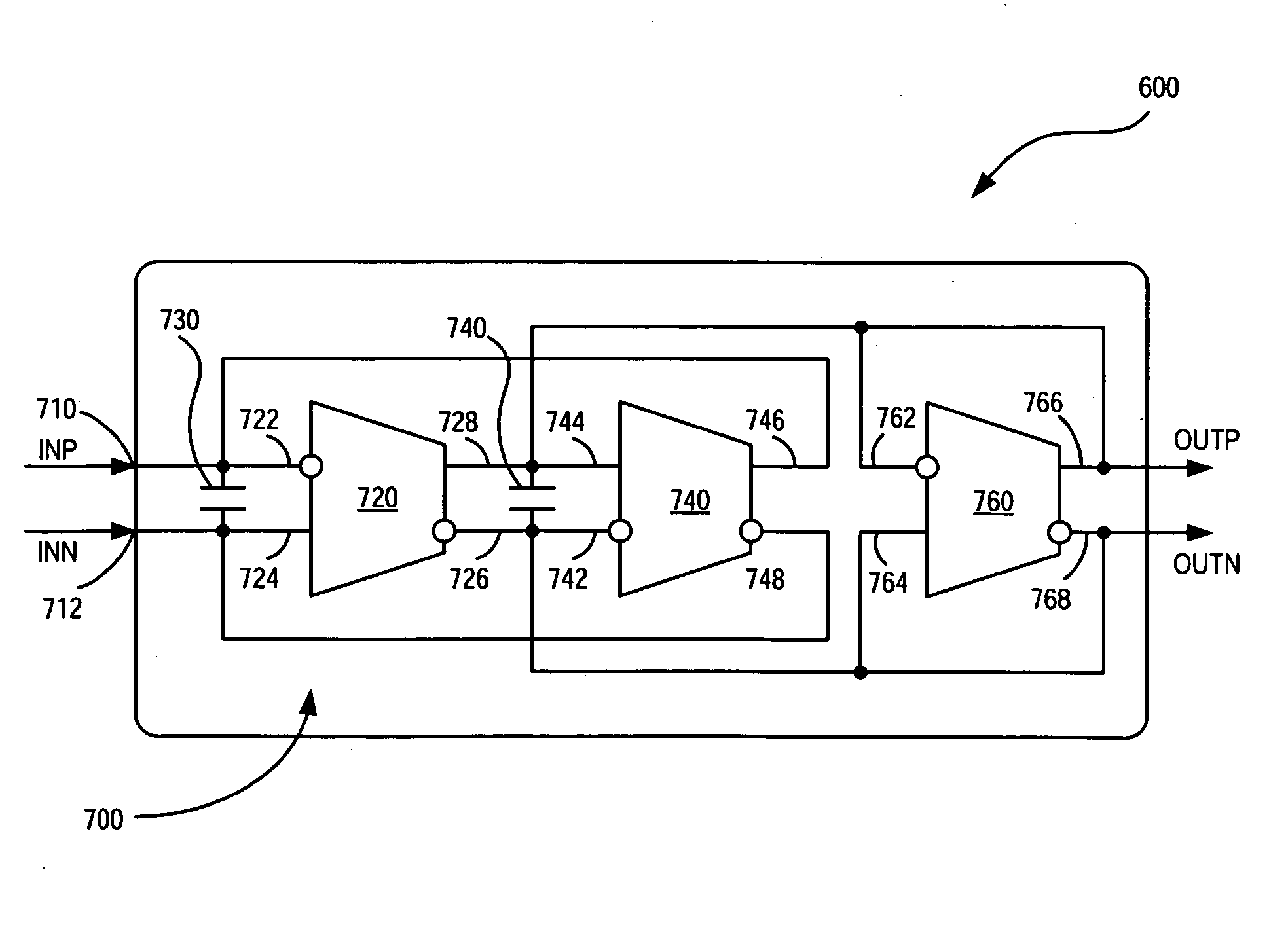
According to one embodiment of the invention, a circuit comprising a plurality of operational transconductance amplifiers (OTAS) is described. The first OTA has differential input and differential output. The second OTA also has differential input, where a first output of the first OTA is coupled to the first differential input of the second OTA, which is an inverting input. A second output of the first OTA is coupled to the second input of the second OTA, which is a non-inverting input. The first differential output being coupled to a first input of the first OTA and the second differential output being coupled to a second input of the first OTA for negative feedback and current biasing.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
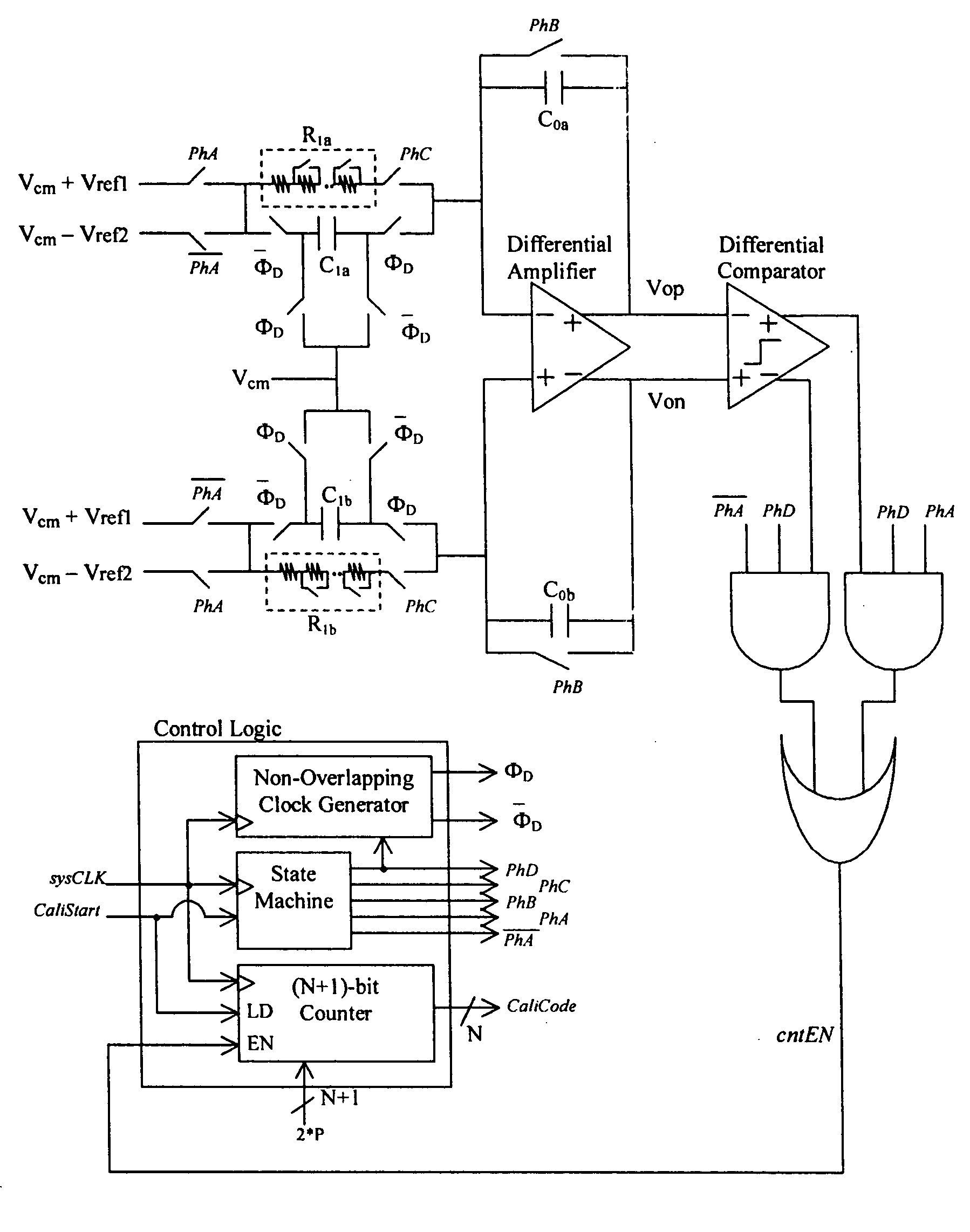
Variable rate RC calibration circuit with filter cut-off frequency programmability
InactiveUS20050118980A1Provide capabilityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsSwitched capacitor networksDifferential amplifierCapacitance
Two reference signals are applied to an RC calibration circuit, which utilizes programmable resistors and switched capacitor resistors in parallel at the inputs of a differential amplifier with feedback capacitors, for the first cycle and then the two reference signals are swapped for the successive cycle. The circuit inherent DC offset is cancelled by these two successive cycles. The time duration when the difference of the differential amplifier outputs in the calibration circuit starts to reverse ramping direction and the time when the difference crosses zero is counted in terms of reference clock cycles by a binary counter. The binary count is used to select the capacitance of the capacitor arrays in an RC filter for time constant calibration. This calibration circuit provides the flexibility for various reference clock rates by adjusting the programmable resistors. By tuning the same programmable resistors, this calibration circuit in addition provides the capability to changing the cut-off frequency of an RC filter circuit to another predetermined value.
