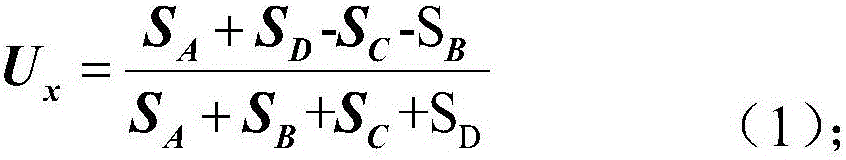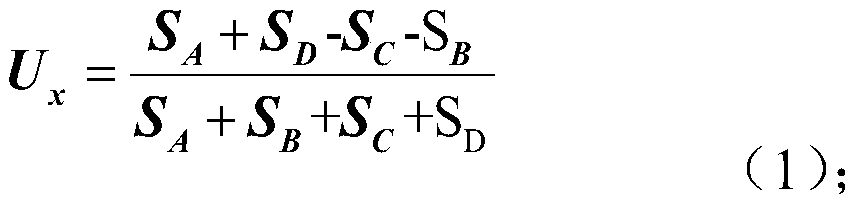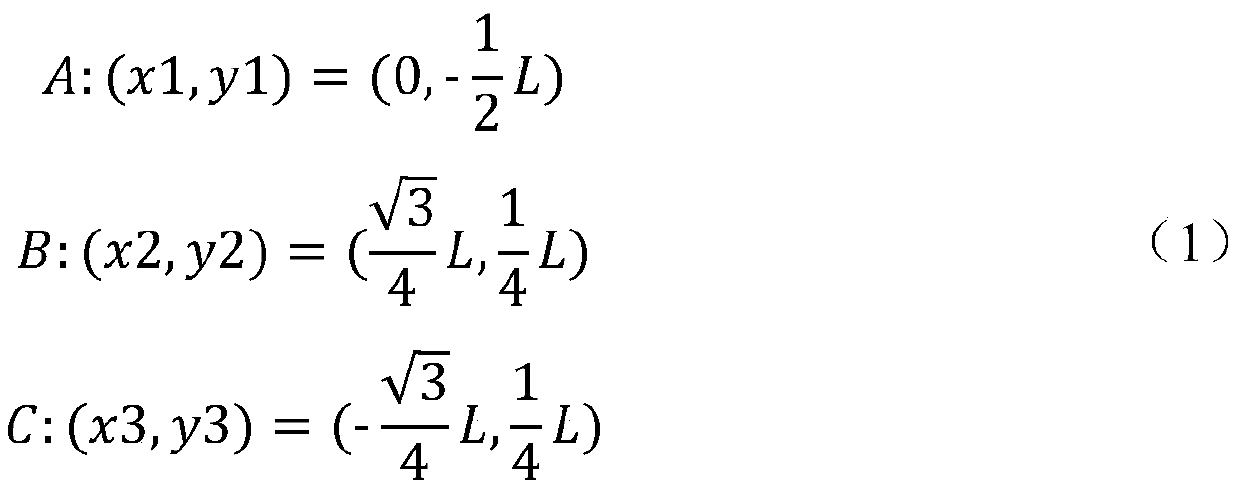Patents
Literature
31 results about "Antenna boresight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
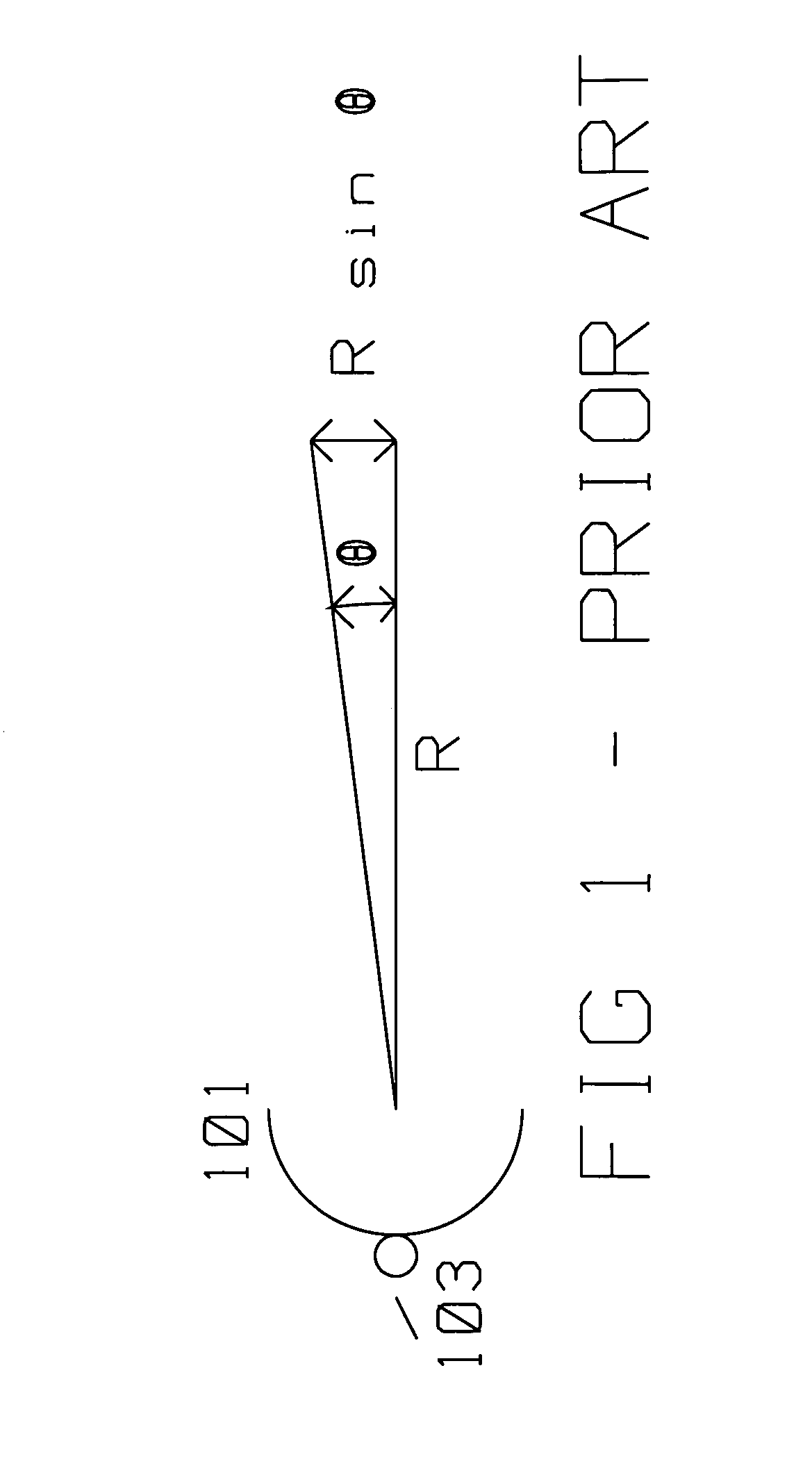
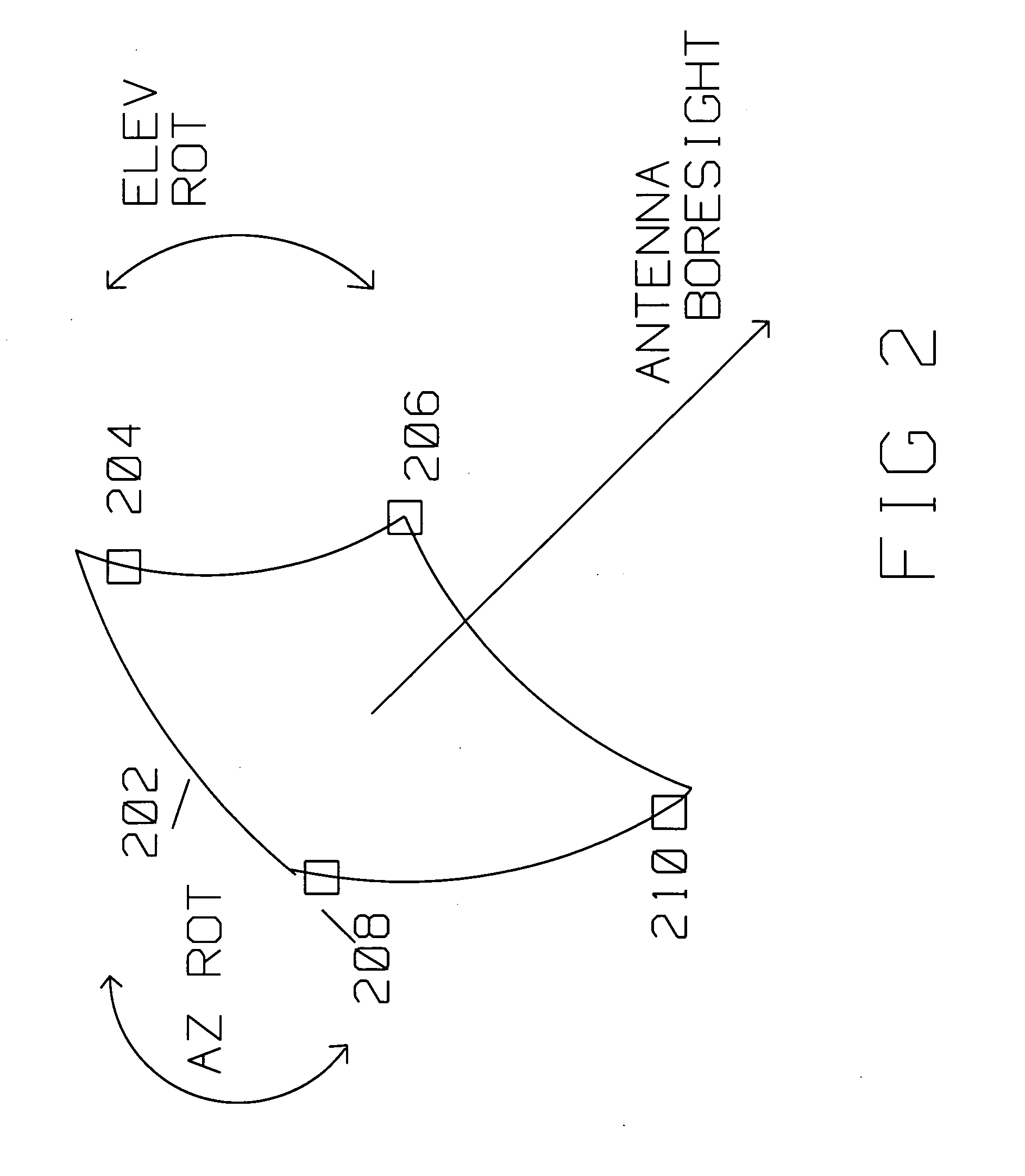
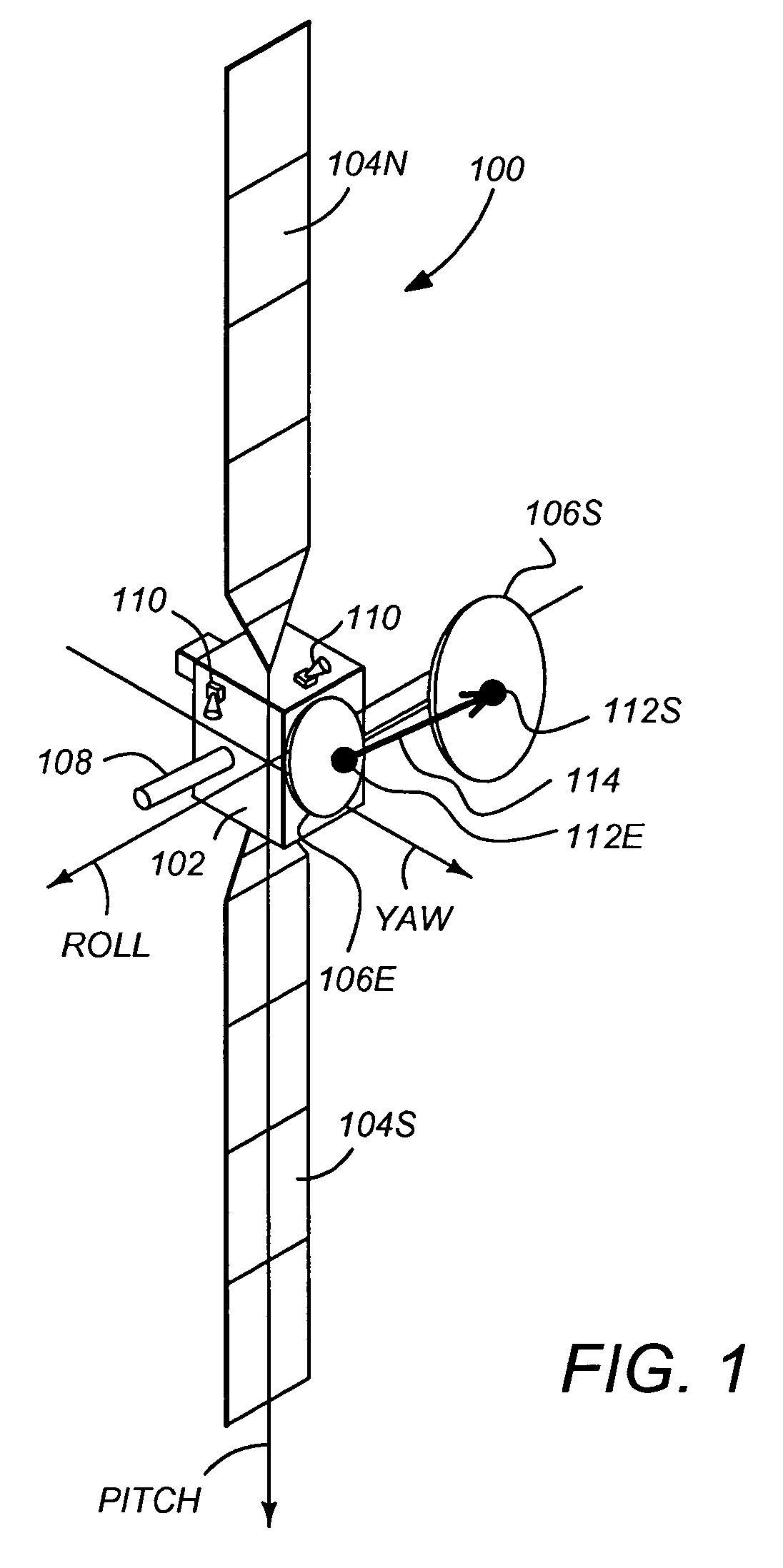
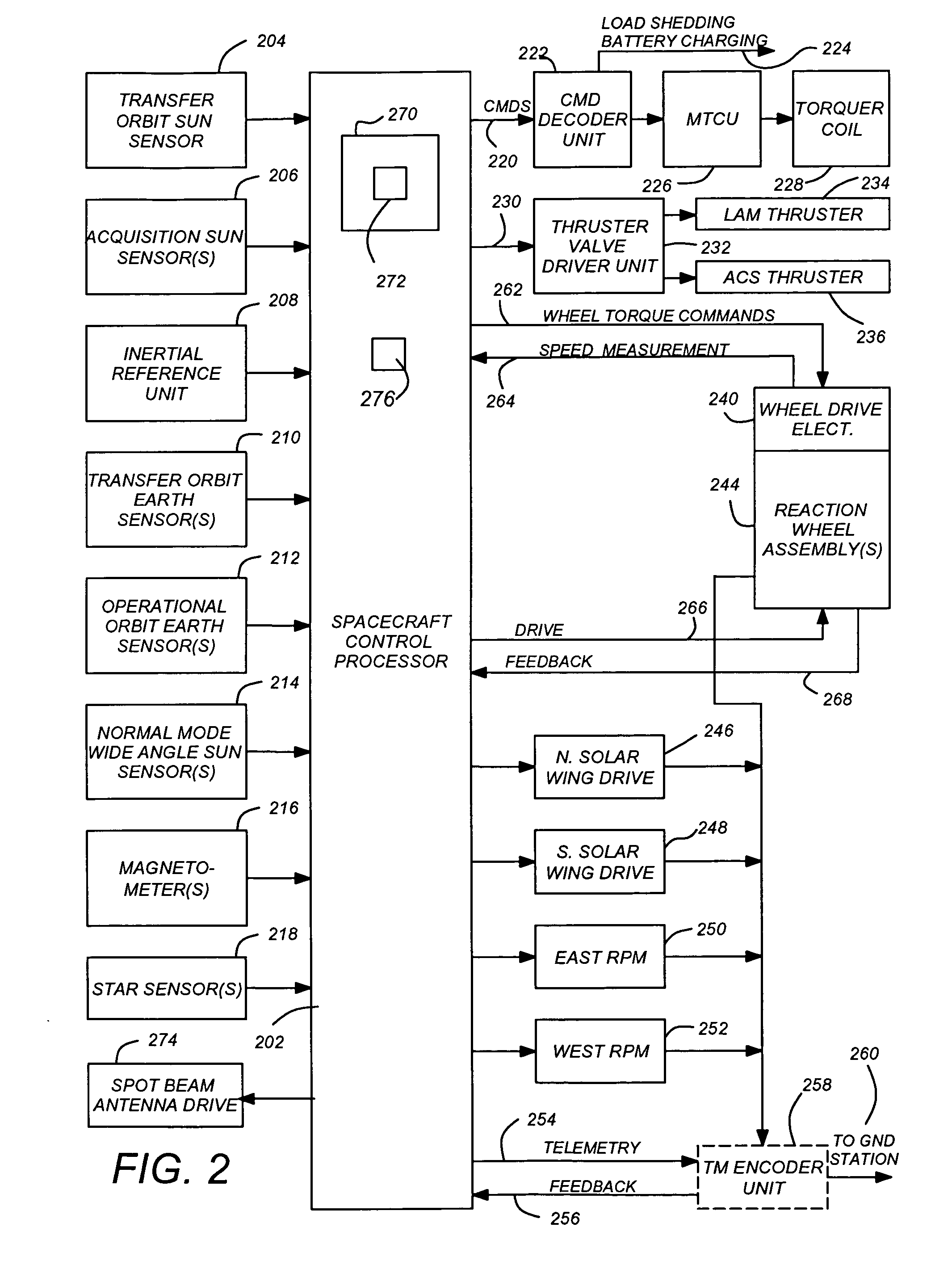
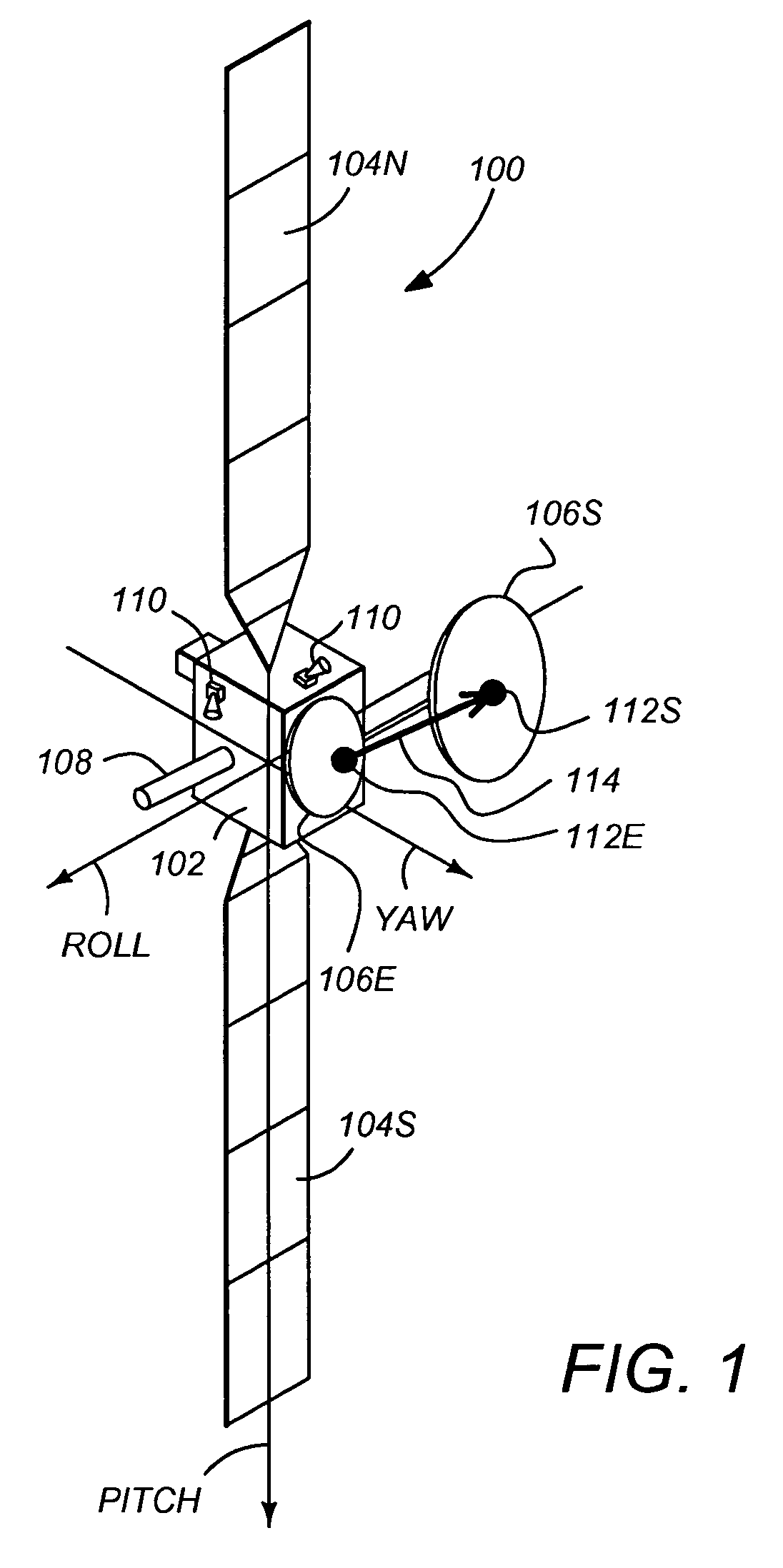
In telecommunications and radar engineering, antenna boresight is the axis of maximum gain (maximum radiated power) of a directional antenna. For most antennas the boresight is the axis of symmetry of the antenna. For example, for axial-fed dish antennas, the antenna boresight is the axis of symmetry of the parabolic dish, and the antenna radiation pattern (the main lobe) is symmetrical about the boresight axis. Most antennas boresight axis is fixed by their shape and cannot be changed. However phased array antennas can electronically steer the beam, changing the angle of the boresight by shifting the relative phase of the radio waves emitted by different antenna elements, and even radiate beams in multiple directions (multiple boresights).
