Method and system for measuring position compensation angles of permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, rotor position technology, applied in the field of control, can solve the problems of small rotor position jitter, complex realization, obvious small rotor position jitter, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
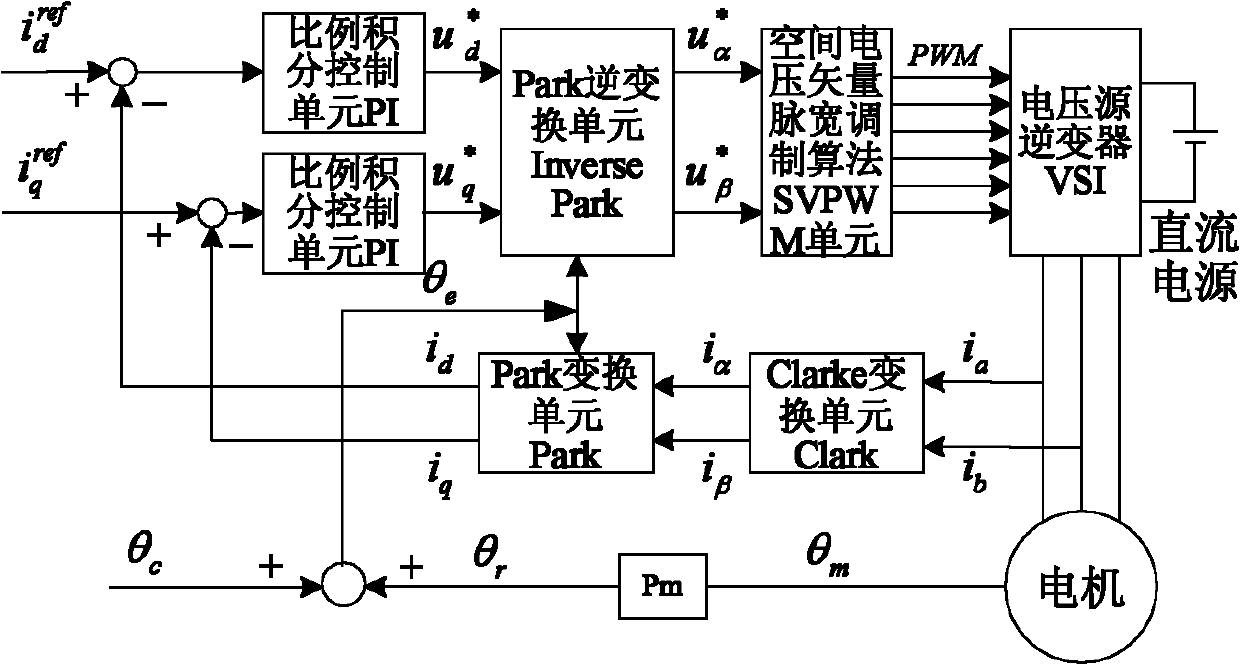
[0063] Embodiment 1, a method for measuring the rotor position compensation angle of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, comprising:
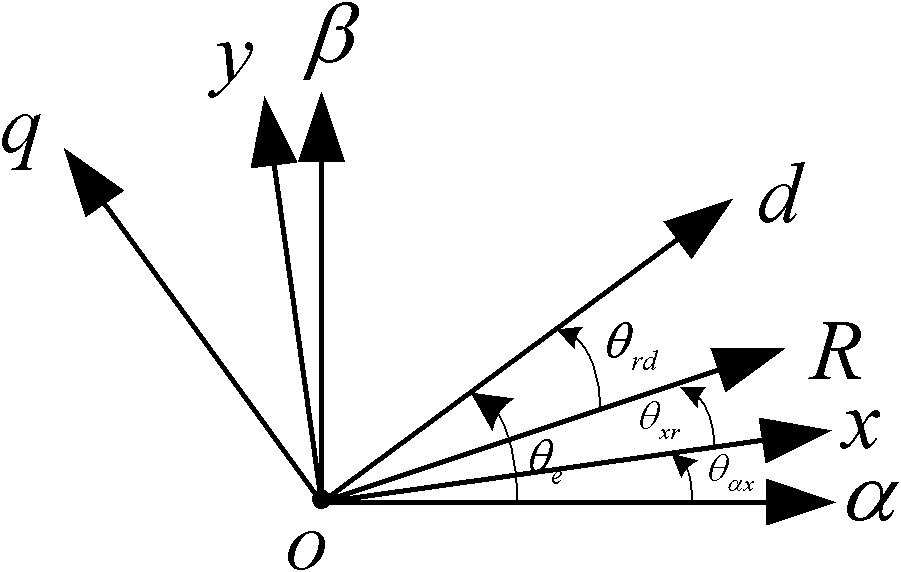
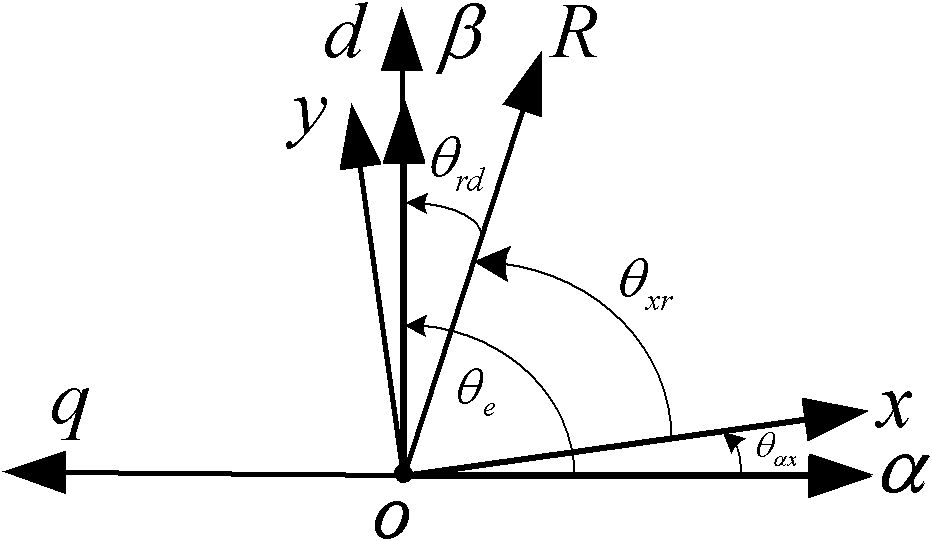
[0064] Set Forced Field Orientation Angle Let d-axis voltage component command value Input the q-axis voltage component command value that can make the permanent magnet synchronous motor enter the zero-speed lock shaft state
[0065] According to the orientation angle of the forced magnetic field Will and The voltage vector is obtained by inverse PARK transformation and
[0066] Convert the voltage vector and Generate the power device pulse width signal required by the voltage source inverter through the space voltage vector pulse width modulation algorithm SVPWM;
[0067] The voltage source inverter drives the permanent magnet synchronous motor to rotate to position; can be, but not limited to, drive a permanent magnet synchronous motor to rotate in a manner similar to a stepper motor stable position;
[0068] Obtain...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Embodiment 2, a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position compensation angle measuring device, such as Figure 4 shown, including:
[0093] The input unit is used to input the q-axis voltage component command value that can make the permanent magnet synchronous motor enter the zero-speed shaft-lock state and the d-axis voltage component command value equal to 0
[0094] Inverse Park Transformation Inverse Park unit for orientation angles according to a pre-set forced magnetic field right and Perform Park inverse transformation to get and
[0095] Space Voltage Vector Pulse Width Modulation Algorithm SVPWM unit for the voltage vector according to the and Using space voltage vector pulse width modulation algorithm to generate power device pulse width signal;
[0096] The voltage source inverter VSI, by the voltage u dc The DC bus power supply is used to generate the three-phase winding current i according to the pulse width signal of the power ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com