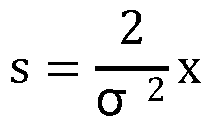Patents
Literature
56 results about "Soft-decision decoder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
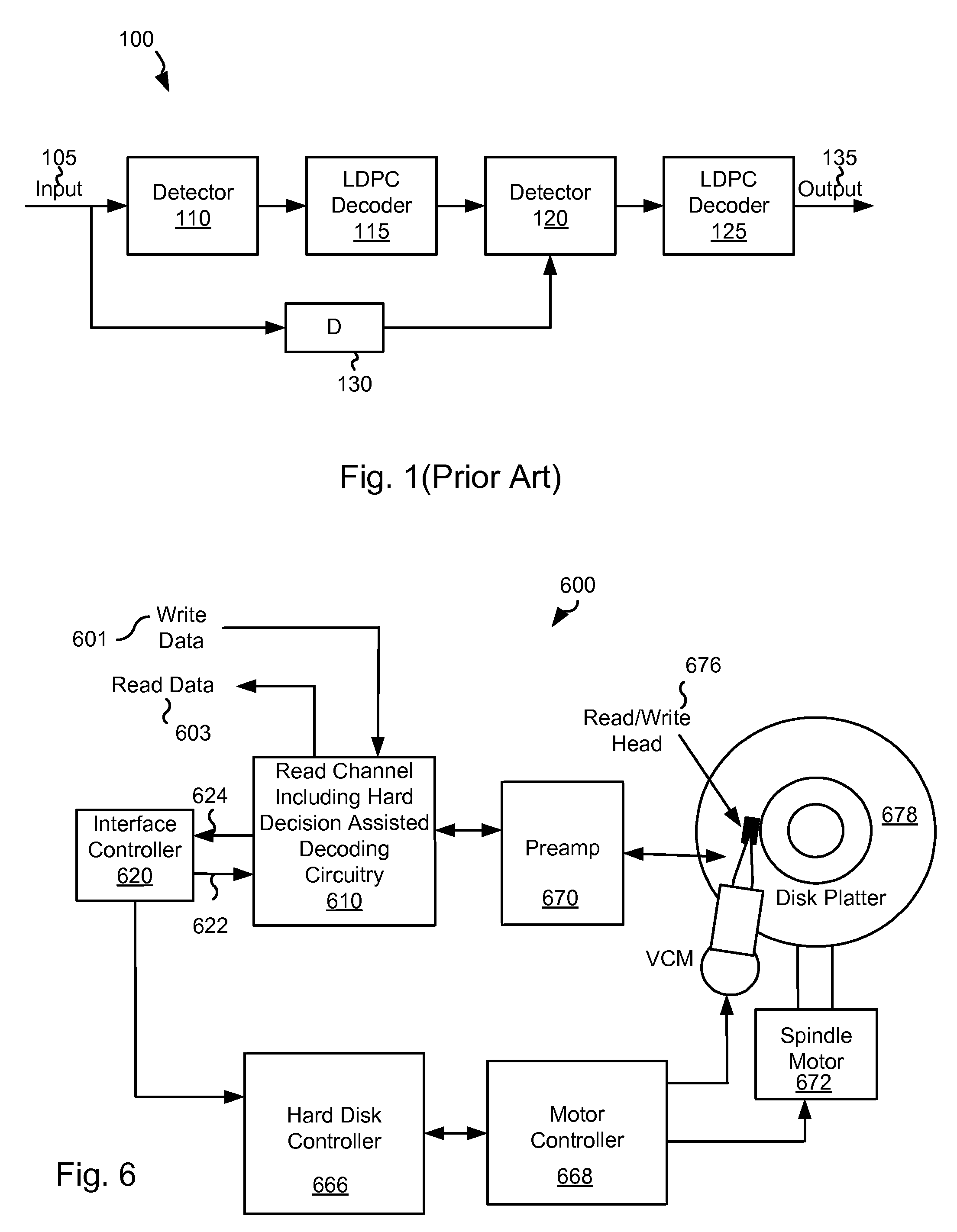
In information theory, a soft-decision decoder is a kind of decoding methods – a class of algorithm used to decode data that has been encoded with an error correcting code. Whereas a hard-decision decoder operates on data that take on a fixed set of possible values (typically 0 or 1 in a binary code), the inputs to a soft-decision decoder may take on a whole range of values in-between. This extra information indicates the reliability of each input data point, and is used to form better estimates of the original data. Therefore, a soft-decision decoder will typically perform better in the presence of corrupted data than its hard-decision counterpart.
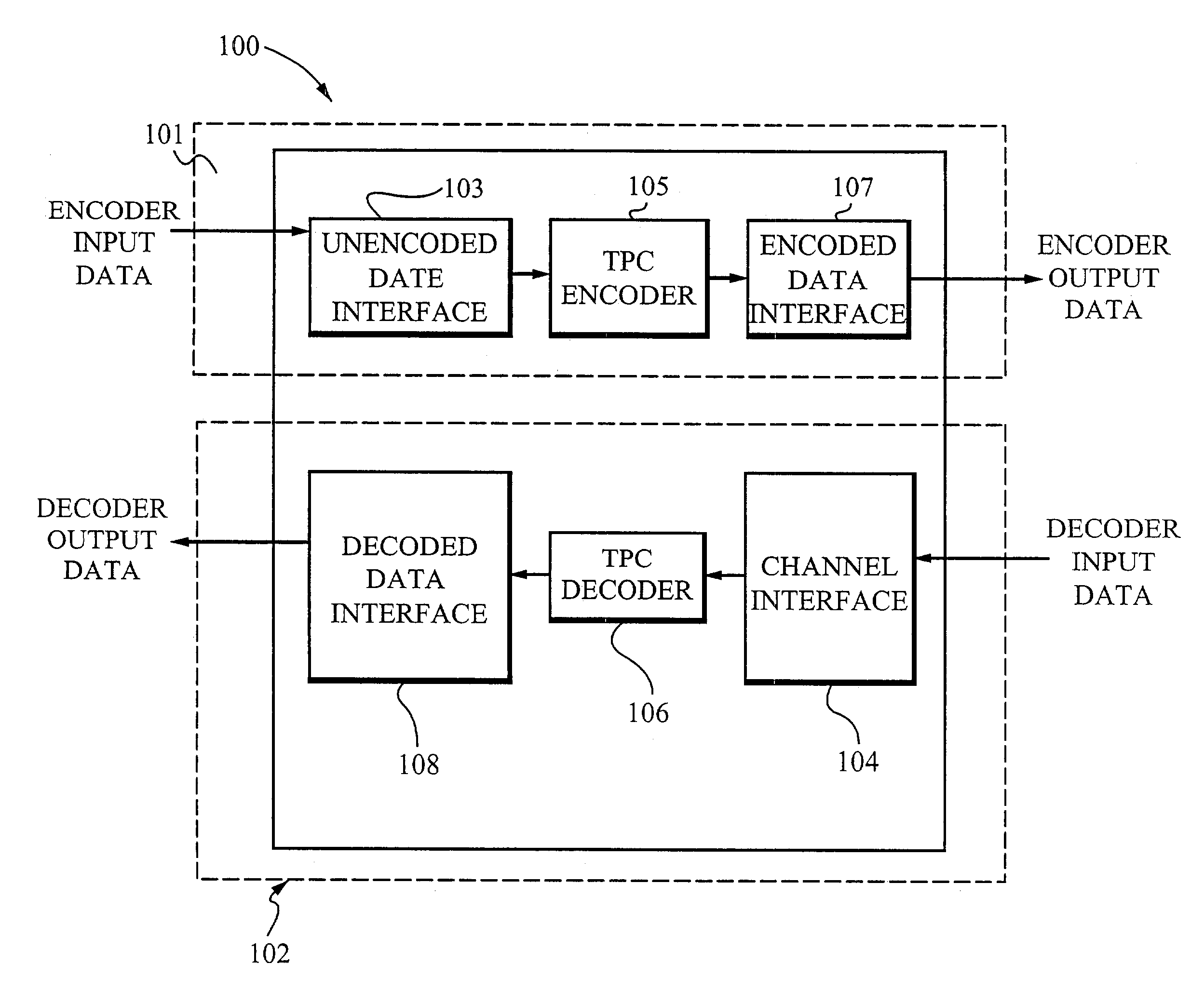
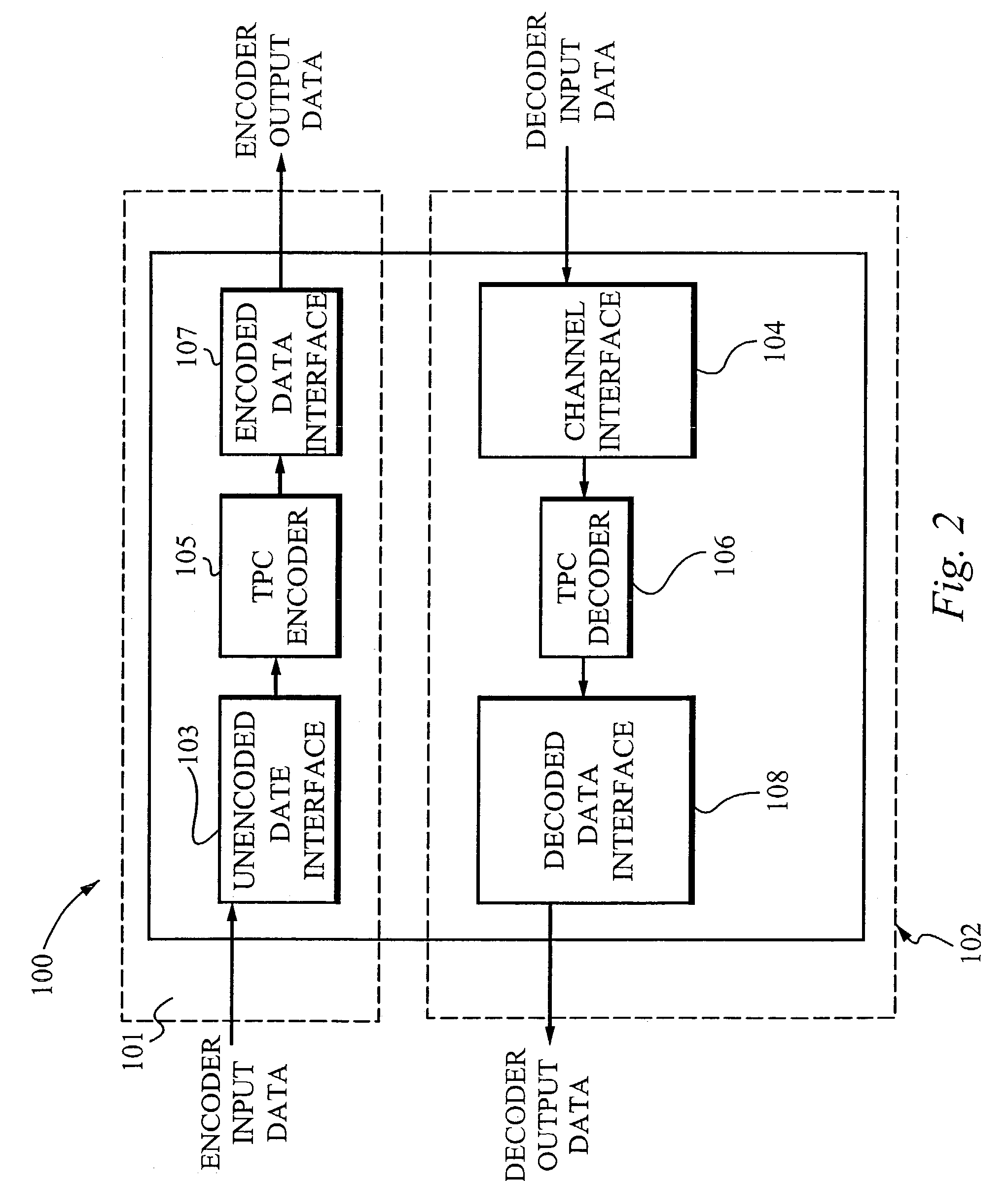
Enhanced turbo product code decoder system utilizing a codeword organization method
InactiveUS7039846B2Error preventionOther decoding techniquesMemory addressTheoretical computer science
A method and apparatus for decoding a linear block encoded string of information bits comprising: converting the string into a plurality of codewords. Performing hard and soft decisions on each codeword to generate a hard and soft decision vector. Computing the syndrome and finding the location of the two minimum values by Galois Field Arithmetic. Designating these values LOW1 and LOW2 and xoring with a Nc1, thus generating Nc2. Swapping Nc1 with Nc2 and determining the lowest soft decision value, Min1 and a next lowest value, Min2. The two bit locations creating Min1 are designated as MinA and MinB. MinA being replaced with Min2 minus the value MinA. MinB being replaced with Min2 minus the value at MinB. Generating an output codeword by subtracting Min1 from all other bit locations values and 2's complementing all soft values with 0 in their location. Creating the new soft value vector. Some embodiments include a system and method that organizes an encoded codeword. The encoded codeword has several codeword bits. The method receives the encoded codeword, assigns multiple codeword bits to at least one memory address in a plurality of memory addresses, and iteratively decodes the received codeword by utilizing the plurality of memory addresses in a predetermined order. The predetermined order is based on a dimension of the received codeword.
Owner:COMTECH TELECOMM CORP
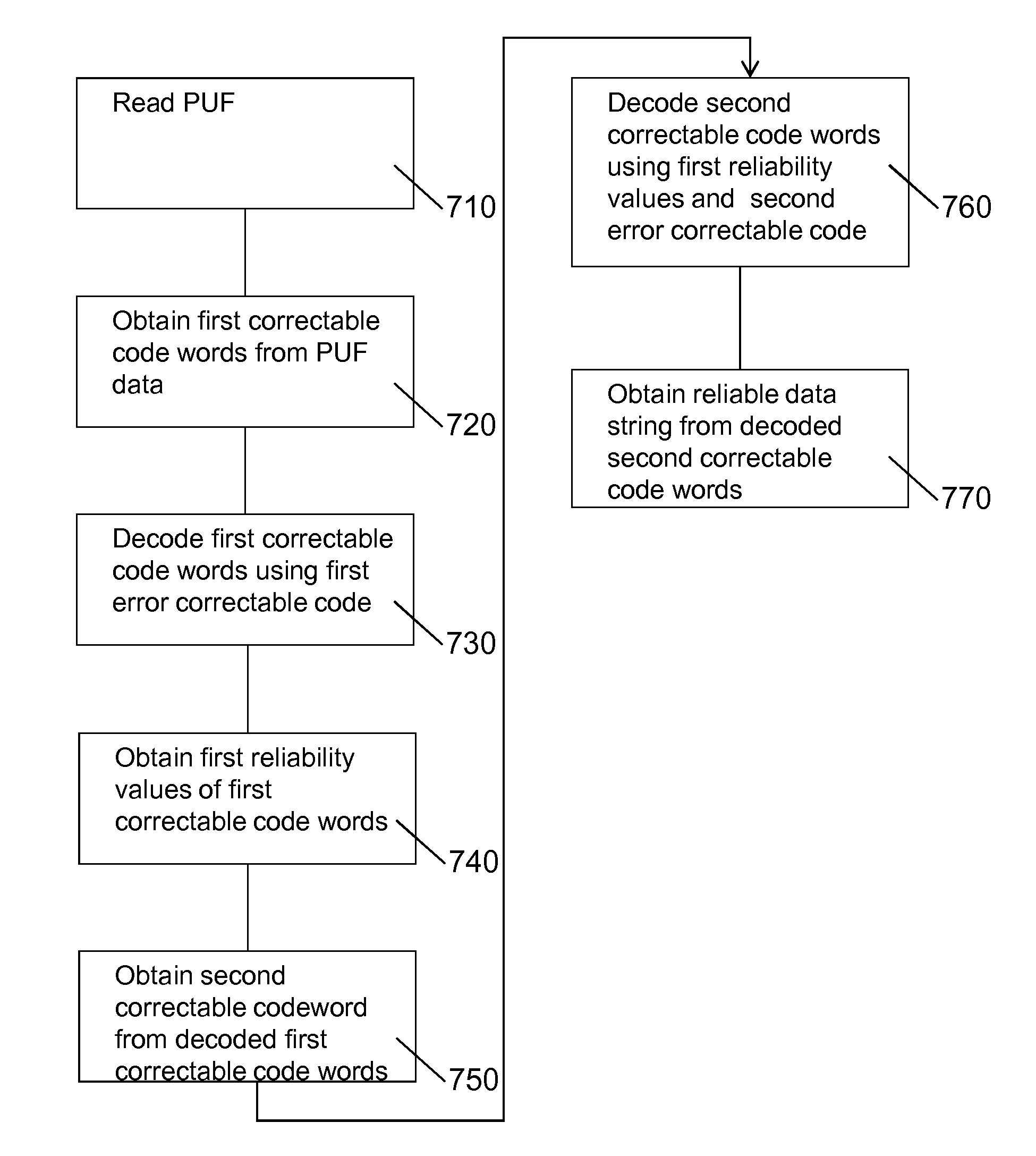
Physically unclonable function (PUF) with improved error correction
ActiveUS20140325237A1Avoid excessive errorMore informationUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringSoft-decision decoderDependability
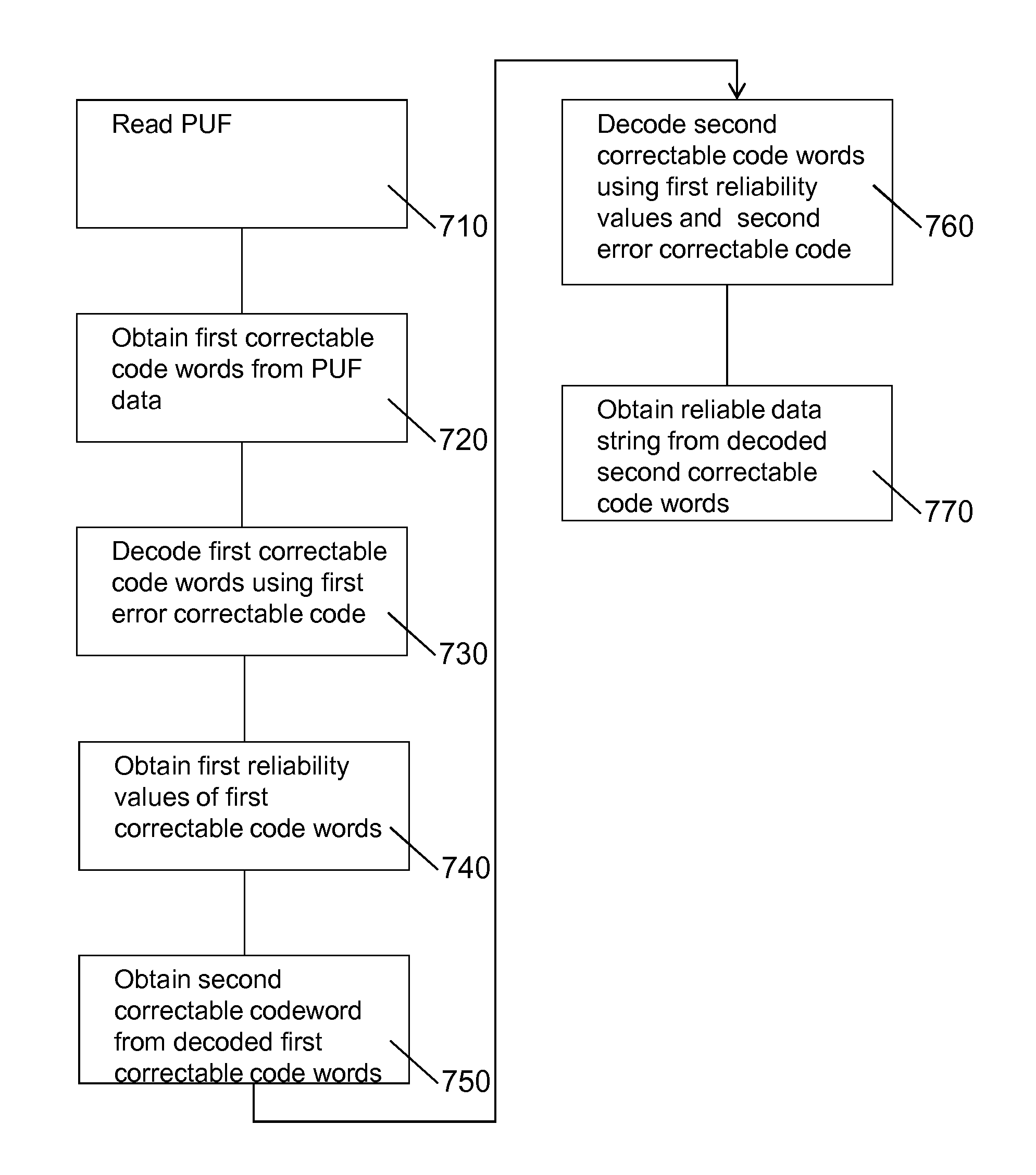
A cryptographic system for reproducibly establishing a reliable data string, such as a cryptographic key, from a noisy physically unclonable function (PUF, 110) is provided. The system comprises a hard decision decoder (150) to decode a first multiple of error correctable data words to obtain a second multiple of corrected and decoded data words and a reliability information extractor (180) to determine reliability information, e.g. soft decision information, that is indicative of a reliability of corrected and decoded data words. The system further comprises a soft decision decoder (160) configured to use the reliability information to decode at least one further correctable data word. Error correcting a PUF using reliability information decreases the false rejection rate.
Owner:INTRINSIC ID
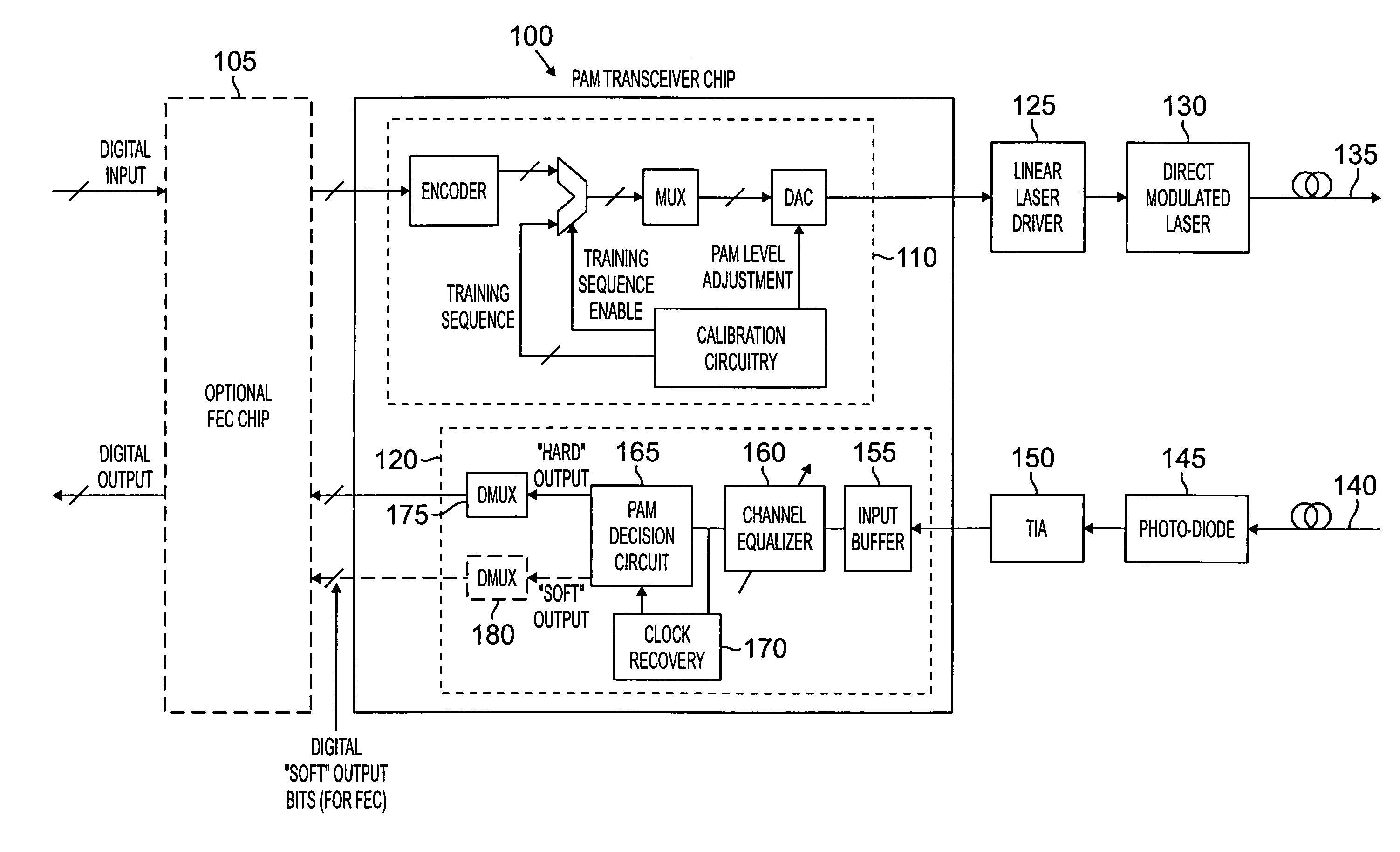
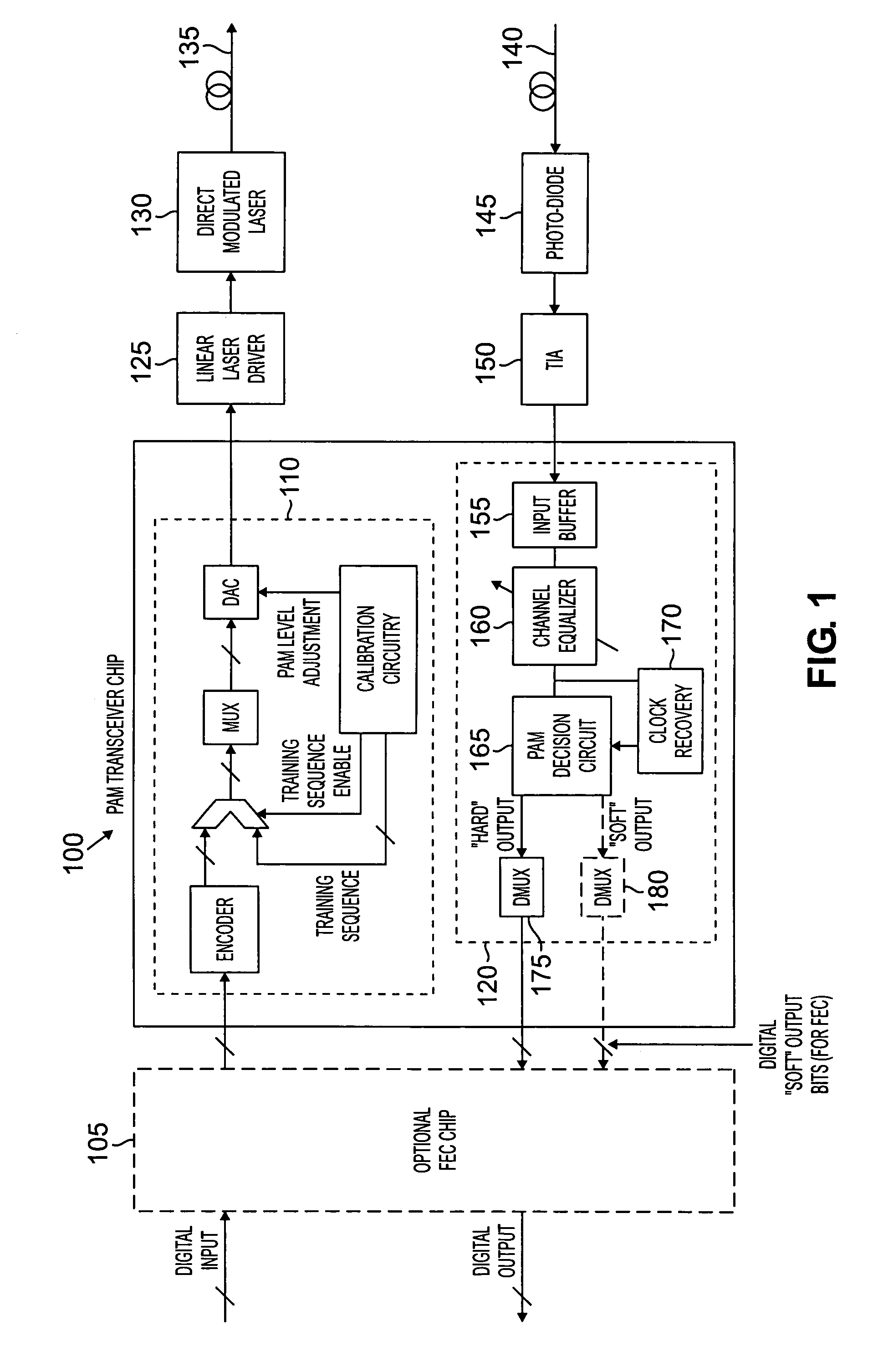
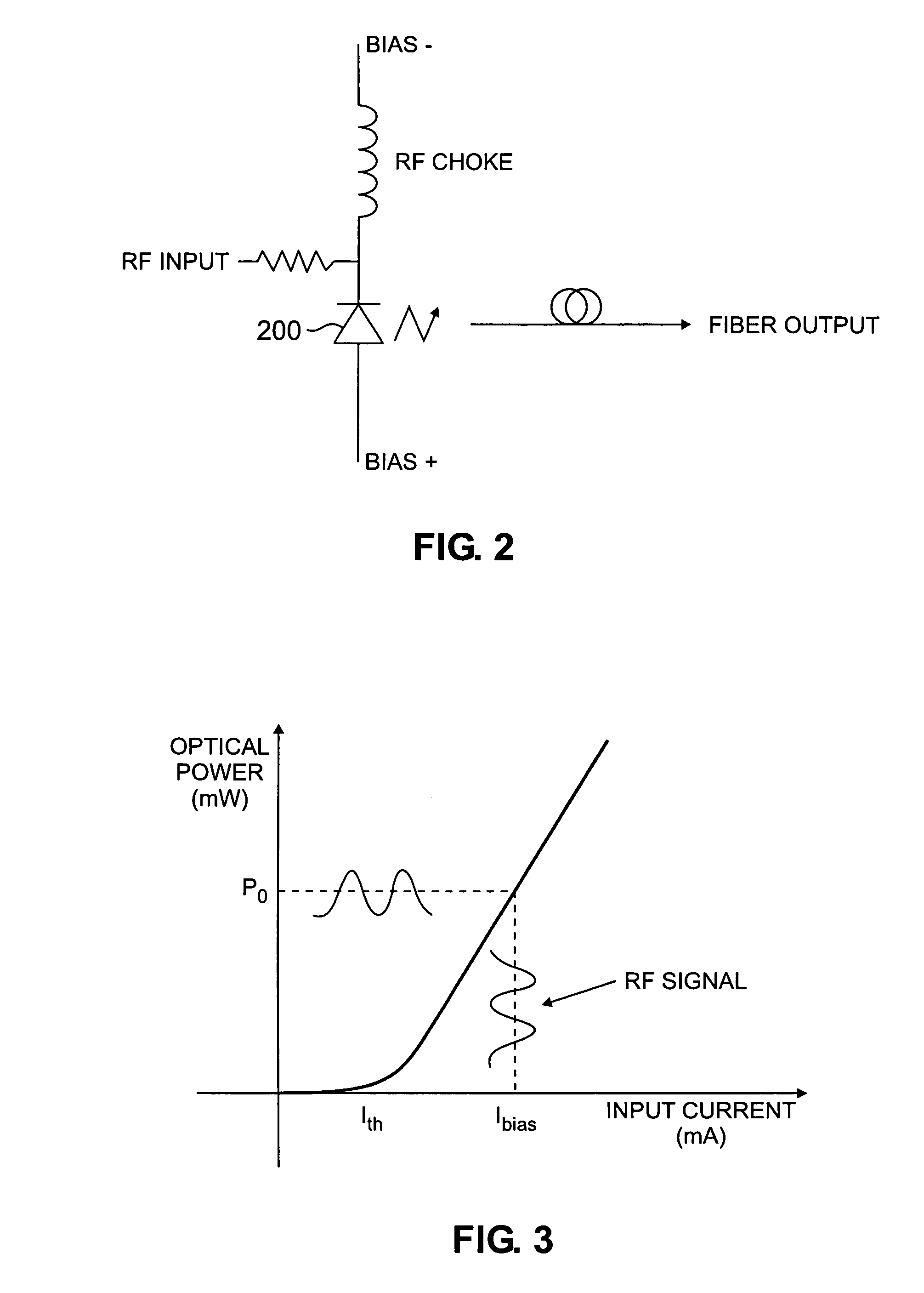
Pulse amplitude modulated transmission scheme for optical channels with soft decision decoding
InactiveUS7155134B2Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationCommunications systemBandwidth compression
An amplitude modulated optical communication system and method are disclosed that achieve bandwidth compression by making use of an n level amplitude modulation scheme in one or more frequency bands. A soft decision decoder is disclosed that provides at least two soft slicing levels between each signal level in the multiple level transmission scheme to define an “uncertainty” region therebetween. The soft slicing levels are used to evaluate the reliability of a given bit assignment. In addition to assigning a digital value based on the received signal level, one or more soft bits are assigned indicating a “reliability” measure of the output code.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
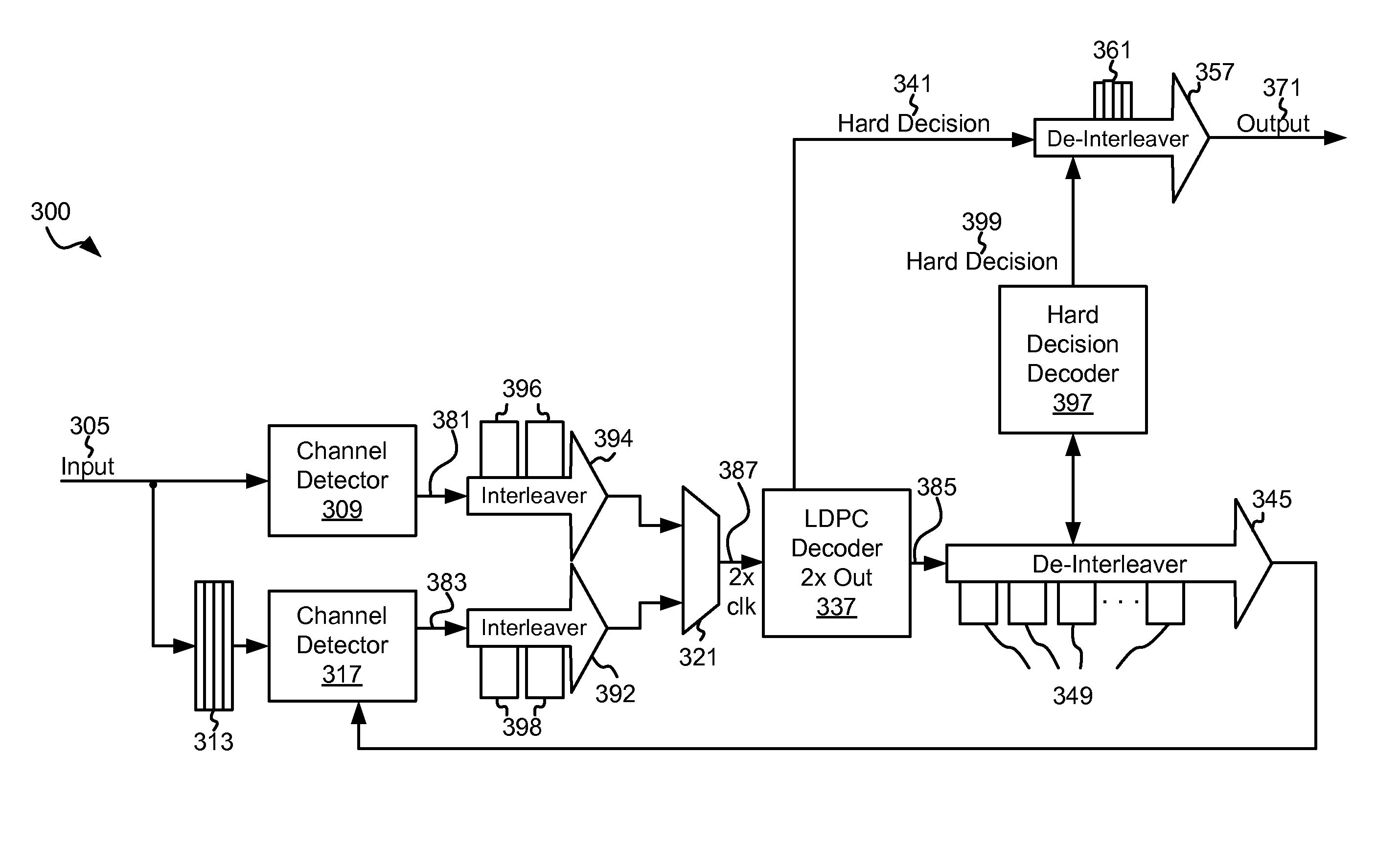
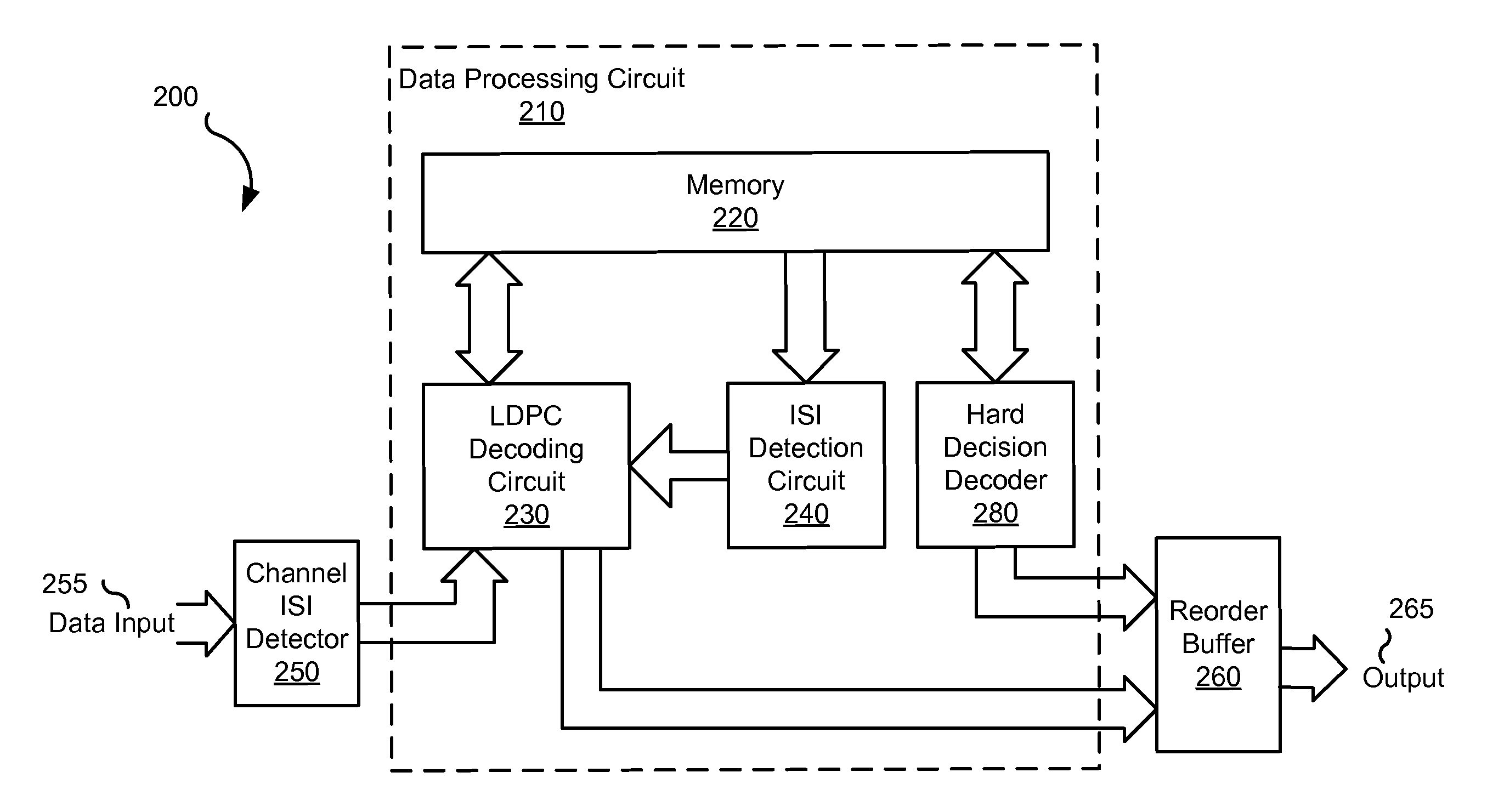
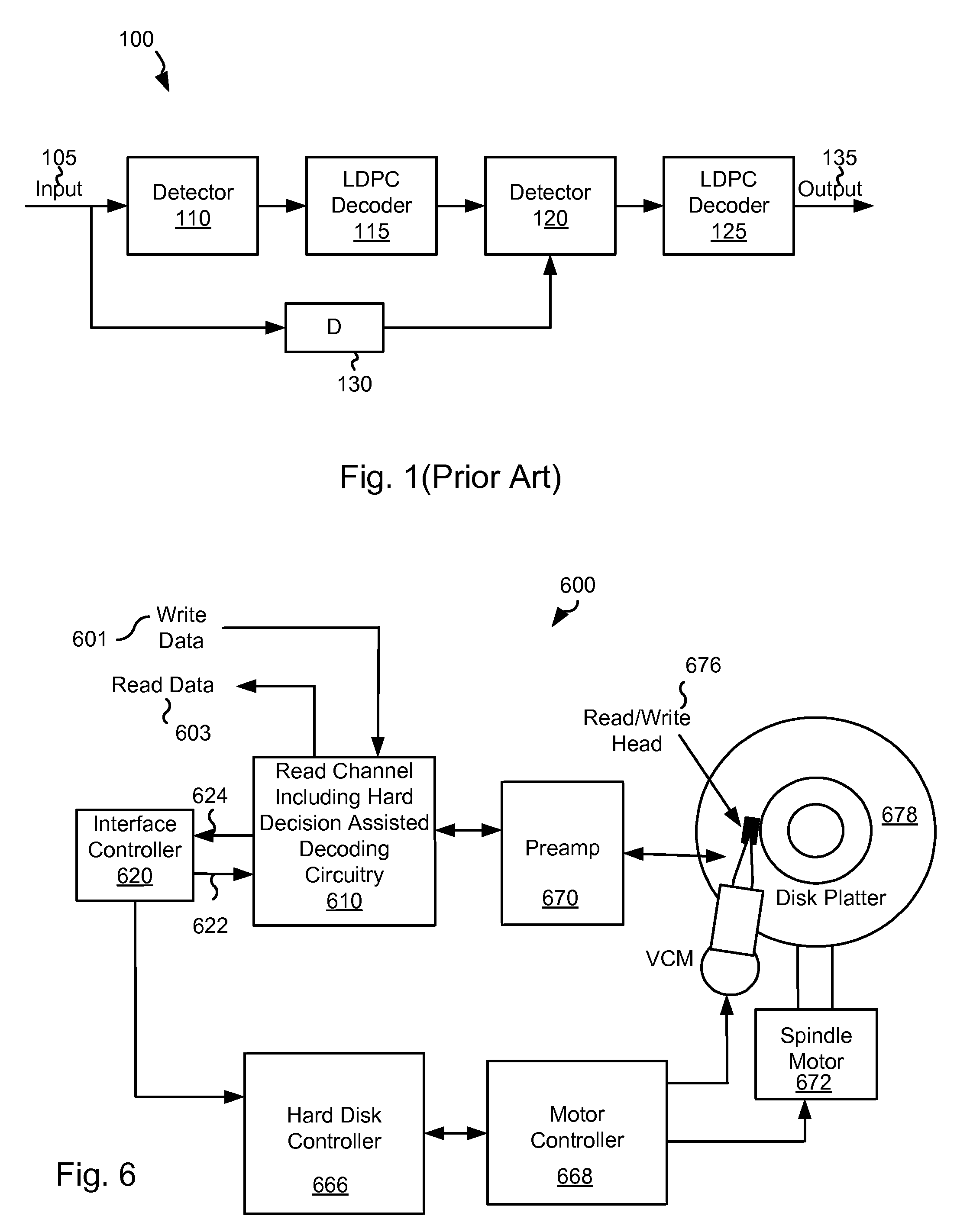
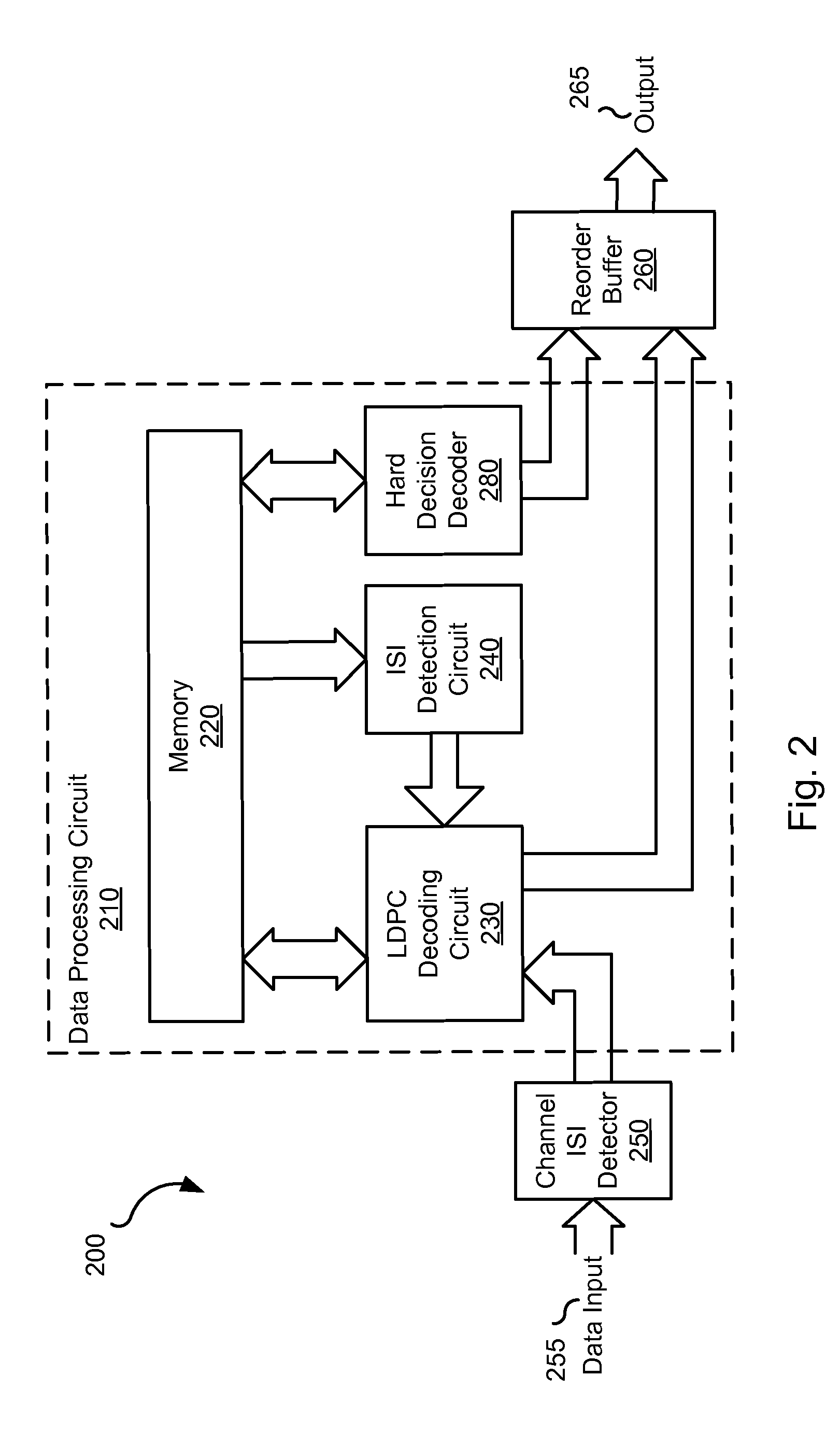
Systems and methods for hard decision assisted decoding
