Phase-differential quantum key allocation and allocating system
A key distribution system and key distribution technology, applied in the field of one-way, stable, fast phase difference quantum key distribution method and its system, can solve the problem of limited transmission distance, poor stability, easy to receive interference from external environment, etc. problem, to achieve high communication security, avoid theft, and fast quantum key distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
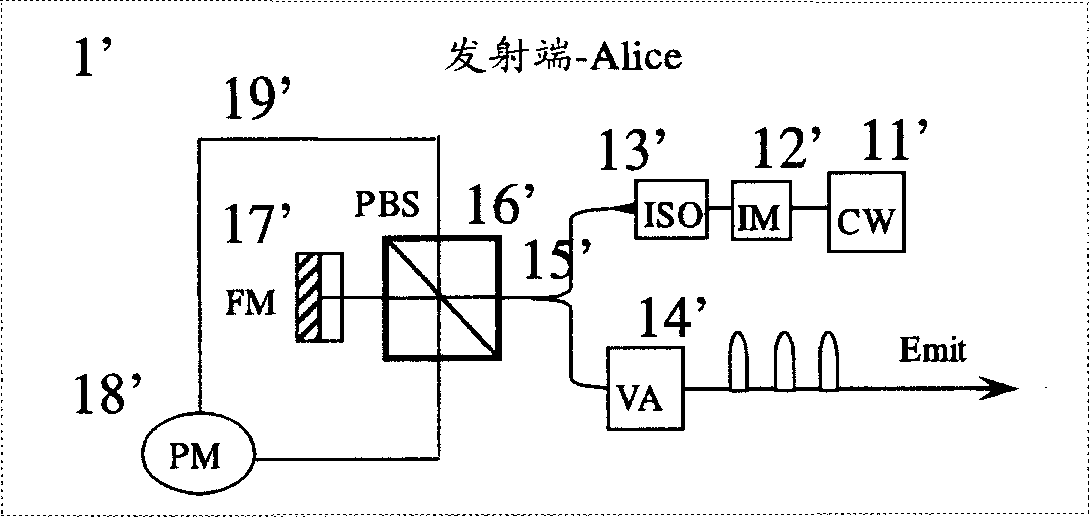
[0050] Such as figure 1 The shown signal modulation transmitter 1'uses an intensity modulator 12' to modulate the laser light emitted by the continuous laser light source 11' into coherent pulsed light with equal time intervals of Δt, and then enters the four-port polarization beam splitter 16' to be divided into horizontal and vertical Two beams of polarized light. One beam of light directly enters the phase modulator 18', and the other beam of light passes through the Faraday rotator mirror 17' to rotate the polarization plane by 90 degrees, and then enters the phase modulator 18' from the other end. The distance of the optical fiber 19' is designed so that the two The beam of light reaches the phase modulator 18' at the same time. Since the two beams experience the same optical path, they are recombined at the 16' port of the polarization beam splitter. Therefore, according to the phase modulation information {0,π}, a random quantum code is output, and then it is attenuated to...
Embodiment 2
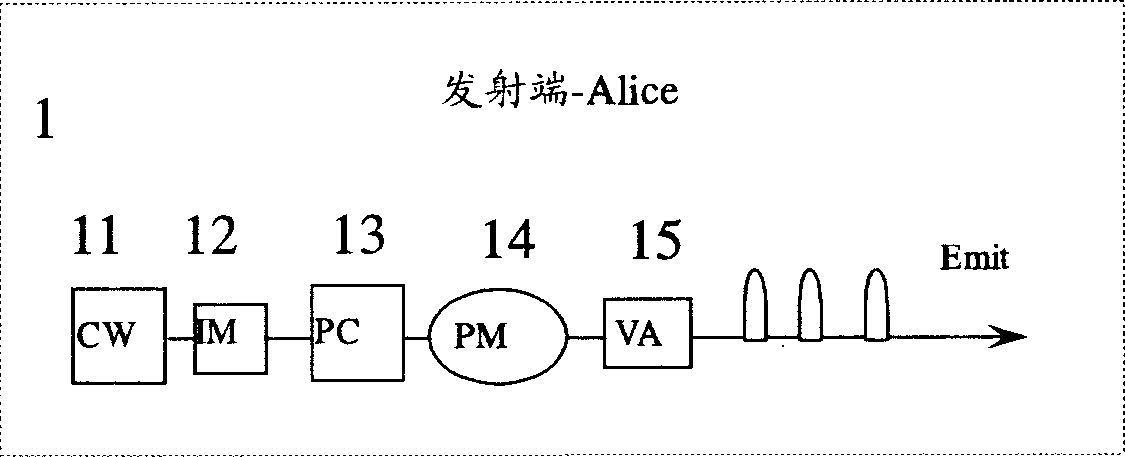
[0055] Such as figure 2 The signal modulation transmitter 1 shown directly uses the intensity modulator 12 to modulate the laser light emitted by the continuous laser light source 11 into coherent pulsed light with equal time intervals of Δt, and enters the phase modulator 14 after being controlled by the polarizer 13. After loading the phase modulation information {0, π}, it is attenuated to a single quantum state μ=0.1 through the optical attenuator 15. In this way, the structure is simple, the devices used are less, the price is low, and the stability is good. The receiving end of the system is exactly the same as in the first embodiment.