Owner:PROCOMM
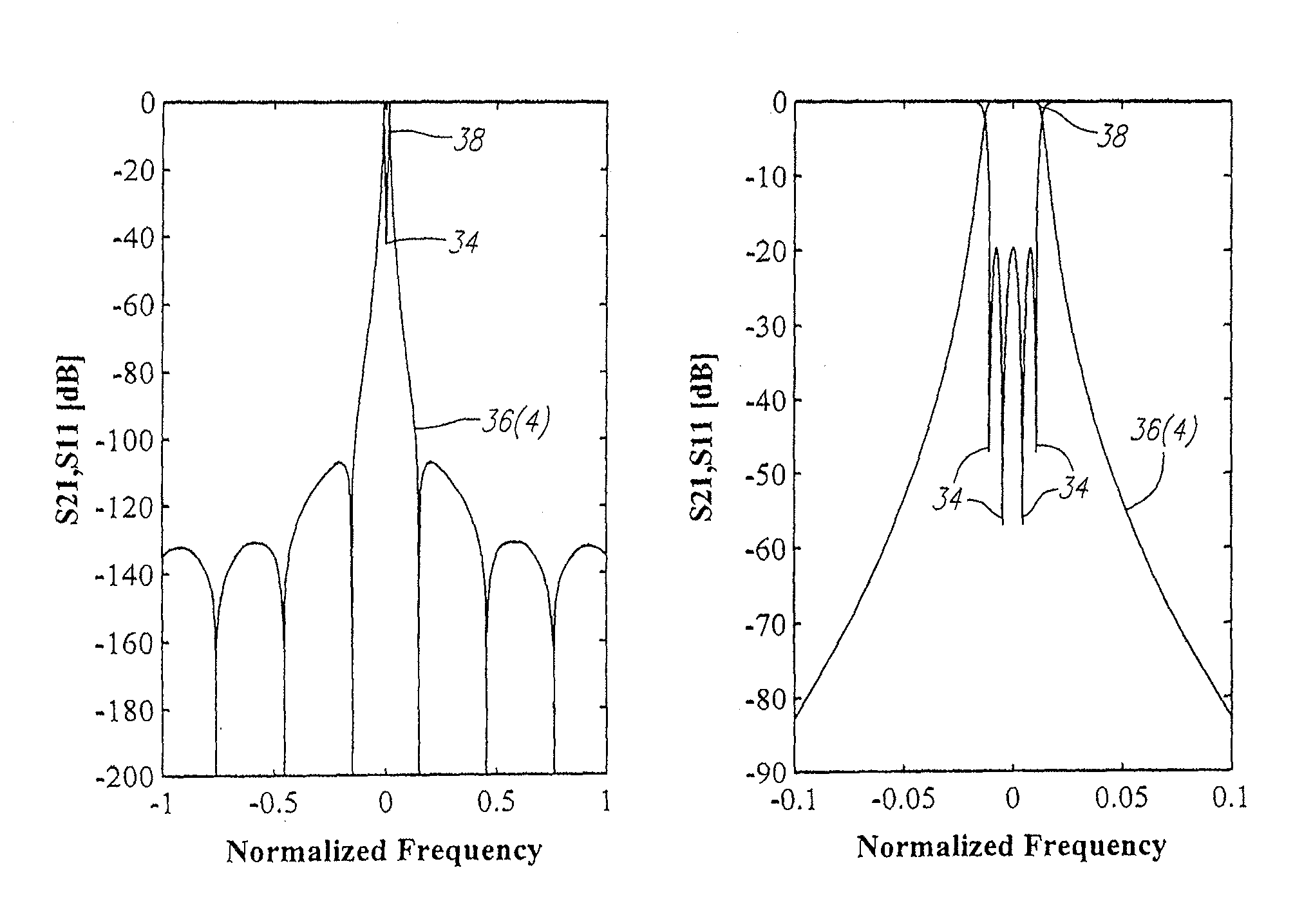
Low-loss tunable radio frequency filter
ActiveUS20070247261A1Minimizing insertion lossDifferent bandwidthMultiple-port networksWaveguidesTransmission zerosEngineering
A tunable radio frequency (RF) filter is provided. The RF filter comprises a signal transmission path having an input and an output, a plurality of resonant elements disposed along the signal transmission path between the input and the output, and a plurality of non-resonant elements coupling the resonant elements together. The resonant elements are coupled together to form a stop band having a plurality of transmission zeroes corresponding to respective frequencies of the resonant elements, and at least one sub-band between the transmission zeroes. The non-resonant elements comprise at least one variable non-resonant element for selectively introducing at least one reflection zero within the stop band to create a pass band in one of the sub-bands(s). The variable non-resonant element(s) may be configured for displacing the reflection zero(es) along the stop band to selectively move the pass band within the one sub-band or within selected ones of the sub-bands.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Low-loss tunable radio frequency filter
ActiveUS7639101B2Different bandwidthReduced insertion lossMultiple-port networksConfiguration CADTransmission zerosRf filters
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
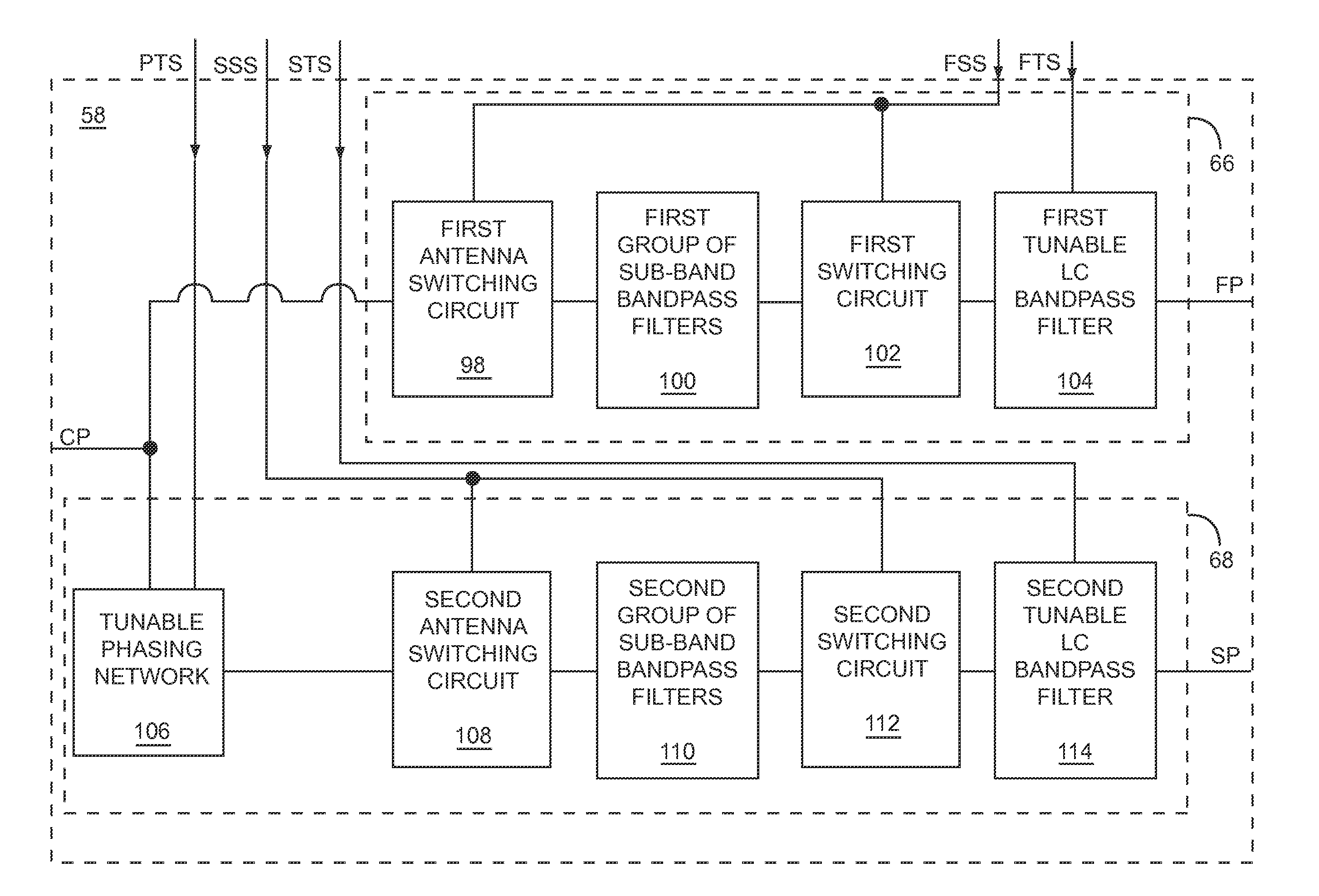
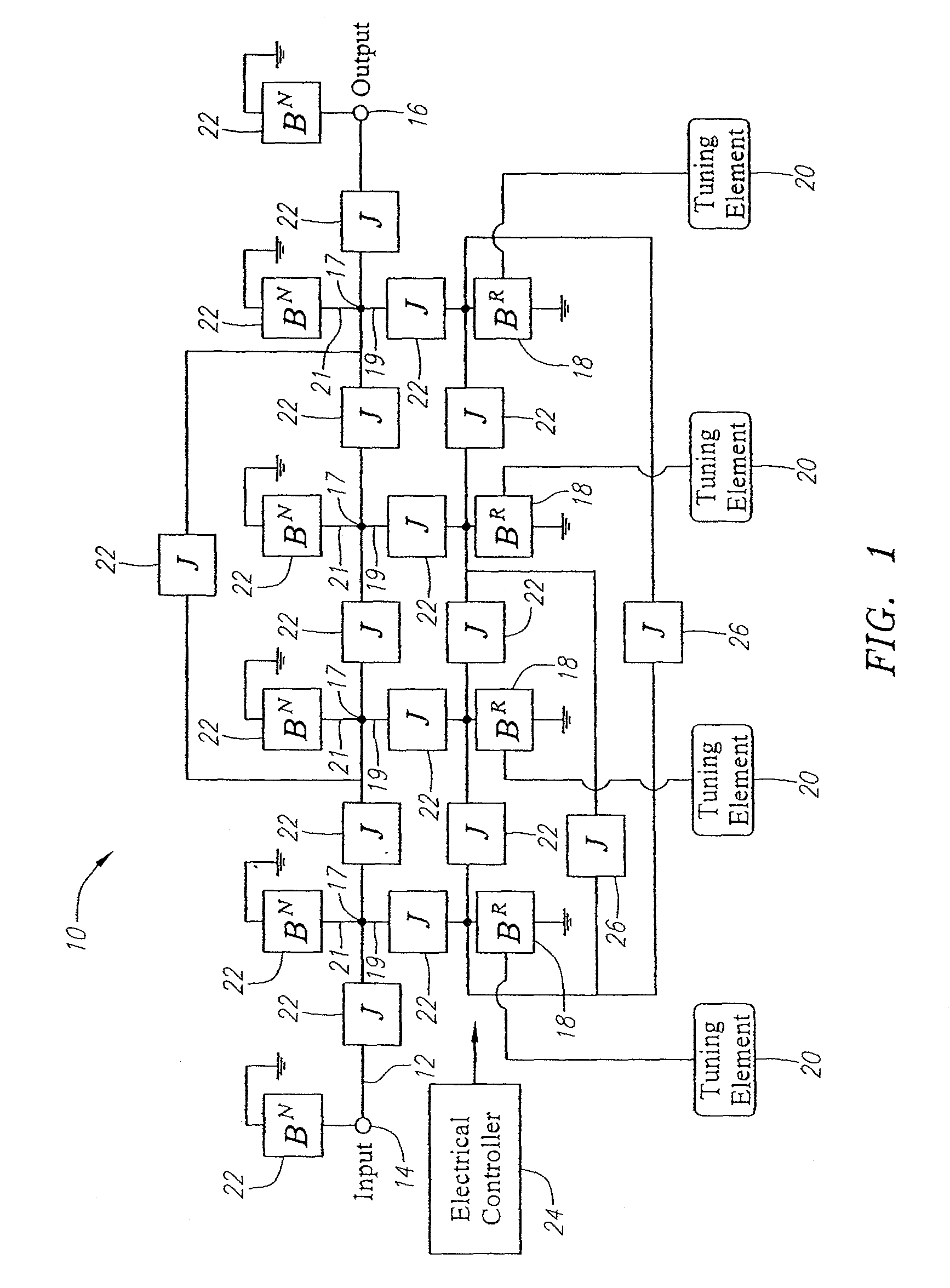
Passive multi-band duplexer
ActiveUS8680947B1Small sizeLow costMultiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesBandpass filteringMulti band
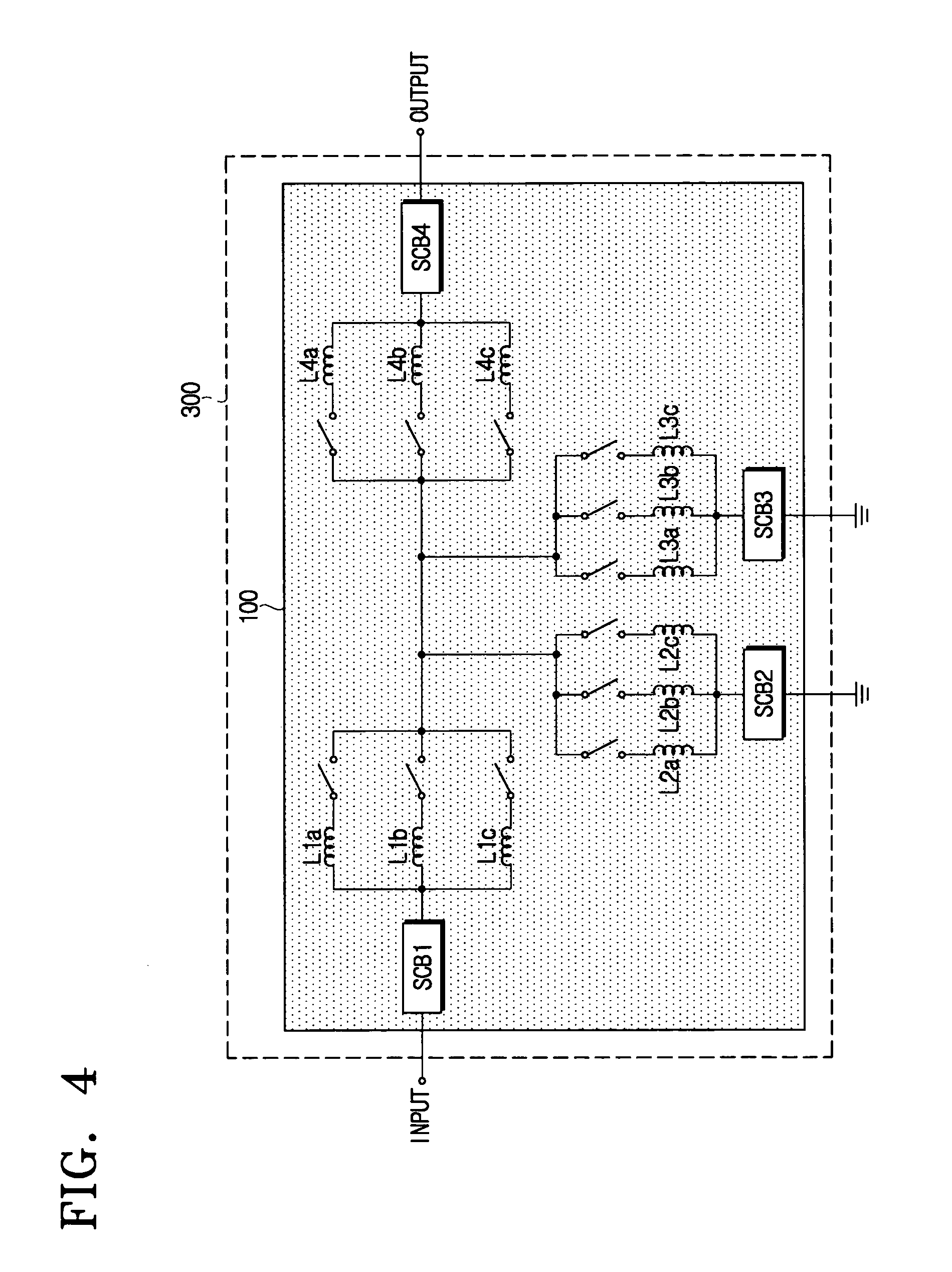
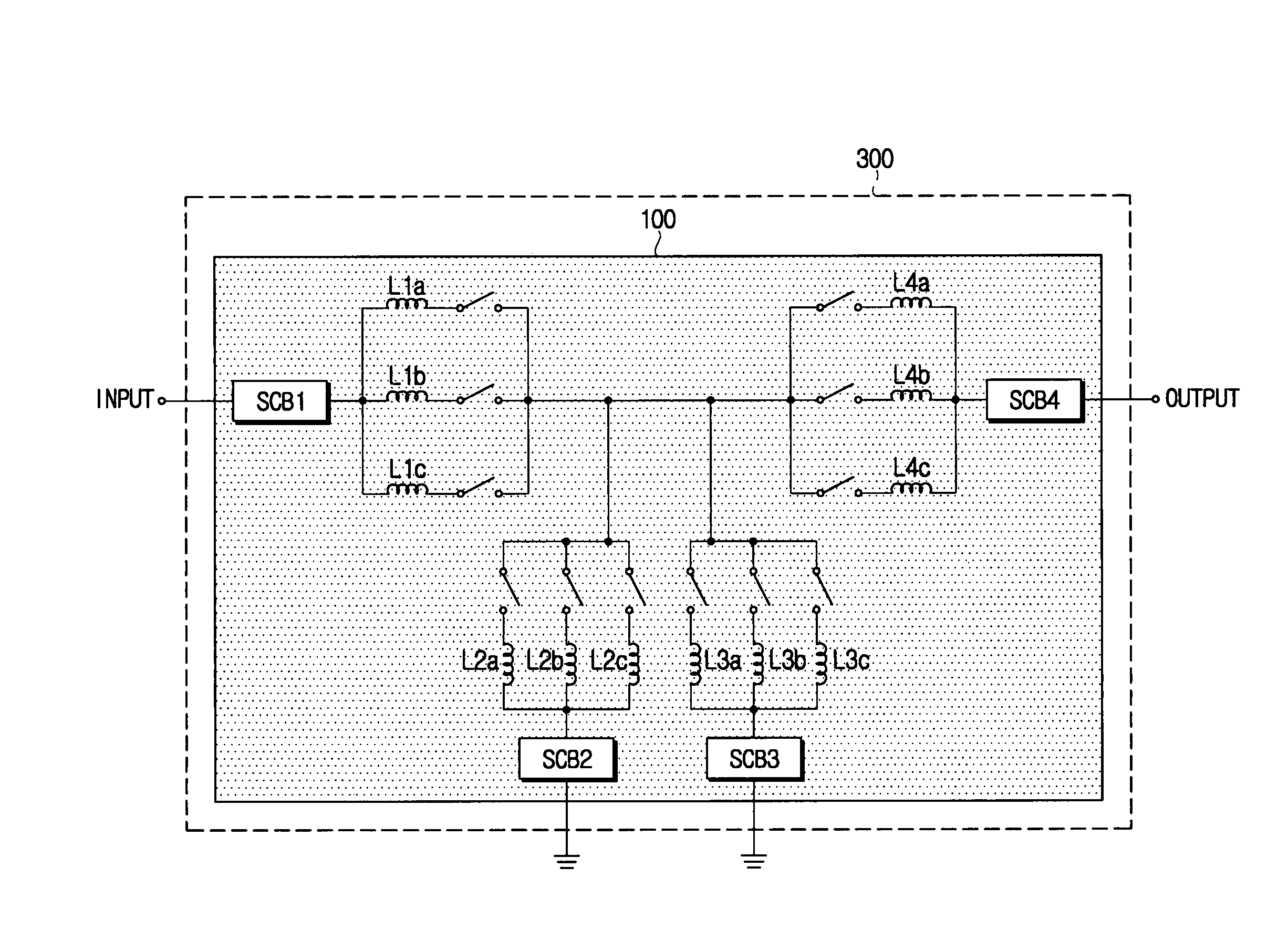
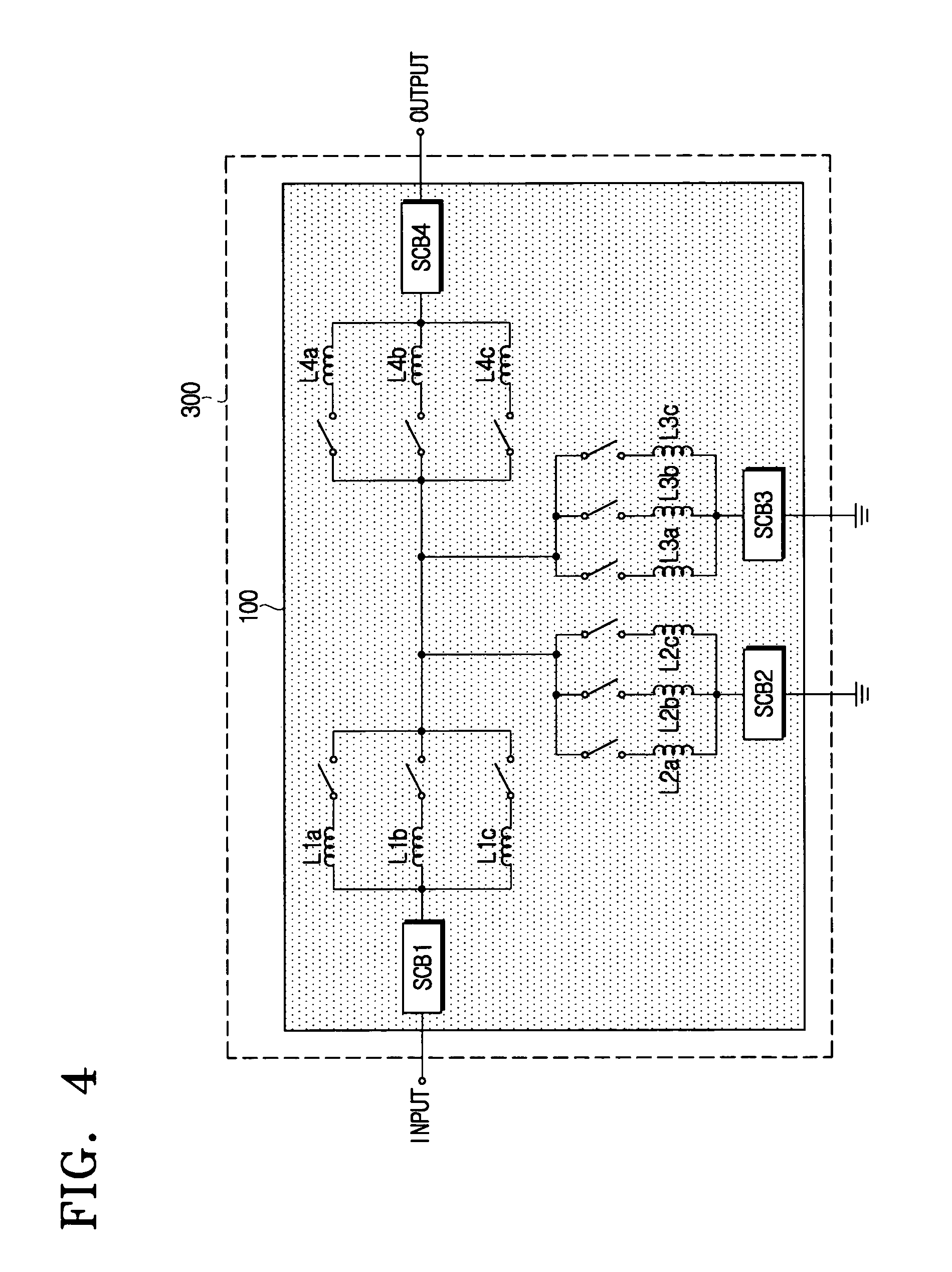
The present disclosure relates to a passive multi-band duplexer having a first bandpass filter and a second bandpass filter. The first bandpass filter includes a first group of sub-band bandpass filters, a first switching circuit, and a first tunable LC bandpass filter. Similarly, the second bandpass filter includes a second