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Systems and Methods for Hard Decision Assisted Decoding
ActiveUS20100275096A1Error preventionTransmission systemsData processing systemSoft-decision decoder
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data processing. For example, a data processing system is disclosed that includes a processing loop circuit having a data detector and a soft decision decoder. The data detector provides a detected output, and the soft decision decoder applies a soft decoding algorithm to a derivative of the detected output to yield a soft decision output and a first hard decision output. The systems further include a queuing buffer and a hard decision decoder. The queuing buffer is operable to store the soft decision output, and the hard decision decoder accesses the soft decision output and applies a hard decoding algorithm to yield a second hard decision output. The data detector is operable to perform a data detection on a derivative of the soft decision output if the soft decision decoder and the hard decision decoder fail to converge
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
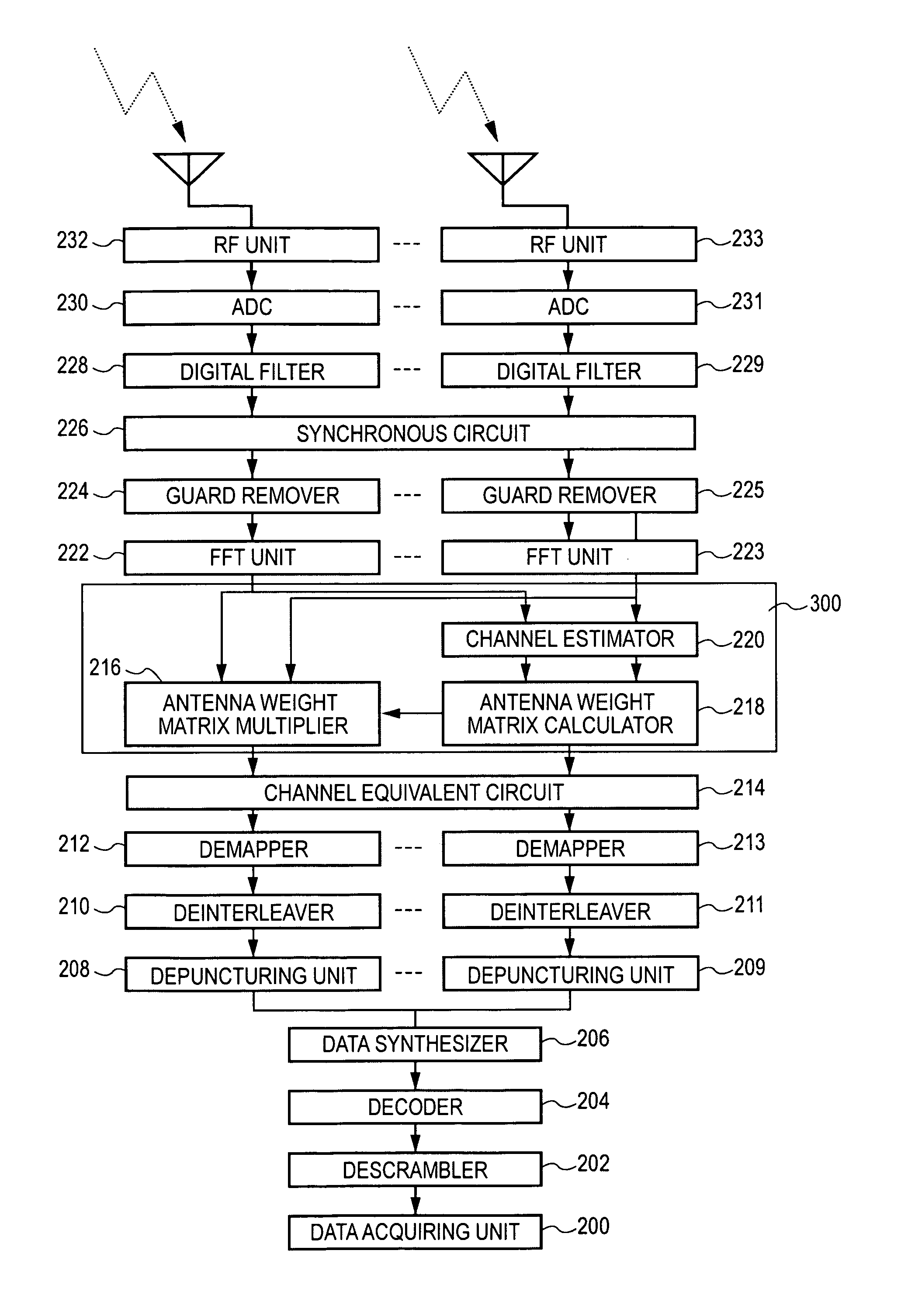
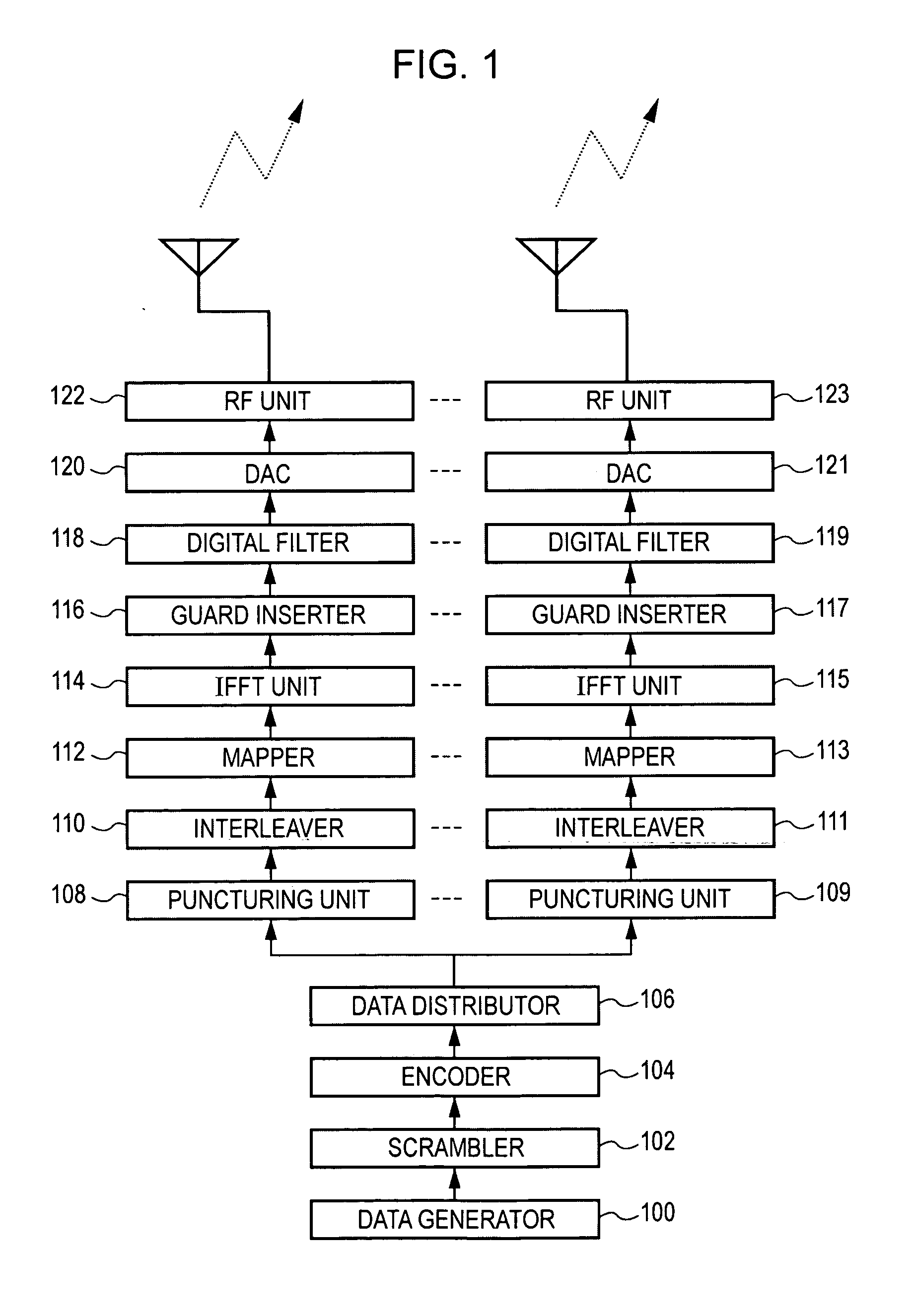
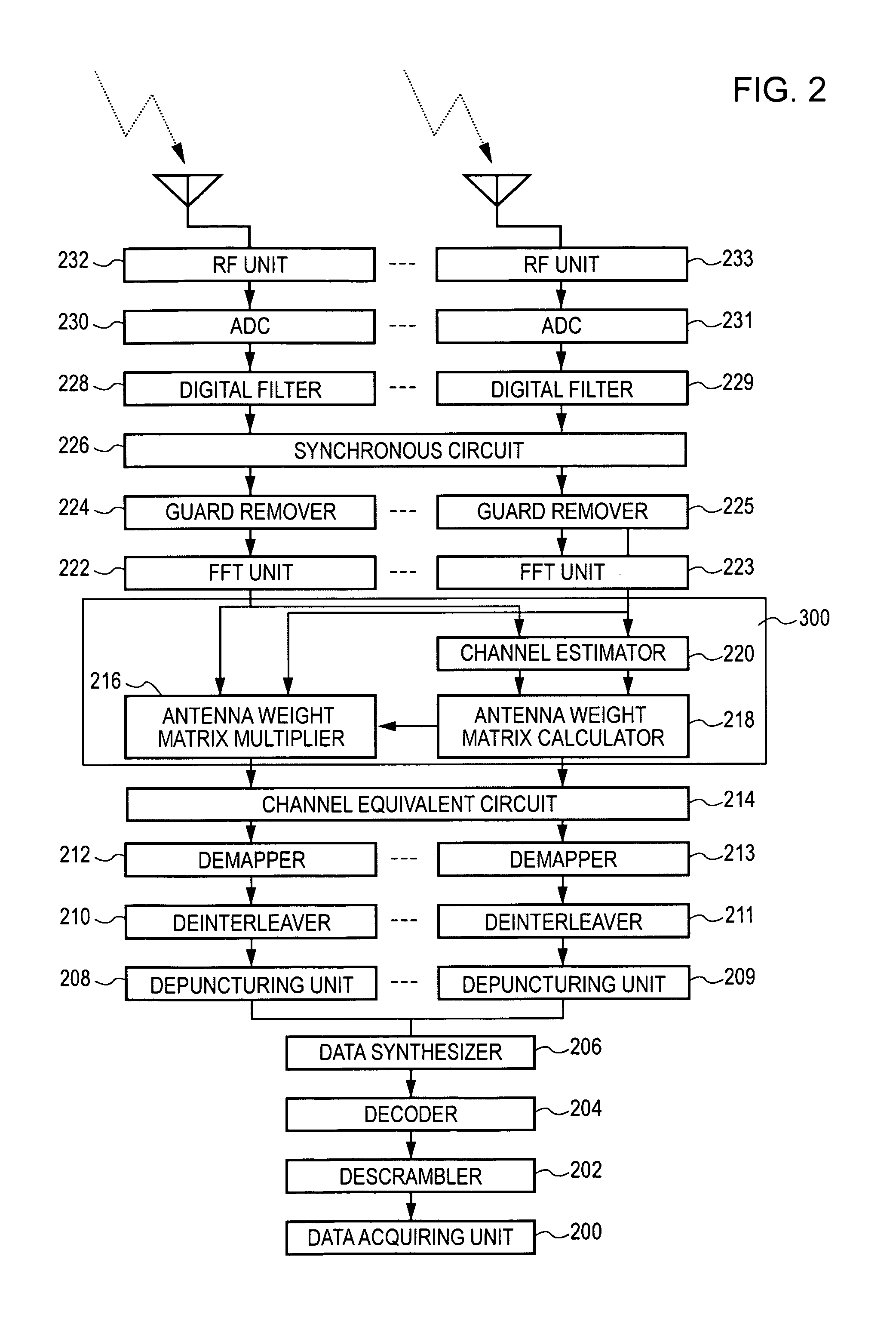
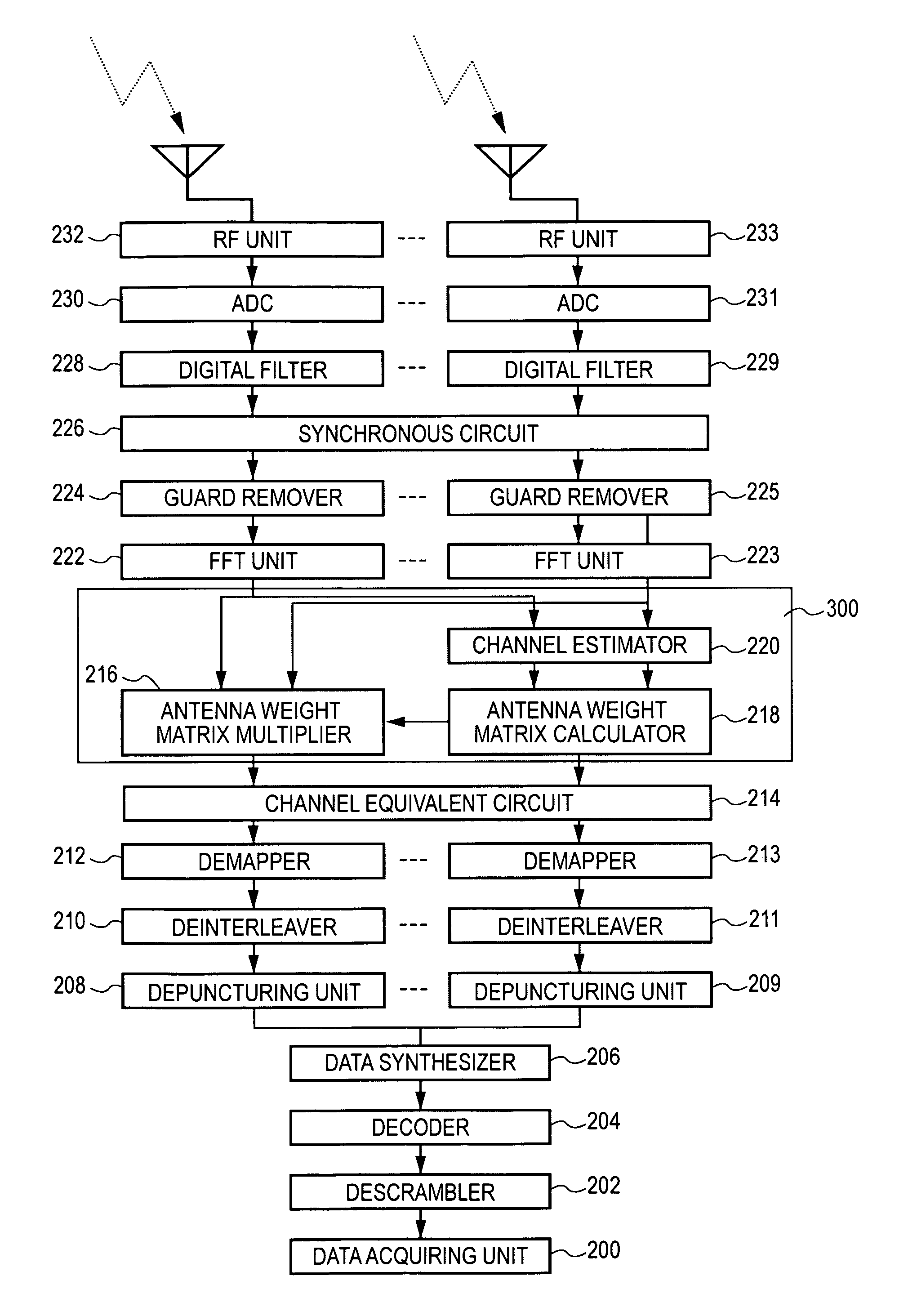
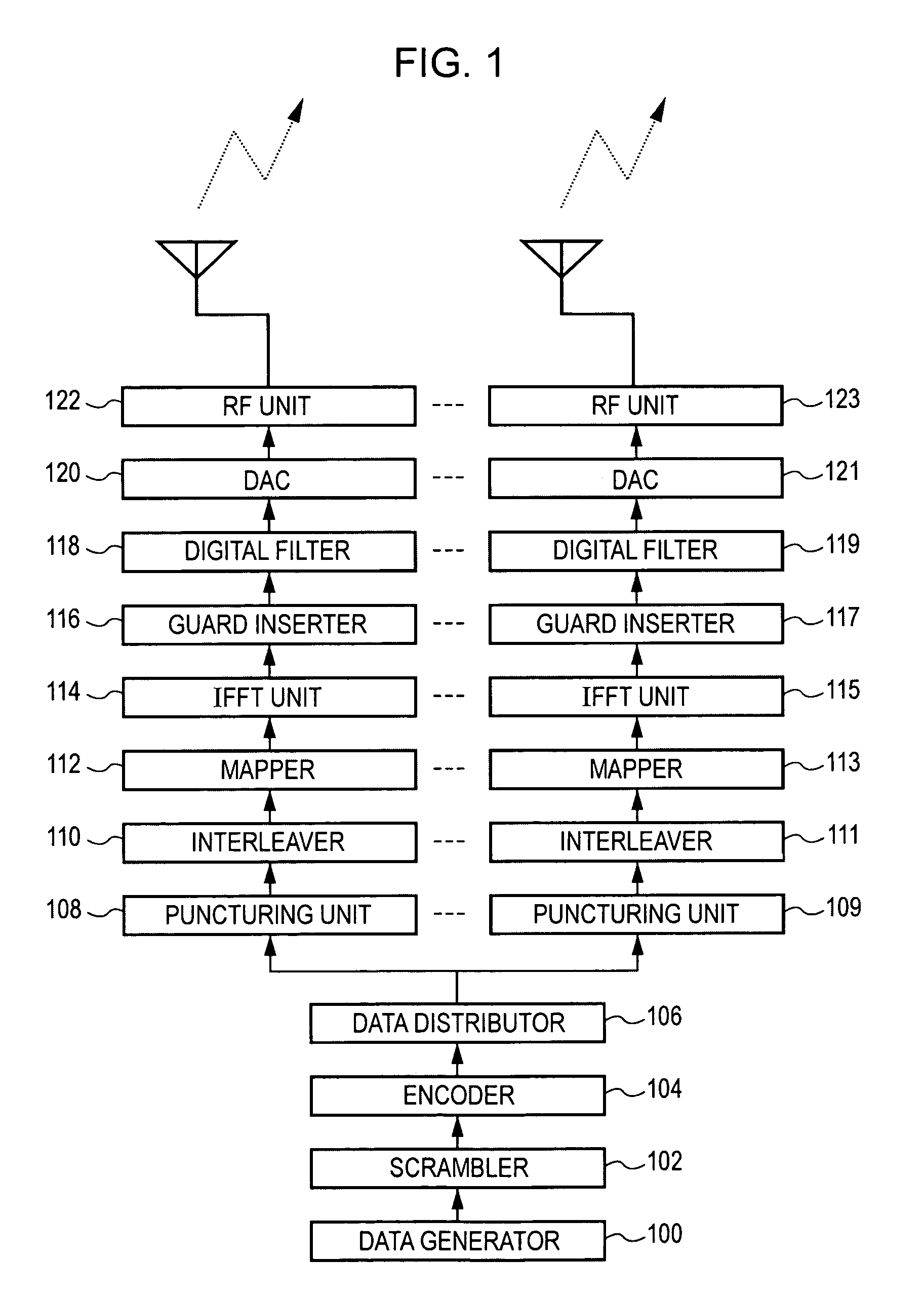
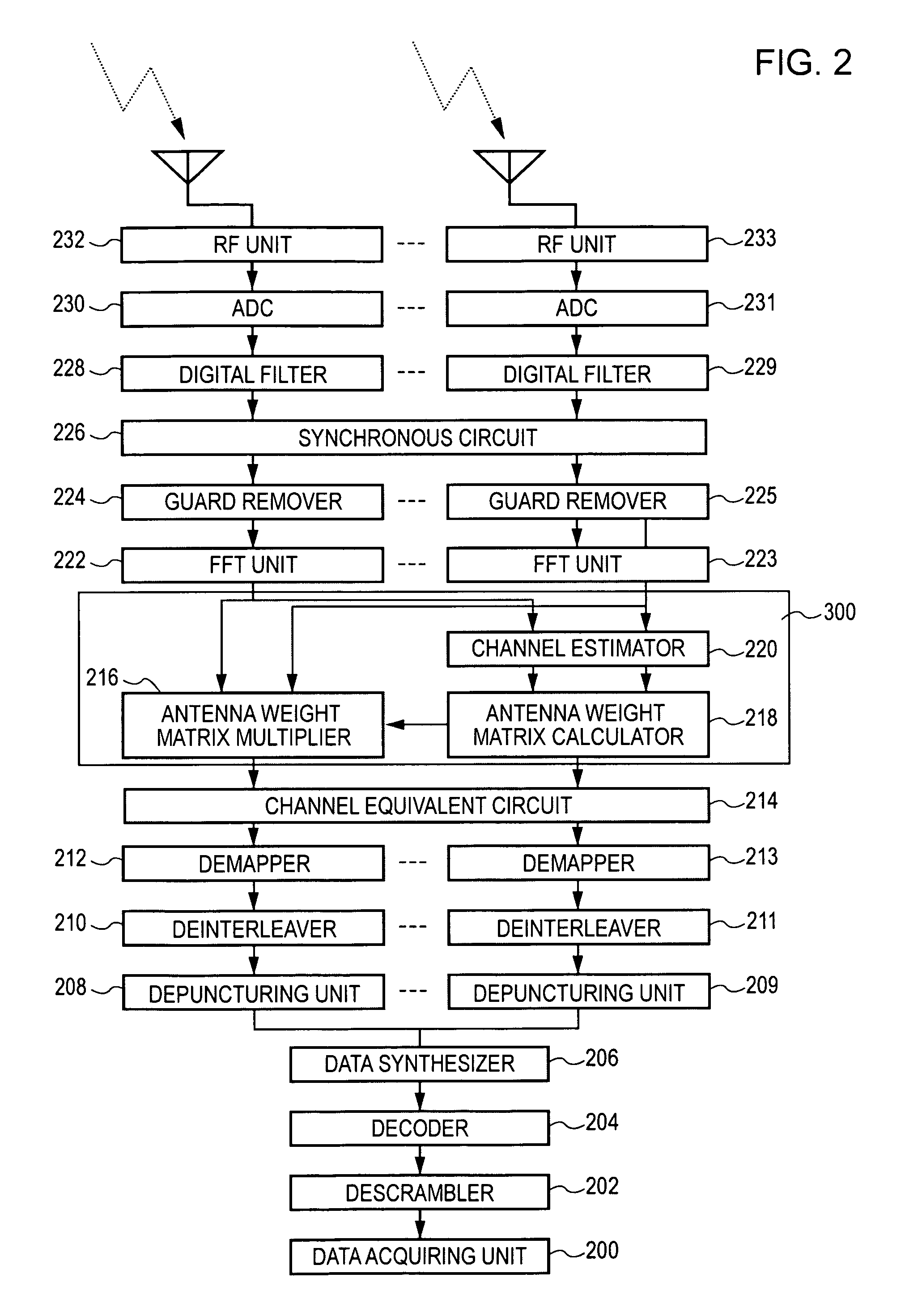
Wireless communication apparatus and wireless communication method
ActiveUS20060269006A1Avoid performance degradationHighly reliable likelihood estimationMultiplex communicationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSignal onEngineering
A wireless communication apparatus for receiving spatially multiplexed signals in which a plurality of streams are spatially multiplexed, using a plurality of antennas, includes the following elements: a channel matrix estimator for estimating a channel matrix for multiplexed channels; a spatial decoder for spatially decoding received signals each of which has been received by a corresponding antenna so as to separate the received signals into individual stream signals by obtaining an antenna weight matrix from the estimated channel matrix, and then multiplying each received signal by the antenna weight matrix; a likelihood information estimator for estimating likelihood information using the estimated channel matrix, the antenna weight matrix, and estimated noise power; and a soft decision decoder for performing soft decision decoding on each stream signal on the basis of the estimated likelihood information.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
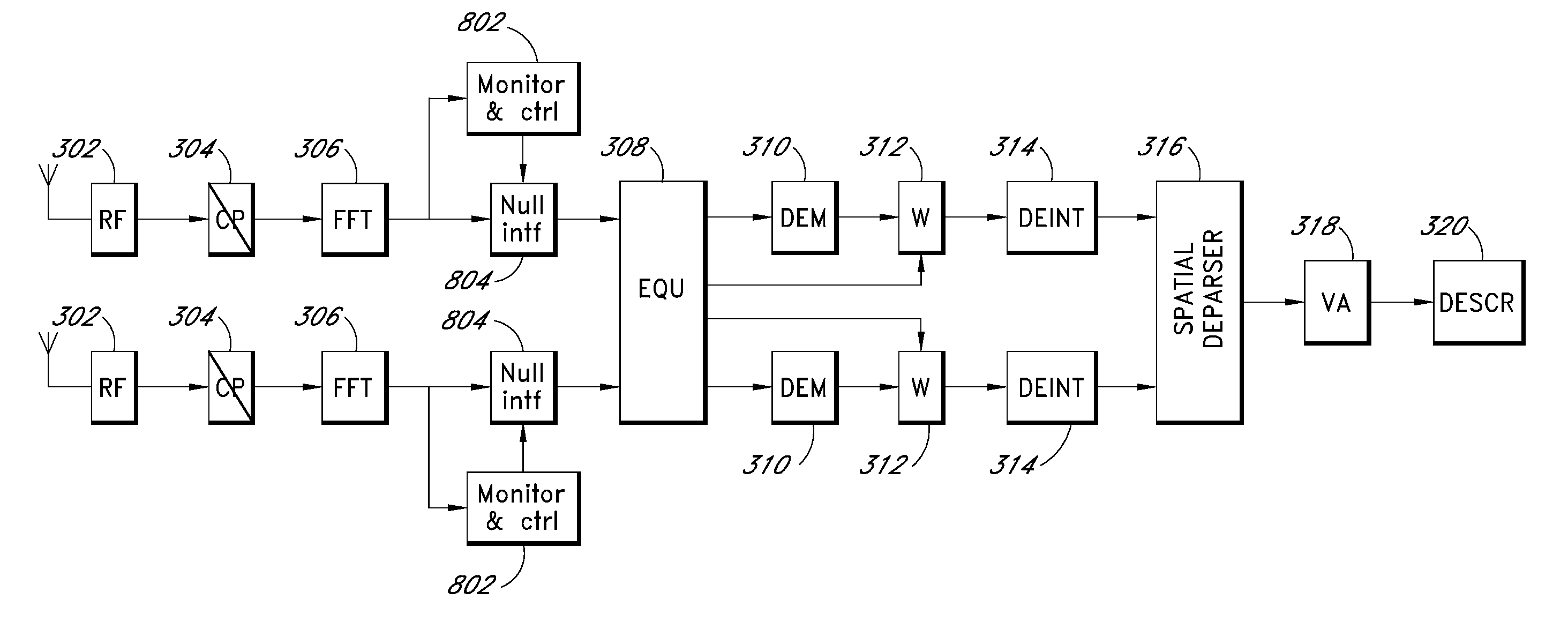
Interference erasure using soft decision weighting of the Viterbi decoder input in OFDM systems
InactiveUS8019029B1Reduce impactLow signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR)Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsViterbi decoderSignal quality
Disclosed is a technique for mitigating the effect of an in-band interferer in Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) wireless or wired networks that employ soft decision Viterbi decoder in the physical layer. The technique uses an independent estimation of the signal quality, which is passed to the Viterbi algorithm decoder so that it is able to discard the corrupted subcarriers. This improves the error correction capability of the Viterbi algorithm decoder in a receiver, which leads to fewer retransmissions and into higher information throughput.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Polar code error correction scheme applied to NAND flash memory
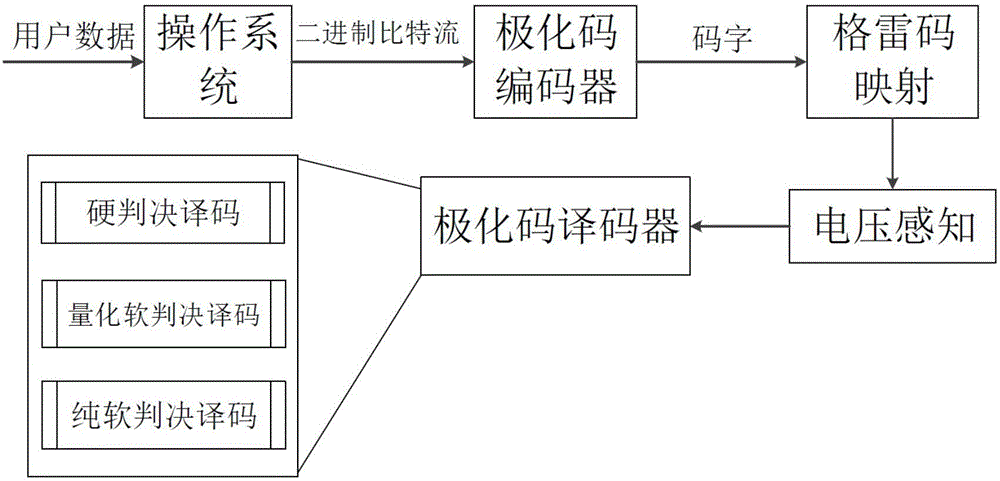
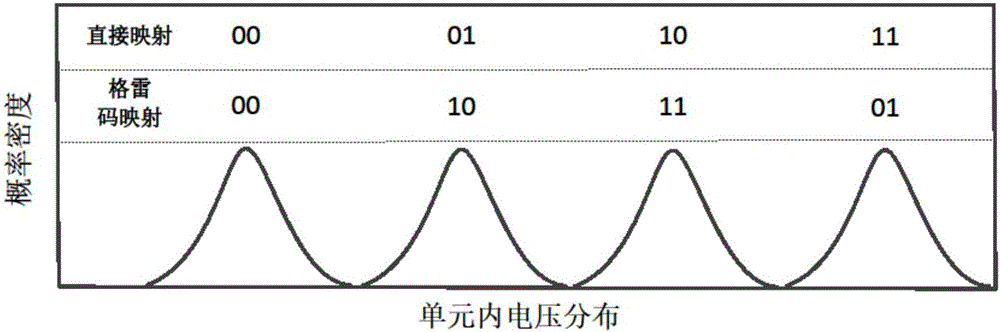
InactiveCN106504796AExtended service lifeSolve the speed problemError correction/detection using linear codesStatic storageDiffusionSoft-decision decoder
The invention provides an efficient multi-scheme ECC technology based on a polar code. The technology is called as a pre-detection scheme and used for meeting the actual application requirements and reducing decoding delay. According to the technology, balance between the decoding speed and the performance requirements can be achieved by judging the voltage diffusion condition of a current NAND flash memory and selecting a corresponding polar code decoder (such as a hard decision decoder, a quantitative soft decision decoder and a pure soft decision decoder) for different voltage distribution states.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
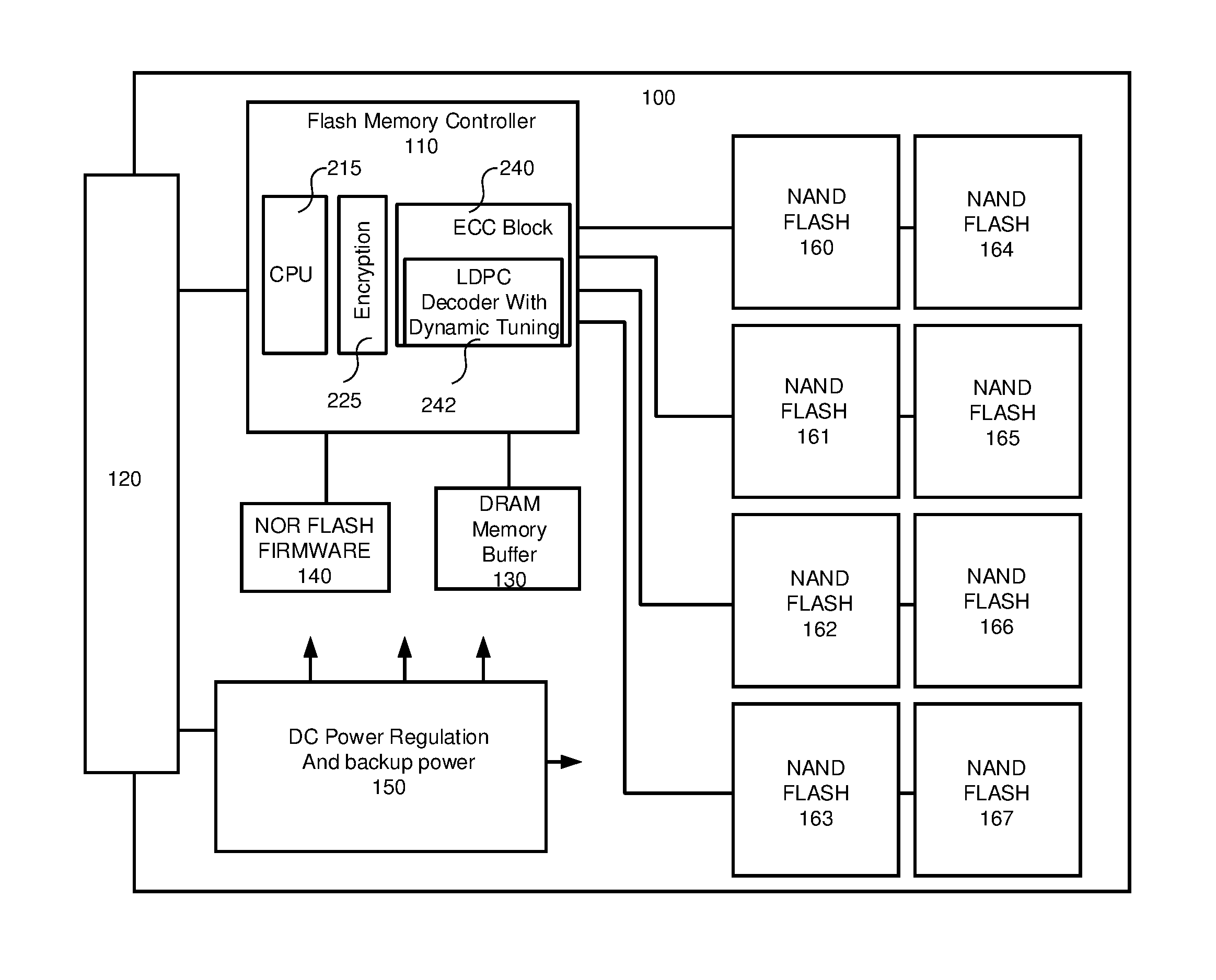
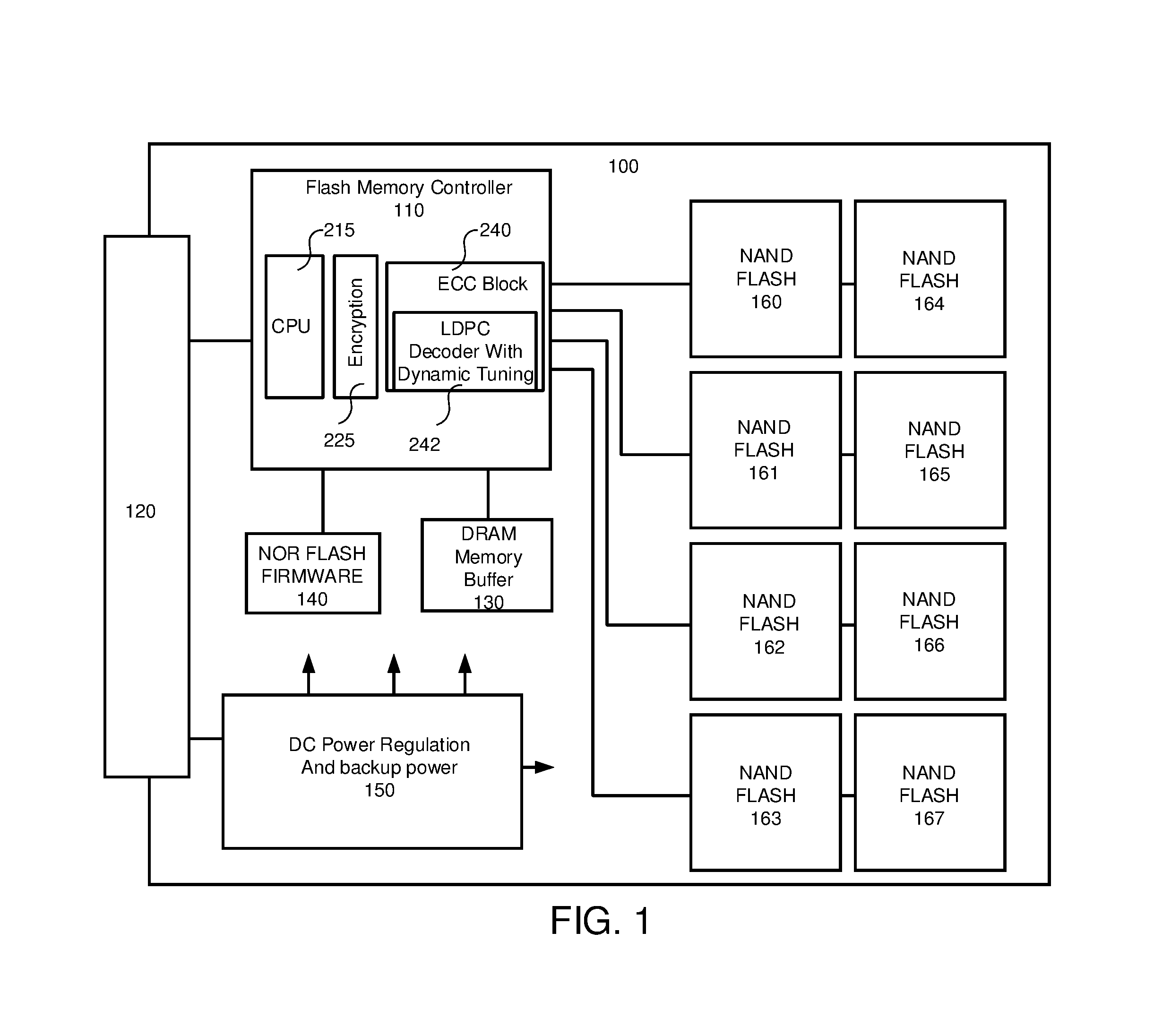
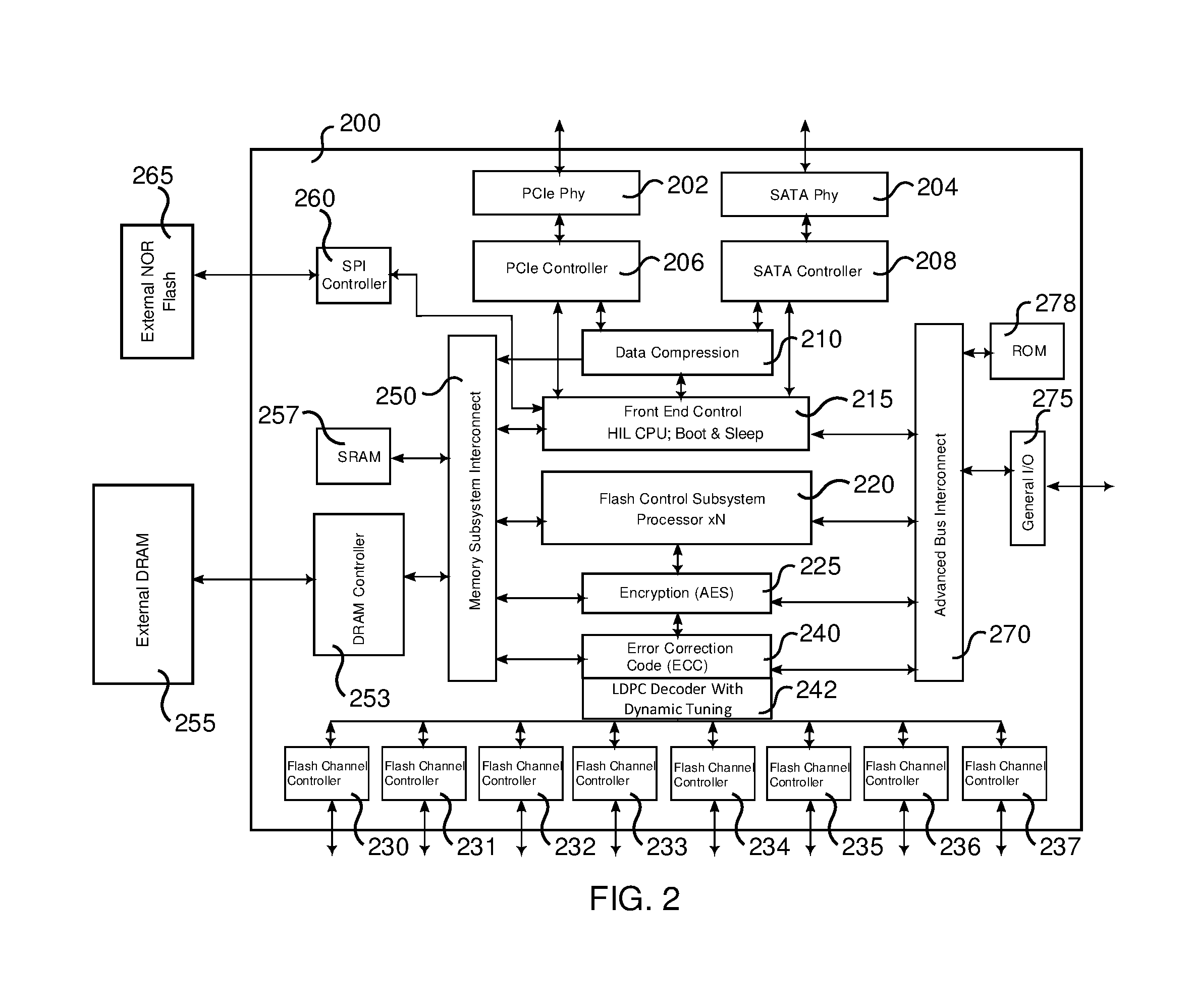
Non-volatile memory controller with error correction (ECC) tuning via error statistics collection
ActiveUS9407294B2Easy to operateImprove performanceOther decoding techniquesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsForward error correctionSolid-state drive