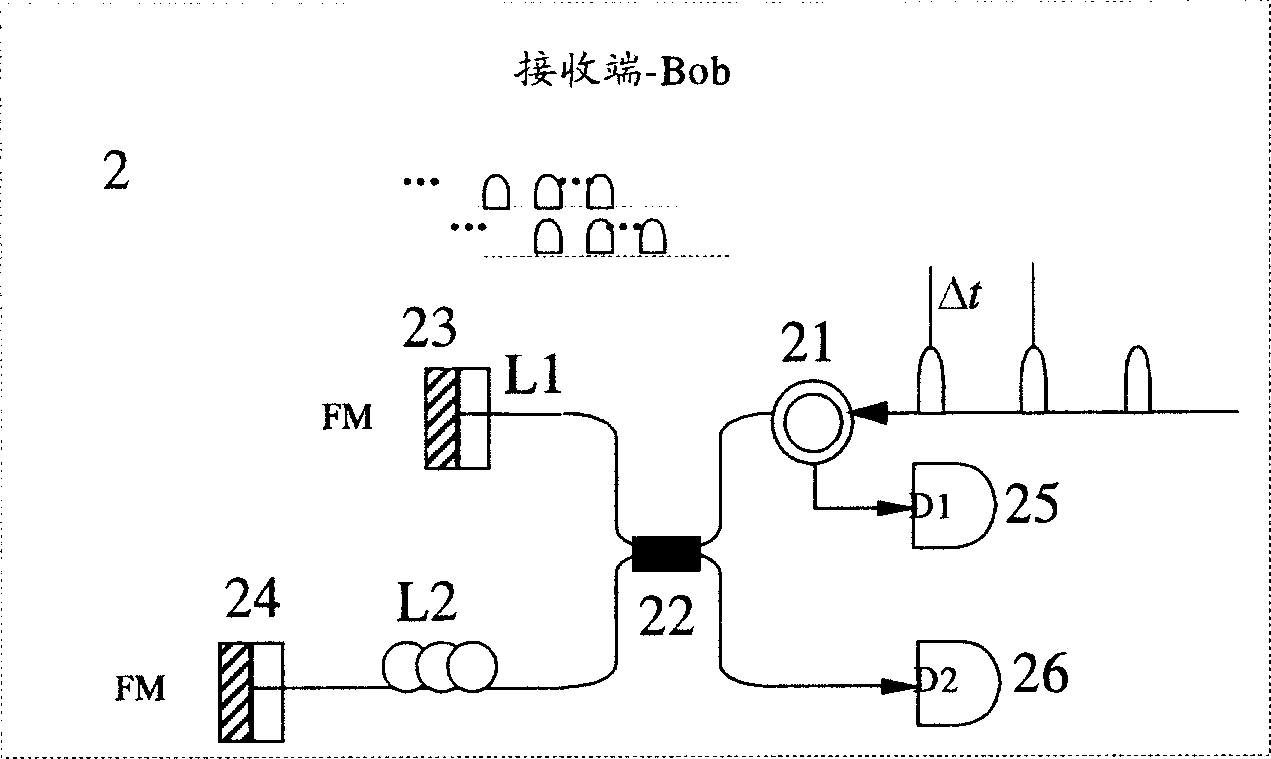
[0056] Light path like Figure 5 As shown, at the transmitting end, Alice modulates each pulse with 0 or π random phase. It is specified that when the phase is 0, the code is "0", and when the phase is π, it is the code "1". The signal is transmitted to the receiving end through the optical fiber 10. At the receiving end, Bob uses the detect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com