group of sub-band bandpass filters, a second switching circuit, and a second tunable LC bandpass filter. A first band of the passive multi-band duplexer, such as a transmit band, is chosen by selecting one of the first group of sub-band bandpass filters and tuning the first tunable LC bandpass filter to the first band. Similarly, a second band of the passive multi-band duplexer, such as a receive band, is chosen by selecting one of the second group of sub-band bandpass filters and tuning the second tunable LC bandpass filter to the second band.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Low-loss tunable radio frequency filter
ActiveUS7719382B2Different bandwidthReduced insertion lossMultiple-port networksWaveguidesTransmission zerosEngineering
A tunable radio frequency (RF) filter is provided. The RF filter comprises a signal transmission path having an input and an output, a plurality of resonant elements disposed along the signal transmission path between the input and the output, and a plurality of non-resonant elements coupling the resonant elements together. The resonant elements are coupled together to form a stop band having a plurality of transmission zeroes corresponding to respective frequencies of the resonant elements, and at least one sub-band between the transmission zeroes. The non-resonant elements comprise at least one variable non-resonant element for selectively introducing at least one reflection zero within the stop band to create a pass band in one of the sub-bands(s). The variable non-resonant element(s) may be configured for displacing the reflection zero(es) along the stop band to selectively move the pass band within the one sub-band or within selected ones of the sub-bands.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Electronically tunable, absorptive, low-loss notch filter
InactiveUS8013690B2Fast tuningHigh levelMultiple-port networksCoupling devicesWireless routerHybrid coupler
Owner:TERASYS TECH
Active filter circuit with dynamically modifiable gain
InactiveUS6958644B2Large dynamic rangeAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationSignal processingControl unit