A non-volatile memory controller for a solid state drive includes a soft-decision LDPC decoder. The soft-decision LDPC decoder includes a probability generation module. A processor reads collected statistics collated from decoded frames and tunes the performance of the soft-decision LDPC decoder performance. Additional parameters may also be taken into account, such as the scramble seed and the type of non-volatile memory. An asymmetry in errors may also be detected and provided to a hard-decision LDPC decoder to adjust its performance.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
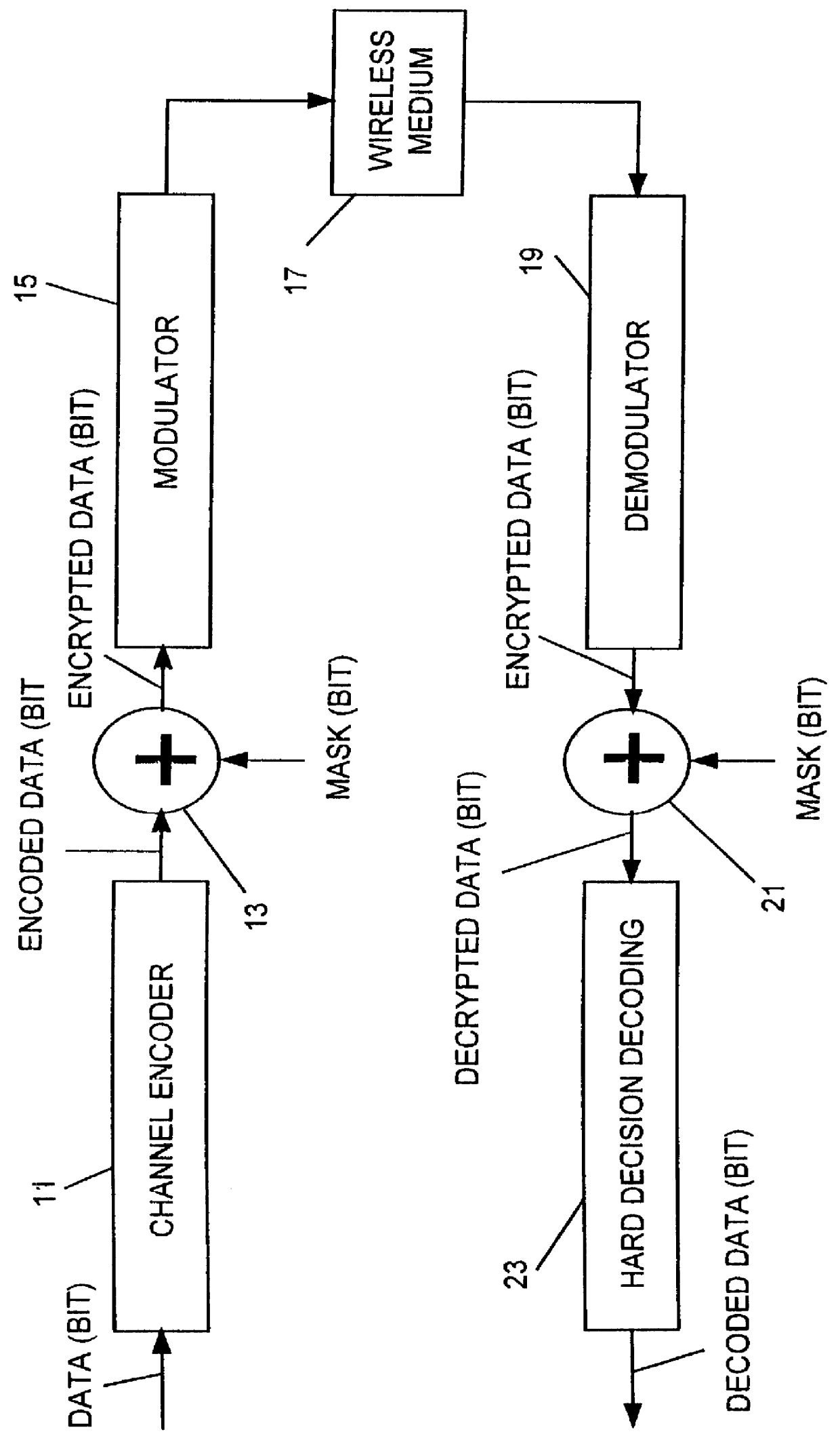
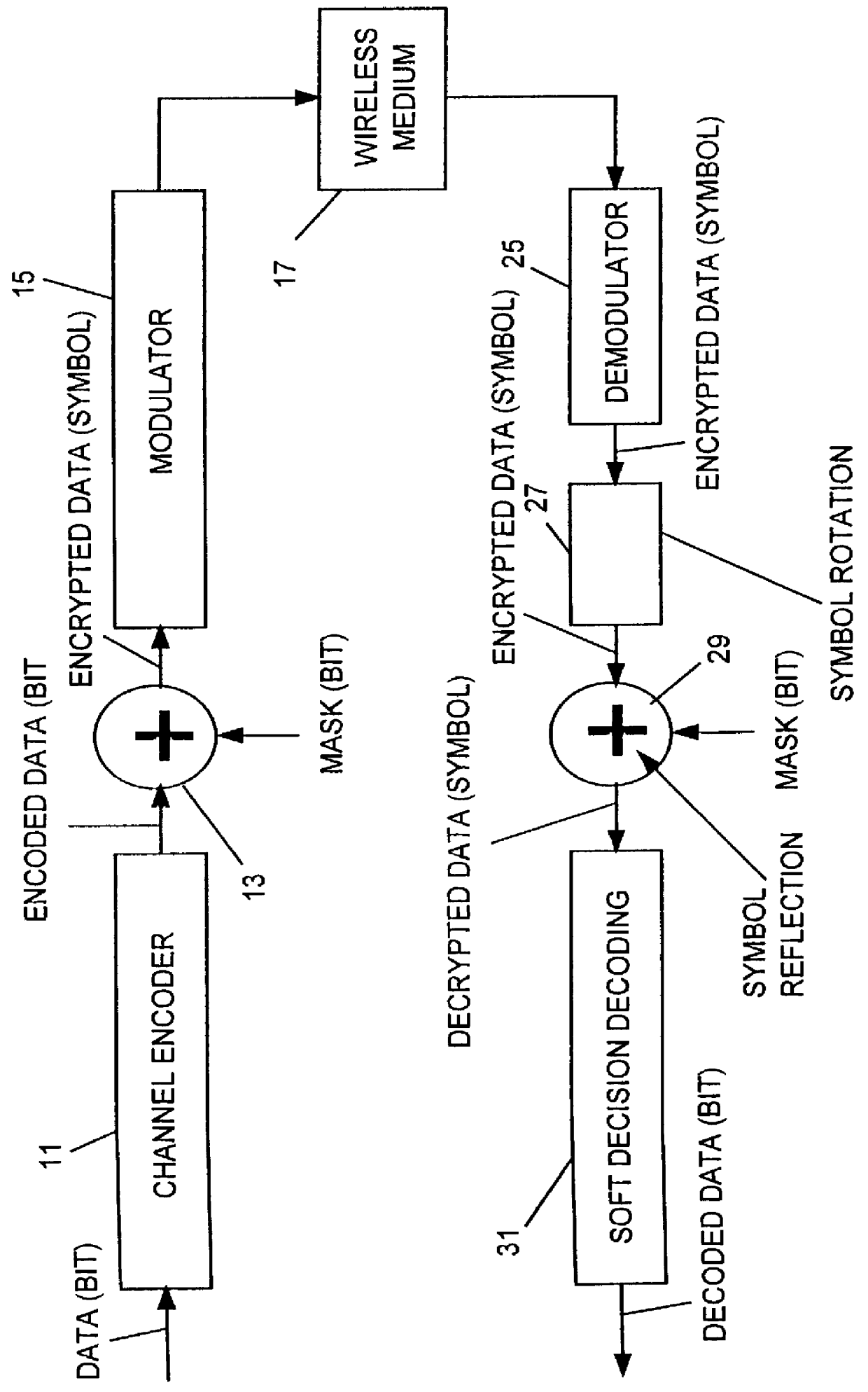
System and method for decryption in the symbol domain
A method of decrypting data comprising encrypting bit-wise data, using a first plural bit mask, modulating the data into symbol format, and transmitting the symbol format data to a receiving apparatus, in a receiving apparatus, rotating a current received symbol sample by an amount equal to one of (i) its difference in phase from an immediately preceding received symbol sample toward the phase of the immediately preceding received symbol sample phase, and (ii) by an amount equal to estimated carrier phase towards zero phase, generating a second bit mask subset derived from values of the first bit mask, comprising plural bits for each symbol, reflecting the rotated symbol by a phase defined by the plural bits to form a symbol which is devoid of encryption, and providing the symbol devoid of encryption to a soft-decision decoder.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
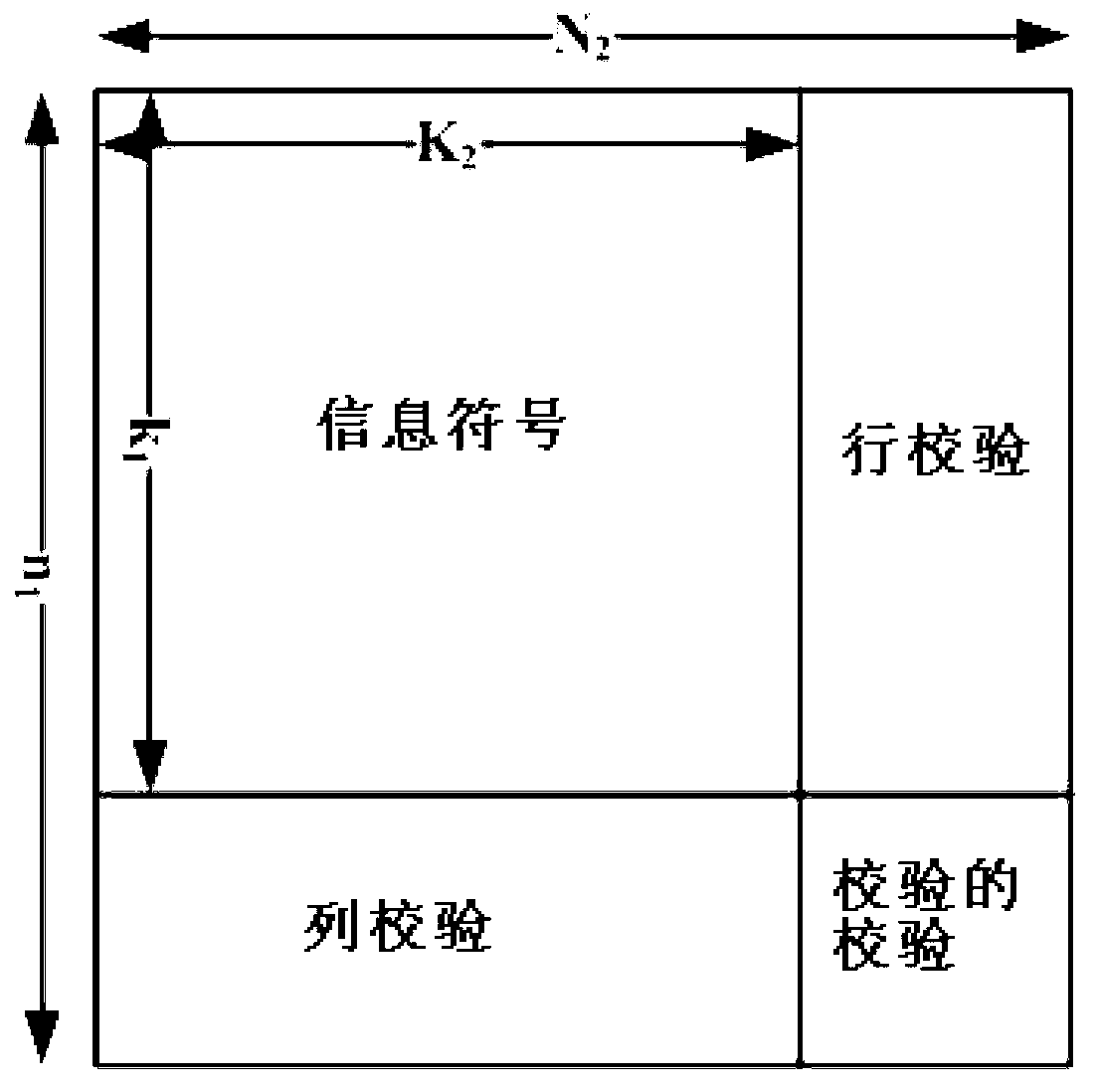
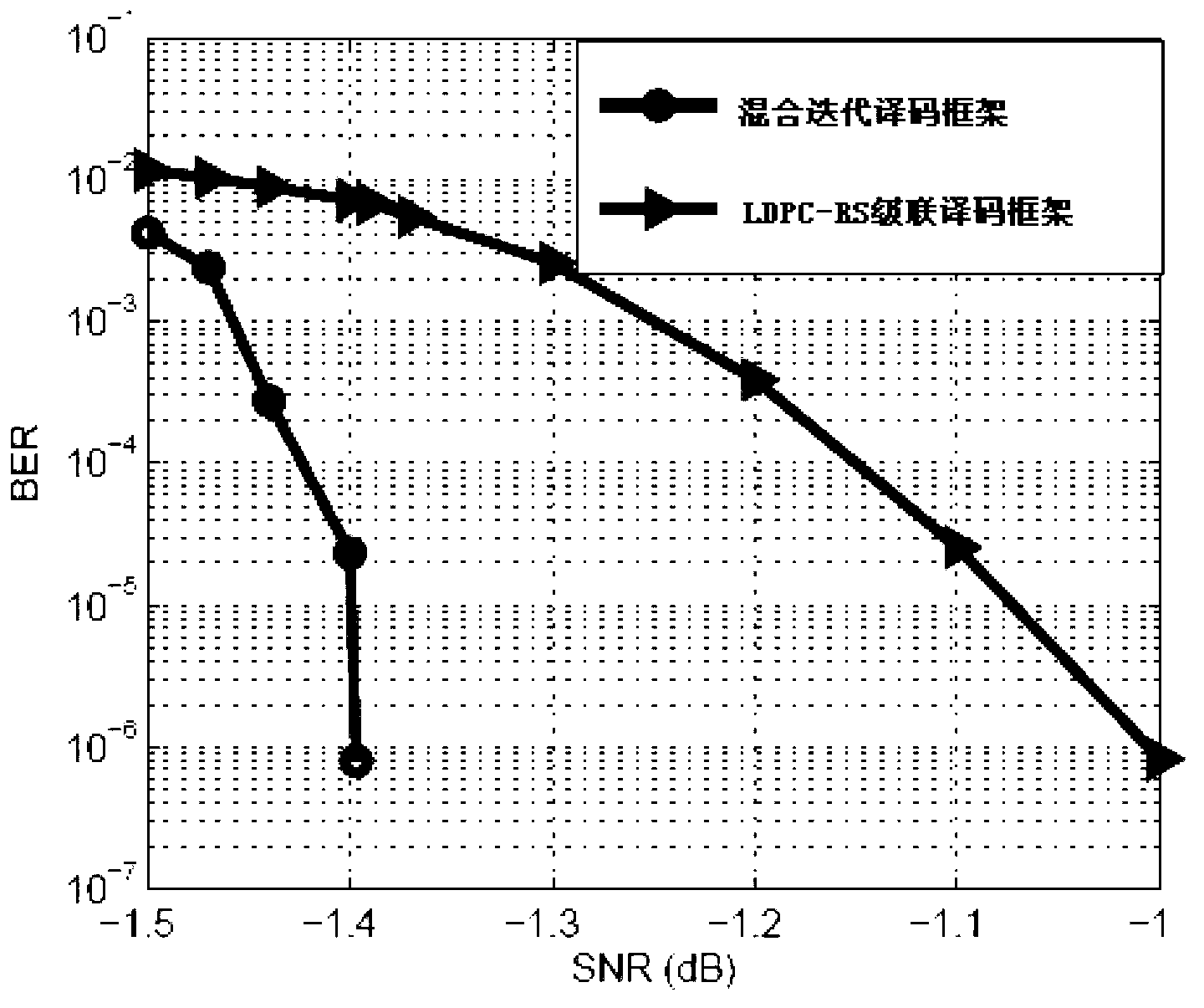
Mixed iterative decoding method for LDPC-RS two-dimensional product code
InactiveCN103269229AFast convergenceReduce iterative processError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCoding blockCommunications system
The invention relates to a mixed iterative decoding method for an LDPC-RS two-dimensional product code in the technical field of communication system channel decoding. According to a received LDPC-RS product code block, log-SPA soft-decision decoding is conducted on LDPC codons of each row, bit soft value information after the decoding and soft value information corresponding to the edge of a bipartite graph are stored; improved WBF decoding is conducted on LDPC rows failed in the log-SPA soft-decision decoding and estimated bit error patterns of the rows failed in decoding can be returned through an improved WBF algorithm; when the estimated error patterns can be corrected by following RS, LDPC hard-decision decoding, RS+LDPC hard-decision decoding is converted; if all errors can not be corrected after one time of iteration is finished, bit soft values corresponding to the rows which is confirmed to be right after the hard-decision decoding are corrected and iteration of the next round is conducted. According to the mixed iterative decoding method for the LDPC-RS two-dimensional product code, the problem that when LDPC-RS is decoded through an SISO decoding structure, an RS soft-decision decoder is high in complexity. Meanwhile, compared with simple LDPC+RS cascading decoding, the mixed iterative decoding method for the LDPC-RS two-dimensional product code improves codon correction performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hard decision decoding method based on genetic algorithm and neural network
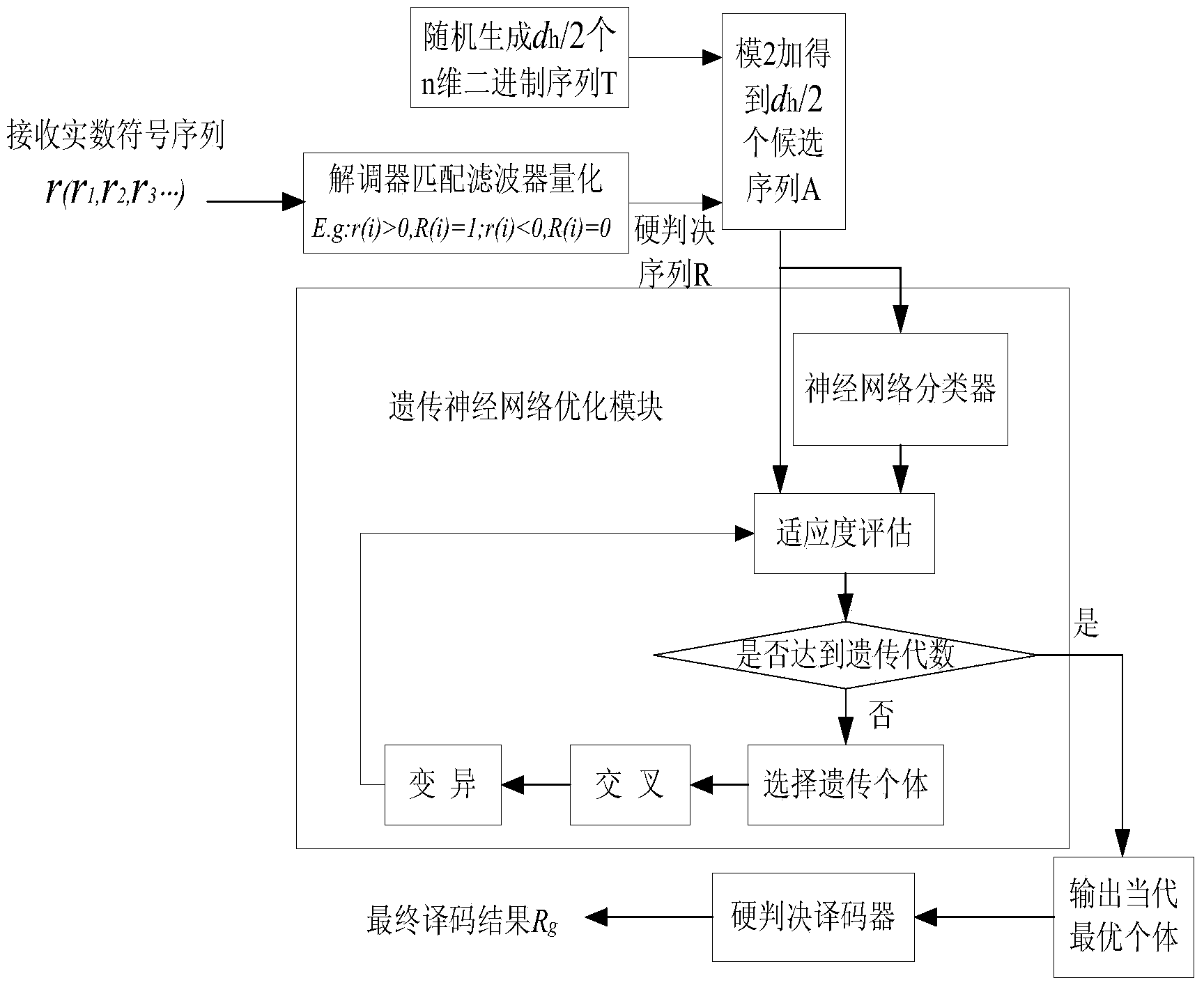
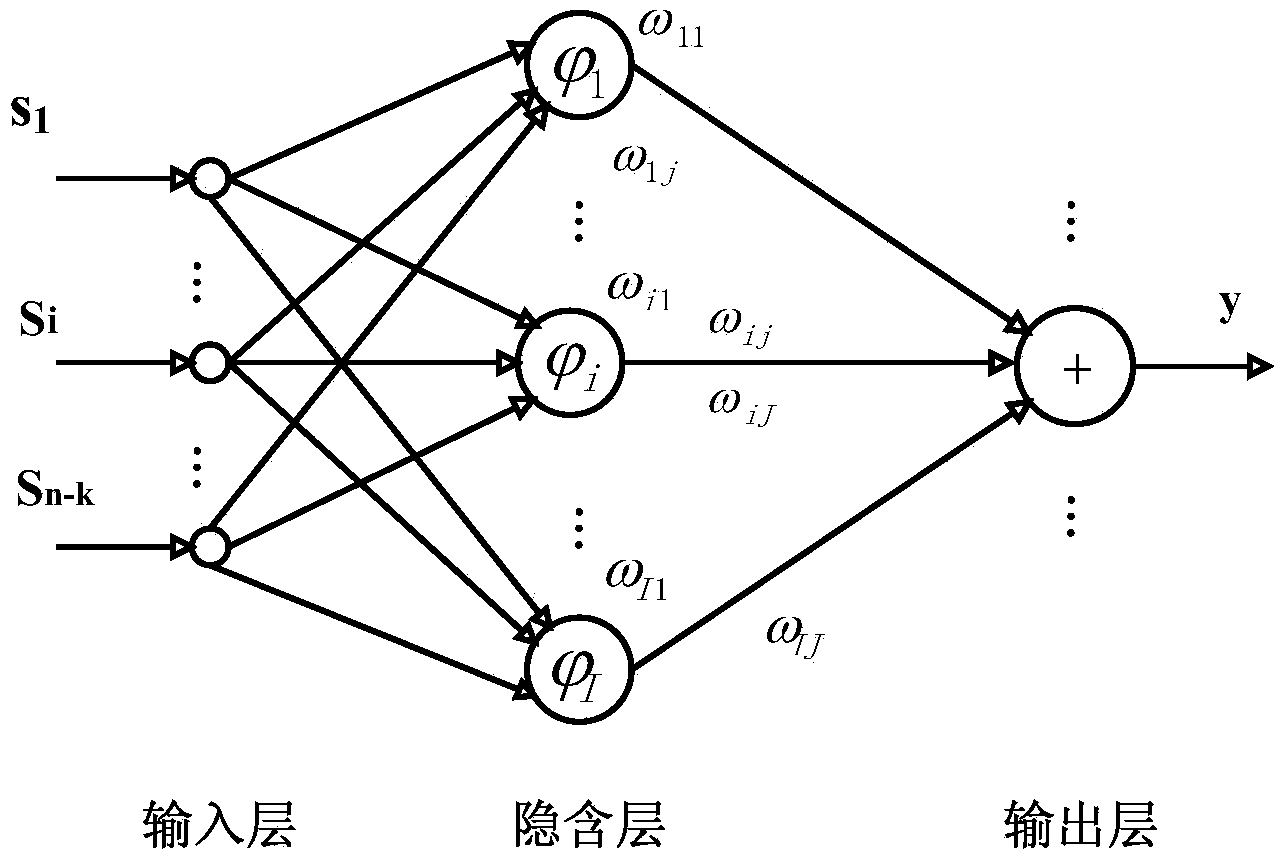
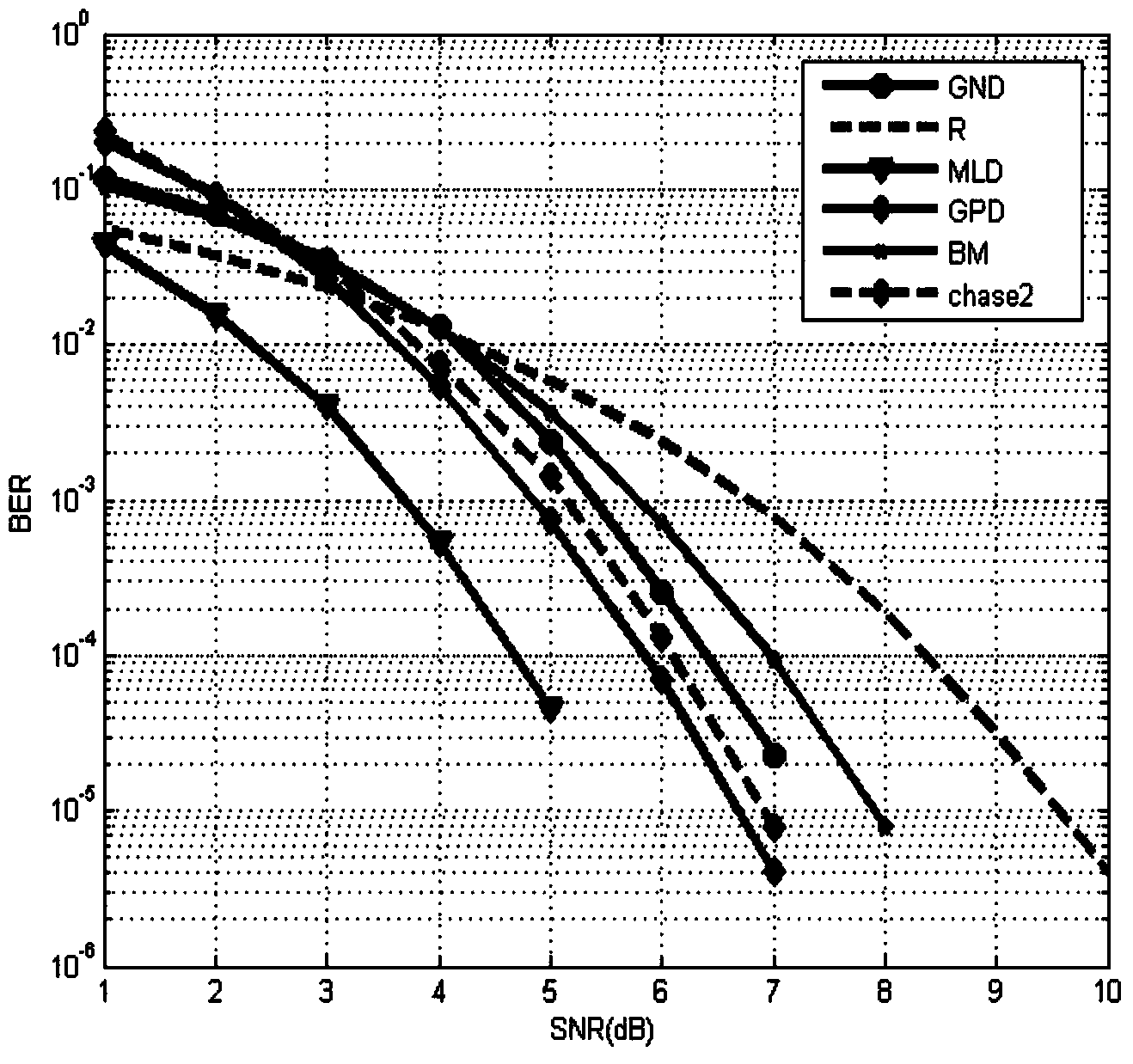
ActiveCN103929210AMake up for loss of reliabilityGood decoding resultCyclic codesGenetic algorithmSoft-decision decoder
The invention relates to the field of signal processing in communication, in particular to a hard decision decoding method based on a genetic algorithm and neural network, namely, a genetic neural-network decoding (GND) method. The method makes full use of self-optimizing capability of the genetic algorithm and a model classifying function of the neural network to perform optimizing processing on output of hard decision quantization of a matching filter in order to make up for a reliability loss of decoding caused by transmission errors of a channel and hard decision quantization, and therefore, code words more similar to a transmission sequence are recovered out to serve as input of a hard decision decoder in order to obtain a better decoding result. As you can see from theoretical analysis and computer analog simulation, error correction performance of the GND method is similar to that of a traditional soft decision decoding method. Due to the fact that no soft information is needed to be calculated through the channel during decoding, compared with the traditional soft decision decoding method, complexity of the GND method is reduced greatly.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