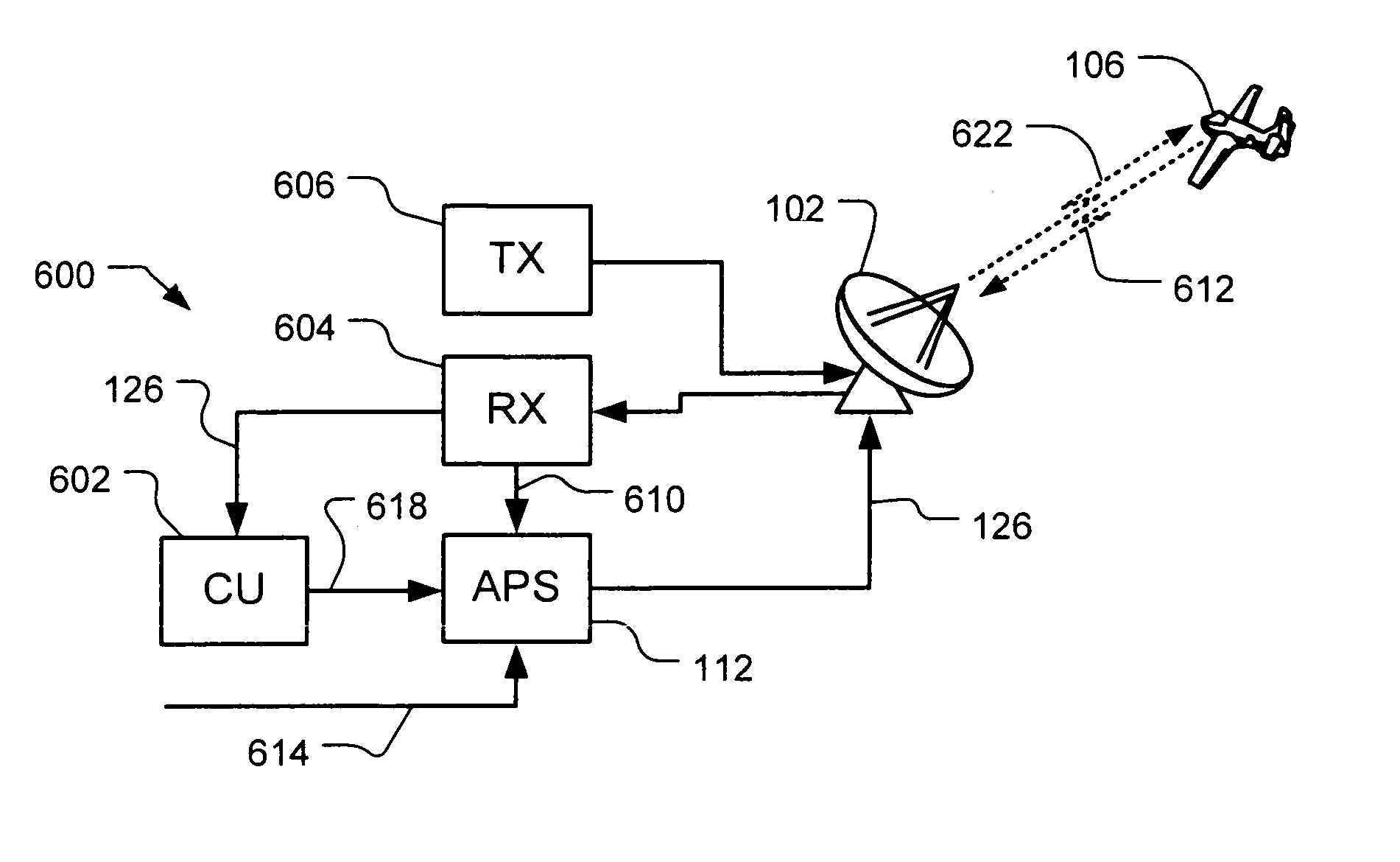
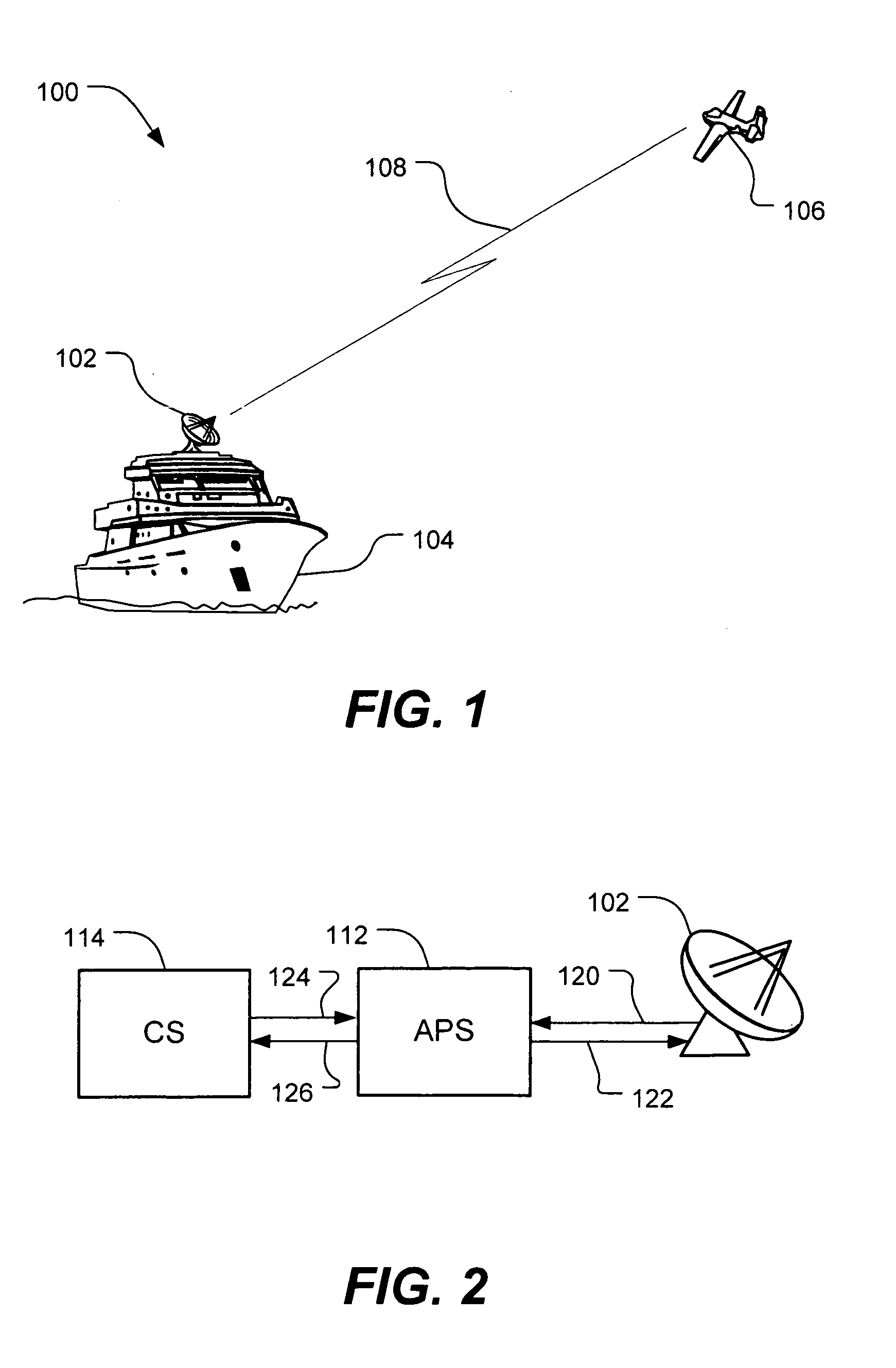
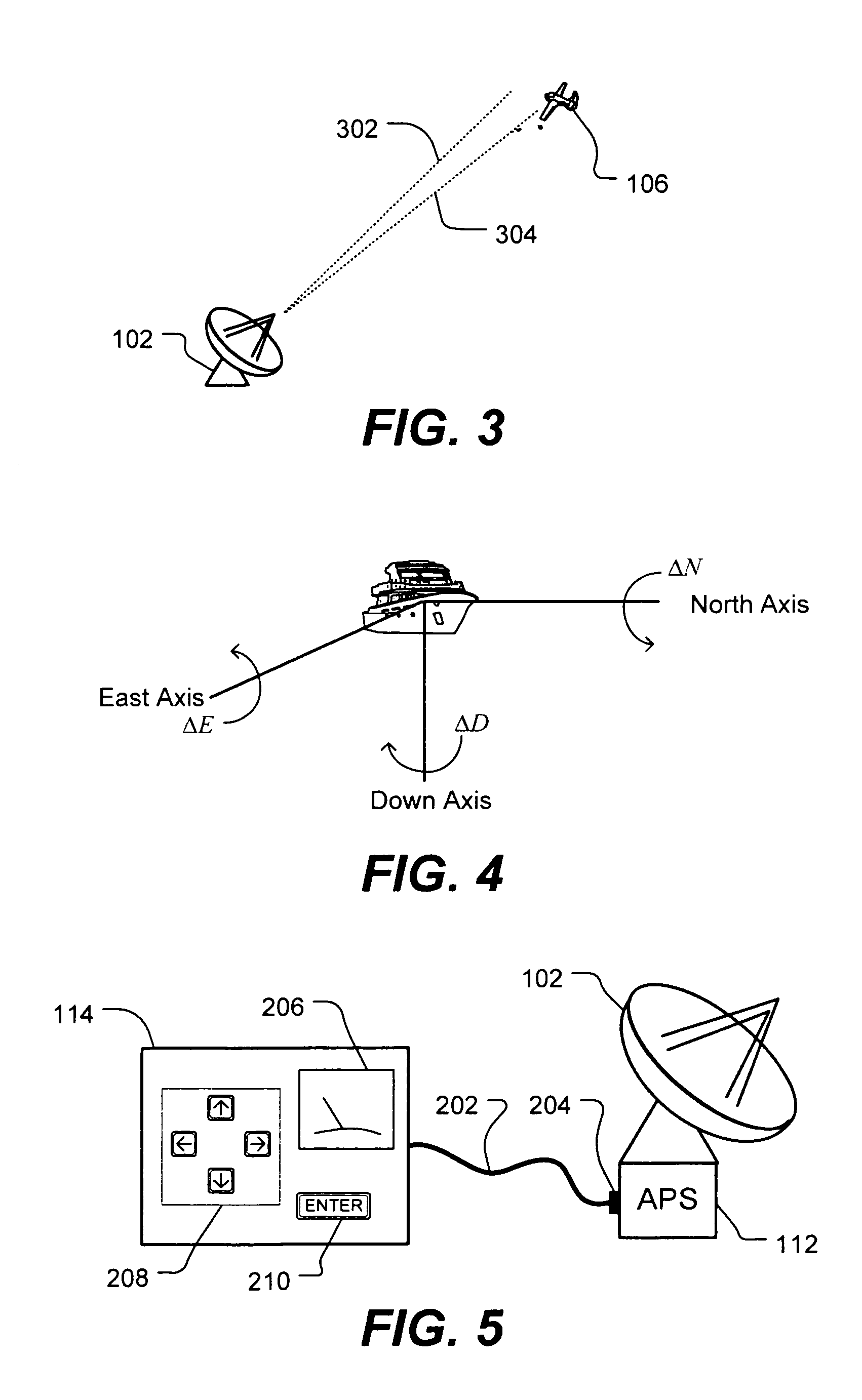
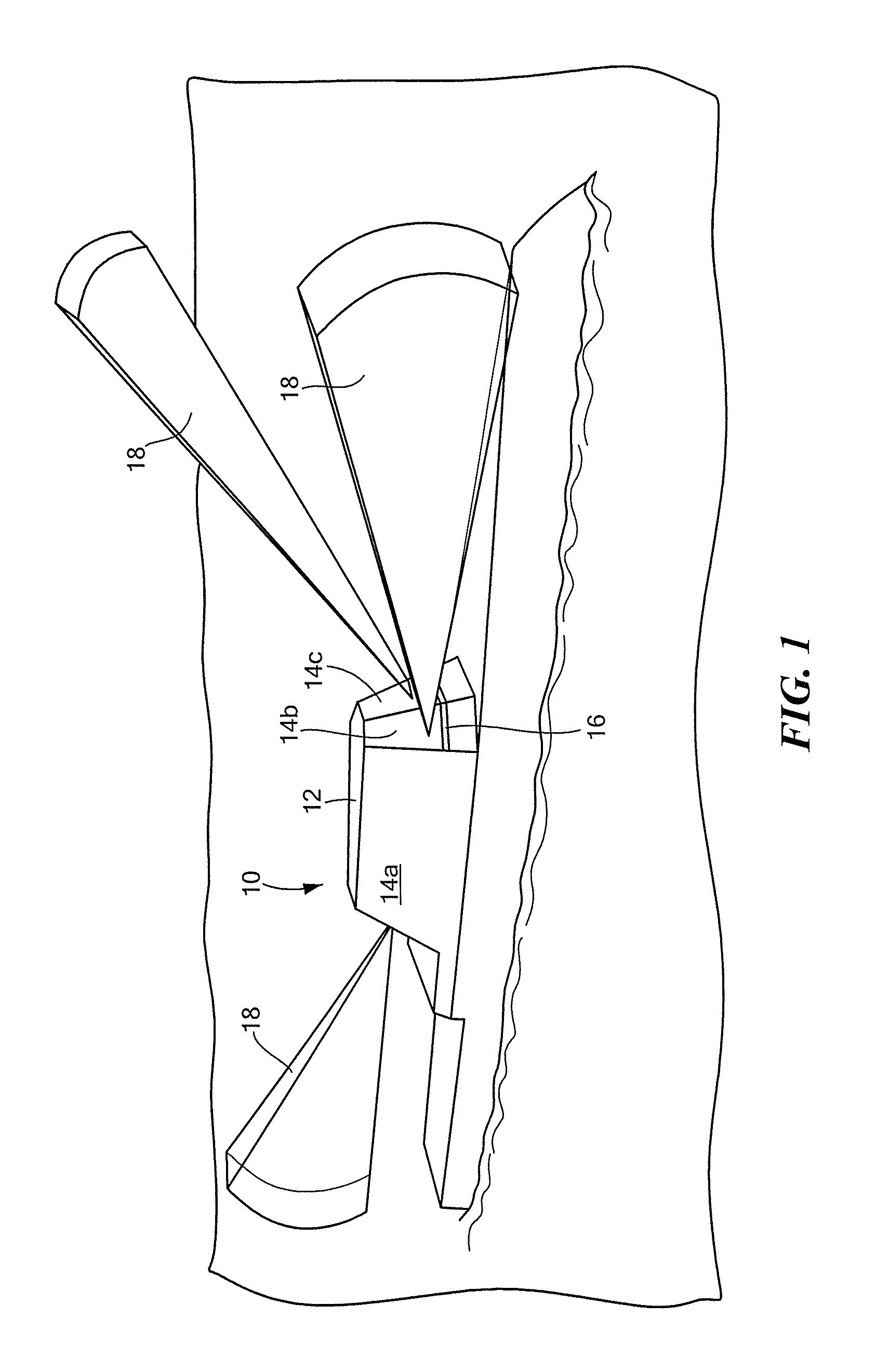
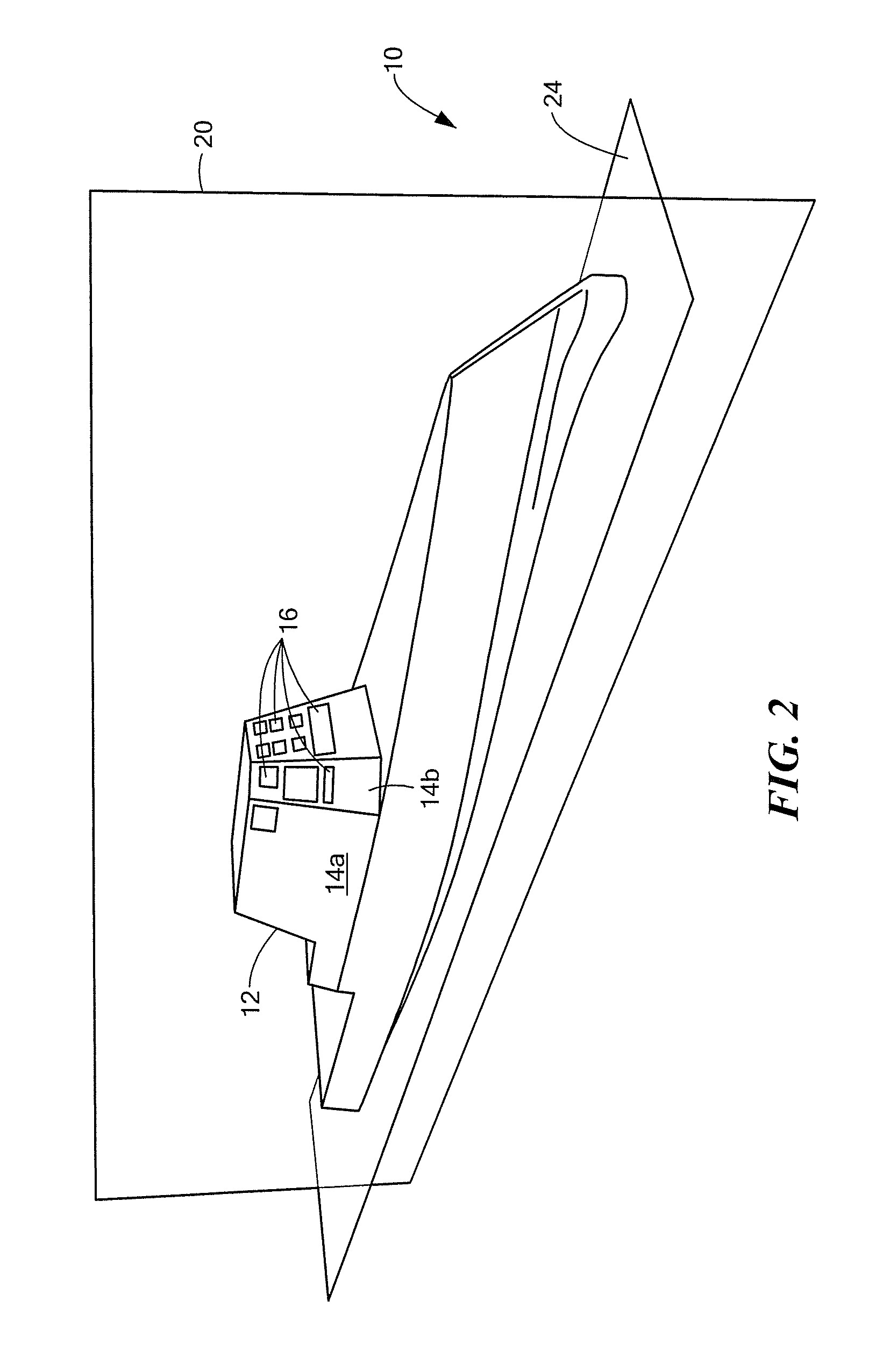
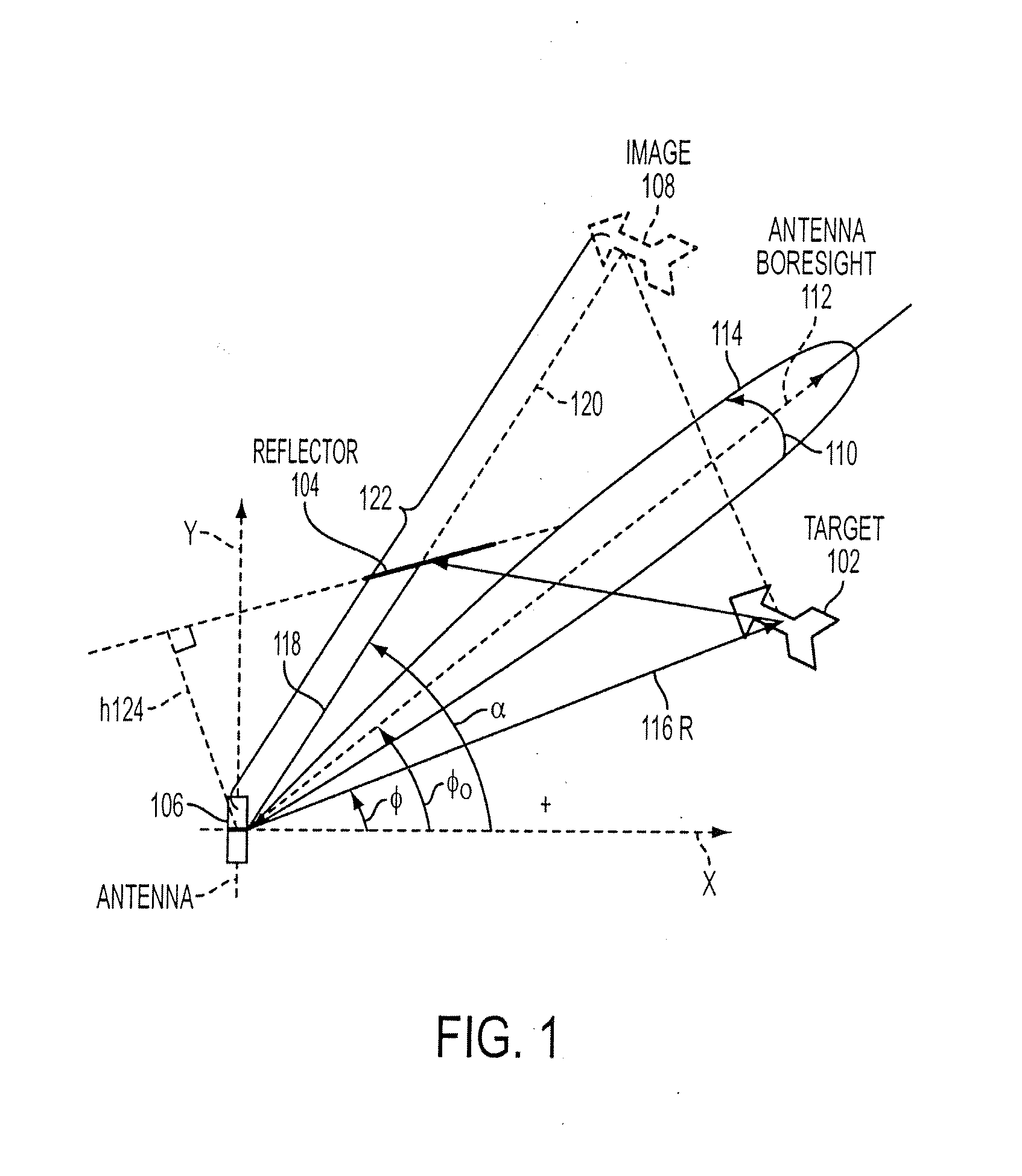
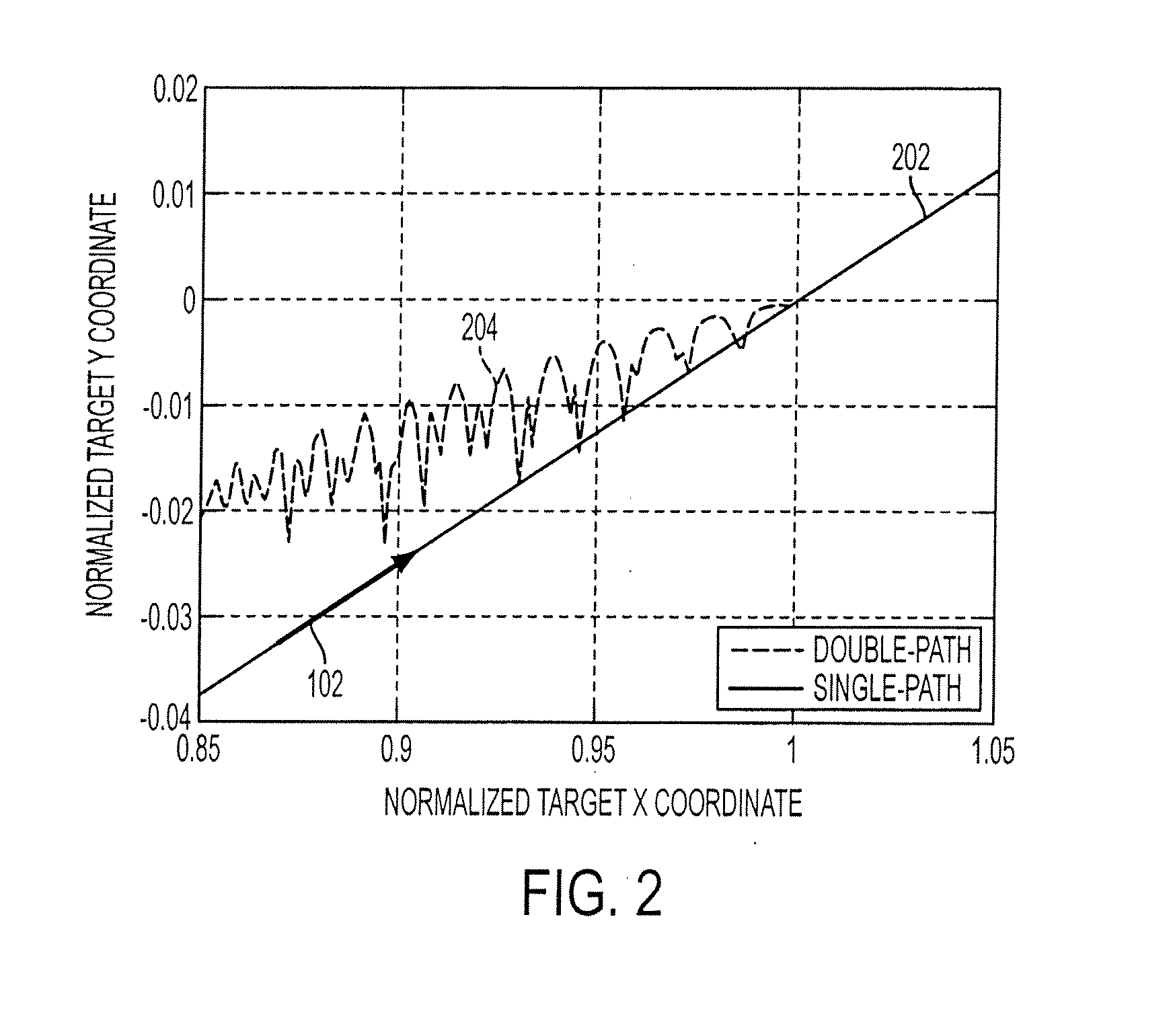
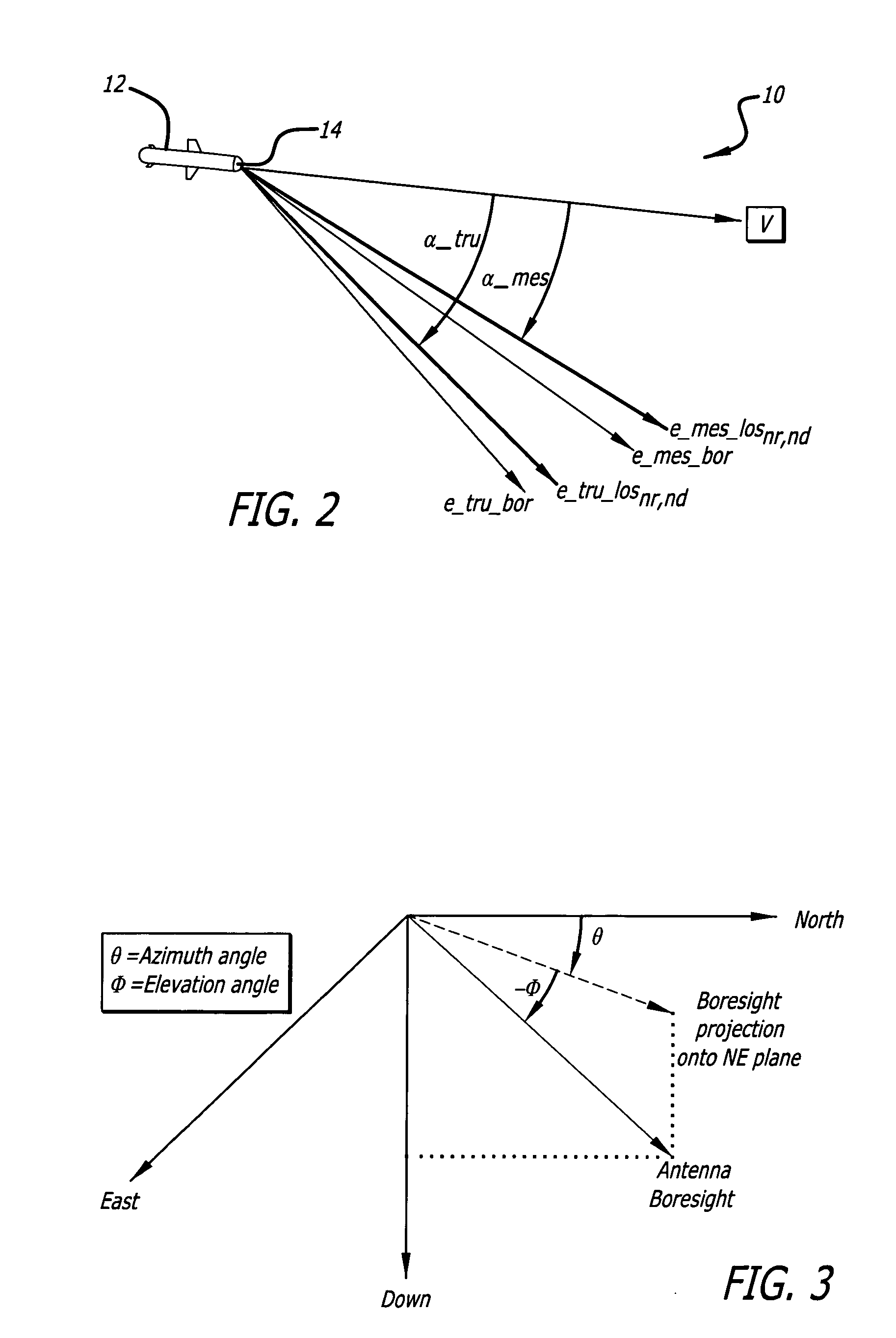
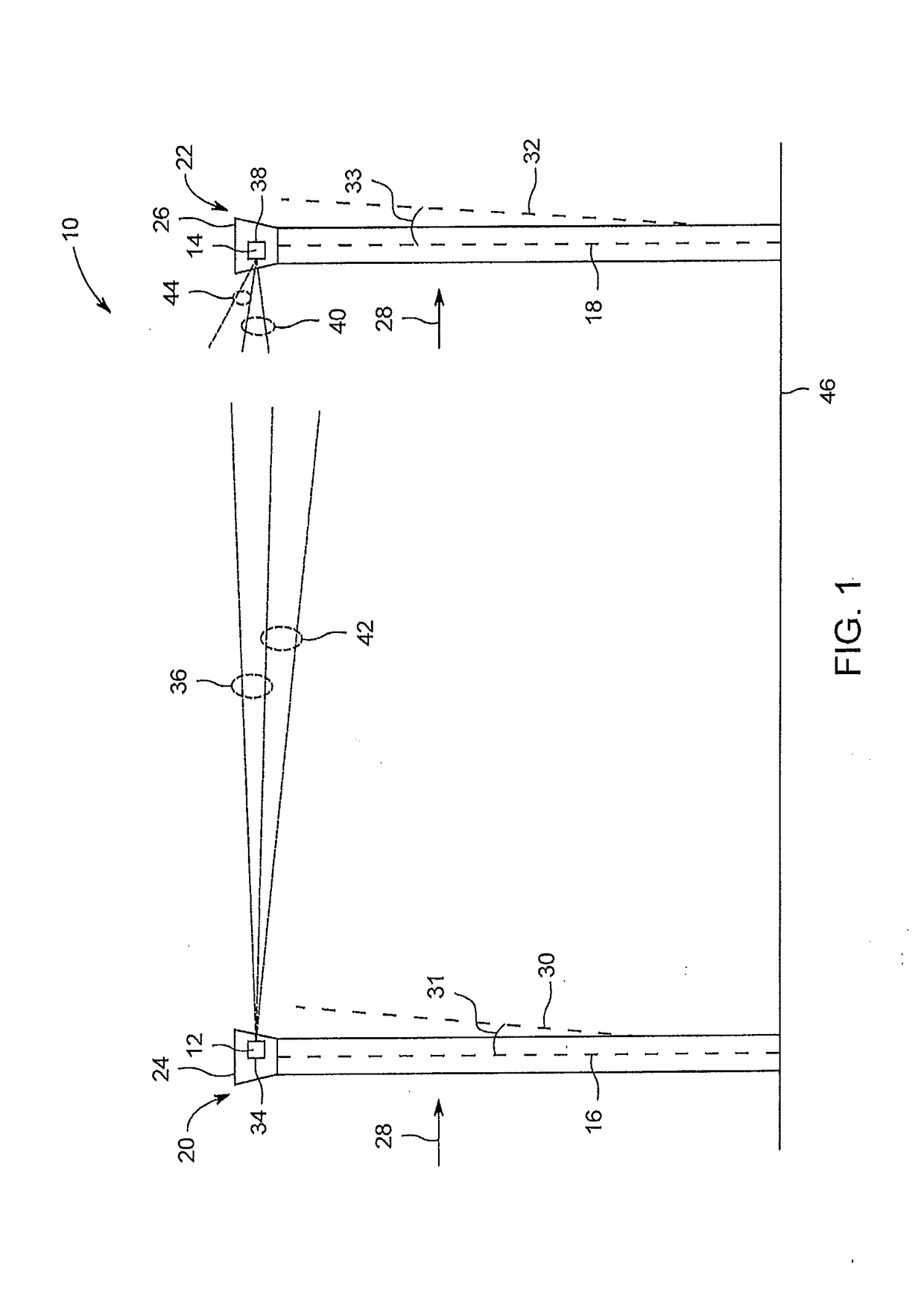
Method and device for boresighting an antenna on a moving platform using a moving target
ActiveUS7218273B1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio transmissionSignal qualityMarine navigation
A technique for boresighting an antenna mounted on a moving platform is described. The technique uses a concurrently moving calibration target. Target navigation data and platform navigation data are used to compensate for movement of the target and the platform. The antenna pointing direction is biased in a direction which provides a best signal quality, and the bias used to determine antenna boresight calibration factors. The boresight correction factors can be used for open loop pointing.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
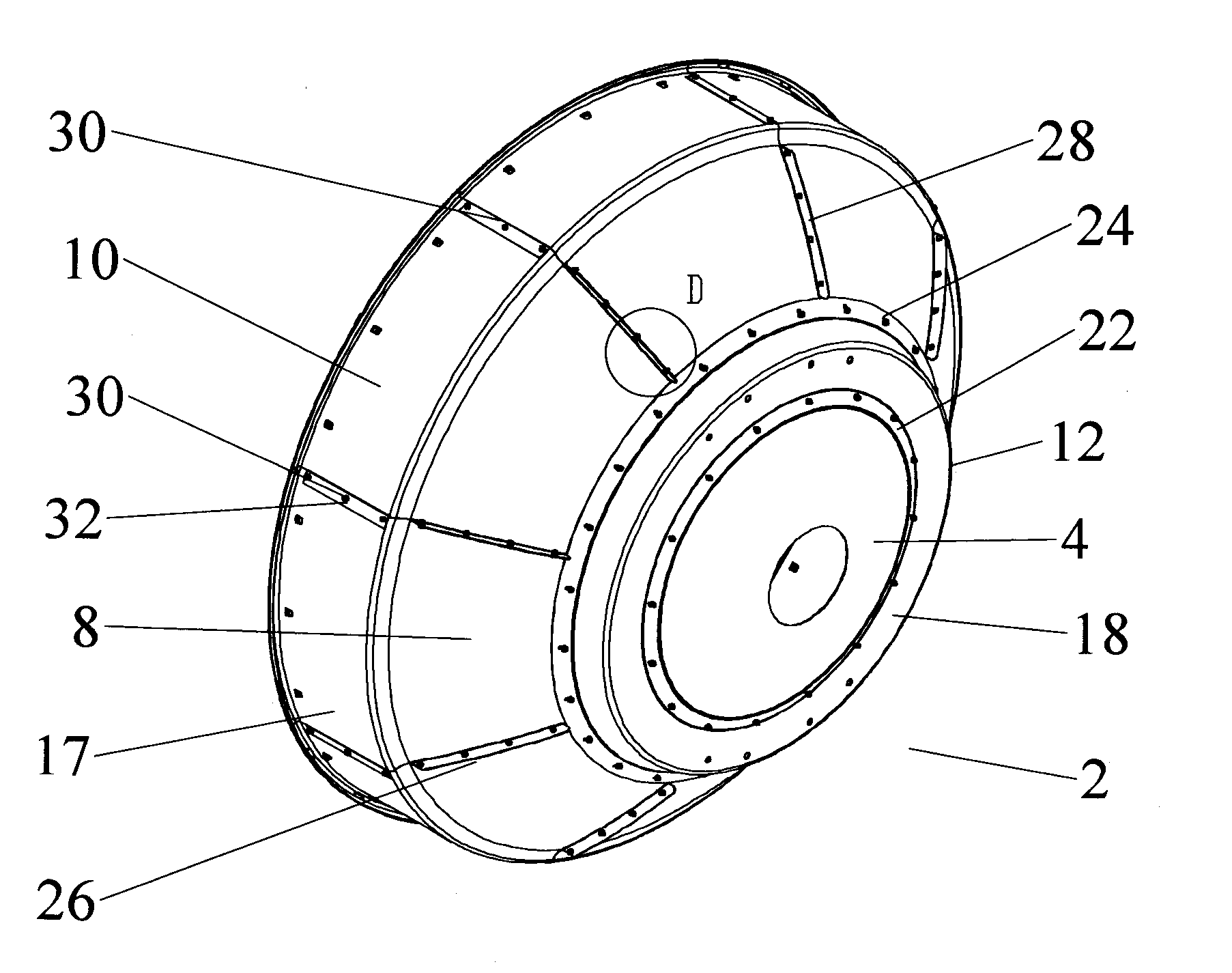
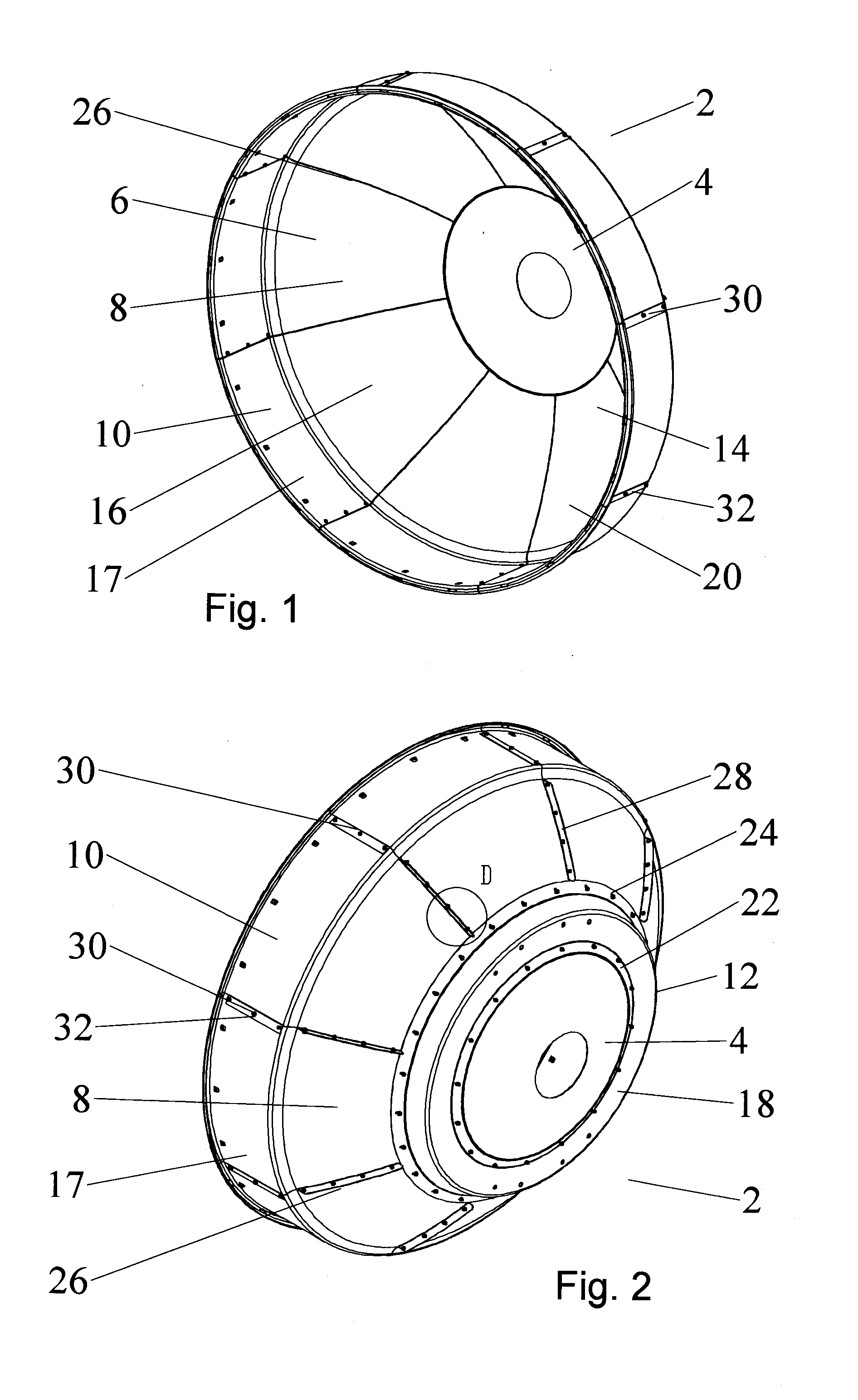
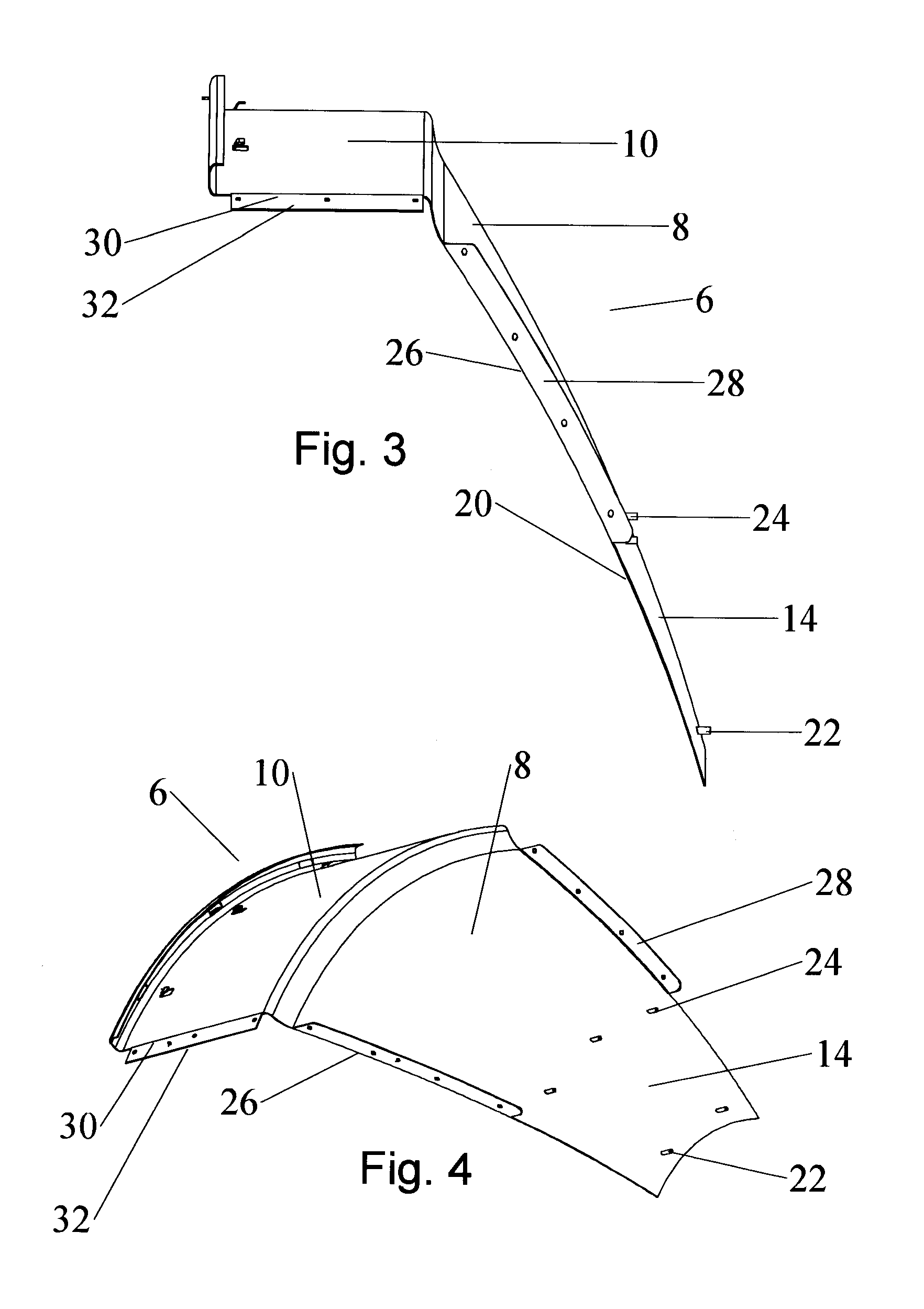
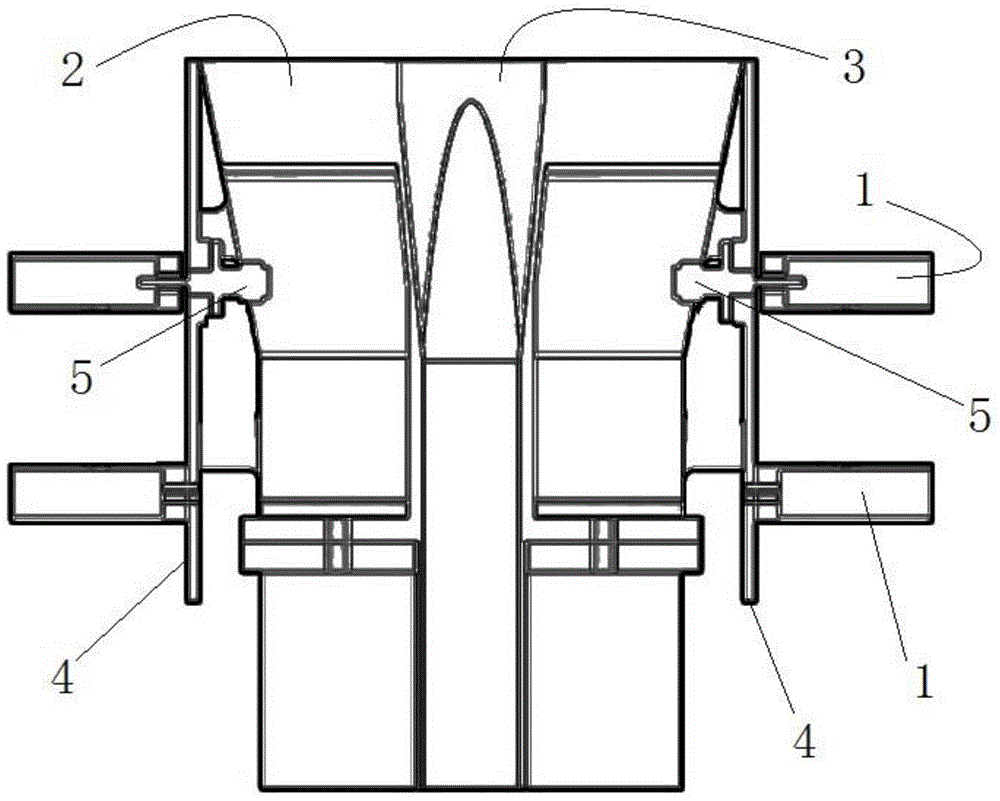
Segmented antenna reflector with shield
InactiveUS20110291914A1Improve rigidityImprove the level ofCollapsable antennas meansAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
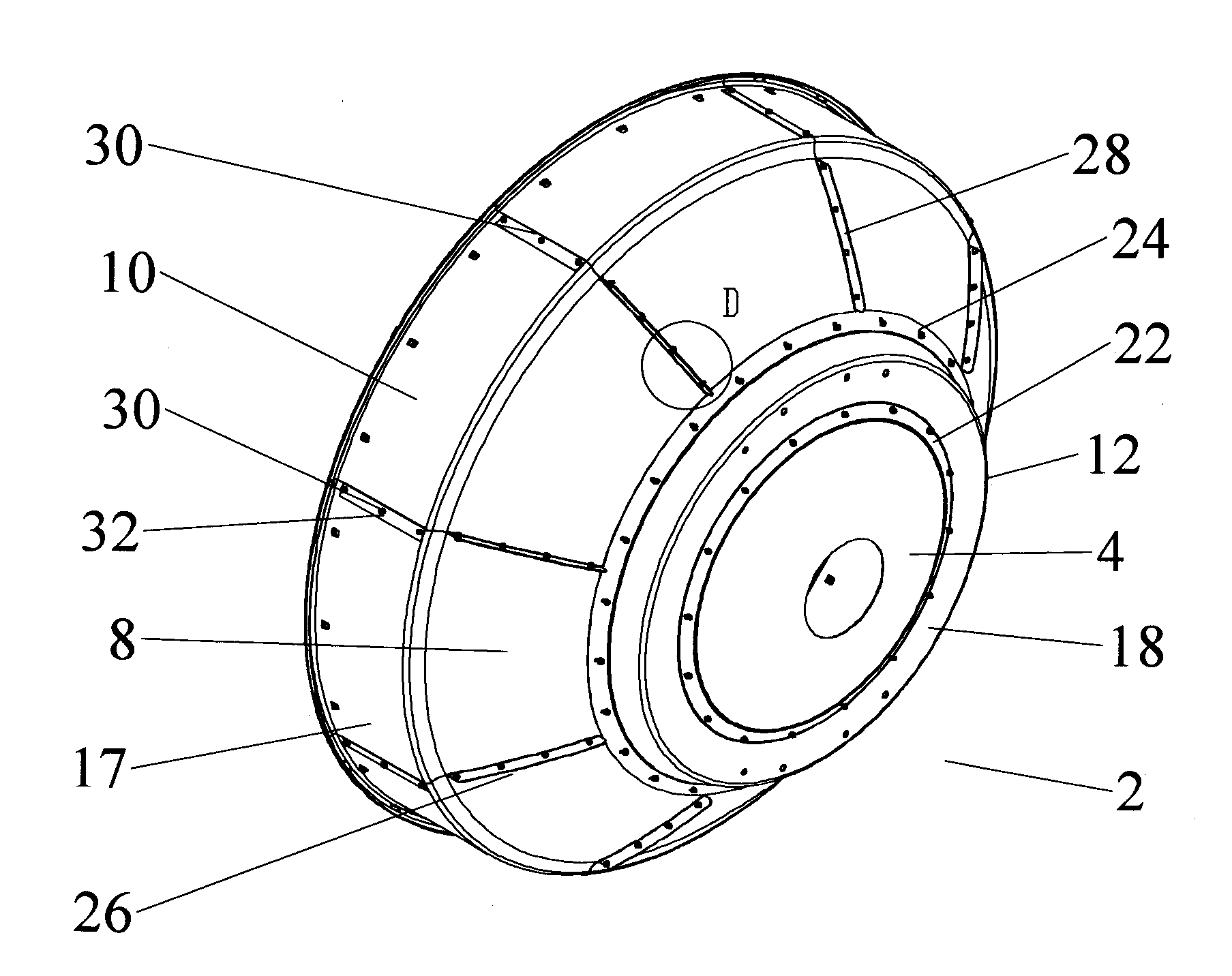
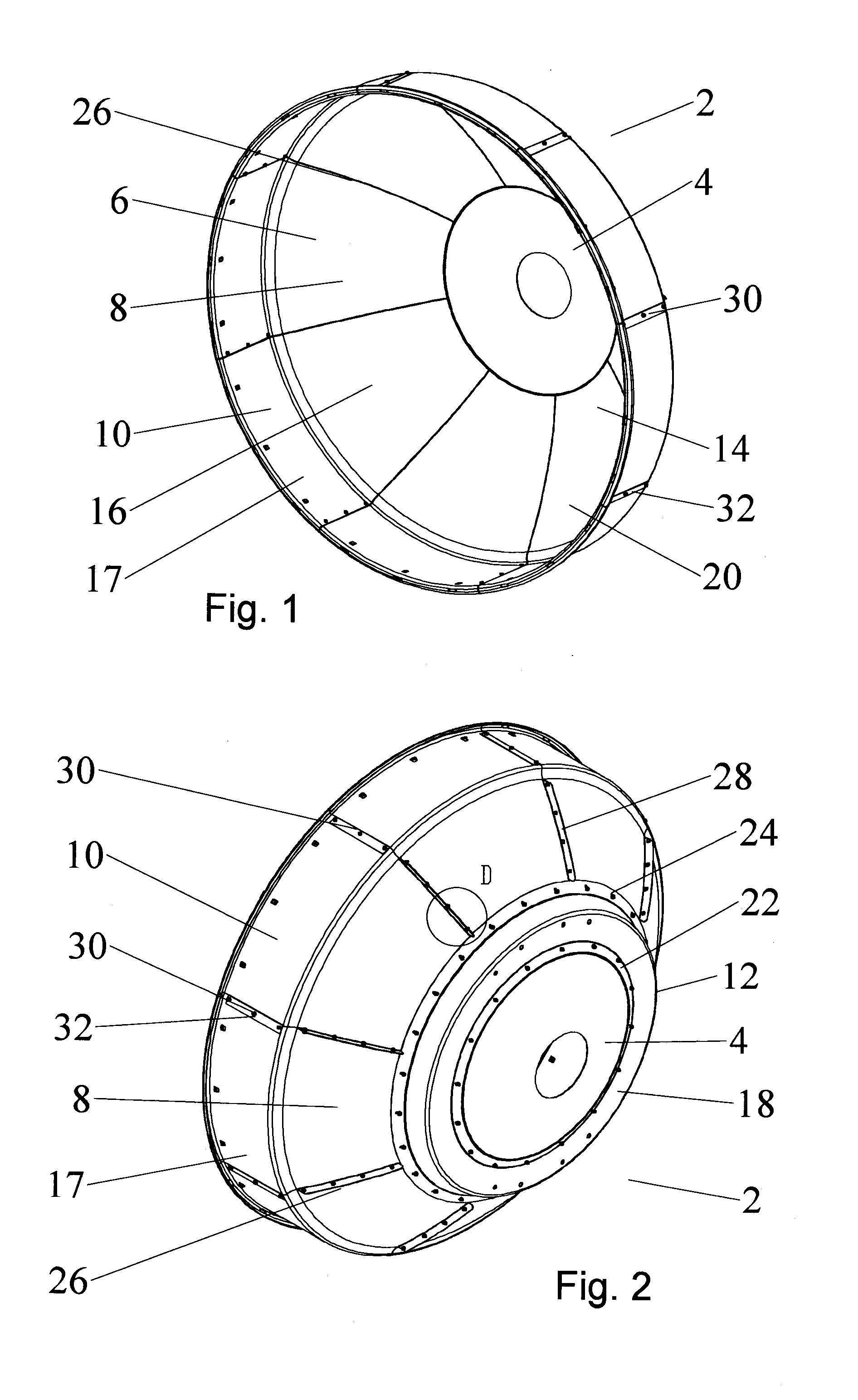
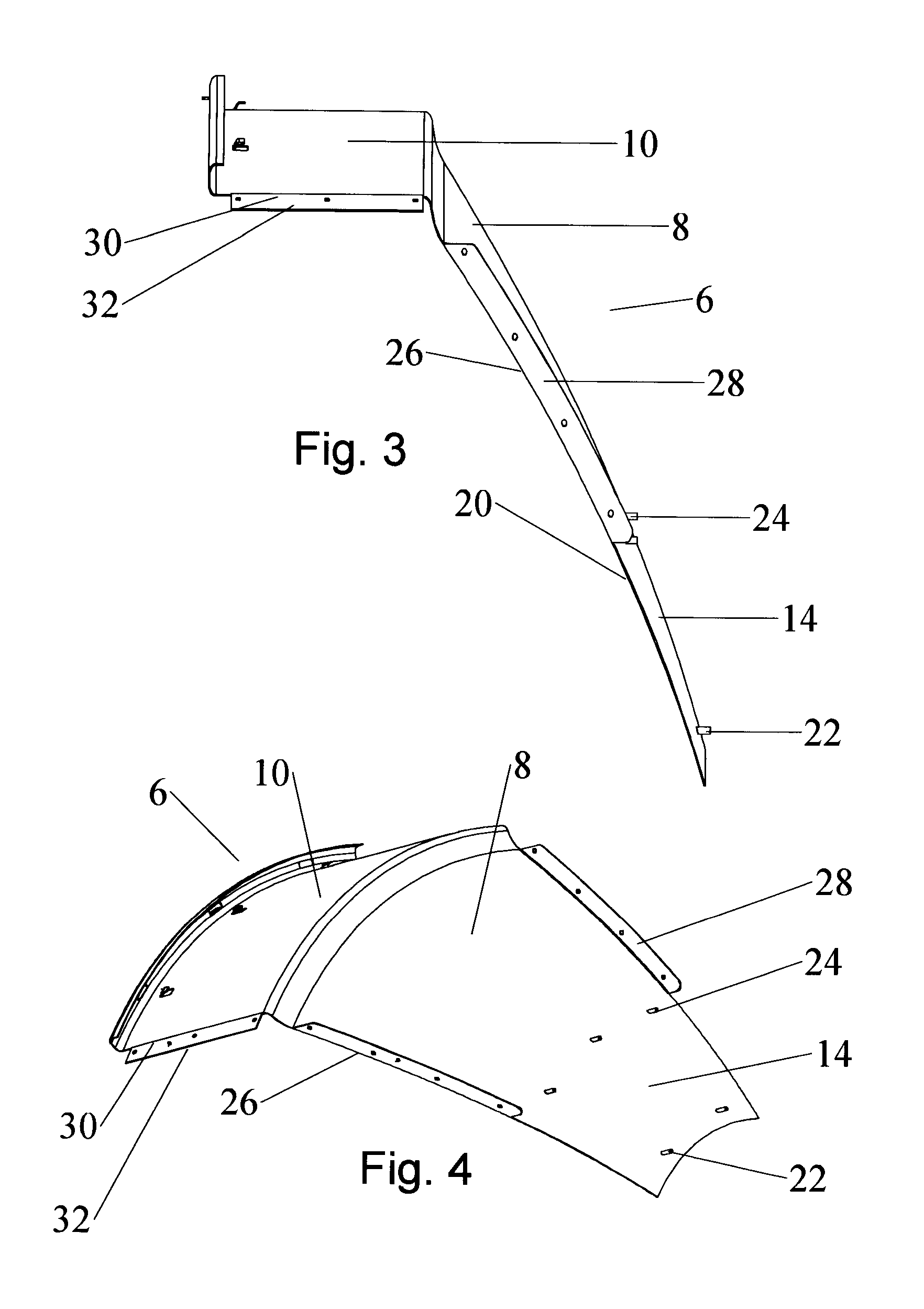
An antenna reflector includes a central segment with a peripheral coupling portion and a plurality of peripheral segments, each provided with a reflector portion and a shield portion. A proximal portion of each shield portion is dimensioned to couple with the peripheral coupling portion, a reflector portion edge of each peripheral segment is dimensioned to couple with adjacent reflector portion edges and a shield portion edge of each peripheral segment is dimensioned to couple with adjacent shield portion edges. The central segment and the reflector portion of the peripheral segments together form a reflector dish. The shield portions together provide a circumferential shield extending from a periphery of the reflector dish along an antenna boresight of the reflector dish.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Directed dipole antenna
InactiveUS7358922B2Optimized horizontal plane radiation patternImproved roll-offAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysDipole antennaRoll-off
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna having a superior Sector Power Ratio (SPR). The antenna may have slant 45 degree dipole radiating elements including directors, and may be disposed on a plurality of tilted element trays to orient an antenna boresight downtilt. The directors may be disposed above or about the respective dipole radiating elements. The antenna has a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, a high-roll off, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
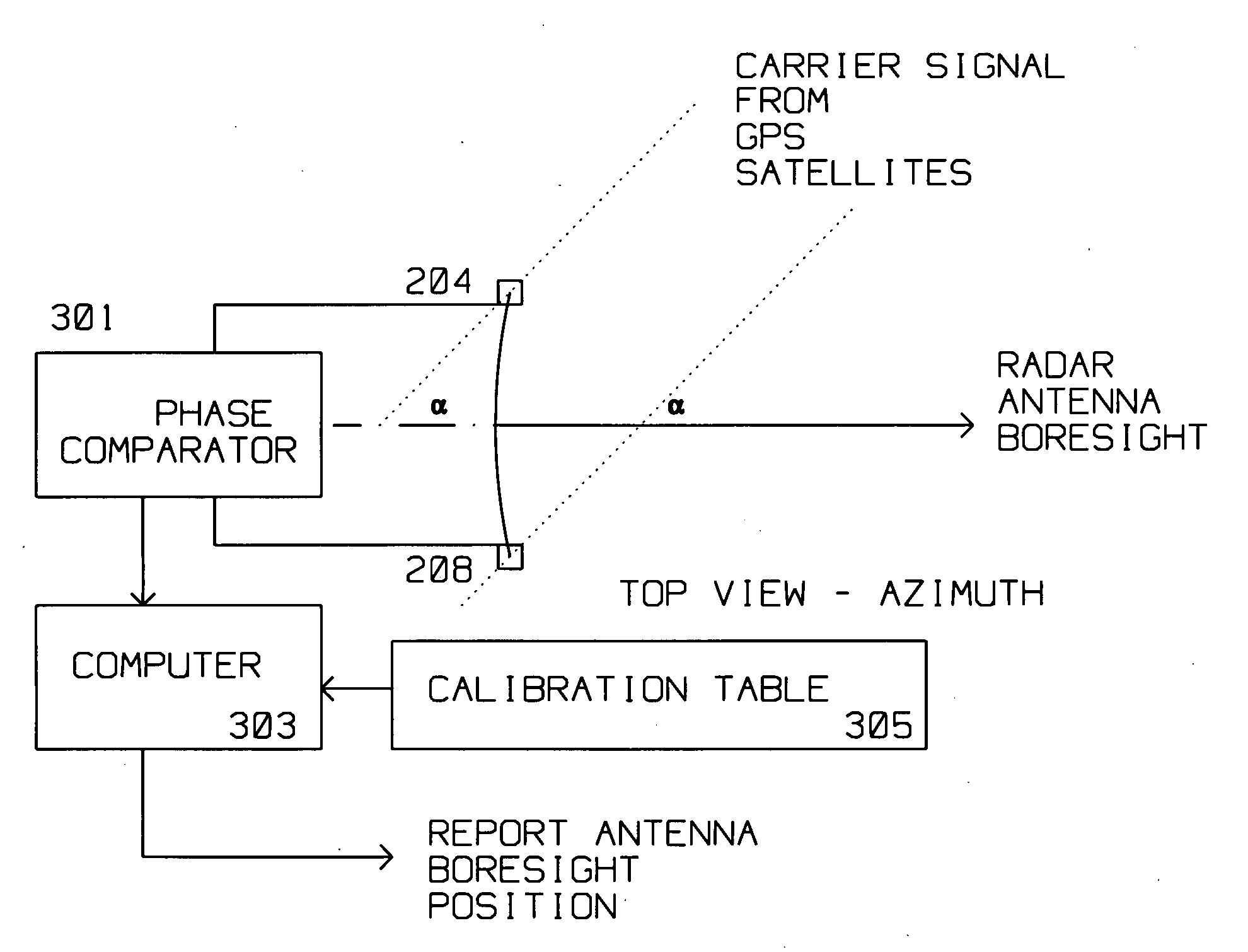
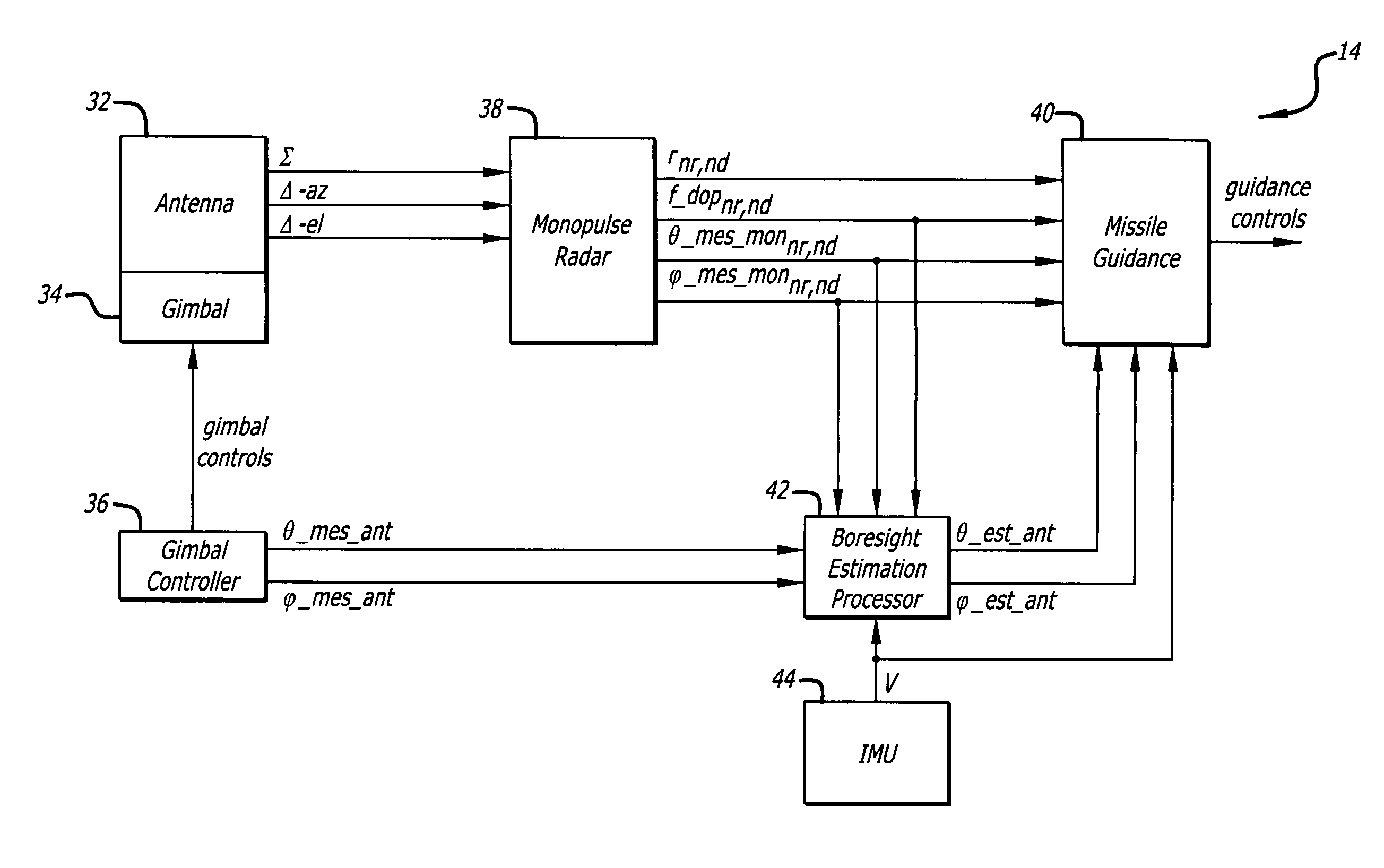
Technique for accurate estimate of large antenna inertial two dimensional orientation using relative GPS spatial phase
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Laser Tracker System And Technique For Antenna Boresight Alignment
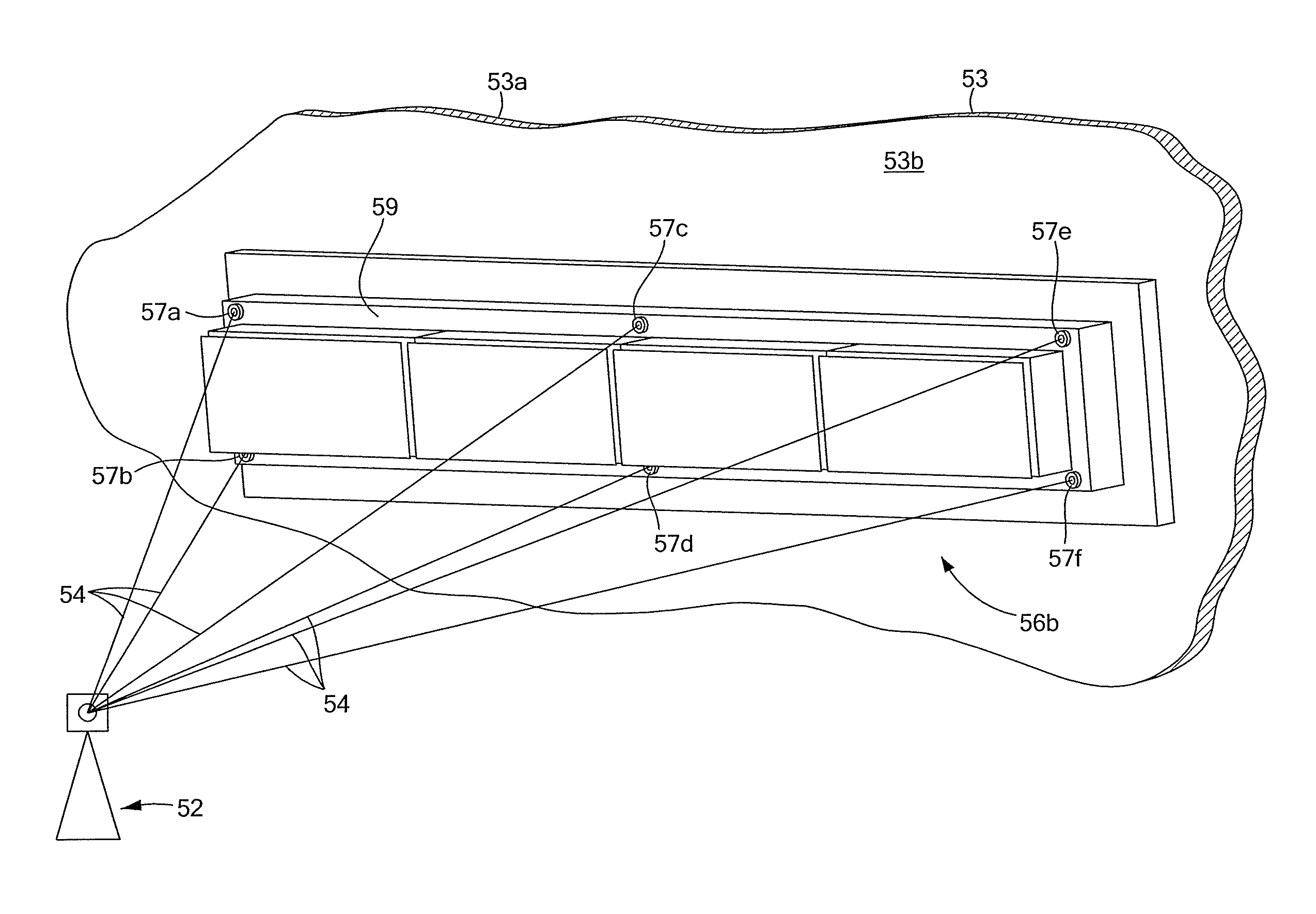
