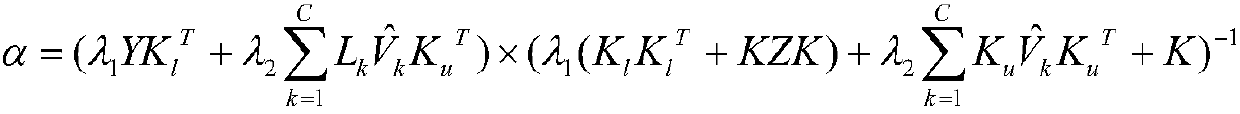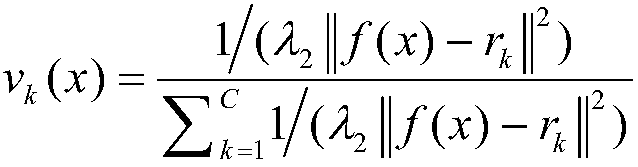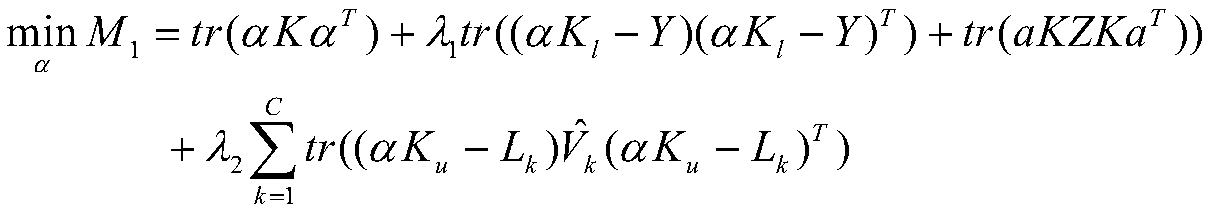Semi-supervised classification method of modified clustering assumption combined with pairwise constraints
A classification method and semi-supervised technology, applied in the fields of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of low performance of algorithms, lack of effectiveness and correctness, neglect of deep cultivation and utilization, etc., to achieve high effectiveness and correctness performance, good fuzzy division ability, and improved algorithm performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] In order to make the technical means, creative features, achievement goals and effects realized by the present invention easy to understand, the present invention will be further described below with reference to the specific embodiments.
[0024] This specific embodiment adopts the following technical solutions: the revised clustering hypothesis is combined with a pairwise constraint semi-supervised classification method, and the steps are:
[0025] Input: l labeled samples u unlabeled samples The iteration termination threshold ε, the maximum number of iterations Maxiter;
[0026] Output: classification decision function f(x) and membership function v(x);
[0027] ①Initialize the class membership of unlabeled samples through the FCM method, and select the appropriate parameter λ 1 , λ 2 , and calculate the initialized α according to the formula, and M;
[0028] ②Pass-through
[0029]
[0030] update α;
[0031] ③ According to the formula
[0032]
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com