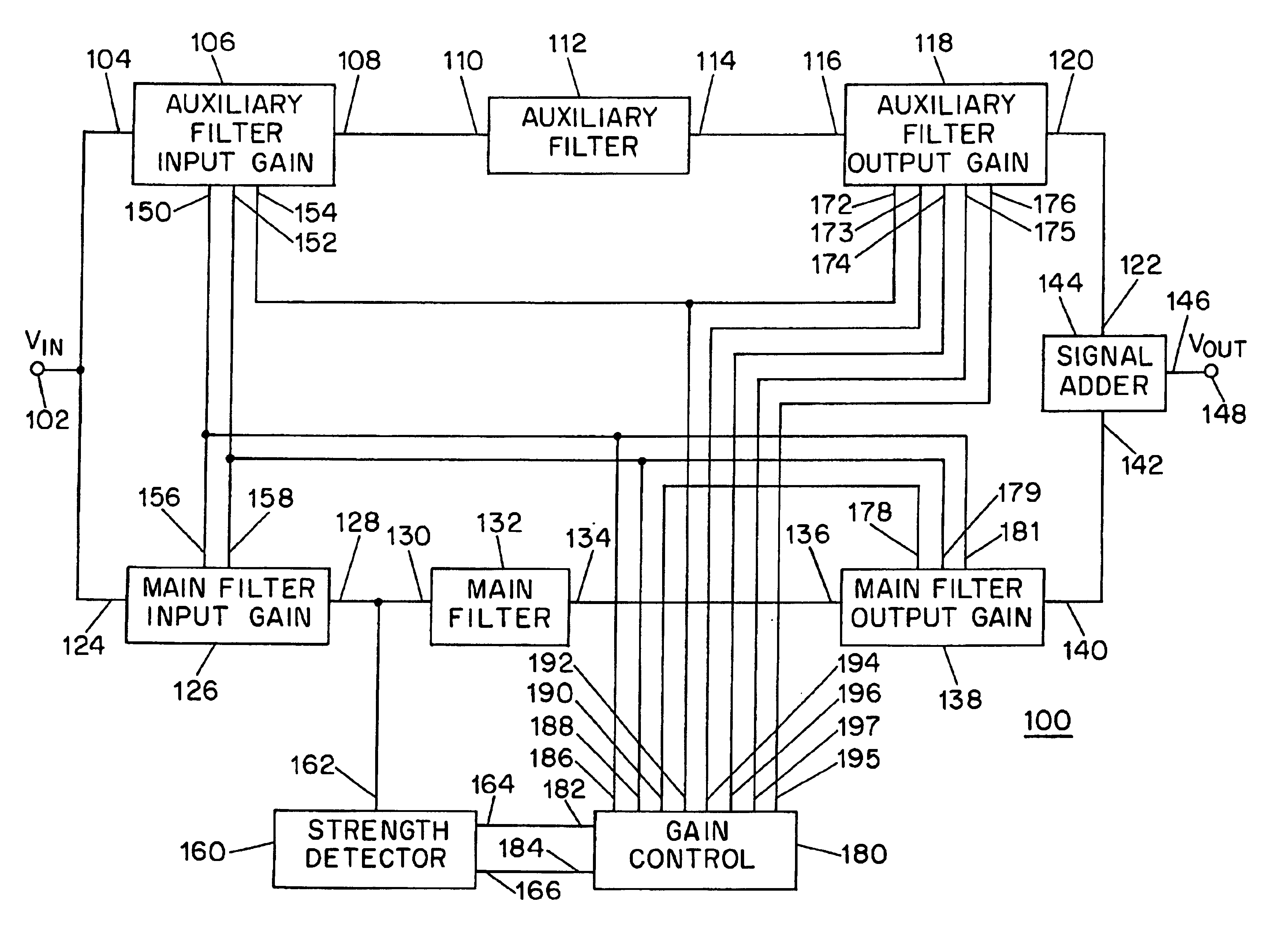
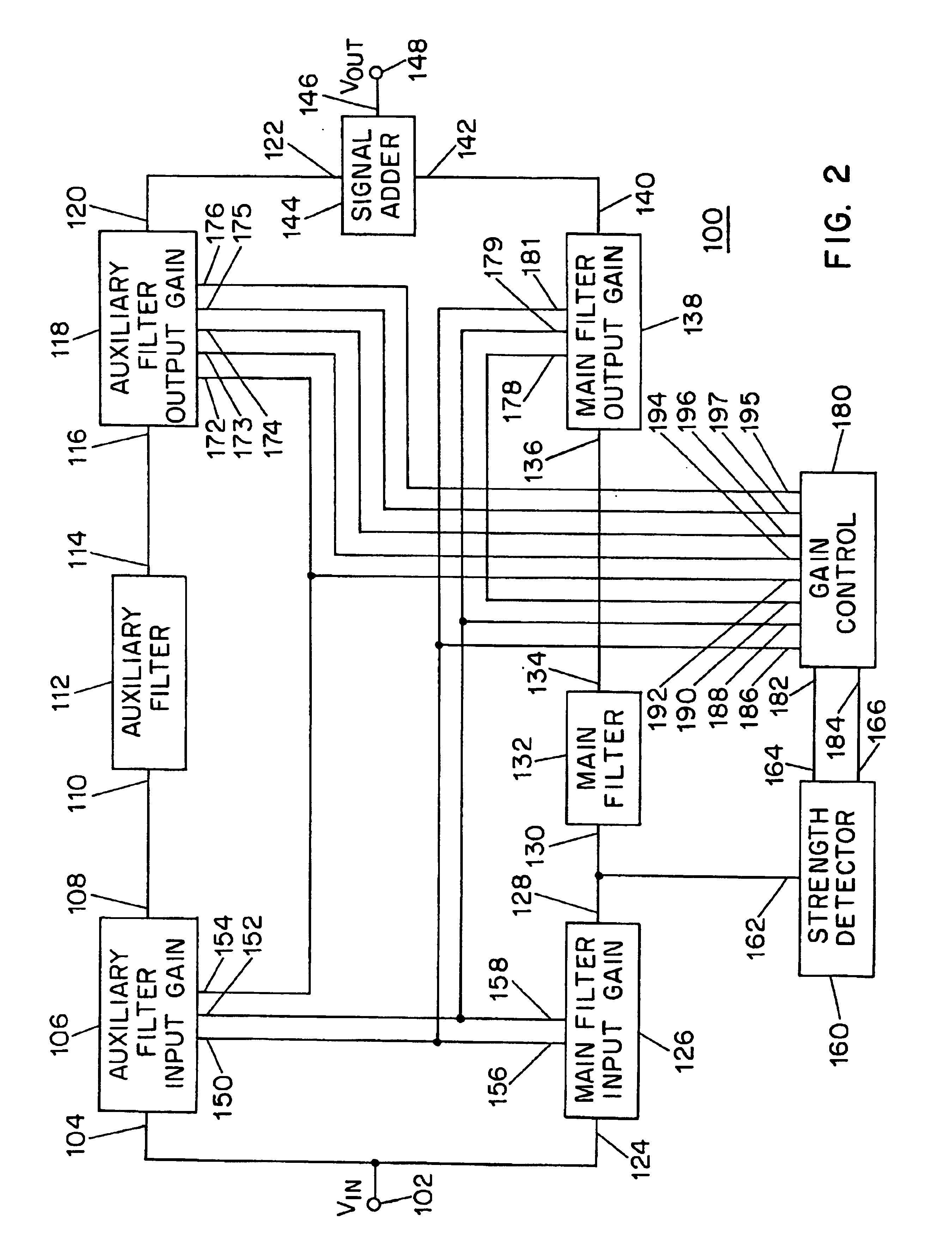
A signal processing system (100) comprises an input terminal (102), and a main path having a main filter input gain unit (126) coupled to said input terminal (102), a main filter (132) and an output gain unit (138). An auxiliary path includes an auxiliary filter input gain unit (106) coupled to the input terminal (102), an auxiliary filter (112) and an auxiliary filter output gain unit (118). An adder (144) is coupled to the output gain units (118, 138) for generating an output signal to an output terminal (148). The gains of the gain units are adjusted by a control unit (18) responsive to a detecting signal from a detector (160).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
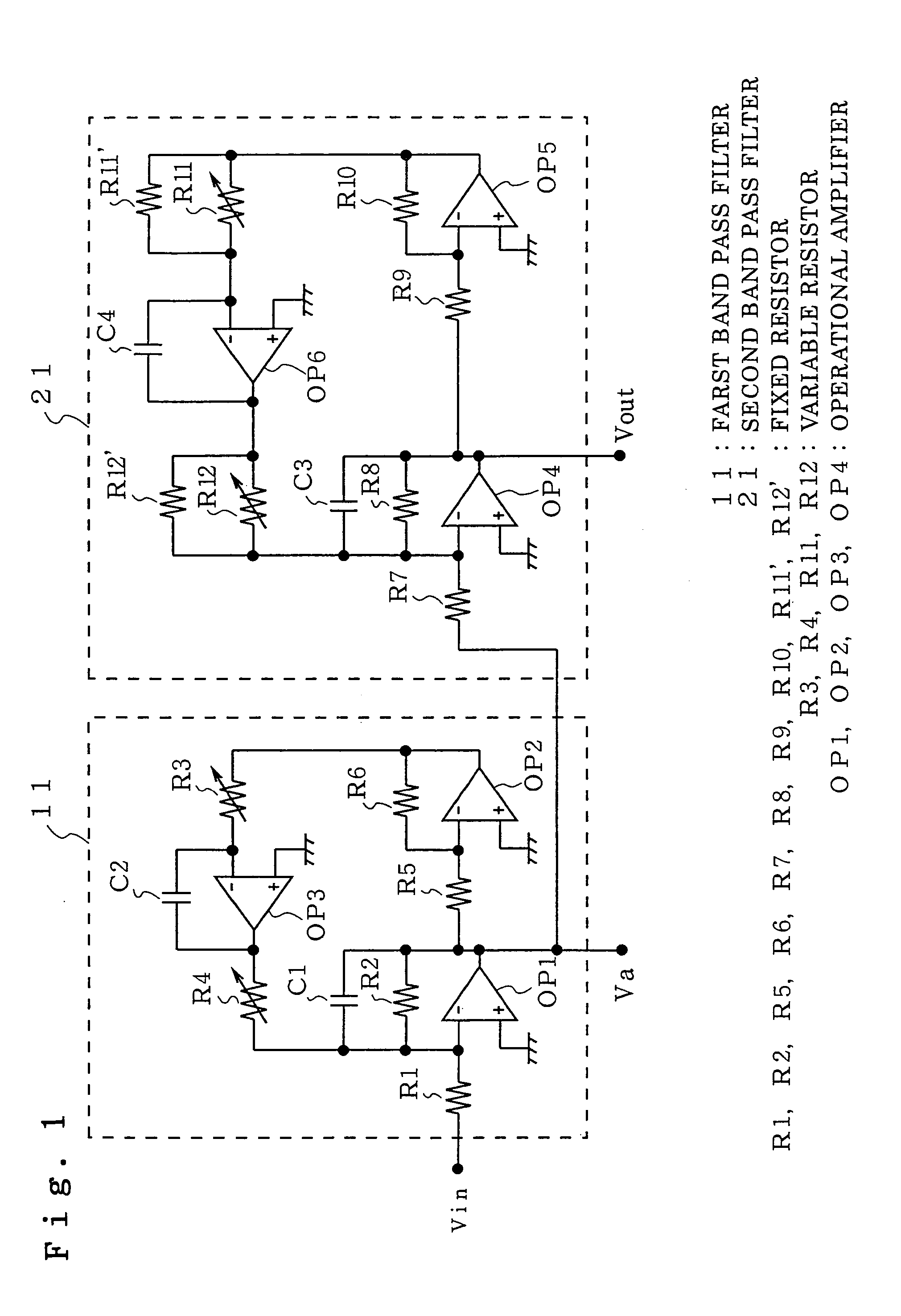
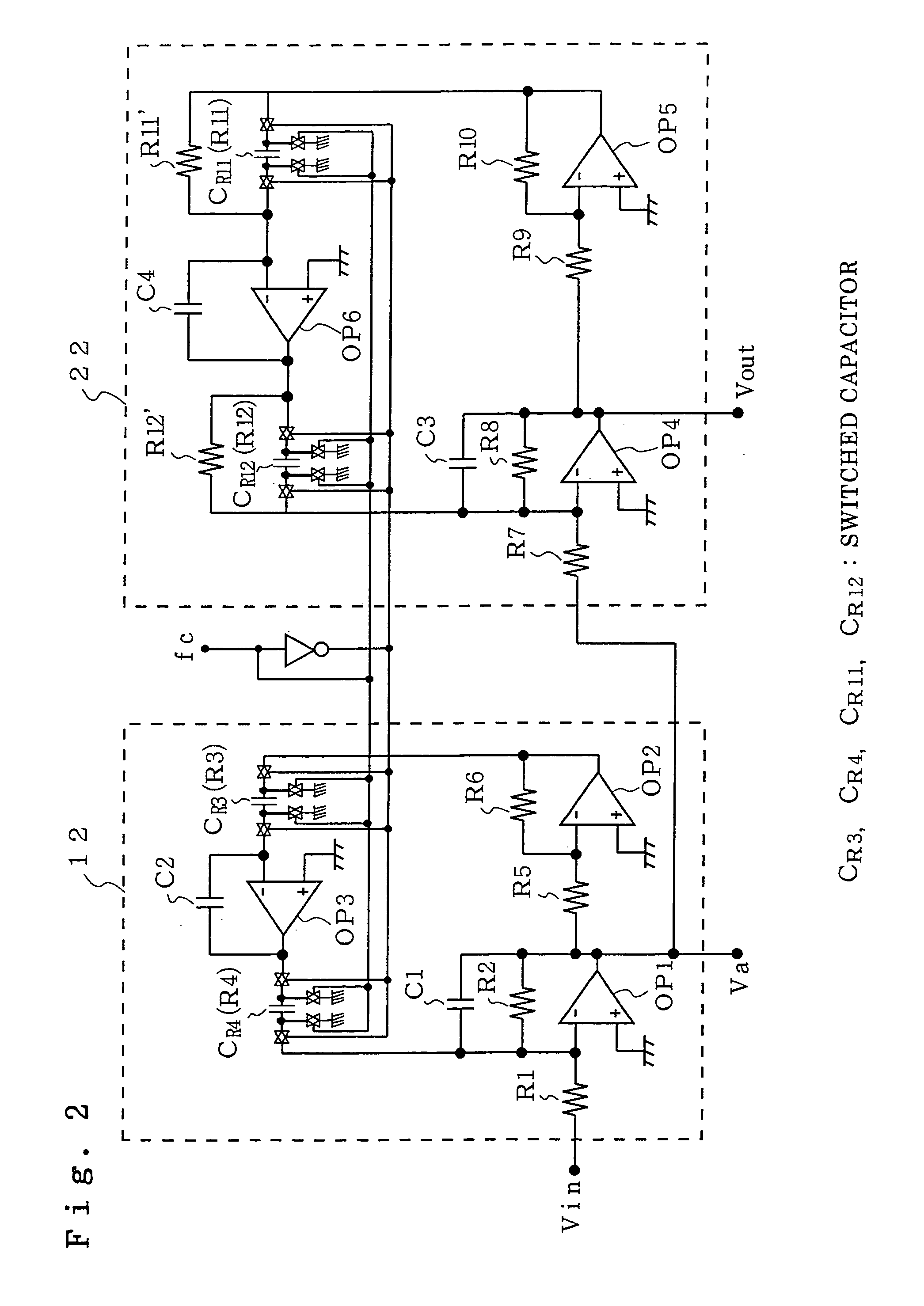
Band pass filter
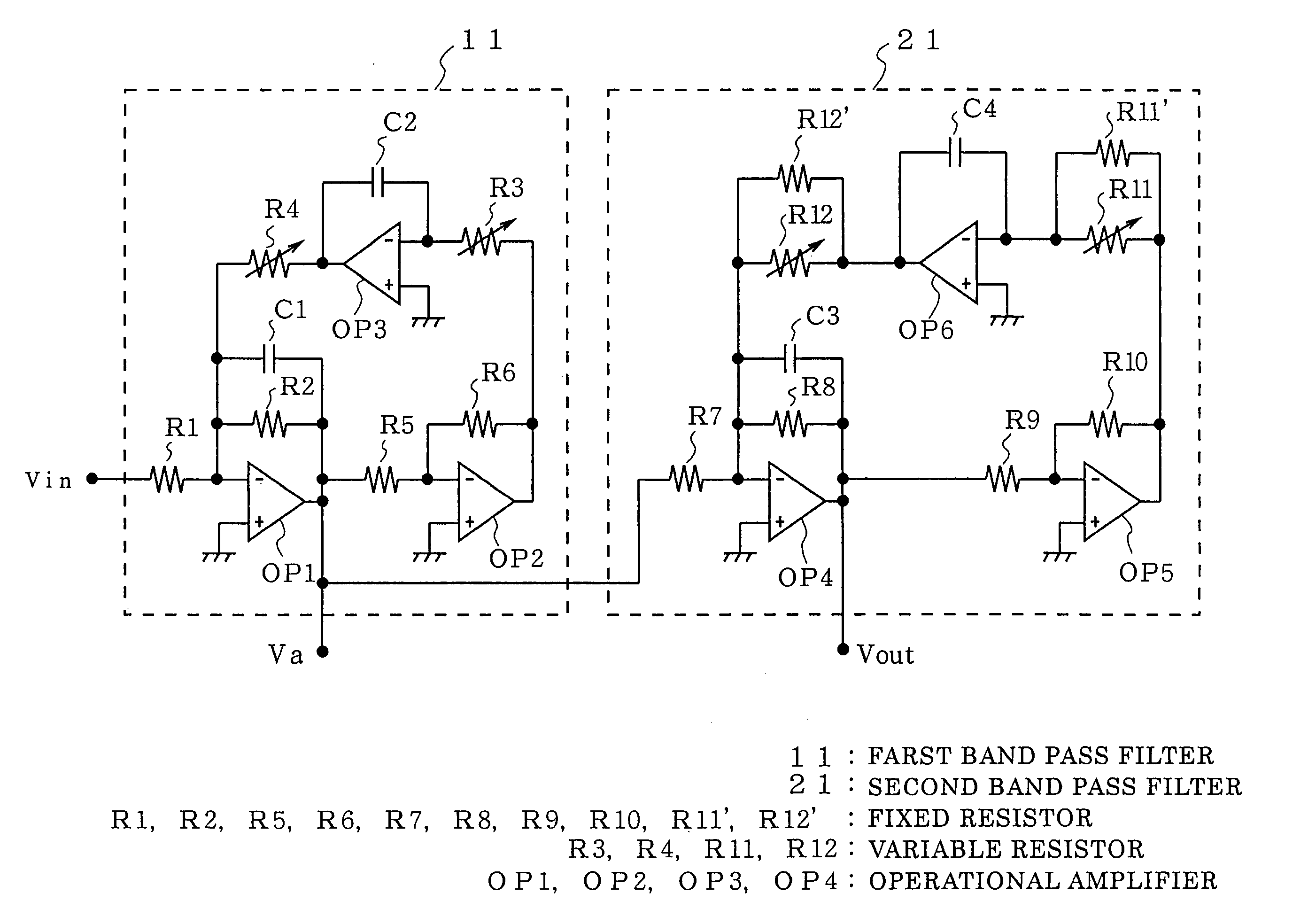
InactiveUS7081788B2Easily variableOscillations generatorsTransmissionBandpass filteringCenter frequency
A band pass filter includes a first band pass filter constructed of a biquad circuit and having a first center frequency, and a second bandpass filter constructed of a biquad circuit and having a second center frequency different from the first center frequency, and the first band pass filter and the second band pass filter are series connected, in which the first band pass filter and the second band pass filter have center frequency adjusting variable resistors varied at the same time, and a fixed resistor is connected in parallel to the center frequency adjusting variable resistor of one of the first band pass filter and the second band pass filter. As a result, the center frequency and / or the maximum gain can be made variable while the band width is fixed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
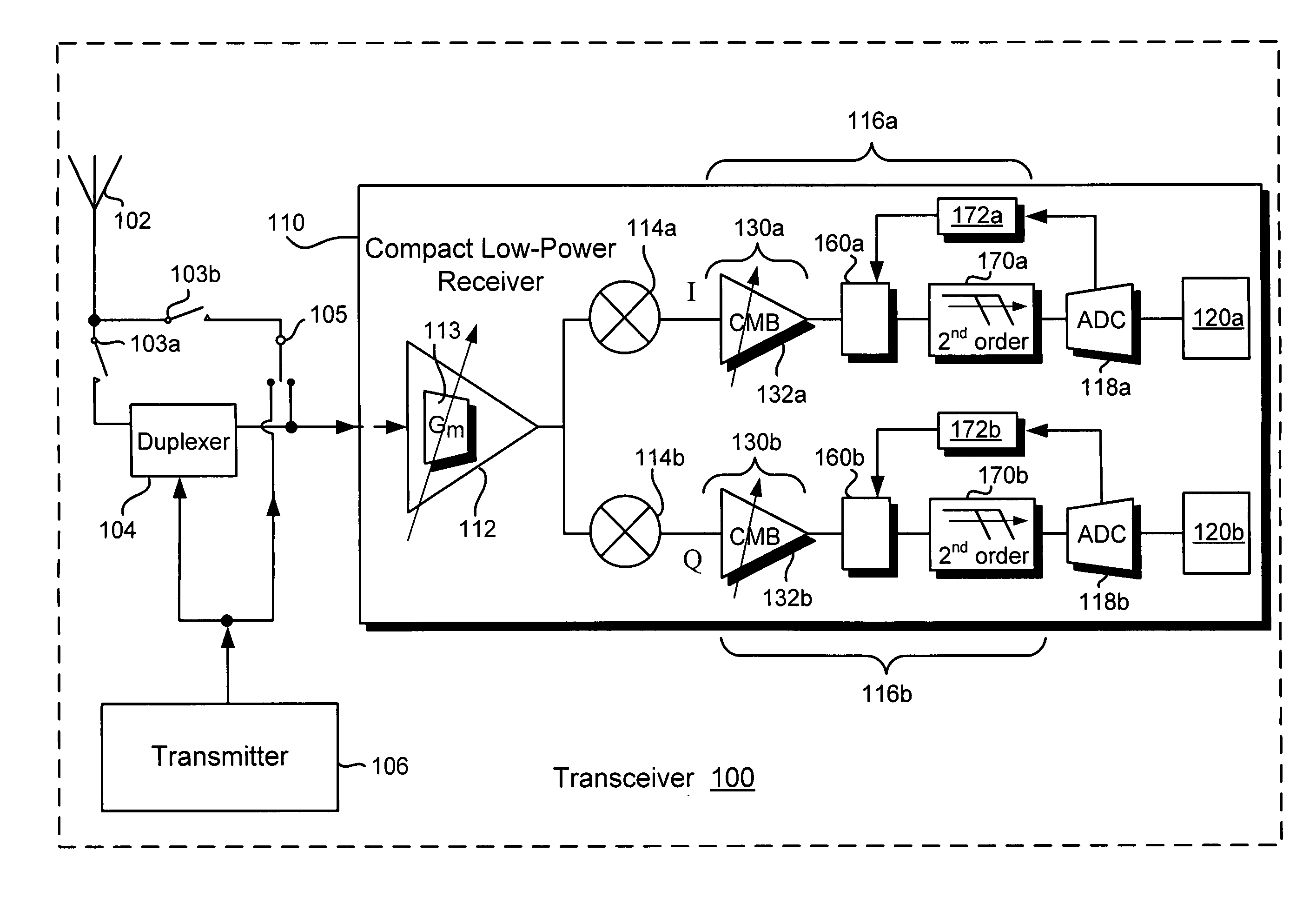
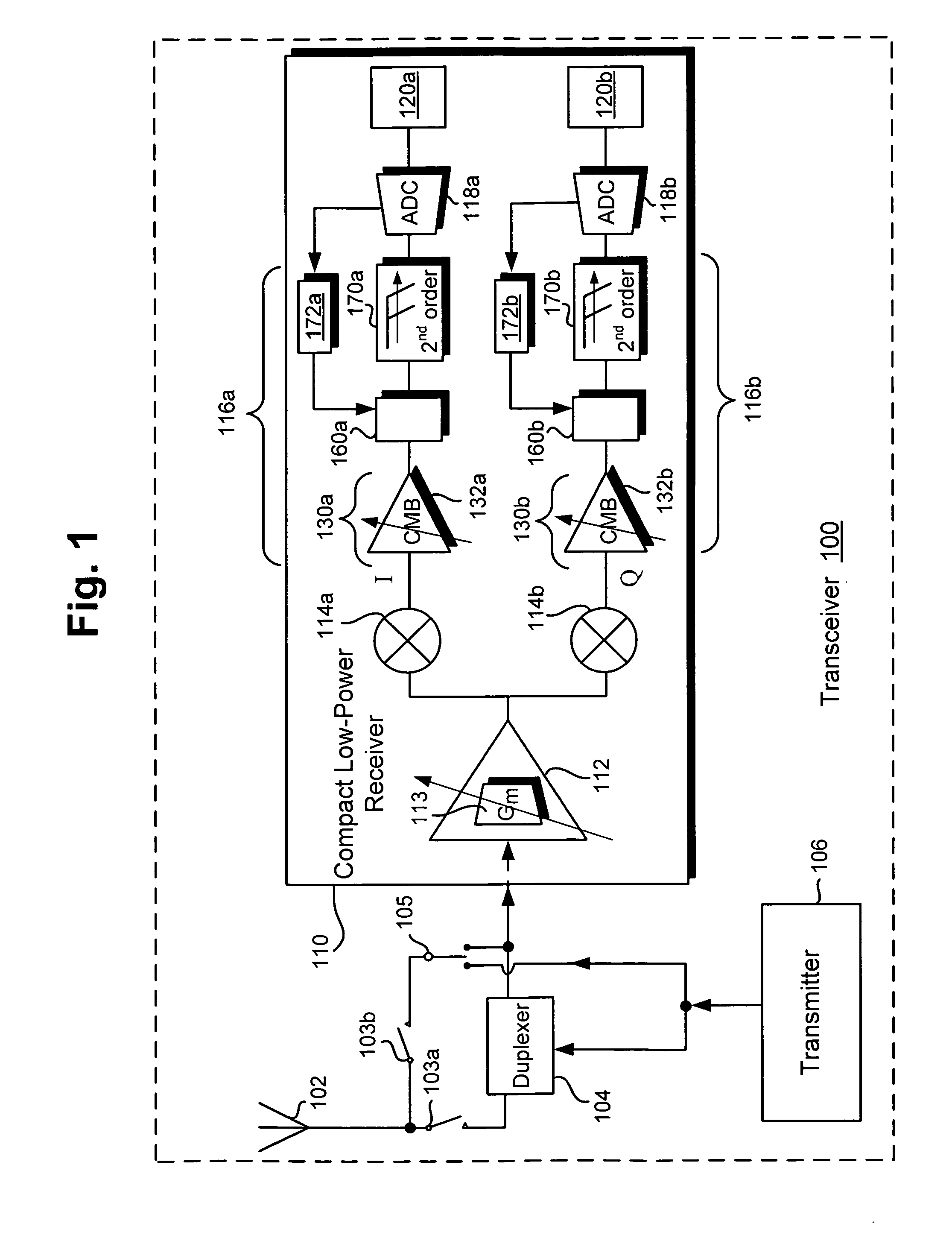
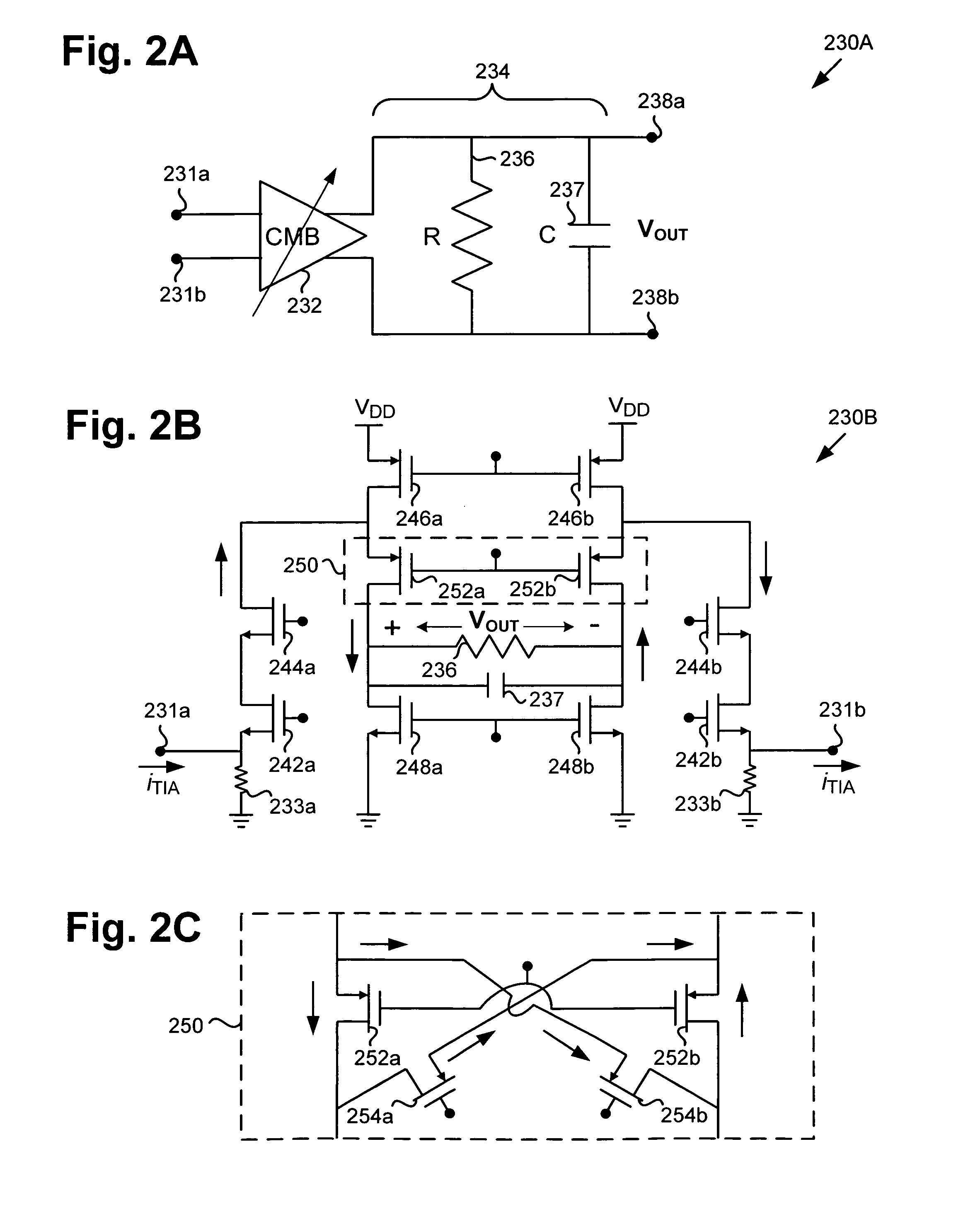
Compact low-power receiver including transimpedance amplifier, digitally controlled interface circuit, and low pass filter