ActiveUS20130097880A1Repeatable accurate dataThe process is simple and fastAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSurveying instrumentsEngineeringLaser tracker
A system and processes for aligning an antenna boresight from a position which is internal to a structure on which the antenna is mounted is described. The system includes a laser tracking system and a plurality of targets disposed on a surface of the antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Technique for accurate estimate of large antenna inertial two dimensional orientation using relative GPS spatial phase
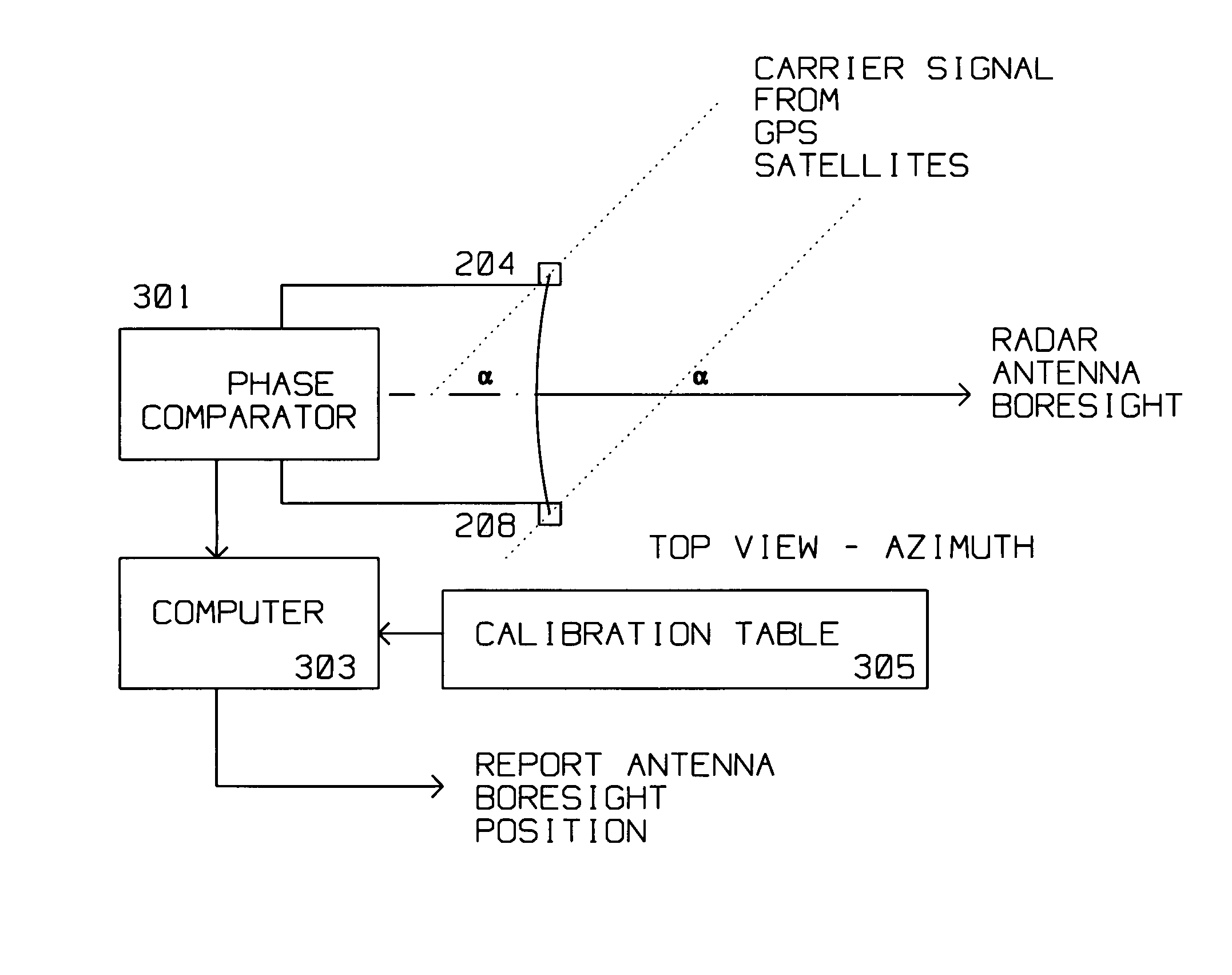
A radar antenna has a reflector and maximum gain along its boresight. The reflector has a periphery, typically circular, rectangular or elliptical. A plurality of Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite signal receiving antennas are rigidly, mechanically attached to the reflector near its periphery. The plurality of GPS satellite signal receiving antennas are connected pairwise to a phase comparator for comparing a plurality of first phase differences induced by a first GPS satellite signal received concurrently between the plurality of GPS satellite signal receiving antennas. A Phase comparator measures the phase difference of the signal received at GPS satellite signal receiving antennas pairwise thus performing a differential phase measurement. This differential phase measurement is supplied to a computer for identifying an ambiguous boresight position using the phase differences measured by the phase comparator. The position of the GPS satellites is known with respect to the geo-location of the antenna. Thus, the boresight angle is derived from the phase difference of the carrier signal from the GPS satellite being received and the mechanical alignment information between the GPS satellite receiving antennas and radar antenna boresight stored during calibration / manufacture of the radar antenna. The ambiguity in the computed boresight position is resolved by making differential phase readings using the same GPS antennas from a second GPS satellite signal supplied by a second satellite.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
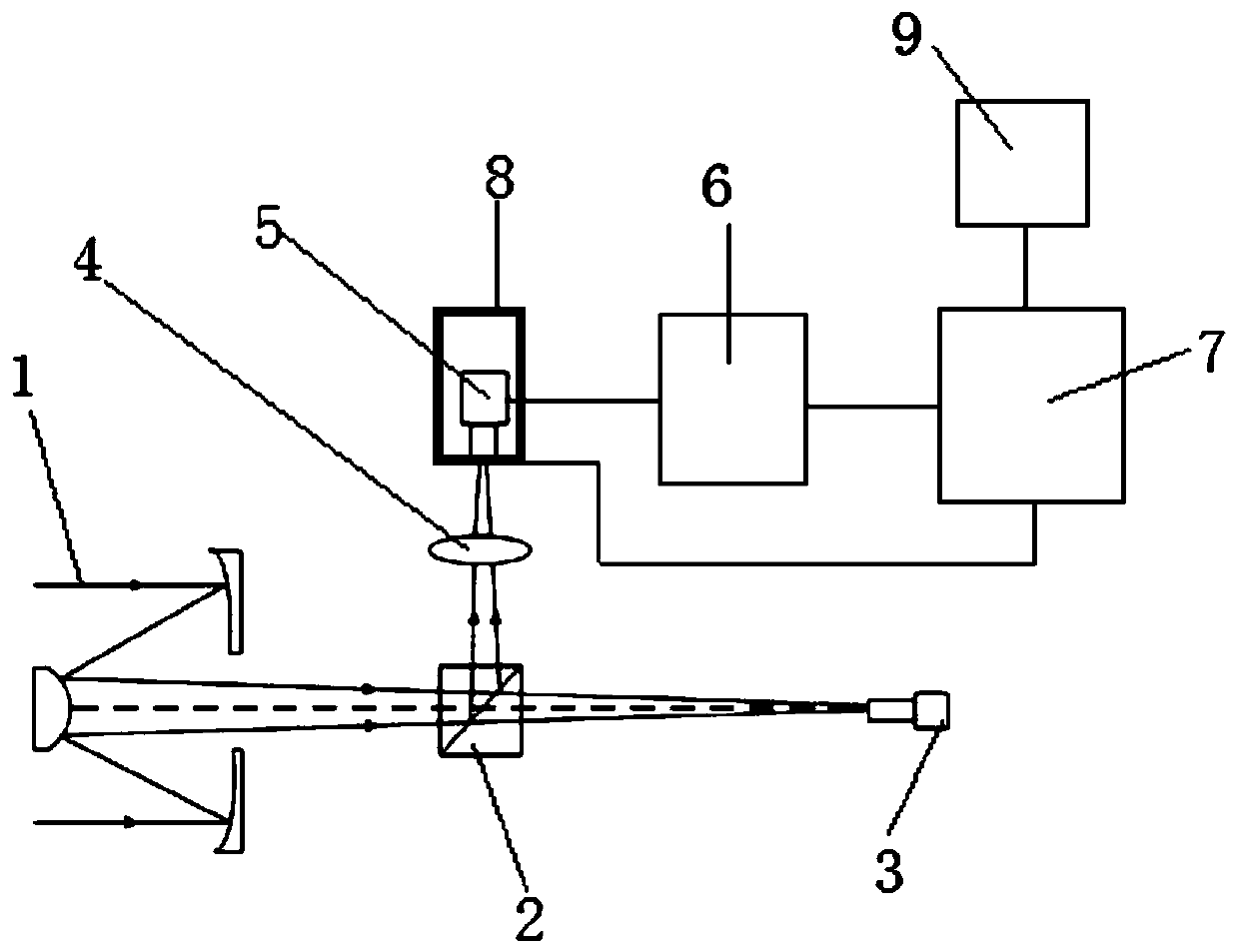
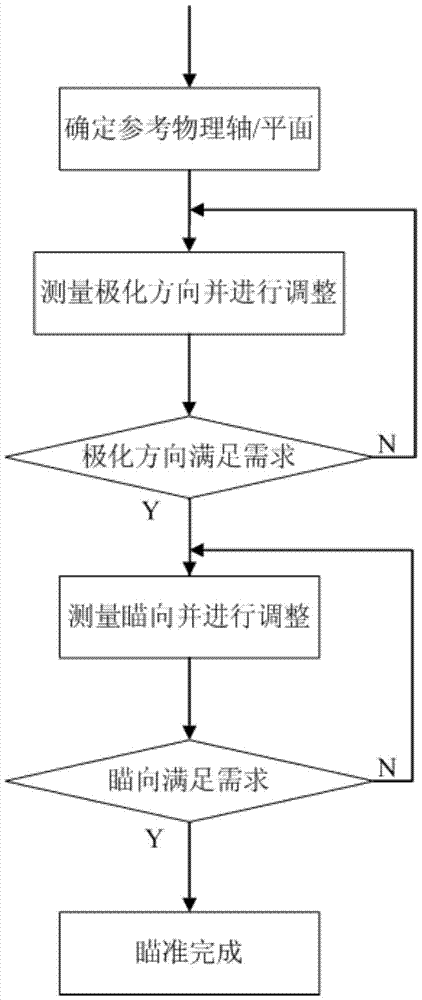
Light spot aligning method based on four-quadrant detector
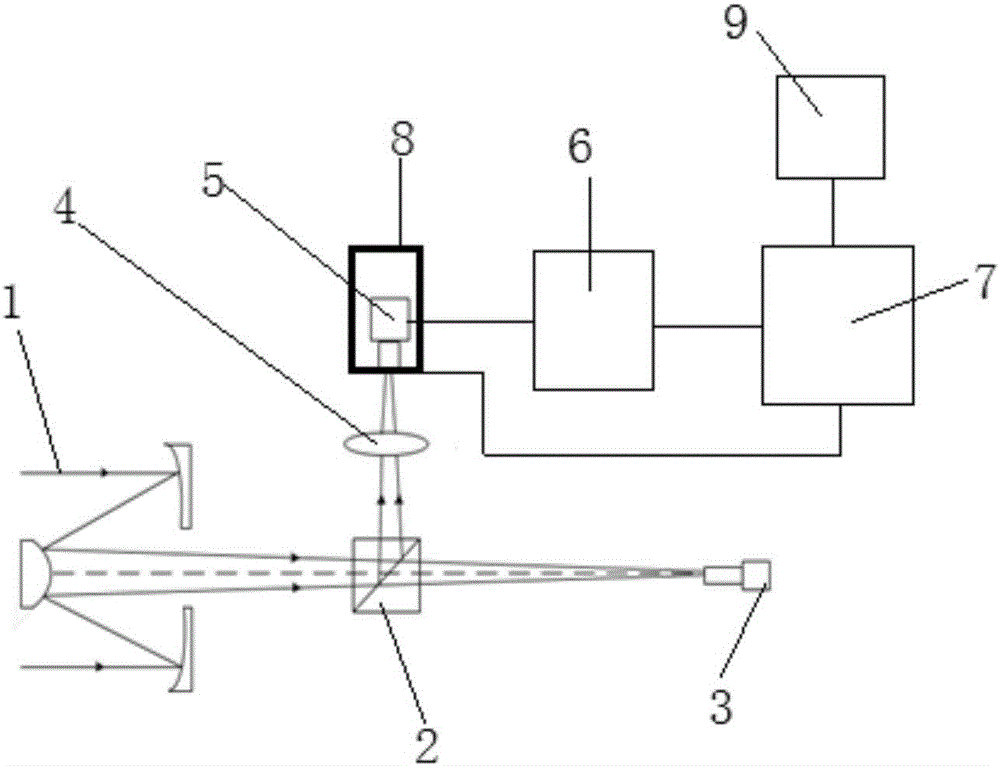
The invention discloses a light spot aligning method based on a four-quadrant detector. The light spot aligning method specifically comprises the following steps of focusing an incident beam onto a photo-sensitive surface of the four-quadrant detector by a lens, and enabling the four-quadrant detector to convert a received light signal into four paths of electric signals; amplifying the obtained four paths of electric signals by an amplifying circuit, transmitting the signals to the signal processing unit, and sequentially performing A / D (analog to digital) conversion and Kalman filtering on the four paths of amplified electric signals in the signal processing unit; performing self-adaptive threshold judging on the four paths of processed electric signals, controlling the action of a cradle head according to judging results, and enabling the cradle head to drive the four-quadrant detector to act, so as to adjust the position of the incident light beam, and align the incident light spot. The light spot aligning method solves the problem of difficulty in aligning of the light spot due to simultaneous existence of light spot drifting and malalignment between light beam and antenna visual axis.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