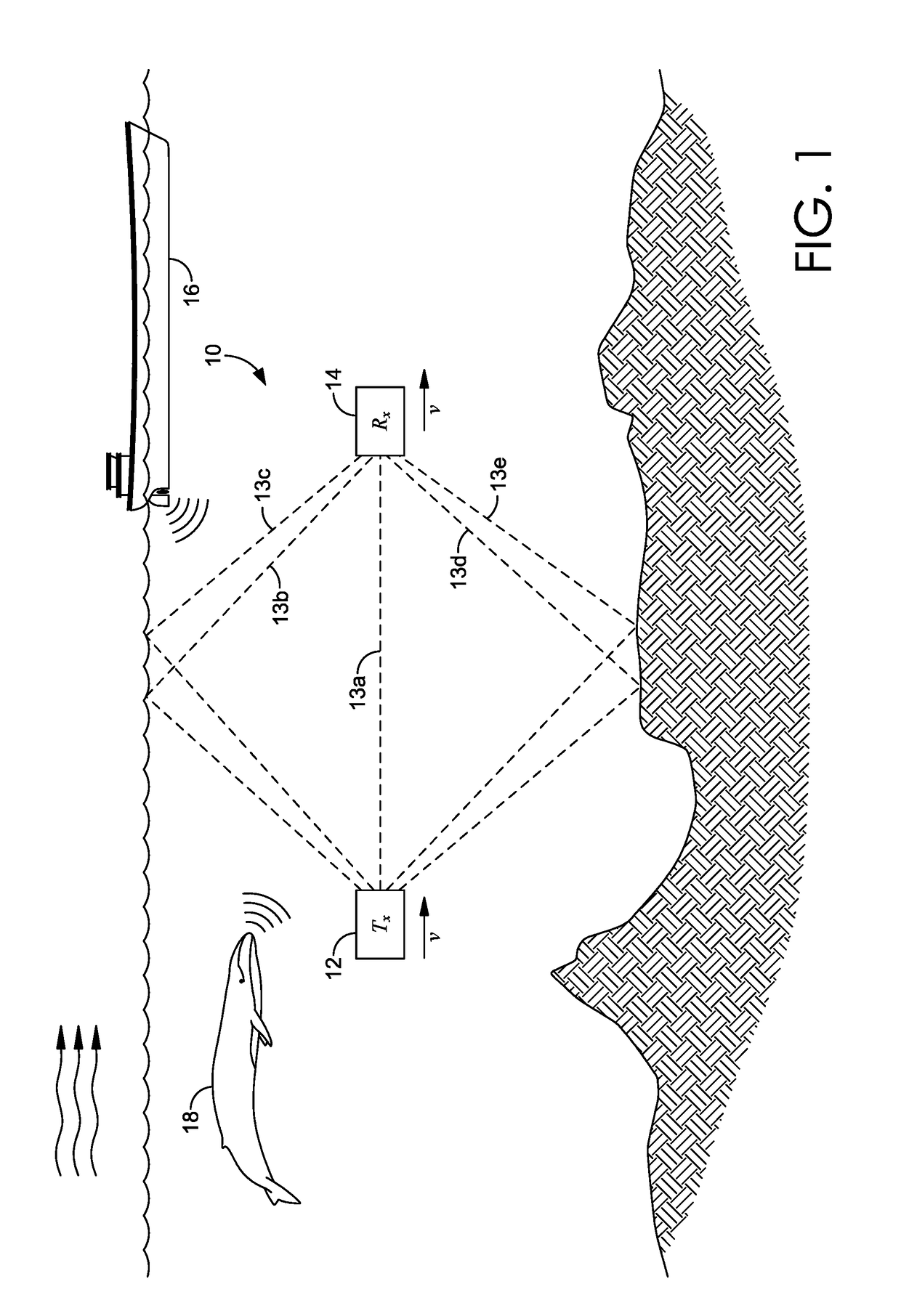
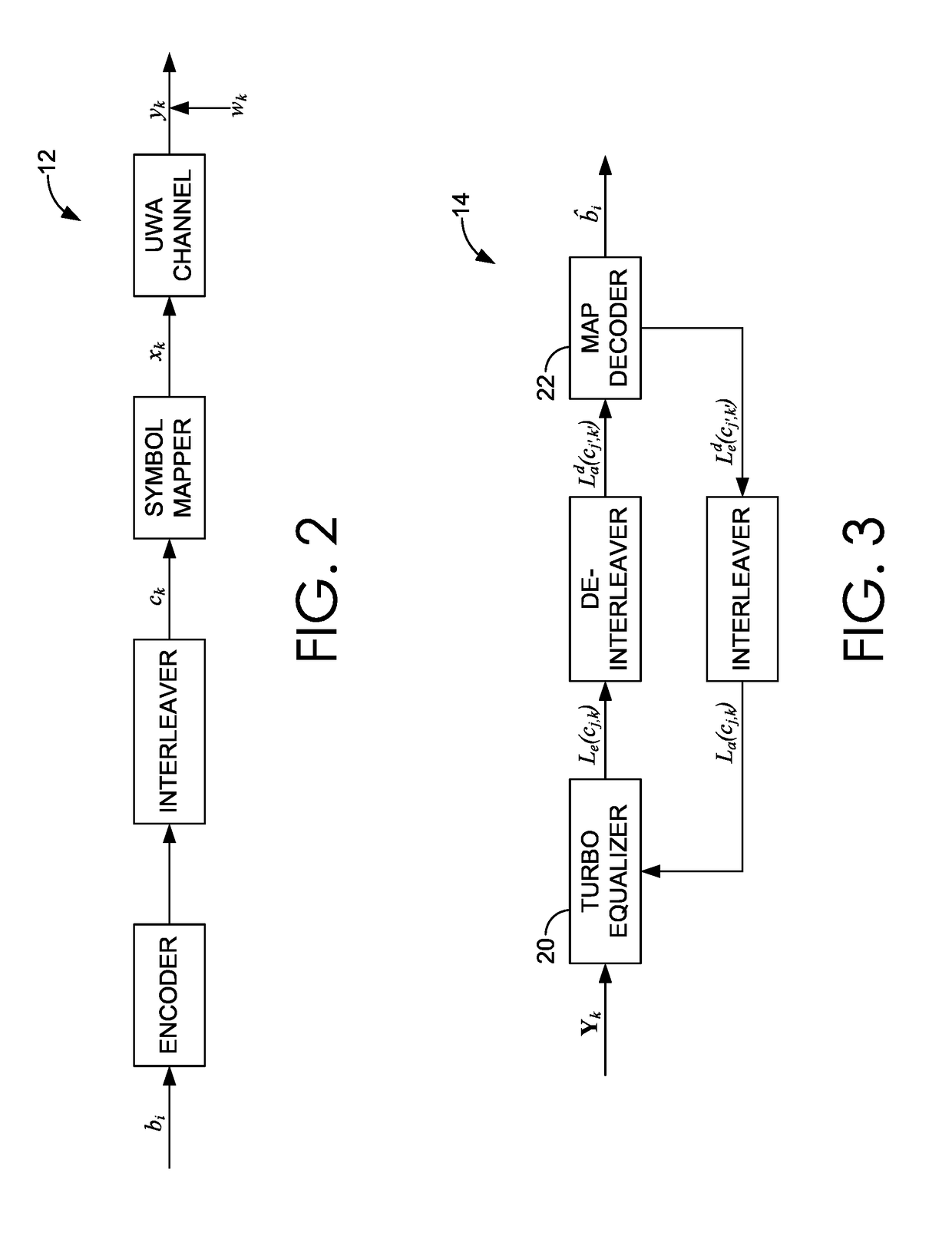
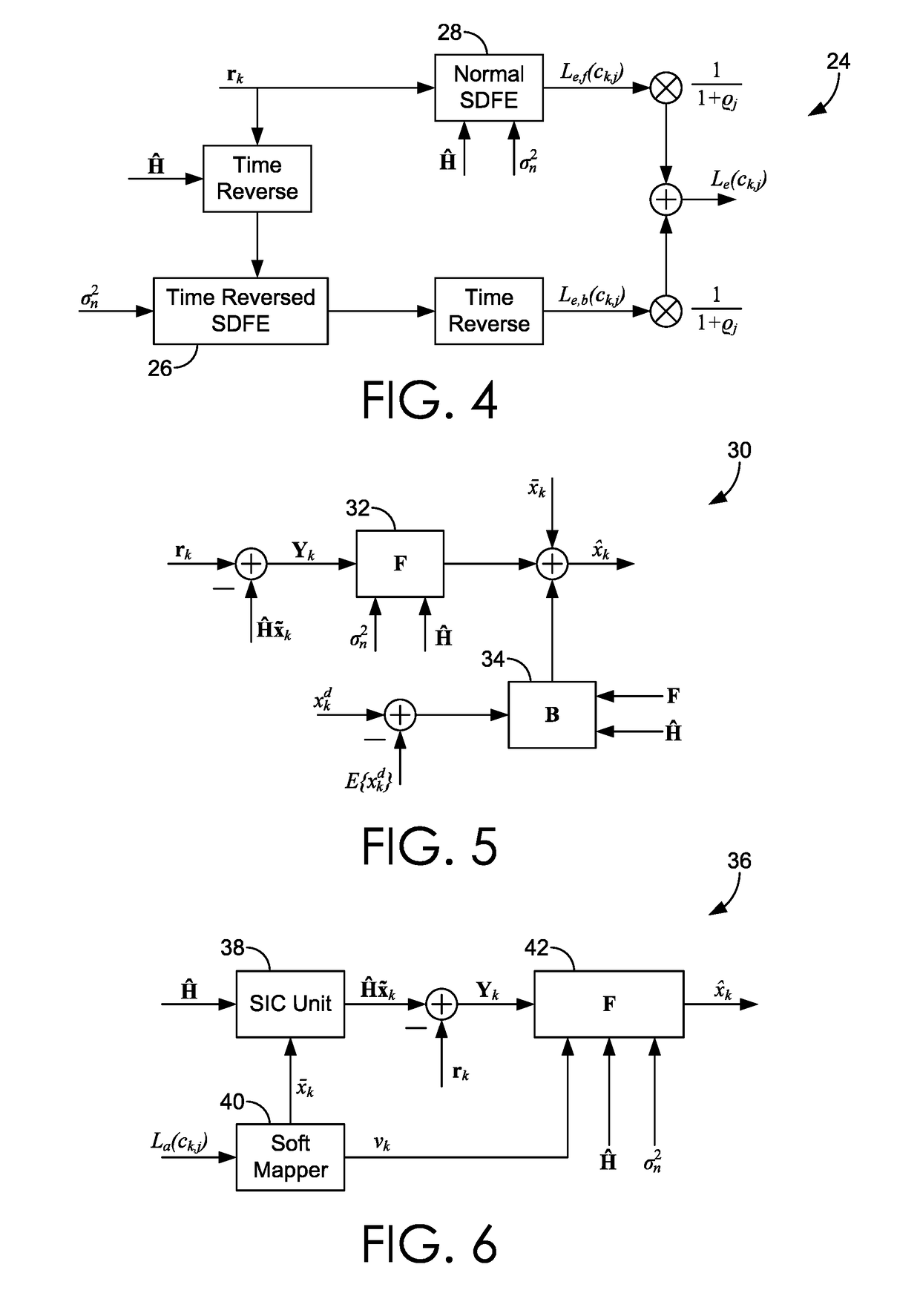
Turbo receivers for single-input single-output underwater acoustic communications
InactiveUS20190058529A1Good robustness and performanceFacilitate communicationError preventionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSoft-decision decoderComputer science
Systems and methods for underwater communication using a SISO acoustic channel. An acoustic receiver may receive a signal comprising information encoded in at least one transmitted symbol. Using a Bi-SDFE, the at least one transmitted symbol is estimated. The Bi-SDFE may include a SDFE and a time-reversed SDFE that each output bit extrinsic LLRs, which are combined into combined bit extrinsic LLRs. The estimated symbol is then mapped to the combined bit extrinsic LLRs, the result of which is de-interleaved. Iterative bit extrinsic LLRs are generated with a MAP and / or soft-decision decoder using the mapped, combined bit extrinsic LLRs as a priori LLRs for the Bi-SDFE in another iterative estimation. The iterative bit extrinsic LLRs are interleaved and transmitted for use by the Bi-SDFE in another iterative estimation. After a plurality of iterations, a hard decision of the transmitted symbol is generated with the MAP and / or soft-decision decoder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
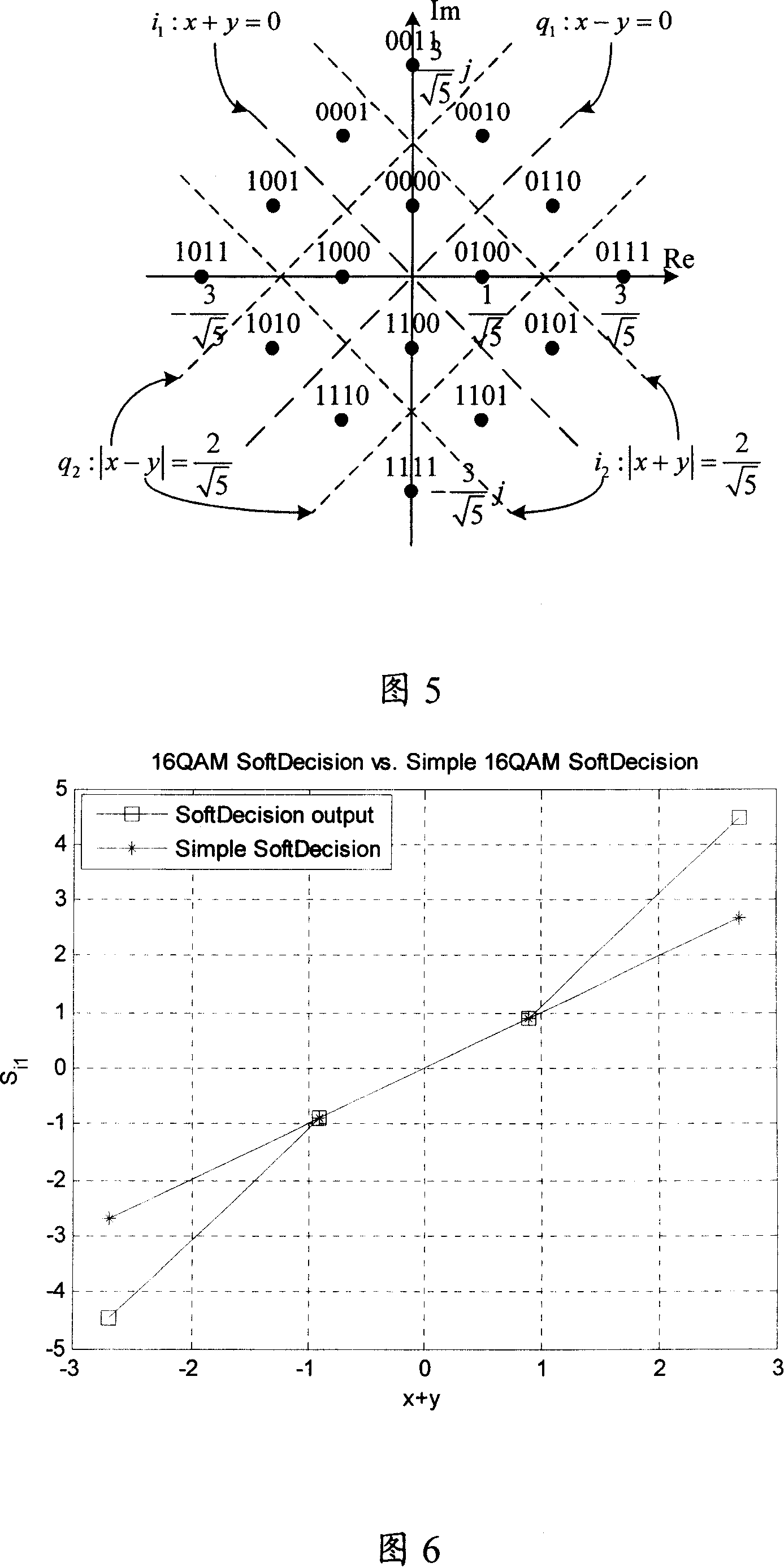
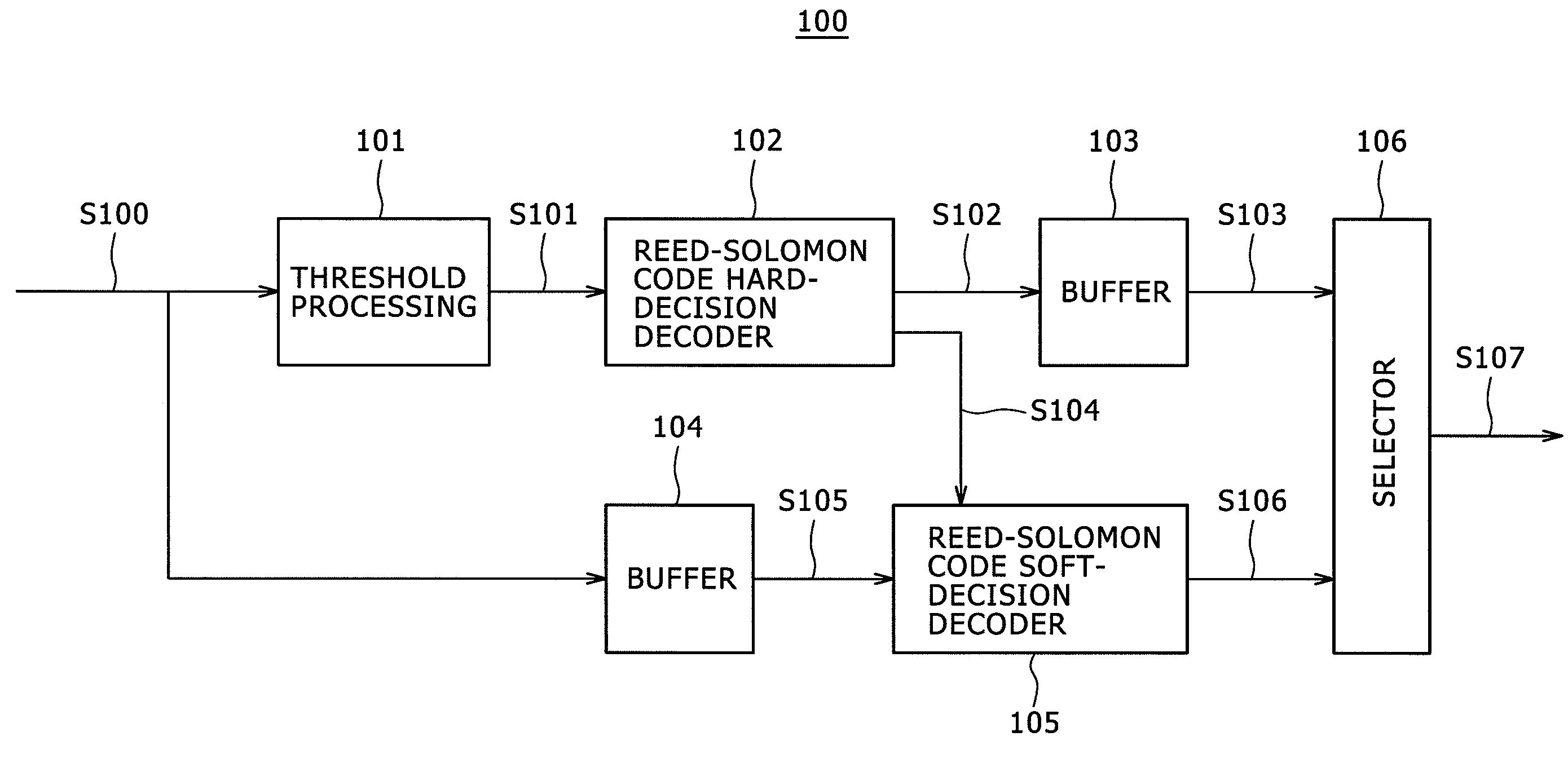
Quadrature amplitude modulated soft decision method and apparatus
ActiveCN101136898ASimple calculationSimplify the soft decision processCode division multiplexMultiple carrier systemsCommunication interfaceDecision boundary
Being applicable to solve the issue that in current technique, demodulation procedure is too complex, the invention discloses simplified schemes for two algorithms. Scheme 1 is that using LLR algorithm and MAX-log algorithm simplifies current demodulation procedure into piecewise functions. Scheme 2 is that using minimum distance between the received signal and hard decision boundary determines amplitude of soft bits to simplify demodulation procedure further. First, the invention decomposes signal in orthogonal into first branch component, and second branch component, and then calculates their soft bits so as to accomplish soft decision-making procedure. In scheme 1, the equipment includes communication interface (CI), decomposition module (DM), judgment module (JM), computing module (CM), and output module (OM). In scheme 2, the equipment includes CI, DM, JM, CM, and OM.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
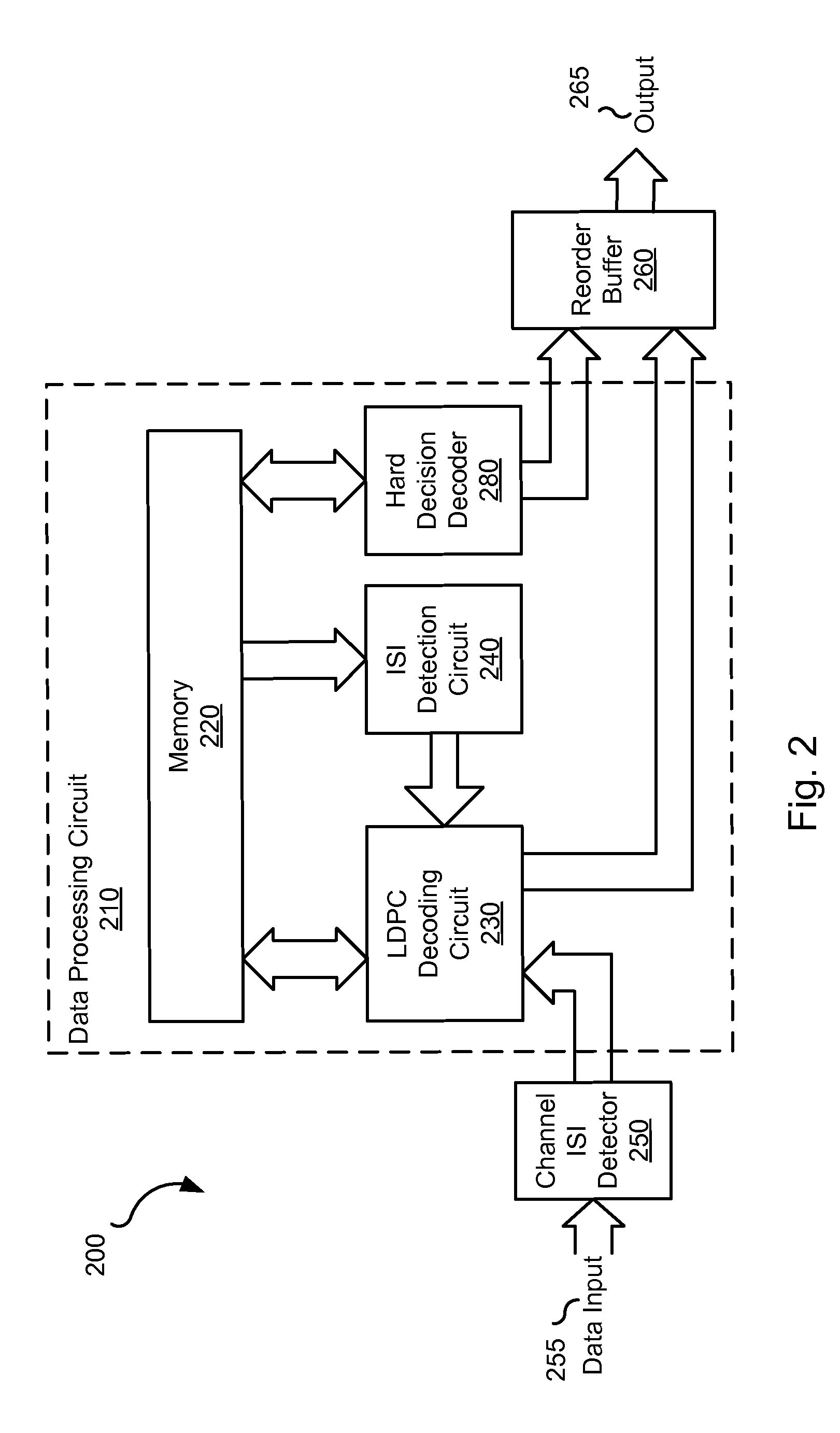
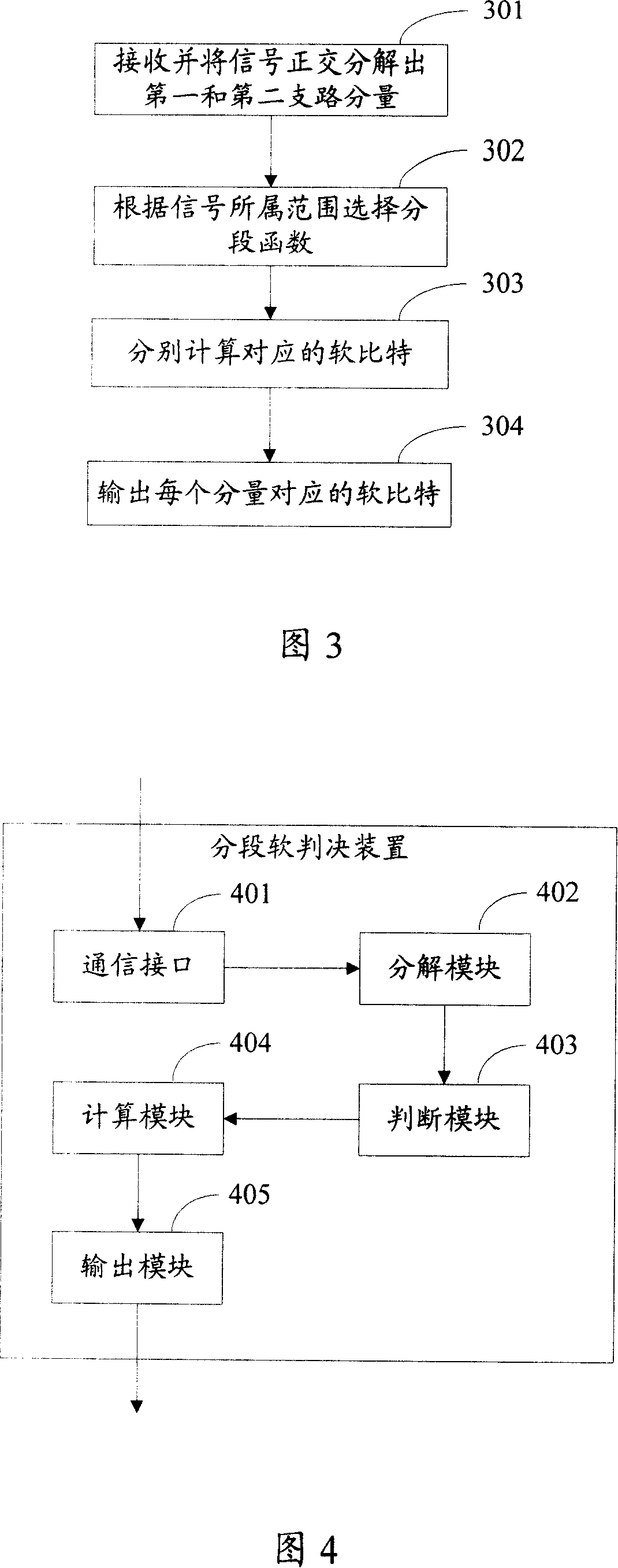
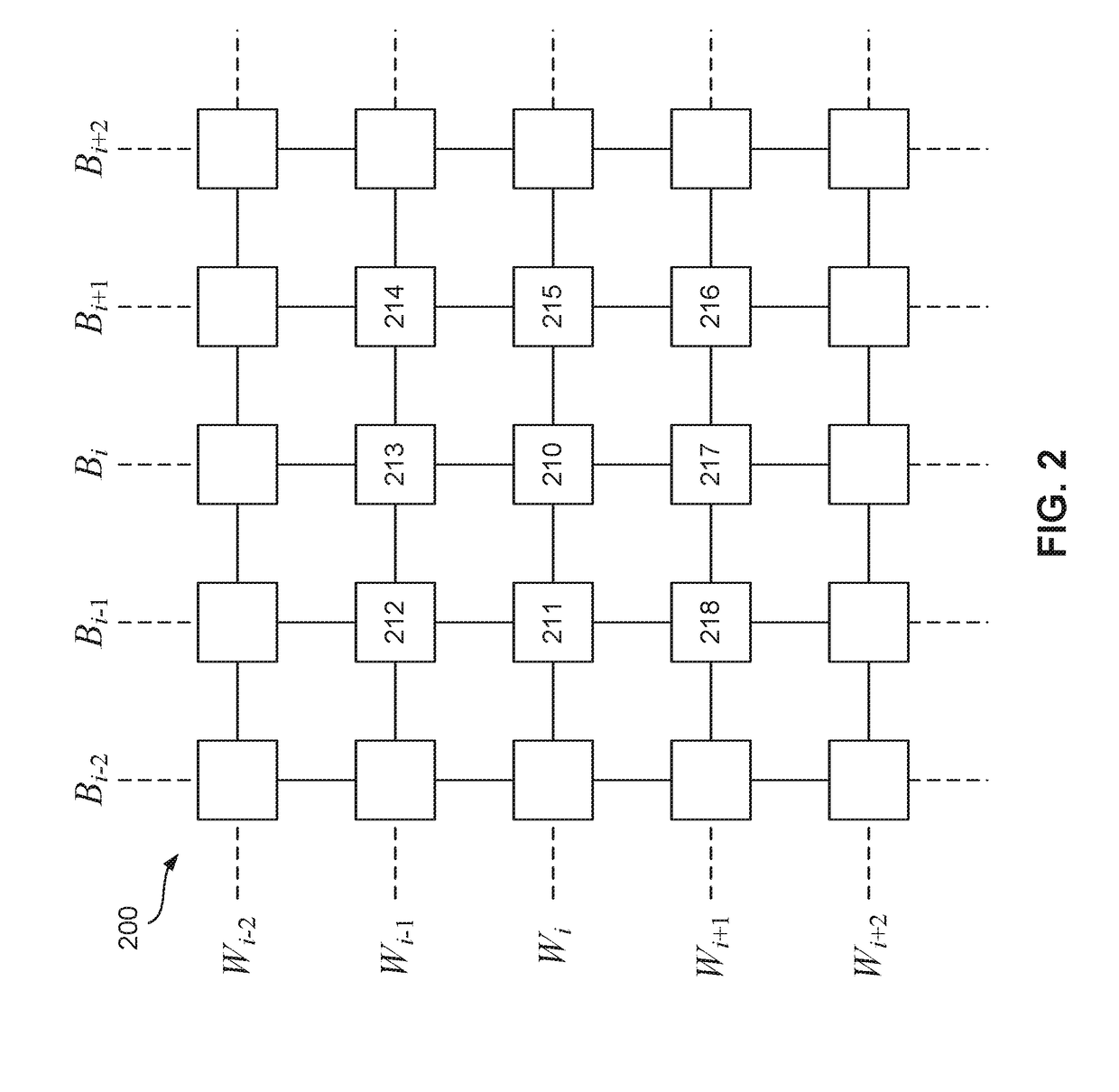
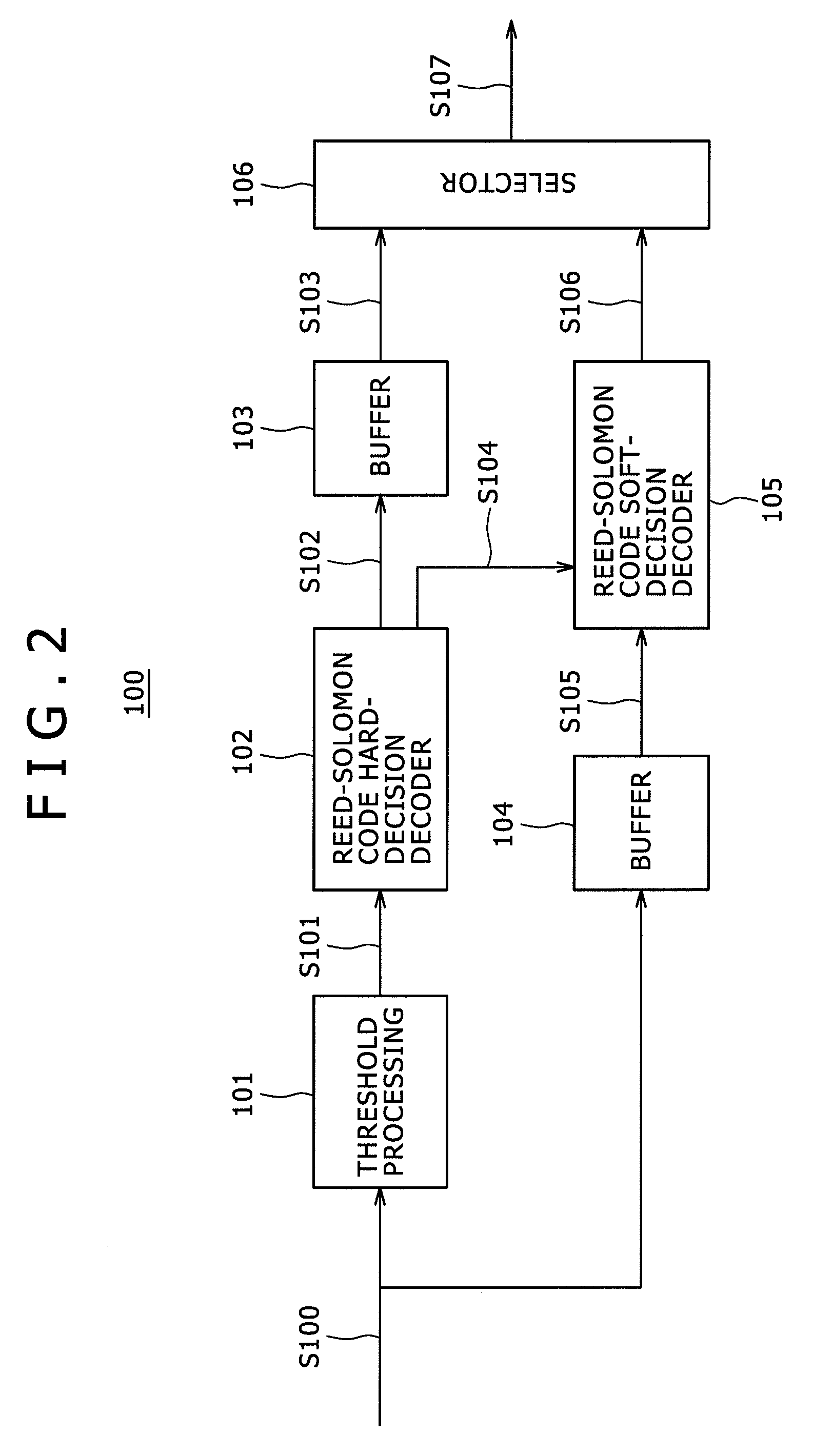
Decoding apparatus and decoding method
InactiveUS20090158127A1Eliminate needReduce circuit sizeFault responseOther decoding techniquesBlock codeSoft-decision decoder
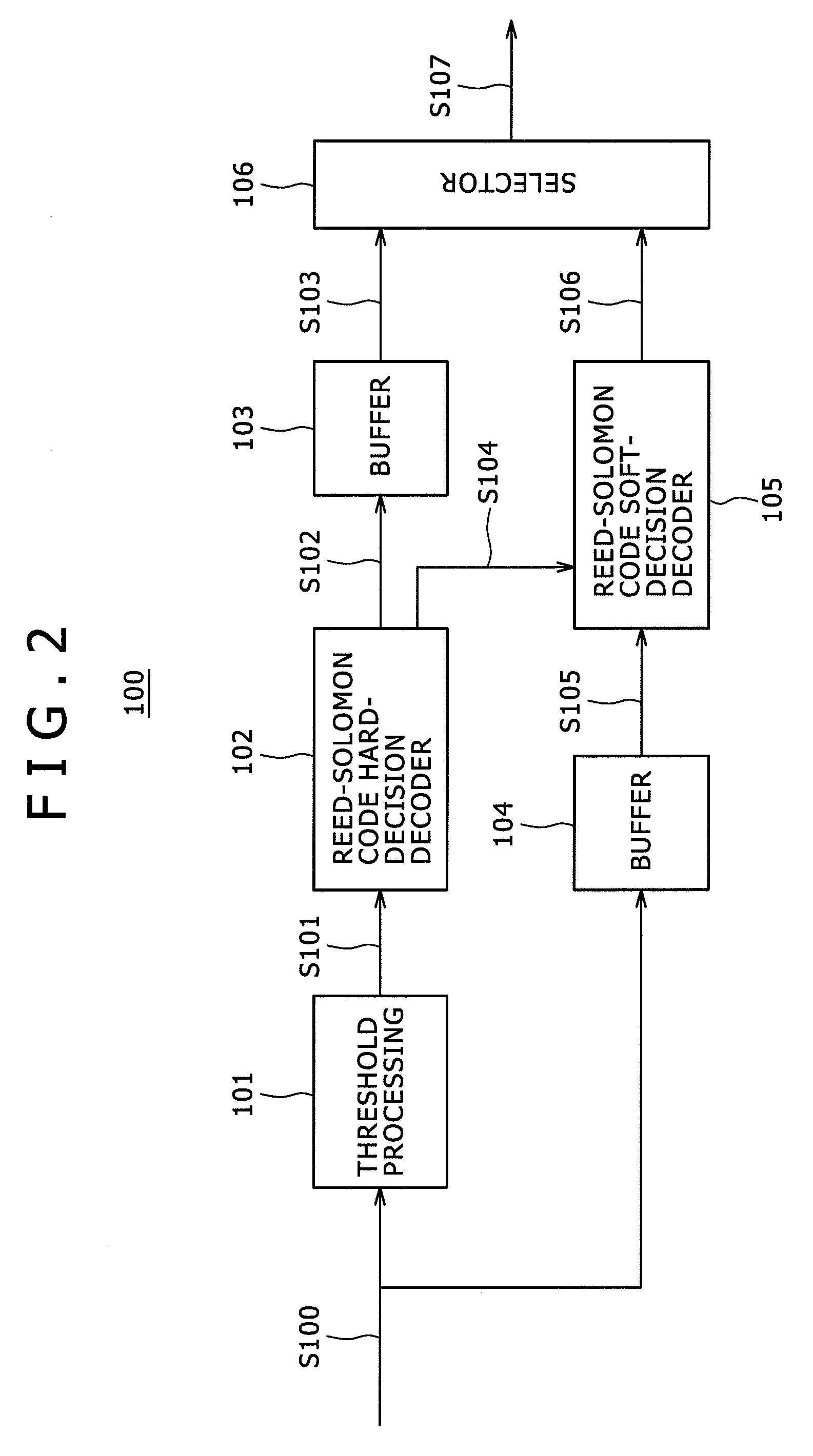
Disclosed herein is a decoding apparatus that performs soft-decision decoding on a linear block code, the apparatus including a hard-decision decoder configured to perform hard-decision decoding on a received word using a hard-decision decoding algorithm; and a soft-decision decoder configured to perform, using a soft-decision algorithm, soft-decision decoding merely on a received word for which the hard-decision decoder has failed in the hard-decision decoding.
Owner:SONY CORP
Physically unclonable function (PUF) with improved error correction
ActiveUS9396357B2Improve reliabilityReduce the amount of informationKey distribution for secure communicationInternal/peripheral component protectionPhysical unclonable functionForward error correction
A cryptographic system for reproducibly establishing a reliable data string, such as a cryptographic key, from a noisy physically unclonable function (PUF, 110) is provided. The system comprises a hard decision decoder (150) to decode a first multiple of error correctable data words to obtain a second multiple of corrected and decoded data words and a reliability information extractor (180) to determine reliability information, e.g. soft decision information, that is indicative of a reliability of corrected and decoded data words. The system further comprises a soft decision decoder (160) configured to use the reliability information to decode at least one further correctable data word. Error correcting a PUF using reliability information decreases the false rejection rate.
Owner:INTRINSIC ID
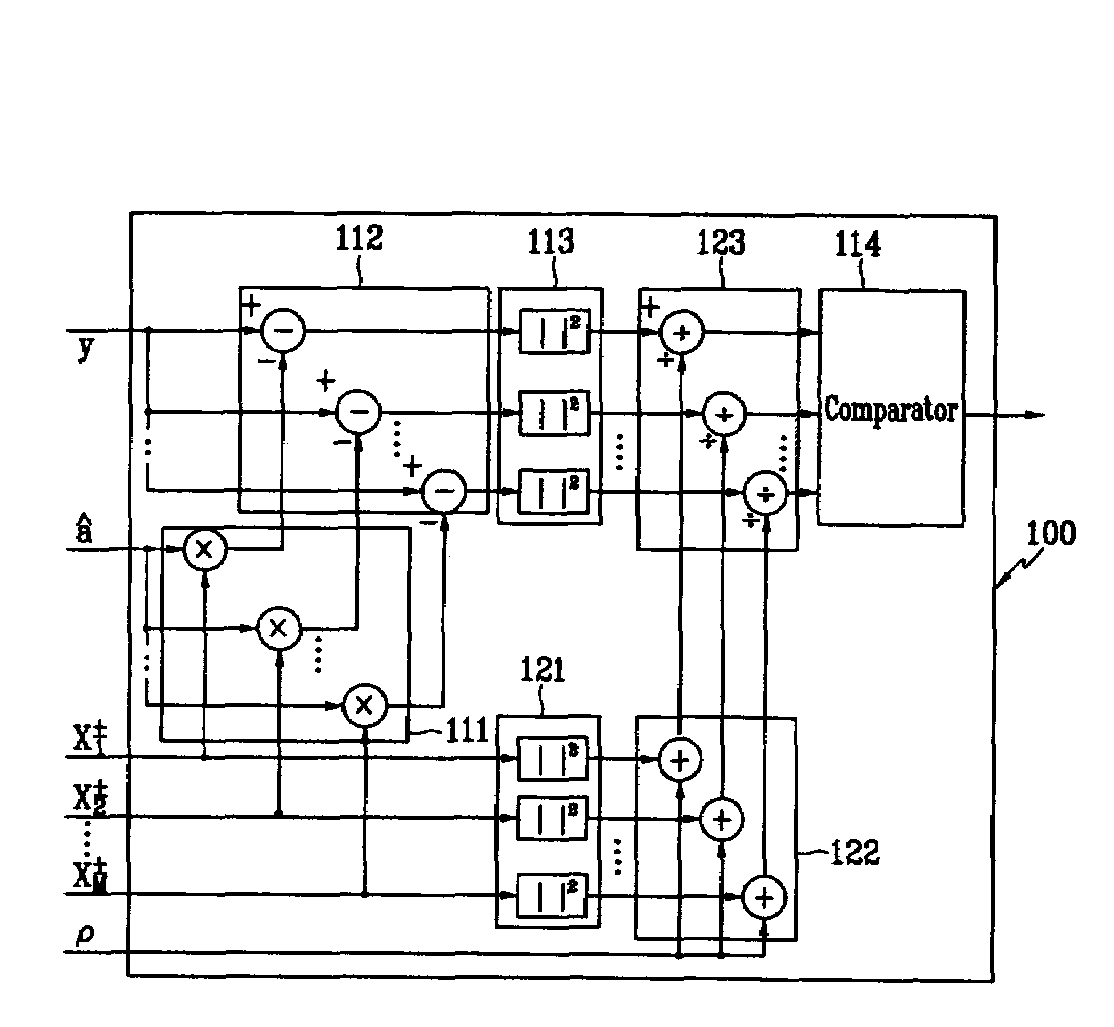
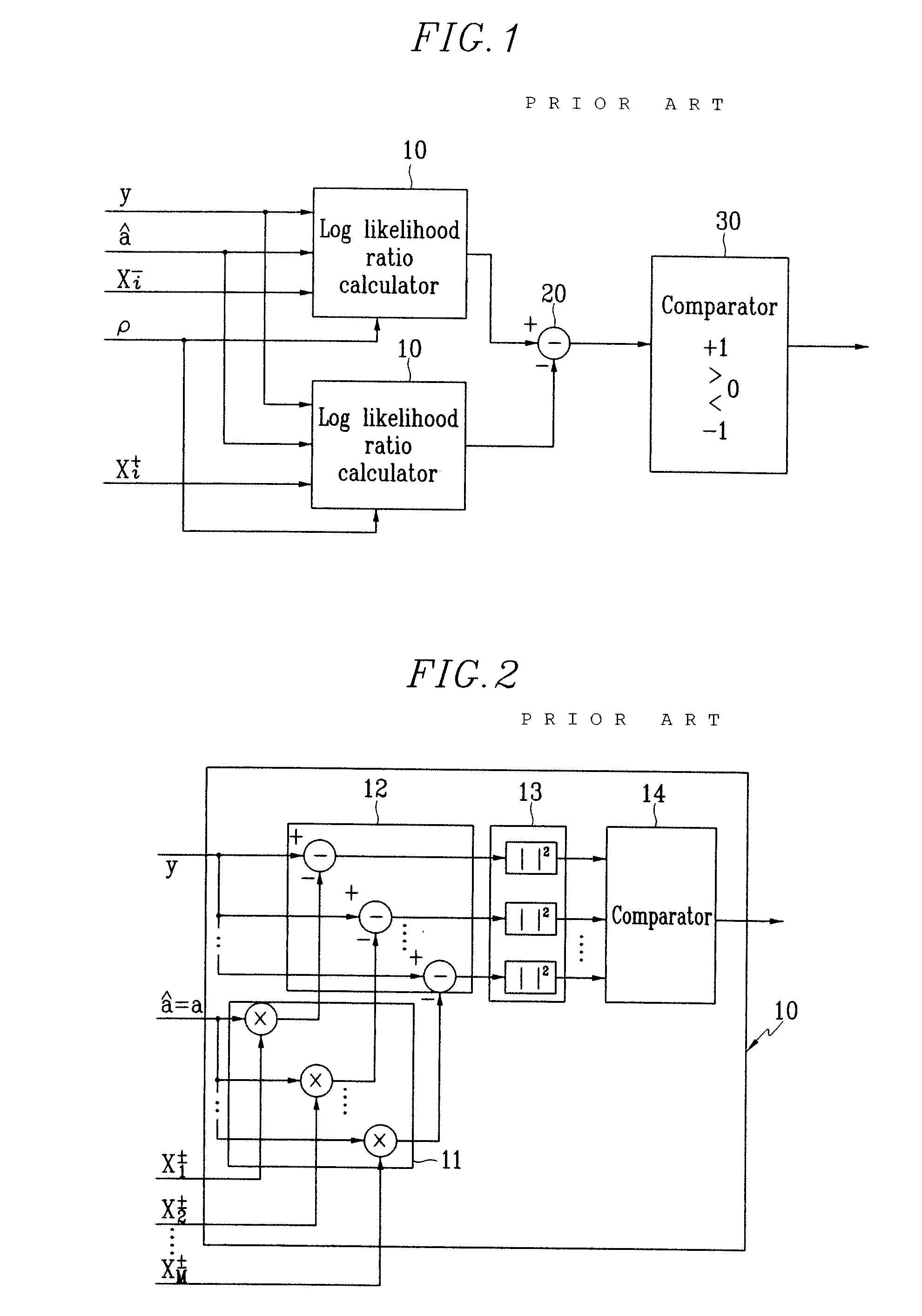
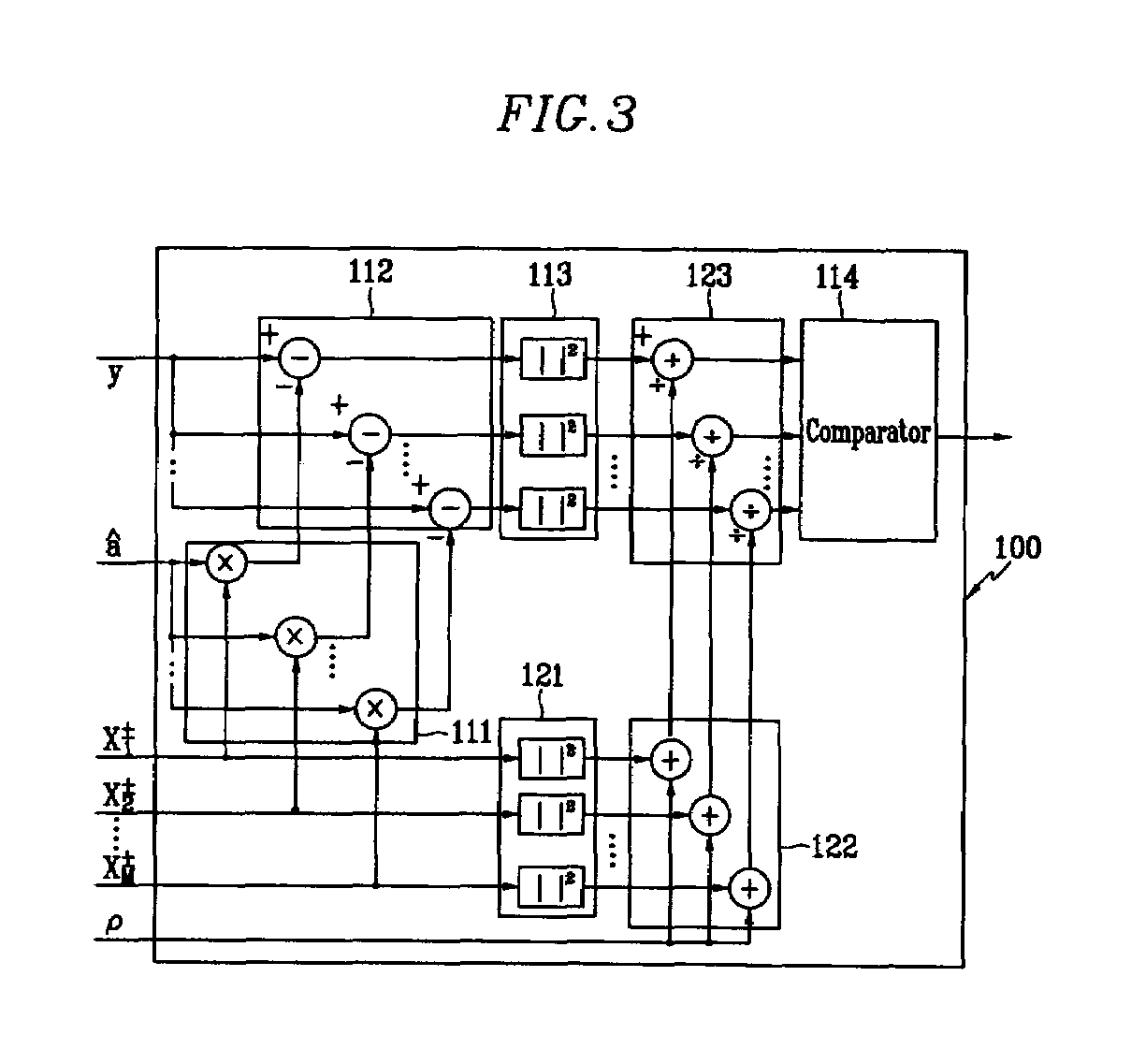