According to one embodiment, a compact low-power receiver comprises first and second analog circuits connected by a digitally controlled interface circuit. The first analog circuit has a first direct-current (DC) offset and a first common mode voltage at an output, and the second analog circuit has a second DC offset and a second common mode voltage at an input. The digitally controlled interface circuit connects the output to the input, and is configured to match the first and second DC offsets and to match the first and second common mode voltages. In one embodiment, the first analog circuit is a variable gain control transimpedance amplifier (TIA) implemented using a current mode buffer, the second analog circuit is a second-order adjustable low-pass filter, whereby a three-pole adjustable low-pass filter in the compact low-power receiver is effectively produced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Filter circuit and receiver using the same
ActiveUS20110026507A1Reduction in DC offsetHigh-speed gain settingMultiple-port networksActive element networkGain settingCapacitor
Gain setting can be performed at high speed while reducing DC offset due to a filter cutoff frequency changeover without the need for input signal muting. A filter circuit having first and second filters is capable of allowing settings of first and second cutoff frequencies. First and second filter switch circuits and a charging circuit including a charging resistor and a charging switch are provided. For a first time period, the first switch circuit is controllably turned on while the second switch circuit is controllably turned off, thereby providing the first filter function. For a second time period, the first switch circuit is controllably turned off while the second switch circuit is controllably turned on, thereby providing the second filter function. For the first time period, the charging switch is controllably turned on so that the second capacitor is charged via the charging resistor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Complex filter with automatic tuning capabilities