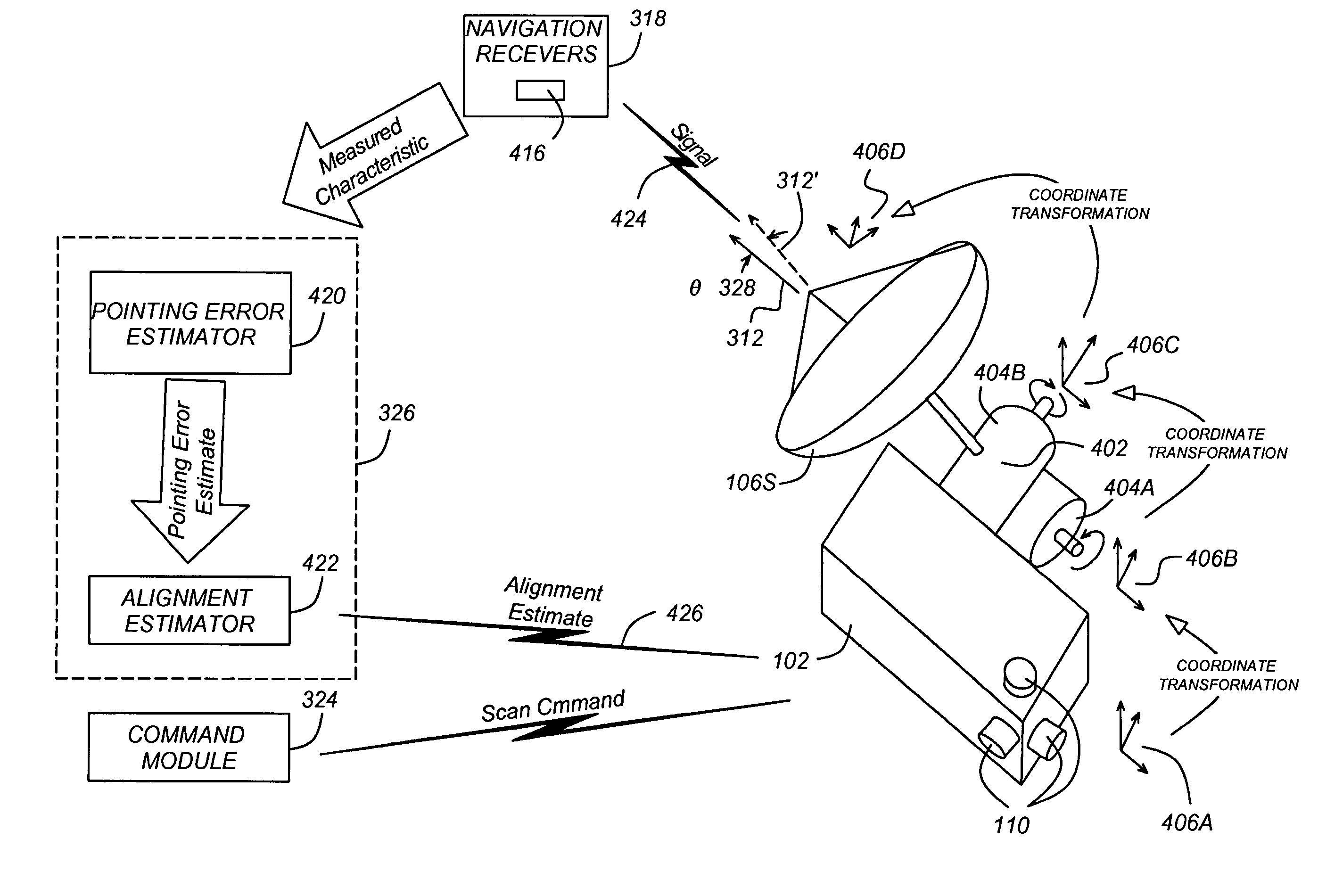
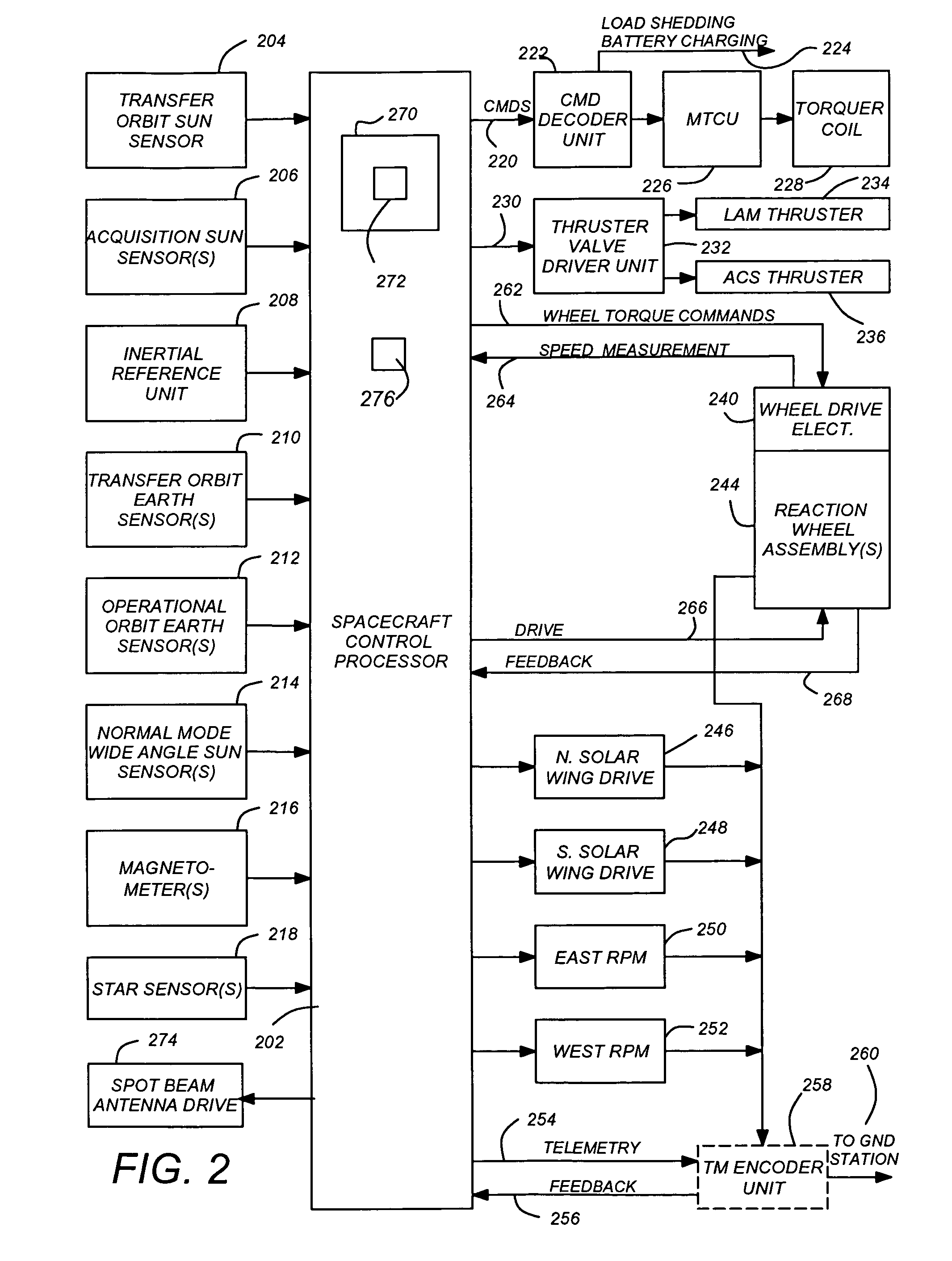
Spot beam antenna boresight calibration using GPS receivers
ActiveUS20070046537A1Reduce the impact of noiseMaximizes alignment error observabilitySatellite radio beaconingRadio transmissionGps receiverSignal characteristic
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Integrated six-frequency-range multipurpose composite feed source
ActiveCN105161862AImprove Radiation PerformanceExcellent electrical performanceSeparate antenna unit combinationsLoudspeakerVisual axis
The invention provides an integrated six-frequency-range multipurpose composite feed source. The feed source comprises four reflecting plates, L / S oscillators, four X frequency range loudspeakers and a Ku / K / Ka frequency range loudspeaker, wherein the four X frequency range loudspeakers are arranged symmetrically by taking a visual axis of an antenna as the center, the Ku / K / Ka frequency range loudspeaker is embedded to the symmetrical center of the four X frequency range loudspeakers and shares loudspeaker walls with the X frequency range loudspeakers, the four reflecting plate is arranged in the surrounding of the X frequency range loudspeakers, a plane where the central axes of two adjacent X frequency range loudspeakers are placed is parallel with corresponding reflecting plate, the L / S oscillators are vertically mounted on the reflecting plates respectively, and the length of the L / S oscillator in the direction vertical to the reflecting plate is 22-26mm.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACEFLIGHT INST OF TT&C & TELECOMM
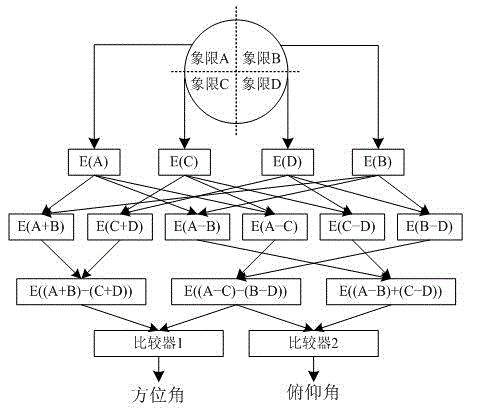
Double-difference beam angle measurement method and system
InactiveCN104931958AImprove performance indicatorsPrecise positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam angleDouble difference
The present invention relates to a double-difference beam angle measurement method and system for achieving angle measurement for an object by utilizing double difference beam channels formed by four quadrants of an antenna. According to four quadrants of an antenna array surface, two sum signal channels, four difference signal channels, a secondary difference signal channel, an azimuth difference channel and a pitching difference channel are obtained; an azimuth angle is obtained through comparison between a signal of the secondary difference signal channel and a signal of the azimuth difference channel; and a pitch angle is obtained through comparison between the signal of the secondary difference signal channel and a signal of the pitching difference channel. The method and the system of the present invention can effectively suppress external interference, and can perform accurate angle measurement for an object within a large angle range deviating from a visual axis direction of the antenna, thereby ensuring accurate positioning for multiple objects by a phased array radar.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
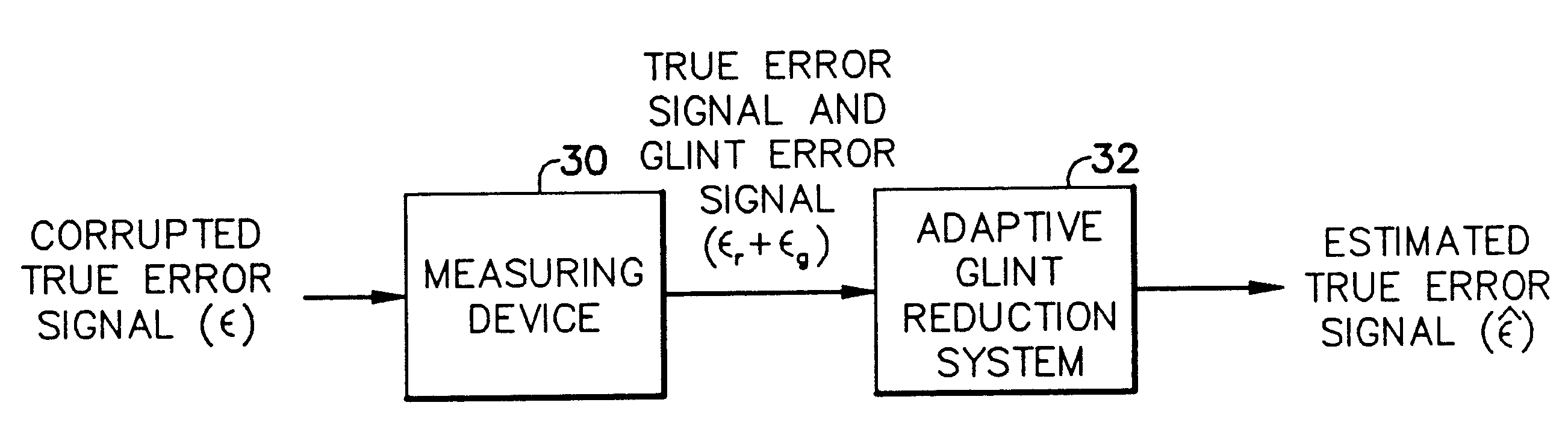
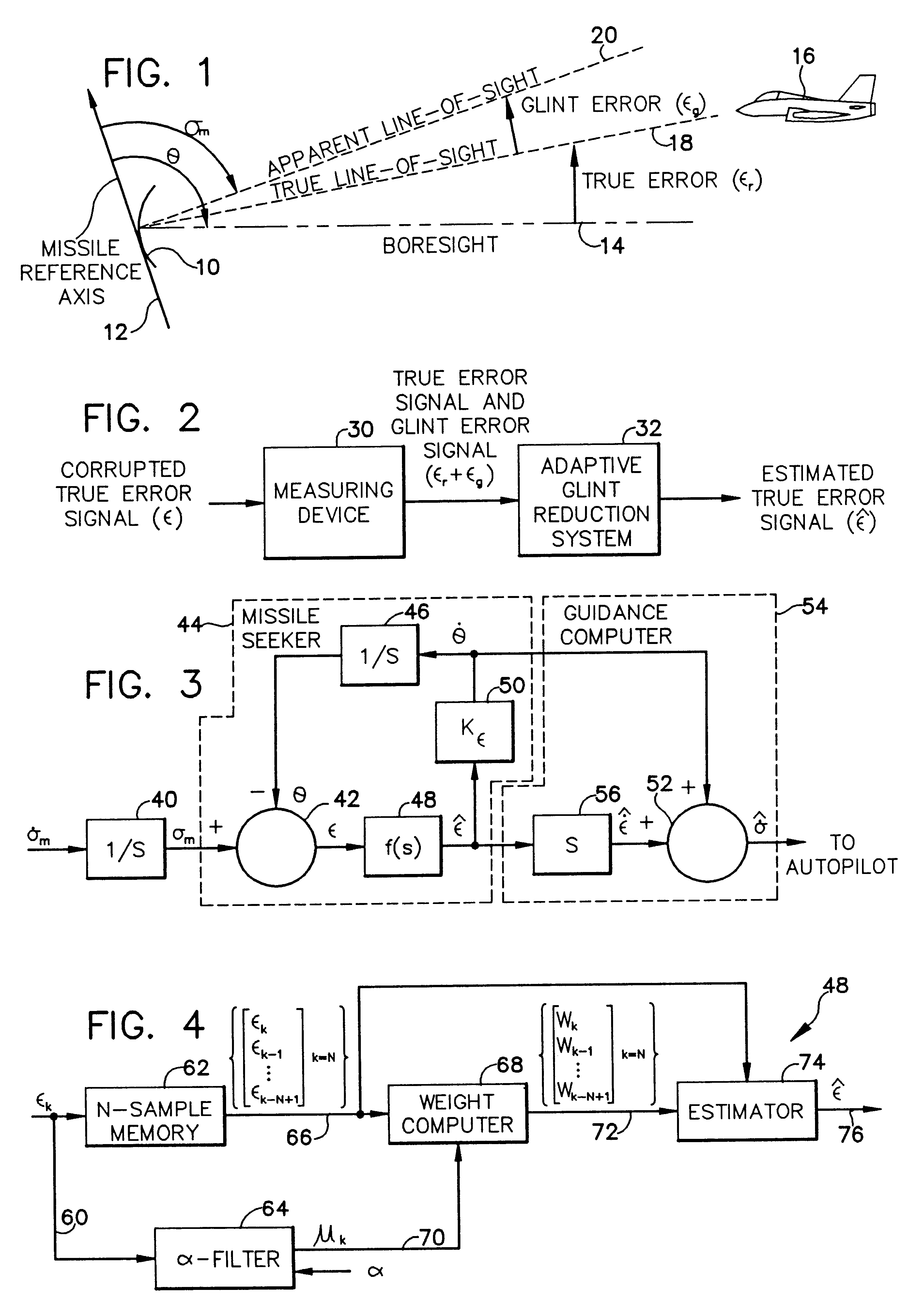
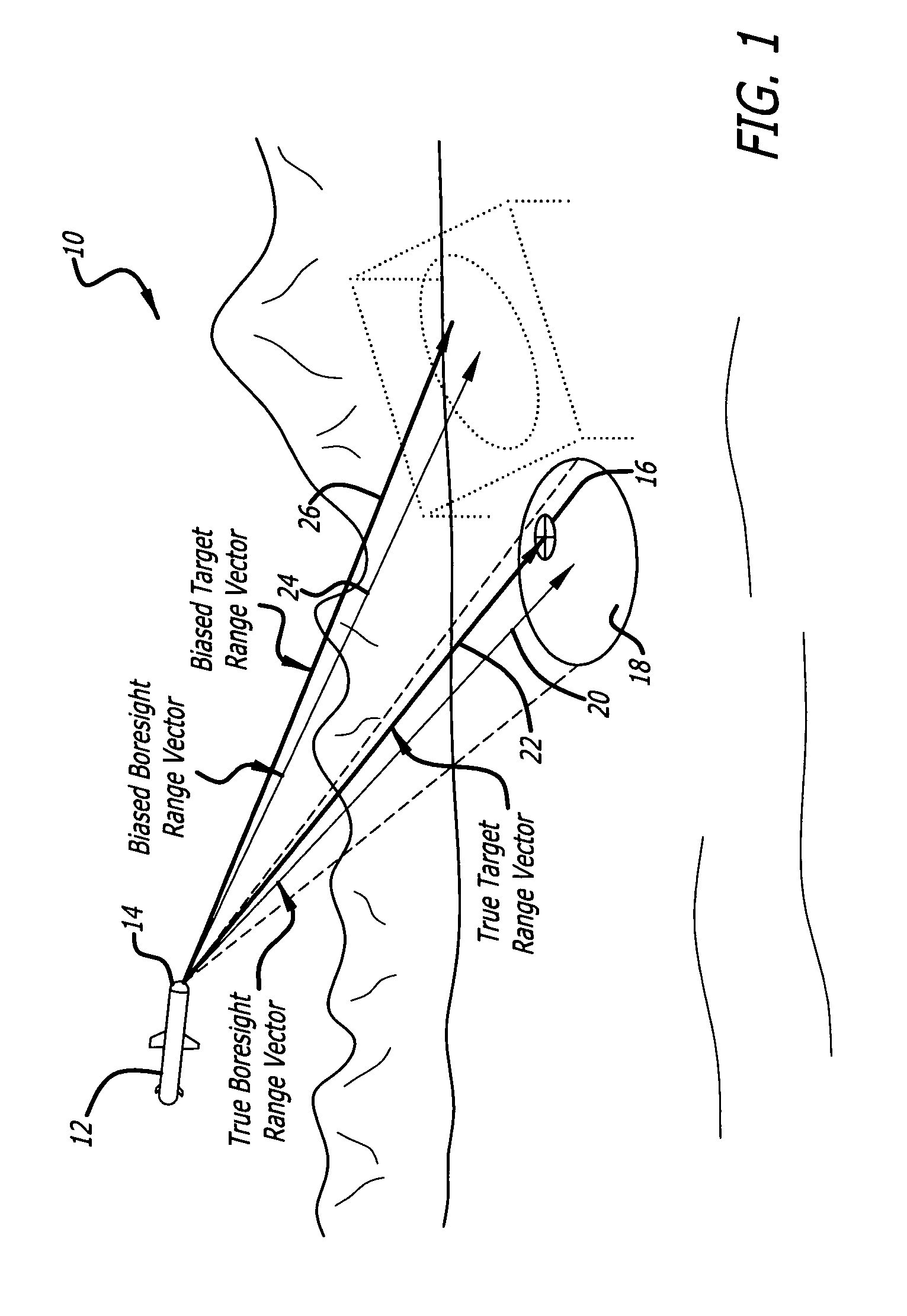
Adaptive glint reduction method and system
InactiveUS6930633B1Easy to trackReduce mistakesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSelf adaptiveAcoustics