Soft decision decoder, and log likelihood ratio calculator and method thereof for enhanced performance in soft decision decoding
InactiveUS7321643B2Optimal signal recoveryImprove decoding performanceDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSoft-decision decoderLog likelihood
Disclosed is a soft decision decoder, and a log likelihood ratio calculator for soft decision decoding and a method thereof, for realizing a generalized log likelihood ratio algorithm in consideration of channel estimation errors for performing soft decision decoding on QAM signals, which comprises multipliers for multiplying reference signals and channel estimation signals, subtractors for subtracting a receive signal of a receiver from output signals of the multipliers, first and second square calculators for squaring the subtractors' output signals and reference signals, dividers for dividing output signals of the first and second square calculators by addition values, and a comparator for comparing output signals of the dividers.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Wireless communication apparatus and wireless communication method
ActiveUS7680203B2Highly reliable likelihood estimationAvoid performance degradationMultiplex communicationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSignal onSoft-decision decoder
A wireless communication apparatus for receiving spatially multiplexed signals in which a plurality of streams are spatially multiplexed, using a plurality of antennas, includes the following elements: a channel matrix estimator for estimating a channel matrix for multiplexed channels; a spatial decoder for spatially decoding received signals each of which has been received by a corresponding antenna so as to separate the received signals into individual stream signals by obtaining an antenna weight matrix from the estimated channel matrix, and then multiplying each received signal by the antenna weight matrix; a likelihood information estimator for estimating likelihood information using the estimated channel matrix, the antenna weight matrix, and estimated noise power; and a soft decision decoder for performing soft decision decoding on each stream signal on the basis of the estimated likelihood information.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
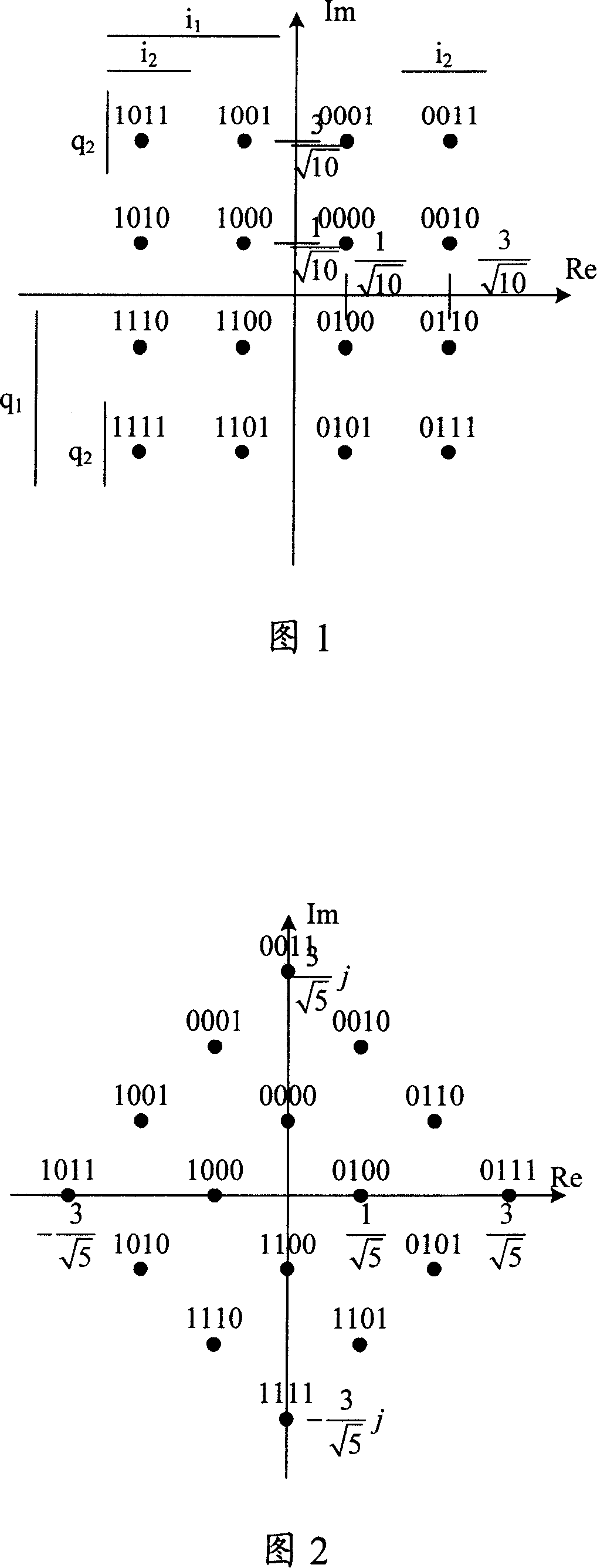
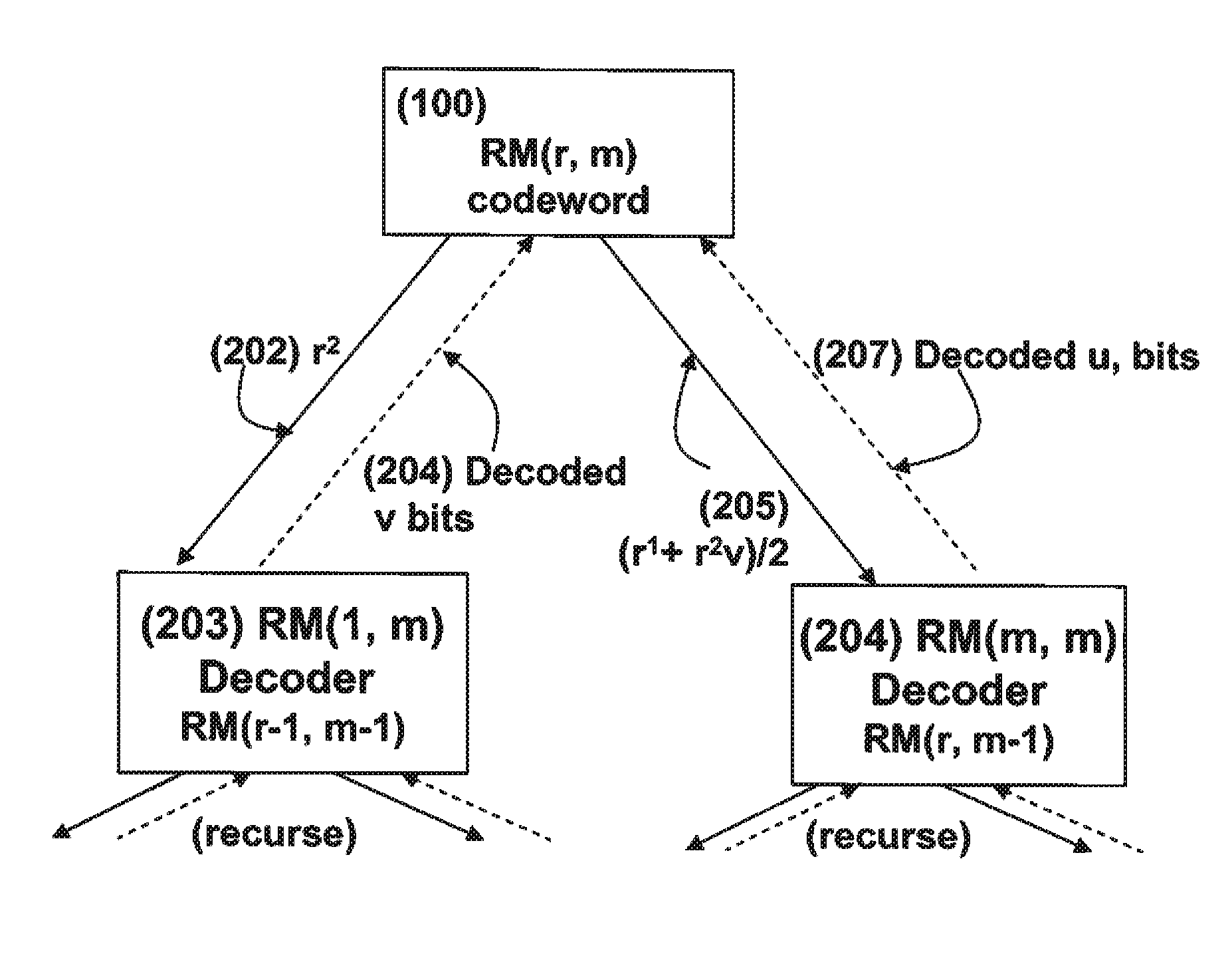
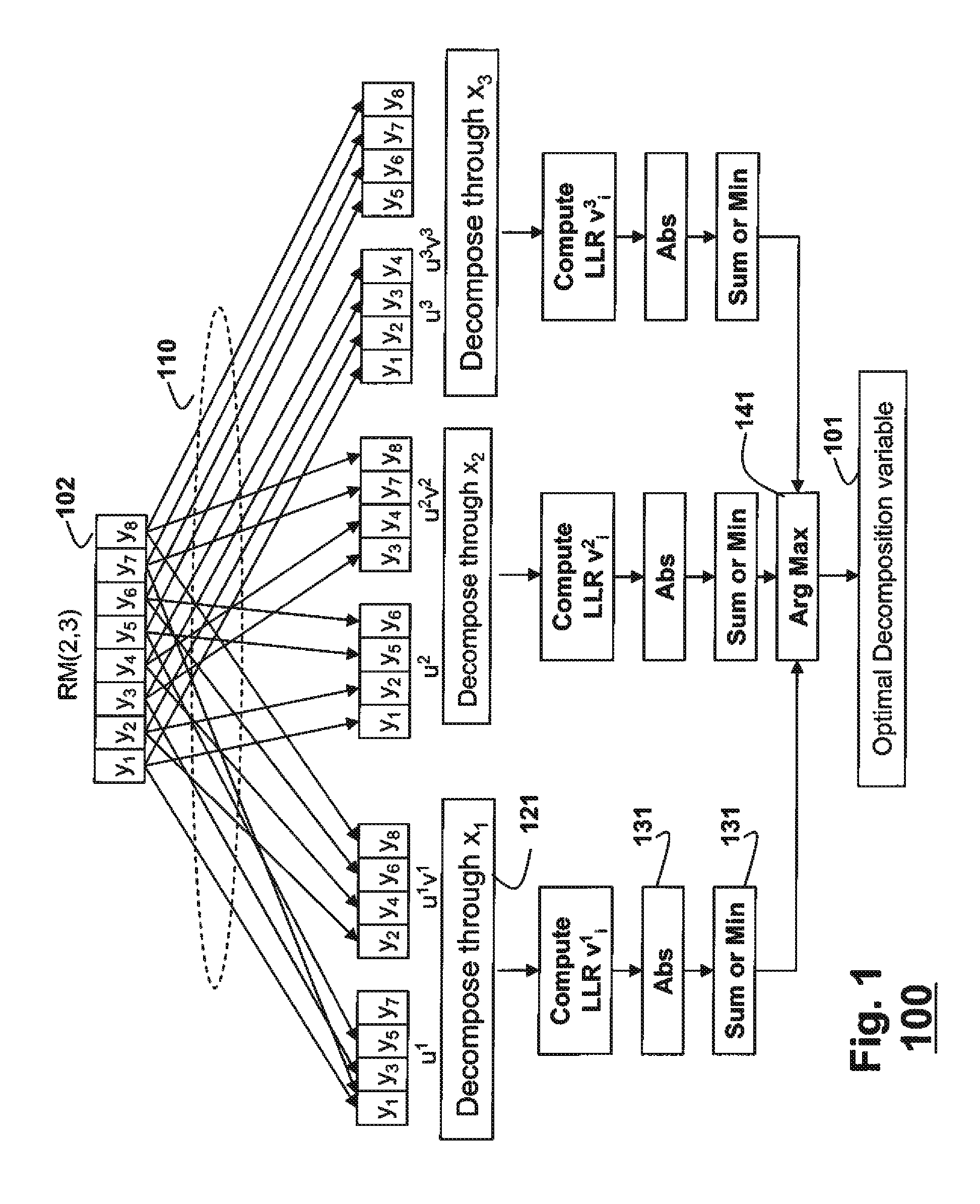
Method for performing soft decision decoding of Euclidean space Reed-Muller codes
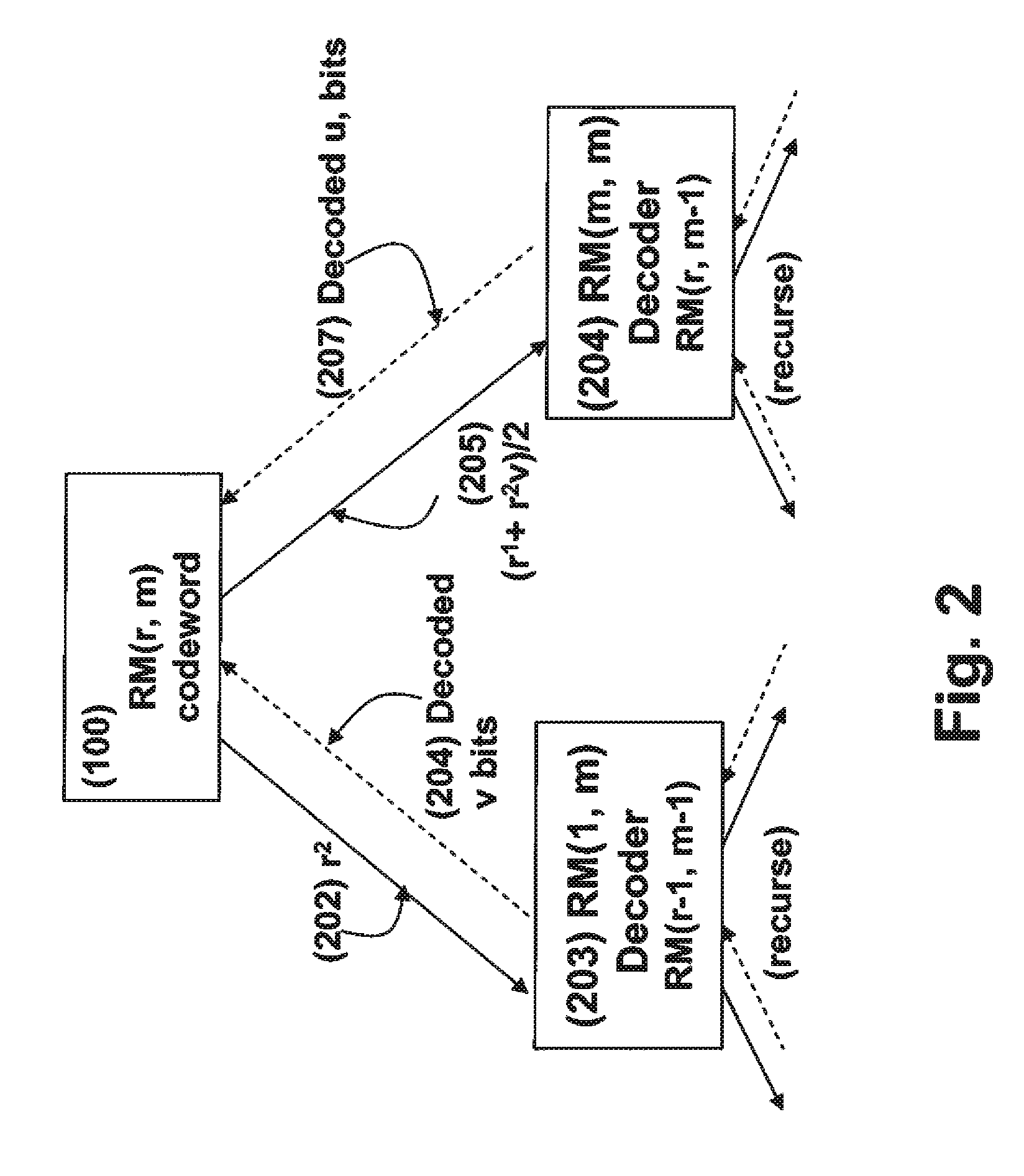
Soft decision decoding of a codeword of a Reed-Muller (RM) code byselecting an optimal decomposition variable i using a likelihood calculation. A code RM(r, m) is expressed as {(u, uv)|uεRM(r, m−1) and vεRM(r−1, m−1)}, where uv denotes a component-wise multiplication of u and v, and (u, uv)=(r1, r2). A receive codeword is separated into r1=u and r2=uv based on the optimal decomposition variable, and r2 is decoded according to the optimal decomposition variable, using a RM(r−1, m−1) decoder to obtain a decoded v and a first set of decoded bits. The decoded v is combined with r1 using (r1+r2v) / 2, and(r1+r2v) / 2 is decoded using a RM(r, m−1) decoder to obtain a decoded u and a second set of decoded bits.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Impulse noise suppression and demapping soft decision method and system in multi-carrier system
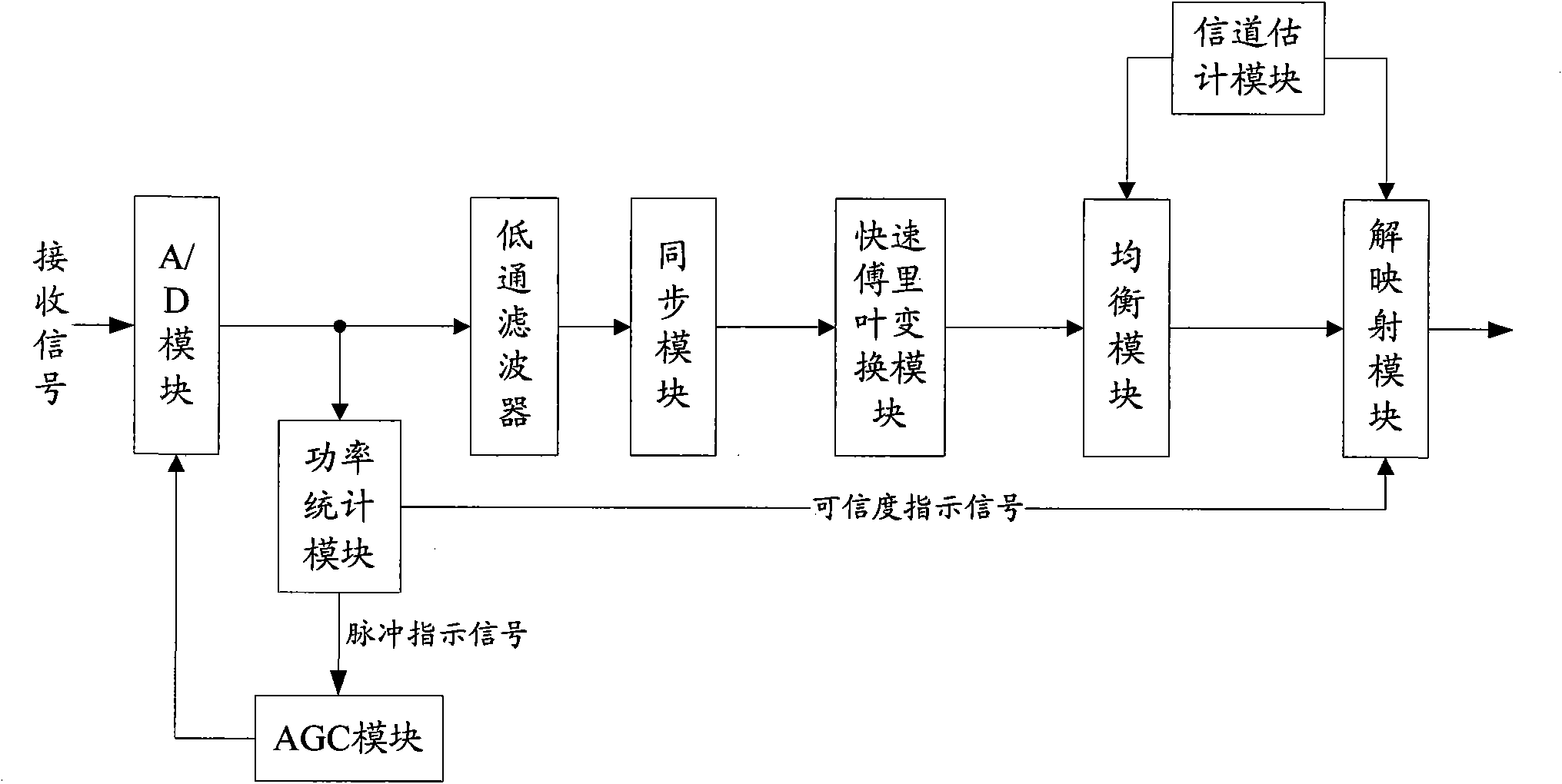
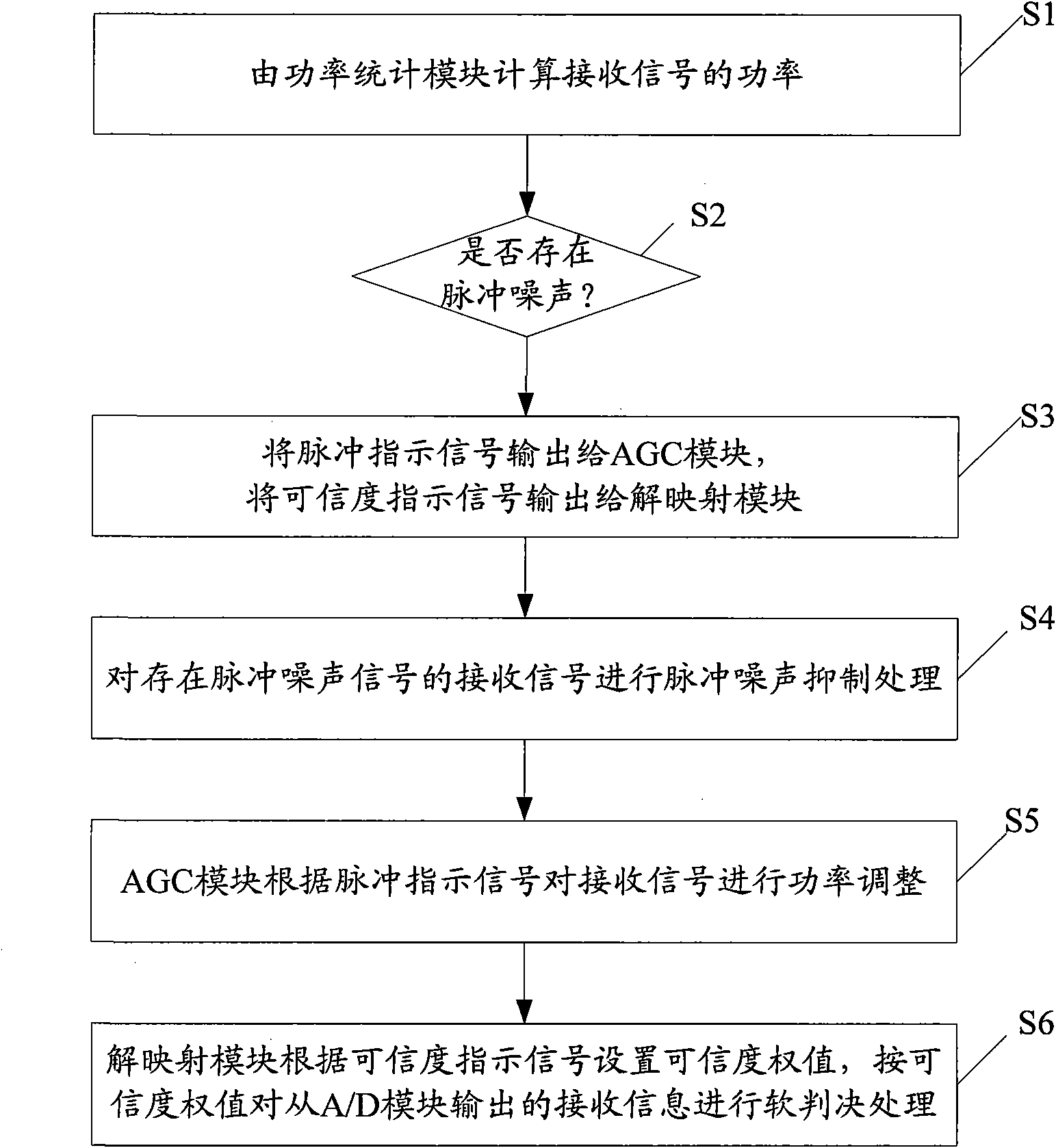
ActiveCN101860512AGuaranteed reliabilityImpulse noise suppressionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDecision methodsEngineering
The invention provides impulse noise suppression and demapping soft decision method and system in a multi-carrier system, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: carrying out statistics on power of receiving signals by an A / D (Analog to Digital) module by a power statistical module, comparing the power with a set threshold, judging whether impulse noise exists in the received signals or not, and if the impulse noise exists, generating an impulse indication signal and a confidence indication signal by the power statistical module; carrying out impulse noise suppression processing on the received signals which are judged to have the impulse noise by an AGC (Automatic Gain Control) module and carrying out power regulation on the receiving signal according to the impulse indication signal; feeding back the power-regulated receiving signal to the A / D module; setting up a confidence weight number according to the confidence indication signal by a demapping module, and carrying out soft decision processing on received information output from the A / D module according to the confidence weight number. The invention can effectively suppress the impulse noise and provides different confidence indications according to different impulse noise types to ensure the reliability of the demapping soft decision.