A complex filter with automatic tuning capabilities for filtering a complex signal is disclosed. The complex filter includes a first lowpass filter, a second lowpass filter, a plurality of resistors, an integrator, a comparator, and a digital unit. The complex filter includes an imaginary component and a real component. The integrator, the comparator and the digital unit forms a tuning circuit. The tuning circuit can generate a plurality of control signals to tune the complex filter to a predetermined frequency. The tuning circuit can be turned off after a predetermined period.
Owner:O2 MICRO INC
Multi band pass filters
A multi-band band pass filter, including: first and second multi-order asynchronous resonators connected to each other by a coupling resonator and connected to respective first and second matching resonators, the first matching resonator connected to a signal-in terminal and second matching resonator connected to a signal-out terminal respectively; a first reference resonator connected between the signal-in terminal and a reference-in terminal and a second reference resonator connected between the signal-out terminal and a reference-out terminal, the first multi-order asynchronous resonator connected between the first matching resonator and the coupling resonator to the first reference terminal and the second multi-order asynchronous resonator connected between the second matching resonator and the coupling resonator to the reference-out terminal, the reference-in terminal connected to the reference-out terminal; and a feedback resonator connected between the signal-in terminal and the signal-out terminal.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and Systems for Interference Rejection for Low Signals
ActiveUS20120171978A1Multiple-port networksActive element networkRadio equipmentElectromagnetic interference
A radio device and a method to operate a non-heterodyne receiver are provided. The radio device is configured to receive a signal waveform and to provide a wake-up signal to a second communication circuit when the signal waveform is a valid communication request; wherein the second communication circuit switches from a power saving state to an operating state upon receiving the wake-up signal from