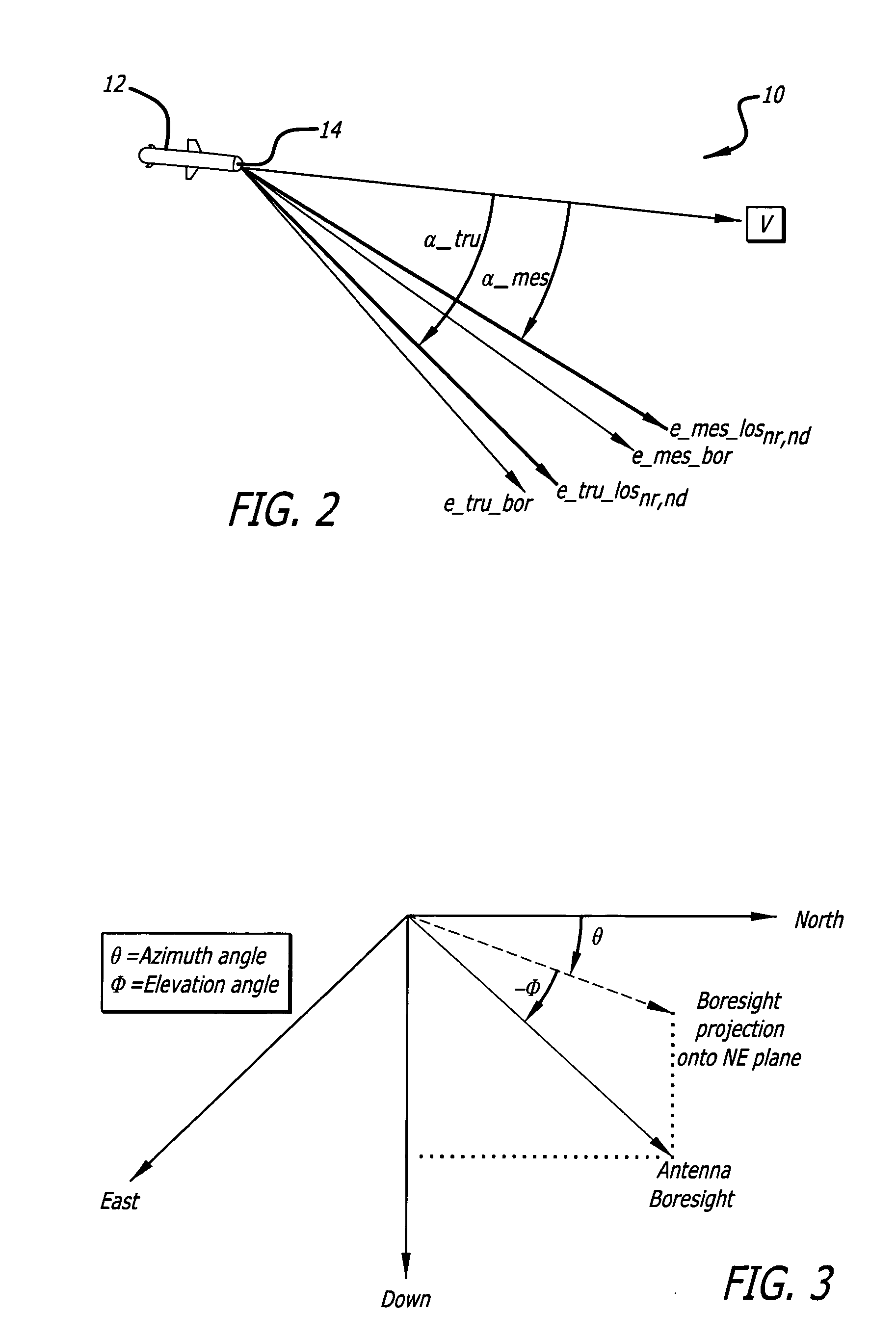
A method and system for adaptively reducing, in a displacement signal having a value indicative of a measured angular displacement between an antenna boresight and an apparent line of sight to a target, a noise signal having a value indicative of an angular error induced by a shift in the target radar centroid so as to provide an output signal having a value indicative of an estimate of a true angular displacement signal between the antenna boresight and a true line of sight to the target.
Owner:HUGHES MISSILE SYST CO
Directed dipole antenna having improved sector power ratio (SPR)
InactiveUS20080088521A1Optimized horizontal plane radiation patternImproved roll-offPolarised antenna unit combinationsAntennasDirectional antennaDipole antenna
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna having a superior Sector Power Ratio (SPR). The antenna may have slant 45 degree dipole radiating elements including directors, and may be disposed on a plurality of tilted element trays to orient an antenna boresight downtilt. The directors may be disposed above or about the respective dipole radiating elements. The antenna has a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, a high-roll off, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
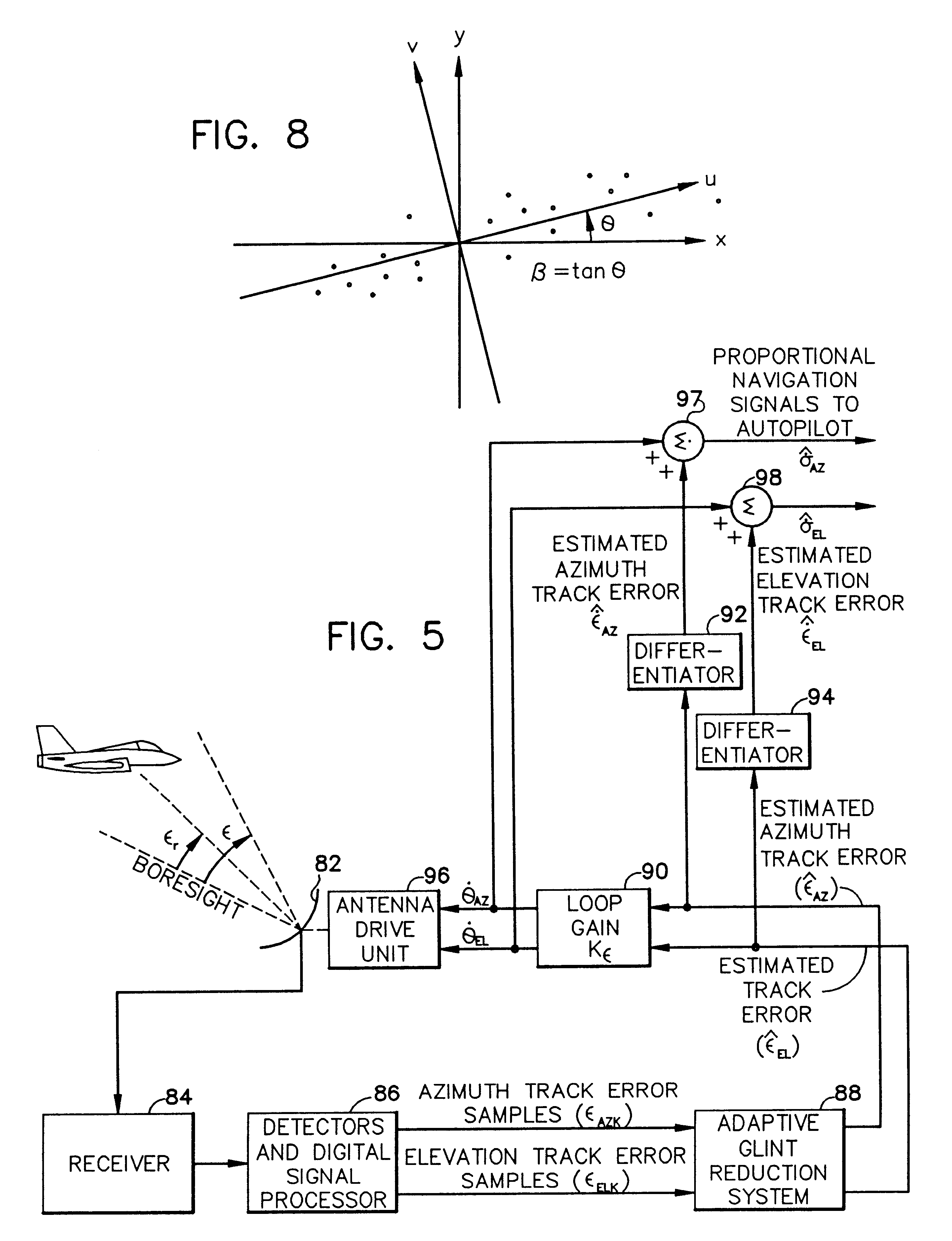
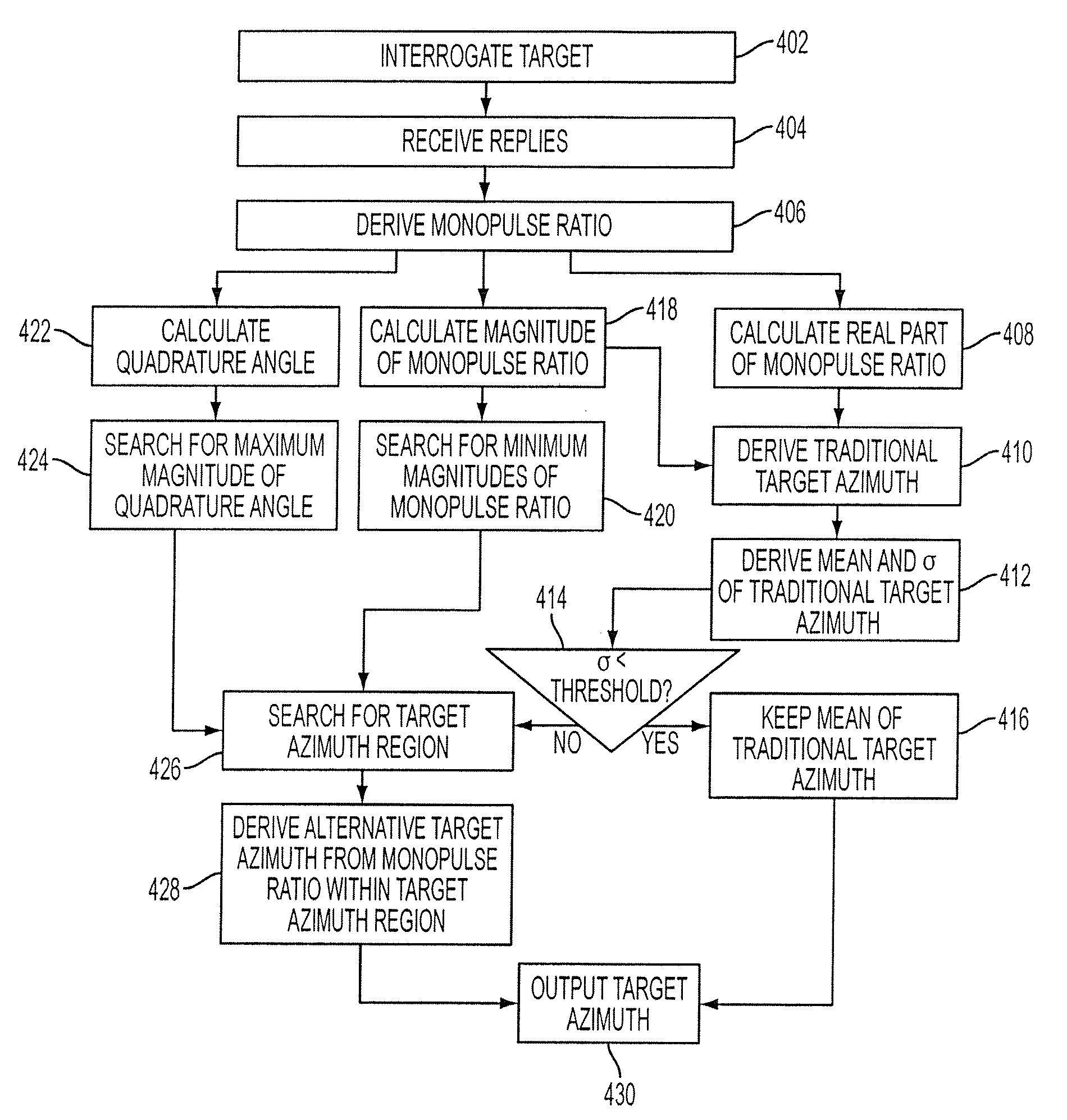
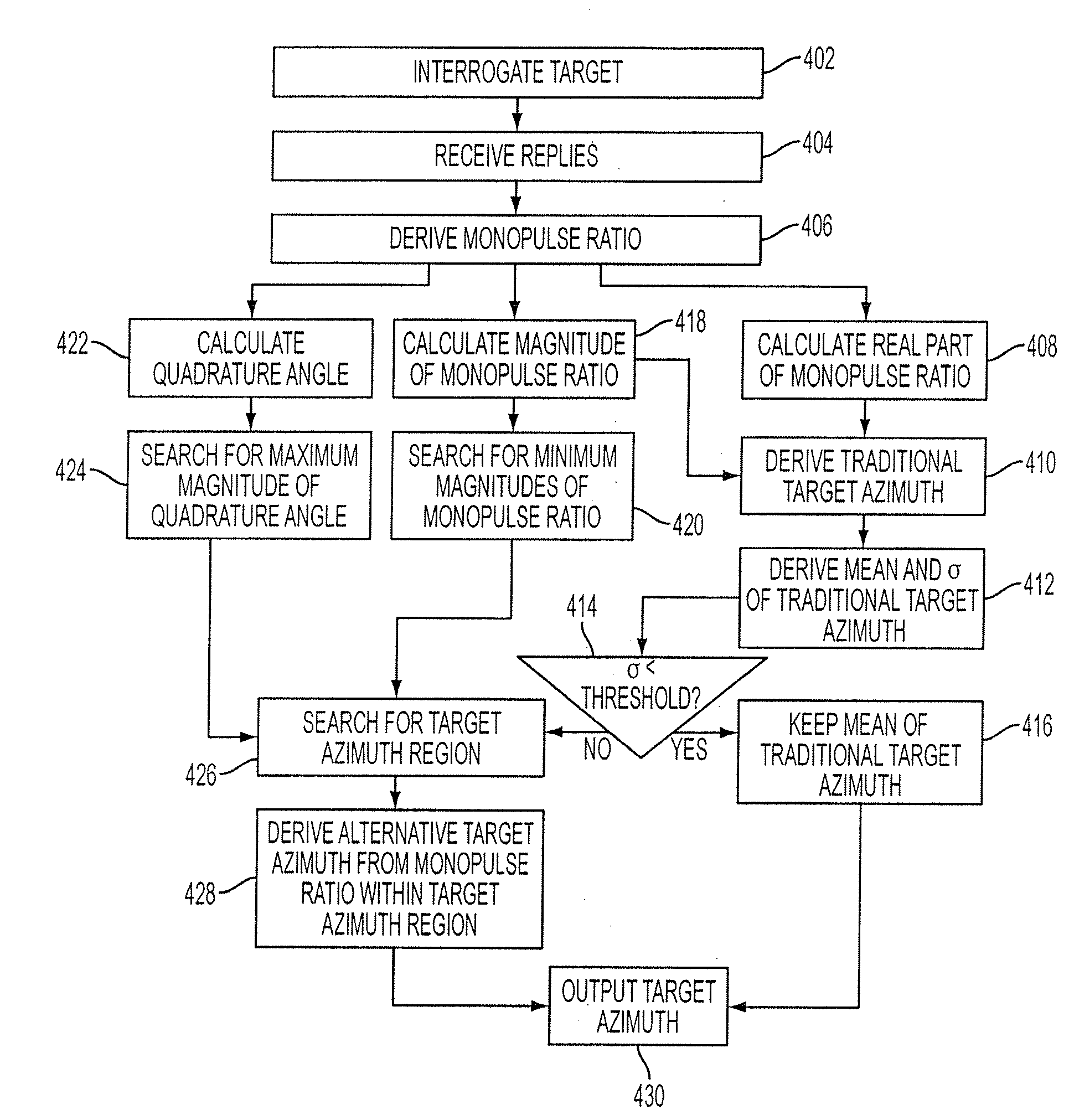
Technique for mitigating multipath impacts on azimuth accuracy in a monopulse interrogator
InactiveUS7675456B2Reduce impactPosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhysicsAntenna boresight
A method for mitigating multipath impacts on azimuth accuracy in a monopulse interrogator is accomplished by calculating samples of monopulse ratio for samples of antenna boresight angles based on data received from an interrogation of a target. Samples of traditional target azimuth from the samples of monopulse ratio are calculated. A mean of the samples of traditional target azimuth is calculated. An alternative target azimuth from the samples of monopulse ratio is calculated. Whether a multipath signal exists is determined from observing a standard deviation of the samples of traditional target azimuth, and using the mean of the traditional target azimuth if a multipath signal does not exist and using the alternative target azimuth if a multipath signal does exist.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
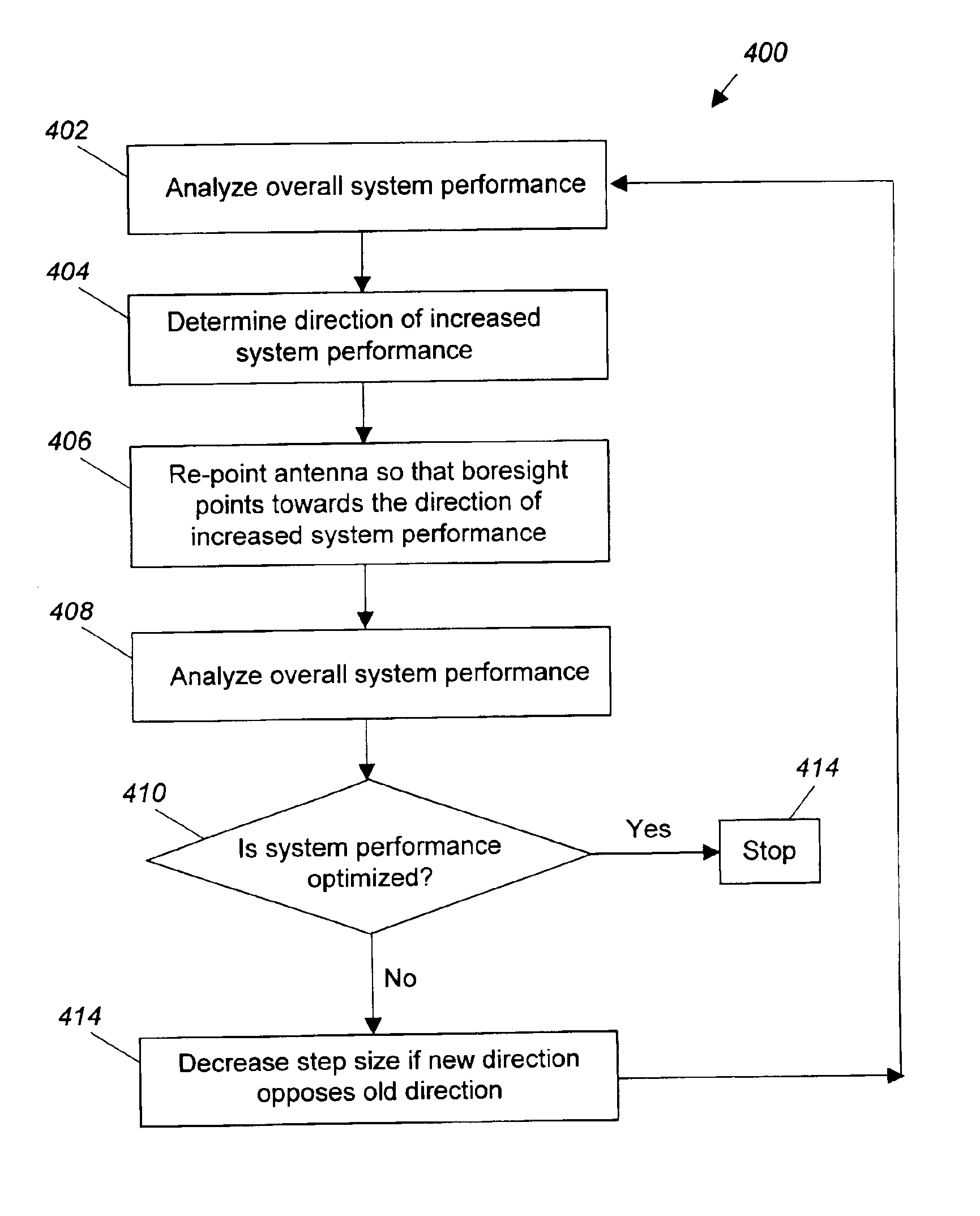
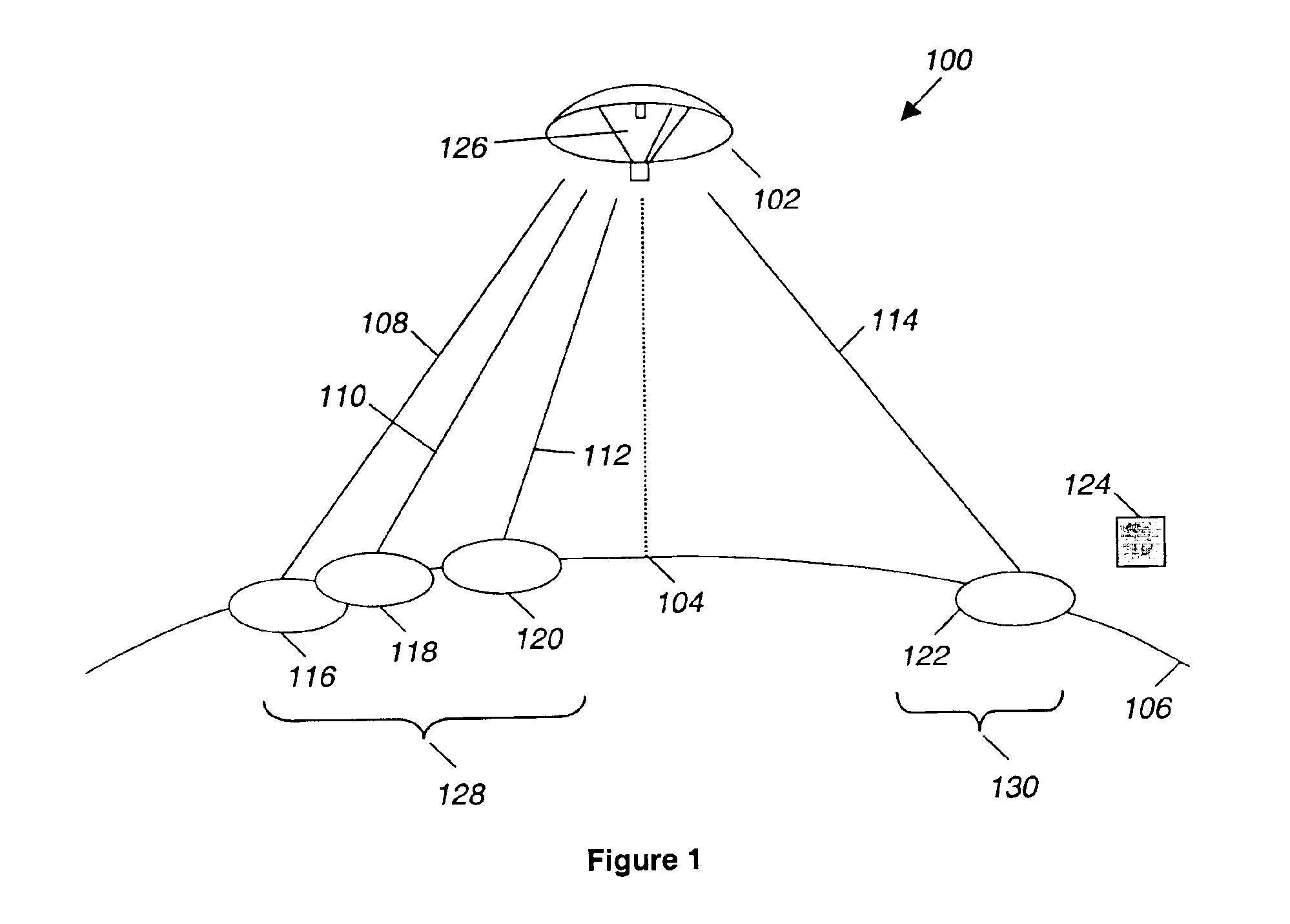
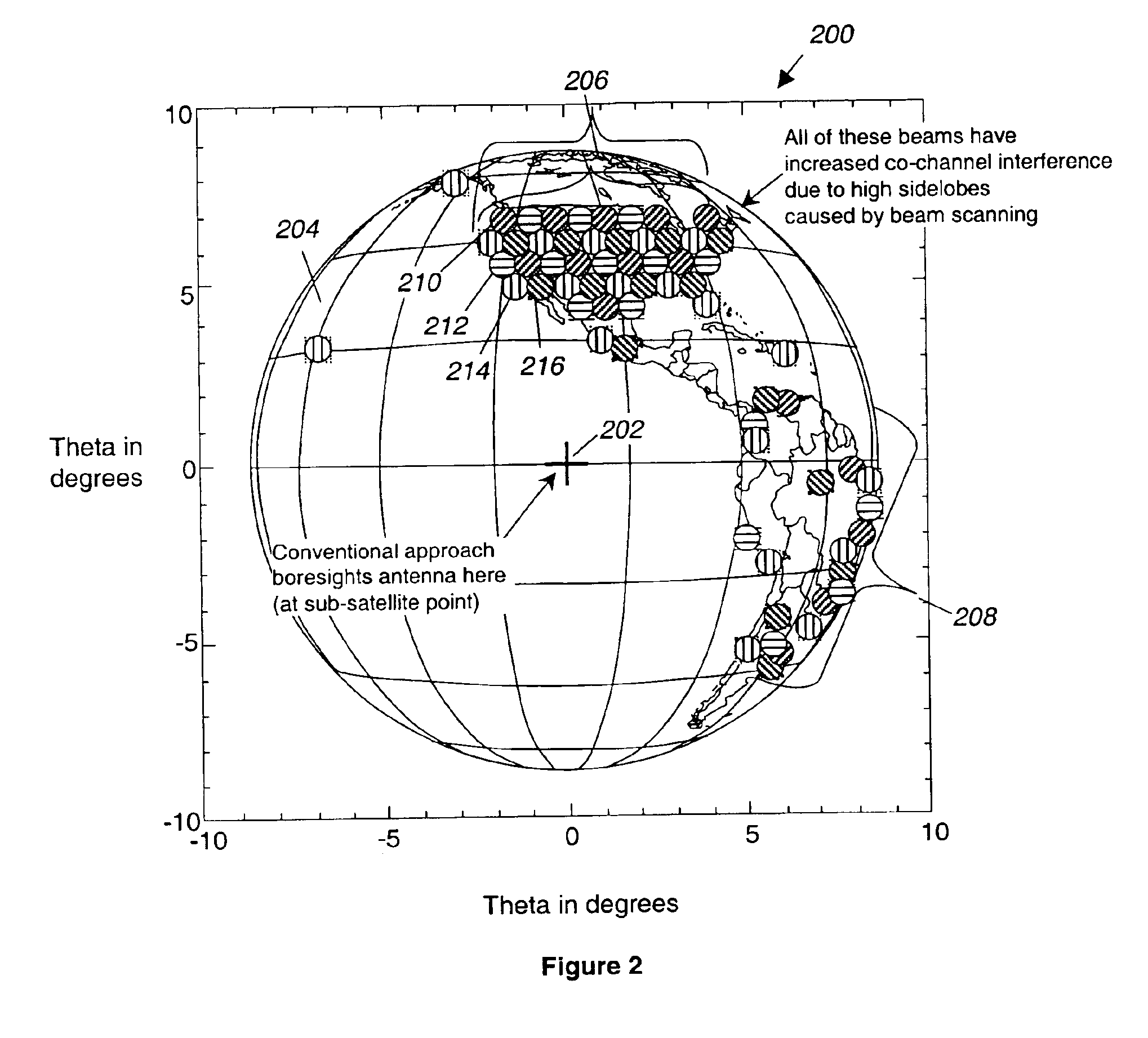
Reducing co-channel interference in satellite communications systems by antenna re-pointing
InactiveUS6940452B2Improve performancePoint to optimizationAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio transmissionCommunications systemHigh density
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Technique for mitigating multipath impacts on azimuth accuracy in a monopulse interrogator
InactiveUS20090096674A1Reduce the impactReduce impactPosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhysicsAntenna boresight
