Electric motor control device
A technology of a control device and a motor, which is used in motor control, motor generator control, AC motor control, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to correctly calculate the limit torque value, inability to eliminate voltage saturation, and inability to obtain sufficient torque.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
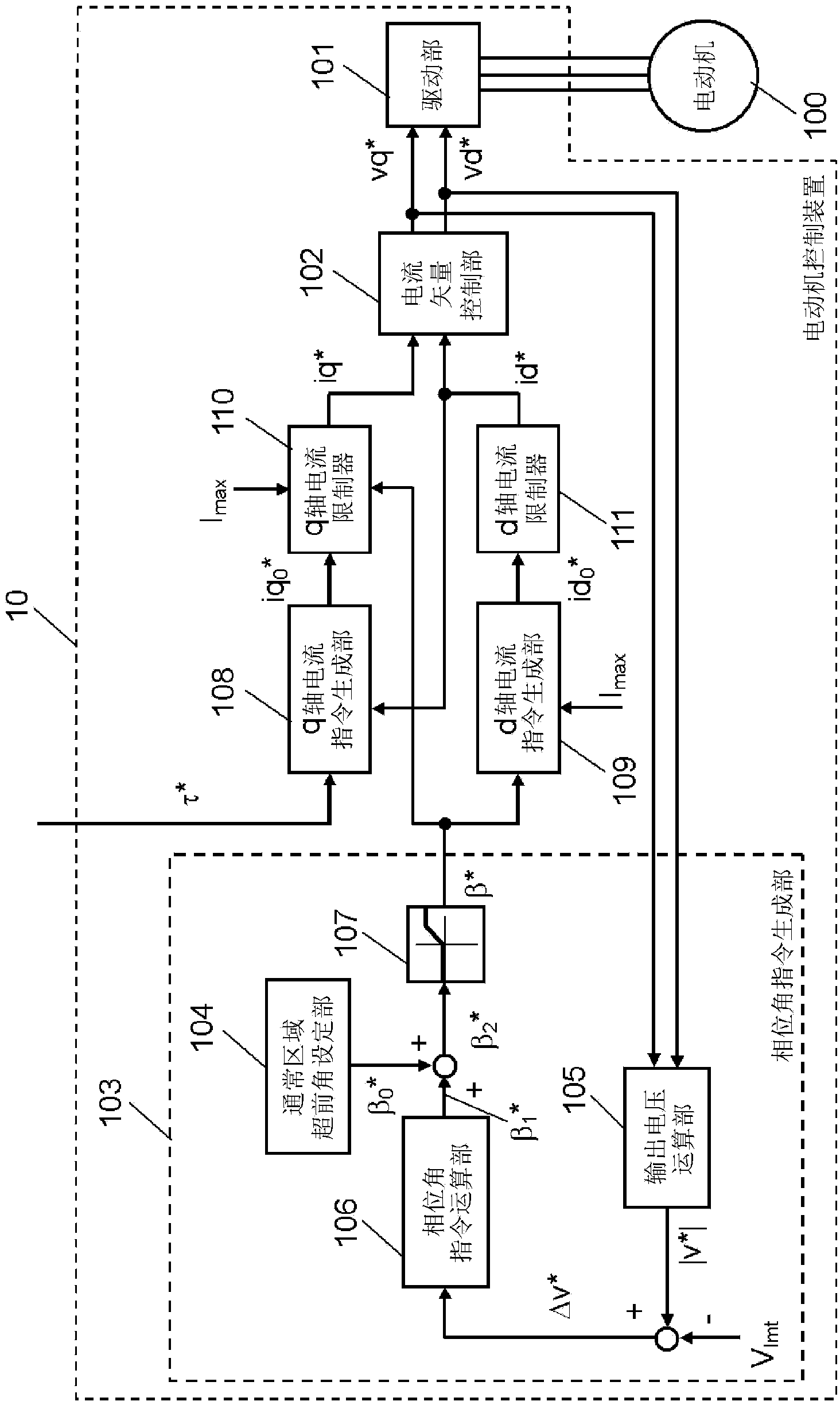
[0033] figure 1 It is a block diagram of the motor control device 10 in Embodiment 1 of this invention. The present motor control device 10 is constituted by a drive control system that drives a permanent magnet synchronous motor 100 in accordance with an external torque command τ*.
[0034] First, in figure 1Among them, the motor 100 has a permanent magnet (not shown) and a winding (not shown) wound around an iron core or the like. The rotor rotates by applying AC power to the winding from the motor control device 10 . exist figure 1 In , an example of the configuration in which the motor 100 is driven by three-phase AC power, which is a U phase, a V phase, and a W phase, is given.
[0035] Next, explain figure 1 The configuration and operation of each part of the present motor control device 10 are shown.