Owner:SHENZHEN STATE MICRO TECH CO LTD
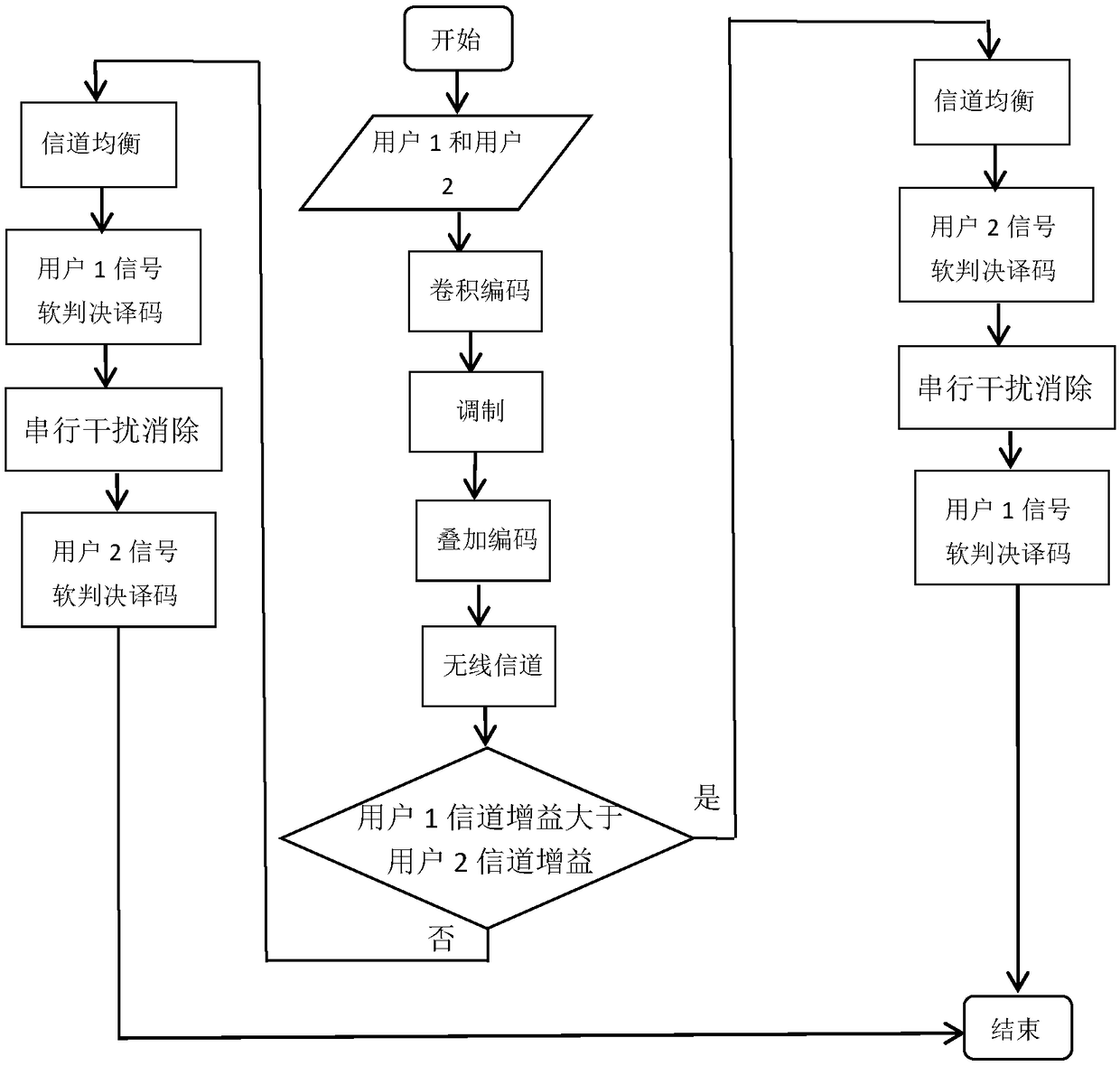
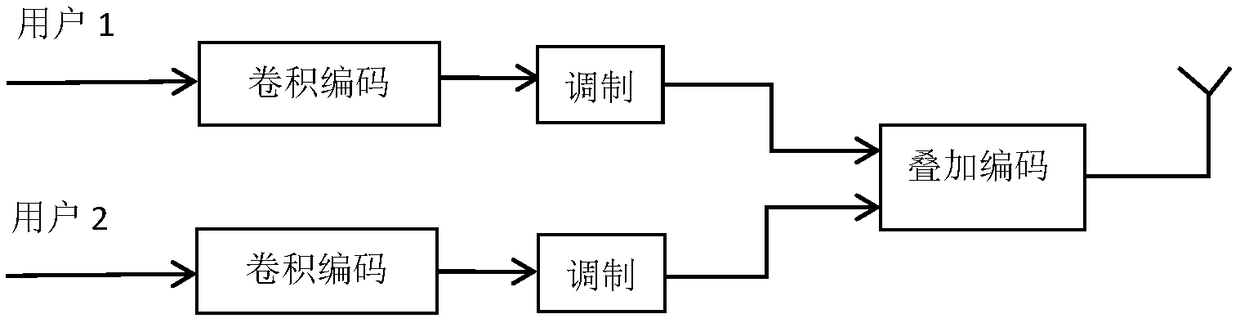
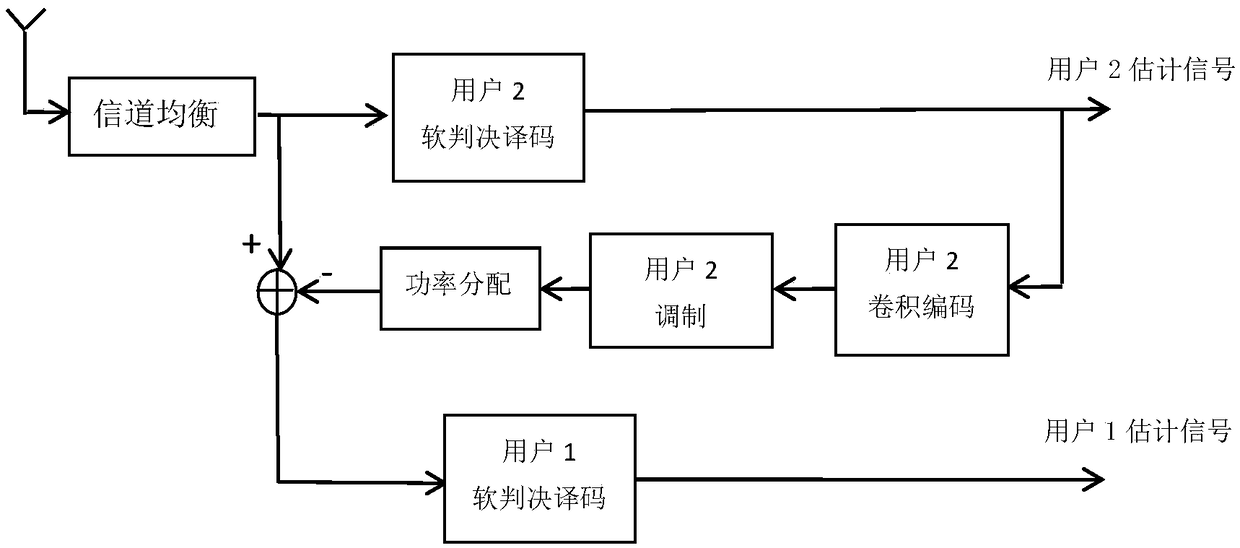
Non-orthogonal multiple access serial interference cancellation method based on soft decision decoding
ActiveCN109347771AImprove reliabilityImprove bit error performanceError preventionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksInterference cancelationSuperposition coding
The invention discloses a non-orthogonal multiple access serial interference cancellation method based on soft decision decoding, which solves the problem of poor reliability of serial interference cancellation technology. The method comprises the following implementation steps: encoding the power domain user by using channel encoding to obtain an encoded signal; modulating the encoded signal by abinary frequency shift keying modulation method to obtain a modulated signal; using a superposition encoding technique to allocate power to the modulated signal for superimposing to obtain a transmitted signal; obtaining a received signal by the transmitted signal through a channel; performing channel equalization on the received signal; determining a decoding order of the serial interference cancellation according to the channel gain; and obtaining an estimated signal of the target user by using the soft decision decoding and the serial interference cancellation method. The method provided by the invention fully utilizes the information of channel error statistical characteristics in the received signal based on the soft decision decoding technology, and combines with the serial interference cancellation to improve the reliability of the non-orthogonal multiple access system, which is used in the downlink of multi-user non-orthogonal multiple access systems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
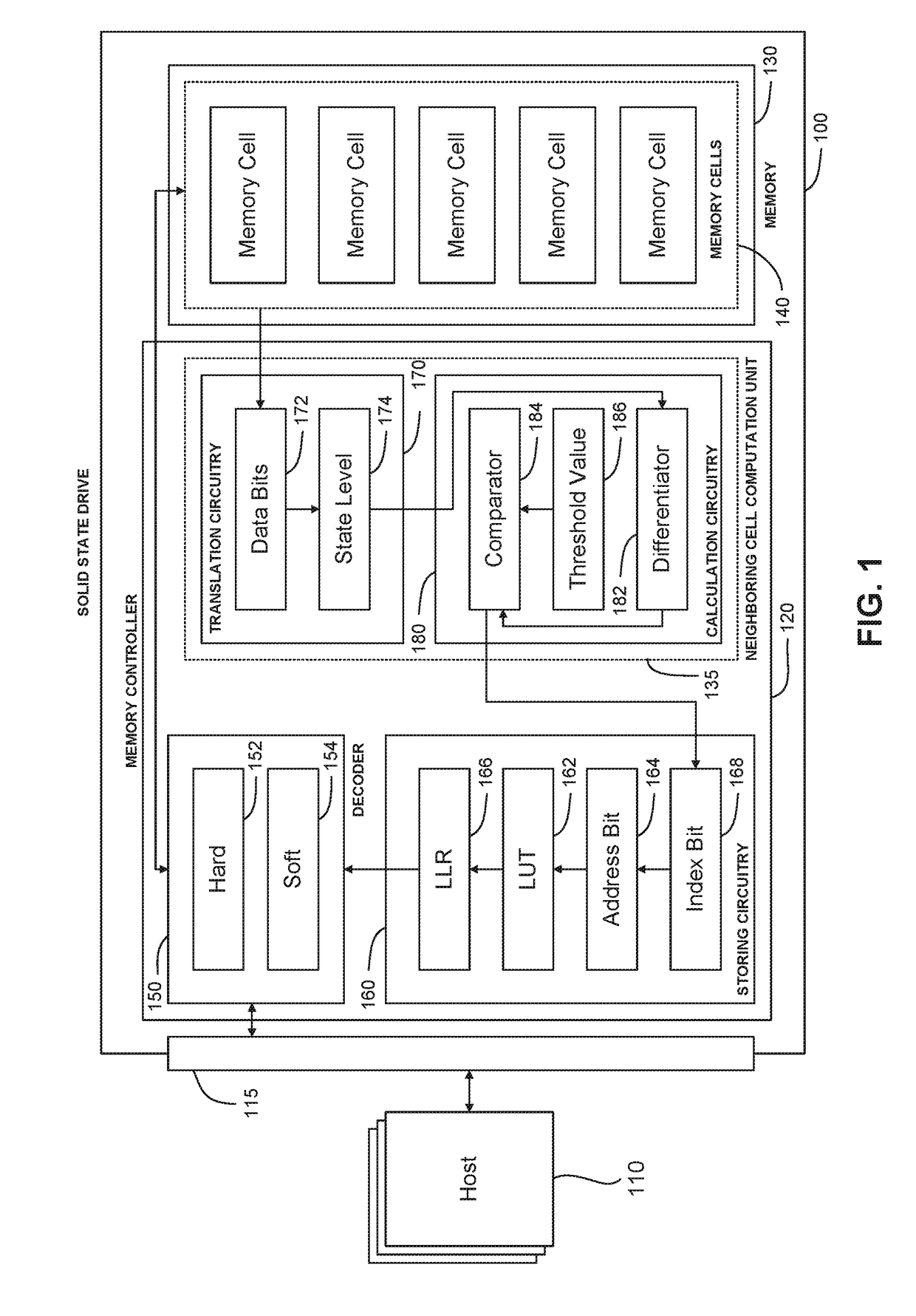
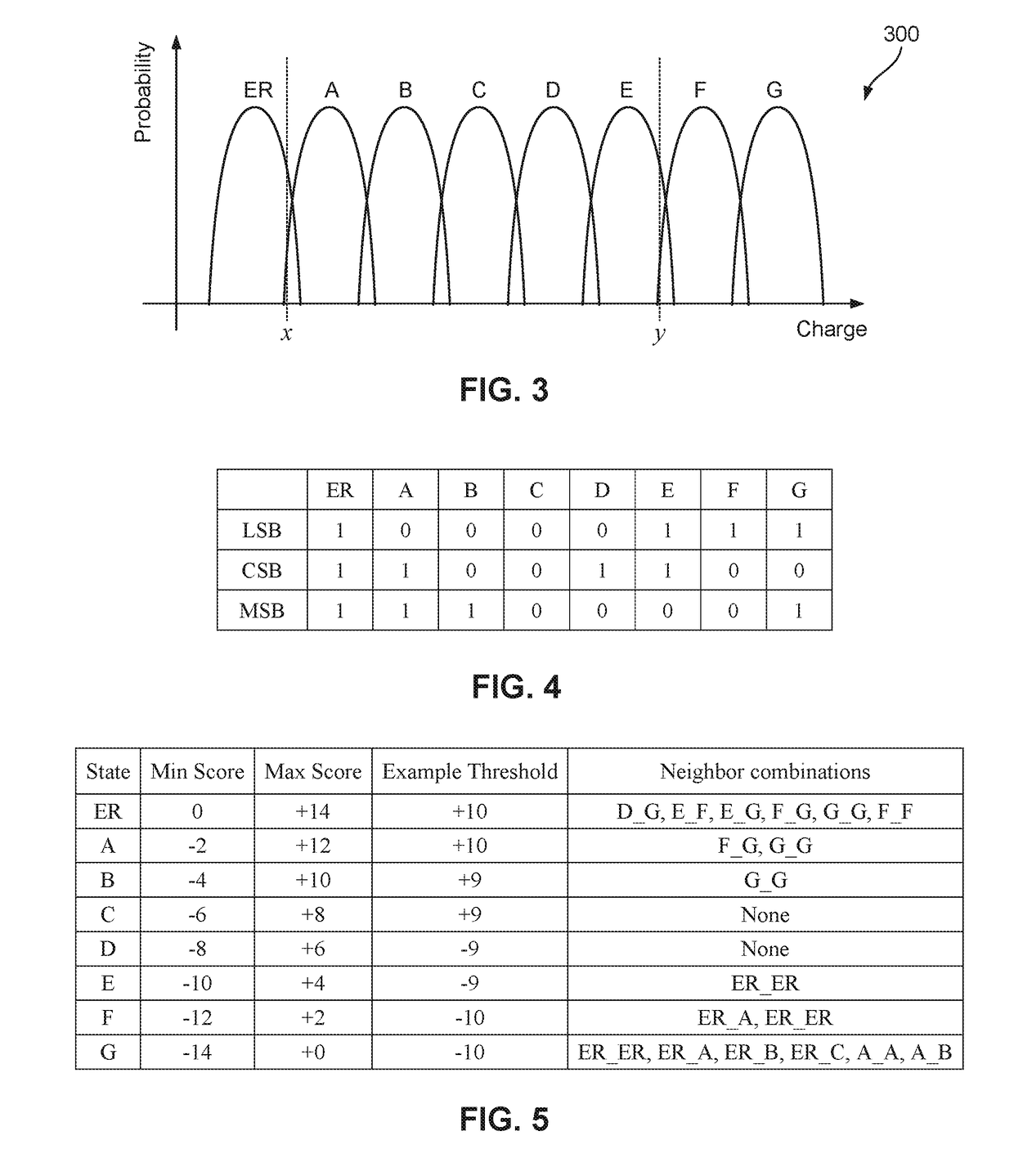
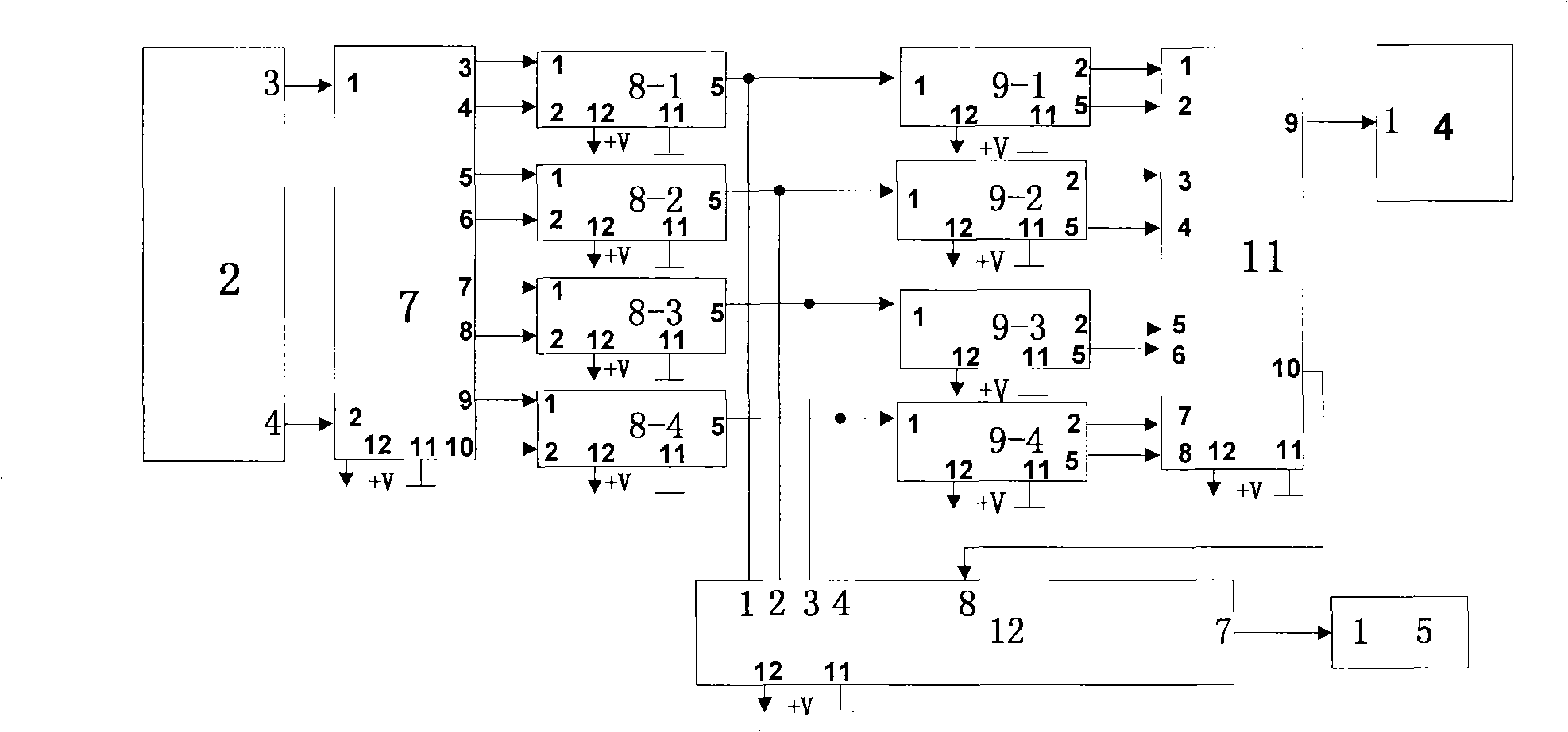
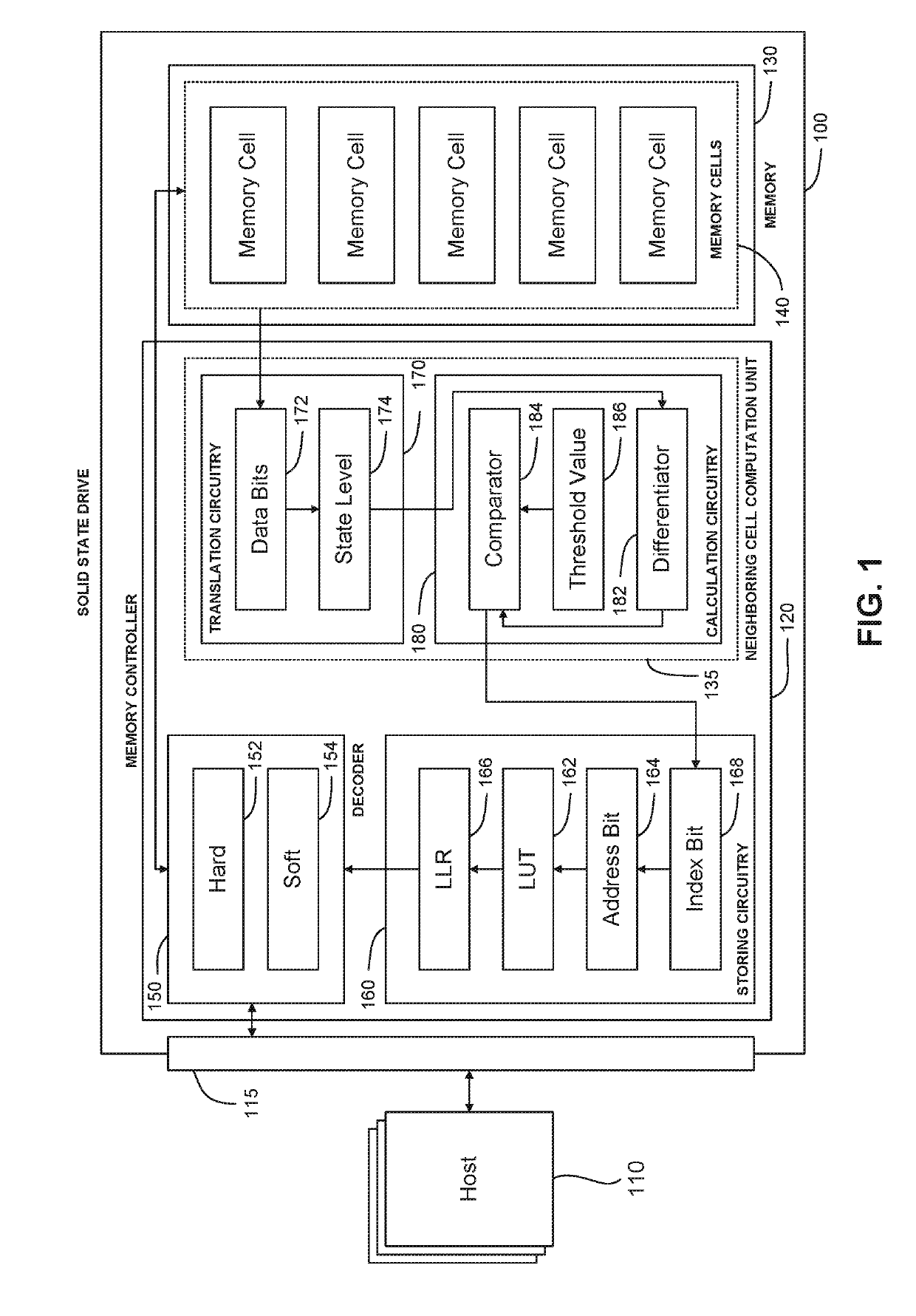
Soft Decision LDPC Decoder With Improved LLR From Neighboring Bits
ActiveUS20190081641A1Input/output to record carriersError detection/correctionSoft-decision decoderLow density
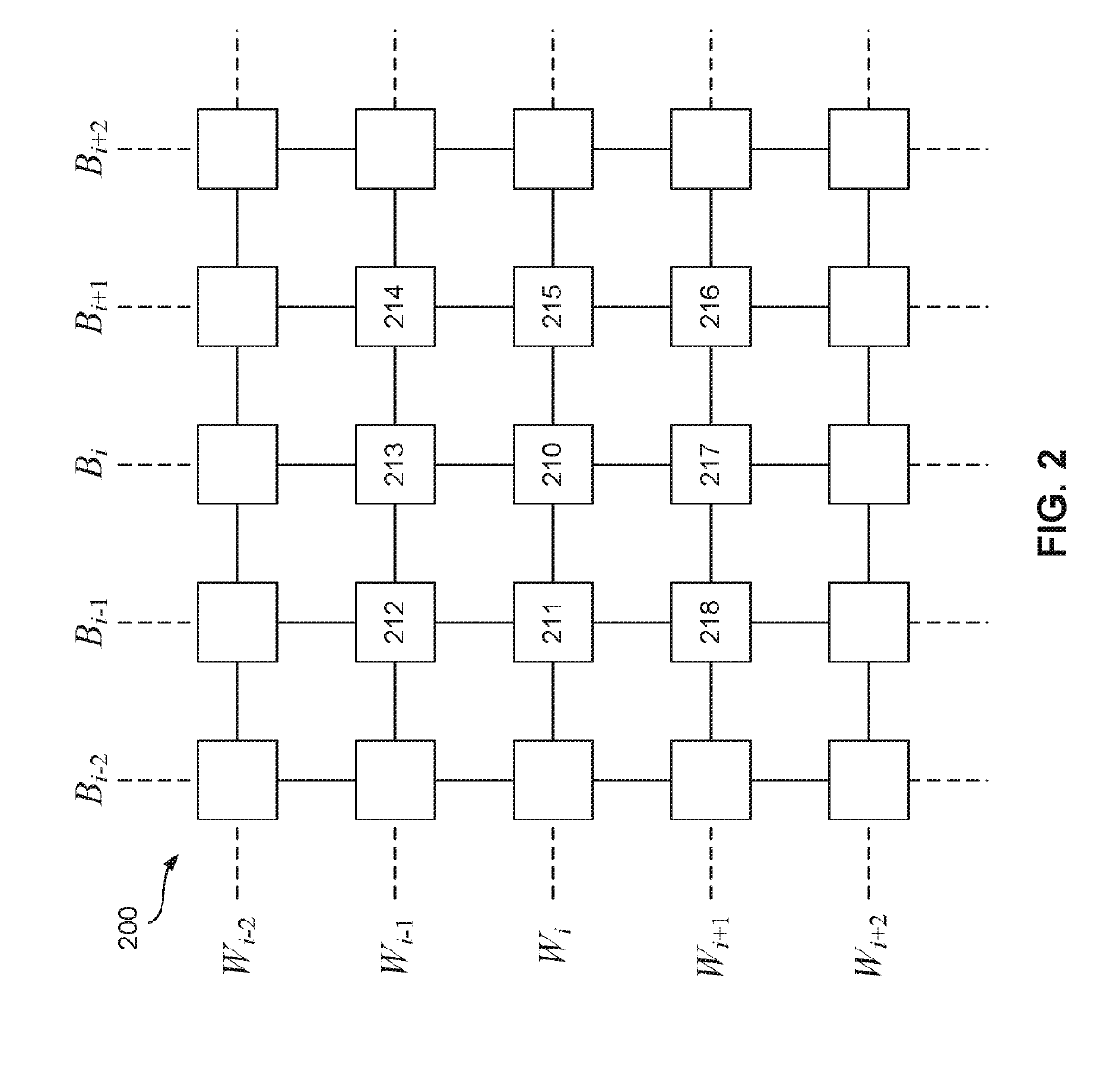
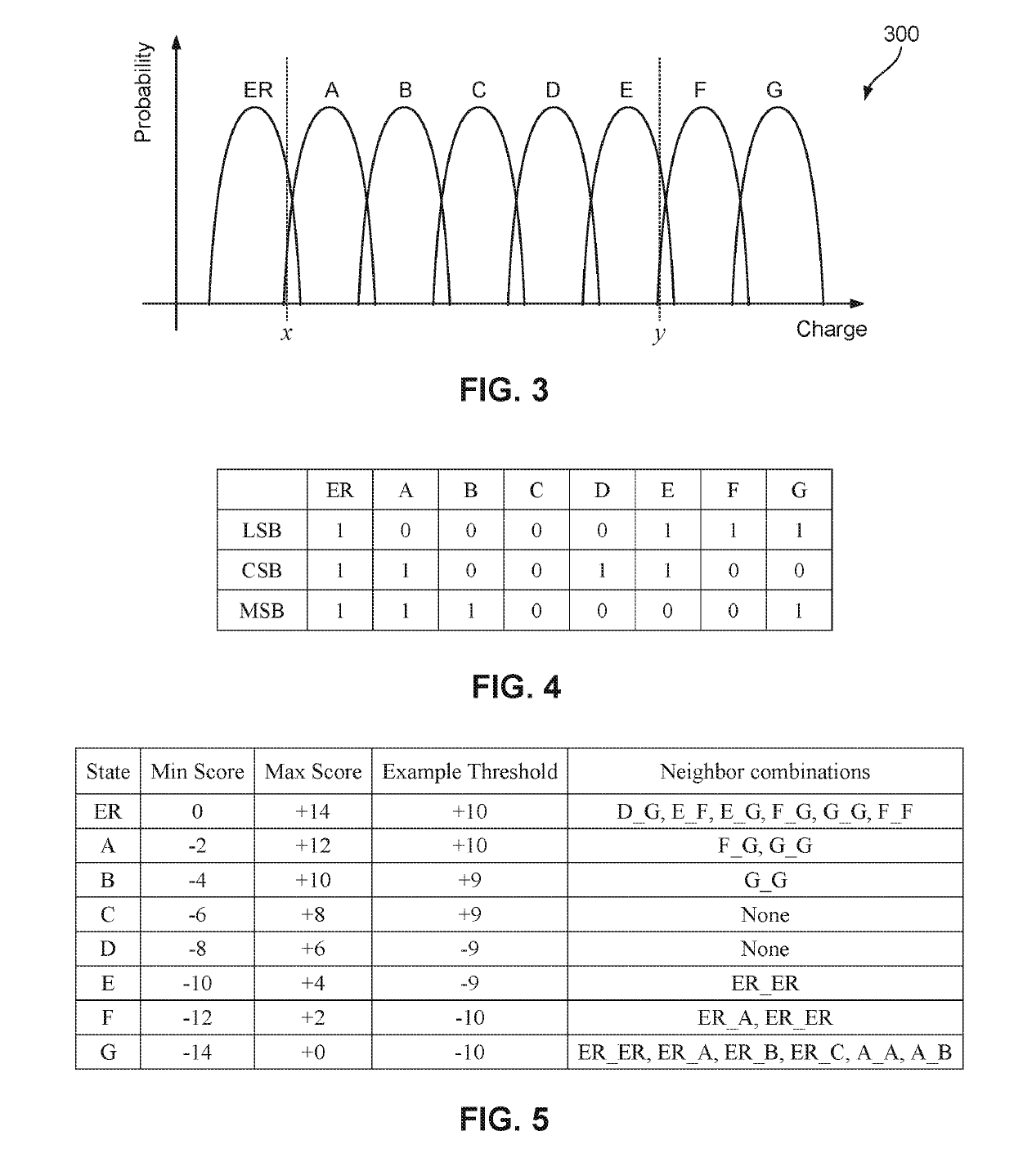
A method of providing, by a controller, a log likelihood ratio (LLR) to a low-density parity check (LDPC) decoder, the method comprising storing, in a non-volatile memory controller, a look-up table for storing LLR values of at least one bit representing a charge state of a cell of the plurality of cells in the memory. The controller determines a cell charge state of the target cell, calculates a value representative of the difference in charge states of the target cell and at least one of a plurality of neighboring cells. The controller compares the calculated value with at least one predetermined threshold value, and sets at least one address bit of an address to the look-up table if the calculated value exceeds the at least one threshold value. The controller extracts a new LLR value from the look-up table, and provides the new LLR value to the LDPC decoder.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Decoding apparatus and decoding method
InactiveUS8640010B2Improve decoding performanceIncrease the amount of calculationOther decoding techniquesError detection/correctionBlock codeSoft-decision decoder
Owner:SONY CORP
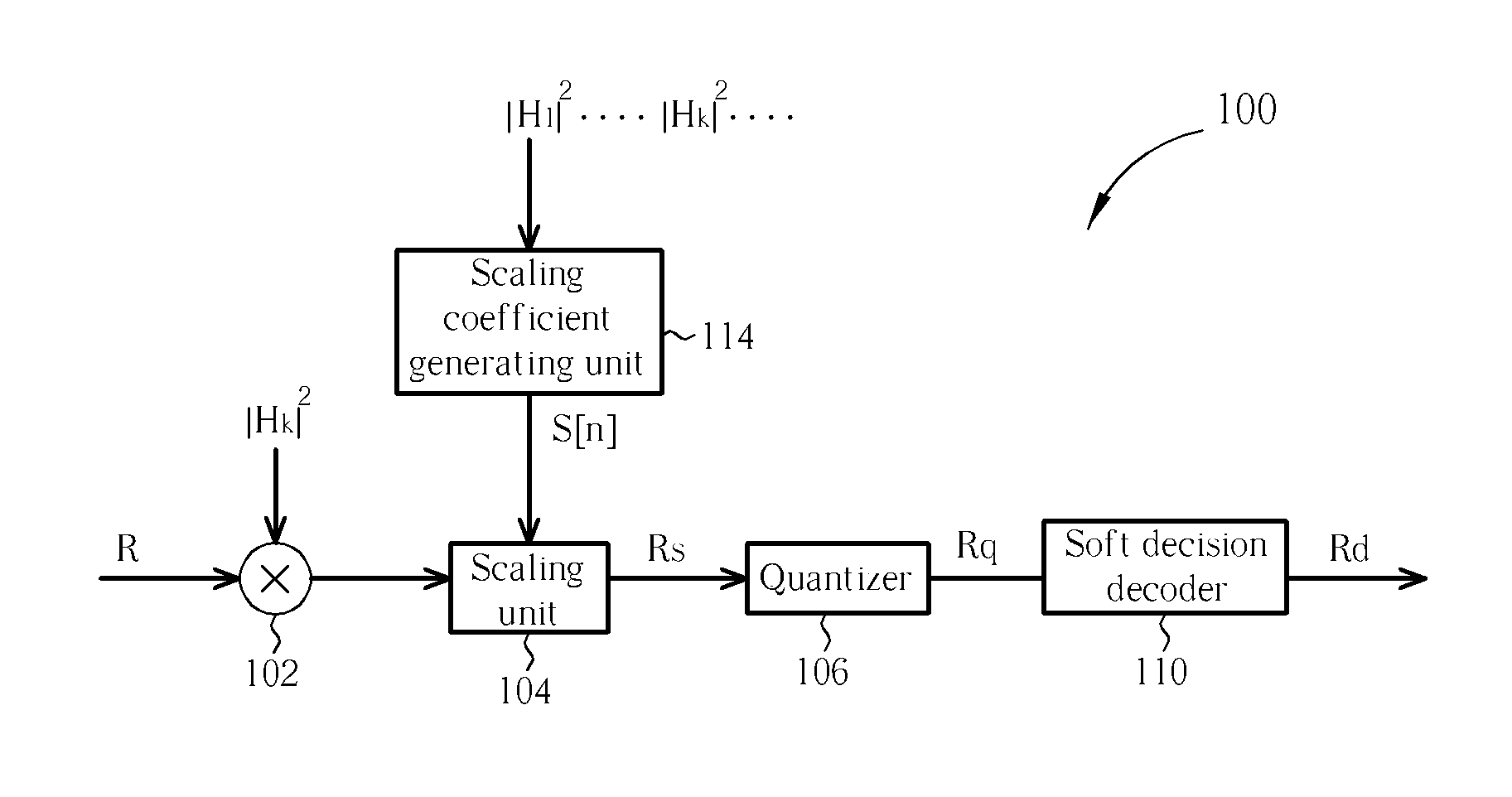
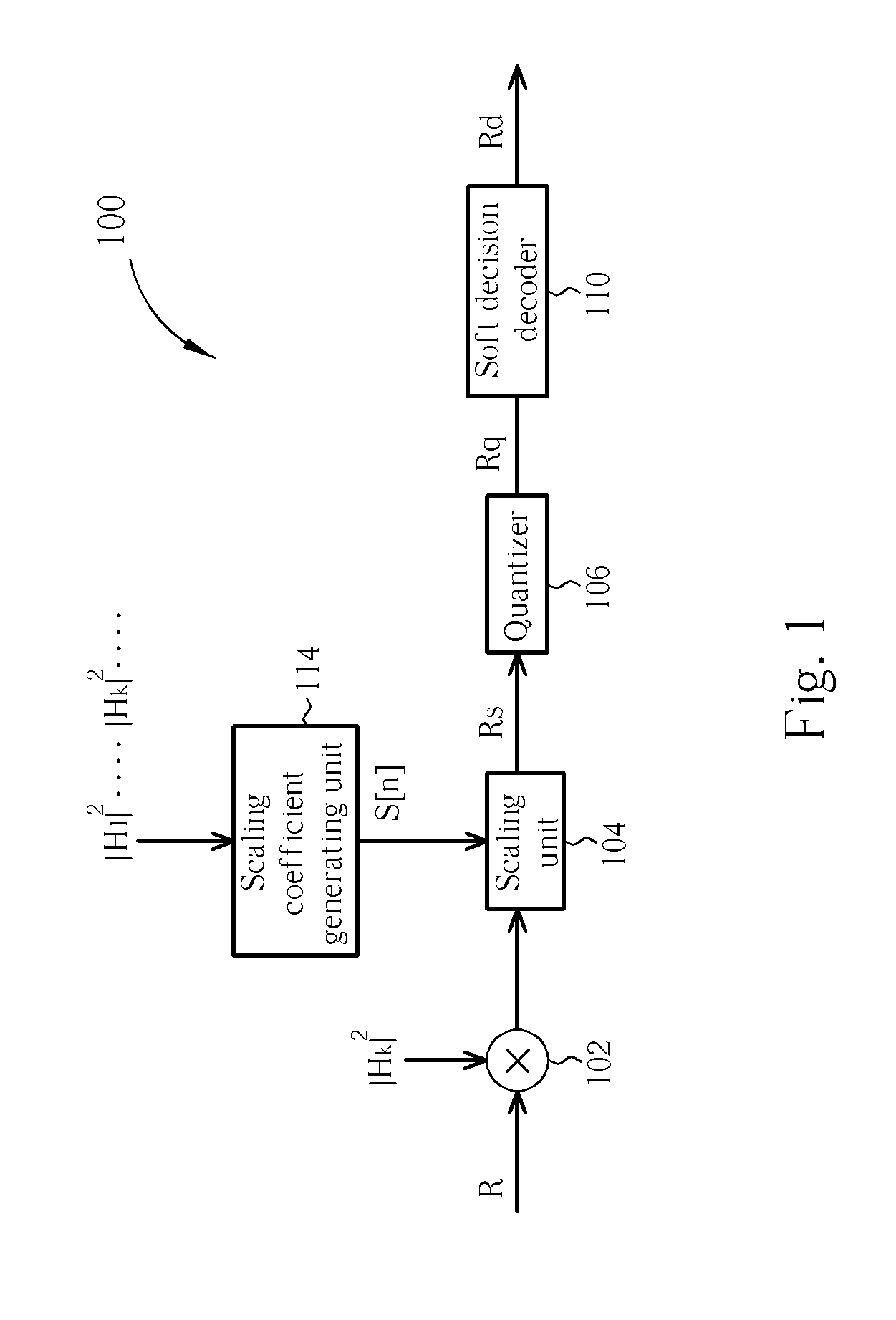
Decoding device and method
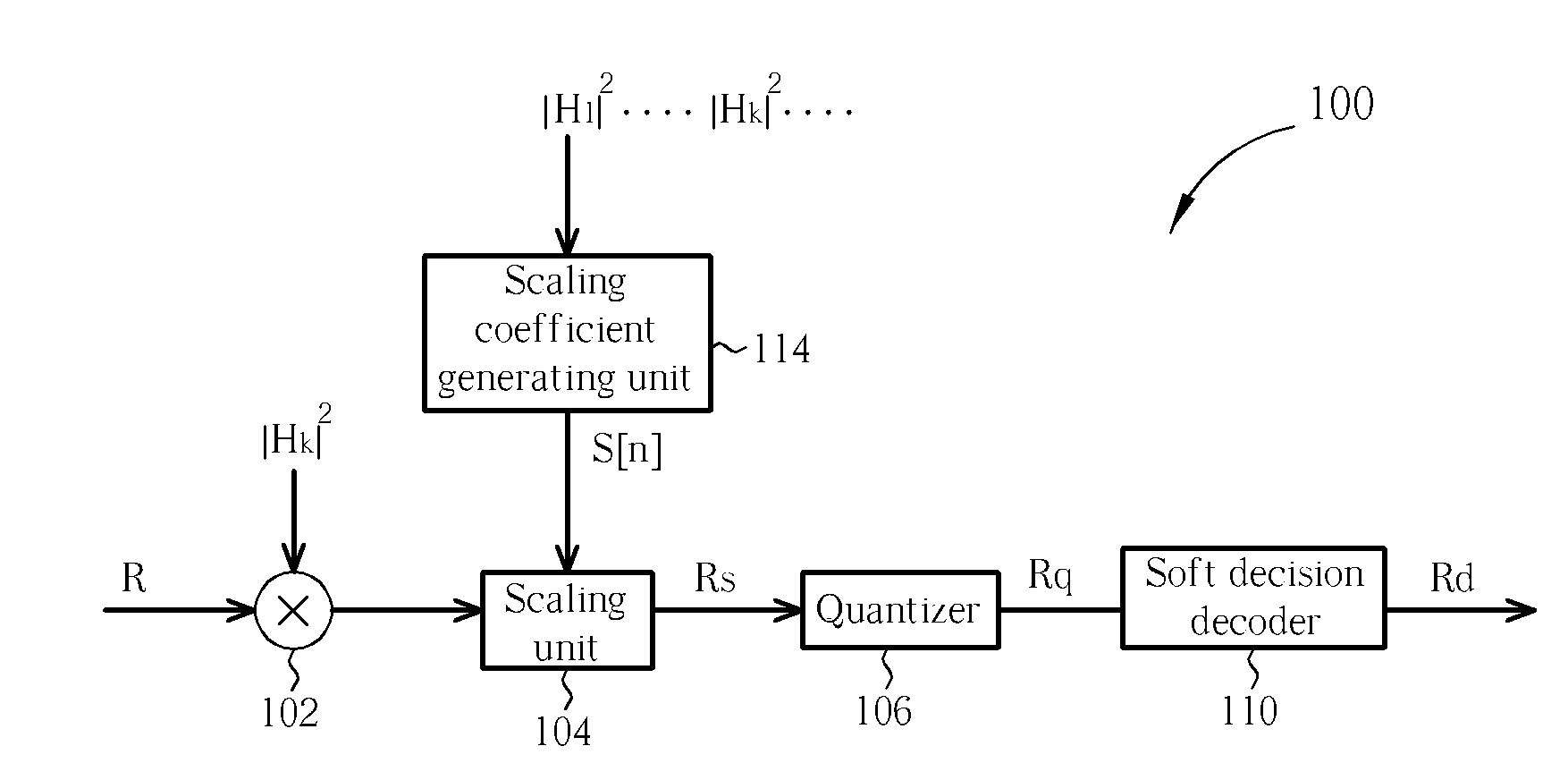
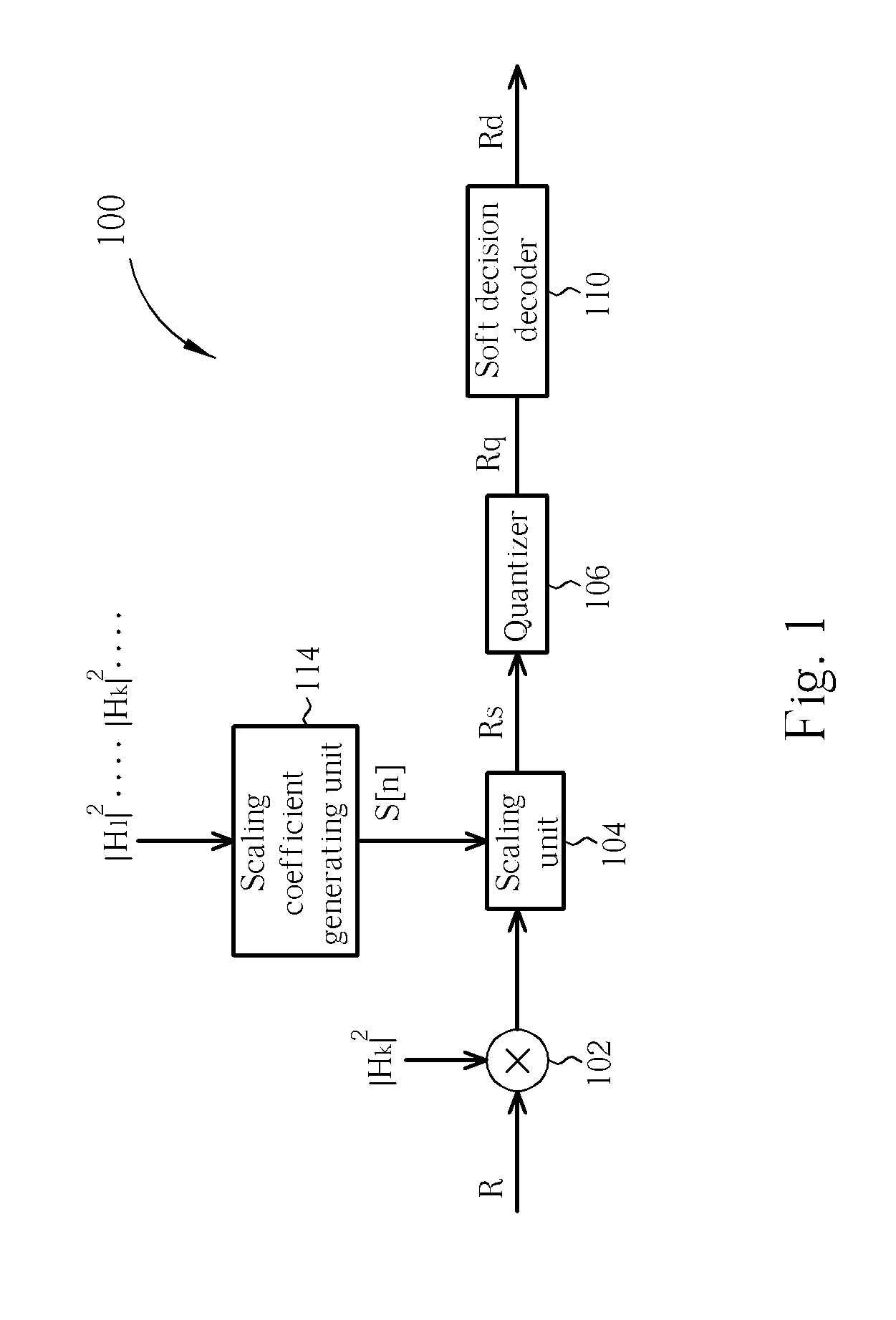
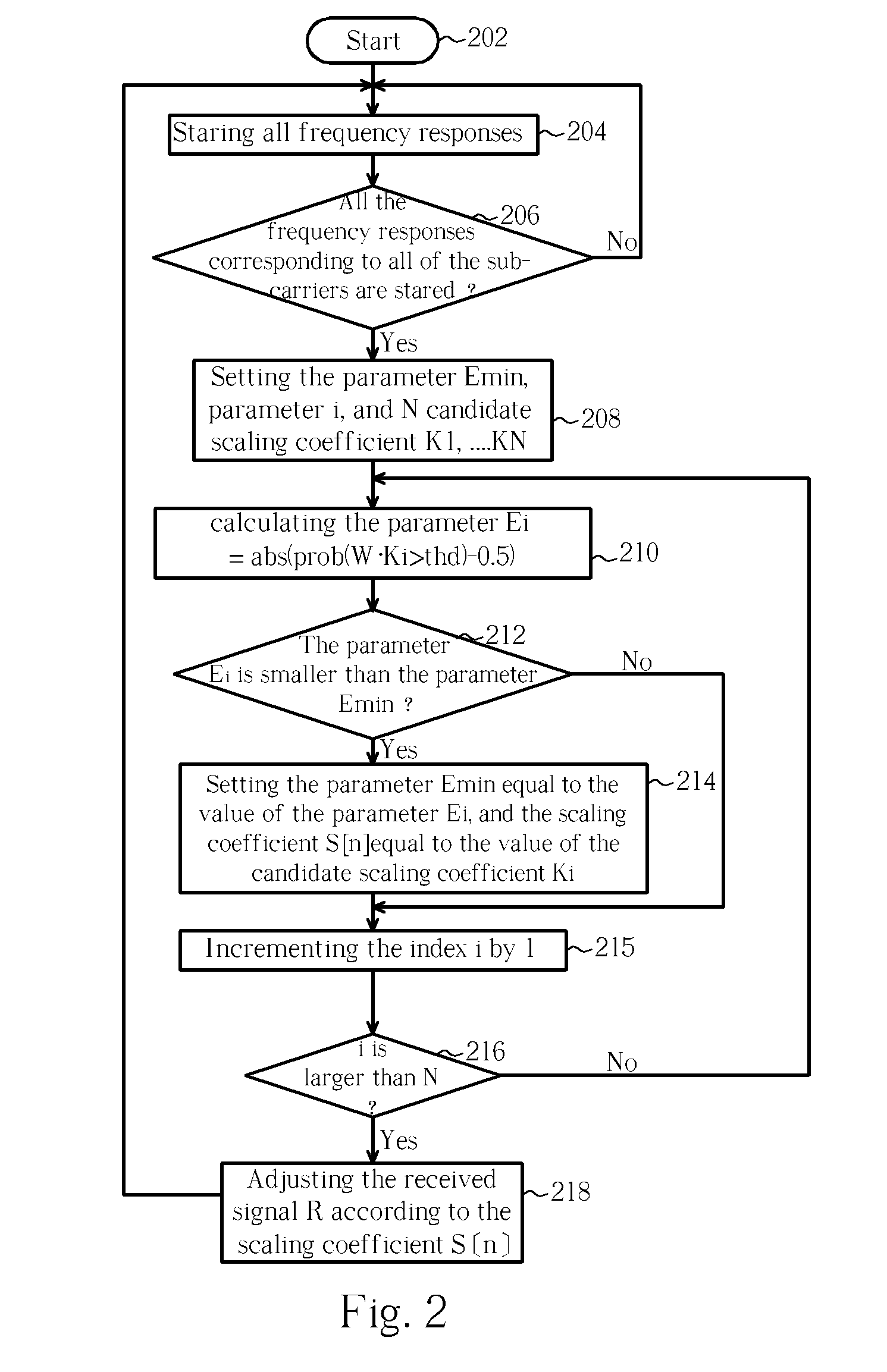
The present invention discloses a decoding device. The decoding device includes a scaling unit for adjusting a received signal according to a scaling coefficient to generate a scaled signal; a quantizer coupled to the scaling unit for generating a quantized signal by quantizing the scaled signal; a soft decision decoder coupled to the quantizer for decoding the quantized signal to generate a decoded signal; and a scaling coefficient generating unit coupled to the scaling unit for generating the scaling coefficient according to a system information of the decoding device.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
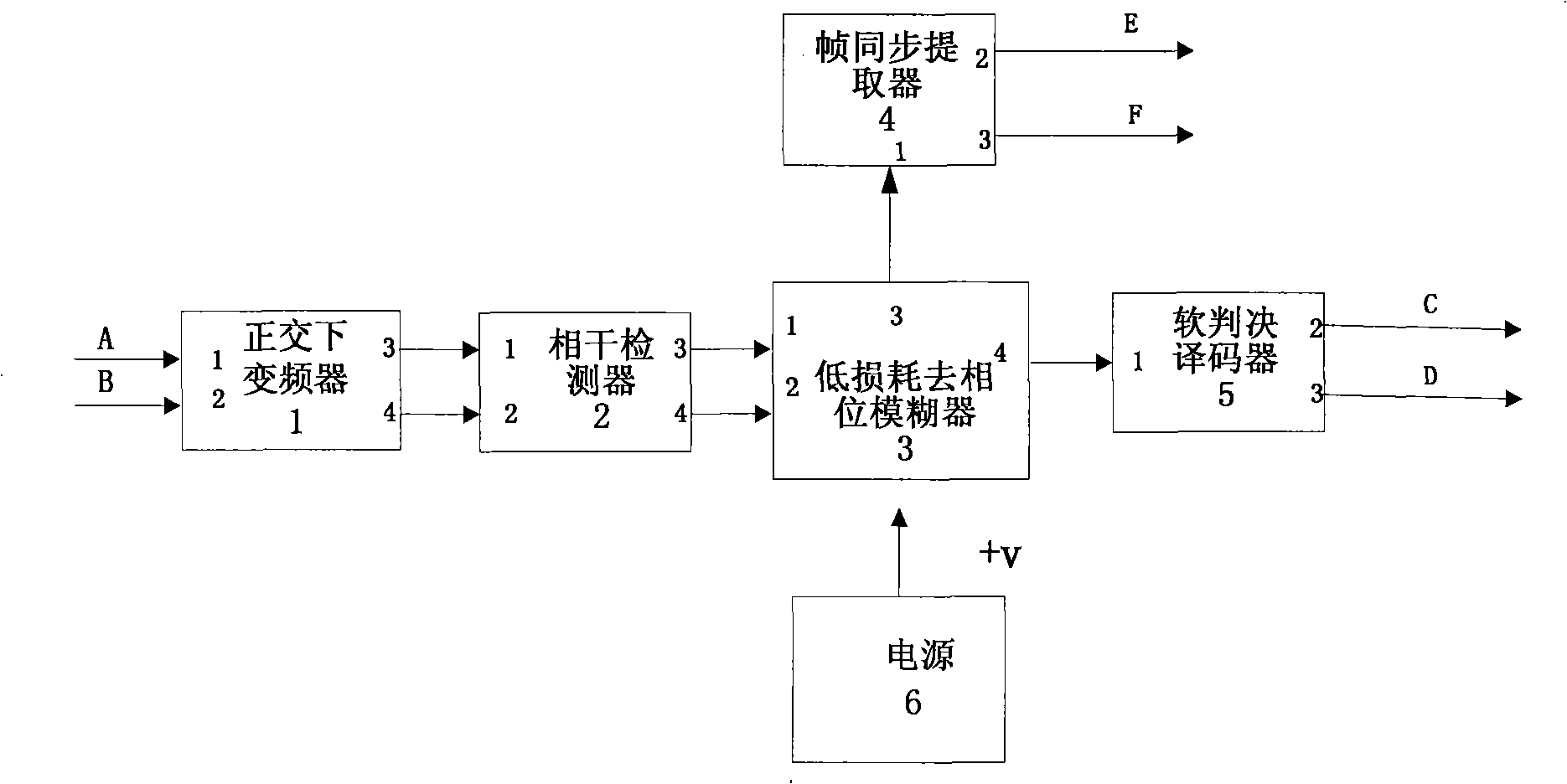
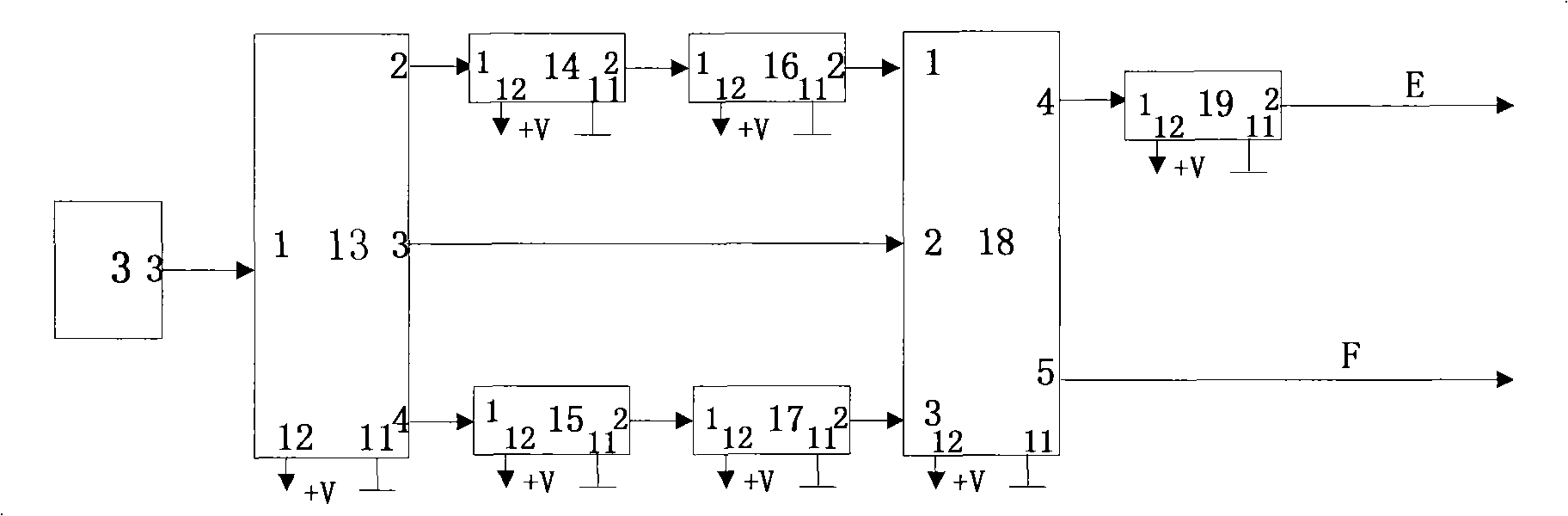
Low loss interface apparatus between combined frame synchronization coherent detection and soft judgment decoding