A method for mitigating multipath impacts on azimuth accuracy in a monopulse interrogator is accomplished by calculating samples of monopulse ratio for samples of antenna boresight angles based on data received from an interrogation of a target. Samples of traditional target azimuth from the samples of monopulse ratio are calculated. A mean of the samples of traditional target azimuth is calculated. An alternative target azimuth from the samples of monopulse ratio is calculated. Whether a multipath signal exists is determined from observing a standard deviation of the samples of traditional target azimuth, and using the mean of the traditional target azimuth if a multipath signal does not exist and using the alternative target azimuth if a multipath signal does exist.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
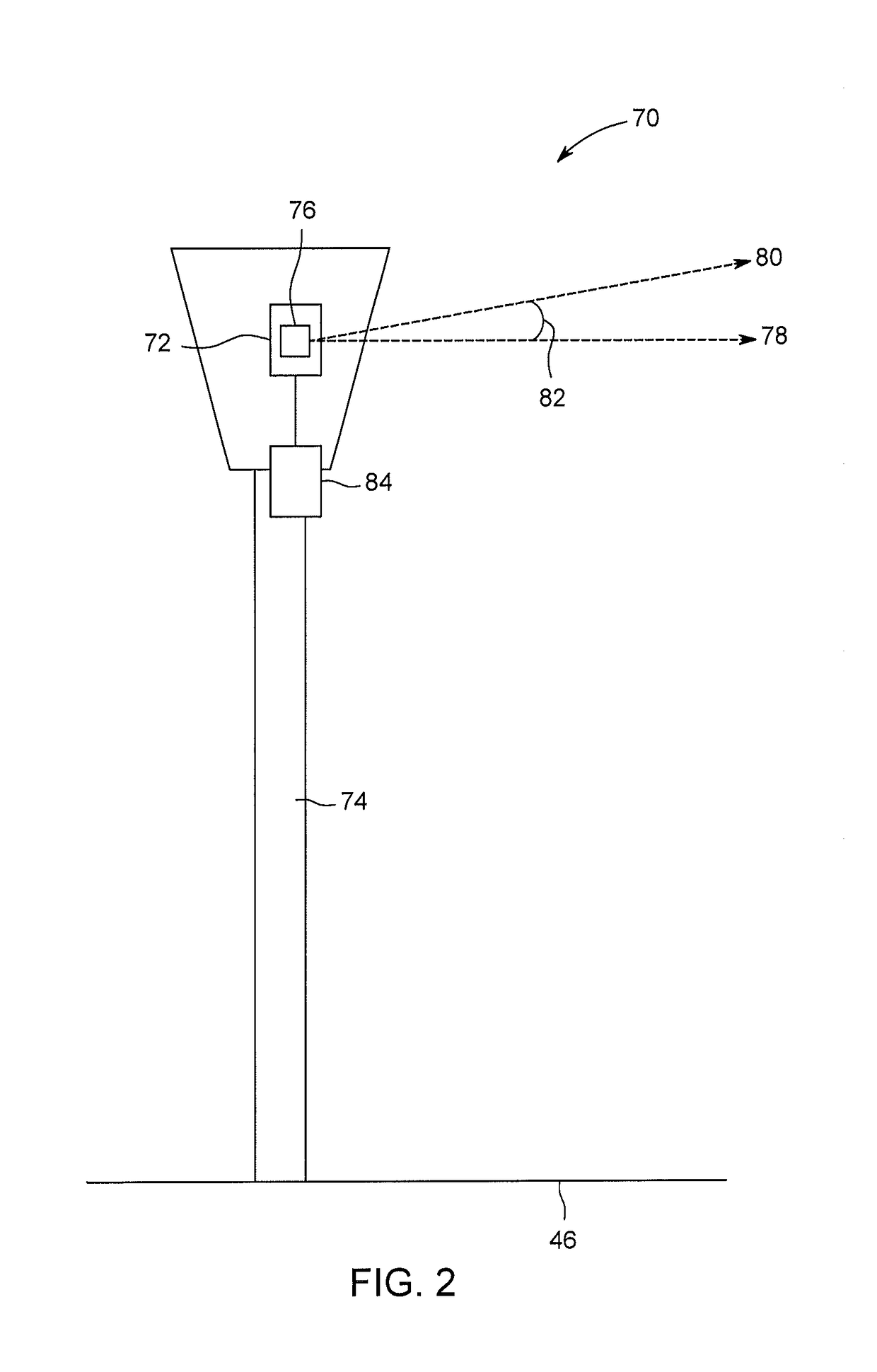
Antenna pointing bias estimation using radar imaging
ActiveUS20100282894A1Error minimizationDirection controllersAntenna supports/mountingsRadar imagingAtmospheric sciences
A system for estimating an antenna boresight direction. The novel system includes a first circuit for receiving a Doppler measurement and a line-of-sight direction measurement corresponding with the Doppler measurement, and a processor adapted to search for an estimated boresight direction that minimizes a Doppler error between the Doppler measurement and a calculated Doppler calculated from the estimated boresight direction and the line-of-sight direction measurement. The line-of-sight direction measurement is measured relative to the true antenna boresight, and the calculated Doppler is the Doppler calculated for a direction found by applying the line-of-sight direction measurement to the estimated boresight direction. In a preferred embodiment, the first circuit receives a Doppler measurement and a line-of-sight direction measurement from each of a plurality of pixels, and the processor searches for an estimated boresight direction that minimizes a sum of squares of Doppler errors for each of the pixels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Directed dipole antenna having improved sector power ratio (SPR)
InactiveUS7535430B2Optimized horizontal plane radiation patternImproved roll-offPolarised antenna unit combinationsDipole antennaRoll-off
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna having a superior Sector Power Ratio (SPR). The antenna may have slant 45 degree dipole radiating elements including directors, and may be disposed on a plurality of tilted element trays to orient an antenna boresight downtilt. The directors may be disposed above or about the respective dipole radiating elements. The antenna has a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, a high-roll off, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
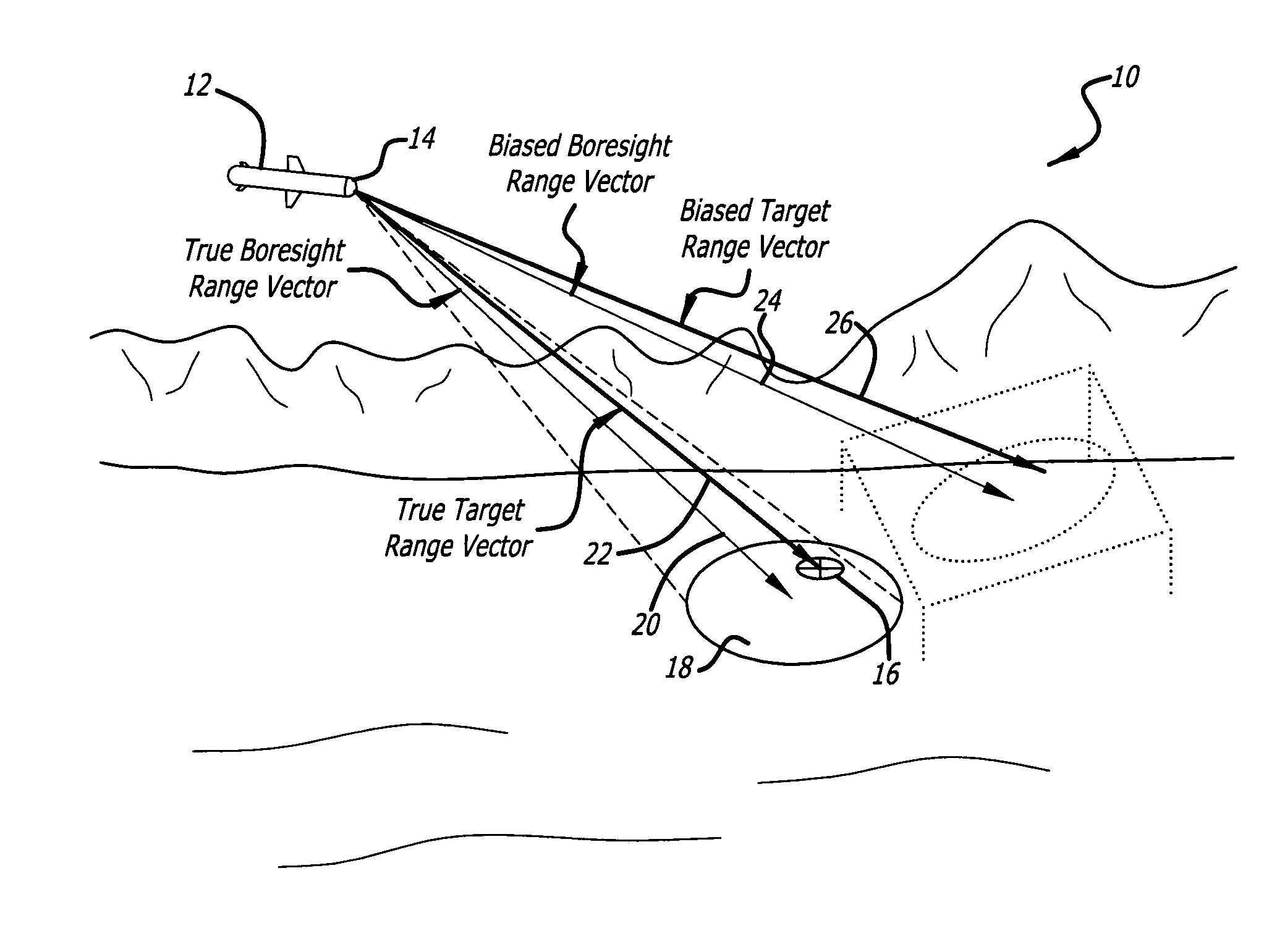
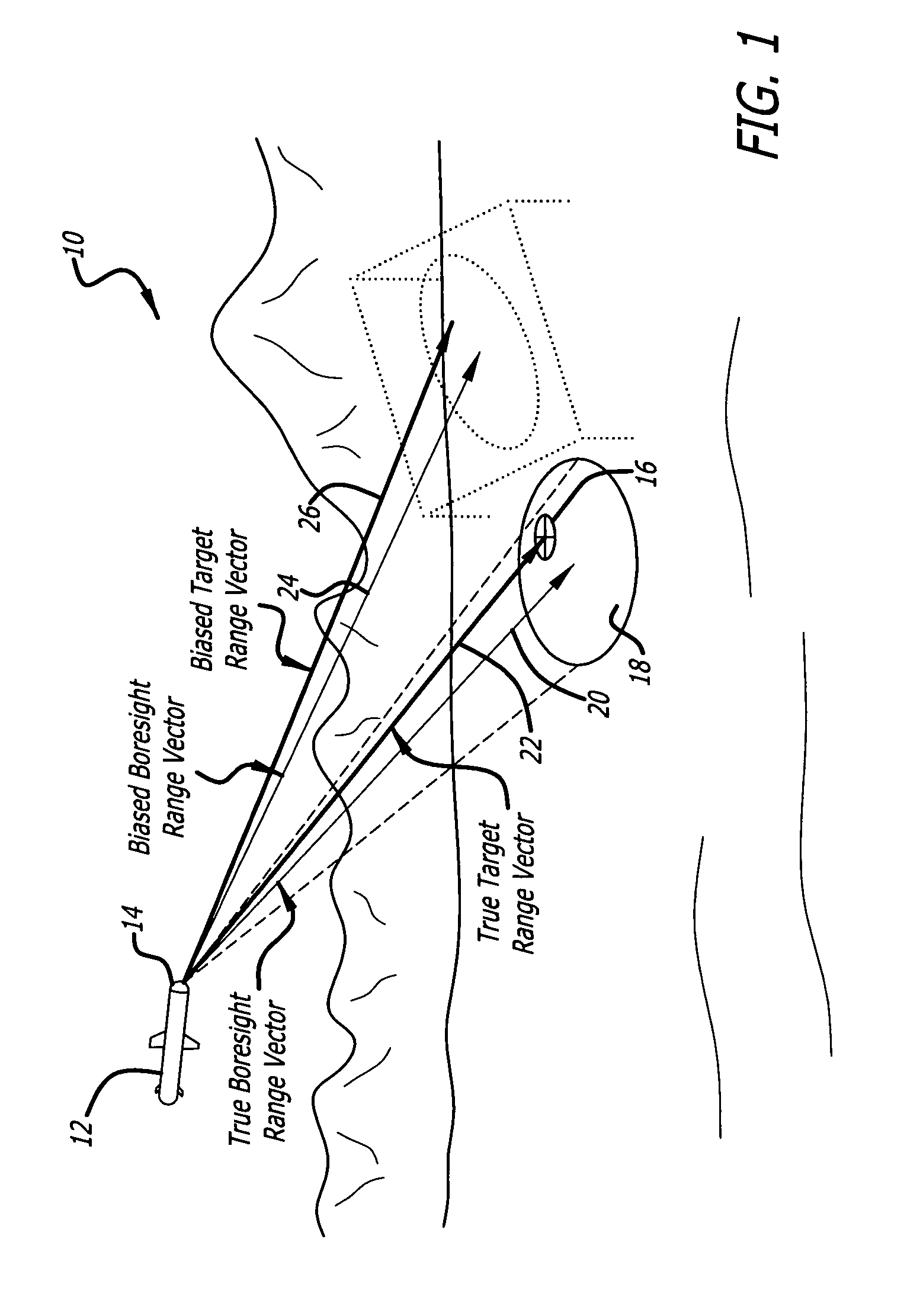
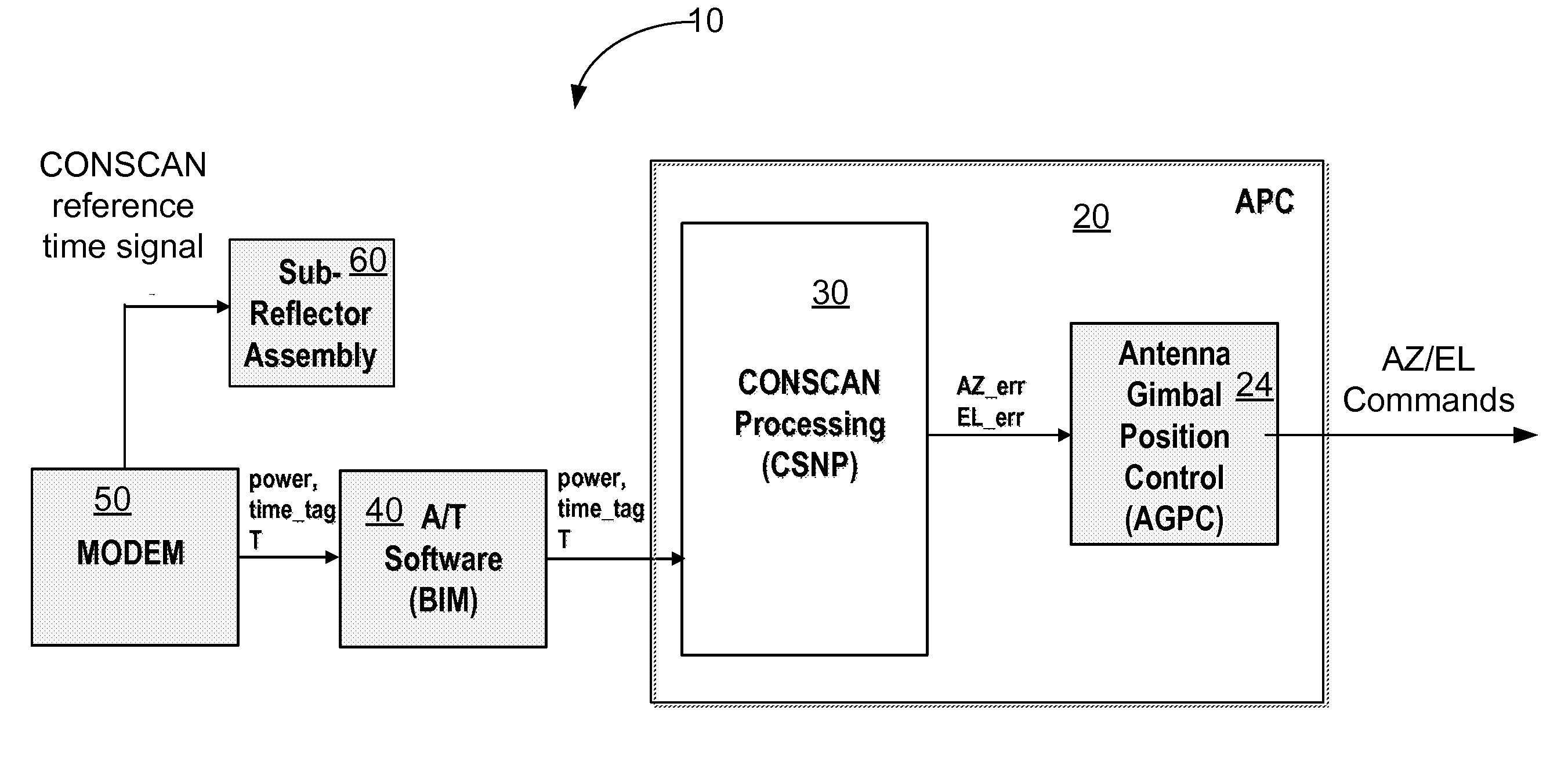
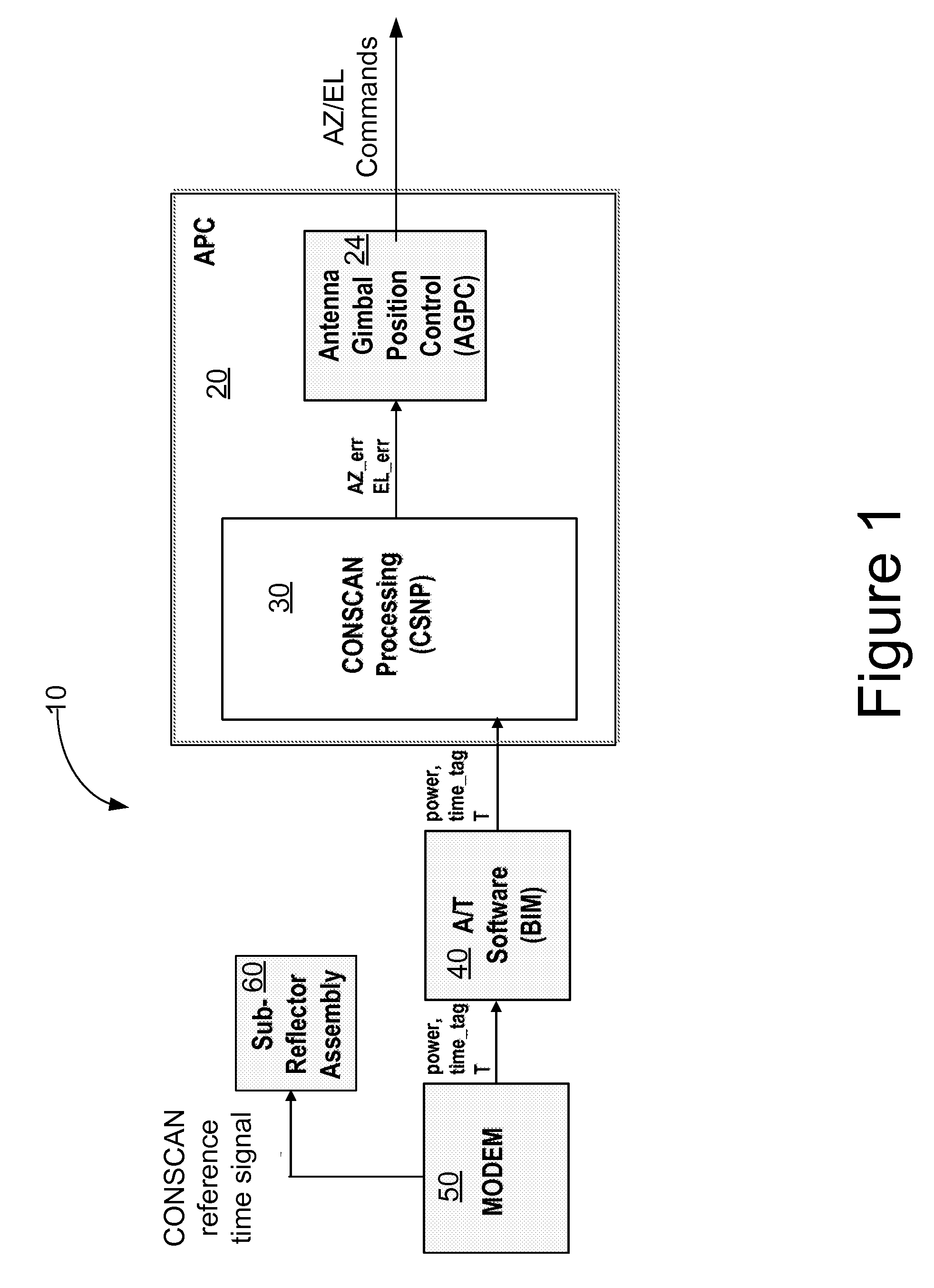
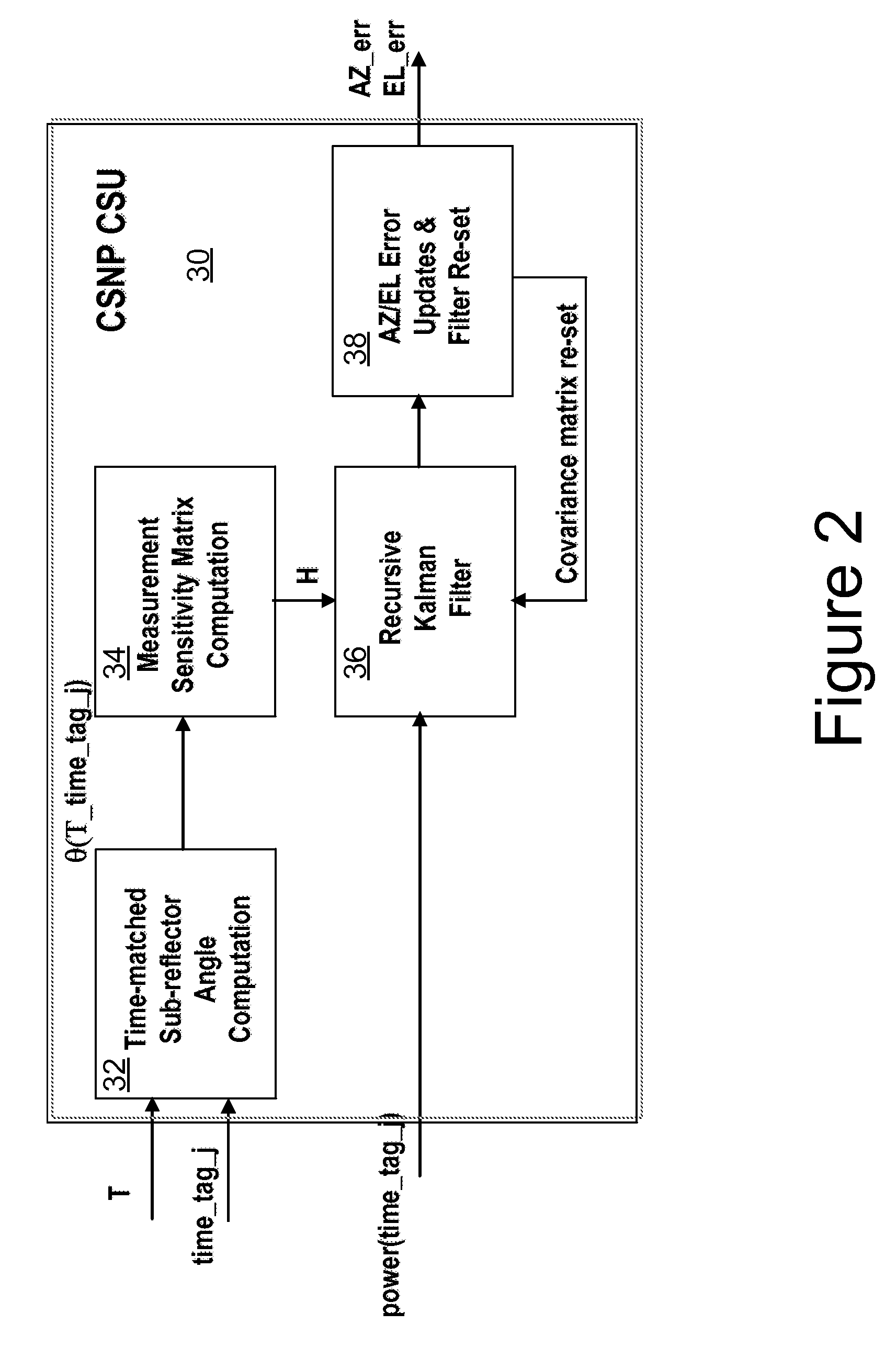
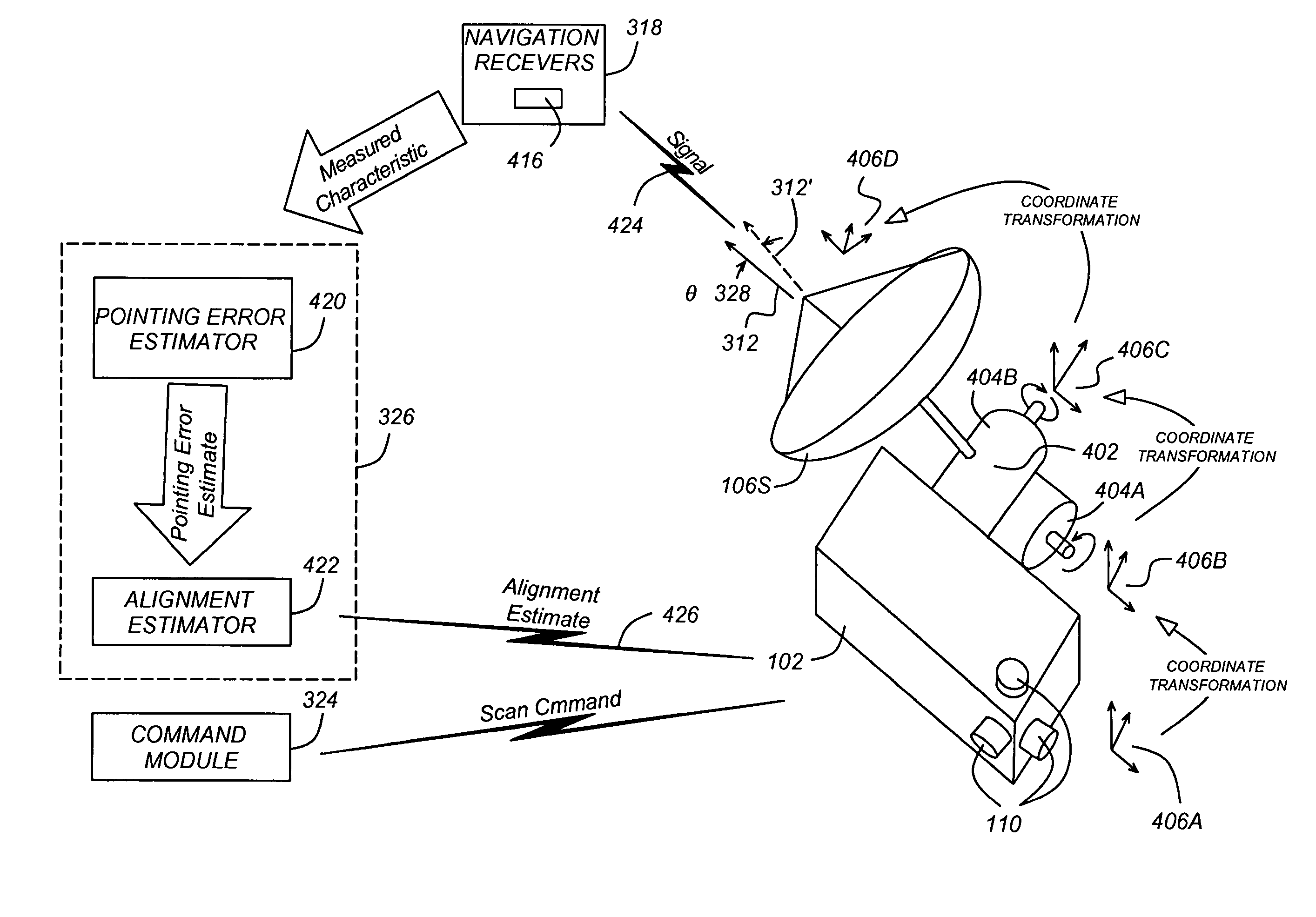
Method and apparatus for precision antenna boresight error estimates
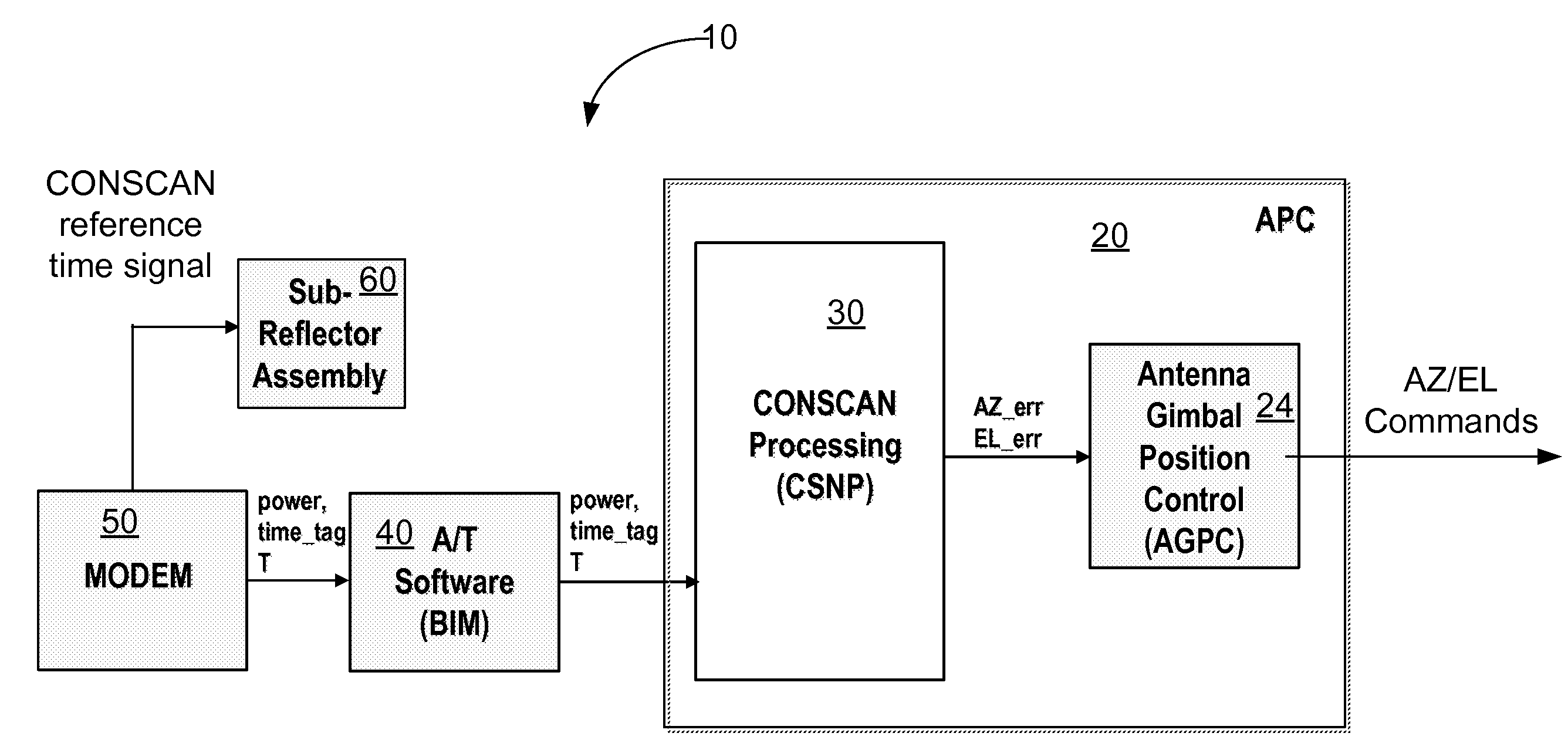
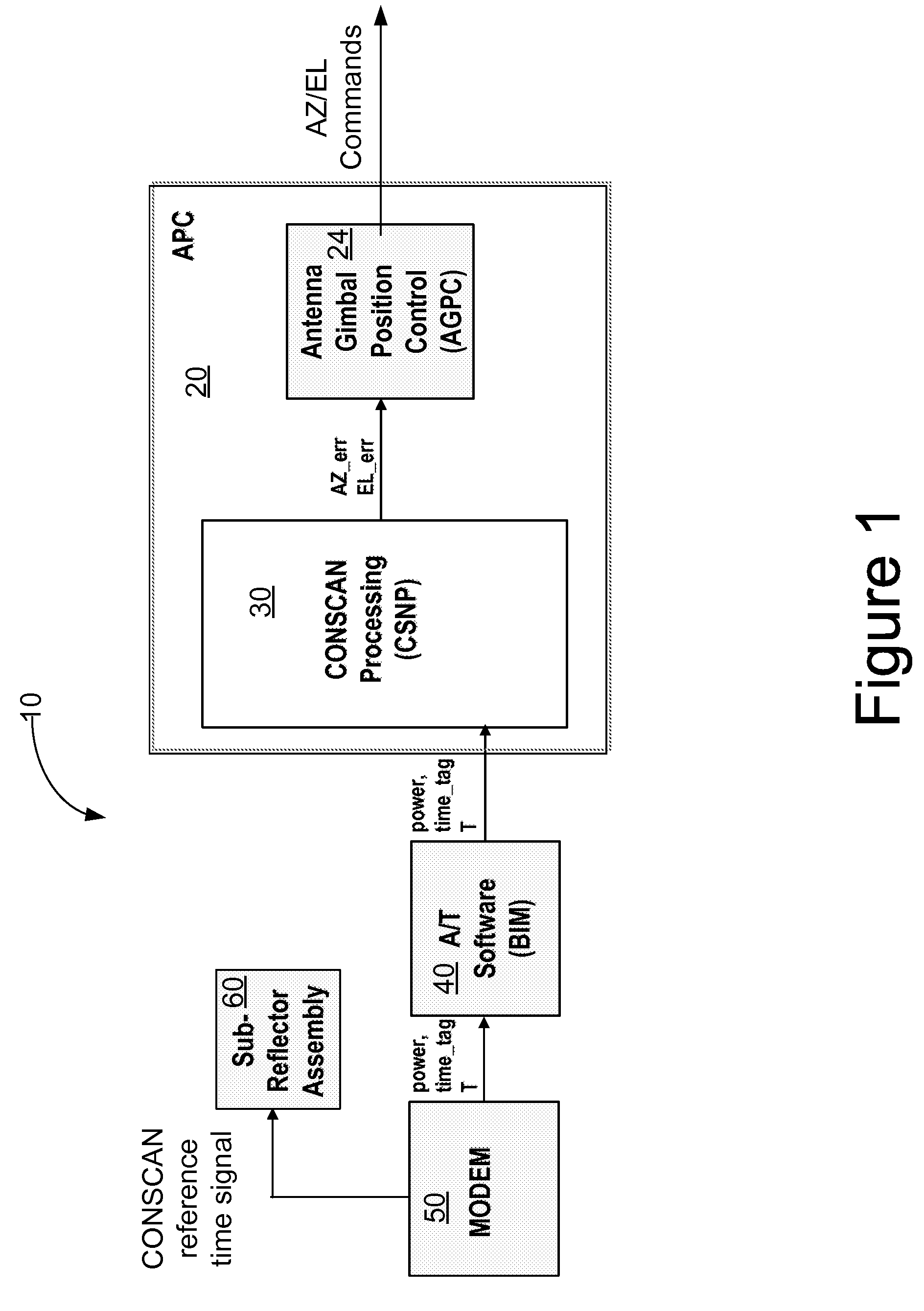
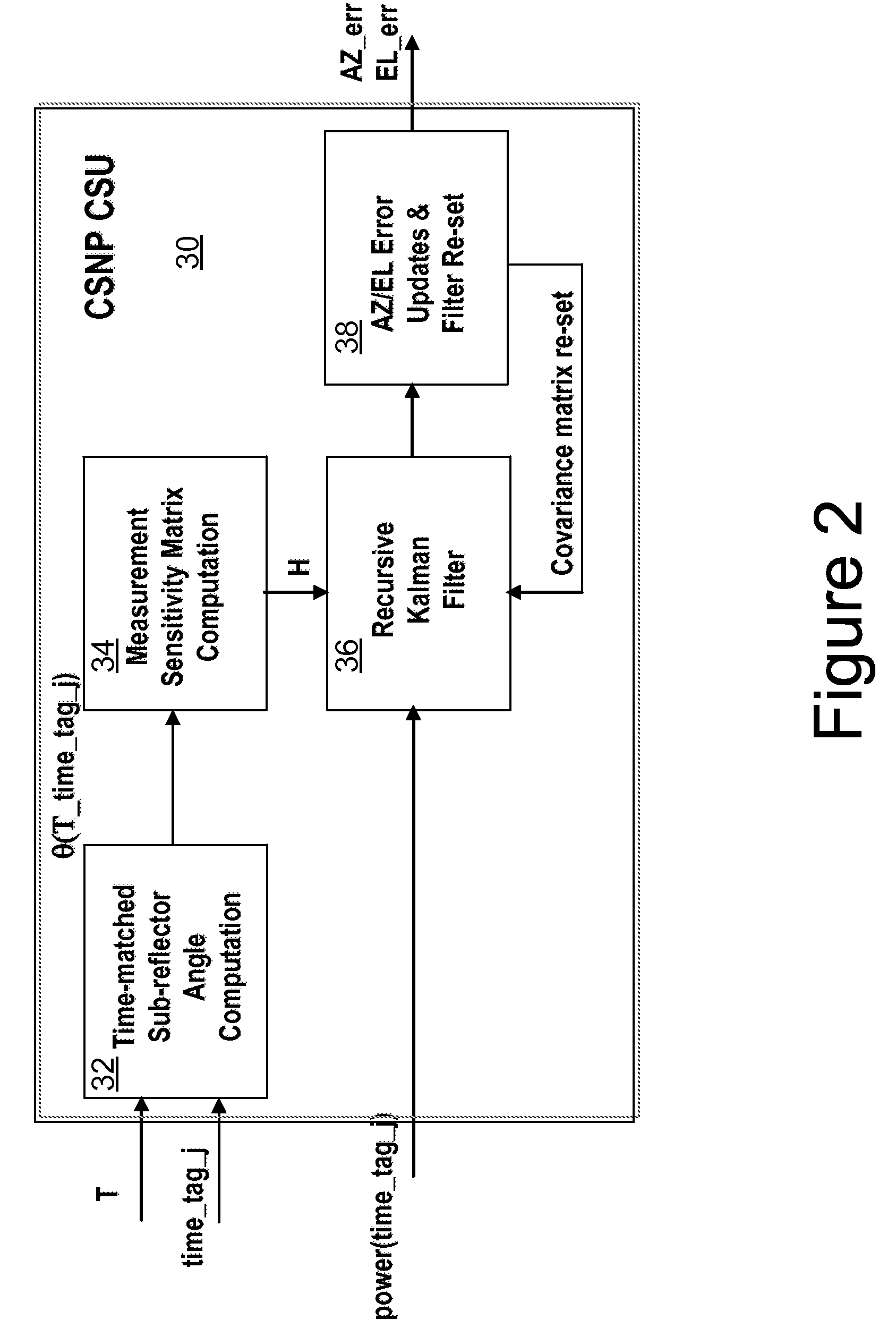
Methods, systems and devices are disclosed for positioning an antenna having a sub-reflector assembly. A conical scan processor receives a period for a reference time pulse and a time tag. The processor calculates a rotation angle of the sub-reflector assembly using the received period for the reference time pulse and the received time tag. The processor may also receive a power measurement associated with the time tag. The processor may calculate and then output antenna boresight errors based on the calculated rotation angle of the sub-reflector assembly and the power measurements associated with the time tag.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Sensed situation millimeter-wave communications beam control
