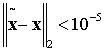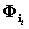Blind reconstructing method of block sparse signal with unknown block size
A block sparse and block size technology, applied in the field of block sparse signal reconstruction, can solve problems such as high complexity, over-matching, and difficulty in obtaining, and achieve the effect of blind reconstruction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
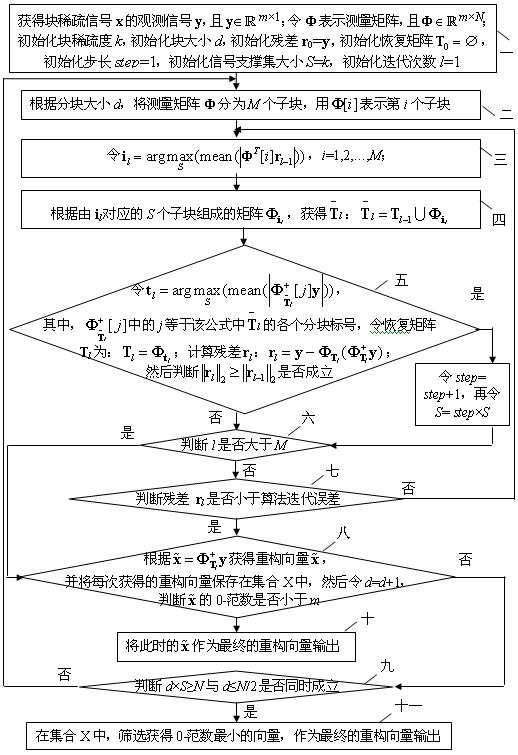
[0023] Specific implementation mode one : the blind reconstruction method of the block sparse signal of unknown block size of the present embodiment, its specific process is as follows:
[0024] Step 1. Obtain block sparse signal x observation signal y ,and y ;make Φ represents the measurement matrix, and ; Initialize block sparsity k , the initial block size d , initialize the residual r 0 = y , initialize the recovery matrix , the initial step size step =1, initialize the signal support set size S = k , the number of initialization iterations l =1;
[0025] Step 2. According to the block size d , will measure the matrix Φ Divided into M block, use Indicates the first i sub-block;
[0026] Step three, order , i =1,2,…, M ;
[0027] The meaning of this formula is: first obtain and multiplied by , to get a The vector of this vector N The elements are divided into blocks according to the block method of the block vector M block, then find ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Specific implementation mode two: This embodiment is a further description of the blind reconstruction method of the block sparse signal whose block size is unknown in Embodiment 1. The block sparsity described in step 1 k The initialized range is ,in K is the true block sparsity of the source signal.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0042] Specific implementation mode three: This embodiment is a further description of the blind reconstruction method of the block sparse signal whose block size is unknown in the second embodiment, the block sparsity k Initialized to 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com