ActiveCN101345735ALow loss phase deblurringLow phase blurError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsDigital signal processingSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The present invention discloses a low loss interface device between coherent detection of combined frame synchronization and soft-decision decoding, which relates to a digital signal processing apparatus of anti-fading frame synchronization and low signal-noise ratio loss fading phase ambiguity demodulation. The low loss interface device is composed of an orthogonal down converter, a coherent detector, a soft-decision decoder, a low loss phase ambiguity demodulator, a frame synchronization extractor, a power supply and other components. The low loss interface device adopts a digital signal processing technique, uses frame header information of an encoder / decoder to perform phase recognizing, combines frame synchronization extraction and realizes the low loss interface between the low loss interface between the coherent detection and soft-decision decoder. And the present invention also has features of simple circuit structure, high integration degree, stabilized and reliable performance, portability, low-cost and so on. The low loss interface device is specially suitable as an interface circuit device between the coherent detection and soft-decision decoding in the long-term fading large-capacity communicating system required for low signal-noise ratio loss.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Soft decision LDPC decoder with improved LLR from neighboring bits
ActiveUS10340951B2Input/output to record carriersError detection/correctionSoft-decision decoderLow density
A method of providing, by a controller, a log likelihood ratio (LLR) to a low-density parity check (LDPC) decoder, the method comprising storing, in a non-volatile memory controller, a look-up table for storing LLR values of at least one bit representing a charge state of a cell of the plurality of cells in the memory. The controller determines a cell charge state of the target cell, calculates a value representative of the difference in charge states of the target cell and at least one of a plurality of neighboring cells. The controller compares the calculated value with at least one predetermined threshold value, and sets at least one address bit of an address to the look-up table if the calculated value exceeds the at least one threshold value. The controller extracts a new LLR value from the look-up table, and provides the new LLR value to the LDPC decoder.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Decoding device and method
The present invention discloses a decoding device. The decoding device includes a scaling unit for adjusting a received signal according to a scaling coefficient to generate a scaled signal; a quantizer coupled to the scaling unit for generating a quantized signal by quantizing the scaled signal; a soft decision decoder coupled to the quantizer for decoding the quantized signal to generate a decoded signal; and a scaling coefficient generating unit coupled to the scaling unit for generating the scaling coefficient according to a system information of the decoding device.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Method of soft decision decoding and apparatus for soft decision decoding
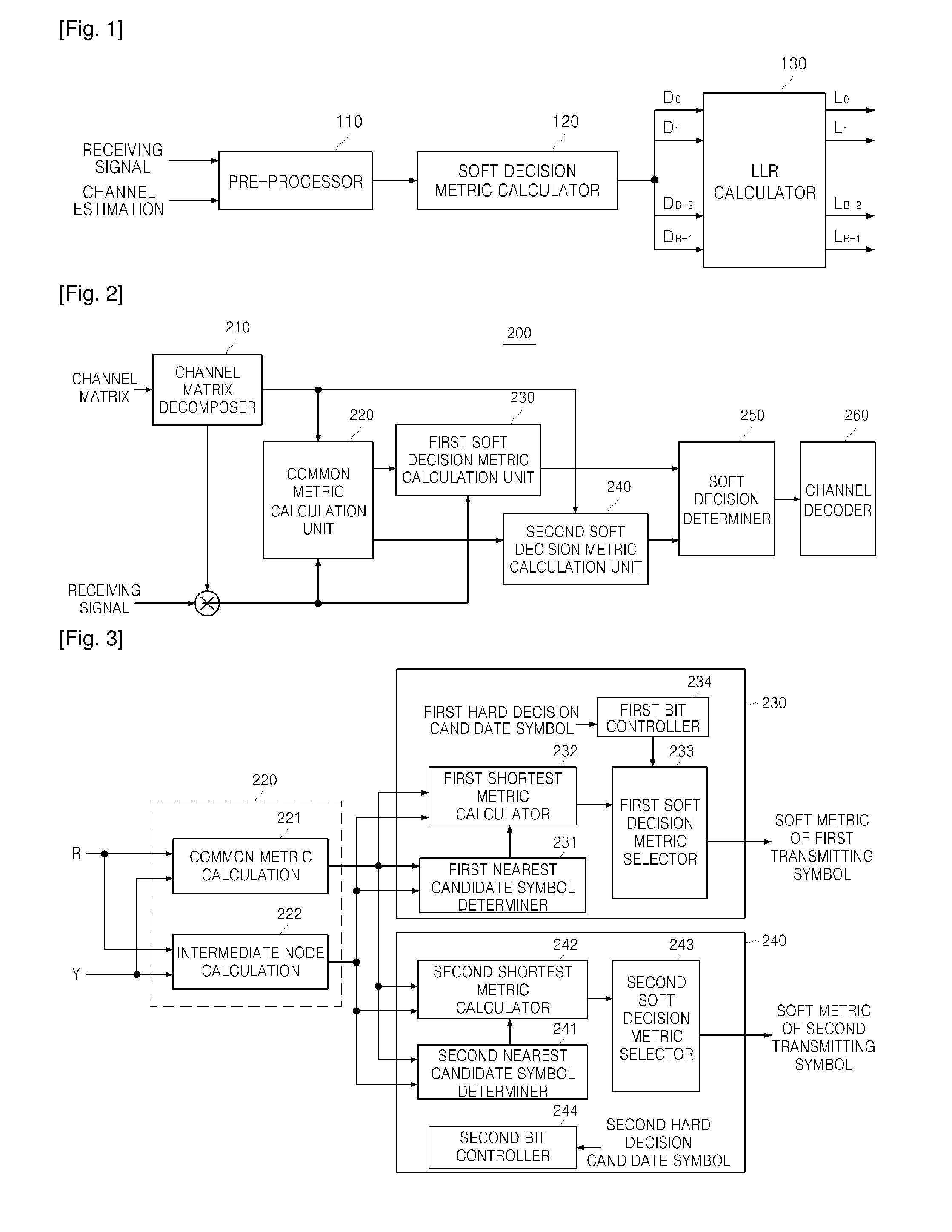
ActiveUS20100272200A1Reduce the amount of calculationReduce complexityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsData streamShortest distance
A soft decision decoding method in a multiple-input multiple-output system which respectively receives two simultaneously transmitted data streams, a first transmitting symbol and a second transmitting symbol, in a first receiving signal and a second receiving signal is provided. The soft decision decoding method includes calculating common metrics corresponding to distances between first candidate symbols, which correspond to combinations of all bits that the first transmitting symbol can have, and the first receiving signal using a channel matrix corresponding to a communication channel through which the first and second transmitting symbols are transmitted and determining intermediate nodes between the second receiving signal and the first candidate symbols and nodes between the second receiving signal and second candidate symbols corresponding to combinations of all bits that the second transmitting symbol can have; selecting first nearest candidate symbols that are at a shortest distance from the intermediate nodes on a signal constellation from among the second candidate symbols and determining a soft decision metric for each bit value of the first transmitting symbol based on the first nearest candidate symbols and the common metrics; and determining second nearest candidate symbols based on a logic value of a predetermined bit of each of the second candidate symbols and the positions of the intermediate nodes on the signal constellation and determining a soft decision metric for each bit value of the second transmitting symbol using the second nearest candidate symbols and the common metrics.