the non-heterodyne receiver. The non-heterodyne receiver further including an Electromagnetic interference (EMI) rejection circuit, including a narrow band filter and a broadband filter to reject an EMI signal. A filter circuit for a narrow passband circuit is also provided. The filter including a buffer circuit; a crystal oscillator coupled to the output of the buffer circuit; and an inverting amplifier coupled in parallel to the crystal oscillator.
Owner:SECUREALL CORP
Controlling the bandwidth of an analog filter
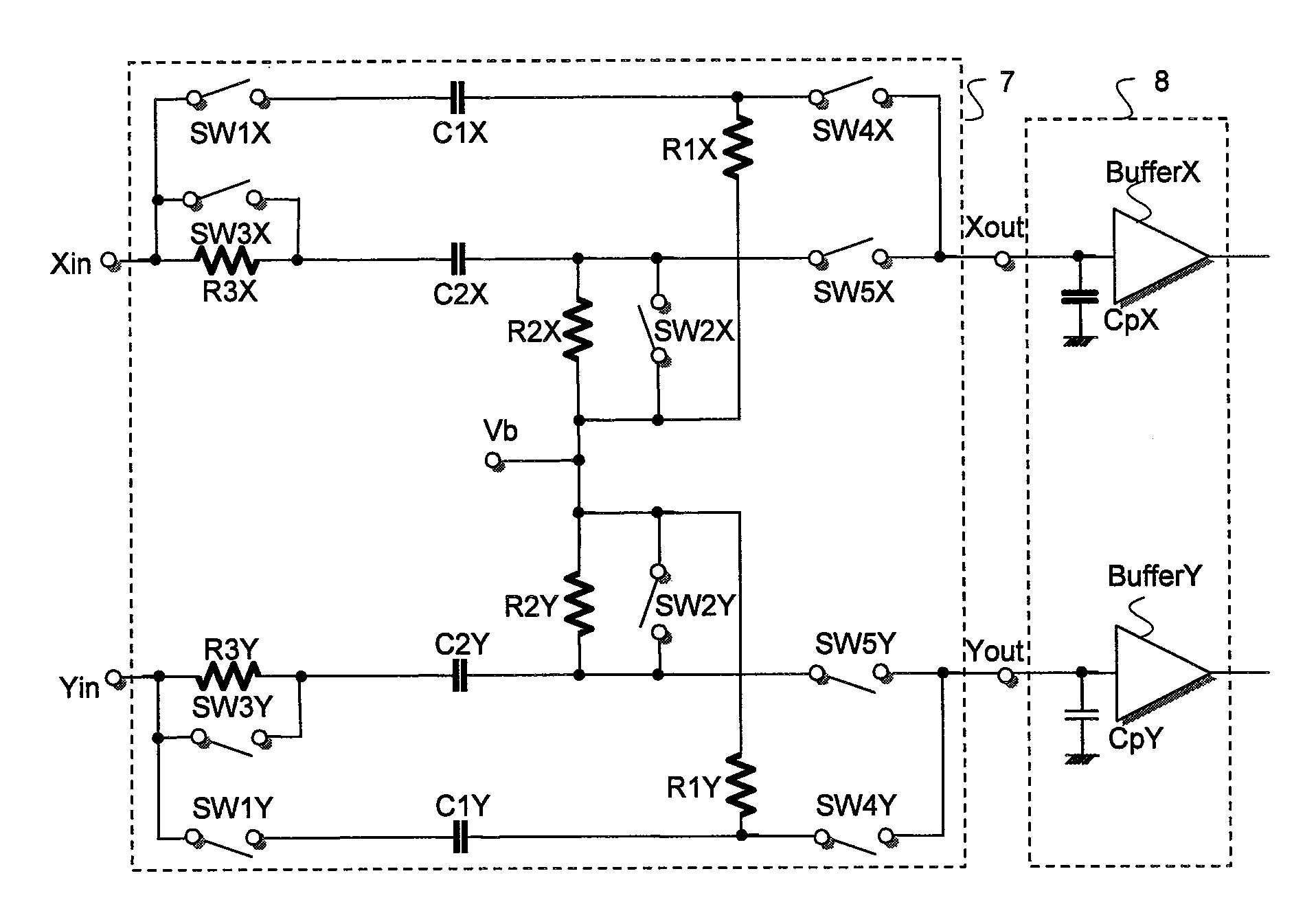
ActiveUS20080096514A1Radio transmissionFrequency selective two-port networksDigital tuningCapacitance
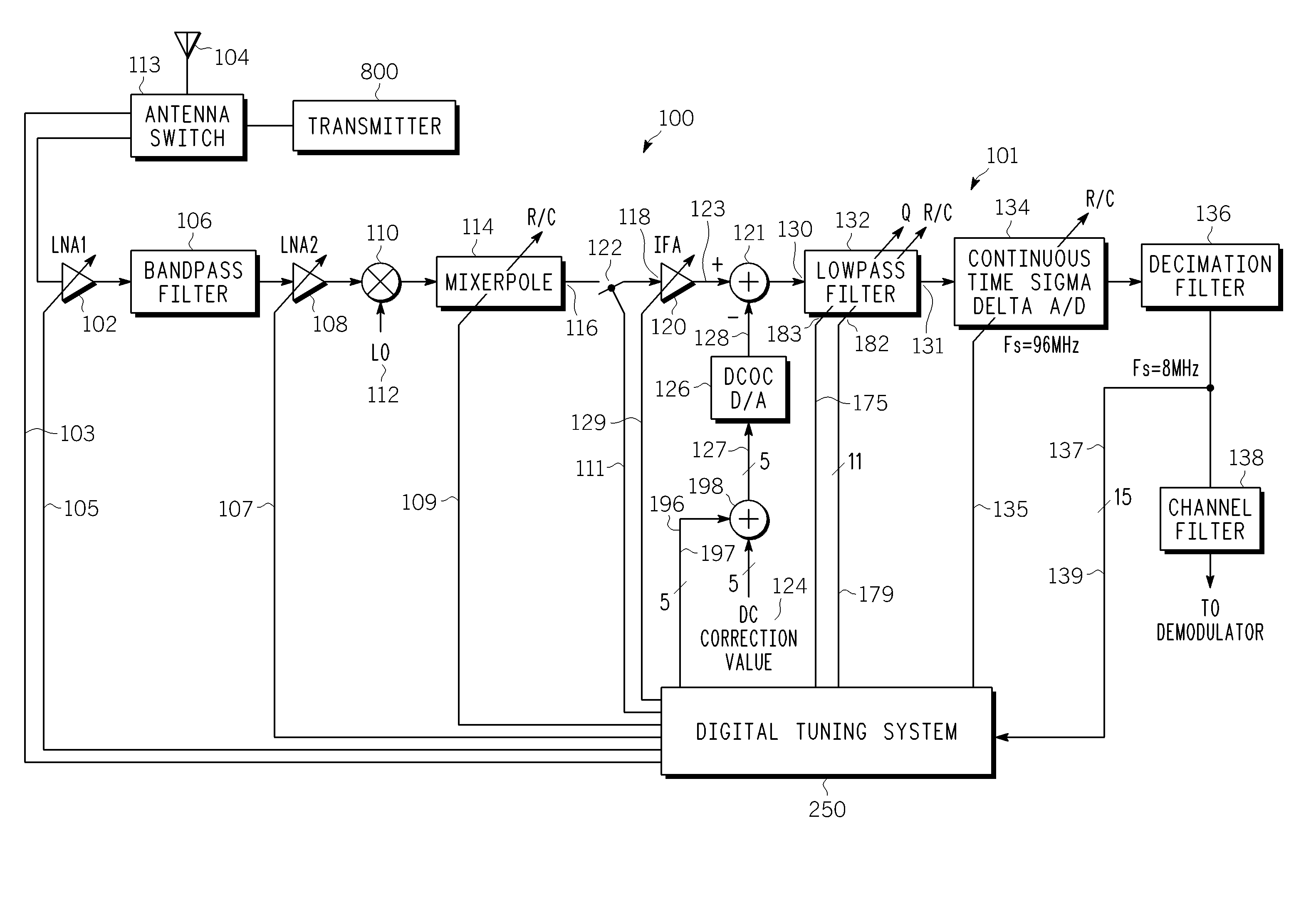
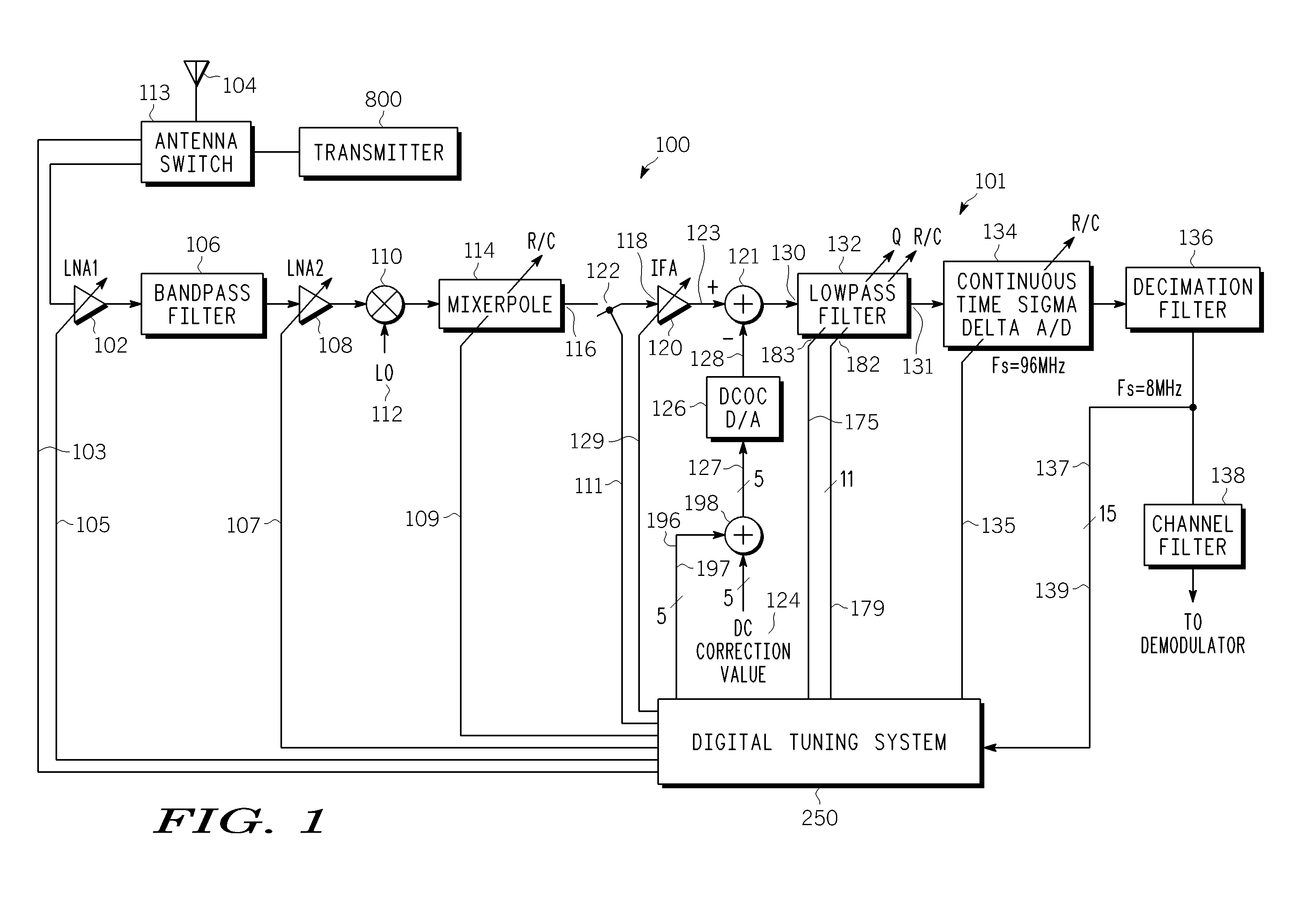
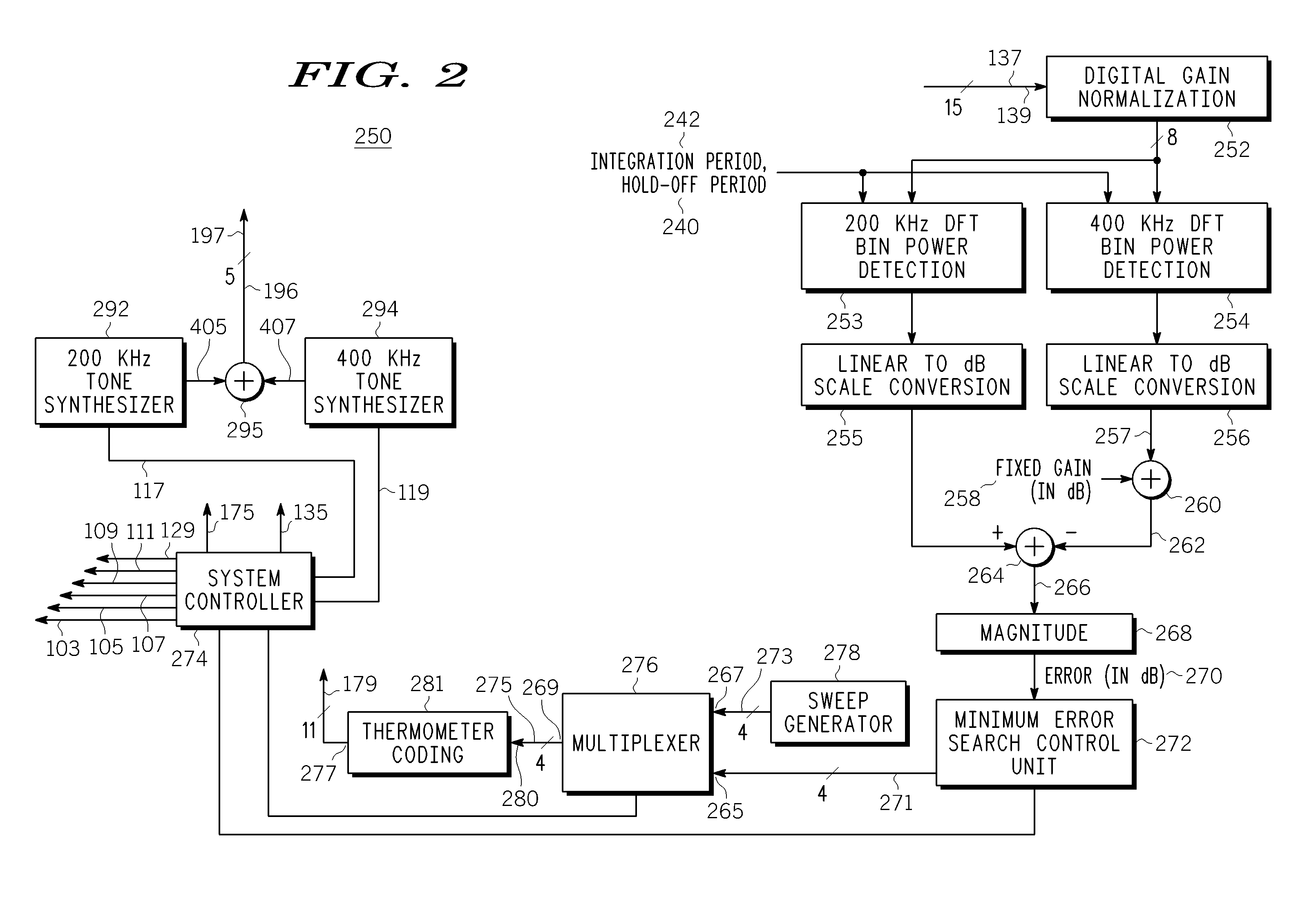
A digital tuning system (250) for changing a cutoff frequency of an analog filter (132) includes digital synthesizers (292 and 294) for producing a two-tone calibration signal (196) applied to an input of the filter after a quality factor of the filter is increased. The filter includes at least one R / C circuit with two resistors (304 and 306) for changing the quality factor and arrays (308 and 310) of capacitors for changing the cutoff frequency. The amplitude of the magnitude responses (409 and 411) of the filter to each tone (405 and 407) is measured by a two discrete Fourier transform single-frequency bin power detection circuits (253 and 254) while the filter is sequenced through a plurality of capacitance settings. An optimal capacitance for the R / C circuit is selected by comparing, to a pre-selected value, a difference between the responses of the filter to each tone, for each capacitance setting.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for tuning an active filter
ActiveUS20080191795A1Batteries circuit arrangementsActive element networkCapacitanceVoltage generator
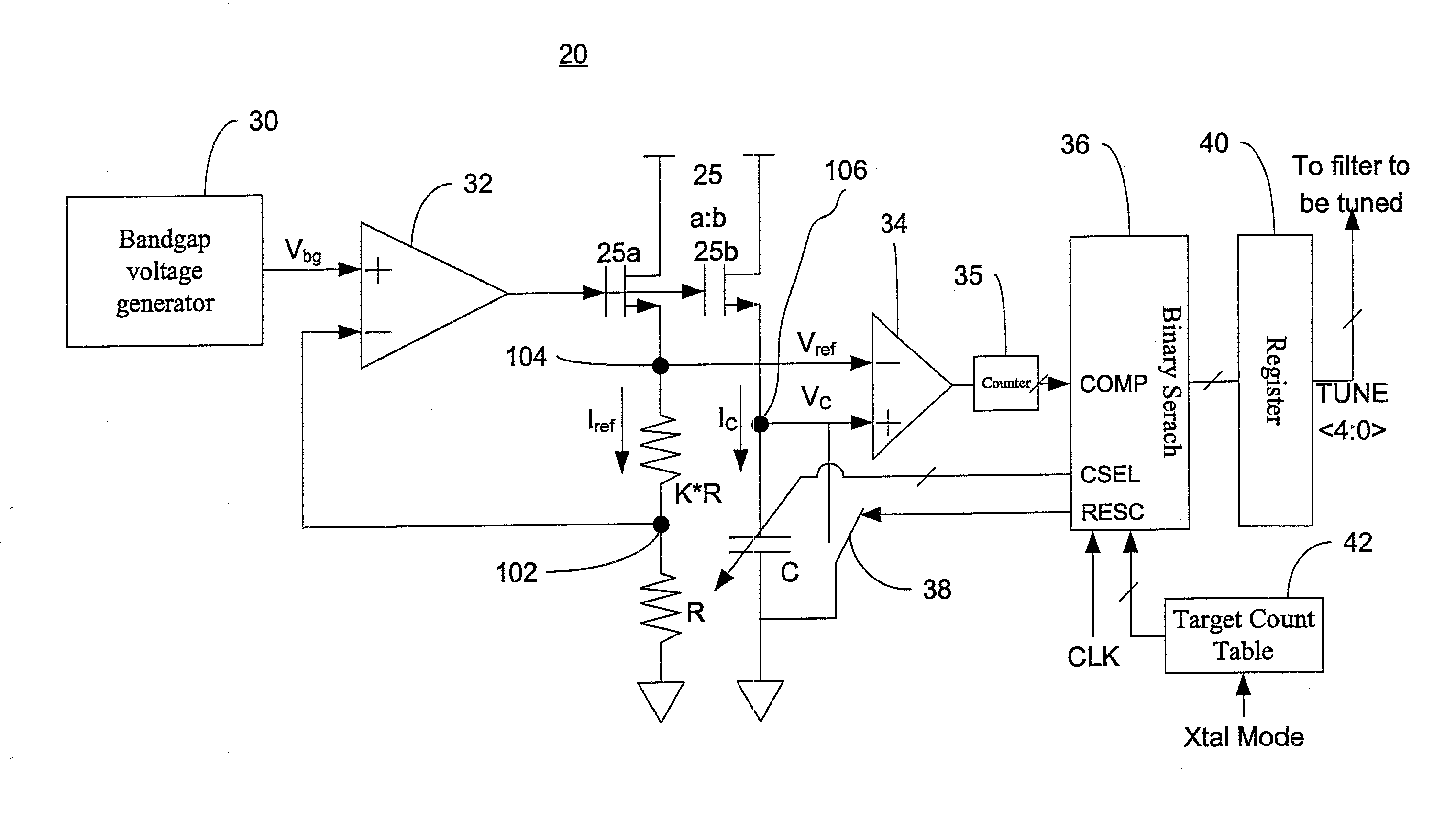
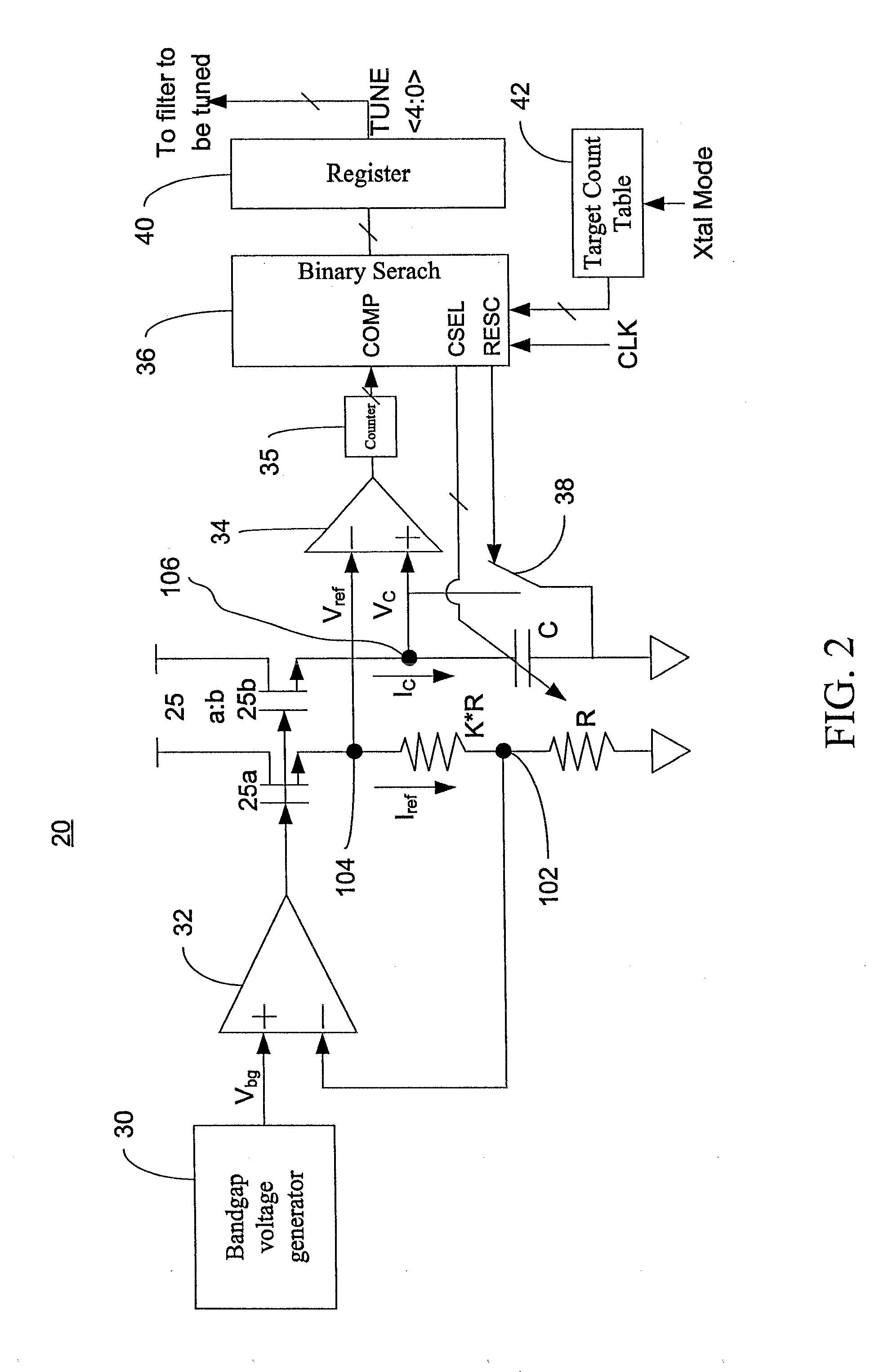