The present disclosure relates to a system includes an antenna disposed on a pole and a beam control unit disposed on the pole and operably coupled to the antenna. The beam control unit includes one or more sensors configured to detect one or more parameters related to tilting or bending of the pole. In addition, the beam control unit is configured to determine a misalignment of an antenna boresight as compared to an initial antenna boresight direction and to re-align the antenna boresight to the initial antenna boresight direction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Antenna pointing bias estimation using radar imaging
A system for estimating an antenna boresight direction. The novel system includes a first circuit for receiving a Doppler measurement and a line-of-sight direction measurement corresponding with the Doppler measurement, and a processor adapted to search for an estimated boresight direction that minimizes a Doppler error between the Doppler measurement and a calculated Doppler calculated from the estimated boresight direction and the line-of-sight direction measurement. The line-of-sight direction measurement is measured relative to the true antenna boresight, and the calculated Doppler is the Doppler calculated for a direction found by applying the line-of-sight direction measurement to the estimated boresight direction. In a preferred embodiment, the first circuit receives a Doppler measurement and a line-of-sight direction measurement from each of a plurality of pixels, and the processor searches for an estimated boresight direction that minimizes a sum of squares of Doppler errors for each of the pixels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Route-based directional antenna
The present disclosure relates to an antenna device for a vehicle for optimizing the signal strength or quality from a mobile network having at least one fixed transceiver. The device comprises: at least one directional antenna; at least one turning device, such as an electric motor, for rotating the directional antenna around an axis substantially perpendicular to the antenna boresight; and a microprocessor configured to calculate an azimuthal rotation angle for pointing the directional antenna to at least one selected fixed transceiver. The calculated azimuthal rotational angle is based on: directional and positional data of the vehicle; positional data of the selected fixed transceivers; and a route for navigating the vehicle between a starting point and a destination. The azimuthal rotation angle of the directional antenna is calculated continuously or at intervals, such that the signal strength or quality from the mobile network is continuously optimized along the route. The present disclosure is further related to a directional wireless hotspot device for communication in a mobile network, wherein the device comprises at least two directional antennas The present disclosure further relates to a method for automatically pointing a directional antenna on a vehicle to a fixed transceiver in a mobile network for optimizing the signal strength or quality, wherein the antenna is pointed to a transceiver based a calculated route for navigating between a starting point and a destination.