Owner:I&C TECH
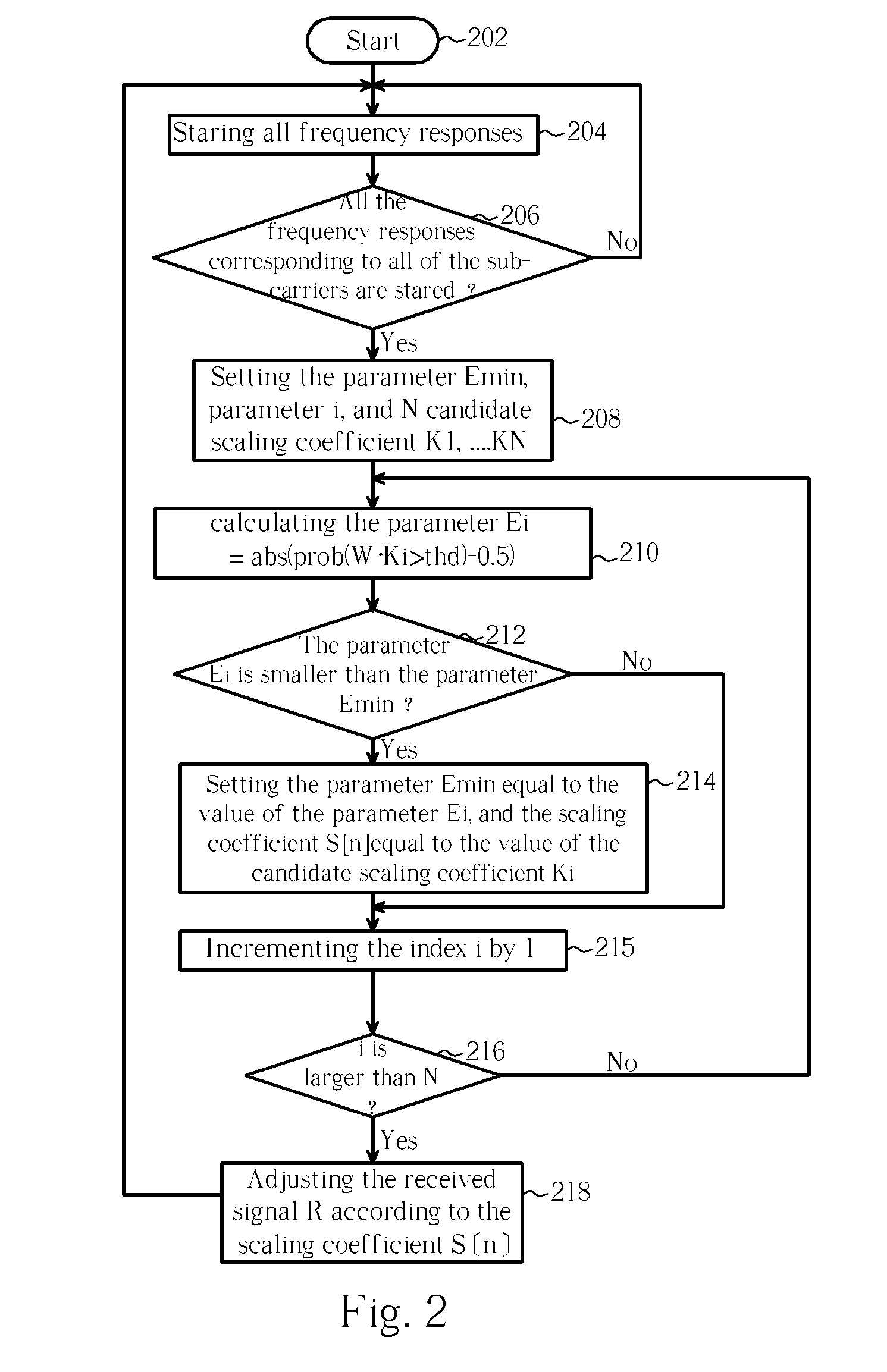
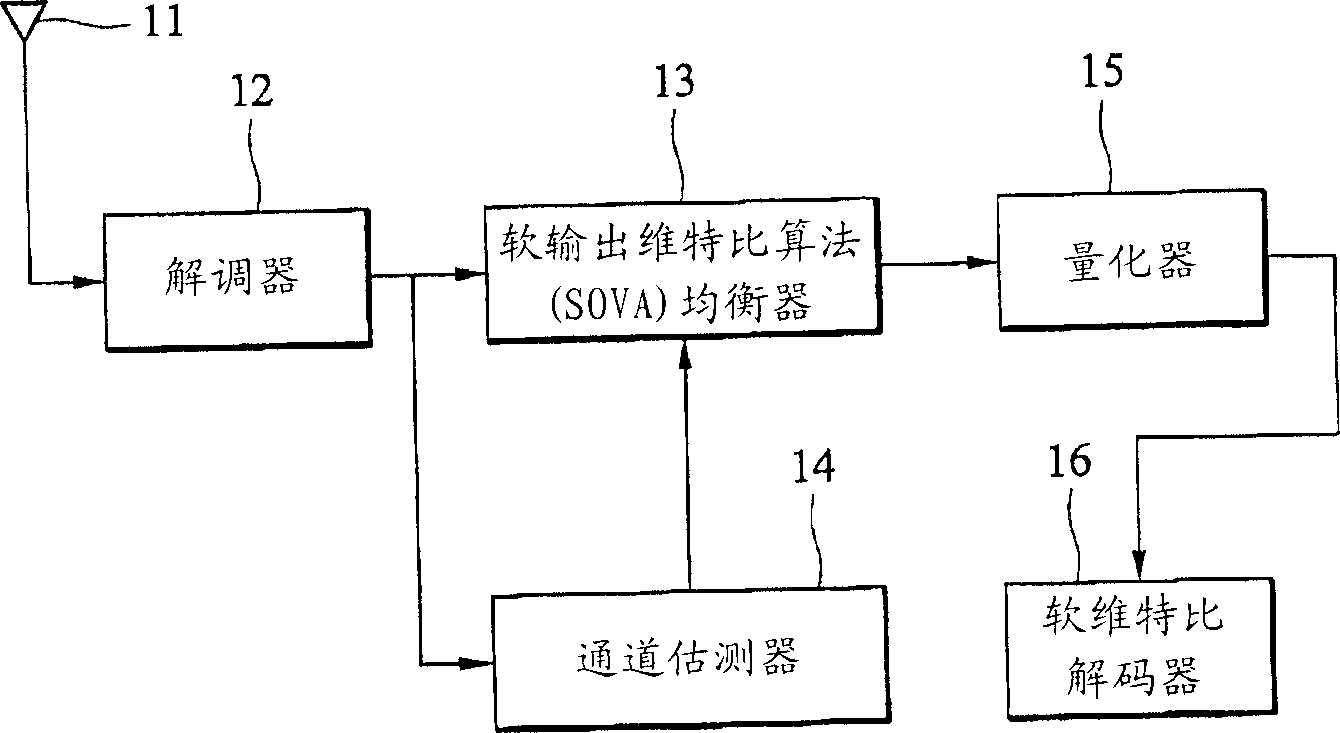
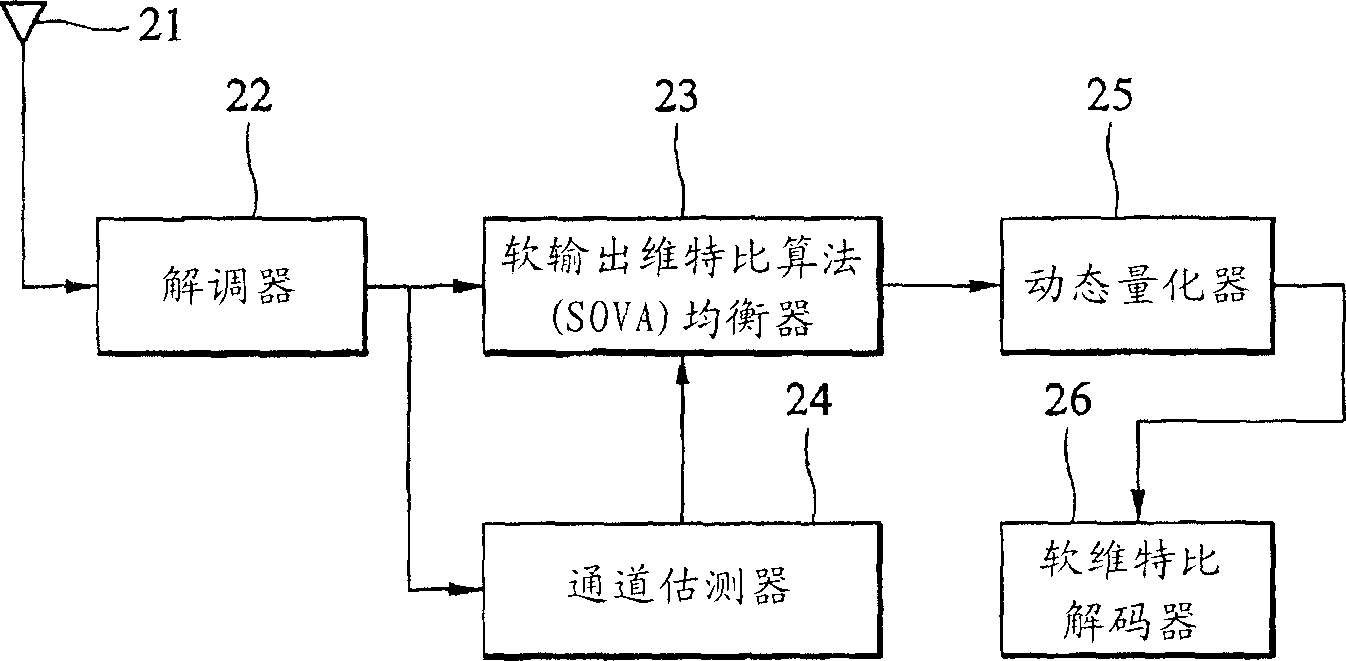
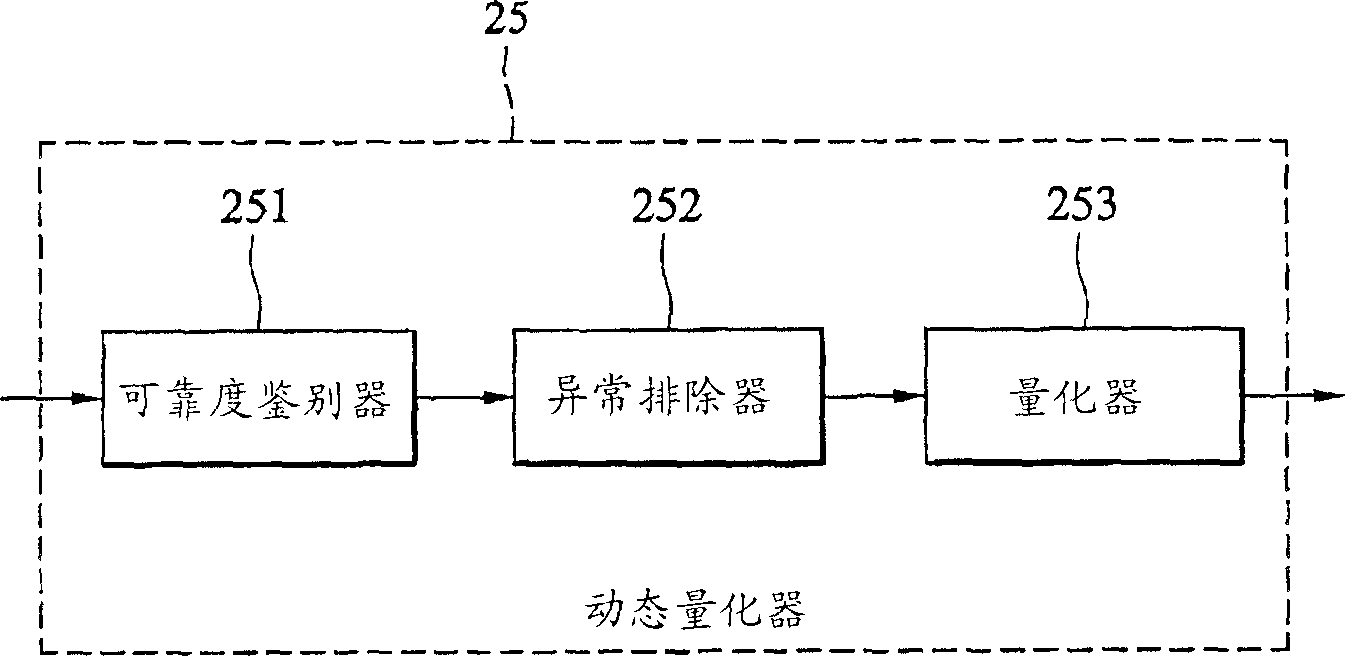
Methods and devices for dynamic quantizing input of a soft decision decoder
Dynamic quantization methods and dynamic quantizers for quantizing soft outputs of an equalizer according to the channel condition in order to alleviate the computational load on a soft decision decoder. The dynamic quantizer assigns only a few bits to represent the equalized signals when the channel condition is good, thus reducing computational burden on the soft decision decoder.
Owner:BENQ CORP
Method for generating soft decision measurement in Turbo-STBC system
InactiveCN103326968ASolve the problem of high implementation complexityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSoft-decision decoderComputer science
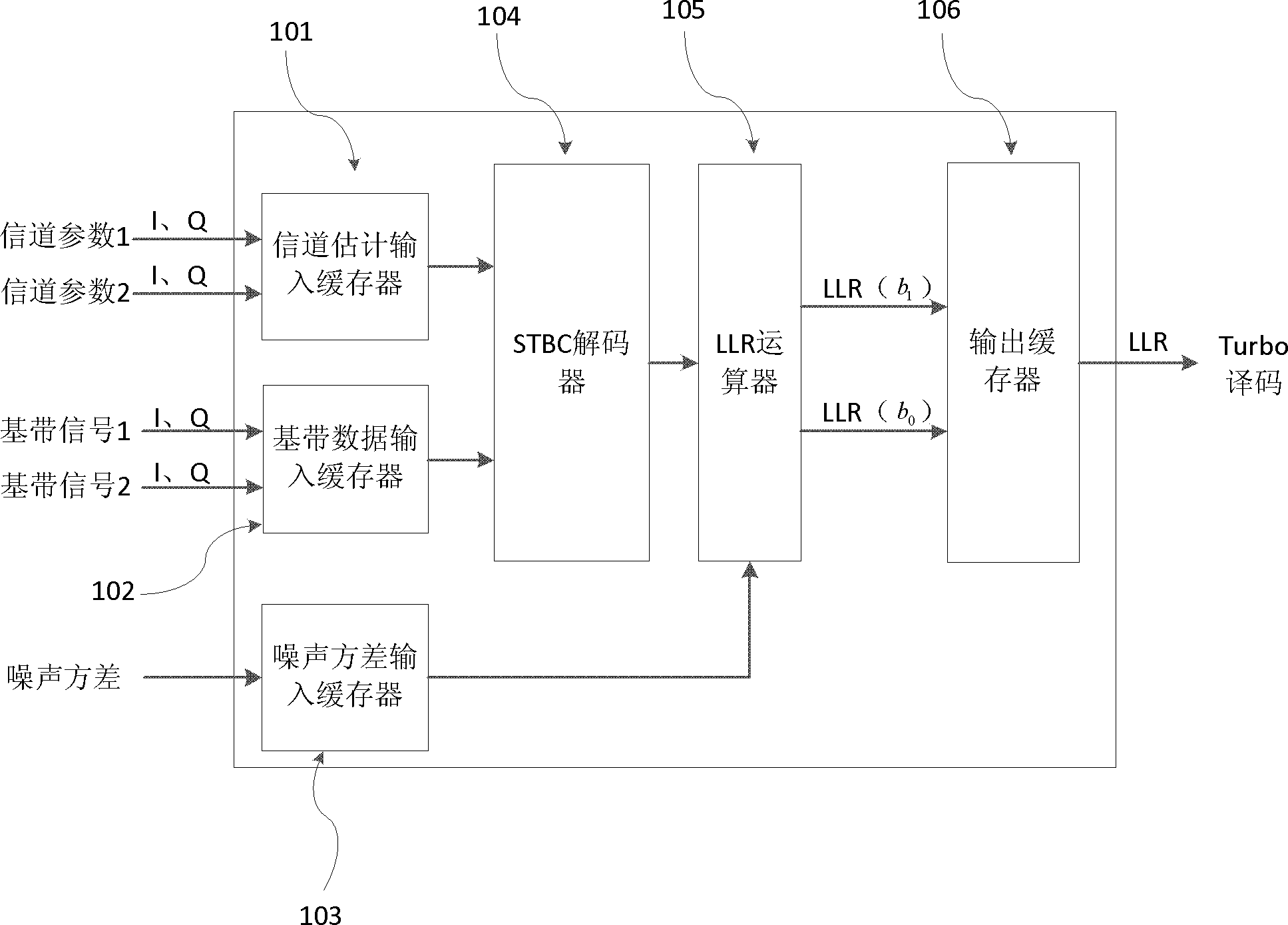
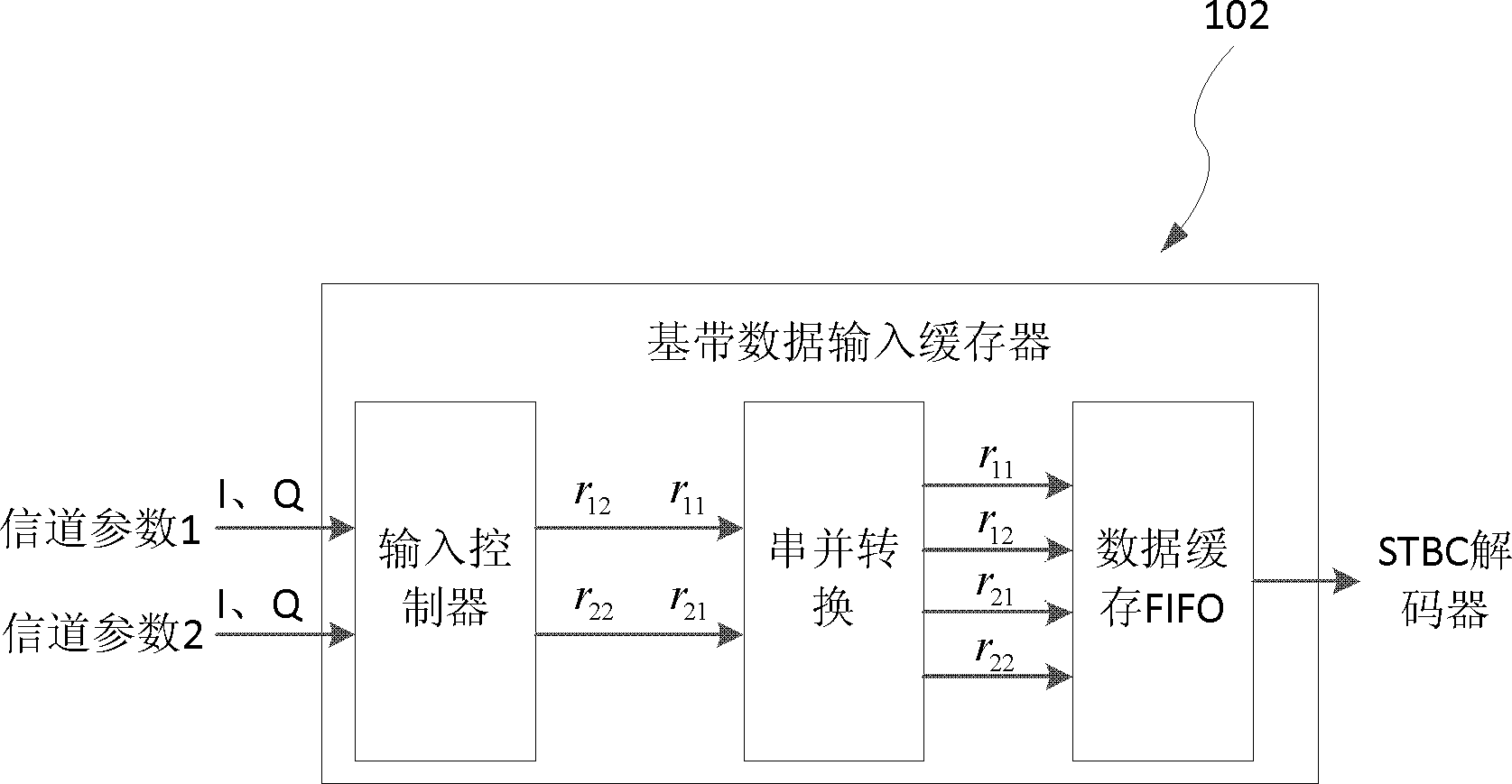
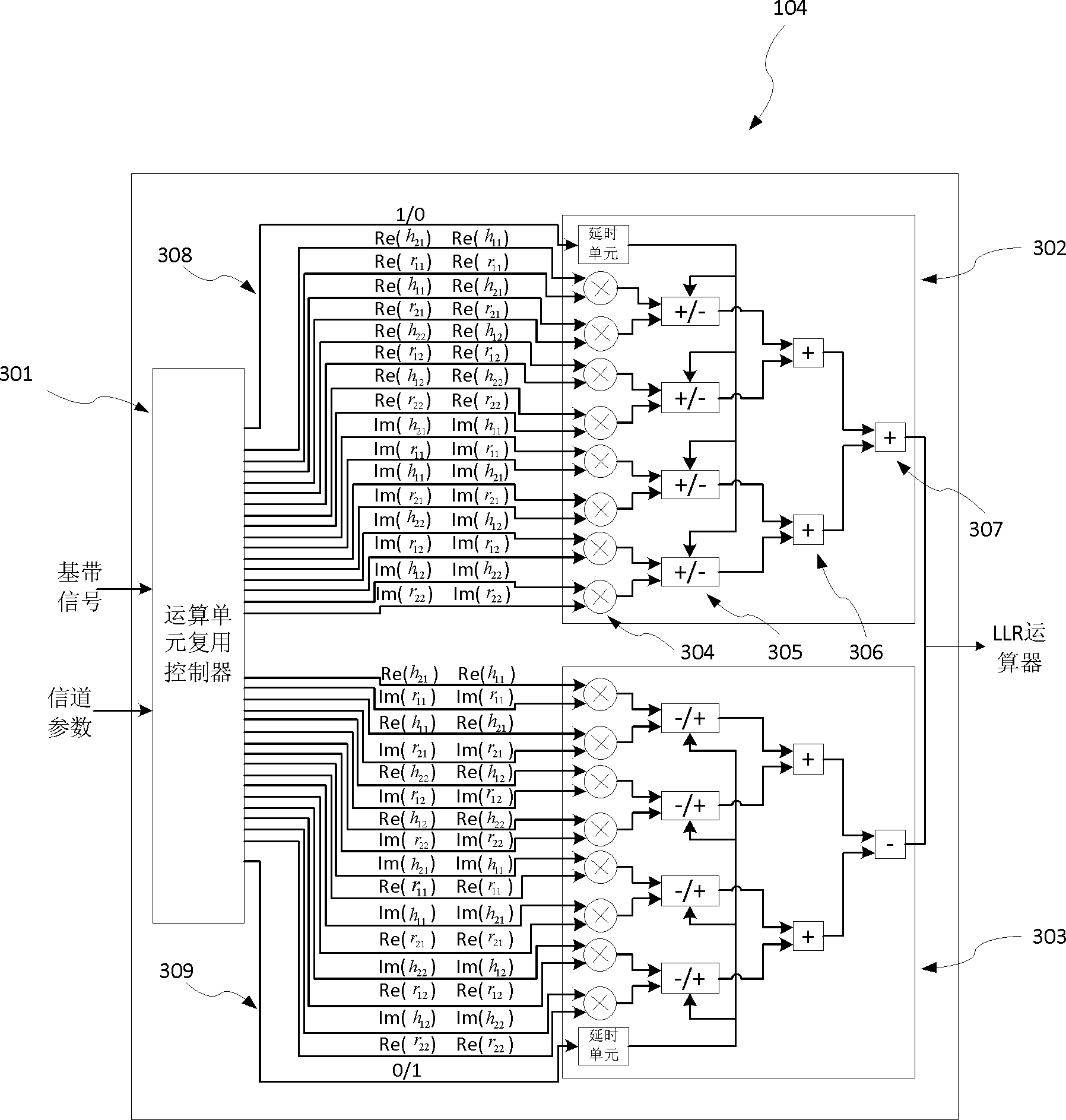
The invention provides a method for generating LLR soft decision measurement in a Turbo-STBC system, wherein the Turbo-STBC system is composed of two transmitting antennas and two receiving antennas. The method is achieved through the fact that an LLR generator module is designed to be arranged on an FPGA. In a Turbo-STBC cascade system, an LLR generator enables baseband signals of a receiving end to be decoded through an STBC decoder and then inputs the baseband signals to an LLR arithmetic unit for calculations, and generated LLR soft decision measurement is used as the input of a follow-up Turbo soft decision decoder for conducting Turbo decoding. When an internal arithmetic module is designed, a parallel arithmetic idea is completely used, and the throughput of the system is improved. A hardware reusing technology is used in the design of the STBC decoder, the arithmetic unit function is guaranteed to be achieved, and meanwhile the consumption to hardware resources of the arithmetic unit is saved. A simple algorithm is used in the design of the LLR arithmetic unit, and compared with a traditional algorithm, the complexity for achieving arithmetic unit hardware is lowered.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com