[0036] The drive unit 101 energizes and drives the windings of the motor 100 to rotationally drive the rotor. The drive unit 101 first performs a 2-phase-3-pha...
Embodiment approach 2
[0093] Figure 8 It is a block diagram of the motor control device 20 in Embodiment 2 of this invention.
[0094] This embodiment is constituted in figure 1 A filter 200 is further inserted in the preceding stage of the q-axis current command generator 108 in the first embodiment shown. Other configurations are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and detailed descriptions of the same configuration elements are omitted.
[0095] The filter 200 smoothes the torque command τ* input from the outside as a target command value. The smoothing algorithm is not particularly limited, for example, a one-order lag low-pass filter. Smoothed torque command τ LPF * is input to the q-axis current command generator 108 .
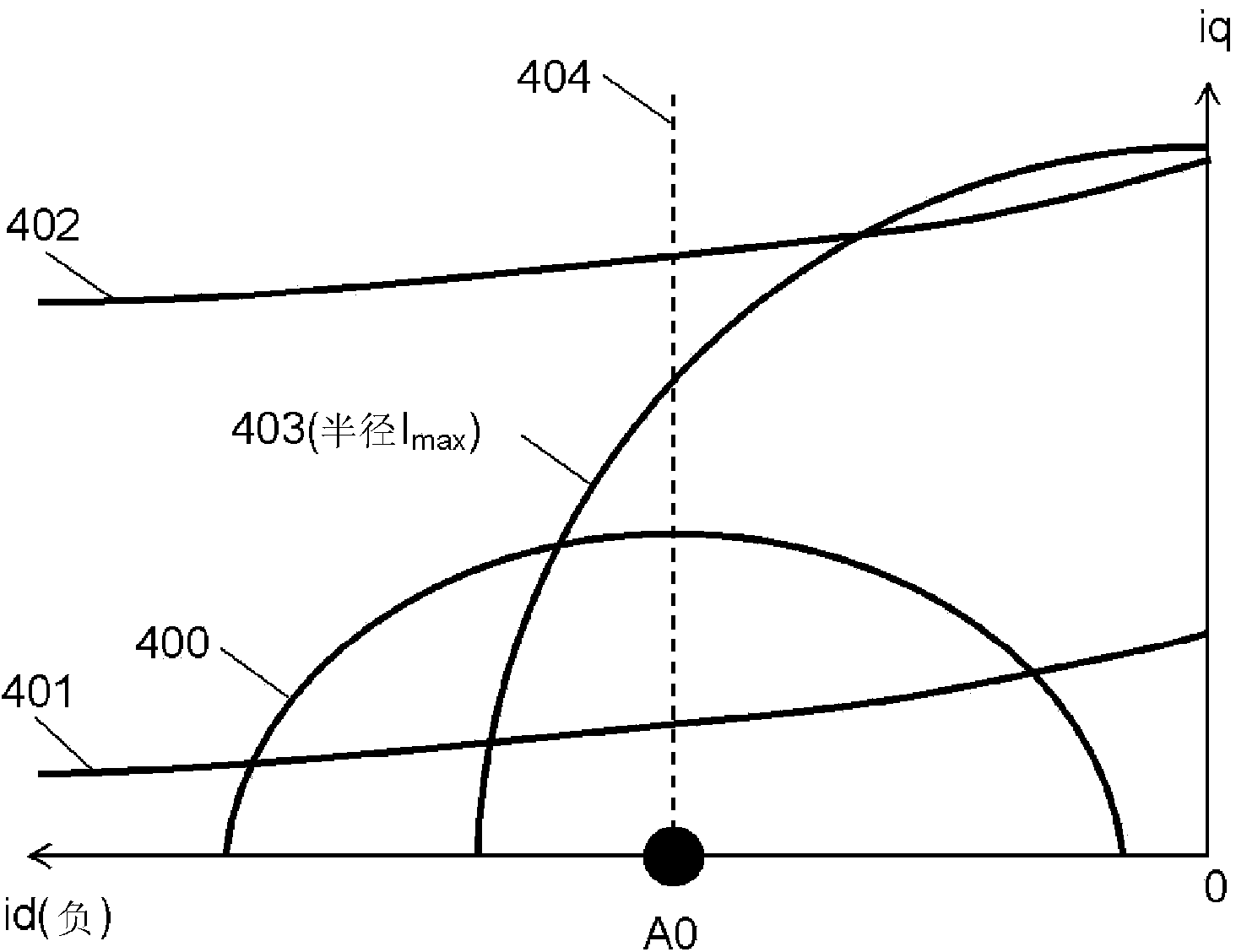
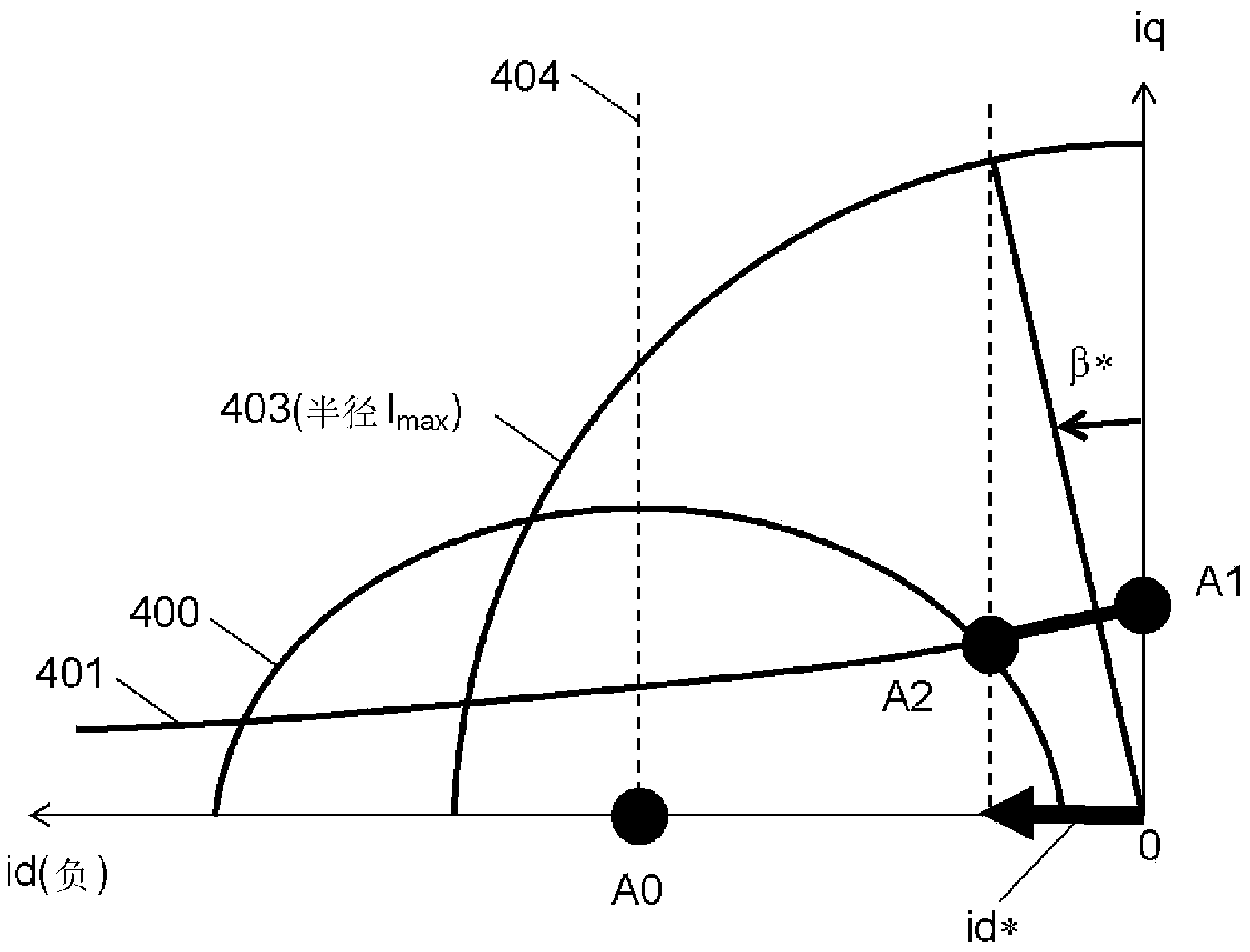
[0096] use Figure 9 The function and effect of the filter 200 are illustrated by the current vector locus of the filter 200. exist Figure 9 A voltage limit ellipse 900 , a constant torque curve 901 of an external torque command, a current limit circle 902 and a d-a...
Embodiment approach 3
[0105] Figure 10 It is a block diagram of the motor control device 30 in Embodiment 3 of this invention.
[0106] This embodiment is transformed into Figure 10 The structure shown in the phase angle command generator 300 is replaced by figure 1 An embodiment of the phase angle command generator 103 in Embodiment 1 is shown. Other configurations are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and detailed descriptions of the same configuration elements are omitted.
[0107] Figure 10 The phase angle command generating unit 300 in the above uses the q-axis component vq* of the voltage command instead of the absolute value |v*| of the voltage command in the first embodiment. In addition, the reference voltage correction unit 301 adjusts the predetermined reference value V lmt Make corrections. Then, from the corrected reference value vq lmt The difference Δvq* obtained by subtracting the d-axis component vq* is output to the phase angle command calculation unit 106 .
[0108] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com