Owner:MIWIRE APS
Method for correcting direction-finding coning effect of one-dimensional interferometer
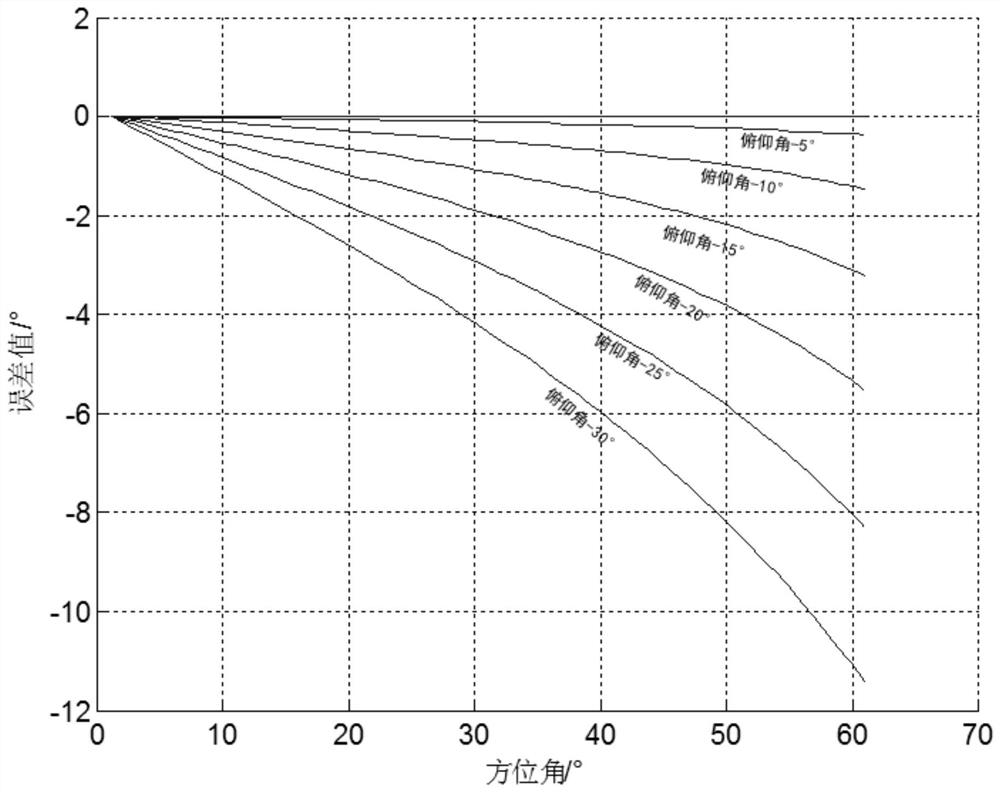
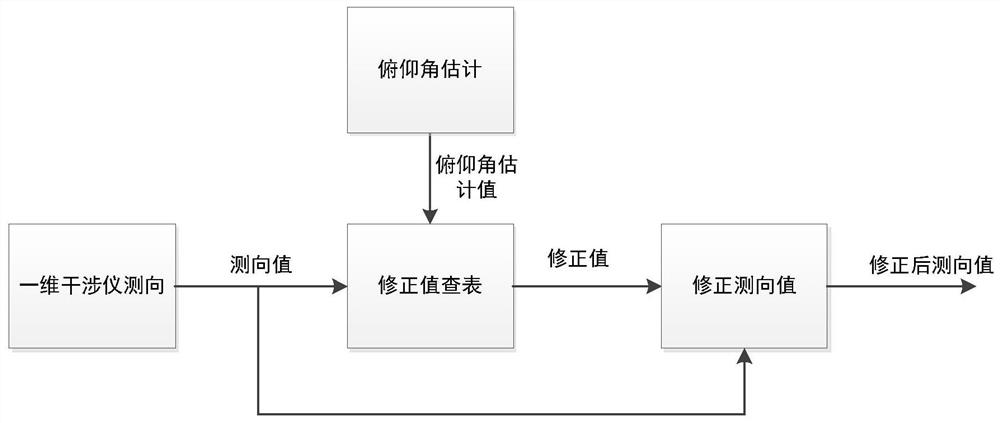
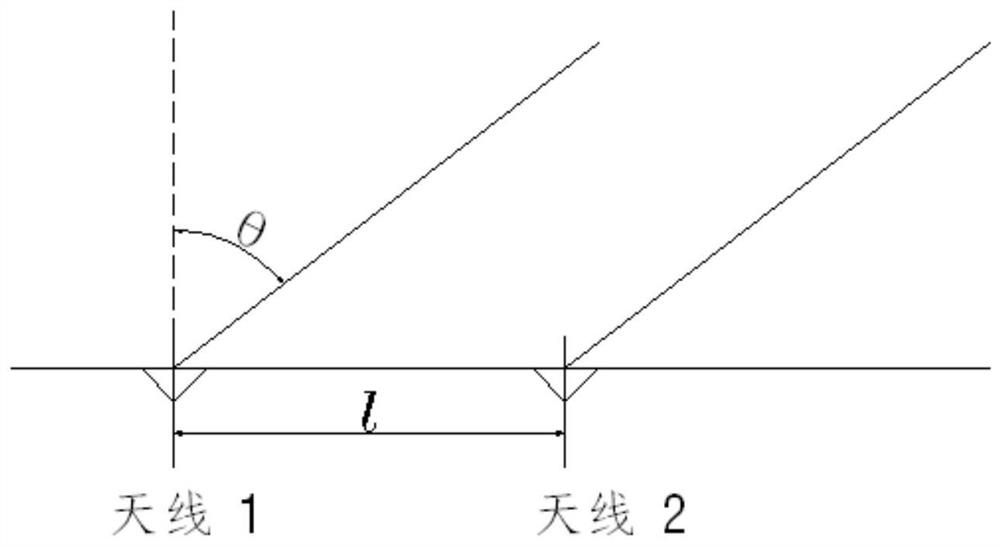
ActiveCN113884977AHigh precisionSave computing resourcesRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadio wave finder monitoring/testingSignal wavePhase difference
The invention discloses a method for correcting the direction-finding coning effect of a one-dimensional interferometer, based on the direction-finding principle of the one-dimensional interferometer, a signal arrival angle theta is shown in the specification, phi is the phase difference of two paths of signals, lambda is the signal wavelength, l is the antenna spacing, and when an incident signal and an antenna visual axis are not in the same plane, the coning effect exists. The correction method comprises the following steps: based on an obtained signal pitch angle beta and a measured signal arrival angle theta, completing correction calculation of an azimuth angle alpha through the following formula: alpha = sin-1 (sin theta / cos beta). According to the method, the influence of a coning effect caused by a large pitch angle can be avoided, and the azimuth direction finding precision of the one-dimensional interferometer can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST CHINA RES INST OF ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Method and apparatus for precision antenna boresight error estimates
Methods, systems and devices are disclosed for positioning an antenna having a sub-reflector assembly. A conical scan processor receives a period for a reference time pulse and a time tag. The processor calculates a rotation angle of the sub-reflector assembly using the received period for the reference time pulse and the received time tag. The processor may also receive a power measurement associated with the time tag. The processor may calculate and then output antenna boresight errors based on the calculated rotation angle of the sub-reflector assembly and the power measurements associated with the time tag.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Laser tracker system and technique for antenna boresight alignment
ActiveUS8567077B2Fast processingEasy to implementAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSurveying instrumentsEngineeringLaser tracker
A system and processes for aligning an antenna boresight from a position which is internal to a structure on which the antenna is mounted is described. The system includes a laser tracking system and a plurality of targets disposed on a surface of the antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Segmented antenna reflector with shield
InactiveUS8405570B2Improve rigidityImprove the level ofCollapsable antennas meansAntenna supports/mountingsCouplingEngineering
An antenna reflector includes a central segment with a peripheral coupling portion and a plurality of peripheral segments, each provided with a reflector portion and a shield portion. A proximal portion of each shield portion is dimensioned to couple with the peripheral coupling portion, a reflector portion edge of each peripheral segment is dimensioned to couple with adjacent reflector portion edges and a shield portion edge of each peripheral segment is dimensioned to couple with adjacent shield portion edges. The central segment and the reflector portion of the peripheral segments together form a reflector dish. The shield portions together provide a circumferential shield extending from a periphery of the reflector dish along an antenna boresight of the reflector dish.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Spot beam antenna boresight calibration using GPS receivers
ActiveUS7256734B2Reduce the impact of noiseMaximizes alignment error observabilitySatellite radio beaconingRadio transmissionGps receiverSignal characteristic
Owner:THE BOEING CO
A Spot Alignment Method Based on Four-quadrant Detector
Owner:浙江慧眼光电科技有限公司
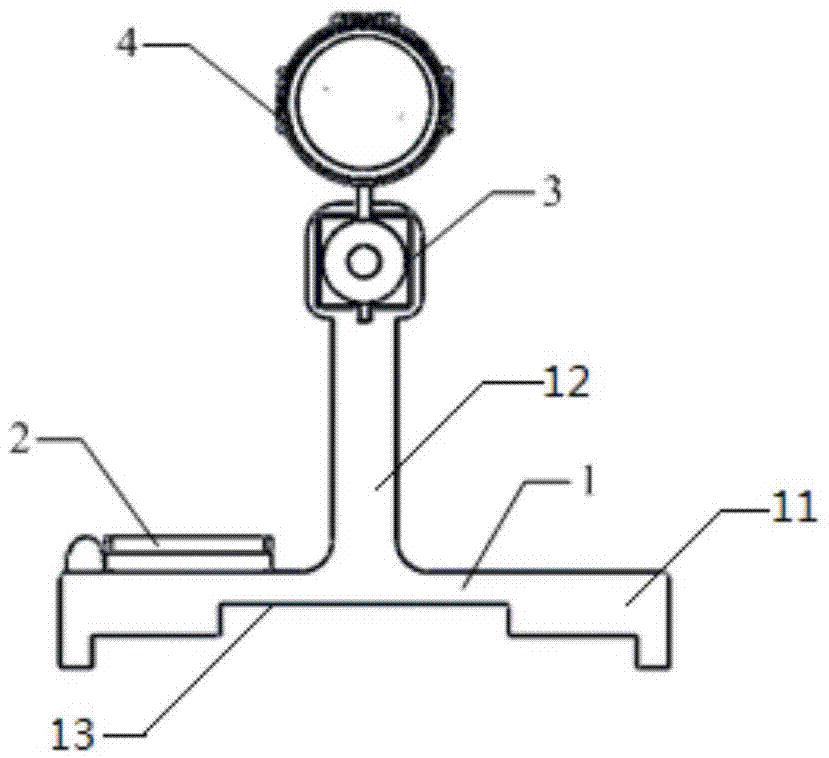
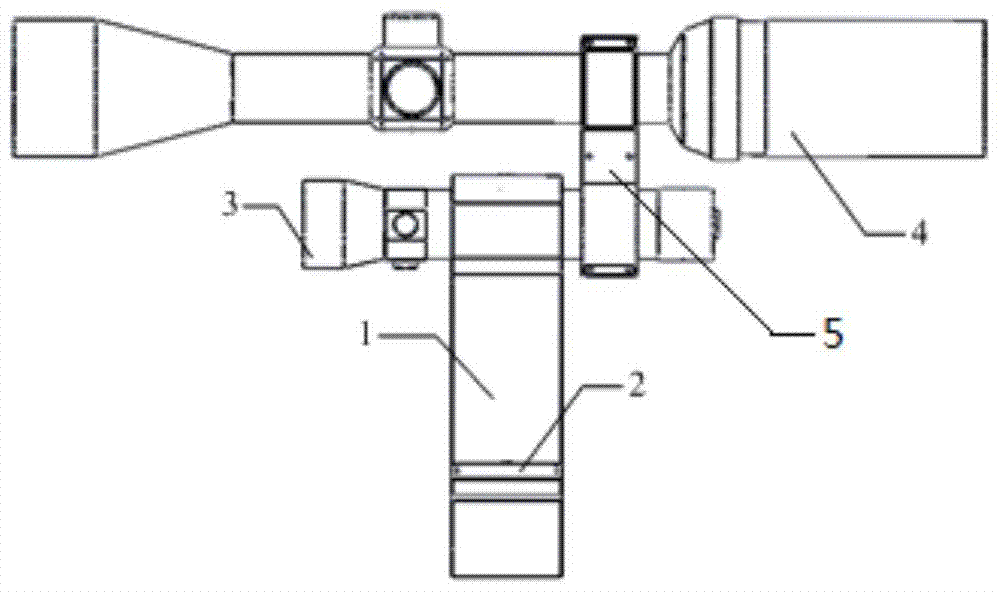
A fast aiming device and method for a waveguide antenna
The invention discloses a fast aiming device for a waveguide antenna, which includes an aiming base, an angle indicating device and an aiming point indicating device. The aiming base is an inverted T-shaped structure, which includes a base and an installation shaft vertically connected to the base. The surface is flat, and the lower surface of the base is recessed with a card slot, which is connected with the waveguide antenna; the angle indicating device is fixed on the upper surface of the base; the aiming point indicating device includes a laser pointer and an optical sight; the laser pointer is set on the installation shaft On the upper end, the optical sight is arranged directly above the laser pointer, the laser pointer is provided with an optical axis adjustment device, and the optical sight is provided with a visual axis adjustment device. The invention can realize fast aiming of visible aiming points at different distances on the premise of ensuring the aiming accuracy of the waveguide antenna in the measurement of the microwave radiation field, and improve the convenience of aiming the waveguide antenna in the measurement of the radiation field.
Owner:中国人民解放军63660部队
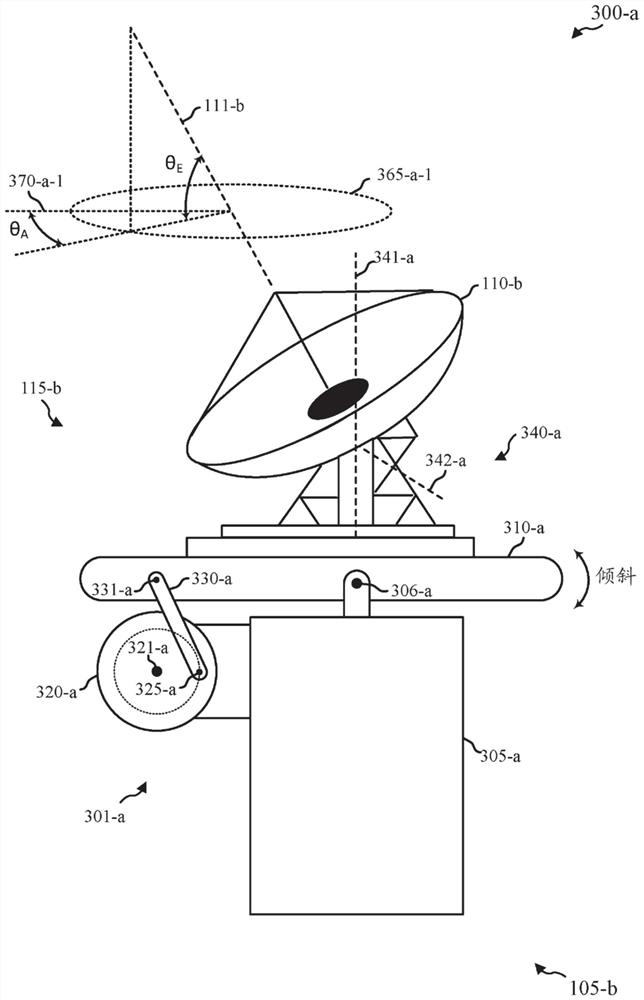
Antenna positioner with eccentric tilt position mechanism
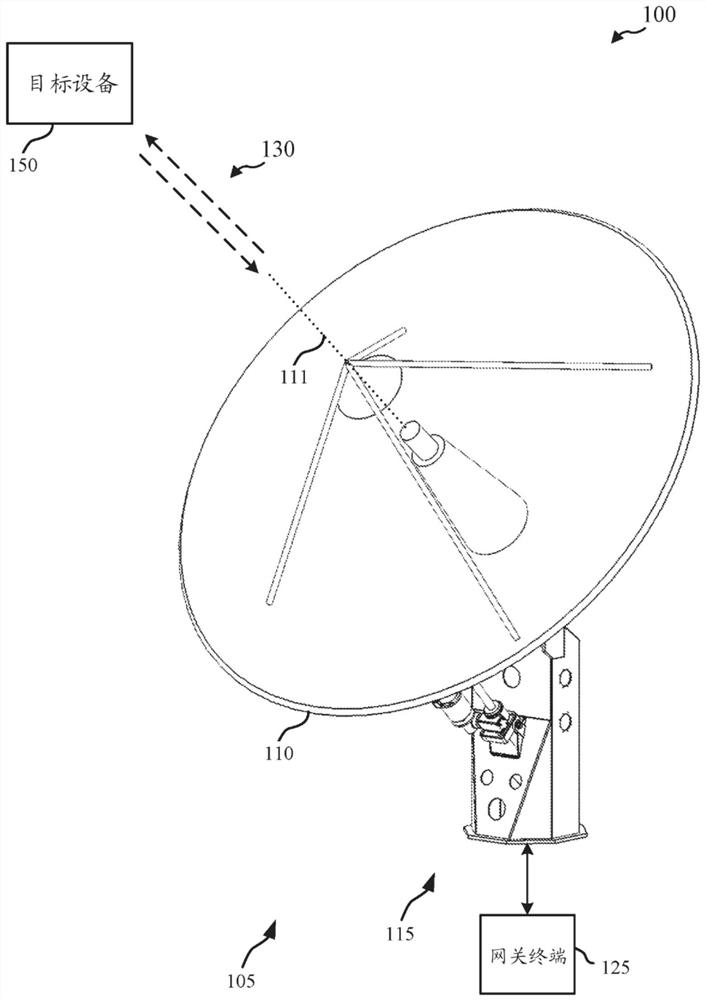
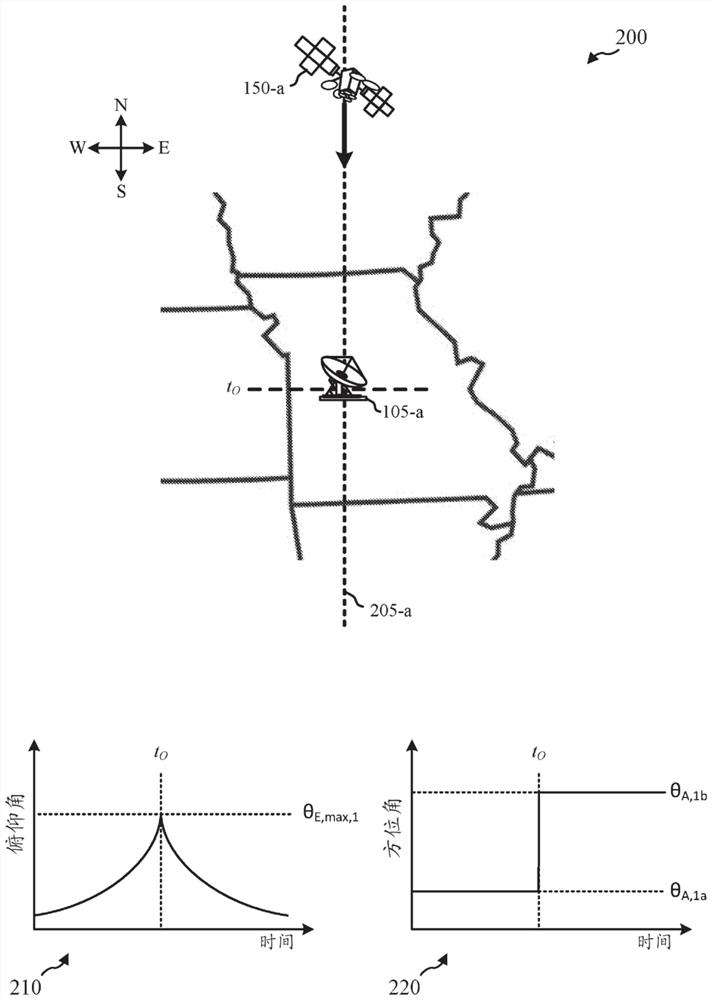
Methods, systems, and devices are described for antenna positioning with an eccentric tilt pointing mechanism. For example, a system in accordance with the present disclosure may include a base structure and an intermediate structure that is rotatably coupled with the base structure about a first axis (e.g., a tilt axis). The system may also include a positioning system that is coupled with the intermediate structure and configured to orient an antenna boresight about at least two angular degrees of freedom with respect to the intermediate structure (e.g., in an elevation-over-azimuth configuration). The system may also include an actuator between the base structure and the intermediate structure that is configured to set, change, or maintain an angle between the base structure and the intermediate structure, which, in some examples, may include a rotation of an eccentric element based on a predicted path of a target device.
Owner:VIASAT INC
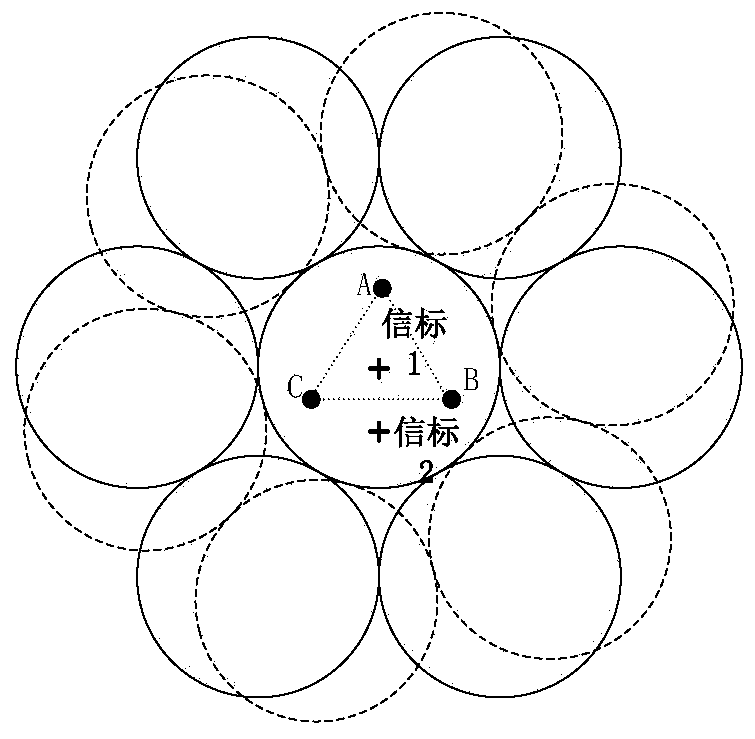
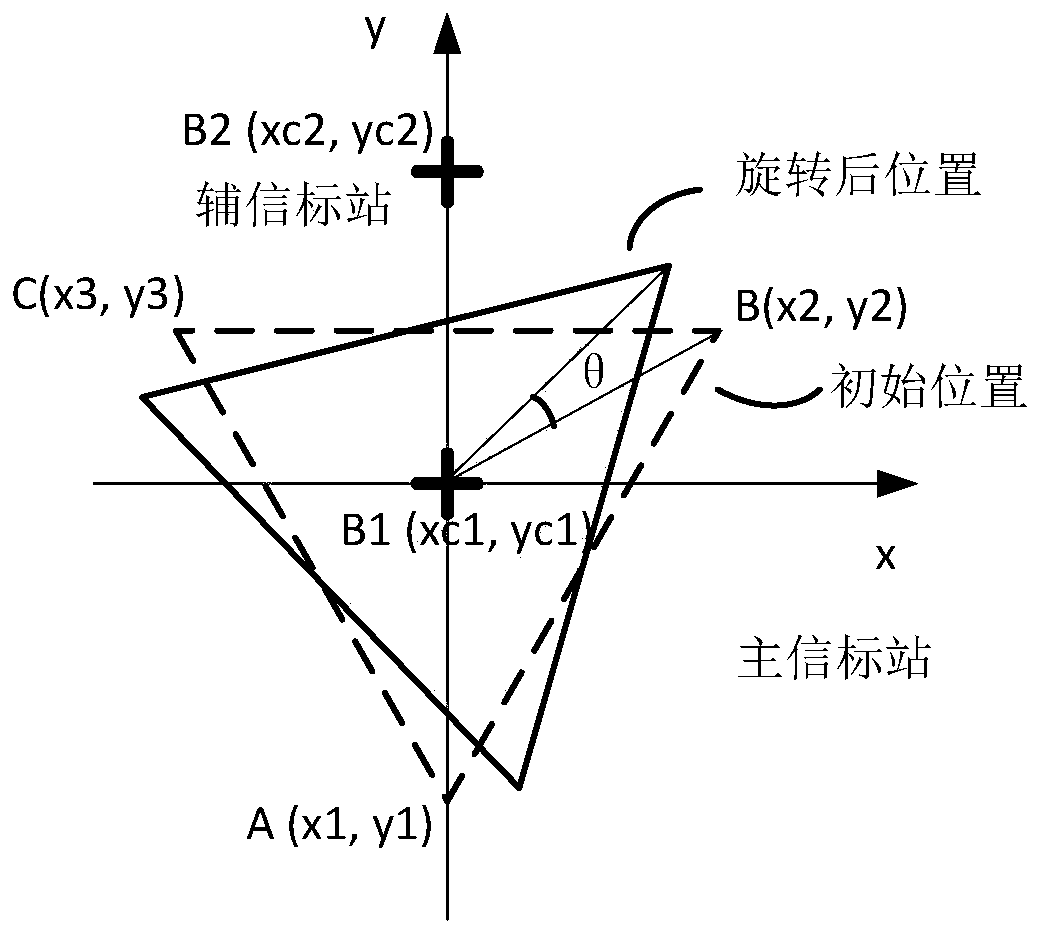
Method and system for measuring satellite antenna rotation angle around visual axis
ActiveCN110514107BCalibration pointingReduce computationUsing electrical meansSatellite antennasPower sensor
The invention discloses a measurement method of a rotation angle of a satellite antenna about an optical axis. Three feed source power sensors are arranged on a satellite, a ground leading beacon station is correspondingly arranged on the ground for three feed source optical axis centers; each antenna optical axis is fixedly pointed to the ground leading beacon station; the method is characterizedby comprising the following steps: setting one or more ground auxiliary beacon stations in an optical axis center beam ground coverage range, wherein a satellite feed source receives a ground beaconsignal, and the receiving signal power is the function of the distance between the feed source center and the beacon station; computing the rotation angle about the optical axis by measuring the signal power of the beacon station. An measurement system disclosed by the invention is mainly composed of the ground leading beacon station, the auxiliary beacon stations and three on-satellite feed source power sensors; the rotation about optical axis of the satellite antenna can be measured and the pointing of the multi-beam satellite antenna can be calibrated, and the computation burden can be greatly reduced when only one ground beacon station is existent.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com