A tuning circuit for tuning an active filter includes a resistor-capacitor circuit comprising a variable capacitor and a resistor equivalent to a first resistor and a second resistor serially connected to the first resistor, a voltage generator for providing a constant reference voltage to the first resistor, a current replicating unit for replicating a current based on the constant reference voltage, a comparator for comparing a charging voltage as the current is charging a variable capacitor with the constant reference voltage, a counter for counting a number of cycles of a clock signal until the charging voltage reaches the constant reference voltage, a adjustment unit for calibrating a capacitance of the variable capacitor based on the number of cycles of a clock signal and a target count value associated with a predetermined RC time constant.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
Method and Apparatus Adapted to Transmit Data
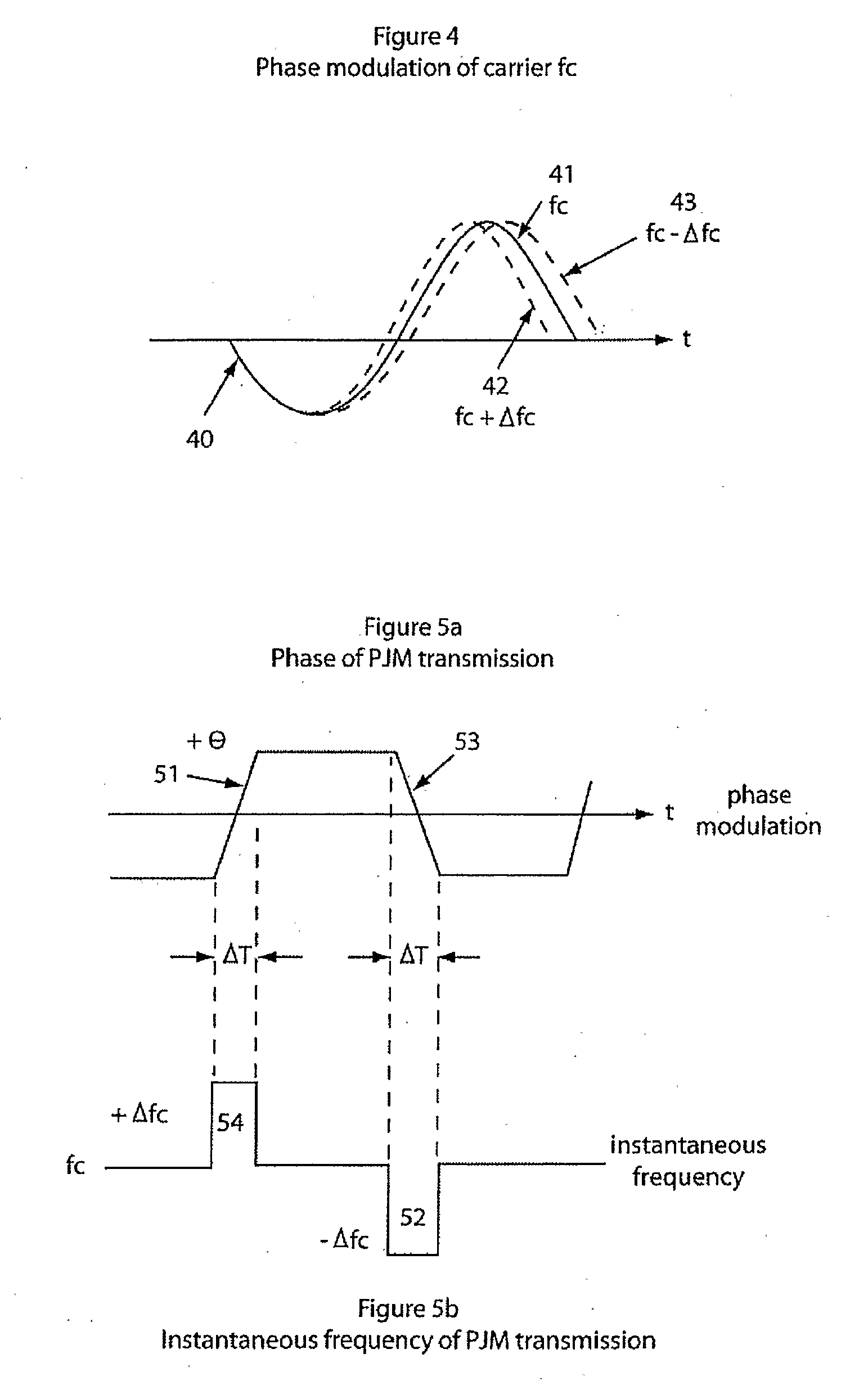
ActiveUS20090010360A1Easy to adjustLow phase modulationAngle modulation by variable impedenceNear-field transmissionAudio power amplifierRadiotransmitter
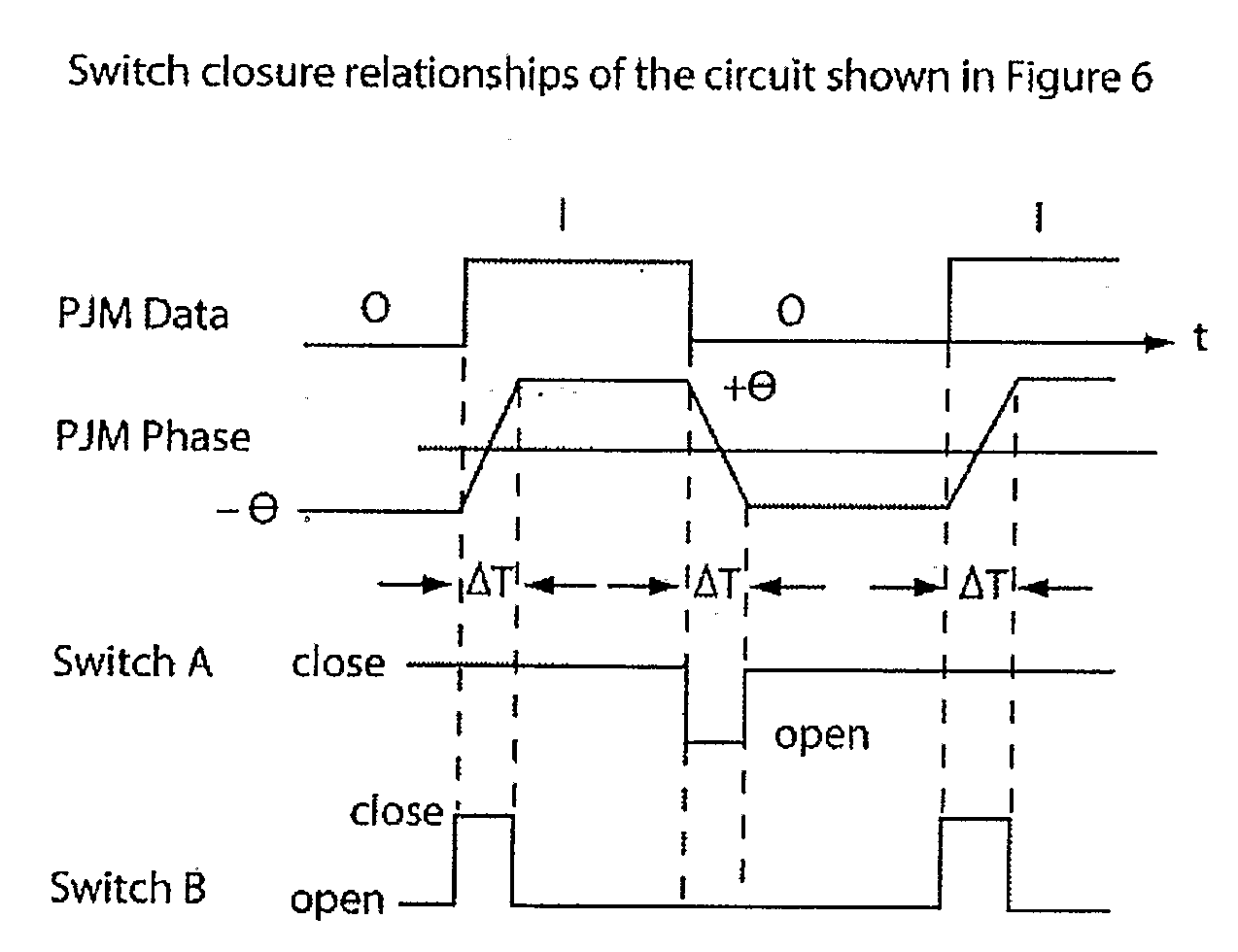
The present invention relates to the field of data transmission. The invention has application to amplifiers, the transmission of data modulated signals, filters and / or matching circuits connected between an amplifier and a load, radio transmitters, the transmission of data modulated radio signals, filters and / or matching circuits used between a transmitter's power amplifier and an antenna and the field of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), such as in the transmission of data between a tag and an interrogator. The present invention enables the transmission of phase modulated signals, by adjusting a device's tuning to substantially match the instantaneous frequency of the phase modulated signal.
Owner:SATO HLDG CORP
Popular searches
Single resonant circuit with varying inductance/capacitance only Resistance/reactance/impedence Electronic circuit testing Digital differential analysers Special data processing applications Error prevention Analogue adaptive filters Amplifier input/output impedence modification Baseband systems Pulse slope modification
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com